Patents
Literature
58 results about "Xylulose kinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transformed eukaryotic cells that directly convert xylose to xylulose
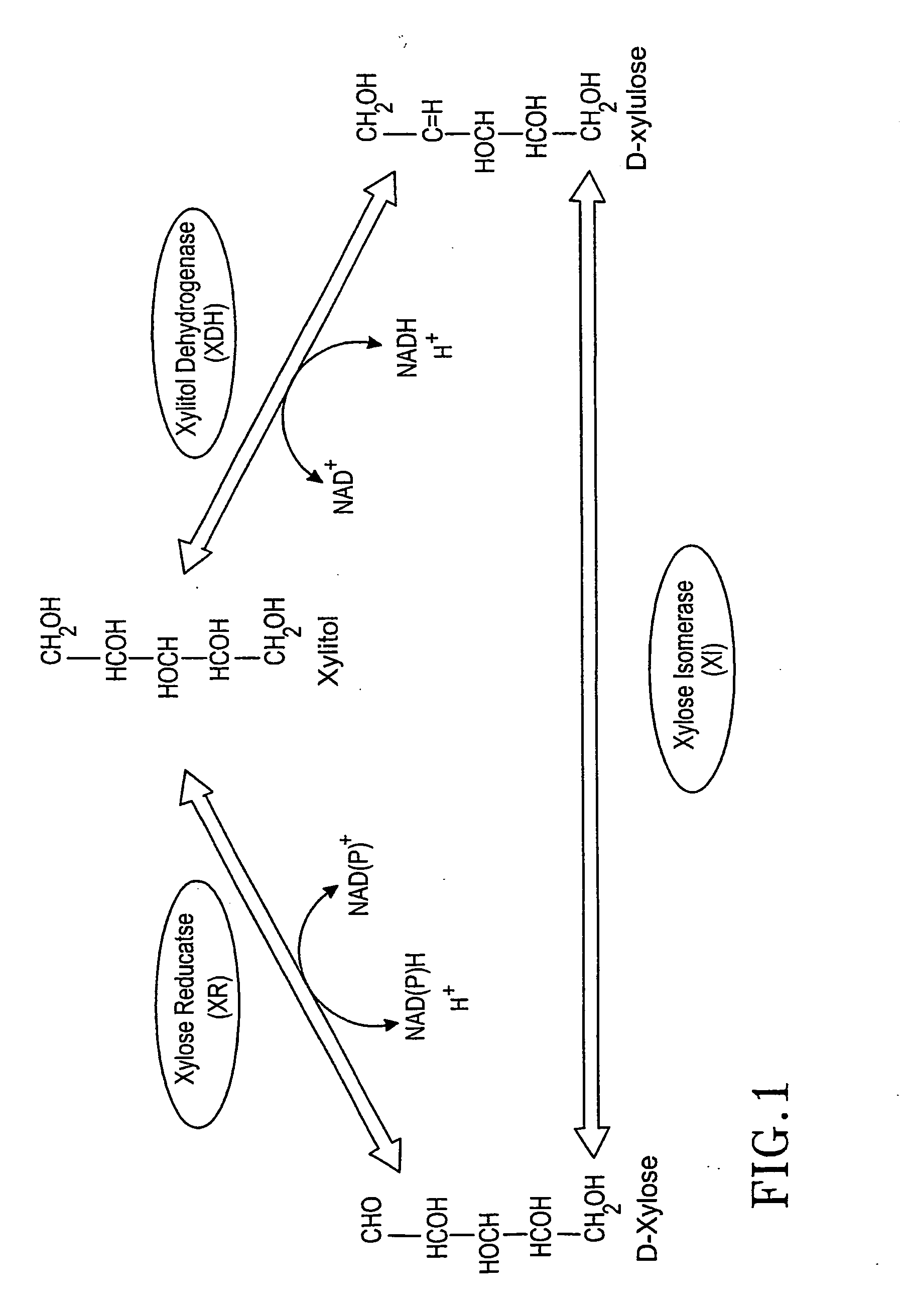
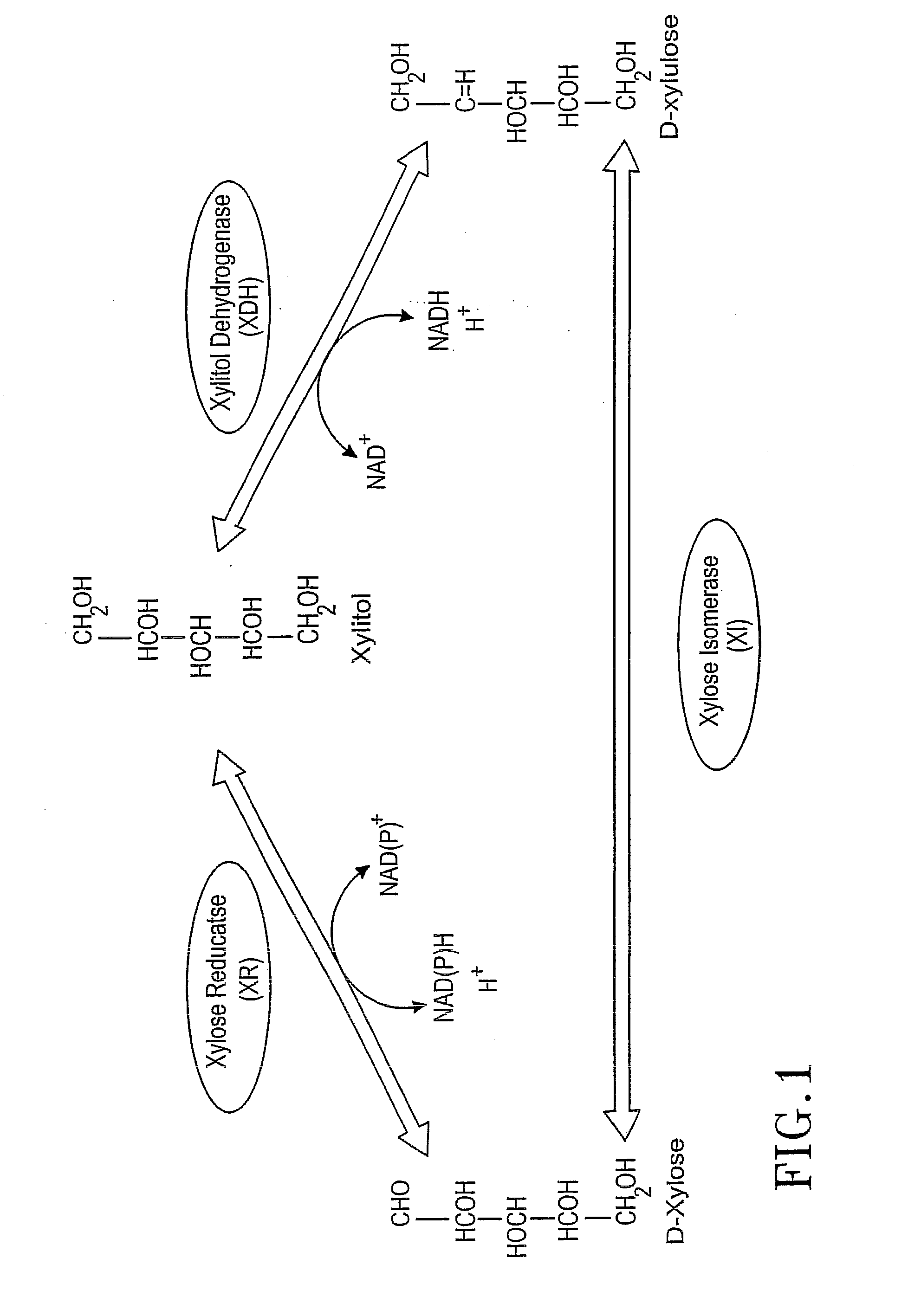
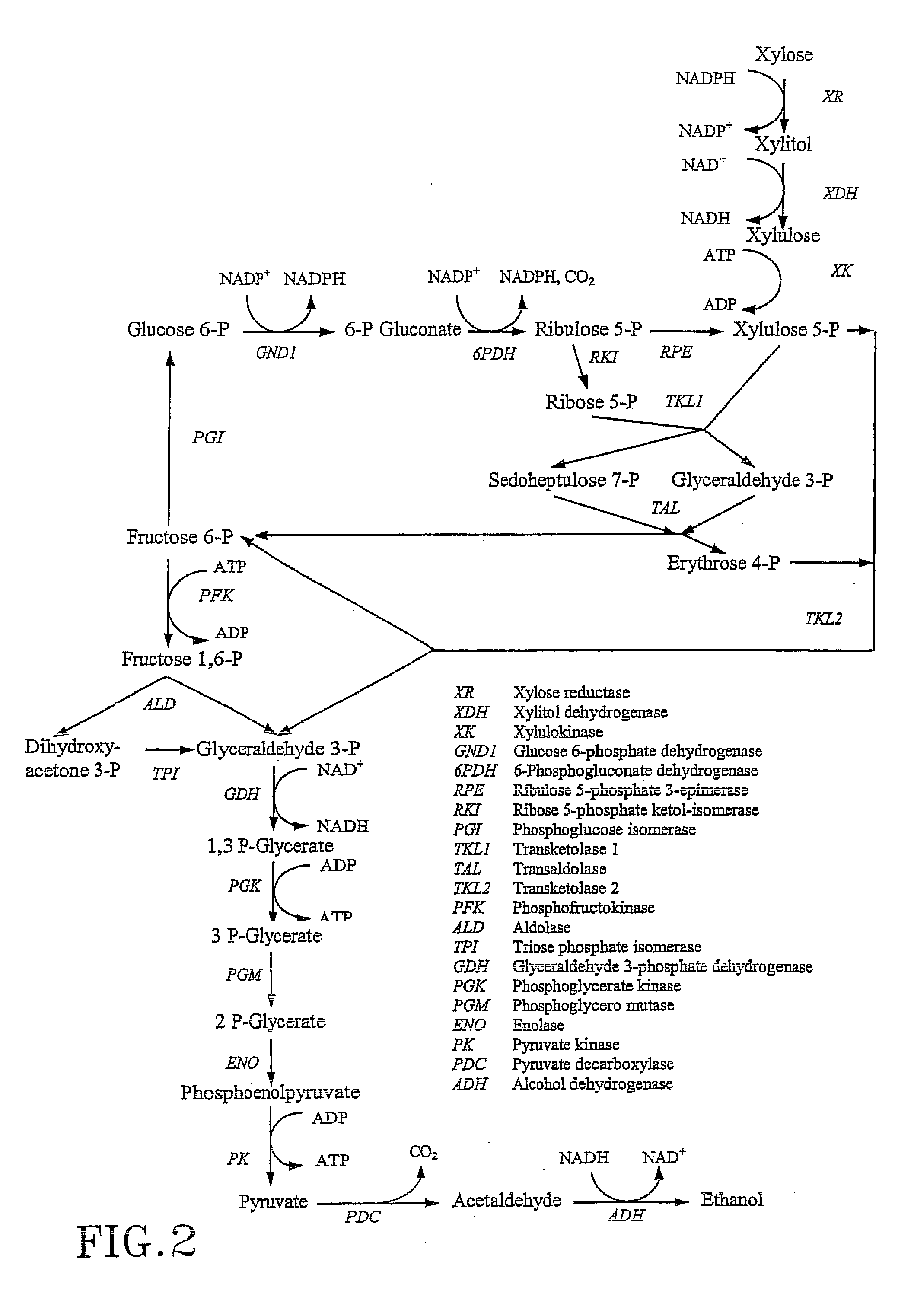
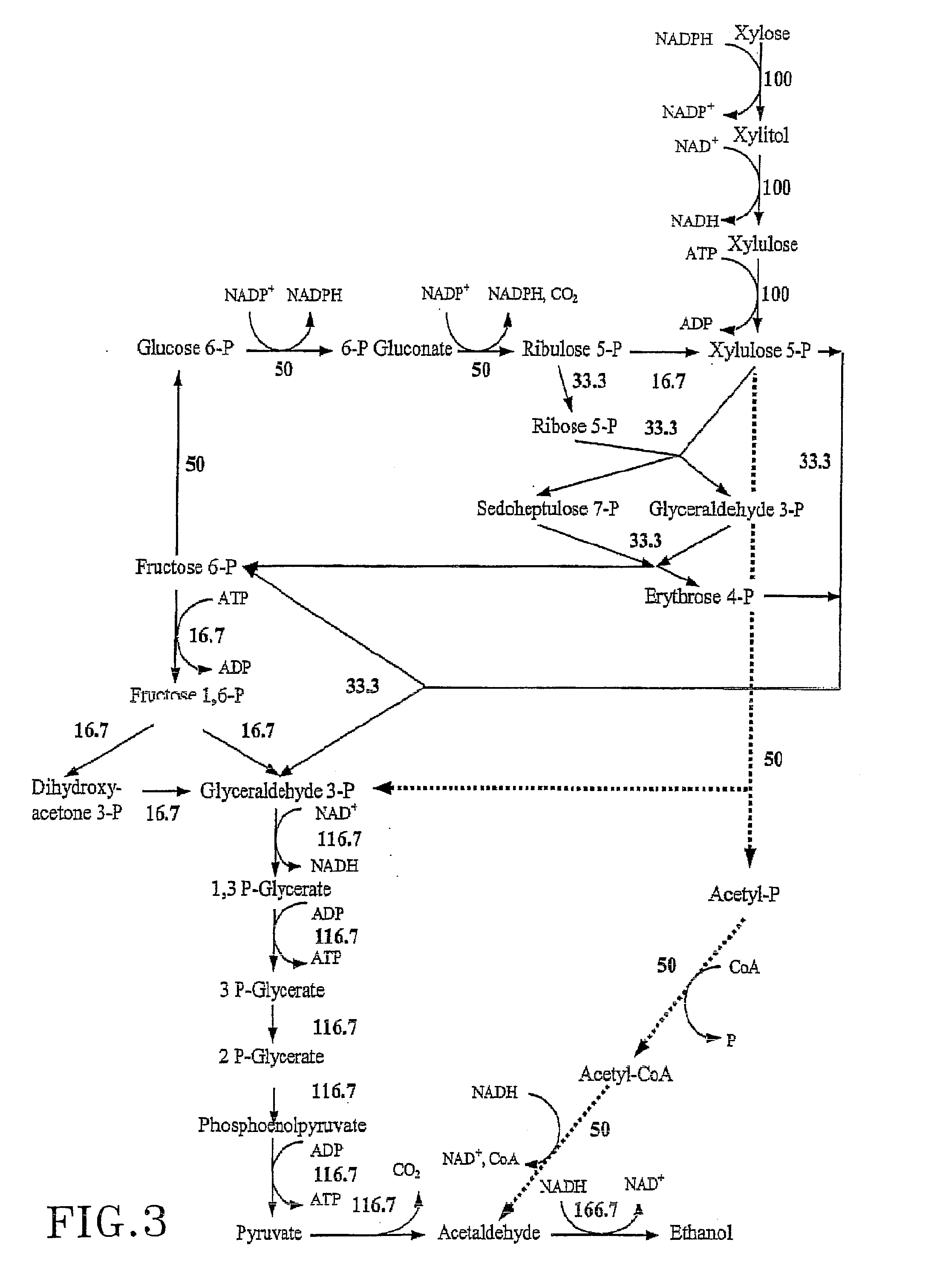
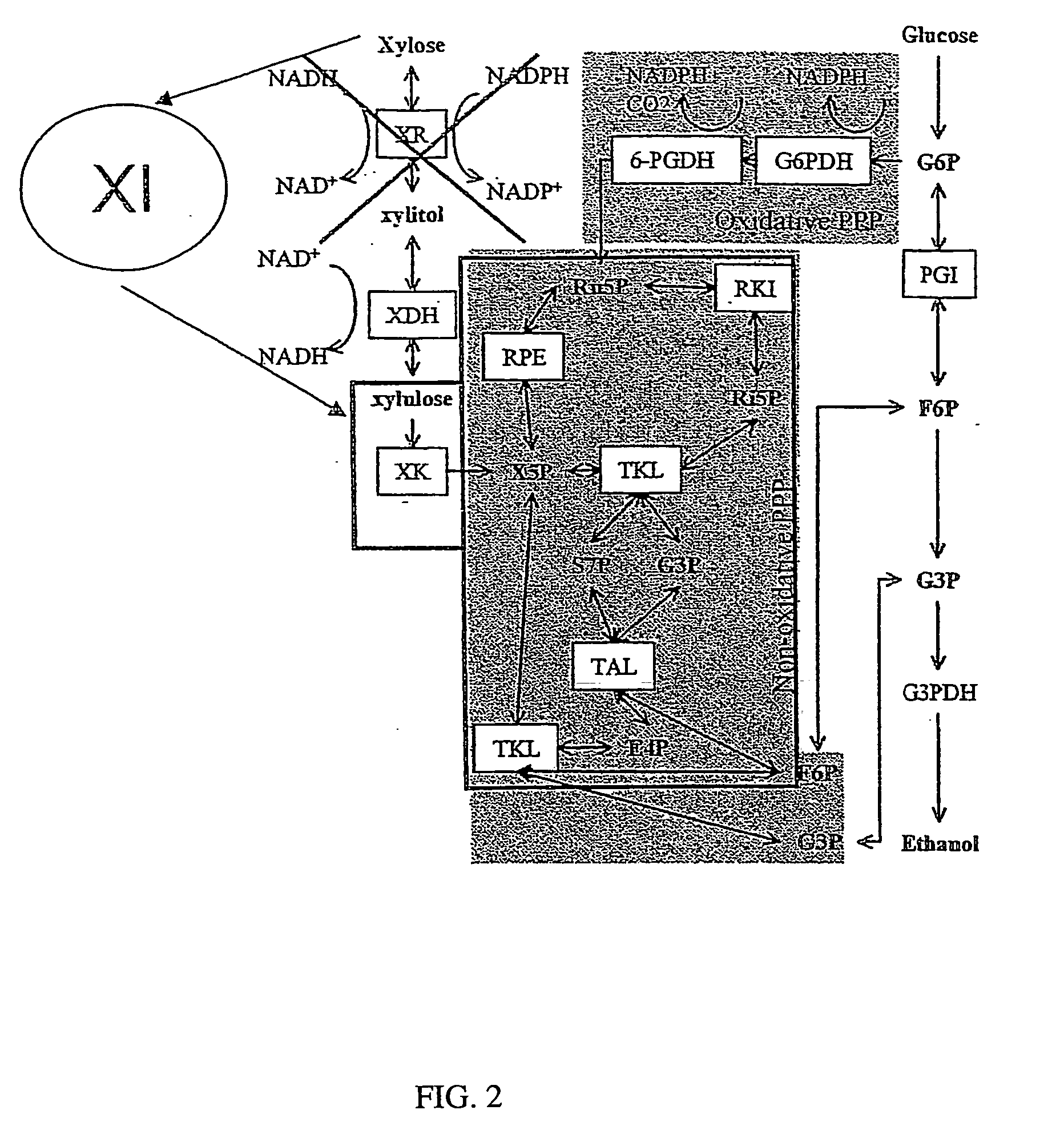
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization
ActiveUS20090246846A1High expressionImproved xylose utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaTransketolaseGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
Strains of Zymomonas were engineered by introducing a chimeric xylose isomerase gene that contains a mutant promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The promoter directs increased expression of xylose isomerase, and when the strain is in addition engineered for expression of xylulokinase, transaldolase and transketolase, improved utilization of xylose is obtained.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
Fermentation of pentose sugars
The present invention relates to host cells transformed with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a eukaryotic xylose isomerase obtainable from an anaerobic fungus. When expressed, the sequence encoding the xylose isomerase confers to the host cell the ability to convert xylose to xylulose which may be further metabolised by the host cell. Thus, the host cell is capable of growth on xylose as carbon source. The host cell preferably is a eukaryotic microorganism such as a yeast or a filamentous fungus. The invention further relates to processes for the production of fermentation products such as ethanol, in which a host cell of the invention uses xylose for growth and for the production of the fermentation product. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding eukaryotic xylose isomerases and xylulose kinases as obtainable from anaerobic fungi.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Stable recombinant yeasts for fermenting xylose to ethanol
InactiveUS7527927B1Easy to keepIncrease lossFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyXylitol dehydrogenase
Described are recombinant yeast which ferment xylose to ethanol and which maintain their ability to do so when cultured for numerous generations in non-selective media. The preferred yeast contain multiple copies of integrated genes encoding xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase fused to promoters which are non-glucose inhibited and which do not require xylose for induction. Also described are preferred methods for integrating multiple copies of