Antagonists of BMP and TGF beta signalling pathway
A transforming growth factor, active technology, applied to the nucleic acid, oligonucleotide or nucleic acid encoding the Smurf protein of the present invention, the antibody that specifically binds to the Smurf protein, and the human Smurf protein field, which can solve the problems of elusive mechanism and purpose.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
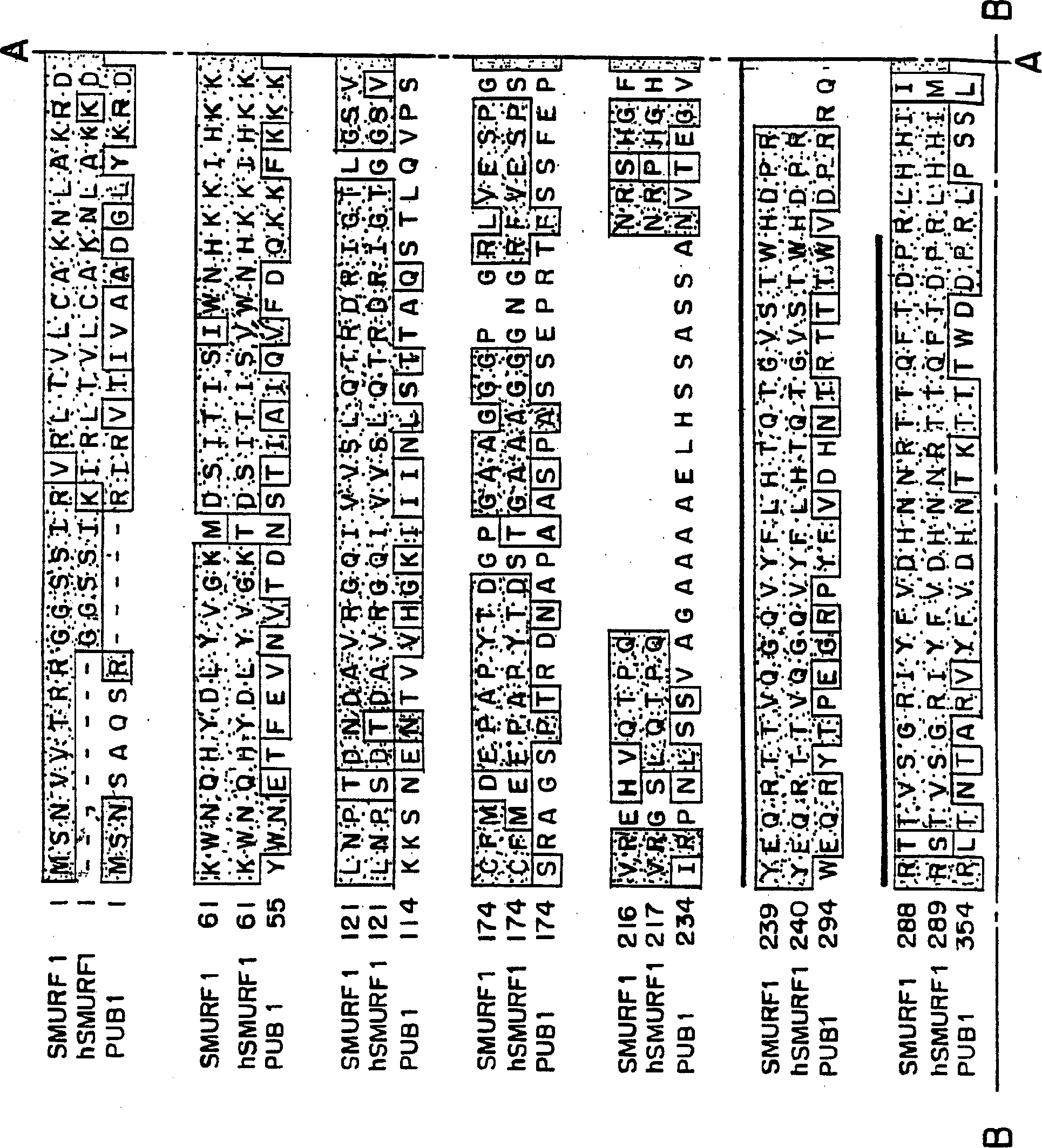
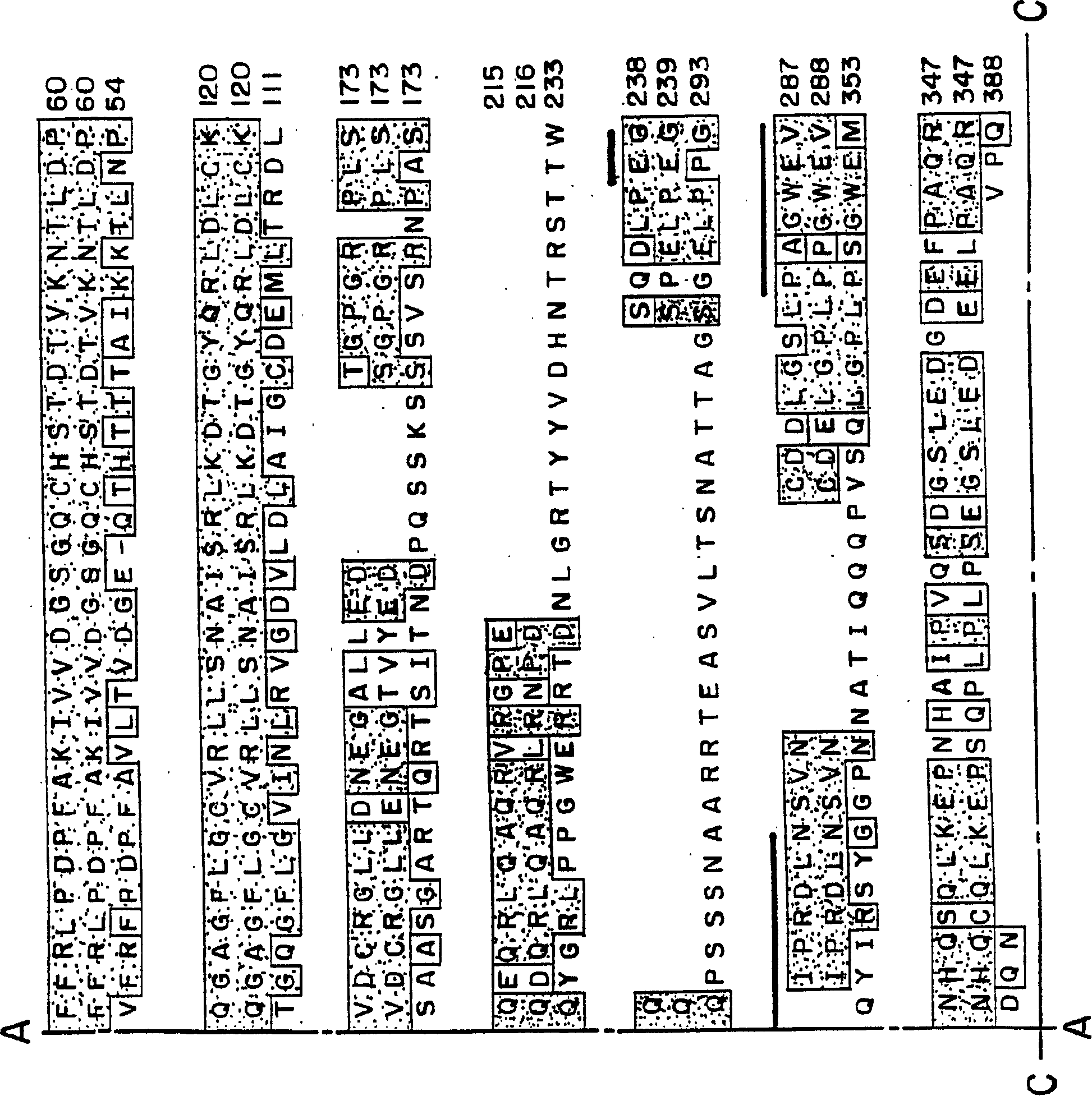
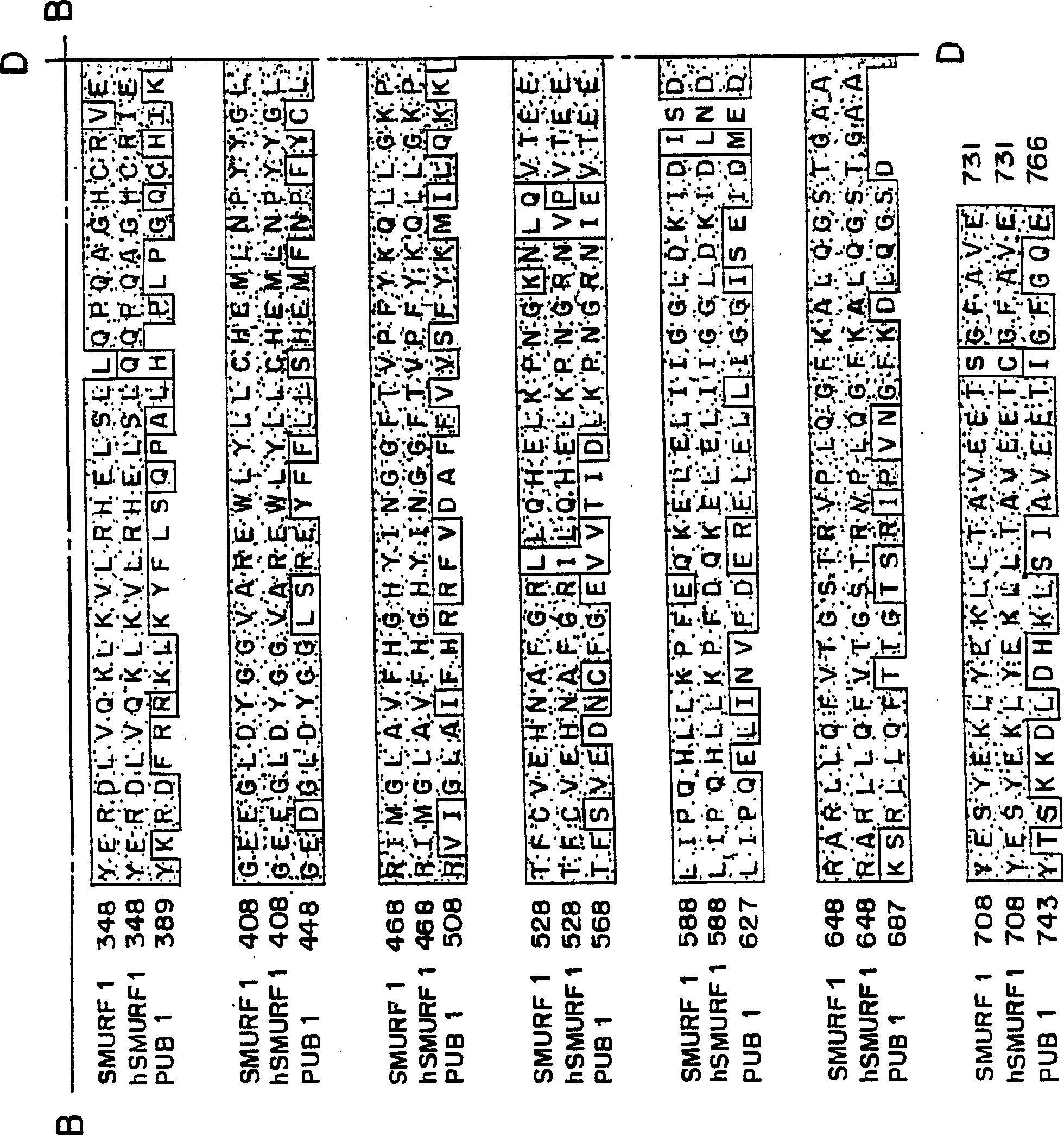
[0216] Smurf1 targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic patterning The TGFβ superfamily regulates various biological processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and patterning. Any dysregulation of TGFβ signaling may cause disease. The signal to activate the TGFβ receptor is directly transduced