Patents
Literature
38 results about "Post-prandial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Post·pran·di·al (pōst-prăn′dē-əl) adj. Following a meal, especially dinner: took a postprandial walk through the woods. post·pran′di·al·ly adv. postprandial (pəʊstˈprændɪəl) adj of or relating to the period immediately after lunch or dinner: a postprandial nap.
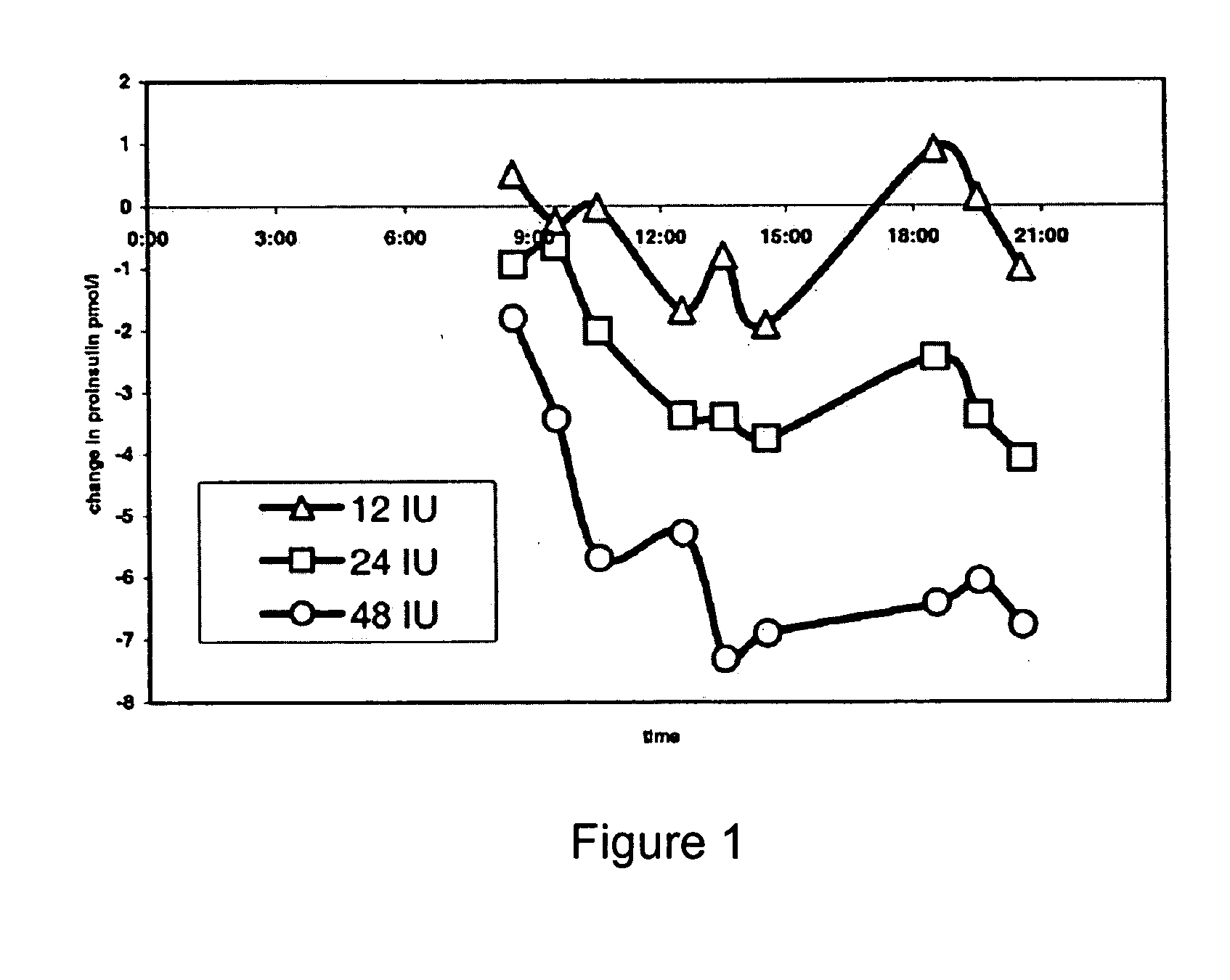
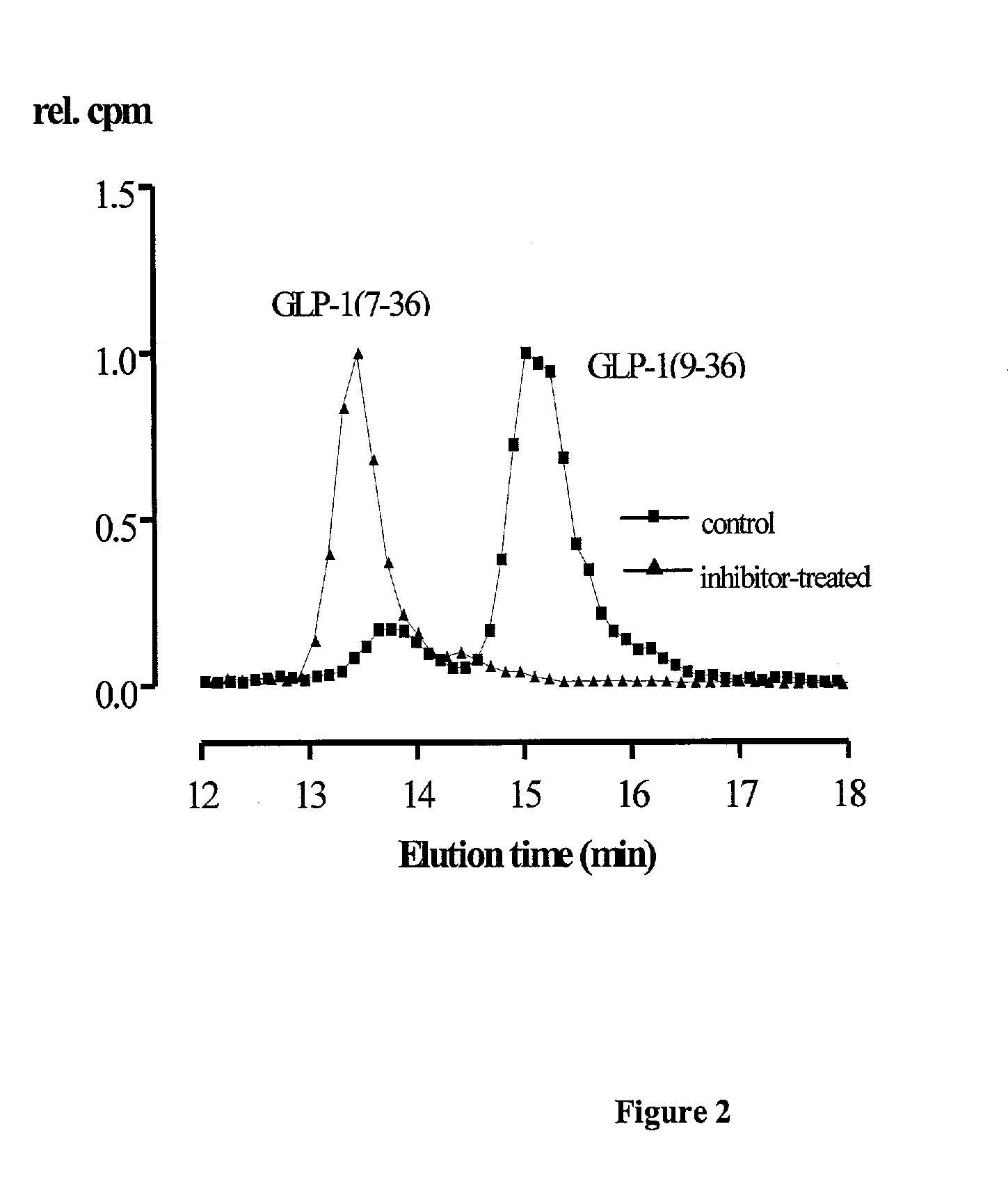
Method of reducing serum proinsulin levels in type 2 diabetics
InactiveUS20050153874A1Lower Level RequirementsLow serum levelsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin responseLevel insulin
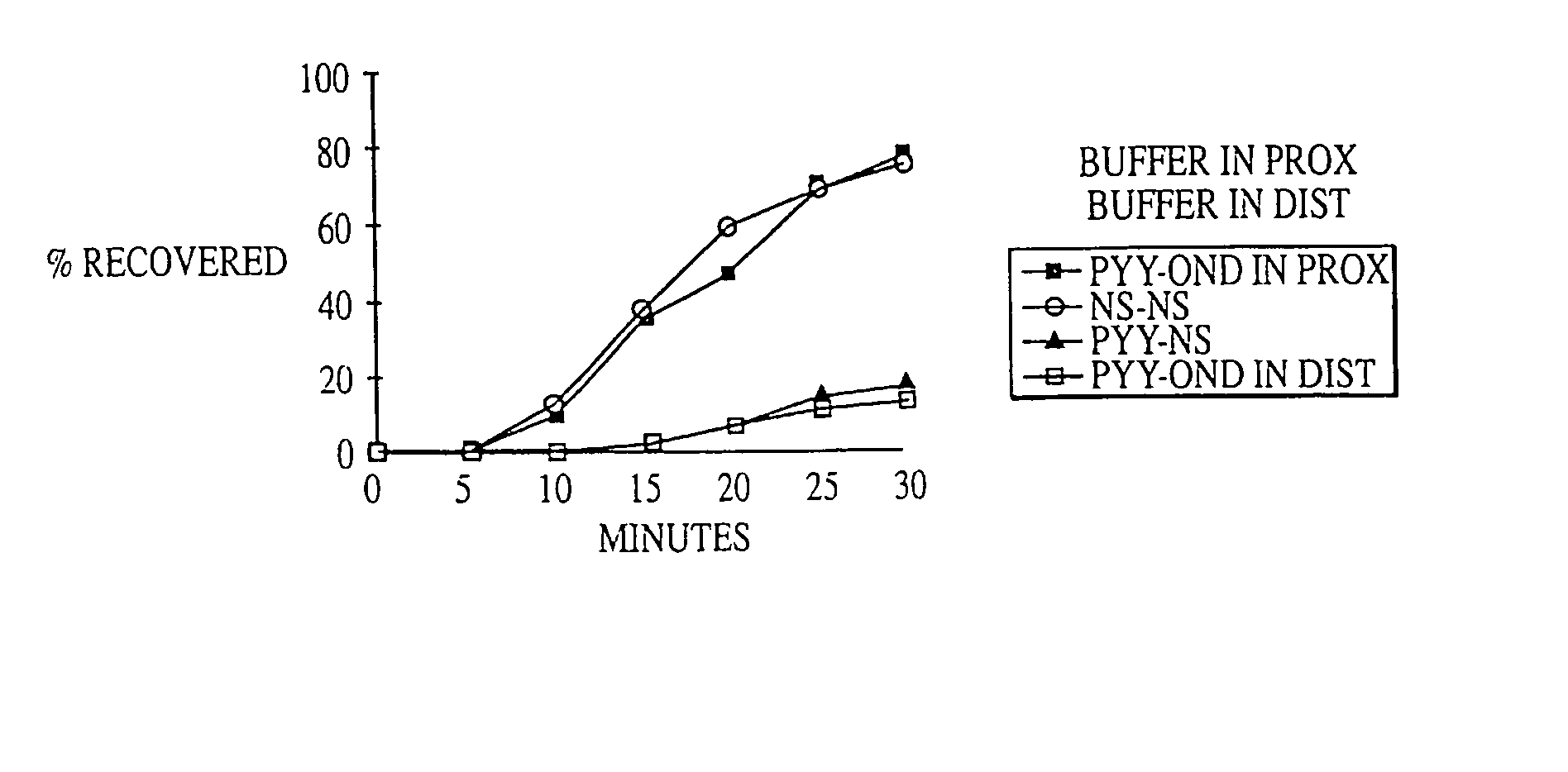
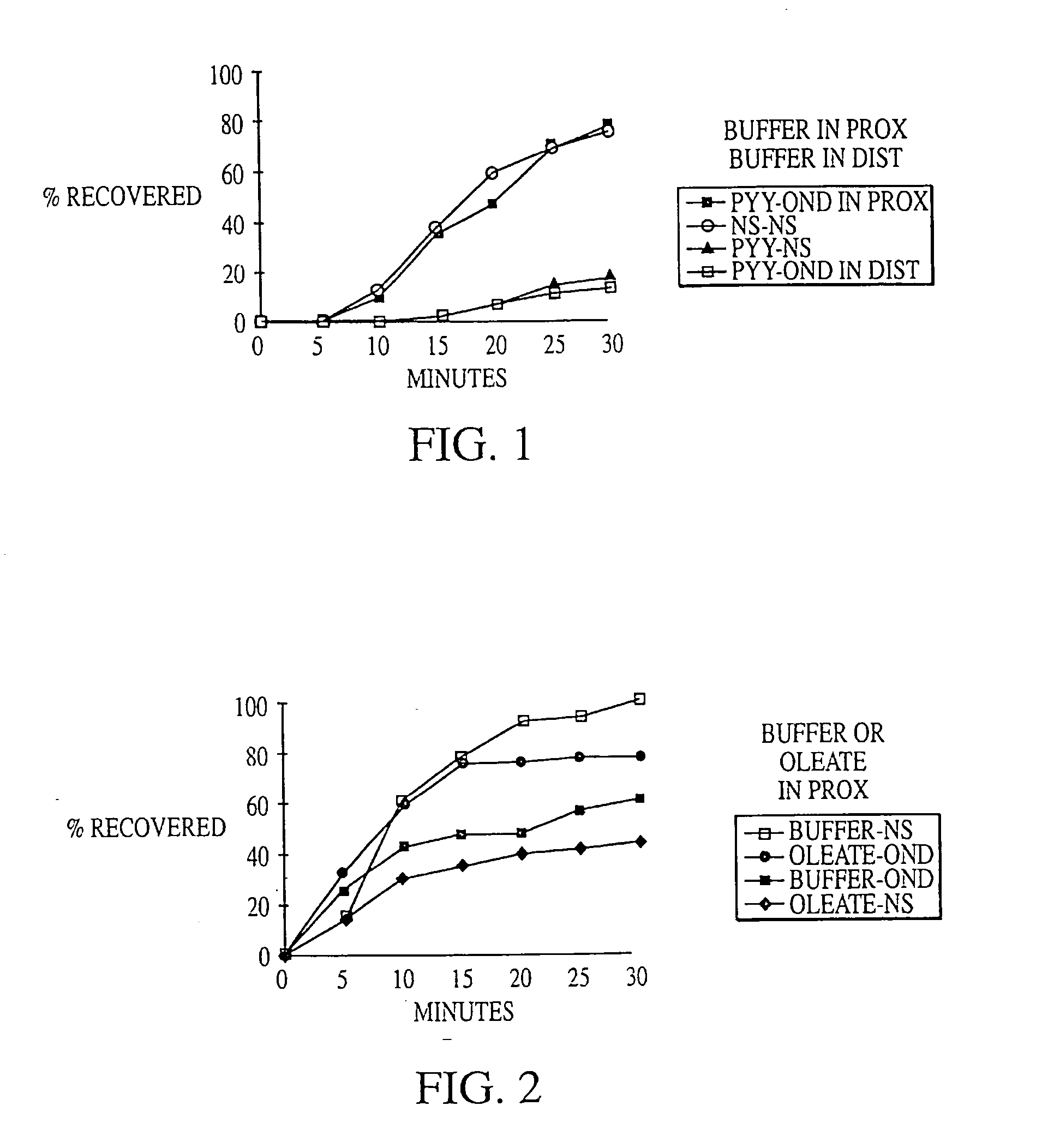
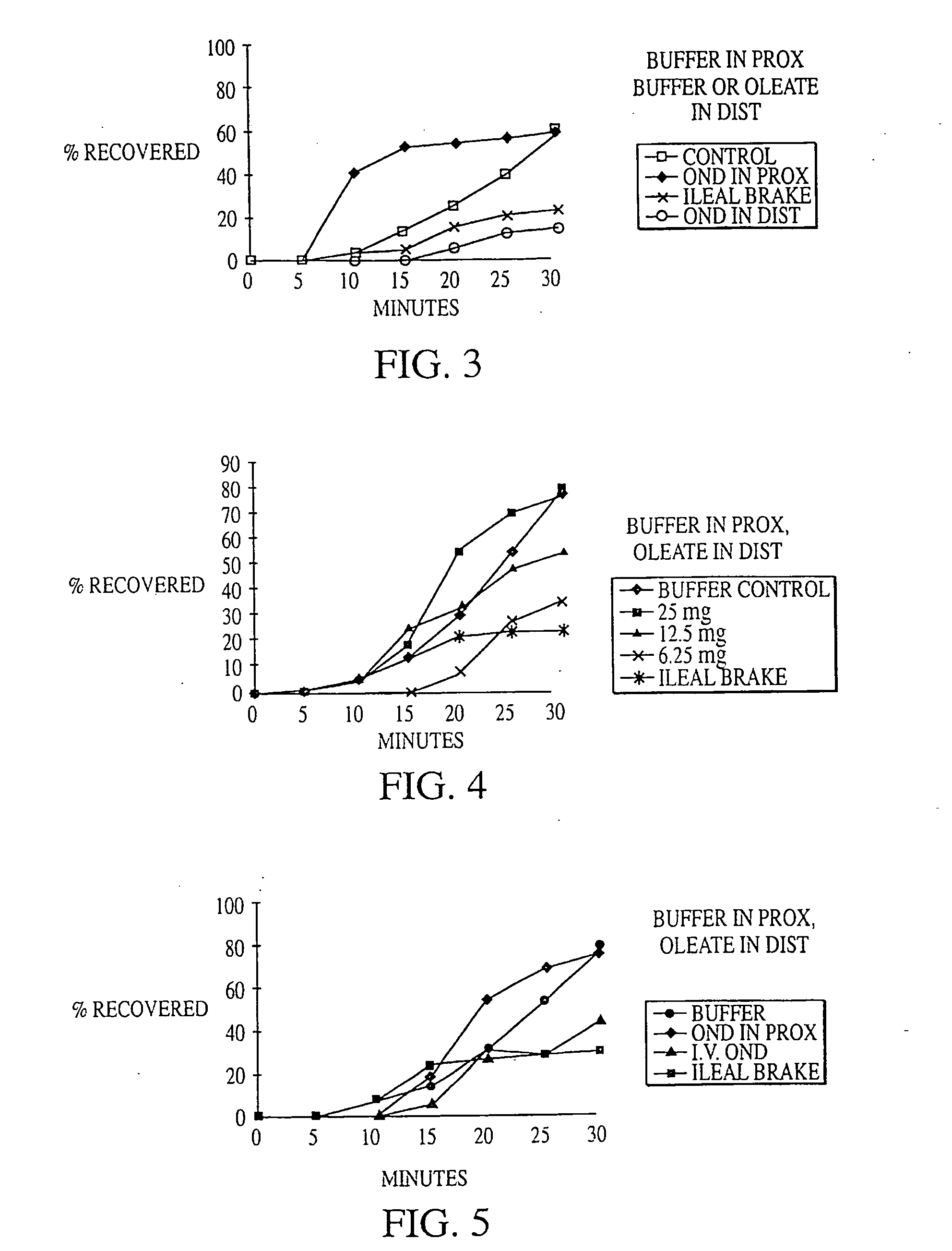
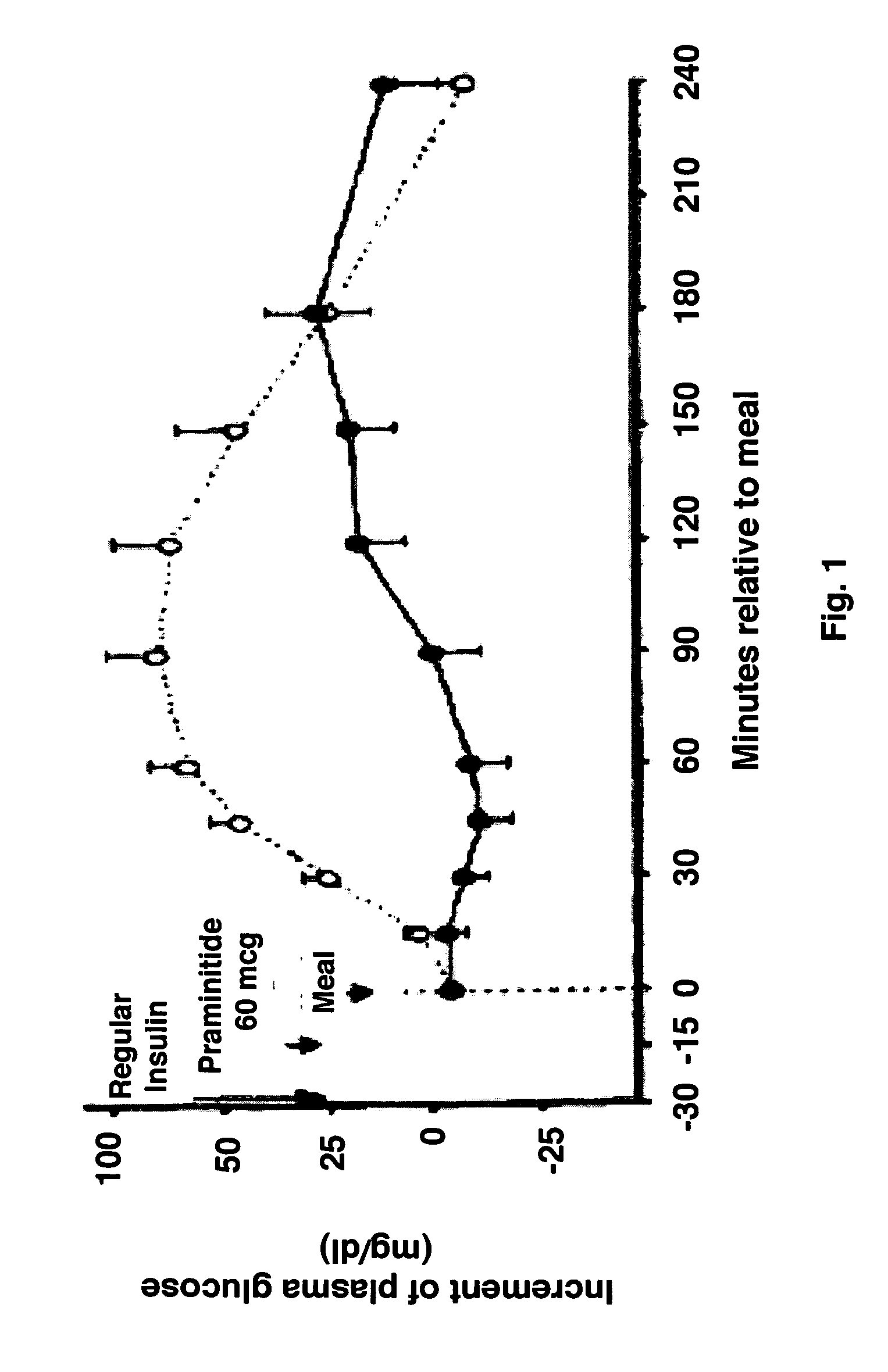
Methods are provided for reducing serum proinsulin levels, lessening post-prandial pancreatic stress, and reducing risk factors for atherosclerosis in subjects with diabetes mellitus, type 2. The method includes administration of insulin in a manner that mimics the meal-related first phase insulin response, using a dose sufficient to reduce serum levels of proinsulin. In some embodiments of the method insulin administration is commenced early in the course of the disease. Mimicking first phase kinetics, peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 18 minutes of administration. In increasingly preferred embodiments peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 15, 12, or 10 minutes of administration. Serum insulin levels return to baseline within about two hours of administration.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
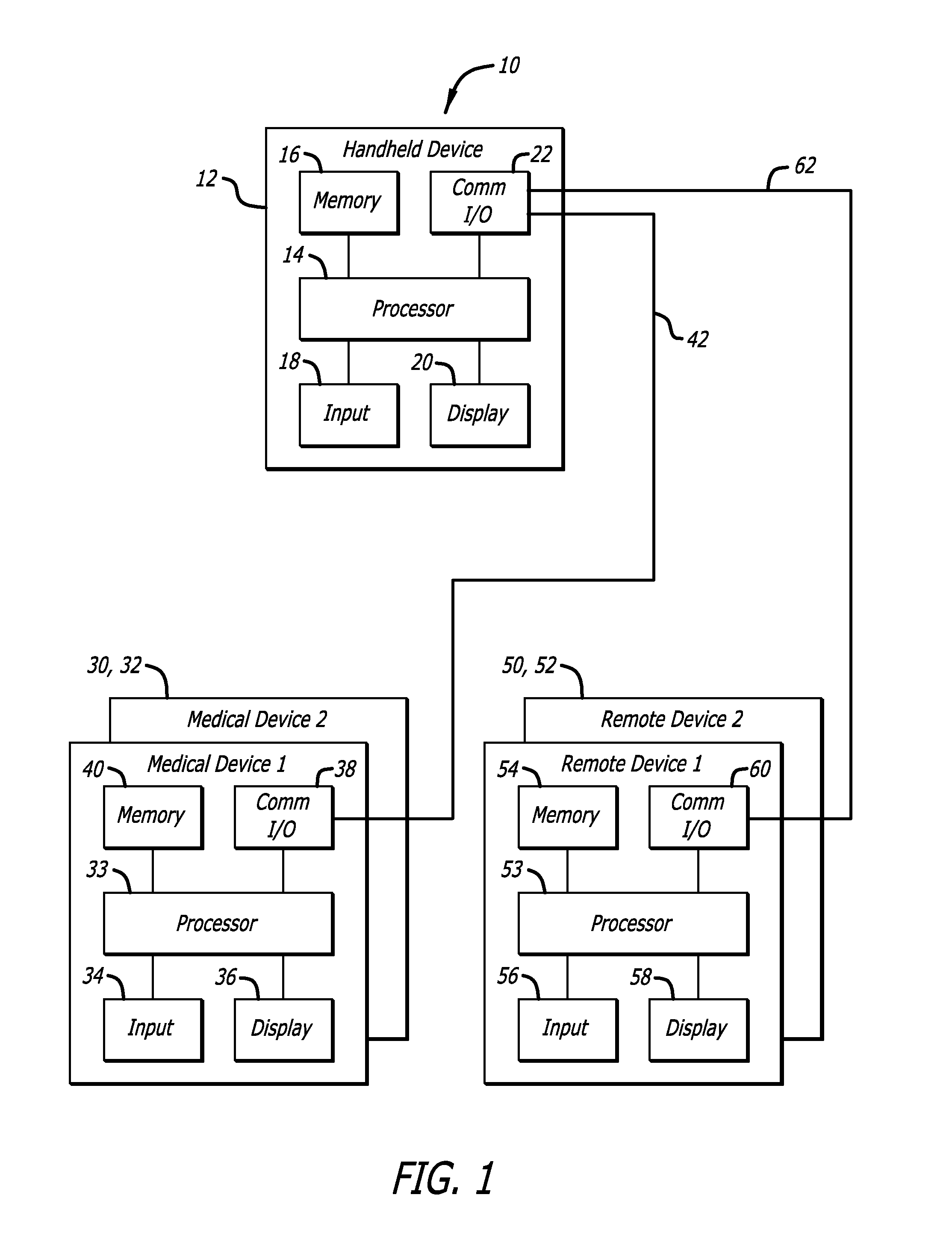
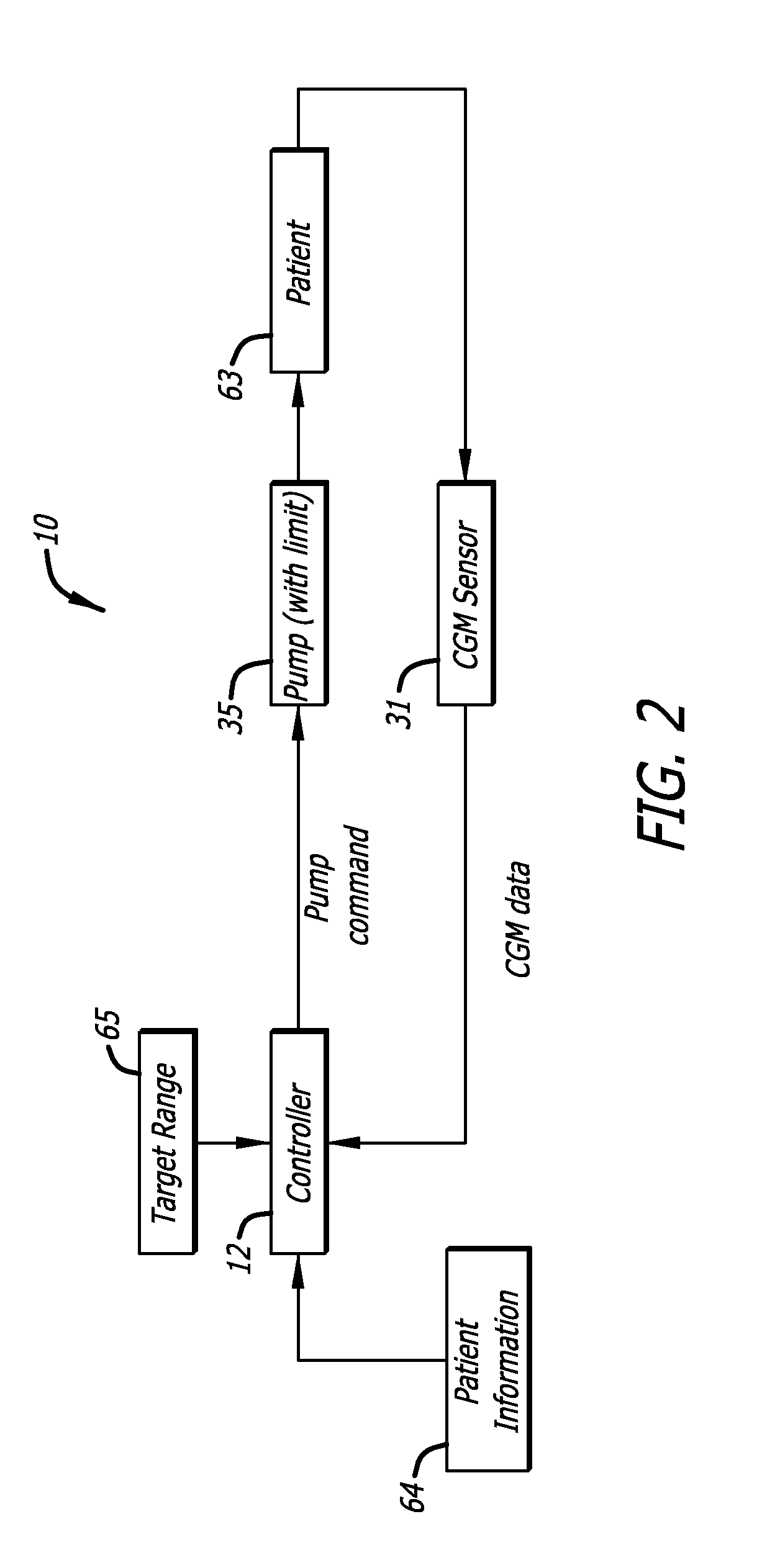
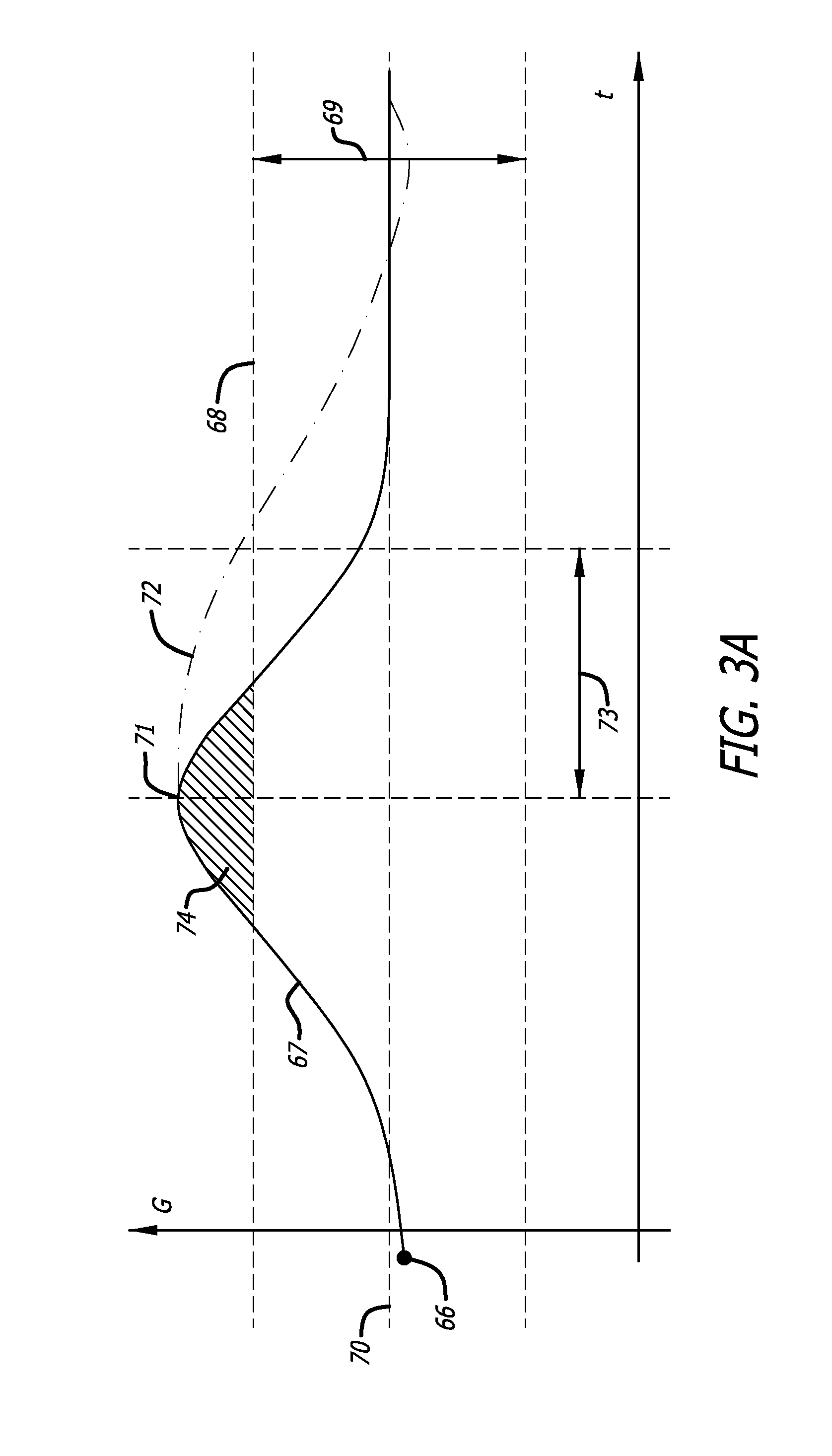
Adaptive insulin delivery system
A proactive system and method in which levels of glucose are monitored after a meal signal and compared to a safe range. If a monitored glucose level is outside the safe range, a post-prandial vertex of the glucose level is identified and an action is provided to more rapidly return the glucose level to a target level within the safe range than if no action was provided. In another aspect a control parameter in an IDM system is adjusted by determining a performance metric of the system as a function of the levels of glucose and a medication administration signal over a first window of time; and, if the performance metric is outside an expected range, adjusting the control parameter to adjust an amount of medication and to bring the performance metric inside the expected range.