exogenous DNA into host cells by transforming cells with replicative / integrative vectors, and then replicating the cells a number of times under selective pressure to promote retention of the vector in subsequent generations. The replicated vectors thus serve to integrate multiple copies of the exogenous DNA into the host cells throughout the replication / selection phase. Thereafter the selective pressure can be removed to promote loss of the vector in subsequent generations, leaving stable integrants of the exogenous DNA.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Metabolic engineering for improved xylose utilisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an ethanol producing, xylose utilizing strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae comprising genes for overexpression of xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase, wherein in addition to said genes for production o phosphoacetyltransferase, and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase are introduced and optionally overexpressed.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Metabolic engineering for improved xylose utilisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Construction of new xylose utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
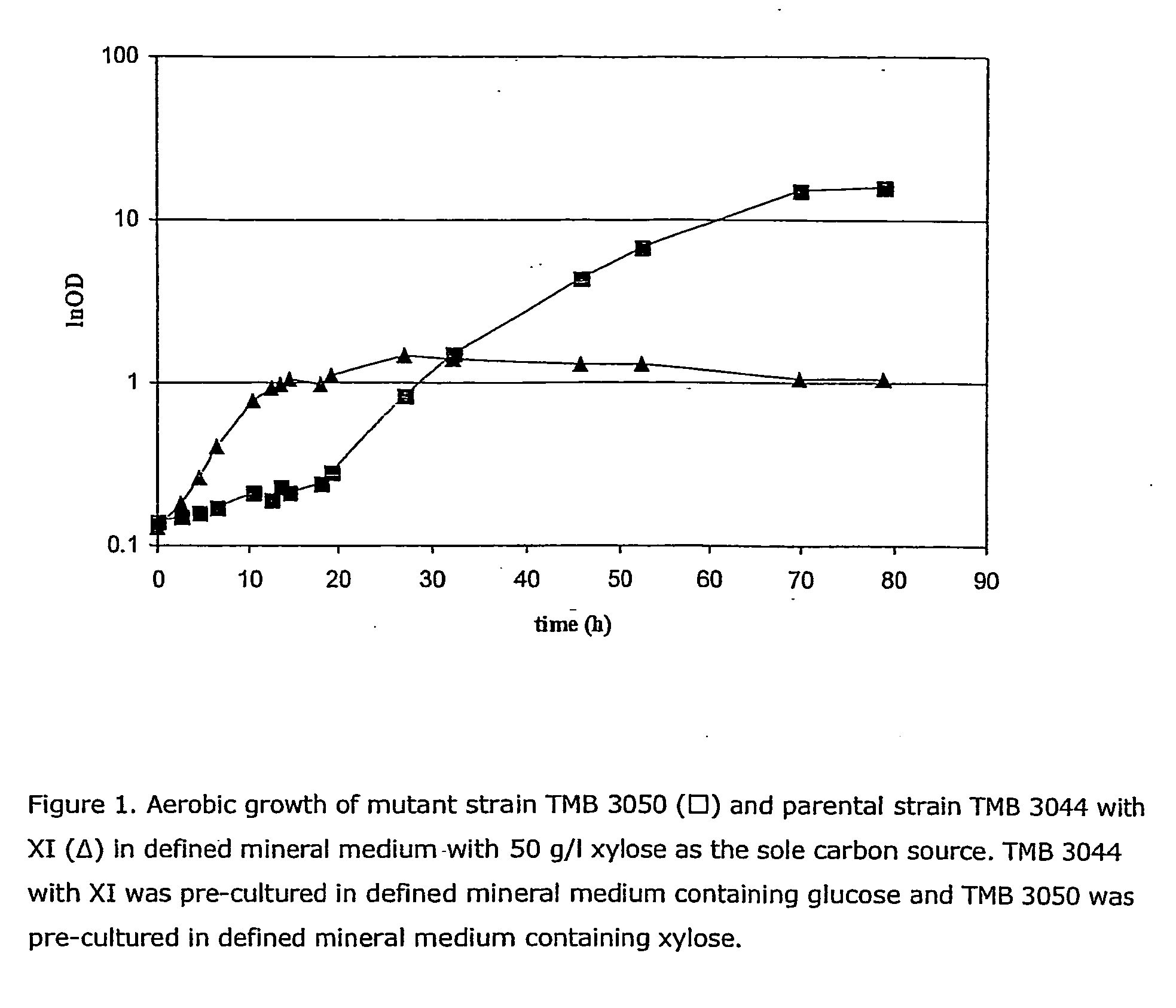
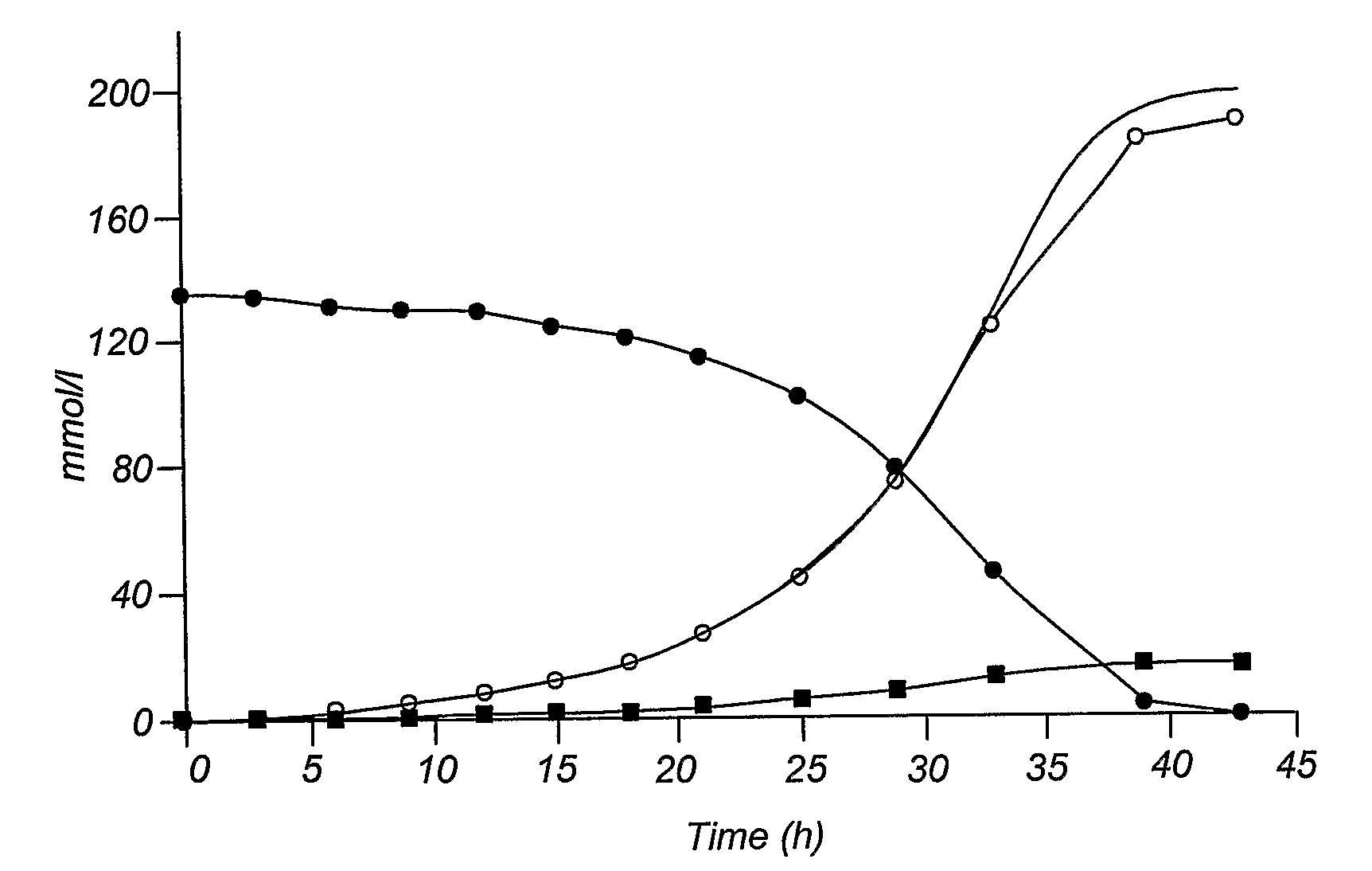
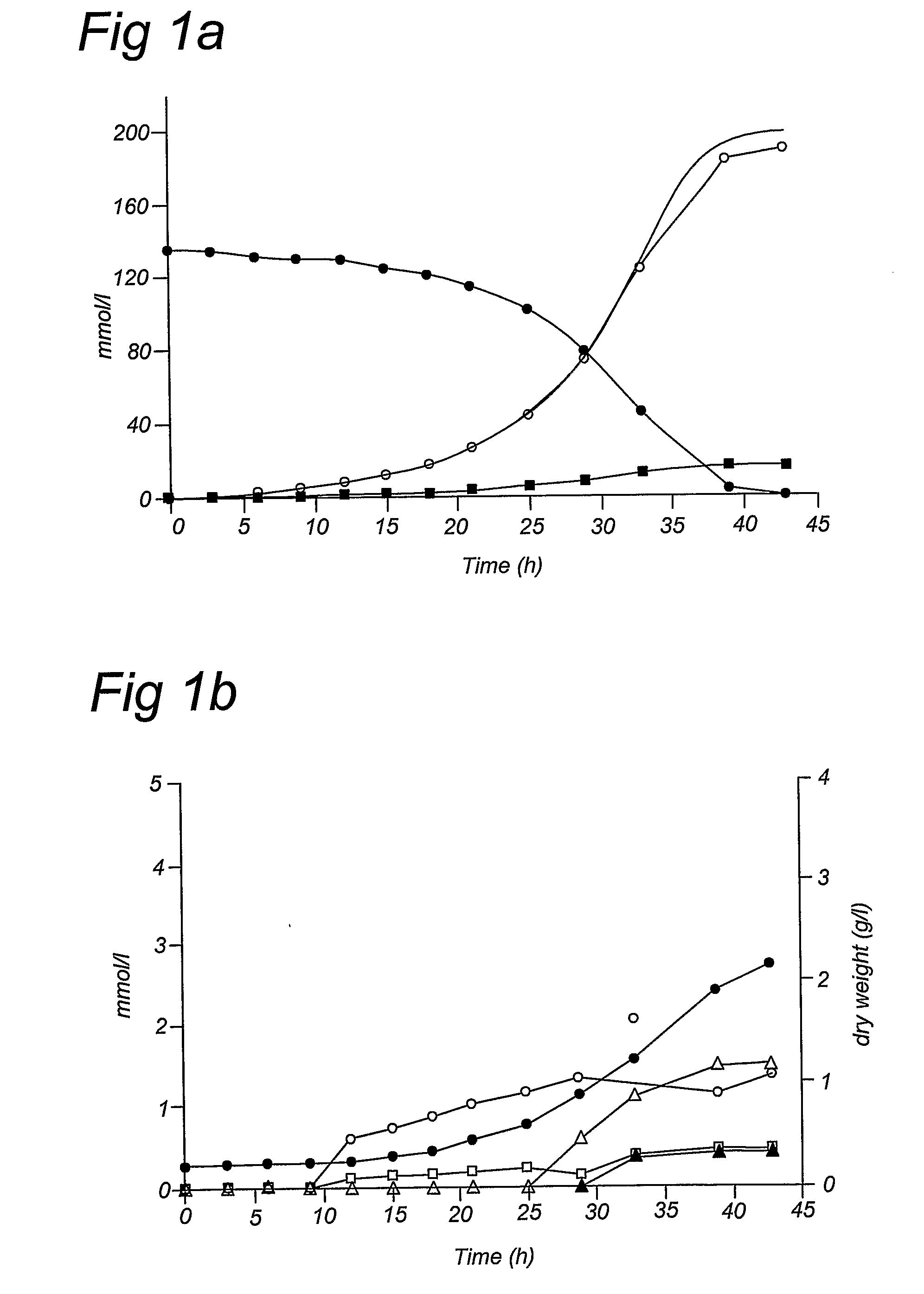
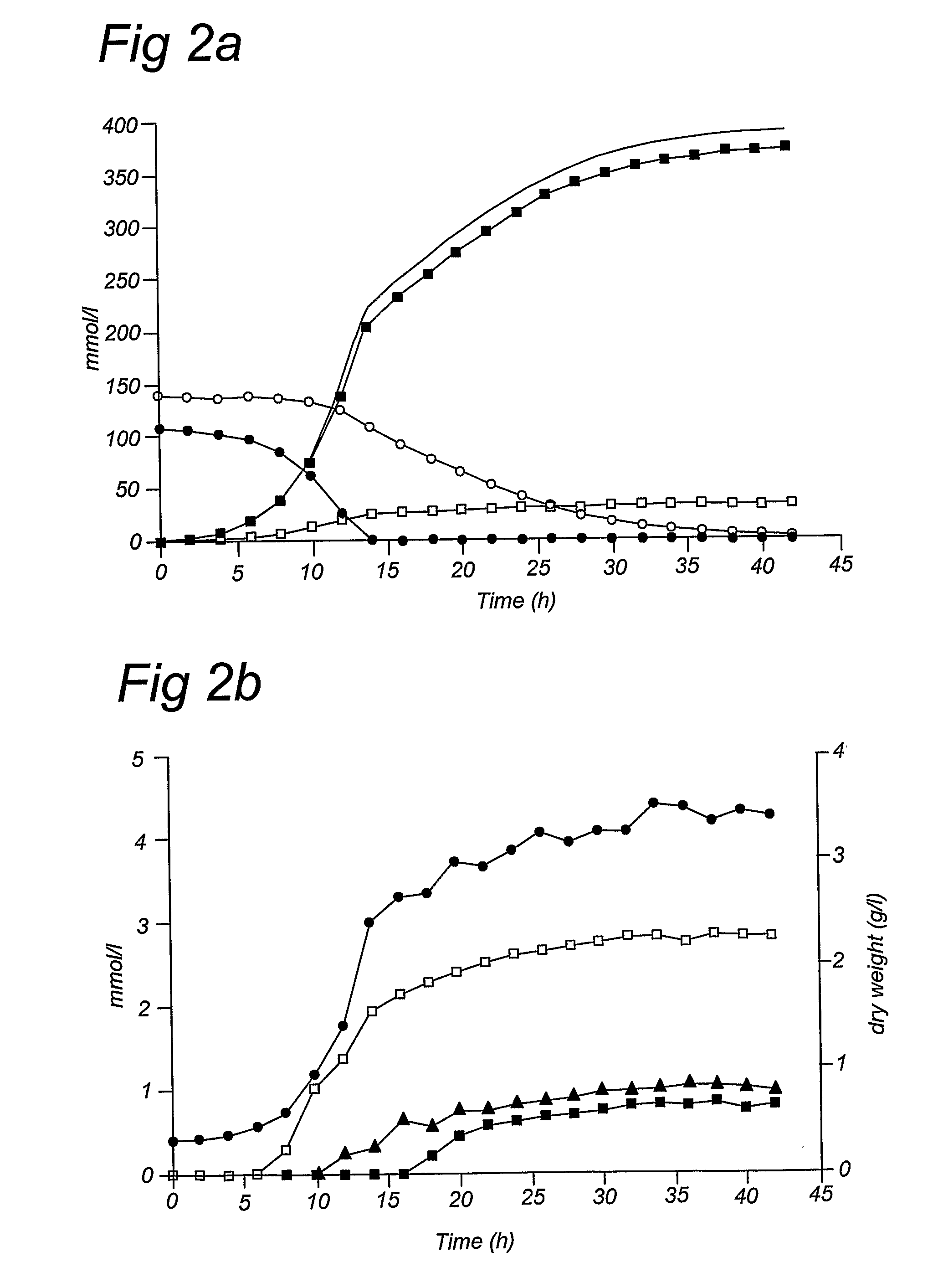
The present invention relates to a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain utilizing xylose for fermenting ethanol expressing xylose isomerase (XI), overexpressing xylulokinase (XK), overexpressing the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and non-expressing aldose reductase (AR) and being adapted to growth in mineral defined medium with xylose as sole carbon source.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Metabolic Engineering of Xylos Fermentation
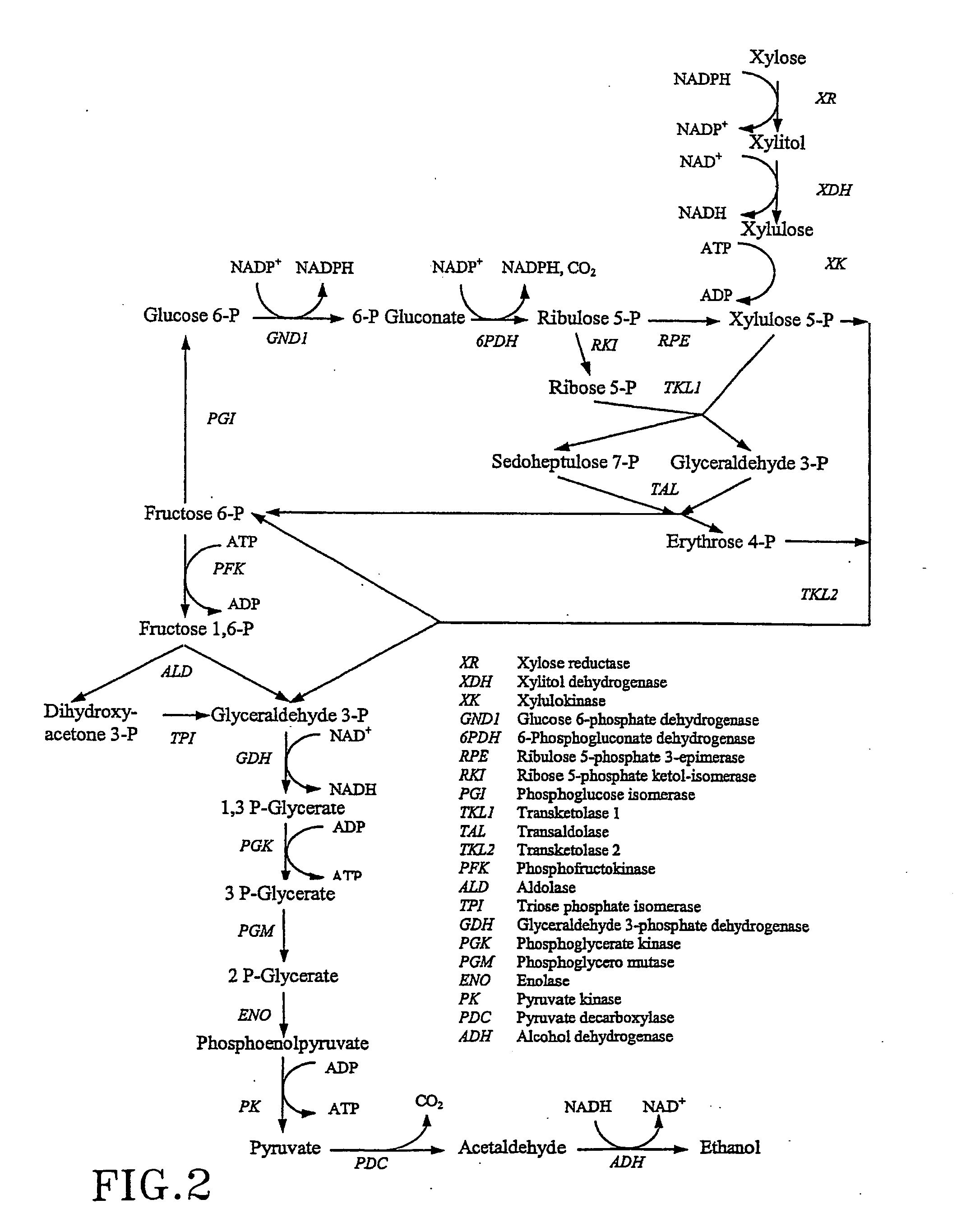
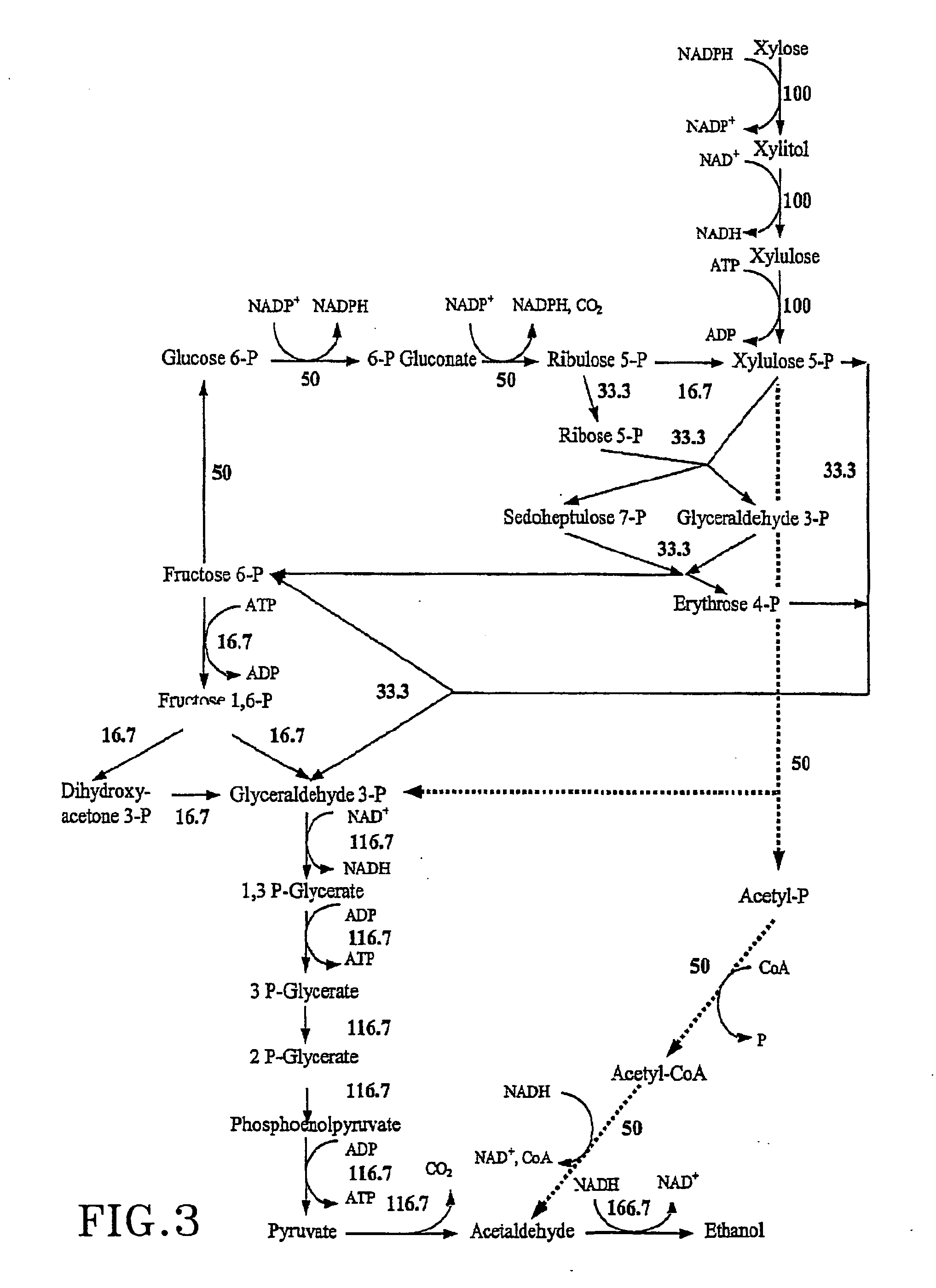
The present invention relates to further genetic modifications in eukaryotic host cells that have been transformed to express a xylose isomerase that confers the host cell the ability of isomerising xylose to xylulose. The further genetic modifications are aimed at improving the efficiency of xylose metabolism and include e.g. reduction of unspecific aldose reductase activity, increased xylulose kinase activity and increased flux of the pentose phosphate pathway. The modified host cells of the invention are suitable for the production of a wide variety of fermentation products, including ethanol, in fermentation processes in which a source of xylose or a source of xylose and glucose are used as carbon source.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Transformed Saccharomyces cerevisiae Engineered for Xylose Utilization
