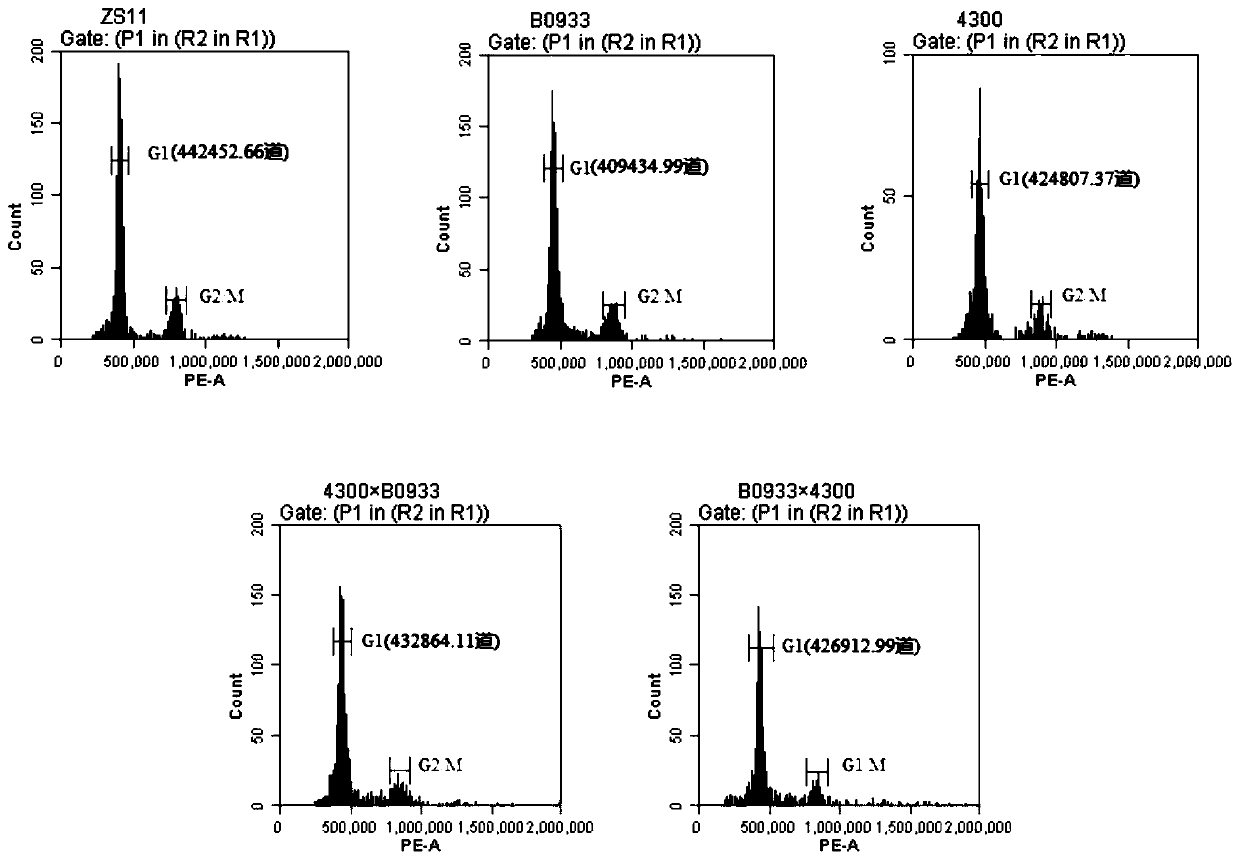
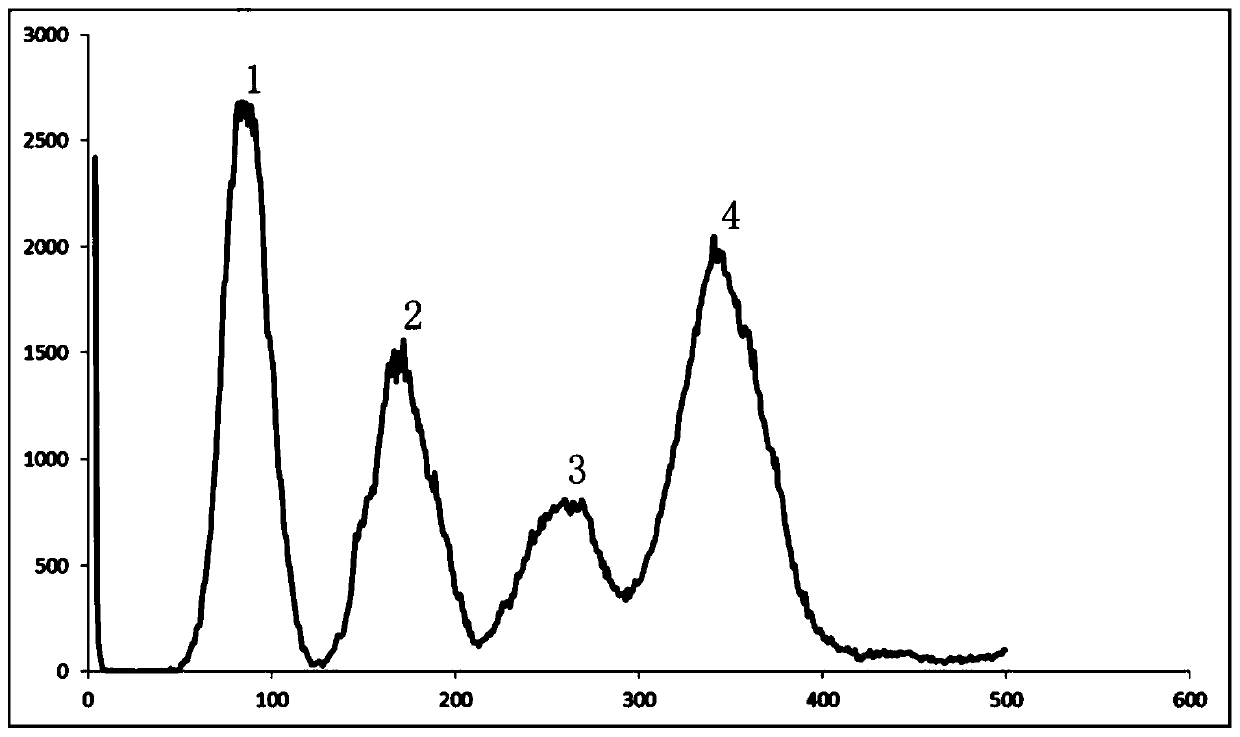
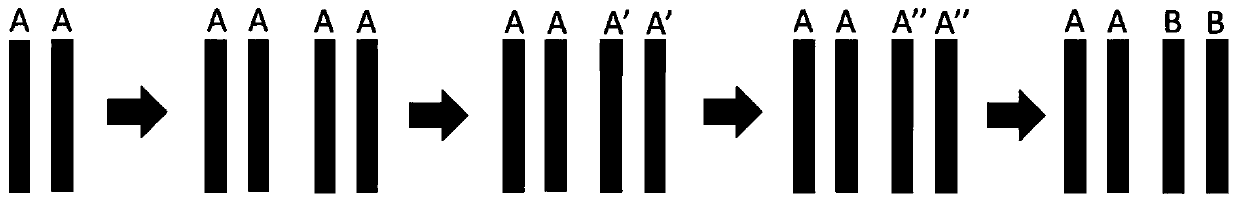
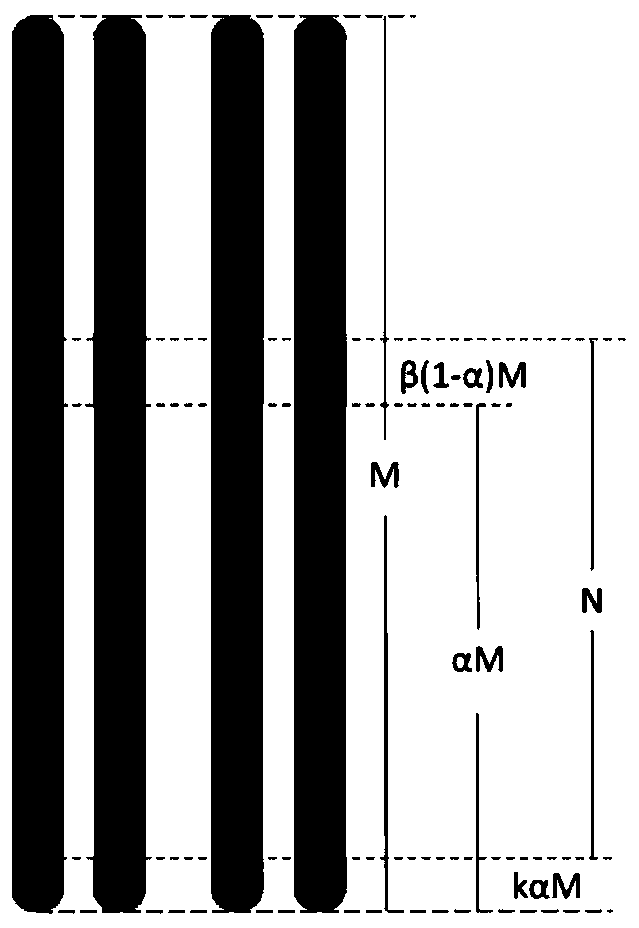
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Genome size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
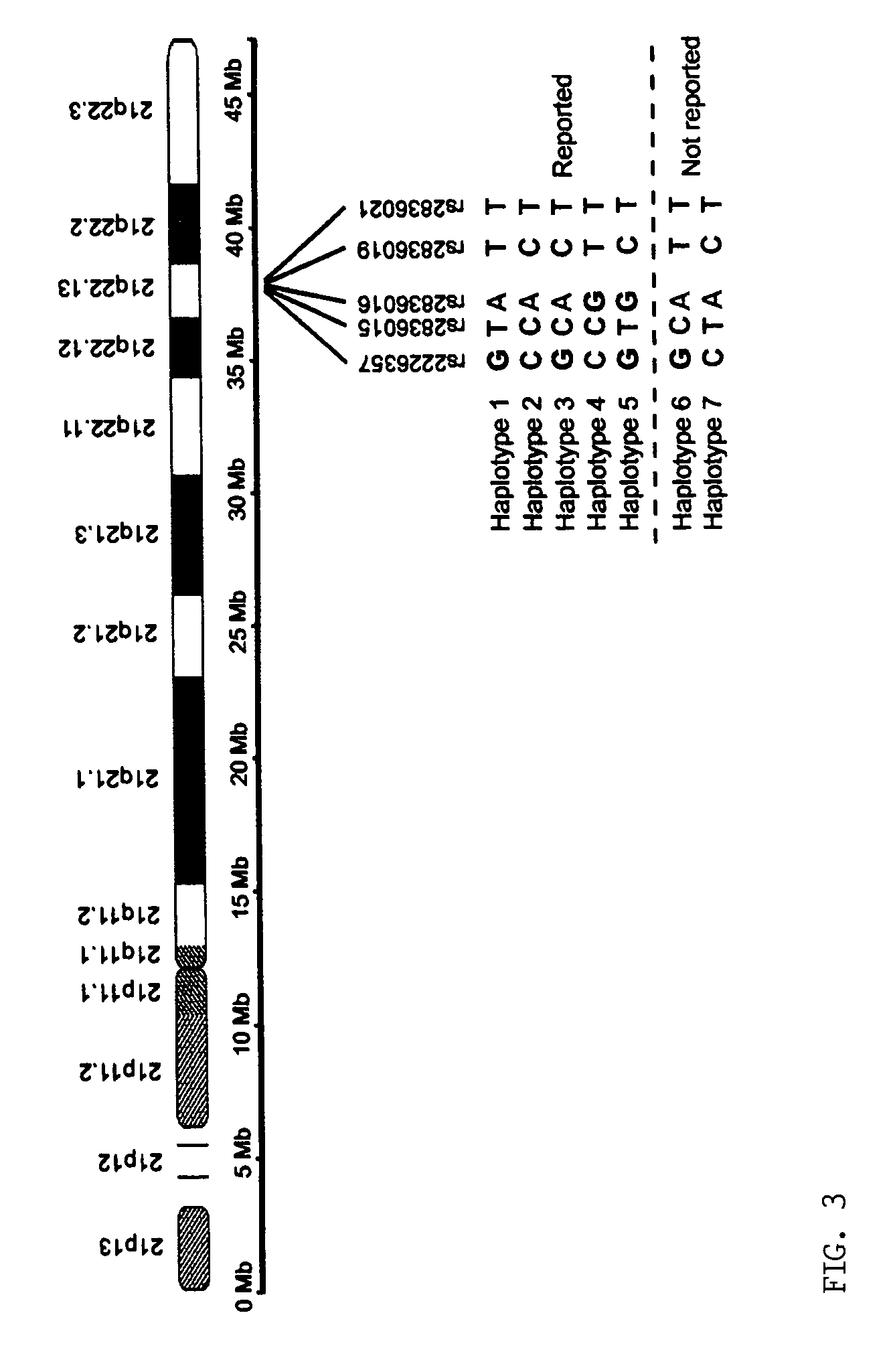
Genome size is the total amount of DNA contained within one copy of a single complete genome. It is typically measured in terms of mass in picograms (trillionths (10⁻¹²) of a gram, abbreviated pg) or less frequently in daltons, or as the total number of nucleotide base pairs, usually in megabases (millions of base pairs, abbreviated Mb or Mbp). One picogram is equal to 978 megabases. In diploid organisms, genome size is often used interchangeably with the term C-value.
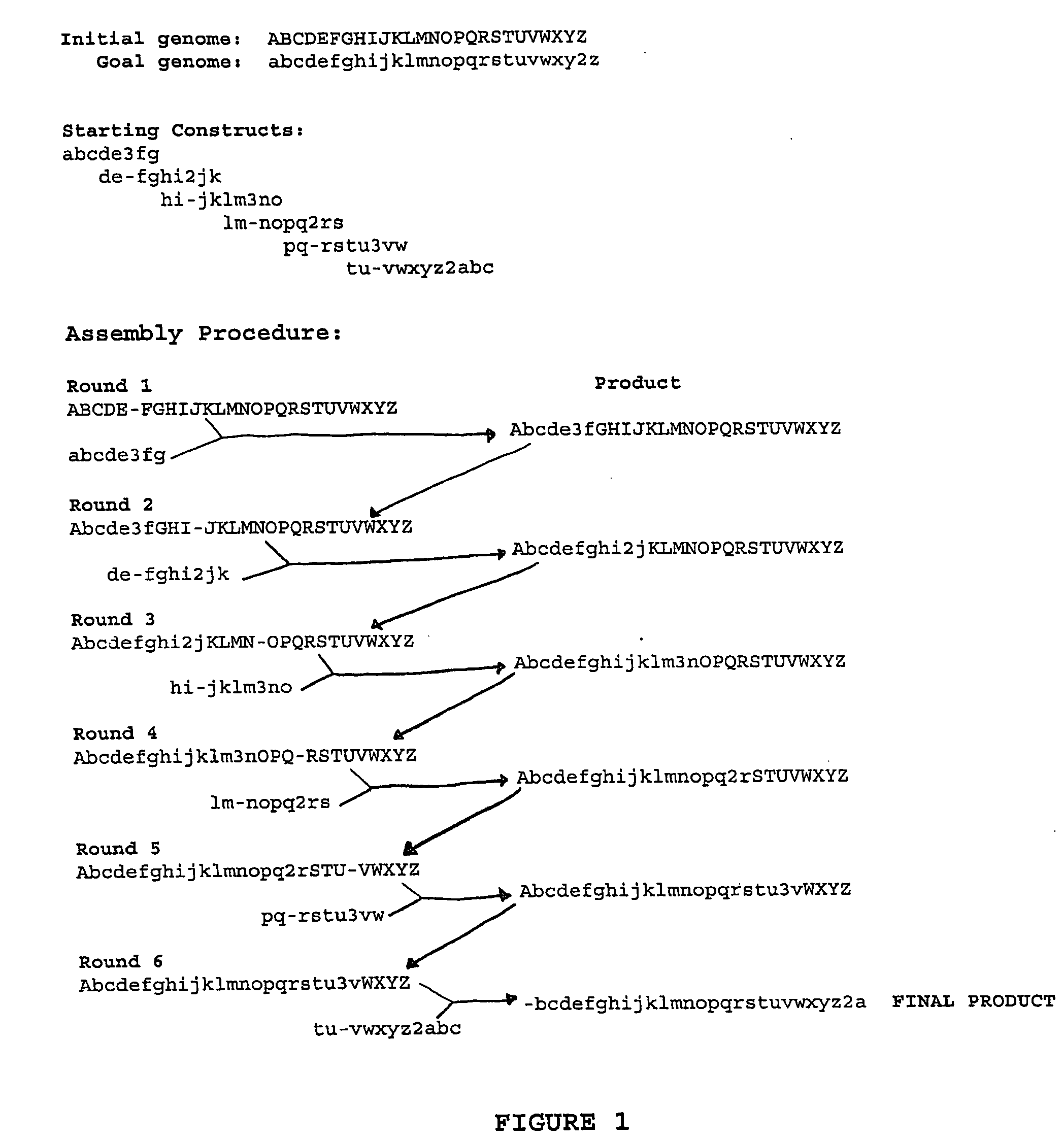
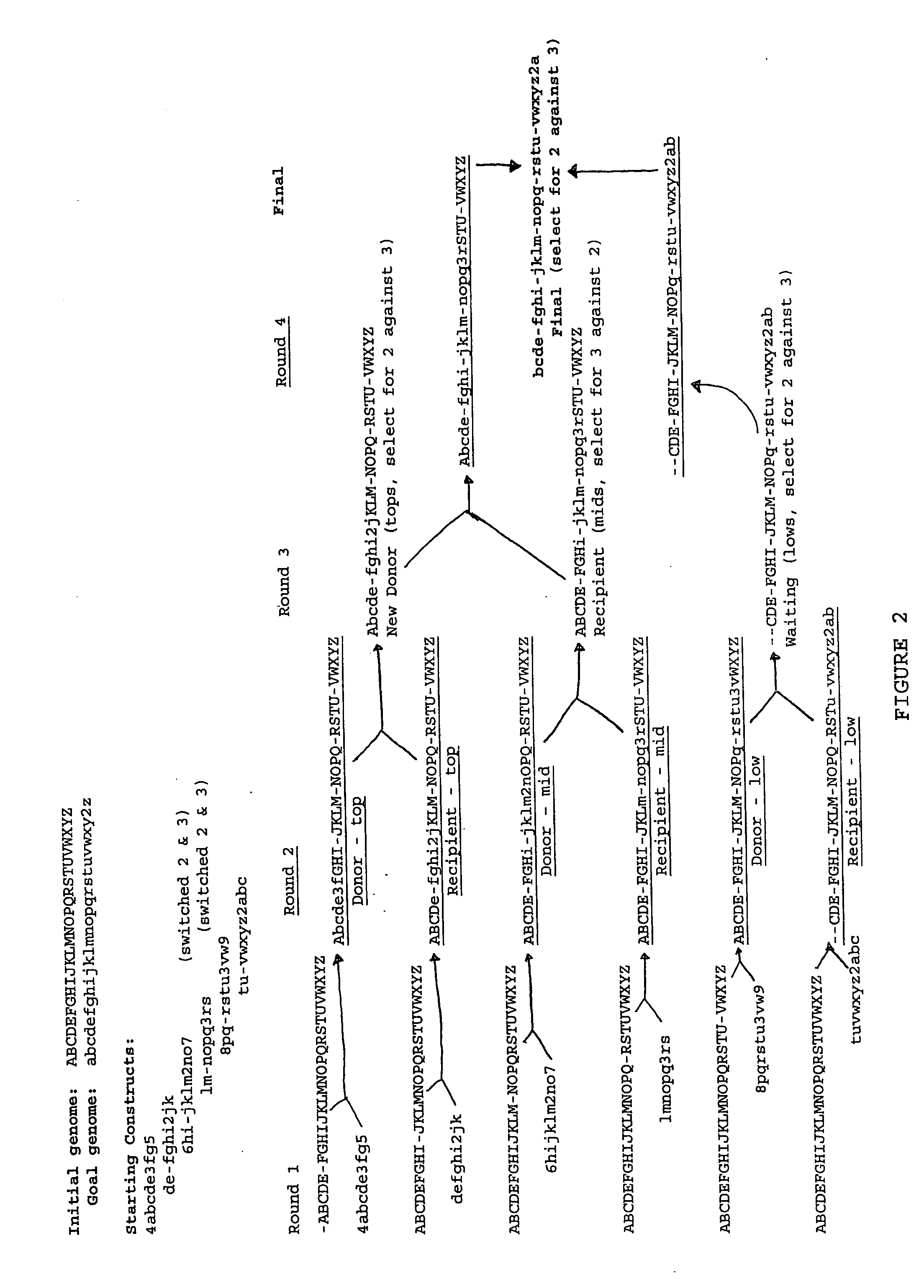
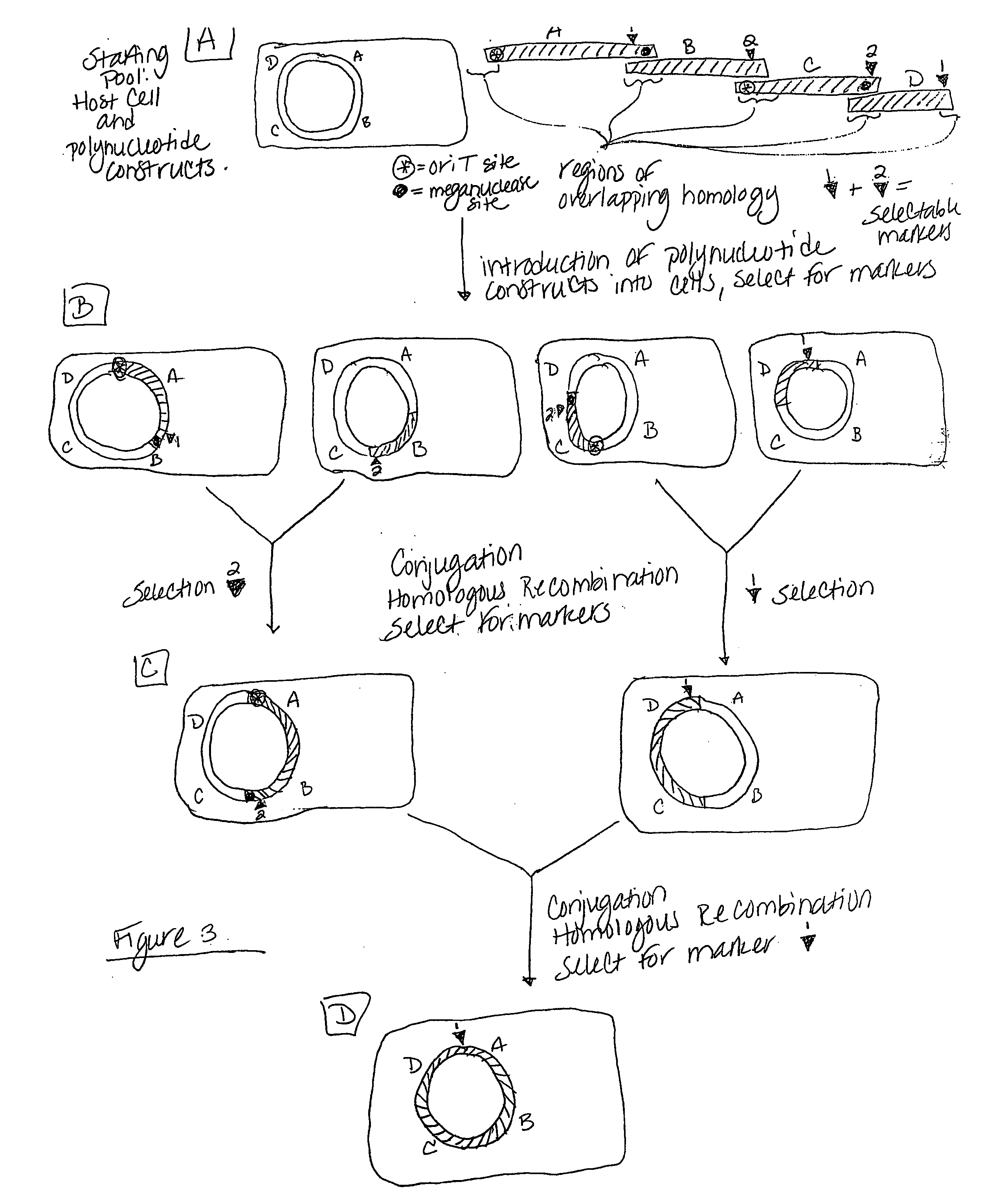
Heirarchical assembly methods for genome engineering
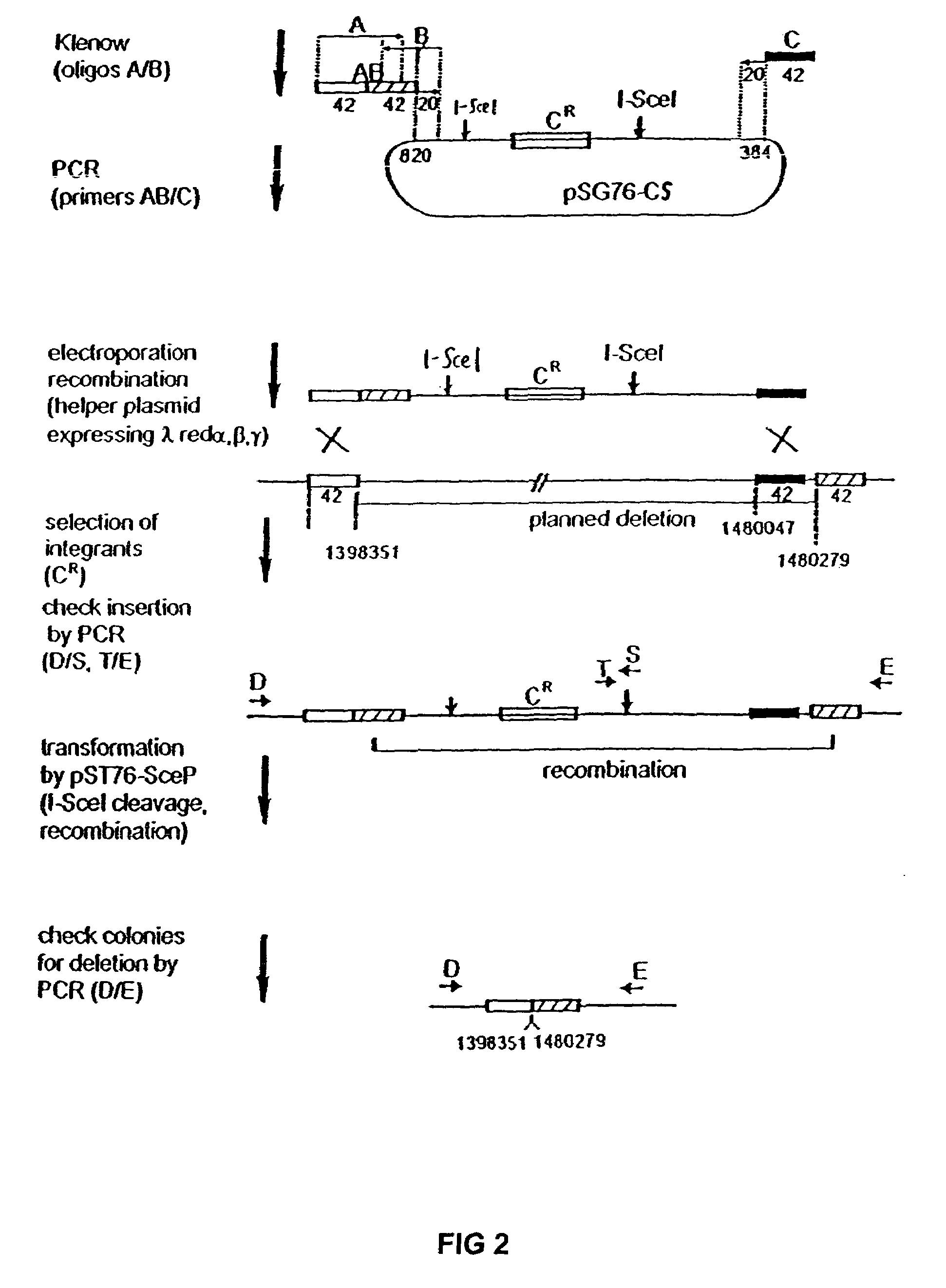
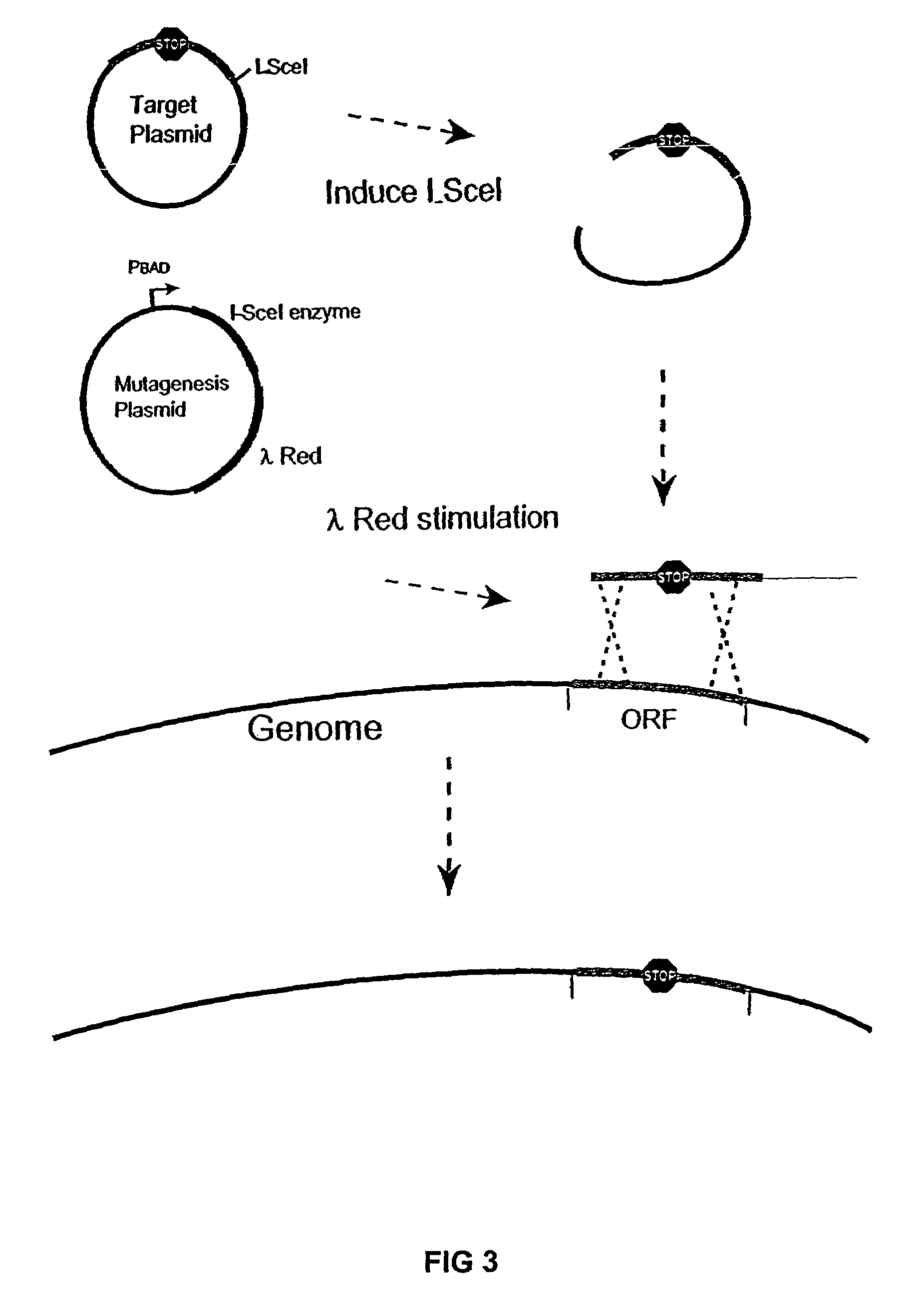
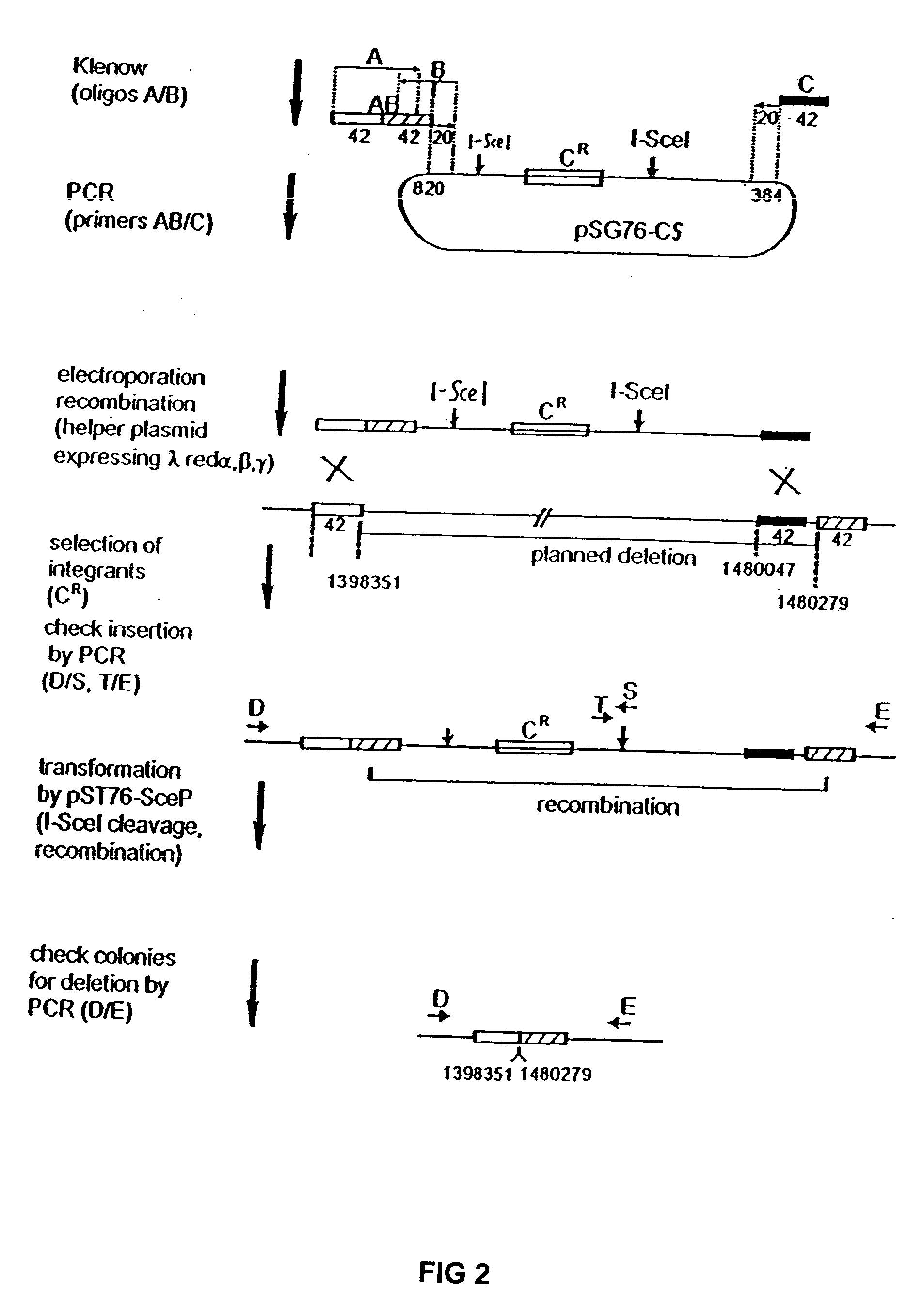
InactiveUS20070004041A1Improve securityImprove propertiesStable introduction of DNAFermentationBiological bodyGenomic Stability
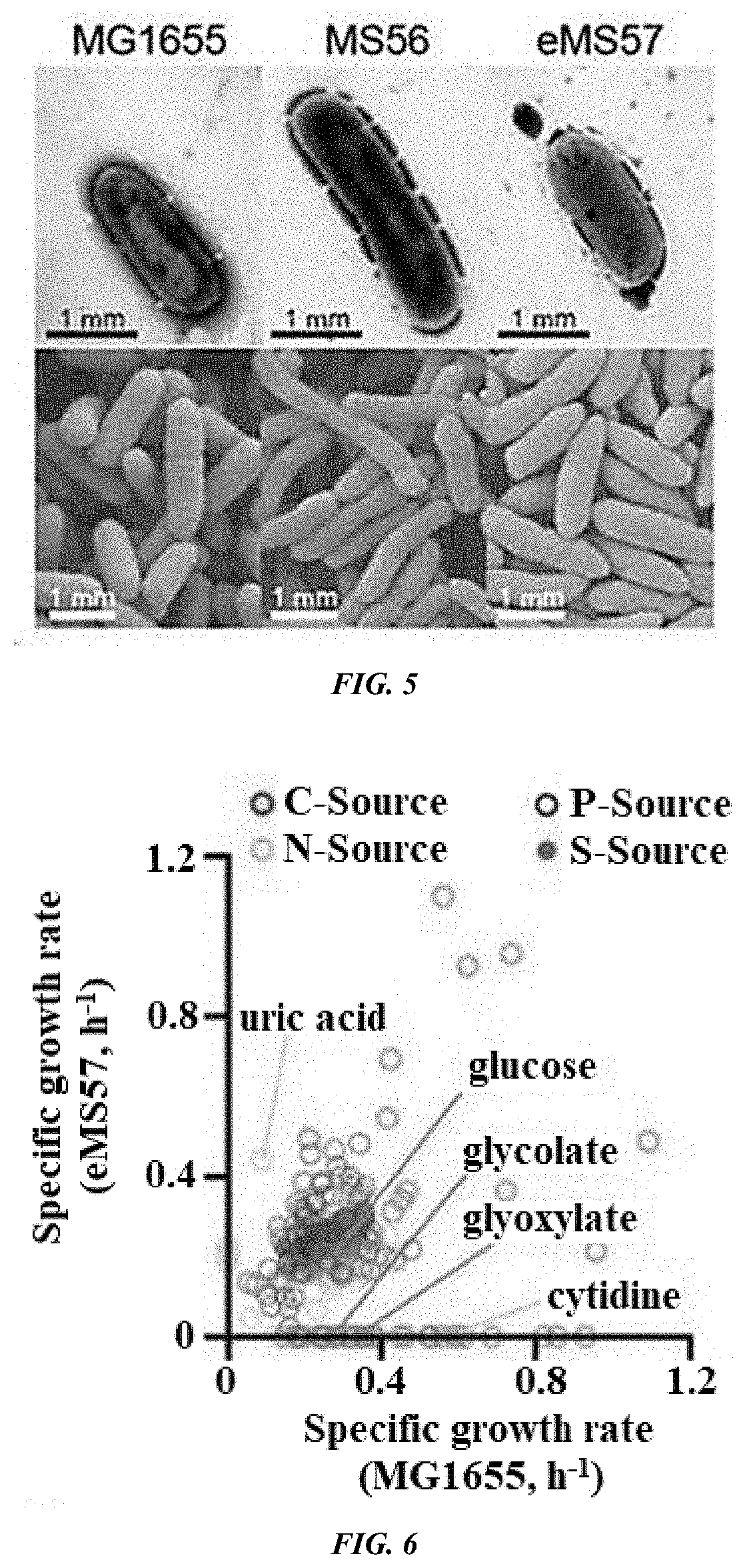
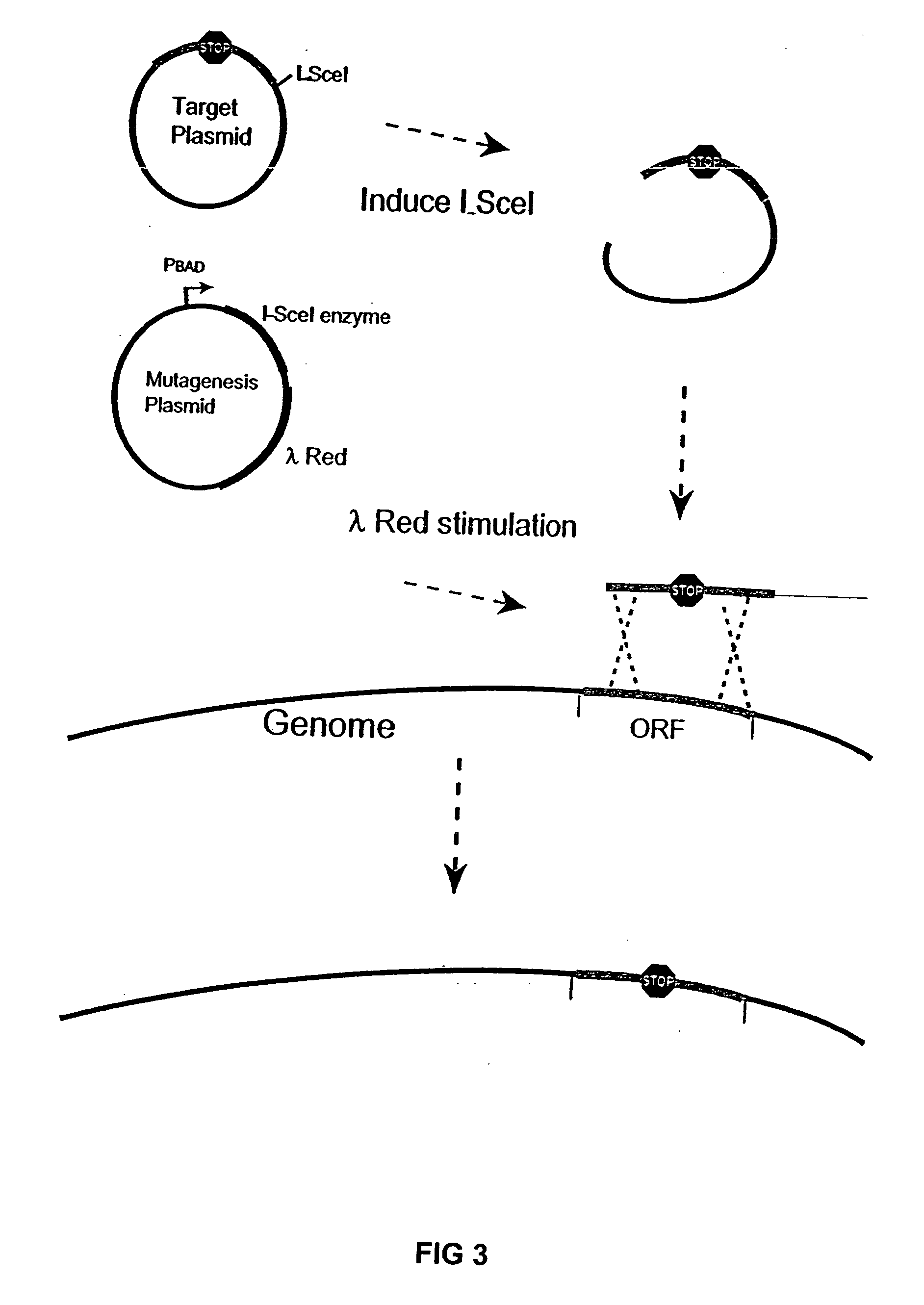
The present invention provides recombination based methods for assembling nucleic acids. In certain aspects the present invention provides hierarchical assembly methods for producing genome sized polynucleotide constructs. The methods may be used for assembling large polynucleotide constructs, for synthesizing