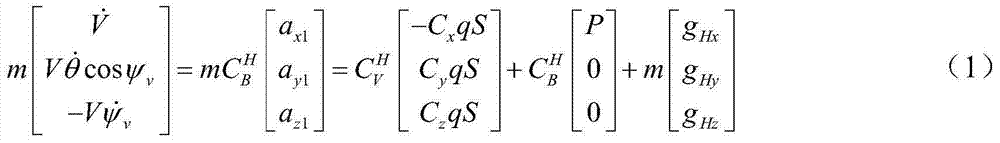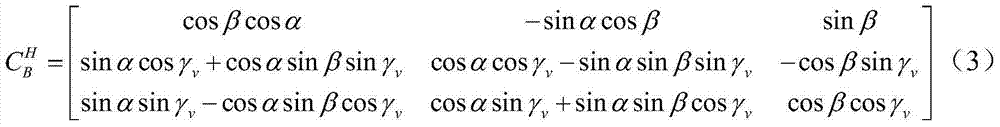Patents
Literature
151 results about "Control oriented" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
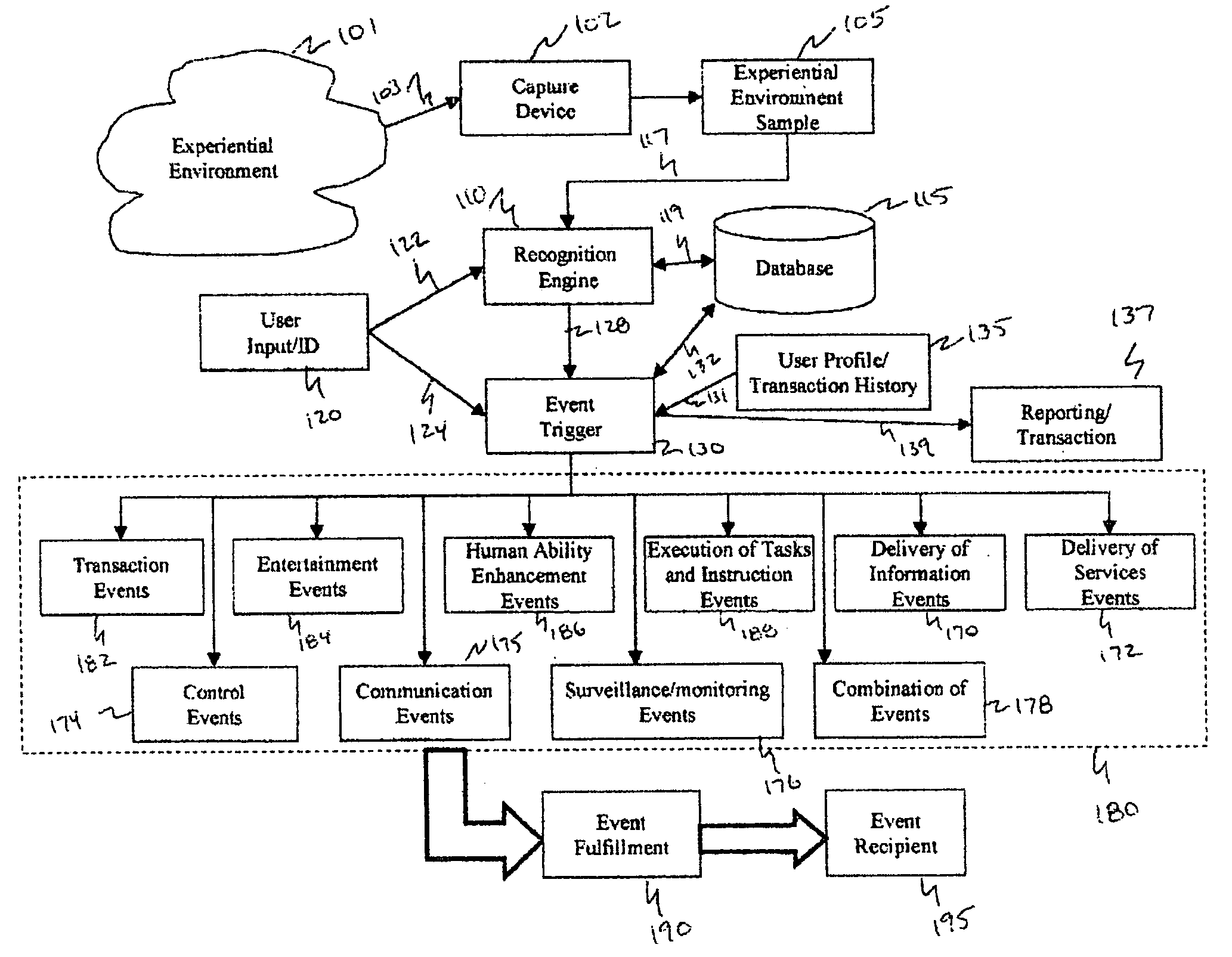
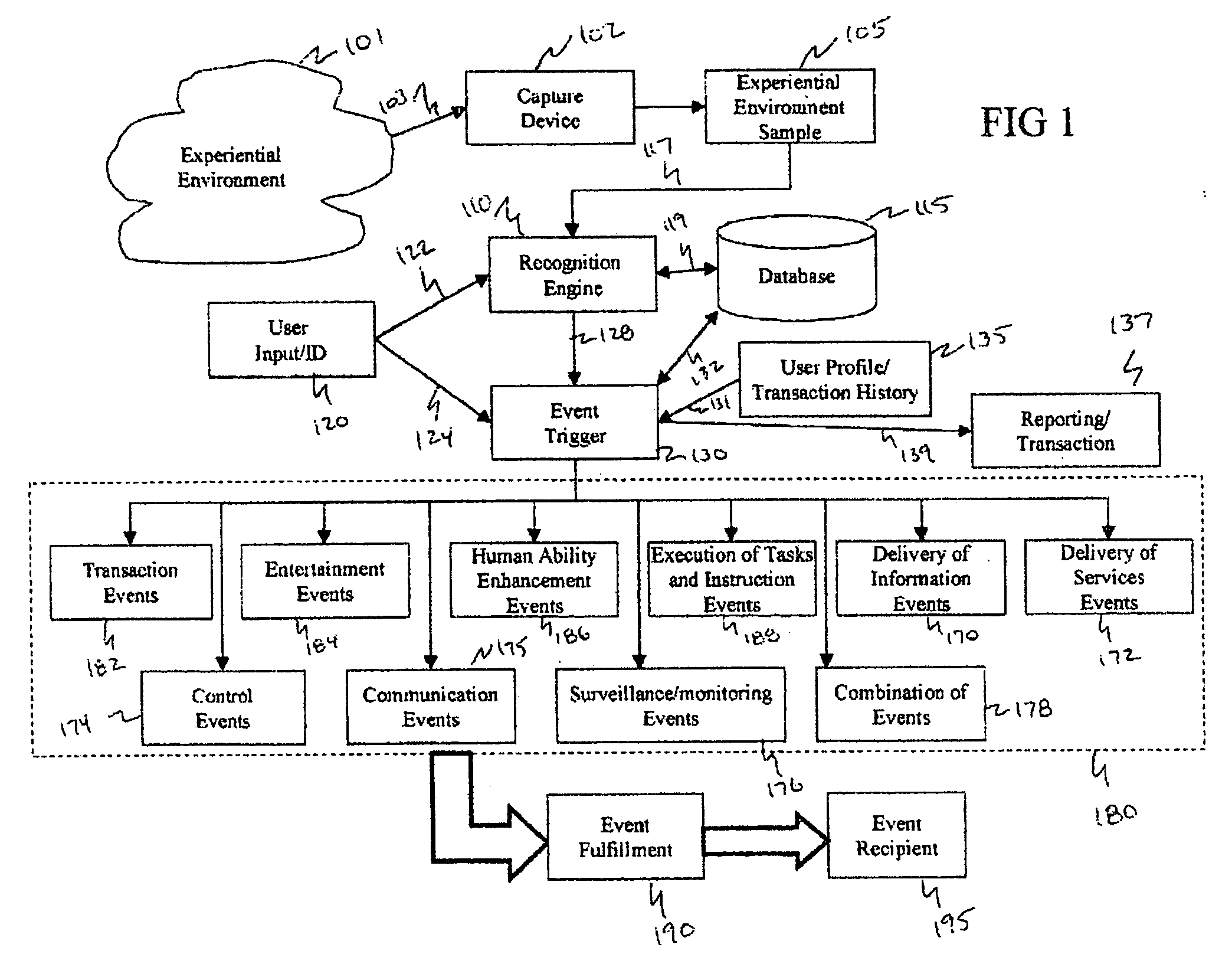
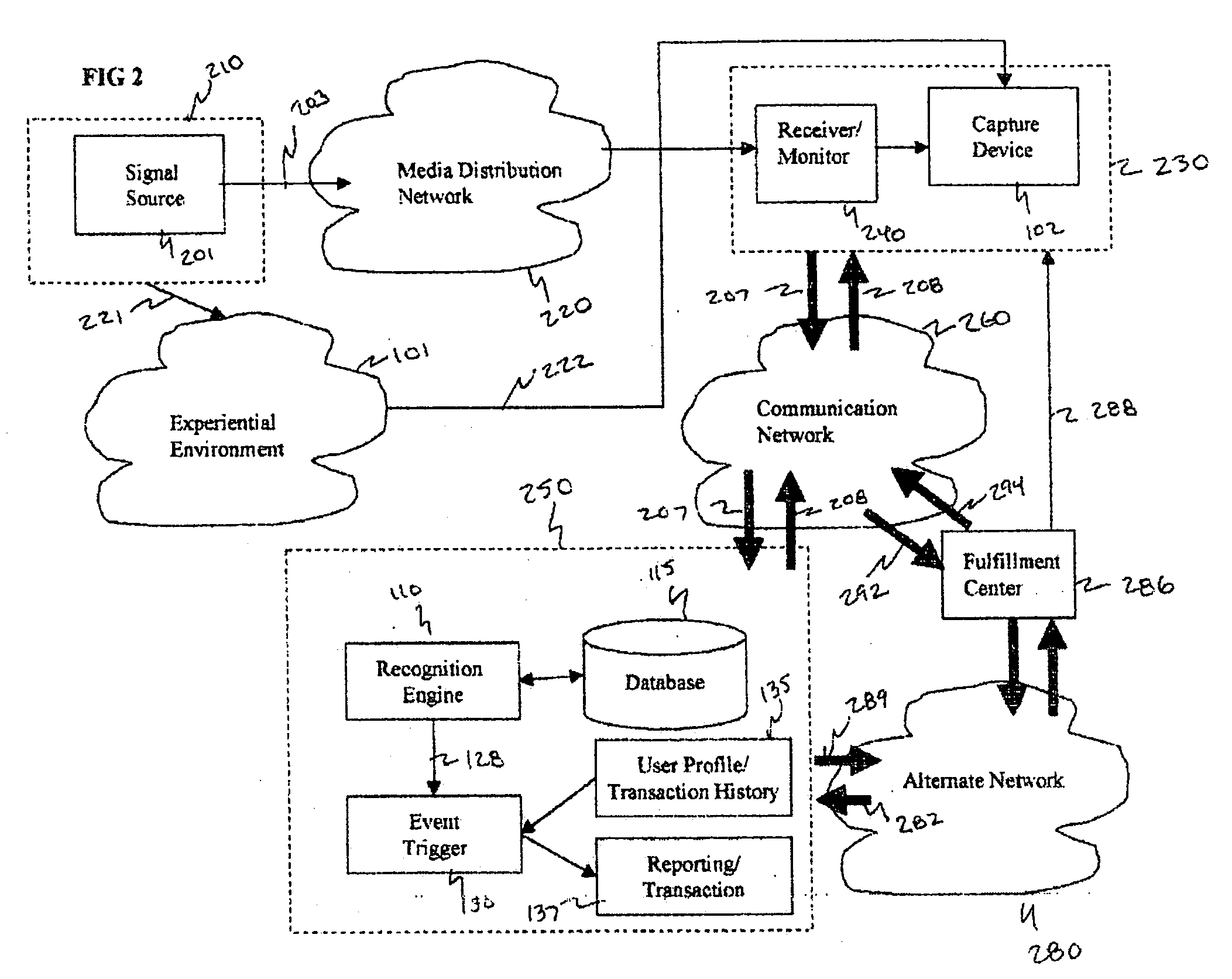
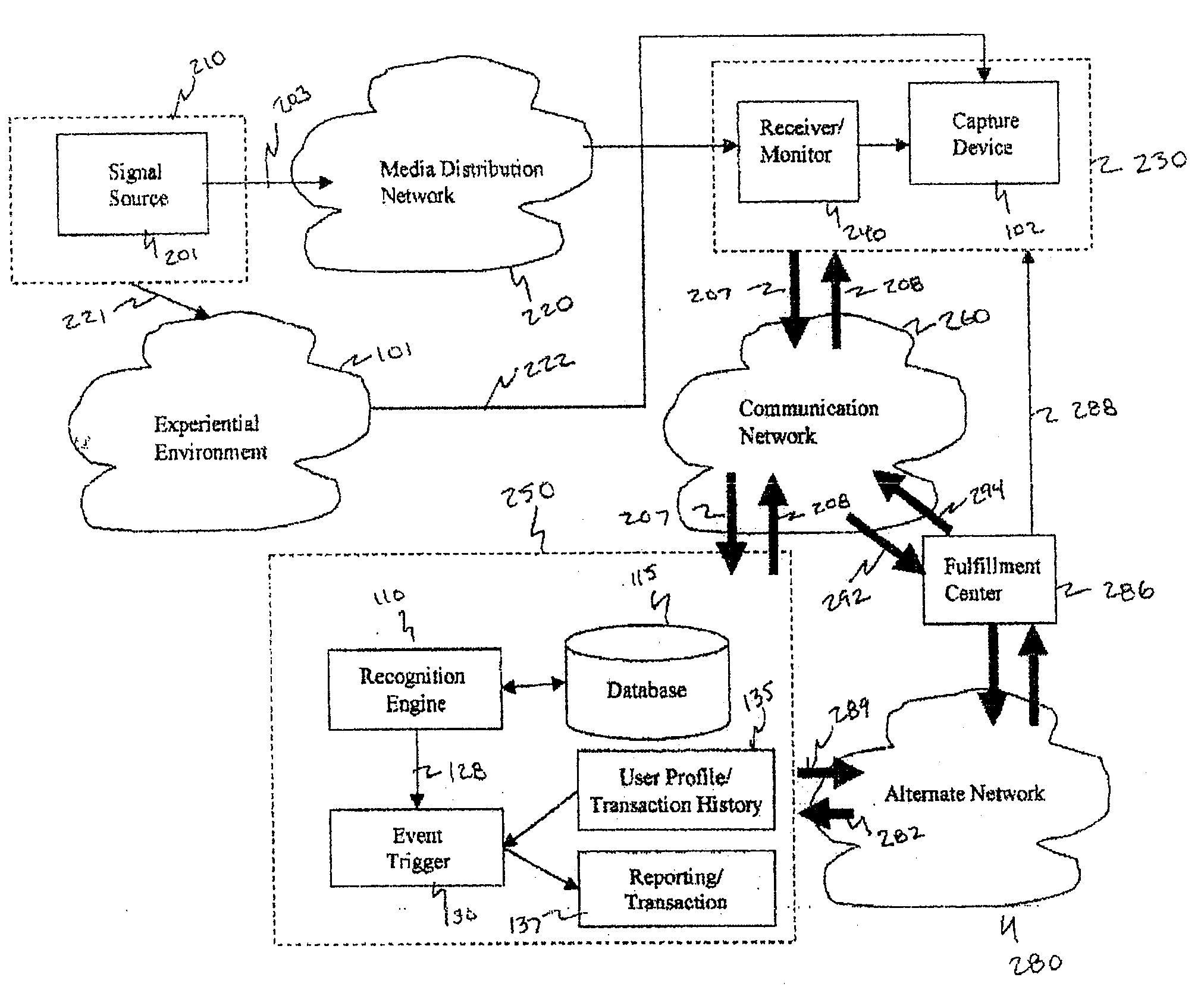
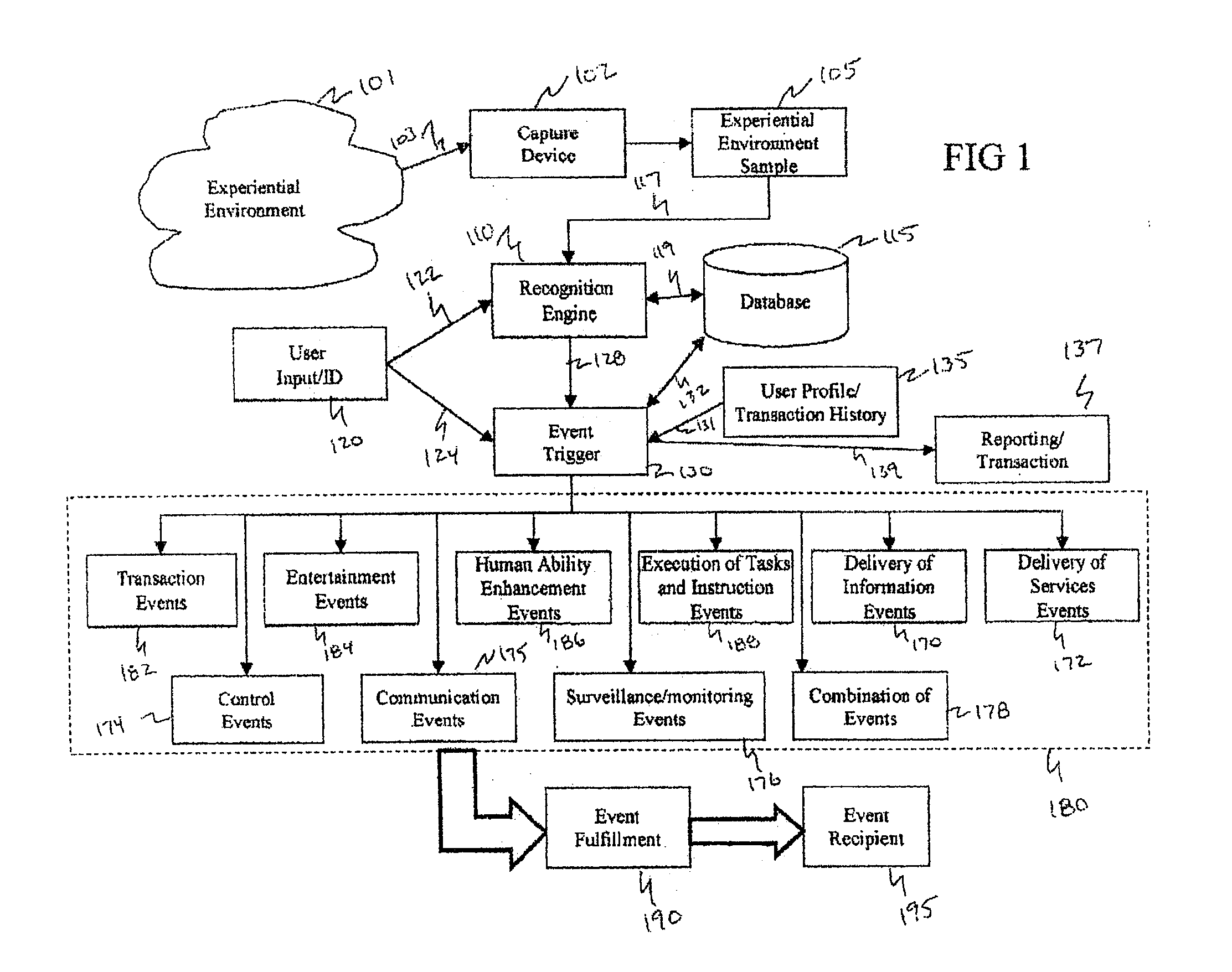
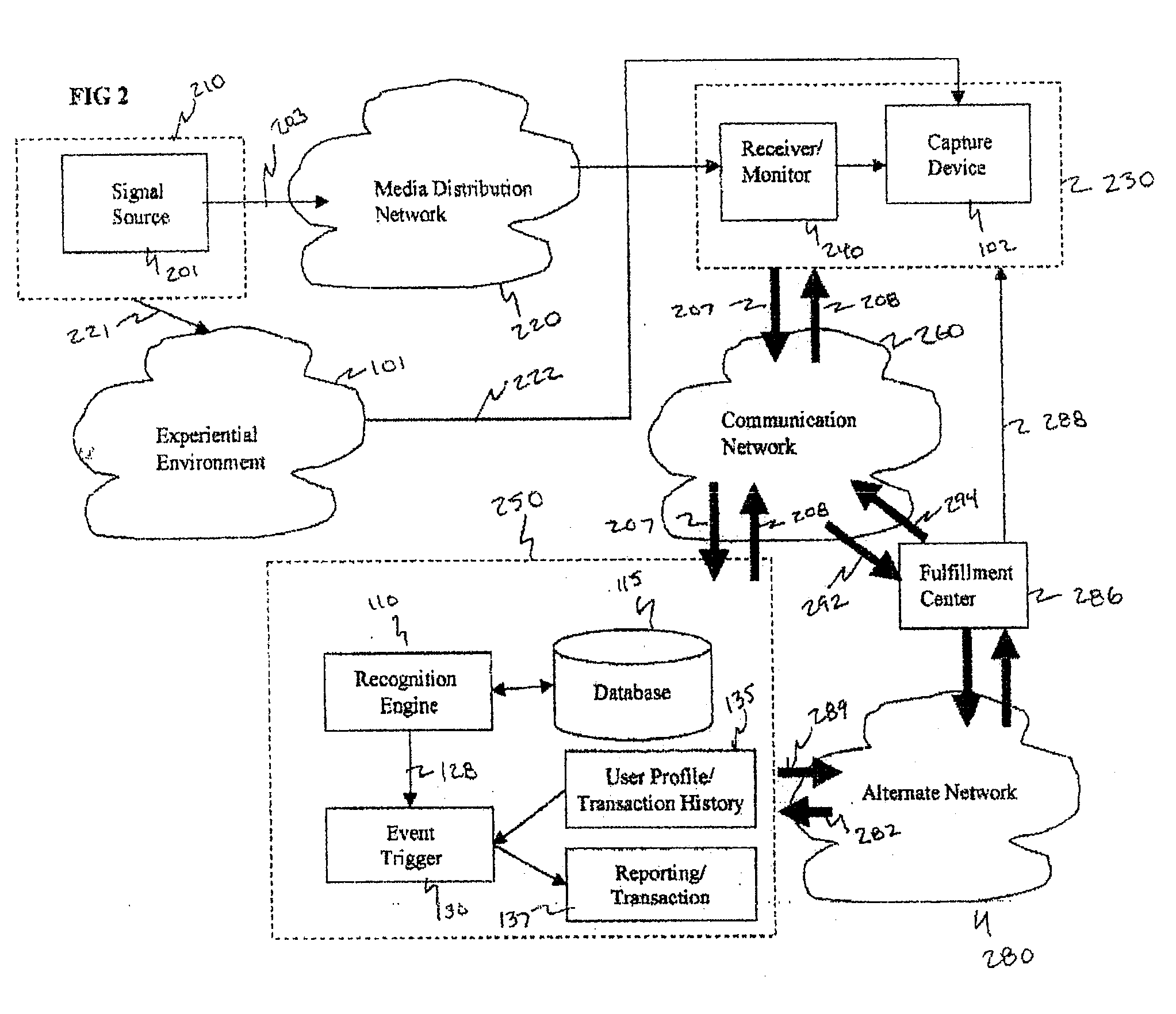
Method and system for interacting with a user in an experiential environment
InactiveUS20050267817A1Improve abilitiesFunction increaseElectrophonic musical instrumentsDiscounts/incentivesControl orientedHuman–computer interaction
A method and system for provides a user with an ability to capture a sample of an experiential environment and deliver that sample to an interactive service to trigger one or more predetermined events. In exemplary embodiments of the invention such triggered events include the delivery of information and services to the user, the execution of tasks and instructions by the service on the user's behalf, communication events, surveillance events and other control-oriented events that are responsive to the user's wishes. In other exemplary embodiments of the invention, the triggered events include transaction-oriented events, entertainment events, and events associated with enhancements to human ability or function.