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Apparatus and method for monitoring blood glucose levels including convenient display of blood glucose value average and constituent values
A method of presenting glucose data to a person with diabetes from a blood glucose meter is provided in which an effective meal average (EMA) value is presented, followed by two or more of the individual values that make up the EMA, to provide improved feedback data for clinical decisions by patients who need to alter their dose of insulin. The EMA can also comprise a measure of the variability of its constituent values. The EMA encompasses those values that occur at specified times such as 1 hour before and 1 hour after a specified meal time. The EMA is calculated over a limited number of days previous to the calculation (e.g., 3 days) and has a minimum number of values that must be obtained within the time and date ranges. An algorithm allows for exclusion of any given reading from the average (e.g., post-prandial or control solution readings). Patients can use 1 to 8 EMA on any given date range (e.g., preferably 4, that is, breakfast, lunch, supper and bedtime snack).
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
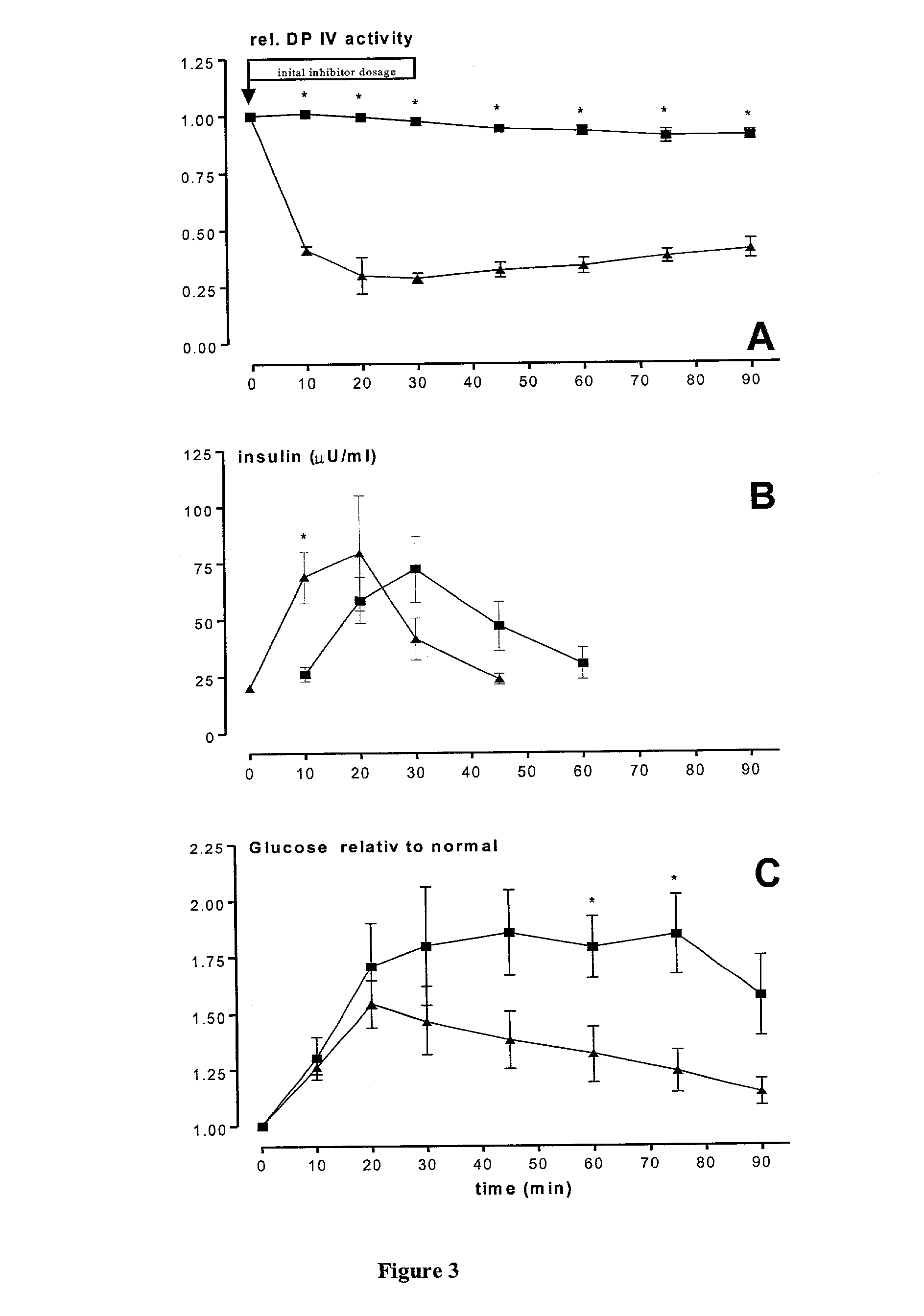
Use of dipeptidyl peptidase IV effectors for normalizing the blood glucose level in mammals
InactiveUS20020110560A1Reduce degradationReduce concentrationDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorderDipeptidyl peptidaseMammal
The present invention comprises the use of activity-reducing effectors of dipeptidyl peptidase (DP IV) and DP IV-analogous enzyme activity in the blood of a mammal to lower elevated post-prandial and basal blood glucose levels in mammalian organisms. The invention further comprises the use of activity-reducing effectors of dipeptidyl peptidase (DP IV) and DP IV-analogous enzyme activity in the blood of a mammal to increase the half-life of incretins in vivo.
