Biosynthetic gene cluster of romatic-polyketide atypical fluostatins and applications of biosynthetic gene cluster
A biosynthetic, atypical technology used in plant genetic improvement, applications, microorganisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
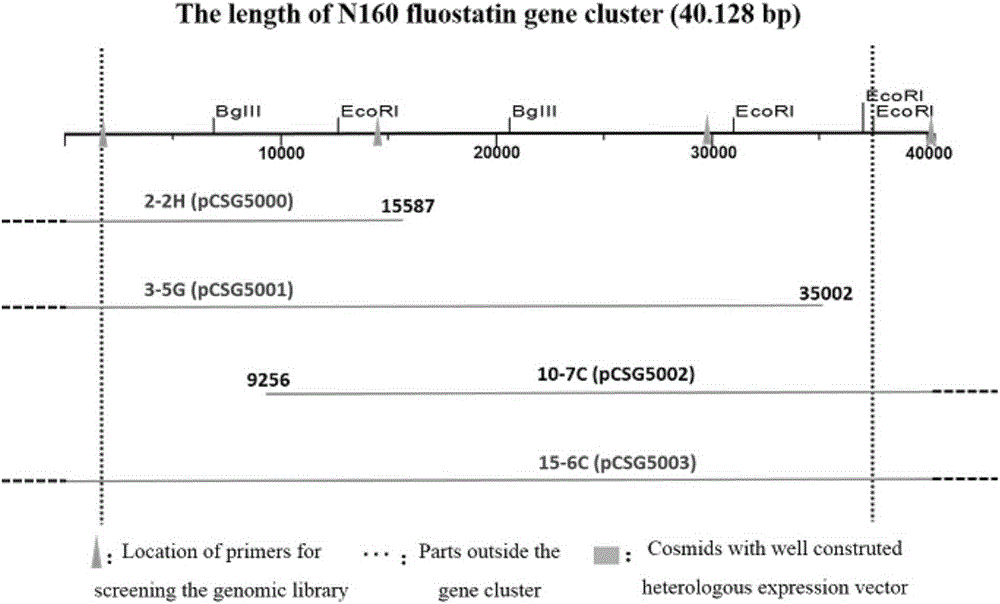
[0113] Example 1: Extraction of Genomic DNA of Micromonospora SCSION160, a Micromonospora SCSION160 Producer of Fluostatins and Related Compounds
[0114] The mycelium of fresh Micromonospora SCSION160 was inoculated in 50mL of 1 # Culture medium (starch 10g, yeast powder 4g, bacteriological peptone 2g, sea salt 10g, add water to 1L, pH7.2-7.4), 28-30℃, shake culture for about 2-3 days, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10 minutes to collect Mycelium. The mycelium was washed twice with STE solution (NaCl75mM, EDTA25mM, Tris-Cl20mM), and 30mL of STE solution and lysozyme with a final concentration of 3mg / mL were added to the washed mycelia, vortexed evenly, and incubated at 37°C for 3 hours. Add proteinase K to a final concentration of 0.1-0.2mg / mL, mix well, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, add SDS to a final concentration of 1-2%, mix well, put in a water bath at 55°C for about 1 hour, and invert several times during the process . Add an equal volume of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl a...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Example 2: Establishment of the Genomic Library of Micromonospora SCSION160, a Fluostatins-producing Bacteria
[0116] First, through a series of dilution experiments to determine the amount of restriction endonuclease Sau3AI, in a 20 μL system, containing 17 μL of Micromonospora SCSION160 genomic DNA, 2 μL of 10× reaction buffer and 1 μL of different dilutions of Sau3AI, The termination reaction is 4 μL 0.5mol / LEDTA and a suitable loading buffer. Through exploration, it is determined that the enzyme activity unit of 0.025-0.05U is more appropriate. On this basis, a 30-42kb genomic DNA fragment was obtained by a large number of partial enzyme digestion, and dephosphorylated with a dephosphorylase.