Owner:SHAZAM INVESTMENTS +1
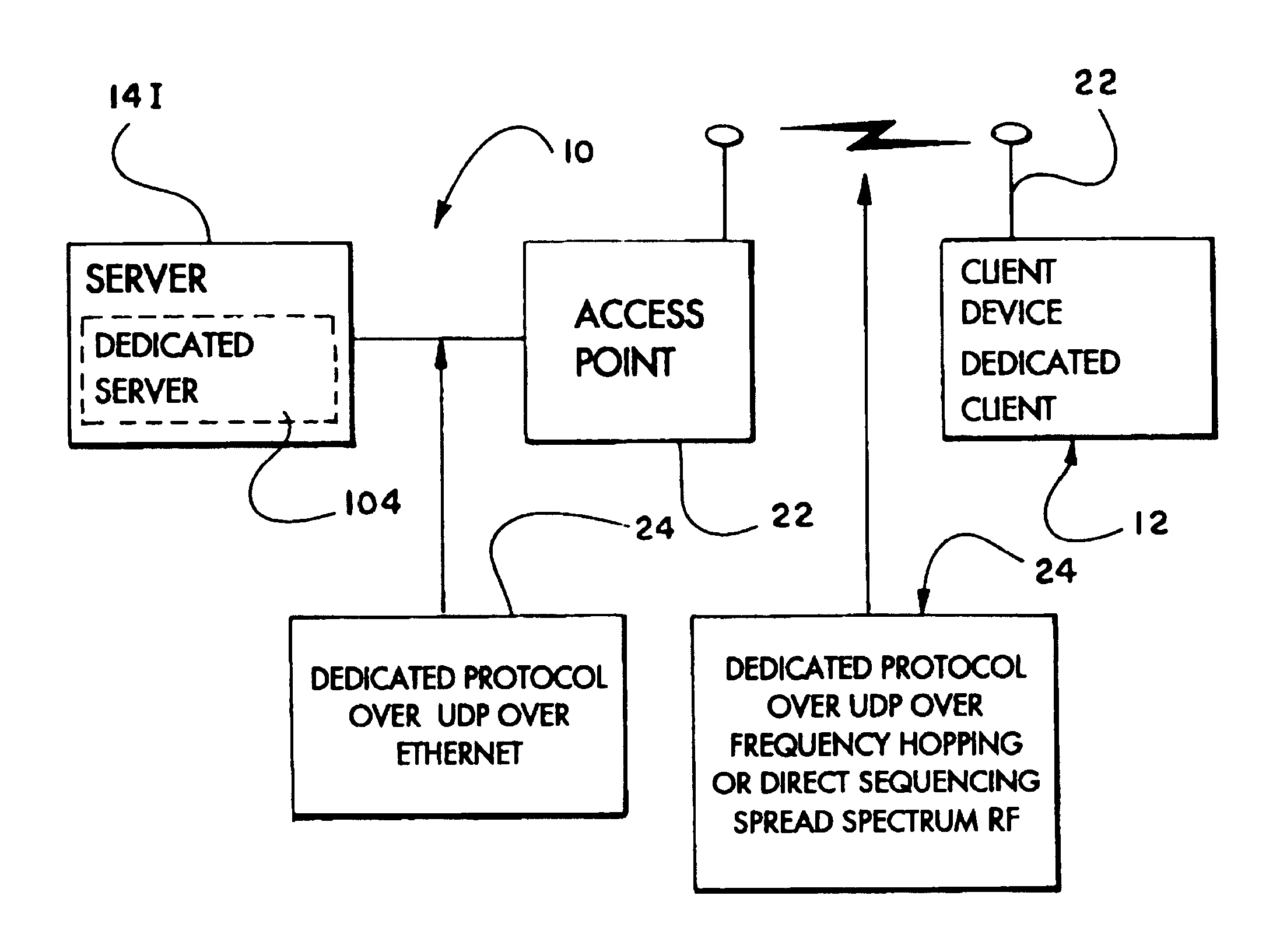
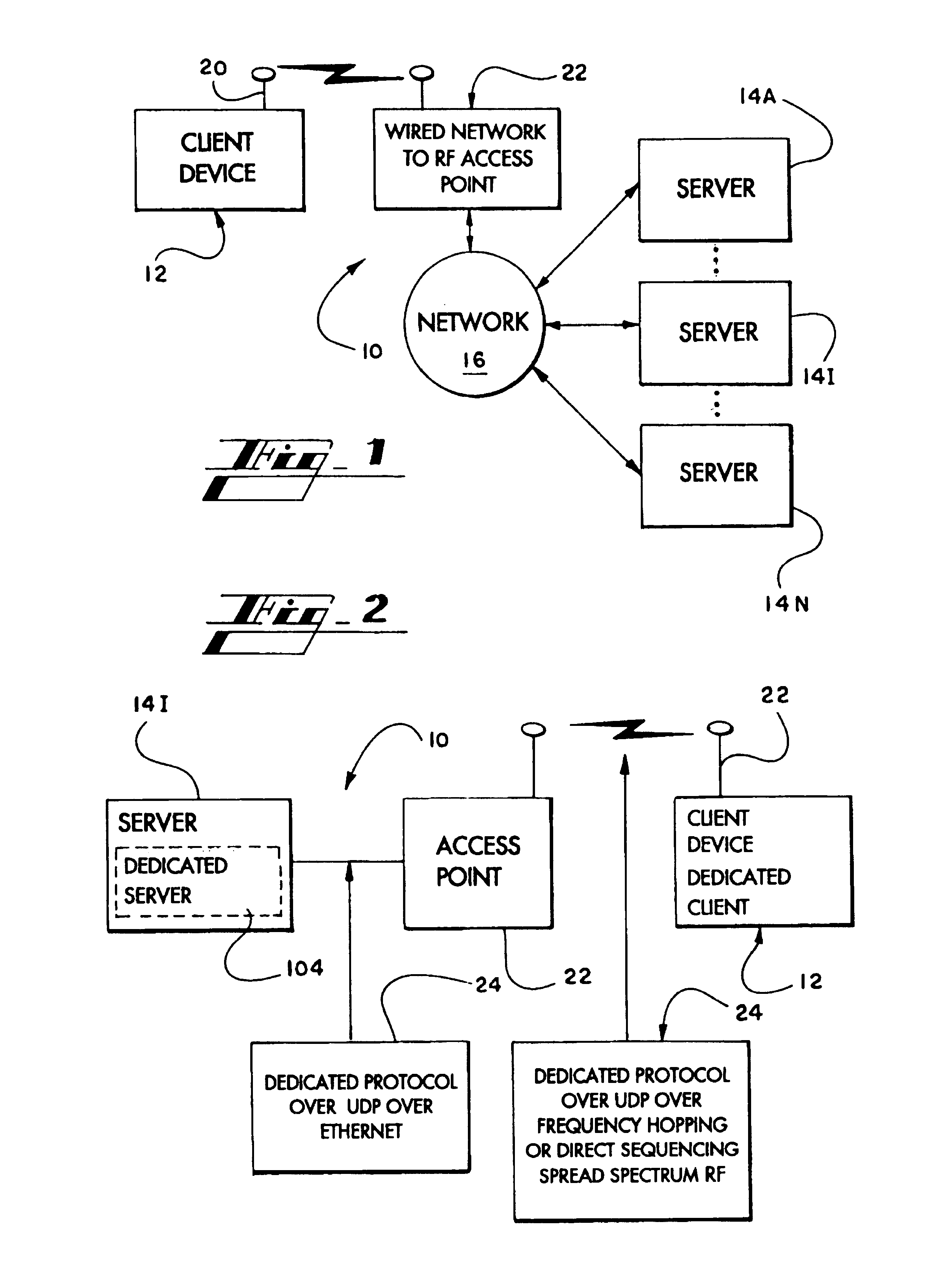
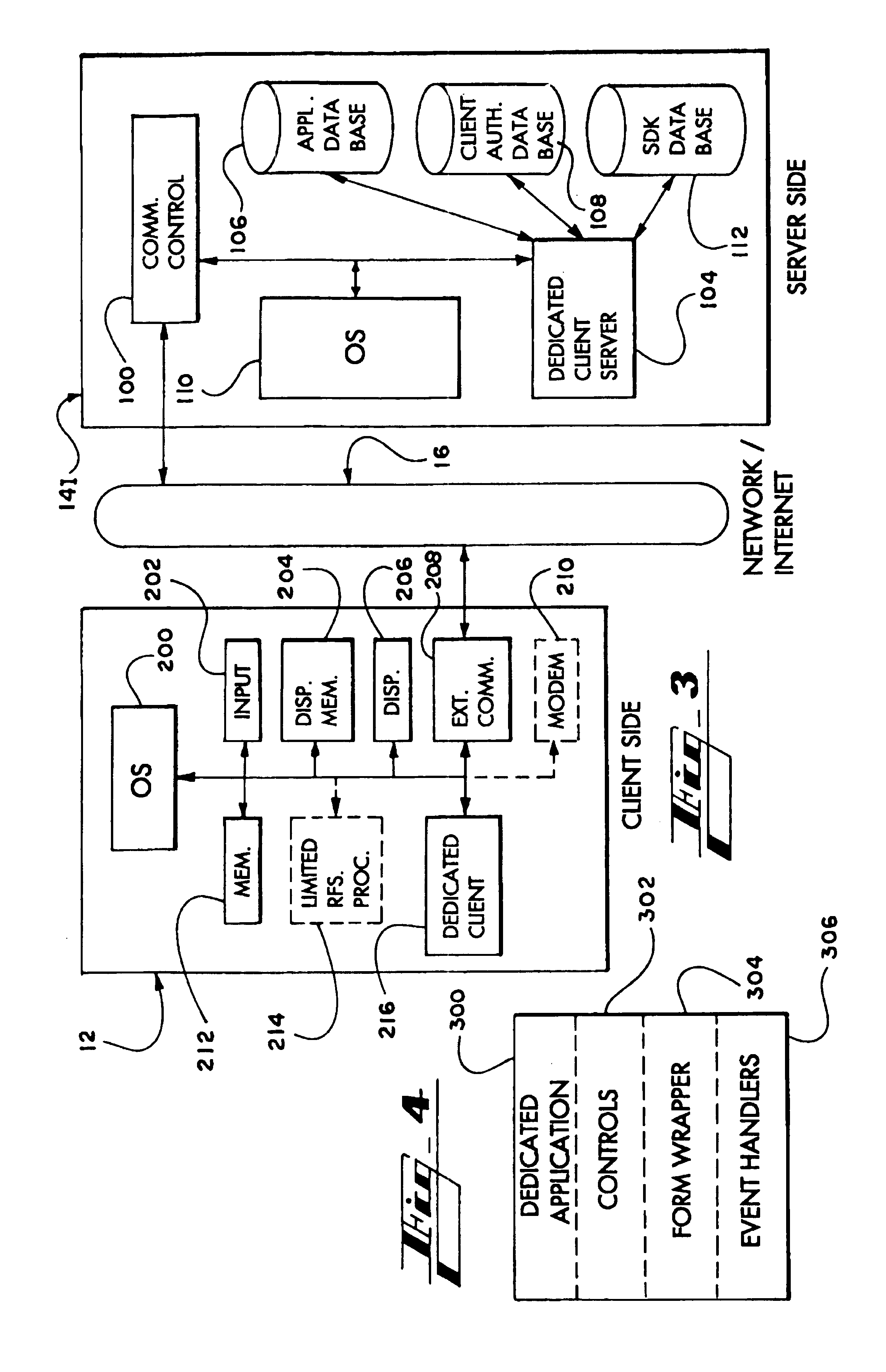
Method and apparatus allowing a limited client device to use the full resources of a networked server
InactiveUS7035912B2Efficiently transmit message compliantImprove efficiencyResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsControl orientedMessage type
A thin-client system operative over a communications network provides a thin-client device with access to a dedicated application present at a server. Messages between the client device and the server conform to a control-oriented protocol that restricts the type of message permissible for transmission to only those descriptive of certain preselected events that are necessary for execution of the dedicated application on the server and excludes transmission of user actions that otherwise would be transmitted to the server from the client device according to conventional display-based protocols.
Owner:CAPGEMINI U S
Cluster UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) locus and attitude cooperative control method for safety domain
ActiveCN108388270AFlight safetyWeakened positioning accuracy requirementsPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl orientedMathematical model
The invention relates to the technology of UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) control, aims at proposing a UAV locus and attitude cooperative control method and ironing out a defect in the locus planning for each UAV of a conventional UAV cluster, and can effectively reduce the requirements for the positioning precision of the UAV. Therefore, the invention provides a cluster UAV locus and attitude cooperative control method for a safety domain, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, control-oriented four-rotor-wing UAV locus and attitude model building: giving full consideration to the inherent characteristics of a four-rotor-wing UAV and the dynamic factors in flight, and building a locus and attitude mathematic model for the four-rotor-wing UAV; 2, cluster center locus planning: achieving the obstacle avoidance path planning for a cluster UAV central point based on a pseudo-spectral method; 3, safety flight region optimization: completing the optimization of a cluster UAV safetyflight envelope and a cluster UAV optimal formation configuration; 4, distributed cooperative controller design. The method is mainly used in a UAV control occasion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
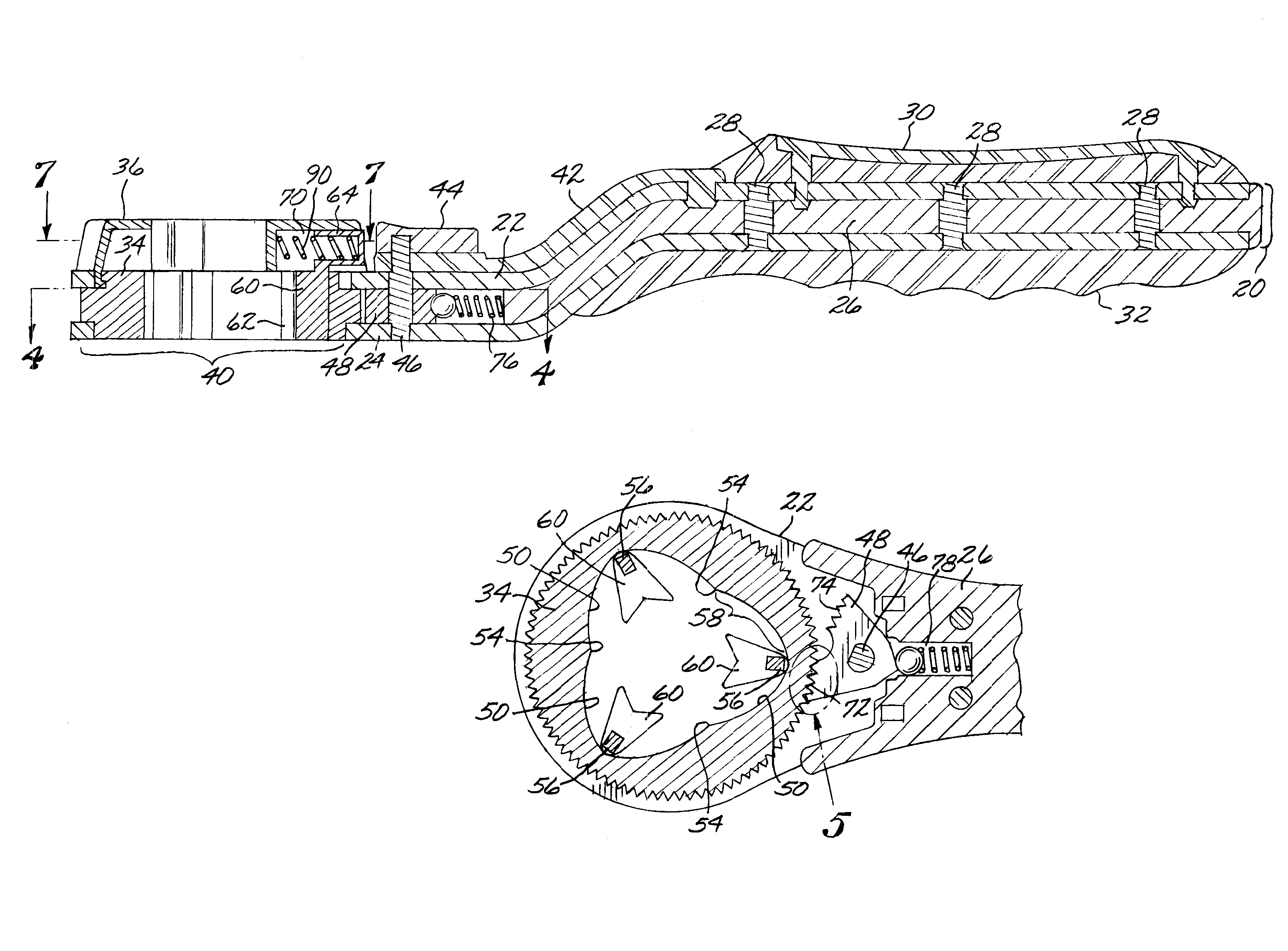
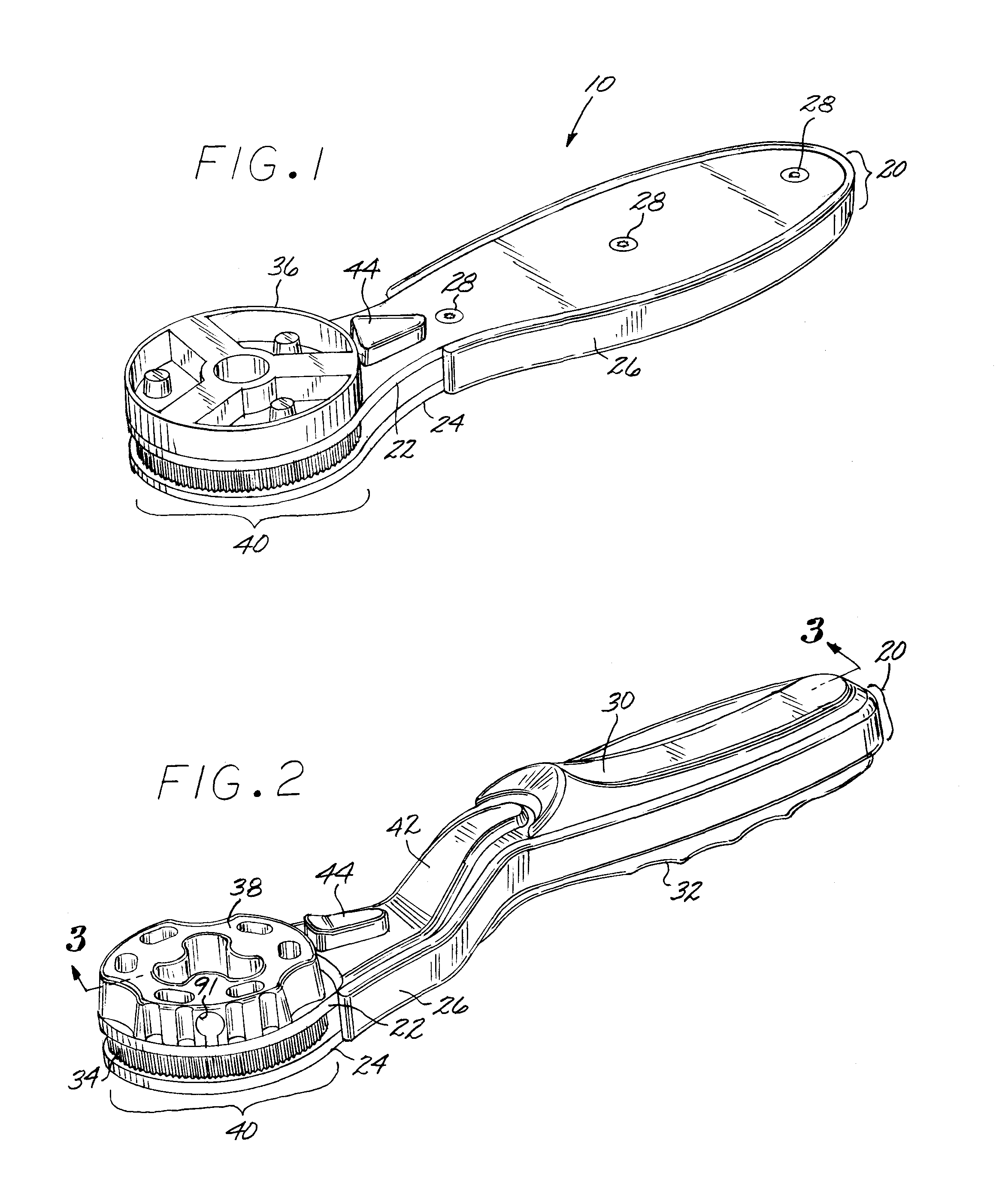
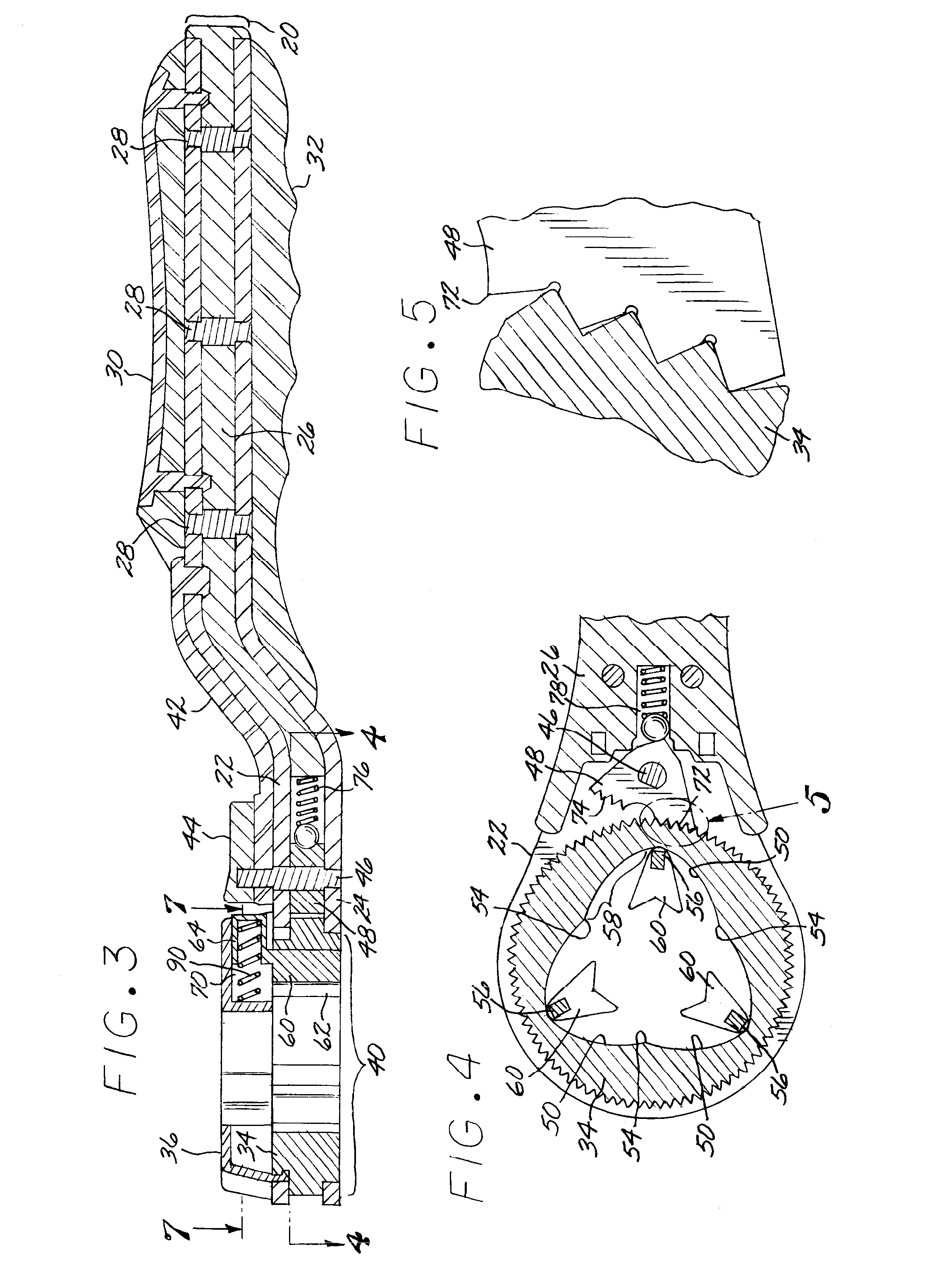
Quick adjust ratcheting wrench with cam actuated clamping
InactiveUS7478577B1Simplify structure and constructionImprove convenienceSpannersWrenchesControl orientedEngineering
The invention is a wrench with jaws adjusted by a cam mechanism and a ratchet mechanism providing a free return stroke of the handle, a simplified construction, convenience of use, durability, effectiveness, and cost and weight reduction; comprising a handle with housing, annular control and adjusting discs, a plurality of radial guide slots in the adjusting disc and cam features in the control disc, a plurality of jaws in the housing, each jaw, having a slider spring loaded, is positioned in said guide slots, and a cam follower interacting with cam features formed on the inner edge of the control disc; radial guide slots on the surface of the adjusting disc facing the control disc, each guide slot limited by the inner arch-shaped edge of the adjusting disc and open on its periphery; cam followers and profiles provide wedging to the rotation of the discs during the return stroke.
