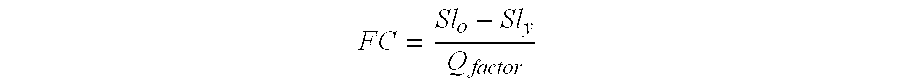Patents
Literature
61 results about "Multicellular organism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organisms. All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social amoebae such as the genus Dictyostelium.
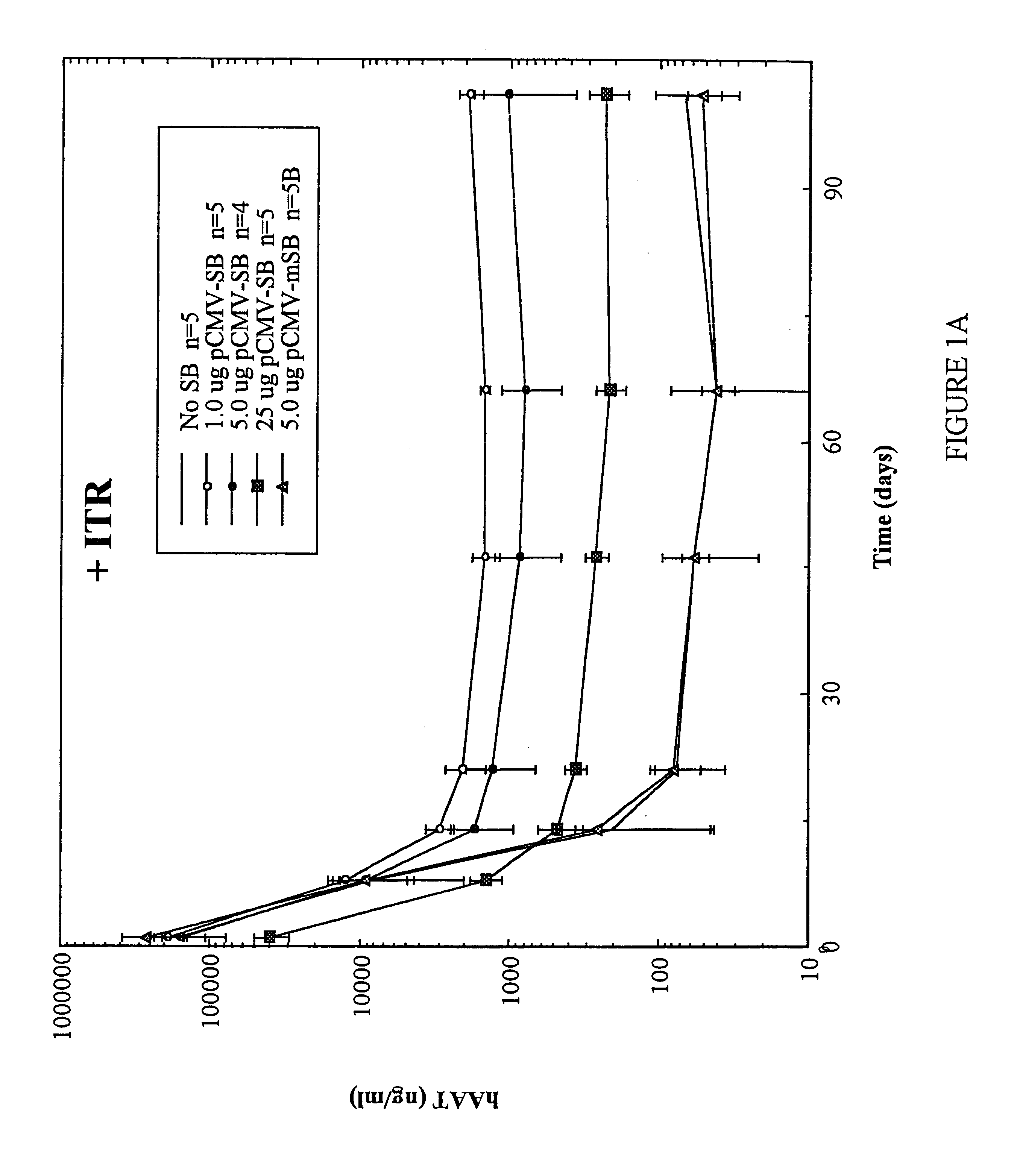
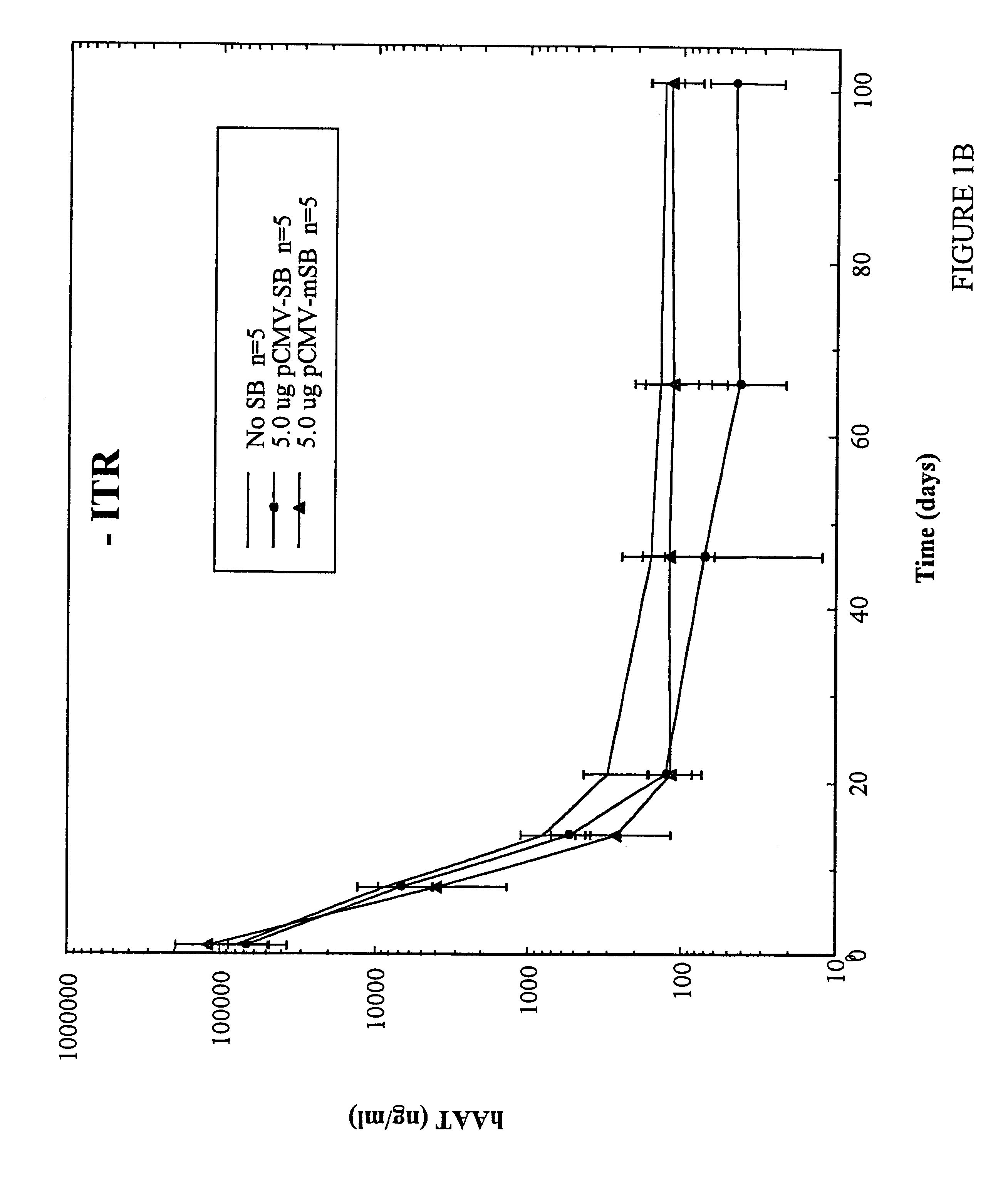
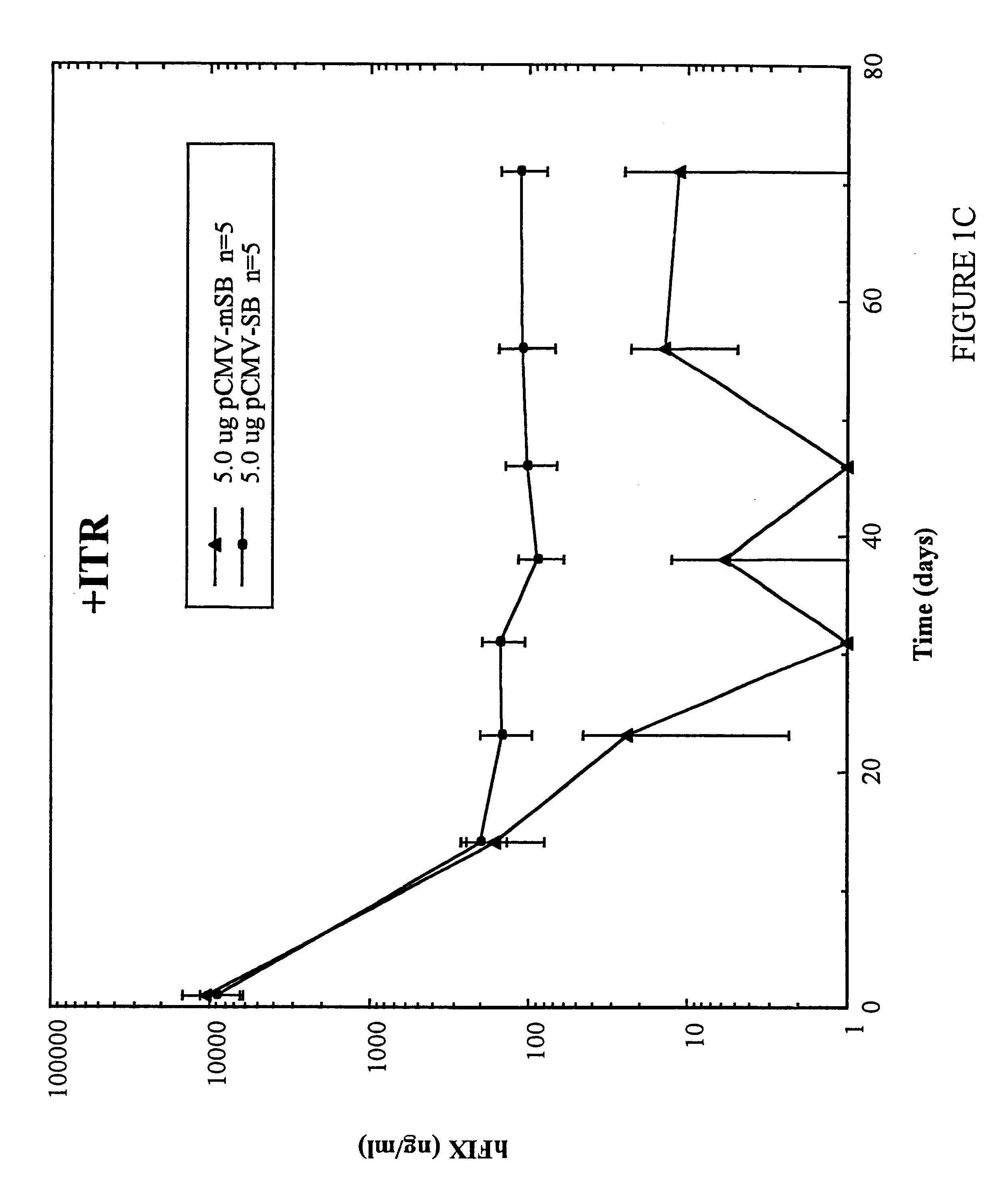
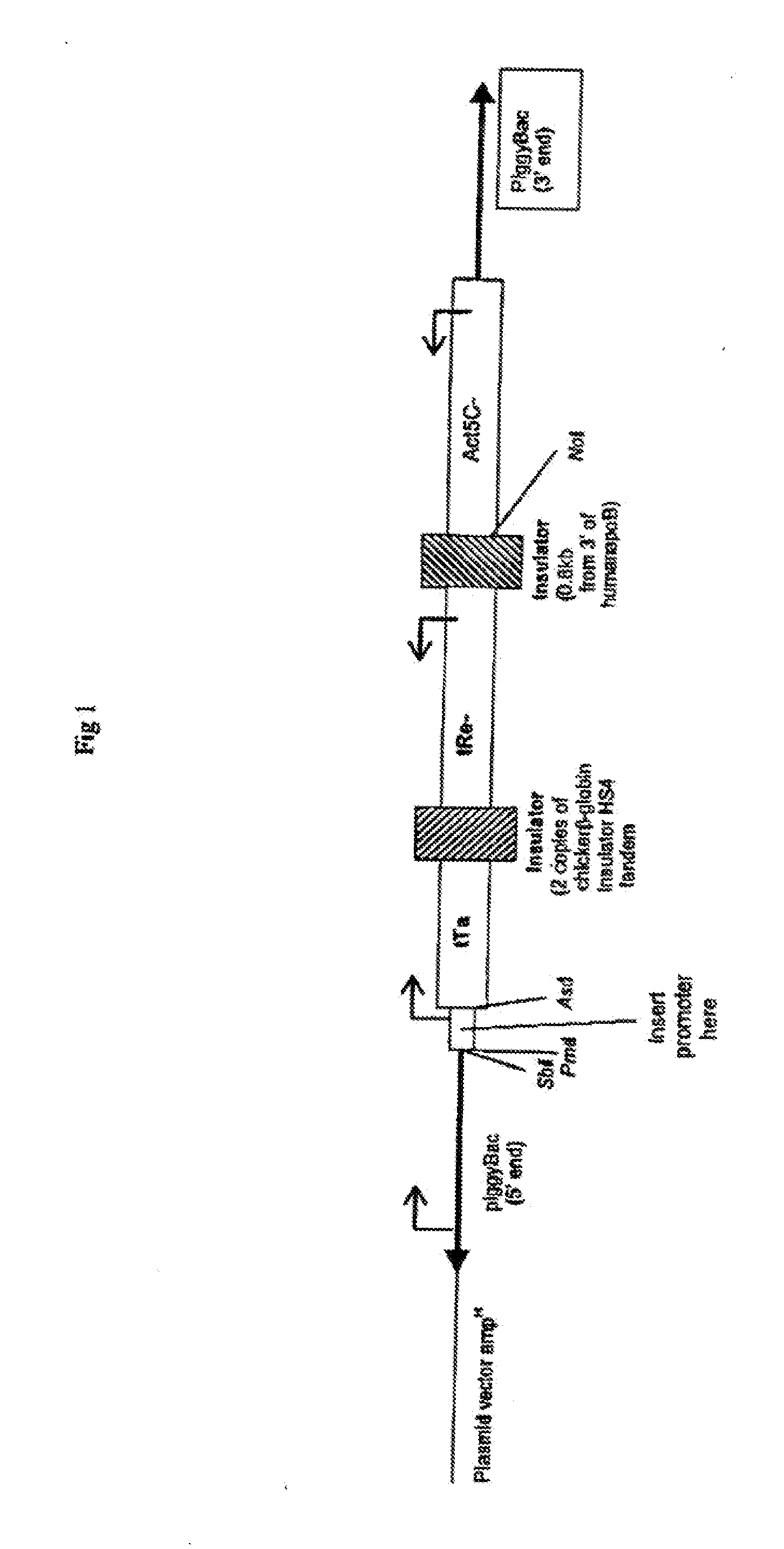
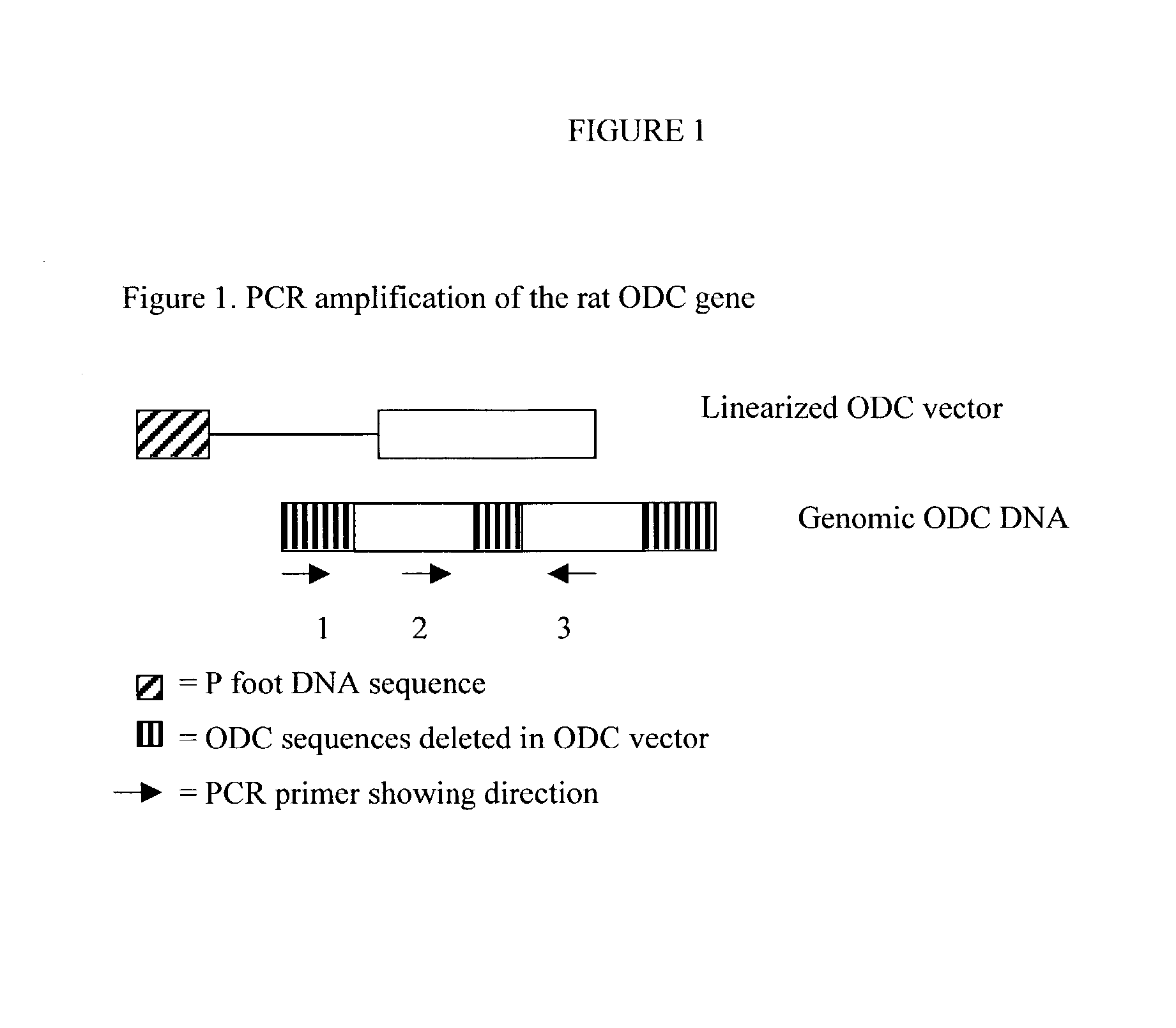
Methods of in vivo gene transfer using a sleeping beauty transposon system
InactiveUS6613752B2Observed effectPromote cloningBiocideHydrolasesSleeping Beauty transposon systemMulticellular organism
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of at least one cell of a multicellular organism are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is administered to the multicellular organism along with a source of a Sleeping Beauty transposase activity. Administration of the transposon and transposase results in integration of the transposon, as well as the nucleic acid present therein, into the genome of at least one cell of the multicellular organism The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the in vivo transfer of genes for use in, among other applications, gene therapy applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microbial production of nuclease resistant DNA, RNA, and oligo mixtures
Owner:FRAYNE CONSULTANTS
Targeted methods of drug screening using co-culture methods
The present invention provides methods of screening for a molecule that inhibits the expression or activity of a protein encoded by a target gene which affects the fitness of a cell. The methods are based on a co-culture assay, and entail culturing together two cell populations, each of which is a population of identical cells, of the same species that differs substantially only in the expression or activity of the gene to be targeted or its encoded protein and the presence or absence of a reporter gene. The screen can be applied to cultured cells, unicellular and multicellular organisms. Manipulating the expression or activity of the target gene sensitizes the host to a molecule which inhibits the target gene or its encoded protein such that the cell or organism comprising the manipulated target gene grows at a different rate from the cell or organism comprising the unmanipulated gene in response to exposure to the molecule. The methods of the invention can be used for identifying drugs, proteins or any other molecules that inhibit the function of proteins encoded by target genes.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