synthetic genomes, or for introducing a plurality of nucleotide changes throughout the genome of an organism. In another aspect, the invention provides cells having increased genomic stability. For example, cells comprising alterations in at least a substantial portion of the transposons in the genome are provided.
Owner:CODON DEVICES
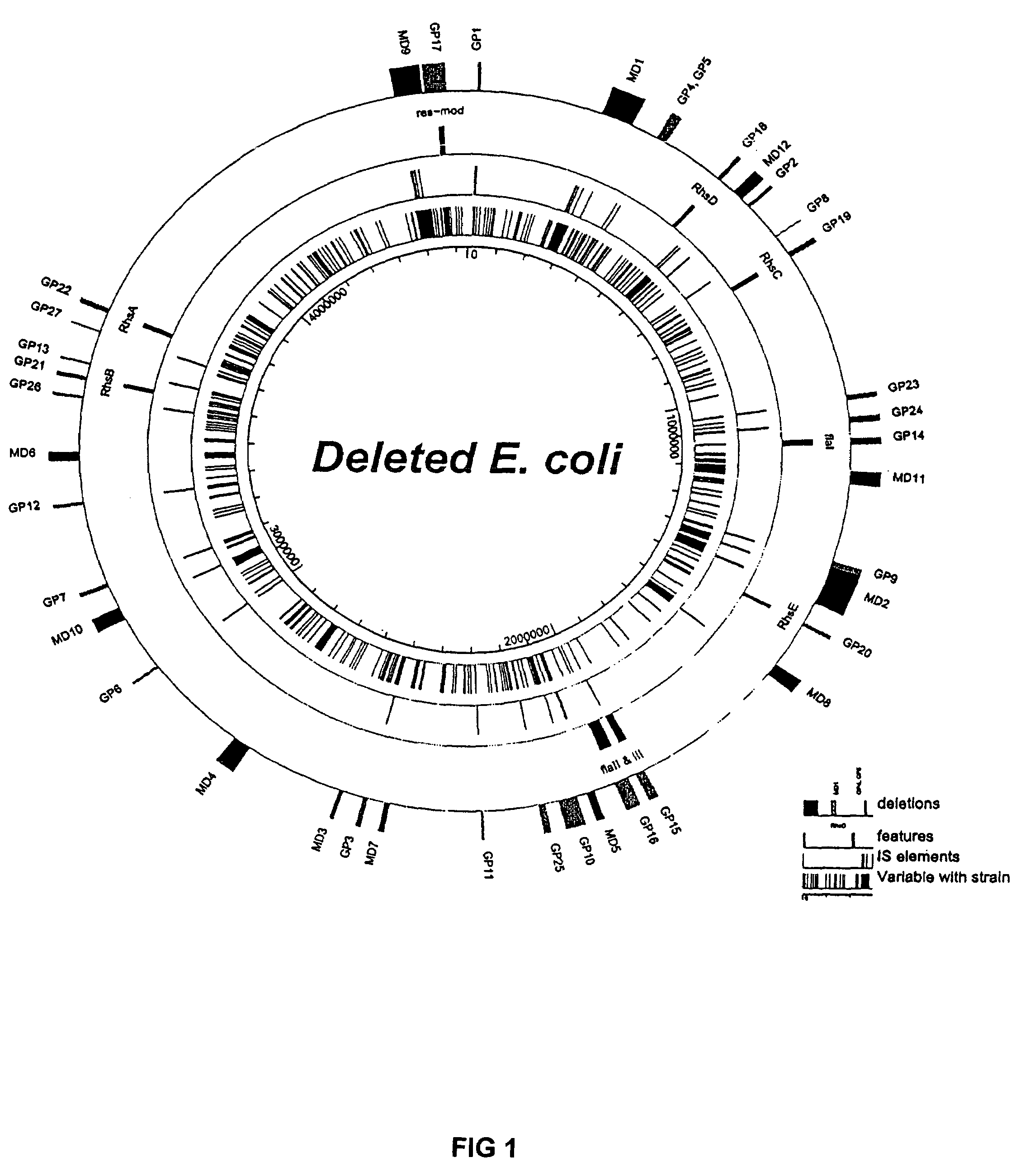
Competent bacteria
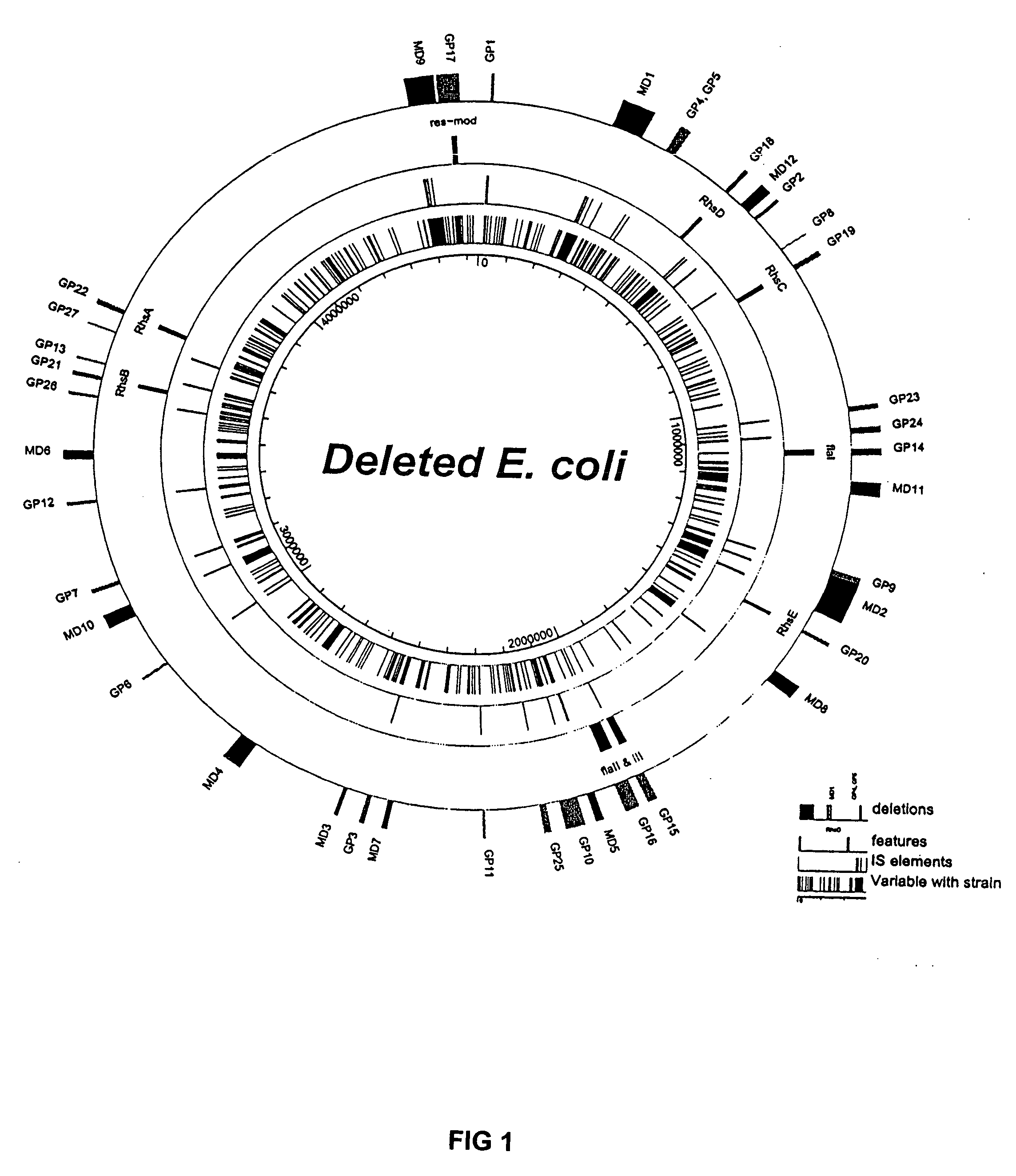
InactiveUS7303906B2Reduced genome bacteriaMaximize efficiencyBacteriaNucleic acid reductionBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The present invention discloses that a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 10% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain has better transformation competence. Specific E. coli strains, having significantly reduced genome sizes, are disclosed which are highly transformation competent. A medium and methodology is taught which enables transformation efficiencies to be increased further.
Owner:SCARAB GENOMICS LLC +1
Competent bacteria
InactiveUS20050032225A1Transformation efficiency can be maximizedReduced genome bacteriaBacteriaNucleic acid reductionEscherichia coliTransformation efficiency
The present invention discloses that a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 10% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain has better transformation competence. Specific E. coli strains, having significantly reduced genome sizes, are disclosed which are highly transformation competent. A medium and methodology is taught which enables transformation efficiencies to be increased further.