InactiveUS20100112658A1High ethanol productionEfficient growth processFungiBacteriaHeterologousNucleotide
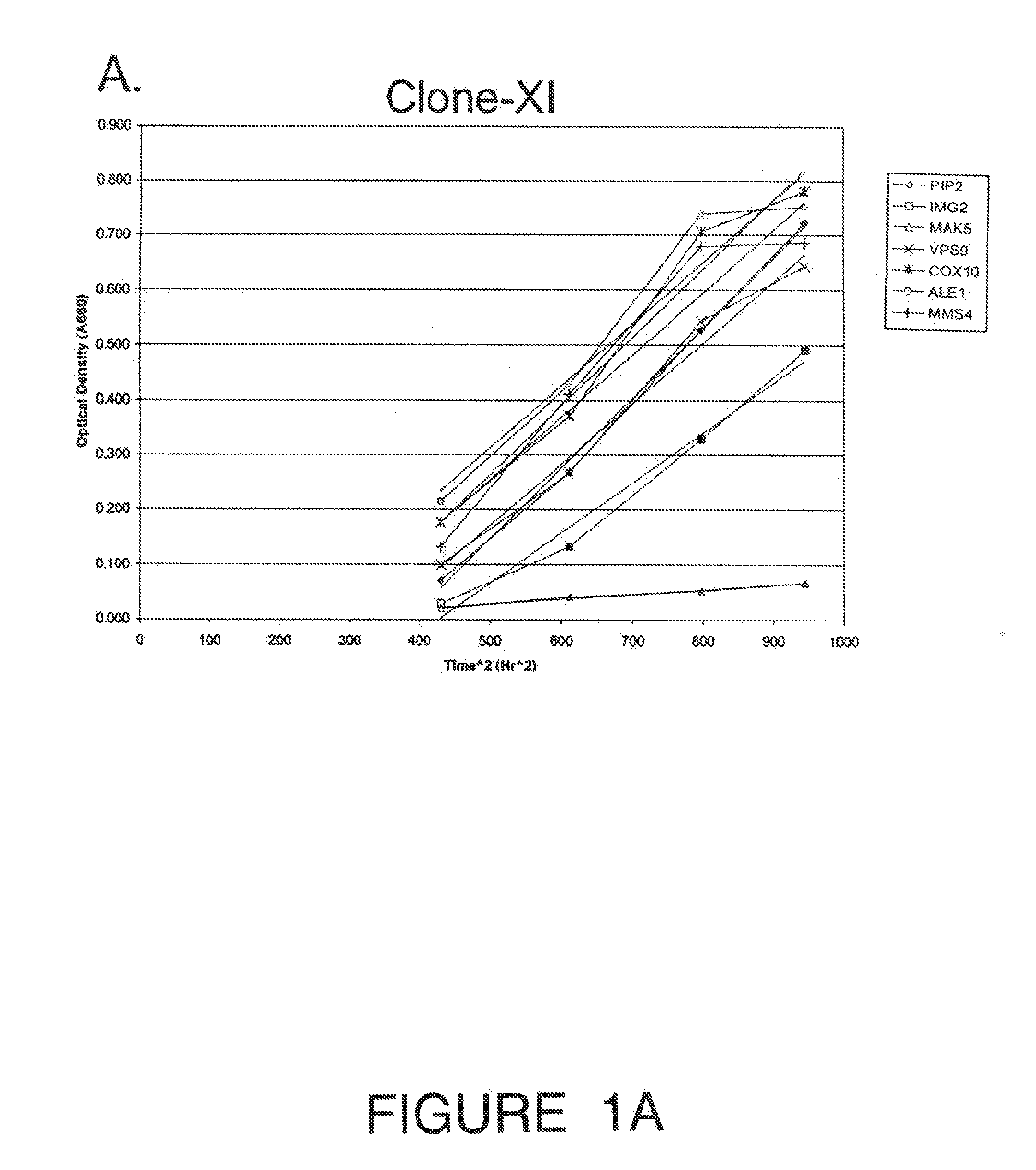
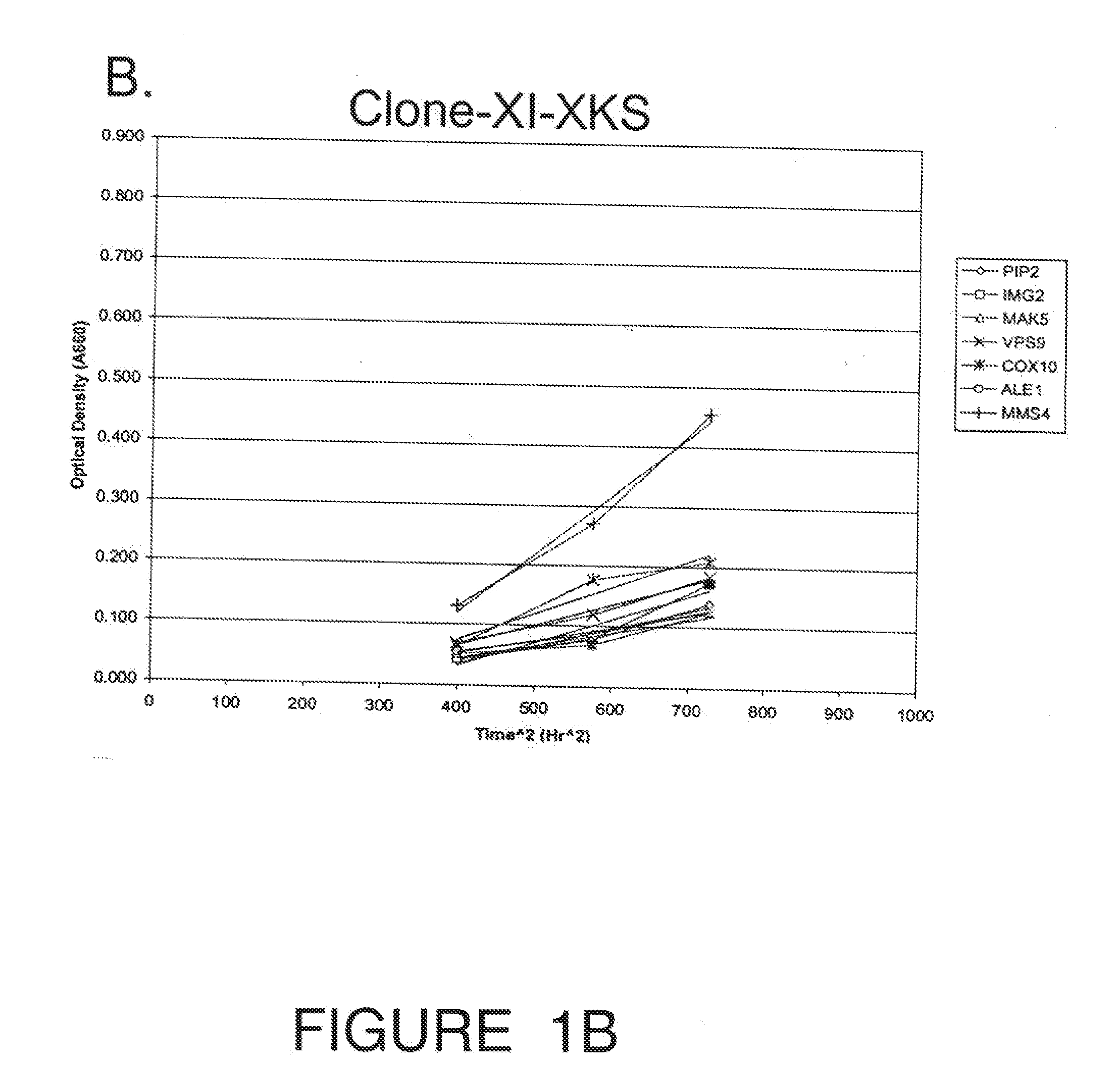
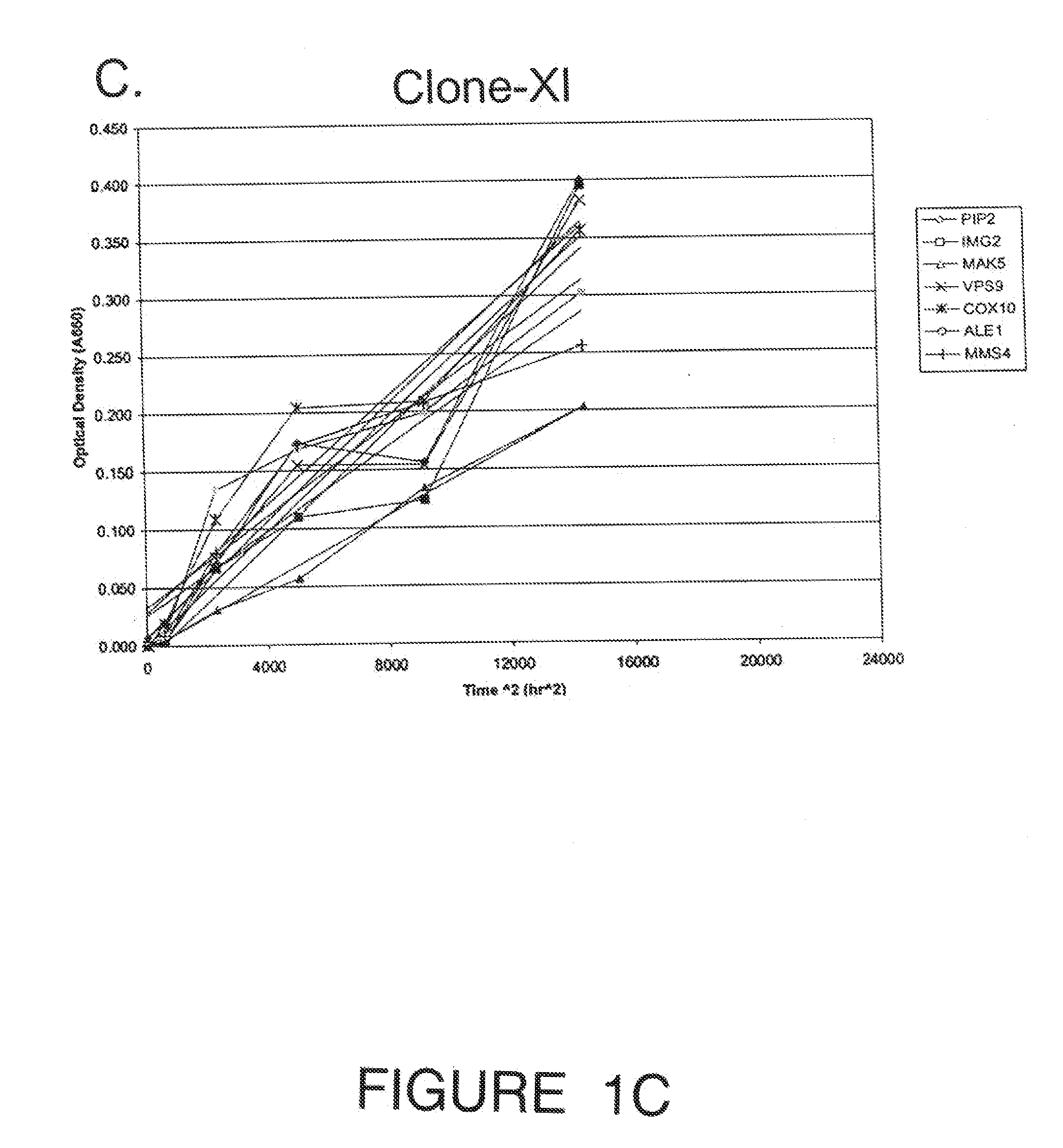
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced by transformation with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding for xylulokinase (XKS) from Yersinia pestis and xylose isomerase (XI) are capable of xylose utilization. The transformants express these heterologous polynucleotides at a sufficient functional level to grow aerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. Further transformation of the recombinant yeasts to overexpress one or more of the S cerevisiae genes PIP2, IMG2, MAK5, VPS9, COX10, ALE1, CDC7, and MMS4, permits the yeast to grow anaerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. When grown under anaerobic conditions on a culture medium comprising both glucose and xylose, the transformed yeast exhibit increased ethanol productivity, with the yeast growing on the xylose to increase their biomass and fermenting the glucose to ethanol.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
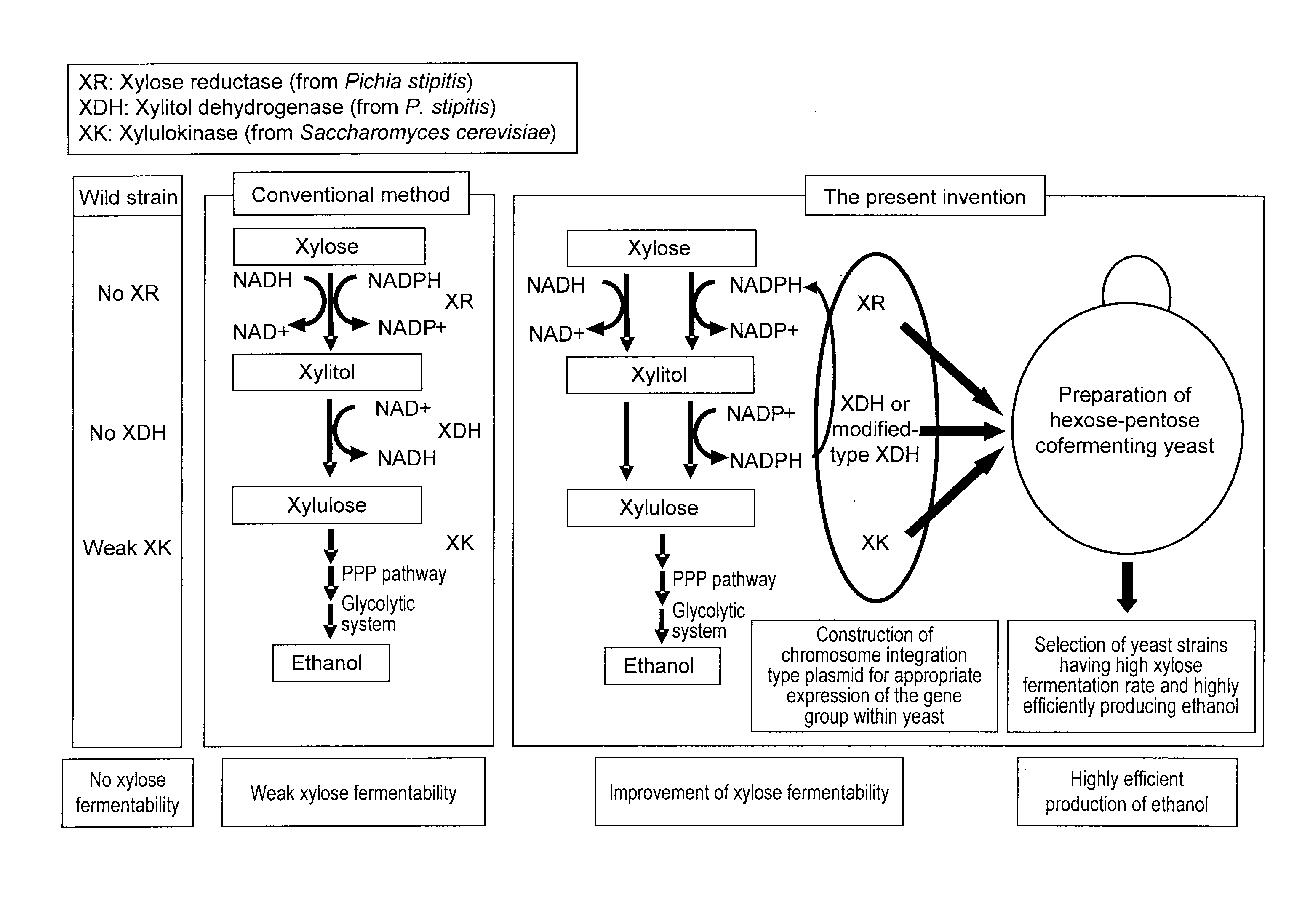
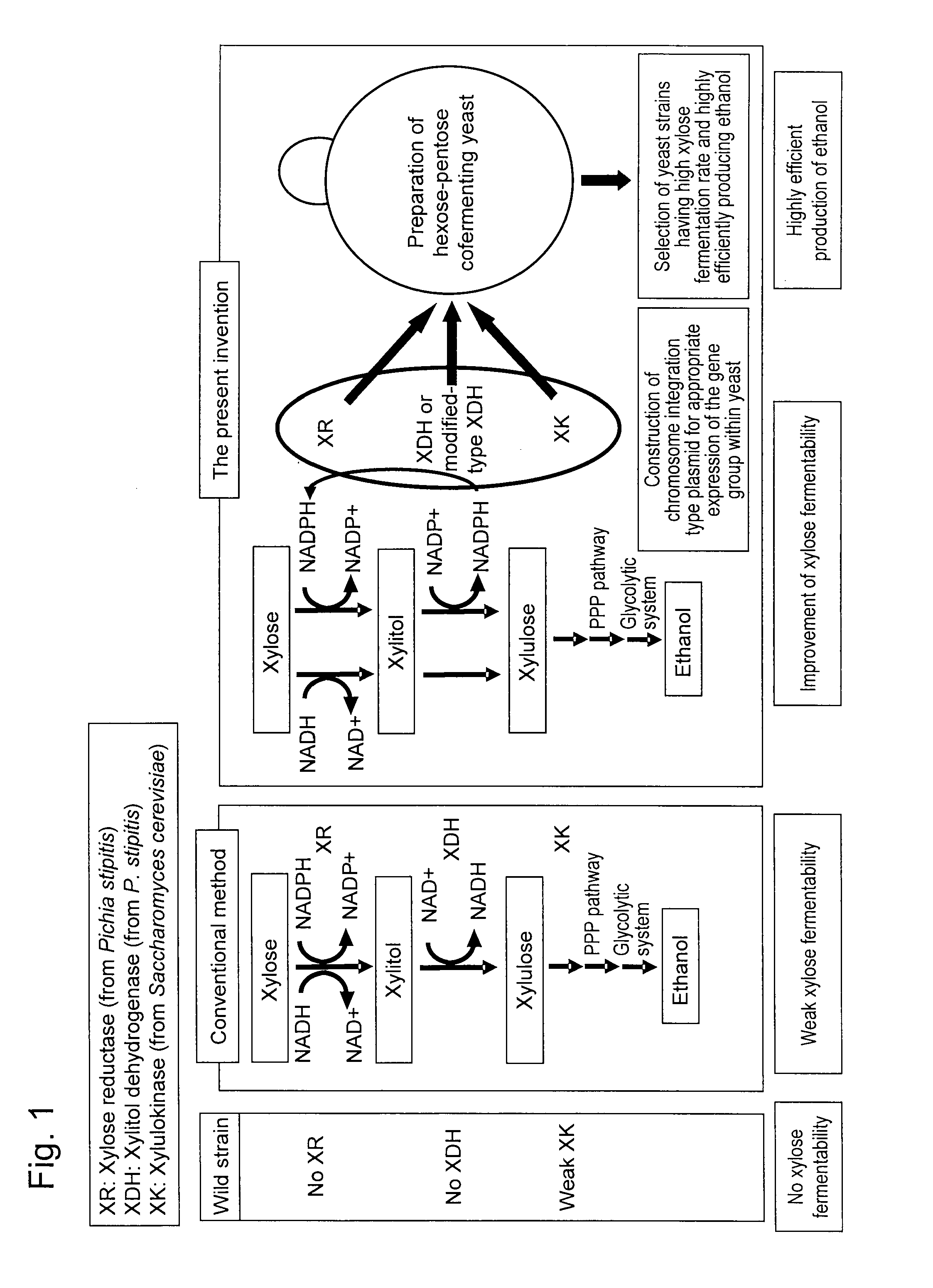
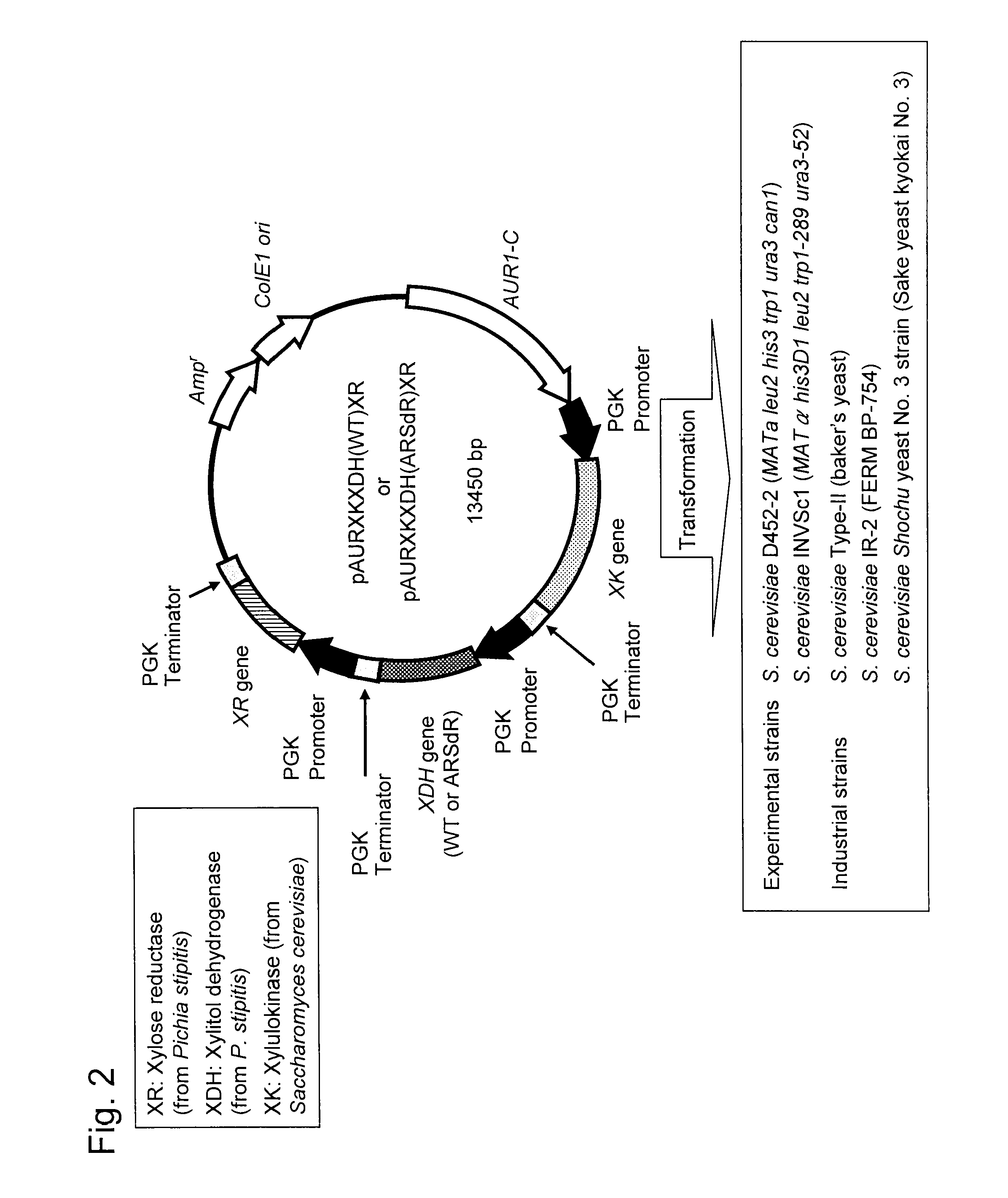
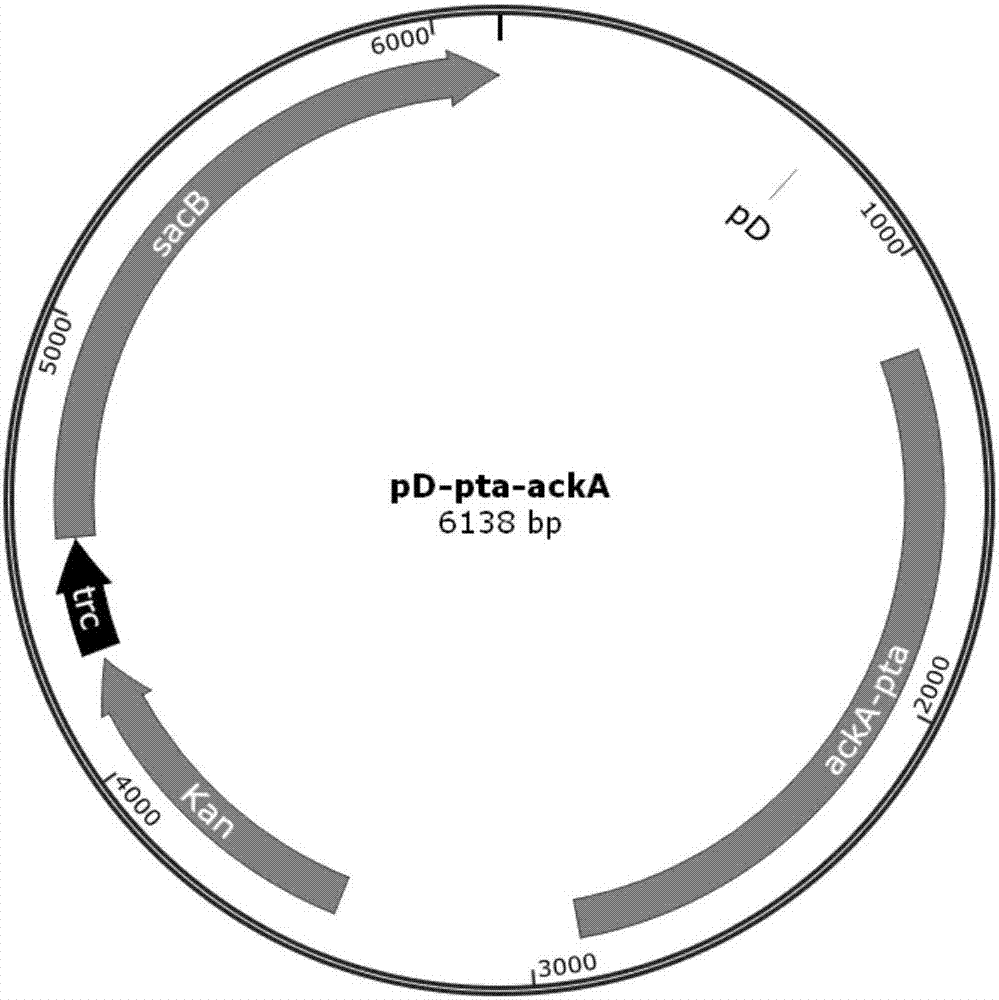
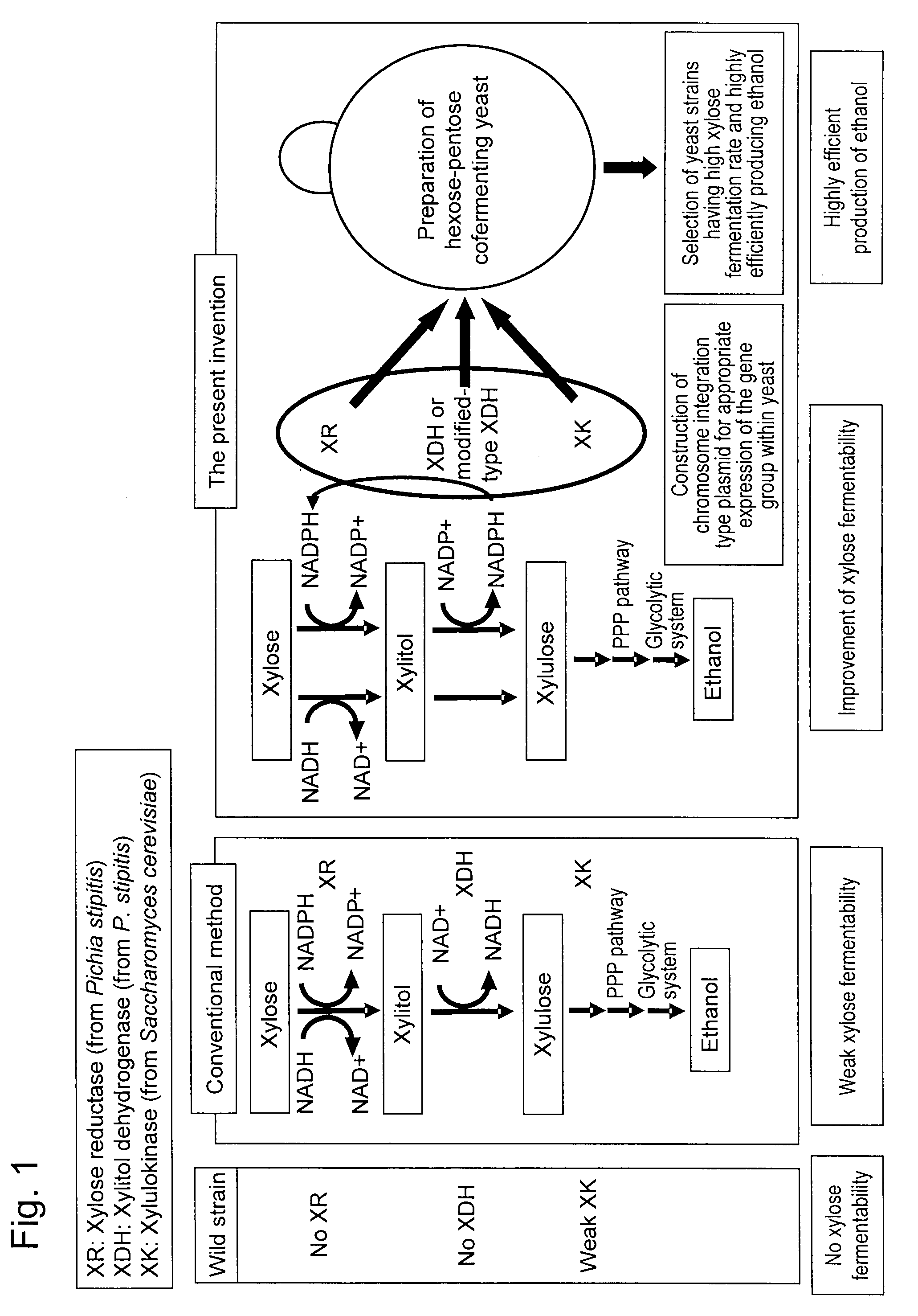
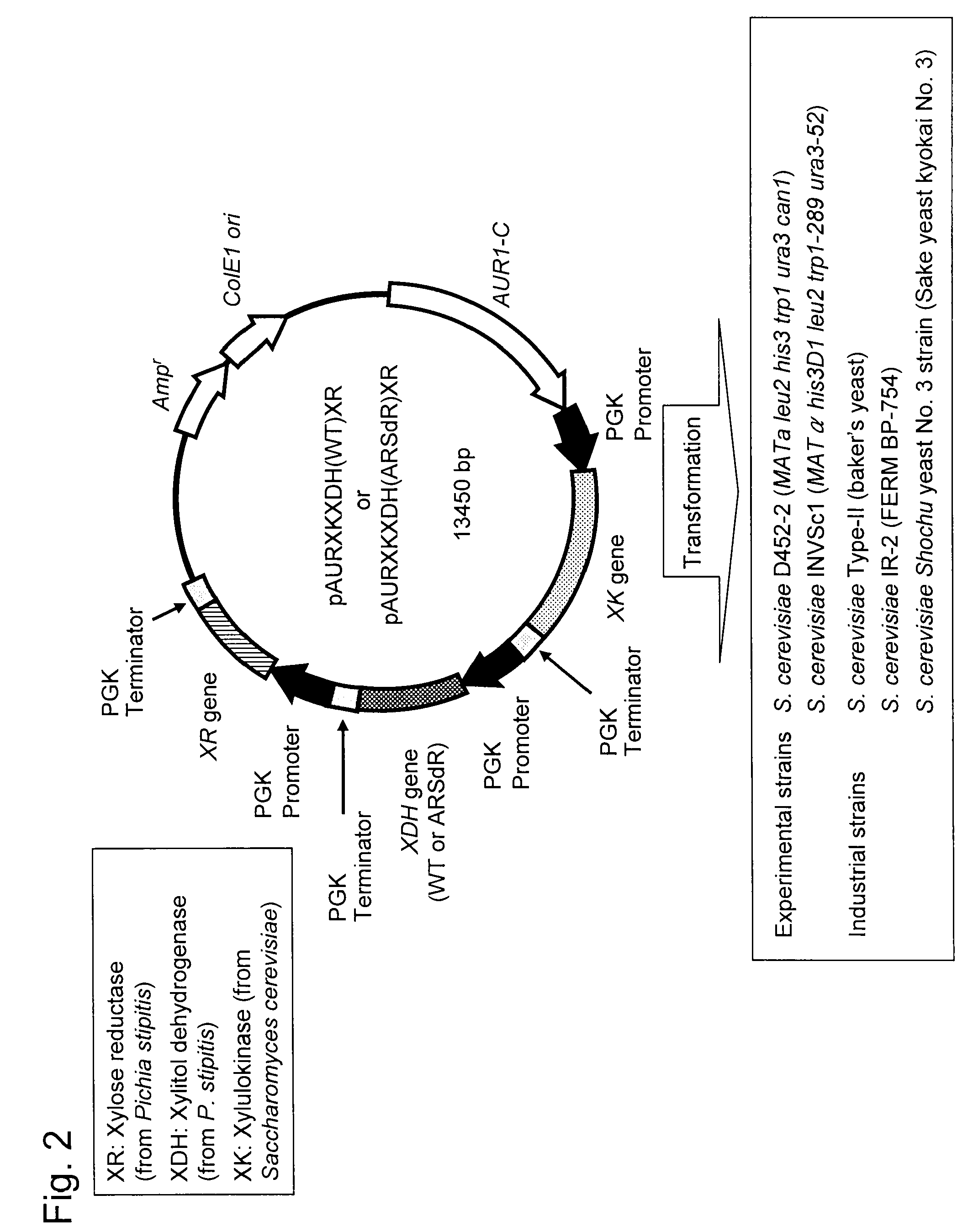
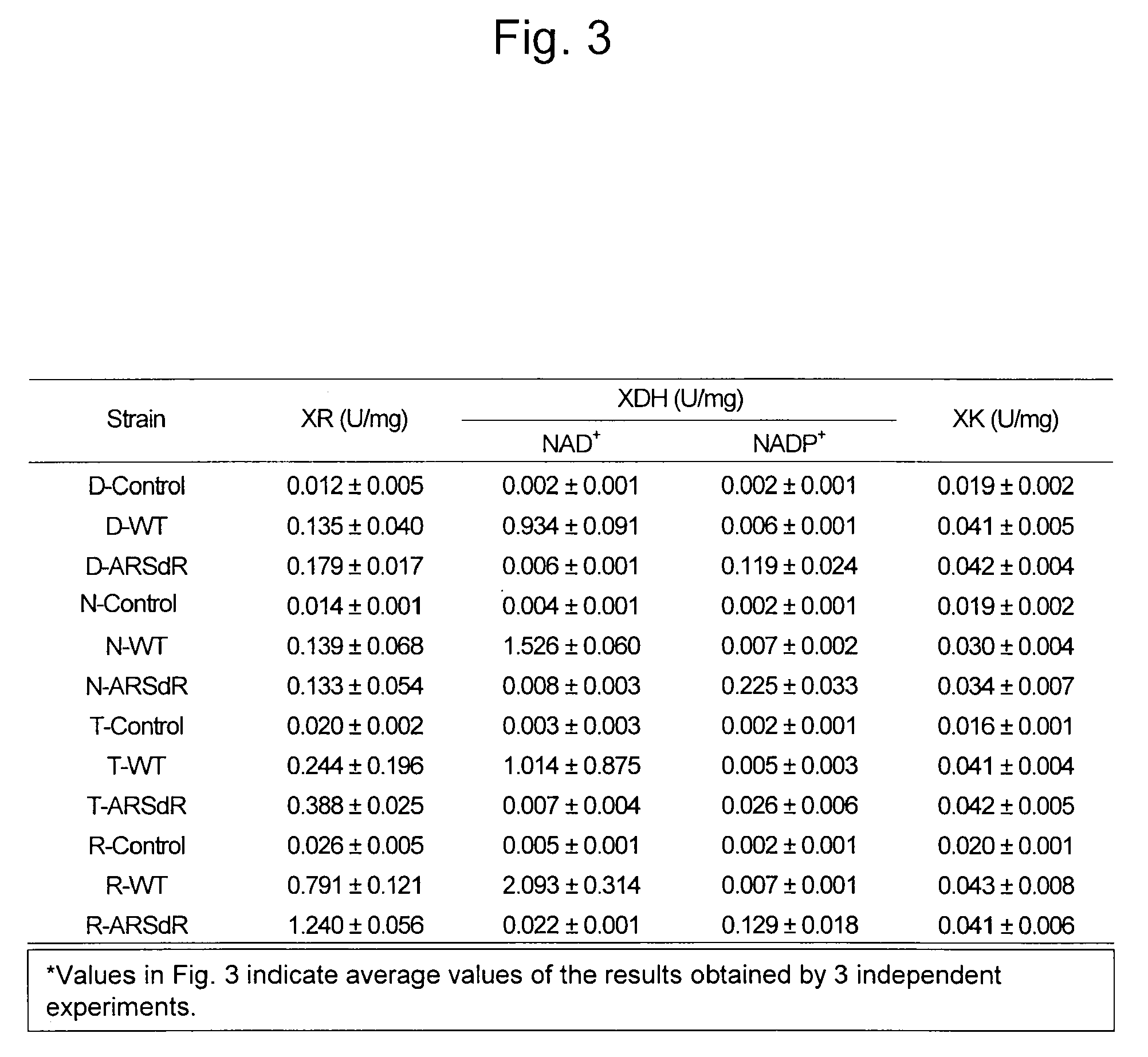
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS20110027847A1Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
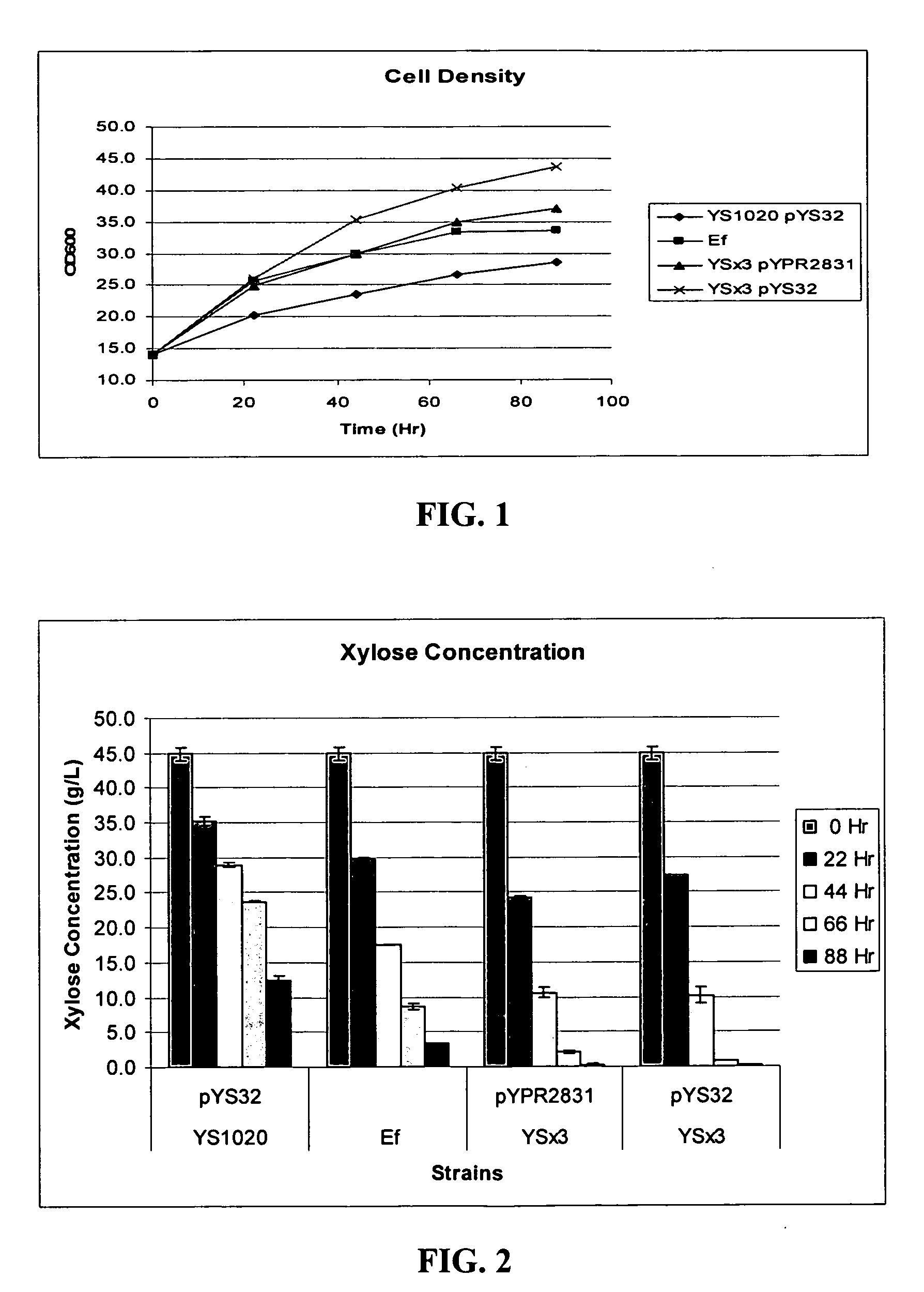
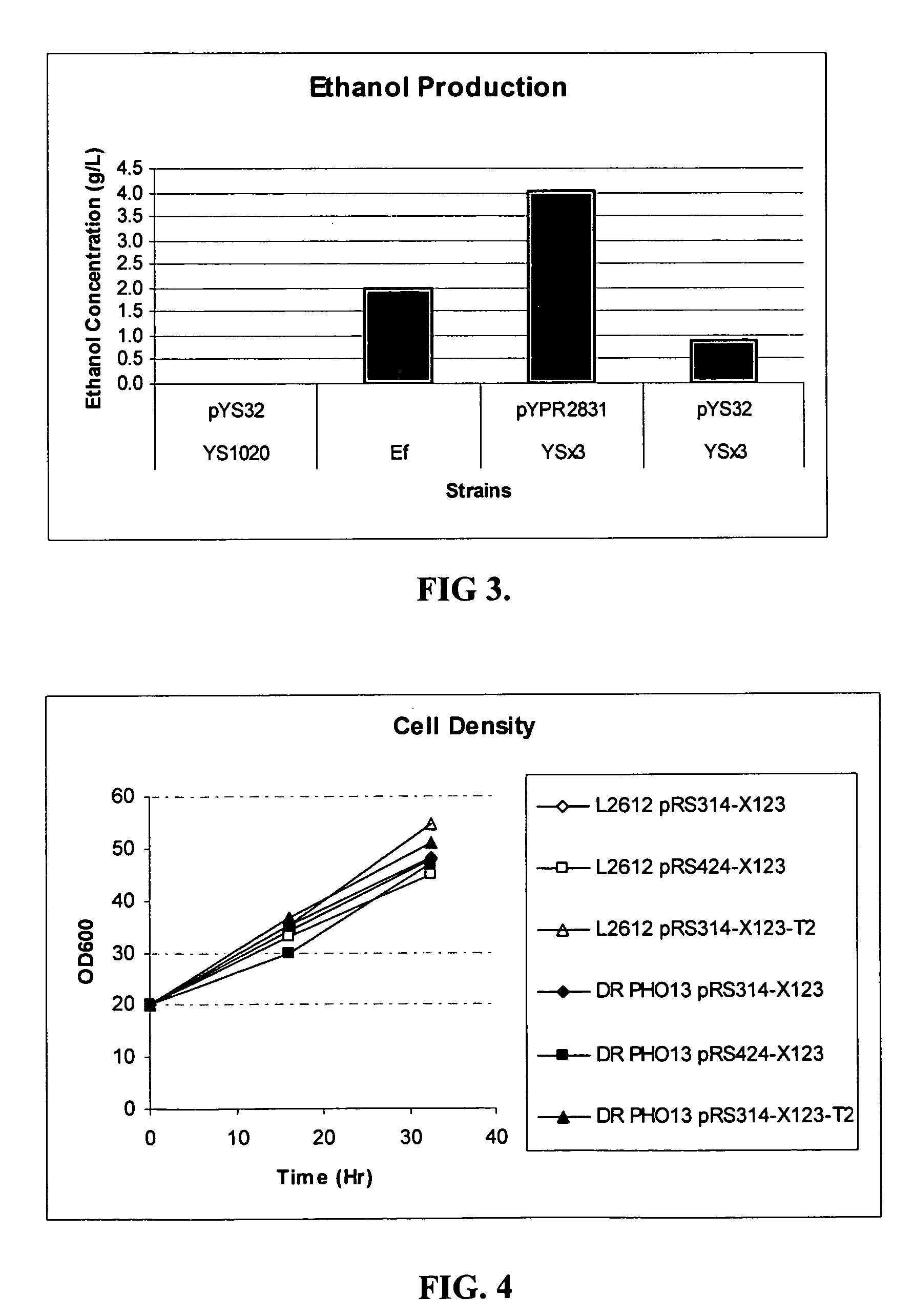
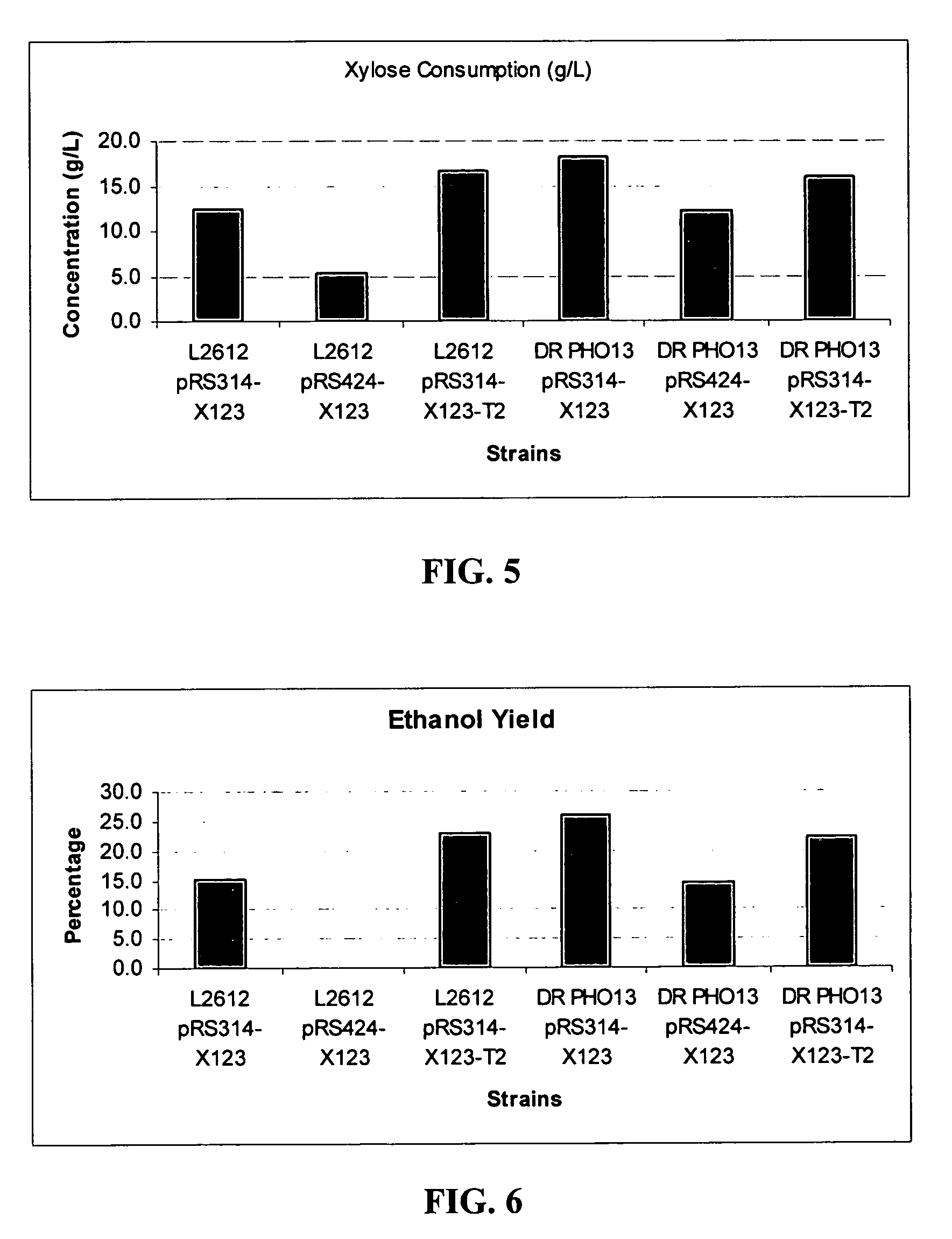
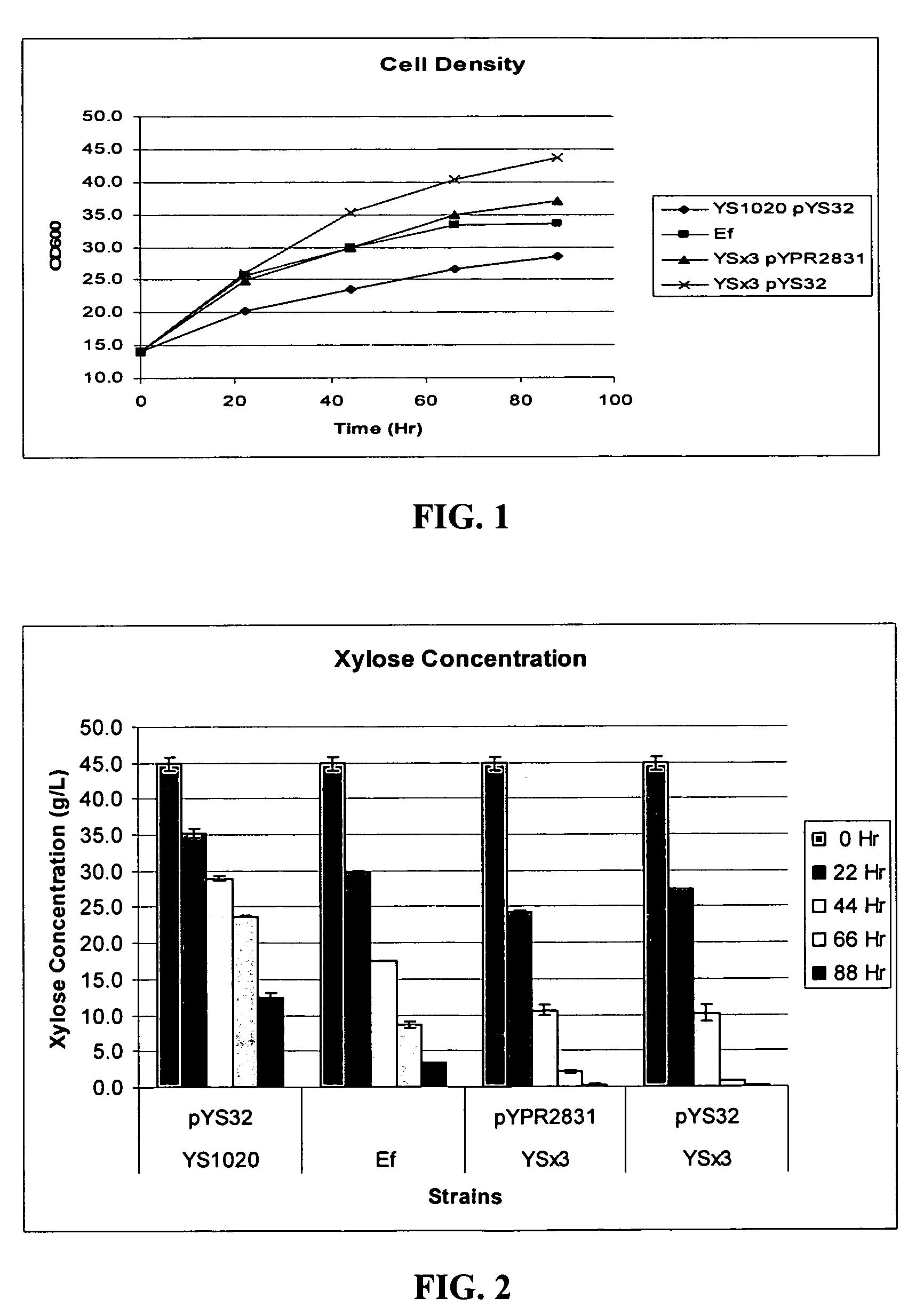
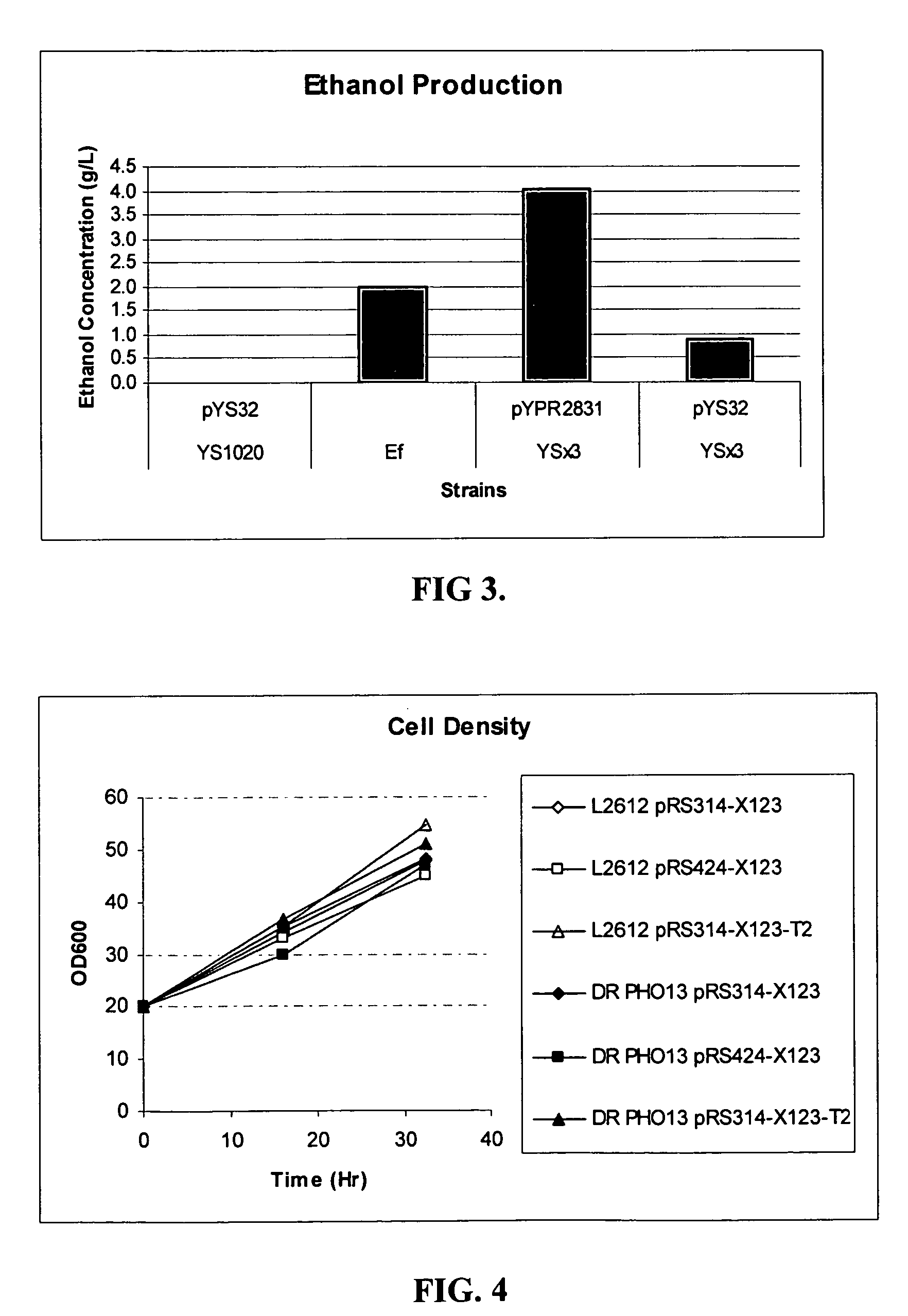
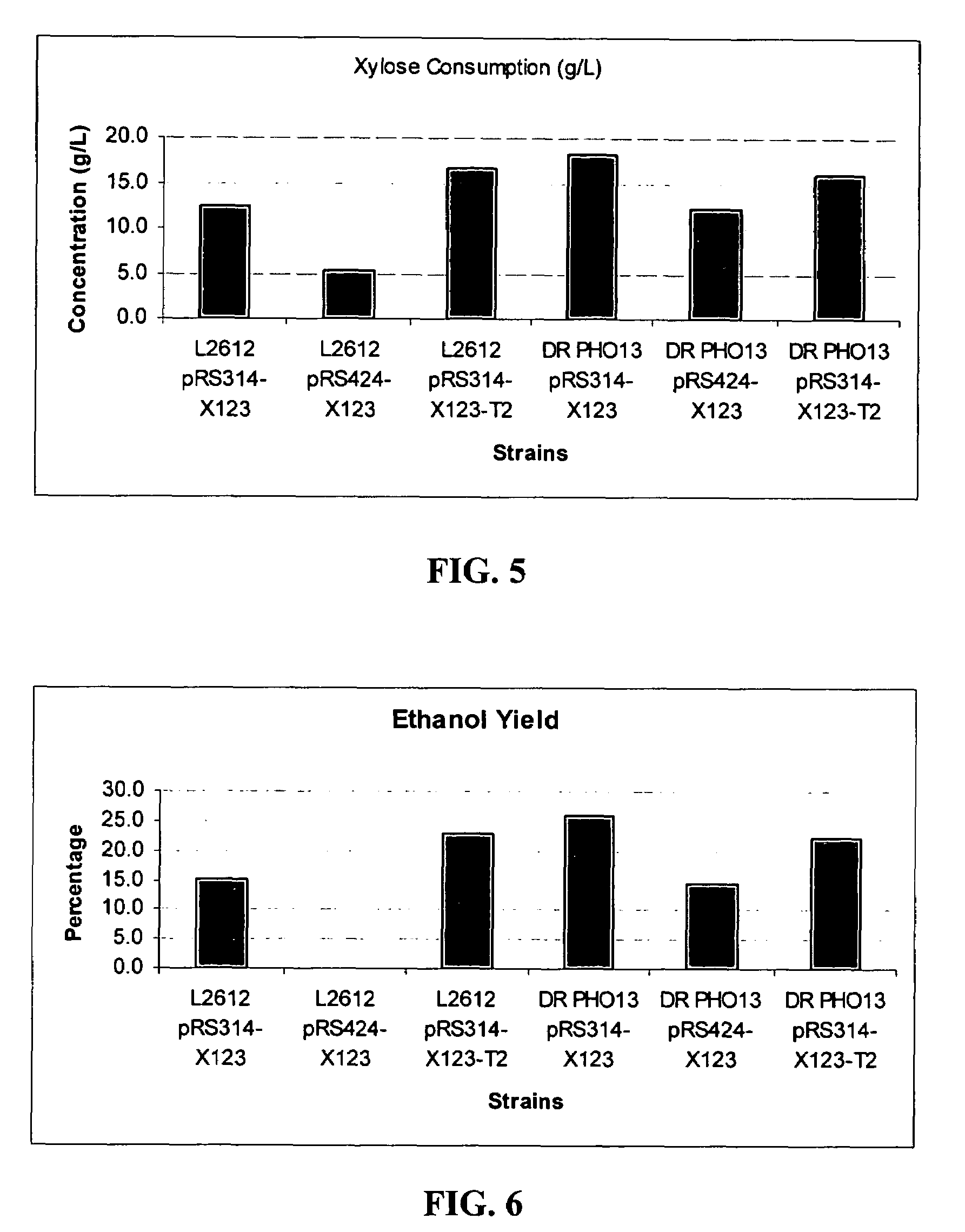
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains expressing xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase and having reduced expression of PHO13 or a PHO13 ortholog, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strains.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains expressing xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase and having reduced expression of PHO13 or a PHO13 ortholog, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strains.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Method for improving sugar utilization rate of clostridium acetobutylicum in fermentation of mixed sugar
