Method for obtaining specified thermodynamic function of nanometer material
A nano-material and thermodynamic technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, etc., can solve the problems of non-thermal conduction, non-representation, and inconsistency, and achieve the effects of accurate measurement results, easy implementation, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
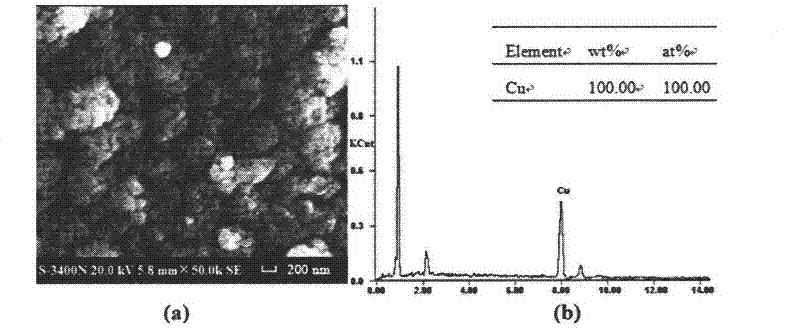
[0014] Use 0.05μm α-Al for copper electrode 2 O 3 The suspension paste is polished to the mirror surface, and then ultrasonically cleaned with absolute ethanol and double distilled water in an ultrasonic cleaner, 100μL 0.4molL -1 Added copper sulfate solution to 10mL 1mmolL -1 The sulfuric acid solution was used as the electrolyte, the copper electrode was used as the working electrode and the counter electrode, and the saturated calomel electrode was used as the reference electrode, and the deposition was carried out at a potential of -1.00V for 60s. Measure the open circuit potential in a two-electrode system and run for 20s.
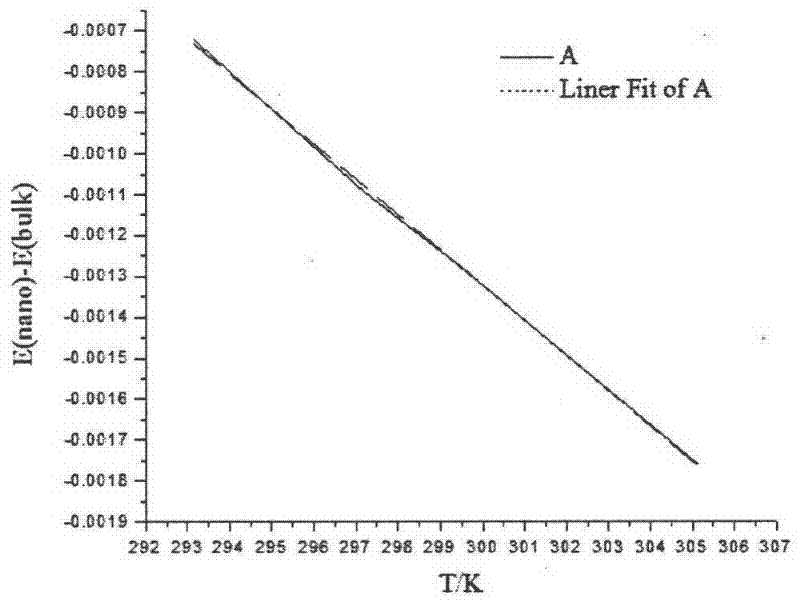
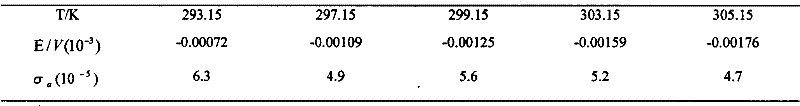
[0015] Measure the open-circuit potential-time curve at 293.15K, 297.15K, 299.15K, 303.15K, and 305.15K respectively, and perform 5 parallel experiments at each temperature and take the average value and statistics as shown in the table below.
[0016] Table 1 Electromotive force changes with temperature (E-T) data
[0017]
[0018] Draw an E-T curve and fit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com