Method for producing L-lactic acid by Bacillus coagulans CGMCC No.2602
A technology of Bacillus coagulans and lactic acid, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of nutritional deficiencies and high production costs, and achieve the effects of simple nutritional requirements, reduced fermentation costs, and reduced risk of contamination by miscellaneous bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
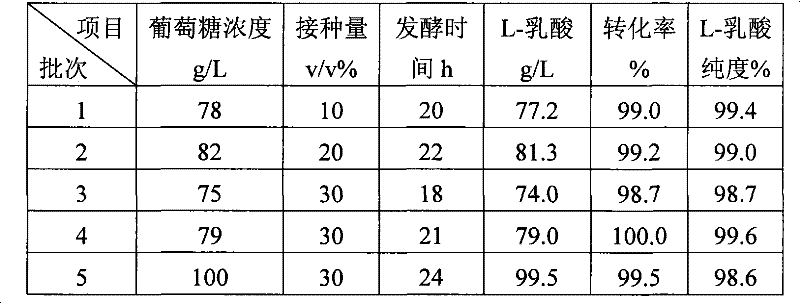
[0023] Embodiment 1. The process of producing L-lactic acid by semi-continuous batch fermentation
[0024] 1. Cell activation
[0025] Aseptically open the freeze-dried strain of Bacillus coagulans, streak and inoculate on the slant of bran nutrient agar in test tubes, culture at 40-50°C for 18-24 hours, then transfer to the slant of bran nutrient agar eggplant bottle by streaking, 40-60 Cultivate at ℃ for 20-24 hours, check under the microscope, when more than 90% of the bacteria form spores, it is mature and ready for transplantation.
[0026] Slant medium (bran nutrient agar medium): peptone 10g / L, beef extract 3g / L, NaCl 5g / L, bran 10g / L, agar 15-20g / L, distilled water 1L, pH 7.0-7.2.
[0027] 2. Seed culture
[0028] 2.1 Incline cultivation
[0029] Use an inoculation loop to dip a small amount of bacteria slime from the slant of the strain, inoculate it on the slant medium by streaking, and cultivate at 40-60°C for 24-48 hours. When the spore rate of microscopic exami...
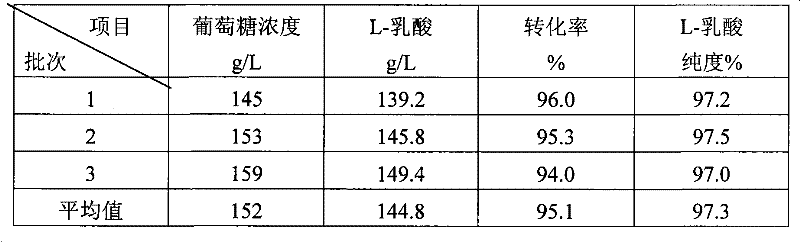
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2. Production of L-lactic acid by intermediate sugar supplementation fermentation
[0044] 1. Cell activation
[0045] Aseptically open the freeze-dried strain of Bacillus coagulans, streak and inoculate on the slant of bran nutrient agar in test tubes, culture at 40-50°C for 18-24 hours, then transfer to the slant of bran nutrient agar eggplant bottle by streaking, 40-60 Cultivate at ℃ for 20-24 hours, check under the microscope, when more than 90% of the bacteria form spores, it is mature and ready for transplantation.
[0046] Incline medium: peptone 10g / L, beef extract 3g / L, NaCl 5g / L, bran 10g / L, agar 15-20g / L, distilled water 1L, pH 7.0-7.2.
[0047] 2. Seed culture
[0048] 2.1 Incline cultivation
[0049] Use an inoculation loop to dip a small amount of bacteria sludge from the slant of the strain, inoculate it on the slant medium by streaking, culture at 40-60°C for 24-48 hours, and microscopically check that the spores > 90% are mature.
[0050] In...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: Corn starch hydrolyzate is the Bacillus coagulans of carbon source and produces L-lactic acid
[0058] Incline medium: peptone 10g / L, beef extract 3g / L, NaCl 5g / L, bran 10g / L, agar 15-20g / L, distilled water 1L, pH 7.0-7.2.
[0059] Seed medium: liquefy cornstarch with high-temperature α-amylase and saccharify with glucoamylase to prepare hydrolyzed sugar. The filtrate is used to measure the hydrolyzed sugar by Fehling’s method, with the hydrolyzed sugar at a concentration of 50g / L as the carbon source, peptone 5g / L, and yeast extract 5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.1g / L, calcium carbonate 30g / L, pH 5.0-6.0.
[0060] Fermentation medium: liquefy cornstarch with high-temperature α-amylase, saccharify with glucoamylase to prepare hydrolyzed sugar, take the filtrate to measure the hydrolyzed sugar by Fehling’s method, use the hydrolyzed sugar at a concentration of 75-80g / L as the carbon source, and peptone 1.0g / L , barley root 3.0g / L, (NH ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com