Owner:WHEELER THOMAS J
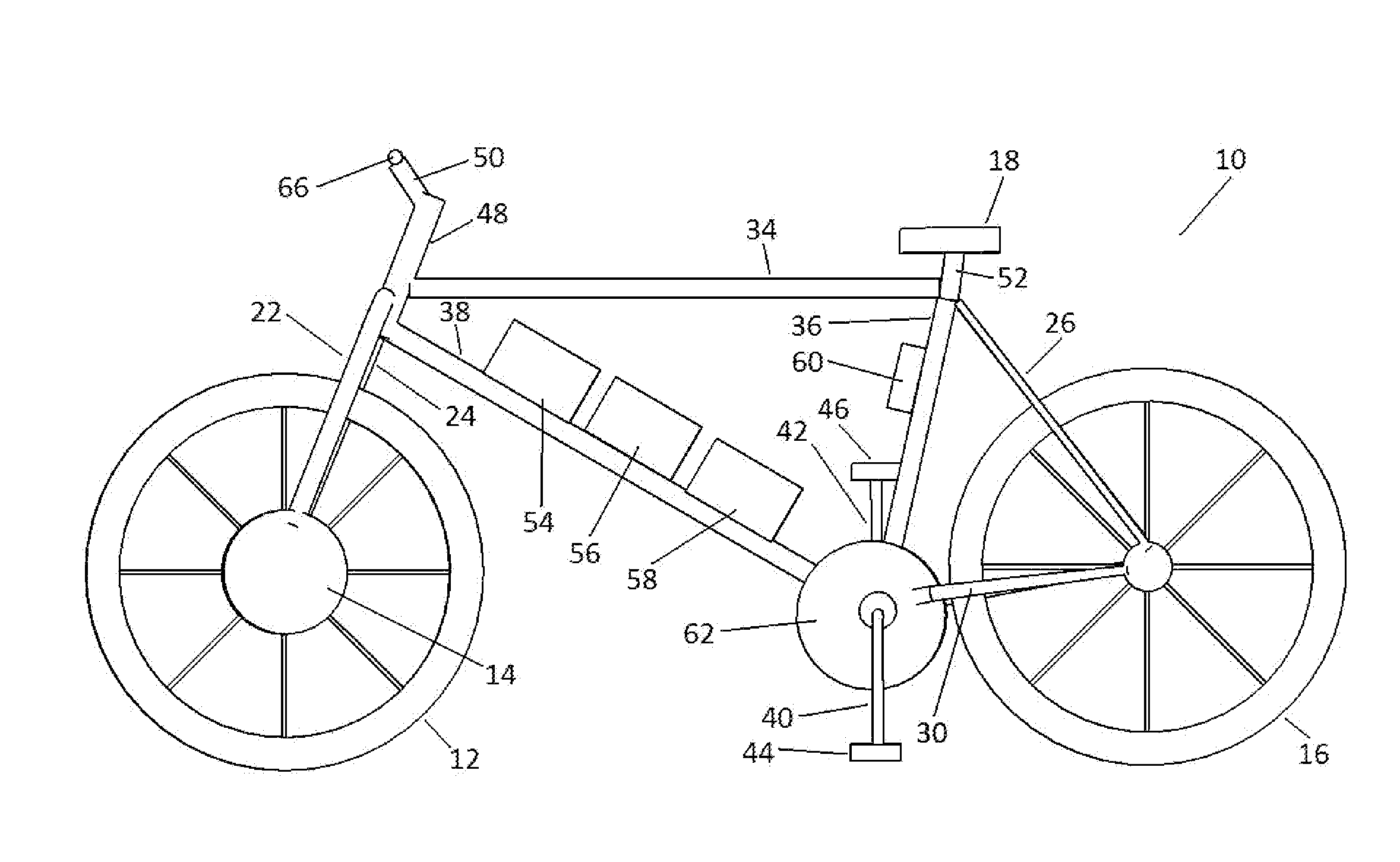
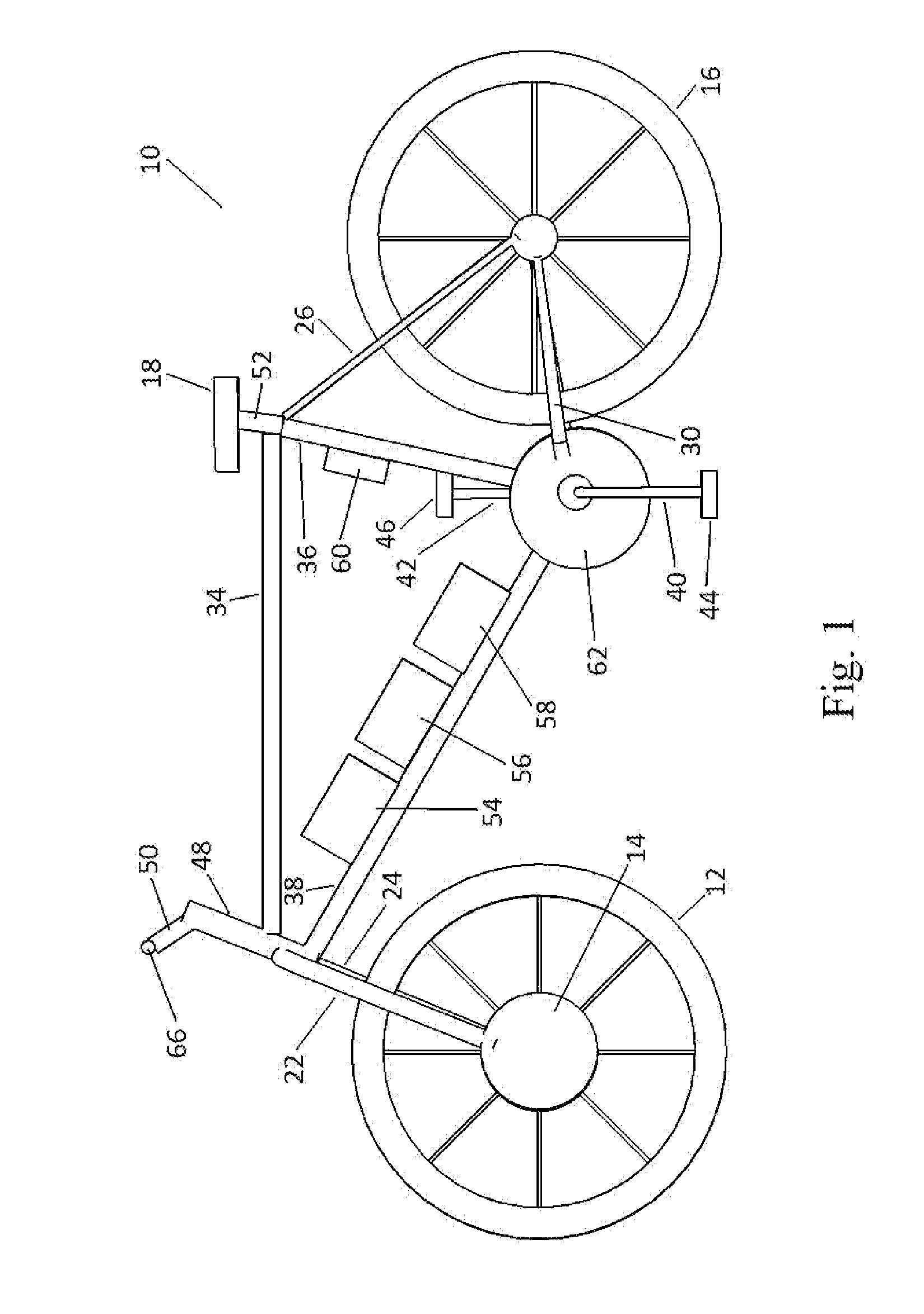
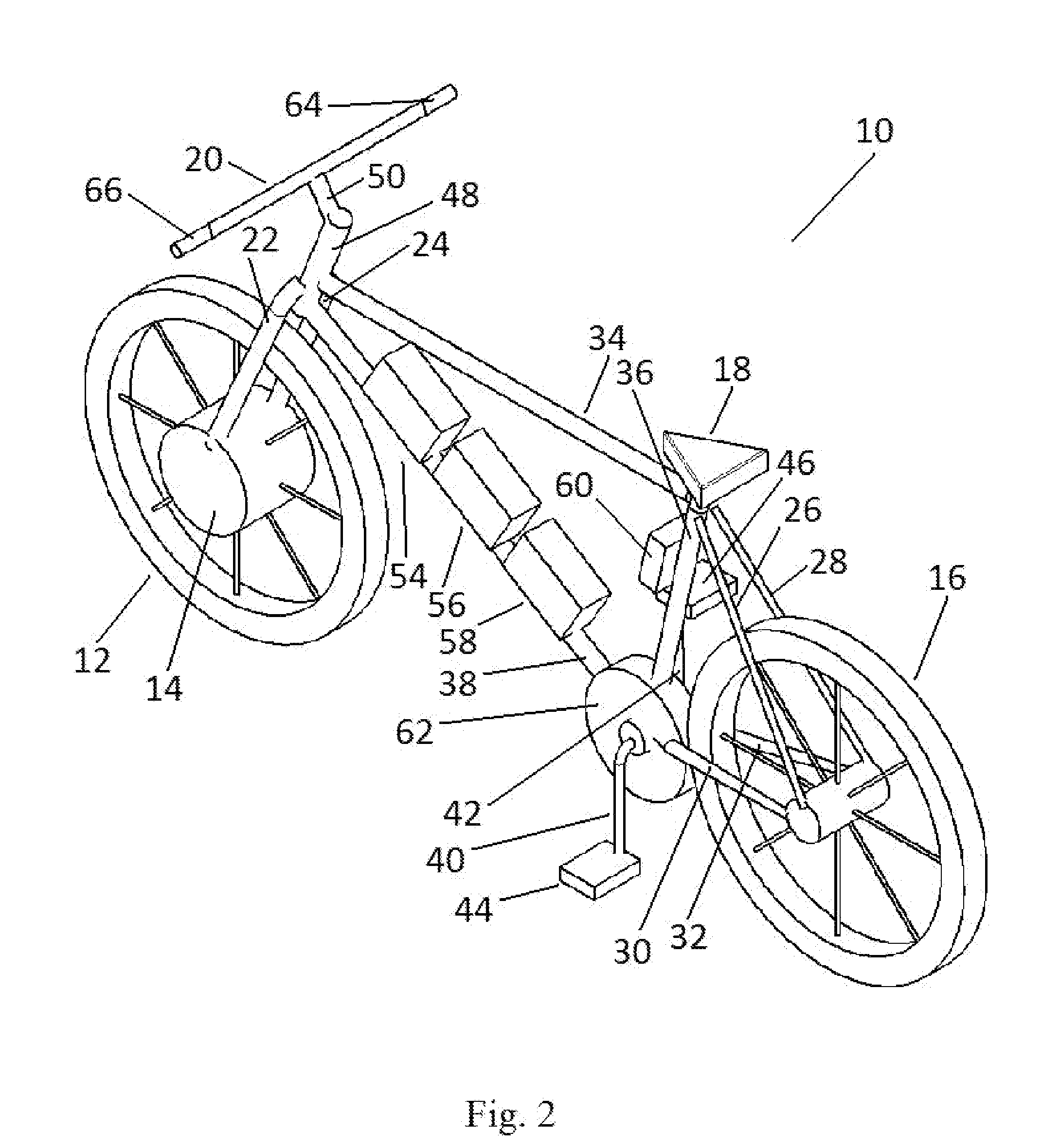
Pedal generator electric bicycle
A chainless electric cycle design that allows a rider / user to pedal a pedal generator to create an electric transmission energy source that either charges the battery or partially powers a hub motor, discharges the battery to the hub motor contained within one of the wheels, allows the user to set a desired level of resistance from the pedal generator using controls oriented about the handlebars, allows the user to activate the hub motor using a speed controlling device oriented about the handlebars, and allows the user to charge the battery by connecting to a standard 110V / 220V AC power supply. A chainless cycle is a cycle where the input power from a rider is not converted into output power by the rear wheel through a gear and chain system connecting the pedals to the rear wheel.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
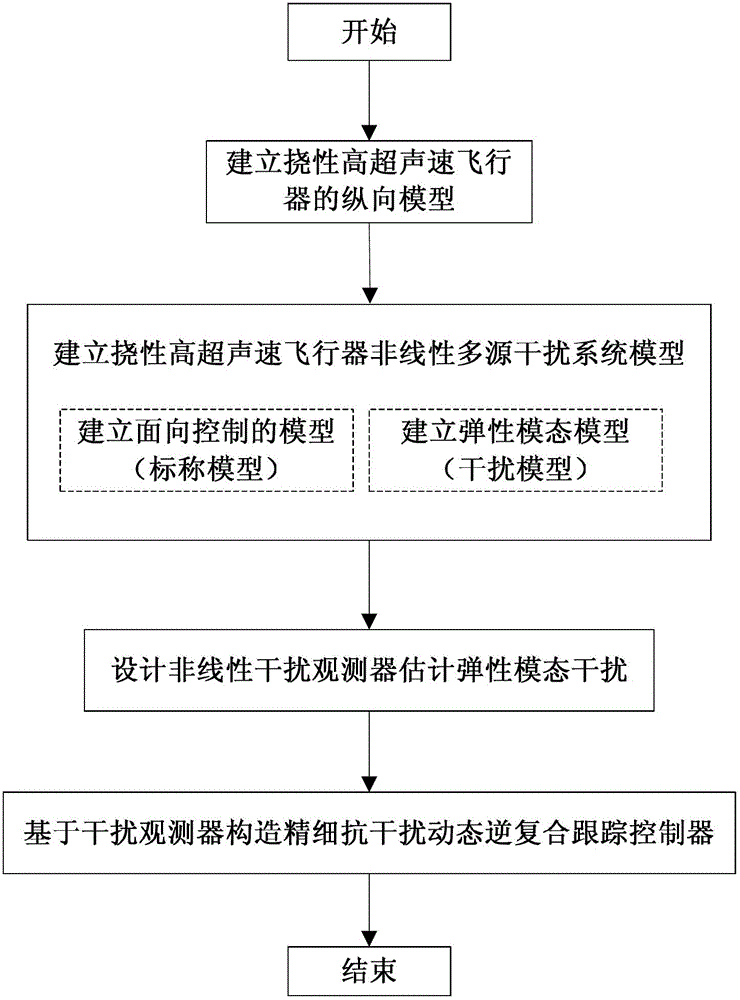
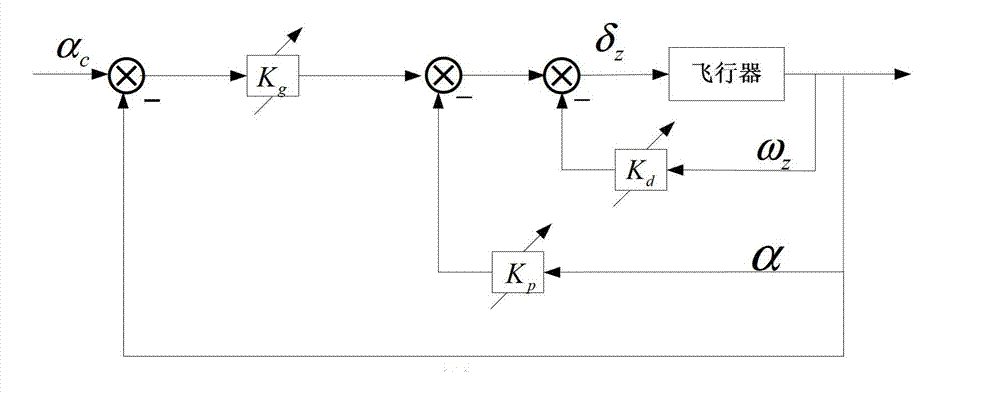
Fine anti-interference tracking controller of flexible hypersonic vehicle
ActiveCN102749851ALittle impact on performanceSuppress interferenceAdaptive controlObservational errorControl oriented
The invention relates to a fine anti-interference tracking controller of a flexible hypersonic vehicle. A method for constructing the fine anti-interference tracking controller comprises the following steps of: (1) building a longitudinal model of the flexible hypersonic vehicle; (2) building a multisource interference system model of the flexible hypersonic vehicle based on the longitudinal model in the step (1): firstly, building a control-oriented nominal model; then regarding an elastic mode as interference and building an elastic mode interference model; and finally, building a multisource interference system model by combining the above two models and considering measurement errors, parameter uncertainty, external interference, etc.; (3) designing a nonlinear disturbance observer to estimate the elastic mode interference based on the multisource interference system model in the step (2); and (4) constructing the fine anti-interference dynamic reverse composite tracking controller based on the nonlinear disturbance observer in the step (3). The fine anti-interference tracking controller has the advantages of high anti-interference performance, rapid tracking speed, high control accuracy, etc., and applies to high accuracy tracking control of the height and the speed of the flexible hypersonic vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High-speed axisymmetric aircraft composite control method
InactiveCN103913991AAvoid Control Coupling ProblemsReduce consumptionSimulator controlControl orientedRudder
The invention discloses a high-speed axisymmetric aircraft composite control method. The high-speed axisymmetric aircraft composite control method is used for solving the technical problem of poor stability in an existing interceptor missile direct force and aerodynamic force composite control method. According to the technical scheme, a varying centroid and pneumatic rudder composite control are adopted, based on defining a varying centroid control mode, an instruct allocation strategy under a composite control scheme is formulated; a dynamical model for control is established through force analysis of a high-speed aircraft; an overall scheme of a varying centroid mechanism is further determined; then ballistic characteristic points are taken to finish design of a control system. According to the high-speed axisymmetric aircraft composite control method, the varying centroid mechanism is introduced, so that the technical problem of poor stability of a background technology control method is effectively avoided, larger control torque is obtained while energy consumption is reduced as much as possible, and reentry flight of the high-speed aircraft for a long time in a large airspace is facilitated; a composite mode with the pneumatic rudder is adopted, so that work pattern of a sliding block executing mechanism is simplified, and system stability is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
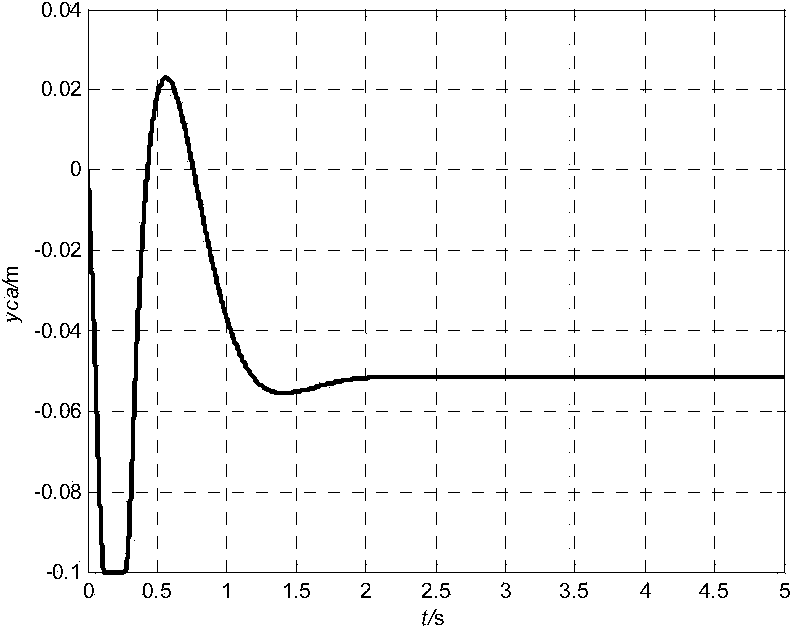
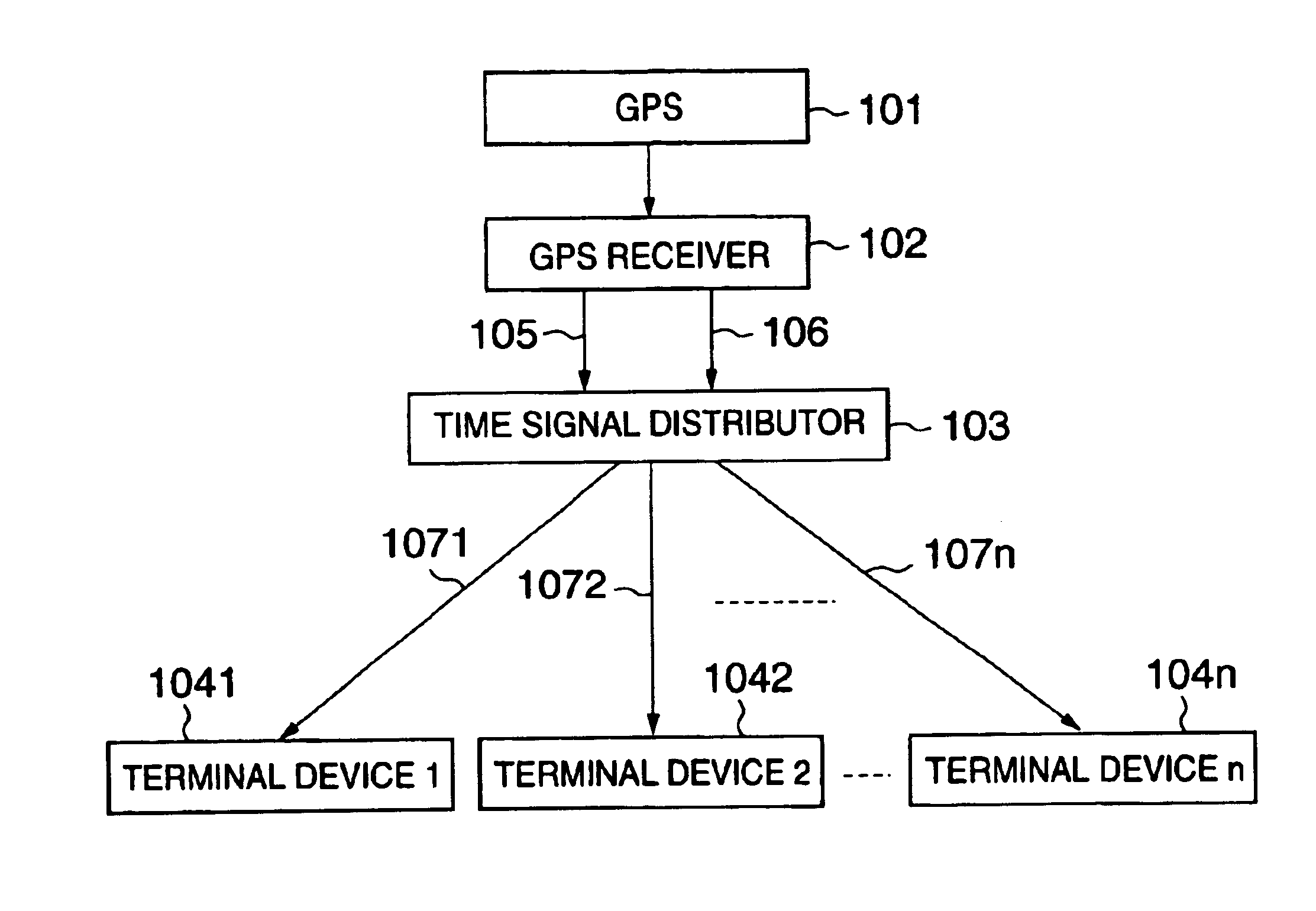
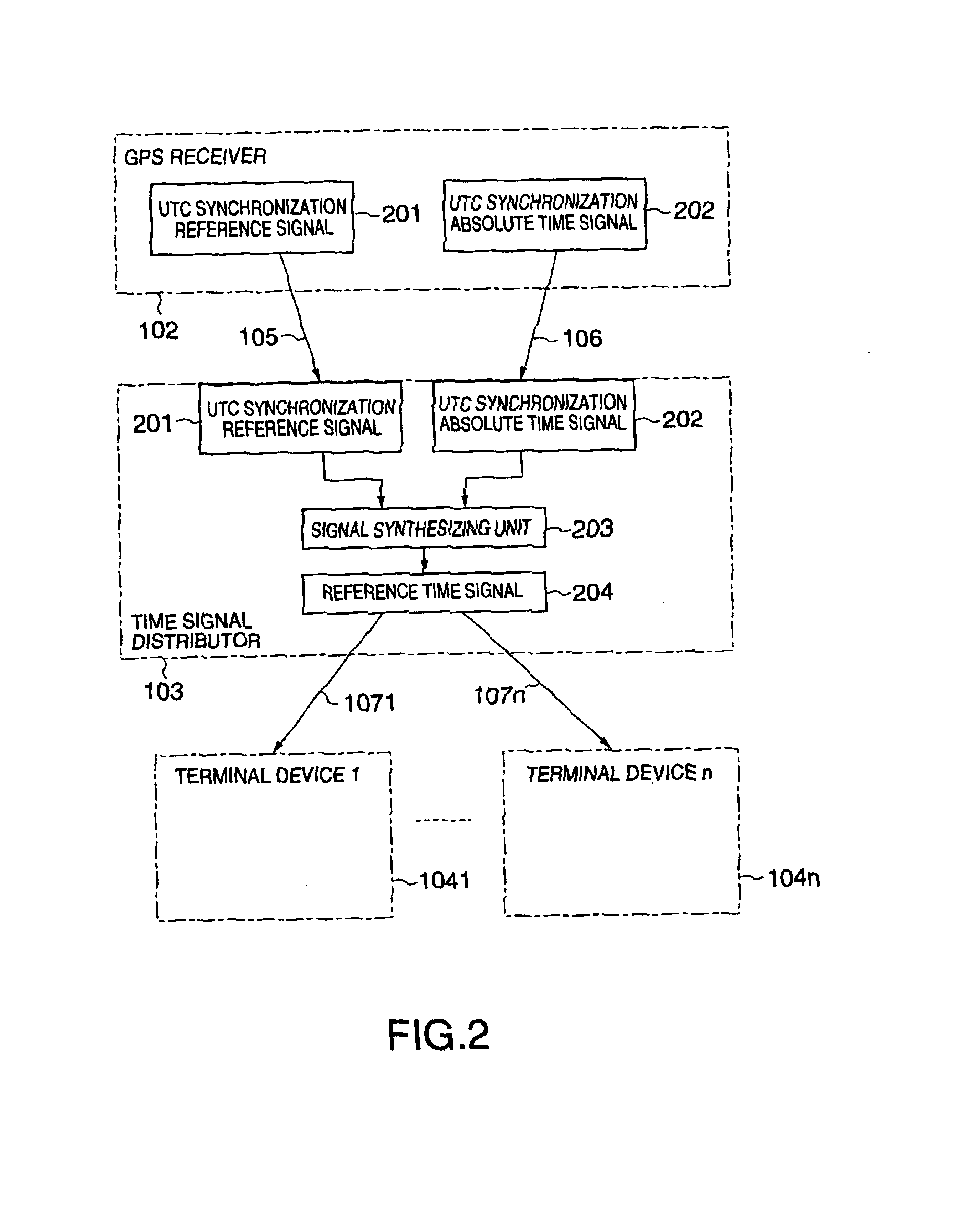
Time synchronizing system
InactiveUS6847691B2Improve accuracyGood economical characteristicSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationControl orientedData synchronization
