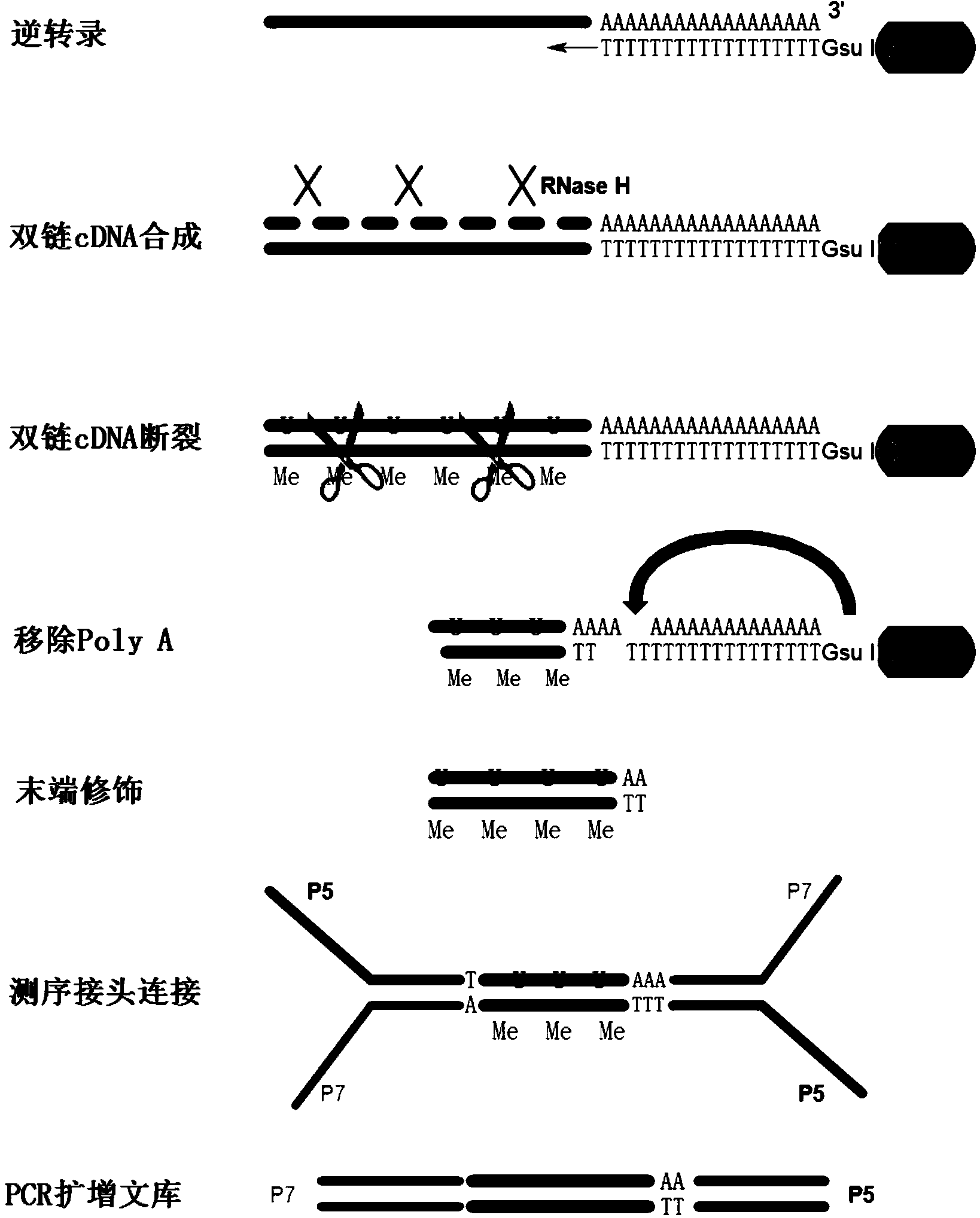
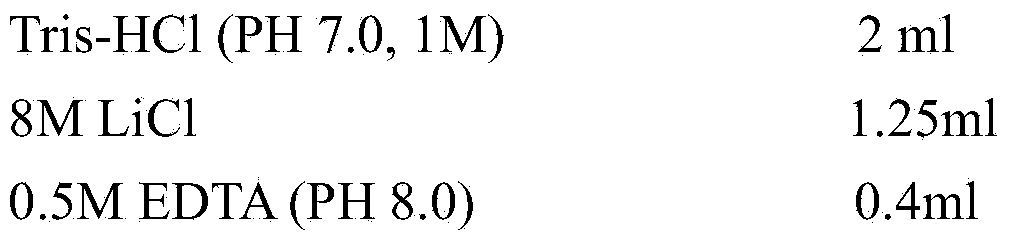Method for analyzing APA (Alternative Polyadenylation) based on 3T-seq (TT-mRNA Terminal Sequencing) within whole-genome range
A 3t-seq, genome-wide technology, applied in the field of RNA PAS (Poly A Site) detection, can solve the problems of unsuitable sample library, complicated RNA level operation, large RNA damage and loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The buffer composition used in the specific embodiment is as follows:
[0025] Reagent storage master solution required for preparing buffer solution (can be purchased from commercial companies, or purchase related reagents to prepare by yourself):
[0026]
[0027] Binding Buffer 1 (20ml):
[0028] DEPC treated water 10ml
[0029] 5M NaCl 8ml
[0030] 0.5M EDTA (PH8.0) 2ml
[0031] Binding Buffer 2 (20ml):
[0032]
[0033]
[0034] Wash buffer A (20ml):
[0035]
[0036] Wash buffer B (20ml):
[0037]
[0038] Wash buffer C (20ml):
[0039]
[0040] Wash buffer D (20ml):
[0041]
[0042] The mother solutions for the following washing buffers are all derived from the products of relevant commercial companies, and the mother solutions need to be purchased from the relevant companies to prepare according to the following formula. It is recommended to prepare freshly for each experiment:
[0043] Wash Buffer 1 (400 μl):
[0044] DEPC treated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com