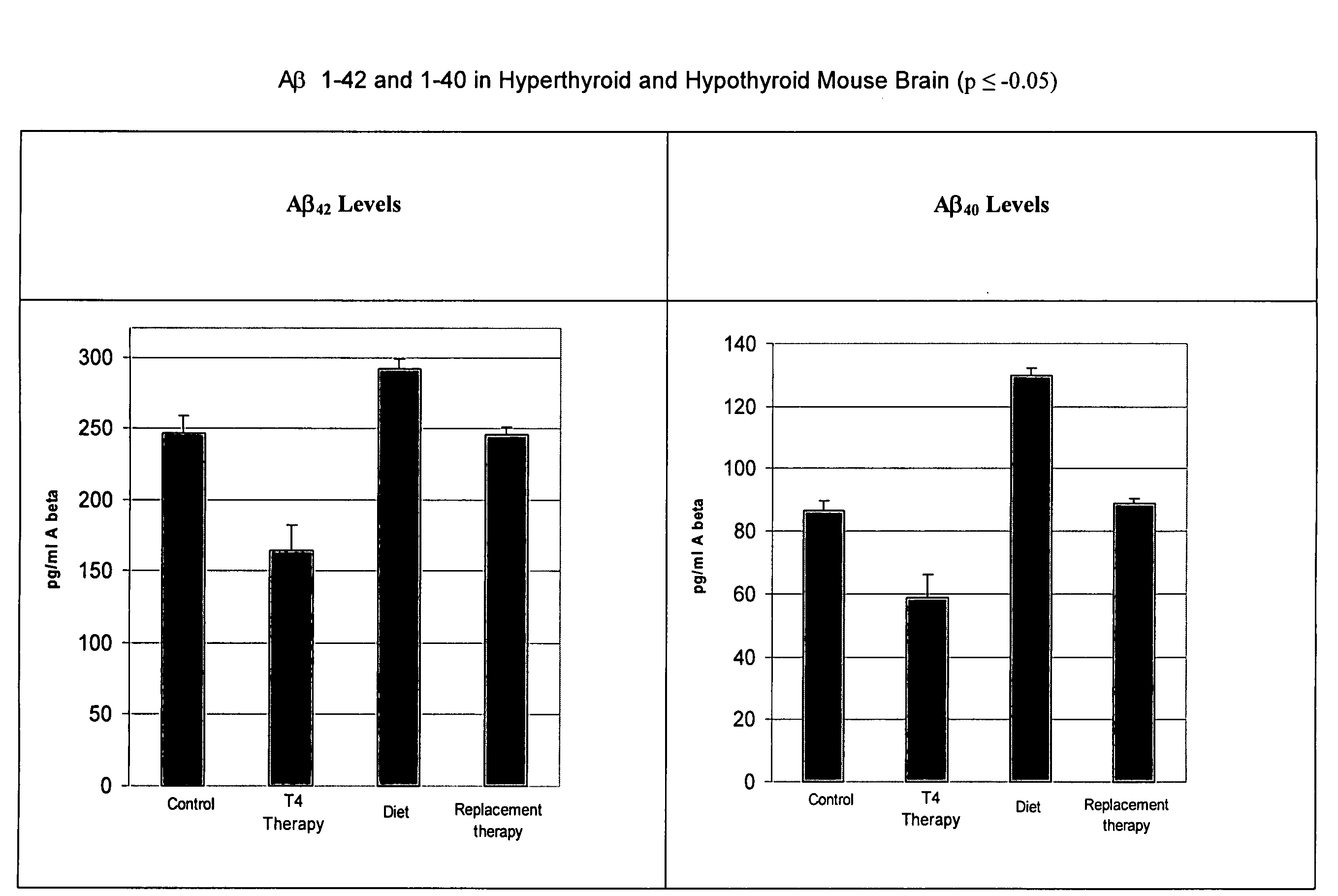
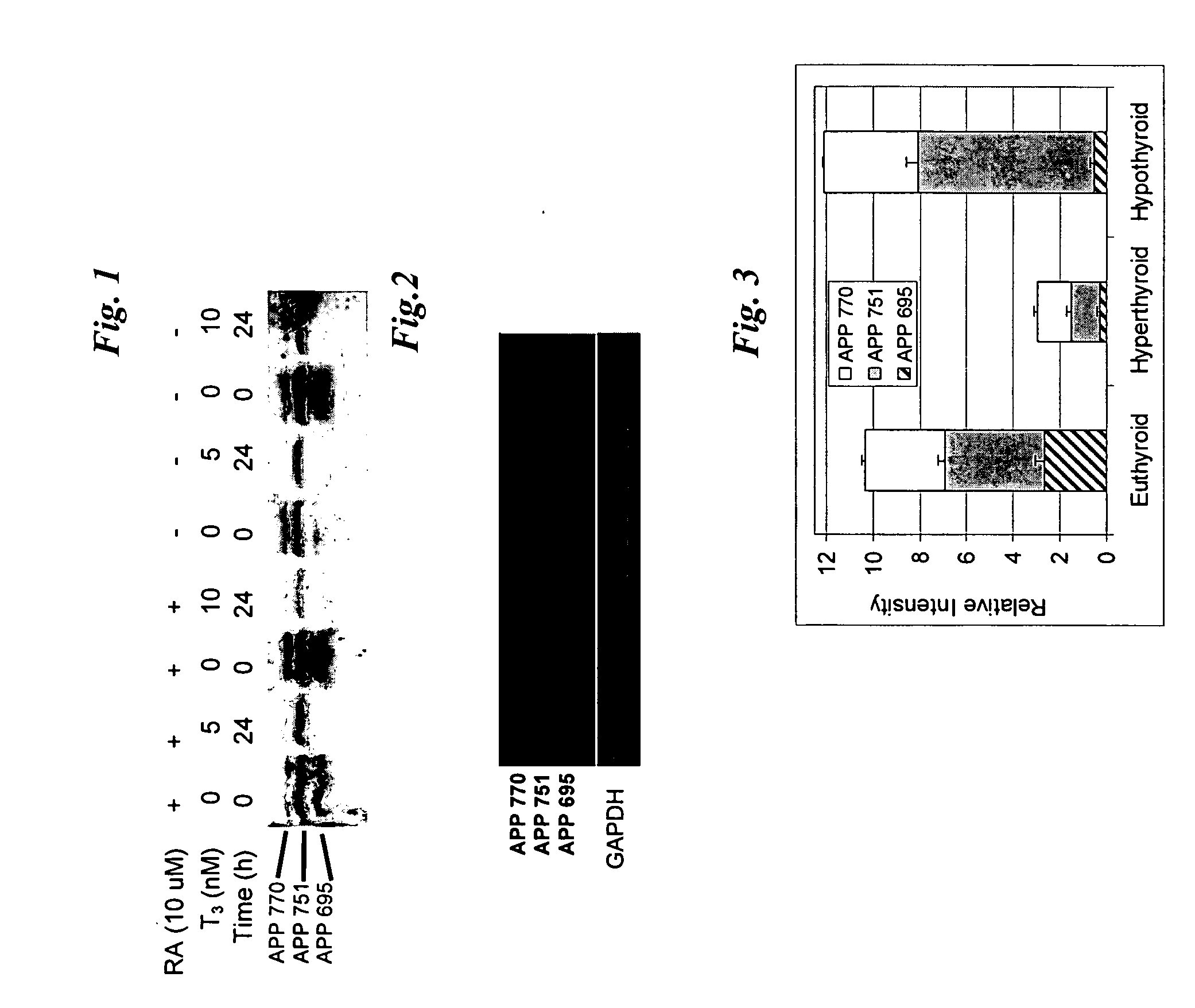
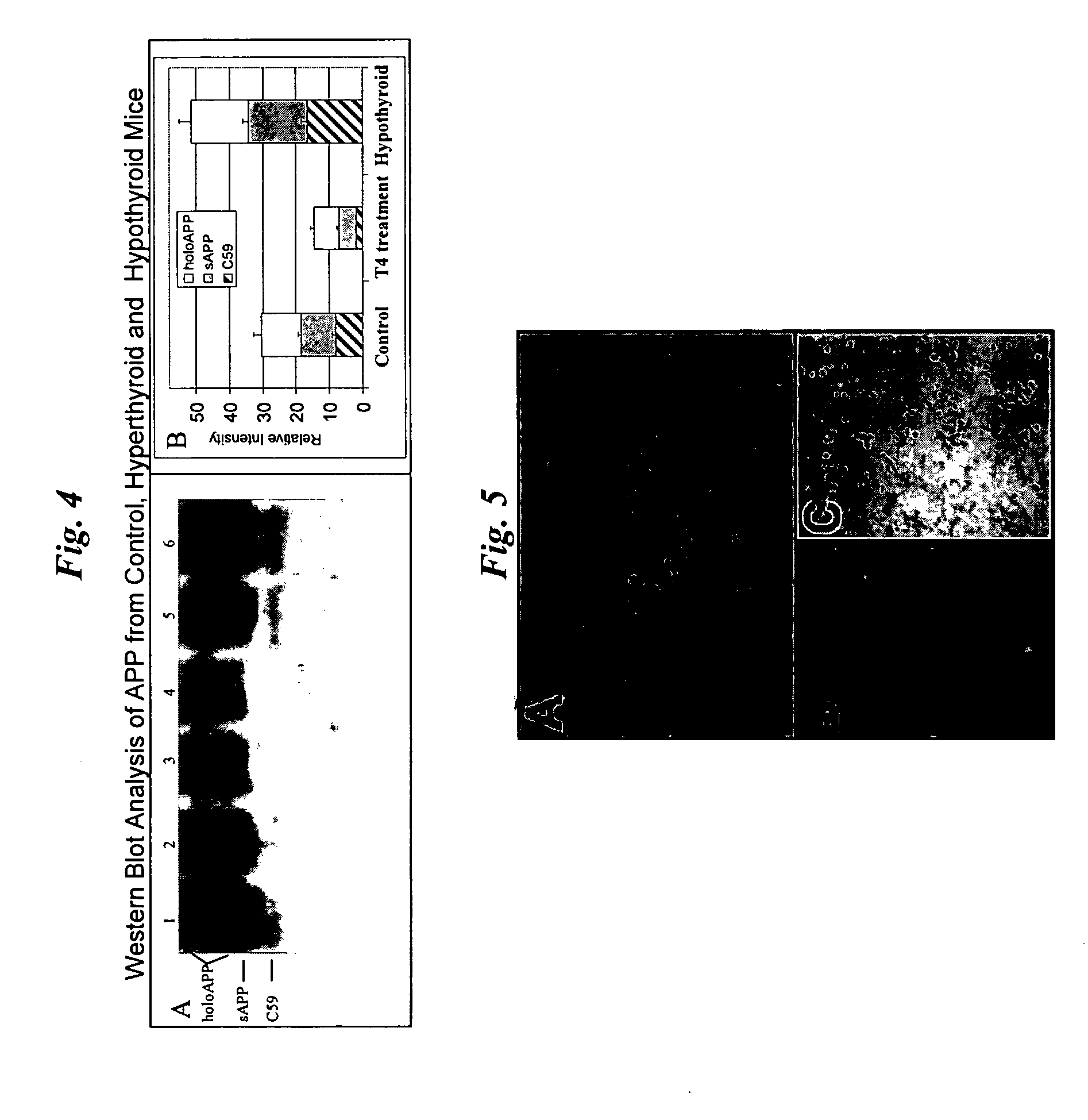
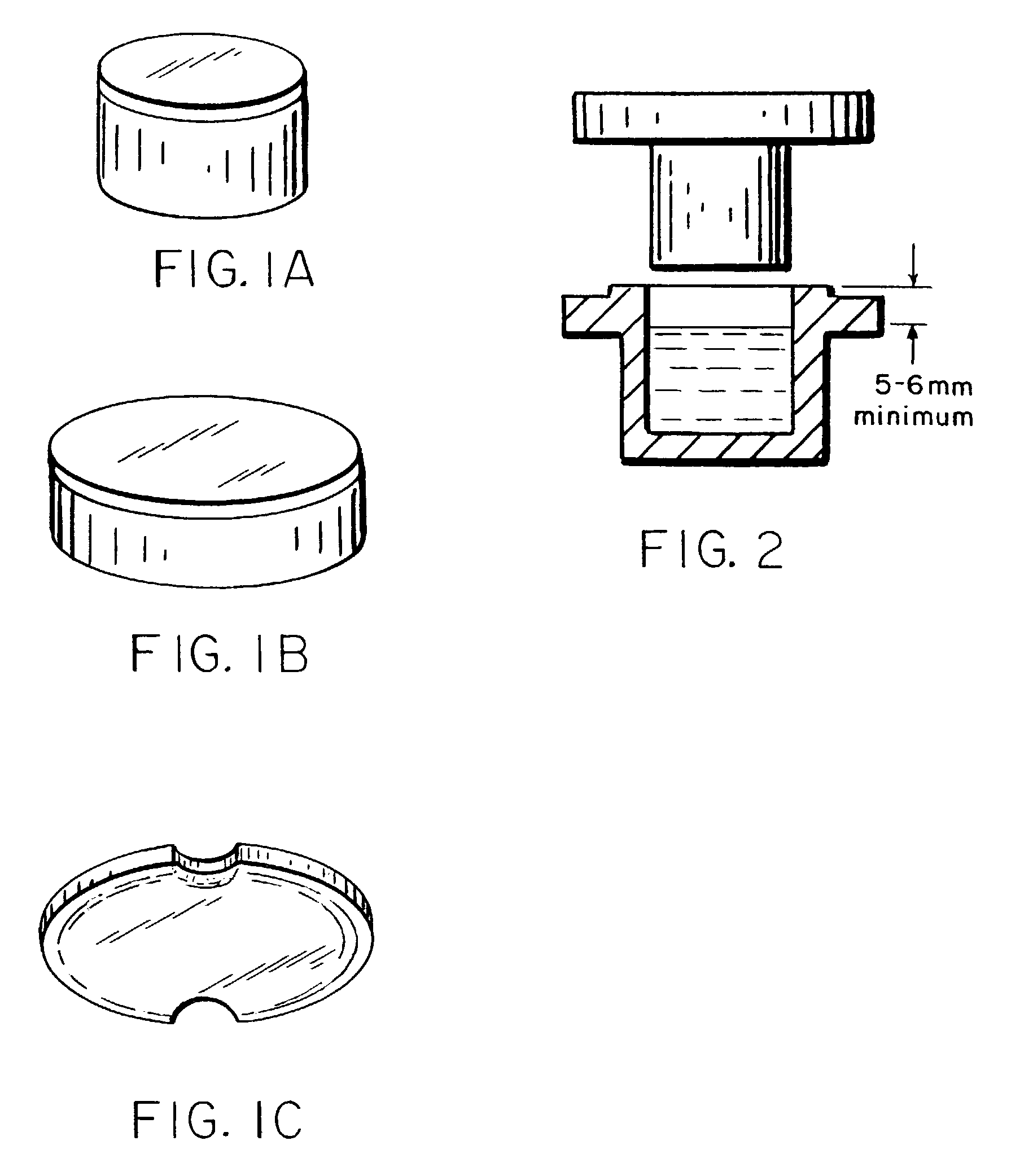
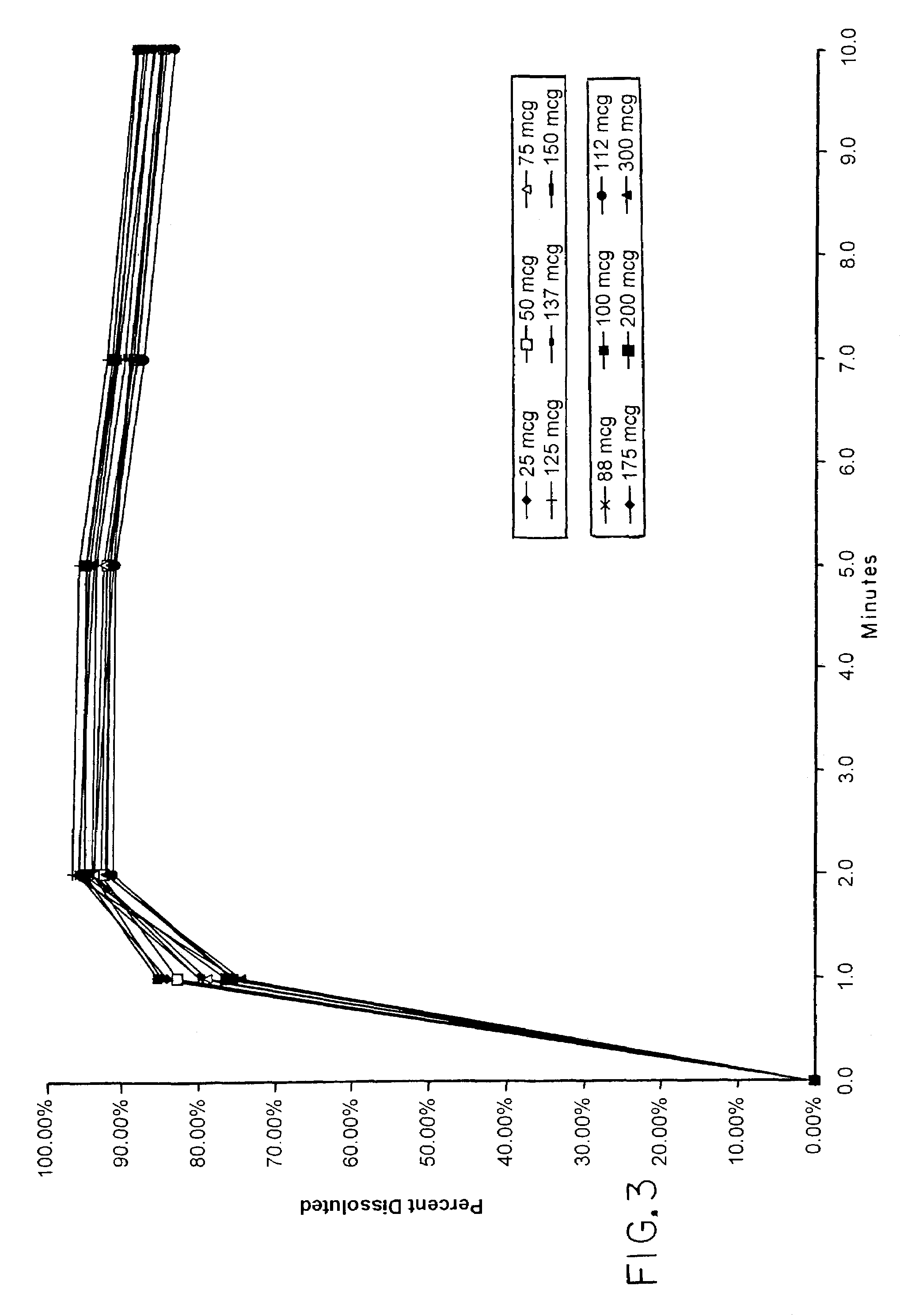
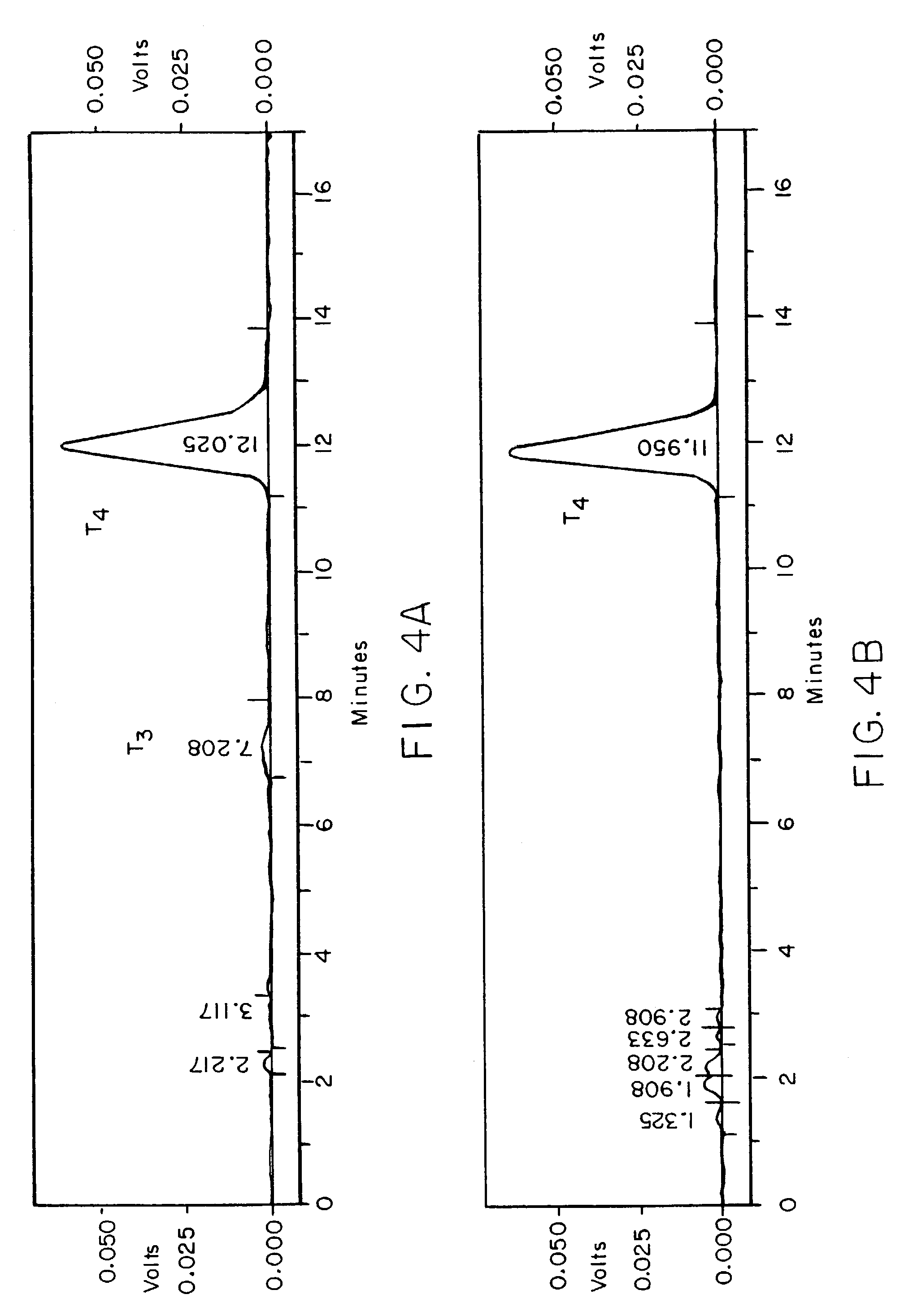
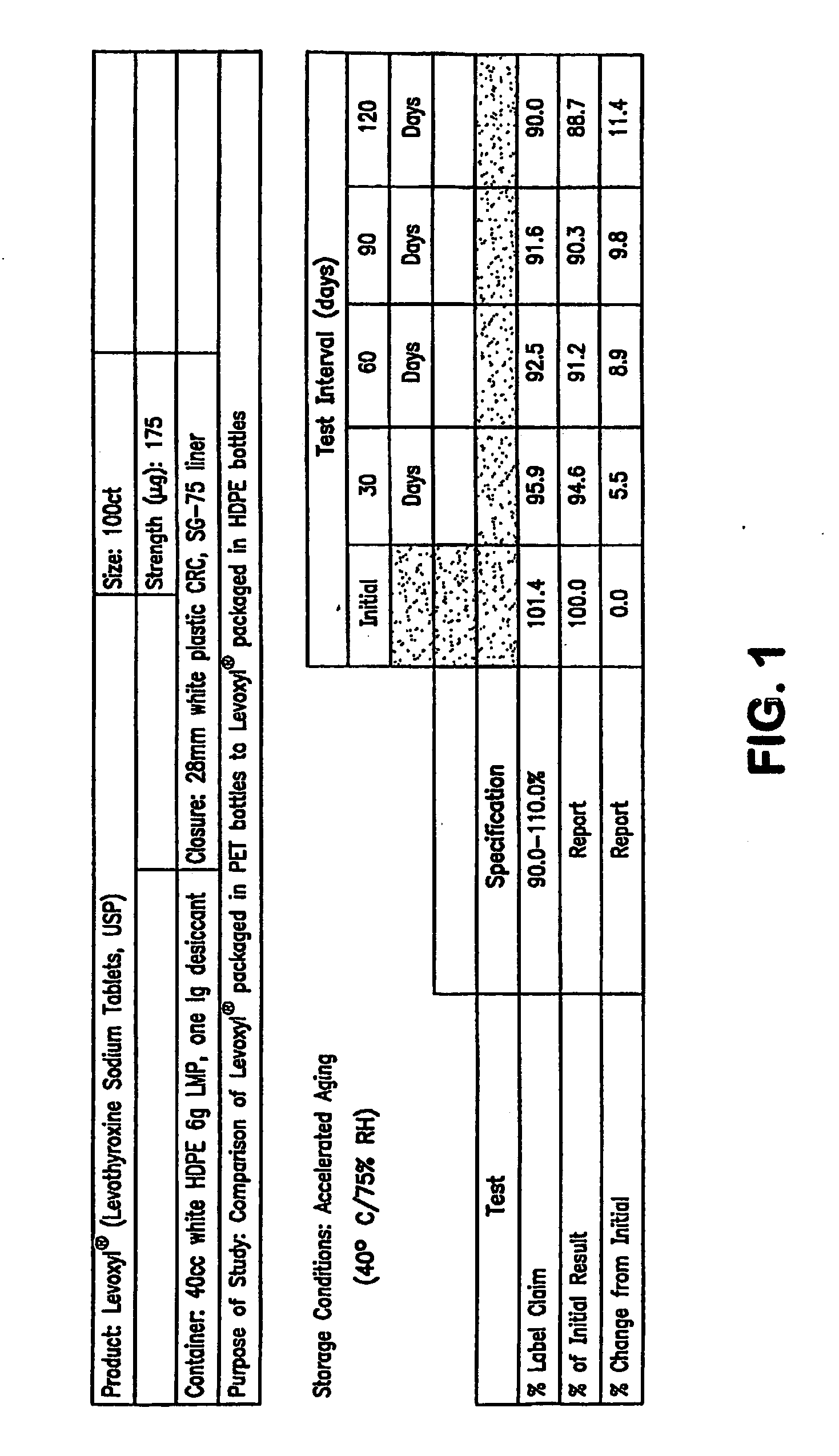
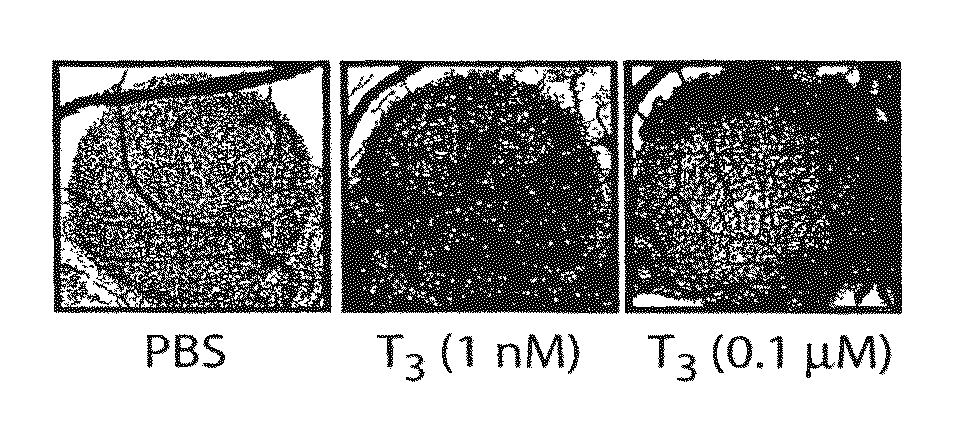Patents
Literature
150 results about "Thyroid hormones" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T₃) and thyroxine (T₄). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T₃ and T₄ are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T₃ and T₄, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T₄), which has a longer half-life than T₃. In humans, the ratio of T₄ to T₃ released into the blood is approximately 14:1. T₄ is converted to the active T₃ (three to four times more potent than T₄) within cells by deiodinases (5'-iodinase). These are further processed by decarboxylation and deiodination to produce iodothyronamine (T₁a) and thyronamine (T₀a). All three isoforms of the deiodinases are selenium-containing enzymes, thus dietary selenium is essential for T₃ production.
Hormone receptor functional dimers and methods of their use
InactiveUS7057015B1Enhance possibility of producingIncrease flexibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesADAMTS ProteinsProtein Unit
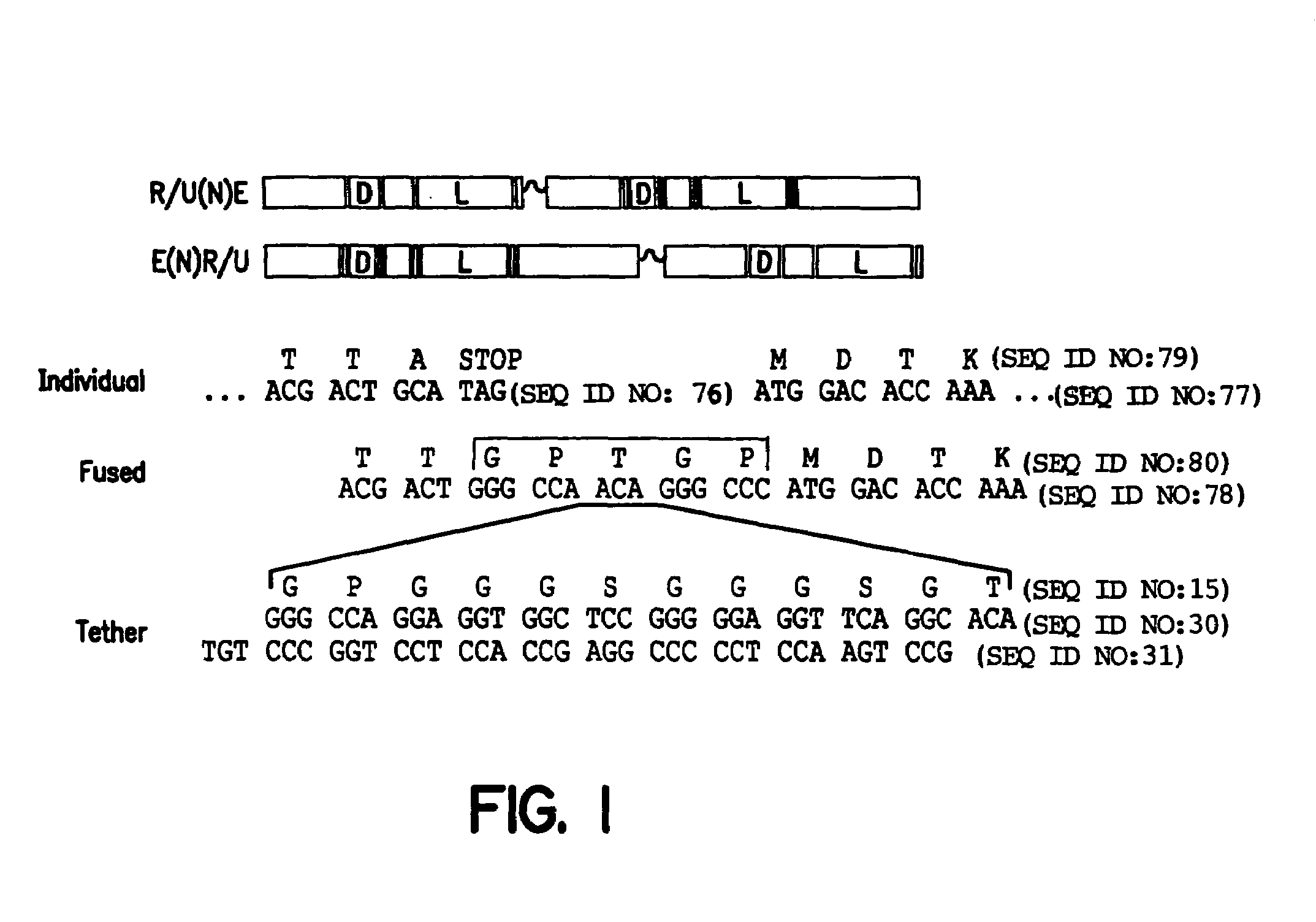
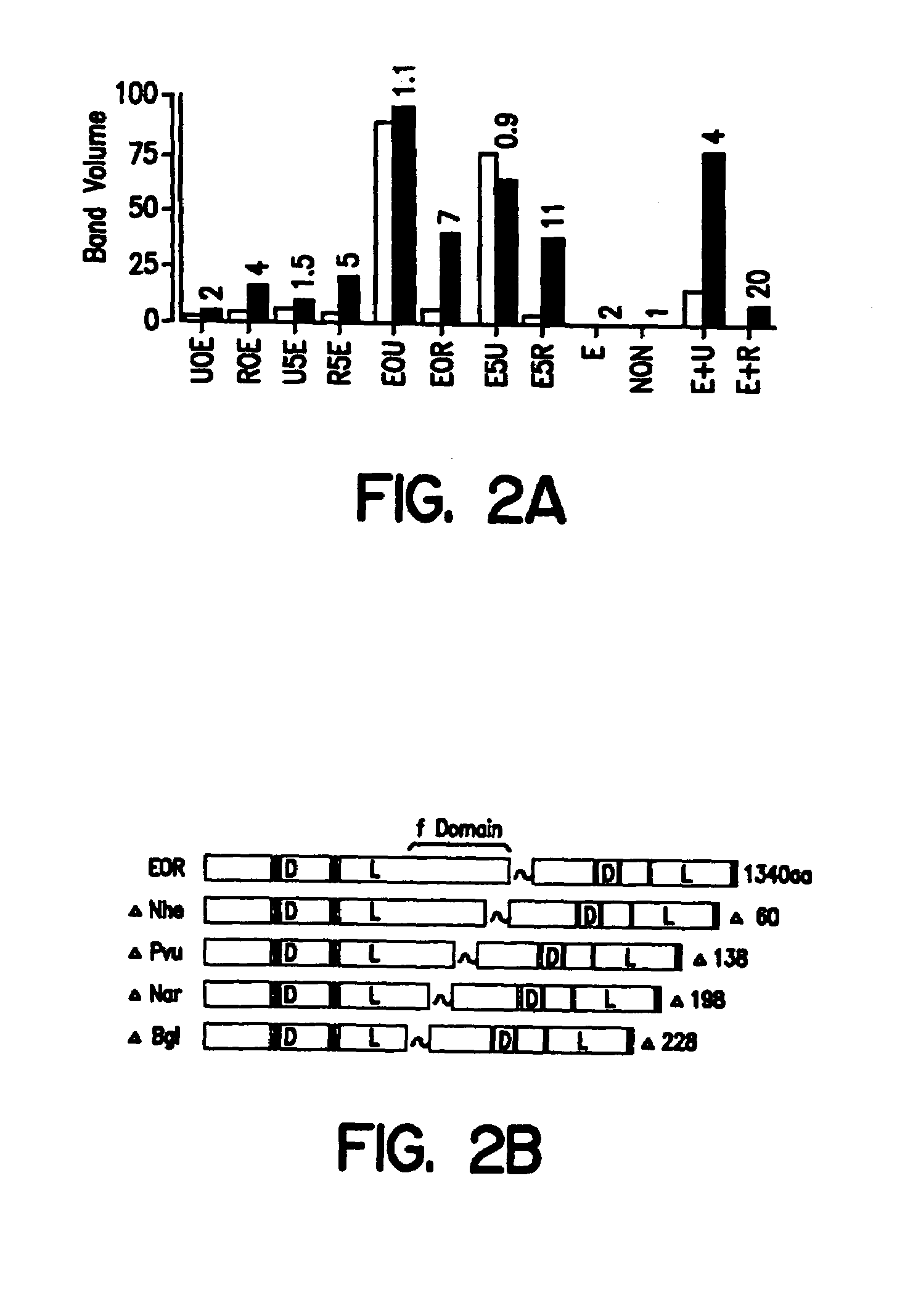
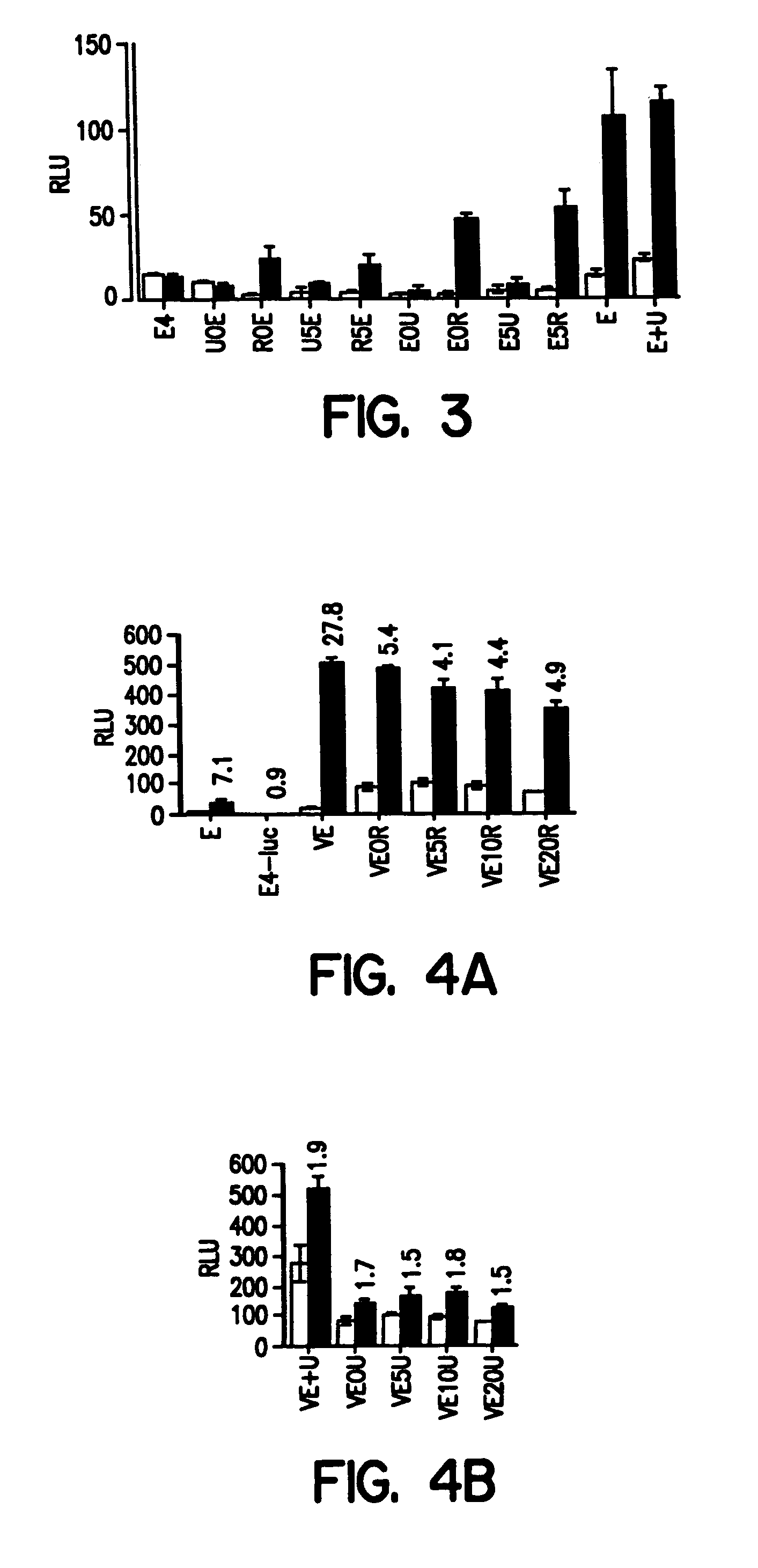
The invention provides chimeric proteins having at least two functional protein units, each containing the dimerization domain of a member of the steroid / thyroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily. The chimeric proteins can fold under crystallization conditions to form functional entities. The functional entities optionally contain a novel flexible peptide linker of variable lengths between at least two of the protein units. In a preferred embodiment, the linker is designed to be increased in increments of 12 amino acids each to aid in preparation of variant chimeric proteins. The DNA binding characteristics of the invention functional entities differ from those of wild-type complexes formed between “monomeric” receptors and their binding partners. Some functional entities, e.g. dimers expressed as fusion proteins, transactivate responsive promoters in a manner similar to wild-type complexes, while others do not promote transactivation and function instead essentially as constitutive repressors. The invention further provides nucleotide sequences encoding the invention chimeric proteins, cells containing such nucleotide sequences, and methods for using the invention chimeric proteins to modulate expression of one or more exogenous genes in a subject organism. In addition, isolated protein crystals suitable for x-ray diffraction analysis and methods for obtaining putative ligands for the invention chimeric proteins are provided.