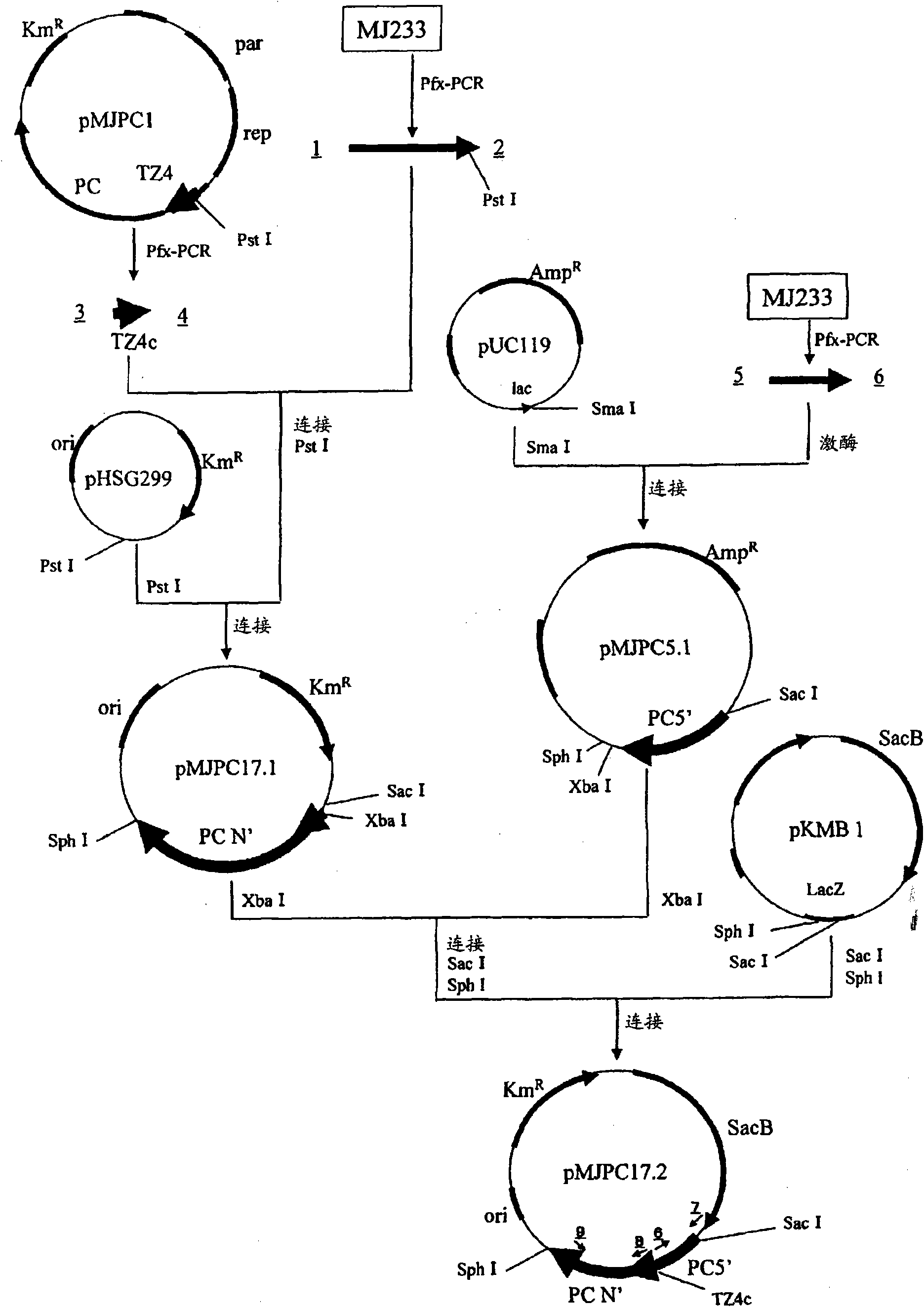
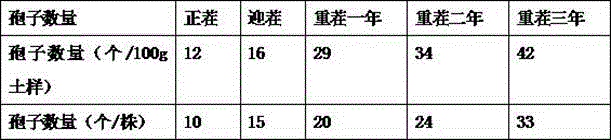
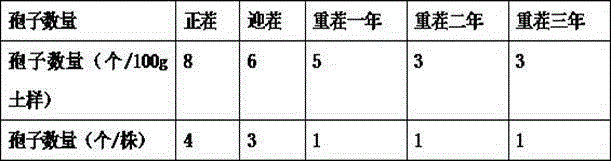
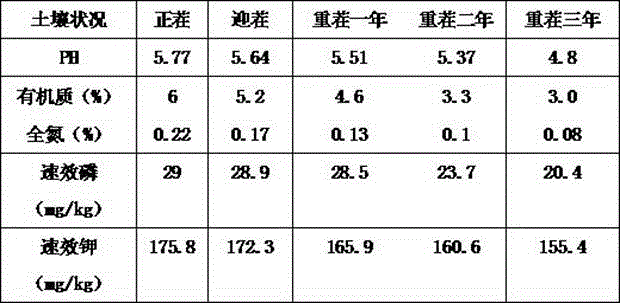
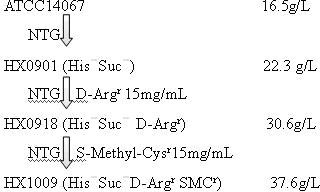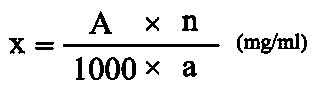Patents
Literature
60 results about "Brevibacterium flavum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A species in the genus CORYNEBACTERIUM, family Corynebacteriaceae, which is used for industrial production of the amino acid LYSINE. It is closely related to Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Method for increasing acid production rate and extracting rate of glutamic acid
ActiveCN109504719AReduce generationHigh transparencyBacteriaOrganic compound preparationProduction rateCeramic membrane
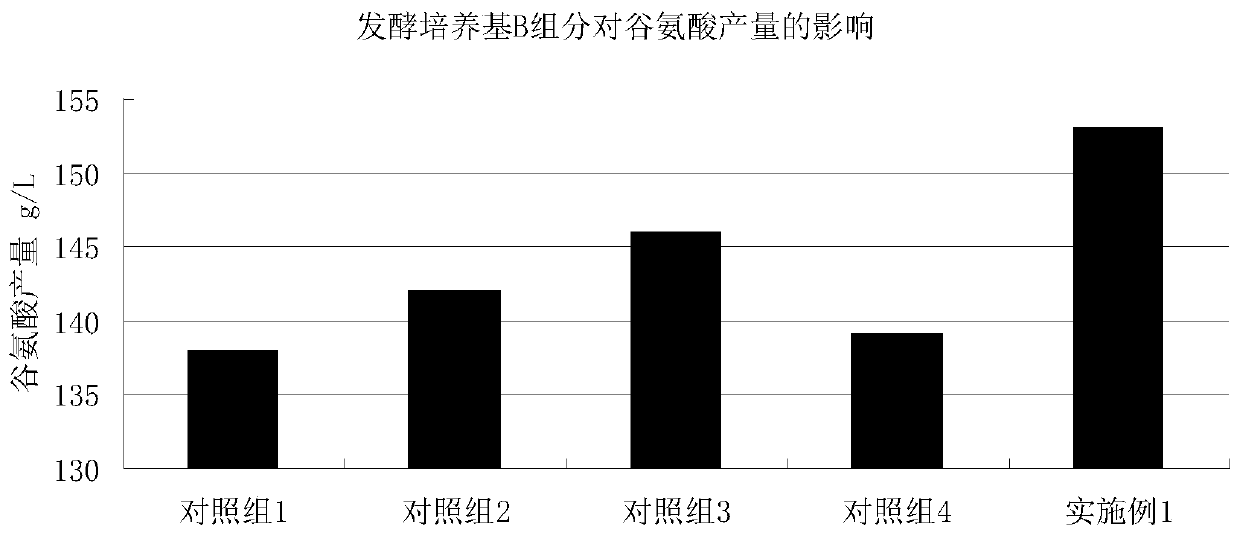
The invention belongs to the technical field of amino acids and discloses a method for increasing an acid production rate and an extracting rate of glutamic acid. The method for increasing the acid production rate and the extracting rate of the glutamic acid comprises the following steps: putting a brevibacterium flavum seed solution for producing the glutamic acid into a fermentation tank filledwith fermentation medium to carry out fermentation cultivation; when the brevibacterium flavum seed solution is fermented for 24 hours, separating out a fermentation solution in the fermentation tankvia a ceramic membrane; draining a filter liquor; putting concentrated thalli back into the fermentation tank; and meanwhile, supplementing a fermentation medium B to the fermentation tank; and continuing to carry out fermentation for 16 h to finish fermentation. The method for increasing the acid production rate and the extracting rate of the glutamic acid, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the glutamic acid fermentation process is more stable and easy to control by optimizing a culture medium; and moreover, the yield and glucose conversion rate of the glutamic acid are increased, the quality of the fermentation solution is improved, the glutamic acid extracting cost is reduced, and the comprehensive benefits are increased.