ActiveCN102796692AElimination of inhibitory effectsImprove xylose utilizationBacteriaTransferasesHigh concentrationWild type
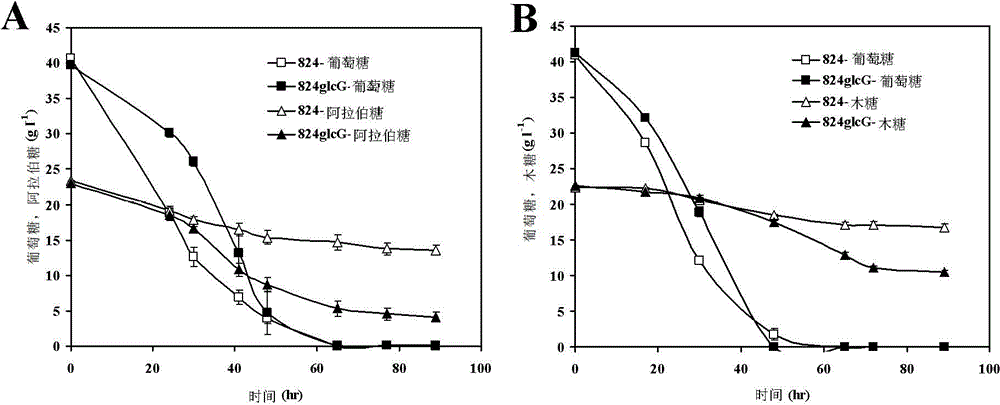
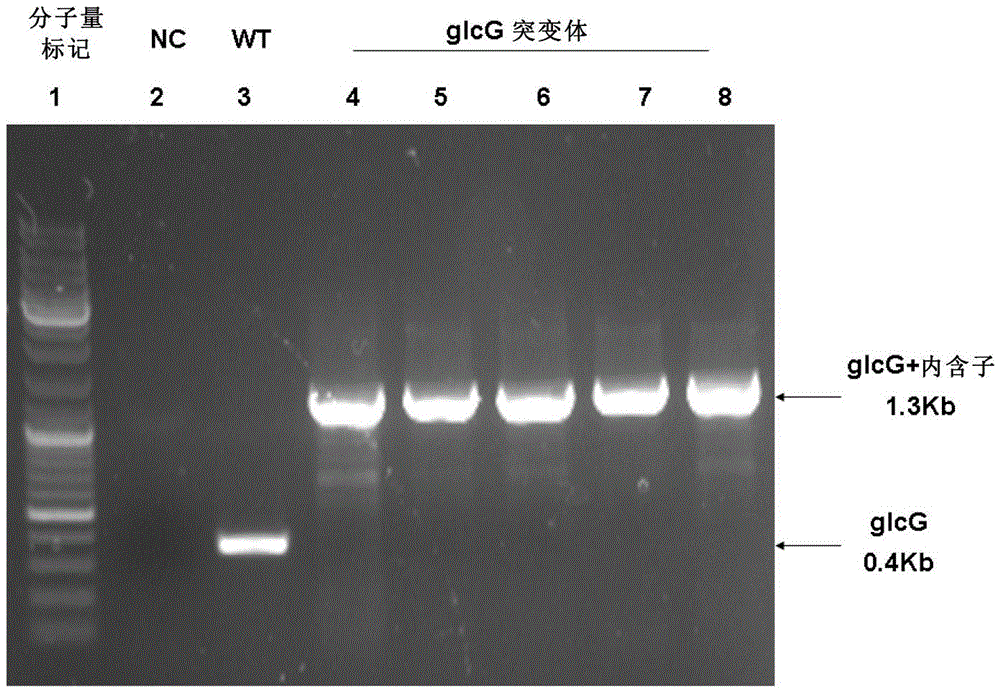
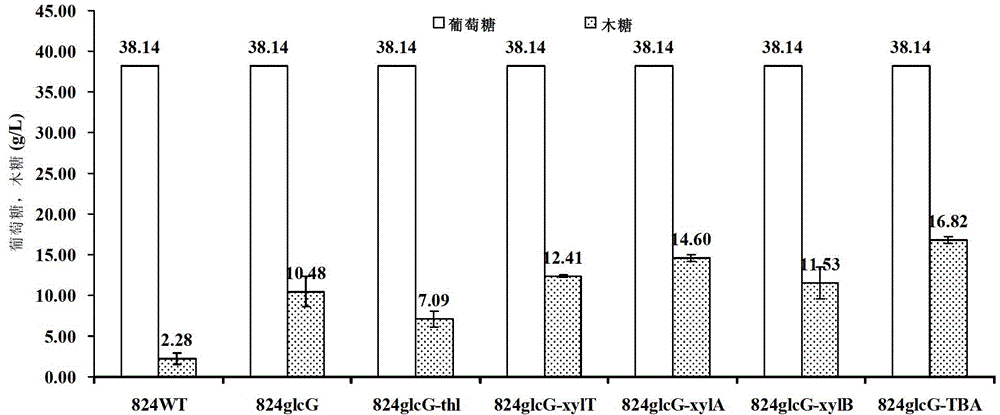
The invention discloses a method for improving the sugar utilization rate of clostridium acetobutylicum in fermentation of mixed sugar. The method comprises the following steps of: performing gene engineering modification on clostridium acetobutylicum, so that compared with wild type clostridium acetobutylicum, the clostridium acetobutylicum has the advantages that expression of g1cG gene can be inhibited, and the expression and activity of xylose transportprotein, xylose isomerase, and / or xylulokinase can be improved; and applying the obtained clostridium acetobutylicum which is subjected to gene engineering to fermentation of sugar. By the method, more xylose and arabinose can be used by clostridium acetobutylicum in the fermentation of the mixed sugar, a solvent product with high concentration can be produced, and the product yield can be improved; and the method has excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:南京食气生化科技有限公司
Stable recombinant yeasts for fermenting xylose to ethanol
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Recombinant yeast for lignocellulose raw materials
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining a recombinant yeast of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which ferments lignocellulose raw materials to ethanol, including introducing DNA into a yeast so as to cause the yeast to have introduced genes encoding xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Xylose-fermenting yeast engineered to increase flux of the pentose phosphate pathway
The present invention relates to further genetic modifications in eukaryotic host cells that have been transformed to express a xylose isomerase that confers the host cell the ability of isomerizing xylose to xylulose. The further genetic modifications are aimed at improving the efficiency of xylose metabolism and include e.g. reduction of unspecific aldose reductase activity, increased xylulose kinase activity and increased flux of the pentose phosphate pathway. The modified host cells of the invention are suitable for the production of a wide variety of fermentation products, including ethanol, in fermentation processes in which a source of xylose or a source of xylose and glucose are used as carbon source.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS8445243B2Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