Owner:SCARAB GENOMICS LLC +1
Bacteriophages useful for the prophylaxis and therapy of vibrio anguillarum
InactiveUS20140105866A1Infection controlEasy to applyBiocideMicroorganismsBacteroidesVibrio anguillarum
An isolated strain of bacteriophage, specific against bacteria belonging to the Vibrio genre, particularly the anguillarum species, deposited on 3 Oct. 2012 at the Polish Collection of Microorganisms (PCM) of the Ludwik Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy of the Polish Academy of Sciences, with access number F / 00072, characterized in that said strain is efficient in the prophylaxis, control and / or treatment of the infection caused by Vibrio anguillarum in all types of species of fish, mollusks and crustaceans that are important for aquaculture susceptible to this bacteria, genome size 48.6 Kb, it is not sensitive to chloroform and its storage temperature is −80° C.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
Method for measuring size of genome of gesneriaceae plant
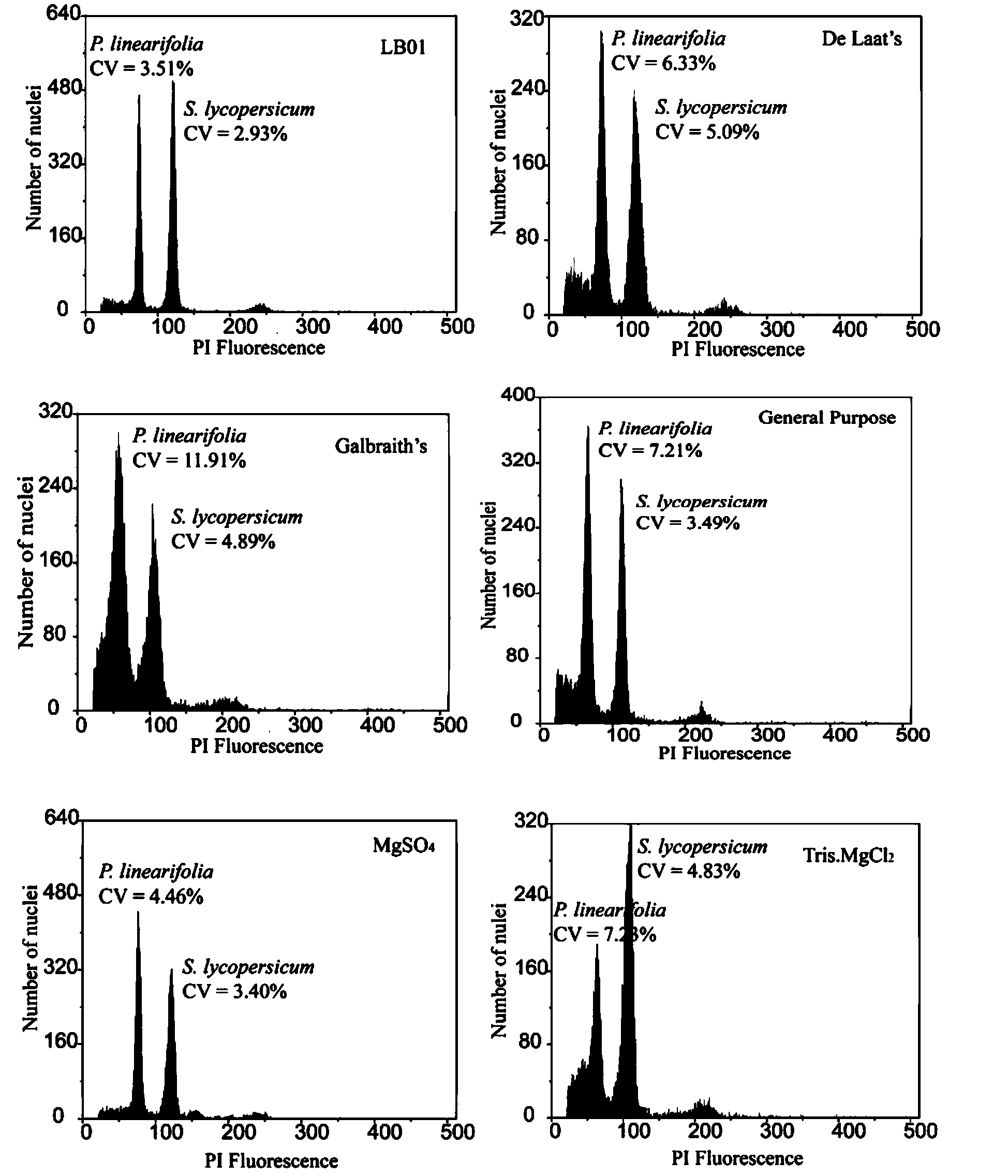
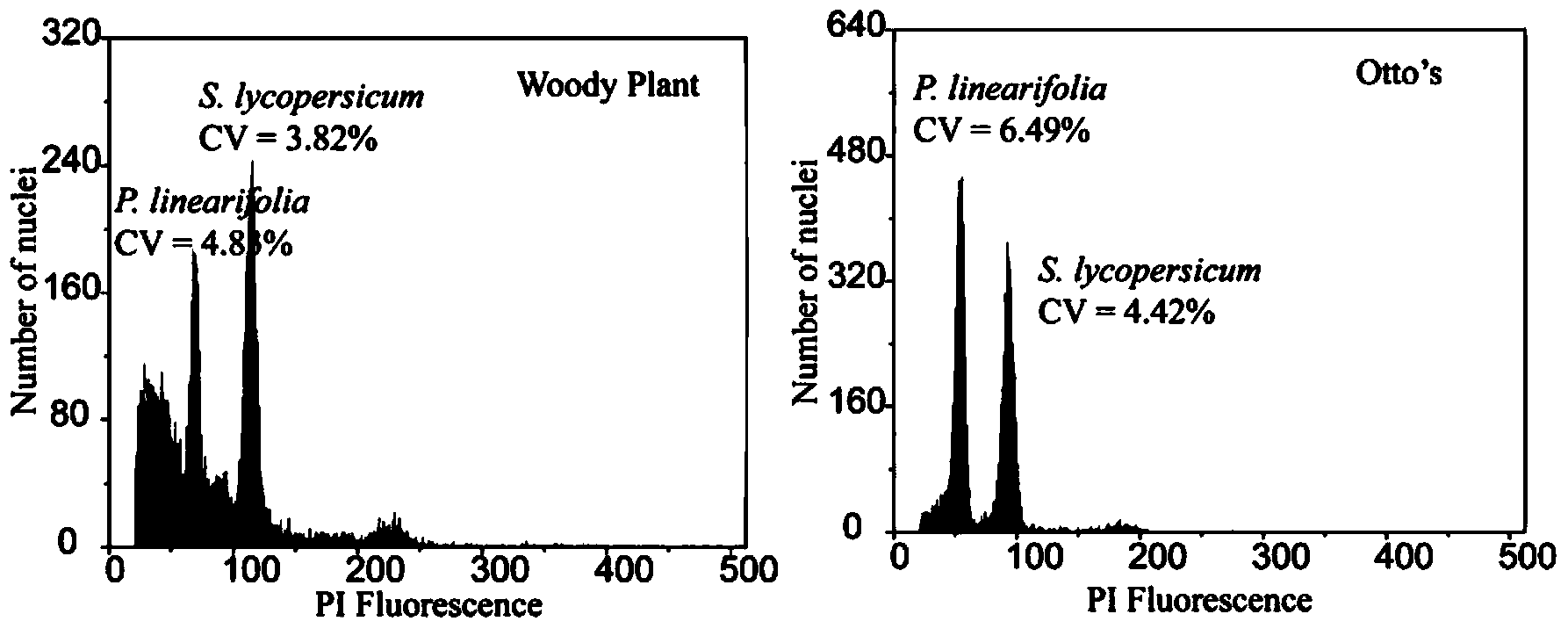
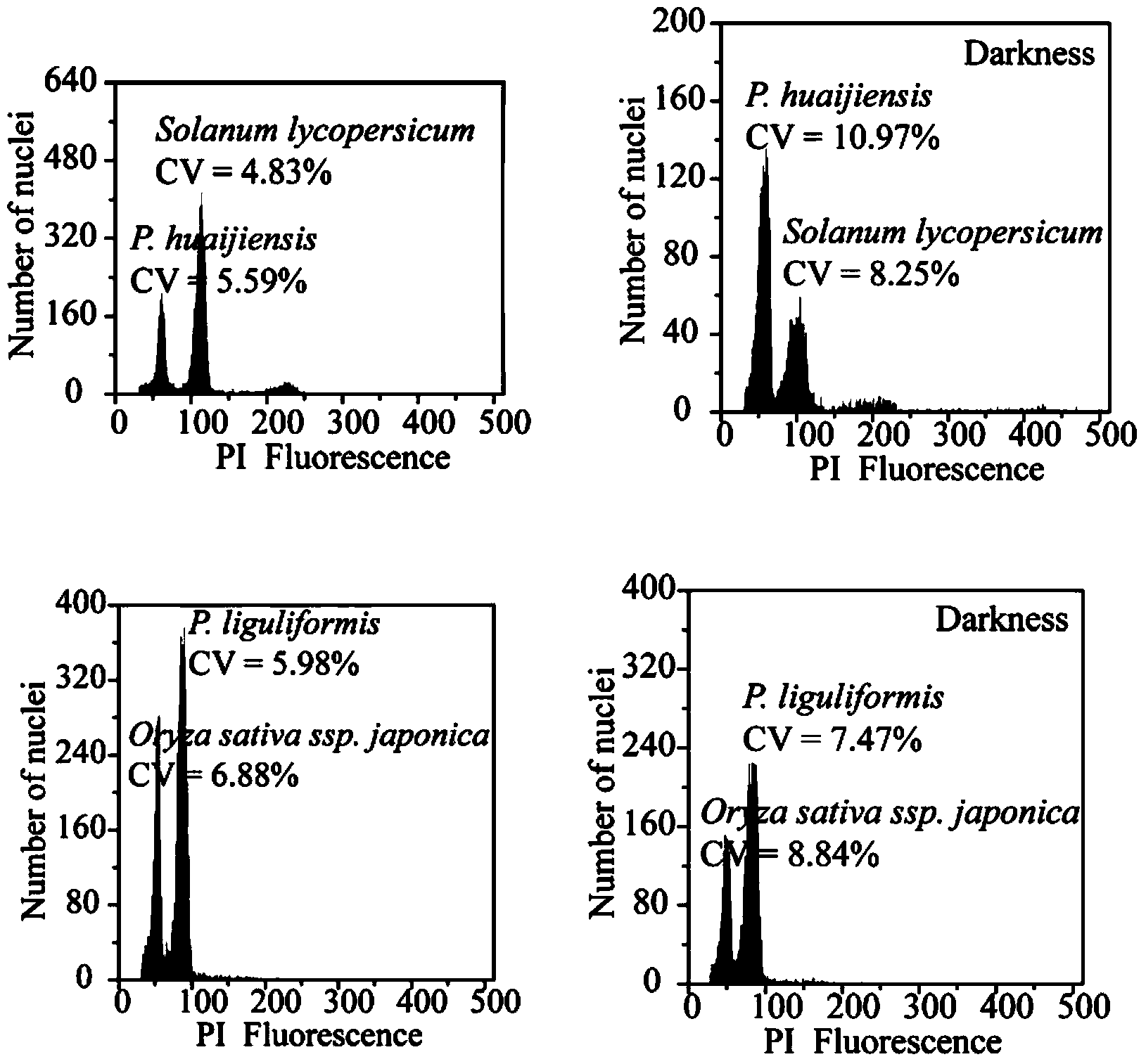
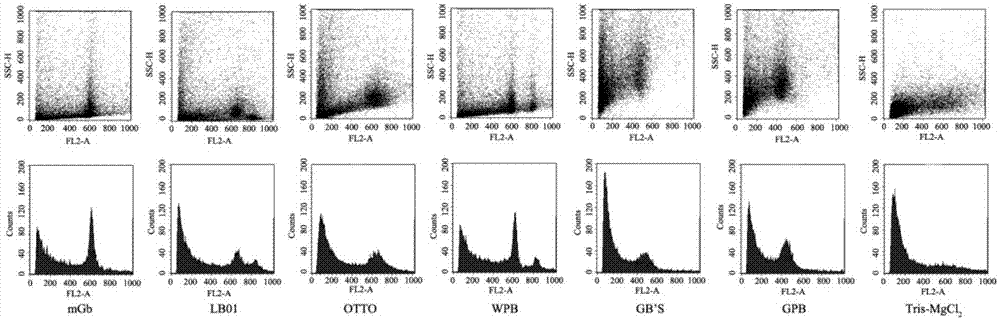
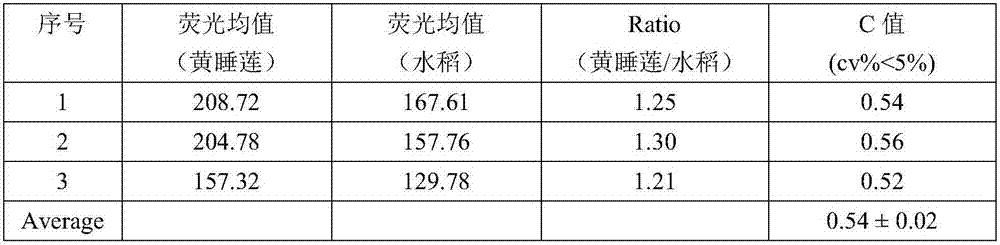
The invention discloses a method for measuring the size of the genome of a gesneriaceae plant. The method comprises the steps of taking fresh tender leaves of the gesneriaceae plant; with a tomato as a main internal reference and rice as a second internal reference, re-correcting the size of the genome of the rice by taking the size of the genome of the tomato as standard; according to the standard of adding 20 milligrams of tender leaves into 1ml of nuclear extraction buffering solution LB01, respectively adding the tender leaves of the target plant and the internal reference species into the nuclear extraction buffering solution LB01, chopping the tender leaves, performing filtration through a filtering net with the aperture of 50 microns to obtain a cell nucleus suspension, and putting the cell nucleus suspension on ice for later use; digesting RNA in the cell nucleus suspension through RNA digestive enzymes till the final concentration of the RNA digestive enzymes is 100 micrograms per ml, and then adding propidium iodide for fluorescence shading dyeing for 40 minutes; and measuring the size of the genome of the target plant through a flow cytometry. The method can measure the accurate sizes of the genomes of various gesneriaceae plants; the CV (Coefficient of Variation) is lower than 5 percent. The method is high in repetitiveness and easy to operate, and is suitable for gesneriaceae botanic research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
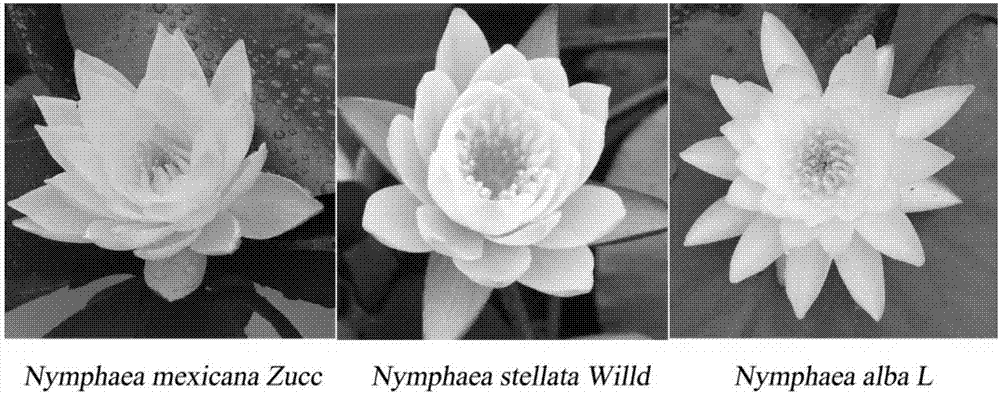
Method for determining genome size of nymphaeaceae plants
InactiveCN107449717AAccurate size measurementAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisGenomicsDatum reference
The invention provides a method for determining the genome size of nymphaeaceae plants. The method is characterized by determining the genome size of three nymphaeaceae plants of NymphaeamexicanaZucc, NymphaeastellataWilld and Nymphaea alba L. by using Oryzasativa nipponbare and Zea mays L B73 as interior labels and utilizing flow cytometry. A result shows that the three plants are different in genome size, wherein the genome size of the Nymphaea alba L. is the largest, and the genome size of the NymphaeamexicanaZucc is the smallest. Basic data reference is provided for genomics and population evolution research of the plants.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
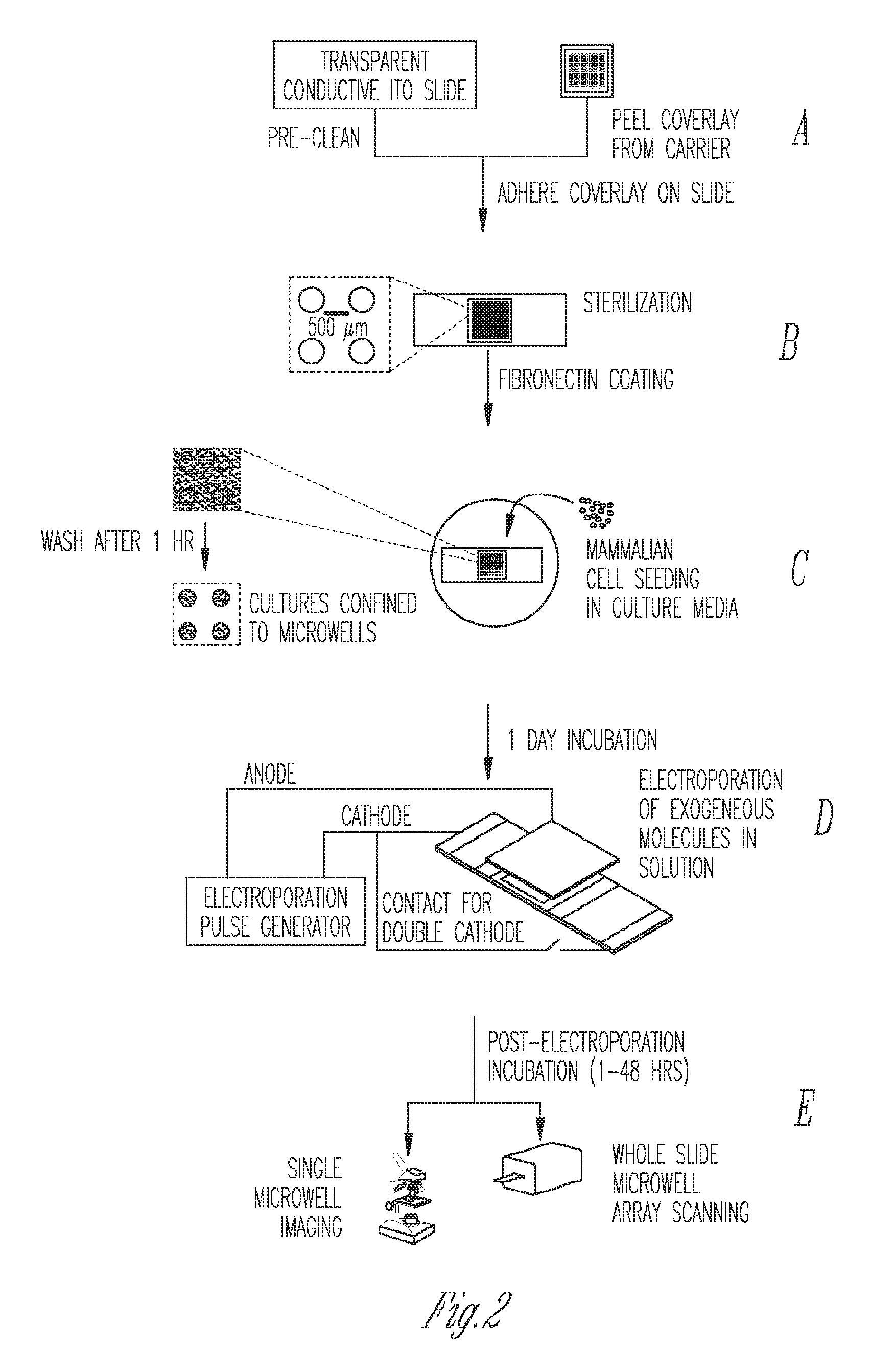
Miniaturized electroporation-ready microwell aray for high-throughput genomic screening
InactiveUS20120231517A1Highly efficient parallel introductionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMiniaturizationPrimary cell
Methods of introducing exogenous molecules into cells including cell lines and primary cells are provided. Additionally, miniaturized electroporation-ready microwell arrays are provided. These tools provide a miniaturized high-throughput functional genomics screening platform to carry out genome-size screens in a variety of cell types.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Process and apparatus for using the sets of pseudo random subsequences present in genomes for identification of species
InactiveUS20050255459A1Rapid increase of computational complexityEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHuman speciesGenomic DNA
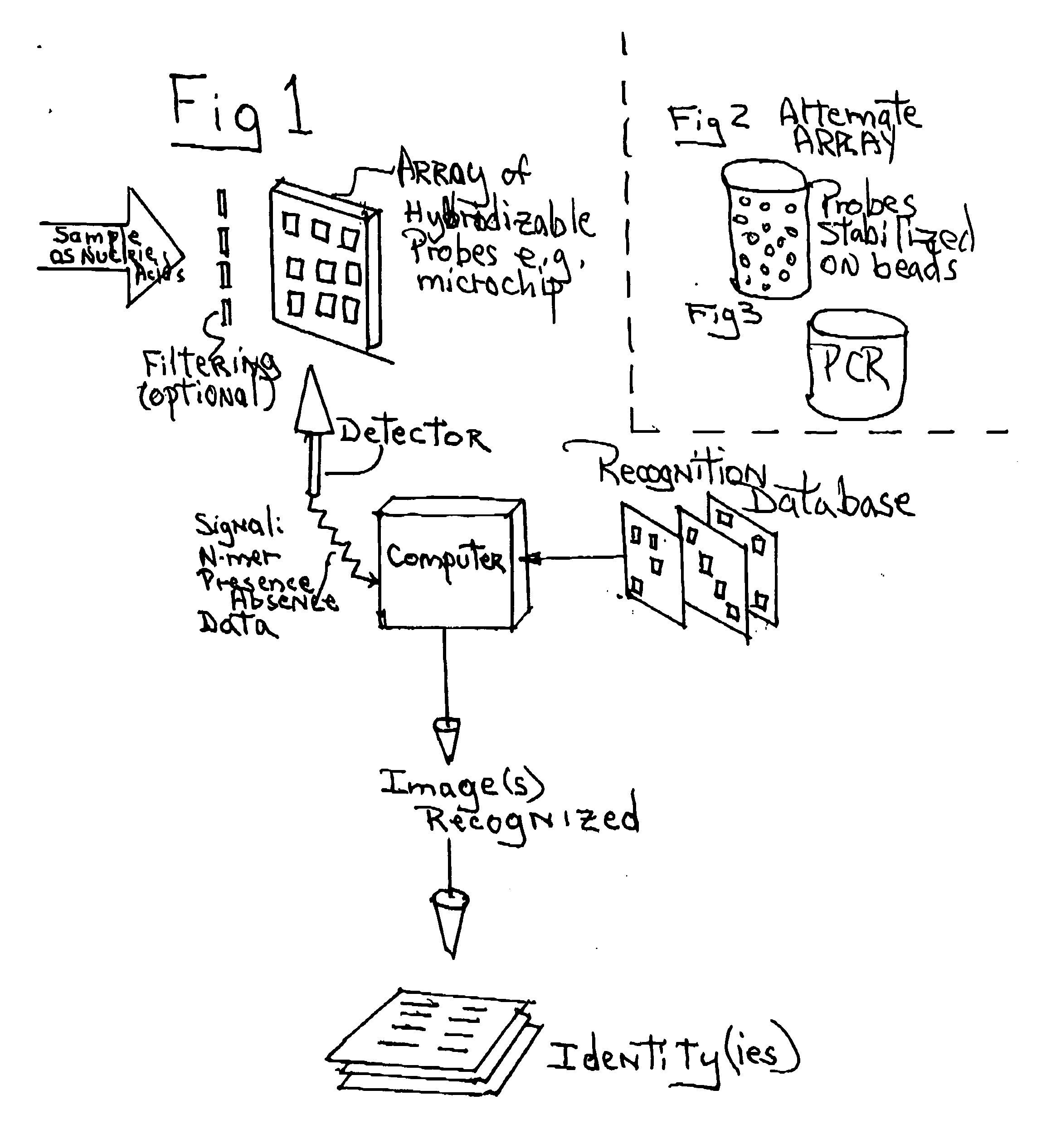
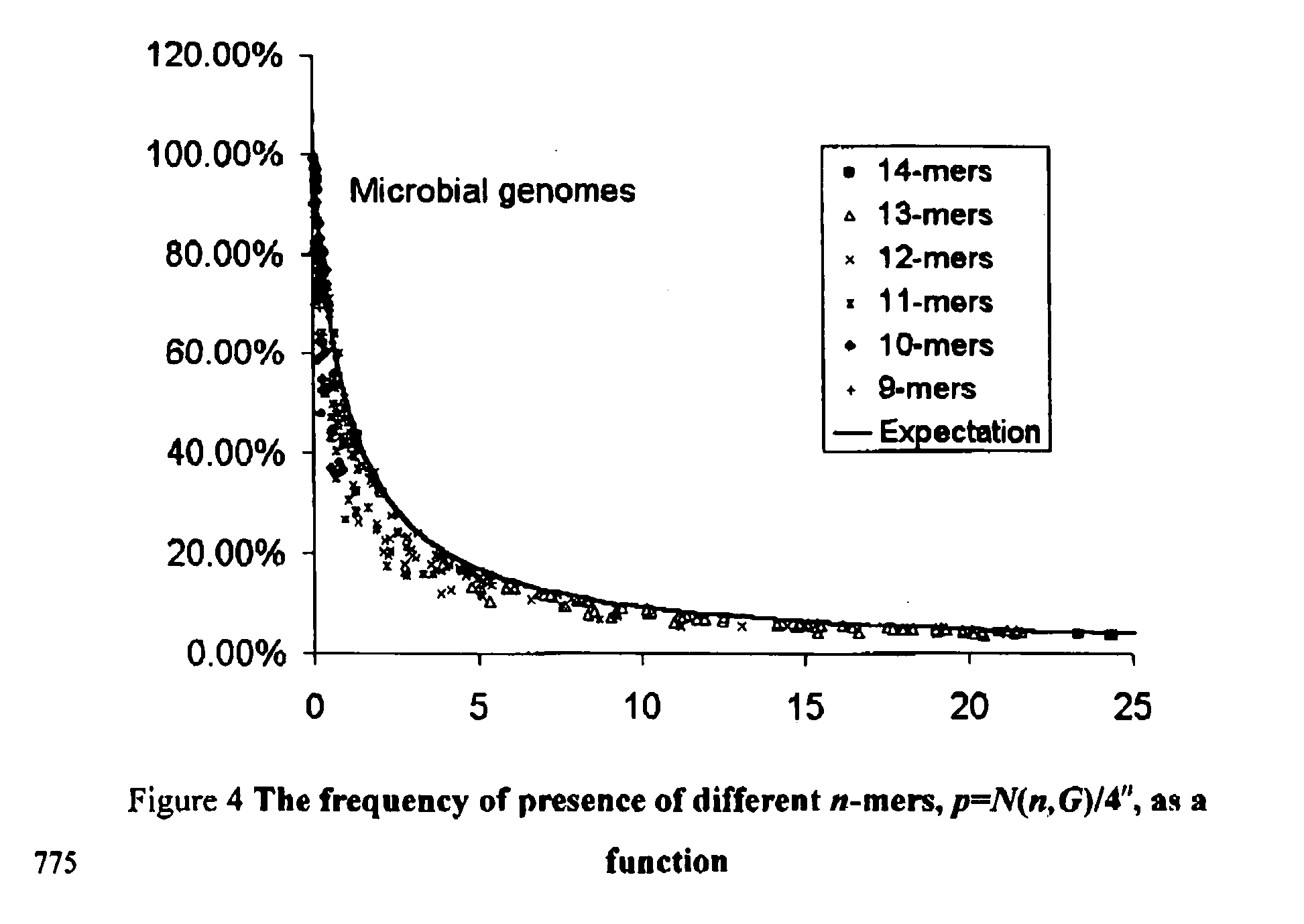
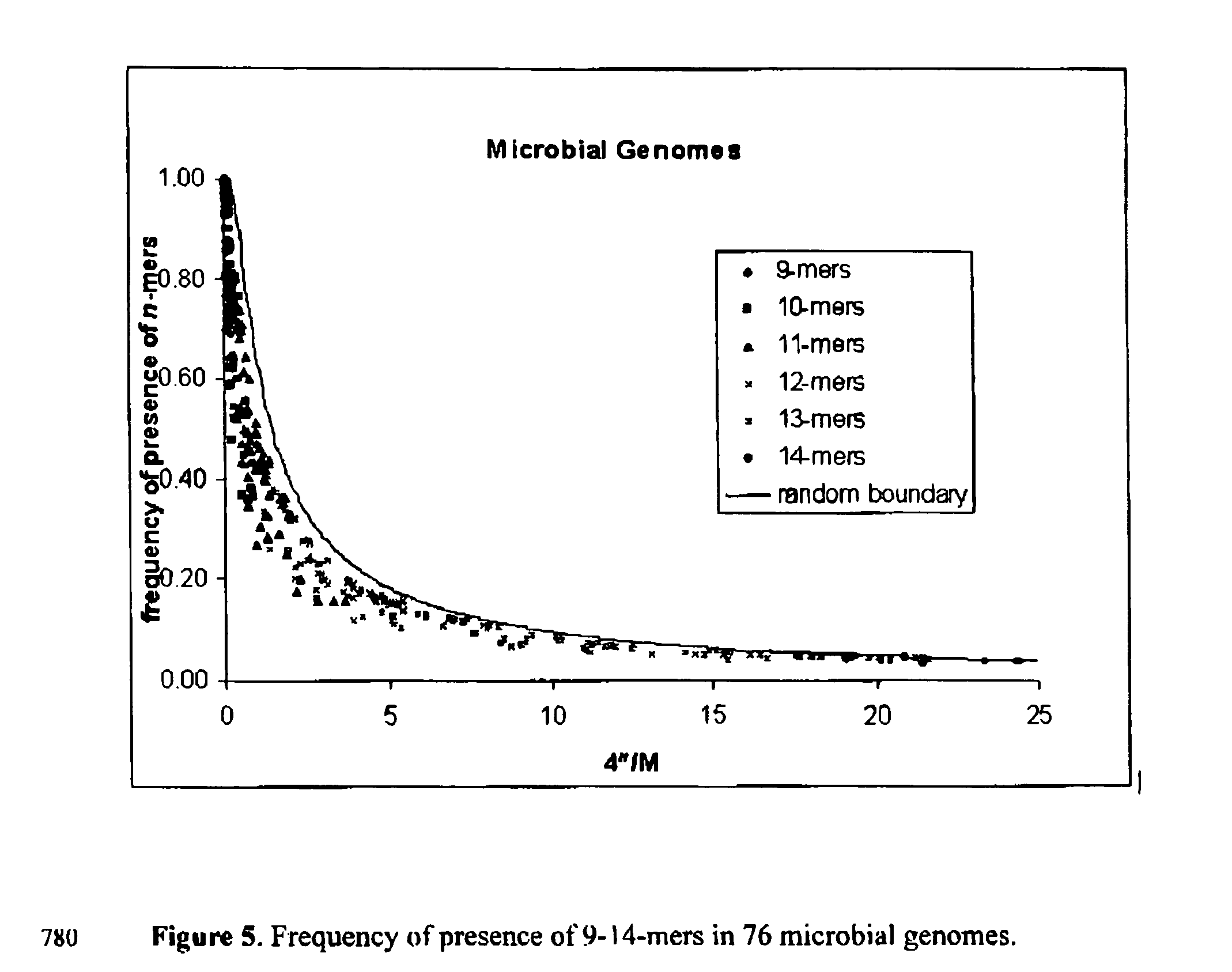
Our research conducted with the genome sequences of more than 250 species of organisms (including viral, microbial, and multi-cellular organisms, and human) results in the discovery that the occurrence of a particular subsequence (the so-called “motifs” or “n-mers,” (n being the length of the subsequences), which can be up to 25 and higher) in the genome of a particular species can be considered as a nearly random event; and that the occurrences of a particular subsequence in the genome sequences of different species can be considered as nearly independent events (with the exception of the cases where extremely closely related species are compared). The set of subsequences that occur in a particular species' genome can therefore be used as a genomic “fingerprint” of this species. This discovery leads to the concept of utilizing a set of pseudo-randomly designed subsequences for species identification or discrimination. These subsequences (probes, primers, motifs, n-mers) can be used with hybridization-based technologies (including, but not limited to, the microarray or PCR technologies) and any other technology allow to identity the fact of presence / absence of particular subsequence in genomic DNA for identification of species. The same approach can also be used to identify individuals of the same species (including the human species), to estimate the genome size of unknown organisms, and to estimate the total genome size in samples containing several viral, microbial, and eukaryotic genomes. The identification methods currently in use for these purposes require sequencing of the genomic sequences of the species or the individuals of interest. The introduction of the proposed computational method eradicates such requirement, and will tremendously reduce the expense of these tests.