Owner:HULUNBEIER NORTHEAST FUFENG BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD +2
Strain capable of producing L-arginine and method for producing L-arginine by same
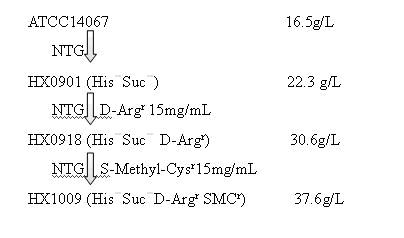
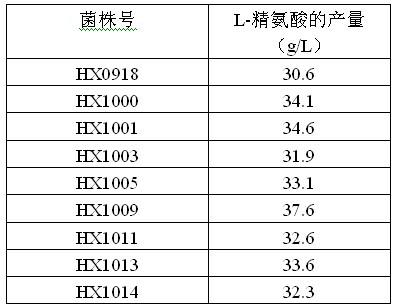
The invention relates to a strain capable of producing L-arginine and a method for producing the L-arginine by the strain and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. For the strain, Brevibacterium flavum ATCC 14067 is used as a starting strain; nitrosoguanidine is adopted to carry out mutagenesis step by step; mutant strains with histidine and succinic acid auxotrophic strains are screened out so as to cut off a competitive metabolic pathway; and mutant strains (His-, Suc-, D-Argr, SMCr) with resistances of arginine structural analogs and cysteine structural analogs are screened out. The strain is named as Brevibacterium flavum HX1009, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4464 and has the genetic characters of histidine auxotroph His-, succinic acid auxotroph Suc-, D-arginine resistance D-Argr and S-methyl cysteine resistance SMCr for improving the yield of the L-arginine. Under the optimized condition, the L-arginine is produced by fermentation on a fermentation tank with the volume of 5L to 5M3 and the arginine production level achieves 50 to 70g / L.
Owner:FUJIAN GUTIAN PHARMA
Method for preparing lysine-rich fermented soybean meal
ActiveCN102763769AAddress nutrient contentSolve two key problems to make up for the lack of lysine in fermented soybean mealFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBrevibacillus borstelensisSaccharomyces
The invention discloses a method for preparing lysine-rich fermented soybean meal, which is simple and can effectively improve the content of nutrients of the soybean meal. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing strains: a, inoculating the brevibacterium flavum into the brevibacterium flavum liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 28-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level brevibacterium flavum strain when the OD590 value of the brevibacterium flavum liquid is 0.25-0.30; b, the inoculating the saccharomycetes into the saccharomycetes liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 28-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level saccharomycetes strain when the OD590 value of the saccharomycetes liquid is 0.25-0.30; and c, inoculating the lactobacillus into the lactobacillus liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 30-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level lactobacillus strain when the OD590 value of the lactobacillus liquid is 0.25-0.30; (2) preparing a fermentation substrate; and (3) inoculating the fermentation substrate. The method for preparing the lysine-rich fermented soybean meal belongs to the technical field of feed preparation.
Owner:广东希普生物科技股份有限公司
Construction and application of high-yield L-valine engineering bacteria
ActiveCN104561074AHigh yieldReduce the rate of contaminationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetohydroxy Acid SynthetaseDihydroxyacid dehydratase
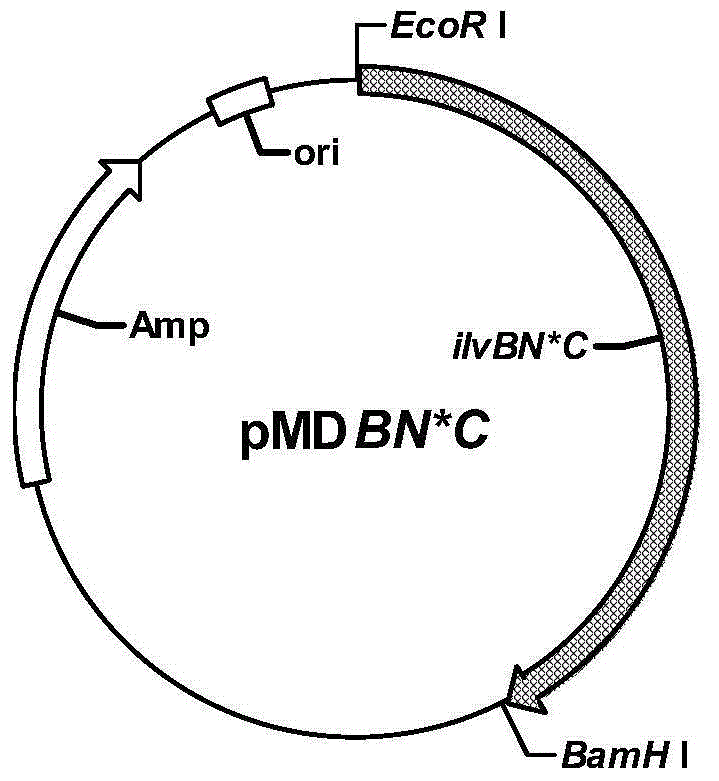
The invention discloses construction and an application of high-yield L-valine engineering bacteria and provides a method for preparing recombinant bacteria. The method comprises steps as follows: an acetohydroxyacid synthase mutant coding DNA module, an acetohydroxyacid isomerism reductase coding DNA module, a branched chain amino acid aminotransferase coding DNA module and a dihydroxy acid dehydrase DNA molecule are introduced into target bacteria and then the recombination bacteria are obtained. An experiment proves that when Brevibacterium flavum MDV-07 is used for fermenting and producing L-valine, the yield of L-valine and a conversion rate can be greatly increased, and great production application value is realized.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum and method for producing L-valine by using brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN110643547APromote reproductionReduce consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The present invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and particularly relates to L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in China Center forType Culture Collection on July 01, 2019, a preservation number is CCTCC M2019496 and a preservation address is Luojia Hill, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province. The present invention also relates to a method for producing L-valine by using the brevibacterium flavum, the brevibacterium flavum strain is subjected to activation culture and seed liquid culture, and obtained seedliquid is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, and the fermentation culture process is firstly aerobic fermentation and then anaerobic fermentation. L-valine production is carried out by using the preserved strain and the production method, yield is high, sugar-acid conversion rate is high, besides, fermentation process takes a short time, and production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BAYANNUR HUAHENG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Process for producing arginine by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN103695487AQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:滨州市生物技术研究院有限责任公司
Preparation method of peanut soy
The invention relates to a preparation method of peanut soy, belonging to the technical field of preparation methods of soy. The peanut soy provided by the invention adopts groundnut kernels as a raw material, bacillus licheniformis, brevibacterium flavum, clostridium acetobutylicum and rhamnose lactobacilli are taken as composite fermentative bacteria of a peanut fungi solution; the special proportional aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus niger and monascus are utilized as fermenting aspergillus of a peanut yeast, and a preparation process of natto soy is adopted. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that the fermentation period is shortened, natto kinase is generated after fermenting of groundnut kernels, the kinase can restrain the browning of the soy in preservation, a maillard reaction is reduced, the nutritive values of the groundnut kernels are high, the flavor is unique, and the color, the aroma and the taste of the prepared soy are good; the content amino acid nitrogen is improved by 43.9%, the full nitrogen content is improved by 17.5%, a soluble salt-free solid is improved by 18.8%, and the preparation method is especially used for preparing ideal soy of pickles.