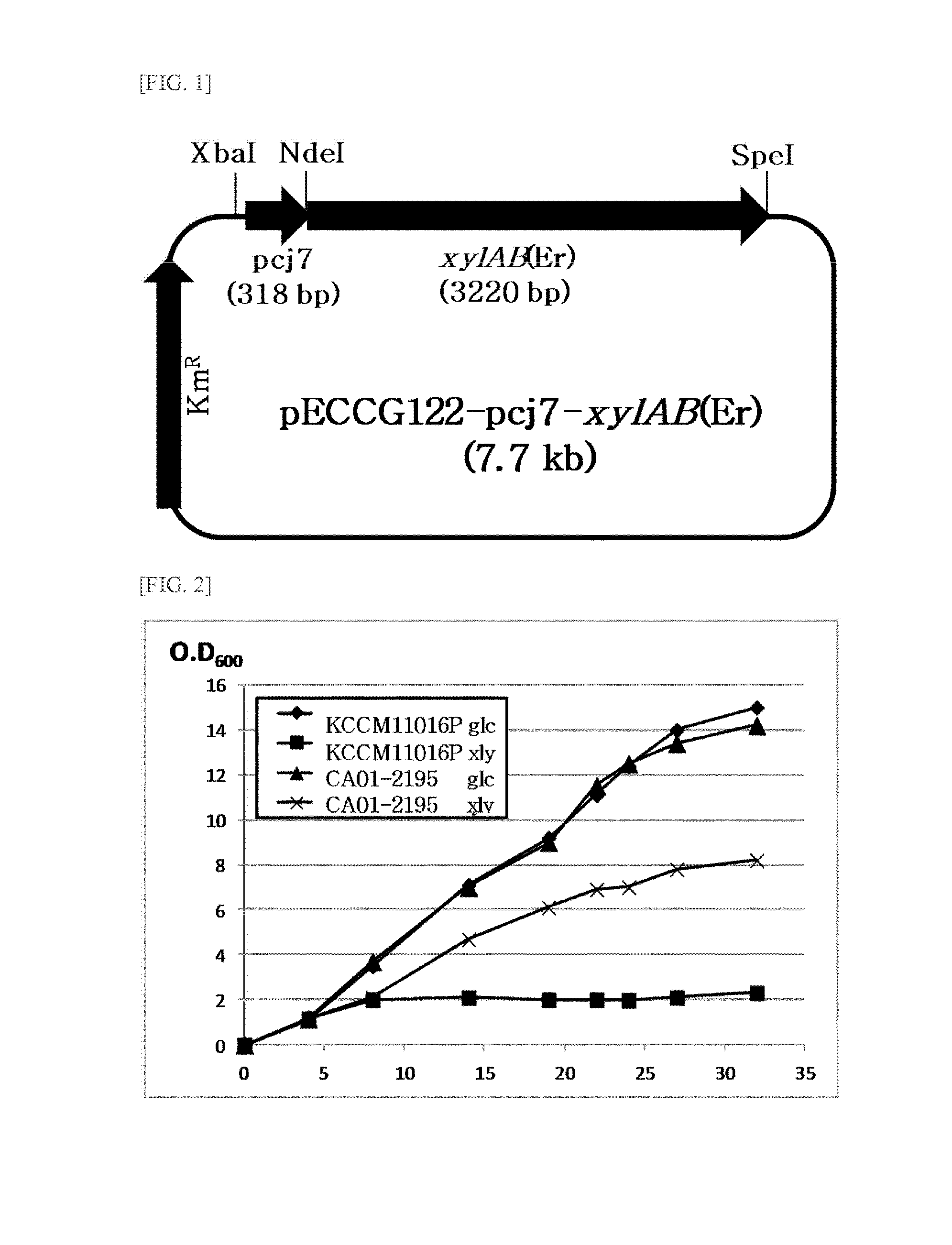
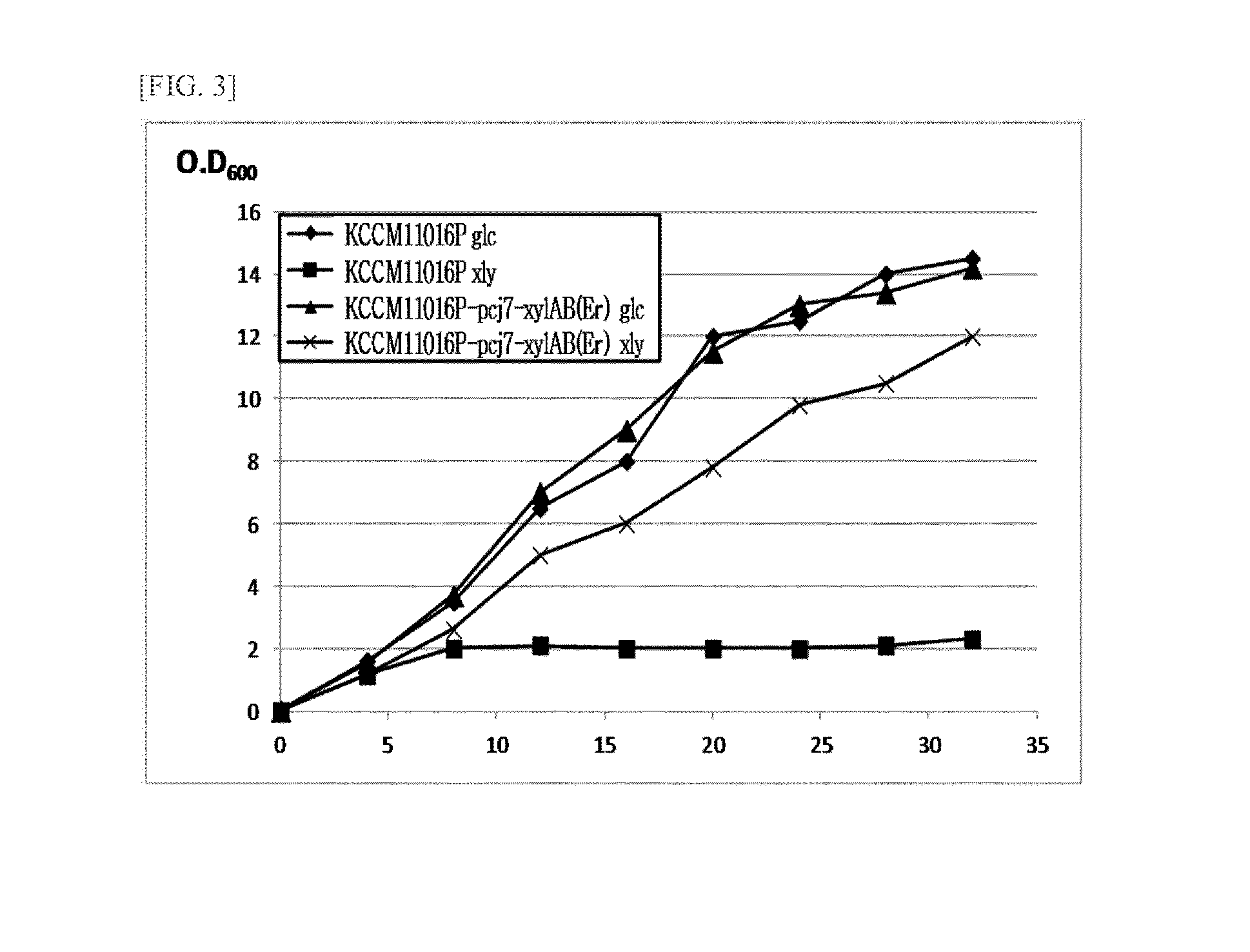
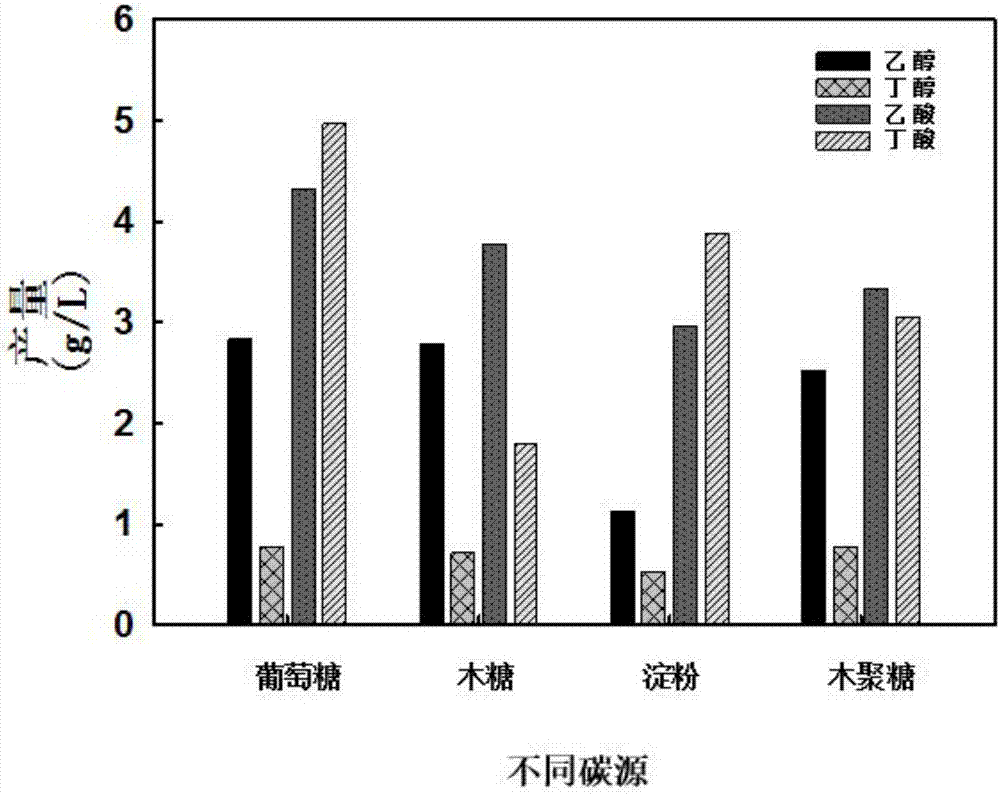
Microorganisms of corynebacterium which can utilize xylose and method for producing l-lysine using same
The present invention relates to microorganisms of corynebacterium which can utilize xylose and to a method for producing L-lysine using same. More particularly, the present invention relates to microorganisms of corynebacterium which are modified, in which genes encoding xylose isomerase and xylulokinase which are xylose synthases are introduced to express the xylose synthase. The present invention also relates to a method for producing L-lysine, comprising a step of culturing the modified microorganisms of corynebacterium using xylose as a carbon source, and recovering L-lysine from the culture.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
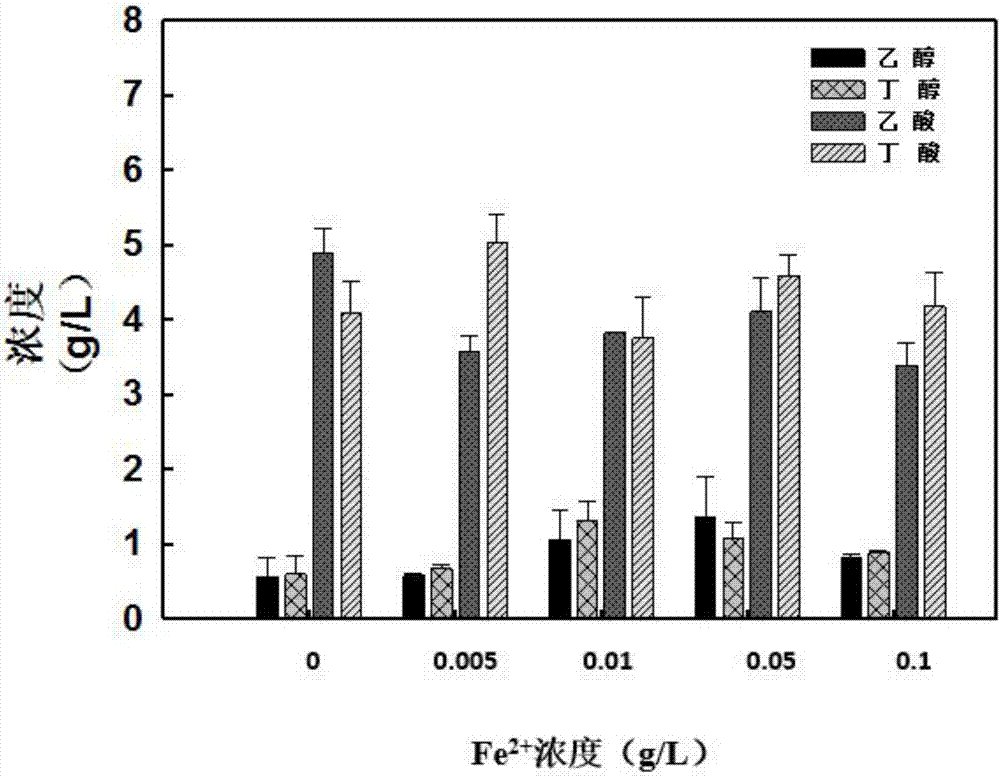
Strain for directly producing butanol by utilizing xylan as sole carbon source and application of strain
The invention discloses a strain for directly producing butanol by utilizing xylan as a sole carbon source. A classification name of the strain is Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum, and the number of the strain is M5; moreover, the strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation date of the strain is 27th February, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2017072. The strain M5 can basically degrade 30g / L of xylan in 3-5 days and can be used as the sole carbon source for growth; after the xylan is degraded into xylose, pyruvic acid is obtained by xylose isomerase and xylulokinase; subsequently, acetic acid, ethanol, butyric acid and butanol are obtained through a series of metabolic pathways. According to the strain and the application of the strain disclosed by the invention, enzymes of all pathways can bear a high temperature of 55 to 65 DEG C, and the strain M5 is the one that can produce the butanol by directly utilizing the xylan, which is the only reported bacterial strain until now; therefore, a series of high-temperature resistant enzymes can be provided for industrial production of the butanol, and the strain has important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, and method for production of bioethanol using the bacterium
InactiveUS8383377B2Strong glucose fermentation capacityImprove fermentation performanceBacteriaBiofuelsTransketolaseEscherichia coli
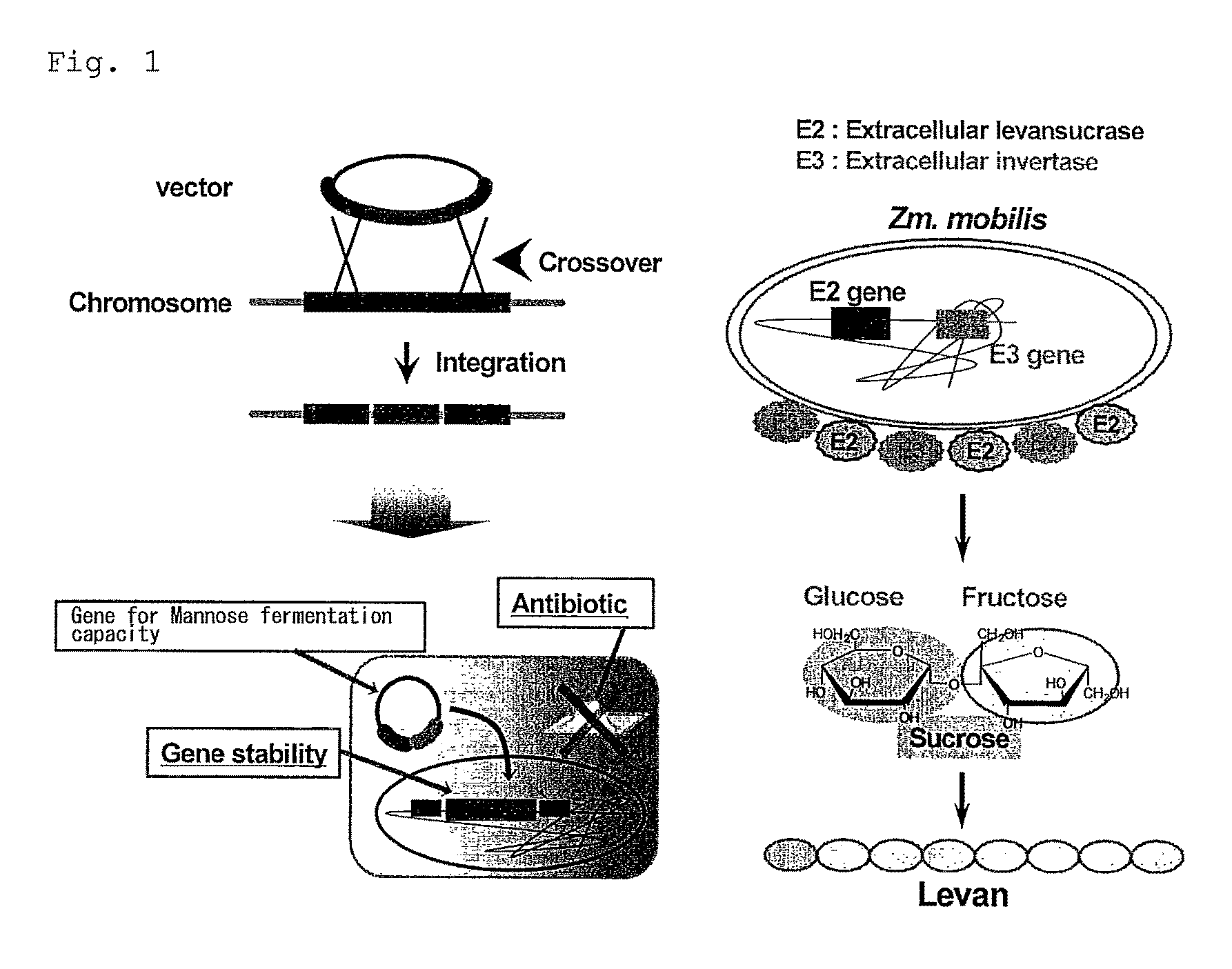
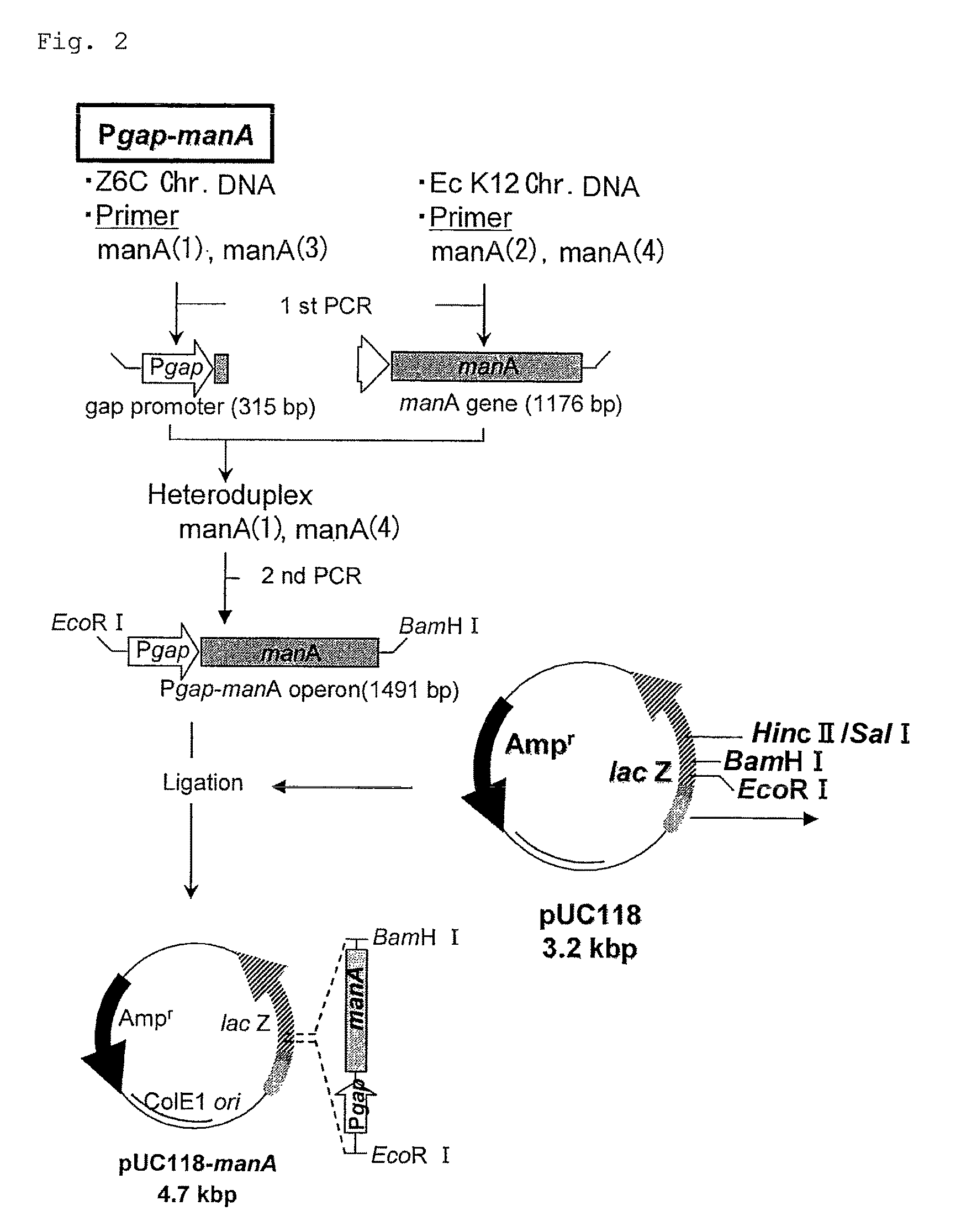
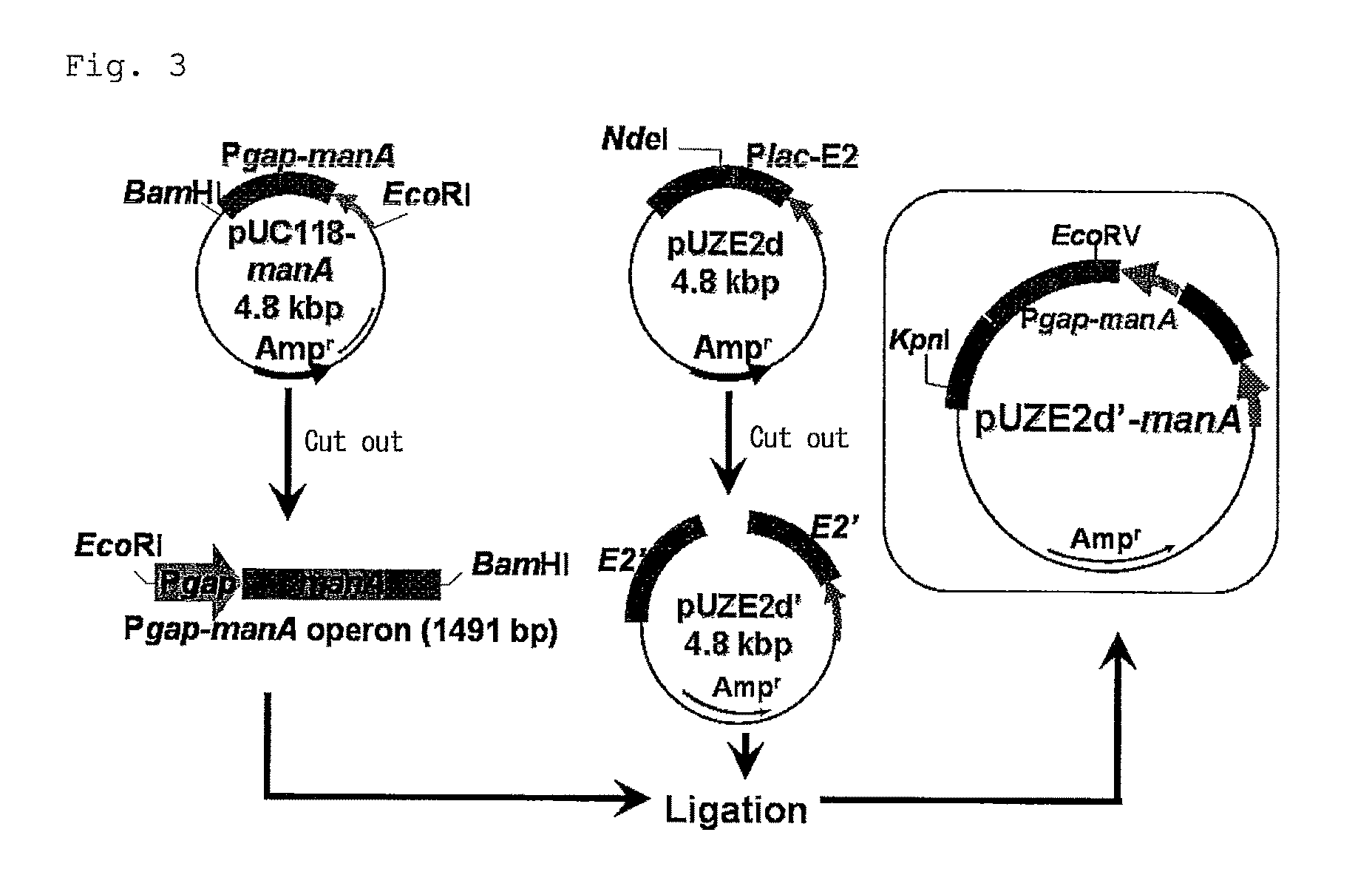
