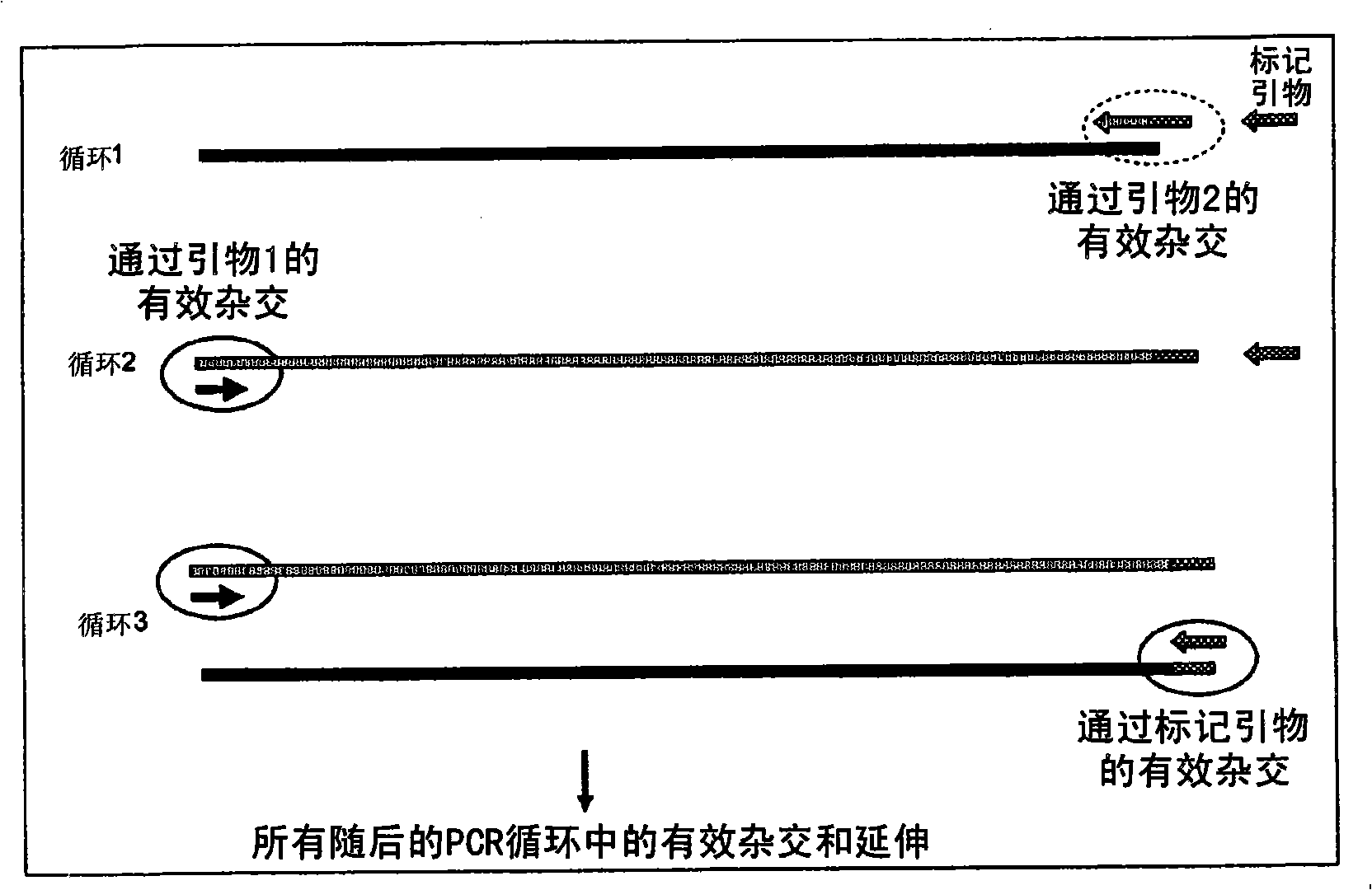
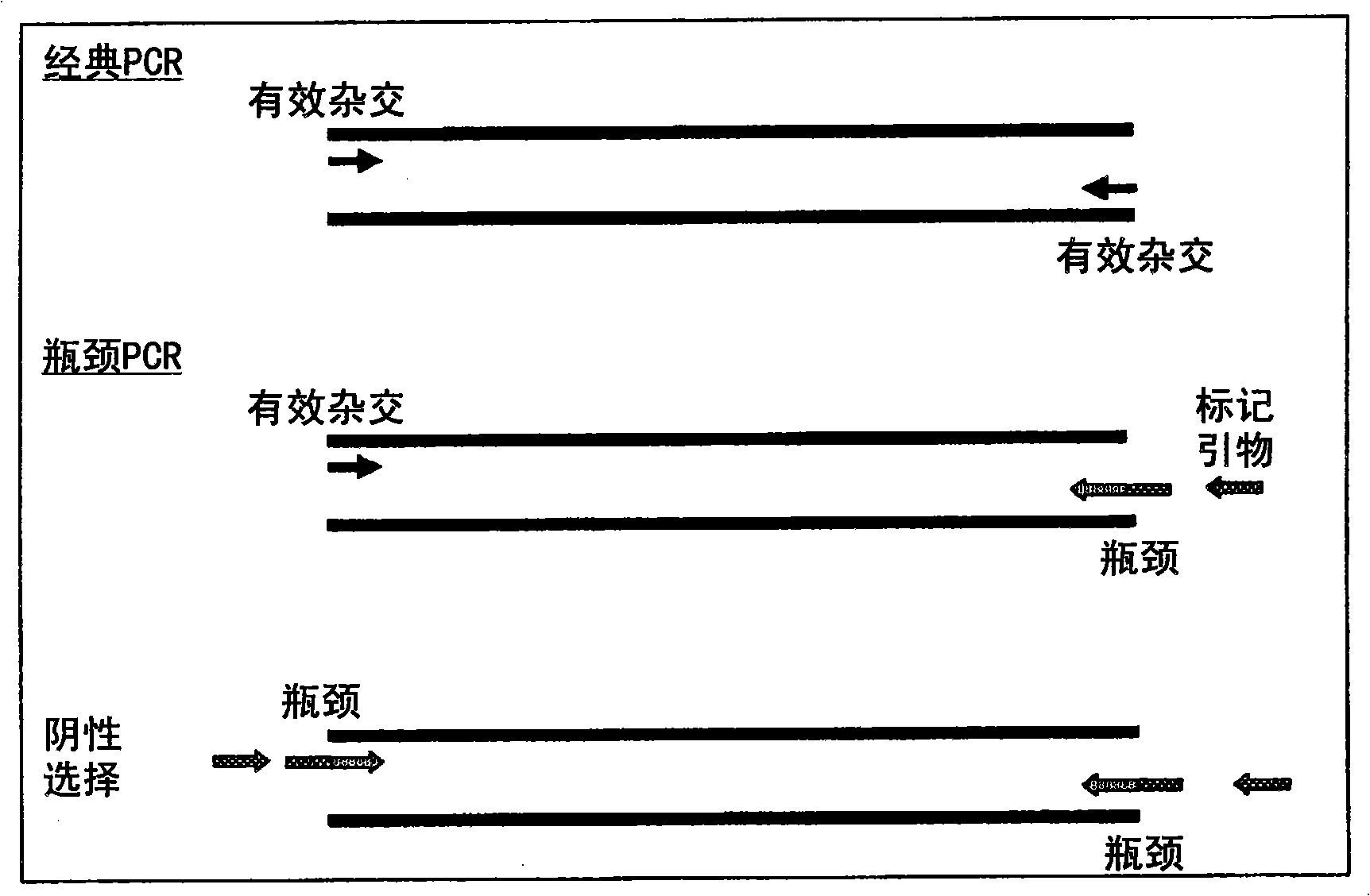
A method of DNA amplification
A nucleic acid, region-based technology for use in the field of amplification of nucleic acid regions of interest
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
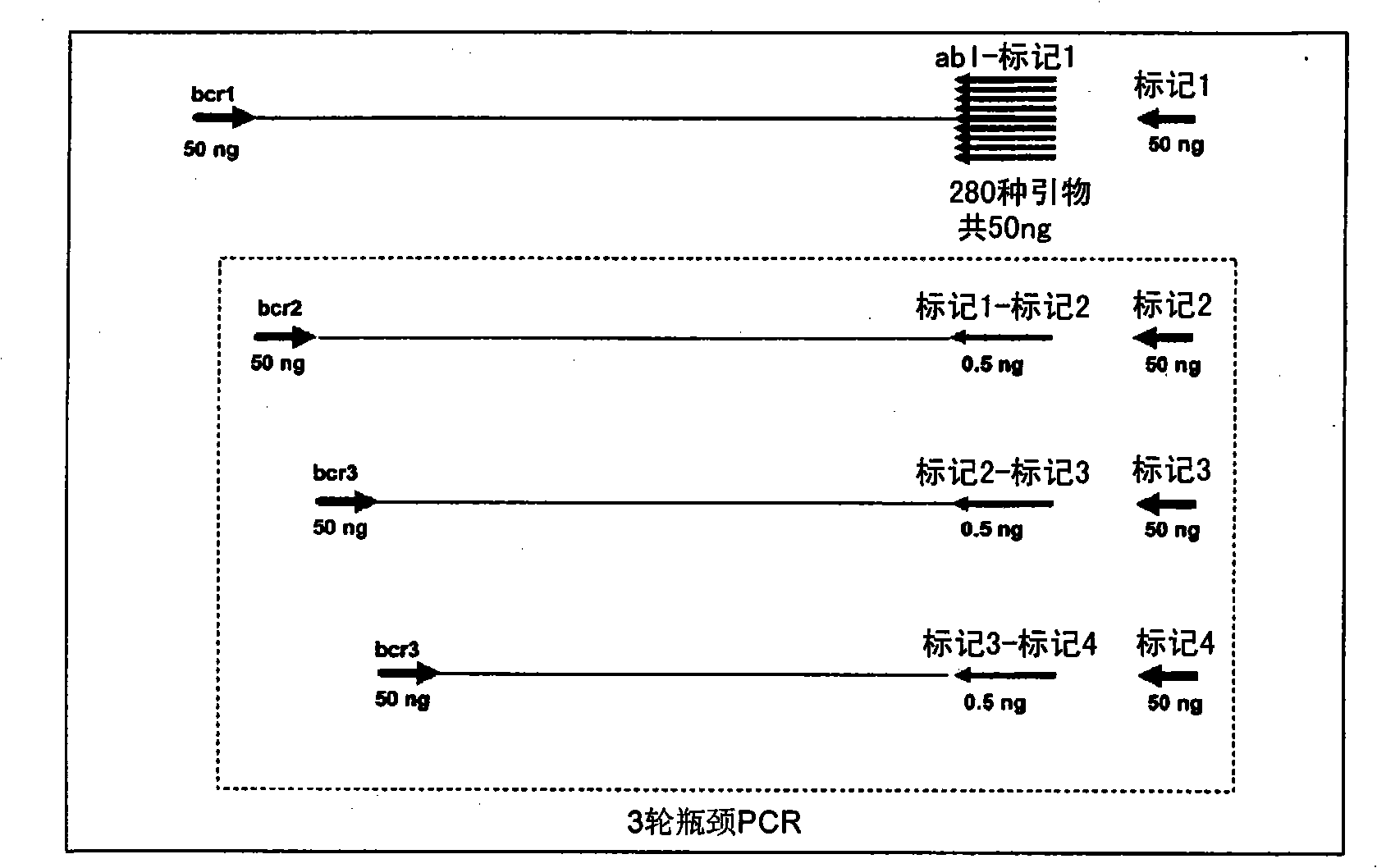
[0247] BCR-ABL DNA Breakpoint Amplification Using Bottleneck PCR
[0248] BCR-ABL DNA breakpoints were amplified in 4 rounds of PCR screening with BCR- and ABL-specific primers. Six BCR-specific primers and 282 ABL-specific primers were designed to span the major breakpoint regions of BCR (3.2kb) and ABL (140kb) DNA, respectively.
[0249] The first round of PCR amplification was performed in 25 μl containing 50 ng of a single BCR-specific primer, 100 ng of all 282 ABL-specific primers (350 pg each), 50 ng Tag A, 50 ng of genomic DNA, 50 mM KCl, 2 mM Tris HCl (pH8.4), 1 U Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen), 5 mM MgCl 2 and 300 μM each of dUTP, dATP, dGTP and dTTP. The amplification