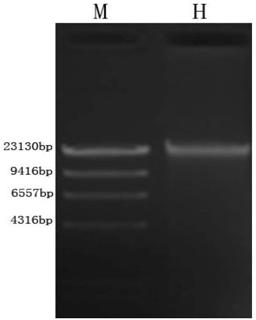
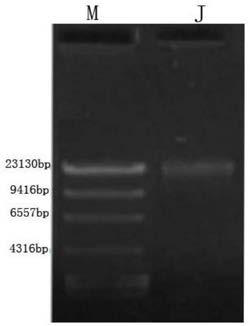
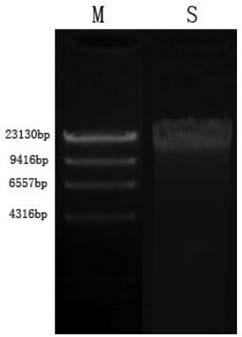
A high temperature compound method for extracting genomic DNA of fish gut microbes
A technology of gut microbiology and genome, which is applied in the field of extracting the genome of fish gut microbes, can solve the problems of high price, DNA degradation, single method, etc., and achieve the effect of simple steps, strong specificity and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Take a healthy koi and wipe the body surface with 75% ethanol. Use blunt-tip scissors to cut the body wall from the anus to the spine, avoiding the tissues in the abdominal cavity, pick the scissors up to prevent tissue damage, cut to the rear edge of the operculum, then cut along the rear edge of the operculum to the lower jaw, and open the body wall. The intestine was separated with ophthalmic scissors, and both ends of the intestine were ligated with sterile cotton thread. Sterile PBS buffer solution washes blood, fat and other substances on the intestinal wall.
[0036] 2. Squeeze out the intestinal contents, cut the intestinal tract longitudinally with ophthalmic scissors, then scrape the intestinal mucosa with a scalpel until the intestinal wall is translucent, and cut the remaining intestinal wall into sections; remove the intestinal contents , mucous membrane and intestinal fragments were placed in a centrifuge tube containing PBS, suspended and shaken 3 ti...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 1. Take a healthy koi and wipe the body surface with 75% ethanol. Use blunt-tip scissors to cut the body wall from the anus to the spine, avoiding the tissues in the abdominal cavity, pick the scissors up to prevent tissue damage, cut to the rear edge of the operculum, then cut along the rear edge of the operculum to the lower jaw, and open the body wall. The intestine was separated with ophthalmic scissors, and both ends of the intestine were ligated with sterile cotton thread. Sterile PBS buffer solution washes blood, fat and other substances on the intestinal wall.
[0046] 2. Squeeze out the intestinal contents, cut the intestinal tract longitudinally with ophthalmic scissors, then scrape the intestinal mucosa with a scalpel until the intestinal wall is translucent, and cut the remaining intestinal wall into sections; remove the intestinal contents , mucous membrane and intestinal fragments were placed in a centrifuge tube containing PBS, suspended and shaken 3 ti...
Embodiment 3
[0055] 1. Take a healthy semi-smooth tongue sole and wipe the body surface with 75% ethanol. Use blunt-tip scissors to cut the body wall from the anus to the spine, avoiding the tissues in the abdominal cavity, pick the scissors up to prevent tissue damage, cut to the rear edge of the operculum, then cut along the rear edge of the operculum to the lower jaw, and open the body wall. The intestine was separated with ophthalmic scissors, and both ends of the intestine were ligated with sterile cotton thread. Sterile PBS buffer solution washes blood, fat and other substances on the intestinal wall.
[0056] 2. Squeeze out the intestinal contents, cut the intestinal tract longitudinally with ophthalmic scissors, then scrape the intestinal mucosa with a scalpel until the intestinal wall is translucent, and cut the remaining intestinal wall into sections; remove the intestinal contents , mucous membrane and intestinal fragments were placed in a centrifuge tube containing PBS, suspe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com