The object is to develop a bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, which can ferment a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type or lignocellulose-type biomass resource to produce ethanol, and to construct an energy-saving high-efficiency bioethanol conversion process. Thus, disclosed is Zymomonas mobilis bacterium which is prepared by integrating a gene encoding a phosphomannose isomerase derived from Escharichia coli into a levansucrase gene located on the chromosome by the double cross-over by means of a homologous recombsination method, and then introducing recombinant DNA prepared by binding a DNA fragment containing genes encoding a xylose isomerase, a xylulokinase, a transaldolase and a transketolase, respectively, all derived from Escherichia coli to a vector. Also disclosed is a method for producing ethanol by continuously fermenting a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type biomass resource in a system on which the Zymomonas mobilis bacterium is immobilized.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for performing alcohol fermentation by using xylose, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for performing alcohol fermentation by using xylose, and a preparation method and application thereof. The strain contains the following nucleotide sequences: xylose reductase gene, xylitol dehydrogenase gene and xylulokinase gene; and the xylulokinase gene is overexpressed. The preparation method comprises the following steps: integrating a constitutive strong promoter to the upstream of the xylulokinase gene of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae initial strain genome by homologous recombination to obtain a xylulokinase-overexpressed strain; and transforming into Candida lusitaniae to obtain xylose reductase gene and xylitol dehydrogenase gene, thereby obtaining the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for performing alcohol fermentation by using xylose. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium can grow by using the xylose as the unique carbon source, and lays foundation for the subsequent construction of alcohol production by xylose / glucose co-fermentation. The engineering strain can be further screened and transformed to produce alcohol from lignocellulose, thereby greatly lowering the alcohol production cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN106434772AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseXylose fermentation