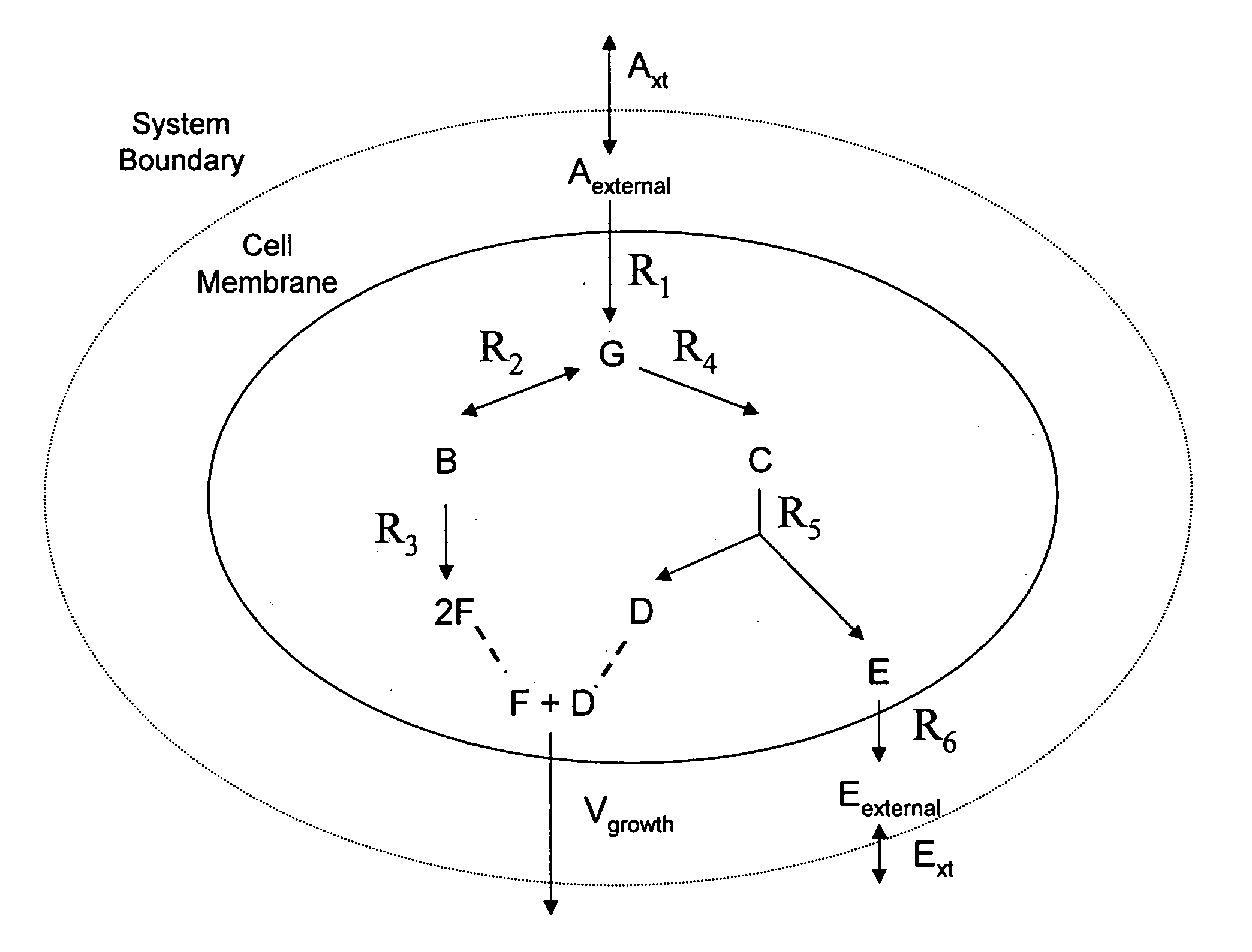
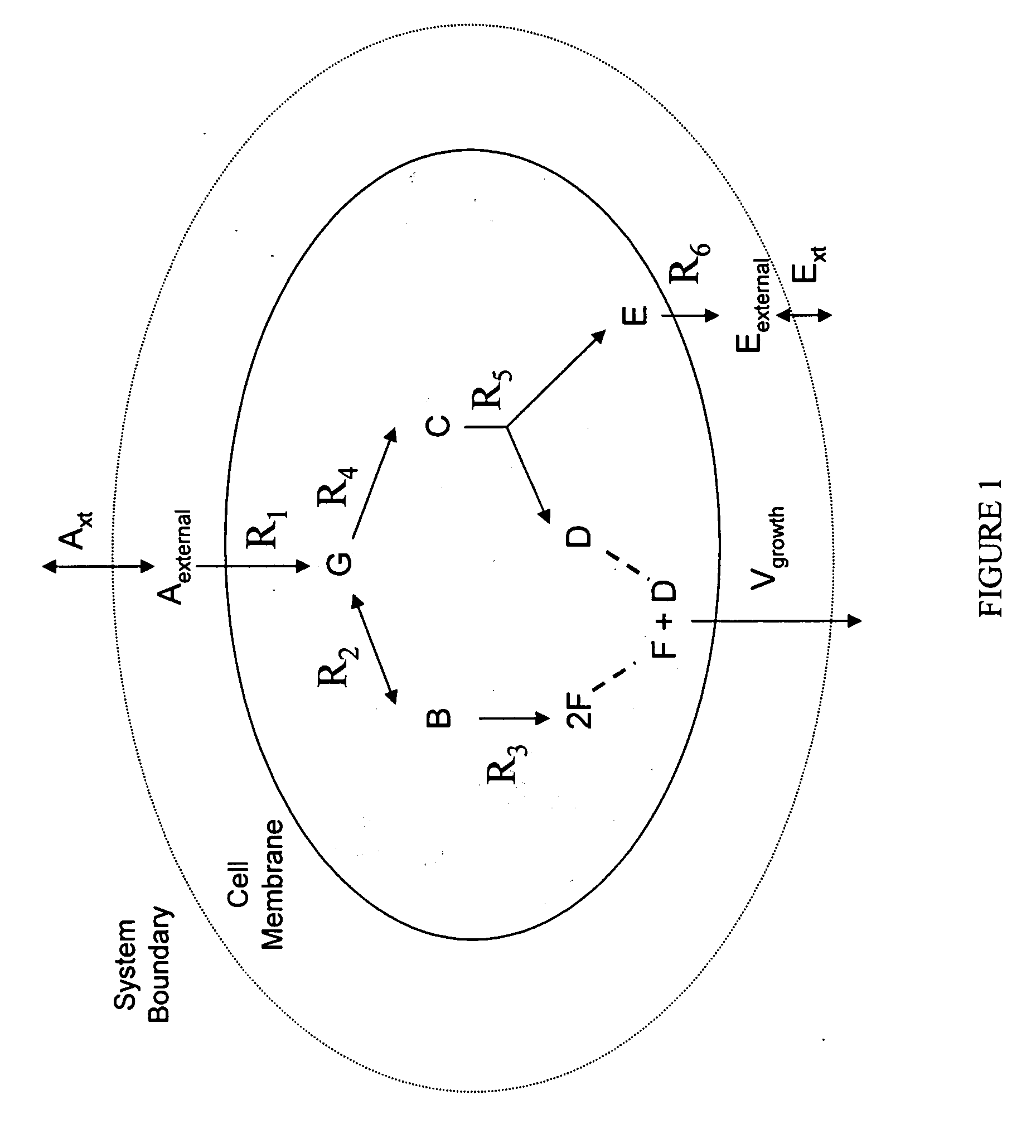
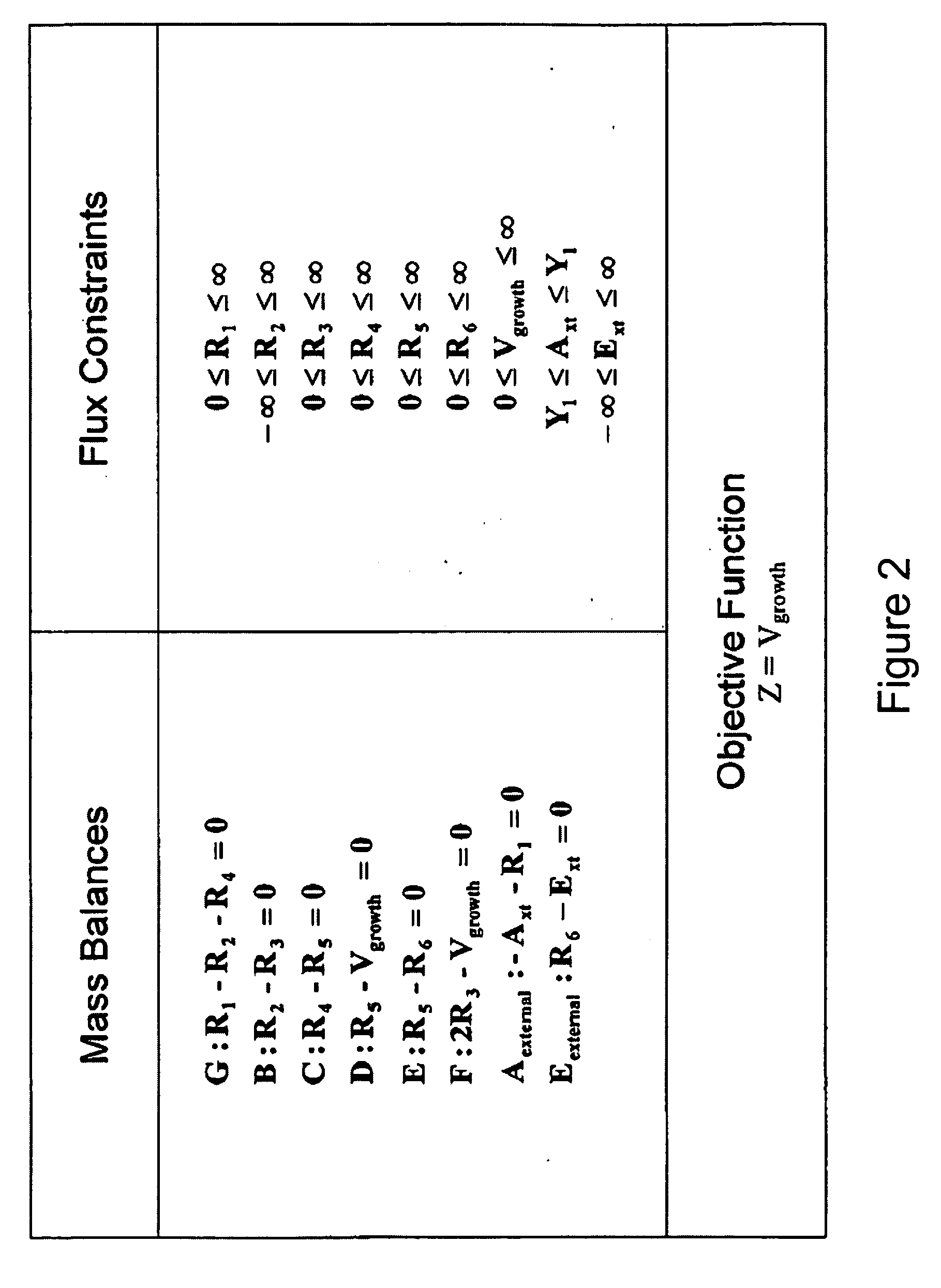
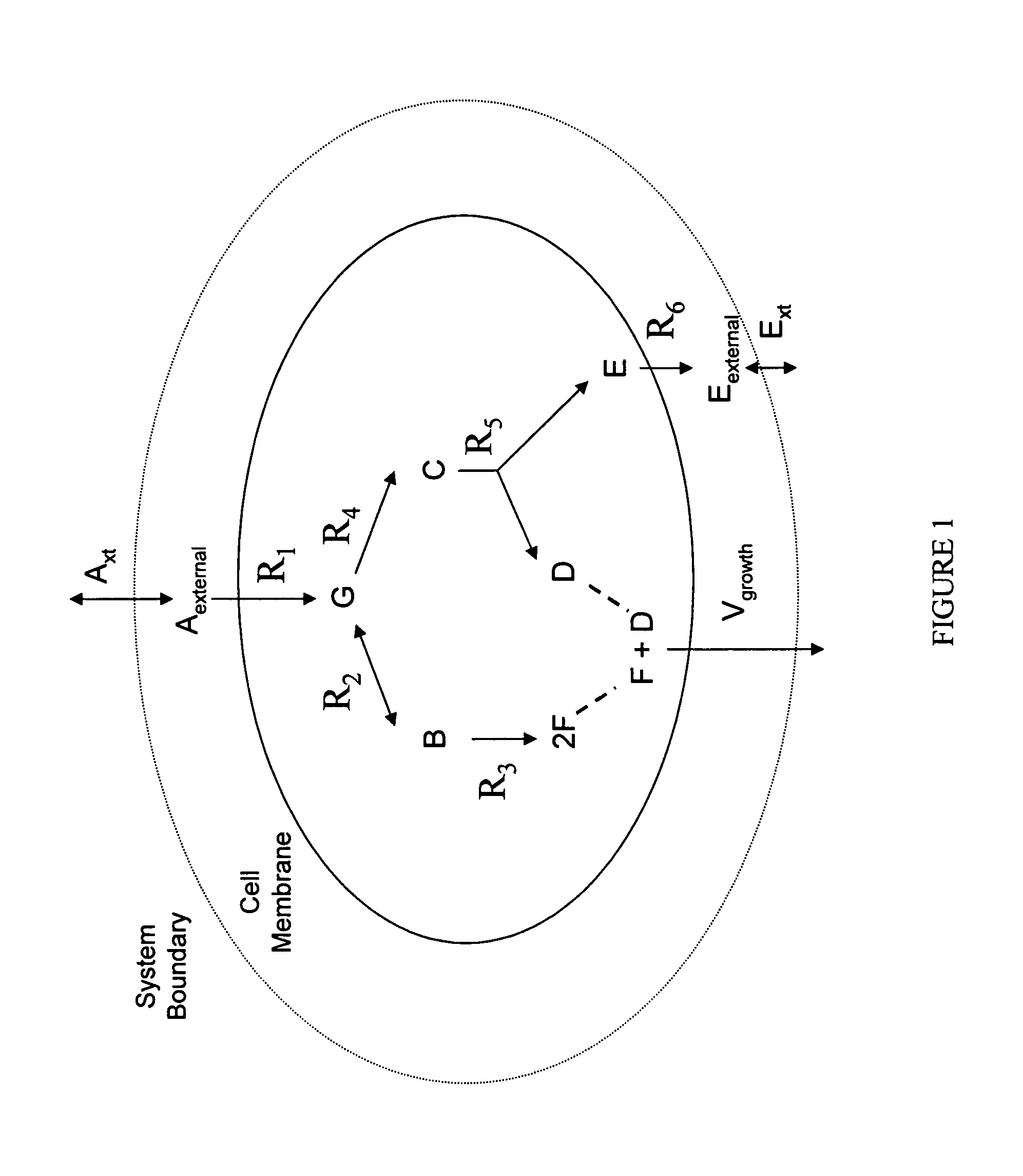
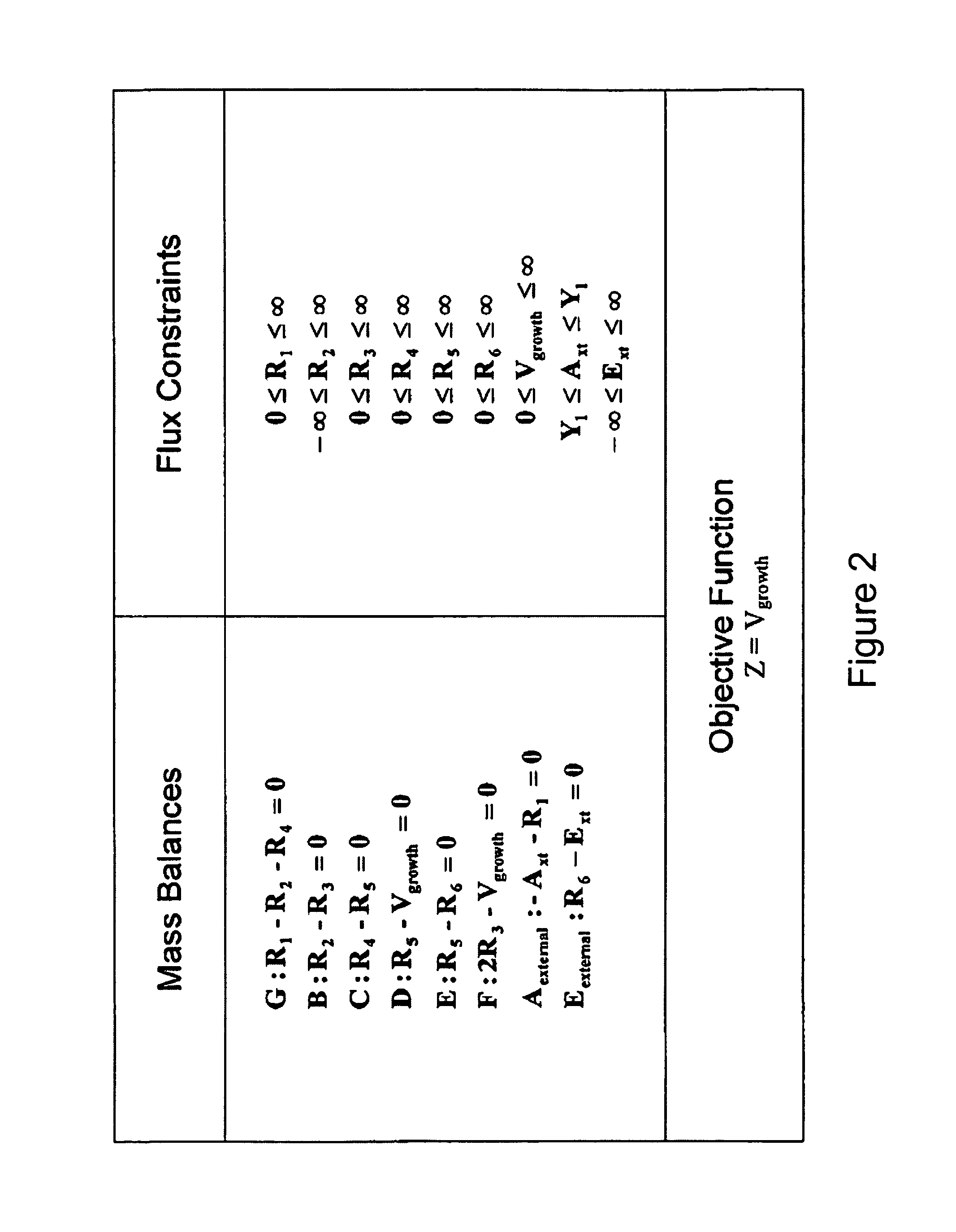
Multicellular metabolic models and methods
ActiveUS20060147899A1Chemical property predictionCompound screeningMulticellular organismMetabolic Model
The invention provides a computer readable medium or media, having: (a) a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures, and (e) commands for determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells. The first, second and third data structures also can include a plurality of data structures. Additionally provided is a method for predicting a physiological function of a multicellular organism. The method includes: (a) providing a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) providing a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) providing a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) providing a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures; (e) providing an objective function, and (f) determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
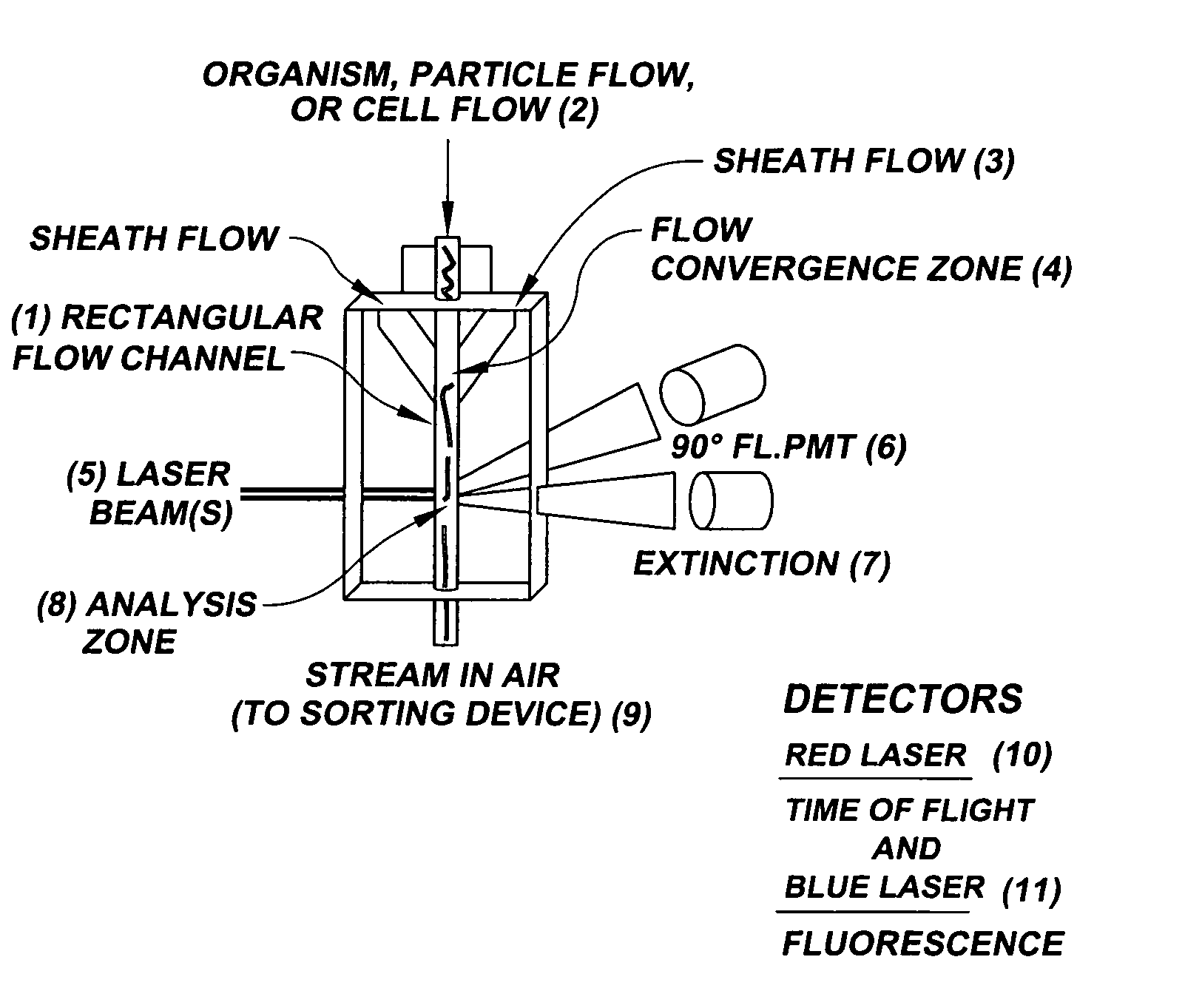
System for axial pattern analysis of multicellular organisms
A method of using elongate multicellular organisms in conjunction with a specialized flow cytometer for drug discovery and compound screening. A stable, optically detectable linear marker pattern on each organism is used to construct a longitudinal map of each organism as it passes through the analysis region of the flow cytometer. This pattern is used to limit complex data analysis to particular regions of each organism thereby simplifying and speeding analysis. The longitudinal marker pattern can be used to alter signal detection modes at known regions of the organism to enhance sensitivity and overall detection effectiveness. A repeating pattern can also be used to add a synchronous element to data analysis. The marker patterns are established using known methods of molecular biology to express various indicator molecules. Inherent features of the organism can be rendered detectable to serve as marker patterns.