[0117] The vector SuperCosl plasmid used to construct the library is first cut from the middle of the two cos sequences with the restriction endonuclease XbaI, then dephosphorylated, and then cut with the restriction endonuclease BamHI from the multiple cloning site , to o...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Example 3: Screening positive clones containing fluostatins synthetic biological genes from the fluostatins producing bacteria Micromonospora SCSION160 genome library
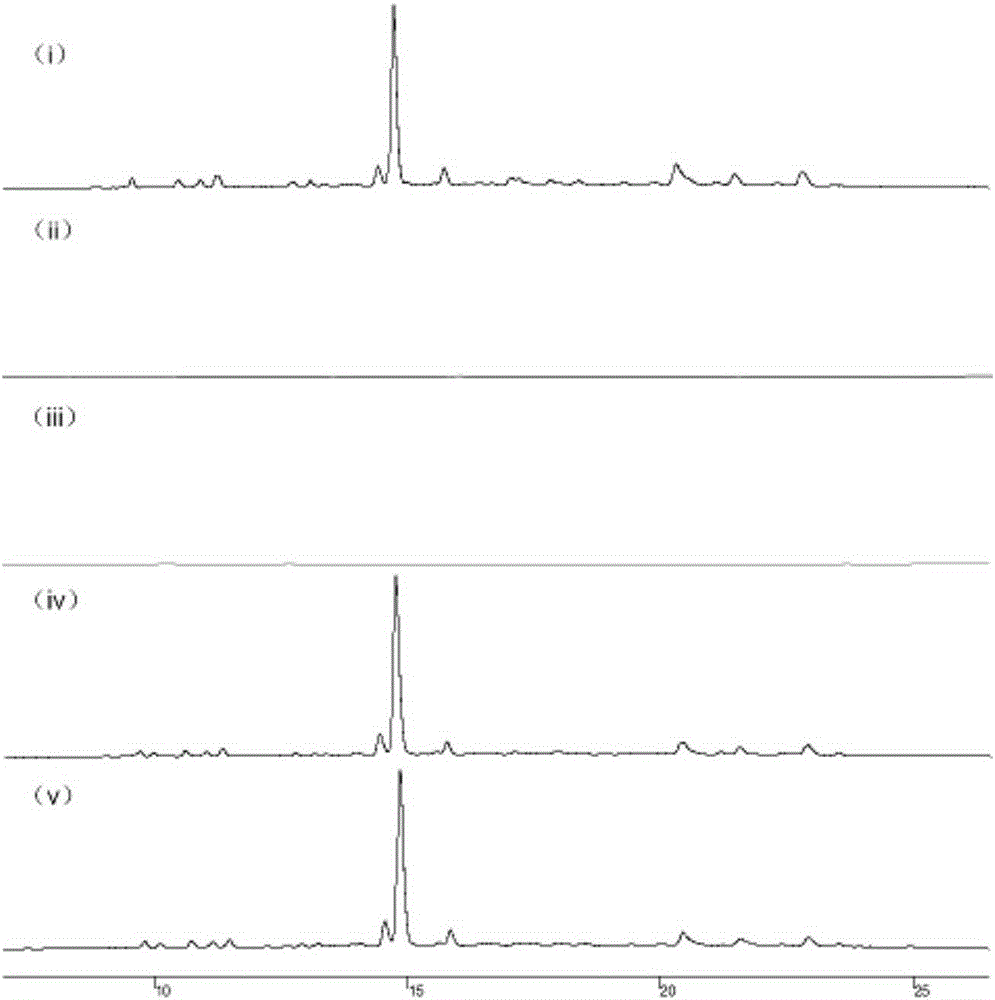
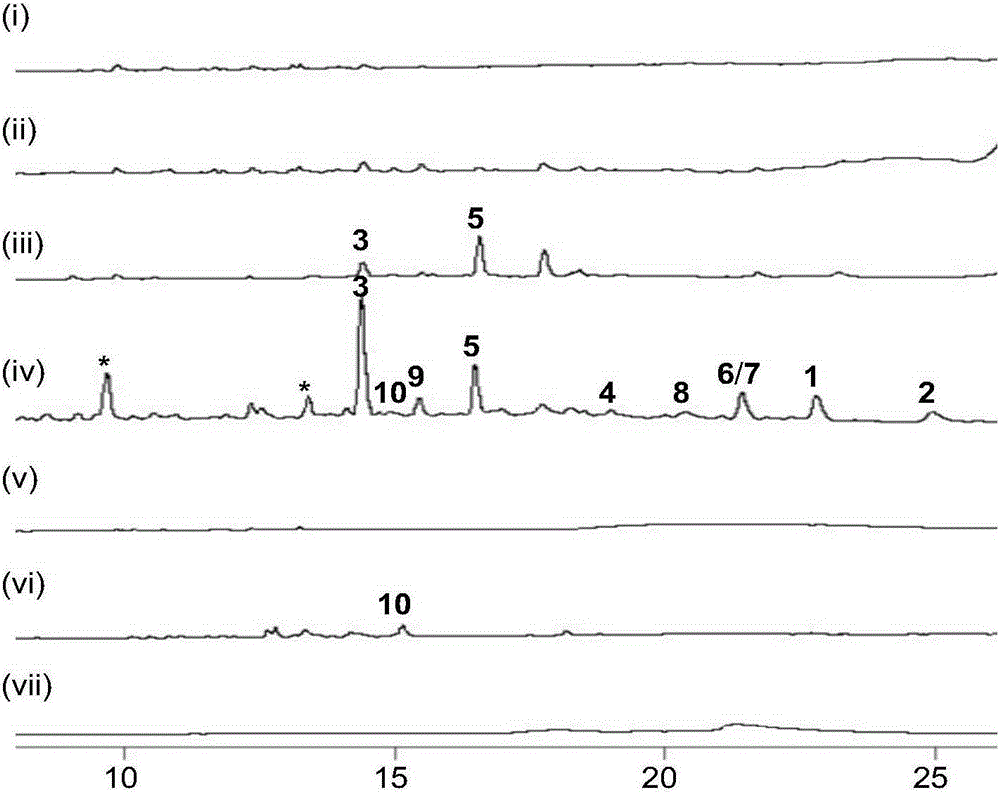
[0120]Genomic DNA of Micromonospora SCSION160 was sent to the National Human Genome South Research Center for genome-wide scanning and annotation. According to the results of scanning and annotation, bioinformatics analysis was used to identify the flsG monooxygenase gene located in the middle of the fluostatins main gene cluster. Sequence design PCR screening primers flsGEF and flsGER (primer sequences are shown in Table 2), screened from 3072 clones in the genomic library of Micromonas sp. SCSION160, and obtained 13 positive clones. Design PCR screening primers: flsF carboxyltransferase gene primers flsFDTF and flsFDTR, flsS adenylosuccinate lyase gene primers flsSEF and flsSER and border gene orf2~3-phosphoshikimate-1-carboxyvinyltransferase gene primer ORF2EF / ORF2ER (primer sequences are shown in Ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com