Owner:松原北大荒食品科技有限公司
Microbe additive for improving beach saline alkali soil structure and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN104762087AAchieve bondingRaise the ratioOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsAmino acid synthesisAlkali soil
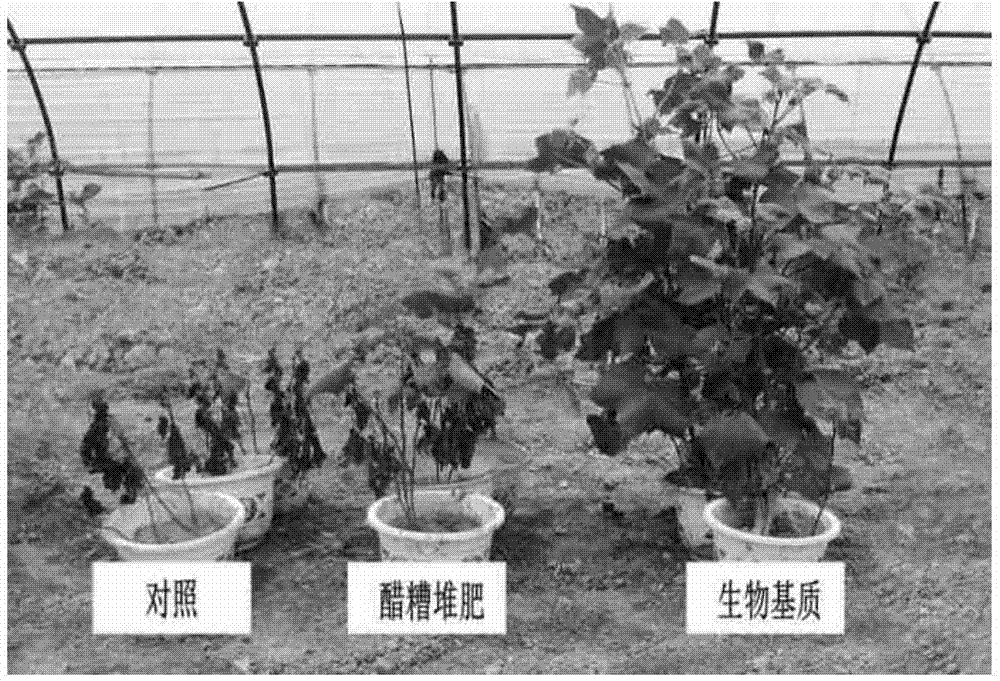
The invention discloses a microbe additive for improving a beach saline alkali soil structure and its preparation method and use. The microbe additive is prepared by combined fermentation of bacillus amyloliquefaciens IAE with an extracellular polypeptide gamma-polyglutamic acid secretion function and brevibacterium flavum IAE with an amino acid synthesis function. A fermentation substrate used for fermentation comprises, by weight, 900-930 parts of vinegar residue, 50-60 parts of (NH4)2SO4, 5-8 parts of K2HPO4, 5-8 parts of MnSO4 and 5-8 parts of MgSO4. The invention discloses a microbe matrix containing the microbe additive. The microbe matrix has an active bacterial strain amount of more than 1.0*10<8> cfu.g<-1>, effective improved substance gamma-polyglutamic acid content of greater than or equal to 20g.kg<-1> by dry weight, water content of less than or equal to 30% and organic matter content less than or equal to 45%. The microbe matrix can effectively improve beach saline alkali soil, has high efficiency and environmental friendliness and is conducive to sustainable development of beach soil.
Owner:江苏农丰宝生物科技有限公司
Construction method and applications of genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine
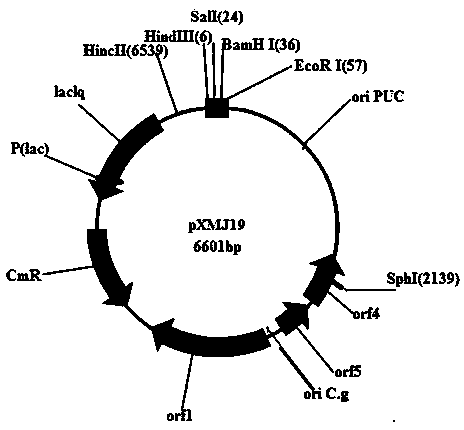
InactiveCN103966151AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColiform bacilli
The invention relates to a construction method and applications of a genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine. The invention discloses a novel genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing L-arginine. Recombinant plasmid pXMJ19-argH can be orderly converted and introduced into colibacillus and auxotroph brevibacterium flavum AN78 by the genetic engineering bacterium strain, and then the argininosuccinase in the AN78 containing recombinant plasmids is over-expressed and fermented to produce L-arginine. The invention further discloses a construction method and applications of the genetic engineering bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can increase the L-arginine production output and reduce the production cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH
Oil field wastewater treatment process
InactiveCN103880250AImprove processing efficiencyEfficient degradationWaste water treatment from quariesMultistage water/sewage treatmentCooling towerWater quality
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for increasing fermentation yield of L-leucine
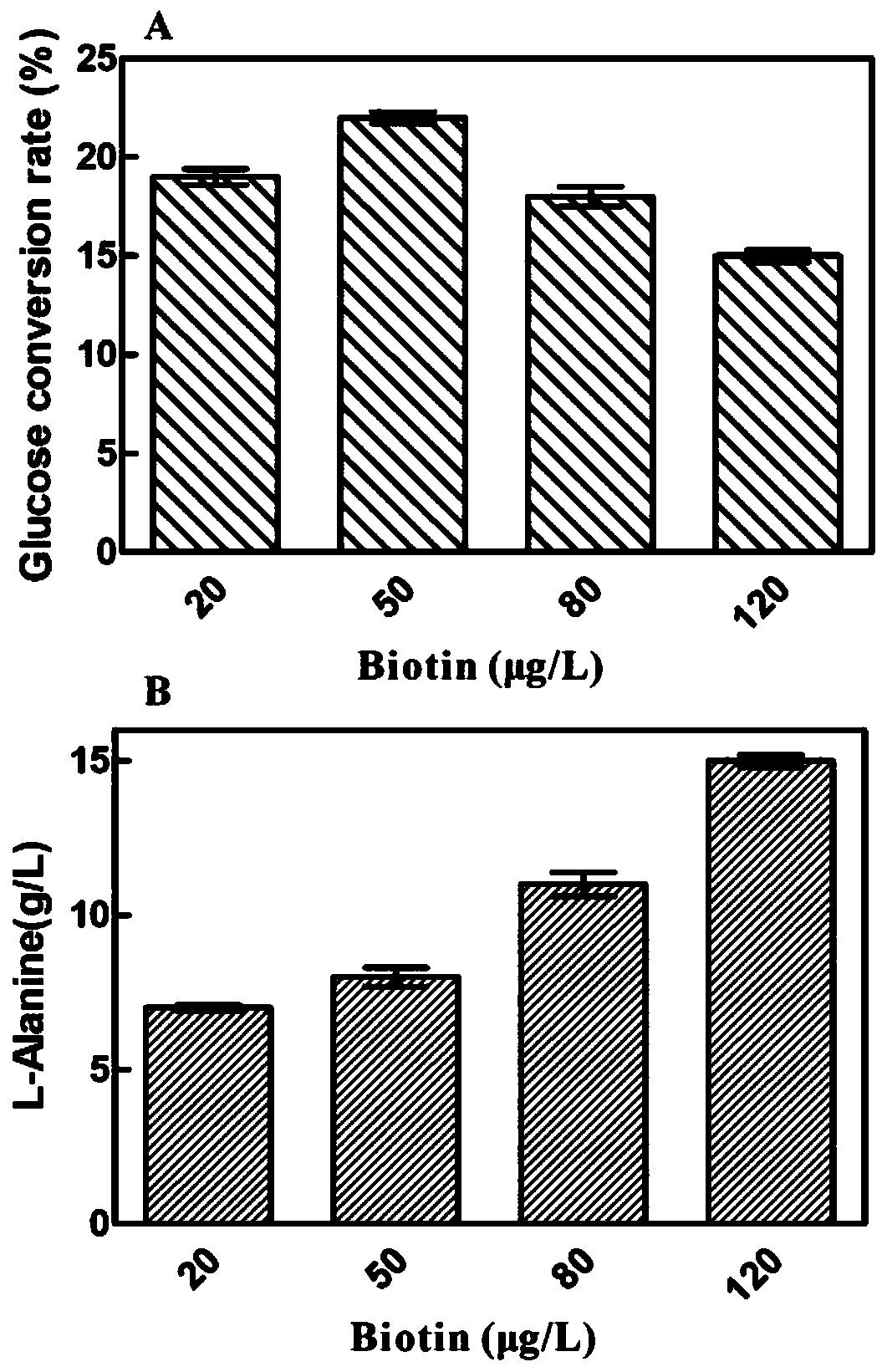
InactiveCN109609564AGood yieldImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBiotin
The invention belongs to the technical field of the production of amino acids, and discloses a method for increasing fermentation yield of L-leucine. The method comprises the following steps of inoculating culture mediums containing biotin in a fermenter with brevibacterium flavum, and performing fermentation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the metabolic pathway of the L-leucine is analyzed, so that the fermentation culture medium is optimized, fermentation steps are optimized, and the acid yield through fermentation can be increased.