A time synchronization system comprises a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver for receiving a time signal from a Global Positioning System (GPS), and outputting a UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) synchronization reference signal synchronizing with UTC and a UTC synchronization absolute time signal, and a time signal distributor for generating a reference time signal synchronizing with UTC from the synchronization reference signal and the absolute time signal, and transmits this reference time signal in distribution to a plurality of distributed control oriented terminal devices. The time synchronization between the plurality of distributed control oriented terminal devices can be thereby taken.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
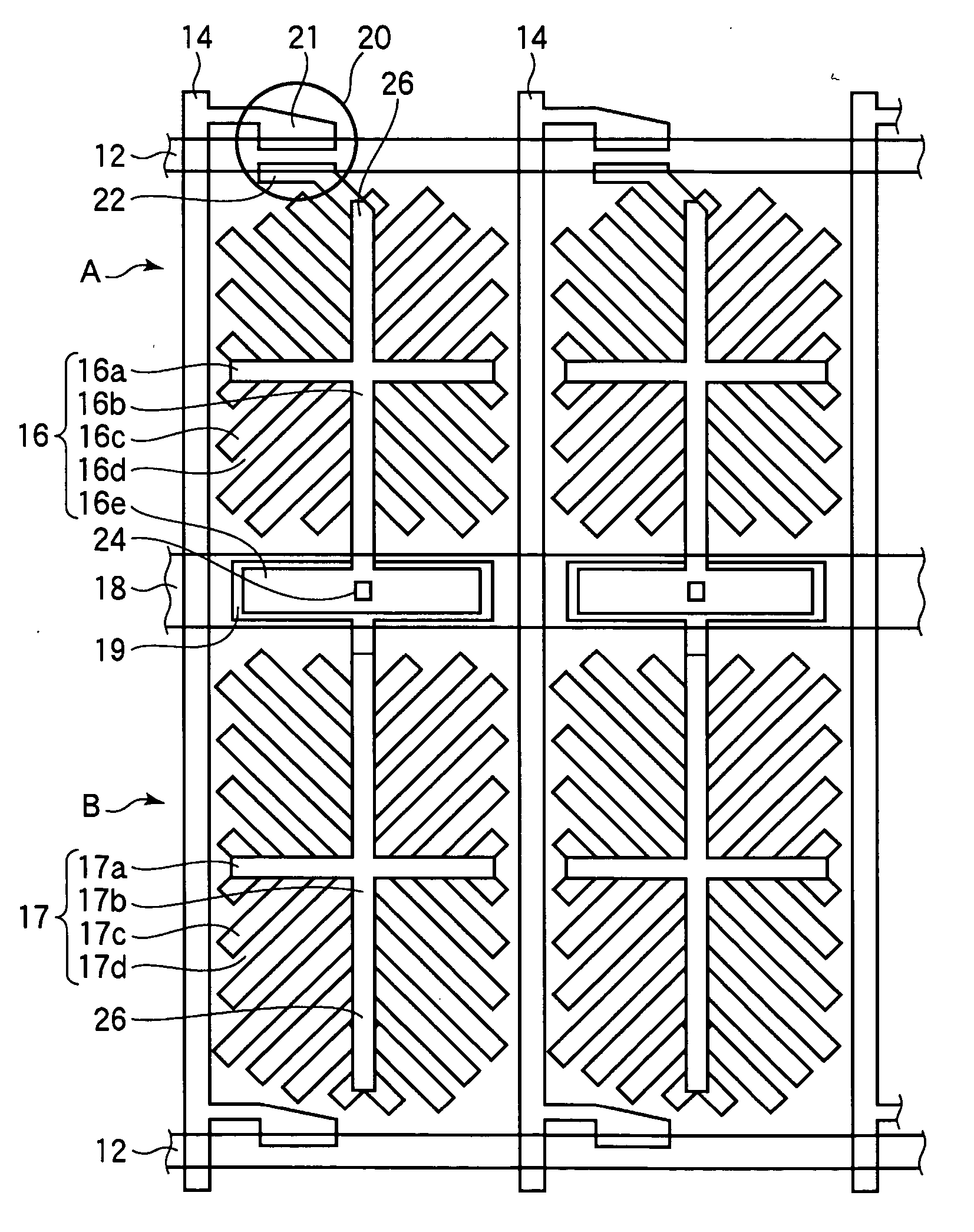
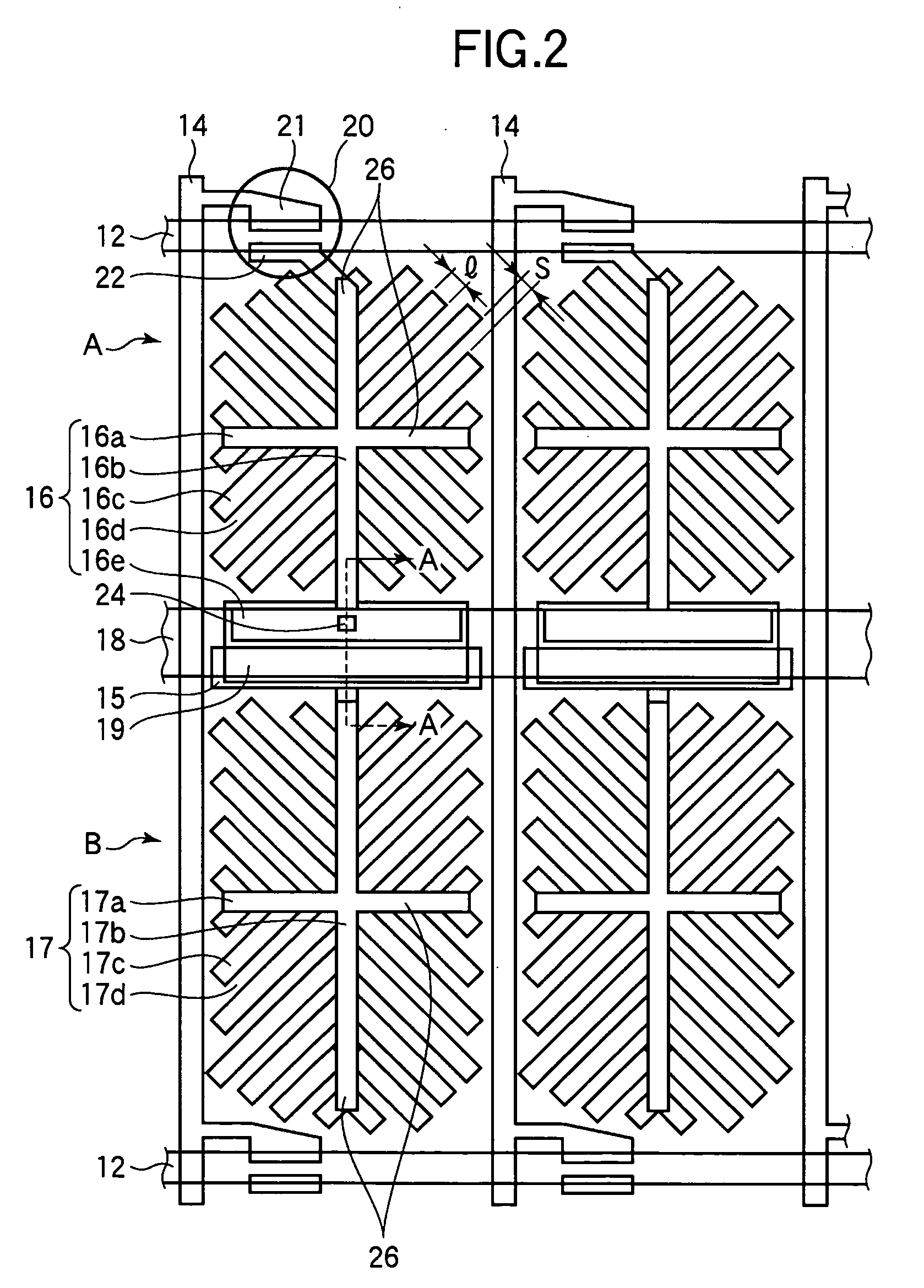
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20070097279A1Improve display qualityEasy alignmentNon-linear opticsCapacitanceControl oriented
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display device for use in a display unit of electronic appliances, which can attain excellent display characteristics, the display device having a control capacitance electrode which is electrically connected to a source electrode of a thin film transistor; a storage capacitance electrode which is electrically connected to the control capacitance electrode; a pixel electrode provided with a direct coupling part which is electrically connected to the control capacitance electrode, and a capacitive coupling part which is disposed and faced to the control capacitance electrode through an insulating film as it is isolated from the direct coupling part; and a dummy capacitive coupling part which is formed in a space between the direct coupling part and the capacitive coupling part, disposed and faced to the storage capacitance electrode through the protective film, and improves alignment defect of liquid crystals on the capacitive coupling part.
Owner:SHARP KK
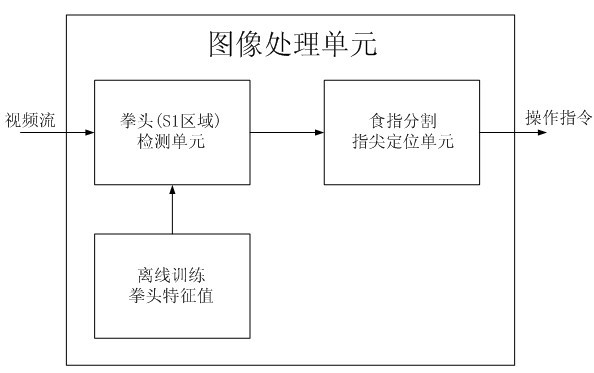
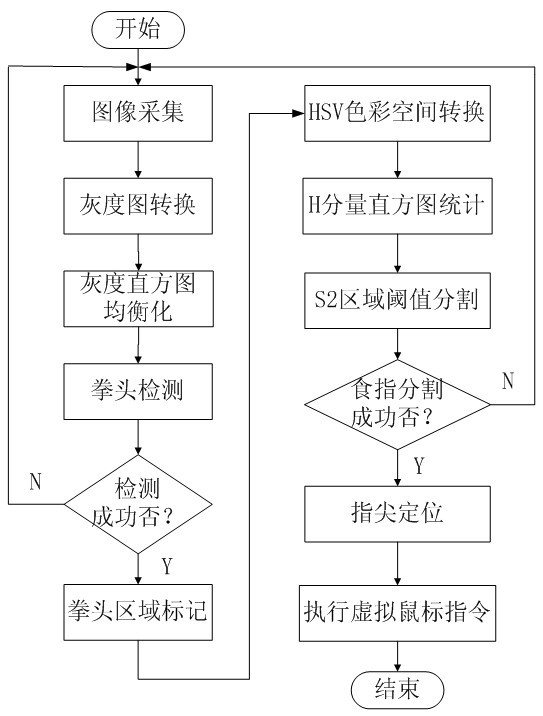
Television control-oriented finger-mouse interaction method
InactiveCN102200834AReduce the effects of light changesImprove detection rateInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsControl orientedInteraction systems
The invention discloses a television control-oriented finger-mouse interaction method. A television interaction system is characterized by comprising the following steps of: acquiring an image by using a built-in camera of a television; performing image detection on the acquired image to obtain a gesture area; and locating a finger and obtaining a motion coordinate of the finger by using a characteristic of the gesture area, so that an execution device in the television completes the corresponding movement and click operation of a mouse pointer according to the coordinate motion trajectory and residence time of the finger. By the method, the remote control operation of the television can be performed through gesture movement, so a man-machine interaction manner of the television is more intelligent and natural. The long-distance natural remote control manner has remarkable promotion effect on the field of television application under a trend of tri-networks integration.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for interacting with a user in an experiential environment
InactiveUS20090012849A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsDiscounts/incentivesControl orientedHuman–computer interaction
A method and system for provides a user with an ability to capture a sample of an experiential environment and deliver that sample to an interactive service to trigger one or more predetermined events. In exemplary embodiments of the invention such triggered events include the delivery of information and services to the user, the execution of tasks and instructions by the service on the user's behalf, communication events; surveillance events and other control-oriented events that are responsive to the user's wishes. In other exemplary embodiments of the invention, the triggered events include transaction-oriented events, entertainment events, and events associated with enhancements to human ability or function.
Owner:APPLE INC
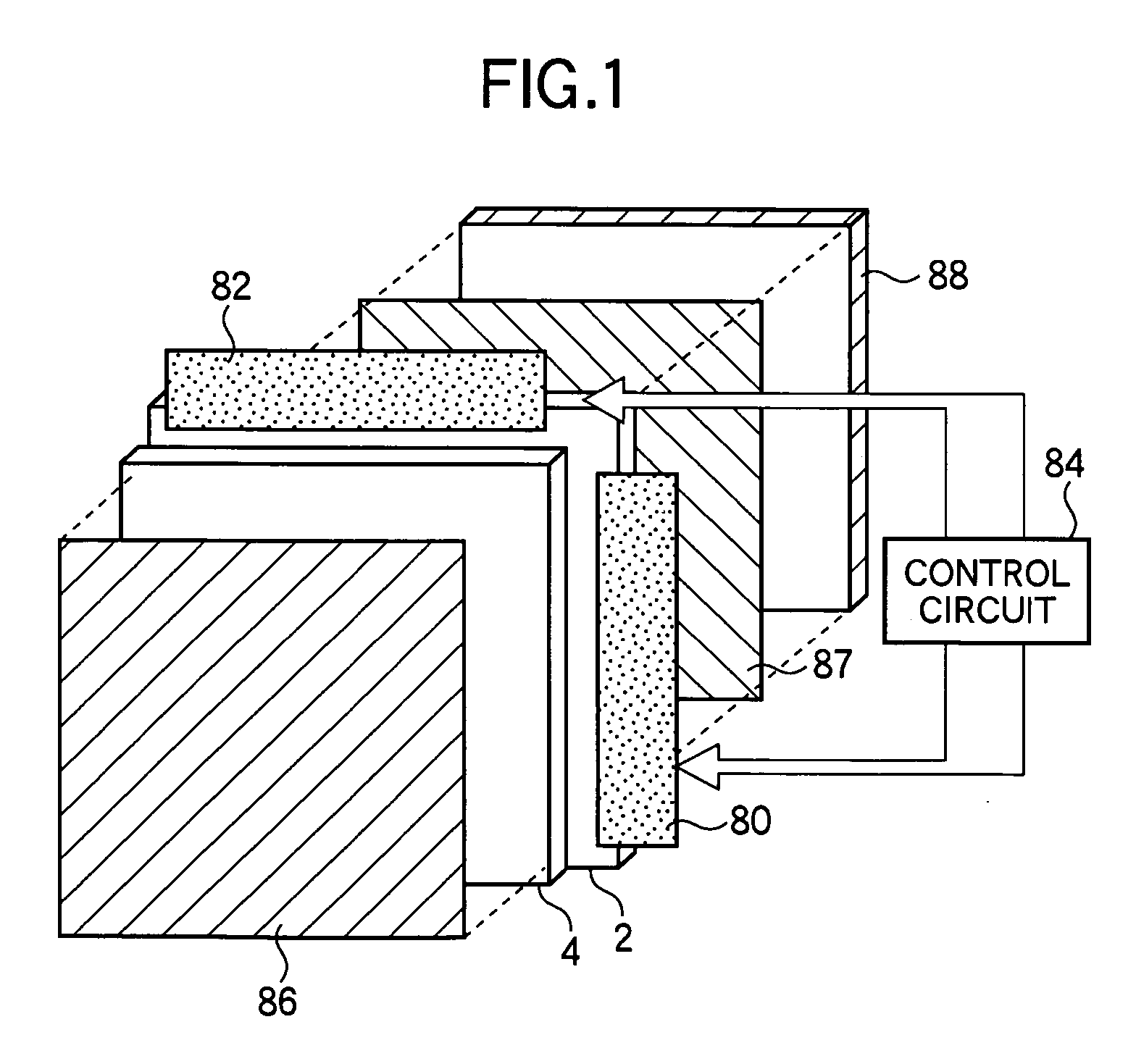
Laboratory apparatus with a control device
ActiveUS20070132723A1Promote exchangeEasy to set upInput/output for user-computer interactionContact mechanismsOperator interfaceControl oriented
A laboratory apparatus having at least one control device (4) comprising an electric printed-circuit board (15) of the control device (4) that is disposed on an instrument body (2) of the laboratory apparatus (1) and has at least one electric control element (16, 18), at least one operator interface (6) of the control device (4) including at least one operator control (11, 33); a retaining device (29, 30) for detachably holding the operator interface (6) on the instrument body (2) with the operator control (11, 33) oriented to the control element (16, 18), and a mechanical and / or magnetic connection for detachably joining the control element (16, 18) mechanically and / or magnetically to the operator control (11, 33).