Owner:UNION BIOMETRICA
Biological control
InactiveUS20030213005A1Not affectAvoidance of sterilisationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyBiological body
The invention relates to a non-human multicellular organism carrying a dominant lethal genetic system, the lethal effect of which is conditional, wherein the lethal effect of the lethal system occurs in the natural environment of the organism.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
High surface cultivation system bag
InactiveUS20080206862A1Increase of available surfaceIncrease gas exchangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesMulticellular organism
An exemplary embodiment of a reversibly closable bag suitable for the cultivation of cells and / or tissues can be provided. The exemplary bag can comprise at least one reversibly closable aperture in the bag wall, and a surface-increasing convection arrangement inside the bag. The convection arrangement is capable to generate and / or modify a convection in a fluid within said bag when at least one of the fluid, the bag, and the convection arrangement is agitated. For example, the surface increasing convection arrangement can be at least one blade, at least one particulate filler and / or at least one surface-increasing substrate being made of a single mould. A system can also be provided comprising at least two bags, whereas the bags may be interconnected via at least one aperture in their bag wall, and a cultivation process using such a bag or system, in which at least one type of cells, tissue, tissue-like cell cultures, organs, organ-like cell cultures, or multicellular organisms are cultivated in the presence of at least one fluid or solid medium provided for growing and / or cultivating the aforesaid culture.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Robotic microscopy apparatus for high throughput observation of multicellular organisms
The present invention relates to a robotic microscopy apparatus that is able to screen, detect, count and image in an automated and high throughput fashion whole multicellular organisms, tissues, individual cells and groups of cells on or embedded within agar, collagen or other defined matrix. To achieve this, the robotic apparatus of the invention images the samples from the top using a microscope with a long working distance. The invention provides robotic systems for plate handling, biological sample immobilization and microscopic examination. The invention also provides for automatic image acquisition, image storage and display, and image analysis.
Owner:ELEGENICS
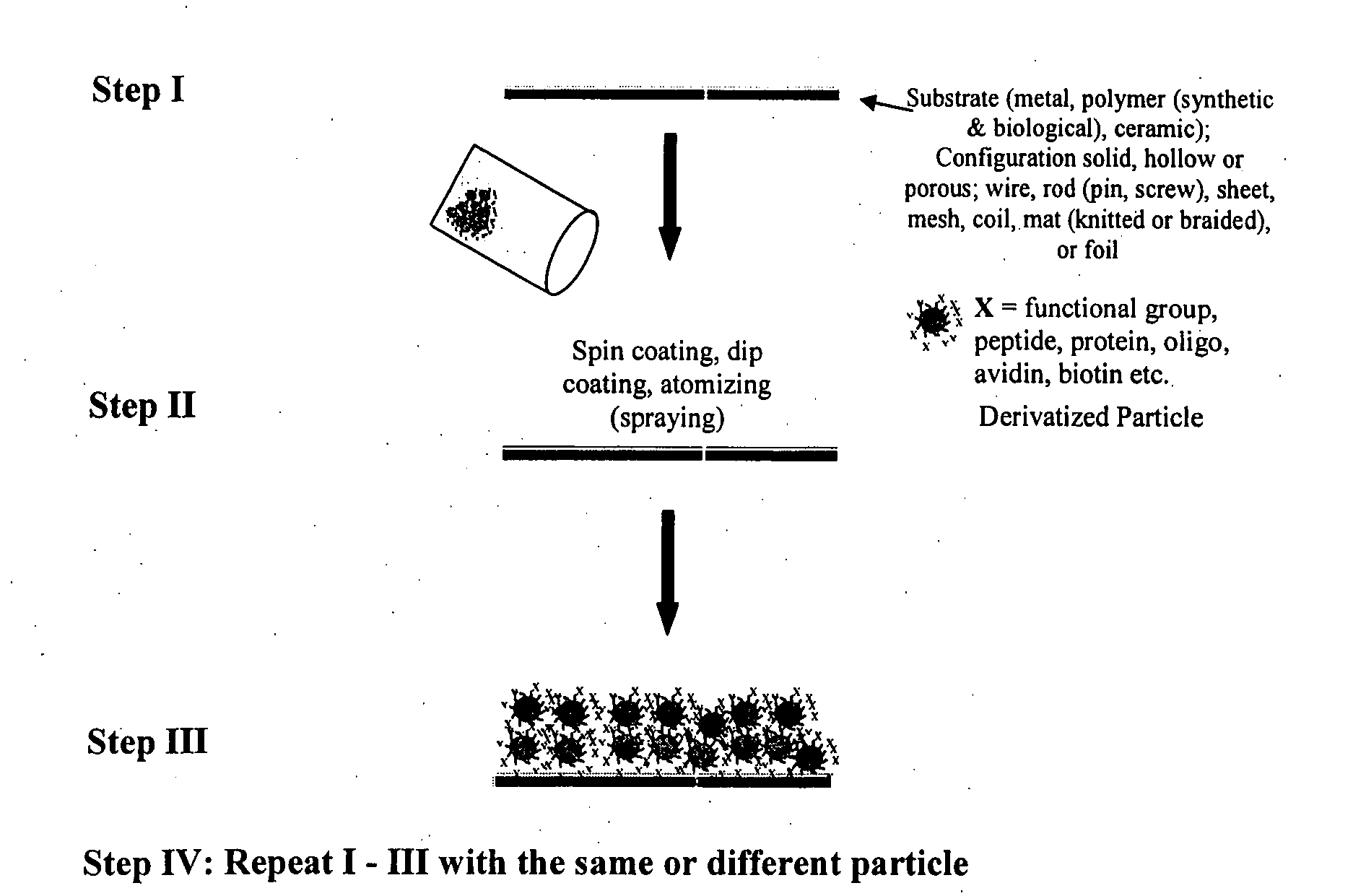
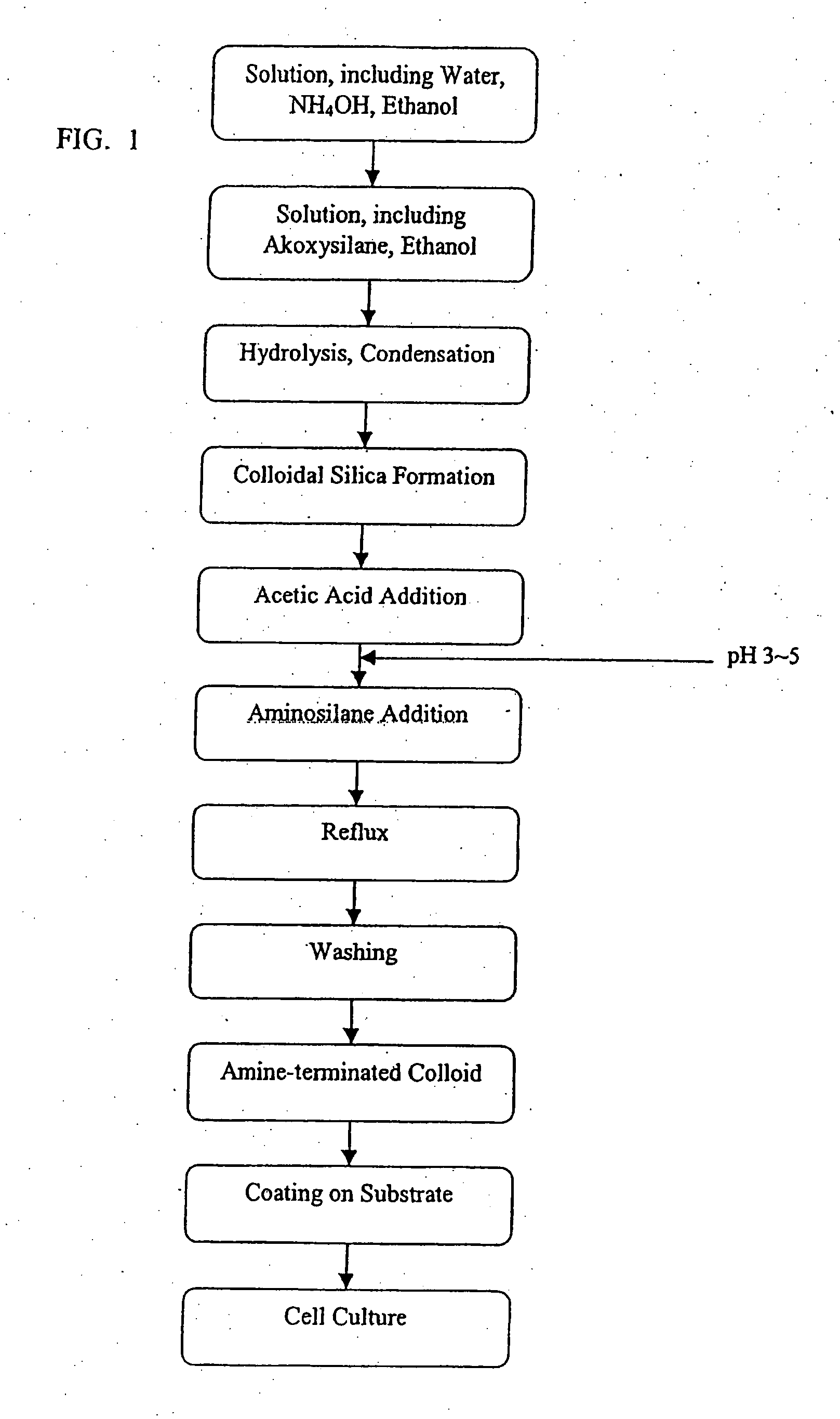
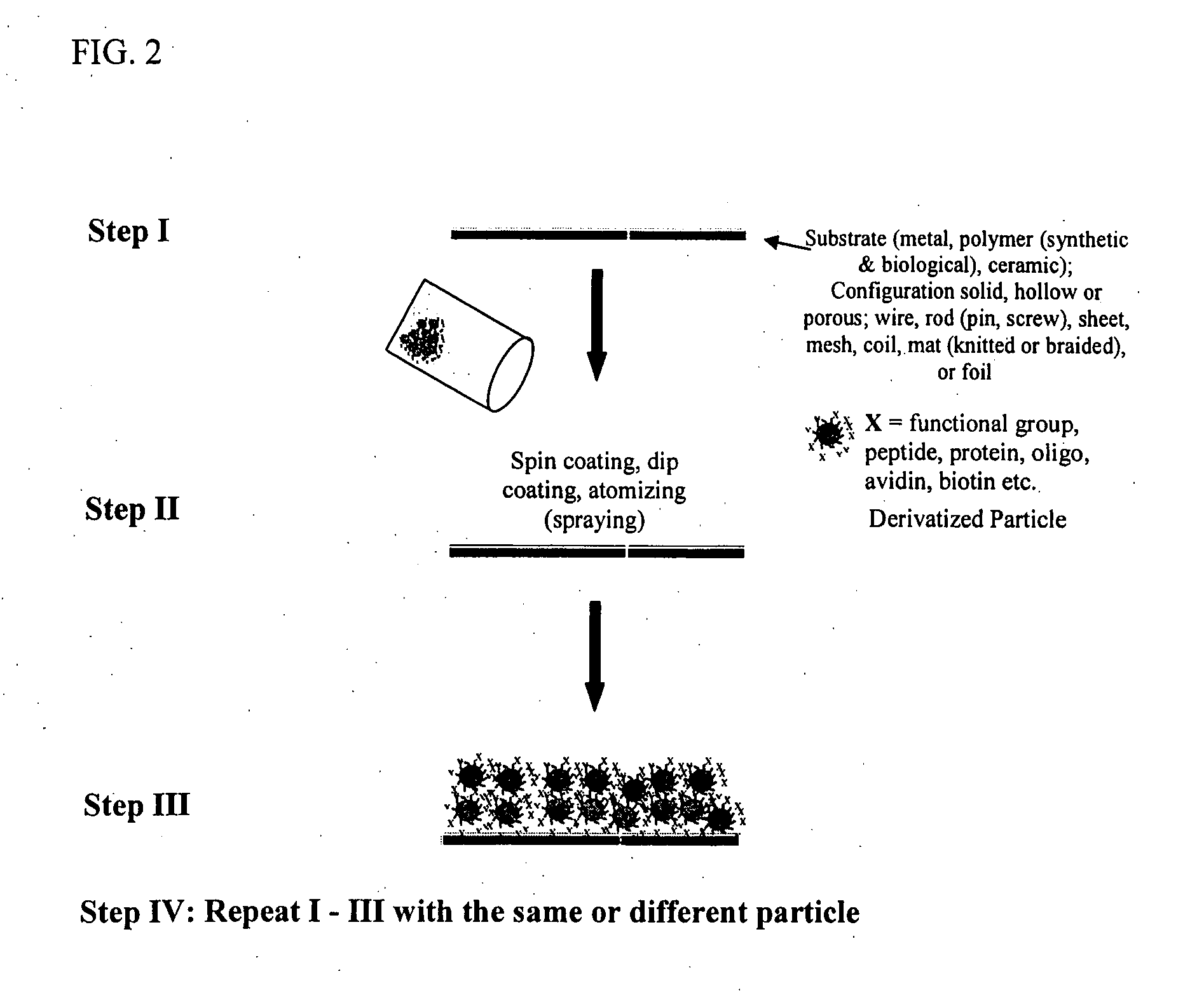
Engineering of material surfaces
InactiveUS20070190100A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMulticellular organismCompatibilization
The invention provides a device having a surface and a functional layer associated with the surface, where the functional layer includes particles having a structure substituted with a functional group, where the functional group is adapted to modify a property of the device, the device is sufficiently biocompatible for application to a multicellular organism and the particles have an average diameter of about 5 nm to about 10 microns.
Owner:SHASTRI VENKASTREETCAR P +3
66 kDa antigen from Borrelia
InactiveUS6054296AReduce sensitivityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtozoaAntigen
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides encoded by the same, antibodies directed thereto and a method of preparing such polypeptides including: (a) inserting an isolated DNA molecule coding for a polypeptide which is immunoreactive with a 66 kDa polypeptide derived from Borrelia garinii IP90 into an expression vector; (b) transforming a host organism or cell with the vector; (c) culturing the transformed host cell under suitable conditions; and (d) harvesting the polypeptide. The isolated DNA molecule is preferably at least 10 nucleotides in length, and the method may optionally include subjecting the polypeptide to post-translational modification. The host cell can be a bacterium, a yeast, a protozoan, or a cell derived from a multicellular organism such as a fungus, an insect cell, a plant cell, or a mammalian cell.
Owner:SYMBICOM
66 kDa antigen from Borrelia
InactiveUS6090586AReduce sensitivityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenProtozoa
Owner:SYMBICOM
66 kDa antigen from Borrelia
InactiveUS6068842AReduce sensitivityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenProtozoa
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides encoded by the same, antibodies directed thereto and a method of preparing such polypeptides including: (a) inserting an isolated DNA molecule coding for a polypeptide which is immunoreactive with a 66 kDa polypeptide derived from Borrelia garinii IP90 into an expression vector; (b) transforming a host organism or cell with the vector; (c) culturing the transformed host cell under suitable conditions; and (d) harvesting the polypeptide. The isolated DNA molecule is preferably at least 10 nucleotides in length, and the method may optionally include subjecting the polypeptide to post-translational modification. The host cell can be a bacterium, a yeast, a protozoan, or a cell derived from a multicellular organism such as a fungus, an insect cell, a plant cell, or a mammalian cell.
Owner:SYMBICOM
Biological Control
InactiveUS20080115233A1Avoidance of sterilisationSolution to short lifeClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionMulticellular organismOrganism
The invention relates to a non-human multicellular organism carrying a dominant lethal genetic system, the lethal effect of which is conditional, wherein the lethal effect of the lethal system occurs in the natural environment of the organism.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
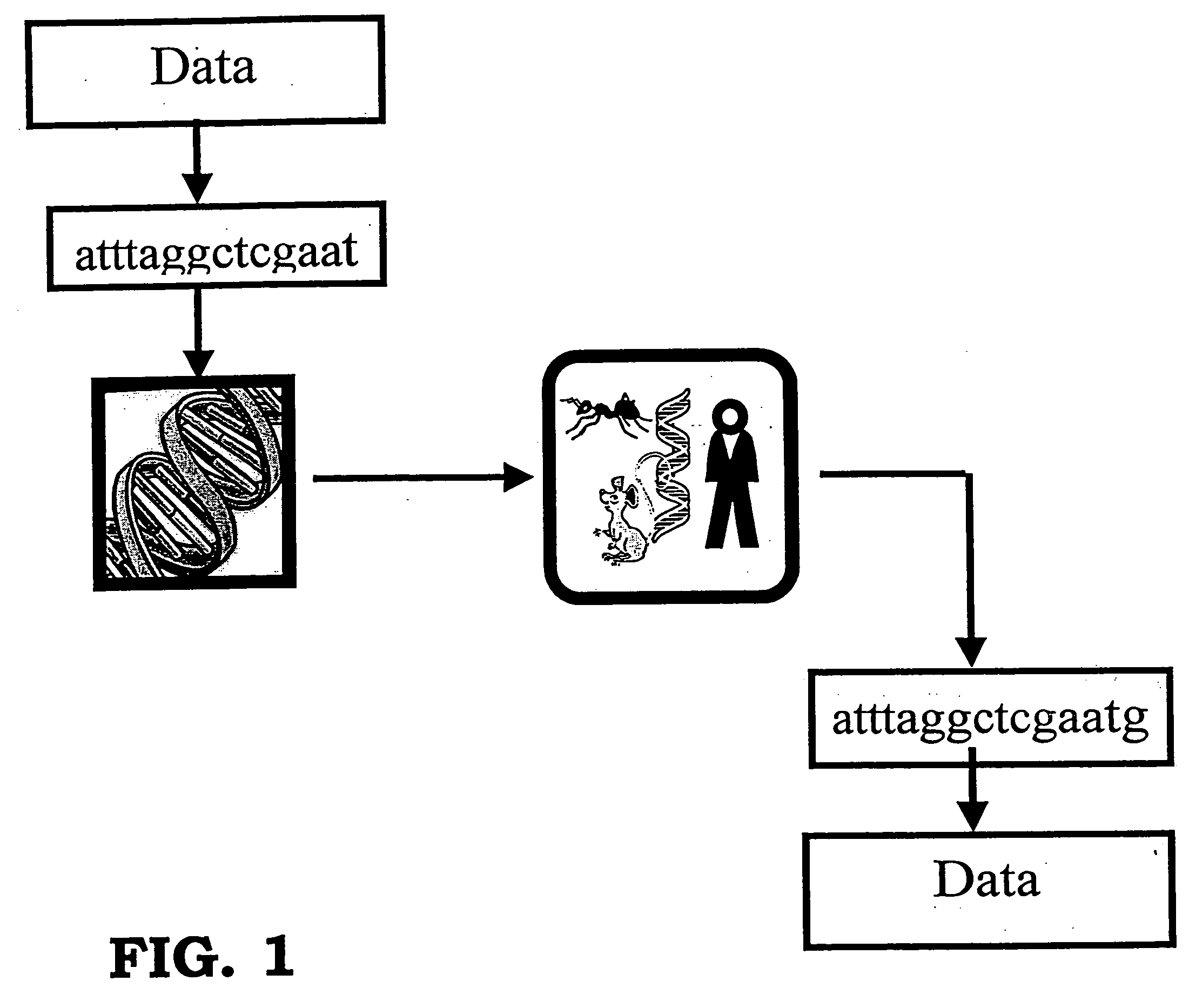
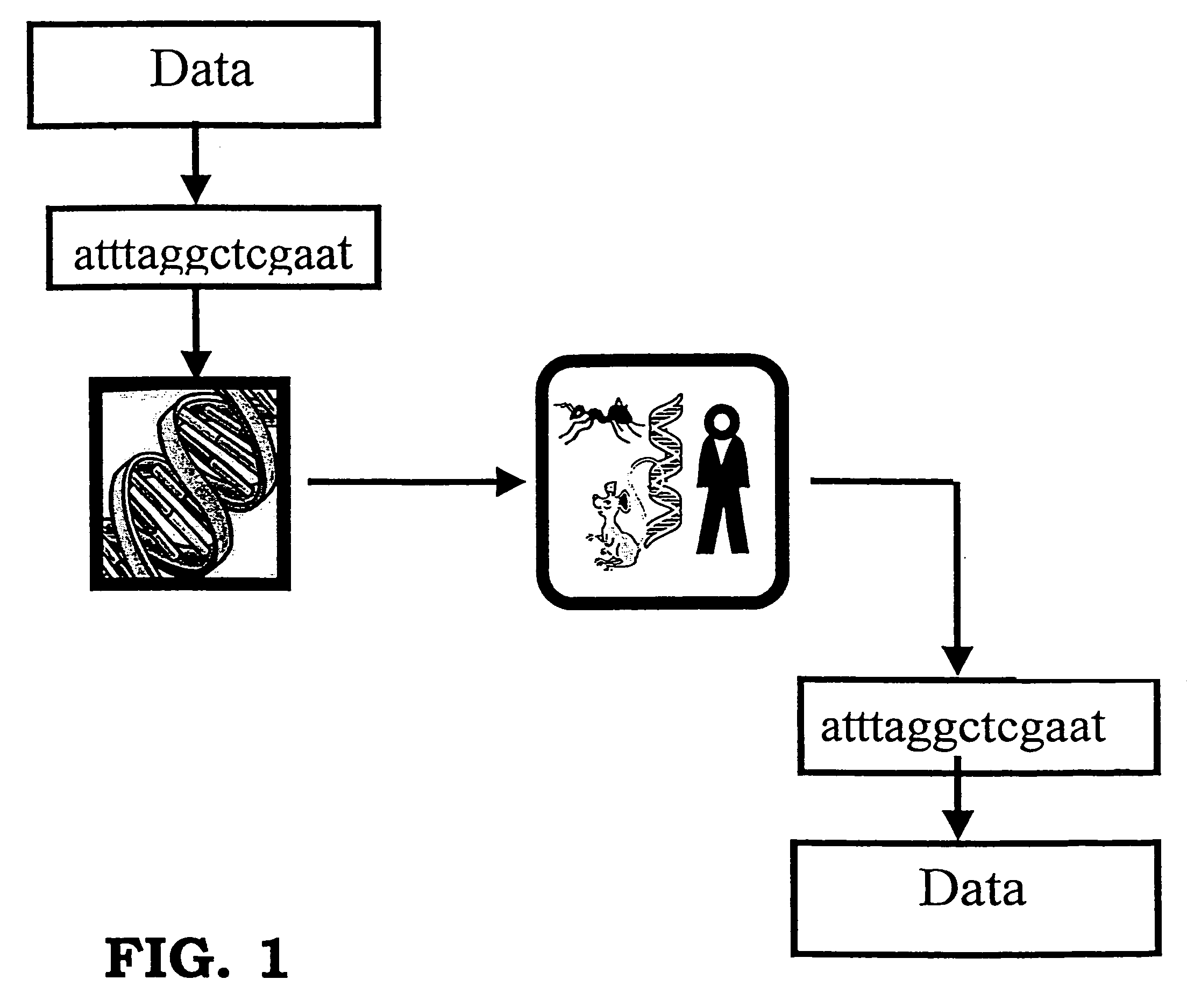
Storing data encoded DNA in living organisms