Owner:FOFANOV YURIY +3
Method for assembling and annotating genome of Hoba Tibetan sheep based on three-generation PacBio and Hi-C technologies
PendingCN113151426AImprove integrityImprove continuityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiotechnologyGenetics
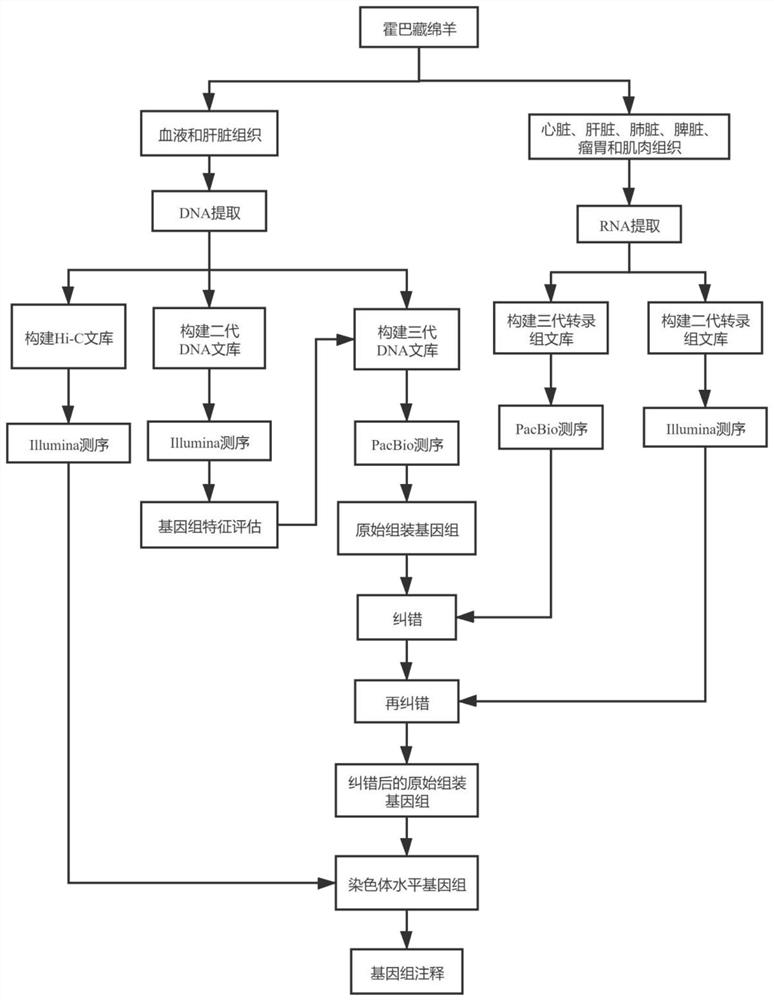
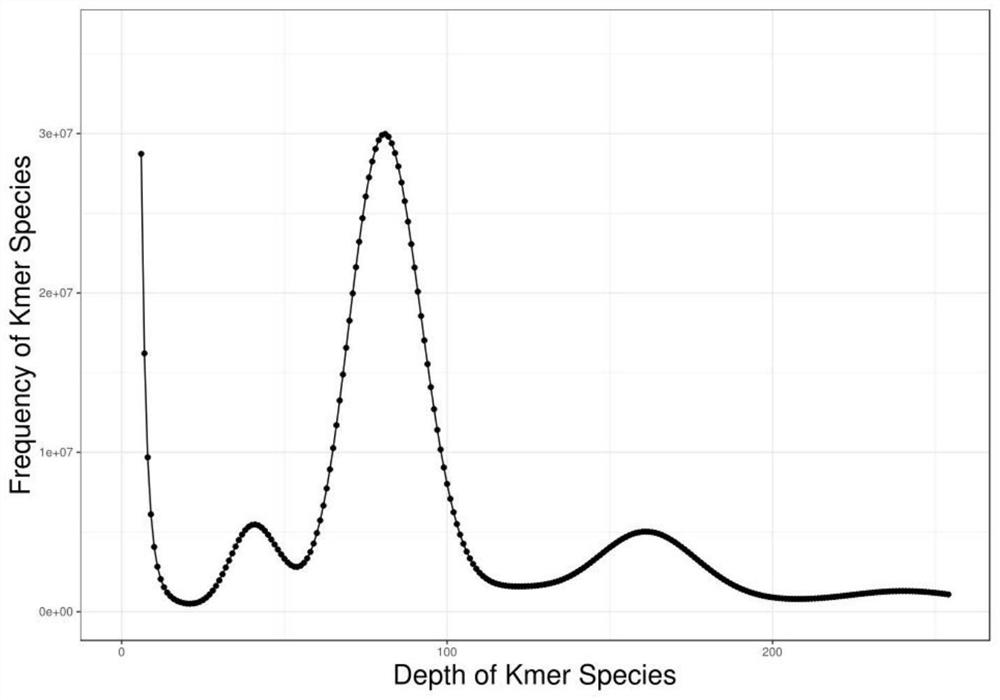
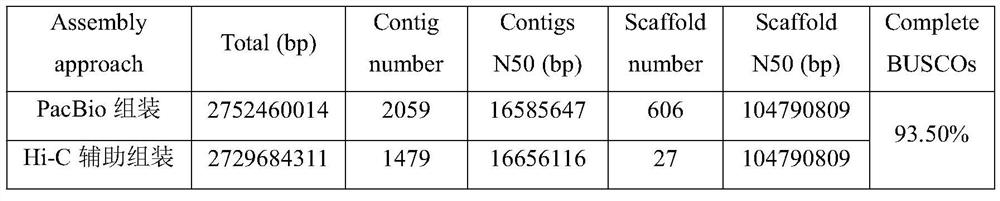
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and particularly relates to a method for assembling and annotating a genome of Hoba Tibetan sheep based on three-generation PacBio and Hi-C technologies. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting blood and tissue samples of Hoba Tibetan sheep; (2) constructing a genome library and a transcriptome library; (3) evaluating genome size and heterozygosity rate; (4) assembling genome, conducting error correction by utilizing a transcription sequencing result; (5) conducting Hi-C assisted assembly and evaluation; and (6) conducting genome annotation and evaluation. According to the method, the high-quality genome of the Hoba Tibetan sheep is assembled at a chromosome level, thereby providing valuable genome resources for studying conservation and innovative utilization of genetic resources of Tibetan sheep populations, and laying a solid foundation for further researches on an environment adaptation mechanism of specific livestock species in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The method of the present invention lays foundation for researches on an alpine and hypoxia adaptive molecular mechanism of the Hoba Tibetan sheep, and provides reference data for researches on human hypoxia-related diseases.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Method for improving efficiency of genome site-directed modification by using small molecular compounds
ActiveCN110499336AImprove the efficiency of fixed-point modificationStable introduction of DNAGenetic engineeringDirect site
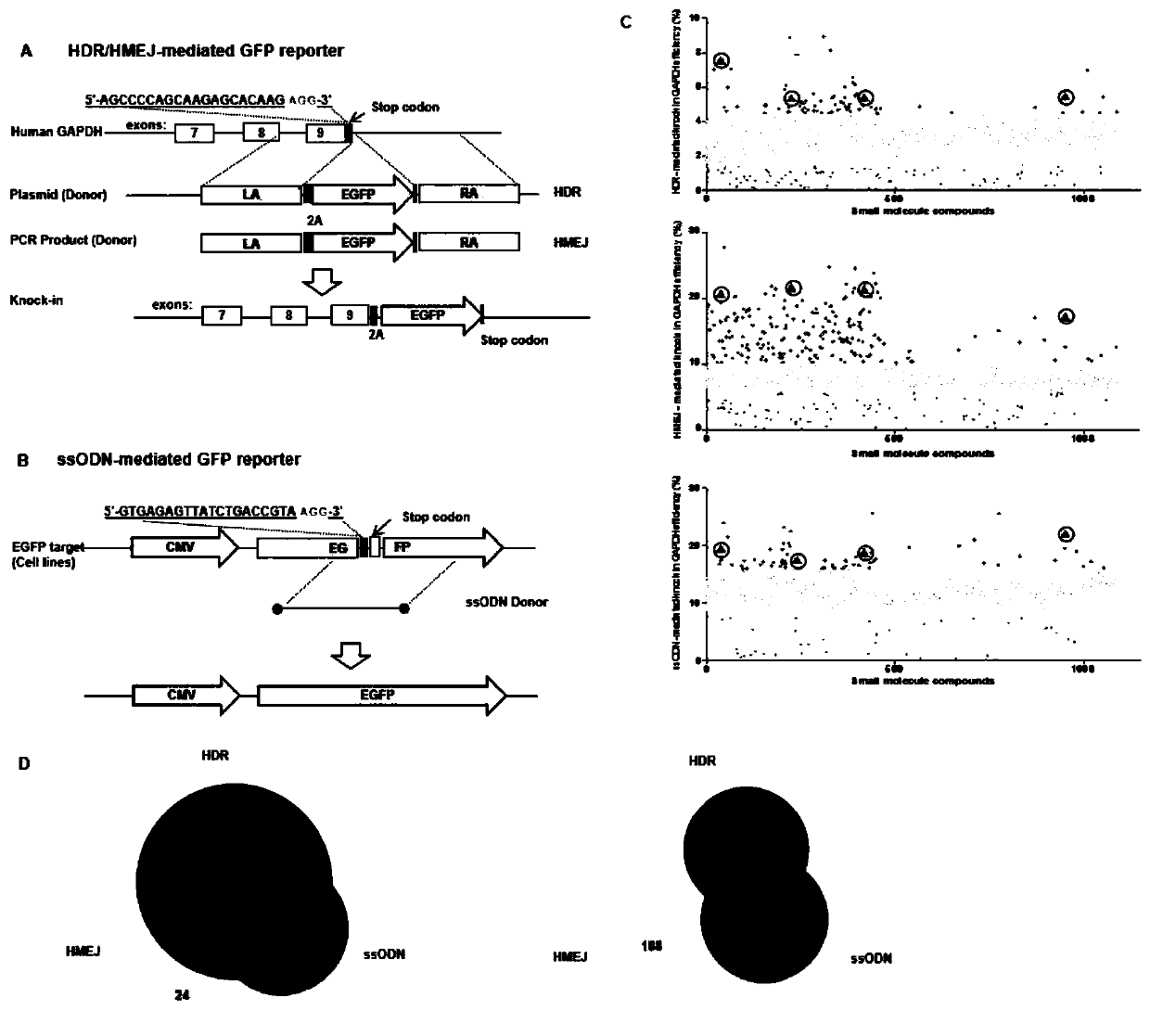
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular to a method for improving the efficiency of genome site-directed modification by using small molecular compounds. A CRISPR / Cas9 system and the small molecular compounds are combined to act on cells to achieve the method. Specifically, the CRISPR / Cas9 system comprises a gRNA fragment of a target gene, the target genecan be identified at a directed site, and the target gene is broken in two chains, and at the break site, the small molecular compounds play a role in homologous recombination repair, the genome site-directed modification is effectively completed, and the efficiency of cell genome site-directed modification treated by the small molecular compounds is significantly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
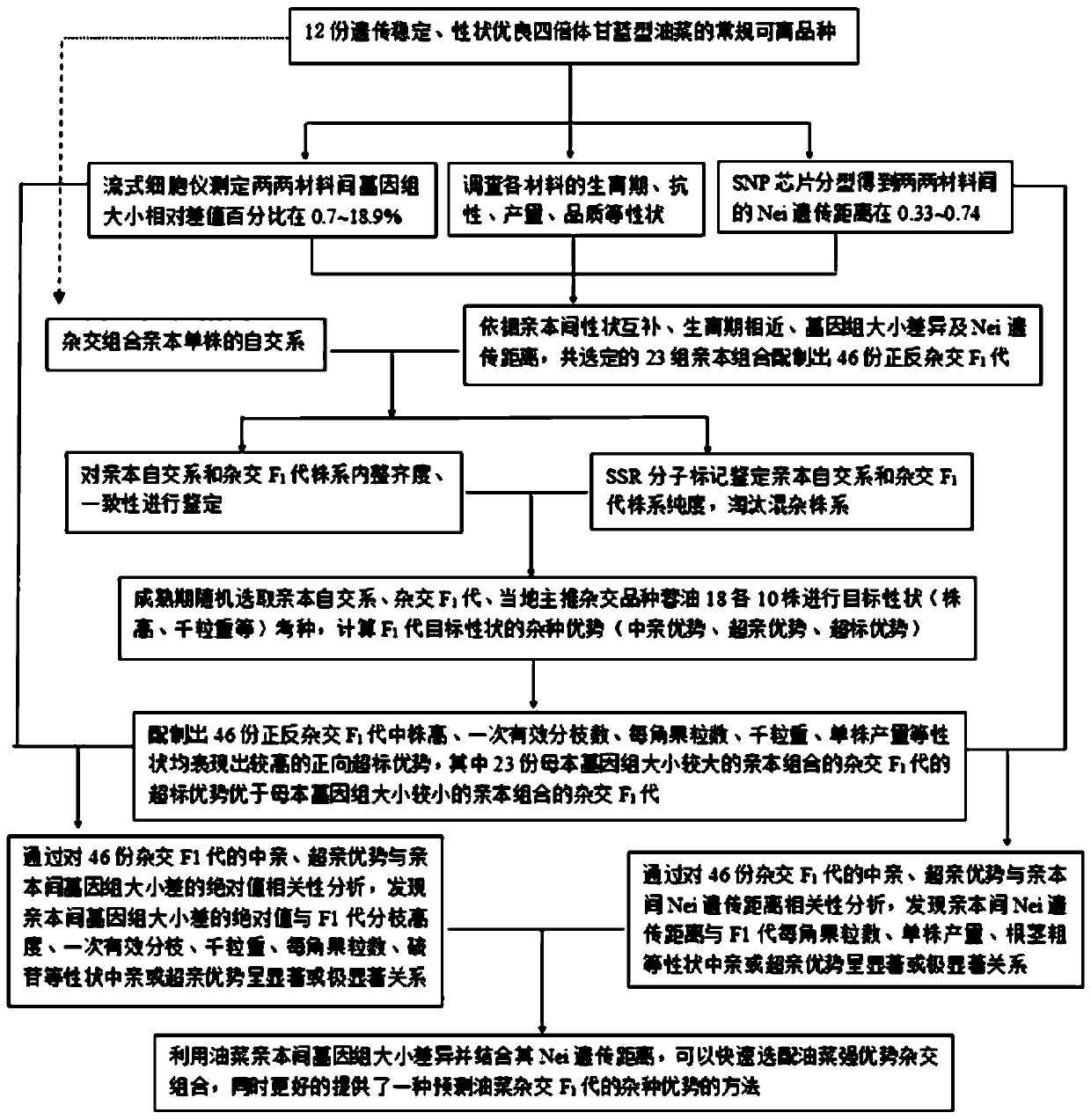
Method based on genome size and for improving cruciferous crop characters
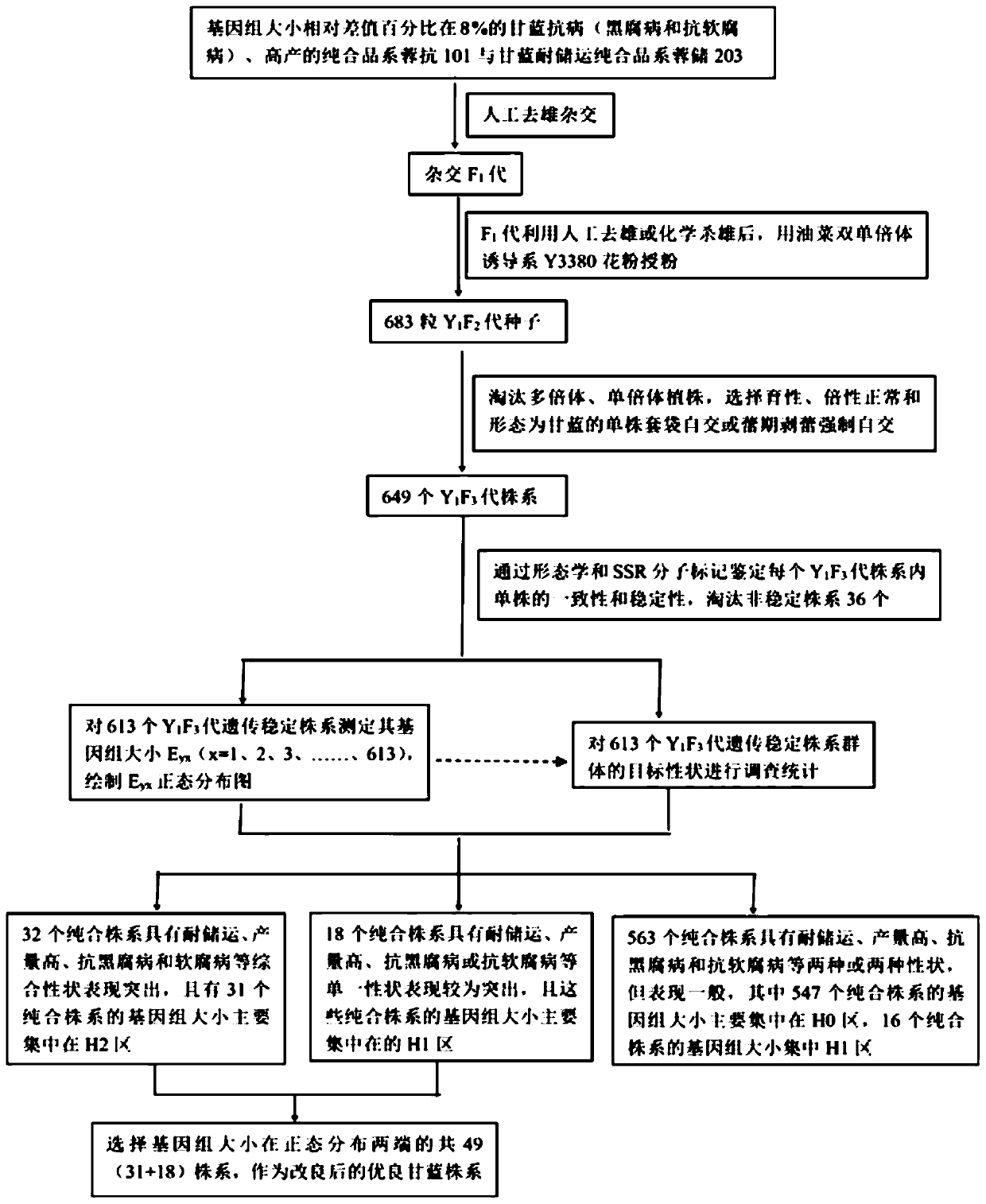
PendingCN110692511AHigh quality traitsEasy to operatePlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
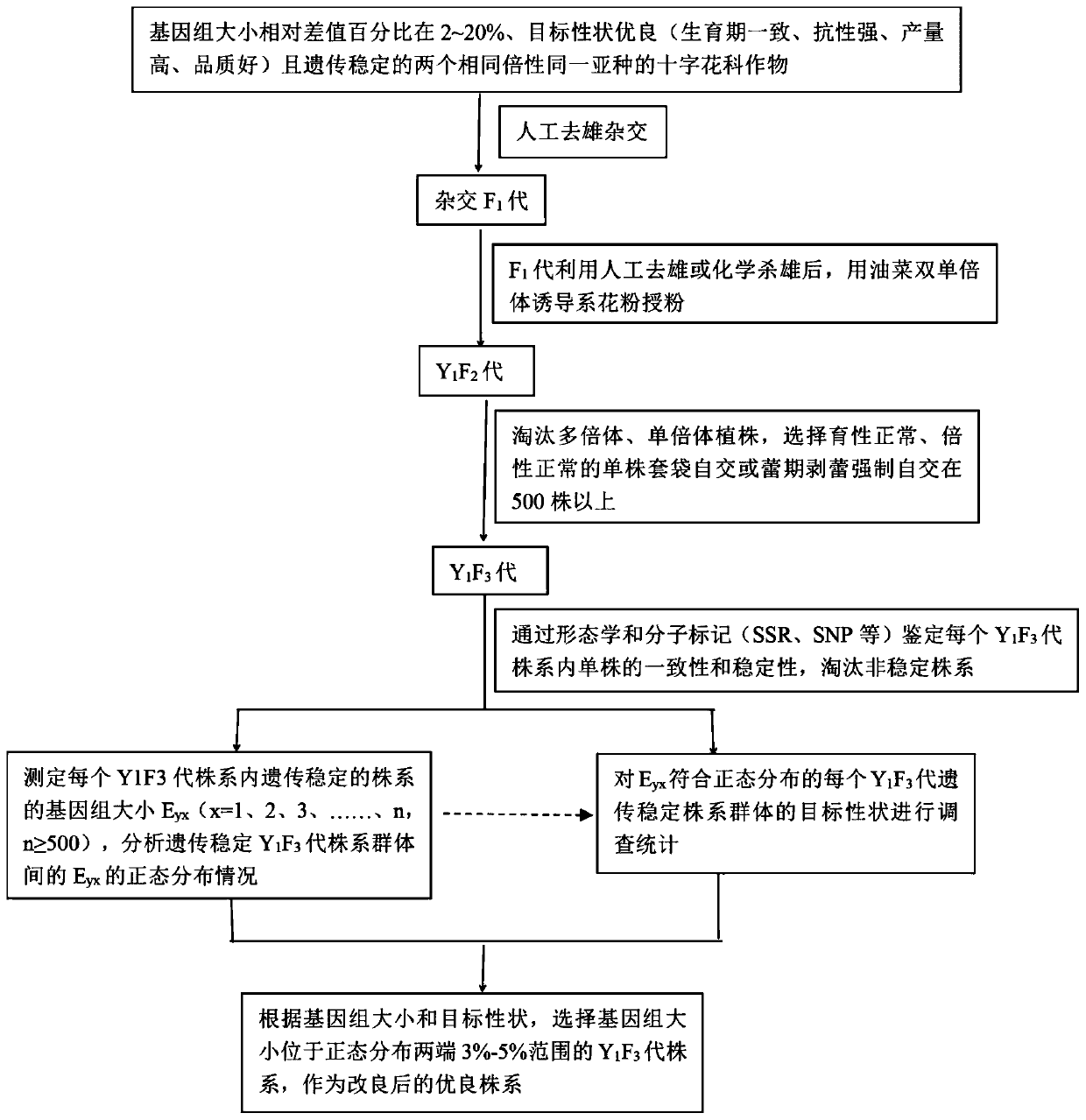
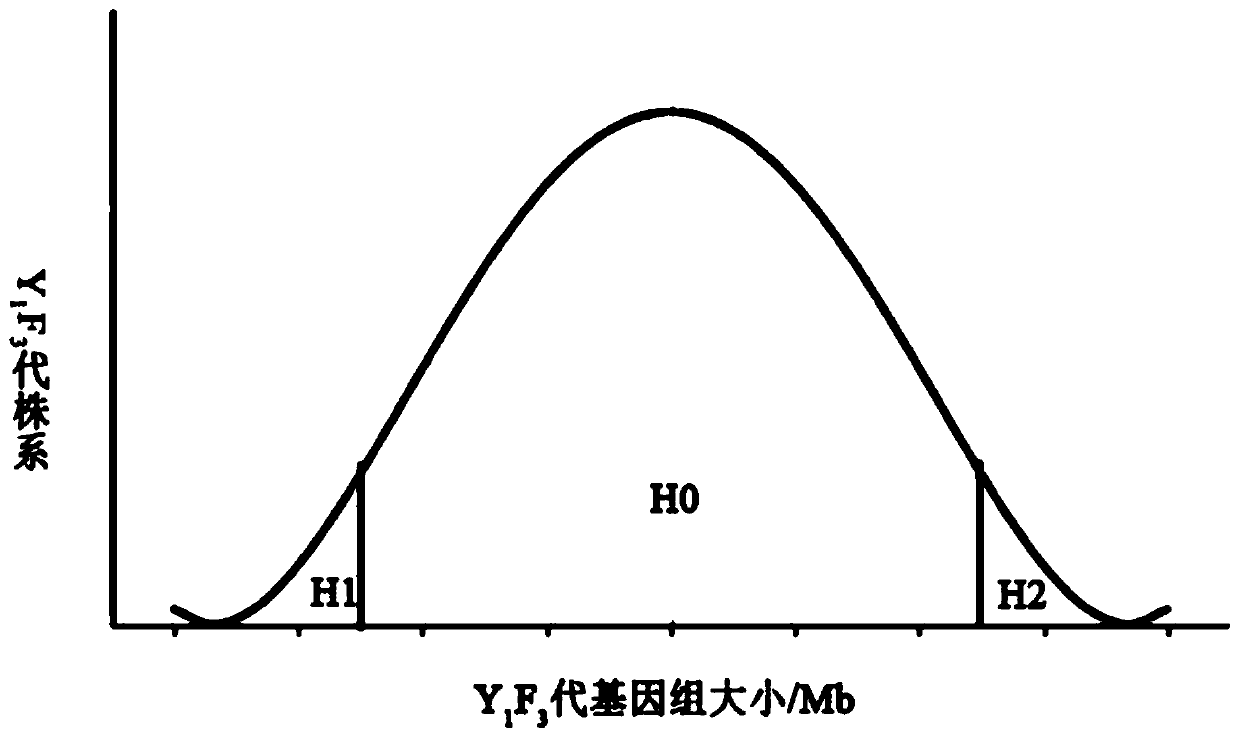