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Antibody against human parathormone related peptides
InactiveUS6903194B1Improve hypophosphatemiaHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsThyroid hormonesA-DNA
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
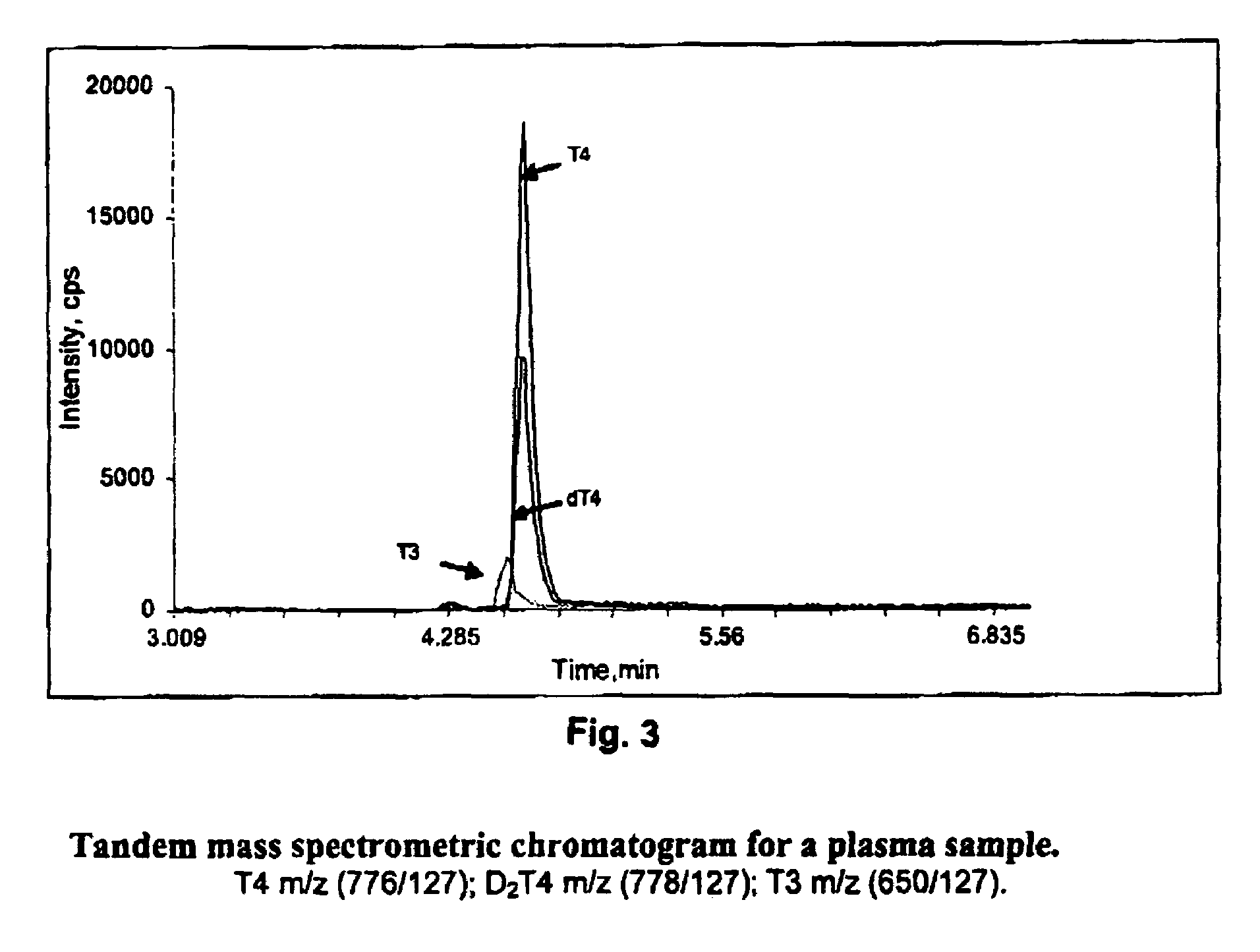
Thyroid hormone analysis by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7618827B2Fast and accurate methodFast and accurate of and quantificationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTransferasesThyroid hormonesMedicine
Methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of one or more hormones by mass spectrometry are disclosed. The methods require minimal sample size and minimal preparation time. The methods include ionizing the hormones and analyzing the hormones by mass spectrometry. In addition, methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of thyroid hormones are disclosed including ionization of the thyroid hormones in the negative mode using an electrospray source.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Method and composition for restoration of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body
InactiveUS20060073178A1Restoring age related tissue lossEasy to produceCosmetic preparationsBiocideInsulin-like growth factorThyroid hormones
A treatment method for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body is disclosed which includes injecting an injectable composition containing a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier into the dermis, the hypodermis, or both, in various areas of the face, or selected areas of the body of a person to stimulate collagen, elastin, or fat cell production, thereby restoring age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body. Further disclosed is an injectable composition for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body, which contains a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier for providing time release of the growth factor into tissues. The growth factor can be insulin, insulin-like growth factor, thyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor, estrogen, retinoic acid, or their combinations.