Owner:XINJIANG FUFENG BIOTECH +2
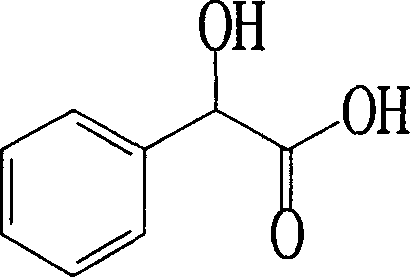
Process for preparing (R)-mandelic acid by microbial asymmetric resolution
InactiveCN1840671AGood conversion effectSimple compositionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMandelic acid
The asymmetrical resolution method for (R)-mandelic acid comprises: screening the (Brevibacterium flavum) AS 1.818 for culture and full cell preparation; with racemic acid as substrate, catalytic converting to obtain the product with optical purity up to 90%e.e. This invention improves product optical purity and has important meaning for enzyme development and resolution.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microorganism microbial inoculum capable of improving continuous cropping obstacles of peanuts
InactiveCN106278569AIncrease productionEffectively adjust PH valueNitrogenous fertilisersOrganic fertiliser preparationDiseaseContinuous cropping
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism microbial inoculum, in particular to the technical field of microorganism microbial inoculum for fertilizers. The microorganism microbial inoculum is prepared by using alfalfa meal, sesbania gum, compound amino acid powder, charcoal powder and a yeast extract as raw materials, inoculating brevibacterium flavum and acetobacter aceti, and performing fermentation under 30-33 DEG C for 68-70 hours. The prepared microorganism microbial inoculum is particularly suitable for continuous cropping planting of the peanuts, can effectively regulate the PH value of soil in the continuous cropping planting period of the peanuts, maintains a microorganism community structure of the soil, improves the activity of soil enzymes, restrains proliferation of harmful fungi, reduces generation of diseases and insect pests, and has positive significance on increase of the yield of continuous cropping peanuts and improvement of continuous cropping soil.
Owner:界首市沃土生物科技有限公司
Brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109554324AIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaHeterologousBrevibacillus borstelensis
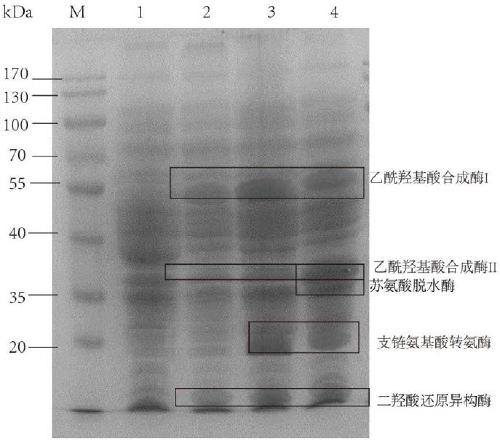
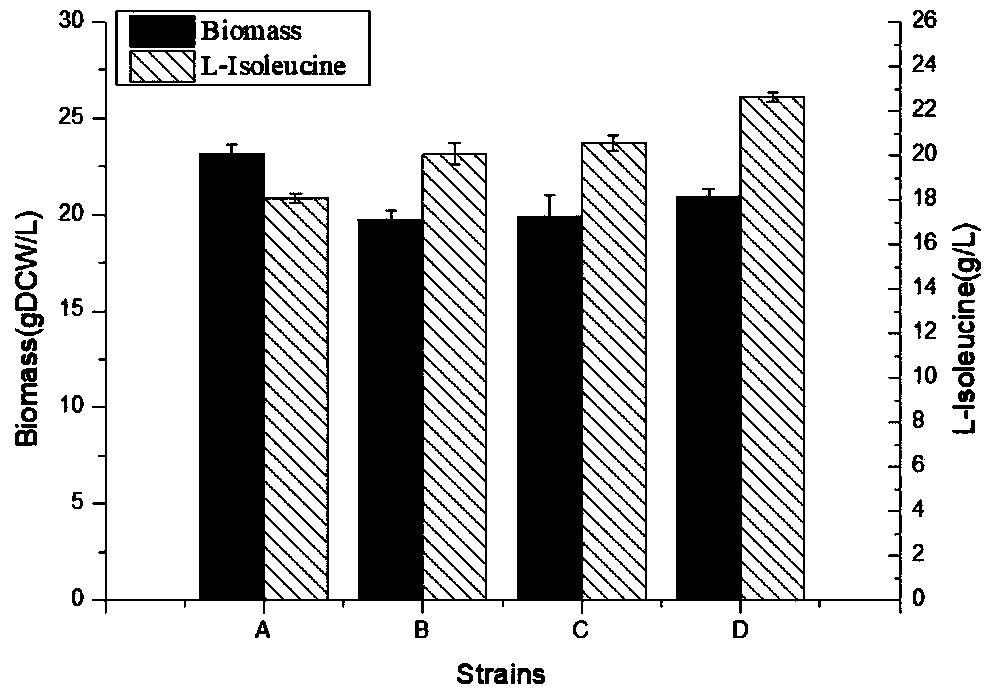
The present invention discloses a brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering means is utilized to strengthen acetohydroxyacid synthase, dihydroxy acid reductoisomerase and branched chain amino acid aminotransferase in the brevibacterium flavum, and heterologously expresses catabolic threonine dehydratase encoded by tdcB, and thus constructs a L-isoleucine high-yield strain B. flavum I12 / pEC-XK99E-ilvBNCE-tdcB. The yield of the accumulated isoleucine is increased to 22.65 g / L in the recombinant strain and is 25.48% higher than that of an original strain, and the maximum biomass reaches 20.95 g DCW / L. The strain can turn lysine pathway carbon source to the L-isoleucine and a brand-new idea for constructing the L-isoleucine high-yield strain is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Phosphoserine phosphatase gene of coryneform bacteria
The present invention provides a DNA coding for a protein defined in the following (A) or (B) is obtained from Brevibacterium flavum chromosomal DNA library by cloning a DNA fragment that complicates serB deficiency of Escherichia coli as a open reading frame in the DNA fragment.(A) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID: 2 in Sequence Listing; or(B) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence including substitution, deletion, insertion, addition or inversion of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, and which has phosphoserine phosphatase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN109943511AHigh yieldHas industrial practical valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrevibacillus borstelensisMicrobiology
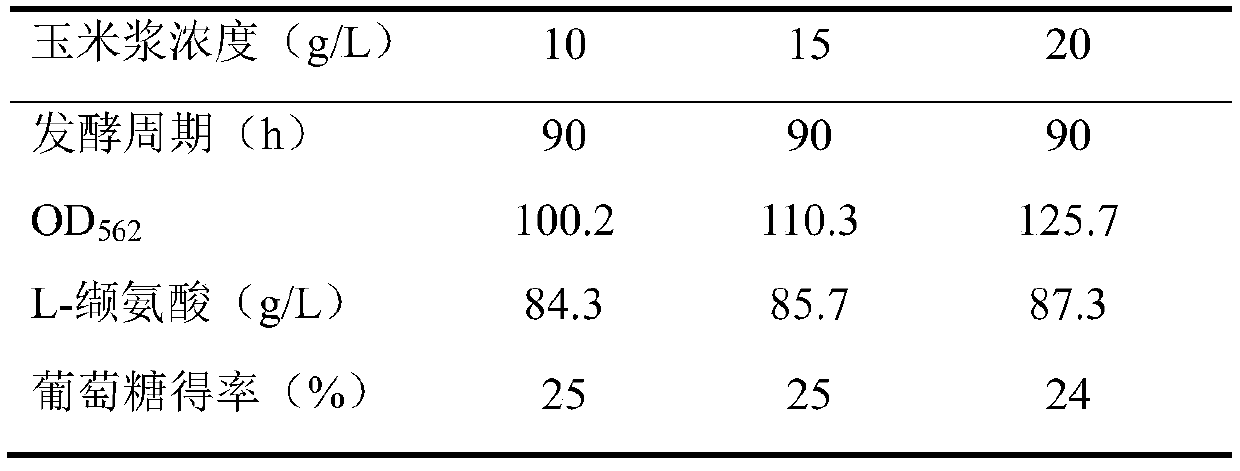
The invention discloses a strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of the brevibacterium flavum, and belons to the technical field of bioengineering. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 17, 2019 under the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2019053, and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.The brevibacterium flavum FMME447 exhibits the ability to accumulate high-level L-valine, and it is verified that the valine tolerance of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 100 g / L. The yield of the L-valine through the fermentation of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 80-90 g / L, the yield of glucose reaches up to about 25-30%, and the brevibacterium flavum has industrial practical value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for producing edible mushroom nutrient solution by fermentation method
The invention discloses a method for producing an edible mushroom nutrient solution by a fermentation method, which relates to the technical field of an organic fertilizer. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing brevibacterium flavum, namely inoculating the brevibacterium flavum, which is taken as an original strain, to a shake flask culture medium for culturing so as to obtain a brevibacterium flavum solution; (2) carrying out submerged fermentation, namely inoculating the brevibacterium flavum solution into a fermentation tank culture medium to carry out the submerged fermentation so as to obtain a fermentation solution; and (3) treating the fermentation solution, namely separating and concentrating the fermentation solution to obtain the edible mushroom nutrient solution. The edible mushroom nutrient solution obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is rich in various nutrition elements including crude proteins, short-chain peptides, amino acids, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin C and the like and is easy to absorb and high in utilization rate; the mushroom growing period can be prolonged and the biotransformation efficiency is improved; the quality and the yield of edible mushrooms are improved obviously.