Owner:PROSIDION LIMITED
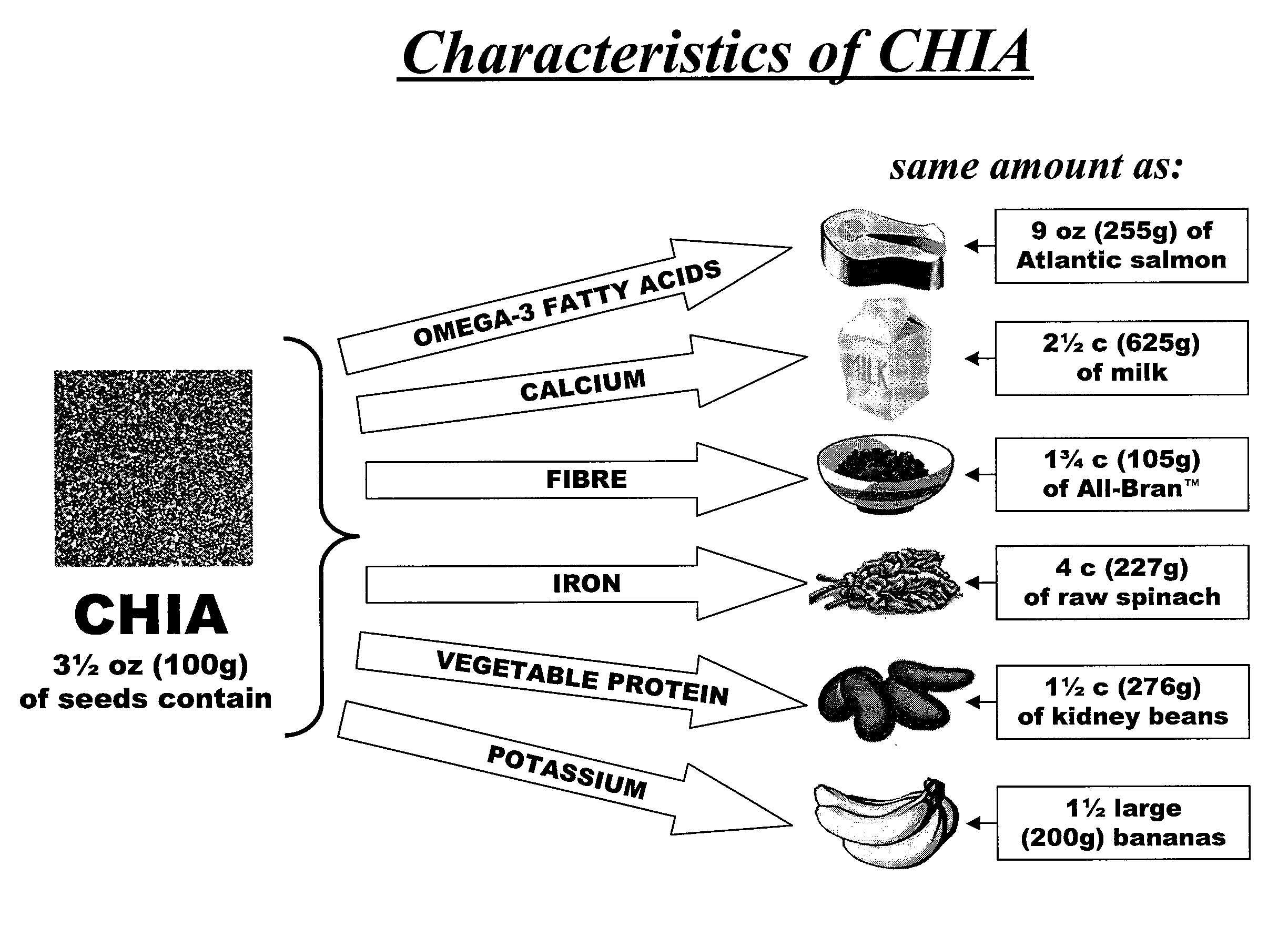
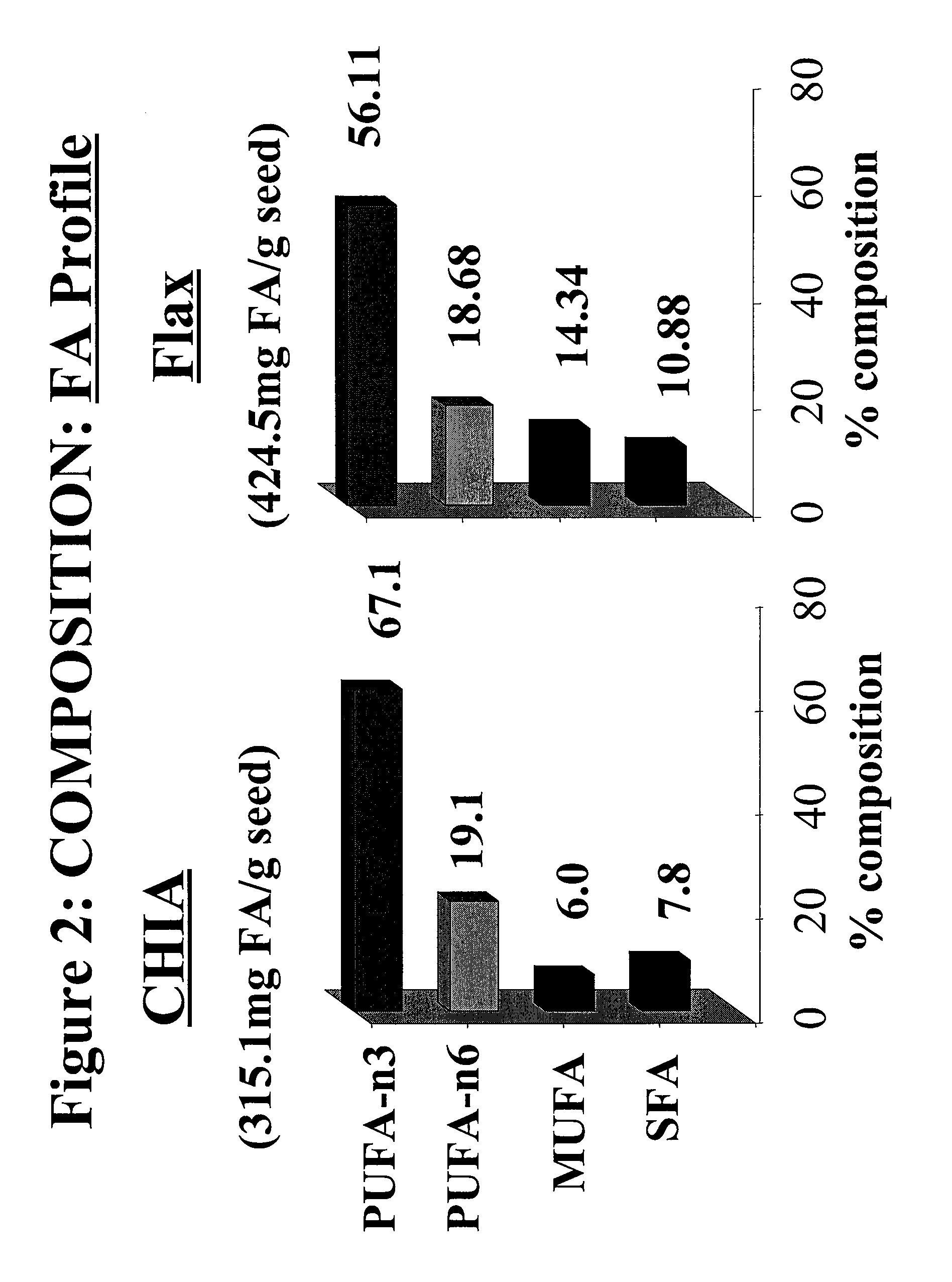
Salvia hispanica I (Chia) in the management and treatment of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and associated risk factors
InactiveUS20080305190A1Improve treatment outcomesReduces fasting and postprandial blood glucoseBiocideMetabolism disorderInflammatory factorsFactor ii
Described is use of Salvia hispanica L. (Chia) for controlling, in one embodiment reducing, blood glucose levels, preferably post-prandial blood glucose levels. This is useful in both non-diabetic and diabetic individuals, but especially in diabetic individuals. Also described is the use of chia in reducing postprandial blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, blood pressure, and oxidative stress in such individuals. The present invention further found that Chia can be used to improve endothelial function, coagulation, fibrinolysis and iron status. The present invention further encompasses the use of Chia in the treatment and / or management of diabetes and / or the treatment and management of diabetes associated conditions or risk factors, such as one or more of the following: blood pressure and blood glucose levels, post-prandial glycemia, inflammatory factors (C-reactive protein), coagulation (fibrinogen, factor VIII, von Willenbrand factor), and fibronolytic factors (such as t-PA), iron status and endothelial function, (such as increase in nitric oxide generation). In one embodiment the invention relates to dietary approaches to such treatment and management.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
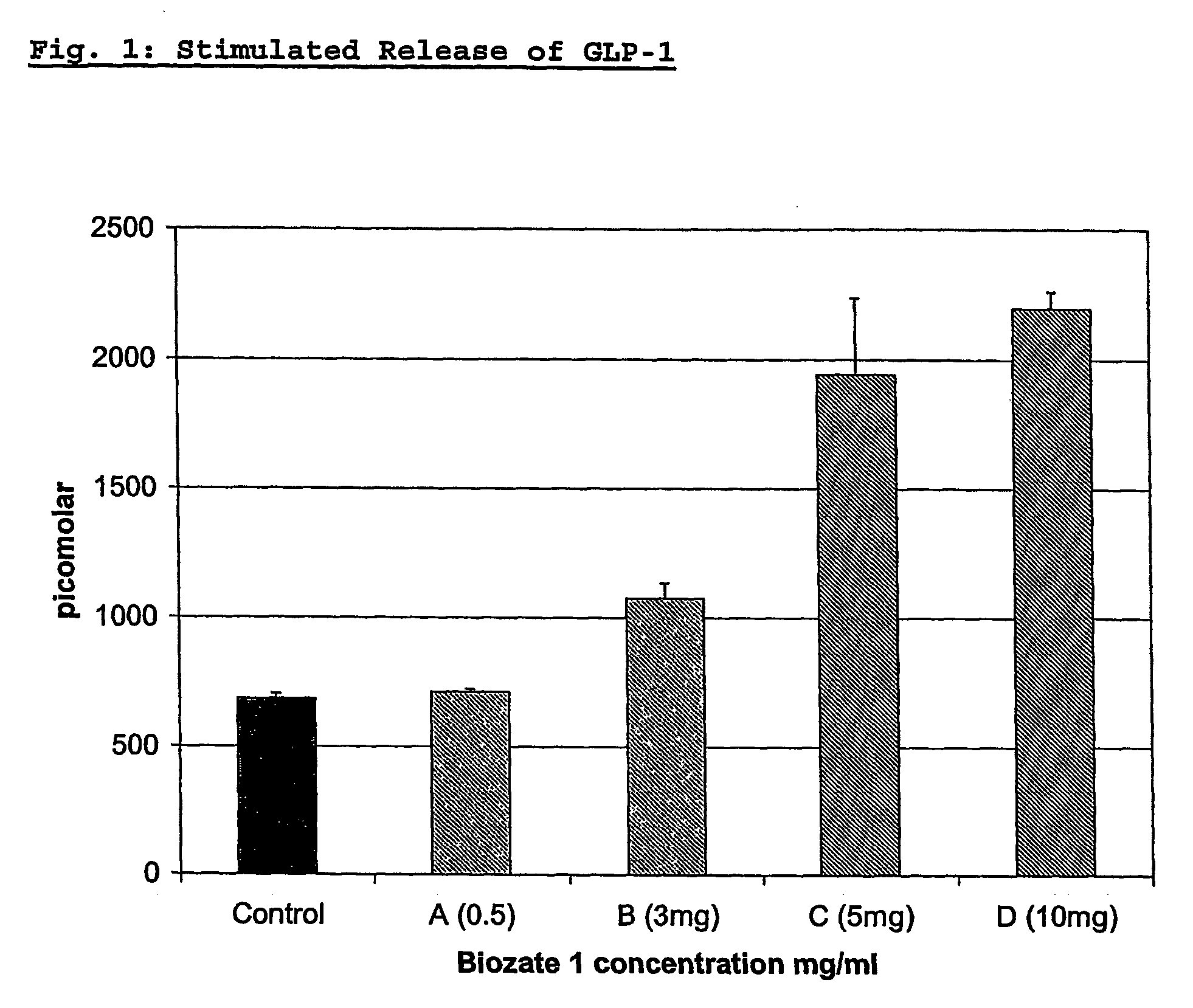
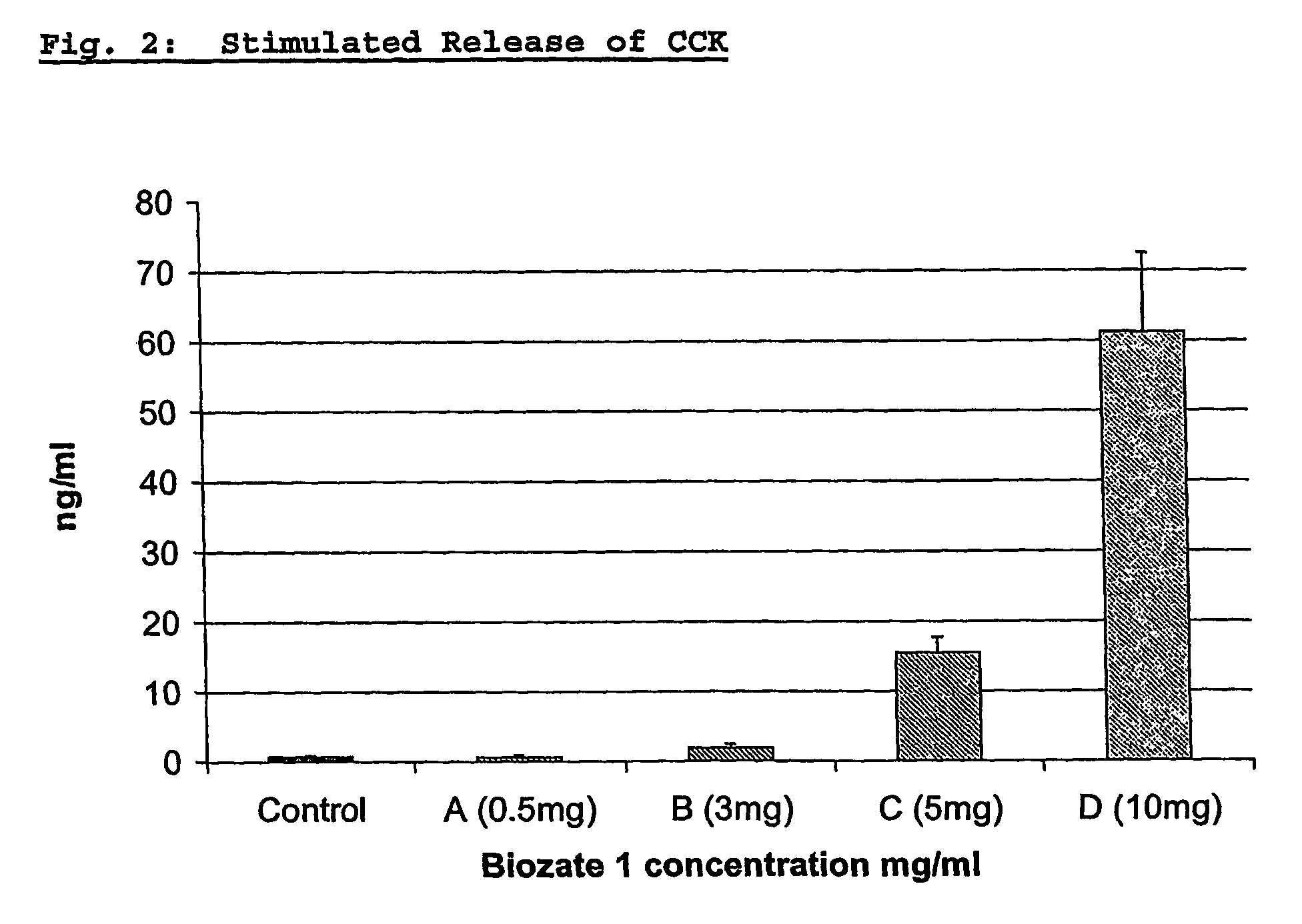
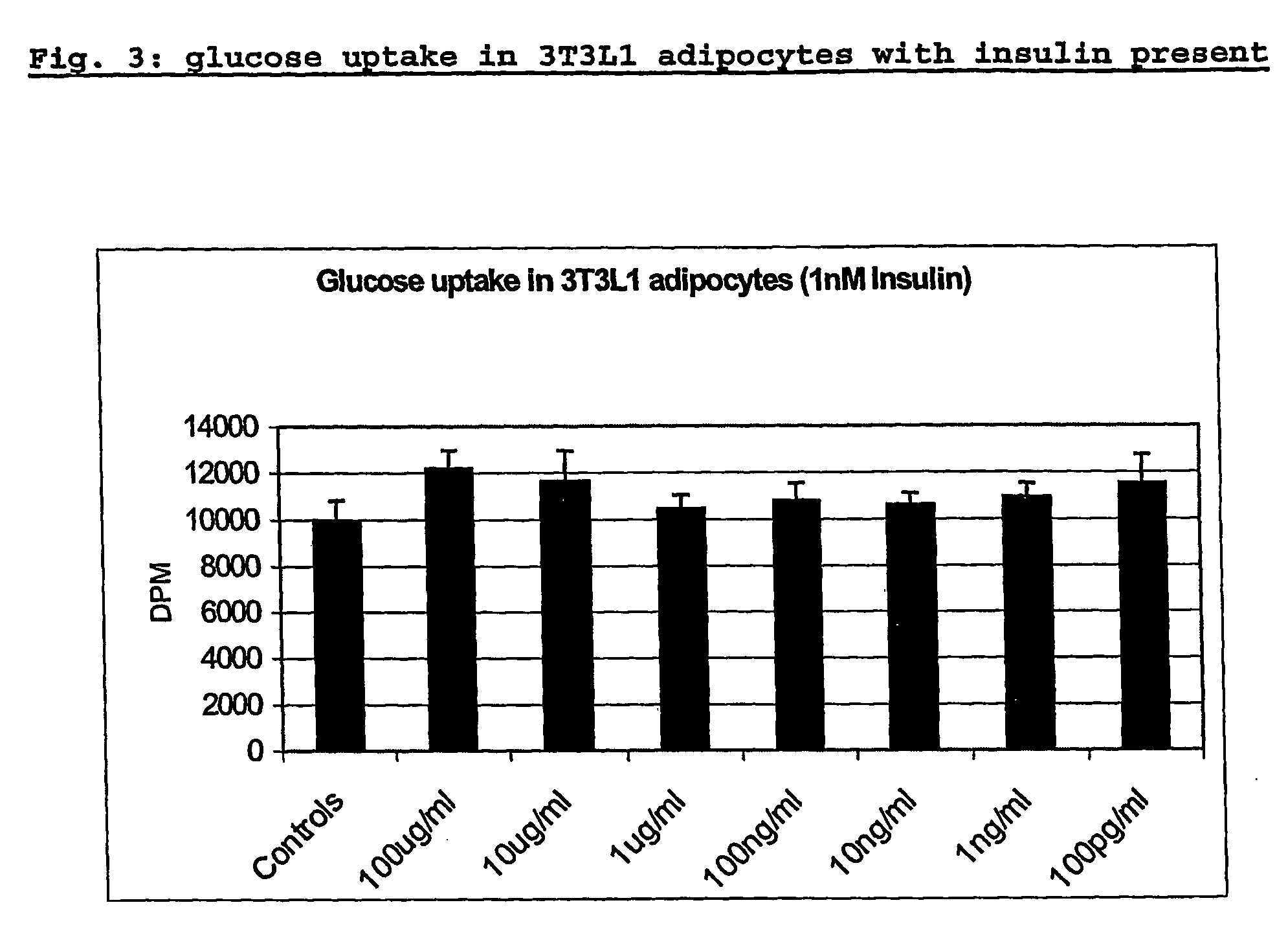
Blood glucose regulating composition
InactiveUS20060171992A1Aids in blood glucose regulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineWhey protein
The invention provides the use of a whey protein hydrolysate in an edible composition the whey protein hydrolysate being able to induce the cellular release of glucagon-like-peptides and cholecystokinins and / or increasing glucose uptake in target tissues, wherein the whey protein hydrolysate regulates blood glucose levels or results in, or is used for, improving or preventing decline in mental performance and / or for providing a sustained feeling of energy and / or for maintaining or providing a feeling of well-being during the post-prandial period in a subject consuming the composition.
Owner:UNILEVER BESTFOODS NORTH AMERICA DIV OF CONOPCO
Use of a chemically modified starch product
InactiveUS20060025381A1Reducing initial acute elevationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlucose polymersD-Glucose
The present invention relates to the use of a chemically modified starch to control and / or regulate the blood glucose level of mammals and post-prandial absorption. Such chemically modified starches, when properly formulated into foods, may be used to provide the consumer with glucose over an extended time period and more constant glucose levels.