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for producing malic acid efficiently by means of xylose fermentation and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. In the recombinant bacterium, hosphopentose isomerase, L-fuculokinase, L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, glycolate oxidase and malate synthase are overexpressed, and meanwhile xylulokinase, malate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase are knocked out, so that a malic acid synthesis route is obtained. According to the recombinant bacterium, the malic acid yield and the xylose conversion rate in shake flask culture and fermentation tank culture can reach ideal levels, and a good industrialized application prospect is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Broad host range plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101475955AEfficient productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTransketolase
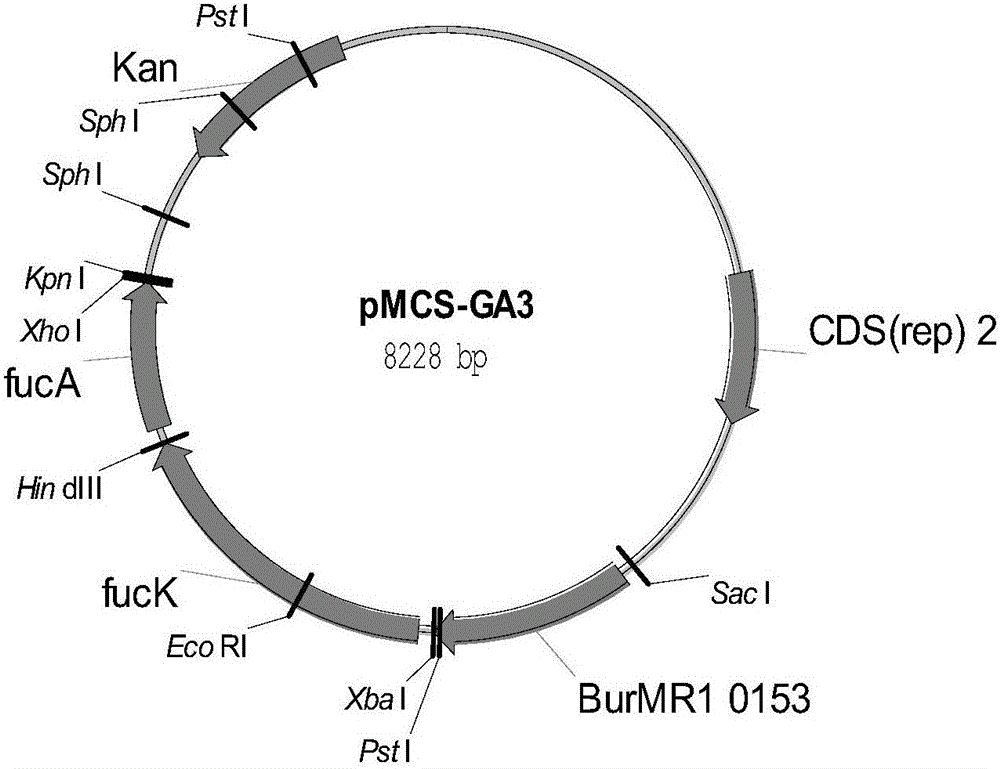
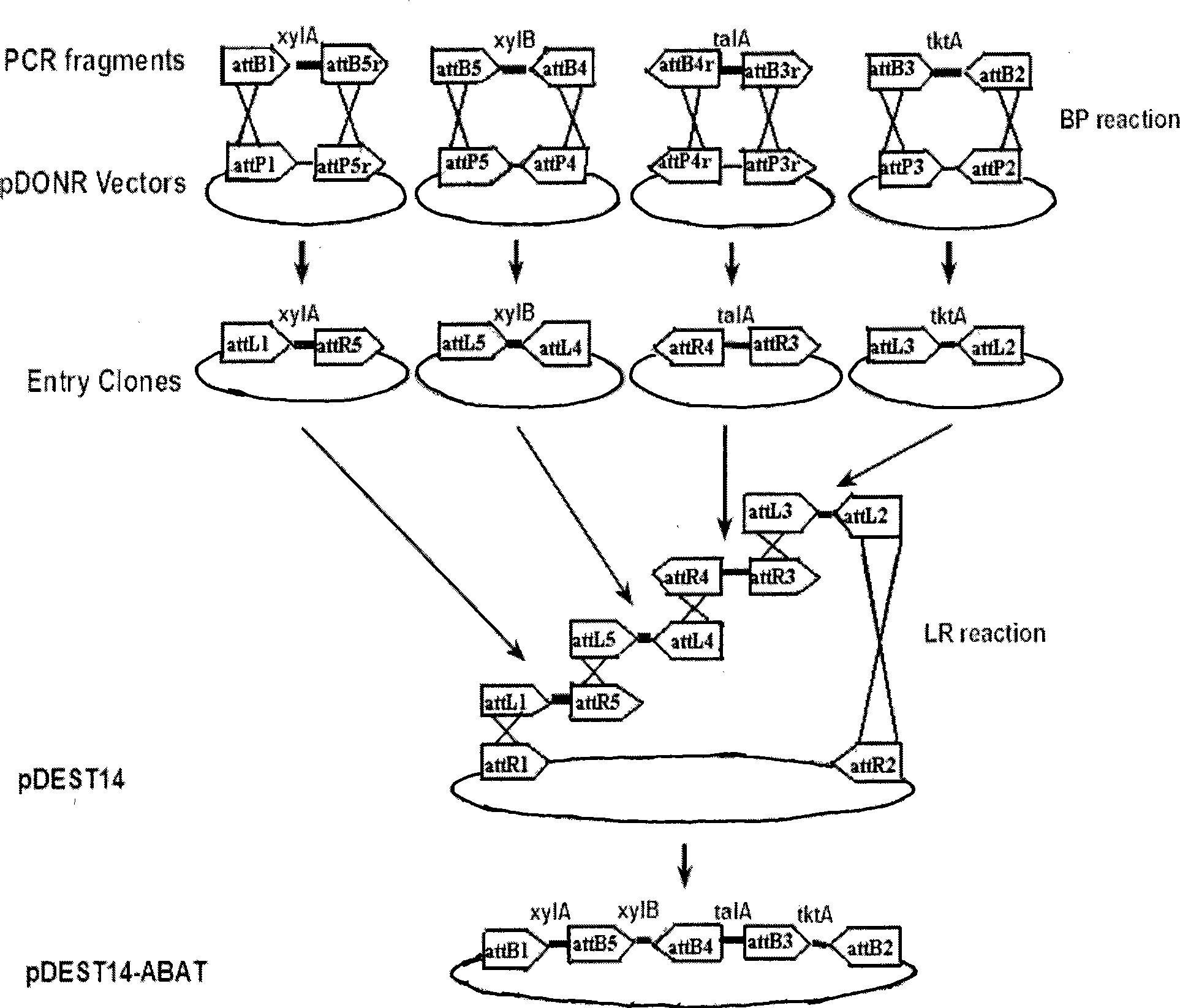
The invention discloses a wide host plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related genes and construction method thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology techniques. The plasmid contains four xylose metabolism related enzyme genes, xylose isomerase (xylA), xylulokinase (xylB), transaldolase (talA) and transketolase (tktA), which are derived from E.coli DH5alpaha strain. The plasmid construction method uses the Gateway technology, to respectively design specific primers of four target genes xylA, xylB, talA and tktA, takes the E.coli DH5alpaha strain as the origin stain of the target genes to amplify the corresponding gene through the PCR; the PCR product performs BP recombination with the corresponding pDONR vector, and then the obtained Entry clones perform LR recombination with the pDEST14, to obtain the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid; the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid is connected to the Xha I single zyme cutting vector pBBR1MCS2 through the Xba I and Nhe I double zyme cutting product to obtained the recombinant plasmid pBBR1MCS2-ABAT. The superior strain shifted in the plasmid can greatly reduce production costs of cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium and its application in production of ethanol
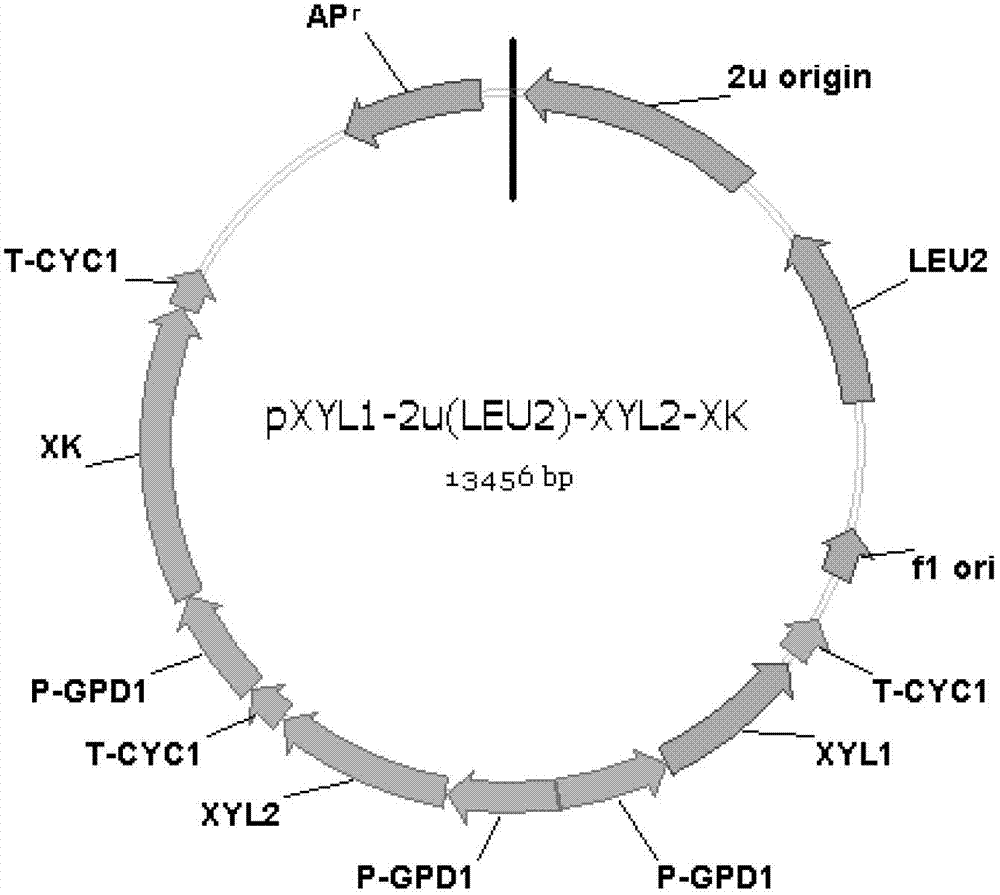
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium and its application in the production of ethanol. The invention provides Saccharomyces cerevisiae W32N55, and the preservation number of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae W32N55 is CGMCC NO.6090. The invention also provides an application of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae W32N55 in the preparation of ethanol. Experiments of the invention prove that the engineering