Current technologies allow the generation of artificial DNA molecules and / or the ability to alter the DNA sequences of existing DNA molecules. With a careful coding scheme and arrangement, it is possible to encode important information as an artificial DNA strand and store it in a living host safely and permanently. This inventive technology can be used to identify origins and protect R&D investments. It can also be used in environmental research to track generations of organisms and observe the ecological impact of pollutants. Today, there are microorganisms that can survive under extreme conditions. As well, it is advantageous to consider multicellular organisms as hosts for stored information. These living organisms can provide as memory housing and protection for stored data or information. The present invention provides well for data storage in a living organism wherein at least one DNA sequence is encoded to represent data and incorporated into a living organism.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
High surface cultivation system with surface increasing substrate
InactiveUS20080206735A1Increase of available surfaceIncrease gas exchangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulticellular organismCulture cell
An exemplary embodiment of a culture vessel suitable is provided for a cultivation of cells and / or tissues. The exemplary vessel comprising at least one reversibly closable aperture in the vessel wall, and at least one surface-increasing substrate within the vessel, with the substrate being made of a single mold. According to another exemplary embodiment, a system can be provided comprising at least two vessels being interconnected via at least one aperture in their vessel wall, and a cultivation process using such a vessel or system, in which at least one type of cells, tissue, tissue-like cell cultures, organs, organ-like cell cultures, or multicellular organisms may be cultivated in the presence of at least one fluid or solid medium, e.g., provided for growing and / or cultivating the culture.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
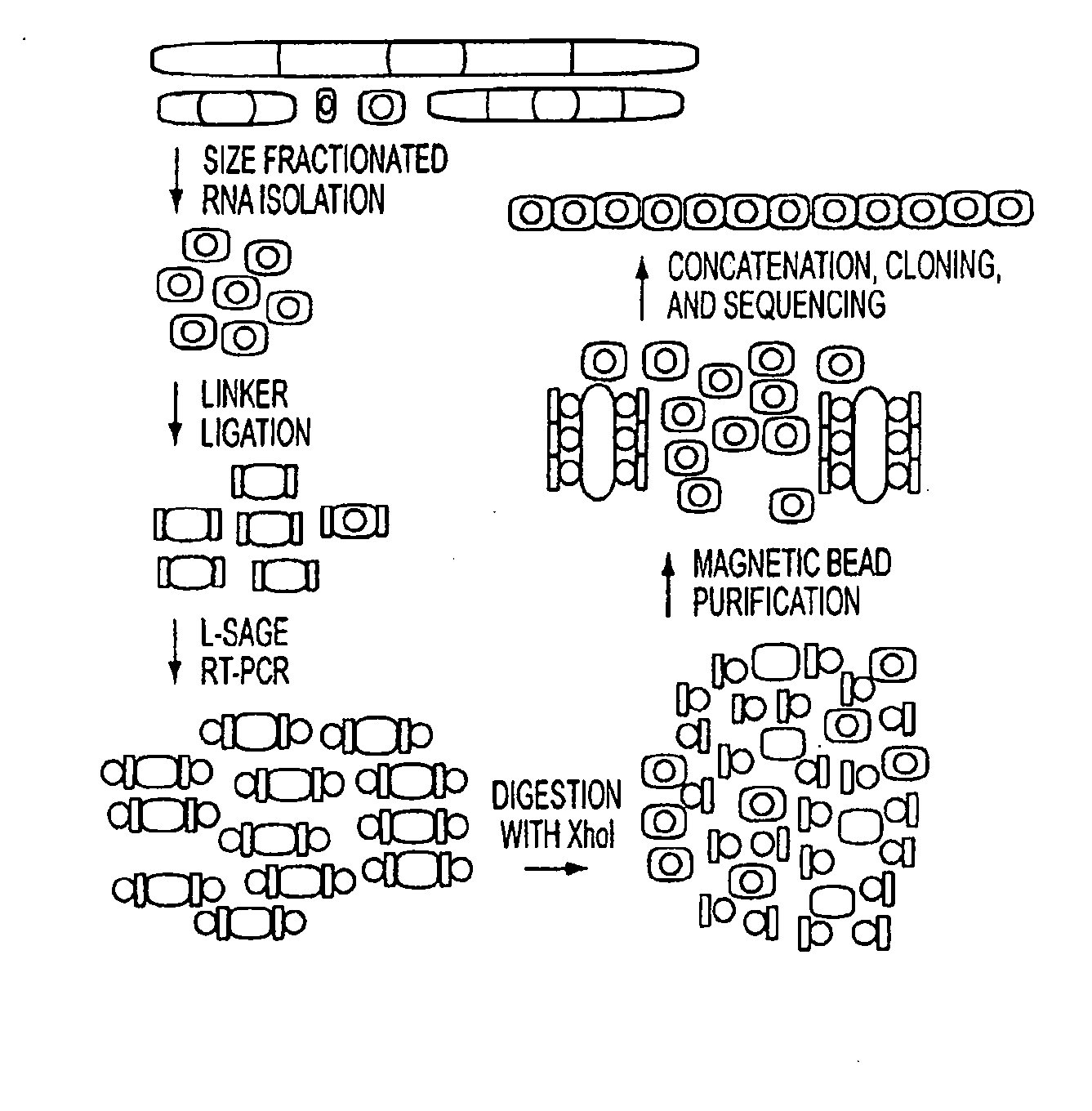
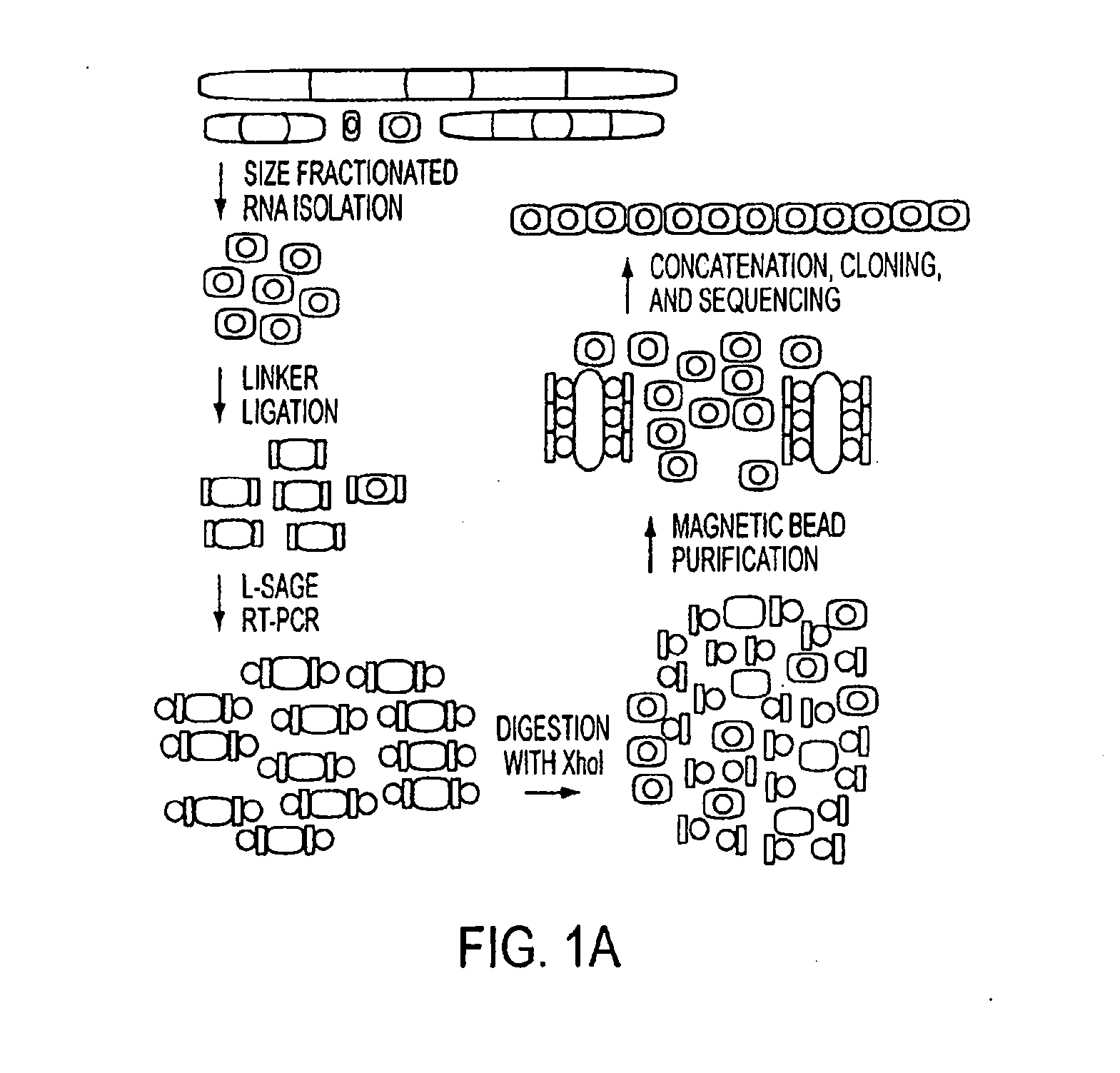
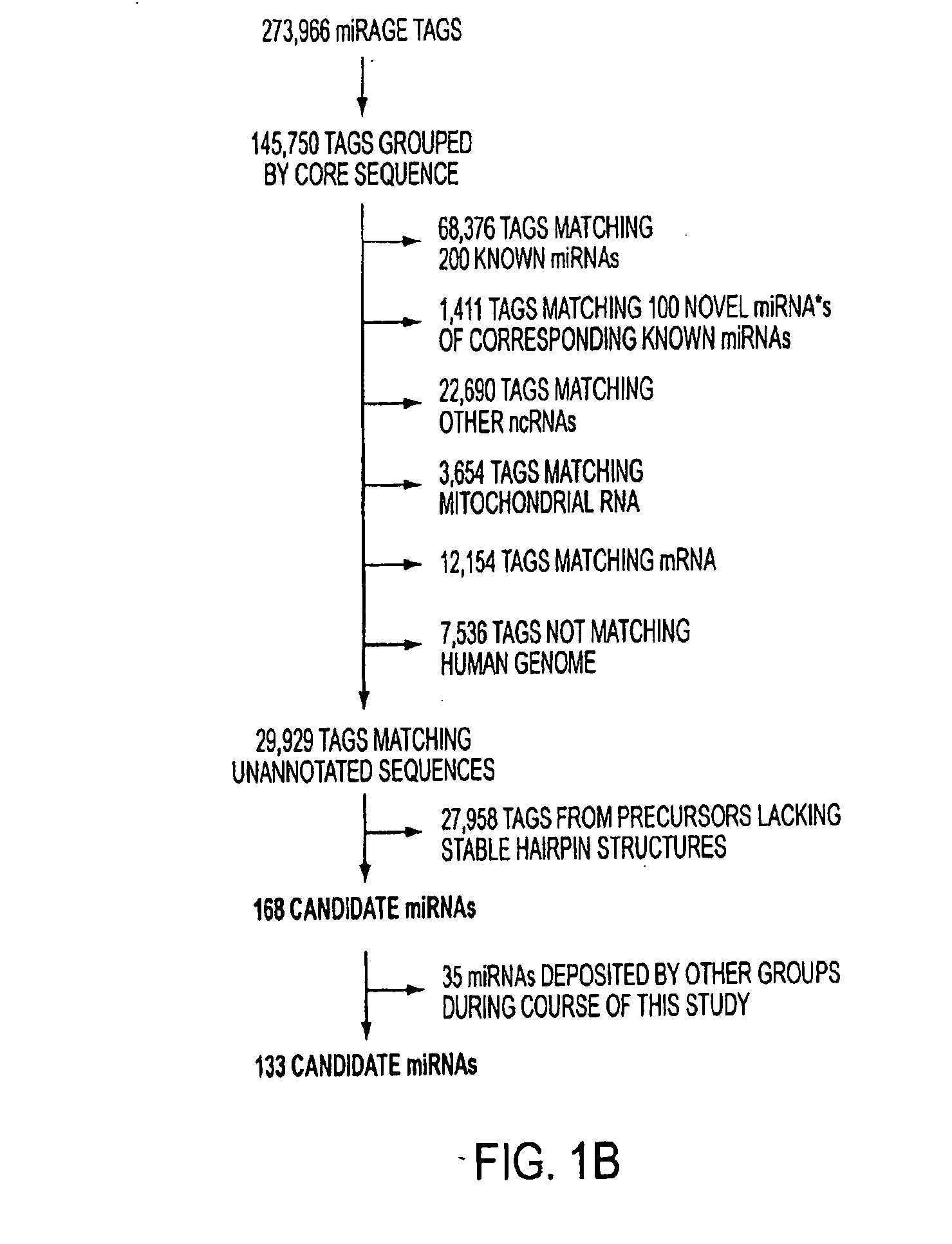
Micrornaome
ActiveUS20100137413A1Reduce generationIncrease volumeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencing
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small noncoding RNAs that have important regulatory roles in multicellular organisms. The public miRNA database contains 321 human miRNA sequences, 234 of which have been experimentally verified. To explore the possibility that additional miRNAs are present in the human genome, we have developed an experimental approach called miRNA serial analysis of gene expression (miRAGE) and used it to perform the largest experimental analysis of human miRNAs to date. Sequence analysis of 273,966 small RNA tags from human colorectal cells allowed us to identify 200 known mature miRNAs, 133 novel miRNA candidates, and 112 previously uncharacterized miRNA* forms. To aid in the evaluation of candidate miRNAs, we disrupted the Dicer locus in three human colorectal cancer cell lines and examined known and novel miRNAs in these cells. The miRNAs are useful to diagnose and treat cancers.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Identification of genetic markers of biological age and metabolism
A method of measuring the biological age of a multicellular organism is disclosed. In one embodiment this method comprises the steps of obtaining a sample of nucleic acid isolated from the organism's organ, tissue or cell and determining the expression pattern of a panel of sequences within the nucleic acid that have been predetermined by either increase or decrease in response to biological aging of the organ, tissue or cell. A method of obtaining biomarkers of aging is also disclosed. This method comprises the step of comparing a gene expression profile of a young multicellular organism subject's organ, tissue or cells; a gene expression profile from a chronologically aged subject's organ, tissue or cell; and a gene expression profile from a chronologically aged but biologically younger subject's organ, tissue or cell and identifying gene expression alterations that are observed when comparing the young subjects and the chronologically aged subjects and are not observed or reduced in magnitude when comparing the young subjects and the chronologically aged but biologically younger subjects.
Owner:WEINDRUCH RICHARD H +2
Storing data encoded DNA in living organisms
Current technologies allow the generation of artificial DNA molecules and / or the ability to alter the DNA sequences of existing DNA molecules. With a careful coding scheme and arrangement, it is possible to encode important information as an artificial DNA strand and store it in a living host safely and permanently. This inventive technology can be used to identify origins and protect R&D investments. It can also be used in environmental research to track generations of organisms and observe the ecological impact of pollutants. Today, there are microorganisms that can survive under extreme conditions. As well, it is advantageous to consider multicellular organisms as hosts for stored information. These living organisms can provide as memory housing and protection for stored data or information. The present invention provides well for data storage in a living organism wherein at least one DNA sequence is encoded to represent data and incorporated into a living organism.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
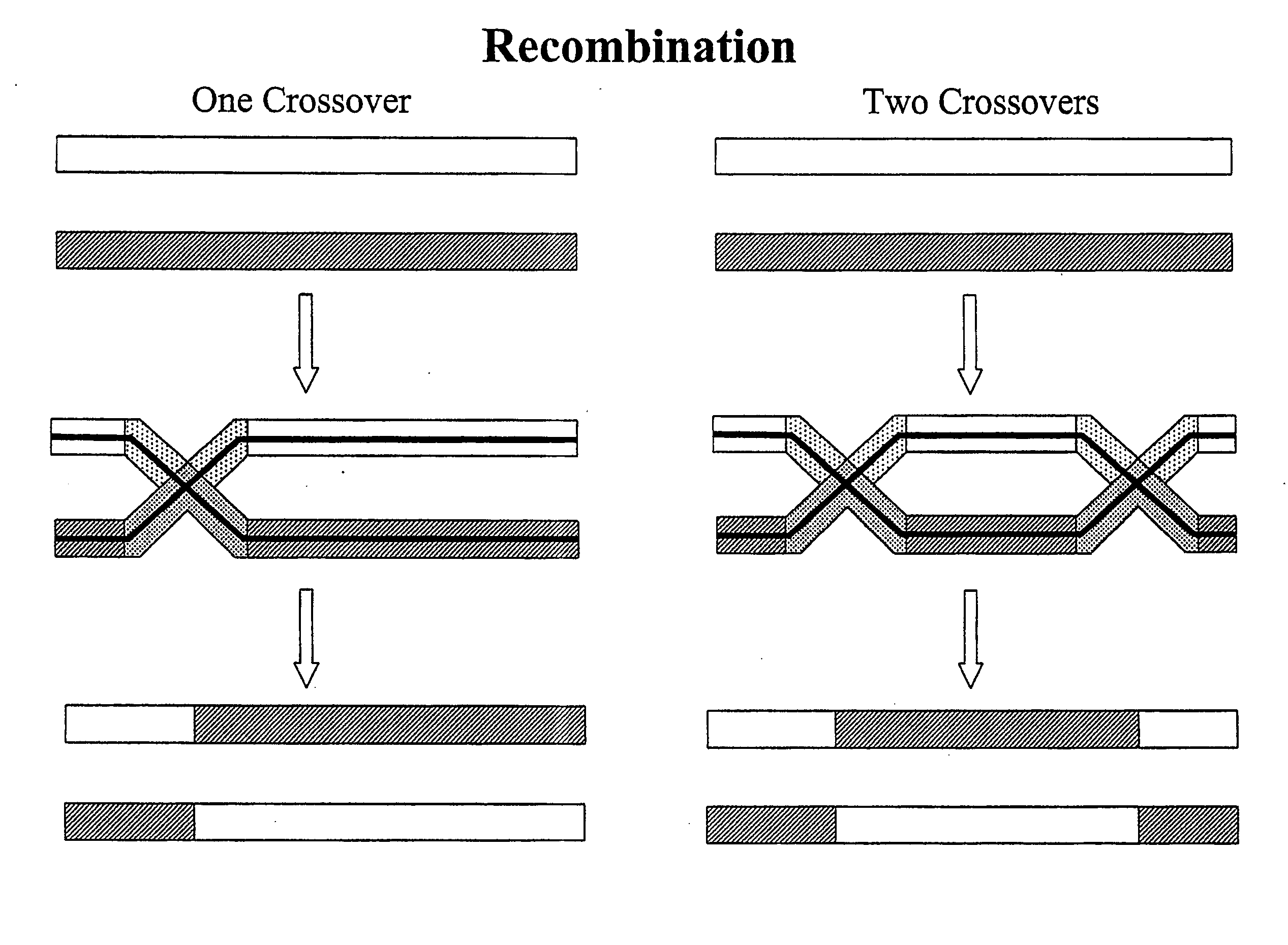
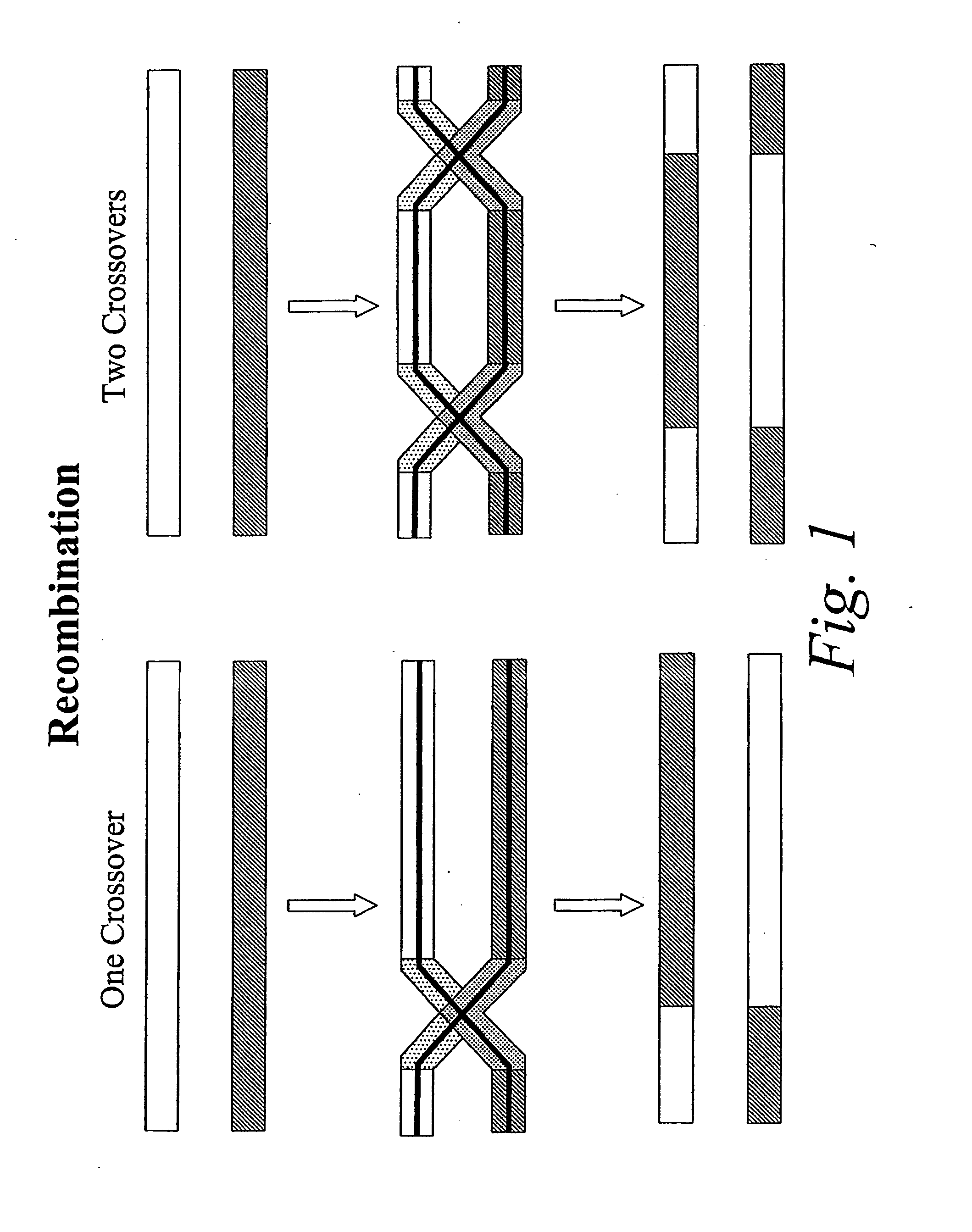
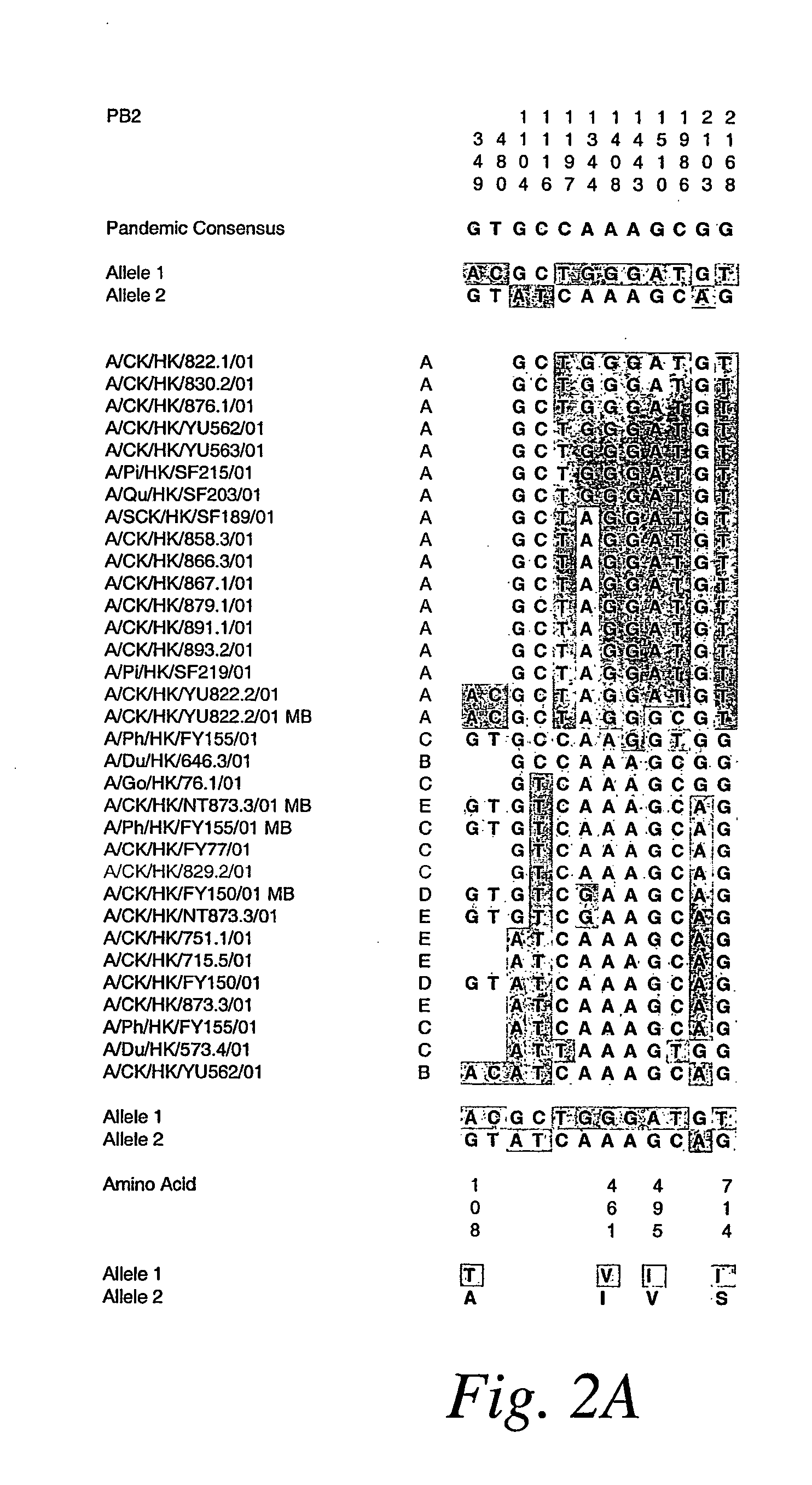
Copy choice recombination and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070253978A1Improve humanImprove animal healthSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMulticellular organismAnimal health
The instant invention provides methods for determining, predicting and characterizing the genetic variability of a range of organisms, including, e.g., viruses, microbes, cells and multicellular organisms. Accordingly, the invention provides methods for identifying virulent pathogens, genetic mutations within pathogens that are relevant to animal health, and methods and compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic intervention against such pathogens.