Owner:BRUNOB II BV
Method for altering insulin pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20060264886A9Increase in hypoglycemic eventImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderClinical efficacySubcutaneous insulin
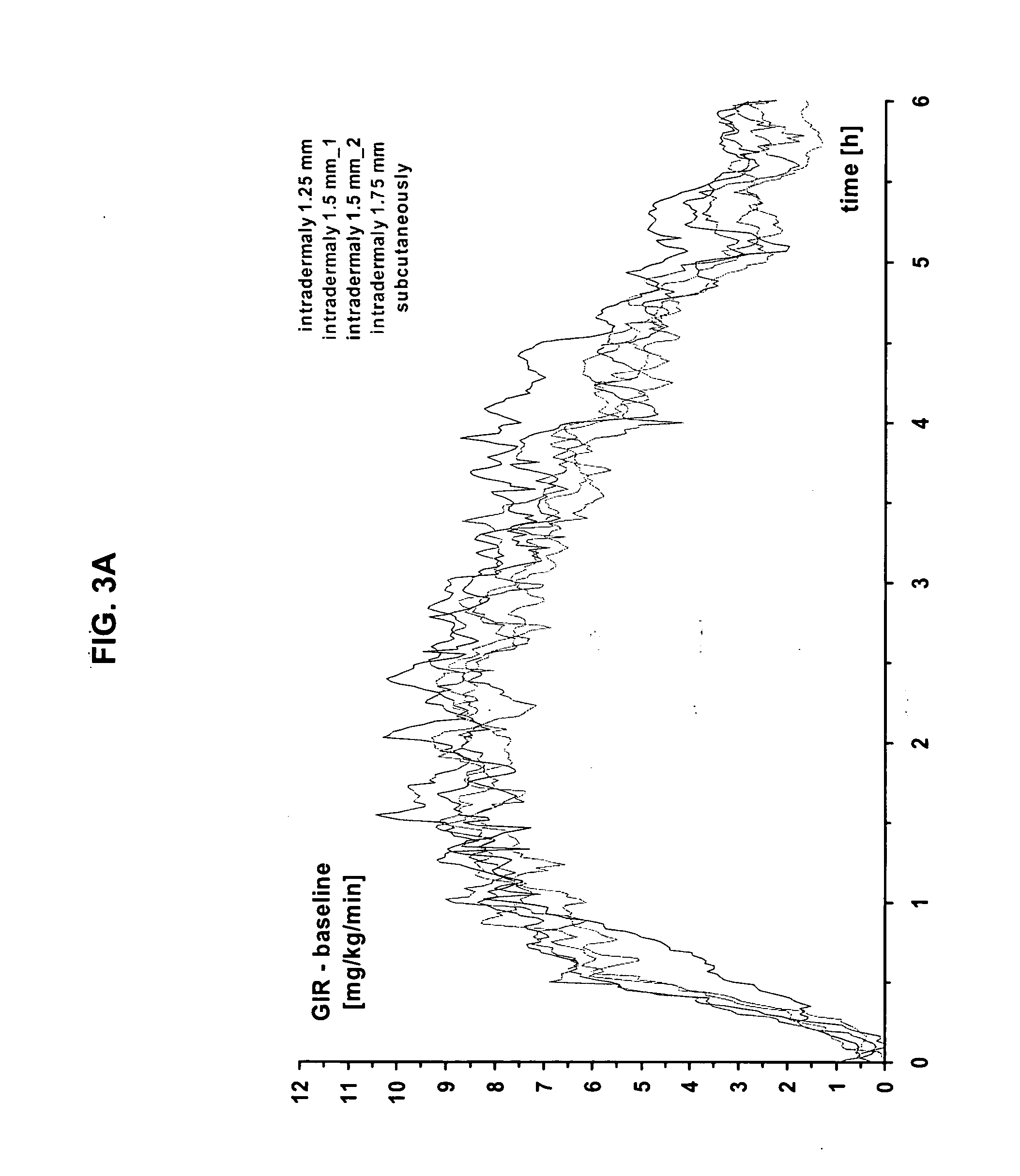
The present invention relates to methods for administration of insulin into the intradermal compartment of subject's skin, preferably to the dermal vasculature of the intradermal compartment. The methods of the present invention enhance the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of insulin delivery and effectively result in a superior clinical efficacy in the treatment and / or prevention of diabetes mellitus. The methods of the instant invention provide an improved glycemic control of both non-fasting (i.e., post-prandial) and fasting blood glucose levels and thus have an enhanced therapeutic efficacy in treatment, prevention and / or management of diabetes relative to traditional methods of insulin delivery, including subcutaneous insulin delivery.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Chromium/biotin treatment of dyslipidemia and diet-induced post prandial hyperglycemia
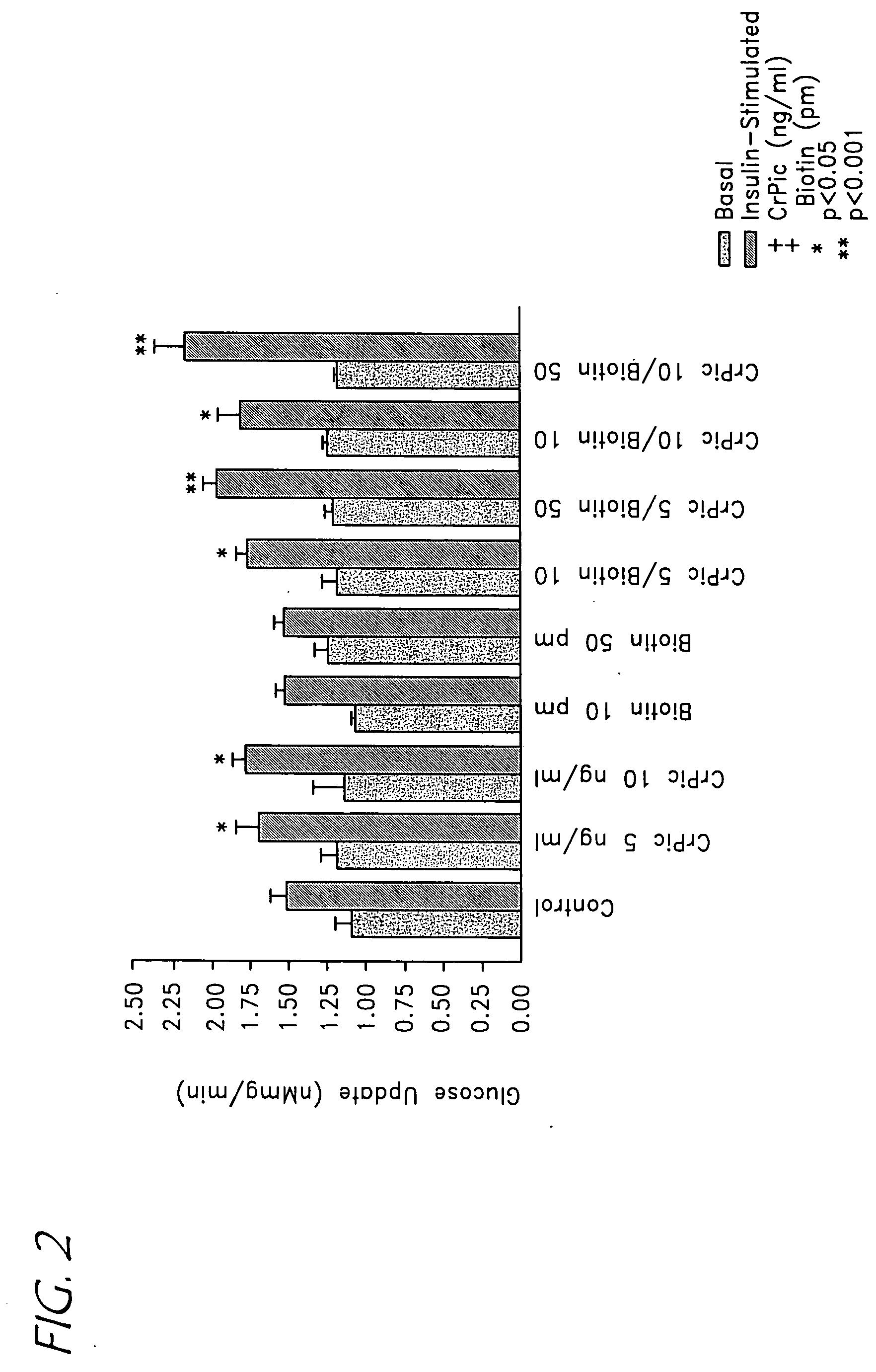
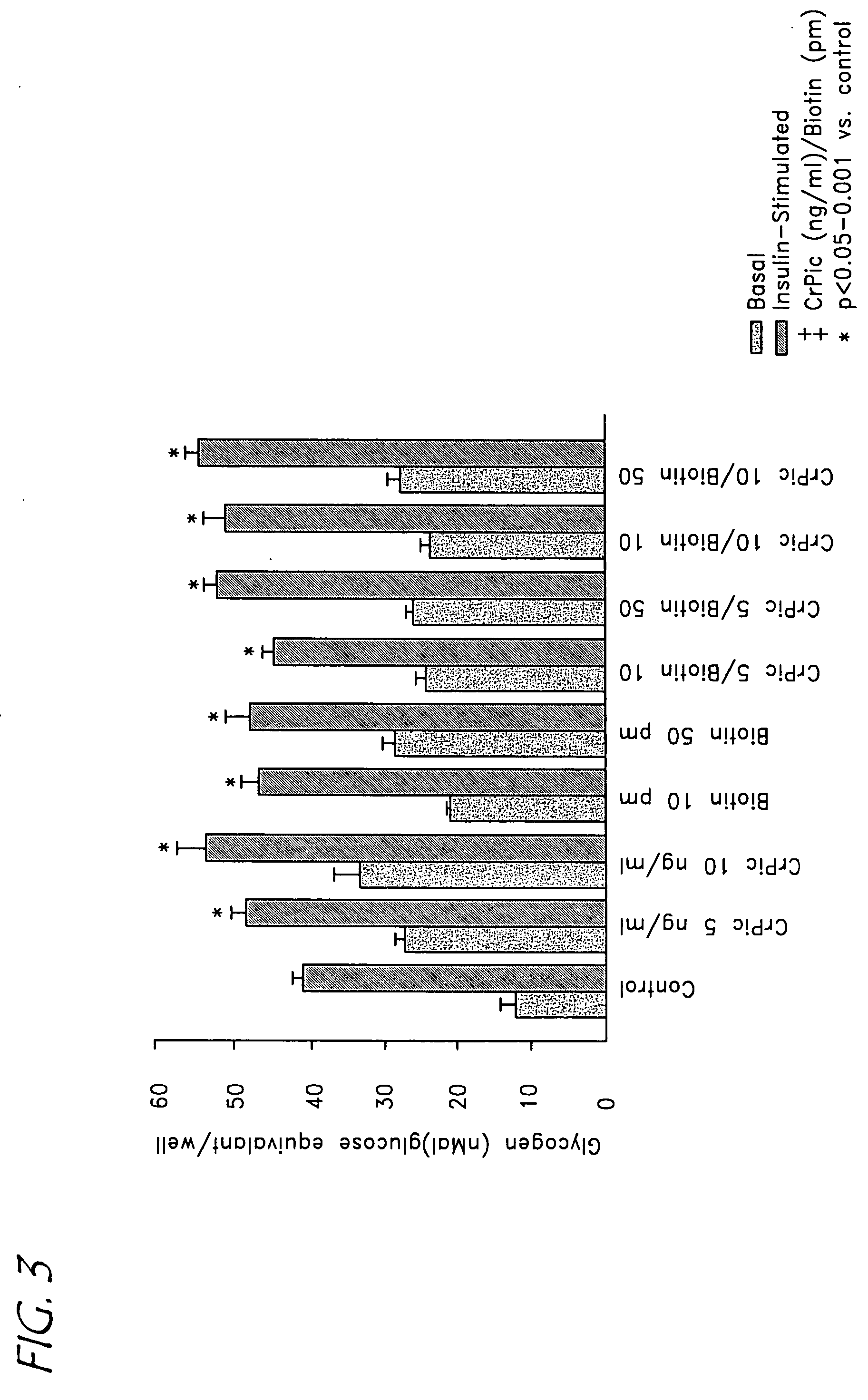
InactiveUS20050214385A1Reducing post prandial hyperglycemiaReduce post-prandial hyperglycemiaHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAcute hyperglycaemiaDyslipidemia
A method for treating dyslipidemia and / or post prandial hyperglycemia by administering a combination of a chromium complex and biotin to an individual in need thereof is disclosed. The two compounds are administered orally or parenterally in daily dosages which provide between 25 μg and 1,000 μg of chromium and between 25 μg and 20 mg biotin. A method for reducing the glycemic index of food is similarly provided.
Owner:JDS THERAPEUTICS
Methods for manipulating upper gastrointestinal transit, blood flow, and satiety, and for treating visceral hyperalgesia
InactiveUS20050014693A1Reduced sensationImprove bioavailabilityCompounds screening/testingAntibacterial agentsAdministered substanceMammal
Disclosed is a method of manipulating the rate of upper gastrointestinal transit of a substance in a mammal. Also disclosed are methods of manipulating satiety and post-prandial visceral blood flow. A method of treating visceral pain or visceral hypersensitivity in a human subject is also described. A method for prolonging the residence time of an orally or enterally administered substance by promoting its dissolution, bioavailability and / or absorption in the small intestine is also described. These methods are related to a method of transmitting to and replicating at a second location in the central nervous system a serotonergic neural signal originating at a first location in the proximal or distal gut of a mammal and / or a method of transmitting to and replicating at a second location in the upper gastrointestinal tract a serotonergic neural signal originating at a first location in the proximal or distal gut.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
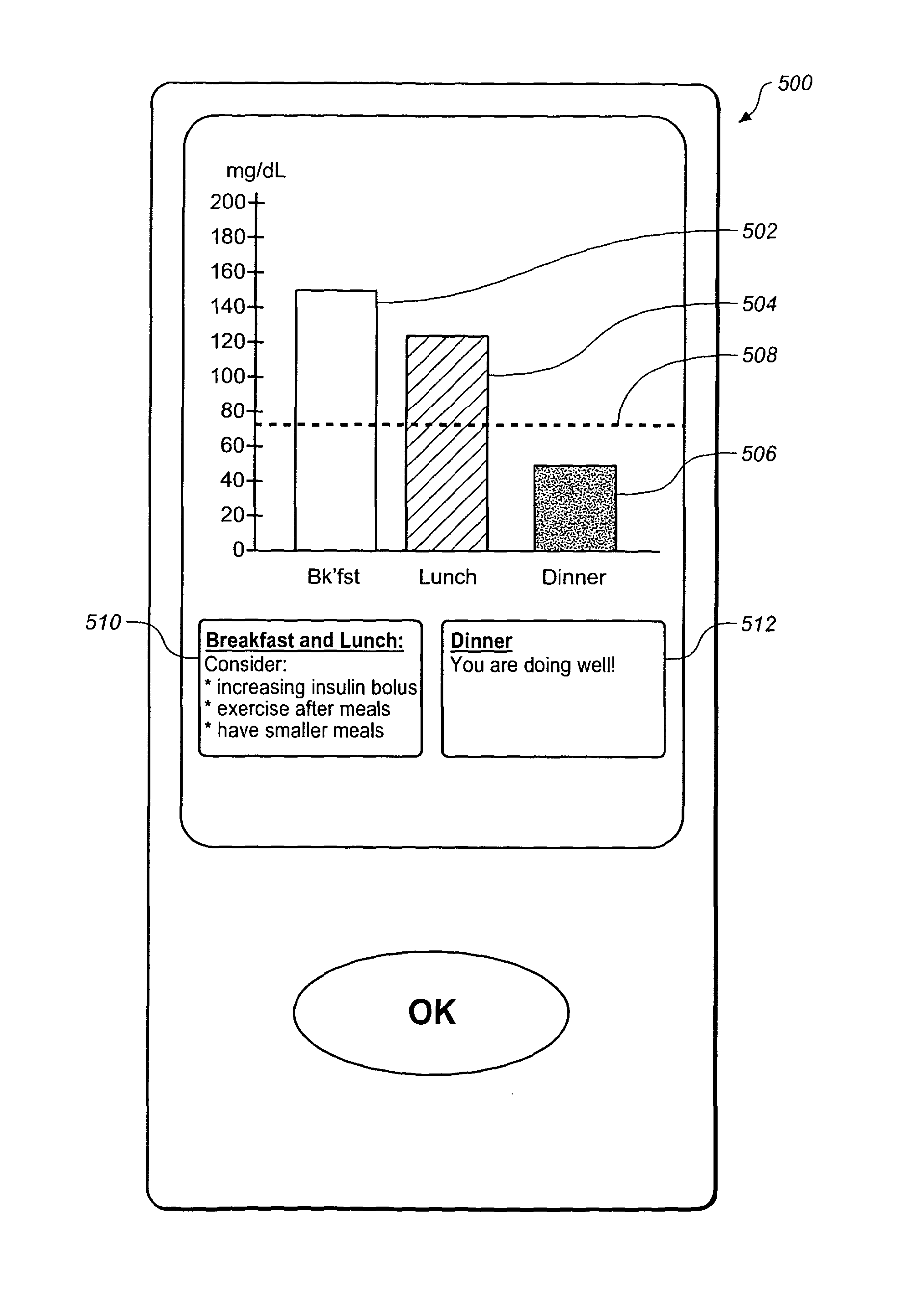
Method, system and device to ensure statistical power for average pre and post-prandial glucose difference messaging
A diabetes management system and method are provided herein that may be used to analyze a patient's level of control of their diabetes, by looking at the difference between blood glucose measurements taken before and after a meal. If the standard deviation of the differences D calculated between pre- and post-prandial results is found to vary significantly from a predetermined threshold value, then a message or graphical indication may be displayed to the user. Messages may provide suggestions to the user as to ways to better manage their condition to ensure compliance of any prescribed diabetes regimen or to guide the patient in managing their diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN SCOTLAND
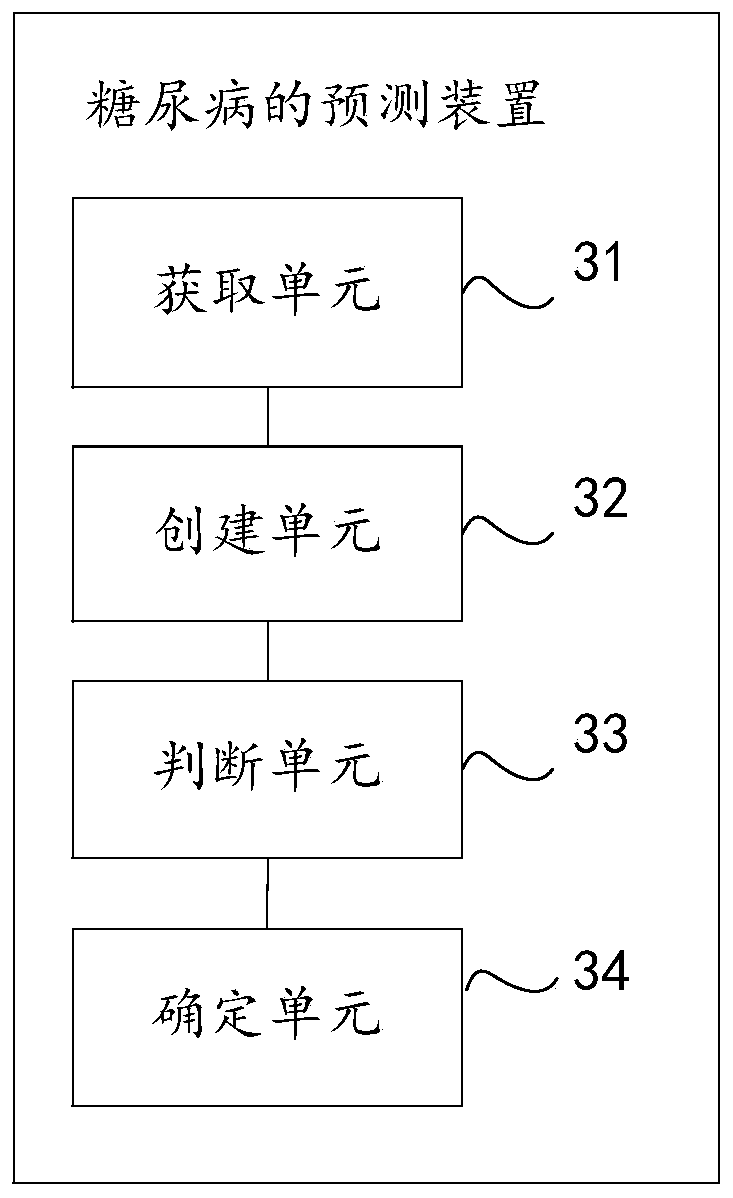
Method and device for predicting diabetes, storage medium, and computer device
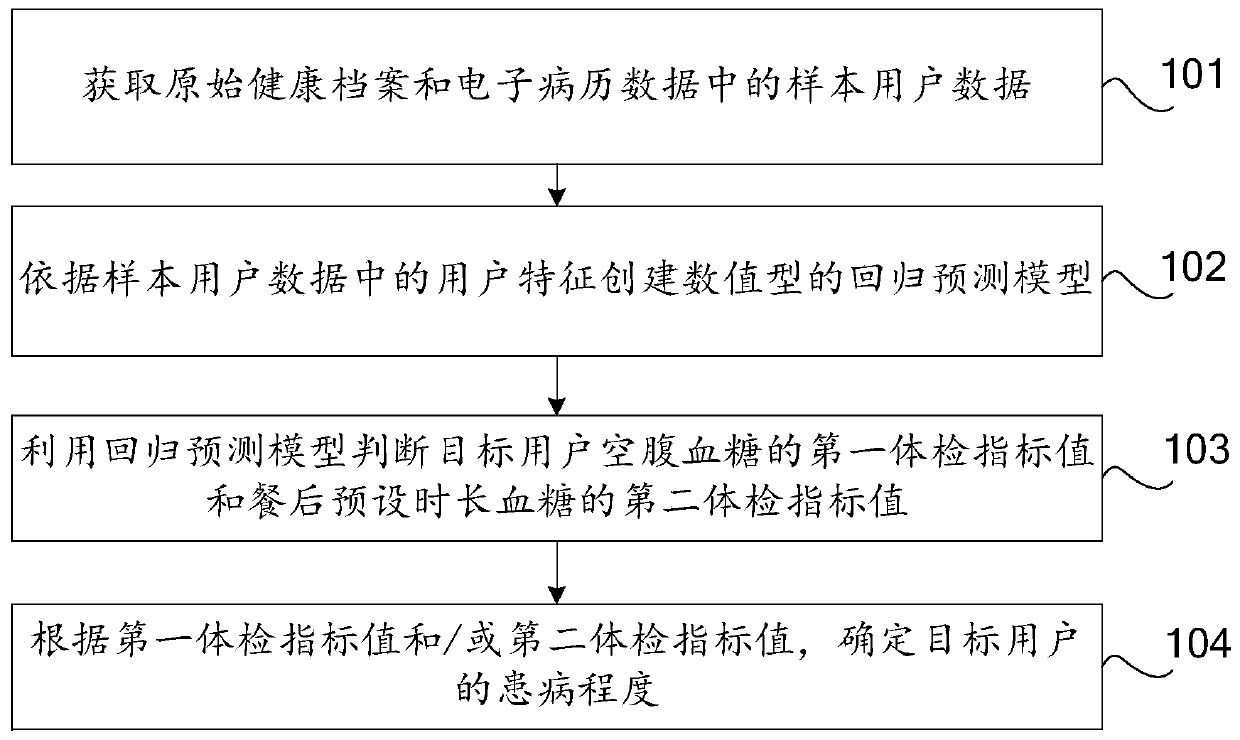
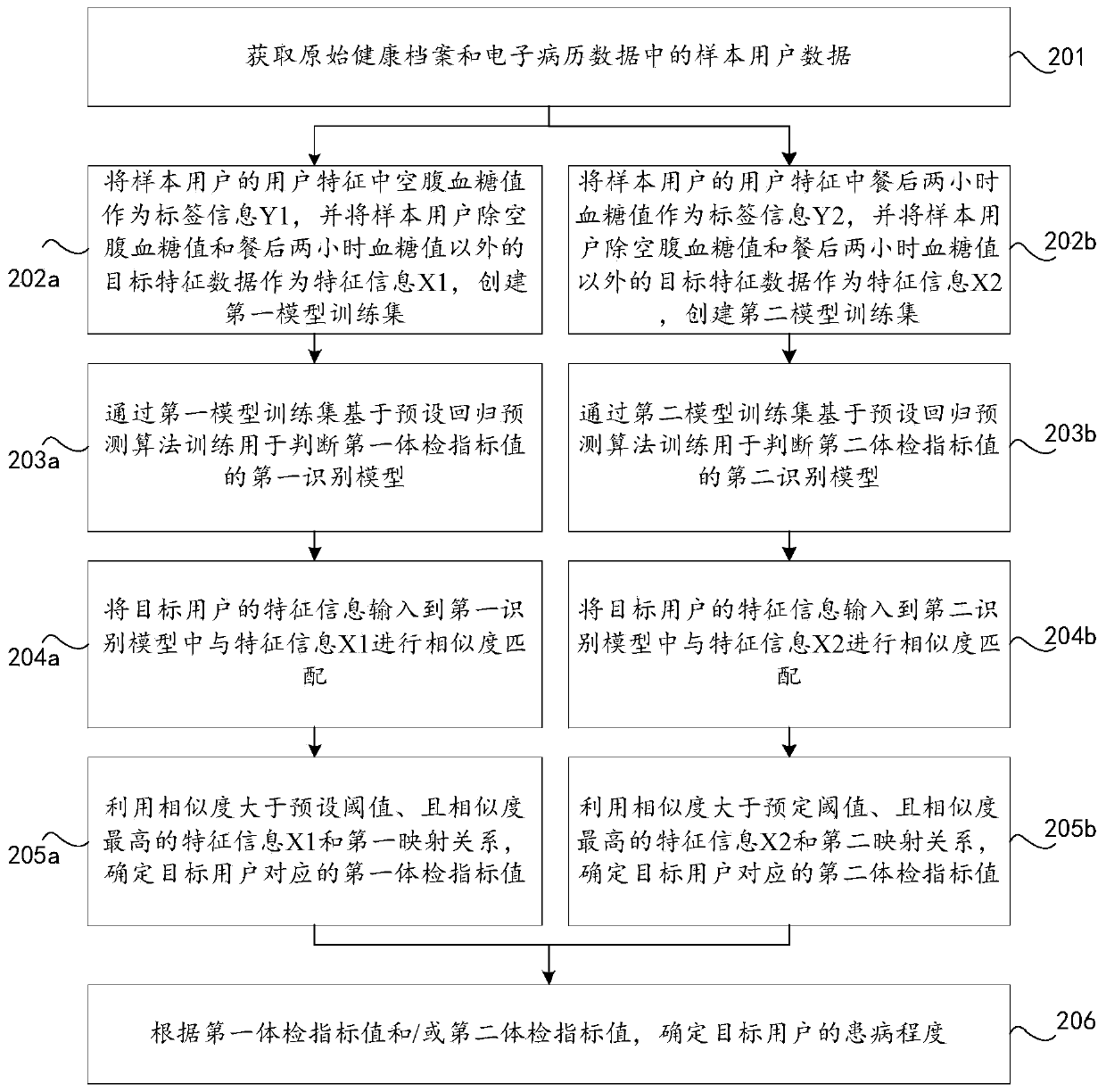
PendingCN110197720AJudging the degree of illnessMedical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical recordDisease
The invention discloses a method and device for predicting diabetes, a storage medium, and a computer device. The invention relates to the field of computer technology, and can effectively solve the problem that the prior art can only judge whether a user has diabetes but cannot judge the severity of the disease. The method includes: obtaining sample user data in an original health record and electronic medical record data; creating a numerical regression prediction model according to the user characteristics in the sample user data; using the regression prediction model to determine a first physical examination index value of the target user's fasting blood glucose and a second physical examination index value of the post-prandial preset duration blood glucose; and determining the degreeof illness of the target user according to the first physical examination index value and / or the second physical examination index value. This application applies to the prediction of diabetes and thedetermination of the extent of diabetes.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Use of a crosslinked or inhibited starch product
InactiveUS20060025382A1Reducing initial acute elevationBlood glucose levelBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlucose polymersD-Glucose
The present invention relates to the use of a starch which is crosslinked or inhibited to control and / or regulate the blood glucose level of mammals and post-prandial absorption. Such chemically modified starches, when properly formulated into foods, may be used to provide the consumer with glucose over an extended time period and more constant glucose levels.