Owner:EPPENDORF SE
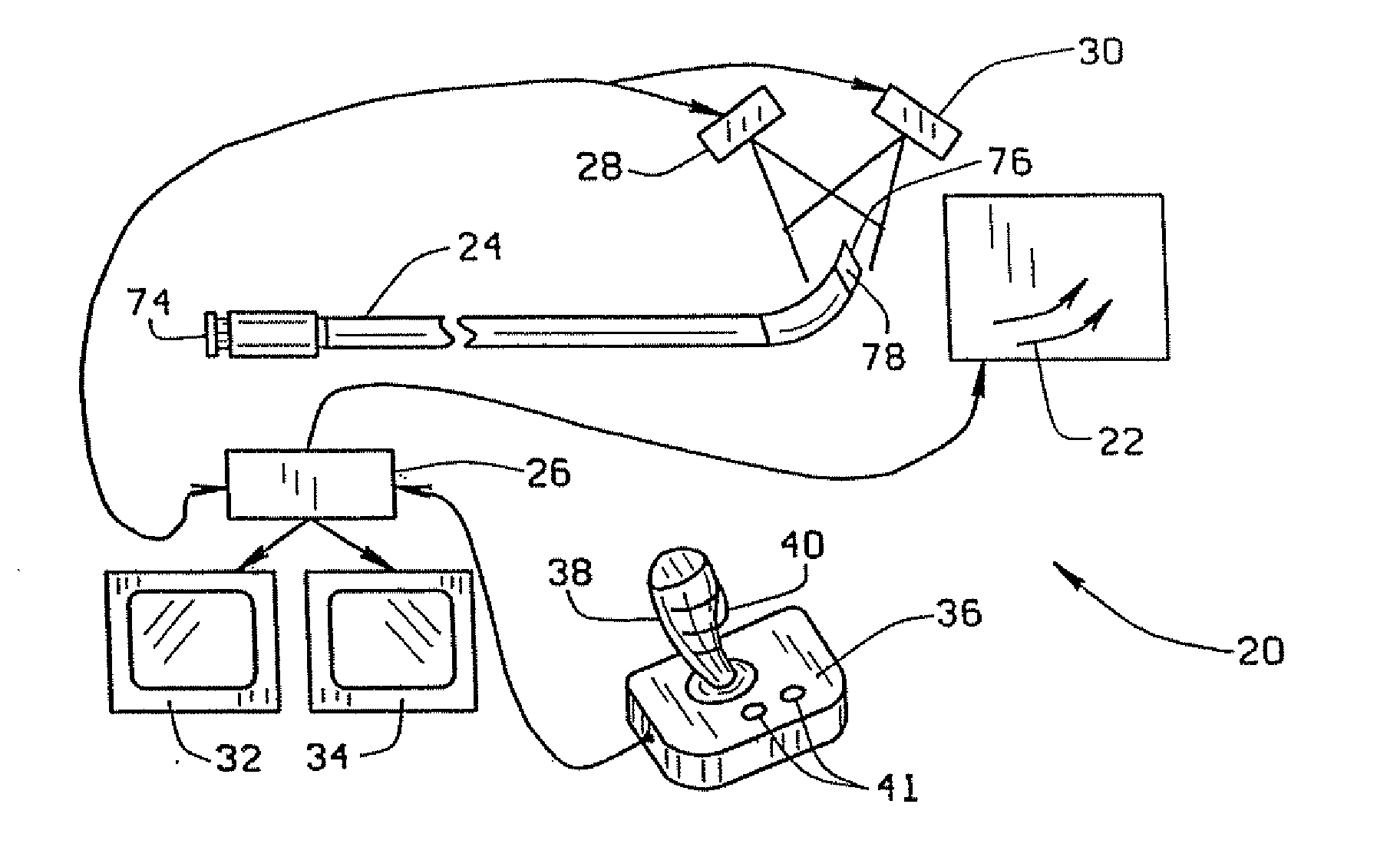
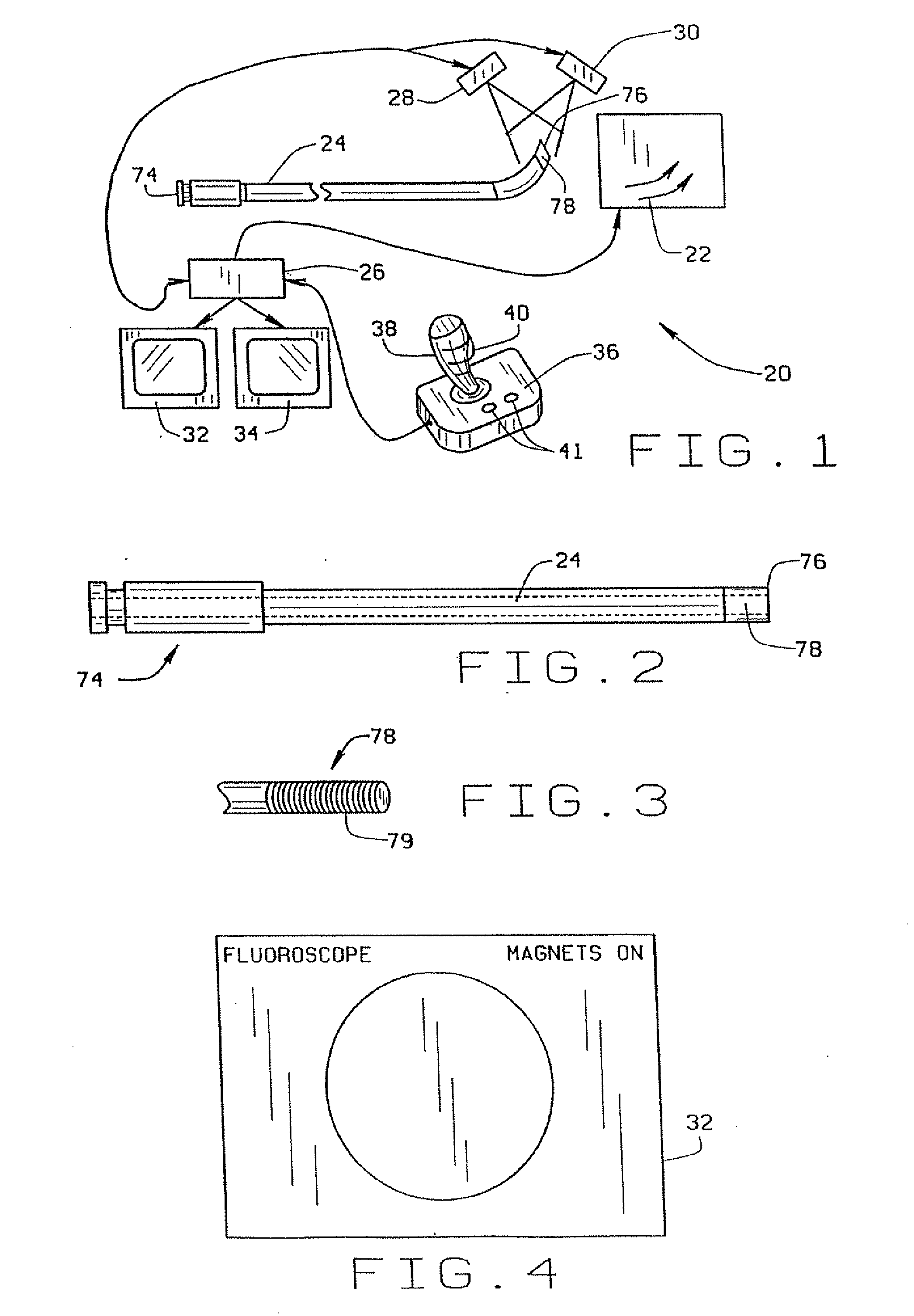
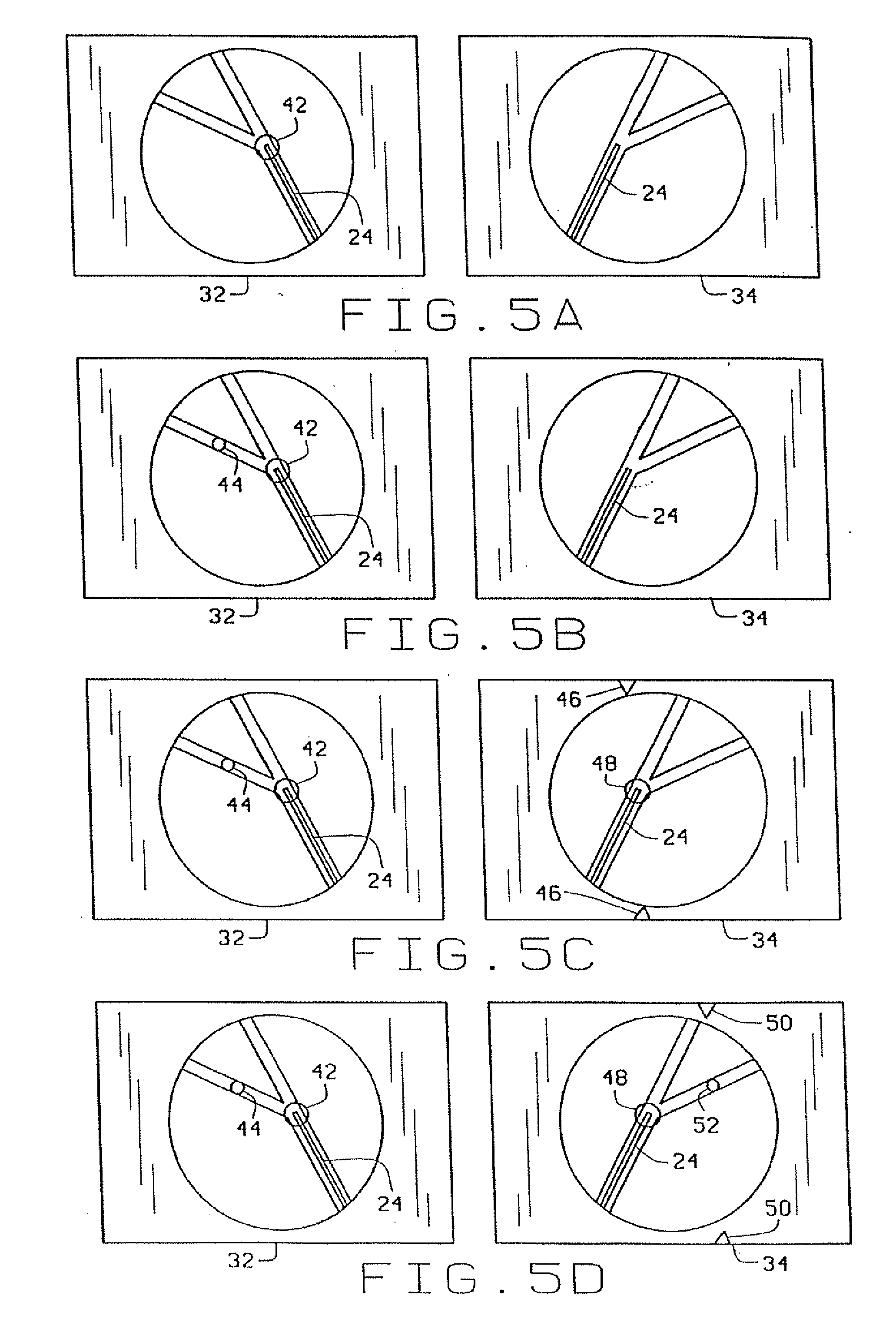
Method and apparatus for magnetically controlling catheters in body lumens and cavities
InactiveUS20100063385A1Fast and efficient navigationEasy to useElectrotherapySurgical adhesivesControl orientedDisplay device
A method of navigating a magnet-tipped distal end of an elongate medical device through the body includes providing an image display of the part of the body through which the medical device is being navigated and using the display to input the desired path of the medical device by identifying points on the desired path on the display. The magnetic field needed to orient the end of the medical device in the direction of the desired path as indicated on the display is then determined. In one embodiment where only points on the desired path are identified, the field direction is the direction indicated by the points on the desired path. In a second embodiment, where points on the current path and the desired path are identified, the desired angle of deflection is determined, and the direction of the magnetic field is set to lead this desired angle of deflection by 90° to over-torque the end of the catheter, and the intensity of the field is determined from a table of experimentally determined field intensities for given angles of deflection.The apparatus for navigating a magnet-tipped medical device through the body in accordance with the invention includes a magnet system for applying a magnetic field to the magnet-tipped distal end of the medical device to orient the distal end of the medical device; a computer for controlling the magnet system to generate a specified magnetic field in the body part; first and second imaging devices connected to the computer, for providing bi-planar images of the body part through which the medical device is being navigated; first and second displays for displaying the images from the image devices; and an input device for inputting points identifying the desired path of the medical device on each of the displays. The computer is programmed to determine the magnetic field necessary to control orient the medical device on the path input on the displays.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
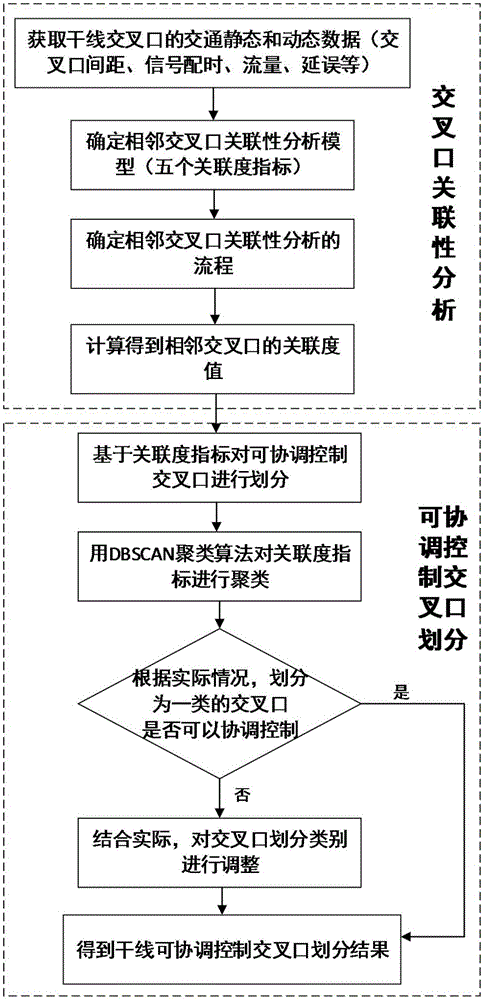
Coordinated control oriented trunk line crossing correlation analysis and division method
InactiveCN105825690AComprehensive correlation analysis methodAccurately quantify the degree of associationRoad vehicles traffic controlControl orientedTraffic capacity
The invention discloses a coordinated control oriented trunk line crossing correlation analysis and division method. The method comprises the steps that 1, traffic parameters used for correlation analysis of crossings of a trunk line are acquired; 2, signal timing plan data generated when single-point control is executed on all the crossings of the trunk line is acquired; 3, the correlation degree of the adjacent crossings is determined; 4, the coordinated control crossings of the trunk line are divided. According to the method, a comprehensive correlation degree index is set up to express the relevancy between the adjacent signal crossings of the trunk line, five key factors influencing the relevancy of the adjacent crossings are comprehensively considered, maximization of the phase coordinating and traffic flow traffic capacity coordinating capacity is adopted as a main target, the correlation degree of the adjacent crossings is accurately quantized, and the scientific and comprehensive correlation analysis method is set up.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
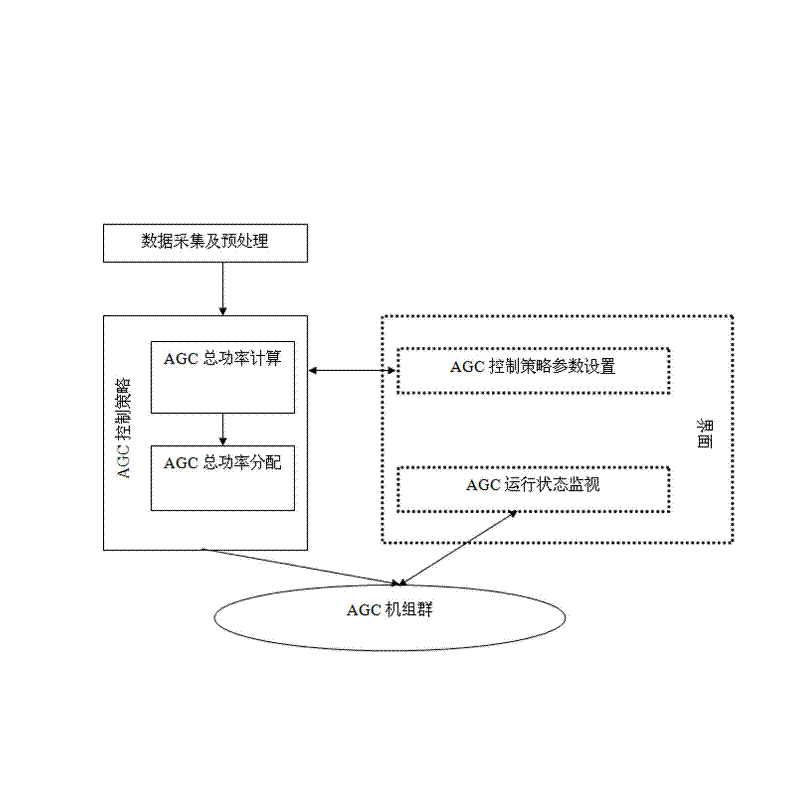
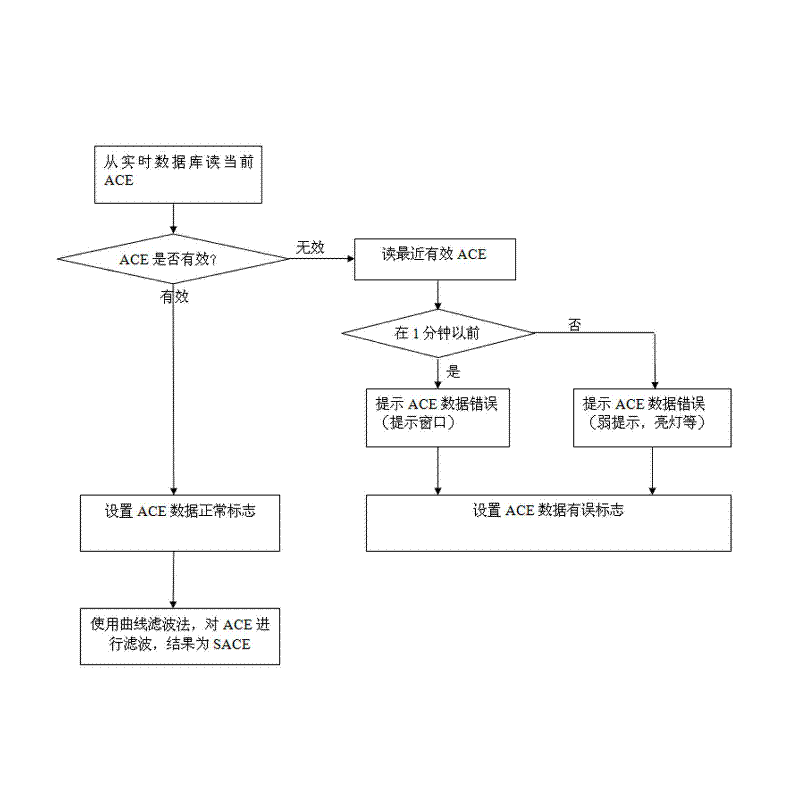
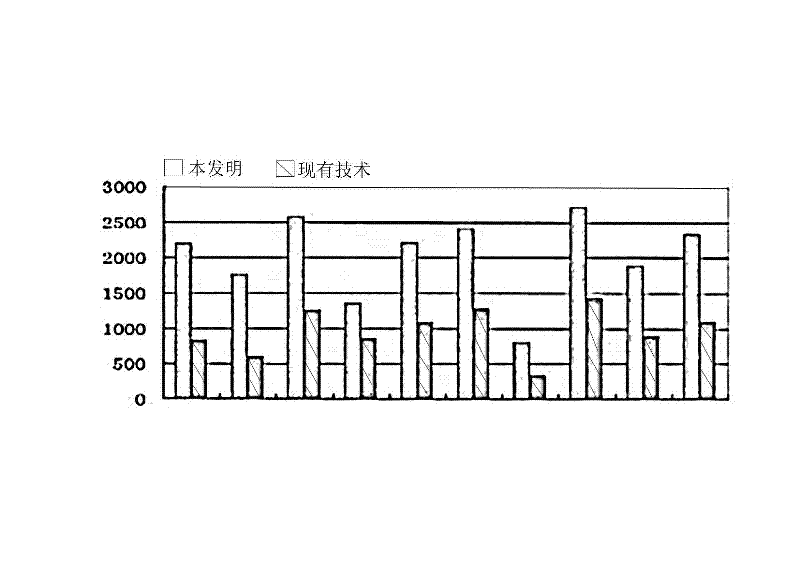
Control method of AGC facing control performance standard (CPS) and control system thereof
InactiveCN102497147AReduce the number of adjustmentsReduce wearElectric generator controlAutomatic Generation ControlControl oriented
The invention relates to a control method of AGC facing a control performance standard (CPS) and a control system thereof. Through setting structures of a data acquisition and pretreatment portion, an AGC total power calculating portion, an AGC total power distribution portion, a parameter set interface, an AGC state monitoring portion and the like, based on a frequency difference expectation, AGC regulating variable can be determined and an integral control link is canceled so that AGC set adjustment times can be effectively reduced. Set wear can be greatly reduced and energy consumption can be effective reduced too. The method and the system are beneficial to realize energy saving and emission reduction for power grid.
Owner:STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Automatic control method of cigarette throwing production flow
InactiveCN101324792ACircumstances Affecting AuthenticityGuaranteed accuracyTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlControl orientedProduction line
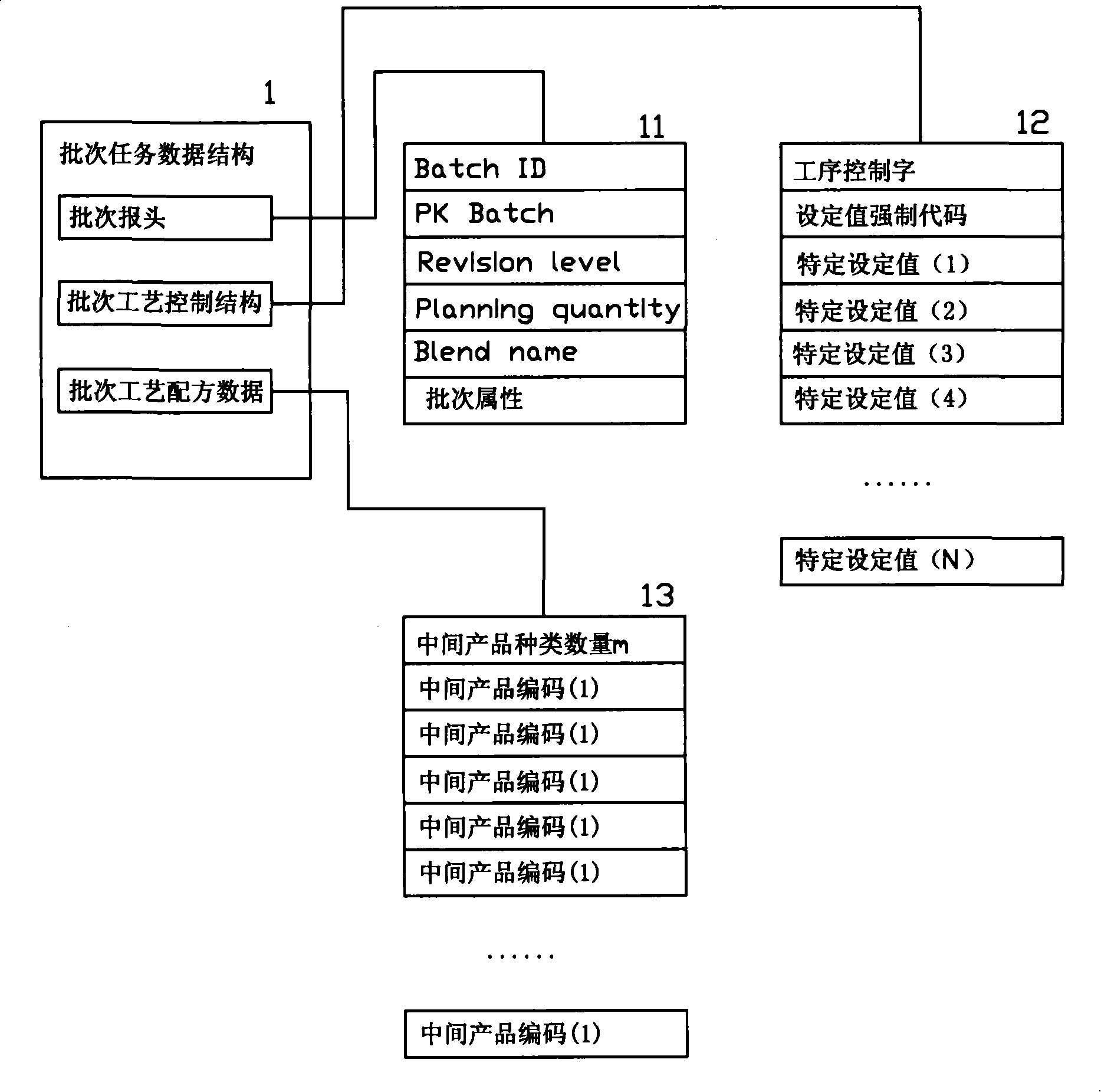
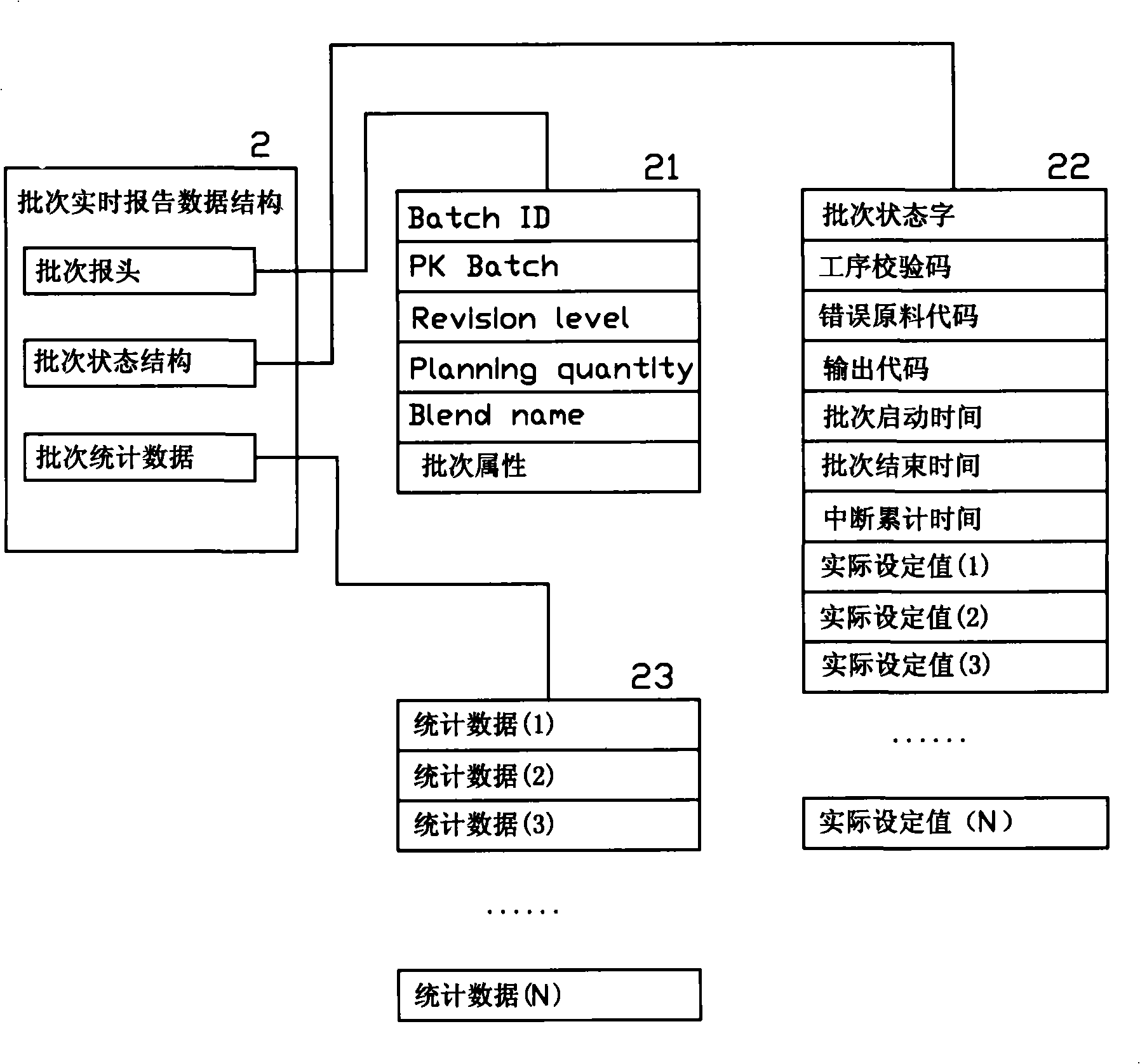
The invention provides an automatic control method for the production flow of cut tobacco of cigarettes, which comprises the steps as follows: an upper system packages the controlling parameters of the production process into controlling parameter packages according to the batches, and issues the controlling parameter packages to production line segment control levels; the production line segment control levels control the control units of the production line segment control levels according to the set controlling parameters of the controlling parameter packages, thus completing the productive tasks of the corresponding batches in turn; during the production process, the production line segment control levels temporarily save the synchronously produced batch data in temporary storage areas thereof, and transmit the batch data to the upper system on completion of the production of the batches. The cut tobacco production line control levels convert control orientation into management orientation by applying batch control to the production line control levels. Besides the automatic control function of the prior production process, the automatic control method further achieves the production management and process quality analysis statistical functions based on the batches.