Owner:NIMAN HENRY L
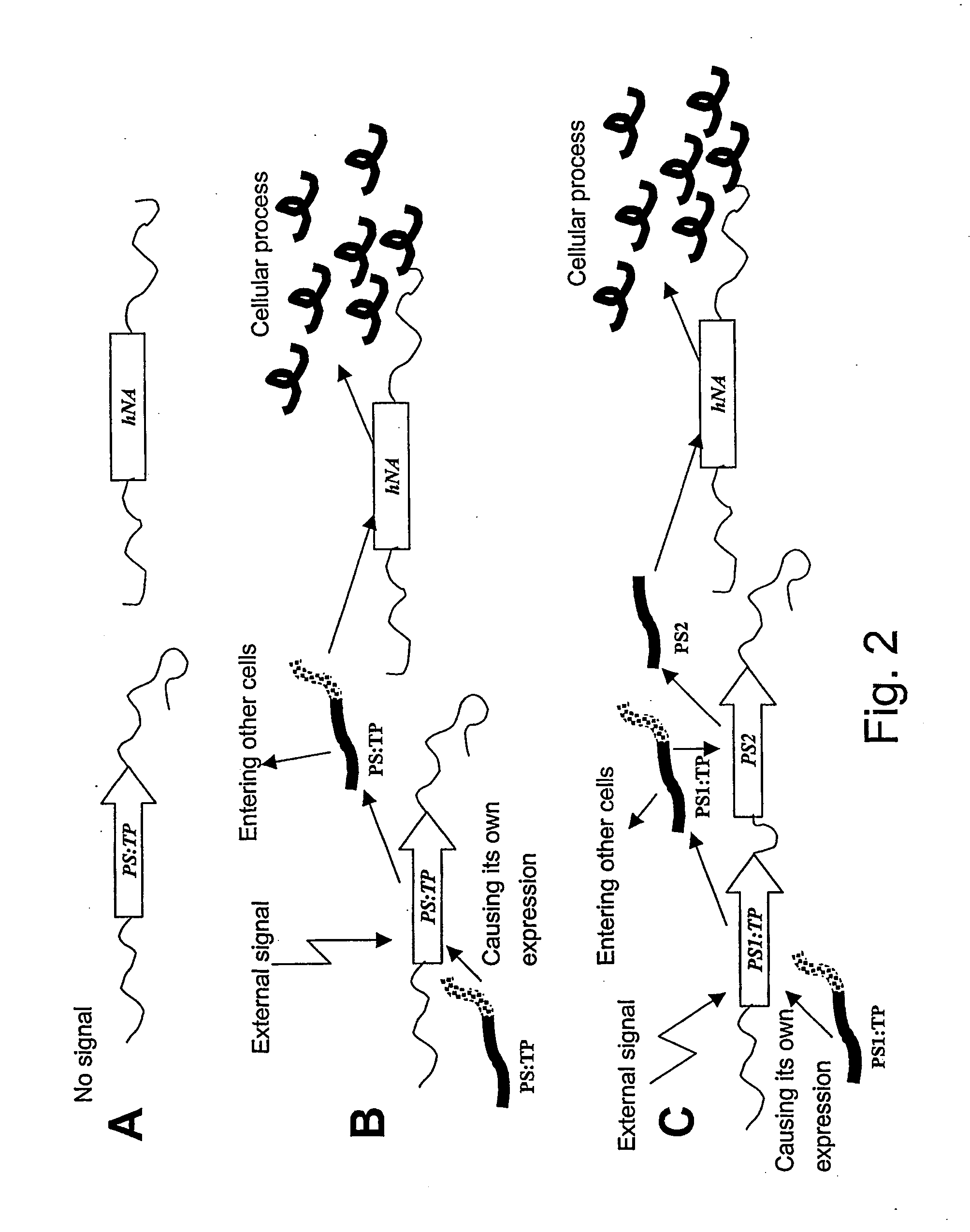
Method of controlling a cellular process in a multi-cellular organism
InactiveUS20060075524A1Slows plant growthHigh efficiencyBryophytesSugar derivativesBiological bodyBiotechnology
A method of controlling a genetically-modified multi-cellular organism or a part thereof, comprising the following steps: (a) providing a multi-cellular organism or a part thereof, whereby cells of said multi-cellular organism or said part contain a heterologous nucleic acid, (b) causing expression of a I protein from said heterologous nucleic acid in at least some of said cells, wherein said protein is capable of (i) leaving a cell and entering other cells of said multi-cellular organism or a part thereof, (ii) causing expression of said protein in cells containing said heterologous nucleic acid, and optionally (iii) controlling a cellular process of interest.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
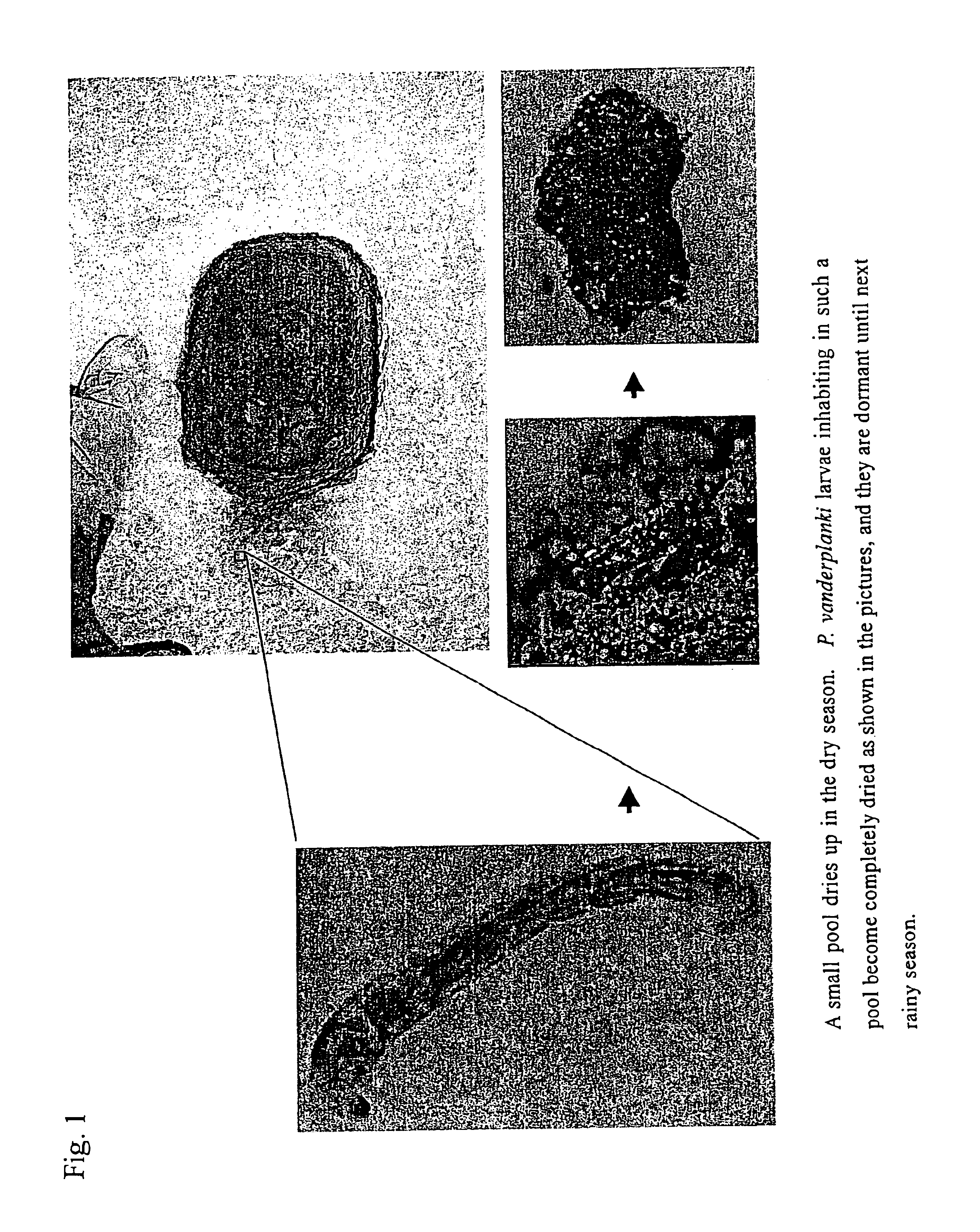
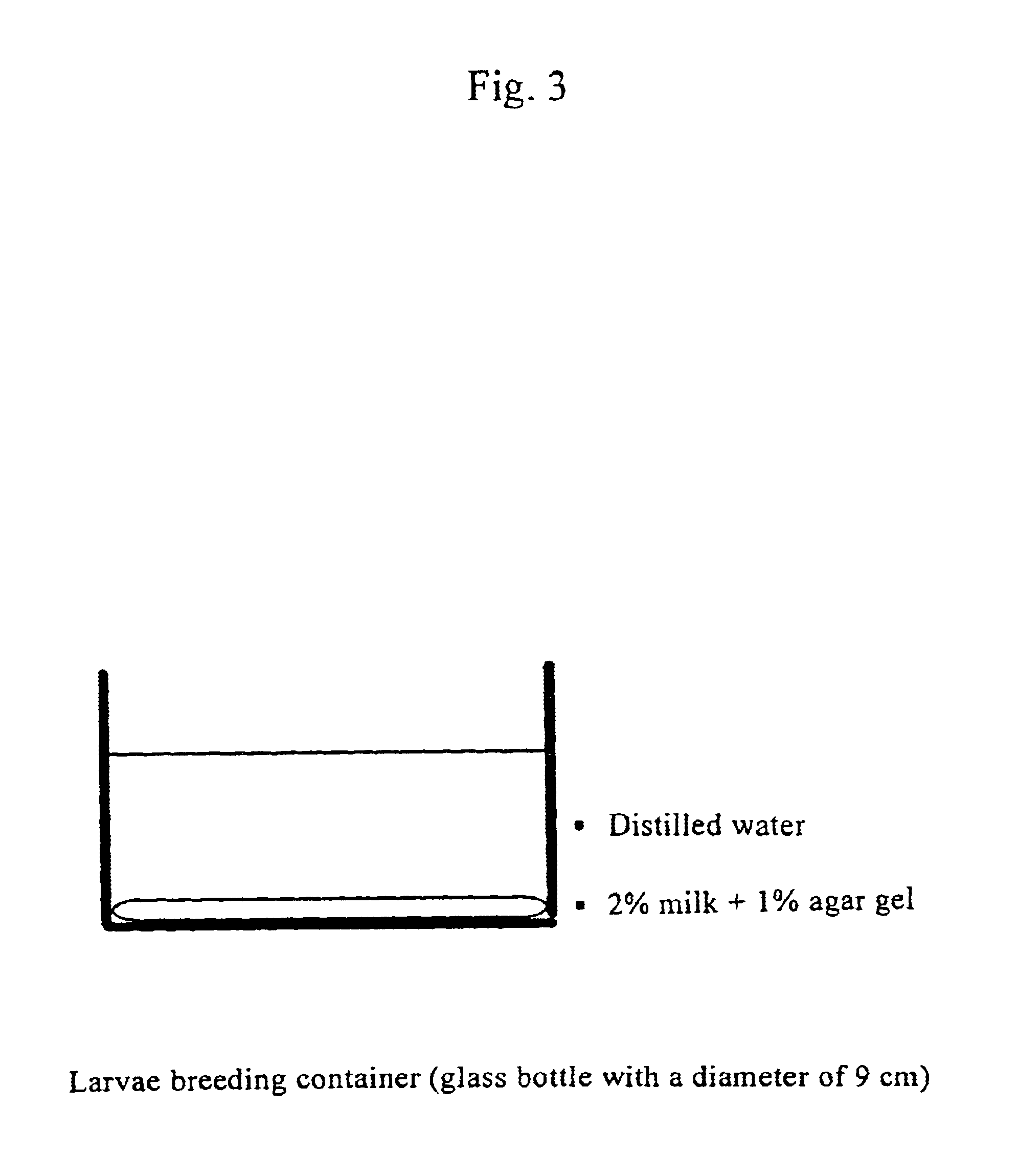
Method for dry-preserving multicellular organism tissue at ordinary temperatures
A tissue of a multicellular organism is gradually dried during cultivation. After the tissue has been completely dehydrated, water is added to the tissue for its recovery. The tissue of the multicellular organism is submerged in an insect body fluid medium treated with heat, and dried for 48 hours or more.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +3
Methods of screening for compounds that inhibit expression of biomarker sequences differentially expressed with age in mice
InactiveUS7041449B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyMulticellular organism
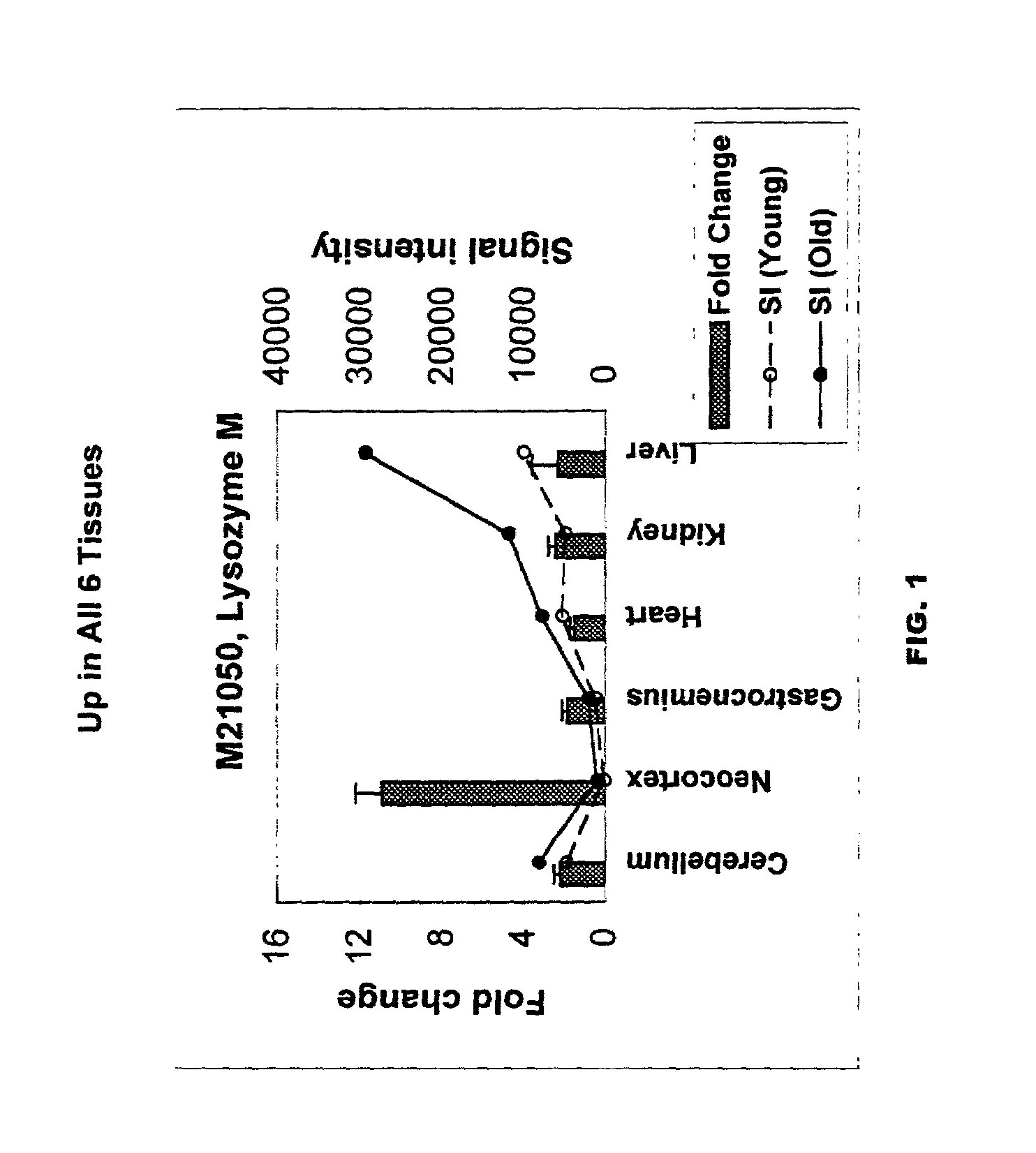
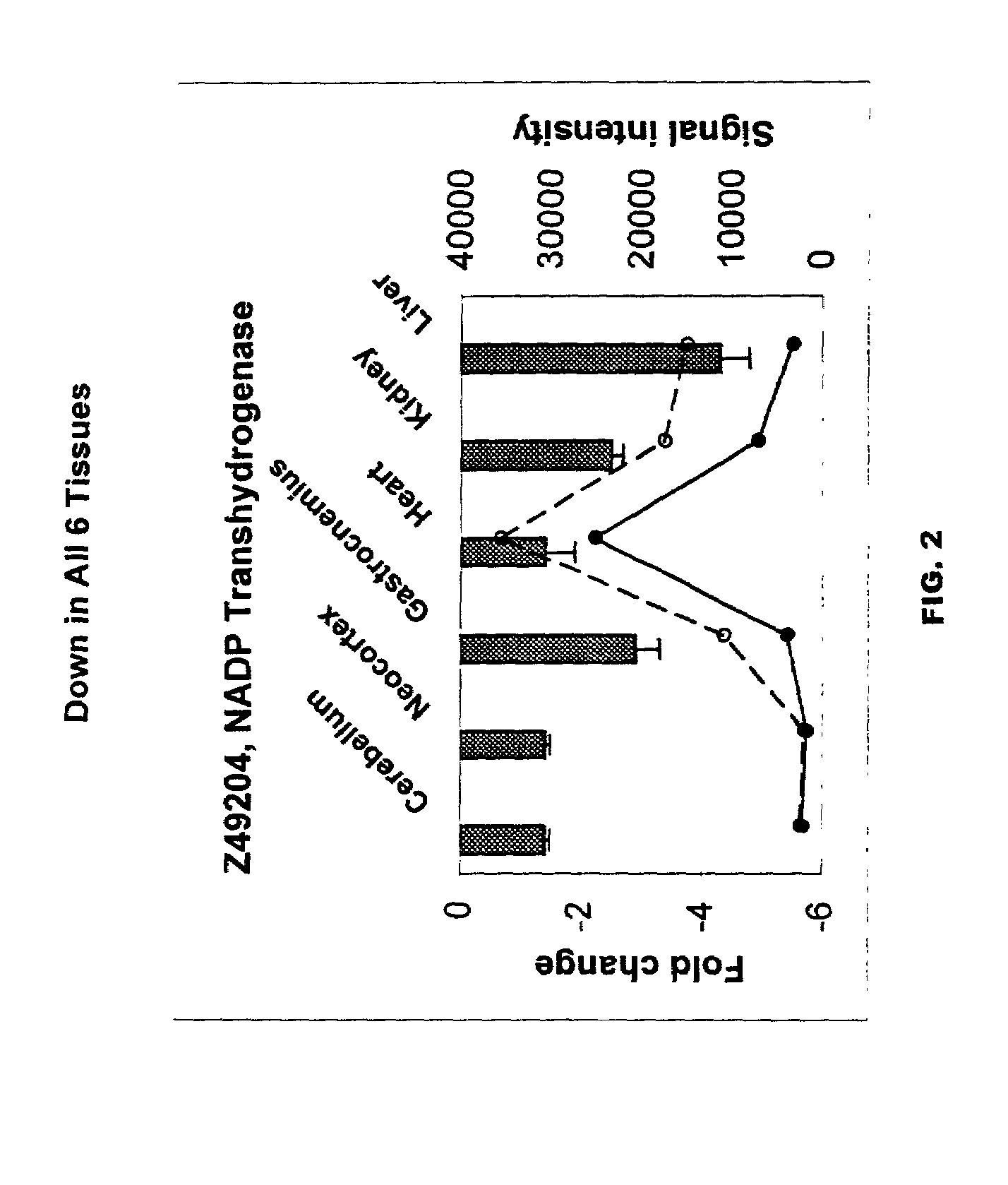
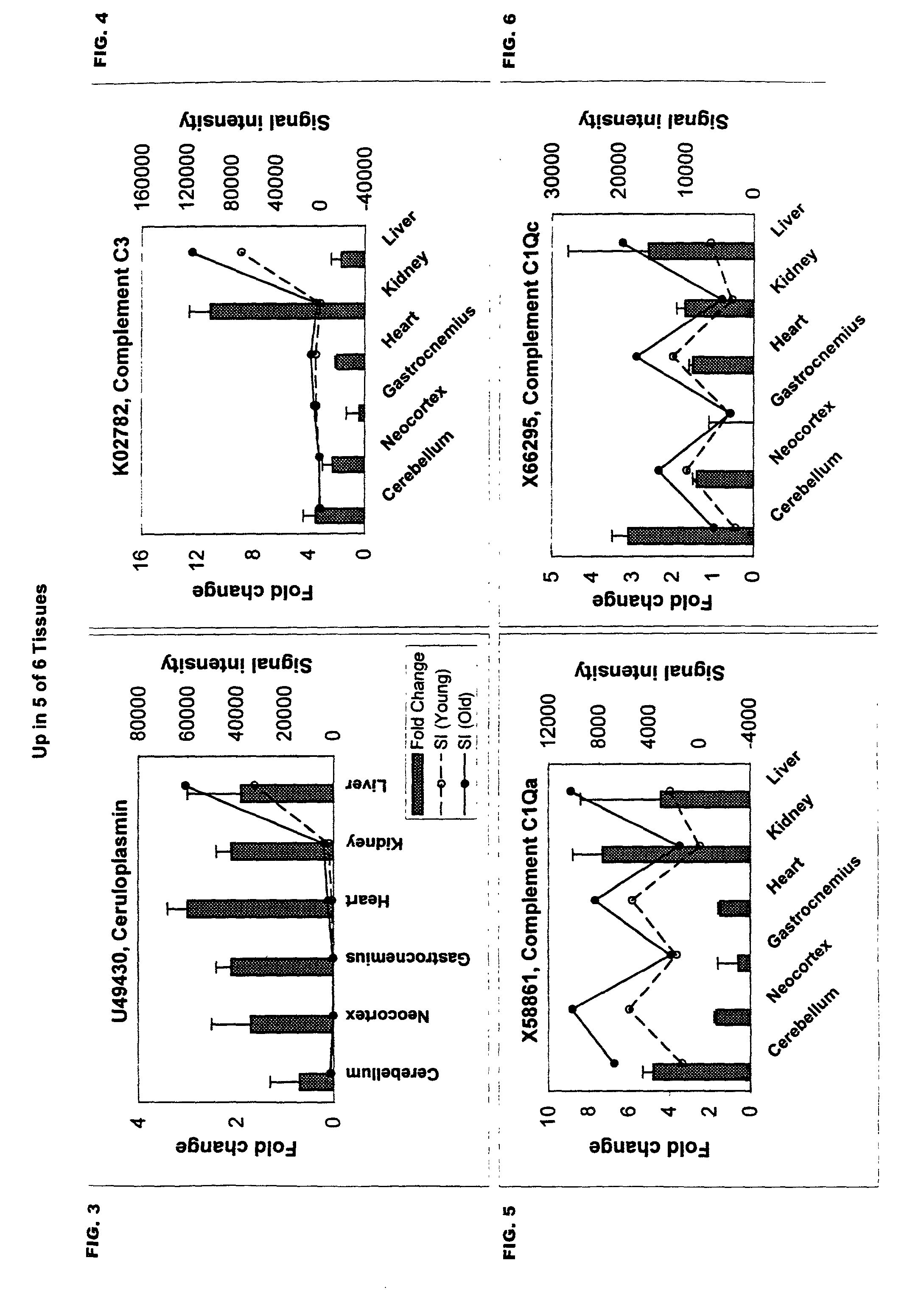
A method of measuring the biological age of a multicellular organism is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining a sample of nucleic acid isolated from the organism's organ, tissue or cell, wherein the nucleic acid is RNA or a cDNA copy of RNA and (b) determining the gene expression pattern of at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of M21050, Z49204, U49430, K02782, X58861, X66295, M22531, X67809, U19118, M64086, M63695, U39066, X92590, X56518, AA182189, X16493, U20344, X16834, X82648, D00754, D16313, L38971 and X15789.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