conditions are: 95°C for 4 minutes; then 6 cycles of 97°C for 1 minute, 65°C for 1 minute, every 2 cycles the temperature is lowered by 1°C, and 72°C for 1 minute; then 4 cycles of 96°C for 30 seconds, 62°C for 1 minute, after the first 2 cycles, the temperature is lowered by 1°C and 72°C f...
Embodiment 2
[0253] Amplification of PML-RARα DNA Breakpoints by Bottleneck PCR
[0254] Isolation of PML-RARα translocation breakpoints from patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia by bottleneck PCR. Patient DNA was amplified with multiple RARα primers and a single PML primer, followed by 2 rounds of bottleneck PCR. The amplified DNA was electrophoresed on a 2% agarose gel ( Figure 9 a). To confirm that the breakpoint was isolated, RARα and PML primers spanning the breakpoint were designed using the breakpoint sequence, and patient DNA was amplified with these primers for one round ( Figure 9 b). also confirmed Figure 9 a The sequence of the amplified band shown on the gel ( Figure 9 c).
Embodiment 3
[0256] Gene Walking Using Degenerate Primers and Bottleneck PCR
[0257] Gene walking along the 3 genes APC, BRCA1 and myocillin was performed with 50 ng of gene-specific forward primer, 50 ng of one of various degenerate reverse primers and 50 ng of reverse marker primer. The degenerate reverse primer has 4-6 random normal residues at the 3' end, followed by 3-6 degenerate residues, followed by a random marker sequence of 12-18, usually 18 normal residues. The most commonly used degenerate primer has 5 fixed bases at the 3' end, followed by 5 degenerate bases, followed by an 18 base marker sequence (5'TGCTAGGATCCAAGGNNNNNATTCG3' (SEQ ID NO: 1)). The reverse marker primer has the same sequence as the marker on the degenerate reverse primer. 5 PCR cycles (annealing at 35°C for 5 minutes), followed by 15 cycles (annealing at 55°C for 3 minutes).
[0258] PCR performed in 25 μl volume with 50 ng total DNA, 5 mM MgCl 2 , 0.1 mM dUTP, 0.2 mM dTTP and 0.3 mM each of dCTP, dATP an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com