Owner:LONGYAN CIGARETTE FACTORY
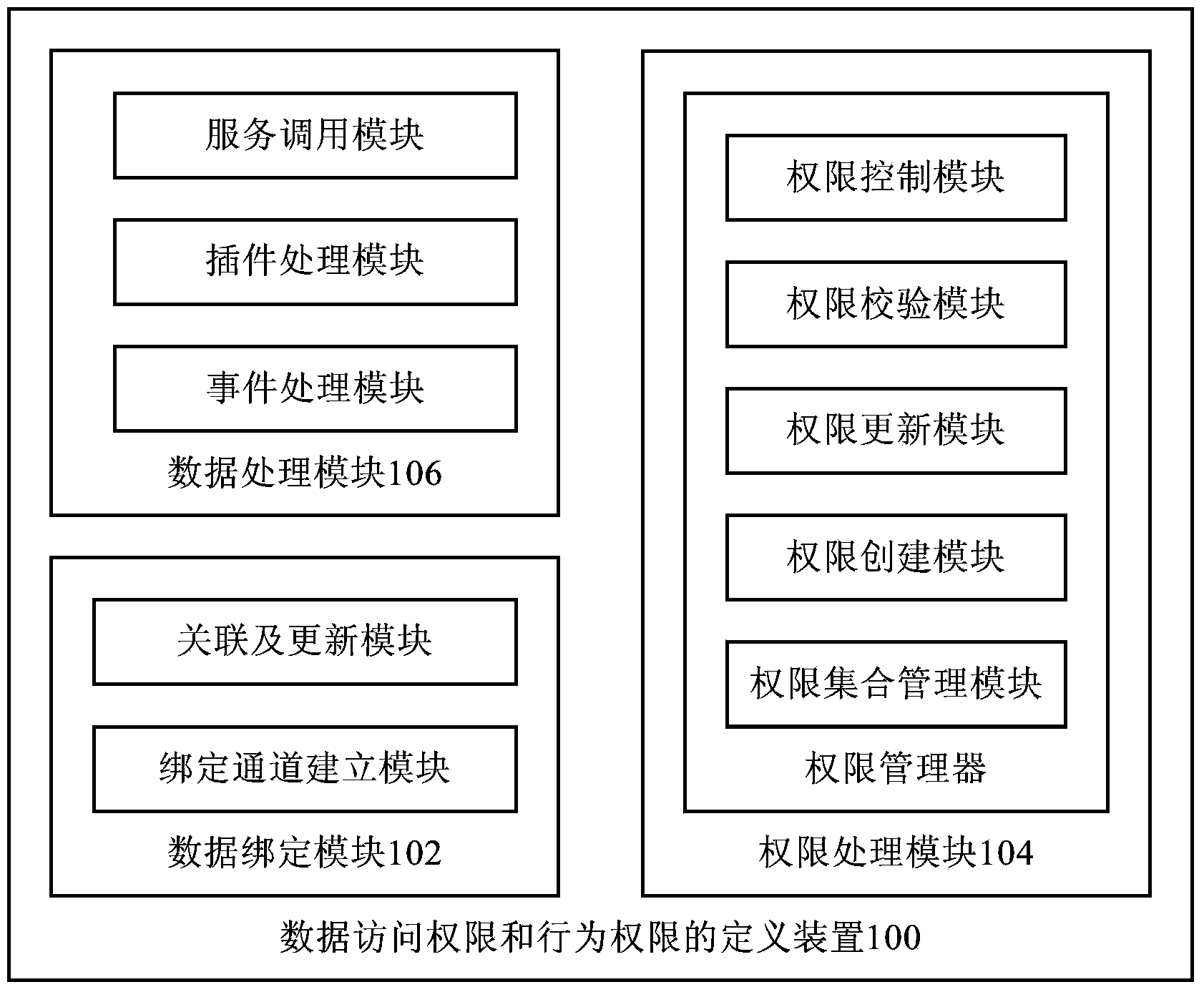
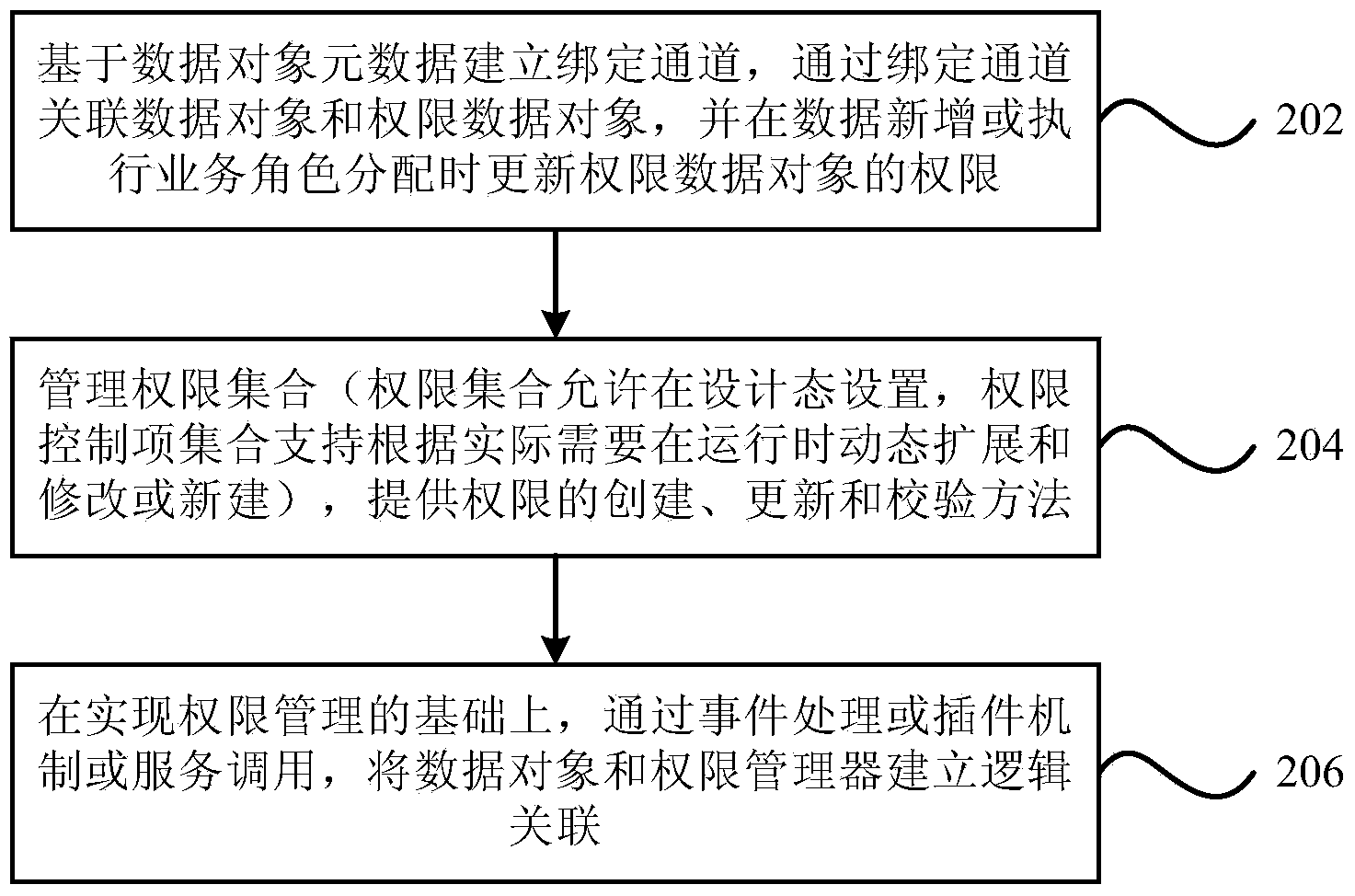
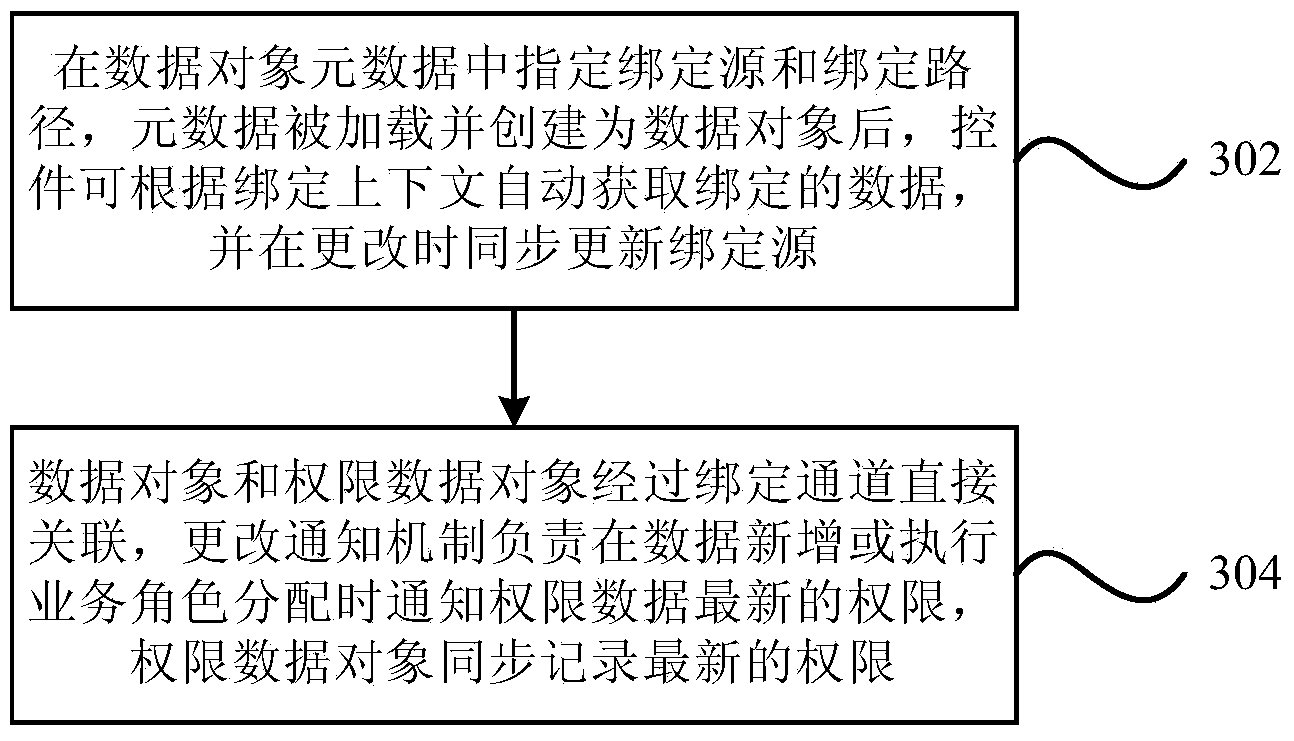
Device and method for defining data access right and behavior right
The invention provides a device for defining a data access right and a behavior right. The device comprises a data binding module, a right processing module and a data processing module, wherein the data binding module is used for linking a data object with a right data object through a binding channel established based on metadata of the data object; the right processing module is used for managing a right set and providing right creating, updating and verifying methods according to the link; and the data processing module is used for establishing a logic link for the data object and a right manager through an event handling or plug-in mechanism or service calling. The invention further provides a method for defining the data access right and the behavior right. According to the technical scheme, definitions of dynamic data access right and behavior right can be finished by sufficiently using static data access right and behavior right on the basis of a conventional defining mode of the data access right and the behavior right, and a general and unified defining thought which the dynamic data access right and behavior right participate in and faces control and dynamic extended data access right and behavior right is established.
Owner:YONYOU NETWORK TECH
Input saturation-considered unmanned surface vehicle full-state constraint trajectory tracking control method
The invention discloses an input saturation-considered unmanned surface vehicle full-state constraint trajectory tracking control method, relates to an unmanned surface vehicle control method, and aims at solving the problem that existing unmanned surface vehicle trajectory tracking control-oriented control methods do not process state constraint and saturation problems. According to the method, akinetic model of a 3-degree of freedom and multiple-input-multiple-output unmanned surface vehicle; a saturated closed-loop system is established and a self-adaptive method is selected to estimate squares of unknown interference upper limits and control input difference upper limits; and self-adaptive laws are designed for unknown interferences and control inputs according to the self-adaptive method, and a controller is designed according to a pseudo-inverse condition so as to control the unmanned surface vehicle. The method is suitable for the control of unmanned surface vehicles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
In-plane-control-based active vibration control method for wrinkled film
ActiveCN108897213AReduce vibrationImprove anti-disturbance abilityAdaptive controlControl orientedIn plane
The invention relates to an in-plane-control-based active vibration control method for a wrinkled film. On the basis of the analysis on the influence on dynamic characteristics of a film structure bya wrinkle form, a dynamic model of a wrinkled film is established; according to a modal superposition method, a space vector based on a natural mode of vibration is obtained and dynamic models of thewrinkled film under different loads are established; condensation polymerization is carried out on the dynamic models according to contributions to system vibration deformation by all orders of modes,so that a control-oriented film structural dynamic model is established; and with a model reference adaptive controller, a PID-MRAC control method based on in-plane-control multi-model switching is proposed. According to the method provided by the invention, no actuator needs to be pasted on the surface of the film; the out-of-plane vibration of the film is suppressed effectively; the characteristics of the film are not affected; the high stability of the film structure is ensured; and compared with the conventional PID control method, the in-plane-control-based active vibration control method enables the vibration time to be shortened by about 39.7%.
Owner:BAOJI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI +1
A terminal based on omnidirectional numbering system
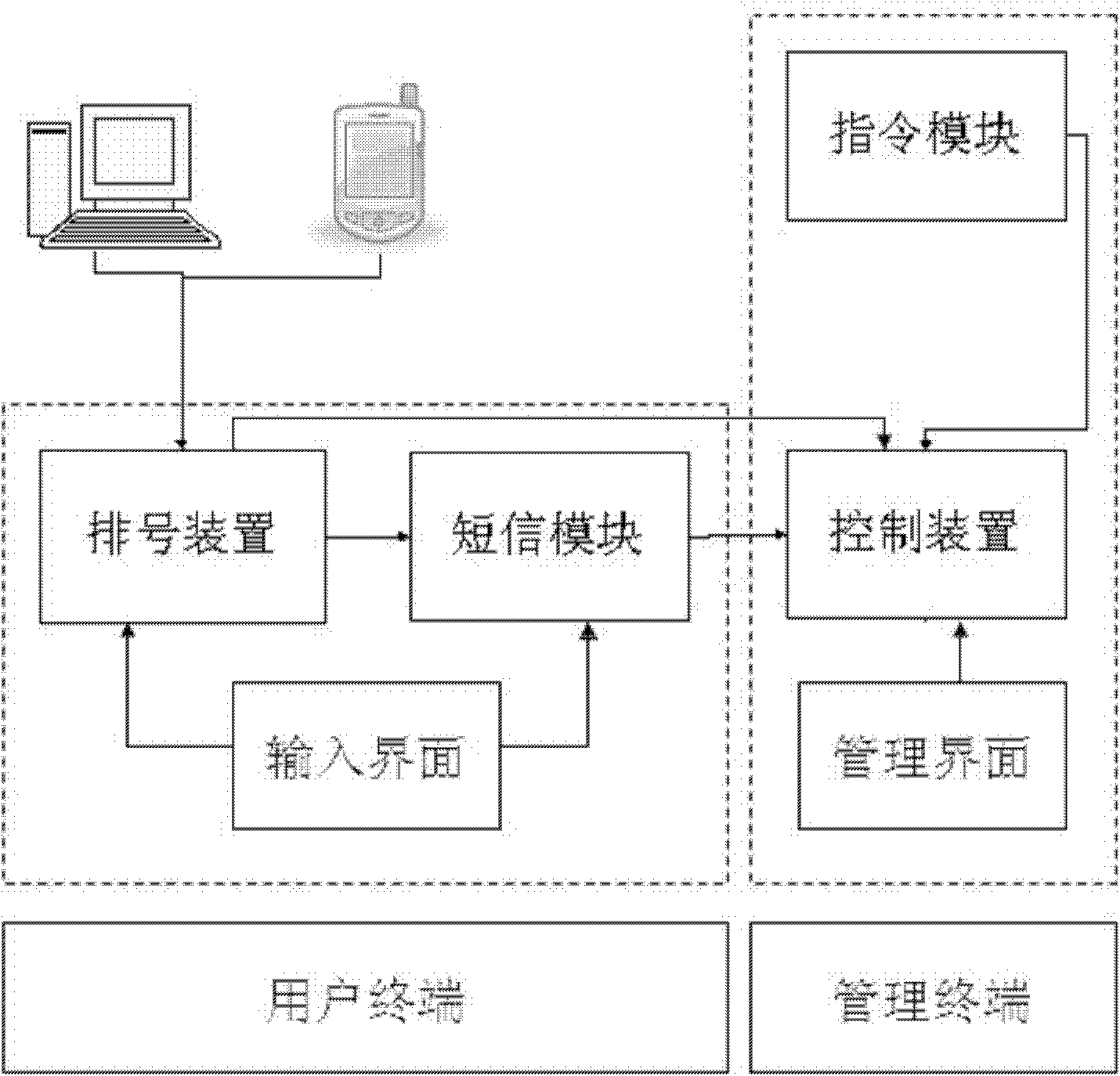
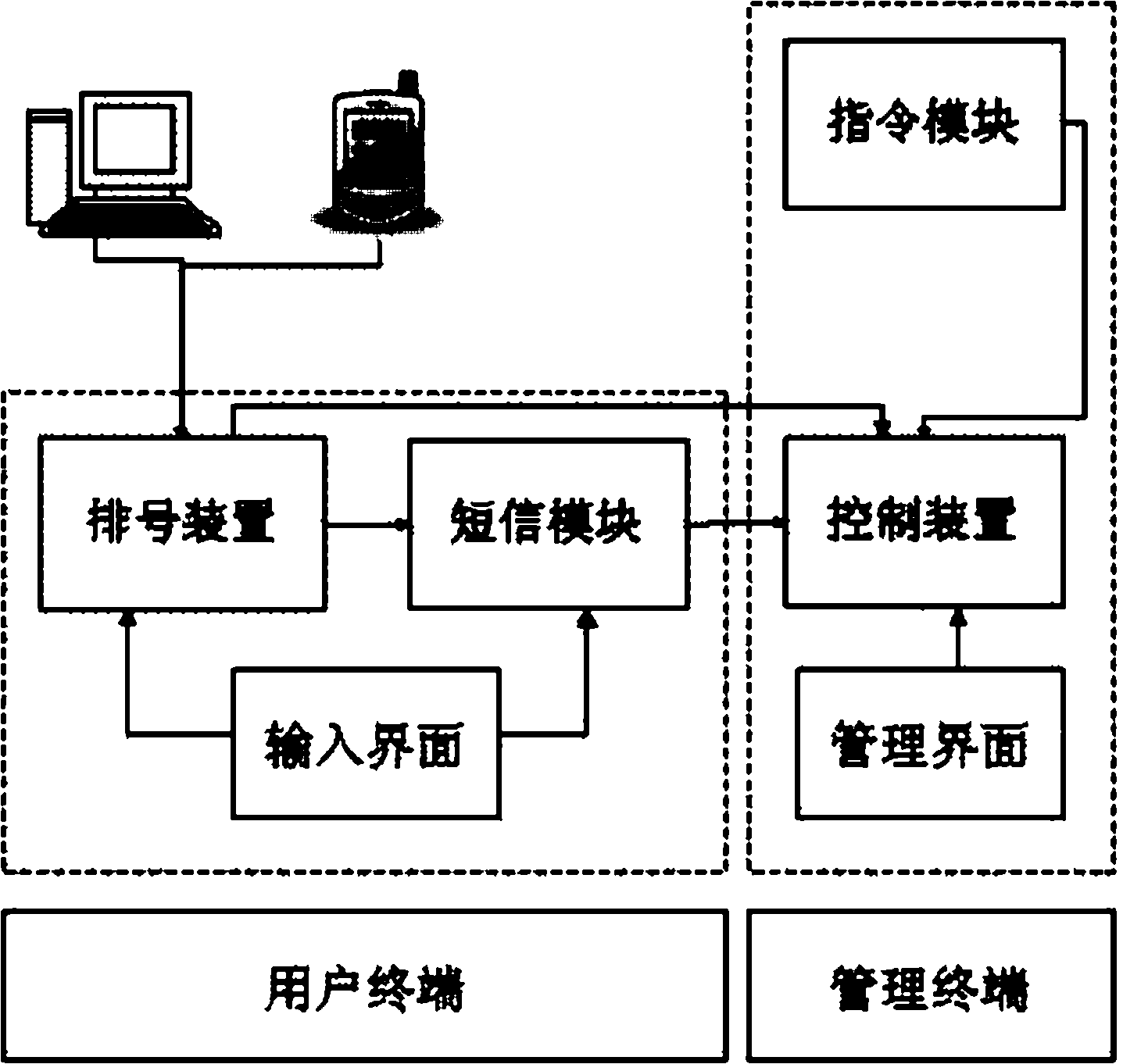
InactiveCN102289854AEasy queuing effectUnderstand qualityChecking apparatusControl orientedUser input
The invention discloses a terminal based on an omnidirectional numbering system, which includes a user terminal and a management terminal. The user terminal includes a numbering device, a short message module and an input interface; the numbering device is equipped with a number-taking module; the short message module is provided with a telephone number input module connected to the numbering device and a short message sending module; The phone number of the mobile phone forms a one-to-one correspondence with the number obtained in the numbering device; the user completes the numbering request through the input interface; the management terminal includes the control device, the command module and the management interface; the control device and the numbering device and the SMS The module is connected to receive the numbering information of the numbering device, and is also connected to the instruction module; the management personnel send instructions to the control device through the management interface. The invention not only realizes the number arrangement through on-site number arrangement and remote number arrangement, but also helps the user to arrange the waiting time more reasonably through the short message reminder near the calling period.