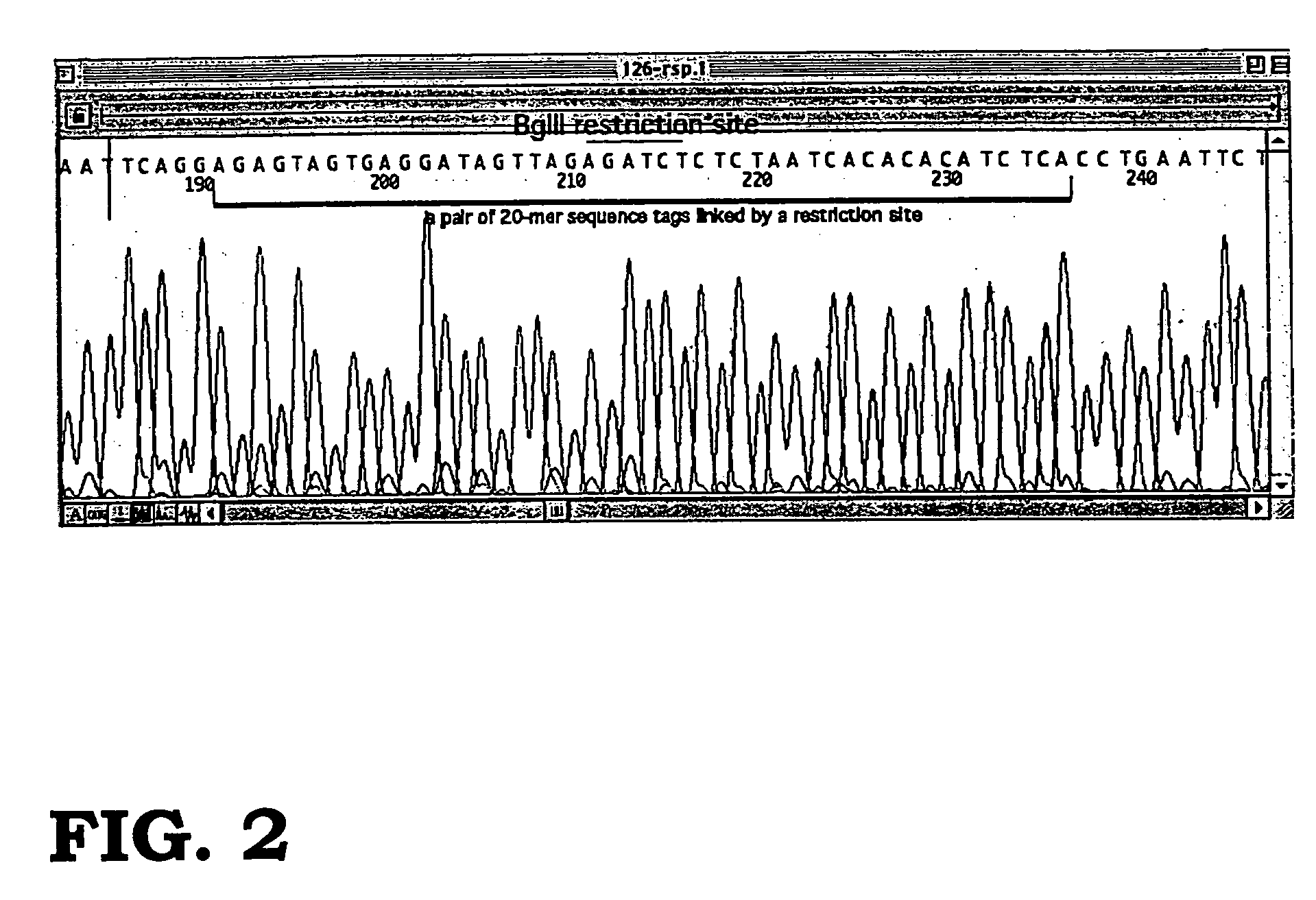
Process and apparatus for using the sets of pseudo random subsequences present in genomes for identification of species
InactiveUS20050255459A1Rapid increase of computational complexityEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHuman speciesGenomic DNA
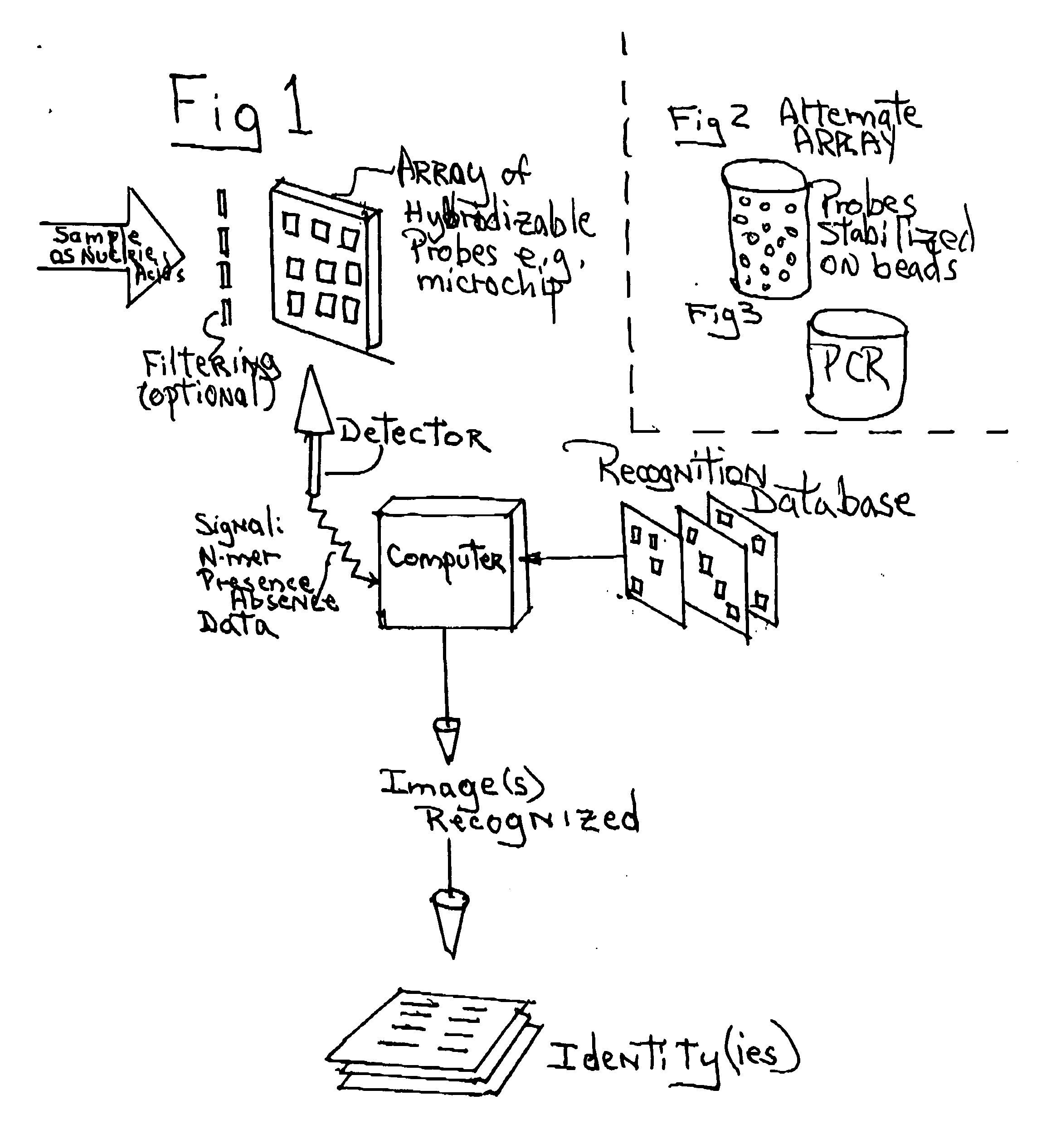
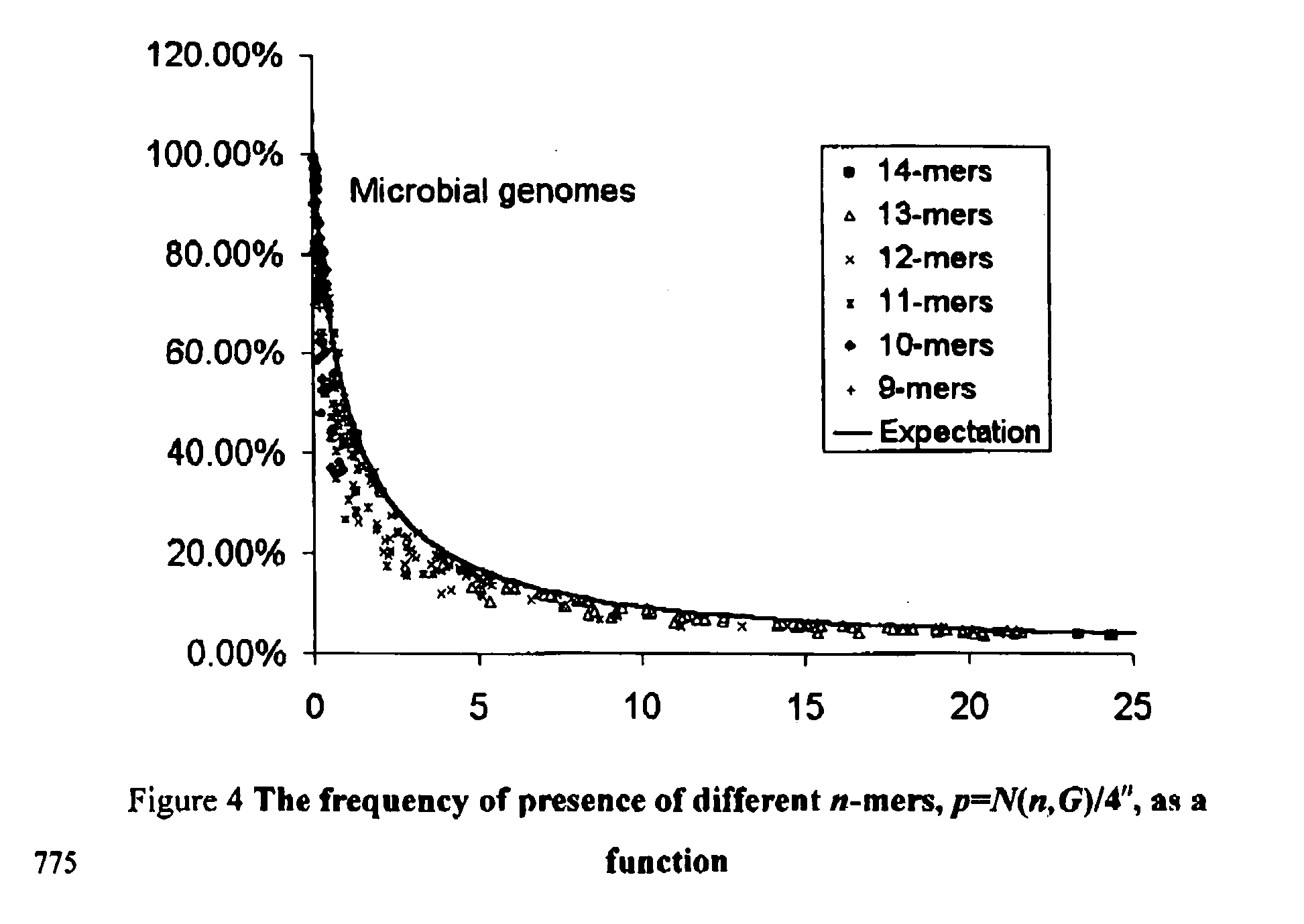
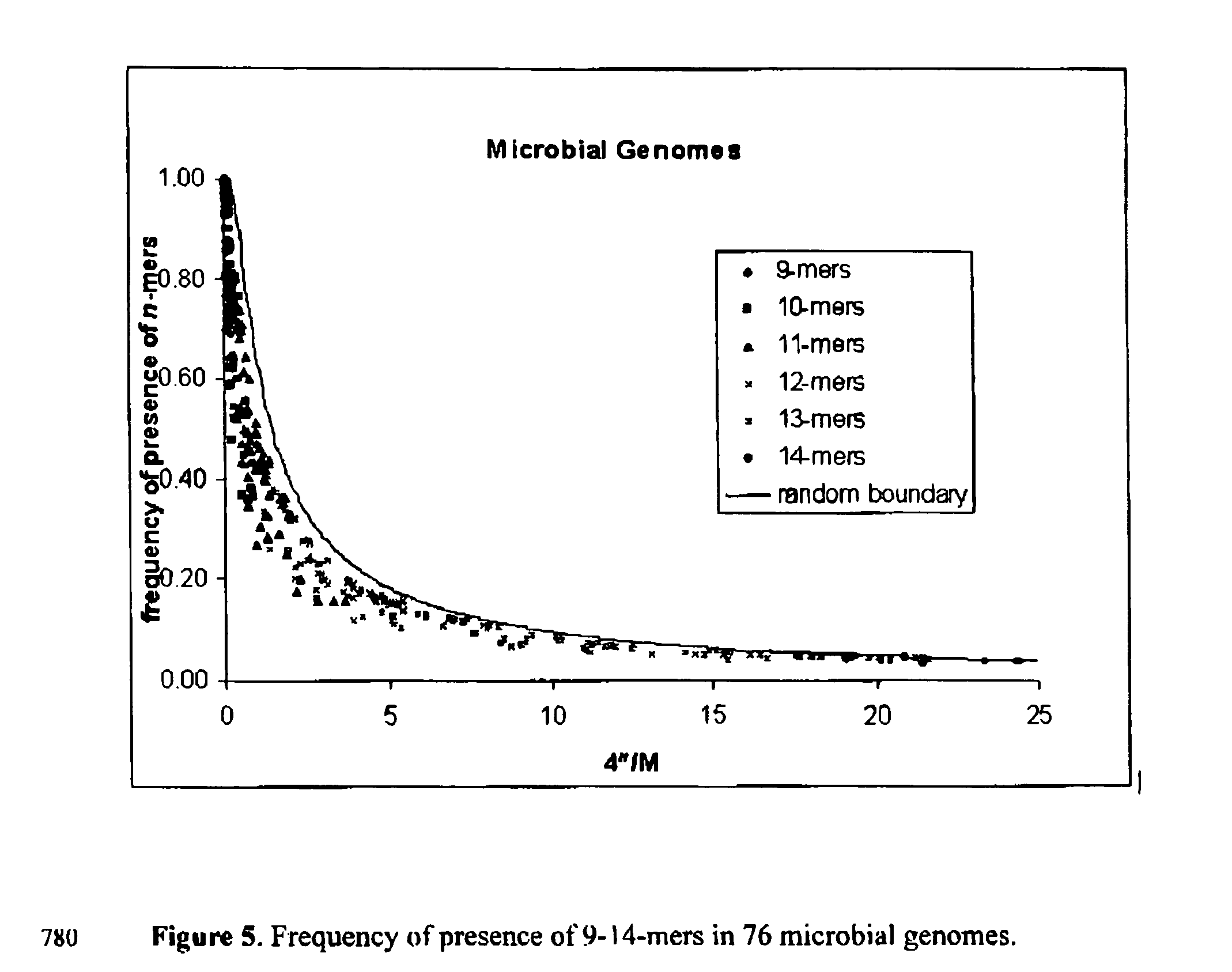
Our research conducted with the genome sequences of more than 250 species of organisms (including viral, microbial, and multi-cellular organisms, and human) results in the discovery that the occurrence of a particular subsequence (the so-called “motifs” or “n-mers,” (n being the length of the subsequences), which can be up to 25 and higher) in the genome of a particular species can be considered as a nearly random event; and that the occurrences of a particular subsequence in the genome sequences of different species can be considered as nearly independent events (with the exception of the cases where extremely closely related species are compared). The set of subsequences that occur in a particular species' genome can therefore be used as a genomic “fingerprint” of this species. This discovery leads to the concept of utilizing a set of pseudo-randomly designed subsequences for species identification or discrimination. These subsequences (probes, primers, motifs, n-mers) can be used with hybridization-based technologies (including, but not limited to, the microarray or PCR technologies) and any other technology allow to identity the fact of presence / absence of particular subsequence in genomic DNA for identification of species. The same approach can also be used to identify individuals of the same species (including the human species), to estimate the genome size of unknown organisms, and to estimate the total genome size in samples containing several viral, microbial, and eukaryotic genomes. The identification methods currently in use for these purposes require sequencing of the genomic sequences of the species or the individuals of interest. The introduction of the proposed computational method eradicates such requirement, and will tremendously reduce the expense of these tests.