Owner:CELLHEALTH TECH
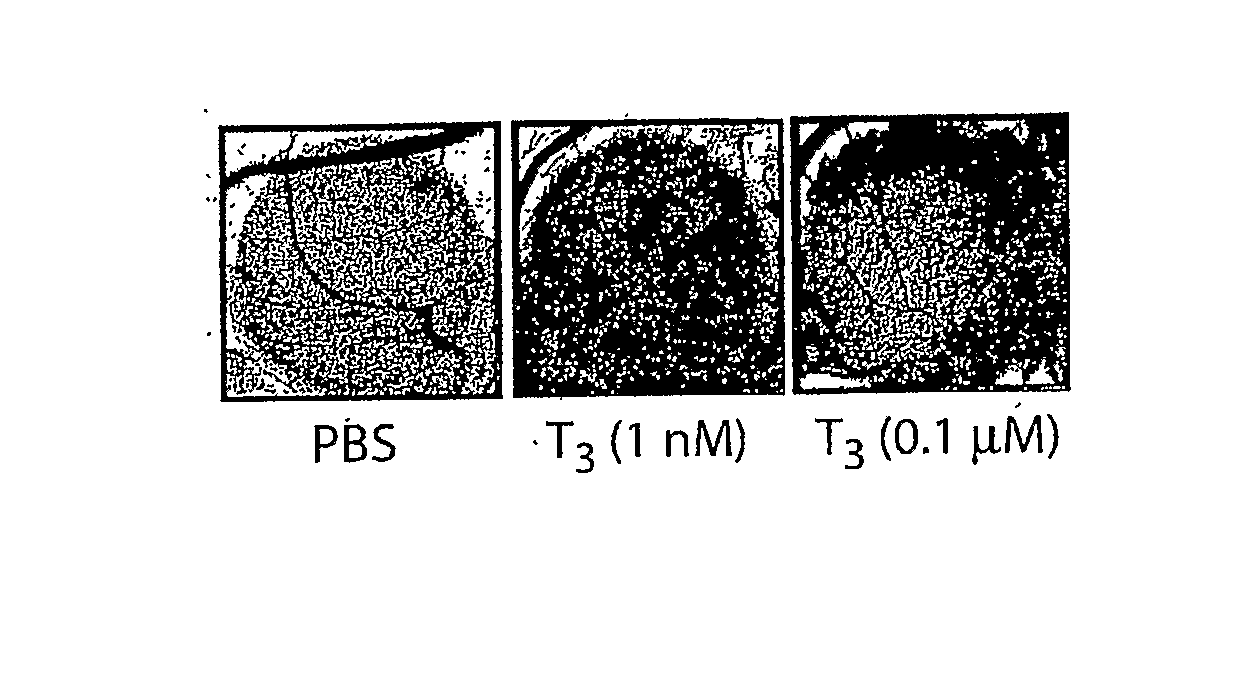
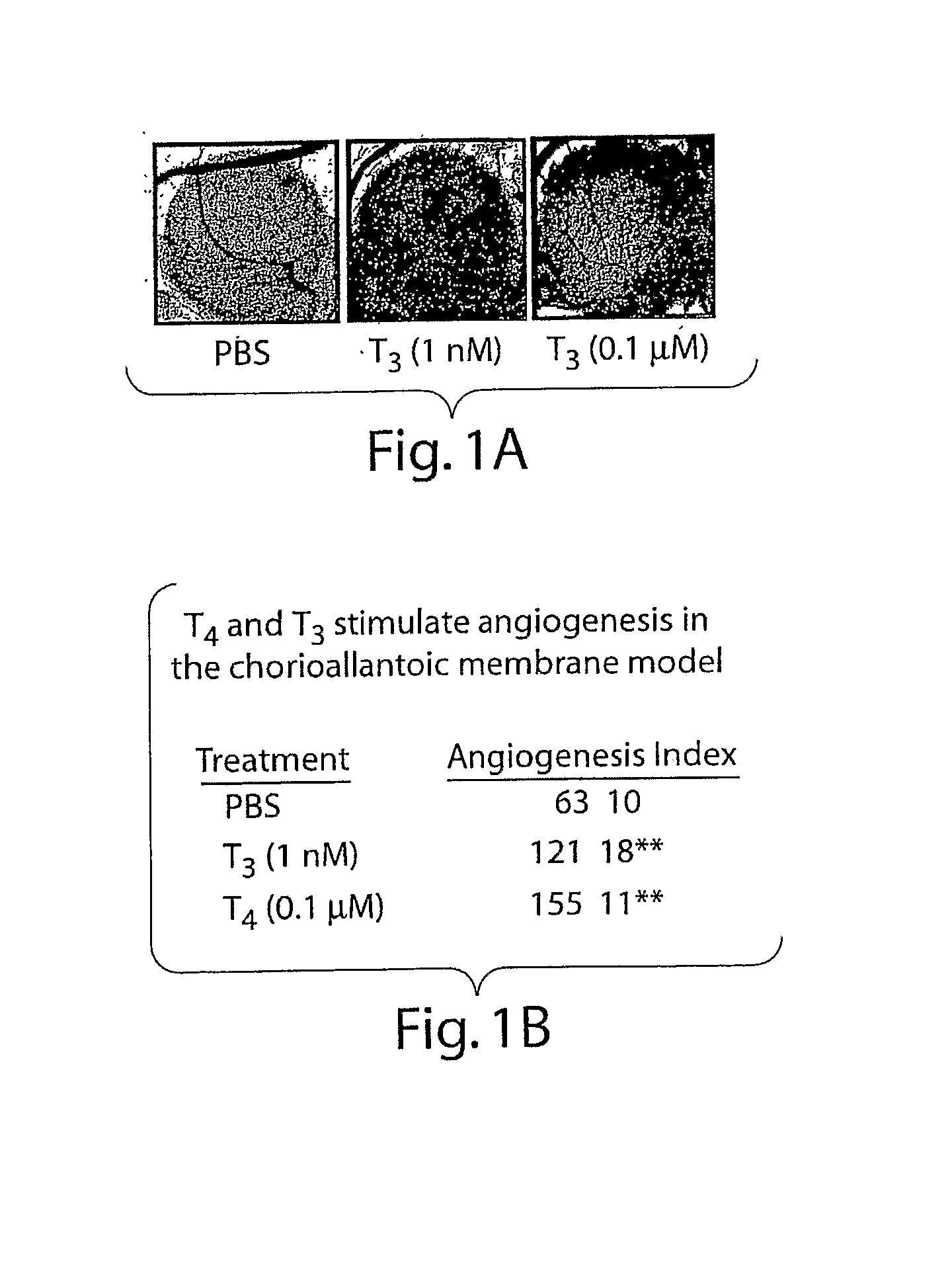
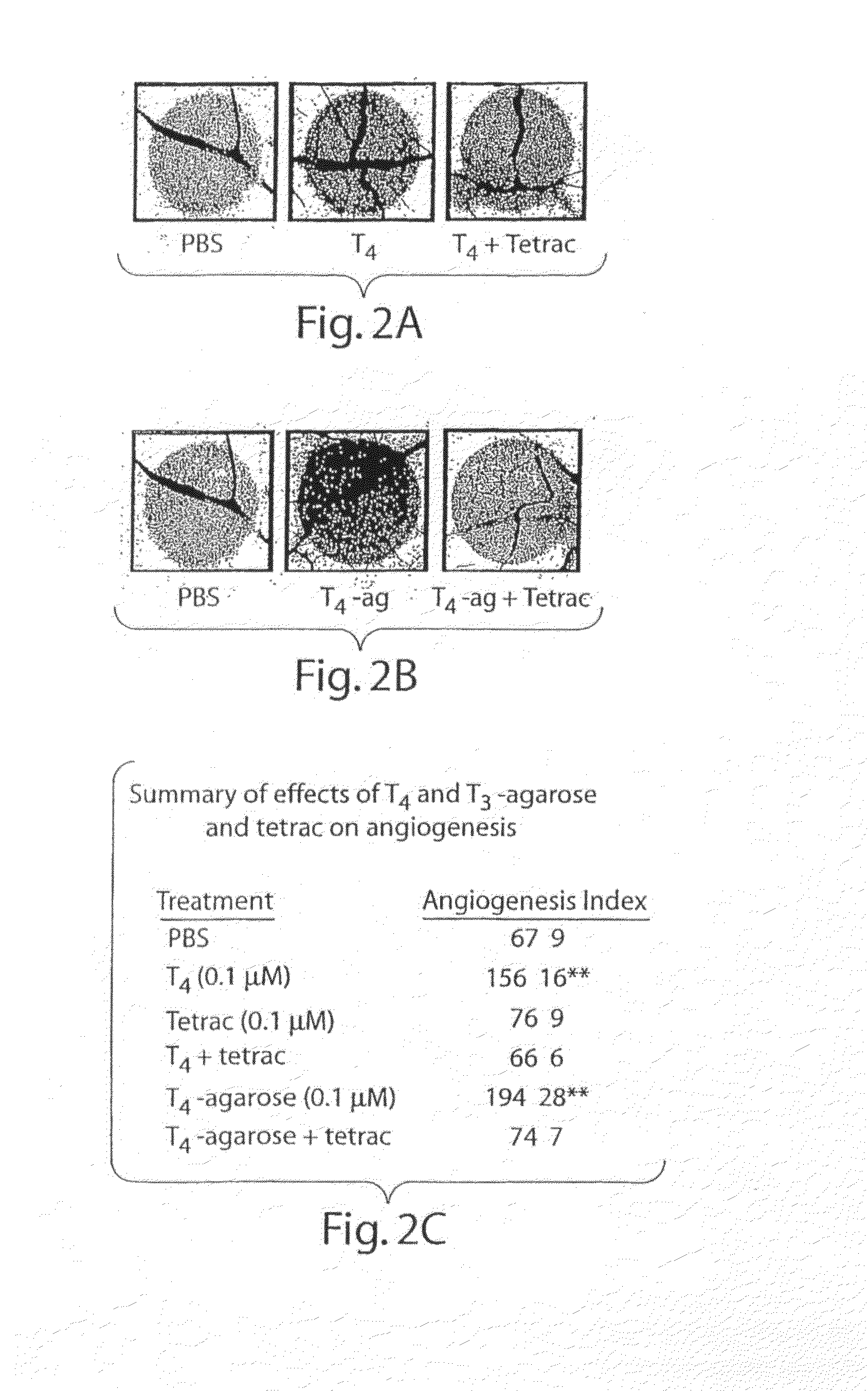
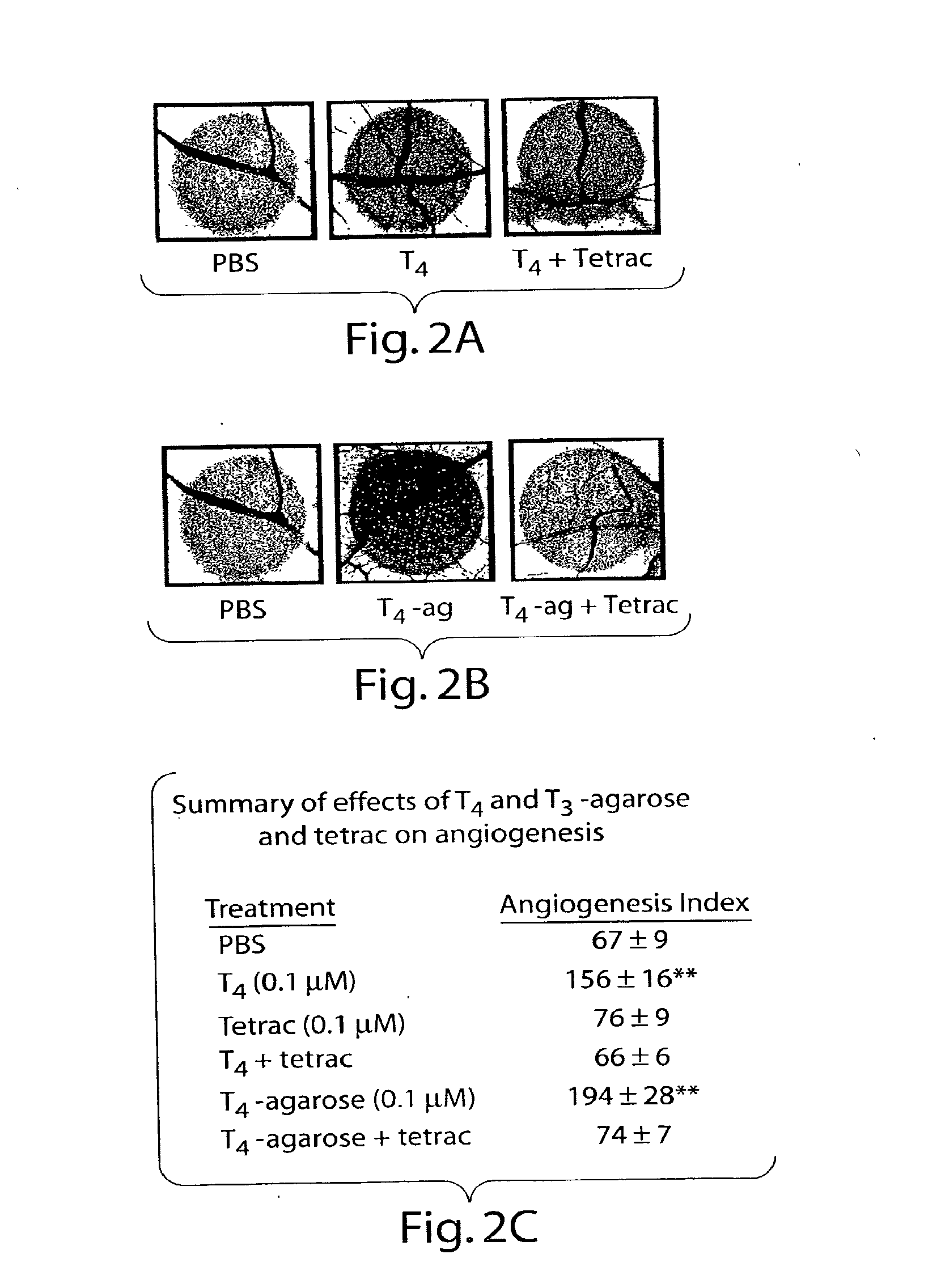
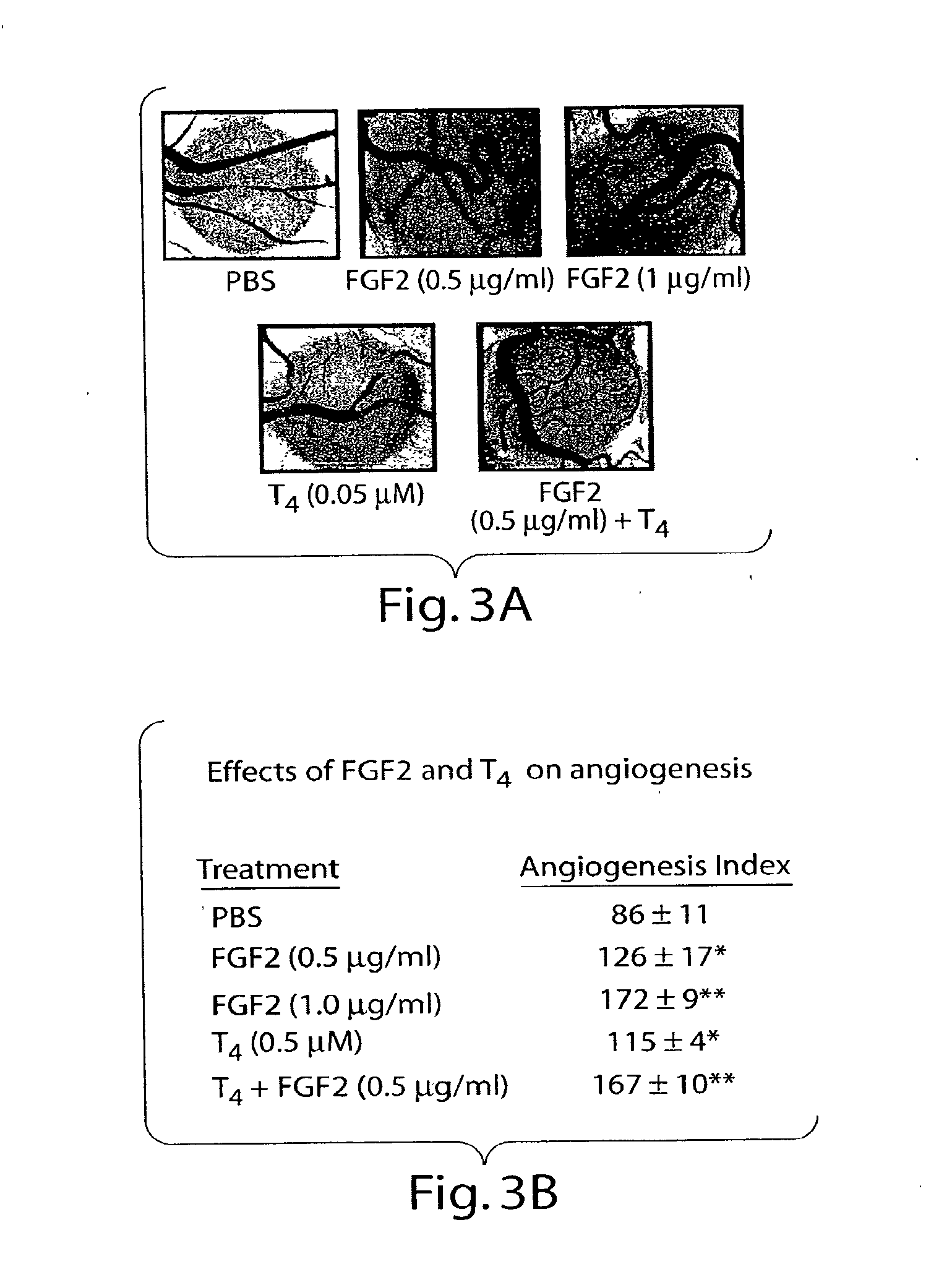
Thyroid Hormone Analogs and Methods of Use
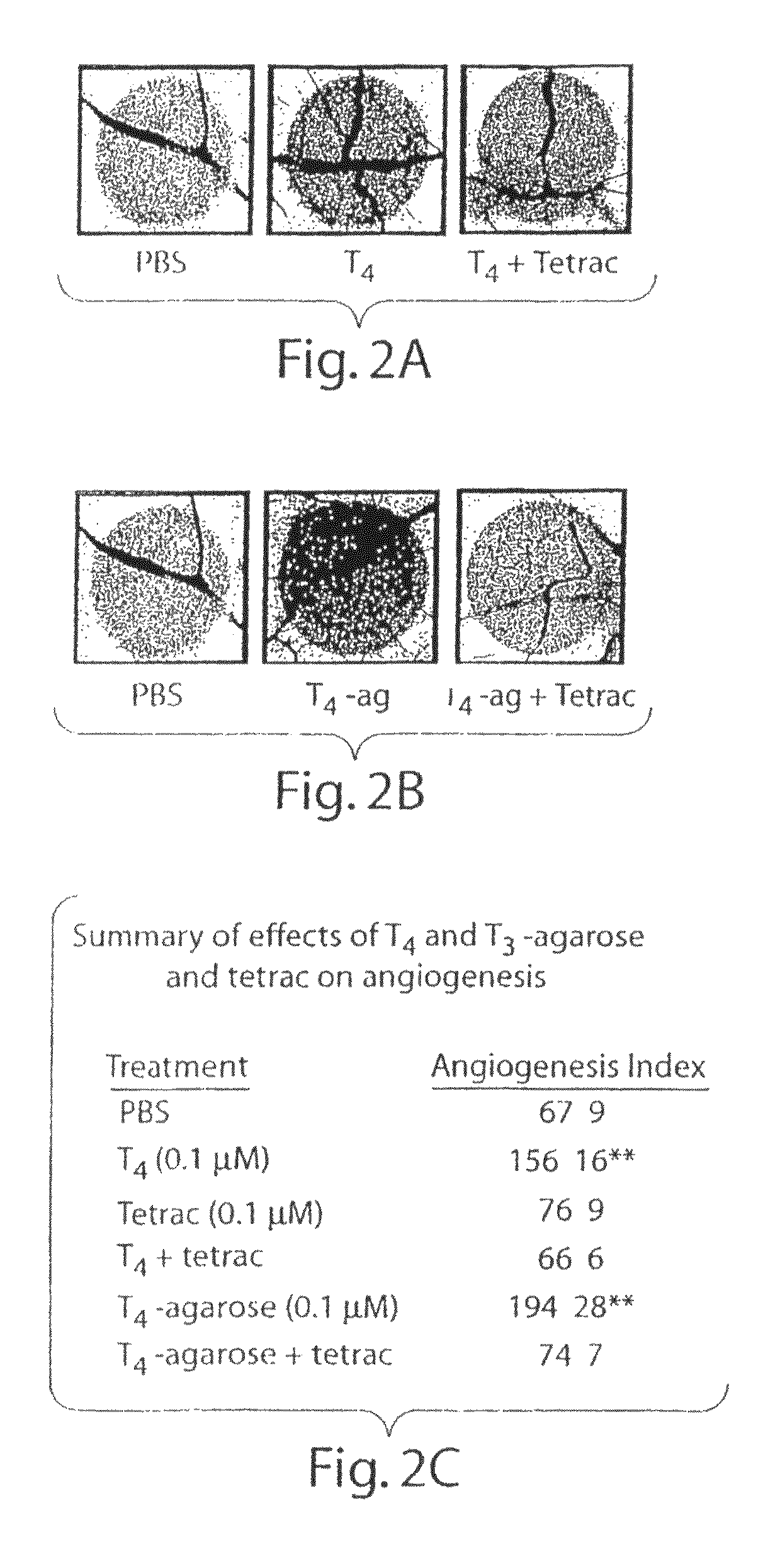
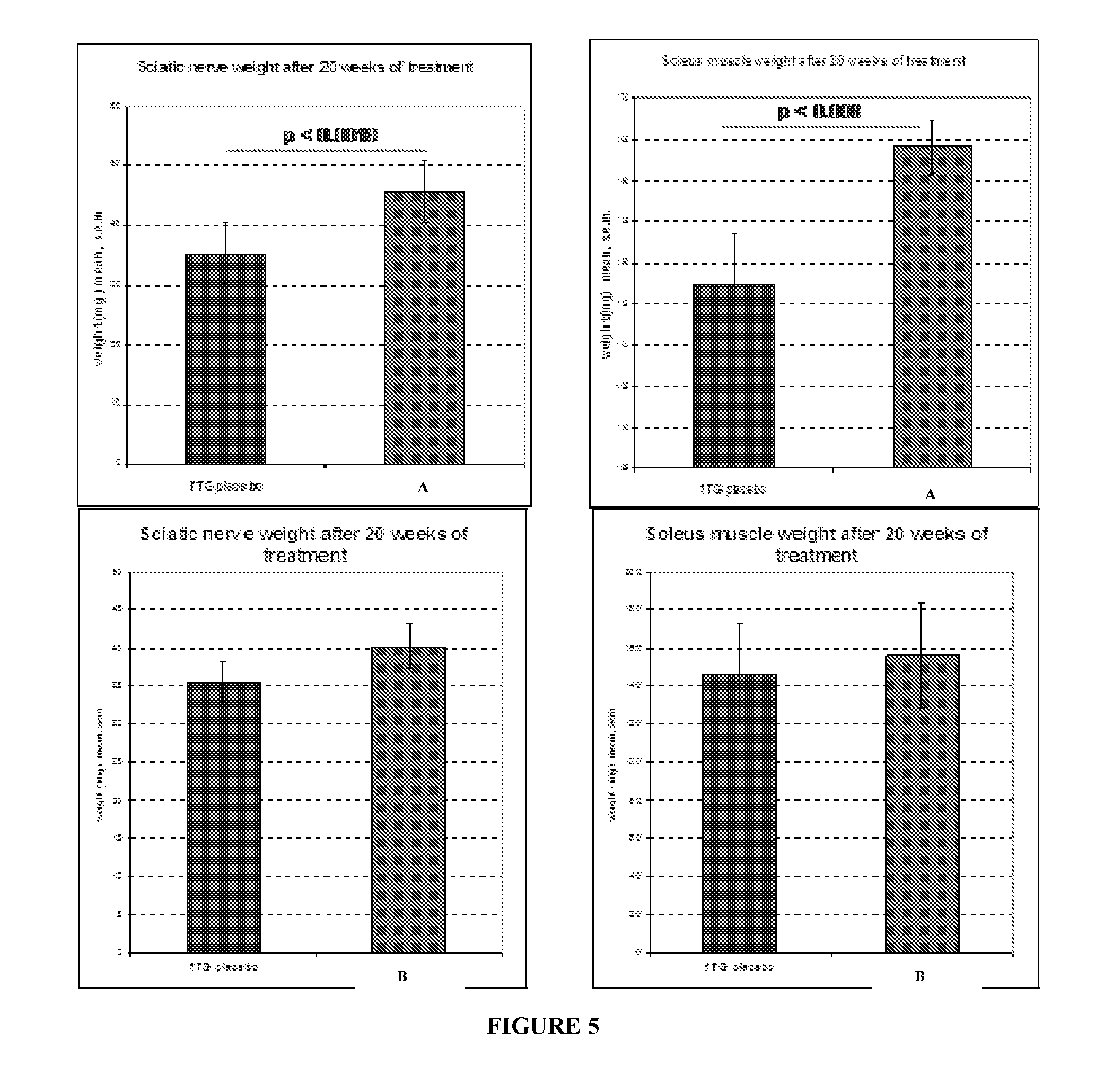
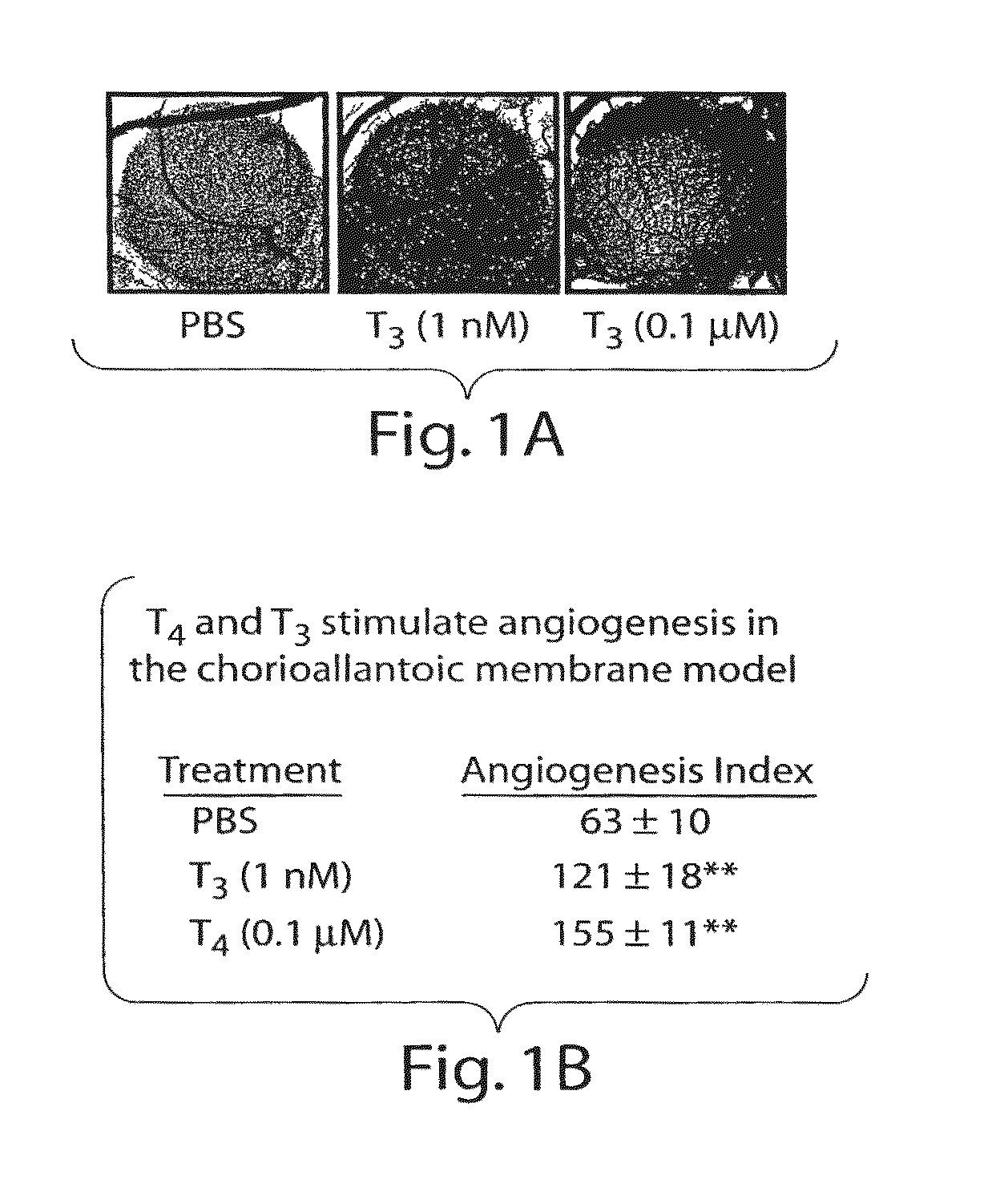
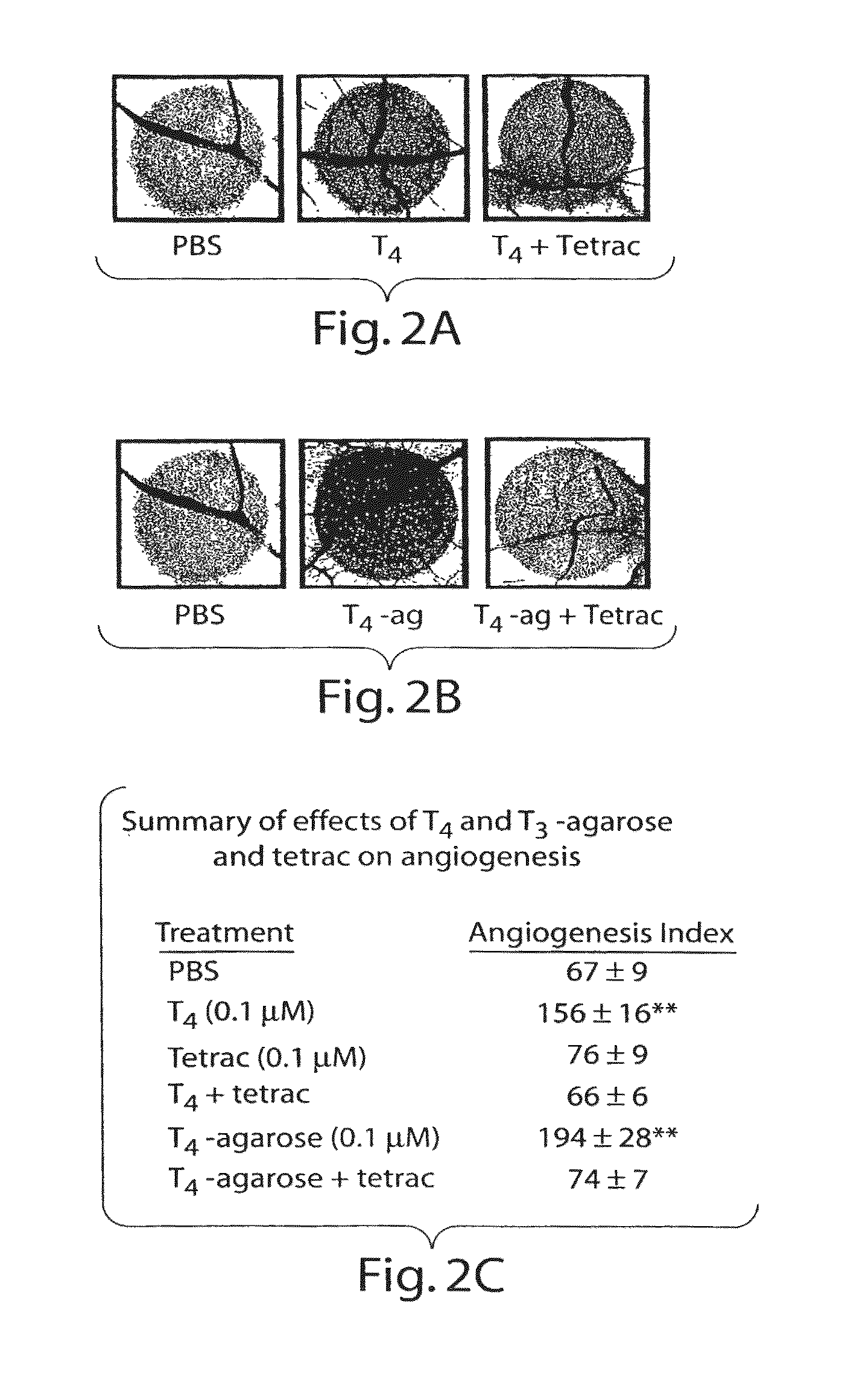
ActiveUS20080124280A1Compounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsThyroid hormonesAngiogenesis growth factor
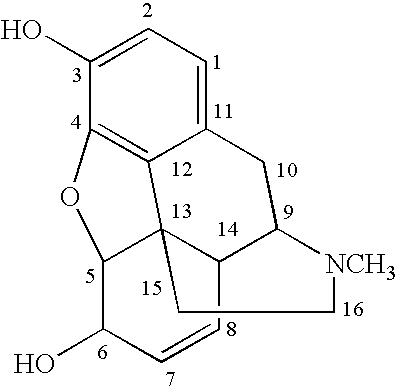
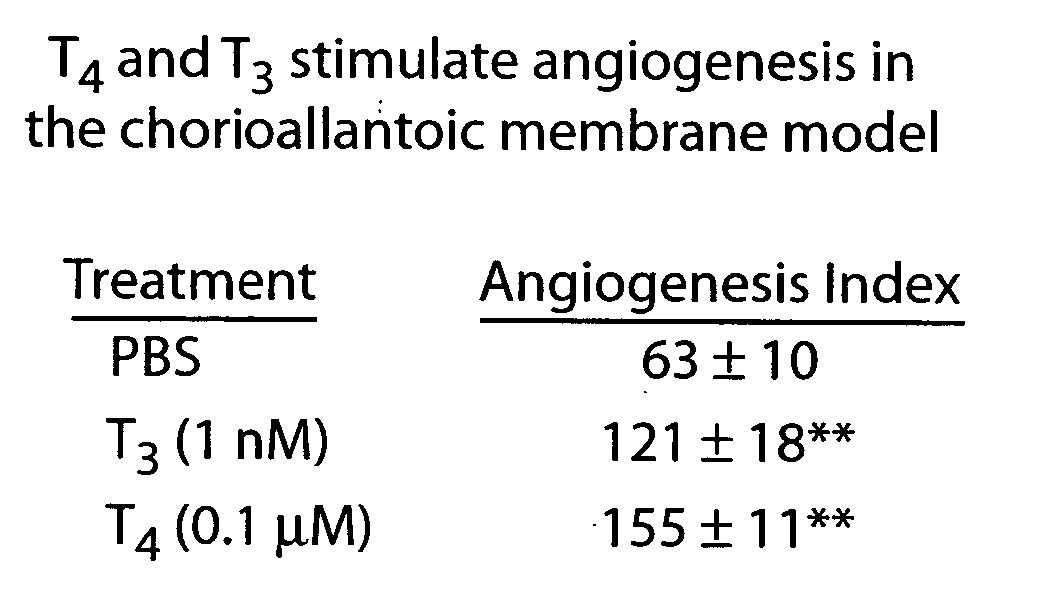
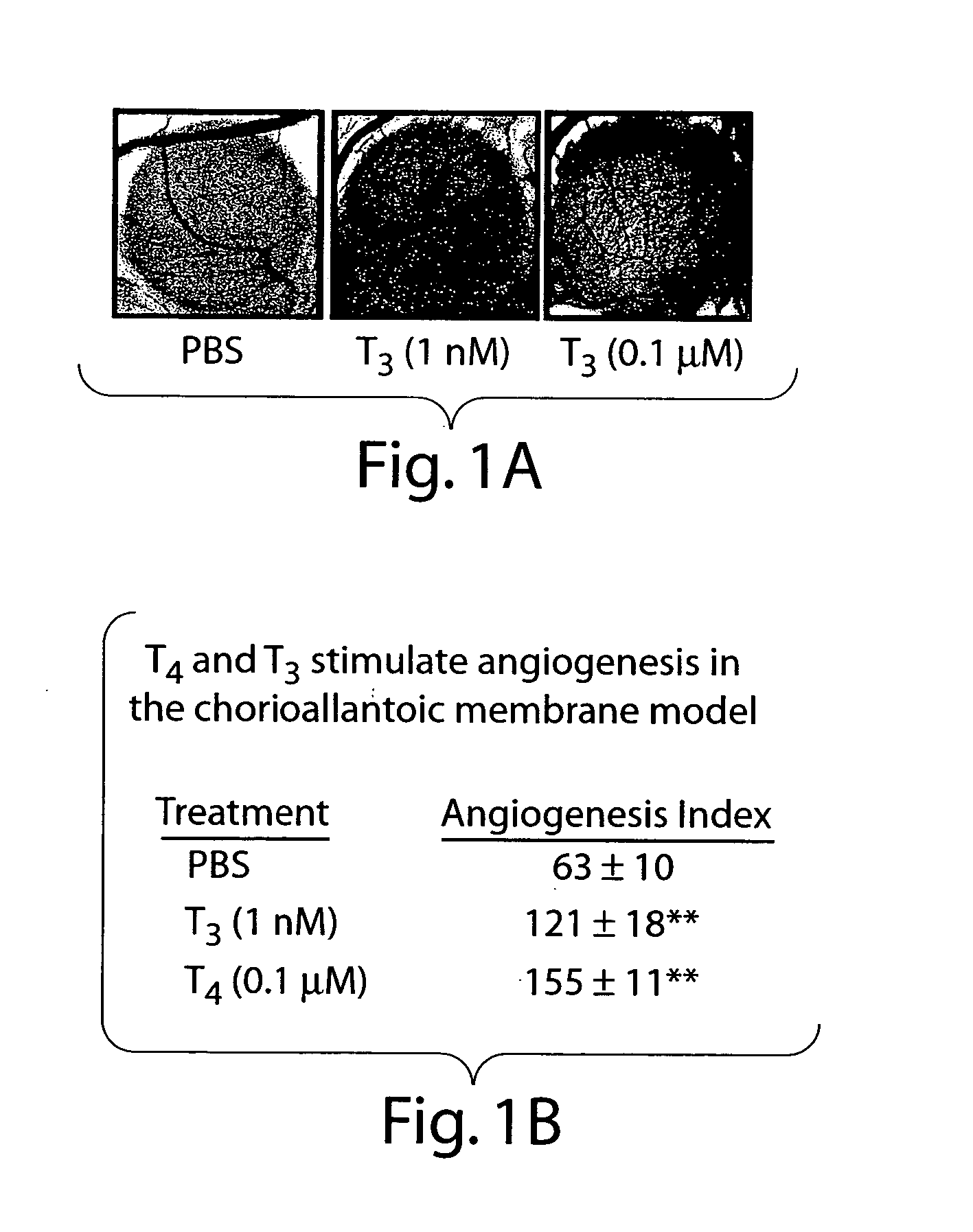
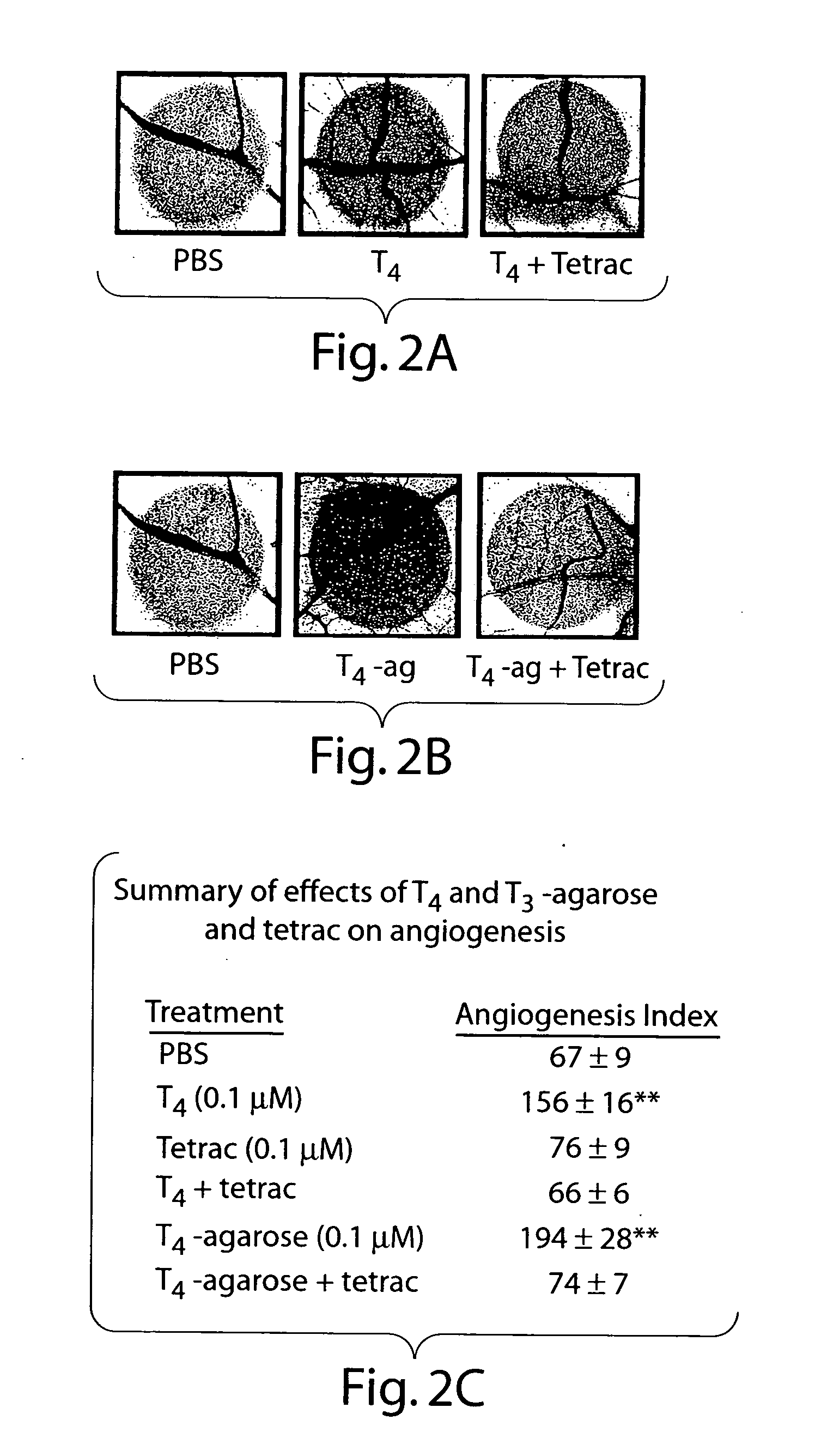
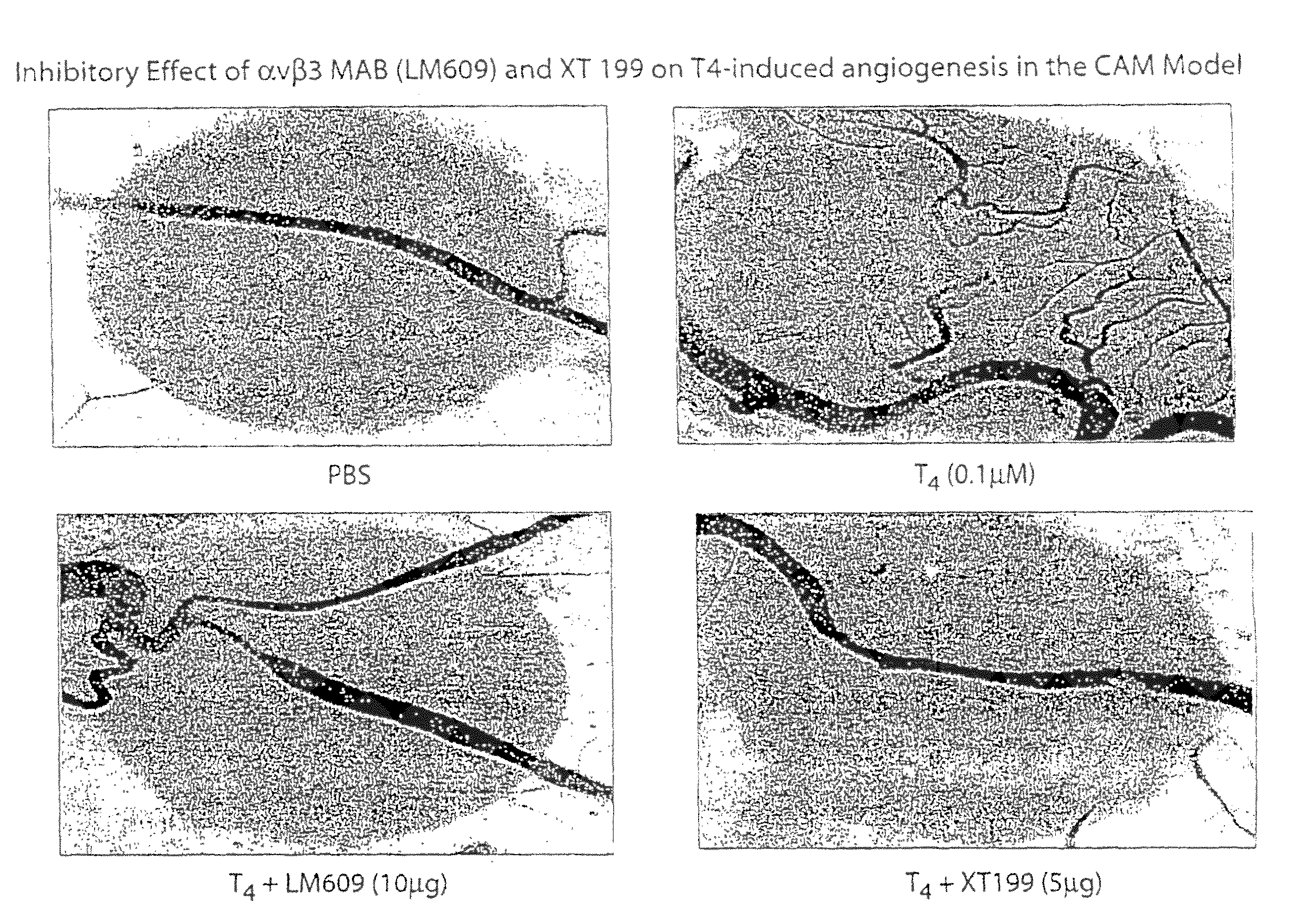
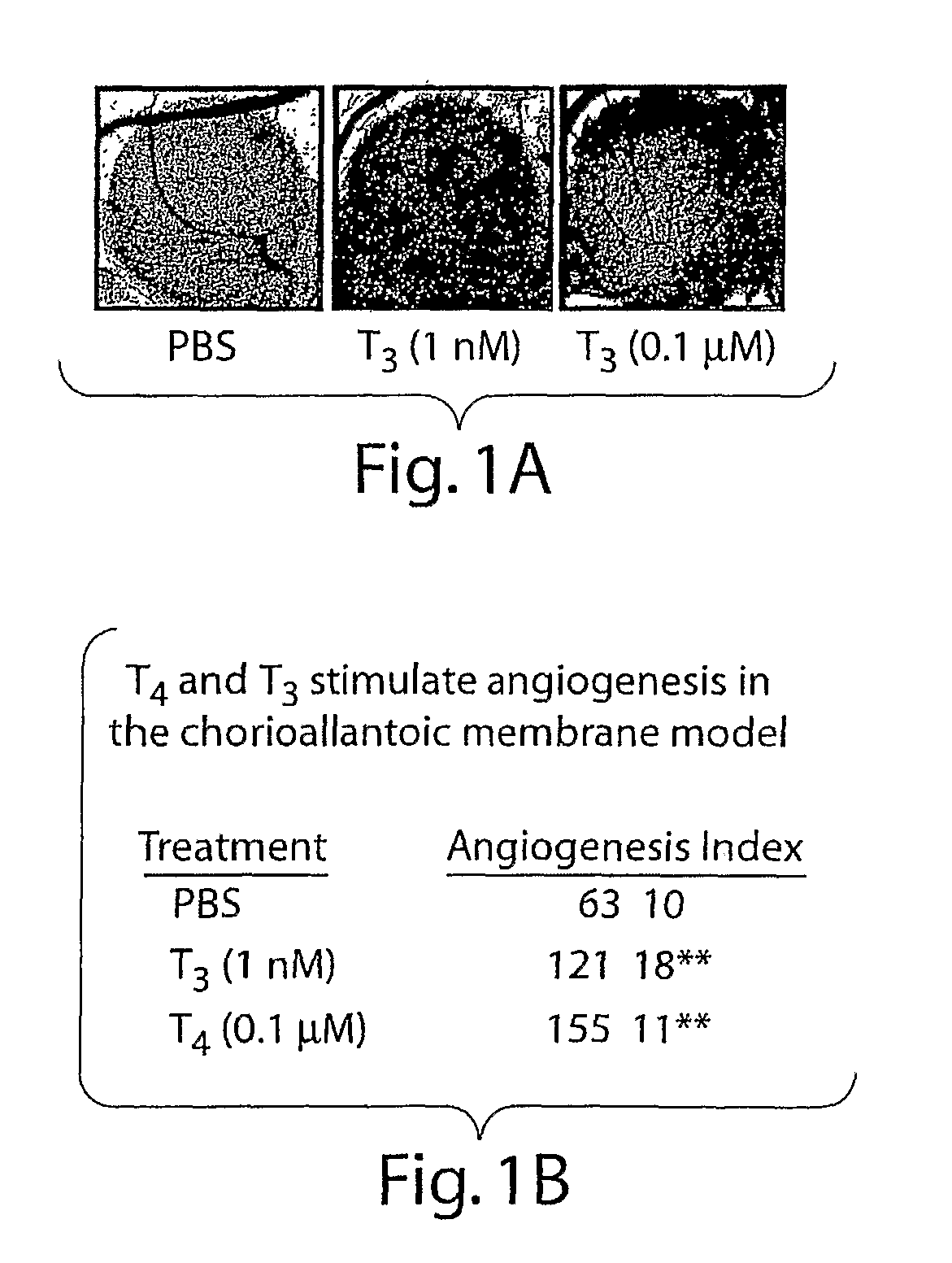
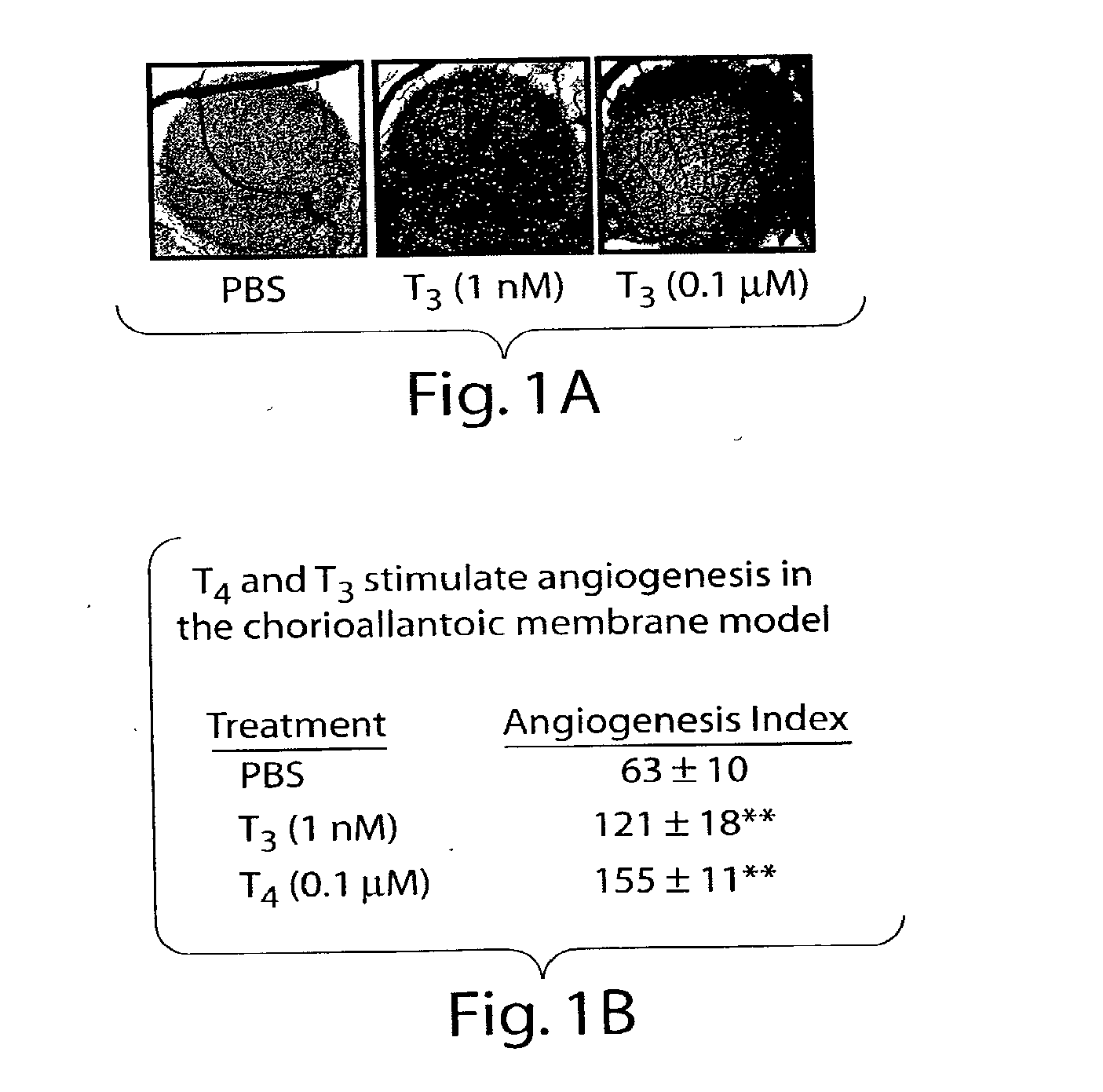
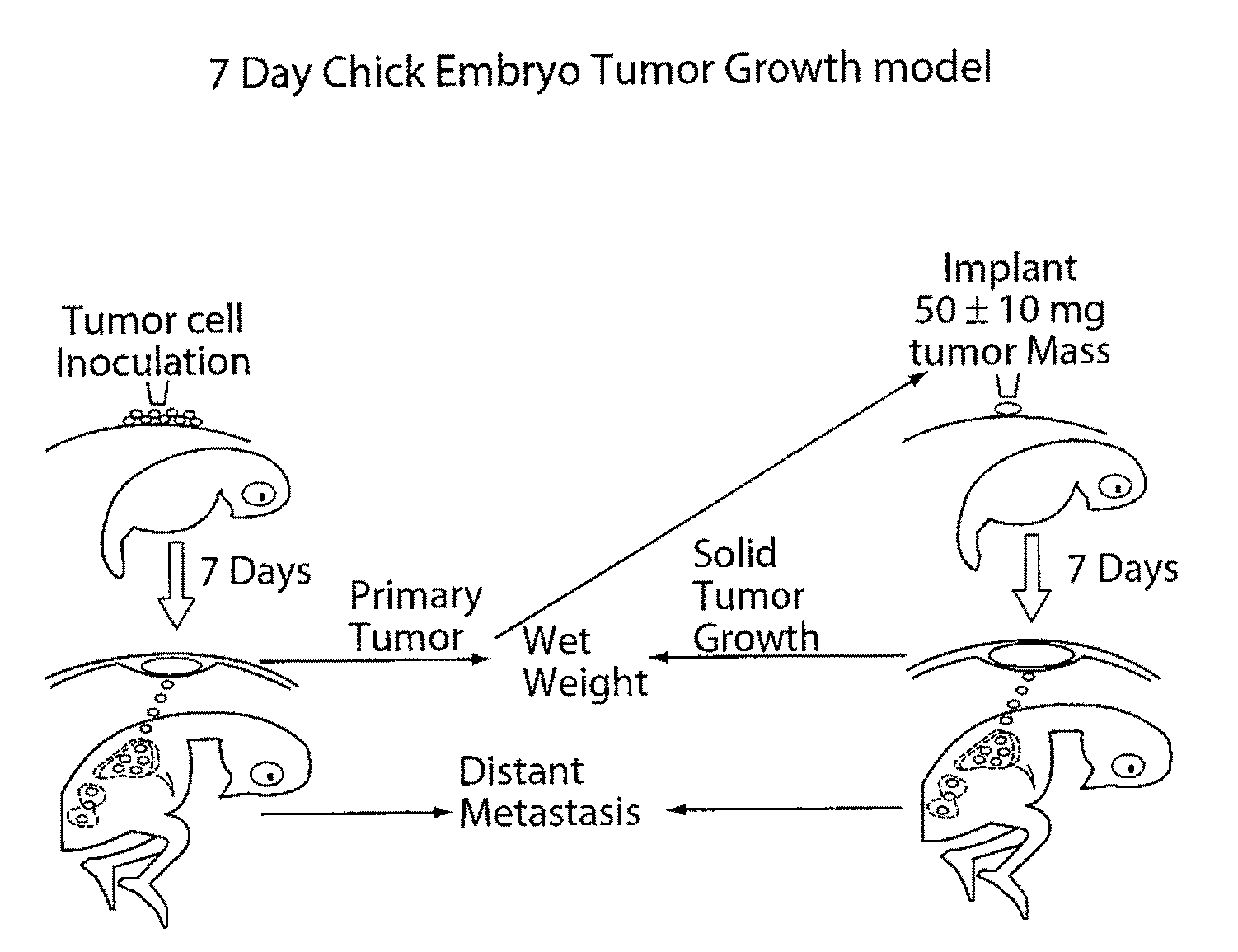
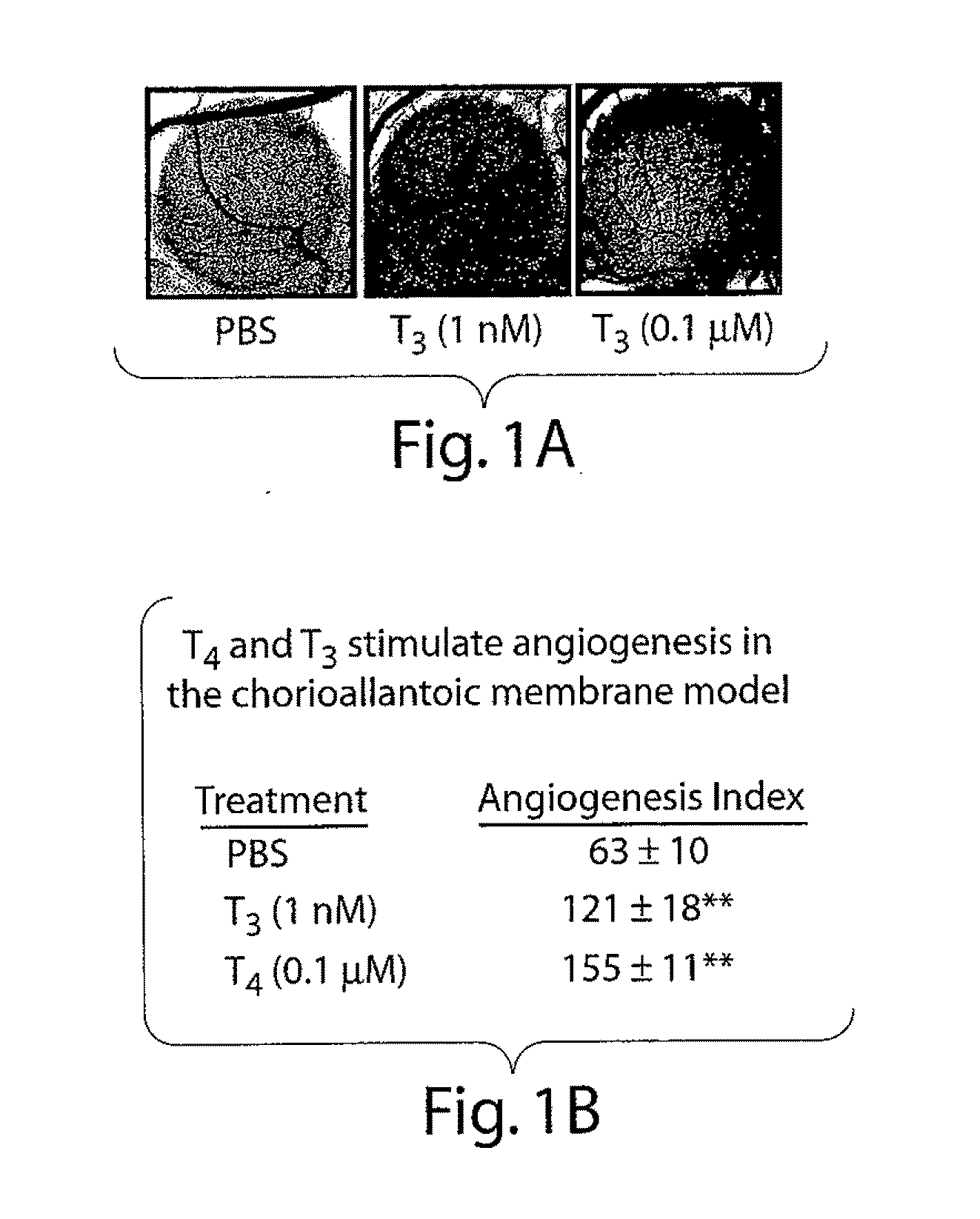
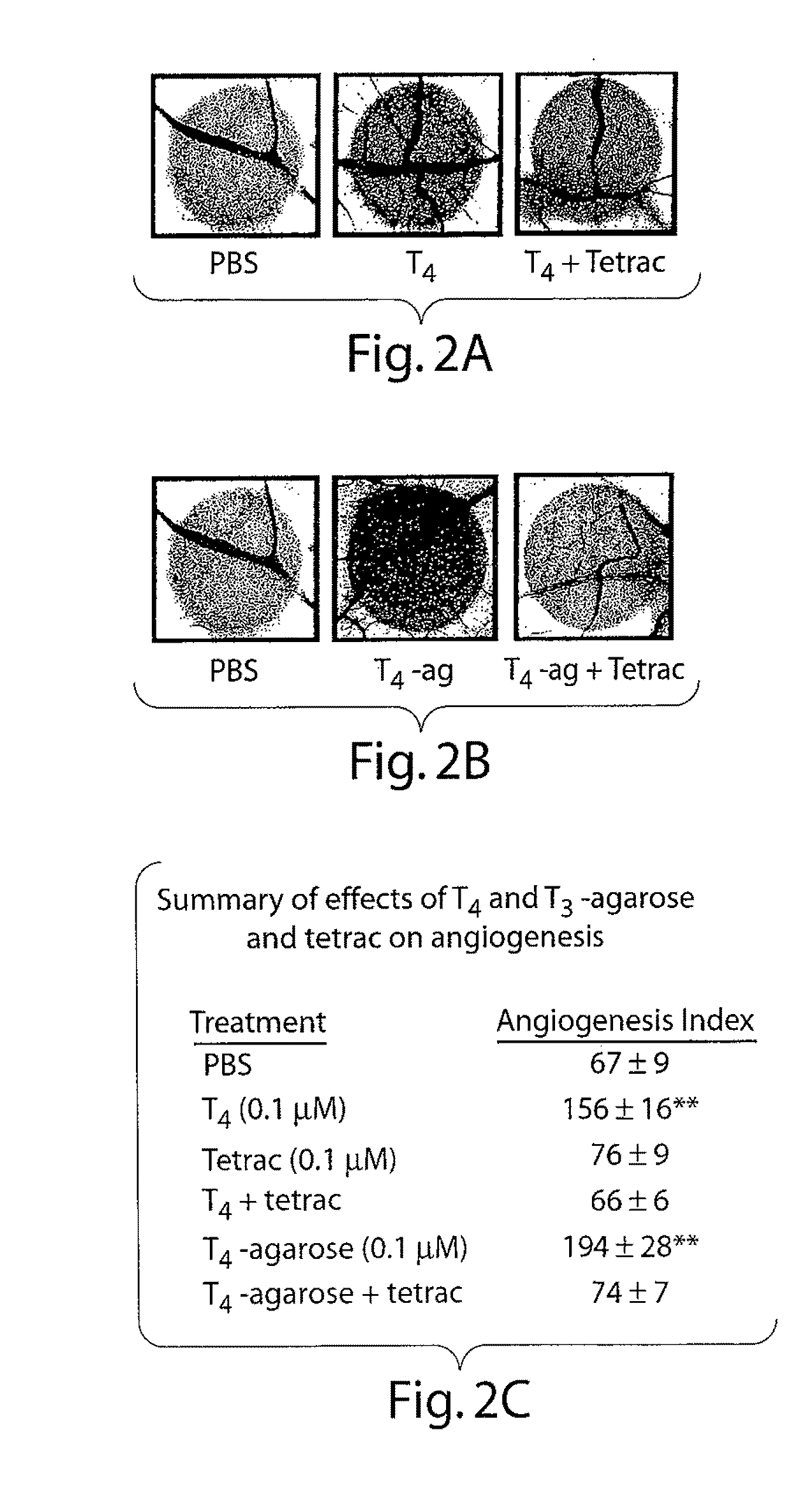
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
Phosphate derivatives of pharmaceutical products
InactiveUS20070042999A1Quick conversionReduce solubilityBiocideNervous disorderAnesthetic AgentPhosphate