Owner:BRUNOB II BV
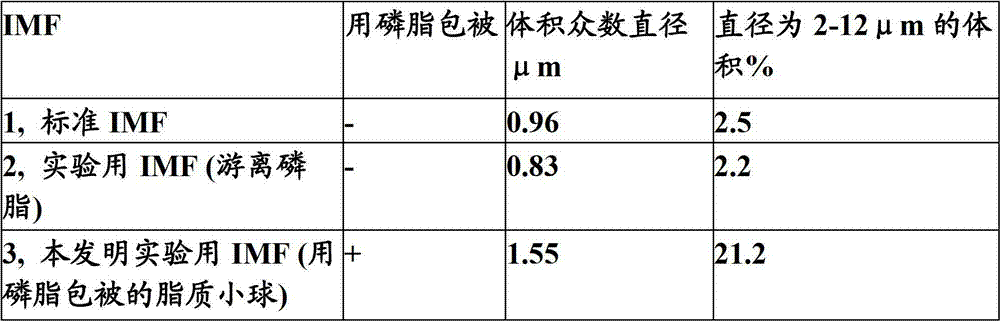
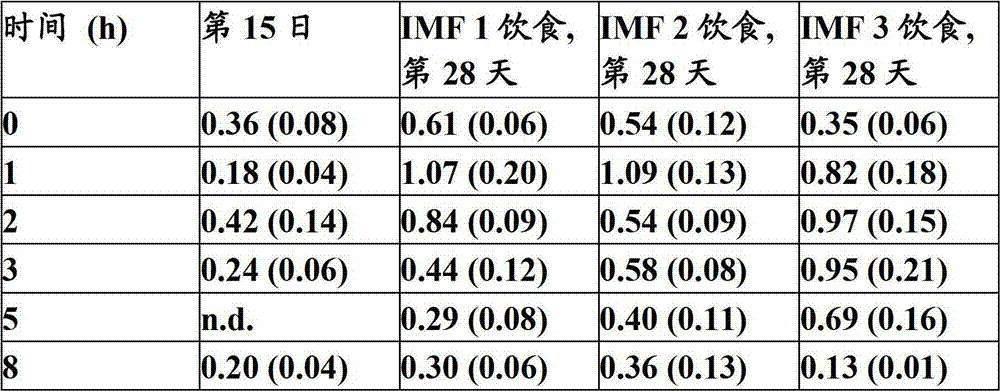
Modulation of post - prandial fat absorption
The invention relates to a method for programming the post-prandial fat handling in an infant by a nutritional composition comprising lipid globules coated with phospholipids.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
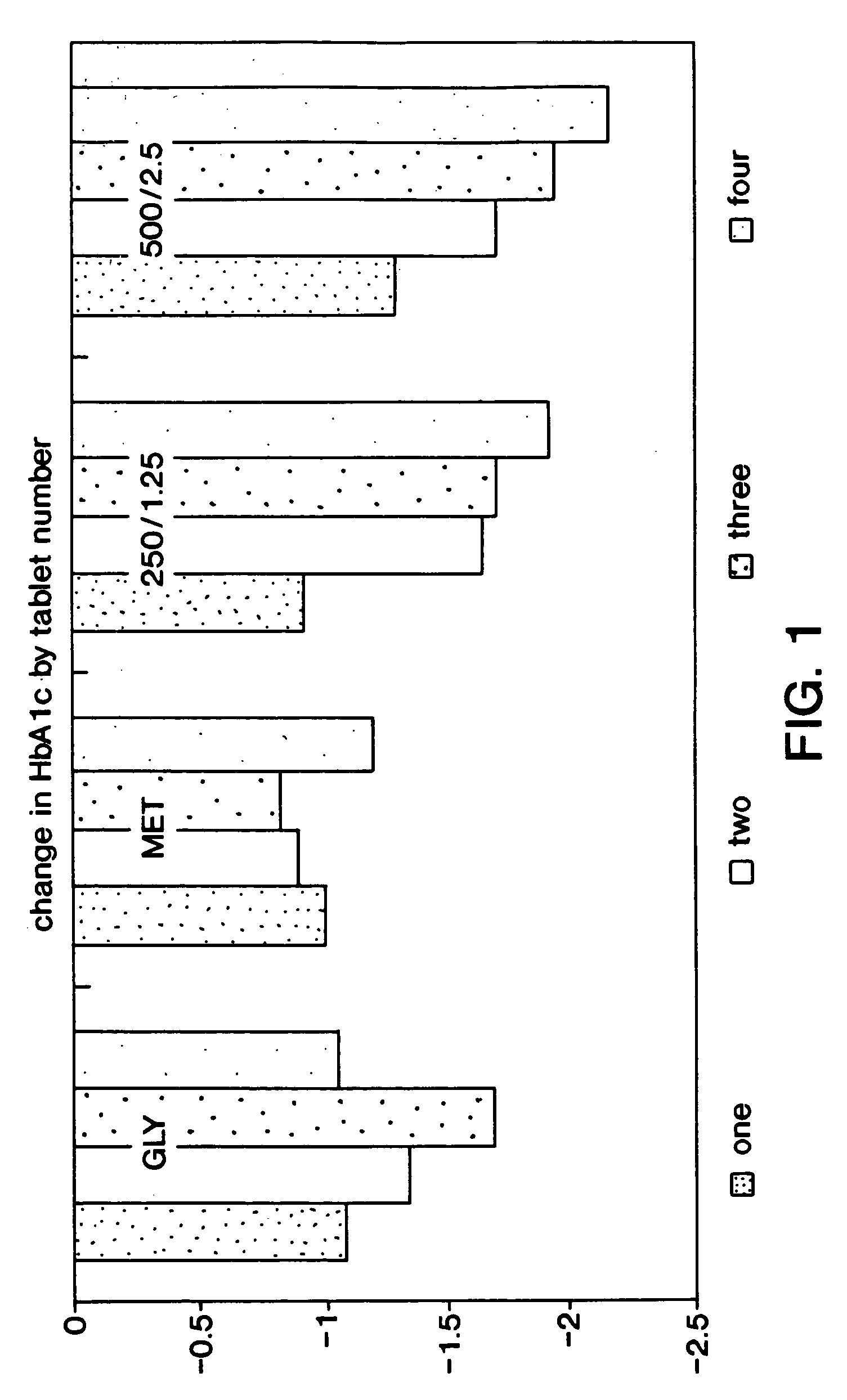
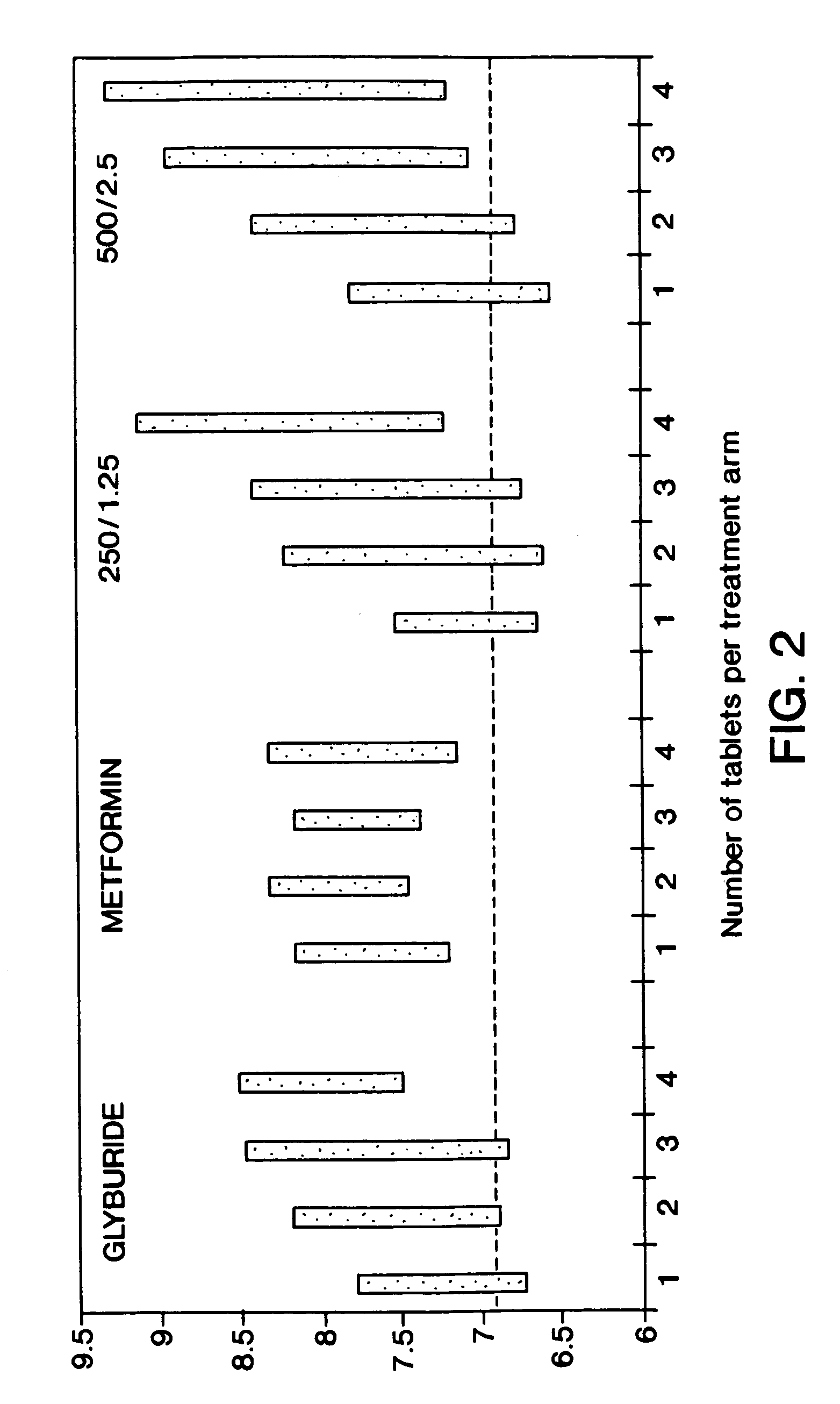
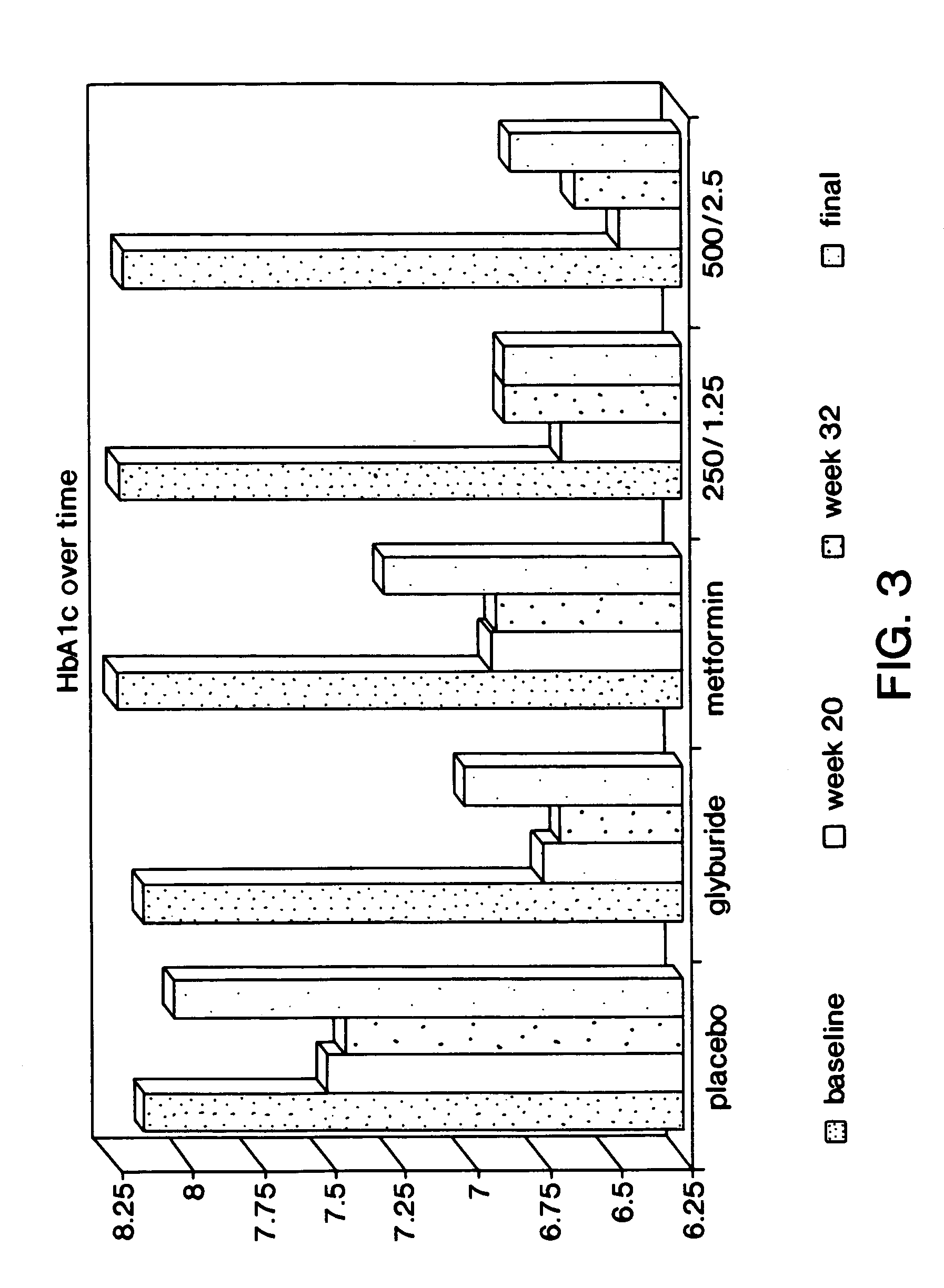
Method for treating diabetes
InactiveUS7598262B2Equivalent efficacy in treating diabetesEliminate side effectsBiocidePowder deliveryFirst line treatmentThird-line therapy
A method is provided for first line treatment of type 2 diabetes employing a combination of metformin and glyburide. A method for treating diabetes in drug naive human patients is also provided employing the above formulation to reduce insulin resistance and / or post-prandial glucose excursion and / or hemoglobin 1Ac, and / or increase post-prandial insulin, thereby treating the diabetes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
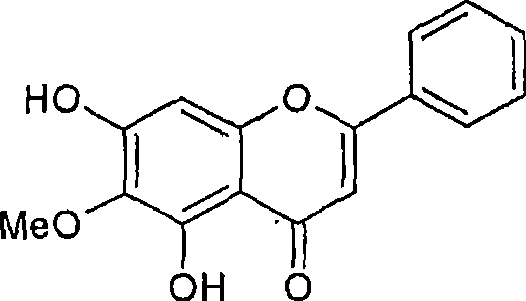
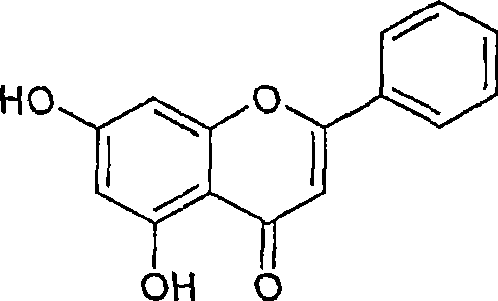
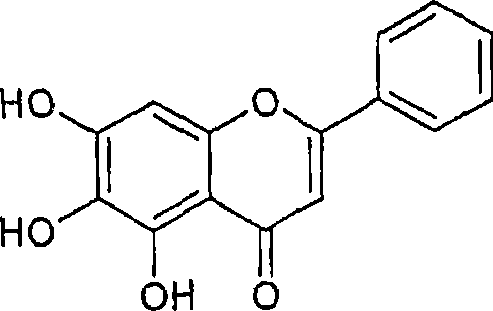
Intestinal alpha-glucosidase inhibitors and a process for the isolation and use thereof
This invention provides a-glucosidase inhibitors isolated from Oroxylum indicum an Indian medicinal plant. Particularly, this invention provides hexane and acetone fraction of Oroxylum indicum wherein the hexane fraction comprises a-glucosidase active compounds of oroxylin A, chrysin and baicalain and acetone fraction comprises the compounds of oroxylin A, chrysin, baicalain, methoxy chrysin and oroxyloside methyl ester. This invention also relates to a process for the isolation of a-glucosidase inhibitory active compounds from the above said hexane and acetone fraction of Oroxylum indicum. This invention also provides the use of potent intestinal a-glucosidase inhibitors as active ingredients that can be used in pharmaceuticals, food products, health foods and specialized health care foods as anti hyperglycemic agent for prevention and treatment of post prandial hyperglycemia, hyperglycemia and related conditions in diabetes mellitus, obesity and disease conditions requiring hyperglycemic control as well as inhibition of a-glucosidase activity.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
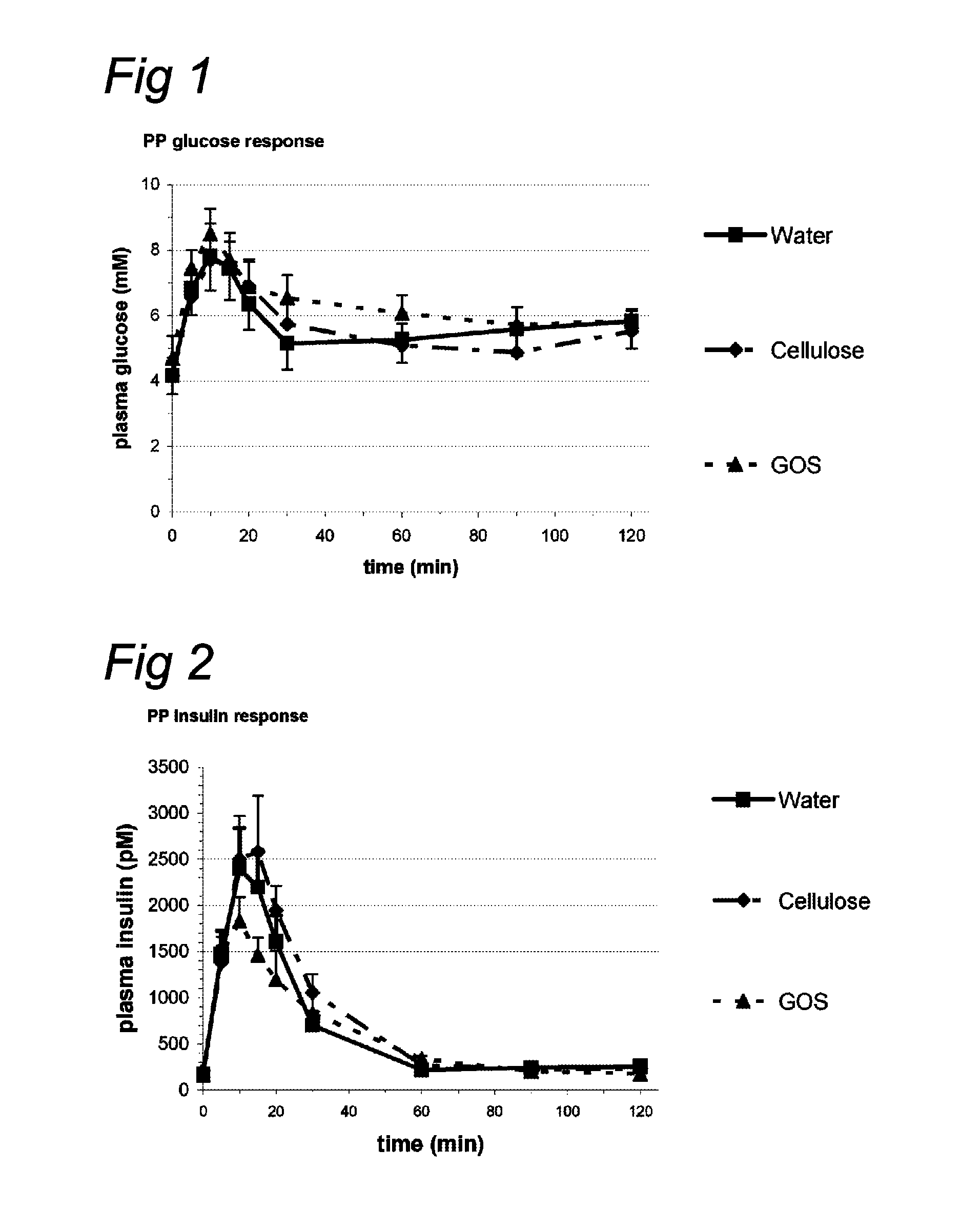
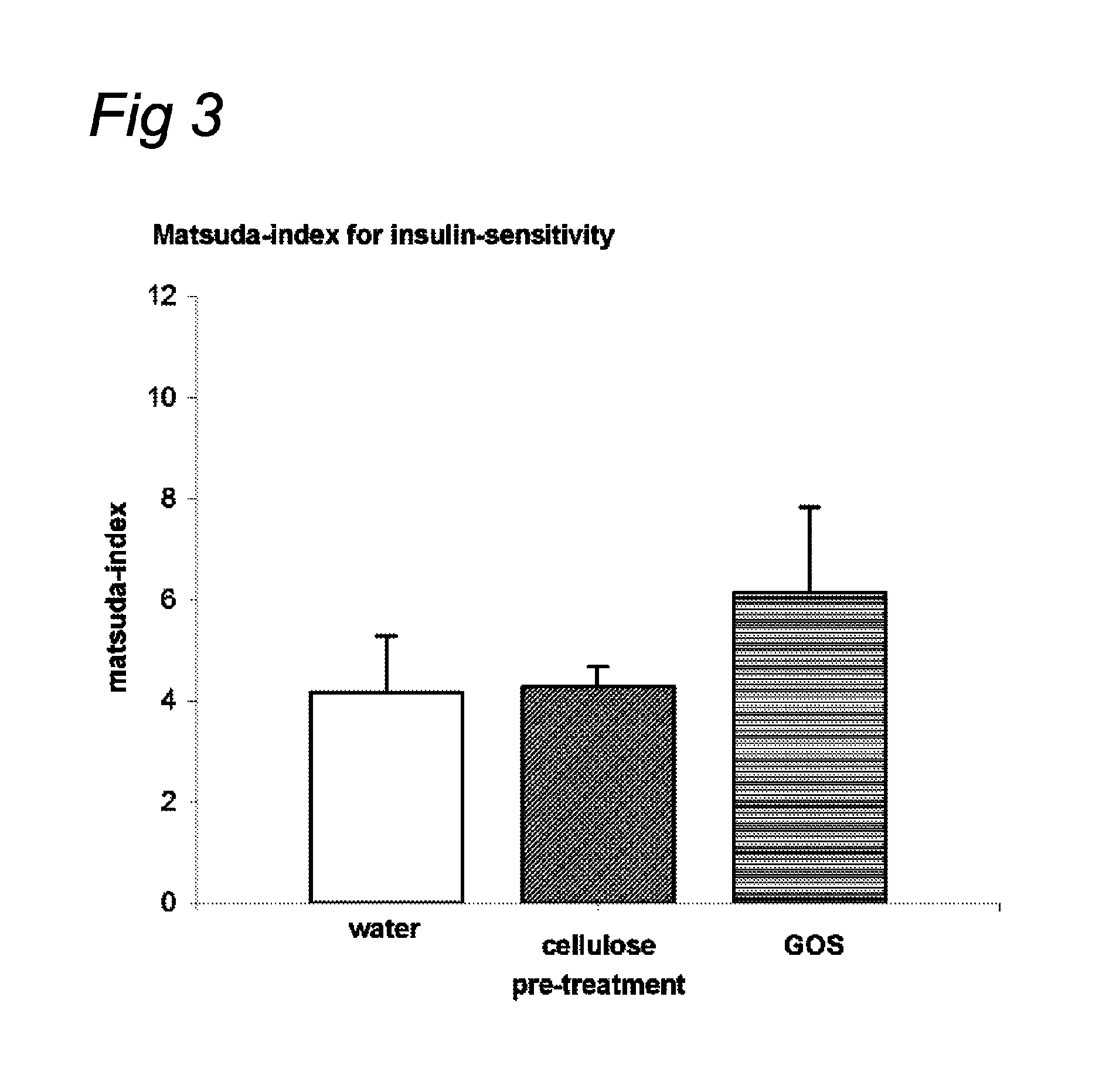
Nutritional products comprising saccharide oligomers
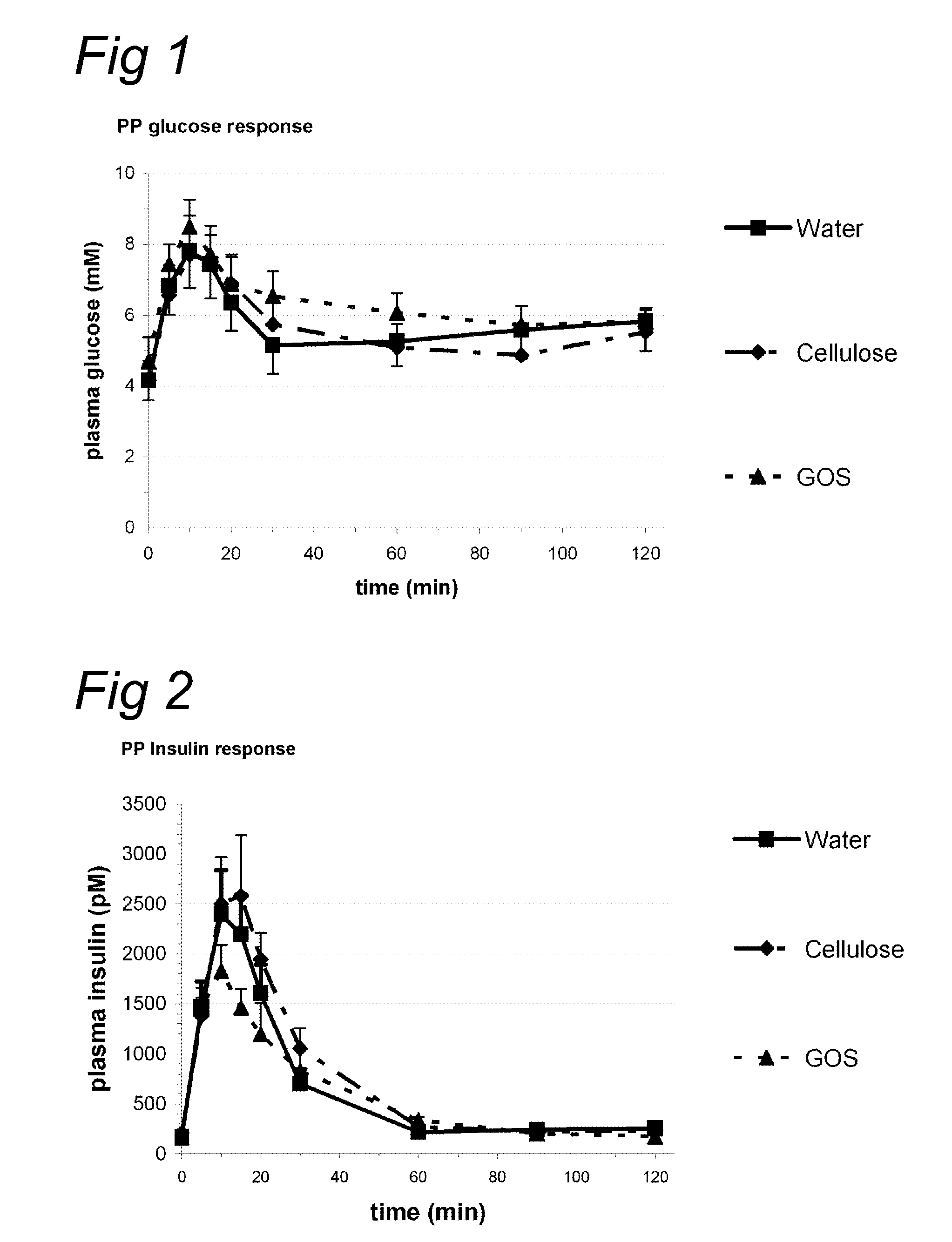
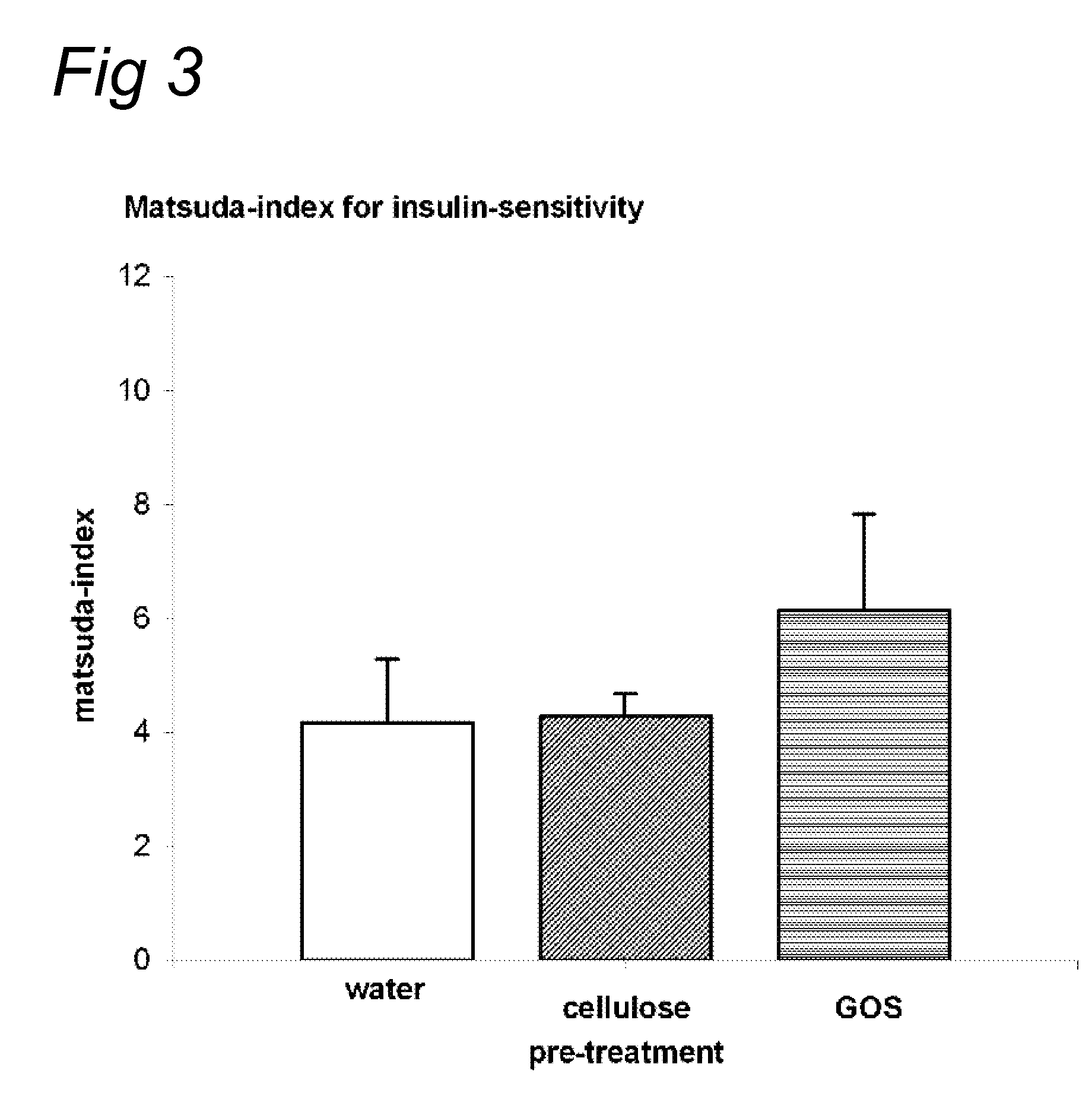
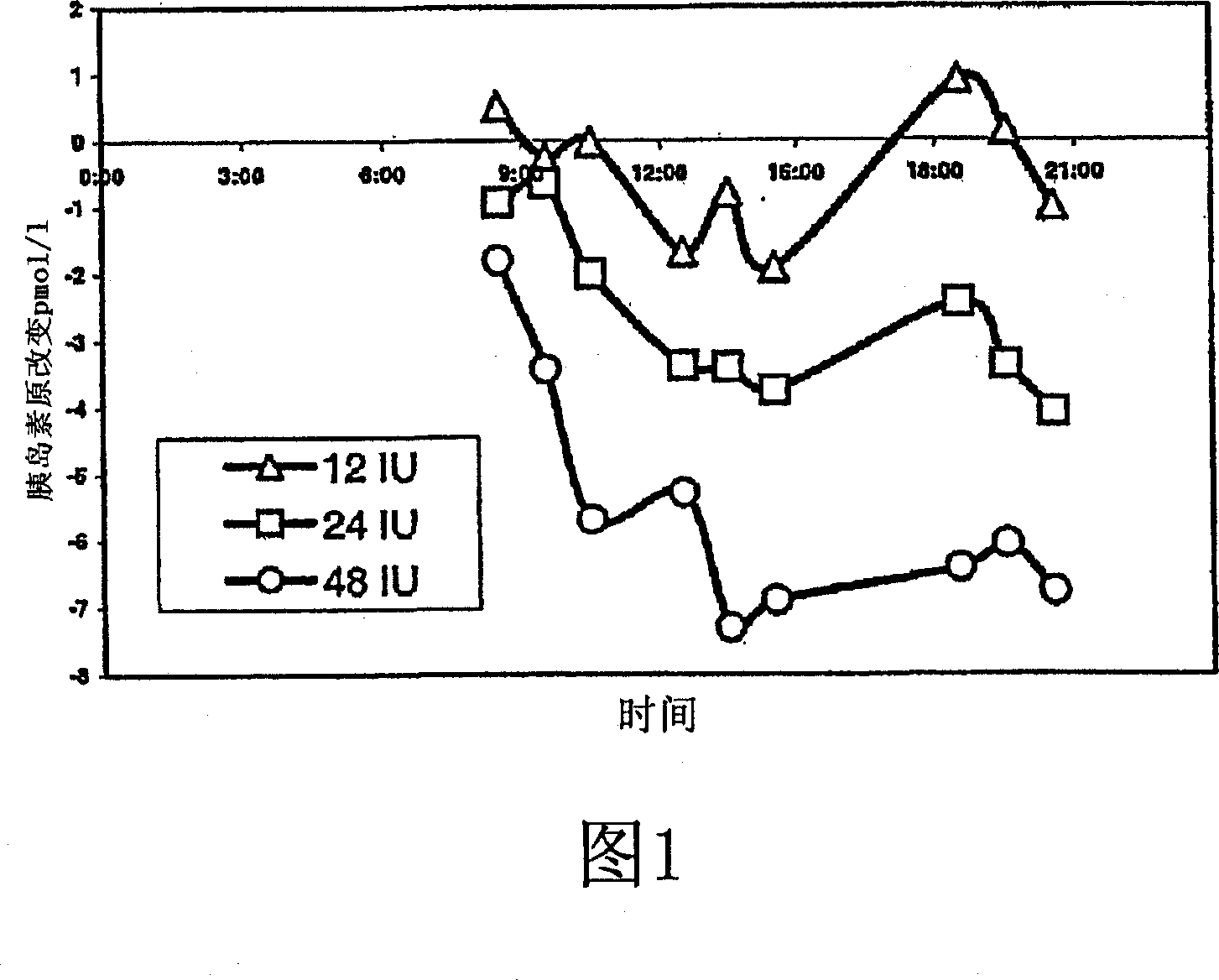