Owner:JING JING PHARMA
Method for improving fermentation efficiency of lysine
PendingCN110777175APromote fragmentationImprove solubilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyLysine fermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of amino acid fermentation and discloses a method for improving the fermentation efficiency of lysine. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating brevibacterium flavum for producing the lysine according to the inoculation quantity of 4 to 8 percent into a fermentation culture medium, wherein the fermentation temperature is 31 DEG C at 0 to 18hours and is 34 DEG C at the end of 18 hours, the ventilation ratio is 1:(0.6-0.8), the stirring rotating speed is 200 to 400 r / min and the fermentation total time is 50 to 60 hours; and in the fermentation process, feeding a glucose solution to maintain the residual sugar content to be 5 to 10 g / L, feeding an ammonium sulfate solution to maintain the ammonia nitrogen content to be 1 to 2 g / L, feeding ammonia water to control the pH to be 7.0 to 7.2 and feeding a defoaming agent to perform defoaming. By the method, the acid producing efficiency of the lysine and the sugar acid conversion rateare increased.
Owner:齐齐哈尔龙江阜丰生物科技有限公司
Conversion method for introducing shuttle plasmids into brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum)
InactiveCN103966251AClear thinkingSimple and fast operationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a rapid and effective method for converting recombinant plasmids that can perform shuttle expression in escherichia coli and brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) into corynebacterium glutamicum and auxotroph brevibacterium flavum. The method comprises two steps namely competent cell preparation and high-temperature culture and conversion: (1) inoculating auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) into a specially-prepared culture medium to enable the auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to carry out rapid proliferation, and then transforming the auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to a culture medium with inefficient nutrients to prepare competent cells; (2) evenly mixing plasmids to be converted and the prepared competent cells, placing the mixture into an ice bath, culturing under a constant temperature, and finally introducing the plasmids into brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to be converted. The method provided by the invention can reduce the restrictive enzyme digestion effect of brevibacterium flavum on shuttle plasmids, the shuttle plasmids can be stably copied and transmitted, and thus the method has the advantages of good conversion effect and convenient operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH +1
Preparation method for cottonseed meal protein fodder
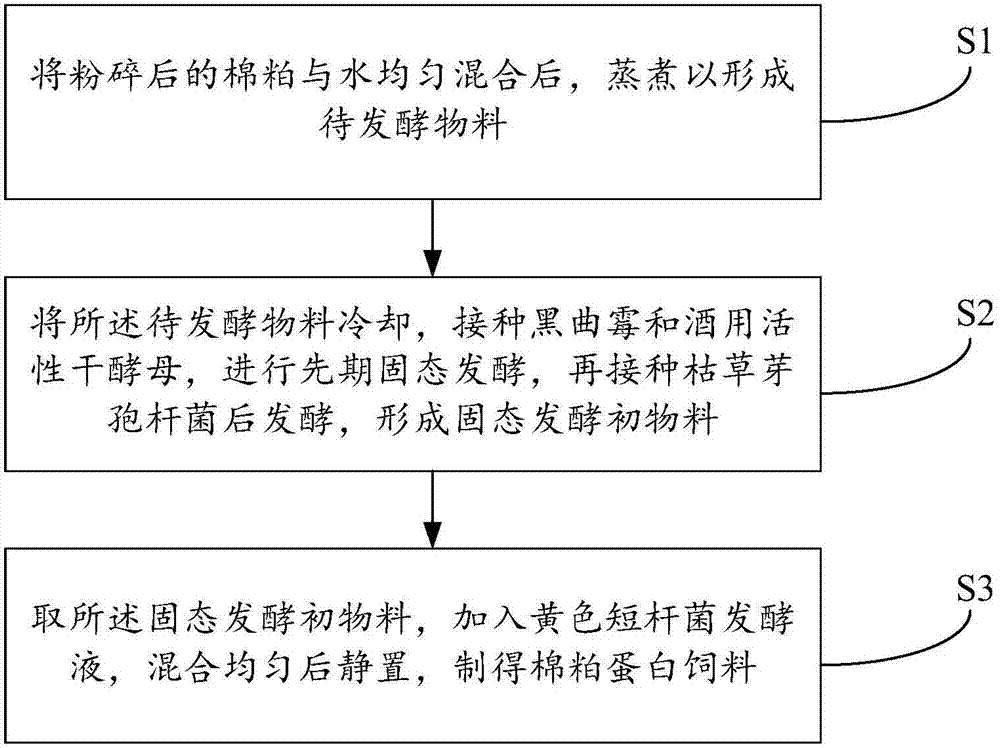
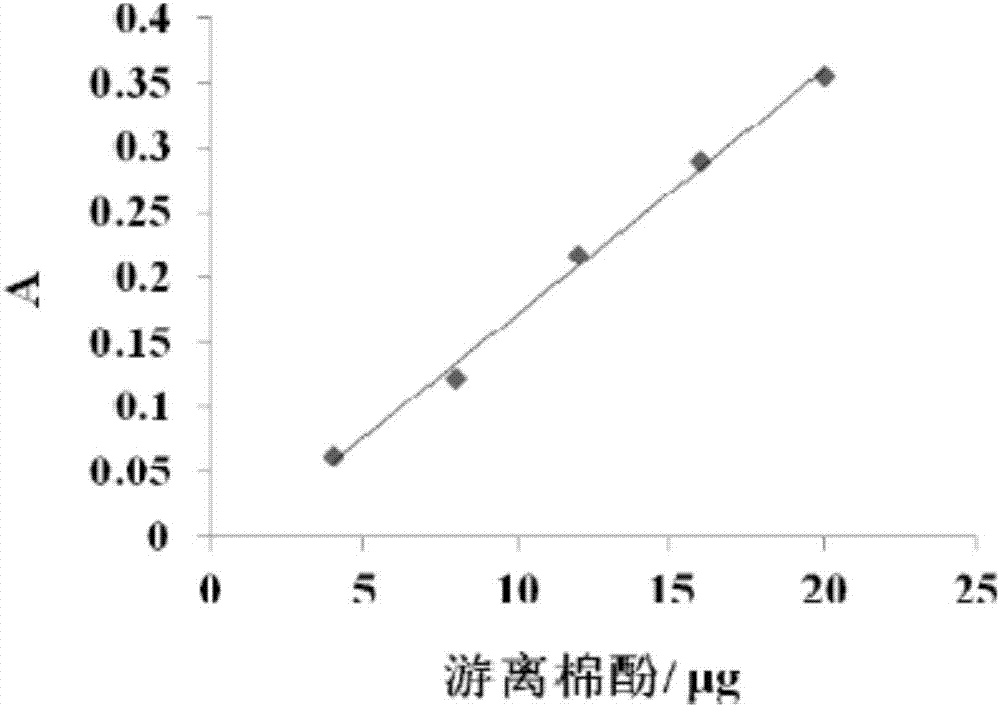
PendingCN107232393AReduce the content of free gossypolHigh in proteinFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAspergillus nigerChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method for a cottonseed meal protein fodder. The preparation method for the cottonseed meal protein fodder comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing crushed cottonseed meal with water and then cooking, thereby forming a to-be-fermented material; cooling the to-be-fermented material, inoculating aspergillus niger and wine active dry yeast, performing early solid state fermentation, inoculating bacillus subtilis and then fermenting, thereby forming a solid fermented primary material; and adding the solid fermented primary material into brevibacterium flavum fermentation liquor, uniformly mixing and then standing by, thereby obtaining the cottonseed meal protein fodder. According to the invention, aspergillus niger and wine active dry yeast are inoculated to the cottonseed meal and are used for synergic fermenting, the bacillus subtilis is inoculated and fermented so as to form the solid fermented primary material, and then the brevibacterium flavum fermentation liquor is added, so that the content of free gossypol in the cottonseed is greatly reduced and the protein content in the cottonseed meal is increased.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
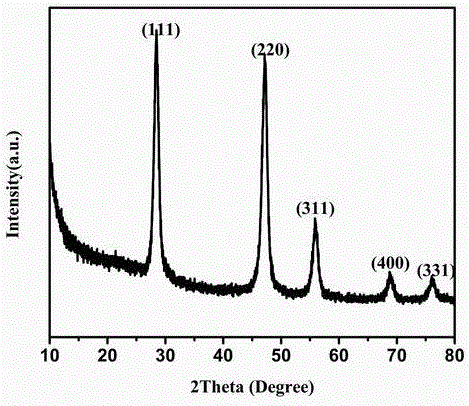
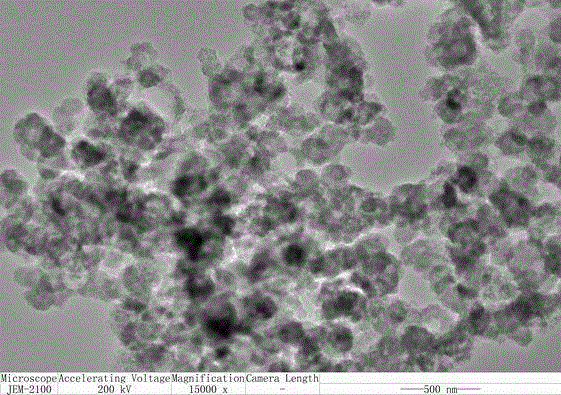
Method for preparing silicon hollow nano-spheres by aid of reducing agent which is secretion of microbial cells
InactiveCN105039420AEasy to operateMild conditionsMicroorganism based processesNanotechnologyEscherichia coliCellulose acetate