According to the invention, there is provided a complex of a pharmaceutical compound selected from the group consisting of opioids, hormones, anaethetics and chemotherapeutic agents comprising the reaction product of: (a) one or more phosphate derivatives of one or more opioids, steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, anaesthetics or chemotherapeutic agents having a phenolic, primary alcohol, secondary alcohol or tertiary hydroxyl group; and (b) a complexing agent selected from the group comprising amphoteric surfactants, cationic surfactants, amino acids having nitrogen functional groups and proteins rich in these amino acids.
Owner:VITAL HEALTH SCIENCES PTY LTD
Thyroid hormone analogs and methods of use
InactiveUS20050124862A1High indexPromote angiogenesisPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsThyroid hormonesAngiogenesis growth factor
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
Compositions and methods for treating alzheimer's disease and dementia
The present invention relates to a method of treating, preventing, or delaying the onset of Alzheimer's disease and / or dementia in mammals. More particularly, the invention relates to method of administration of compositions containing defined chemical species useful for treating, preventing, or delaying the onset of Alzheimer's disease and / or dementia in mammals. In some embodiments, a composition used in connection with such methods comprises one or more of 1) thyroid hormone and 2) cyclo(His-Pro) and a zinc salt. Such compositions may also be used to treat metabolic syndrome and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Use of TGF-beta inhibitors to counteract pathologic changes in the level or function of steroid/thyroid receptors
The invention concerns the use of TGF-beta inhibitors to counteract a pathologic change in the expression level, activity and / or signaling of a receptor of the steroid-thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. In particular, the invention concerns a method for counteracting a pathologic change in a signal-transduction pathway involving a member of the steroid / thyroid hormone super-family, comprising administering to a mammalian subject in need an effective amount of a compound capable of inhibiting TGF-beta signaling through a TGF-beta receptor.
Owner:SCIOS
Pharmaceutical formulations for thyroid hormones