InactiveUS20100069327A1Increase insulin sensitivityLonger effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPost-prandialGlycemic
Indigestible oligosaccharides having a molecular weight of 450 Da to 3700 Da are used for the improvement of insulin resistance, the prevention of post-prandial glycaemic dip, and / or the decrease of the post-prandial glucose response of a meal, which is consumed within 72 hours after the consumption of the first product. The oligo-saccharides are especially galacto-oligosaccharides, and are advantageously administered a few hours prior to having the meal.
Owner:NUTRICIA
Method of reducing serum proinsulin levels in type 2 diabetics
InactiveCN101027082AIncrease inhalationLarge particle sizePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseSerum ige
Methods are provided for reducing serum proinsulin levels, lessening post-prandial pancreatic stress, and reducing risk factors for atherosclerosis in subjects with diabetes mellitus, type 2. The method includes administration of insulin in a manner that mimics the meal-related first phase insulin response, using a dose sufficient to reduce serum levels of proinsulin. In some embodiments of the method insulin administration is commenced early in the course of the disease. Mimicking first phase kinetics, peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 18 minutes of administration. In increasingly preferred embodiments peak serum insulin levels can be reached within about 15, 12, or 10 minutes of administration. Serum insulin levels return to baseline within about two hours of administration.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
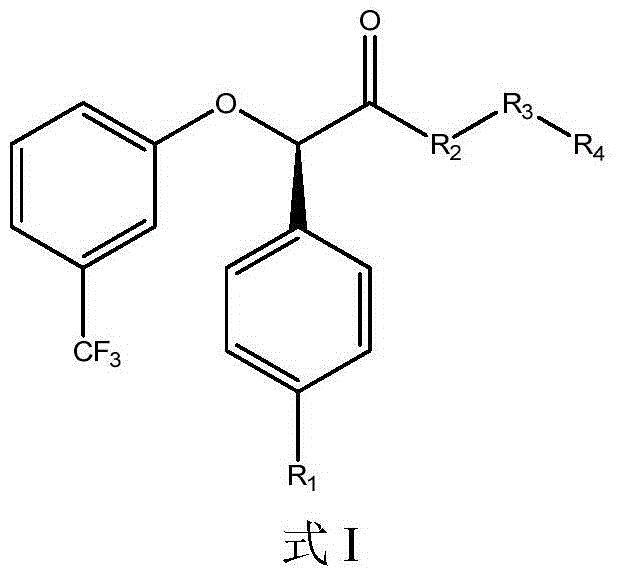
Compositions and methods for the treatment of metabolic syndrome
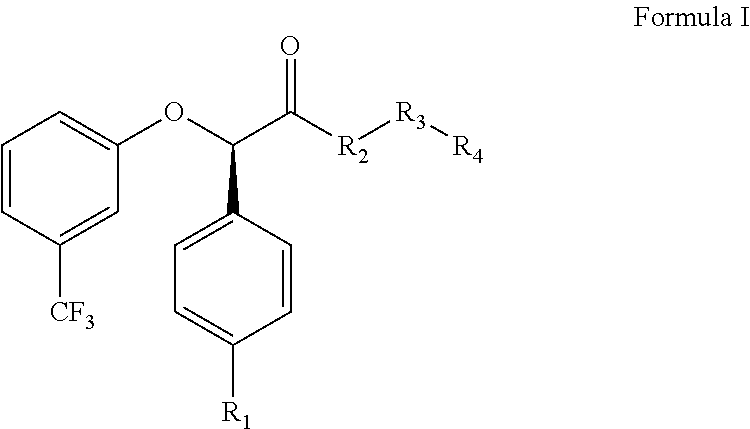
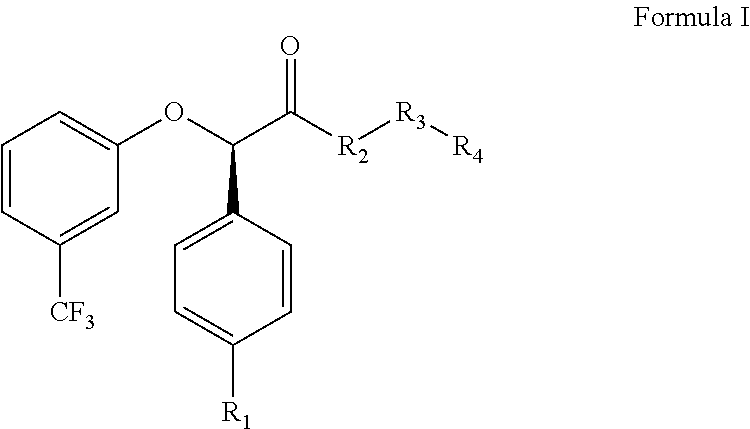
The invention relates to the compounds of formula (I) or its pharmaceutical acceptable salts, as well as polymorphs, solvates, enantiomers, stereoisomers and hydrates thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of compounds of formula (I), and methods for the treatment of metabolic syndrome may be formulated for oral, buccal, rectal, topical, transdermal, transmucosal, intravenous, parenteral administration, syrup, or injection. Such compositions may be used to treatment of hyperuricemia, gout; dyslipidemia, obesity, urea cycle disorders, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, microvascular complications,.macrovascular complications, lipid disorders, prediabetes., obesity, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, stroke, neuropathy, renal complications, hypertriglyceridemia, cardiovascular complications, and post prandial hyperglycemia.