The invention discloses a method for preparing silicon hollow nano-spheres by the aid of a reducing agent which is secretion of microbial cells. The method includes steps of (1), inoculating saccharomyces cerevisiae, brevibacterium flavum, escherichia coli, asperigillus flavus, pseudomonas aeruginosa or aspergillus fumigatus in YPD (yeast peptone dextrose) culture media, LB (luria bertani) culture media, CA (cellulose acetate) culture media or potato dextrose agar culture media, cultivating the saccharomyces cerevisiae, the brevibacterium flavum, the escherichia coli, the asperigillus flavus, the pseudomonas aeruginosa or the aspergillus fumigatus in the culture media for 12h-14d and centrifugally removing the cells to obtain secretion of the cells; (2), adding the secretion of the cells into K<2>SiF<6> or Na<2>SiO<3>, shaking the secretion in a shaking bed at the constant temperature of 20-37 DEG C for 16-72h at the shaking speed of 100-300r / min, centrifugally collecting bottom precipitates, and washing and drying the precipitates to obtain the silicon hollow nano-spheres with the average particle sizes of 200nm. The secretion of the cells is a supernatant. The molar concentration of the K<2>SiF<6> or the Na<2>SiO<3> is 0.011mol / L. The method has a series of advantages of environmental friendliness, simplicity in operation, economic efficiency, good biocompatibility and the like.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Microorganism product for reducing soil alkalinity of low beaches and saline-alkali land
ActiveCN104629768AReduce alkalinityLower pHAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesAlkali soilBiology
The invention discloses a microorganism product for reducing soil alkalinity of low beaches and saline-alkali land, and belongs to the soil improvement technology. The microorganism product is that microorganism fermented solid wastes capable of synthesizing glutamic acid can be utilized to produce a soil improvement product; the functional microorganism strains in the product can be synthesized into glutamic acid while propagating in soil, and meanwhile, the pH of the soil is lowered down, so that the effects of reducing alkalinity and improving the saline-alkali land can be achieved. The microorganism product is produced from brevibacterium flavum solid fermented agricultural wastes; the product contains not less than 0.5*10<8> cfug<-1> of brevibacterium flavum, not greater than 30% of water content, and not less than 45% of organic matters, and the pH is 5.5. The test shows that the bio-organic fertilizer can be applied to the soil in the low beaches and saline-alkali land, the pH can be continuously reduced in salt leaching for a long term; and therefore, the product is able to effectively reduce soil alkalinity of the low beaches and saline-alkali land.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for production of succinic acid
Disclosed is a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by acting a cultured cell of a bacterium selected from Brevibacterium flavum, Brevibacterium lactofermentum and Corynebacterium glutamicum or a treatment product of the cultured cell on an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing the organic raw material to produce succinic acid and collecting succinic acid, wherein the bacterium is so modified as to have an enhanced pyruvate carboxylase activity compared with an unmodified one, and wherein the cultured cell or the treatment product thereof is acted on the organic raw material at 37 to 45 DEG C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Phosphoserine phosphatase gene of coryneform bacteria
The present invention provides a DNA coding for a protein defined in the following (A) or (B) is obtained from Brevibacterium flavum chromosomal DNA library by cloning a DNA fragment that complicates serB deficiency of Escherichia coli as a open reading frame in the DNA fragment.(A) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID: 2 in Sequence Listing; or(B) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence including substitution, deletion, insertion, addition or inversion of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, and which has phosphoserine phosphatase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Microbial agent for improving soybean continuous cropping barrier
InactiveCN106244483AIncrease productionImprove continuous cropping soil qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of a microbial agent, more specifically to the technical field of a microbial agent for fertilizers. The microbial agent is prepared by the following steps: using ryegrass meal, sesbania gum, compound amino acids powder, charcoal dust and yeast extract as raw materials, inoculating brevibacterium flavum and acetobacter aceti, and fermenting at 30-33 DEG C for 68-70 h. The obtained microbial agent is especially suitable for continuous cropping soybean plantation, can effectively adjust pH value of soil during soybean continuous cropping plantation period, raise content of organic matter in the soil, increase contents of total nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus and rapidly available potassium in the soil, increase bacteria number of beneficial bacteria in the soil, inhibit proliferation of harmful fungi and reduce disease pest and weed, and is of positive significance for enhancing yield of continuous cropping soybean and improving properties of continuous cropping soil.