The present invention provides for pharmaceutical formulations based on thyroid hormones enabling a safe and stable oral administration in the framework of the strict therapeutic index prescribed in case of thyroid disorders.
Owner:ALTERGON
Thyroid hormone analogs and methods of use
ActiveUS8071134B2Compounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsThyroid hormonesAngiogenesis growth factor
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
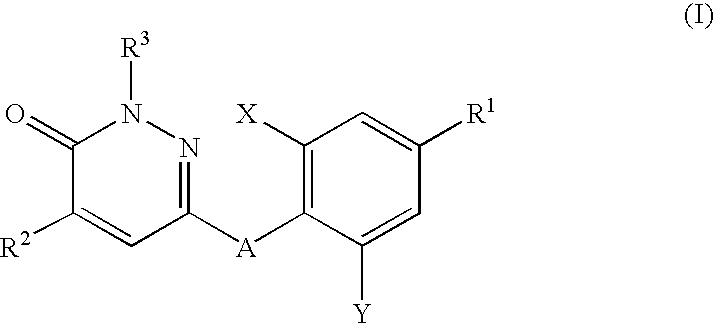
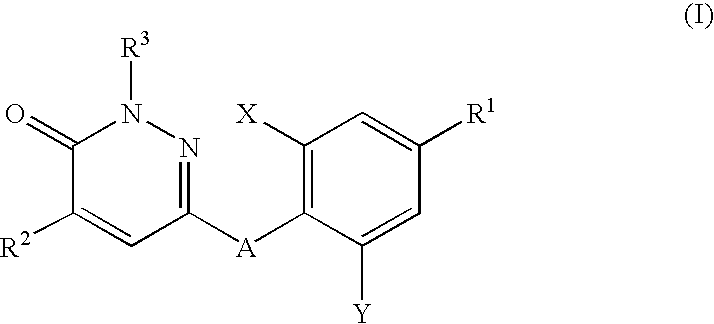
Substituted pyridazinone compound
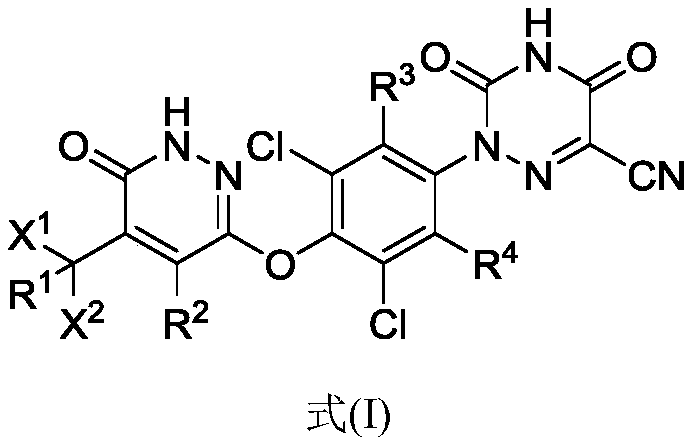
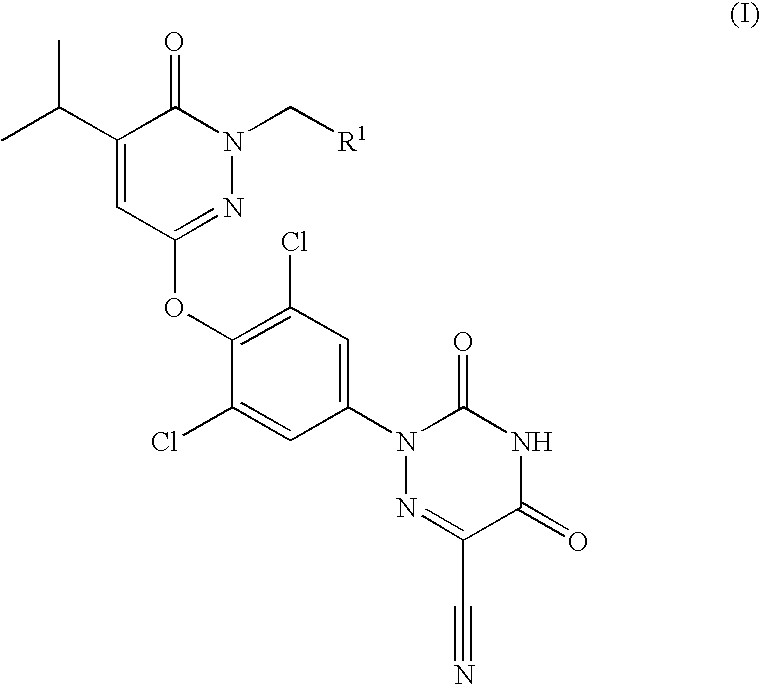
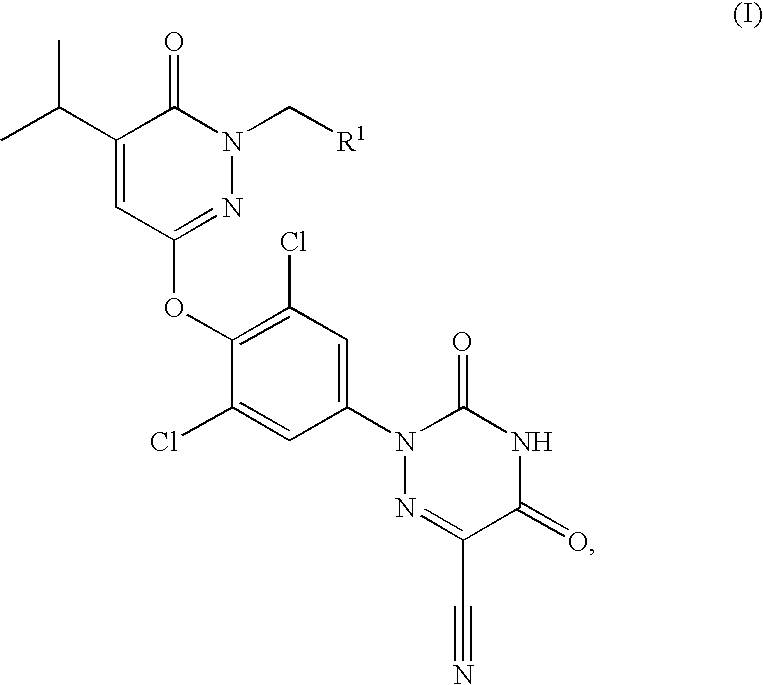
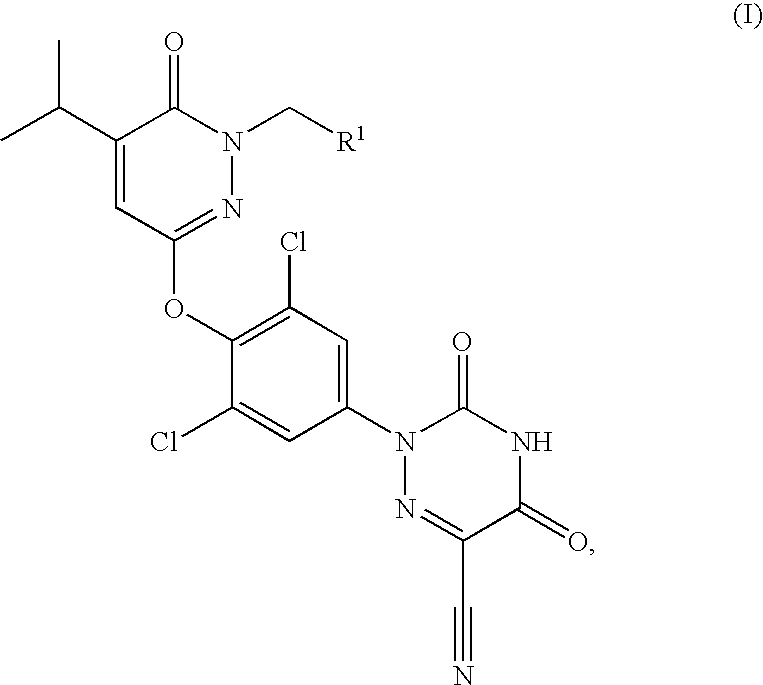
ActiveCN109574995AIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsMetabolism disorderDiseaseThyroid hormones
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition of a substituted pyridazinone compound, and application thereof. The substituted pyridazinone compound is a compound as shown in formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, hydrate or solvent compound, crystalline form, stereoisomer or isotopic variant thereof. The compound, namely a THR-beta agonist, can be used for treating and / or preventing diseases regulated by thyroid hormone analogs.