Owner:FOFANOV YURIY +3
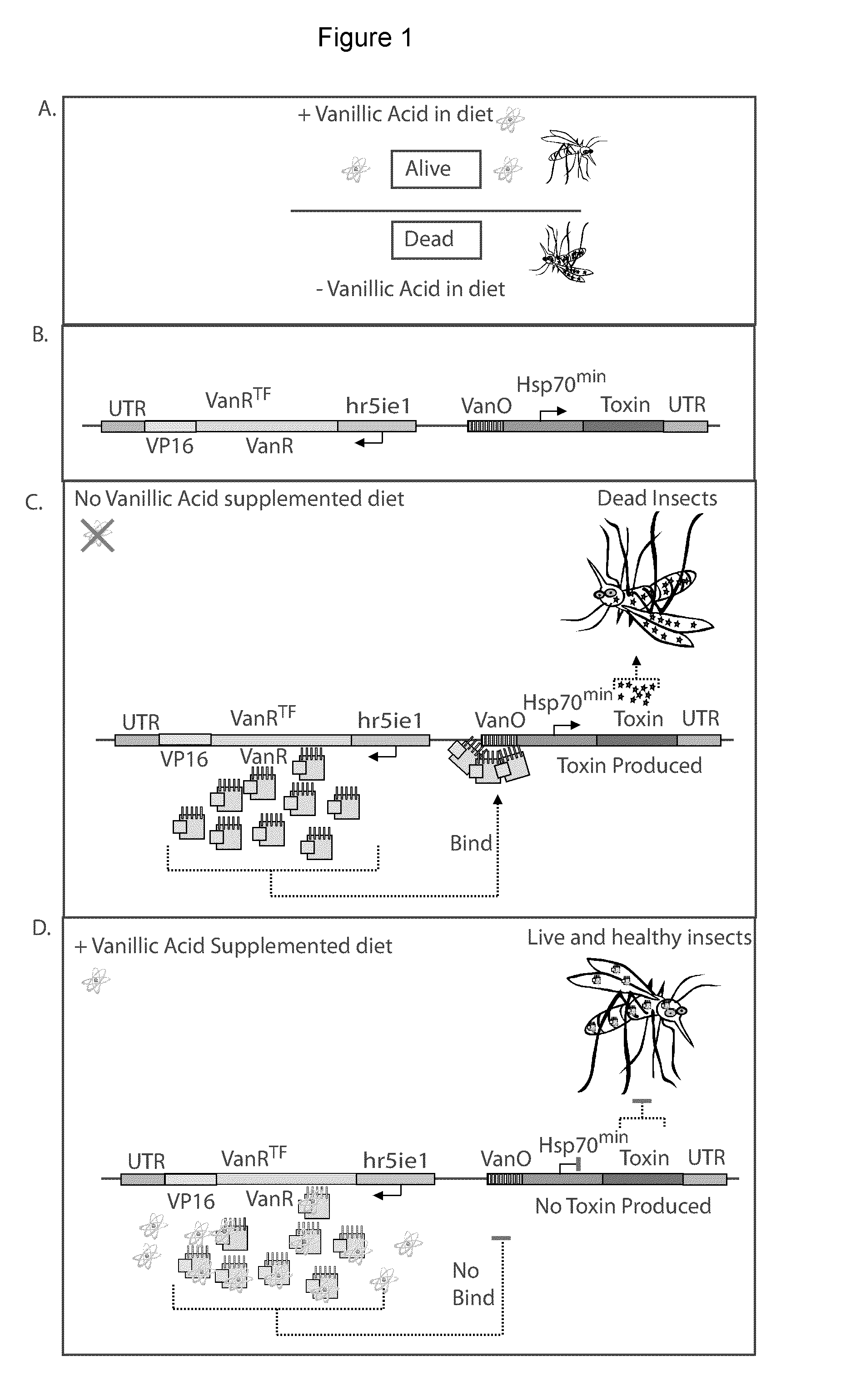
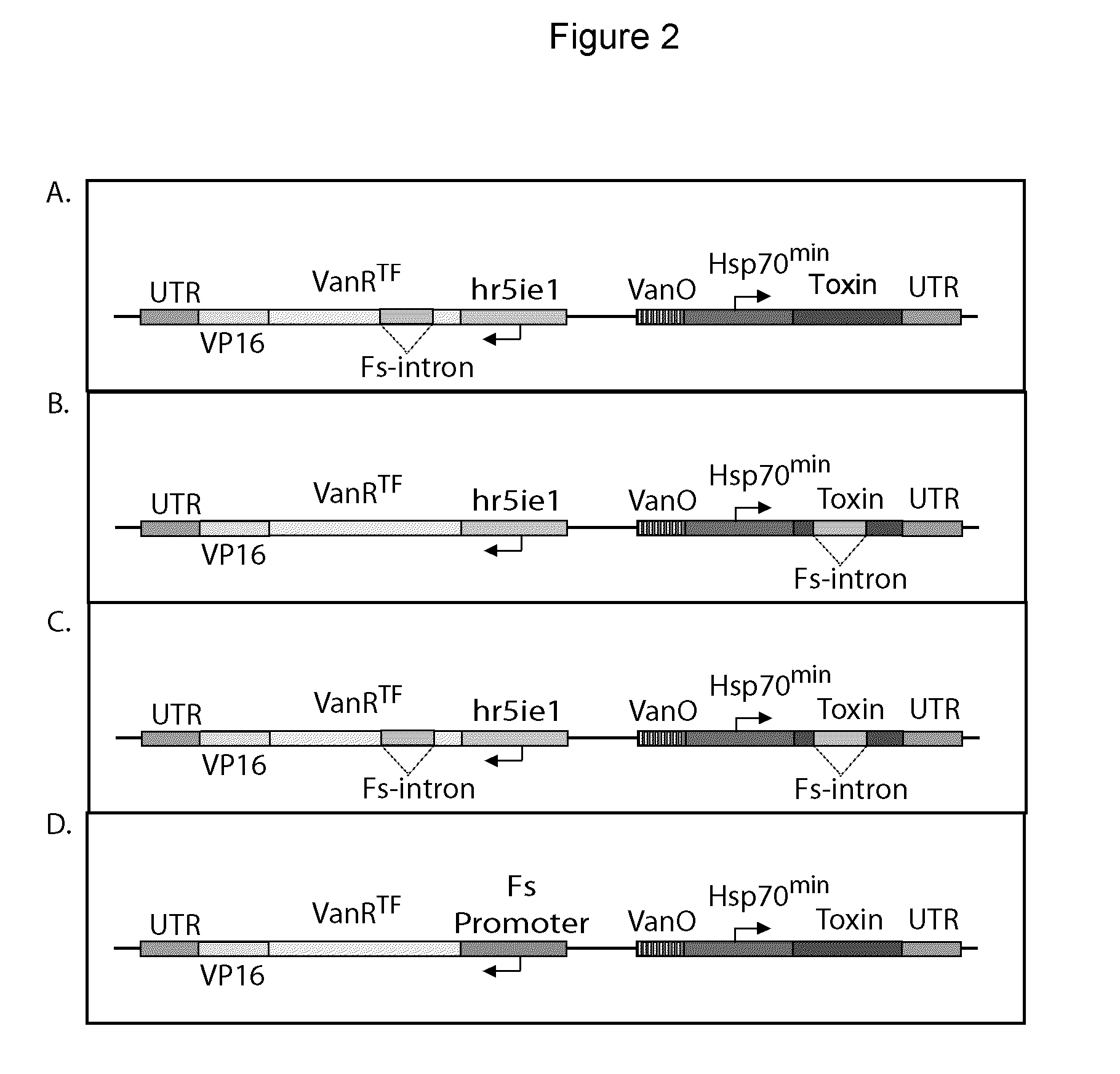
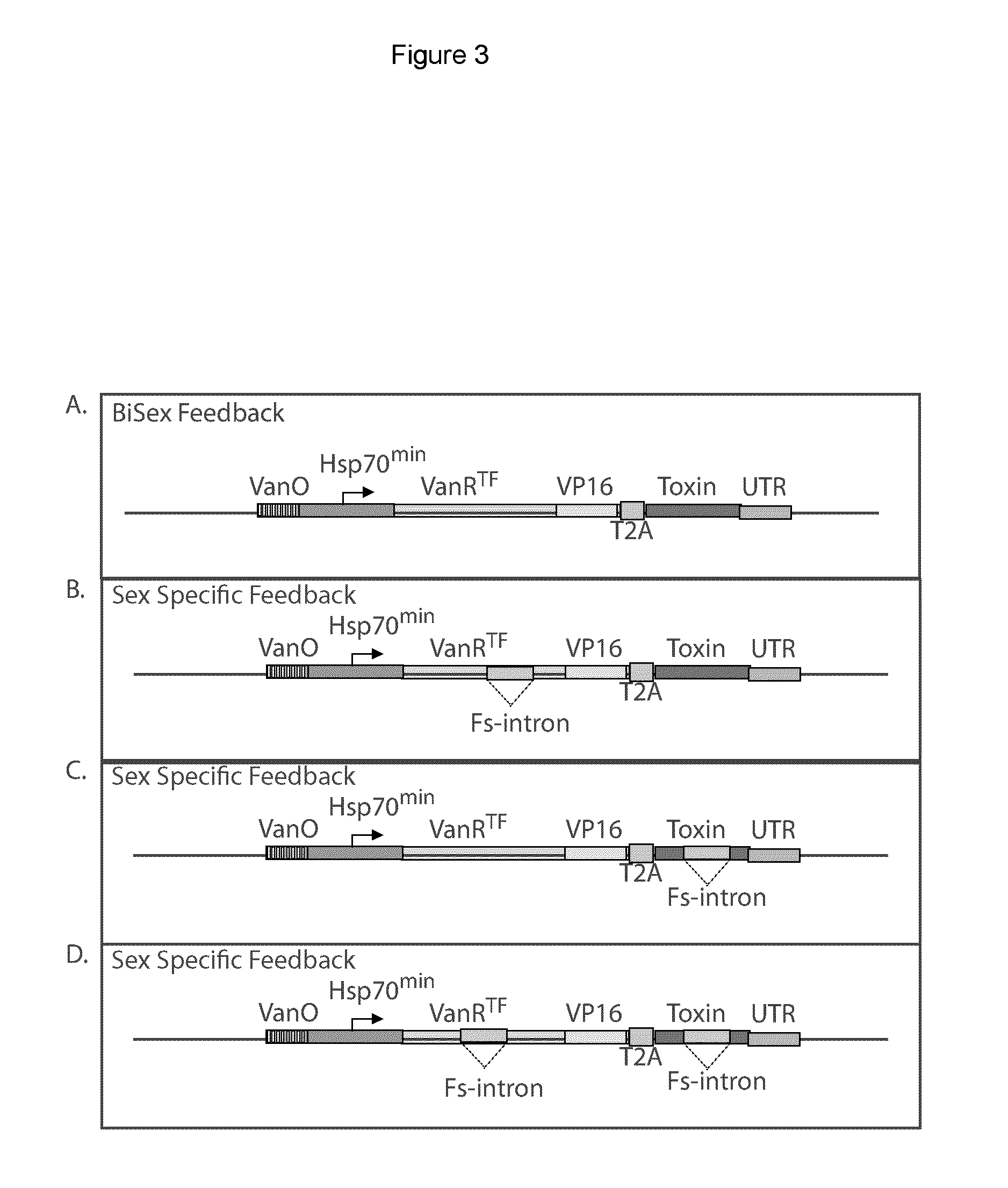
Repressible lethal system for regulating insect populations
Disclosed herein are components, systems and methods for regulating population of multicellular organisms, for example insects.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Human diacylglycerol kinase iota
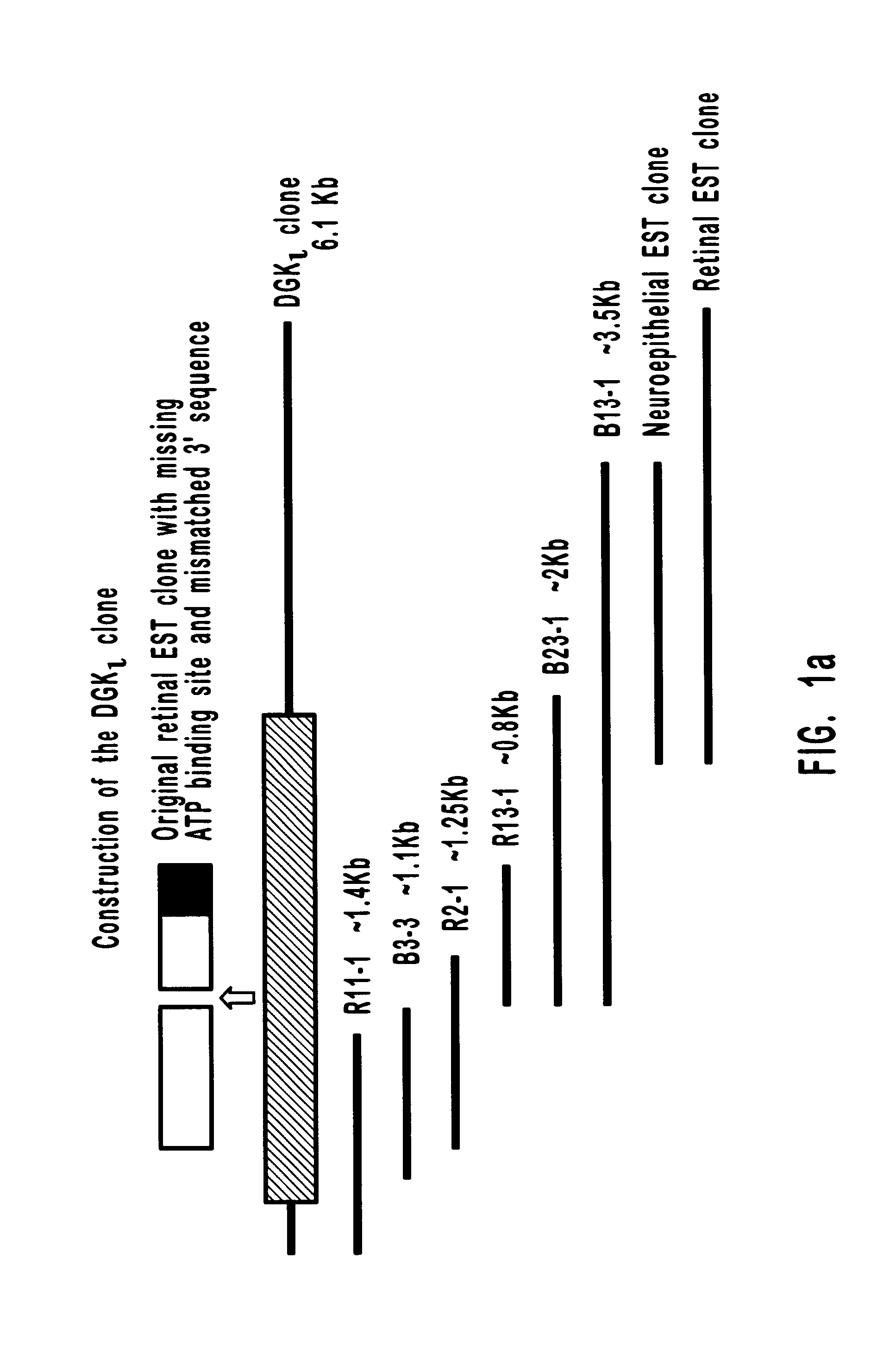
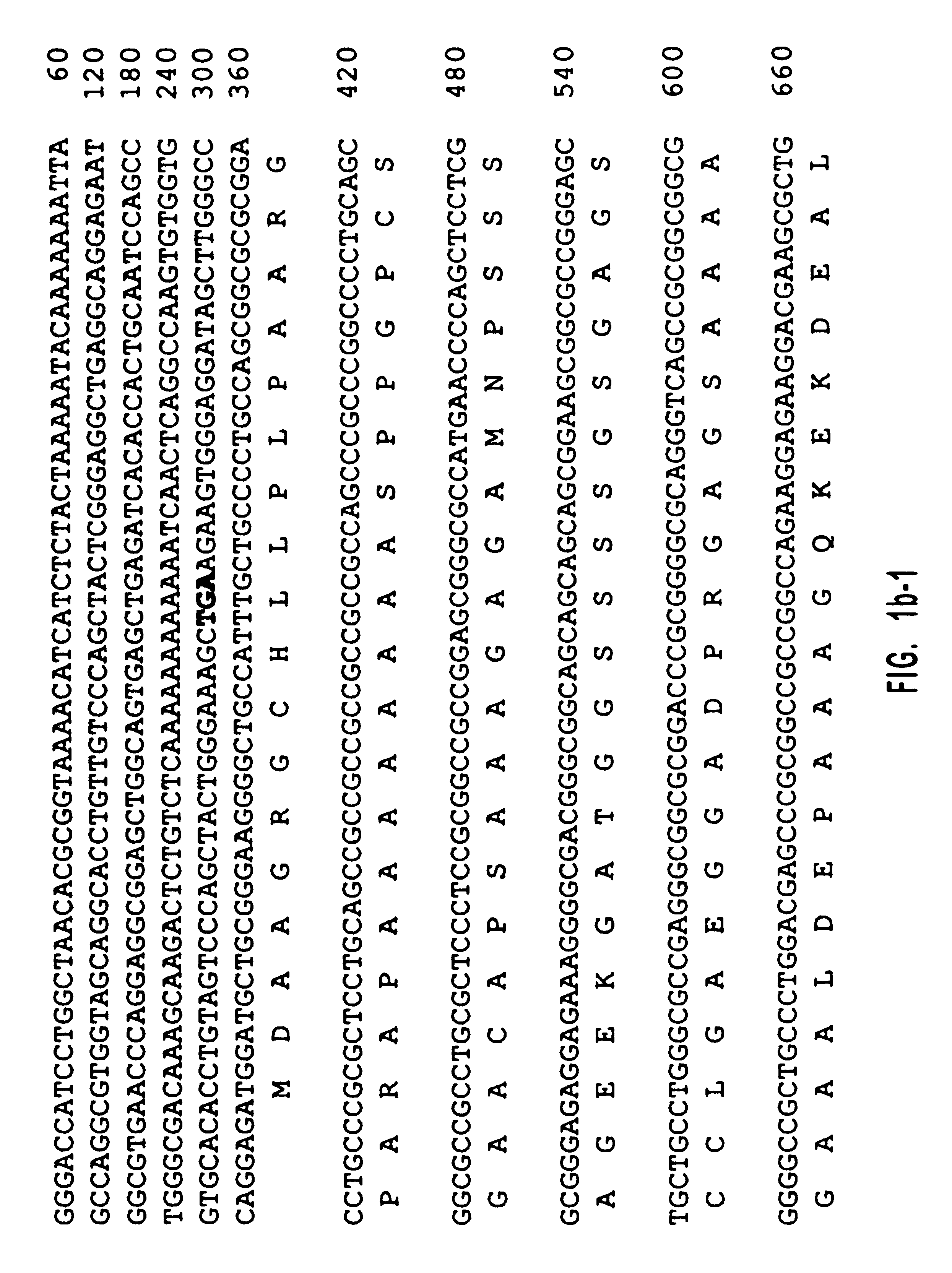
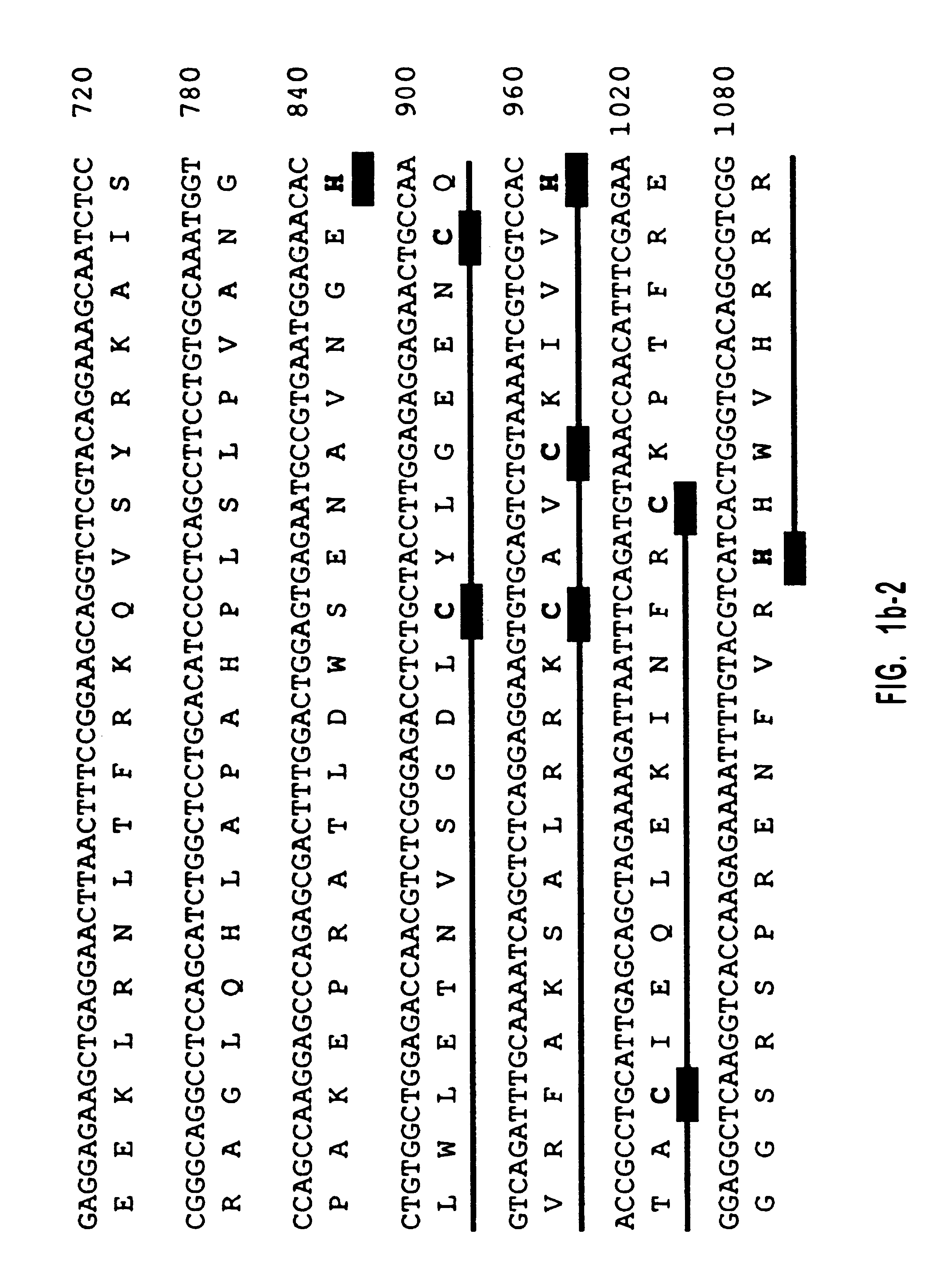
Diacylglycerol (DAG) plays a central role in both the synthesis of complex lipids and in intracellular signaling; diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) catalyzes the phosphorylation of DAG, which yields phosphatidic acid. A family of DGKs has been identified in multicellular organisms over the past few years, but the physiological function(s) of this diversity is not clear. One clue has come from the Drosophila DGK2, rdgA, since mutations in this gene cause retinal degeneration. The present invention relates to a novel DGK, designated DGKι, which was isolated from human retina and brain libraries. DGKι contains two cysteine-rich repeats, a region similar to the phosphorylation site domain of MARCKS, a conserved catalytic domain, and four ankyrin repeats at its C-terminus. By primary structure, DGKι is most similar to human DGKζ and Drosophila rdgA. A>12 kb mRNA for DGKι was detected only in brain and retina among the tissues examined. In cells transfected with the DGKι cDNA, an approximately 130 kDa protein was detected by immunoassay, and activity assays demonstrated that it encodes a functional DAG kinase. The protein was found to be in both the cytoplasm and nucleus, with this localization controlled by PKC isoforms alpha and gamma. The gene encoding DGKι was localized to human chromosome 7q32.3-33, which is known to be a locus for an inherited form of retinitis pigmentosa. These results have defined a novel isoform of DAG kinase, which may have important cellular functions in the retina and brain.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Molecular control of transgene segregation and its escape by a recoverable block of funtion (rbf) system
InactiveUS20040025200A1Leak to environmentInhibition of segregationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructWild type
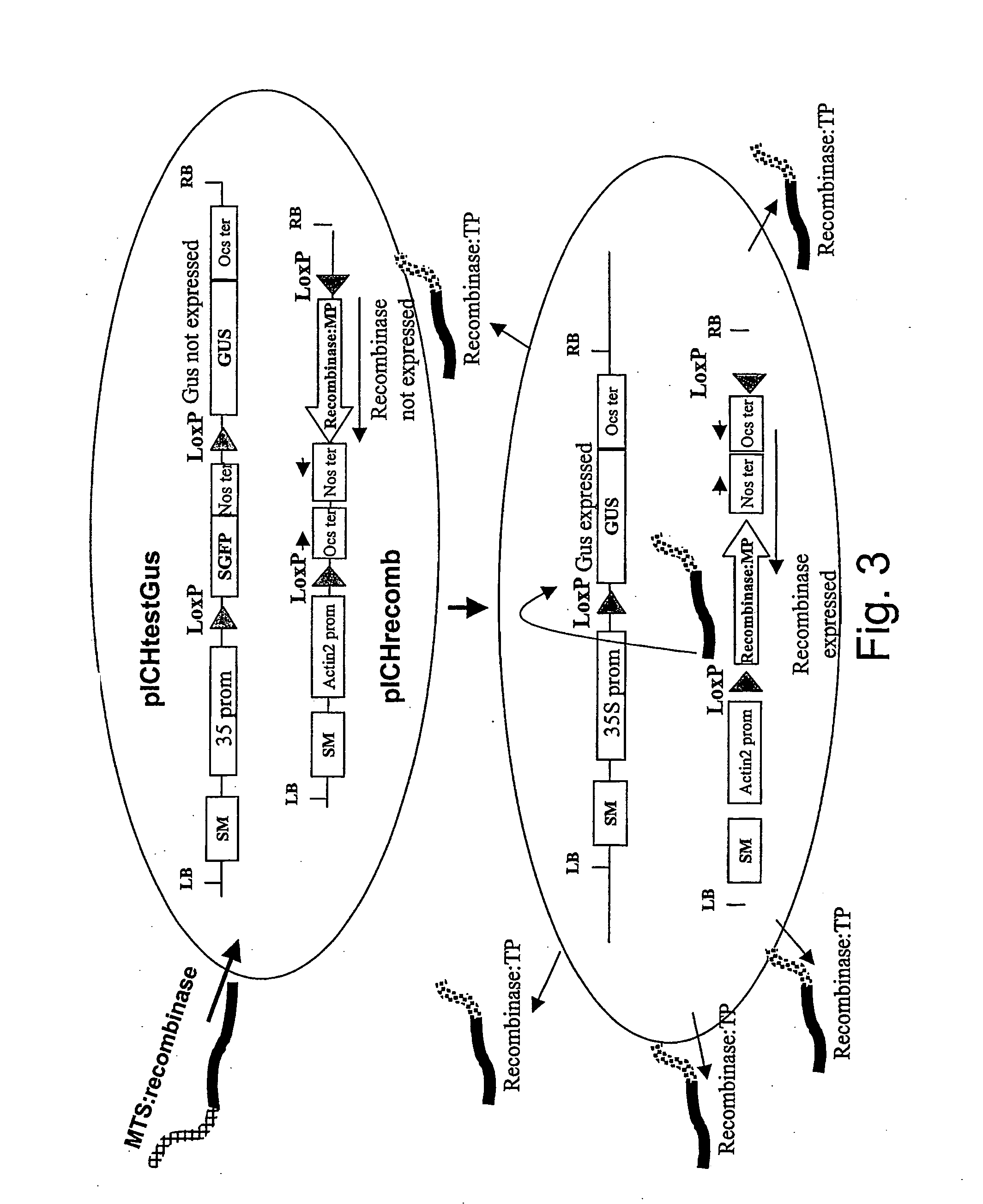
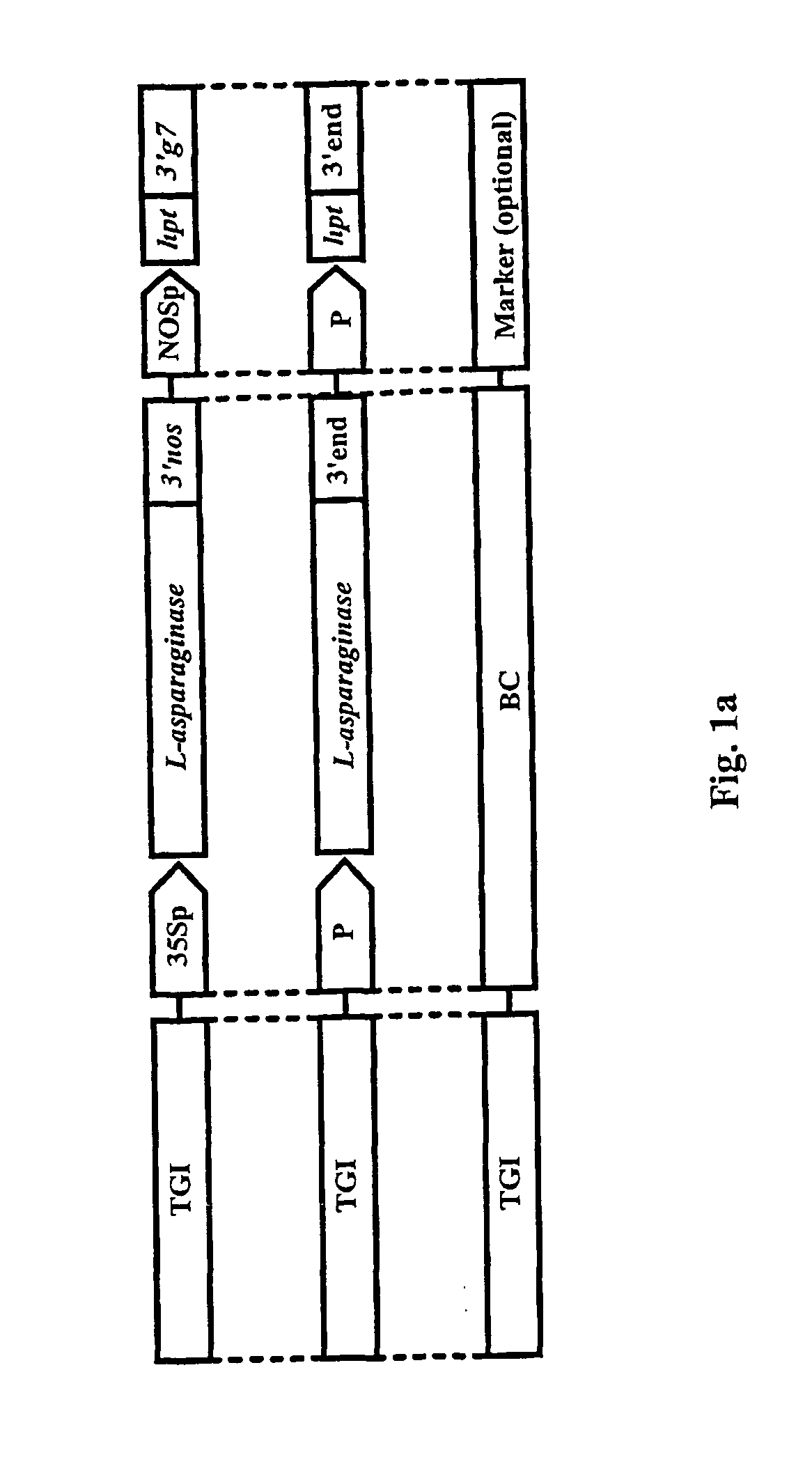
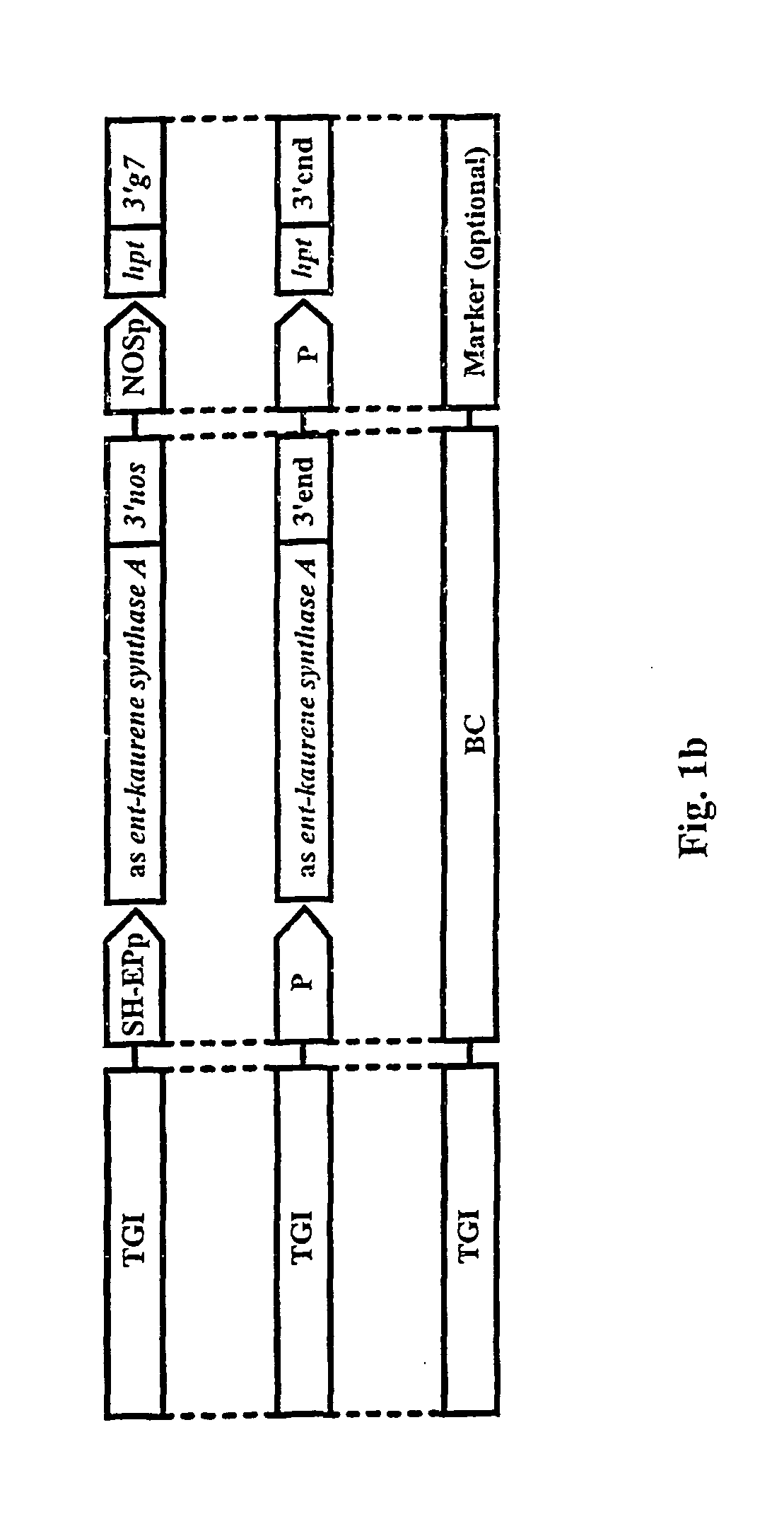
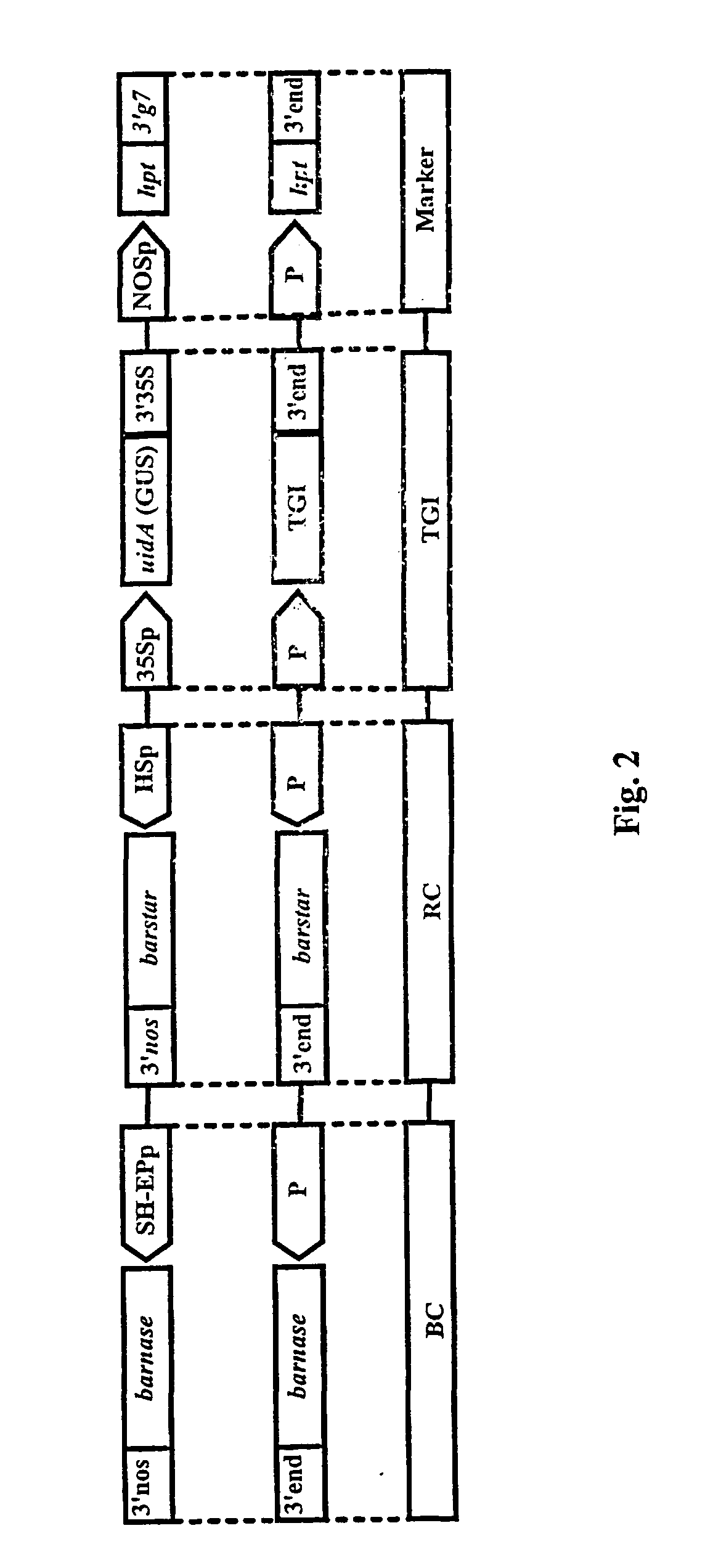
The invention is related to a method and a complex of DNA constructs for providing an increased level of control of transgene segregation in Sexually Reproducing Multicellular Organisms (SRMOs), which are prone to out-crossing with their wild-type or cultivated relatives. The method and constructs allow the farmer to reuse the transgenic crop. without risk. The RBF system comprises one or more Transgenes of Interest (TGIs) encoding desired gene products, one or more Blocking Constructs (BC), and one or more user-controlled means for recovering the blocked functions. The BC has the capacity of blocking at least one function essential for the survival and / or reproduction of the SRMO. Preferably more than one BC flanking the TGIs are used. The BC may be located in close proximity to the TGI, preferably in an intron or flanking the TGIs. The blocked function is recoverable by user-controlled interventions preferably applicable under confined conditions. The intervention is combined with one or more Recovering Constructs (RC). Different types of RBF systems are disclosed. The Double and Triple and Segregating RBF systems and intron-inserted BC are the preferred embodiments of the present invention. The Transgenic Inserts (TI) of the Triple RBF system and their interactions are shown in FIG. 10.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
High surface cultivation system with surface increasing substrate
InactiveCN101646762ATissue/virus culture apparatusSolid phase fermentation bioreactorsMulticellular organismCell organisation