Owner:BEIJING NAVIGATOR SMARTECH CO LTD
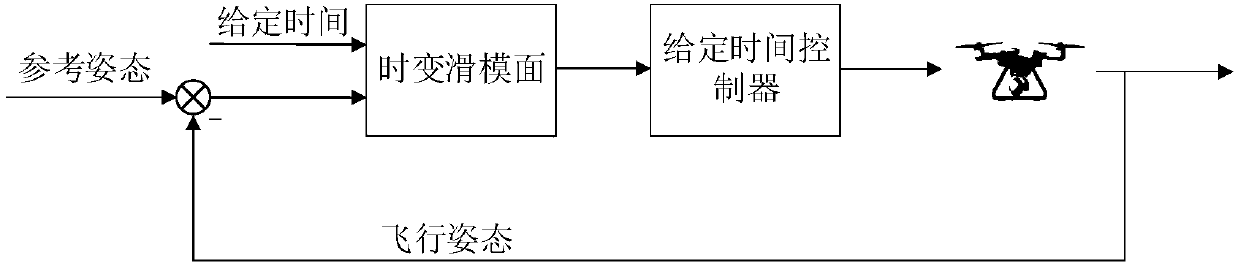
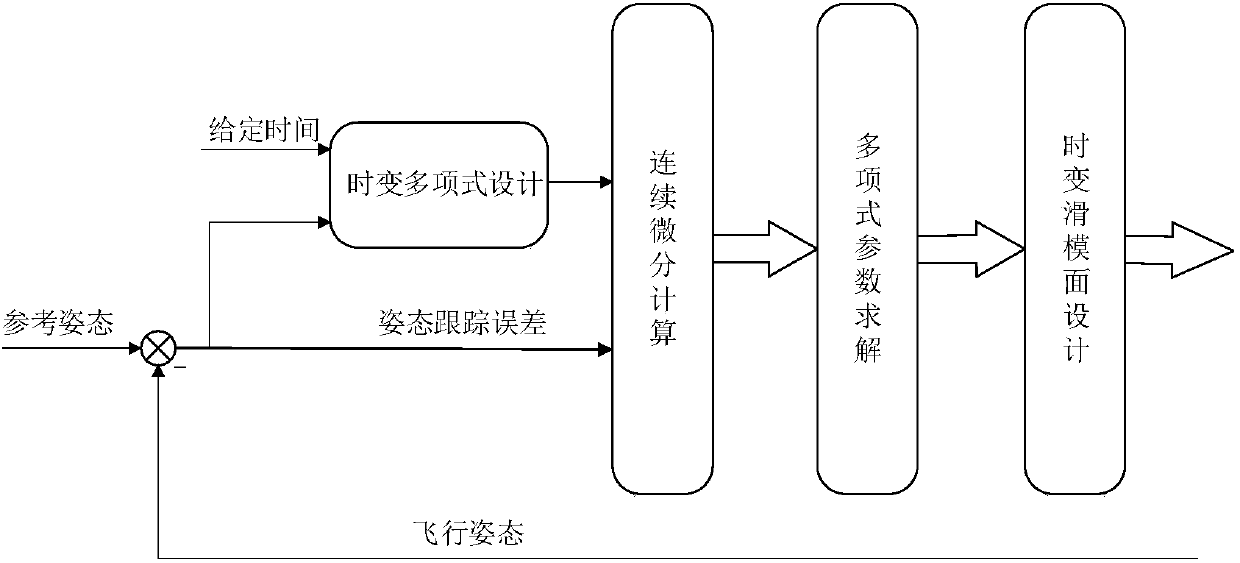
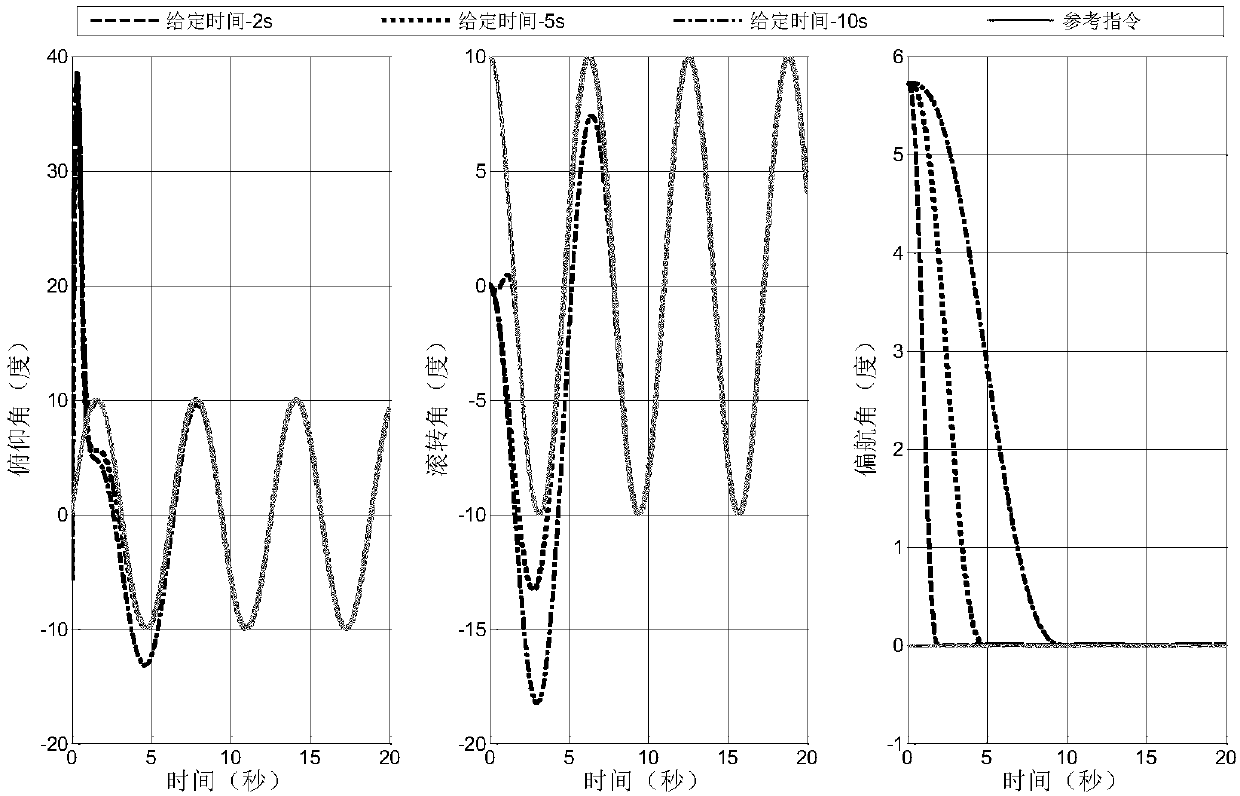
Given time-based quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle high-precision attitude tracking control method
ActiveCN108181920AGood tracking effectImprove robustnessAttitude controlControl orientedAnti jamming
The invention belongs to the unmanned aerial vehicle control technical field and provides a given time-based quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle high-precision attitude tracking control method. With themethod adopted, the convergence time of the attitude tracking of a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle can be manually adjusted, so that the attitude tracking error of the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle can converge within desired time, and the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle can have good tracking performance and anti-jamming capability. The given time-based quadrotor unmanned aerial vehiclehigh-precision attitude tracking control method of the invention has the following steps that: step 1, control oriented quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle attitude model establishment; step 2, given time-based time-varying sliding mode surface design; and step 3, given time-based high-precision continuous controller design. The given time-based quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle high-precision attitude tracking control method of the present invention is mainly applied to the aerial vehicle control conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Comprehensive identification method for motion characteristics of axisymmetric high-speed flight vehicle
InactiveCN103926931AImprove real-time performanceImprove defectsAttitude controlControl orientedMathematical model
The invention discloses a comprehensive identification method for motion characteristics of an axisymmetric high-speed flight vehicle. The comprehensive identification method for the motion characteristics of the axisymmetric high-speed flight vehicle is used for solving the technical problem that an existing self-adaptation attitude control method for a hypersonic flight vehicle is poor in real-time performance. According to the technical scheme, the comprehensive identification method for the motion characteristics of the axisymmetric high-speed flight vehicle comprises the steps that a high-speed flight vehicle full mathematical model is established to deduce a control-oriented attitude motion equation, a characteristic equation is established, a functional relationship between parameters of the characteristic equation and sensor measurement is established, parameters of a control-oriented high-speed flight vehicle characteristic model can be obtained rapidly and directly in an online mode through algebraic calculation, and then the parameters are used for adjusting parameters of a self-adaptation controller. Therefore, an iterative operation process needed by a system identification method is omitted, the efficient and rapid identification method is provided for obtaining of system parameters of the flight vehicle, the requirement of the high-speed flight vehicle for time sensitivity is met, the defects and shortcomings of the system identification method are overcome, and real-time performance of a control method for the hypersonic flight vehicle is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
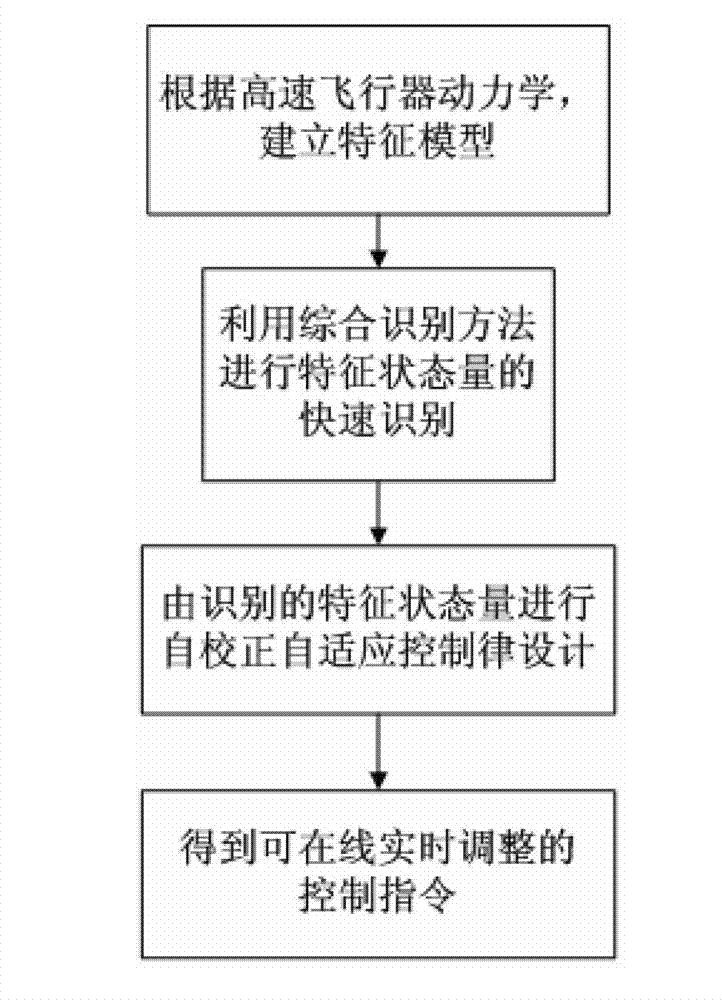
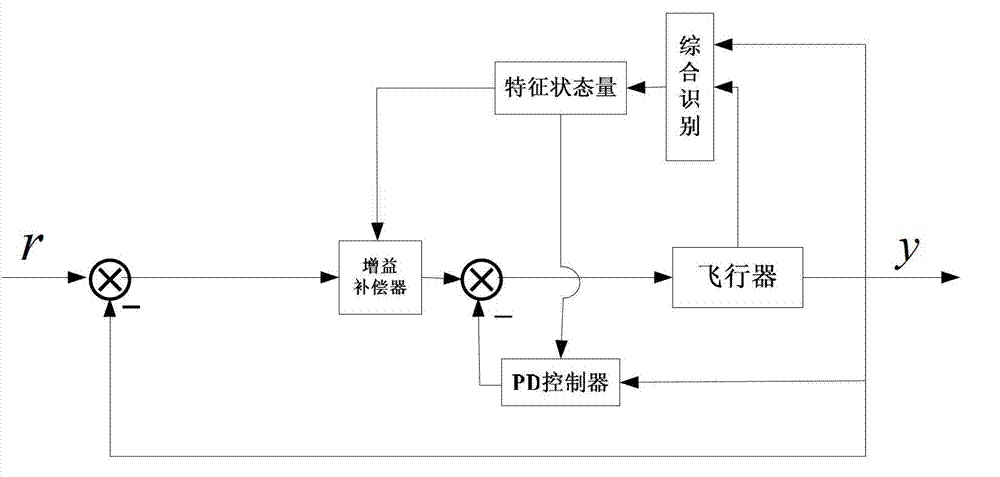
High-speed aircraft self-adaptation control method based on movement state comprehensive identification
The invention discloses a high-speed aircraft self-adaptation control method based on movement state comprehensive identification. The high-speed aircraft self-adaptation control method based on the movement state comprehensive identification is used for solving the technical problem that an existing hypersonic aircraft robust control method based on a characteristic model is long in convergence time. The high-speed aircraft self-adaptation control method based on the movement state comprehensive identification comprises the steps of firstly building a high-speed aircraft model, conducting small perturbation linearization, and obtaining a characteristic model of high-speed aircraft movement states; then on-line building characteristic state quantity of the control oriented characteristic model quickly and measurably; and then designing a self-correcting and self-adaptation control method according to the obtained characteristic model. Due to the fact that the characteristic state quantity of the control oriented characteristic model is quickly obtained through a method of the movement state comprehensive identification, on-line identification is needless, on-line generation of controller parameters can be conducted directly according to real-time dynamic characteristics of an object through a self-correcting and self-adaptation control strategy, and thus the parameters of a controller are enabled to be adjusted in time according to actual situations in an actual fly process.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
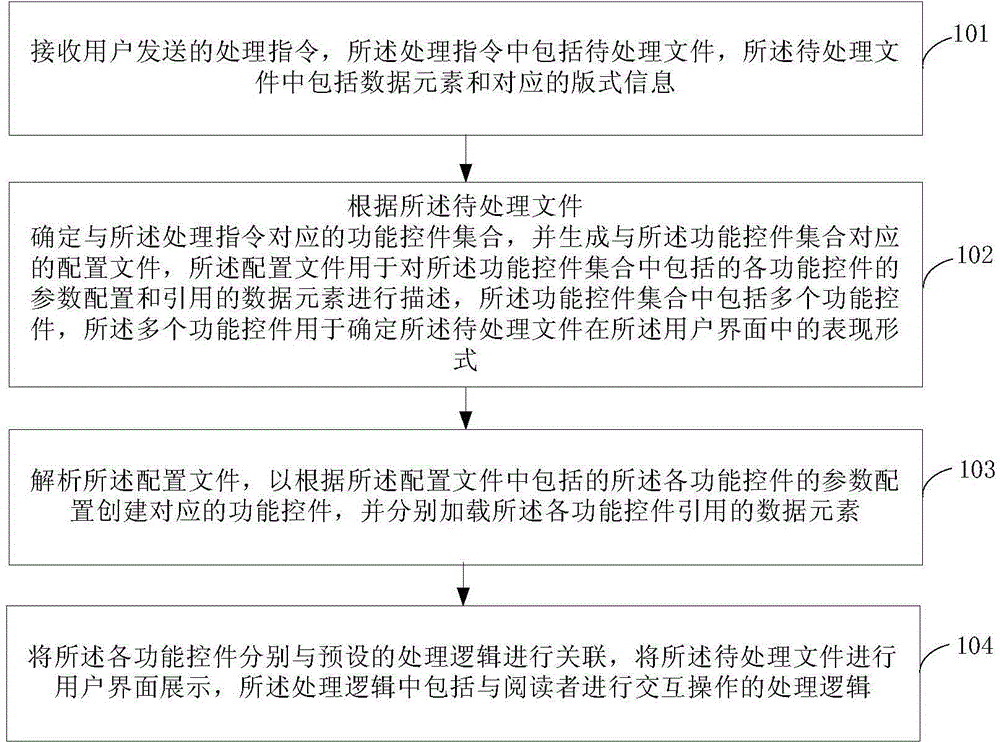
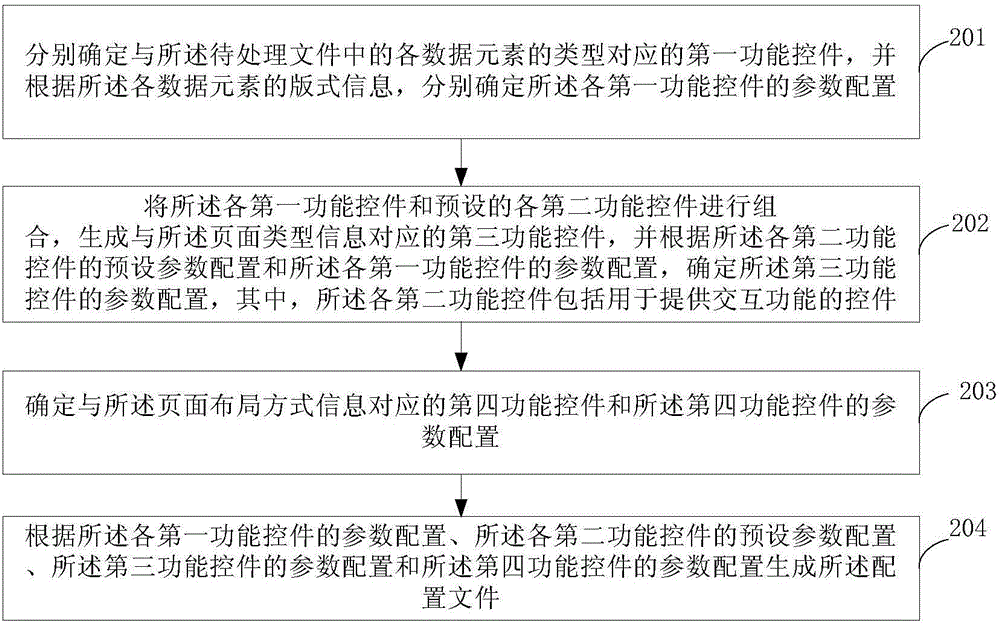
Processing method and apparatus of user interface
InactiveCN105094769AMeet individual needsImprove processing efficiencySpecific program execution arrangementsPersonalizationProcessing Instruction
The present invention provides a processing method and apparatus of a user interface (UI). The method comprises: receiving a processing instruction that comprises a to-be-processed file and that is sent by a user; determining a function control set corresponding to the processing instruction, and generating a configuration file, wherein the configuration file is used for describing parameter configurations and reference data elements of each function control included in the function control set; and parsing the configuration file, creating corresponding function controls according to the parameter configurations of the function controls, and associating the function controls with preset processing logic to show the to-be-processed file in an user interface. The function controls-oriented processing approach facilitates decrease in processing difficulty faced by UI designers, thereby facilitating improvement in the processing efficiency of the user interface. In addition, the processing logic of each function control is configured, so that the display effect of the user interface better meets individual needs of a user.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +1
Information interaction based multi-agent fault detecting and compensating control method
ActiveCN104698839ARealize real-time monitoringResolve interferenceAdaptive controlControl orientedInformation transmission
The invention provides an information interaction based multi-agent fault detecting and compensating control method, and aims at solving the problems that the current distributed multi-agent system easily suffers from fault and simple and feasible real-time fault handling scheme is not provided. The method comprises the steps of modeling for system and fault, wherein the model includes a node dynamics model, an information interaction model and a typical fault model; 2, performing information interaction based multi-agent real-time fault detection; 3, integrating and processing information based on the Gossip algorithm; 4, calculating and applying compensation quantity based on the control quantity; 5, designing binary-loop information based communication, namely, analyzing the communication content of fault nodes starting from an information interaction model, and creating a virtual information transmission channel through the binary-loop information, so as to ensure that the fault handling scheme does not influence the normal work of the system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
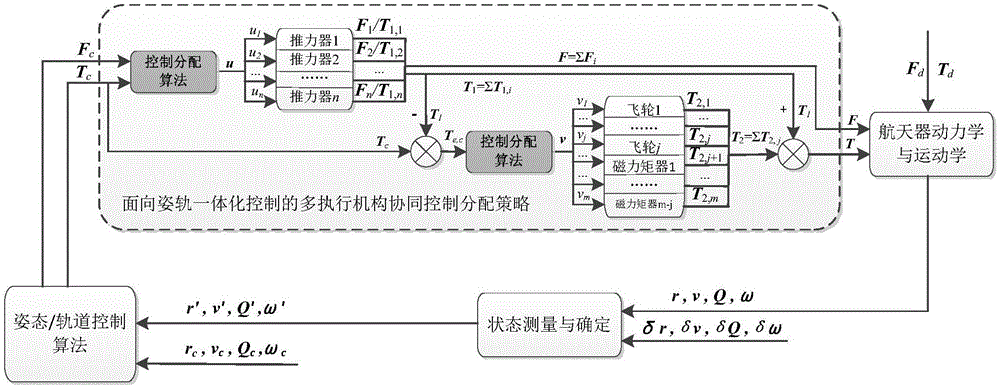
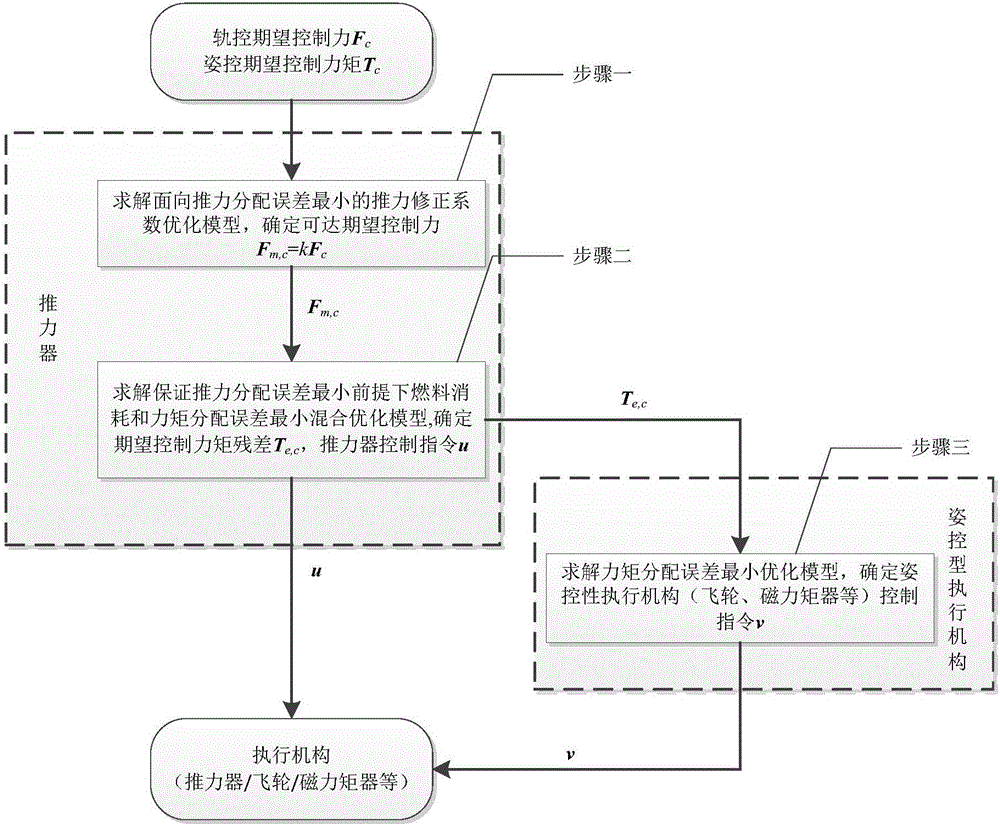
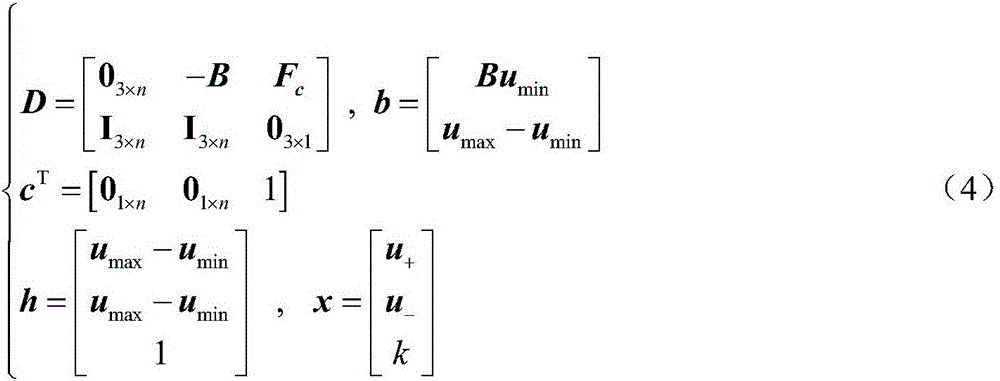
Attitude-orbit integrated control oriented multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method
ActiveCN105892478AEffectively completedImprove efficiencyAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl orientedSpace vehicle control
The invention discloses an attitude-orbit integrated control oriented multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method and relates to a multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method. The invention is aimed at solving the problems of low utilization rate of thruster fuel and little mutual cooperation among execution mechanisms of existing attitude-orbit integrated control oriented distribution strategy. In the invention, the orbit control expectation control force and the attitude control expectation control torque are distributed among the thrusters enabling both orbit control and attitude control; in the distribution process, the needs of track control are met first, and a thruster control distribution scheme proximal to the attitude control expectation control moment is optimally solved without additionally consuming redundant fuel; and after that, the remaining expectation control moment only can be distributed among the attitude-control execution mechanisms. While the attitude-orbit integrated control task is finished, the fuel consumption of the thruster is reduced, the burden on the attitude-control execution mechanisms such as flywheels and magnetic moments is alleviated, and the in-orbit life of spacecraft is prolonged. The method disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of spacecraft control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Experimental device for psychological teaching and psychological testing
InactiveCN106710332AFlow in the right directionCorrect flowDigital data processing detailsPsychotechnic devicesControl orientedPsychological testing
The invention discloses an experimental device for psychological teaching and psychological testing. The experimental device comprises a bracket, a psychological teaching device and a psychological testing device, wherein the psychological teaching device and the psychological testing device are arranged on the bracket and are connected with a cloud data module; a server module is arranged in a control box; the control box comprises a box body, a connecting piece screwed in the box body and used for arranging the server module, the server module arranged on the connecting piece and needing to be cooled, and partial cooling equipment for cooling the server module needing to be cooled. According to the experimental device disclosed by the invention, the defect that the cooling structure cannot easily execute cooling emphatically on the position with highest temperature rise in the control box in the prior art is effectively avoided.