from the receptor to the nucleus by the Smad protein. Several links between ubiquitin-mediated degradation and the regulation of morphogenetic signals during development are now established. This example illustrates a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase, Smurf1, that selectively interacts with BMP pathway-specific Smads, leading to their ubiquitination, degradation and inactivation. In amphibian embryos, Smurf1 specifically blocks BMP signaling to affect patterning. Thus, ubiquitination against Smads may function to control embryonic development and various cellular responses to TGFβ signaling.
[0217] method
[0218] Yeast two-hybrid screening Xenopus Smad1 cDNA (36) was cloned...
Embodiment 2
[0254] Example 2: Characterization and cloning of human Smurf2
[0255] Human Smurf2 was identified and cloned using the Xenopus Smurf1 sequence from the EST database. Two overlapping EST clones corresponding to hSmurf2 were obtained and used to construct the full-length sequence of hSmurf2. Smurf2 is closely related to Smurf1, and its amino acid sequence homology with hSmurf1 is about 75%. Smurf2 contains an amino-terminal C2 domain followed by three WW domains and a HECT ubiquitin ligase domain ( Figure 12 ). Smurf2 is closely related to Smurf1, but has an additional WW domain downstream of the C2 domain ( Figure 13 ). Smurf2 was found to be expressed throughout early development and to be present in most adult tissues, with lower levels in the spleen and skeletal muscle ( Figure 14 A and Figure 14 B). RT-PCR analysis further showed that Smurf2 was expressed in various cell lines including P19, HepG2 and 293T.
[0256] Isolation of human Smurf2 and mouse Smurf2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com