The present invention is directed culture vessel suitable for cultivation of cells and / or tissues comprising at least one reversibly clo sable aperture in the vessel wall, and at least one surface-increasing substrate within the vessel, said substrate being made of a single mold. The invention further provides a system comprising at least two vessels being interconnected via at least one aperturein their vessel wall, and a cultivation process using such a vessel or system, in which at least one type of cells, tissue, tissue-like cell cultures, organs, organ- like cell cultures, or multicellular organisms are cultivated in the presence of at least one fluid or solid medium necessary for growing and / or cultivating the aforesaid culture.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Methods and compositions for use in homologous recombination
Methods for homologously recombining an exogenous nucleic acid into a target cell genome of a multicellular organism, e.g., an animal, are provided. In the subject methods, a targeting vector that includes a linearizing endonuclease site, e.g., a recombinase recognition site, and a homologous recombination integrating element, is contacted with the multicellular organism, e.g., via systemic or local administration, such that the target cell(s) of the multicellular organism takes up the targeting vector. The targeting vector is one that has been linearized by a linearizing endonuclease, e.g., a recombinase, at some point prior to the homologous recombination event, e.g., prior to or after contact with the multicellular organism. Following uptake by the target cell(s), the integrating element then homologously recombines into the target cell genome from the linearized targeting vector. Also provided are targeting vectors, systems and kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:TOSK INC
Multicellular metabolic models and methods
ActiveUS8949032B2Chemical property predictionCompound screeningMulticellular organismMetabolic Model
The invention provides a computer readable medium or media, having: (a) a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures, and (e) commands for determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells. The first, second and third data structures also can include a plurality of data structures. Additionally provided is a method for predicting a physiological function of a multicellular organism. The method includes: (a) providing a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) providing a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) providing a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) providing a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures; (e) providing an objective function, and (f) determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Multicellular biological composite scaffold, preparation method and application thereof
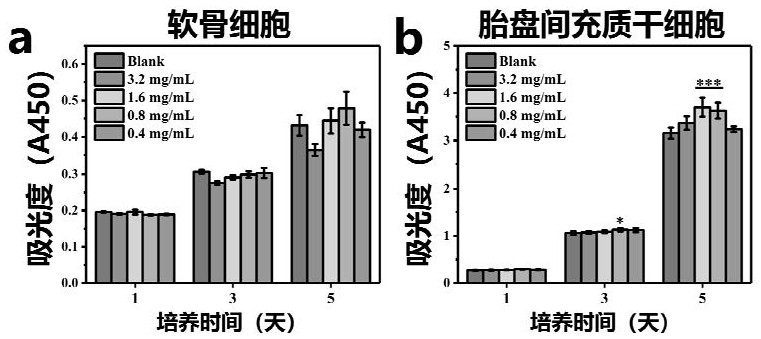
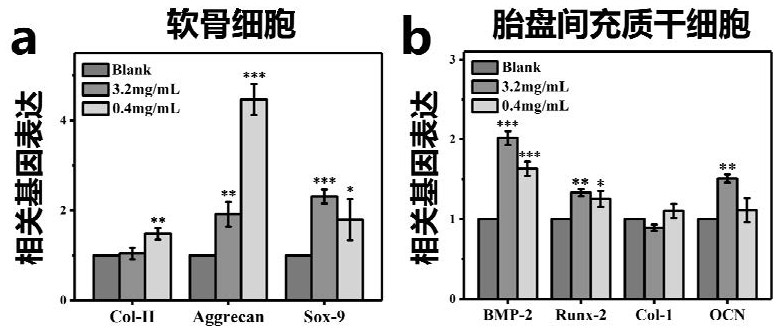
ActiveCN112336920AAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMulticellular organismBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a multicellular biological composite scaffold, a preparation method and application thereof. The scaffold comprises a lower-layer structure for forming a circular permutation mode of (A-B-A)m and an upper-layer structure for forming a circular permutation mode of (C-D-C)n, and A is a lower-layer composite material of bioactive ceramic powder containing three elements of Li,Mg and Si and an organic material with biocompatibility, B is stem cells with osteogenic differentiation potential, C is an upper-layer organic material containing an organic material with biocompatibility, D is chondrocyte, m and n are positive integers between 1 and 100. The multicellular biological composite scaffold can simulate the physiological structure of osteochondral complex tissue andefficiently promote the integrated repair of osteochondral defect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com