The invention discloses a method based on genome size and for improving cruciferous crop characters. The method includes: S1, collecting germplasm resources of cruciferous crops, and measuring genomesize E; S2, subjecting genome size relative difference percent T to reciprocal crossing of 2-20% cruciferous crops to obtain F1 generation; S3, planting the F1 generation, and performing artificial castration; S4, using a rape dihaploid inducer to induce the F1 generation to obtain a Y1F2 generation; S5, planting the Y1F2 generation, selecting orderly single plants with normal fertility and ploidyfor selfing to obtain a Y1F3 generation; S6, planting the Y1F3 generation, identifying its stability, and analyzing normal distribution condition of genome size Eyx of the Y1F3 generation; S7, investigating target character of the Y1F3 generation; S8, selecting a strain with the target character and Eyx positioned within 3-5% of two ends of normal distribution as an improved breeding new material. The method has the advantages of short improving period, high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method of achieving protein expression vector capable of genome site-specific modification
ActiveCN103898099AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationAnimal geneIndividual animal
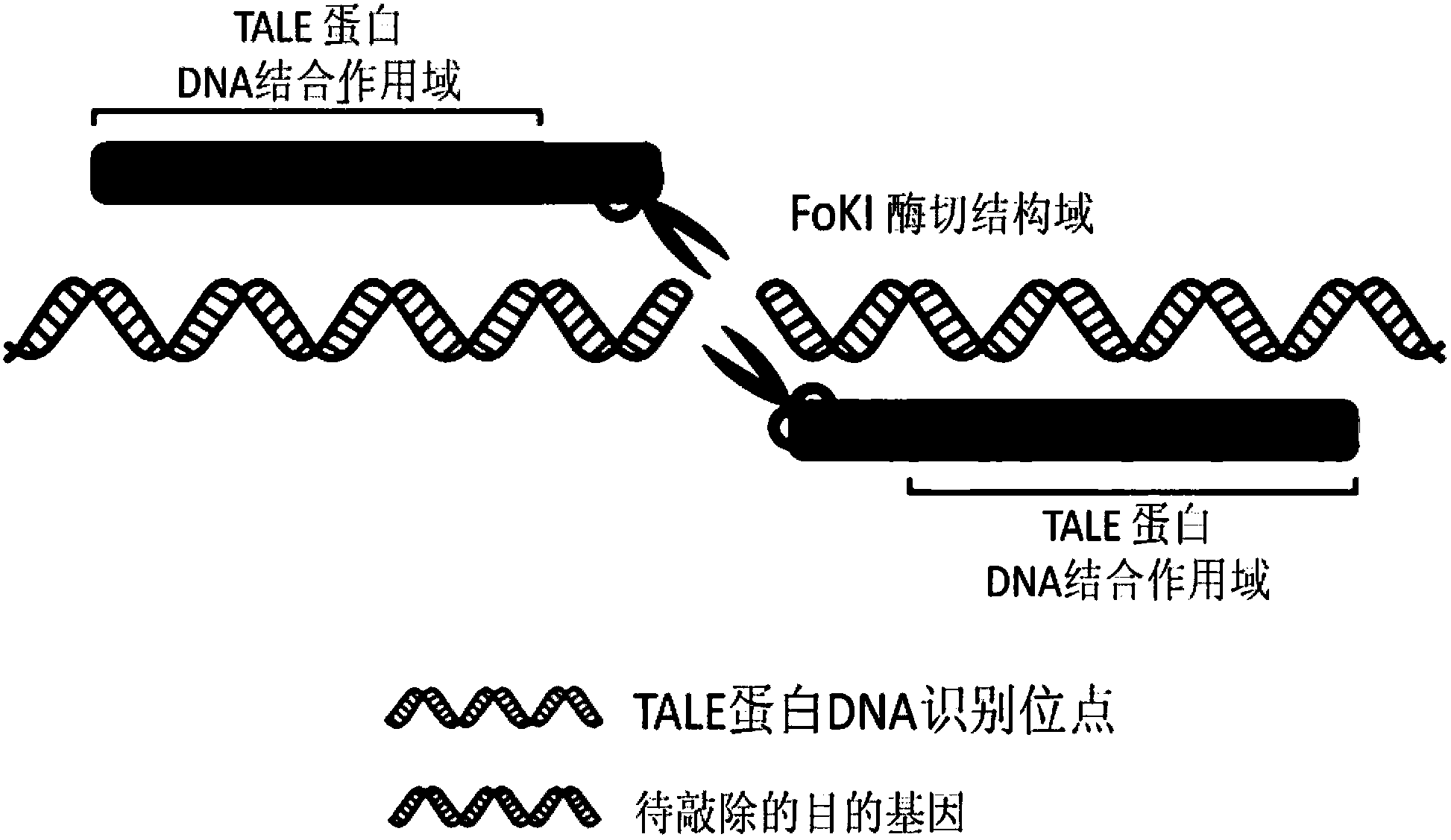
The invention relates to a biological gene clone expression technology, and particularly relates to a method of rapidly and efficiently constructing an expression vector of a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN). The method is particularly suitable for constructing an expression vector aiming at higher animal genome genetic modification in large scale so as to study functions of animal genes.
Owner:BEIJING PERCANS ONCOLOGY CO LTD
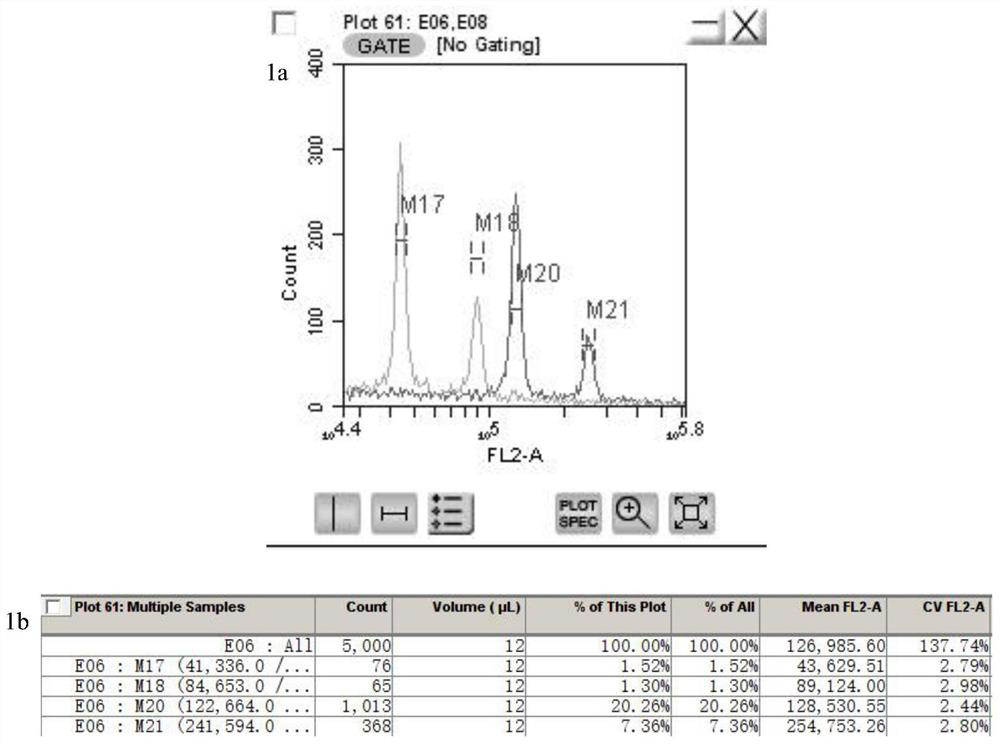
Method for quickly identifying genome size of sweet potatoes and application thereof
ActiveCN109596502ALow costPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisWild speciesNutrient solution
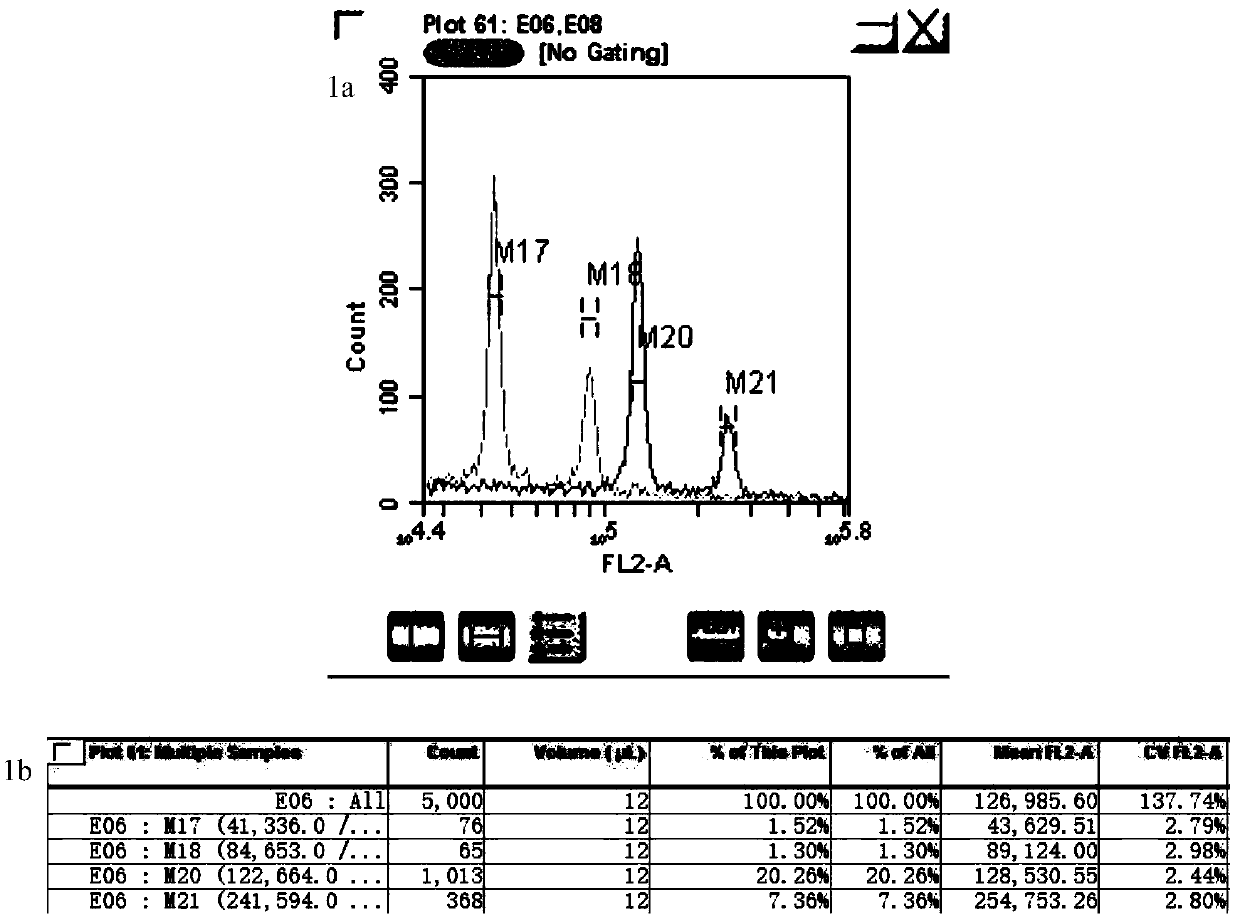
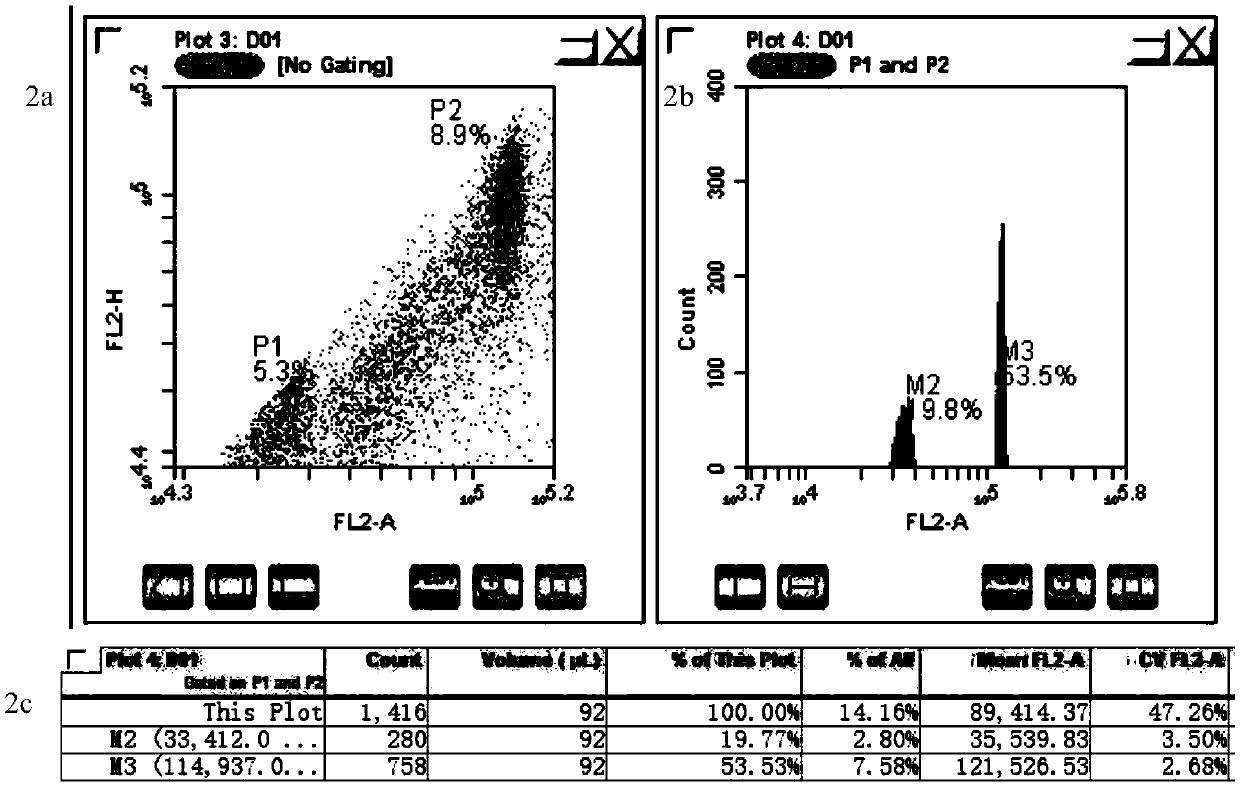
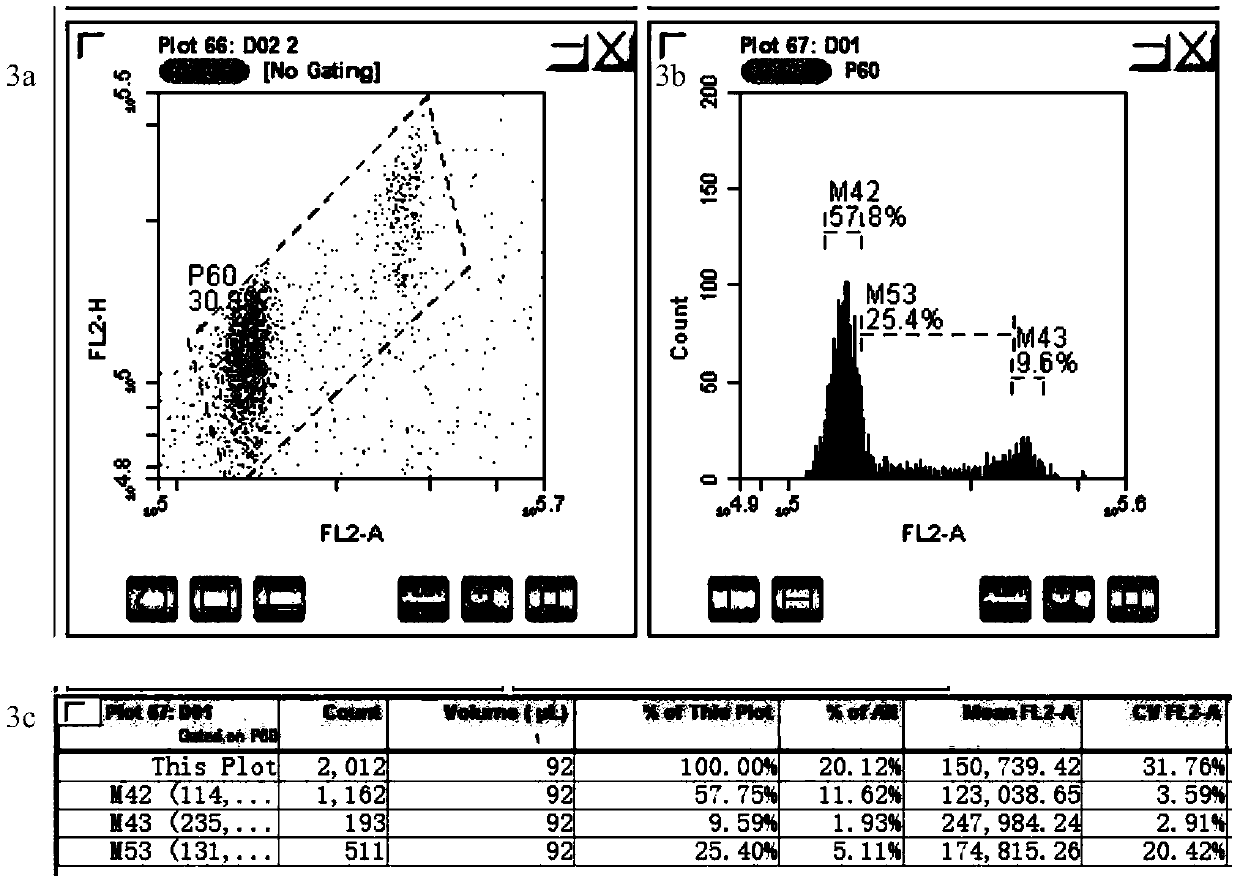
The invention provides a method for quickly identifying the genome size of sweet potatoes, belonging to the technical field of plant ploidy detection. The method comprises the steps of 1) taking sweetpotato tips from a field and performing cottage on the sweet potato tips in aHoagland nutrient solution for culturing for 20-28h; 2) mixing unexpanded leaves or new root tips with a lysis solution special for sweet potatoes for tissue lysis to obtain liquor produced after lysis; 3) filtering the liquor produced after lysis, collecting the filtrate, centrifuging, and collecting the centrifugationproduct as lysed cells; 4) mixing the lysed cells with a dye solution for dyeing, and obtaining a to-be-detected cell solution by vortex oscillation; 5) detecting the FL2-A value of the to-be-detectedcell by a flow cytometer; and 6) calculating to obtain the 1C value of the genome of the to-be-detected cell and the genome size of the to-be-detected cell according to the FL2-A value of the to-be-detected cell. The method can also identify the genome size of other species of ipomoea, and provide a fast, efficient and low-cost determination method for identifying the genome of sweet potatoes andrelated wild species.