Owner:海桂珍
Multichannel transmission control mechanism based on TCP friendliness
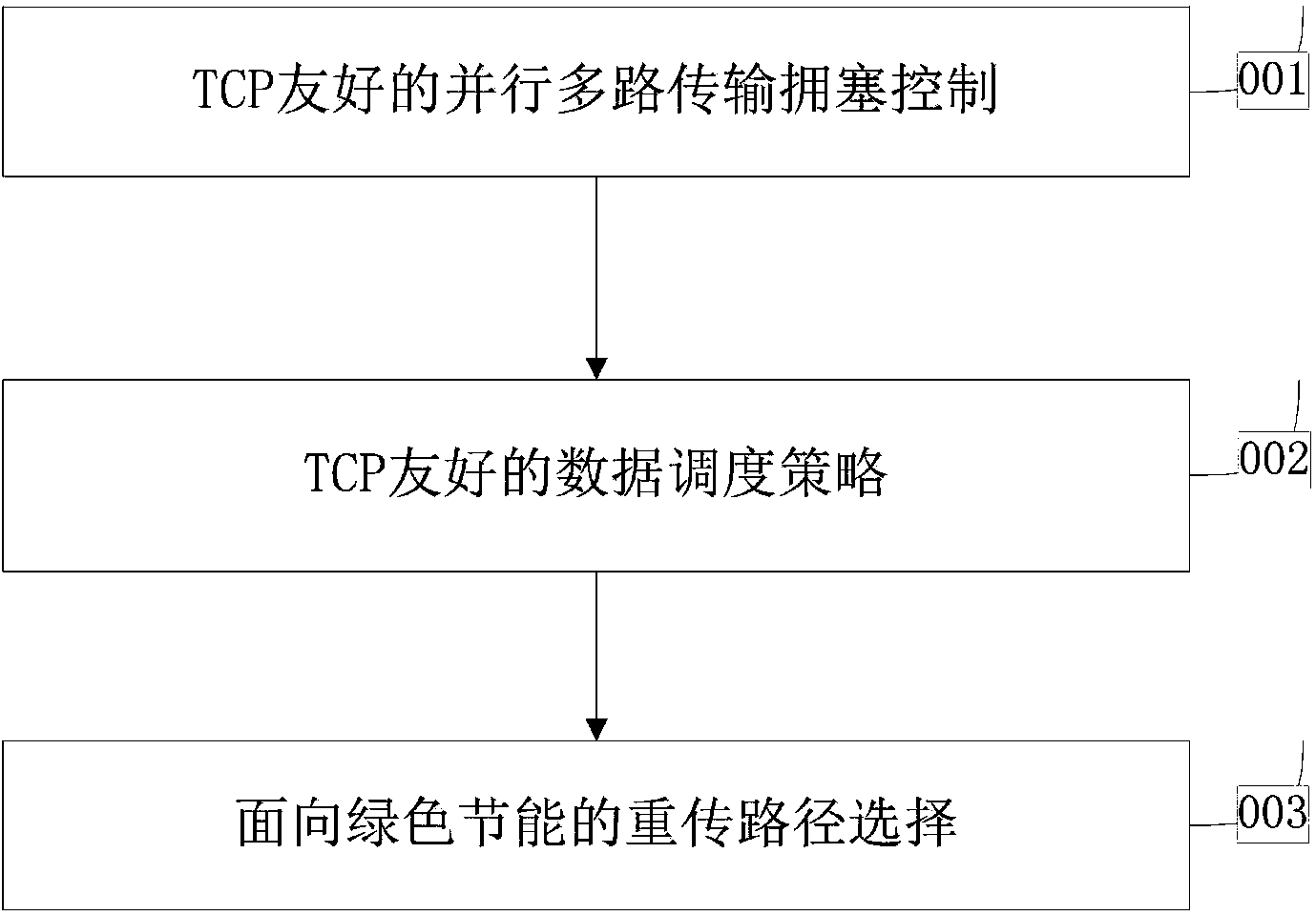
InactiveCN103929369AAchieve fairnessLoad balancingData switching networksControl orientedComputer network technology
The invention provides a multichannel transmission control mechanism based on TCP friendliness on the basis of the prior art, and belongs to the technical field of computer networks. The scheme comprises parallel multichannel transmission congestion control oriented to TCP friendliness, a data scheduling strategy of TCP friendliness and a retransmission path selection scheme oriented to energy saving. The multichannel transmission control mechanism based on TCP friendliness can keep the friendliness and the fairness of a TCP while achieving the parallel multichannel transmission performance, load balancing of all paths in the parallel multichannel transmission process is achieved, data transmission performance is improved, and the demand for wisdom multichannel data transmission with environmental protection, energy saving and the like being as the important features of a user is met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
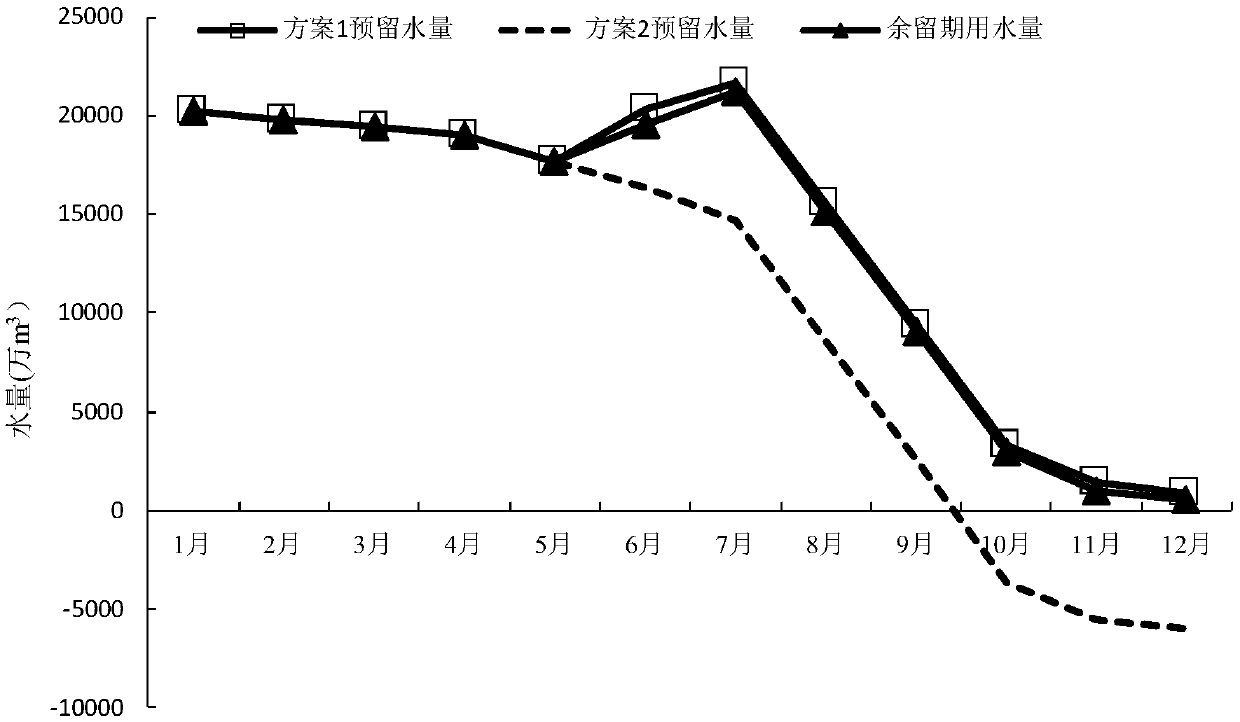
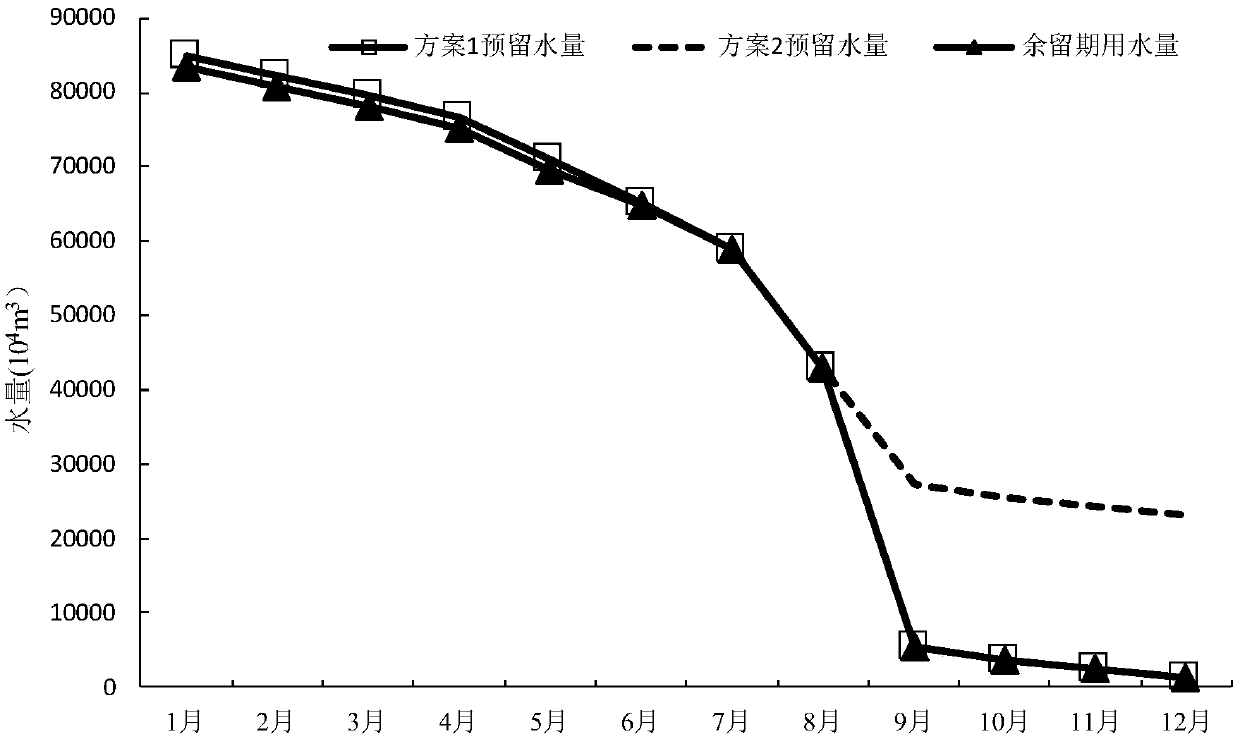
A drainage basin water quantity dynamic optimization distribution method oriented to total quantity control
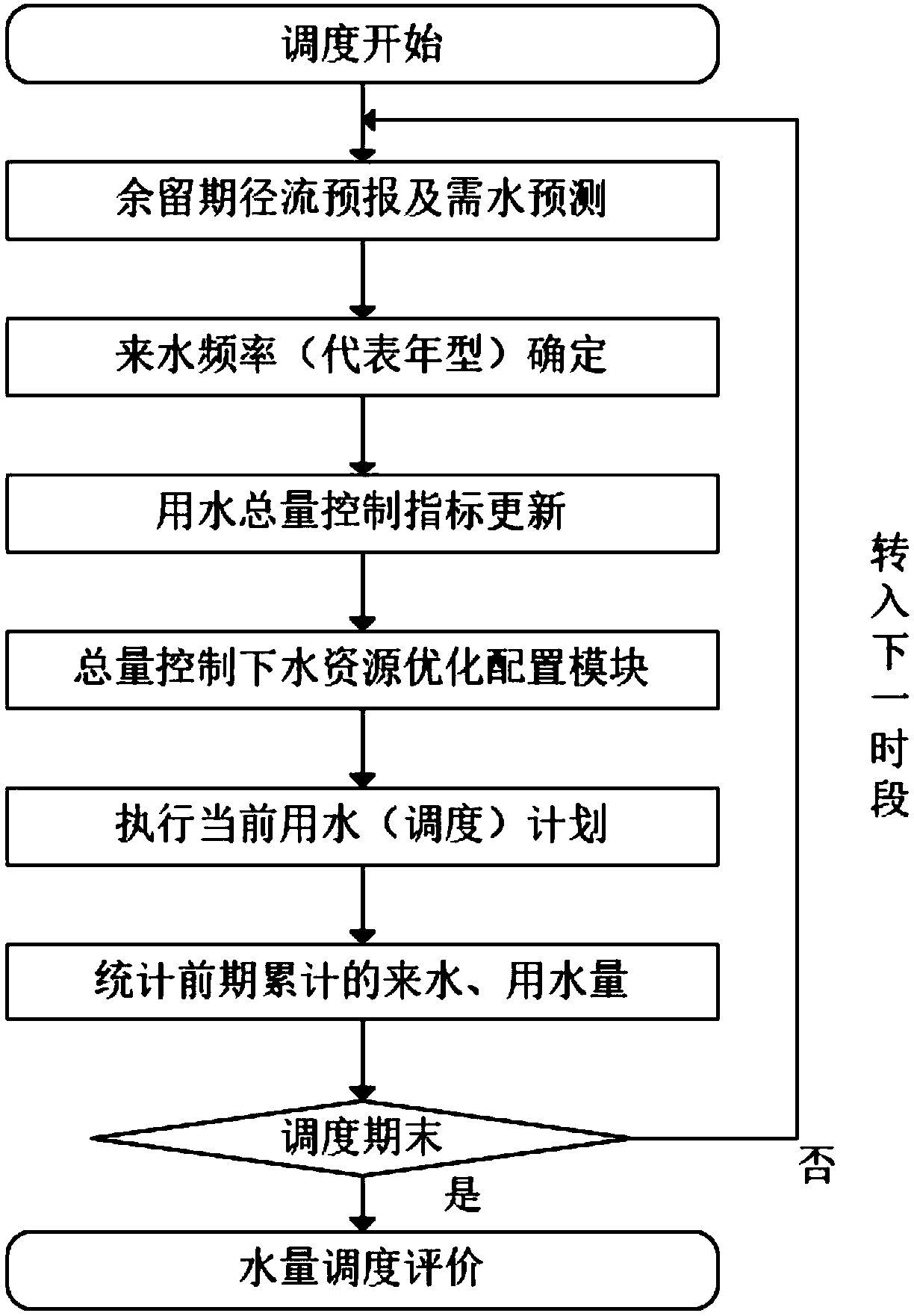
ActiveCN109685256ASimple resultEasy to implementGeneral water supply conservationForecastingControl orientedDistribution method
The invention provides a total amount control-oriented basin water amount dynamic optimization distribution method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, obtaining a typical year incoming water database, a typical year required water database and a water consumption total amount index library; 2, remaining period runoff forecasting is carried out; 3, determining the incoming water frequency of the year; 4, determining an annual total water consumption control index and a remaining period required water sequence of the confronting time period; 5, determining a water resource optimal configuration objective function and constraint conditions; 6, solving the total amount control-oriented water resource configuration model and executing a remaining period flood (scheduling) plan; 7, dynamically updating a water supply (scheduling) plan; And 8, adjusting and evaluating the water quantity at the end of the scheduling period. According to the invention, the annual rolling adjustmentmethod of the total water consumption index in combination with chaotic Volterra runoff forecasting is provided for the first time; The annual total amount control index can be updated month by month,the annual water supply amount of each subarea is controlled within the annual total water consumption index all the time through a real-time monitoring and rolling decision method, and a new idea isprovided for achieving dynamic management of the total water consumption.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
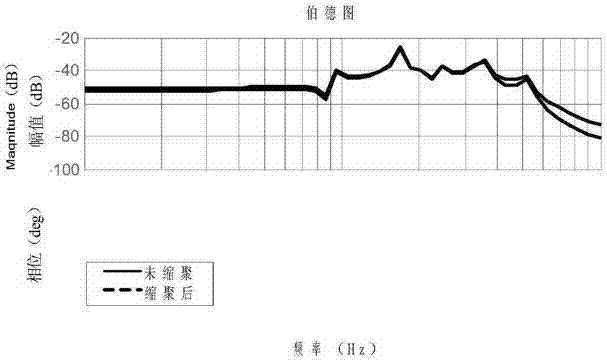
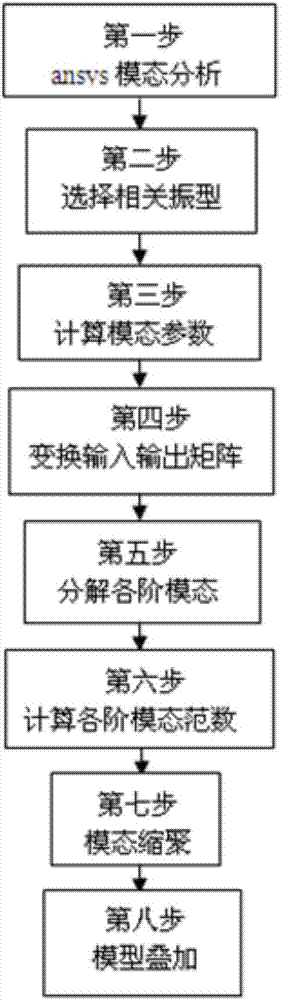
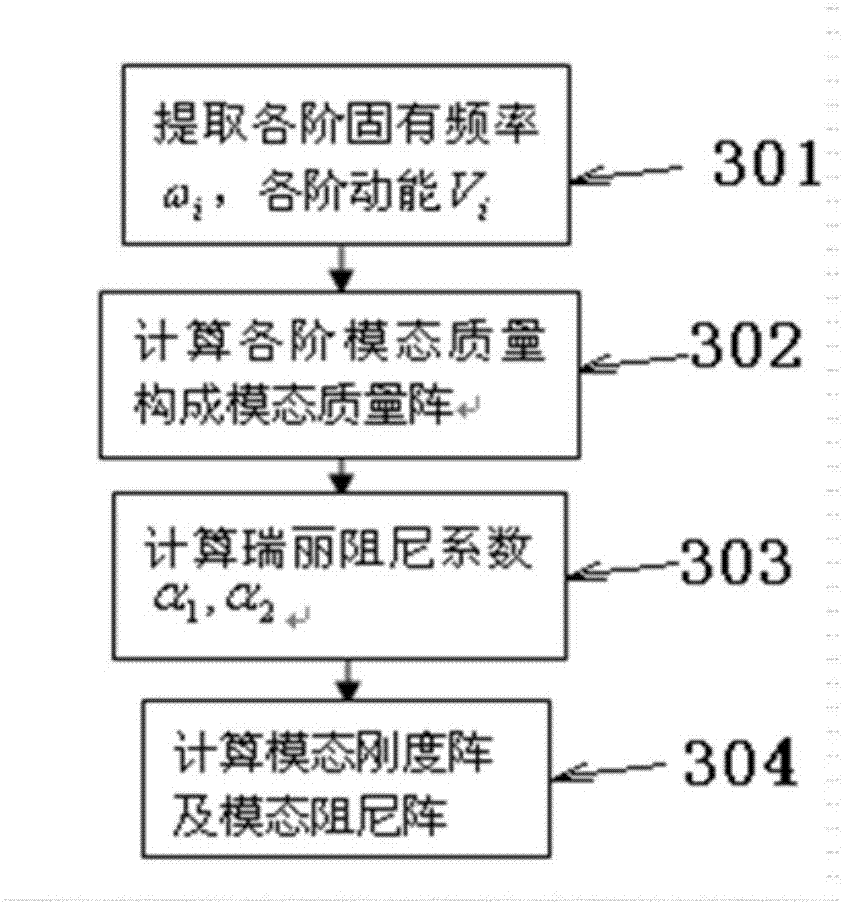
Control-orientated large antenna modeling method
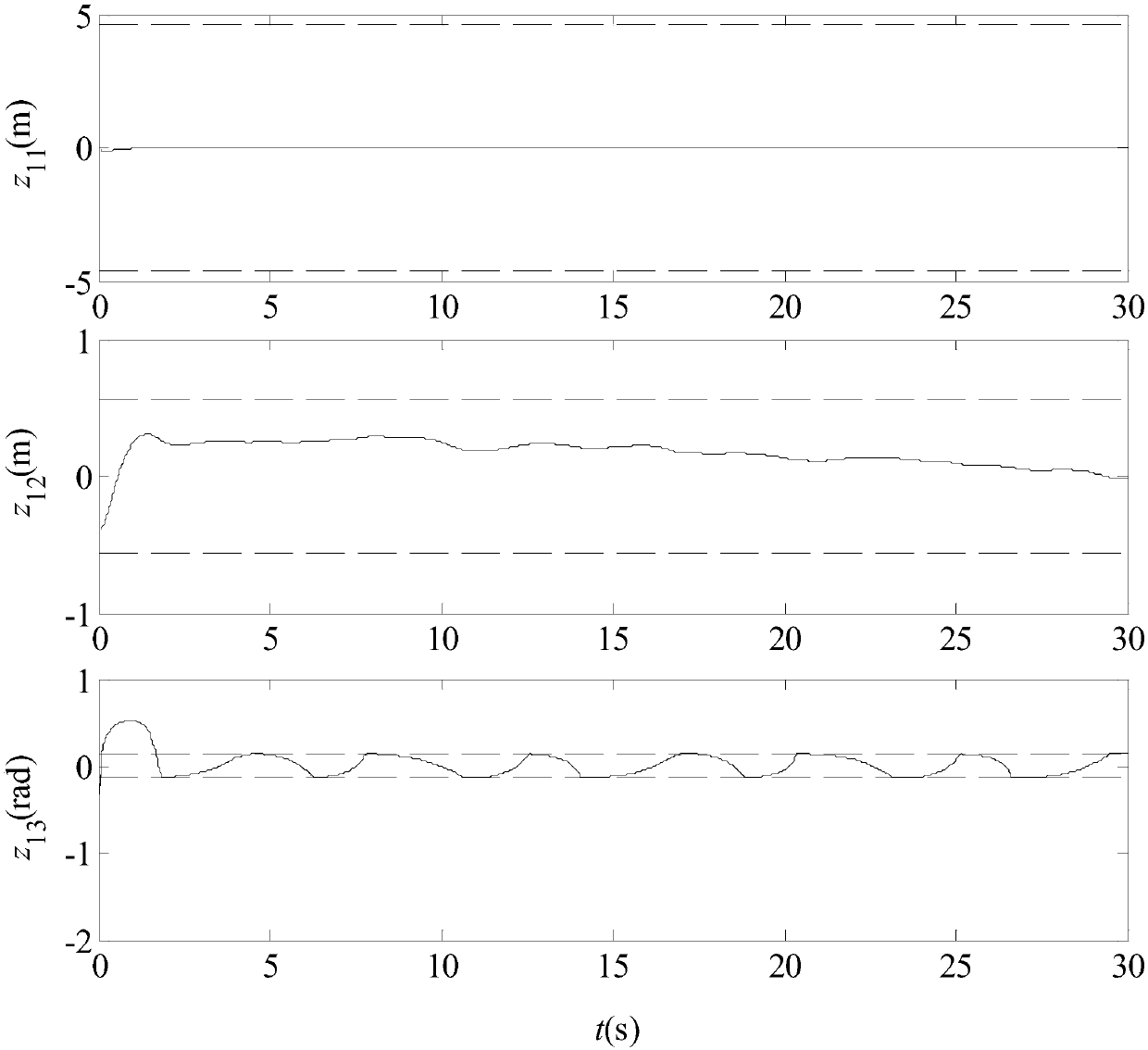
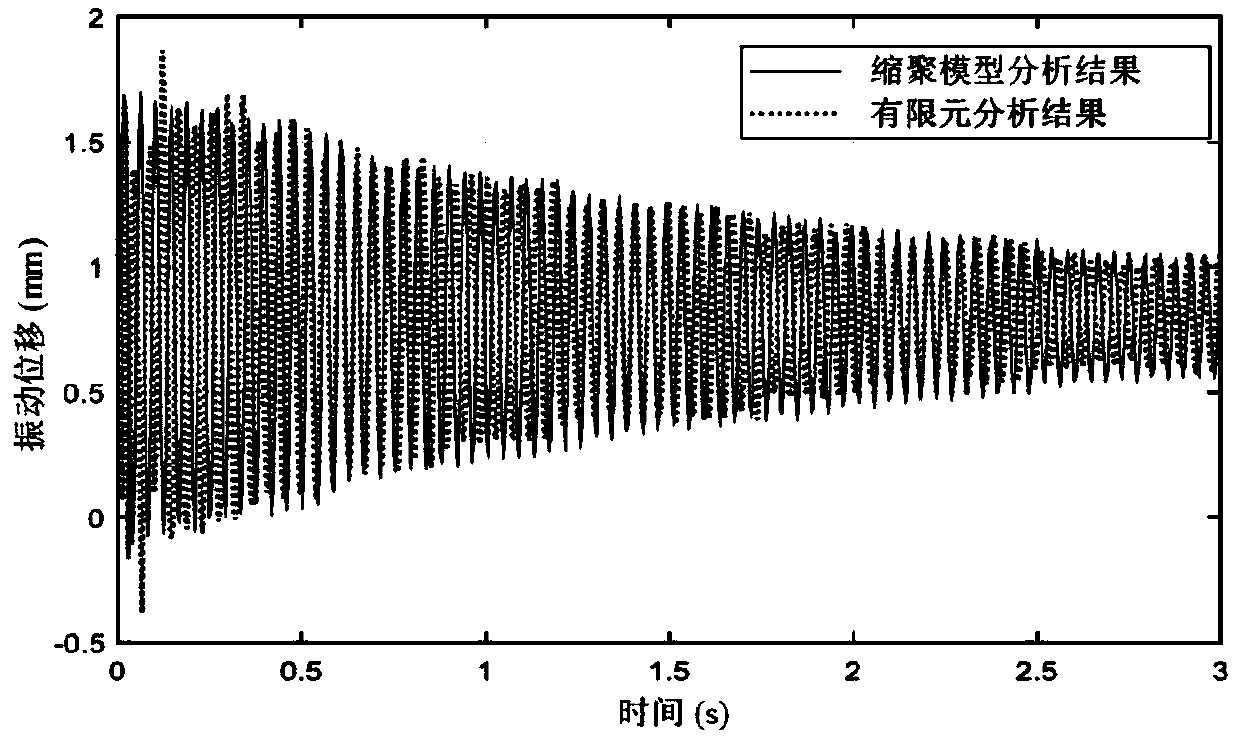
The invention relates to a control-orientated large antenna modeling method which comprises the steps of ansvs modal analysis, relevant vibration mode selection, modal parameter calculation, input and output matrix conversion, decomposition of each order of modality, calculation of the norm of each order of modality, modal polycondensation and modal superposition. The method has the advantages that due to the fact that antenna flexibility information is established in a control model, the model is closer to the reality and pointing error calculation is more accurate; due to the fact that a rigid model and a flexible model are both in a decoupled state, rigid corners and flexible deviation can be output by the rigid model and the flexible model respectively, and output processing can be conducted respectively.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com