Owner:CELLIXBIO PTE LTD
Method, system and device to ensure statistical power for average pre and post-prandial glucose difference messaging
InactiveUS20130277233A1Analysis is limitedEasy to manageMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementRegimenDiabetes management
A diabetes management system and method are provided herein that may be used to analyze a patient's level of control of their diabetes, by looking at the difference between blood glucose measurements taken before and after a meal. If the standard deviation of the differences D calculated between pre- and post-prandial results is found to vary significantly from a predetermined threshold value, then a message or graphical indication may be displayed to the user. Messages may provide suggestions to the user as to ways to better manage their condition to ensure compliance of any prescribed diabetes regimen or to guide the patient in managing their diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Neurotoxin therapy for postprandial hyperglycemia
InactiveUS20100104602A1Effectively treating obesityImpair gastricBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaSmooth muscle
Botulinum toxin is increasingly being injected into visceral smooth muscle for a variety of indications. The present invention discloses intragastric administration of botulinum toxin to delay gastric emptying with the aim of inducing satiety and promoting weight-loss. The present invention also discloses the effects of intragastric administration of Botulinum toxin in reducing post-prandial hyperglycemia in patients suffering from Diabetes Mellitus.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of detection of clinically significant post-prandial hyperglycemia in normoglycemic patients
InactiveUS20140200178A1High riskReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood lipidsPost-prandial
This invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of or likelihood of a patient of developing occult pancreatic beta cell dysfunction, and a method for detecting the presence of or likelihood of a patient of developing clinically significant post-prandial hyperglycemia. The methods involve (a) measuring a level of alpha-hydroxybutyrate (AHB) in a single fasting baseline biological sample of the patient; (b) comparing the level of AHB in the single fasting baseline biological sample to a reference AHB level; and (c) determining the presence of or likelihood of developing the disorder in the patient based on the comparison in step (b). An increased AHB level at fasting baseline indicates that a normoglycemic, normo-insulinemic and / or non-dyslipidemic patient has developed or has an increased likelihood of developing occult pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. An increased AHB level at fasting baseline and an elevated glucose level of at least about 155 mg / dL at 30 minutes and / or 1 hour indicates that a normoglycemic, normo-insulinemic and / or non-dyslipidemic patient has developed or has an increased likelihood of developing clinically significant post-prandial hyperglycemia.
Owner:PRECISION DIABETES INC +1
Nutritional products comprising saccharide oligomers
InactiveUS8637487B2High clinical relevanceEasy to manufactureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOligomerMedicine
Indigestible oligosaccharides having a molecular weight of 450 Da to 3700 Da are used for the improvement of insulin resistance, the prevention of post-prandial glycaemic dip, and / or the decrease of the post-prandial glucose response of a meal, which is consumed within 72 hours after the consumption of the first product. The oligo-saccharides are especially galacto-oligosaccharides, and are advantageously administered a few hours prior to having the meal.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Apparatus and method for monitoring blood glucose levels including convenient diplay of blood glucose value average and constituent values
A method of presenting glucose data to a person with diabetes from a blood glucose meter is provided in which an effective meal average (EMA) value is presented, followed by two or more of the individual values that make up the EMA, to provide improved feedback data for clinical decisions by patients who need to alter their dose of insulin. The EMA can also comprise a measure of the variability of its constituent values. The EMA encompasses those values that occur at specified times such as 1 hour before and 1 hour after a specified meal time. The EMA is calculated over a limited number of days previous to the calculation (e.g., 3 days) and has a minimum number of values that must be obtained within the time and date ranges. An algorithm allows for exclusion of any given reading from the average (e.g., post-prandial or control solution readings). Patients can use 1 to 8 EMA on any given date range (e.g., preferably 4, that is, breakfast, lunch, supper and bedtime snack).
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Administration of a food composition product
InactiveUS20160136124A1Increase satietyReduce postprandial level of blood sugarBiocideDispersion deliveryEnvironmental healthFood composition data