Owner:XUZHOU INST OF AGRI SCI IN JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT (JIANGSU XUZHOU SWEETPOTATO CENT)
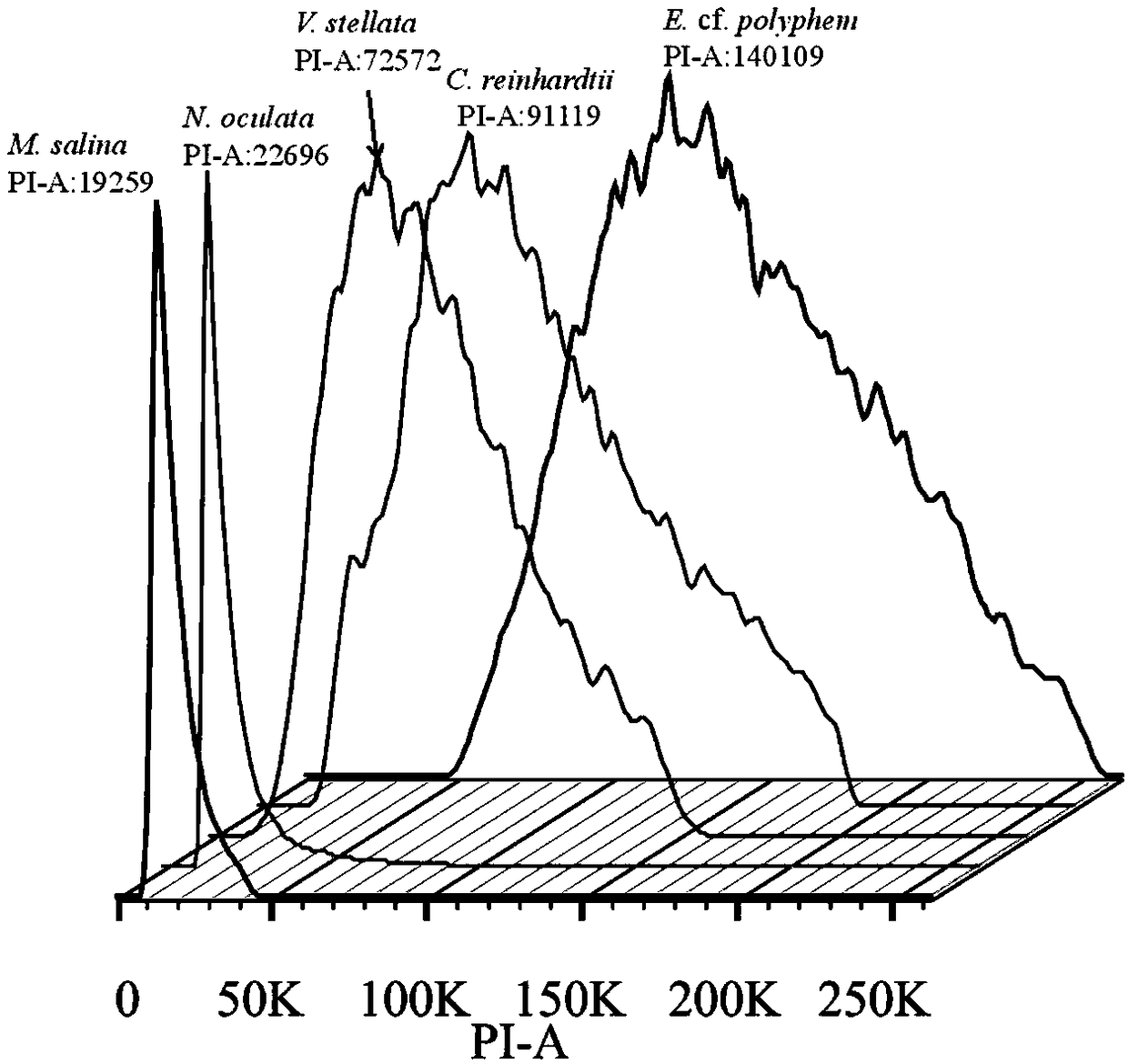
Method for determining size of single-cell eukaryotic algae genome
ActiveCN109295185AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStainingCell wall
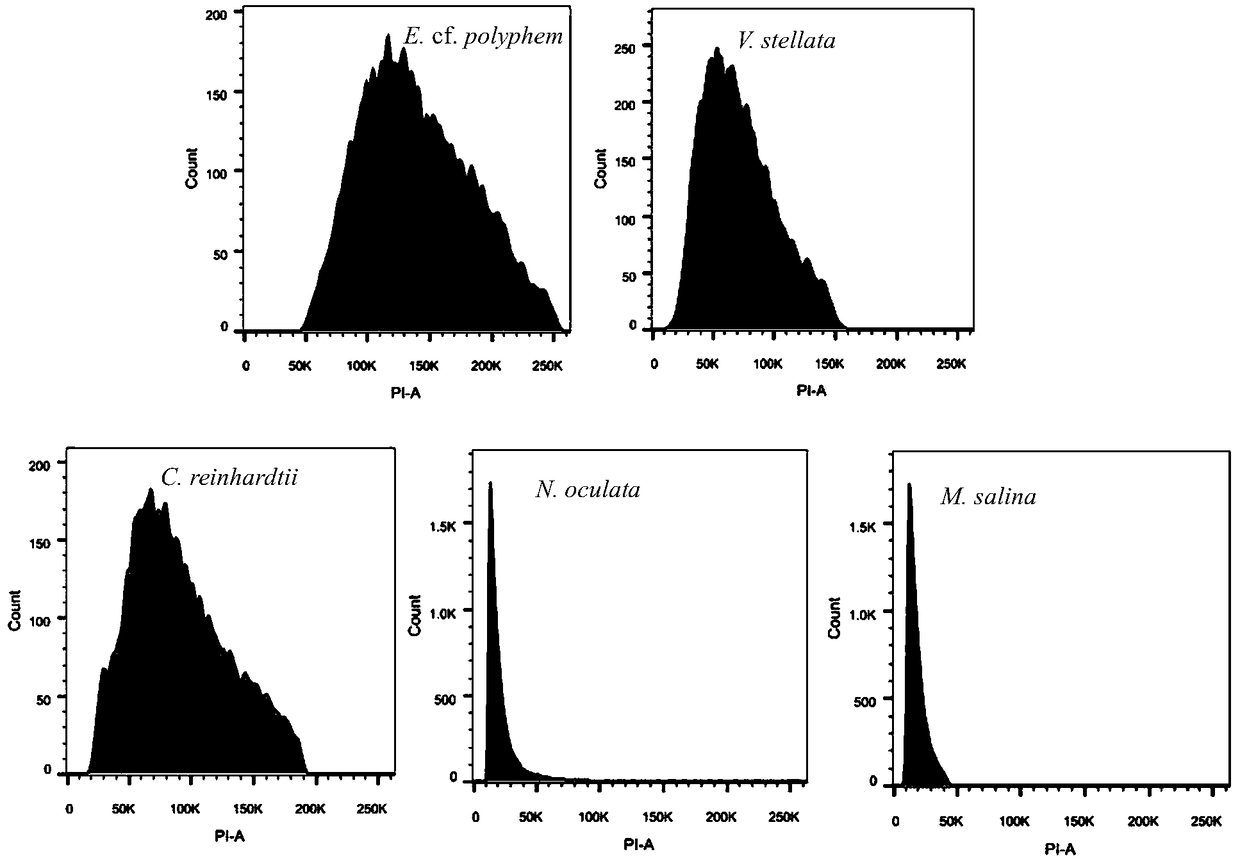
The invention discloses a method for determining size of single-cell eukaryotic algae genome. The method is based on the characteristics of single-cell eukaryotic algae, optimizes an extraction and staining method of the nucleus, and obtains the more accurate flow cytometry analysis result, combined with a high-throughput second-generation illumina sequencing technology, the genome size of algae cells is comprehensively evaluated, and the characteristics of the genome can be clarified. The technical method optimizes the flow cytometry analysis of traditional plants, removes the interference ofalgal cytochrome and cell wall by using methanol, greatly improves the dyeing effect of PI, and improves the accuracy of flow cytometry analysis, and combined with a current leading high-flux sequencing technology, the genome structure characteristics of the to-be-tested species are comprehensively analyzed, which can provide a theoretical basis for a genetic structure research of subsequent species and an assembly strategy of whole genome sequencing.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
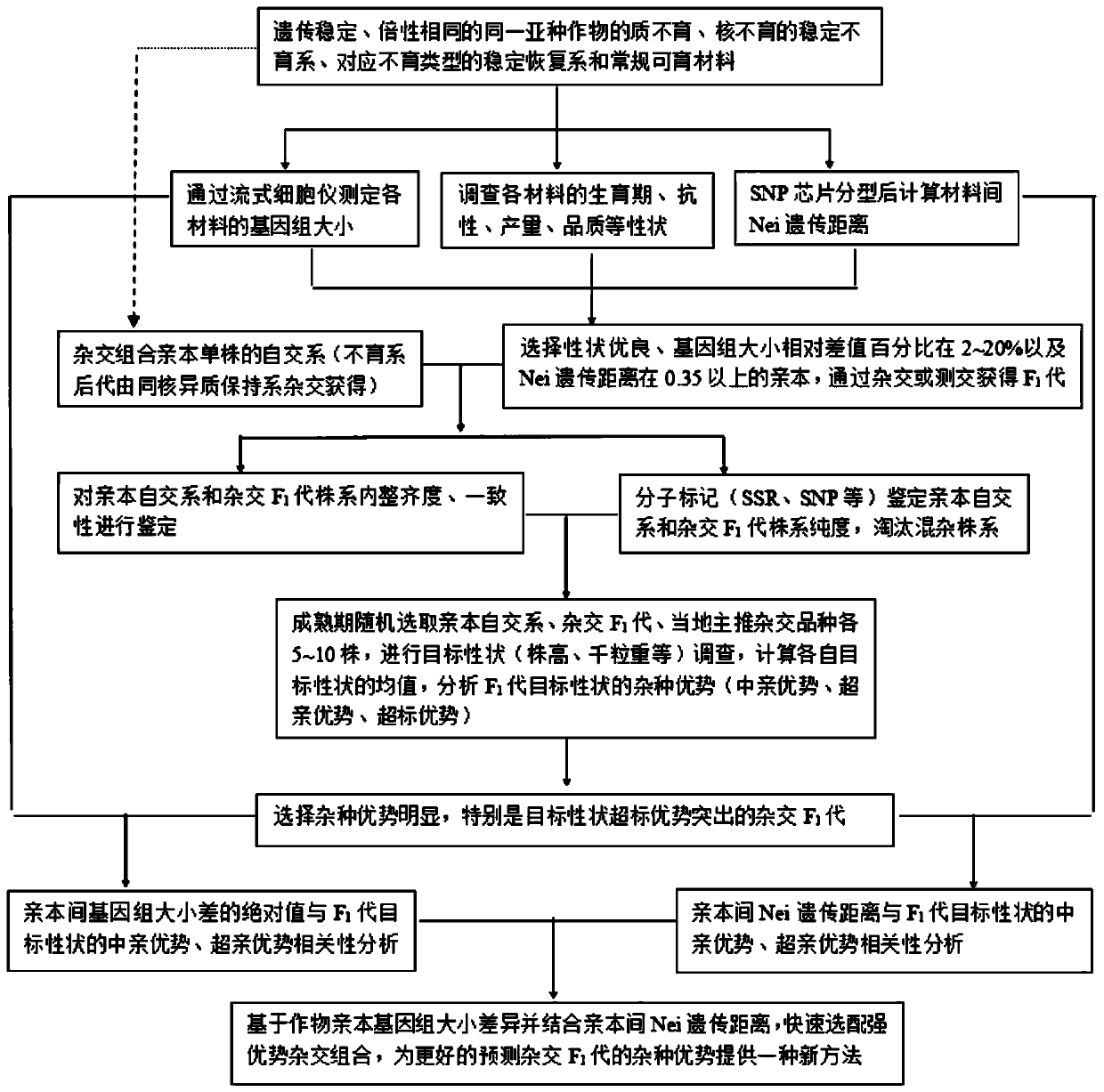
Method for rapidly predicting heterosis based on genome size of crops
The invention discloses a method for rapidly predicting heterosis based on genome size, and belongs to the technical field of crop breeding. The method includes the following steps: S1. selecting a hybrid combination parent according to the relative difference percentage of genome size and Nei genetic distance between crops; S2. emasculating and hybridizing the selected hybrid combination parent to obtain F1 generation; S3. carrying out heterosis analysis on target traits of the F1 generation; S4. analyzing the correlation between heterosis of the target traits of the F1 generation and Nei genetic distance between parents; S5. analyzing the correlation between heterosis of the target traits of the F1 generation and absolute value of genome size difference between parents; and S6. combiningthe above analysis results, selecting strong heterosis hybrid combinations and predicting heterosis of the F1 generation at the same time. The breeding method is beneficial to improving breeding efficiency and reducing breeding cost, and has the advantage of wide applicability.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for polyploidy genome survey
PendingCN111411107ASolve the problem of low evaluation accuracyFill vacancyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic sequencingGenetics
The invention discloses a method for polyploidy genome survey and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. By adopting the method, genome characteristic information of a polyploidy speciescan be accurately obtained through an updating algorithm. The method specifically comprises the following steps: performing genome DNA extraction and sequencing; performing quality control on genomesequencing data; evaluating characteristics of a polyploidy genome; and analyzing ploidy variation of the polyploidy genome. The method already takes complex relationships of genome sequences of polyploidy species into account when being designed, analysis methods aiming at sizes, heterozygosis rates and homologous rates of the genomes of the polyploidy species are specifically designed, and the problem that a conventional method is high in polyploidy genome evaluation fault rate can be effectively avoided. By adopting the method for polyploidy genome survey, survey analysis on any eukaryon polyploidy genome can be theoretically implemented, so that the method for polyploidy genome survey can be widely applied to polyploidy genome evaluation, and accurate and effective analysis methods areprovided for application to evaluation on sizes, heterozygosis rates and homologous rates of polyploidy genomes, and the like.
Owner:武汉古奥基因科技有限公司
Method of carrying out scaffolding based on long fragments
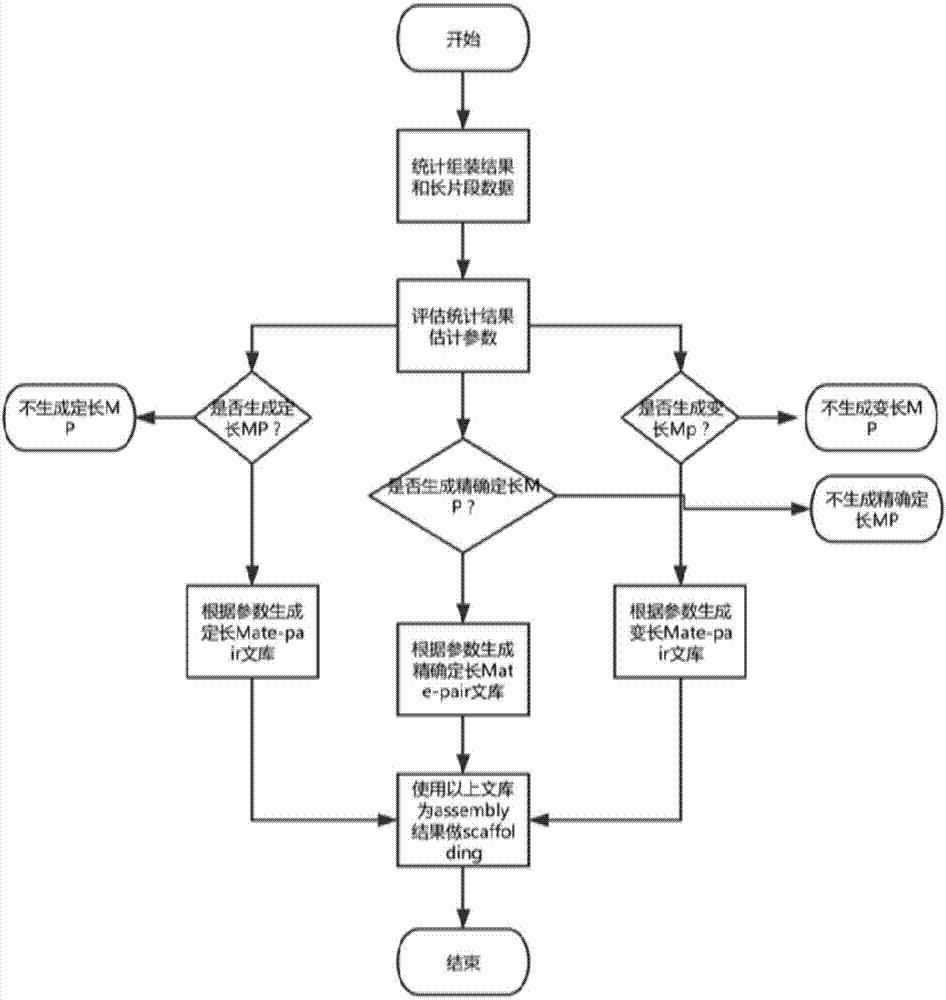
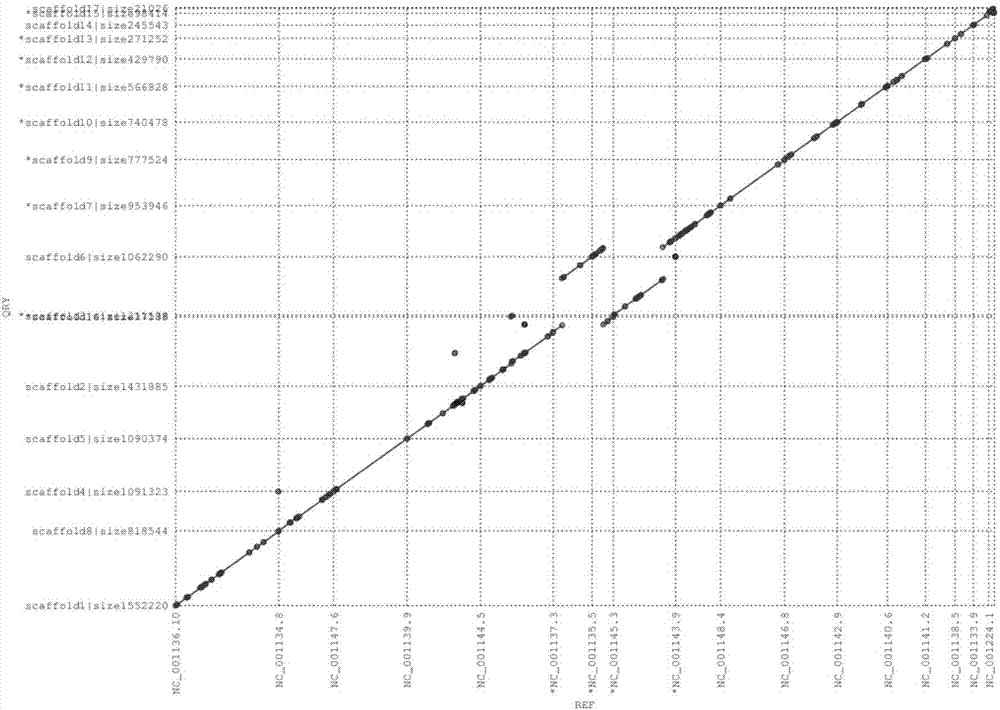
ActiveCN107273716AHigh precisionThe assembly result is complete and more continuousSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsContigComputational biology
The invention relates to a method of carrying out scaffolding based on long fragments. The method is characterized by including the following steps: S1, obtaining long-fragment sequence data and a genome splicing result, and obtaining an estimated genome size, a genome splicing size and a contig number; S2, evaluating an insert length range between a mate pair according to the long-fragment sequence data and the genome splicing result; S3, generating a mate pair library according to the long-fragment sequence data and the insert length range; and S4, using the mate pair library, which is obtained in the S3, to carry out scaffolding on the genome splicing result to obtain a scaffolding result. Through using the method of the invention, an existing long-fragment sequence can be directly utilized to obtain the mate pair library in a case where additional mate pair or pair end sequencing is not needed, and thus next scaffolding is completed.
Owner:WUHAN FRASERGEN CO LTD
Space methylobacterium LCT-S10-2
The invention relates to a strain of downward strain space methylobacterium LCT-S10-2 separated out of a re-entry capsule of the Shenzhou IX airship. The space methylobacterium LCT-S10-2 is an aerobic bacterium, a short-rod-shaped gram stain variable strain (figure 1), a chemoheterotrophic bacterium, a facultative methylotrophic bacterium and a rare facultative methane nutritional bacterium, and the strain grows slowly. The space methyl bacillus LCT-S10-2 is subjected to 16S rRNA sequencing, and is identified as a methylobacterium member. Whole genome sequencing analysis is carried out, the whole genome size is 4.57 Mbp, the GC content is 66.84%, the predicted gene number is 4946, and protein of LCT-S10-2 is classified and annotated as 20 kinds of COG families. The LCT-S10-2 bacterium can grow on the surface of epoxy resin and the surface of vulcanized natural rubber, and a corrosive biological film is generated. The bacterium cannot grow on the surface of ester polyurethane, the surface of ether polyurethane and the surface of polyvinyl formal, and no corrosive biological film is generated. Certain help is provided for studies of species distribution of microorganisms in an airtight aircraft and selection of corrosion-resistant materials.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