Owner:界首市沃土生物科技有限公司
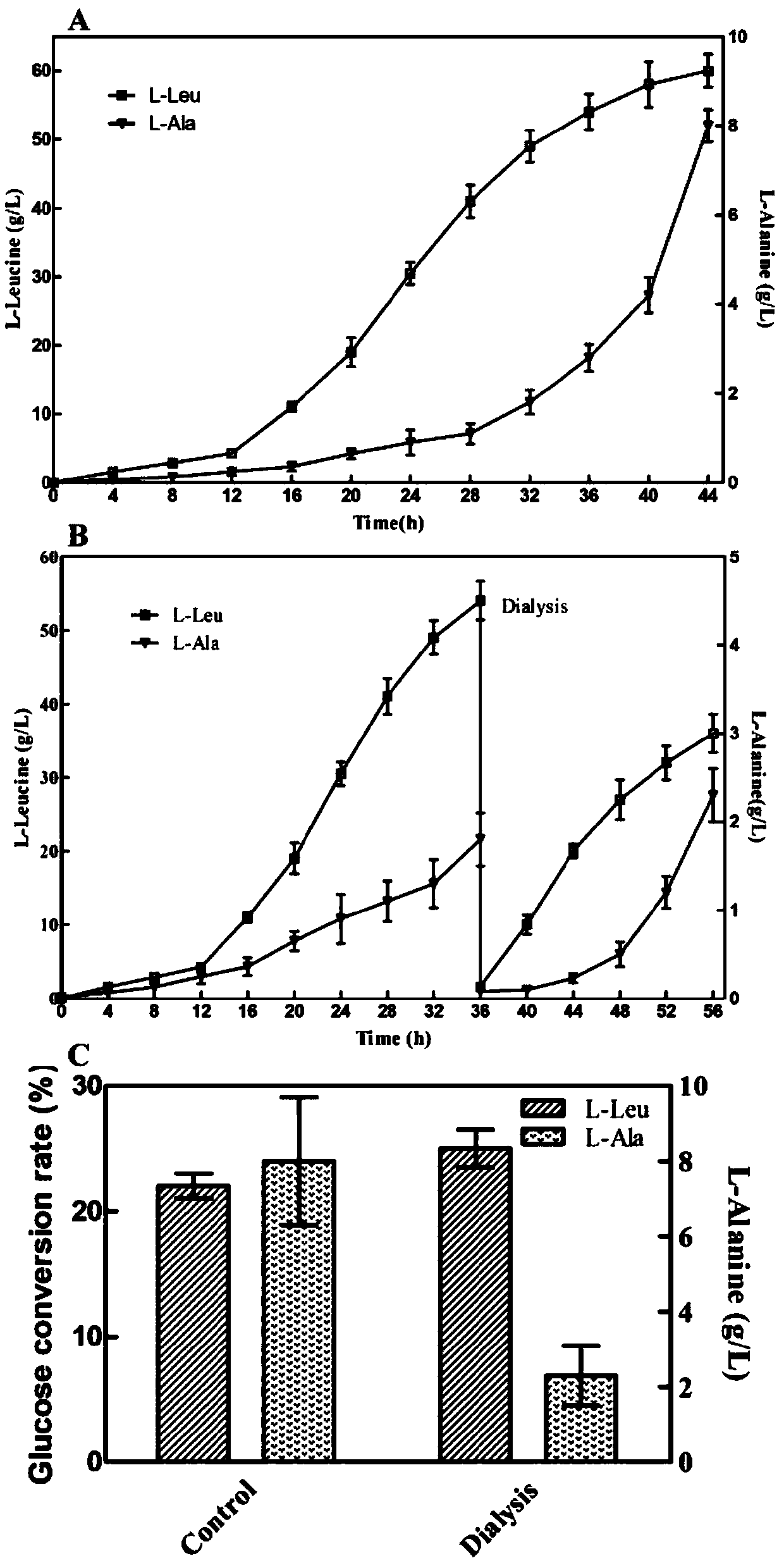
Method for producing L-leucine by fermentation
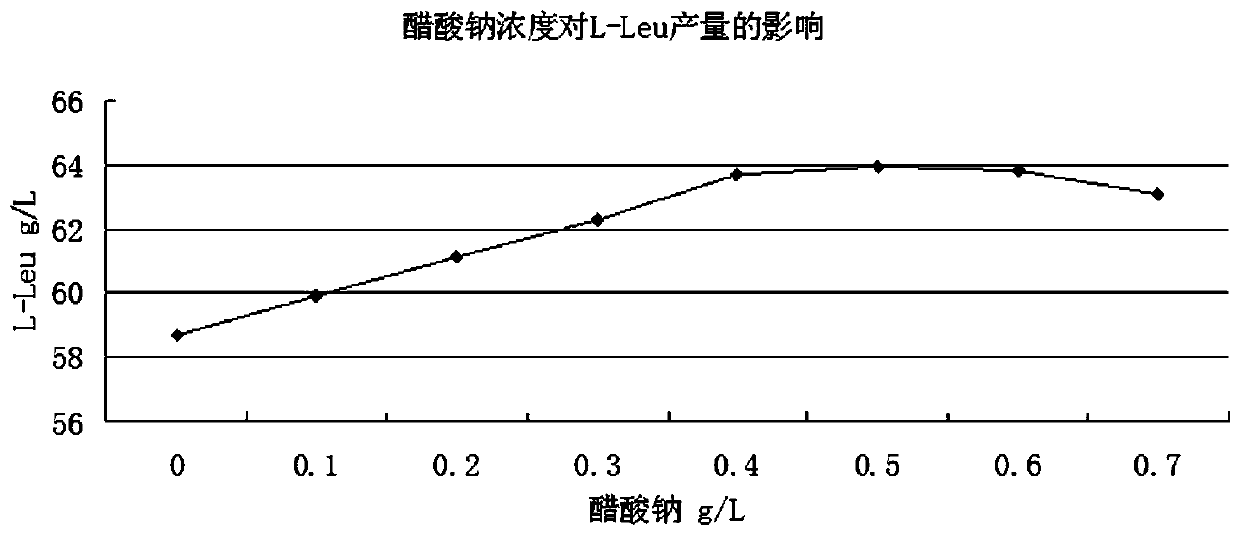
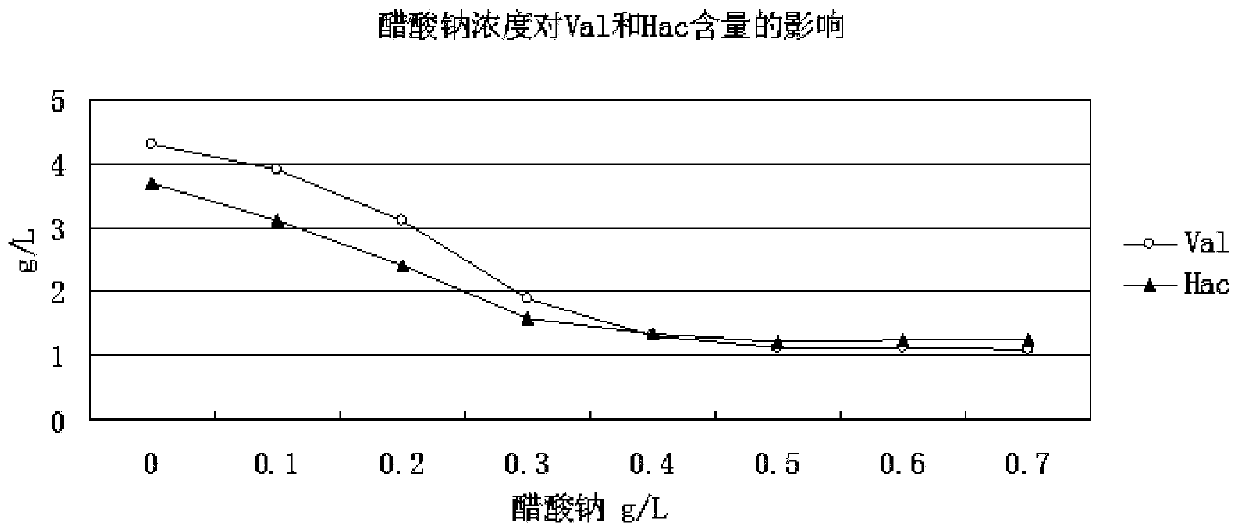
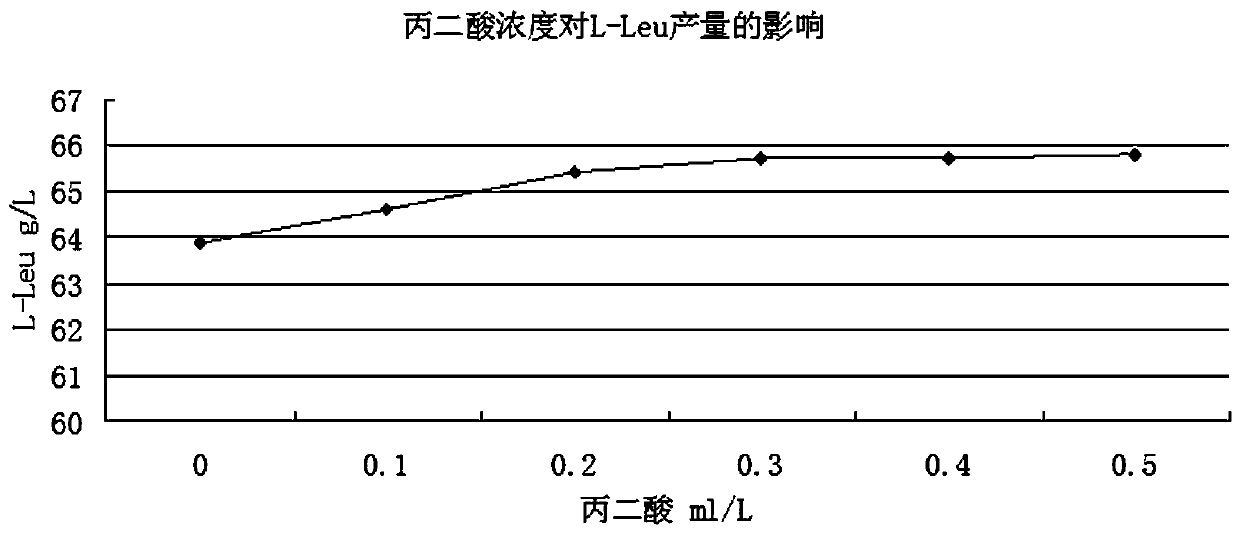
ActiveCN110541013AReduce generationSynthetic pathway blockedMicroorganism based processesFermentationSodium acetateMalonic acid
The invention belongs to the field of production process of L-leucine, and discloses a method for producing L-leucine by fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting brevibacterium flavum producing L-leucine for more than 44 h and feeding a sodium acetate aqueous solution into a fermentation tank at 30 h of the fermentation, controlling concentration of sodium acetate at 0.1-1 g / L in the fermentation solution until the fermentation is completed, wherein the concentration of the sodium acetate aqueous solution is 50-100 g / L; feeding a malonic acid aqueous solution in the fermentation tank at 30 h of the fermentation and controlling concentration of malonic acid at 0.1-0.5 ml / L in the fermentation solution until the fermentation is completed, wherein the concentration of the malonic acid aqueous solution is 10-20%; adding chitosan in the fermentation tank at 40 h of the fermentation and controlling concentration of chitosan at 20-80 mg / L in the fermentation solution. The method of the invention has high fermentation efficiency, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:XINJIANG FUFENG BIOTECH
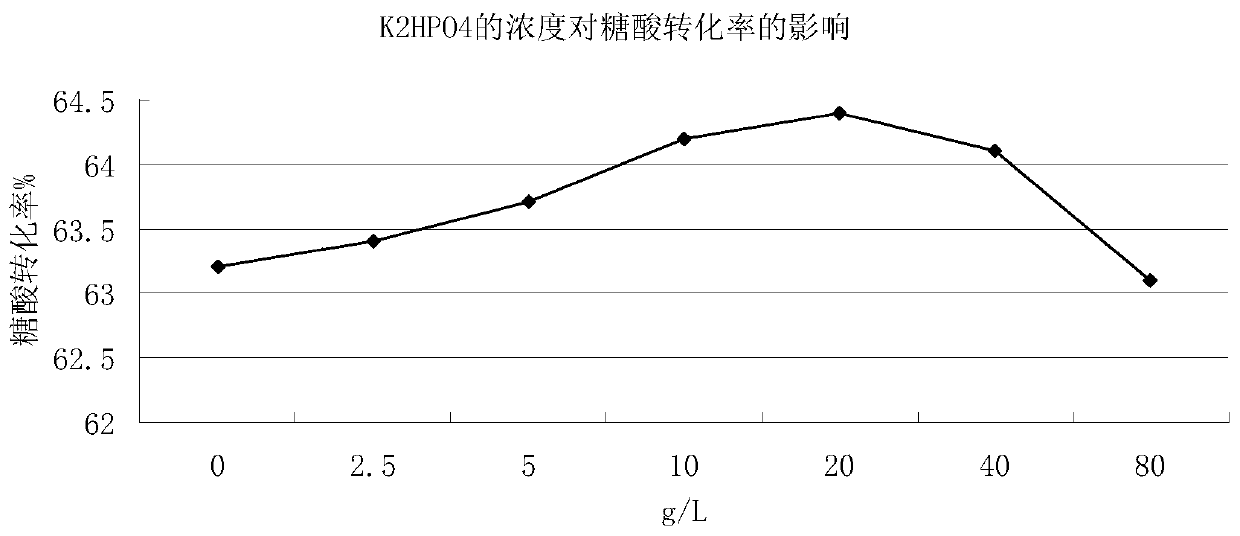
Method for improving glutamic acid fermentation conversion rate
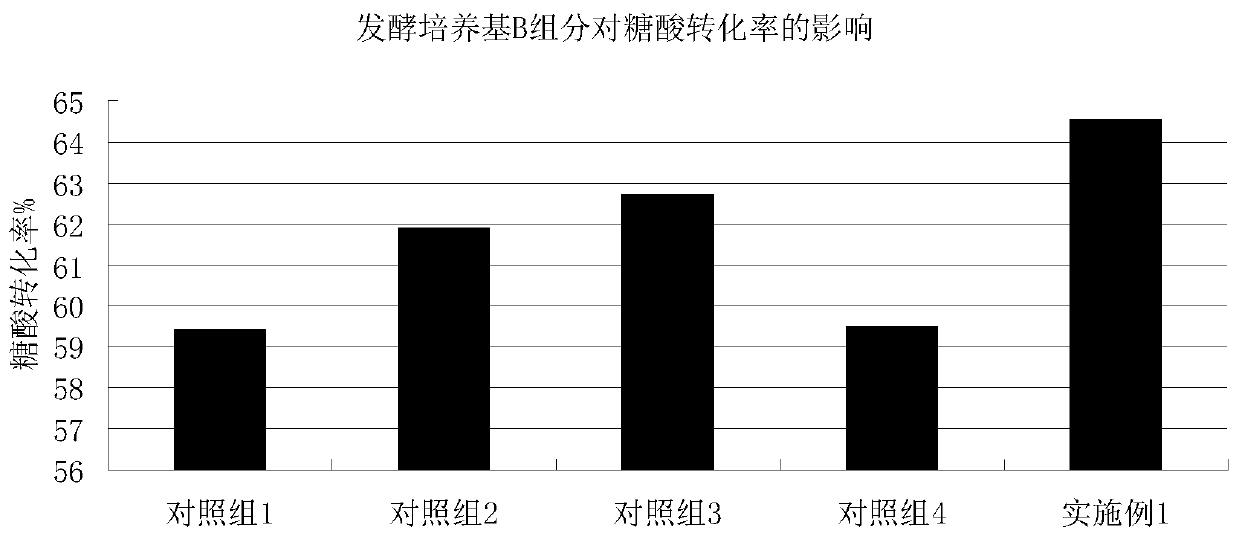
ActiveCN110904168AFacilitated releaseIncrease proliferation rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyAqueous solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of amino acid production, and discloses a method for improving the glutamic acid fermentation conversion rate. The method comprises the following steps: 1)inoculating a fermentation culture medium A with a Brevibacterium flavum seed liquid for producing glutamic acid, and carrying out fermentation culture for 18-24 h; 2) then adding a fermentation medium B, continuing to ferment and culture for 24 h or above, and collecting the obtained fermentation liquor, wherein the total fermentation time is controlled to be 48-50 h; and 3) feeding an aqueous K2HPO4 solution with the concentration of 15-25 g / L at the flow rate of 5 ml / min when fermentation is performed for 30 h, and stopping the feeding before the fermentation is finished. The culture medium and the process are optimized to improve the conversion rate.
Owner:HULUNBEIER NORTHEAST FUFENG BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
How to make a kind of peanut soy sauce