Method for orally administrating a subject a food composition product, referred to as “Preload Meal,” before administering a main meal to the subject. The food composition product includes nutrients that stimulate the release of incretins in the subject prior to administration of the main meal, increasing satiety, lowering total energy intake from both the food composition product and the main meal, and contributing to a biological control of a post prandial blood sugar level and a post prandial insulin level in the subject.
Owner:INDEVEX AB
Compositions and methods for the treatment of metabolic syndrome
ActiveUS9321716B1Organic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaDyslipidemia
The invention relates to the compounds of formula I or its pharmaceutical acceptable salts, as well as polymorphs, solvates, enantiomers, stereoisomers and hydrates thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of compounds of formula I, and methods for the treatment of metabolic syndrome may be formulated for oral, buccal, rectal, topical, transdermal, transmucosal, intravenous, parenteral administration, syrup, or injection. Such compositions may be used to treatment of hyperuricemia, gout, dyslipidemia, obesity, urea cycle disorders, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, microvascular complications, macrovascular complications, lipid disorders, prediabetes, obesity, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, stroke, neuropathy, renal complications, hypertriglyceridemia, cardiovascular complications, and post prandial hyperglycemia.
Owner:CELLIXBIO PTE LTD
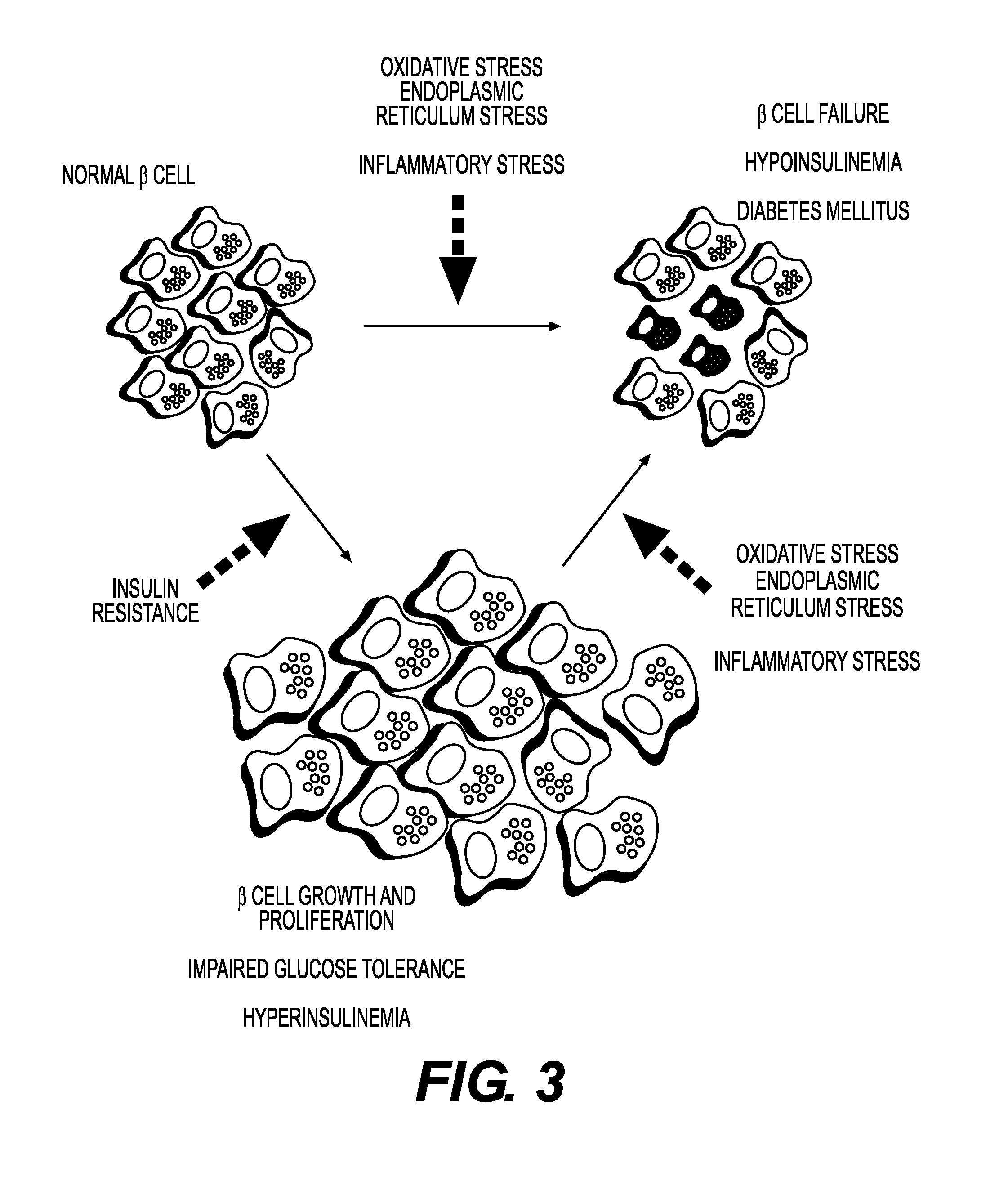
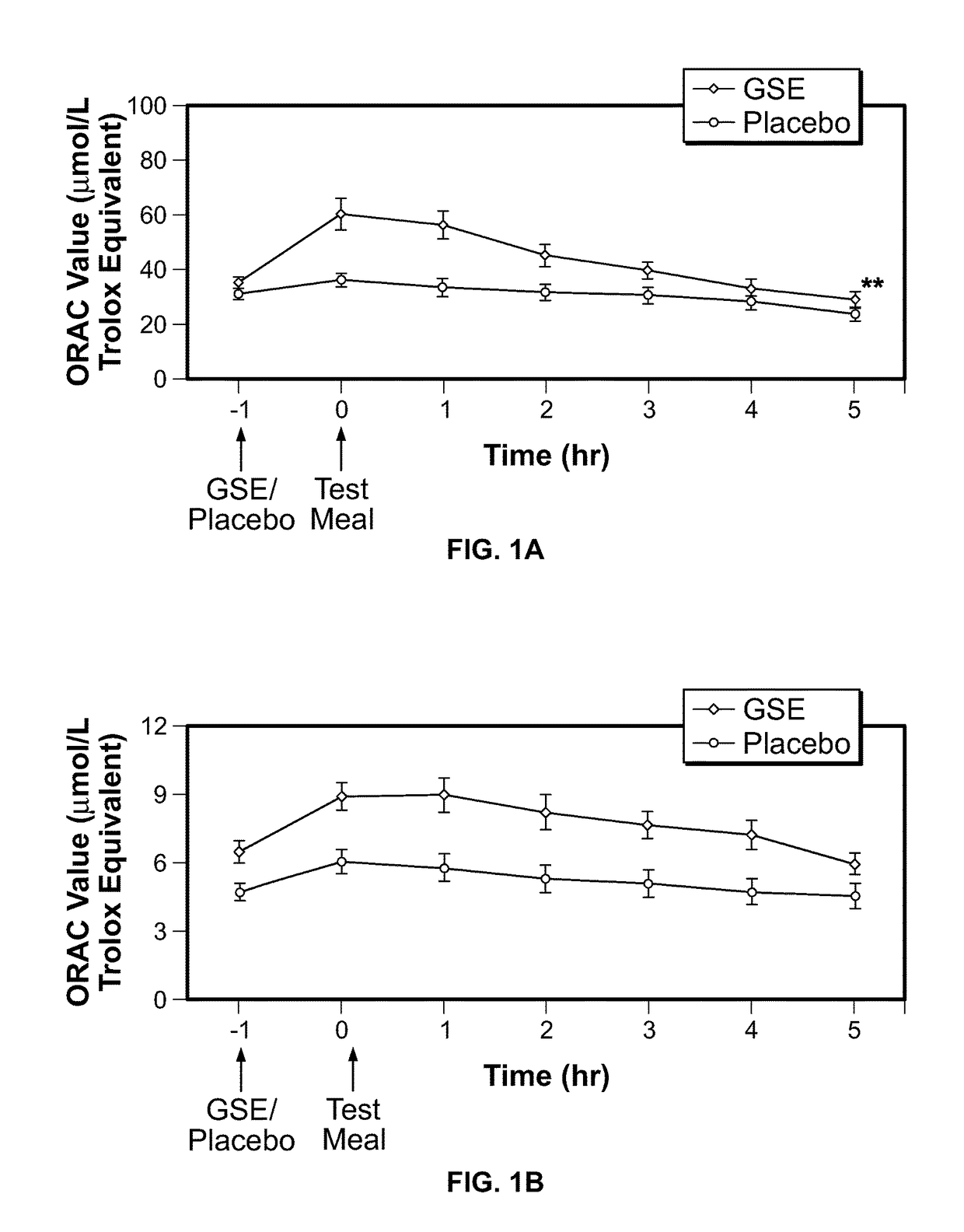
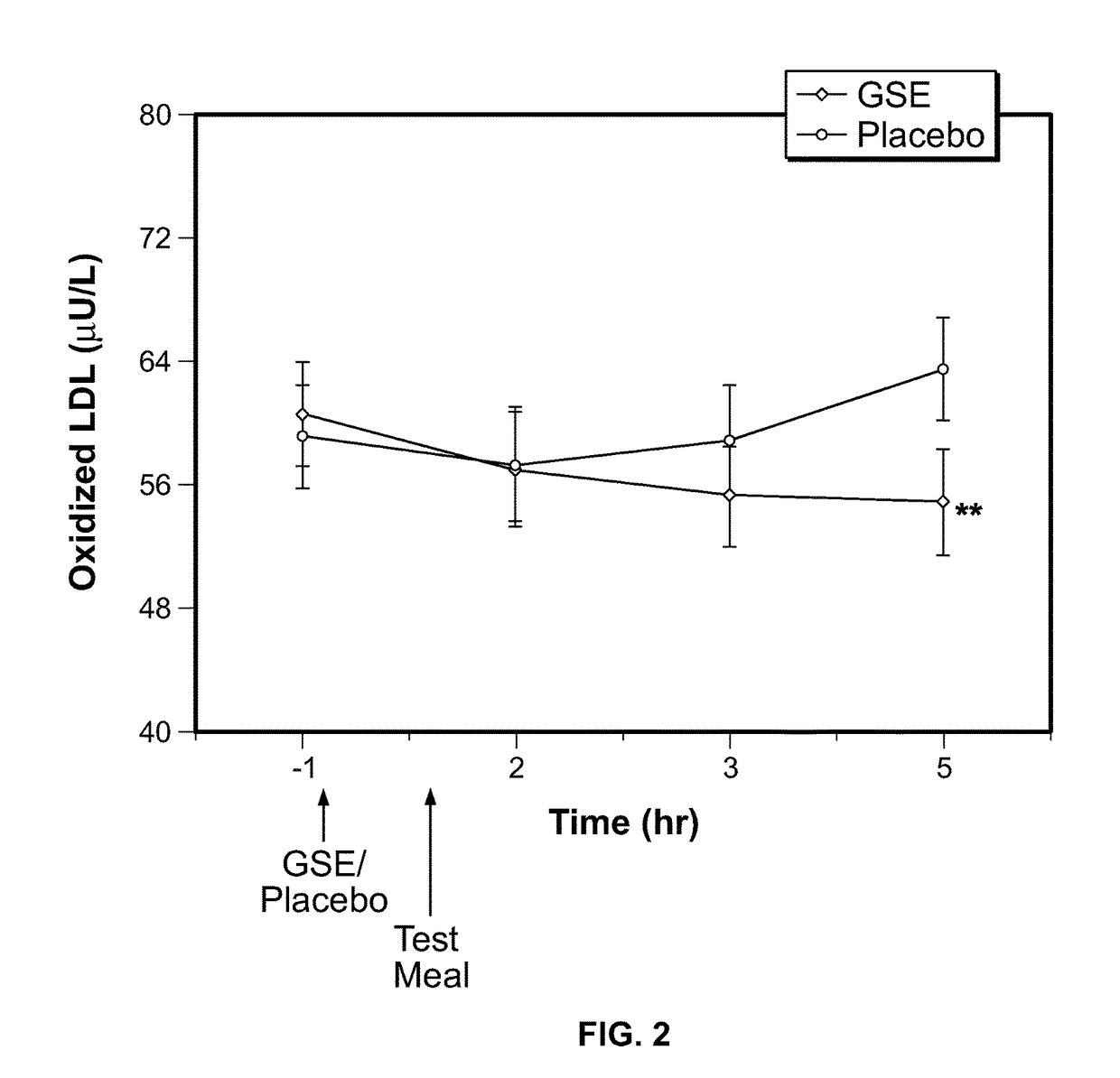
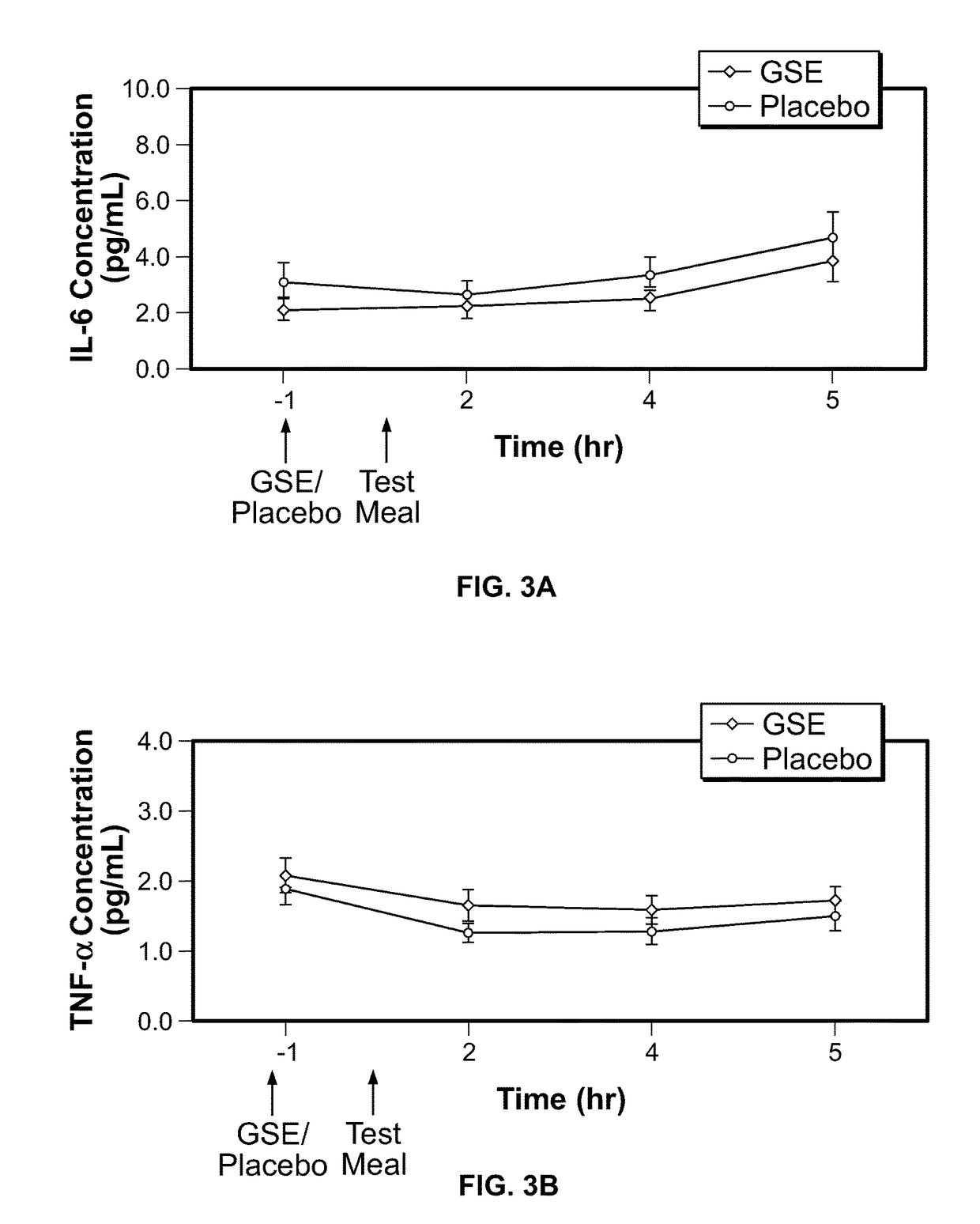
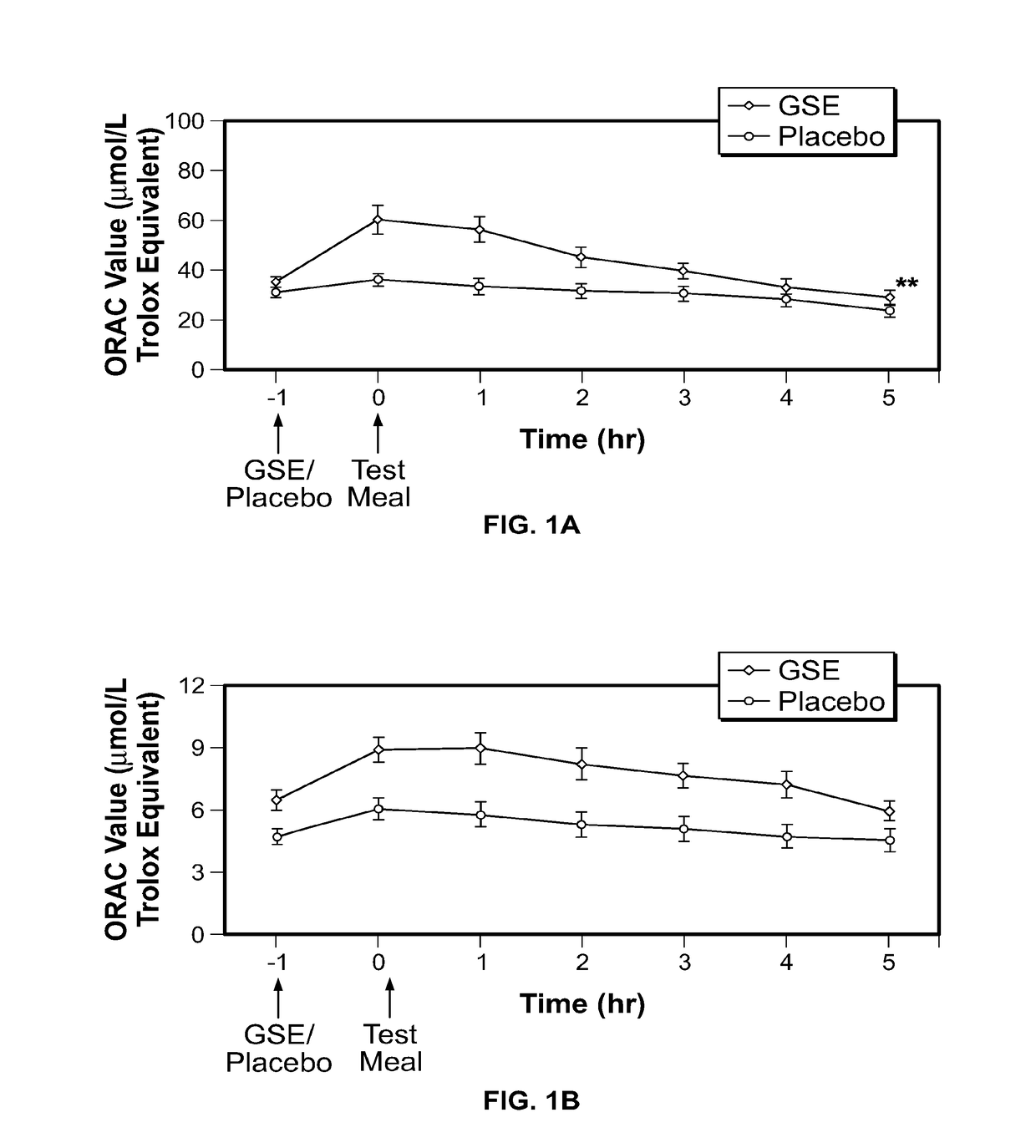
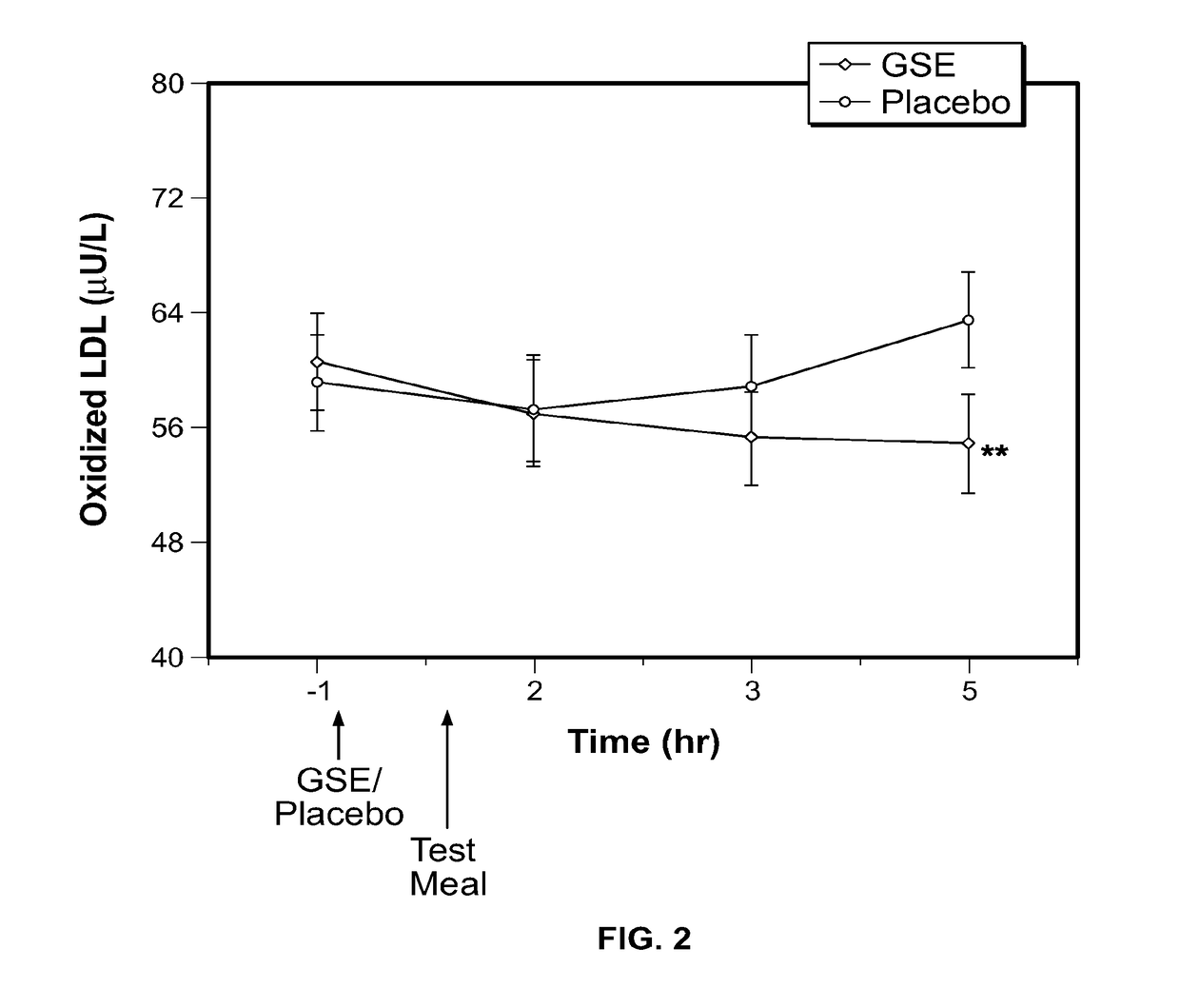
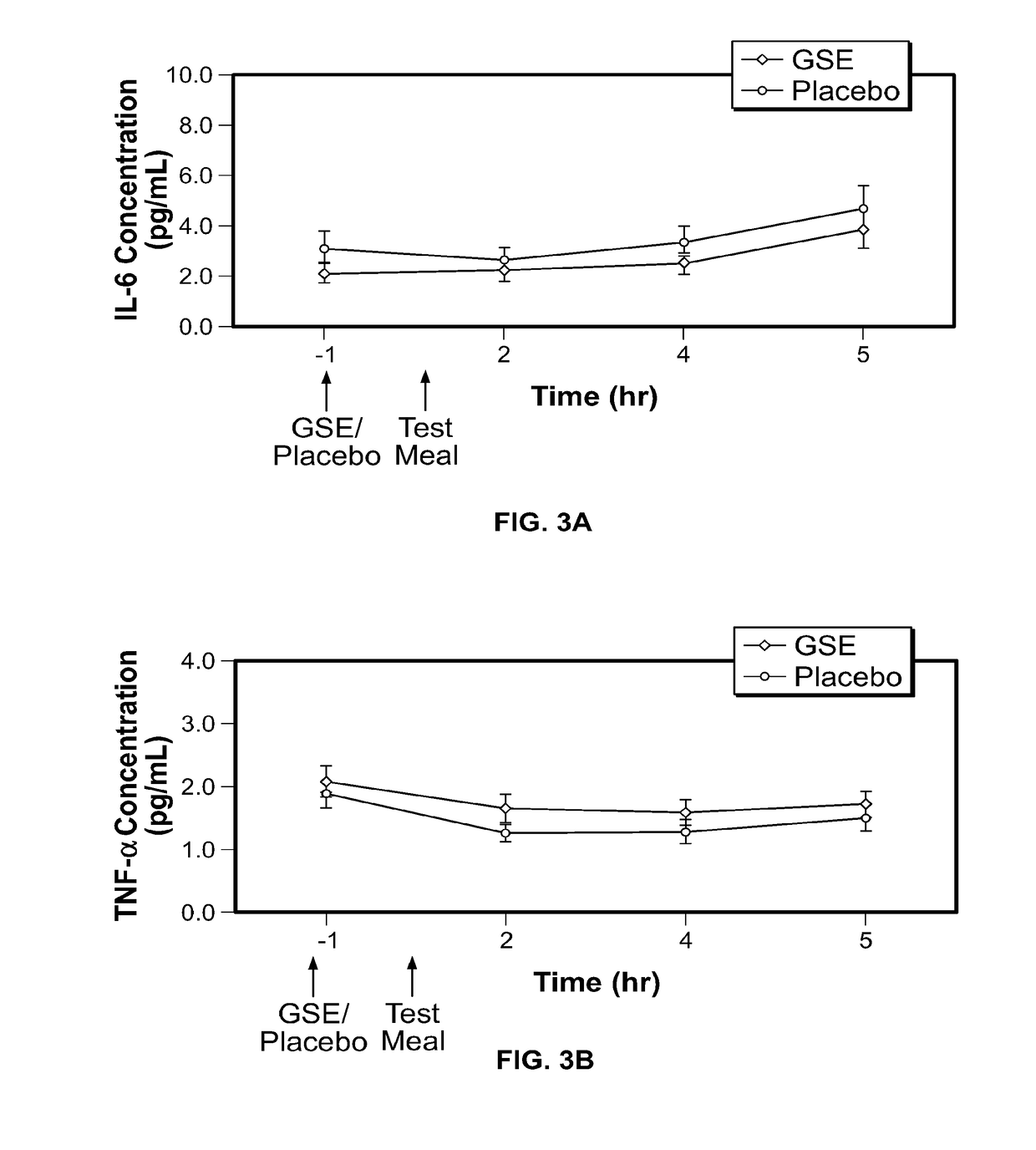
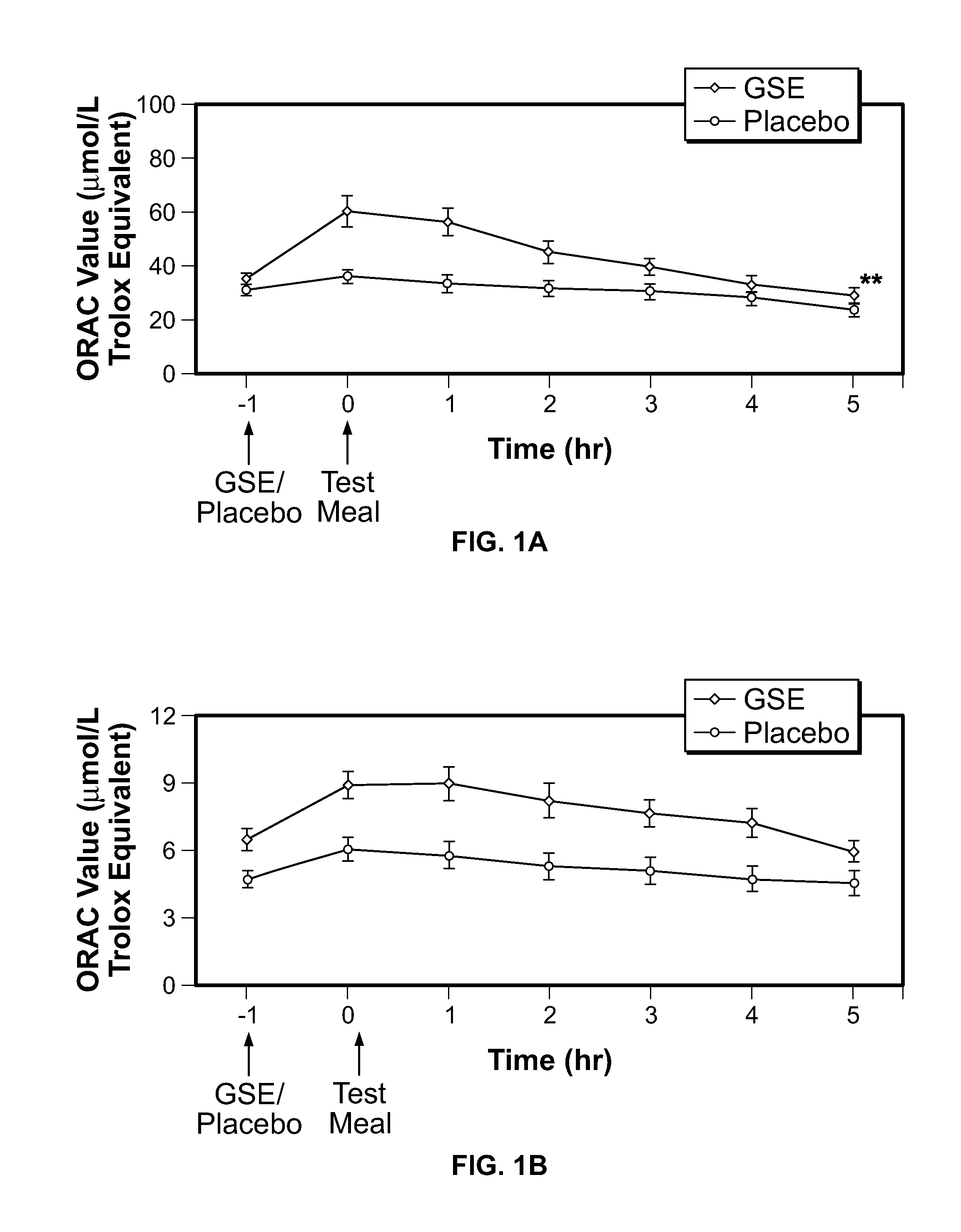
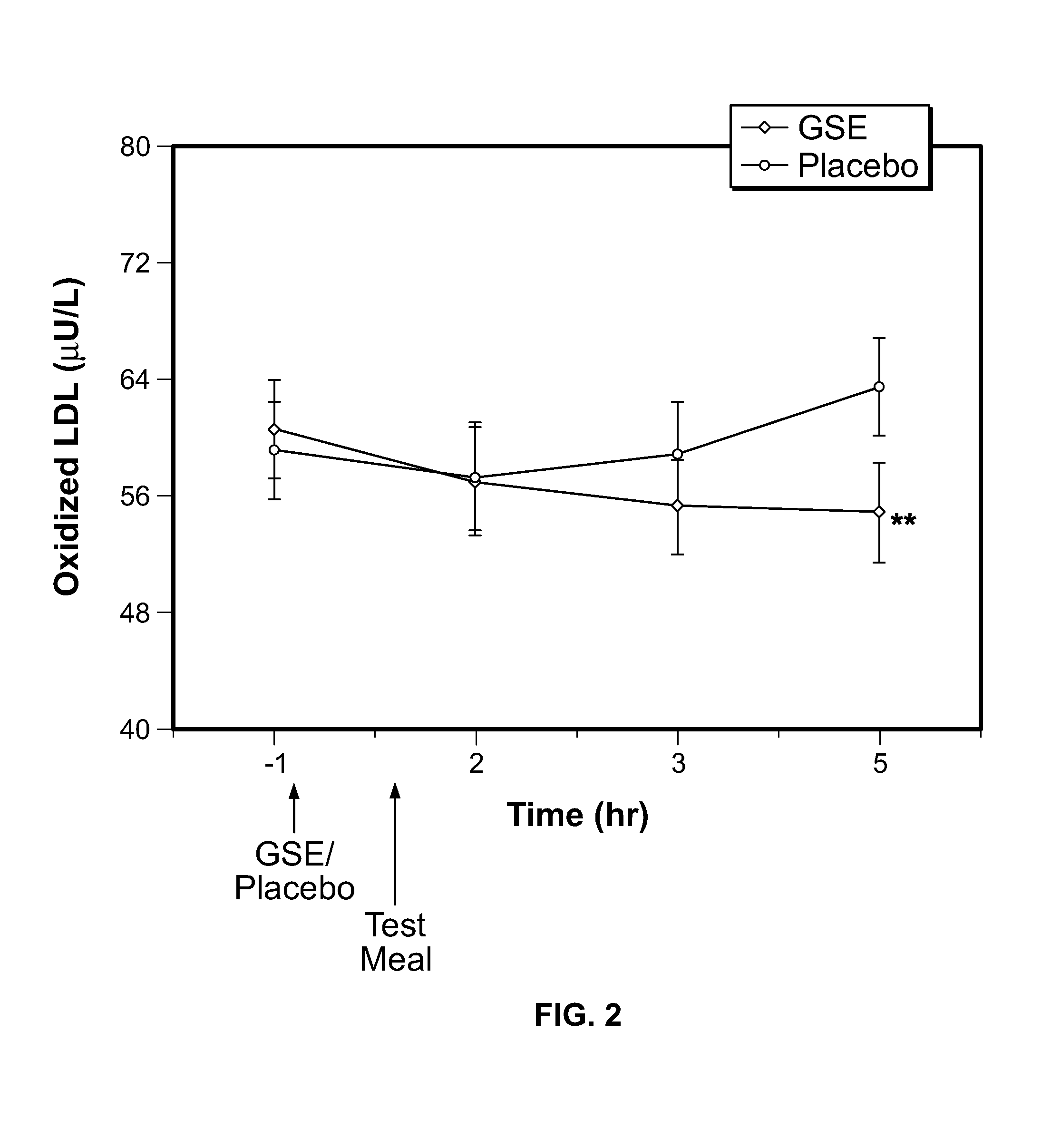
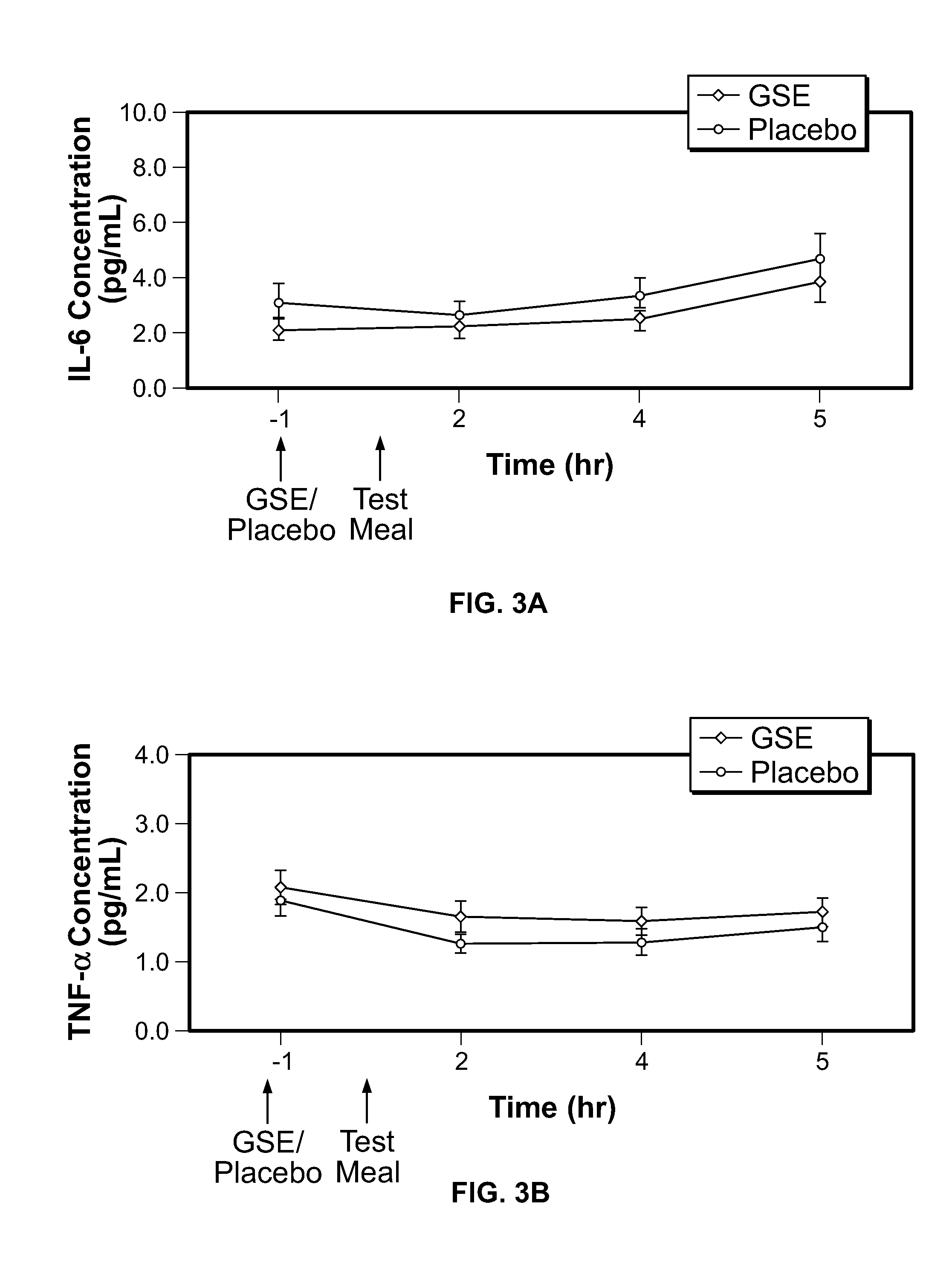
Modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity with grape seed extract
ActiveUS9592265B2Modulating oxidative stressModulating inflammationOrganic active ingredientsPlant ingredientsOxidative stressProanthocyanidin
Method for modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in a subject by using a grape seed extract, the method being useful in modulating post-prandial oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in patients suffering from Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). The method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a grape seed extract and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The grape seed extract is a polyphenolic extract comprising proanthocyanidins and anthocyanidins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method of detection of occult pancreatic beta cell dysfunction in normoglycemic patients
InactiveUS20180156776A1High riskReduce riskDisease diagnosisBiological testingAcute hyperglycaemiaDyslipidemia
This invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of or likelihood of a patient of developing occult pancreatic beta cell dysfunction, and a method for detecting the presence of or likelihood of a patient of developing clinically significant post-prandial hyperglycemia. The methods involve (a) measuring a level of alpha-hydroxybutyrate (AHB) in a single fasting baseline biological sample of the patient; (b) comparing the level of AHB in the single fasting baseline biological sample to a reference AHB level; and (c) determining the presence of or likelihood of developing the disorder in the patient based on the comparison in step (b). An increased AHB level at fasting baseline indicates that a normoglycemic, normo-insulinemic and / or non-dyslipidemic patient has developed or has an increased likelihood of developing occult pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. An increased AHB level at fasting baseline and an elevated glucose level of at least about 155 mg / dL at 30 minutes and / or 1 hour indicates that a normoglycemic, normo-insulinemic and / or non-dyslipidemic patient has developed or has an increased likelihood of developing clinically significant post-prandial hyperglycemia.
Owner:TRUE HEALTH IP LLC
Modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity with grape seed extract
Method for modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in a subject by using a grape seed extract, the method being useful in modulating post-prandial oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in patients suffering from Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). The method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a grape seed extract and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The grape seed extract is a polyphenolic extract comprising proanthocyanidins and anthocyanidins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Impaired Insulin Sensitivity with Grape seed Extract
Method for modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in a subject by using a grape seed extract, the method being useful in modulating post-prandial oxidative stress, inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity in patients suffering from Metabolic Syndrome (MetS).
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com