Combination drug composition for treating liver cancer
A technology for the treatment of liver cancer and its composition, which is applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem that the proliferation of cancer cells cannot be inhibited from the root cause, and achieve the effect of inhibiting proliferation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Establish a reporter mouse model for detecting the efficiency of homologous recombination repair (HR) and non-homologous end joining repair (NHEJ) in vivo and detect the repair efficiency in mouse liver cancer.
[0024] 1. Establishment of reporter mouse model
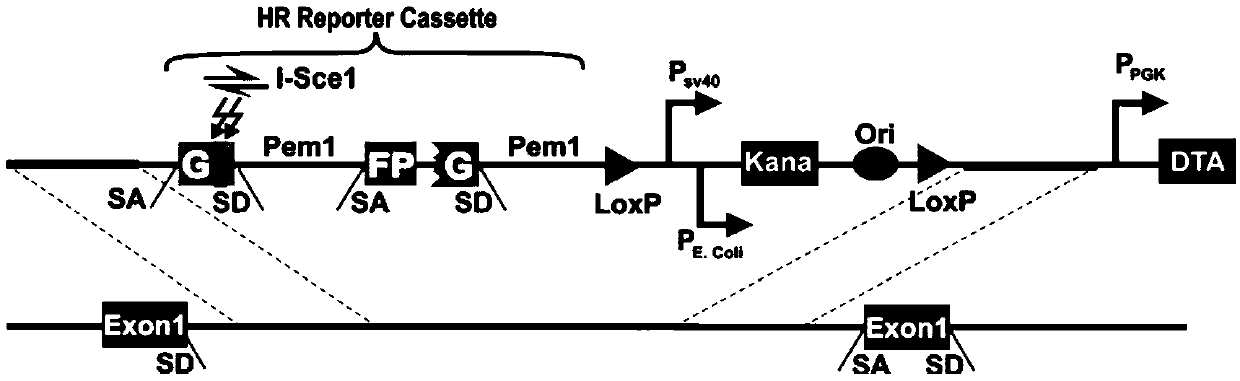
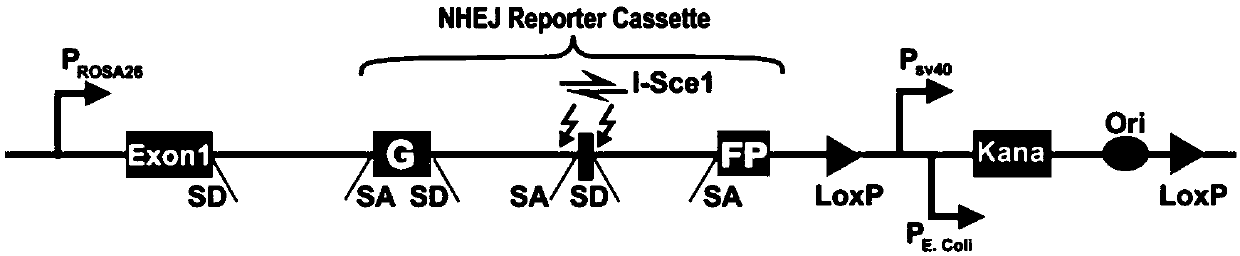
[0025] Both HR or NHEJ reporter vectors are constructed based on the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene and are integrated behind the first exon of the mouse Rosa26 gene. In the HR report vector ( figure 1 ), the GFP gene is split into two exons by the intron Pem1. In the first exon, the 22bp sequence was deleted and two reversed I-SceI sequences were inserted, so that the I-SceI endonuclease can recognize and cut DNA double-strand breaks, and at the same time ensure that even if it is repaired by NHEJ Does not generate complete GFP sequences. Following the second exon is the cognate template GFP-Pem1 lacking the promoter and ATG. The entire HR reporter vector was electrotransfected into mouse e...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Mechanism of up-regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway in liver cancer tissue
[0030] 1. Detection of expression levels of repair-related genes in mouse liver cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues
[0031] Firstly, the proteins of 8 pairs of mouse liver cancer tissues and corresponding paracancerous tissues were extracted and subjected to Western blot experiments and semi-quantitative analysis. The results showed that the expression levels of DNA-PKcs and Parp1 were significantly increased in liver cancer tissues ( Figure 4 ), indicating that DNA-PKcs and Parp1 proteins play a key role in the abnormal up-regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway in mouse liver cancer.
[0032] 2. Detection of expression levels of repair-related genes in human liver cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues
[0033] In order to detect whether this change is also conserved in human liver cancer, 108 pairs of human liver cancer and corresponding pa...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Inhibition of PARP1 and DNA-PKcs can inhibit HR and NHEJ repair efficiency in liver cancer tissue respectively
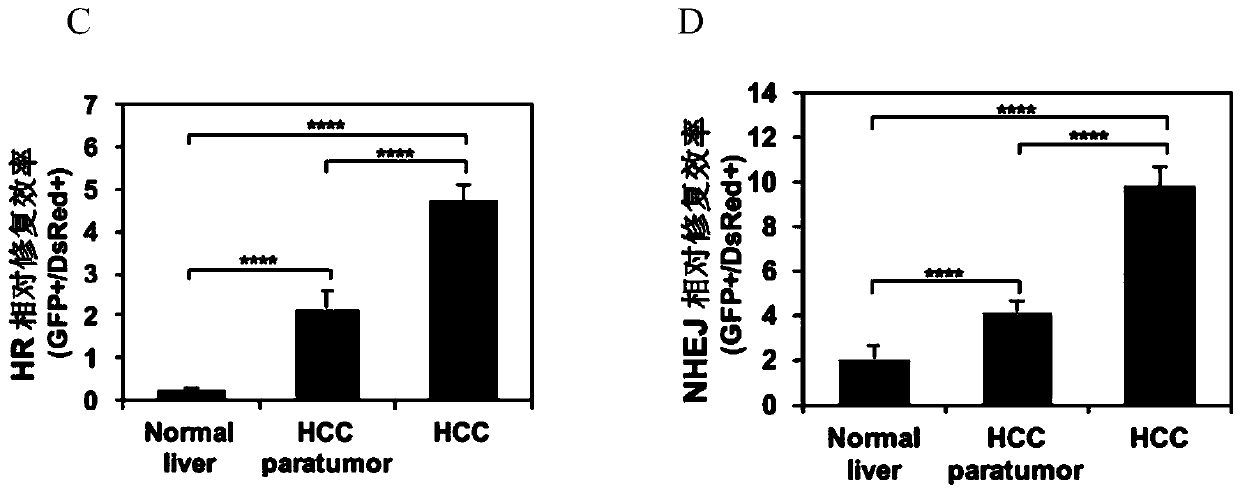
[0035]Olaparib is an inhibitor of PARP1, and NU7441 is an inhibitor of DNA-PKcs. In order to study whether olaparib and NU7441 can block the DNA double-strand break repair pathway, + / Rosa26HR or + / Rosa26NHEJ reporter mice were induced to form orthotopic liver cancer, and then Continuous intraperitoneal injection of 15 days of olaparib or / and NU7441 (olaparib: 50mg / kg / day; NU7441: 4mg / kg / day). On the fifth day of inhibitor injection, 50 μg pCMV-I-SceI and 15 μg pDsRed2-N1 plasmid were injected through the tail vein, and the mice were sacrificed 10 days later to remove liver cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues and digest them into single cells for flow analysis. The results showed that in the liver cancer tissues of + / Rosa26HR mice, both the olaparib and olaparib+NU7441 experimental groups could significantly inhibit the repair efficiency of HR ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com