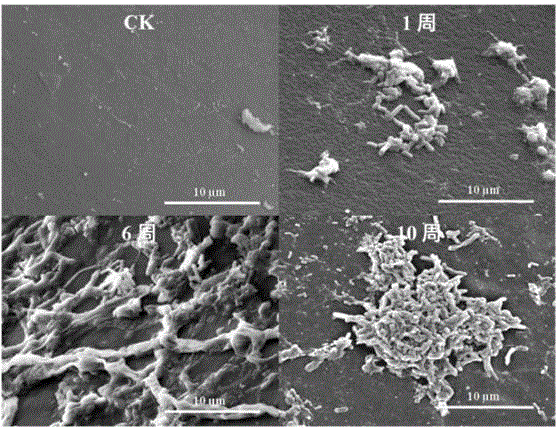
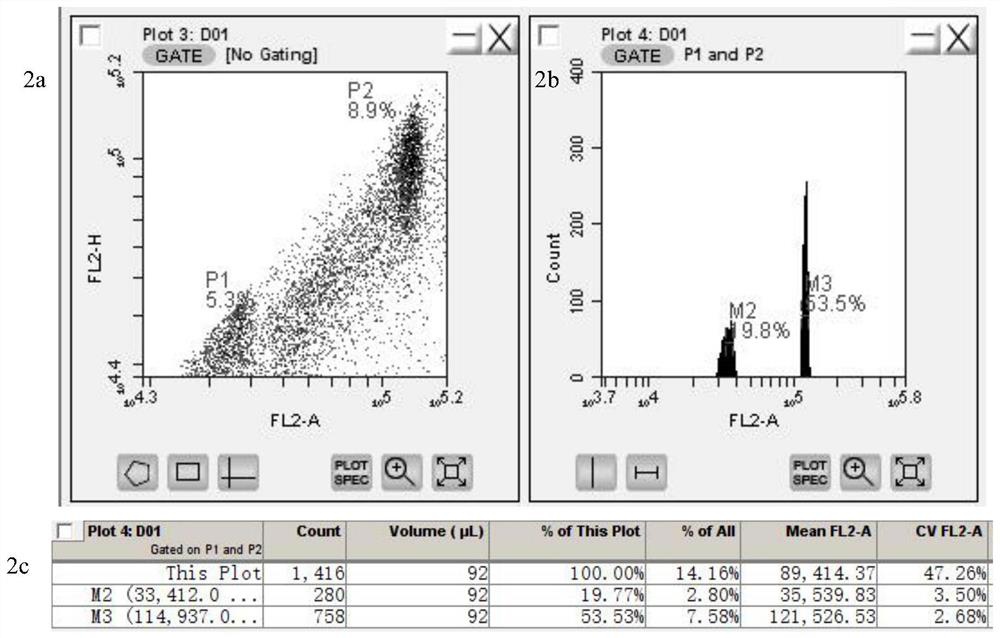
Staphylococcus epidermidis with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity for gram-positive drug resistant bacteria as well as screening method and application of staphylococcus epidermidis
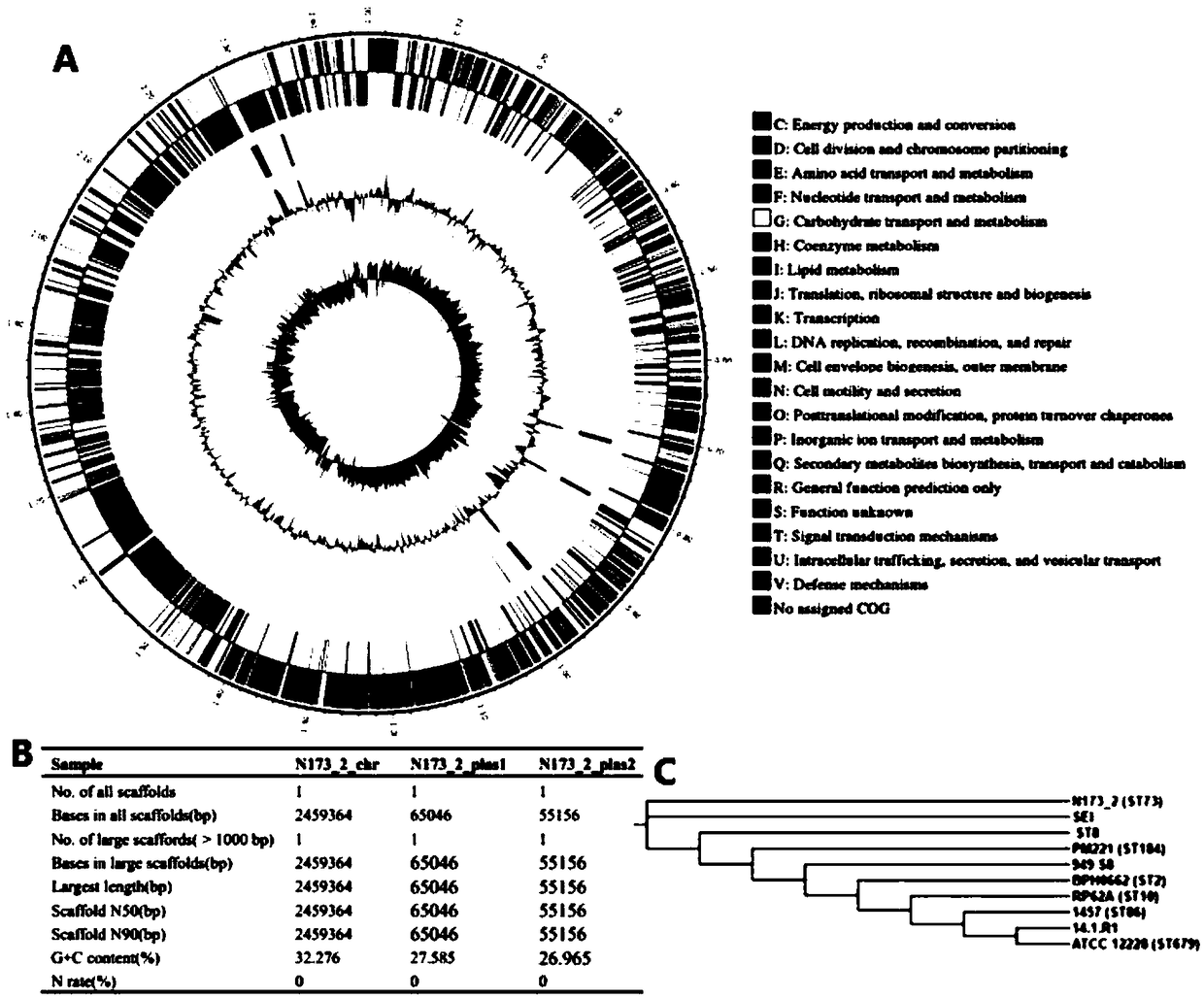
ActiveCN108823124AStrong targetingNew structureAntibacterial agentsBacteriaNasal cavityScreening method
The invention discloses a staphylococcus epidermidis with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity for gram-positive drug resistant bacteria and a screening method of the staphylococcus epidermidis. Thestaphylococcus epidermidis is separated from staphylococcus epidermidis strains colonized in nasal cavity of healthy people, is named N173-2, has obvious bacteriostatic action on clinically common gram-positive drug resistant pathogenic bacteria but has no bacteriostatic action on gram-negative drug resistant bacteria. The genome size of the staphylococcus epidermidis strain N173-2 is 2459364 bp,the staphylococcus epidermidis strain N173-2 contains two plasmids with sizes being 65046 bp and 55156 bp respectively and is preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 3, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 15550. The invention further relates to an application of the staphylococcus epidermidis N173-2 in preparation of drugs resisting gram-positive drug resistant bacteria. The strain with the broad-spectrum antibacterial activity on the clinically common drug resistant pathogenic bacteria is screened from symbiotic / colonized florae of a human body, and a foundation is laid for exploration of novel antibacterial molecules which are non-toxic and harmless to the human body, brand-new in structure and more targeted and do not easily produce drug resistance.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
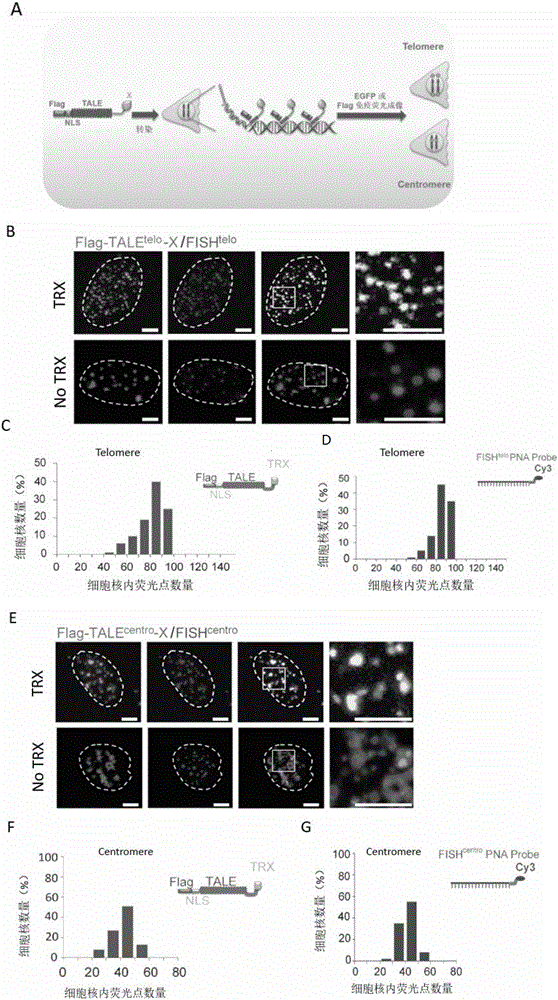
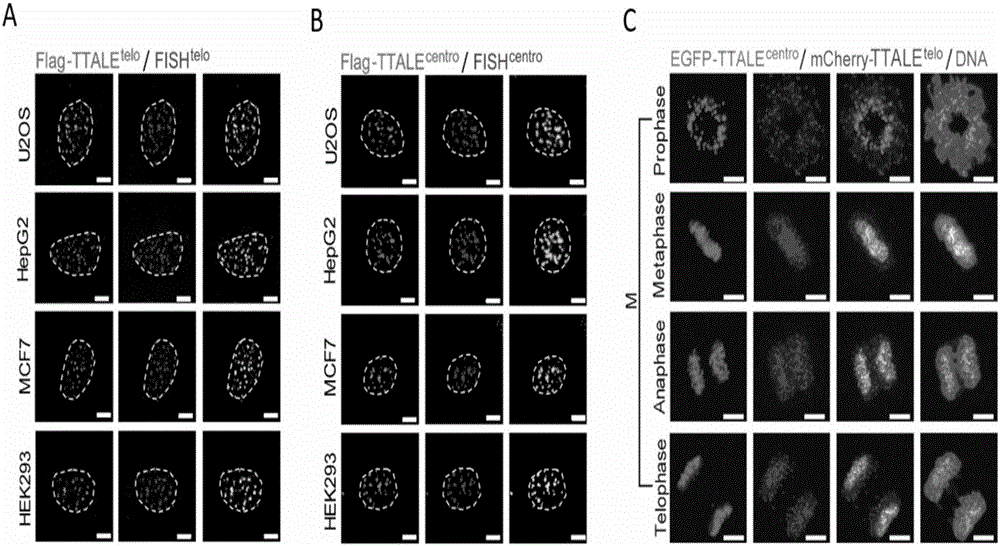
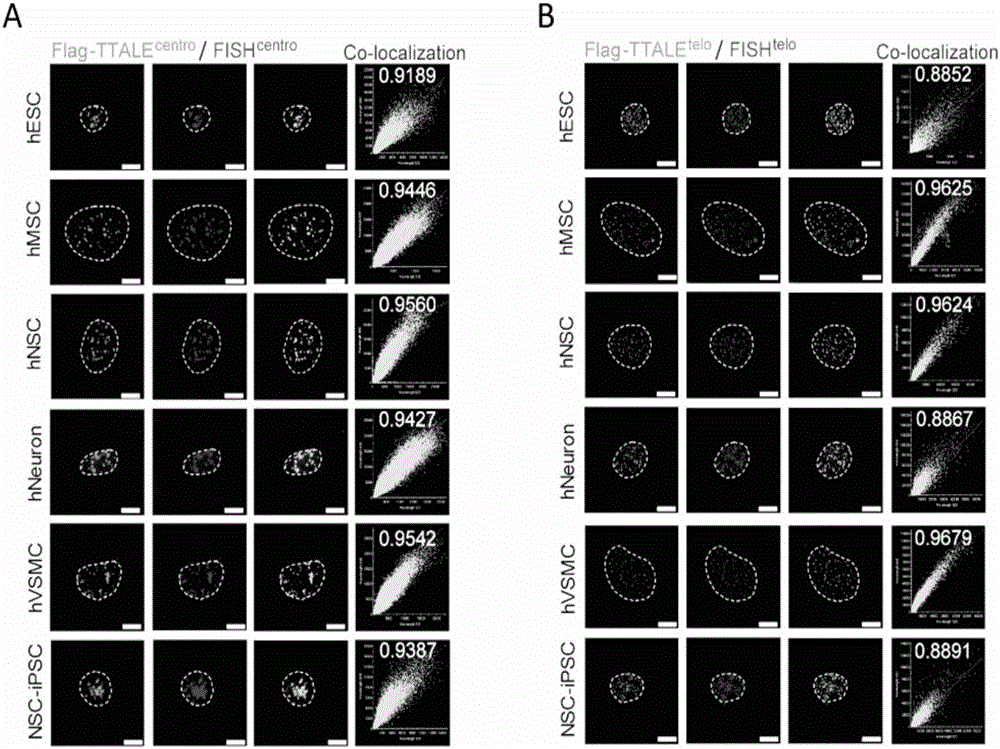
Method for visually marking genome sites
ActiveCN106800602APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNucleic acid vectorDiseaseBasic research
The invention discloses a method for visually marking genome sites. According to the method, a novel visual genome marking tool TTALE is established by fusing thioredoxin (TRX) at the c-terminal of the traditional transcriptional activation-like effect element (TALE) protein. Experiments prove that the TTALE can be used for accurately marking genome repetitive sequences such as telomere, centromere and ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA) coded sequences (ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid (rDNA)) in different types of human cells such as a tumor cell line, embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells and terminally differentiated cells, and coded genetic loci (MUC4). A TTALE technology can make up for the lack of accurate, simple, convenient and long-acting live cell genome visualization marking techniques in the current scientific research and clinical markets, thereby promoting the development of basic research and clinical diagnosis and treatment of human senility and vital diseases.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
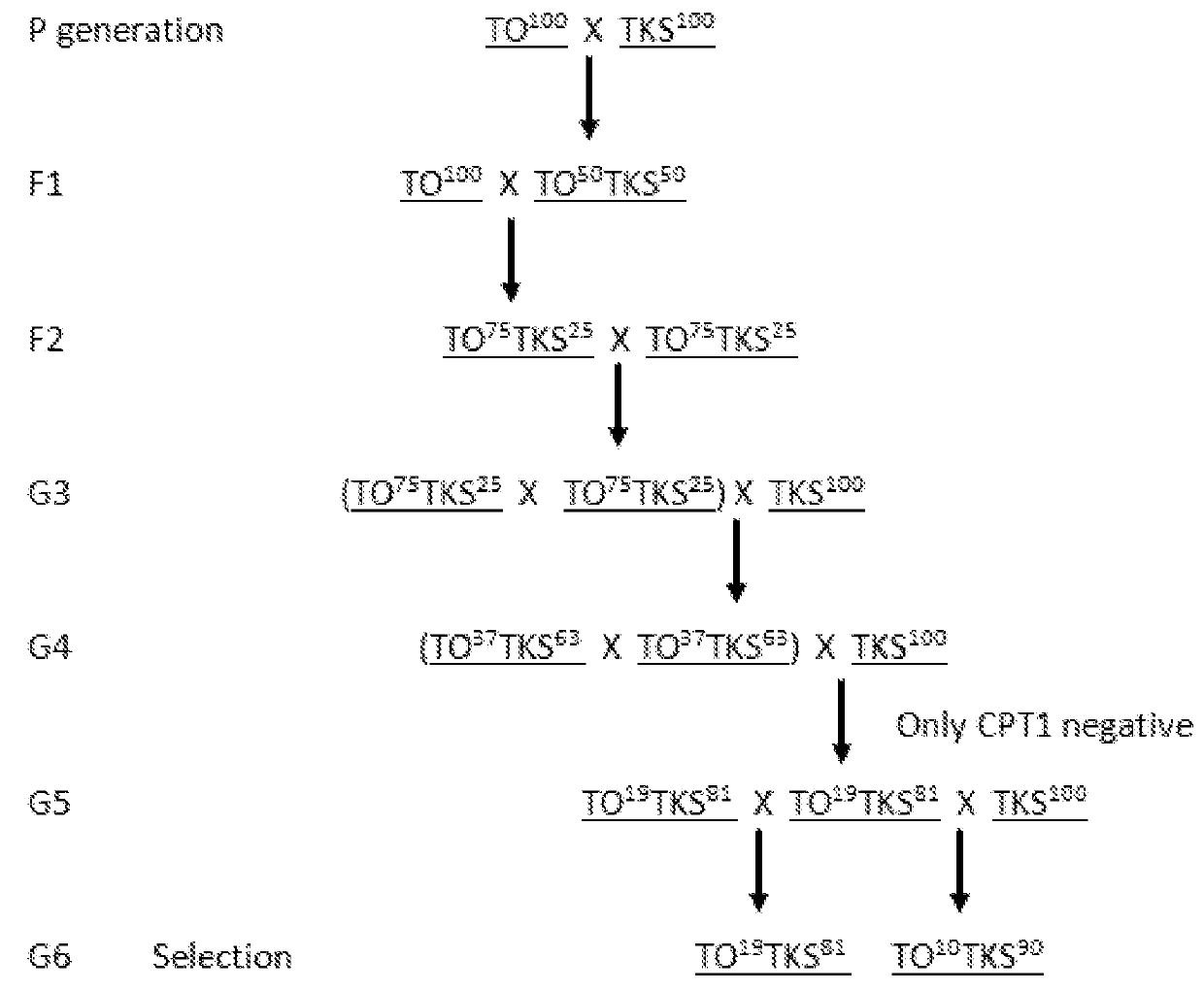
Rubber producing taraxacum plant
InactiveUS20180271043A1Sure easyPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyBotany
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining Taraxacum plants of considerable size and substantial rubber content, preferably by providing Taraxacum plants having a relatively large genome size and / or having a specific percentage of Taraxacum koksaghyz (TKS) derived genes and a specific percentage of Taraxacum officinale (TO) derived genes; selecting these plants for the presence or absence of certain markers; and subsequently selecting the plants on plant size, and on genome size.
Owner:LION FLEX BV
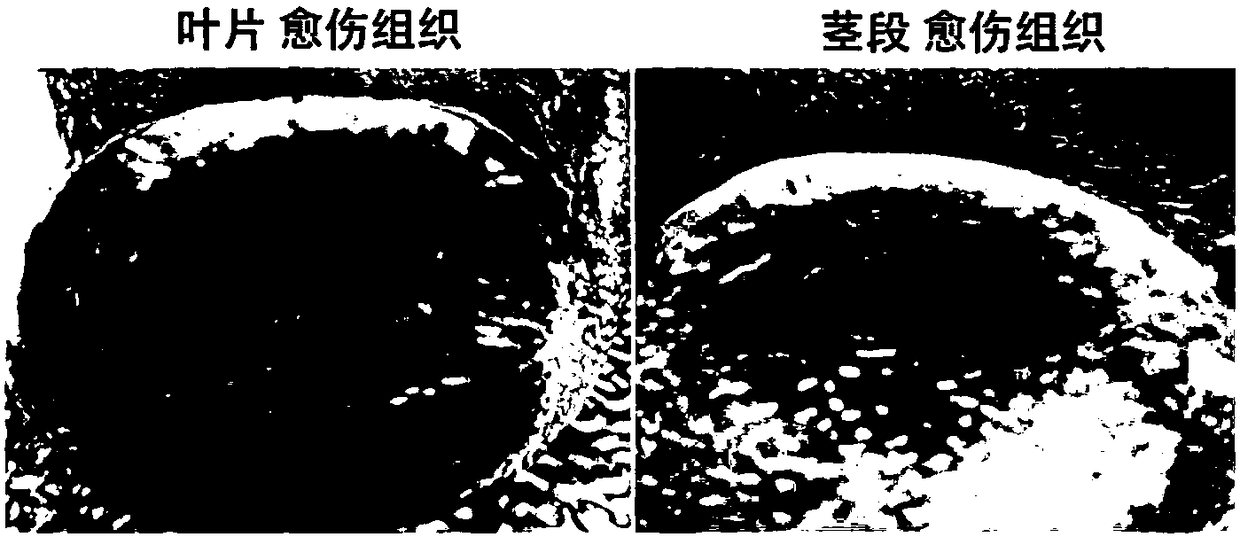
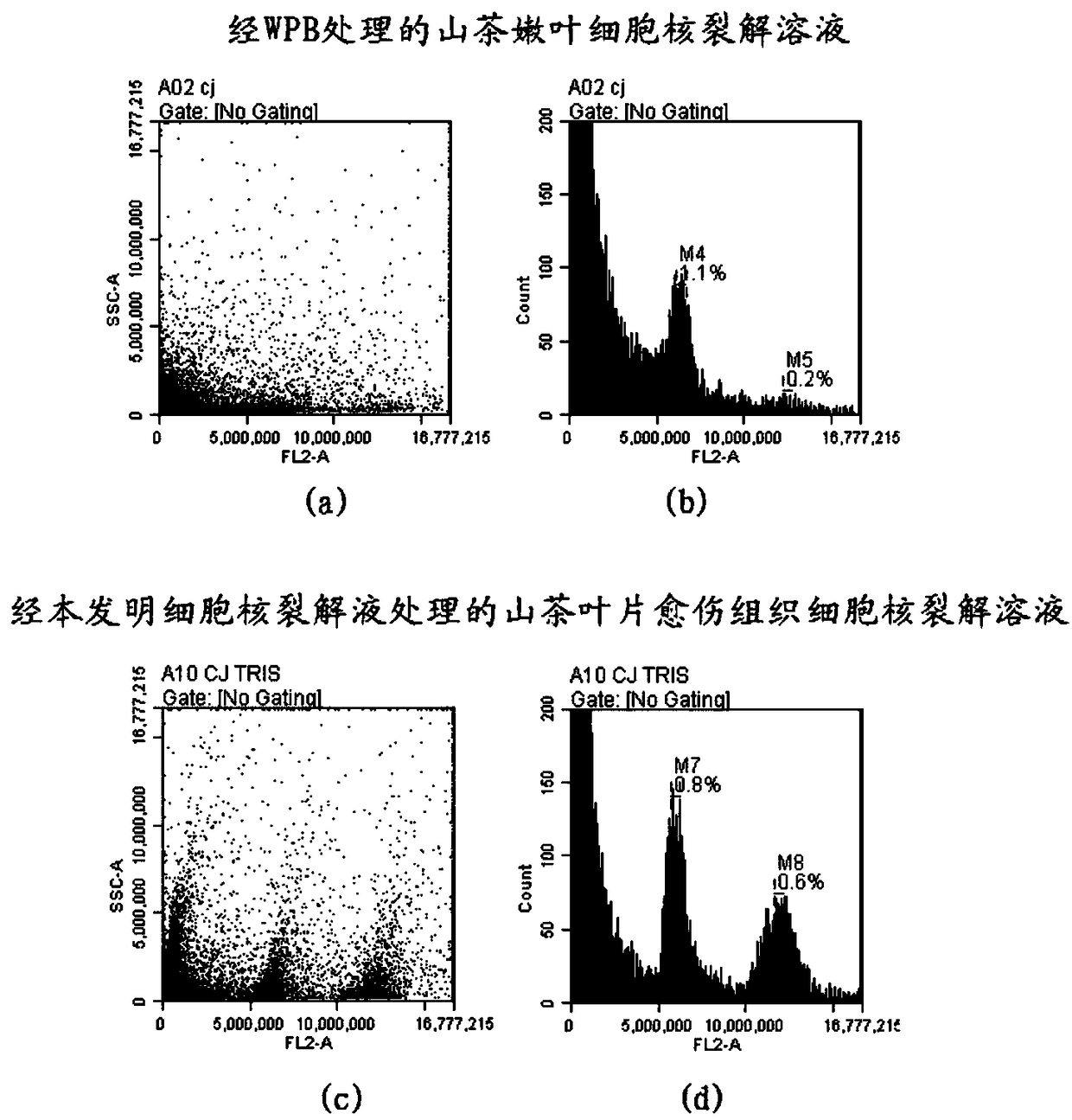
Method for detecting nuclear DNA content of Camellia plant
InactiveCN108165645AAvoid restrictionsOvercome limitationsMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsLysisSkin callus
The invention provides a method for detecting the nuclear DNA content of a Camellia plant. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cutting a Camellia plant blade or stem segment to obtain an explant; (2) performing disinfecting pretreatment on the explant; (3) inducing calluses; (4) processing the induced calluses to achieve nucleus separation, and filtering the processed calluses; (5) staining a filtrate obtained in step (4) to prepare a nuclear lysis solution to be detected; and (5) detecting the nuclear DNA content of the nuclear lysis solution to be detected through a flow cytometer.The method has application significance in ploidy inspection and genome size determination of the Camellia plant, and provides a new analytical technique for polyploid breeding of the Camellia plant.
Owner:RES INST OF SUBTROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
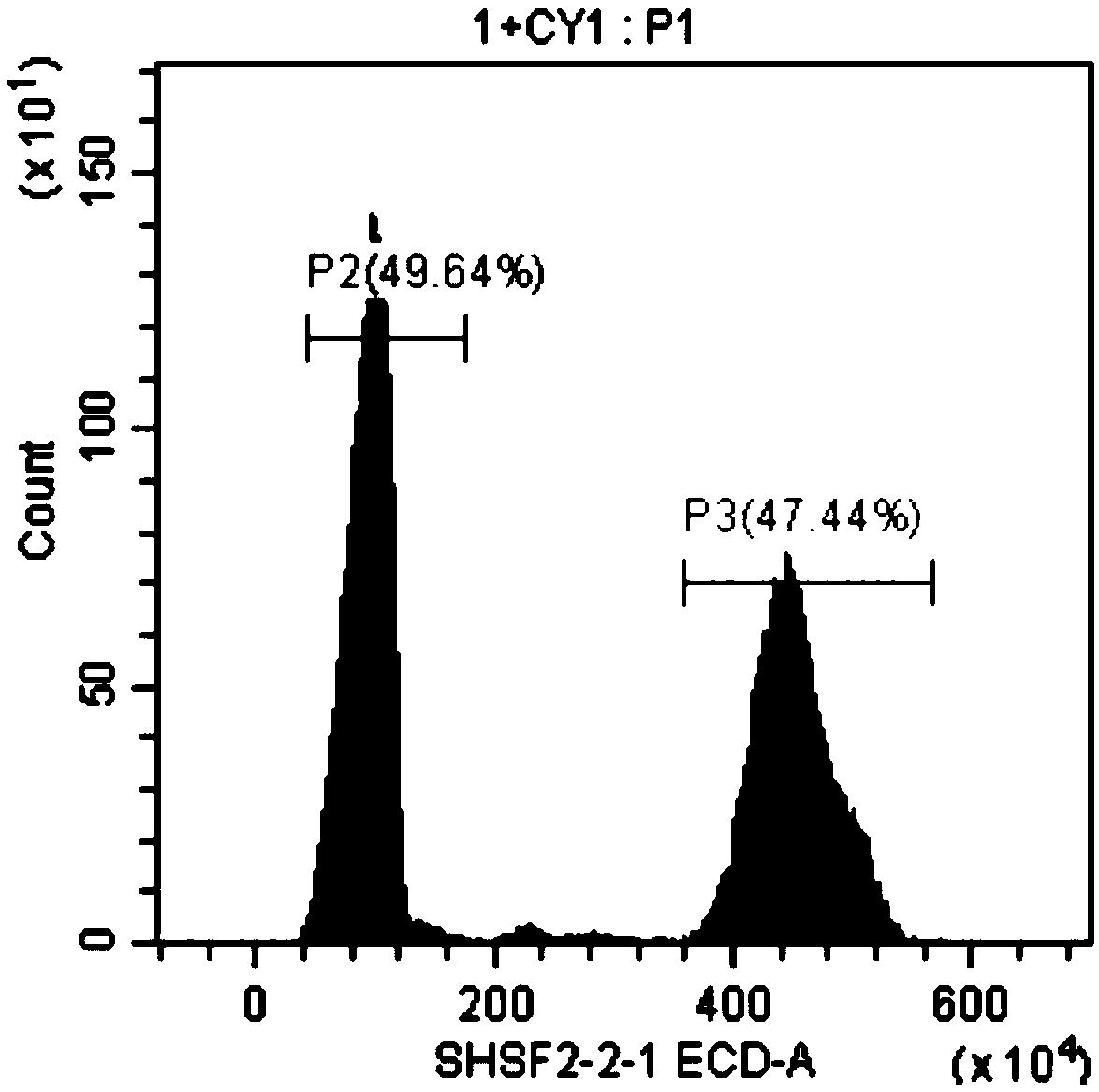
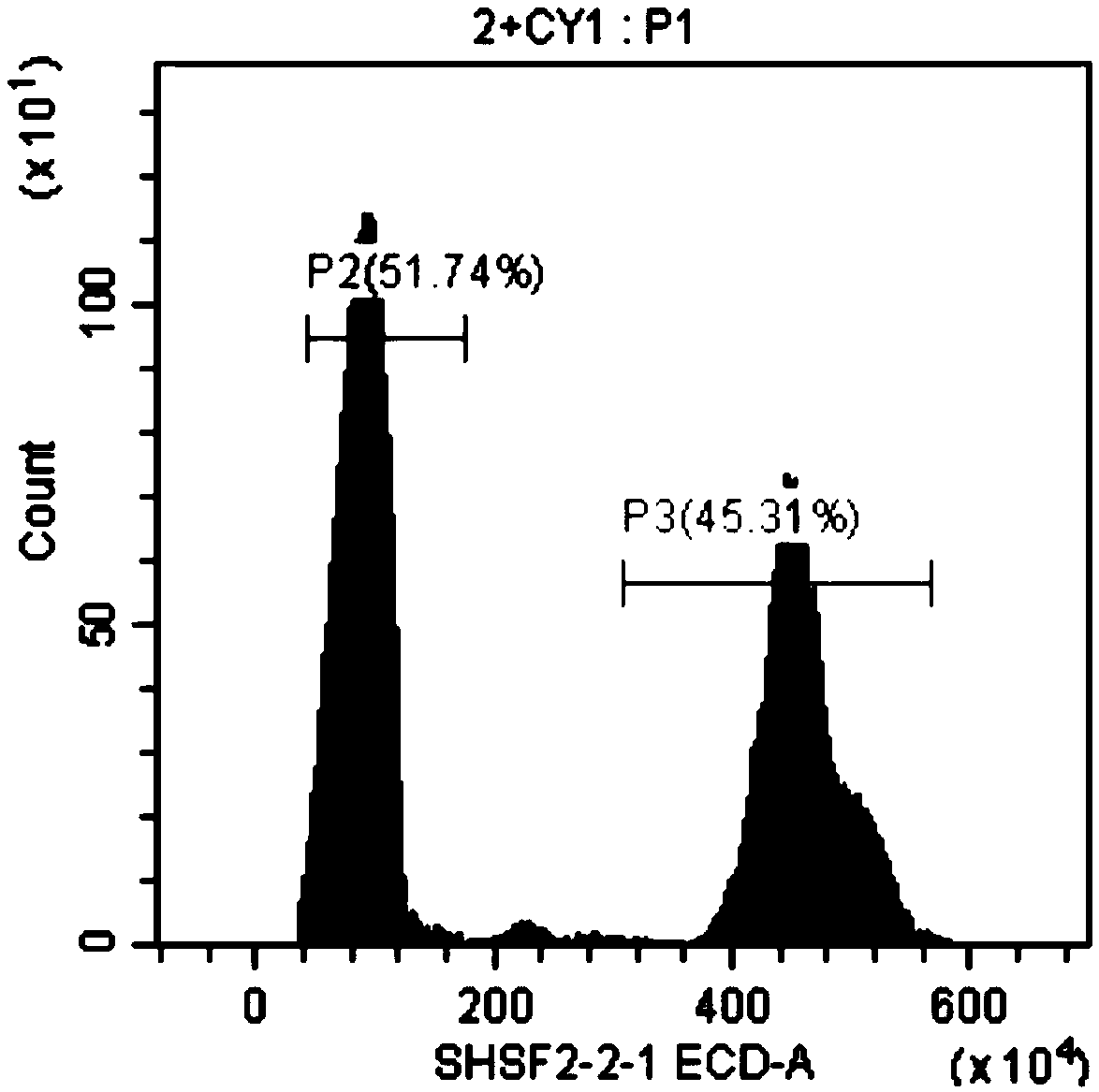
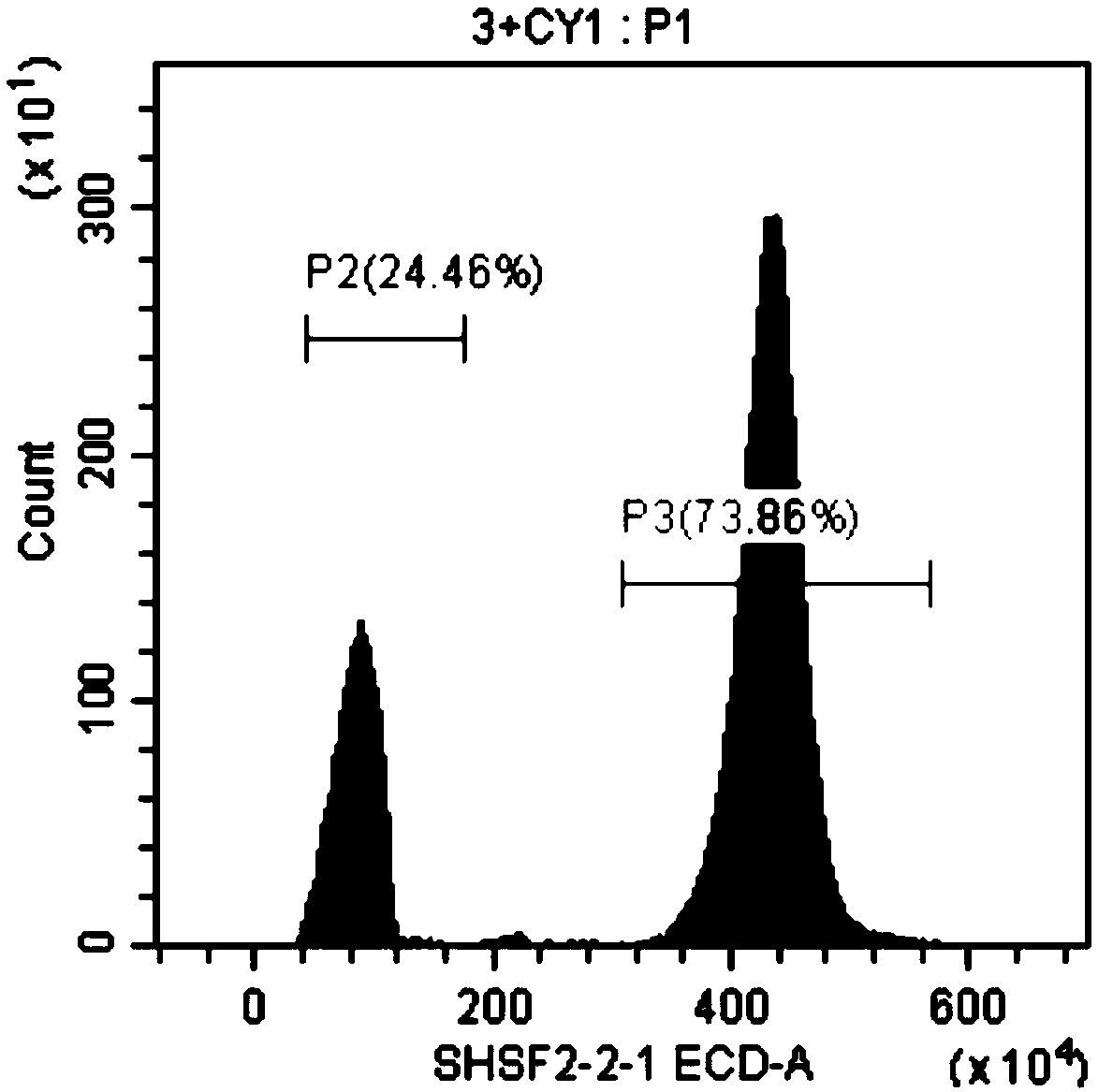
Method for rapidly determining genome size of sturgeons by flow cytometry
InactiveCN108823277ARapid determinationEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological particle analysisGenome sizeBioinformatics
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining the genome size sturgeons of by flow cytometry. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting fish with the genome having a known sizeas a standard control, respectively performing caudal vein blood connection, blood centrifuging, PBS buffer solution washing, 2% paraformaldehyde solution addition, permeabilizing agent addition andstaining on the standard control and a sturgeon to be detected, and detecting the standard control and the sturgeon to be detected by flow cytometry to obtain the fluorescence intensity peak P2 of thestandard control and the fluorescence intensity peak P1 of the sturgeon to be detected; and 2, obtaining the genome size of the sturgeon to be detected according to N1= N2 * P1 / P2, wherein N1 represents the genome size of the sturgeon to be detected, and N2 represents the genome size of the standard control. The method can be used to preliminary determine the genome size of several major speciesof sturgeons bred in China before large-scale genome sequencing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
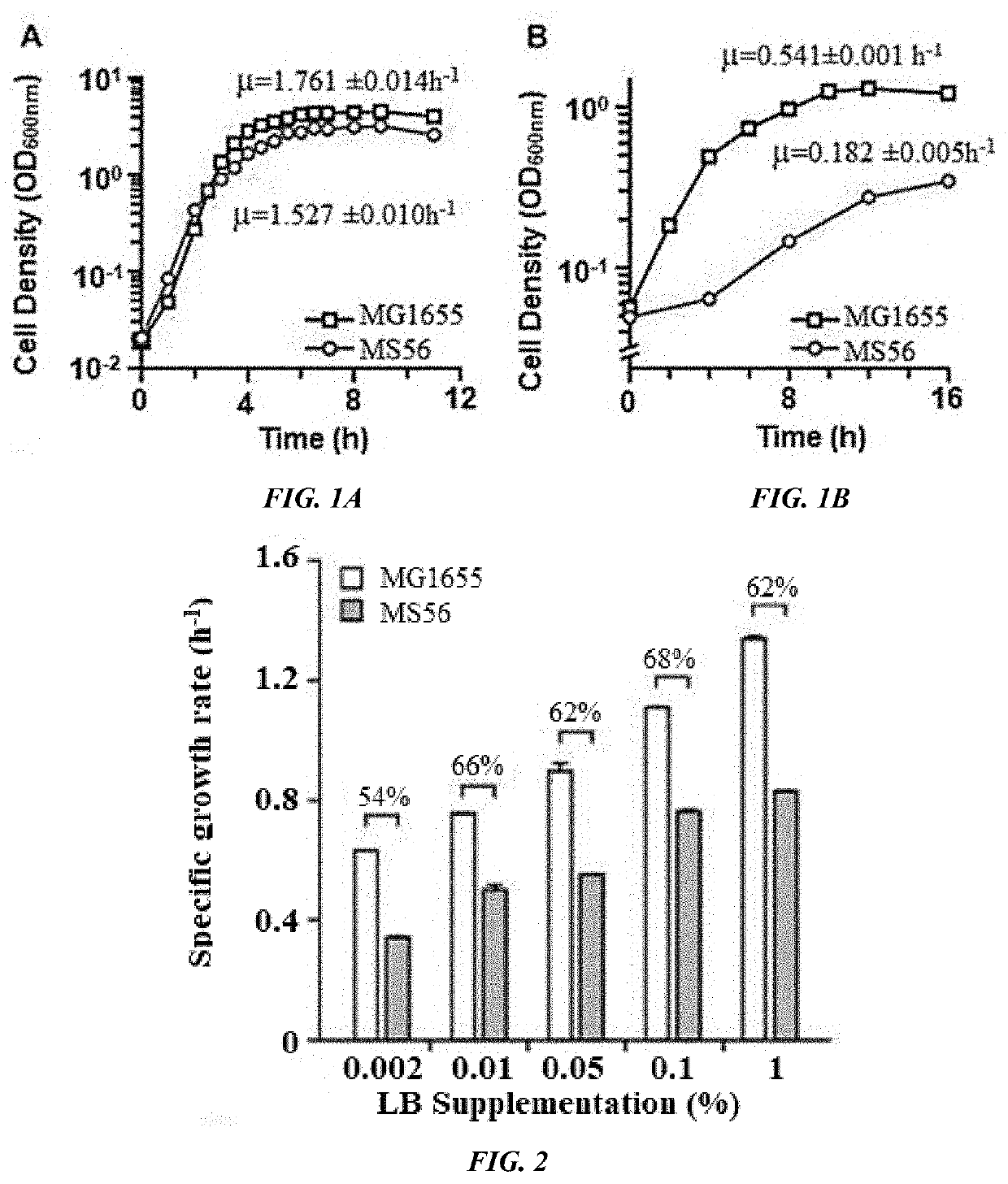
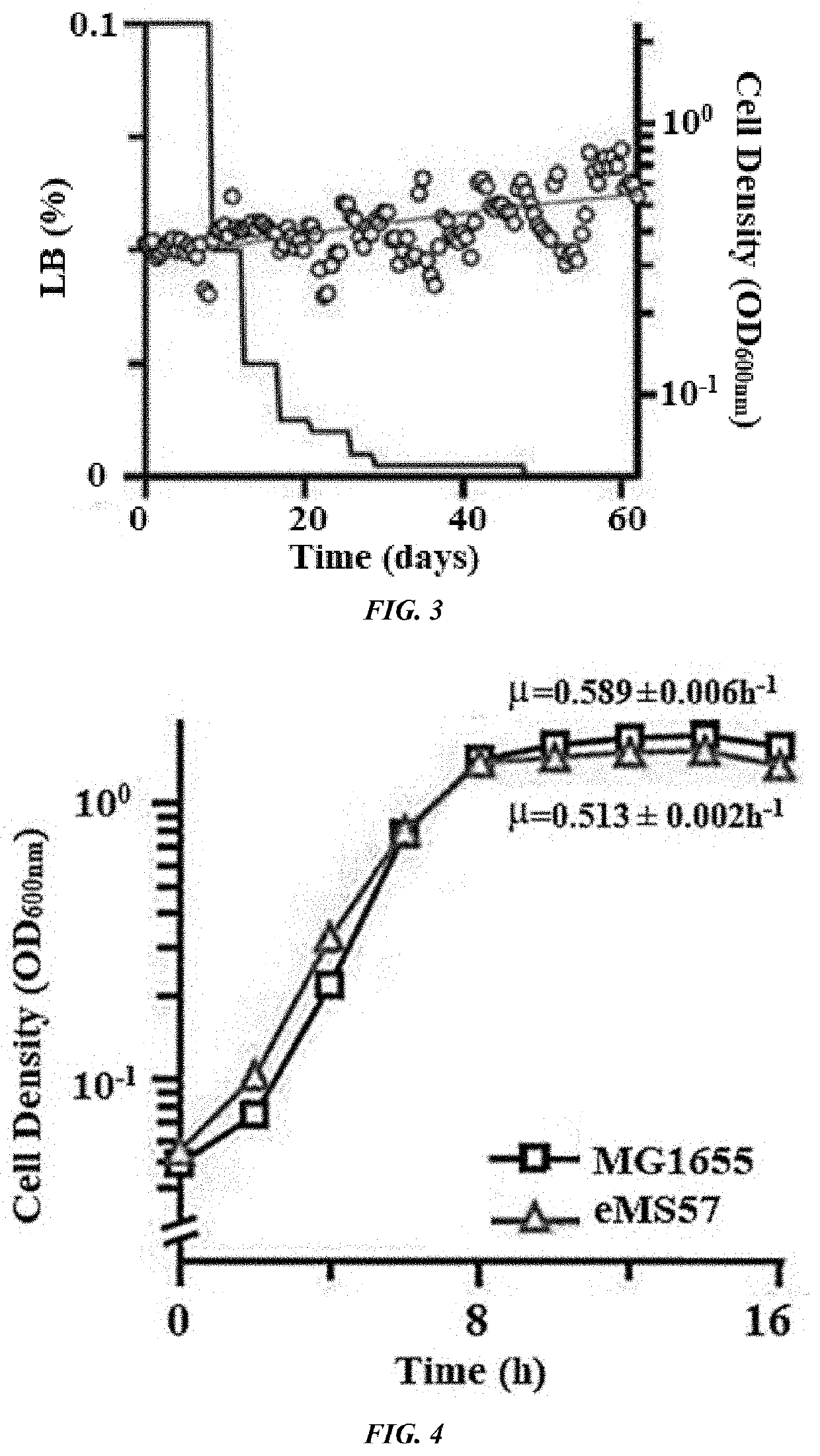
Novel microorganism having minimal genome and method of producing the same
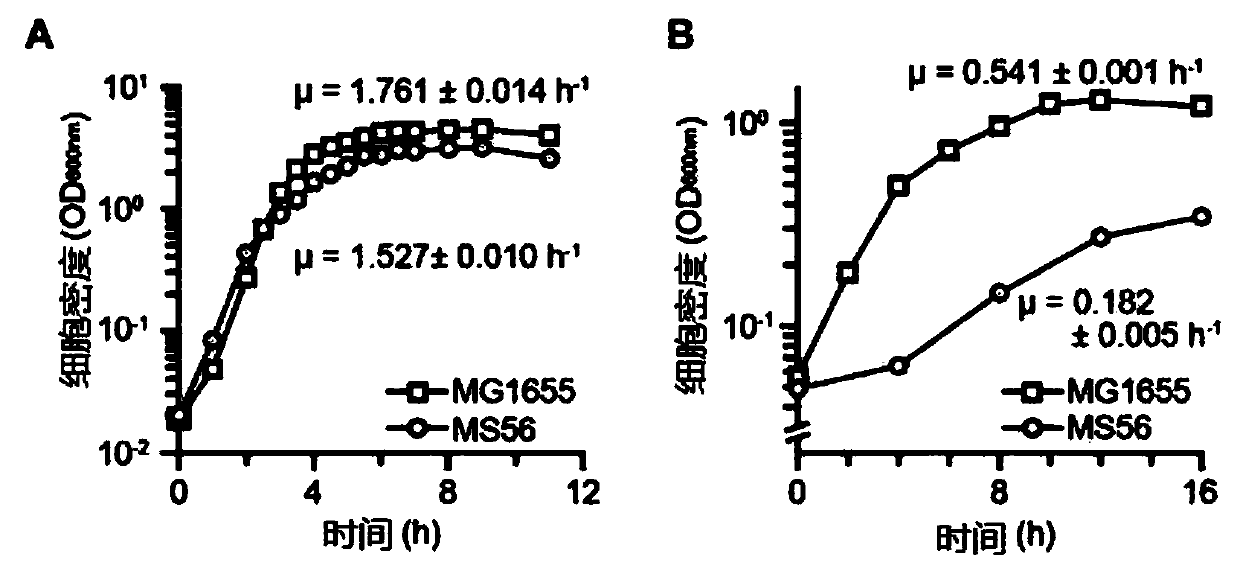