The invention relates to a preparation method of peanut soy, belonging to the technical field of preparation methods of soy. The peanut soy provided by the invention adopts groundnut kernels as a raw material, bacillus licheniformis, brevibacterium flavum, clostridium acetobutylicum and rhamnose lactobacilli are taken as composite fermentative bacteria of a peanut fungi solution; the special proportional aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus niger and monascus are utilized as fermenting aspergillus of a peanut yeast, and a preparation process of natto soy is adopted. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that the fermentation period is shortened, natto kinase is generated after fermenting of groundnut kernels, the kinase can restrain the browning of the soy in preservation, a maillard reaction is reduced, the nutritive values of the groundnut kernels are high, the flavor is unique, and the color, the aroma and the taste of the prepared soy are good; the content amino acid nitrogen is improved by 43.9%, the full nitrogen content is improved by 17.5%, a soluble salt-free solid is improved by 18.8%, and the preparation method is especially used for preparing ideal soy of pickles.
Owner:松原北大荒食品科技有限公司
Preparation method of bionic immobilized 3-cyanopyridine nitrile hydratase
InactiveCN104894092AAdvantages of catalytic hydrolysis performanceImprove repeated use stabilityOn/in organic carrierHydrolysisNitrile hydratase
The invention discloses an indium oxide nanosphere coating brevibacterium flavum nitrile hydratase, a preparation method and application. The multilayered structure of cells is simulated by referring to the existence form of the hydratase in a living body, and the indium oxide nanosphere is prepared through bionic design of components, functions and processes and used for embedding of the brevibacterium flavum nitrile hydratase. The characteristics that the immobilized nitrile hydratase is high in stability, high in activity, easy to recycle and the like are used for catalyzing 3-cyanopyridine to be transformed into nicotinamide in an efficient hydrolysis mode. The preparation method of the bionic immobilized hydratase can provide reference significance for preparation of a microcyst immobilized carrier, and provide a novel research idea for biotransformation of the 3-cyanopyridine.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
A kind of microbial fermentation process to produce arginine
InactiveCN103695487BQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a process for producing arginine by microbial fermentation. Brevibacterium flavum MQA121 is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: preparing fermentation liquid, namely performing slant culture, performing shake-flask culture, performing primary seed culture, performing secondary seed culture, and continuing to ferment; extracting and refining a fermented product, namely preprocessing the fermentation liquid, performing secondary crystallization, performing color and impurity removal, performing membrane concentration and separation, drying, and packaging to obtain arginine as a finished product. The method has the benefits that organic and inorganic matters and bacteria in subsequent extracting and refining liquid of arginine can be remarkably reduced and the arginine yield can be increased; in addition, the product quality is improved and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:滨州市生物技术研究院有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com