Owner:SHENZHEN TARGETRX INC
Thyroid hormone analogs
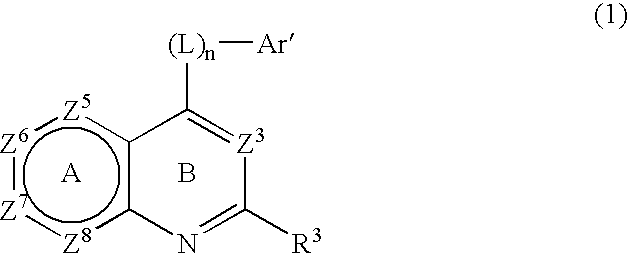
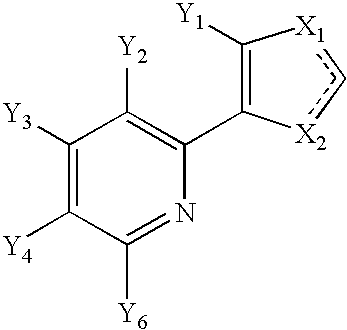
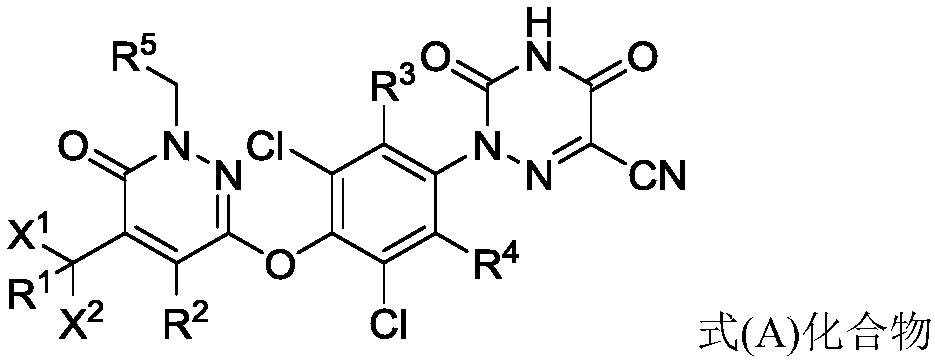
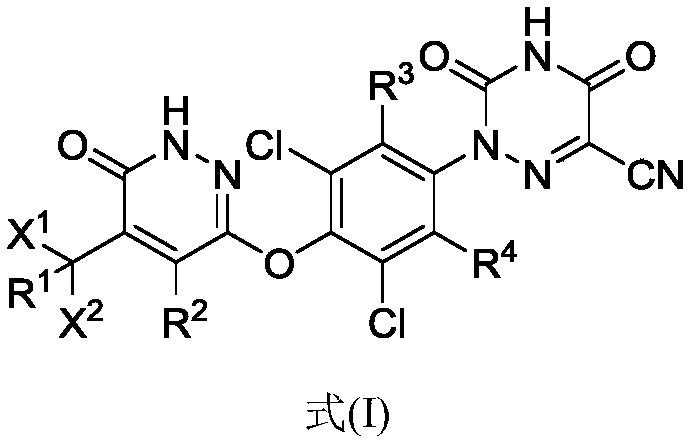
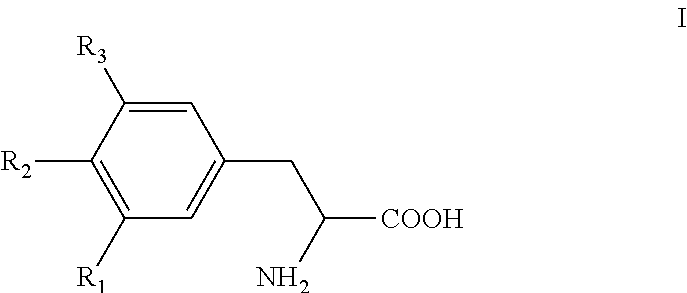
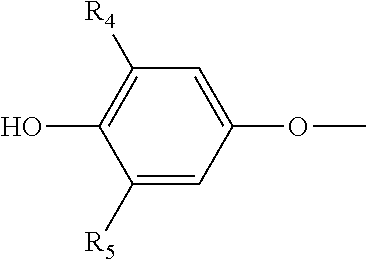
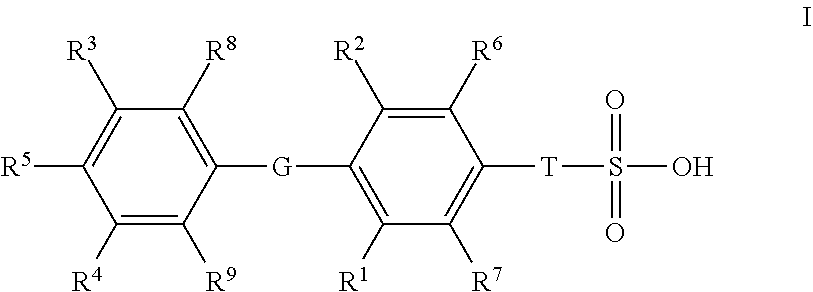
Provided herein are compounds of the formula (I):as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the substituents are as those disclosed in the specification. These compounds, and the pharmaceutical compositions containing them, are useful for the treatment of diseases such as obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes and other related disorders and diseases, and may be useful for other diseases such as NASH, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, hypothyroidism, thyroid cancer and other disorders and diseases related thereto.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Thyroid hormone analogs and methods of use
ActiveUS20140072635A1BiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsThyroid hormonesAngiogenesis growth factor
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
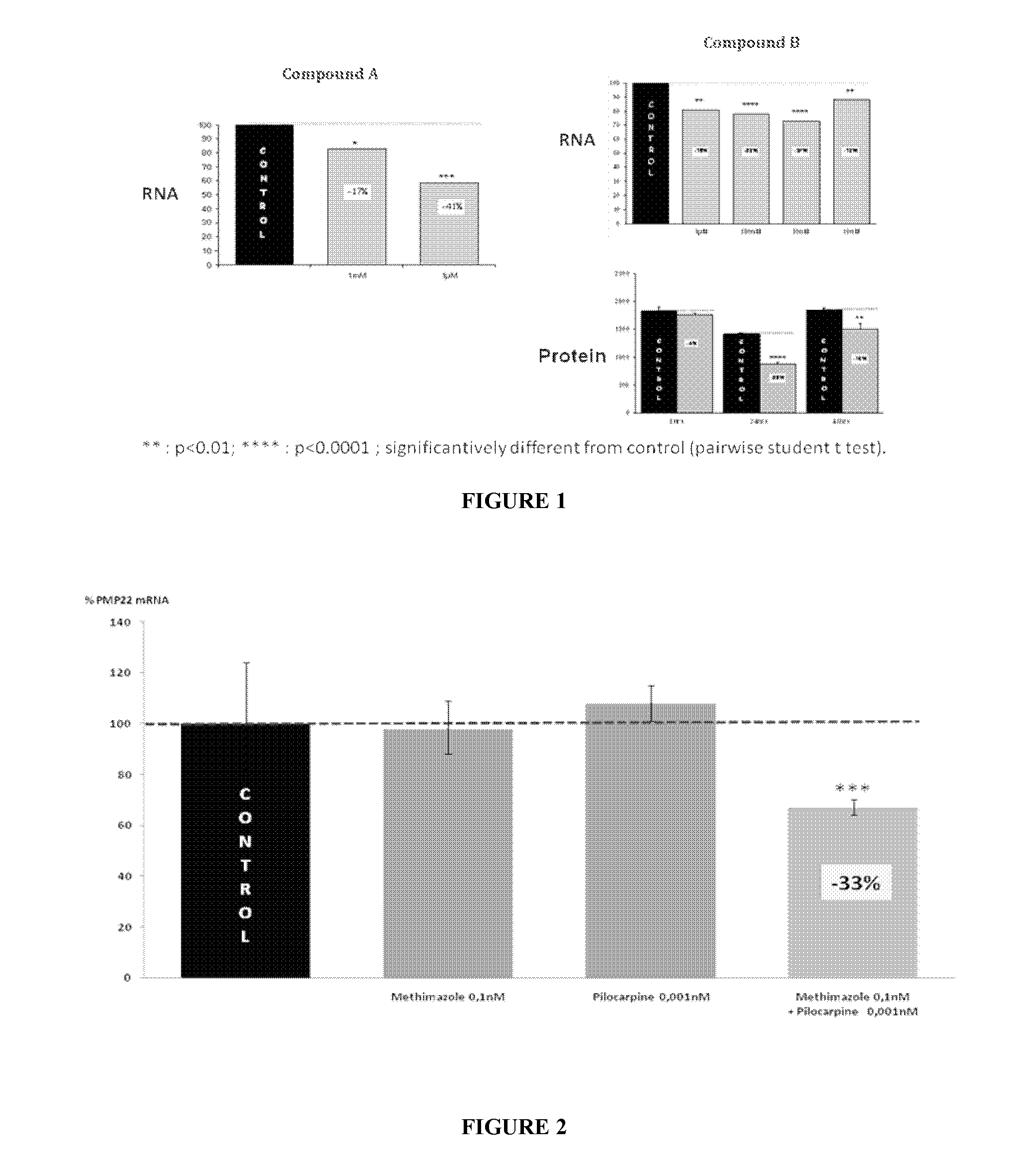
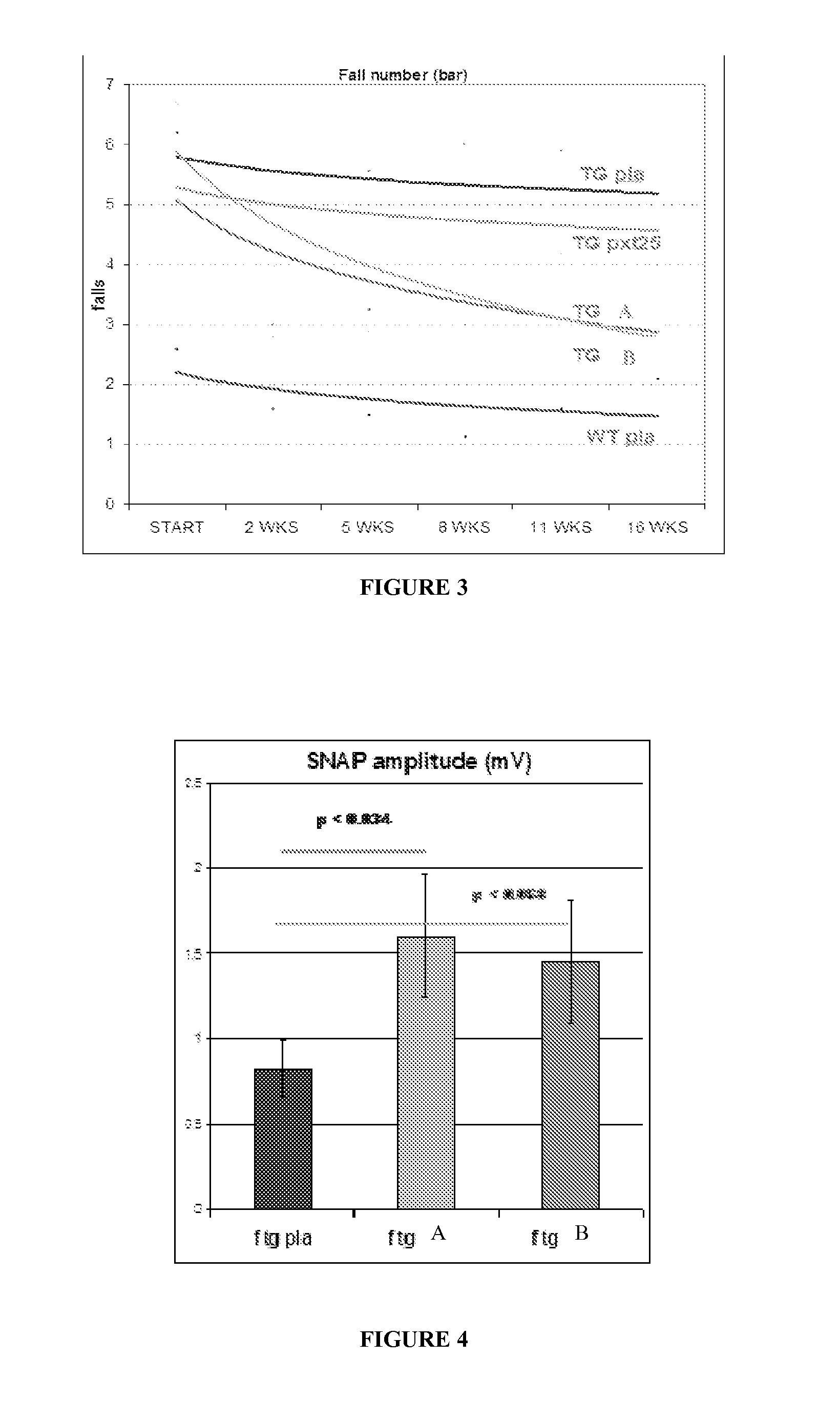
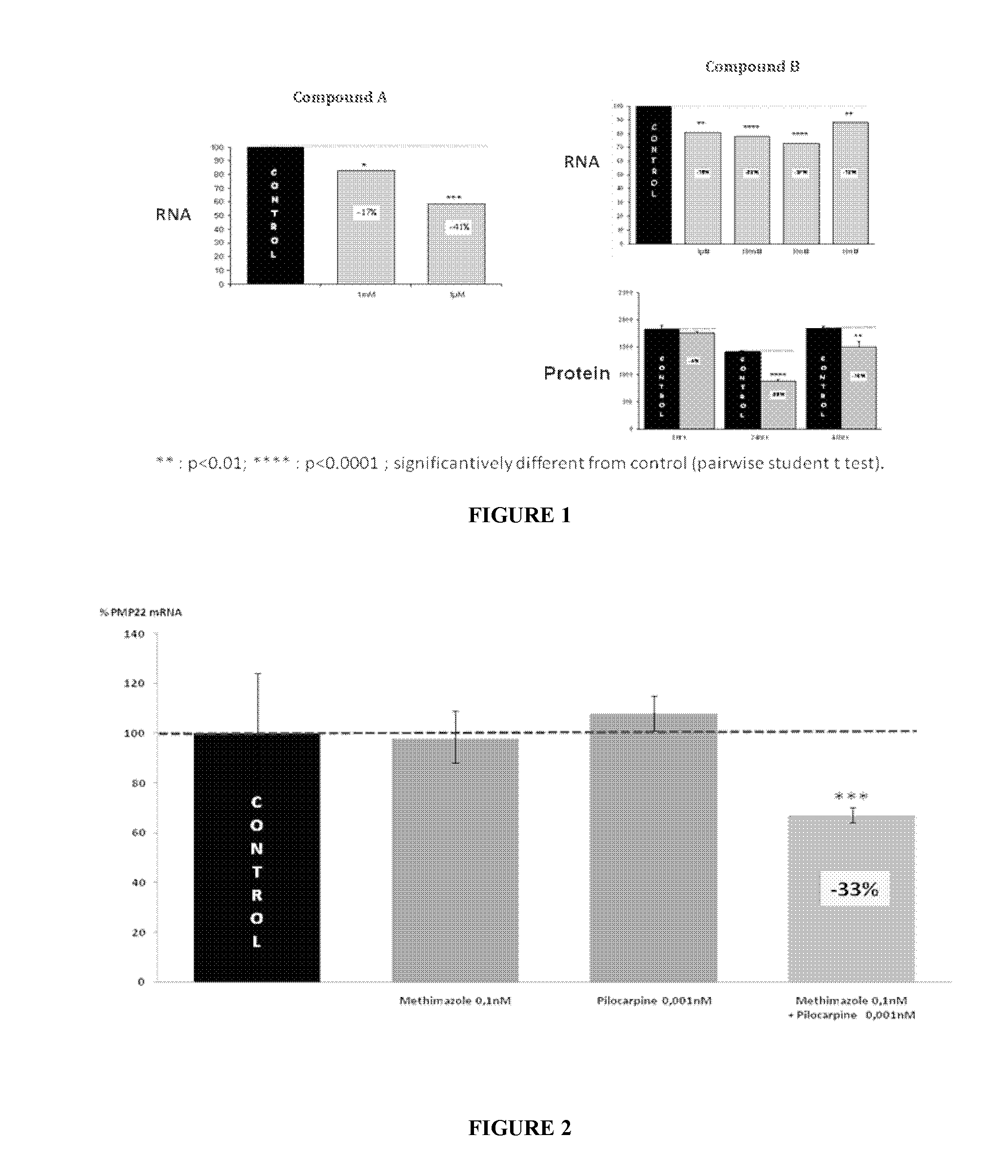
Combination of pilocarpin and methimazol for treating Charcot-Marietooth disease and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting simultaneously muscarinic receptor signaling and thyroid hormone pathway in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Pharmaceutical formulae for thyroid hormones and procedures for obtaining them
The present invention provides pharmaceutical formulation for thyroid hormones which allow safe and stable administration by mouth within the ambit of the narrow therapeutic index prescribed in the case of thyroid dysfunctions, as well as procedures for obtaining
Owner:ALTERGON
Thyroid hormone analogs and methods of use
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
Prodrugs of thyroid hormone analogs
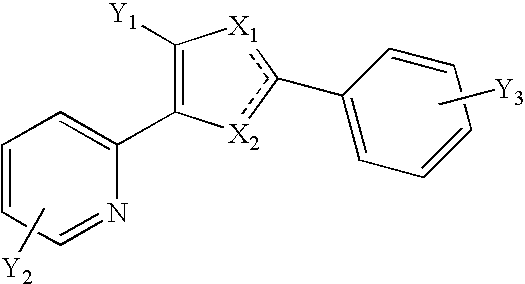
Provided herein are compounds of the formula (I):as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the substituents are as those disclosed in the specification. These compounds, and the pharmaceutical compositions containing them, are useful for the treatment of diseases such as obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes and other related disorders and diseases, and may be useful for other diseases such as NASH, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, hypothyroidism, thyroid cancer and other disorders and diseases related thereto.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Combination of pilocarpin and methimazol for treating charcot-marietooth disease and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting simultaneously muscarinic receptor signaling and thyroid hormone pathway in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Novel methods of treating or preventing fibrotic lung diseases
The invention includes a method of preventing or treating a fibrotic lung disease in a subject, comprising administering to the subject a thyroid hormone by inhalation and / or aerosolization. The invention further comprises compositions and kits comprising compositions useful within the invention.
Owner:YALE UNIV
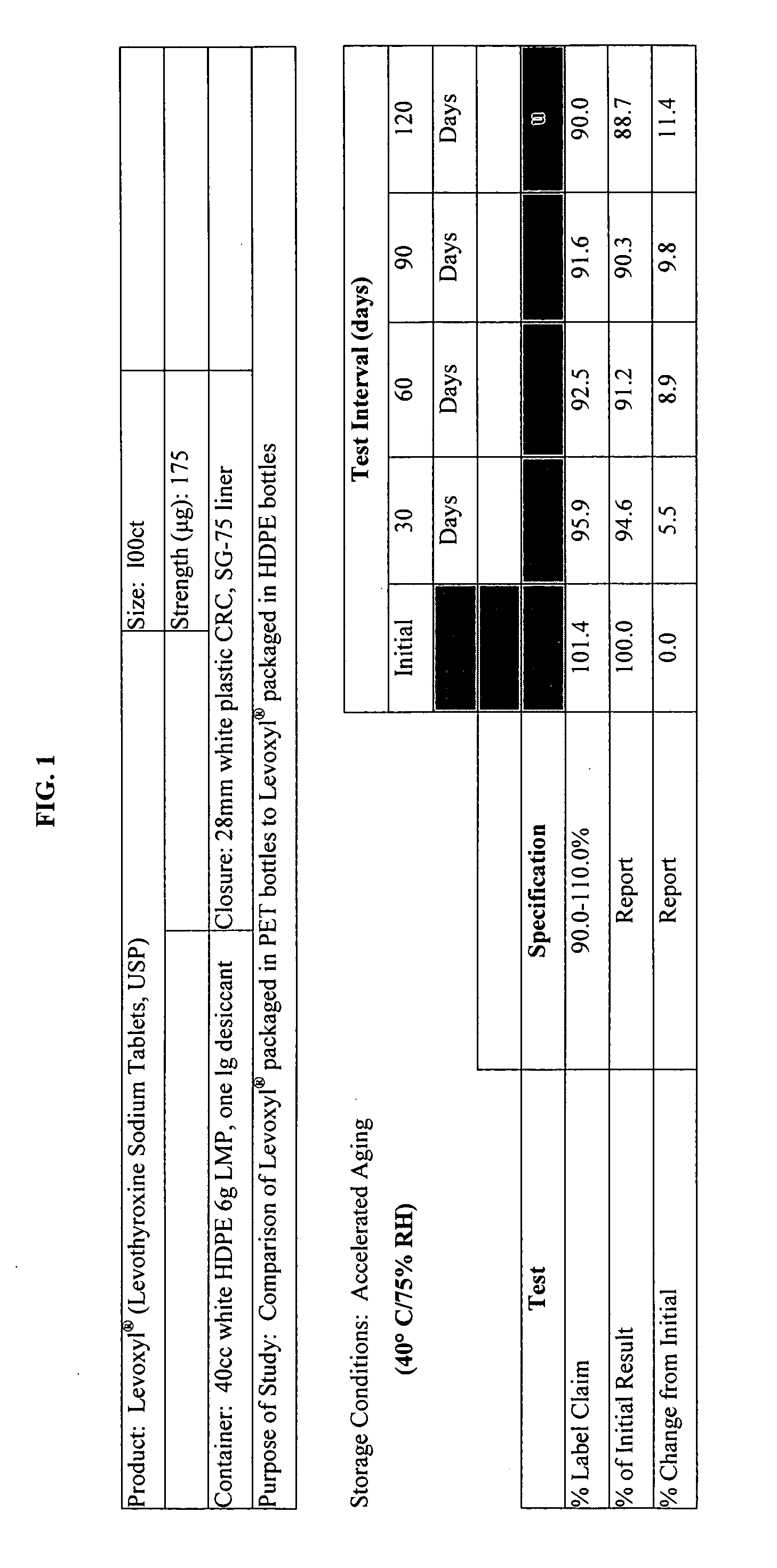
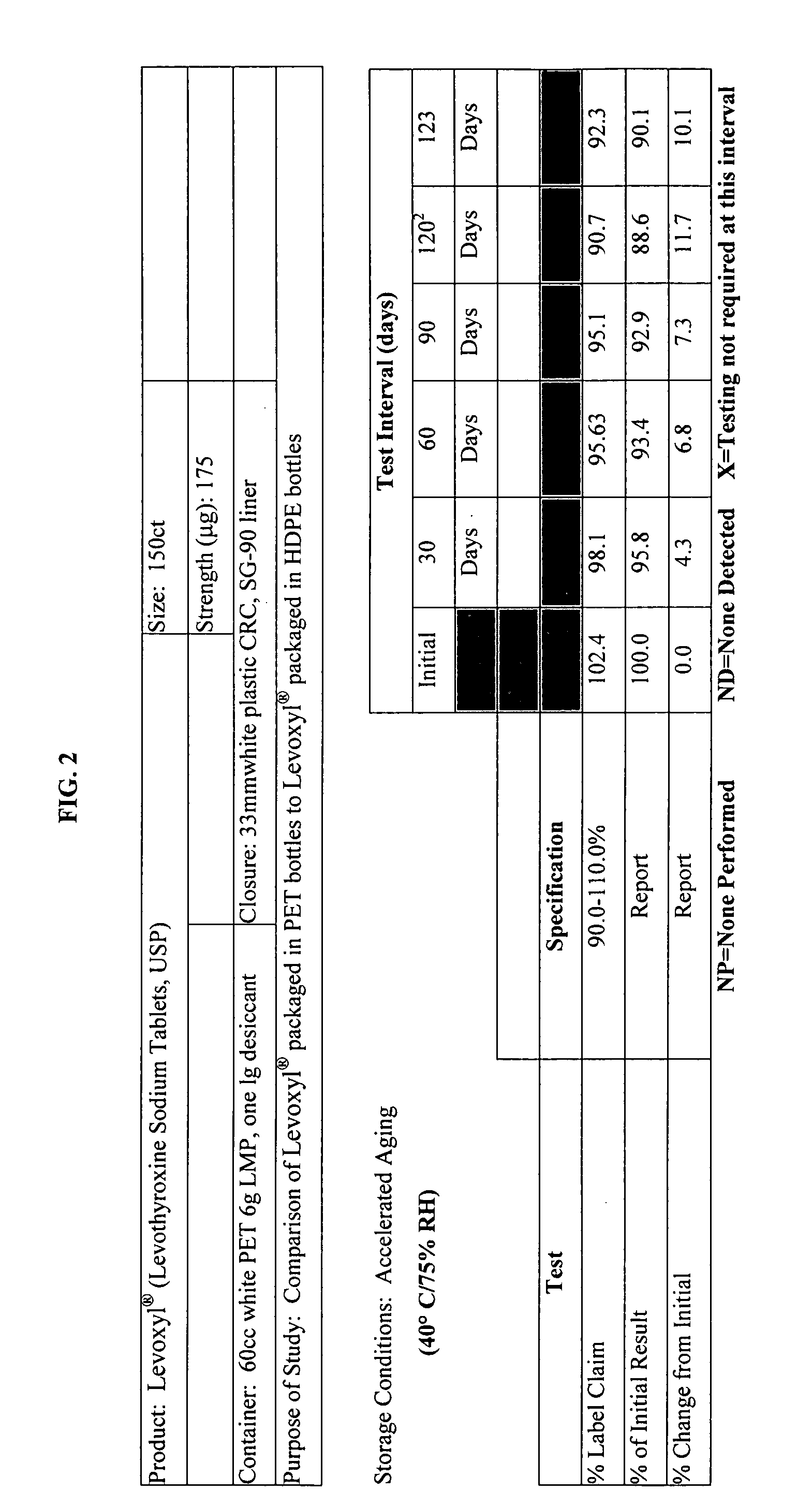
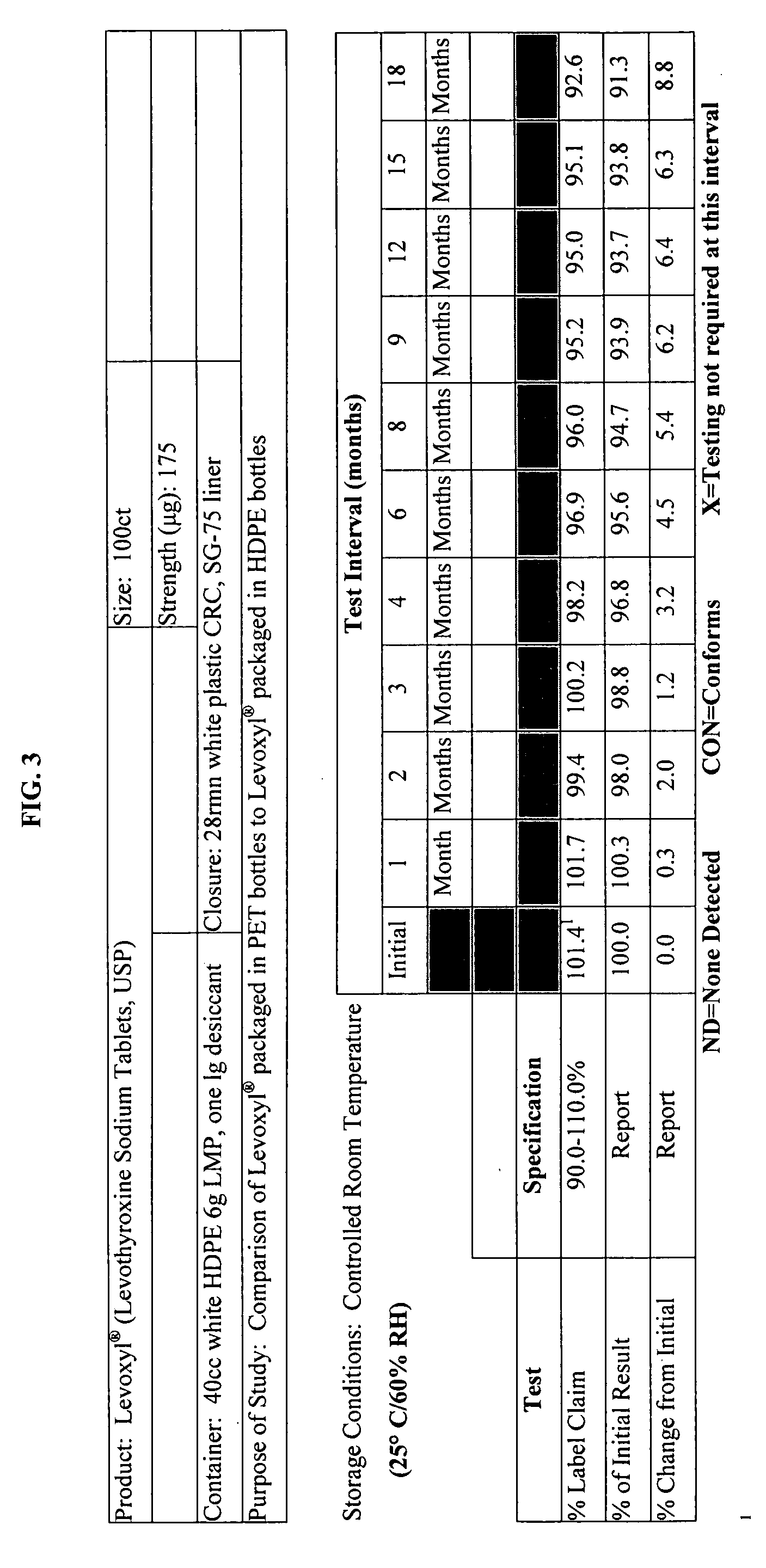
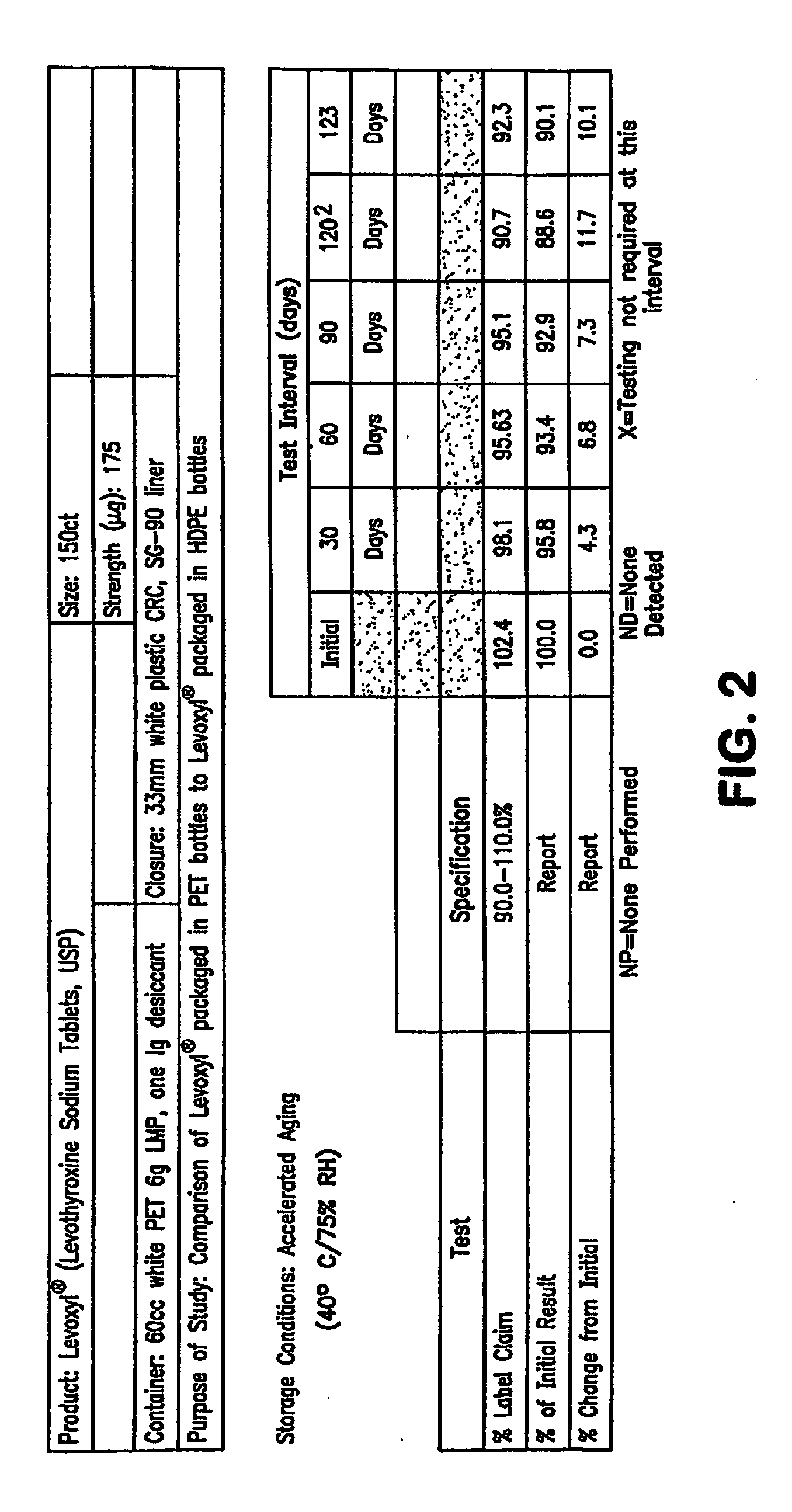
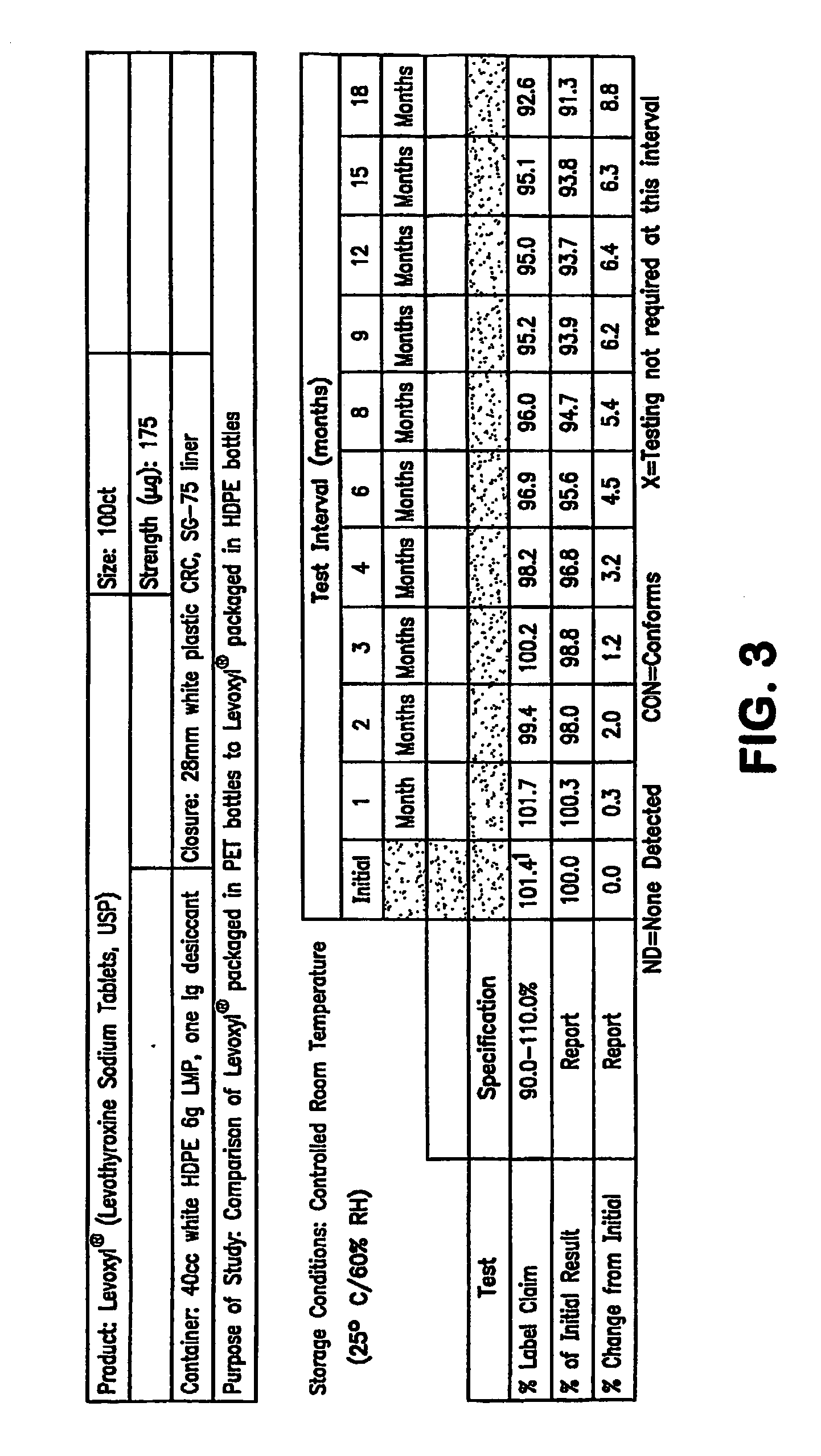
Oxygen-impervious packaging with optional oxygen scavenger, stabilized thyroid hormone compositions and methods for storing thyroid hormone pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20060183804A1Improve performanceHead spaceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsThyroid hormonesLiothyronine Sodium
Novel packaging, methods of packaging and methods for storing thyroid hormone pharmaceutical compositions, such as levothyroxine (T4) sodium and liothyronine (T3) sodium, in reduced oxygen conditions for maintaining the stability and potency of the thyroid hormones during extended shelf life are provided.
Owner:KING PHARMA RES & DEV
Methods of administering levothyroxine pharmaceutical compositions
ActiveUS7101569B2Improve bioavailabilityExtended shelf lifeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideThyroid hormonesImmediate release
The present invention generally relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of making and administering such compositions. In one aspect, the invention features stabilized pharmaceutical compositions that include pharmaceutically active ingredients such as levothyroxine (T4) sodium and liothyronine (T3) sodium (thyroid hormone drugs), preferably in an immediate release solid dosage form. Also provided are methods for making and using such immediate release and stabilized compositions.
Owner:FRANZ G ANDREW +3