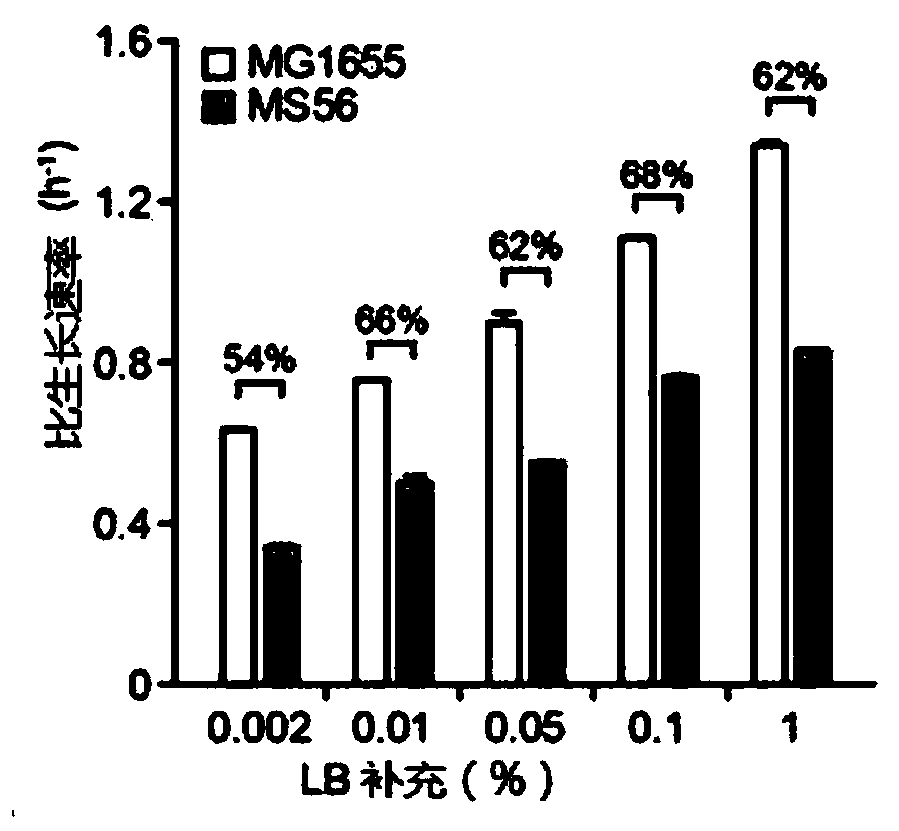
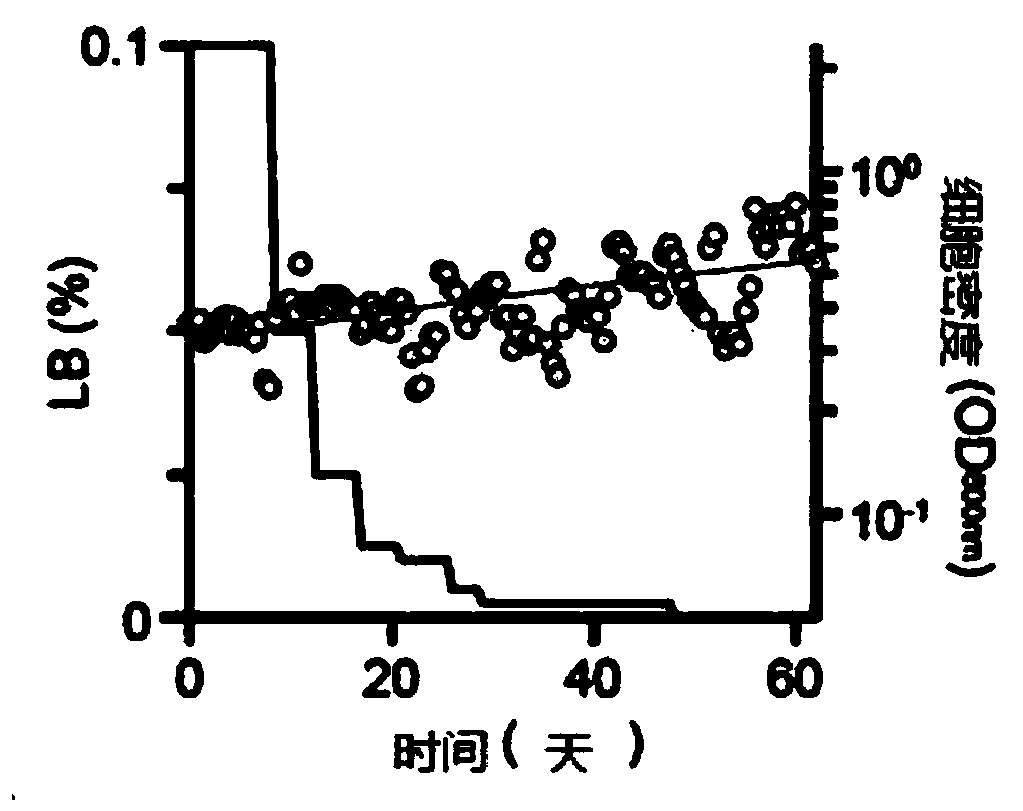
Provided is a method of producing a novel microorganism having a minimal genome. In particular, provided are a method of producing a novel microorganism having a smaller genome size than a wild-type, the method including the step of culturing the microorganism in a medium containing LB broth with stepwise decreasing concentrations of the LB broth; and a novel microorganism having a smaller genome size than a wild-type, produced by the above method.Despite the small genome size, the novel microorganism of the present disclosure may have a high growth rate, pyruvate production capacity, and protein translation efficiency thereby being usefully applied to industry such as production of recombinant proteins or pyruvate.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
A method for rapidly identifying the genome size of sweet potato and its application
ActiveCN109596502BLow costPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisBiotechnologyWild species
The invention provides a method for quickly identifying the size of the sweet potato genome, which belongs to the technical field of plant ploidy detection, and comprises the following steps: 1) taking sweet potato stem tip tissue cuttings from the field and culturing them in Hoagland culture solution for 20 to 28 hours; 2) taking Unexpanded leaves or new root tips are mixed with sweet potato special lysate for tissue lysis; 3) filtering the lysed feed liquid, collecting the filtrate, centrifuging, and collecting centrifuged products as lysed cells; 4) lysing the lysed cells Mix the cells with the dye solution for staining, and vortex to obtain the cell solution to be tested; 5) detect the FL2-A value of the cell to be tested by flow cytometry on the cell solution to be tested; 6) The FL2-A value of the cell to be tested is calculated to obtain the 1C value of the genome of the cell to be tested and its genome size. The method of the invention can also identify the genome size of other species of the genus Ipomoea, providing a fast, efficient and low-cost determination method for genome identification of sweet potato and its close relative wild species.
Owner:XUZHOU INST OF AGRI SCI IN JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT (JIANGSU XUZHOU SWEETPOTATO CENT)
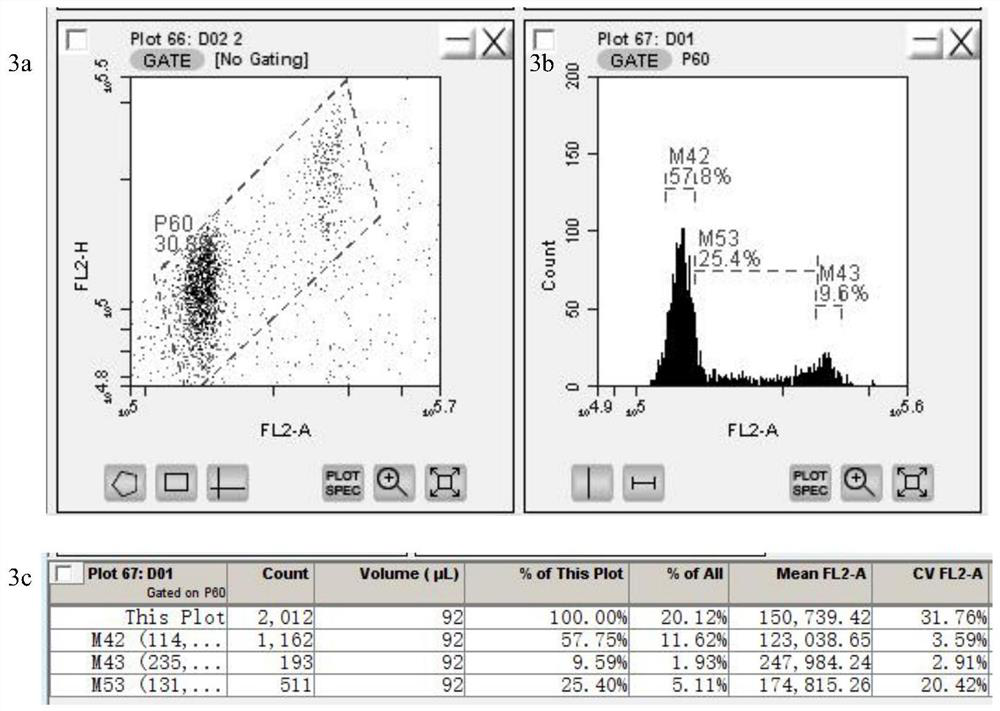
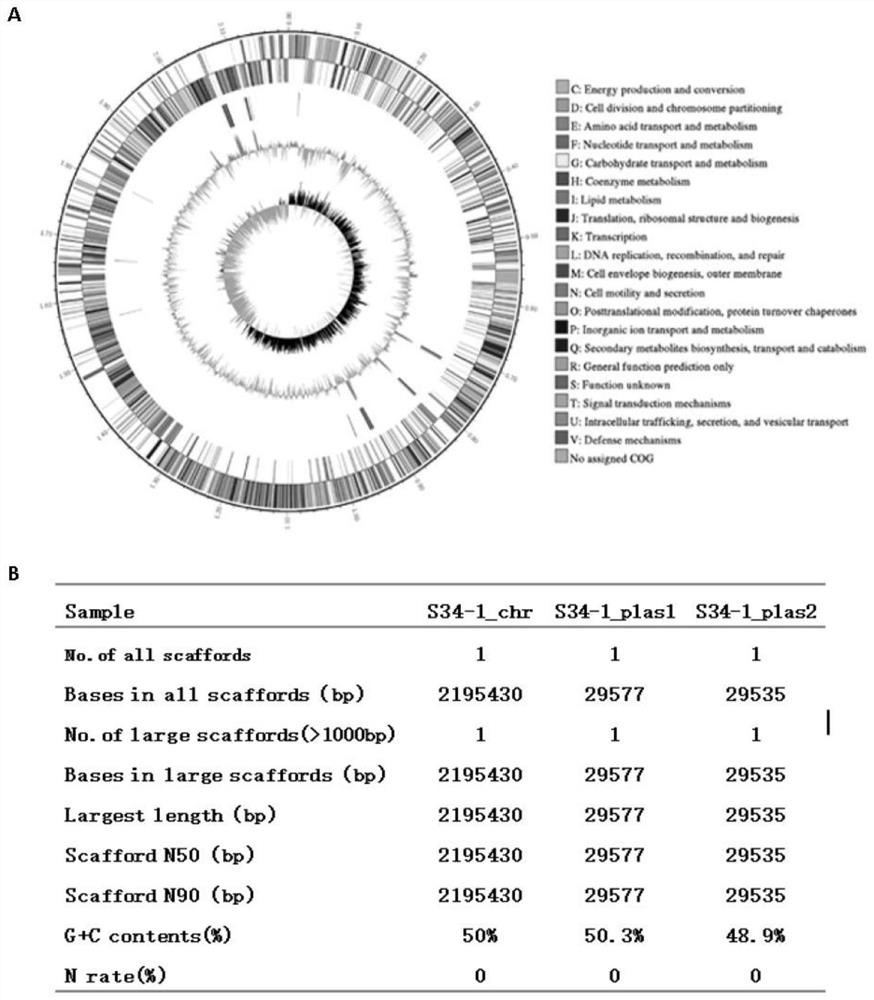
A strain of human staphylococcus with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram-positive drug-resistant bacteria and its screening method and application
ActiveCN108753646BDrug resistance is not easy to produceStrong targetingAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a strain of human staphylococcus with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram-positive drug-resistant bacteria and a screening method thereof. Common gram-positive drug-resistant pathogens have obvious antibacterial effect, but no bacteriostatic effect on gram-negative drug-resistant bacteria. The genome size of the human staphylococcus strain S34-1 is 2195430bp, including 2 plasmids, the size is 29577bp and 29535bp respectively, and it has been deposited in the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for Microbial Culture Collection on April 03, 2018. Its deposit number is CGMCC No.15552. The present invention also relates to the application of the human staphylococcus S34‑1 in the preparation of anti-Gram-positive drug-resistant bacteria. The present invention screens the strains with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against common clinical drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria from the symbiotic / colonization flora of human body. Molecules lay the groundwork.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Host removing method and kit for metagenomes of pathogen microorganisms
PendingCN112322701AIntegrity guaranteedGood enzyme activityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymic digestionNucleic acid
The invention provides a host removing method and kit for metagenomes of pathogen microorganisms, and is particularly suitable for detection of the metagenomes of the pathogen microorganisms includingbronchoalveolar lavage fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, sputum, ascites and the like; by utilizing the characteristics that human cells are inconsistent with bacteria, fungi, viruses and the like in cellstructure and the concentration and the genome size of the human cells are remarkably different from those of the fungi, the bacteria, the viruses and the like, a denaturing agent and an enzyme are selected to respectively dissolve the cells and digest nucleic acid of the human cells, so that the host removal effect is achieved, wherein the denaturing agent at least includes one or more of saponin, Tween 20, Triton X-100, digitonin and CHAPS; and the host removal operation of the metagenomes of the pathogen microorganisms can be completed within 5-20 minutes, and the method can improve the detection sensitivity of the metagenomes of the pathogen microorganisms.
Owner:SHAOXING INGENIGEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Novel microorganism having minimal genome and method of producing the same
Provided is a method of producing a novel microorganism having a minimal genome. In particular, provided are a method of producing a novel microorganism having a smaller genome size than a wild-type,the method including the step of culturing the microorganism in a medium containing LB broth with stepwise decreasing concentrations of the LB broth; and a novel microorganism having a smaller genomesize than a wild-type, produced by the above method. Despite the small genome size, the novel microorganism of the present disclosure may have a high growth rate, pyruvate production capacity, and protein translation efficiency thereby being usefully applied to industry such as production of recombinant proteins or pyruvate.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS7303880B2Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Application of a sphingobacterium hotanense in the control of parasitic nematodes
The invention discloses the application of a strain of Sphingobacterium hotanense in preventing and treating parasitic nematode diseases. The Sphingobacterium hotanense AMCC 101218 provided by the present invention has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19217; this bacterium can effectively control cucumber root-knot nematode disease, and its oocyst number, root-knot number, and insect population density have decreased by 71.28% compared with the blank control , 75.86% and 63.80%; AMCC101218 genome size is 4490254bp, GC content is 41.21%.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com