Oxygen-impervious packaging with optional oxygen scavenger, stabilized thyroid hormone compositions and methods for storing thyroid hormone pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20090297566A1Improve performanceEasy maintenanceBiocideOrganic active ingredientsThyroid hormonesLiothyronine
The present invention provides stabilized thyroid hormone pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of packaging and storing thyroid hormone pharmaceutical compositions, such as levothyroxine (T4) sodium and liothyronine (T3) sodium, in reduced oxygen conditions for maintaining the stability and potency of the thyroid hormones during extended shelf life.
Owner:BRINKMAN KYLE R +2
Saccharide free, storage stable thyroid hormone active drug formulations and methods for their production
Embodiments of the present invention provide pharmaceutical compositions in unit dosage form that comprise a therapeutically effective amount of levothyroxine sodium; an antioxidant in an amount sufficient to stabilize the levothyroxine sodium against oxidation; an amount of an alditol sufficient to stabilize the levothyroxine sodium; and at least two excipients selected from a filler, a binder, and a lubricant. Such compositions are free of added monosaccharide, disaccharide, and an oligosaccharide and are storage stable.
Owner:FAMYGEN LIFE SCI INC
Thyroid Hormone Analogs and Methods of Use
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of thyroid hormone, or an antagonist thereof, to promote or inhibit angiogenesis in the subject. Compositions of the polymeric forms of thyroid hormone, or thyroid hormone analogs, are also disclosed.
Owner:NANOPHARM
Method and composition for restoration of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body
InactiveUS7414021B2Easy to producePromote productionCosmetic preparationsBiocideInsulin-like growth factorThyroid hormones
A treatment method for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body is disclosed which includes injecting an injectable composition containing a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier into the dermis, the hypodermis, or both, in various areas of the face, or selected areas of the body of a person to stimulate collagen, elastin, or fat cell production, thereby restoring age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body. Further disclosed is an injectable composition for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body, which contains a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier for providing time release of the growth factor into tissues. The growth factor can be insulin, insulin-like growth factor, thyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor, estrogen, retinoic acid, or their combinations.
Owner:CELLHEALTH TECH
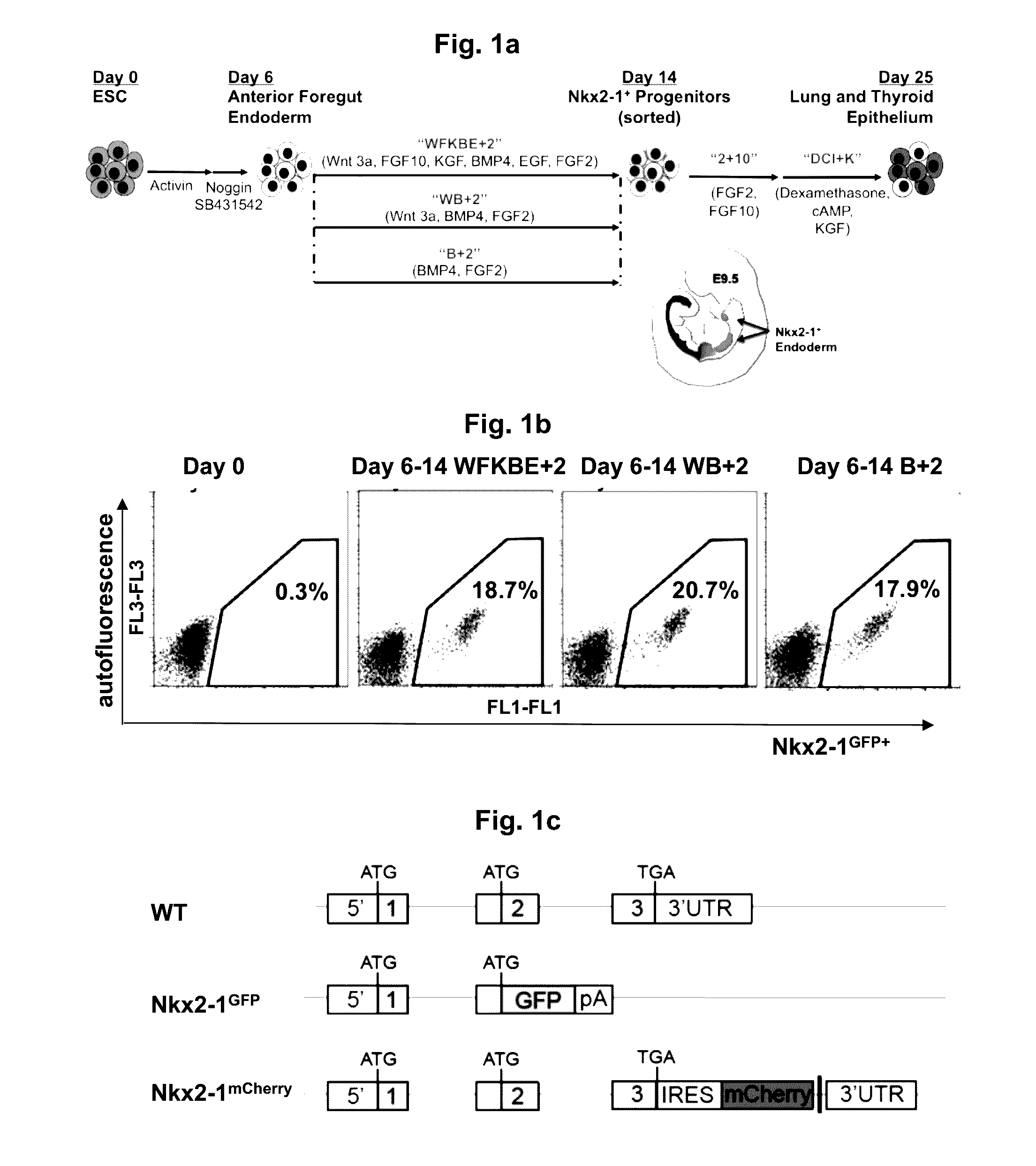
Differentiation of stem cells into thyroid tissue
ActiveUS20170027994A1Reduction amelioration of symptomRetain their thyroid functionPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processThyroid hormonesThyroid Gland Tissue
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
Concentrated Liquid Thyroid Hormone Composition
This invention is directed generally to a liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one thyroid hormone (particularly a composition further comprising at least one cyclodextrin compound), a process for making such a composition and a method of using such a composition to treat a condition associated with impaired thyroid hormone function.
Owner:INTERVET INT BV
Levothyroxine compositions and methos
InactiveUS20080003284A1Improve bioavailabilityExtended shelf lifeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsThyroid hormonesImmediate release
The present invention generally relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of making and administering such compositions. In one aspect, the invention features stabilized pharmaceutical compositions that include pharmaceutically active ingredients such as levothyroxine (T4) sodium and liothyronine (T3) sodium (thyroid hormone drugs), preferably in an immediate release solid dosage form. Also provided are methods for making and using such immediate release and stabilized compositions.
Owner:FRANZ G ANDREW +3
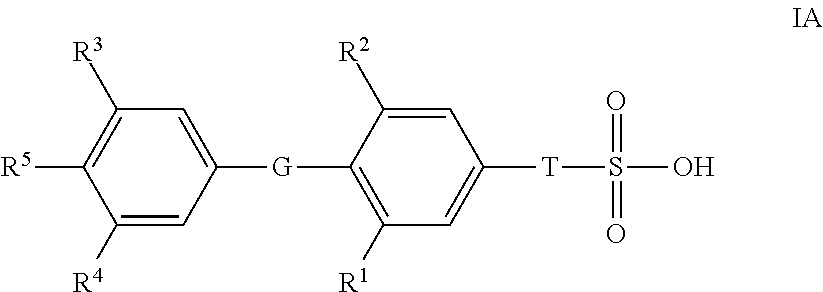
Novel Sulfonic Acid-Containing Thyromimetics, and Methods for Their Use
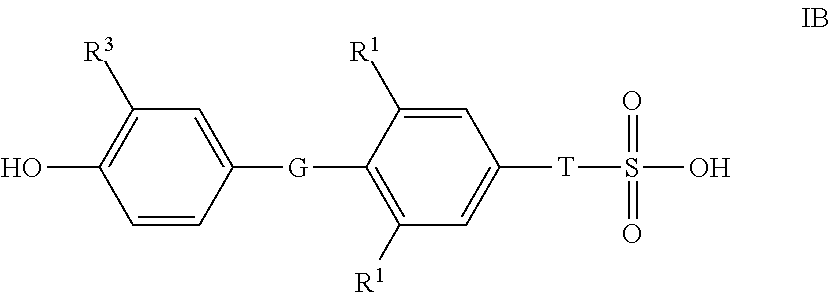
The present invention relates to sulfonic acid containing compounds of formula IB, in which G, R1, R3 and T are as defined in the claims, that bind to thyroid receptors in the liver. Activation of these receptors results in modulation of gene expression of genes regulated by thyroid hormones. The compounds can be used to treat diseases and disorders including metabolic diseases such as obesity, NASH, hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia, as well as associated conditions such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome X and diabetes.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com