bacterium W32N55 provided in the invention is obtained through obtaining the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium by the introducing xylose reductase gene (XYL1) and xylitol dehydrogenase gene (XYL2) to an original strain and by improving the activity of xylulokinase (XK), and through allowing the engineering bacterium containing the XYL1, the XYL2 and XK gene to undergo adaptive acclimation.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for production of substance in candida utilis using xylose as carbon source
InactiveUS20120045803A1Efficient production of L-lacticShort timeFungiTransferasesYeastBiotechnology
Disclosed is a yeast strain of Candida utilis, wherein the yeast strain has been transformed with at least one of three genes that are operatively linked to a promoter sequence and encode polypeptides having activities of xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulose kinase. The yeast strain is useful for producing a metabolic product from xylose with high efficiency.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
Xylitol production from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20140342418A1Reduce expressionIncrease in intracellular NADPH concentrationFermentationCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
The present disclosure relates to host cells containing a recombinant xylose reductase, a recombinant cellodextrin transporter, a recombinant intracellular β-glucosidase, and lacking xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase, and to methods of using such cells for producing xylitol from cellulosic biomass containing cellodextrin and xylose.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Prevotella ruminicola xylose isomerase and co-expression with xylulokinase in yeast for xylose fermentation
A xylose isomerase (XI) enzyme which exhibits increased activity and affinity for xylose is produced by strain TC2-24 of the rumen bacterium, Prevotella ruminicola. The gene encoding this enzyme may be used to produce improved recombinant yeast capable of utilizing xylose. The recombinant yeast are preferably transformed with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding both the P. ruminicola XI, and the xylulokinase (XKS) of a Prevotella species. Yeast transformed with the polynucleotide sequences coding both of these XI and XKS exhibit significantly increased xylose utilization and cell growth on a culture medium containing xylose as the sole carbon source, in comparison to yeast transformed with XKS and XI from other sources.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
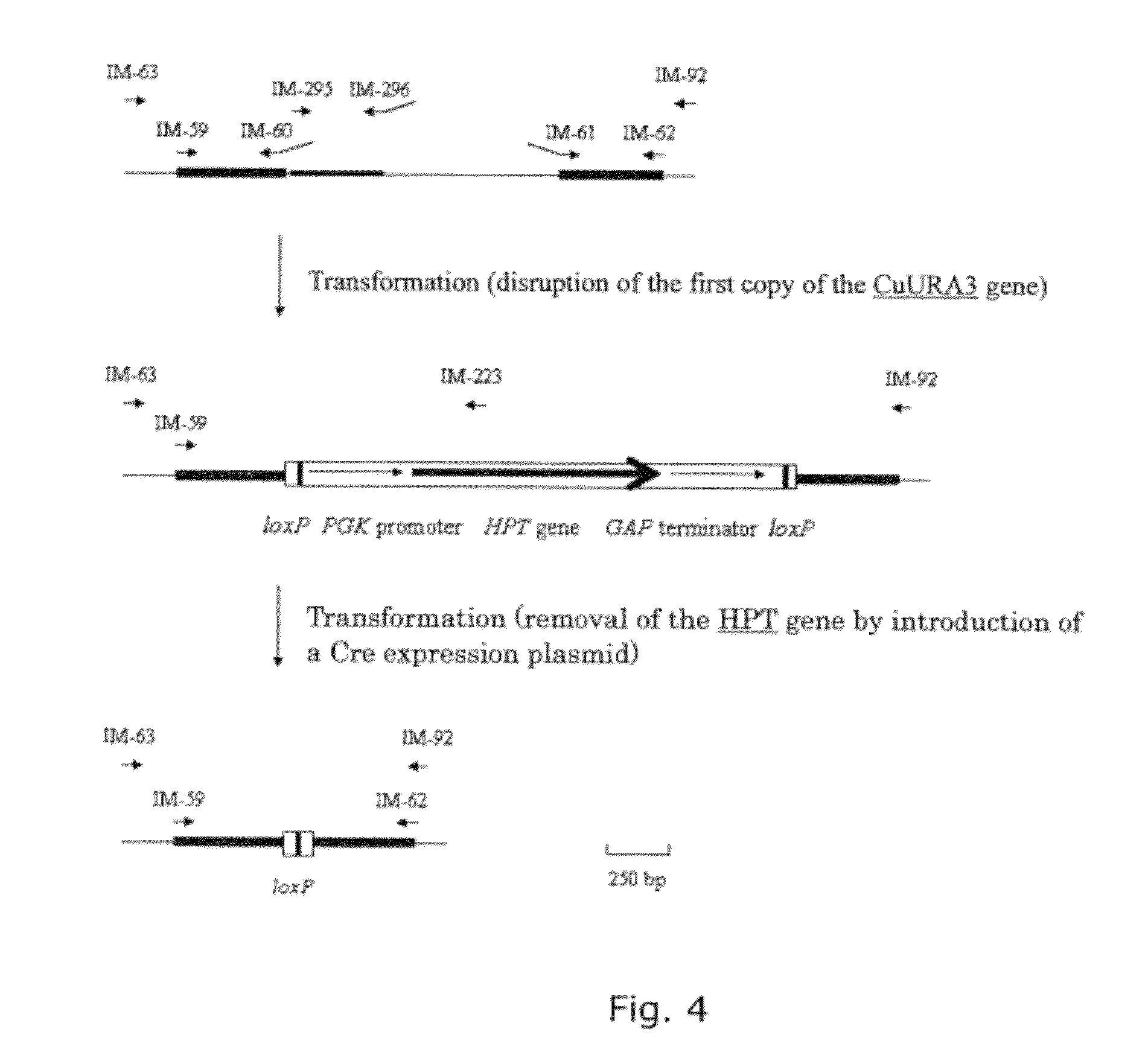
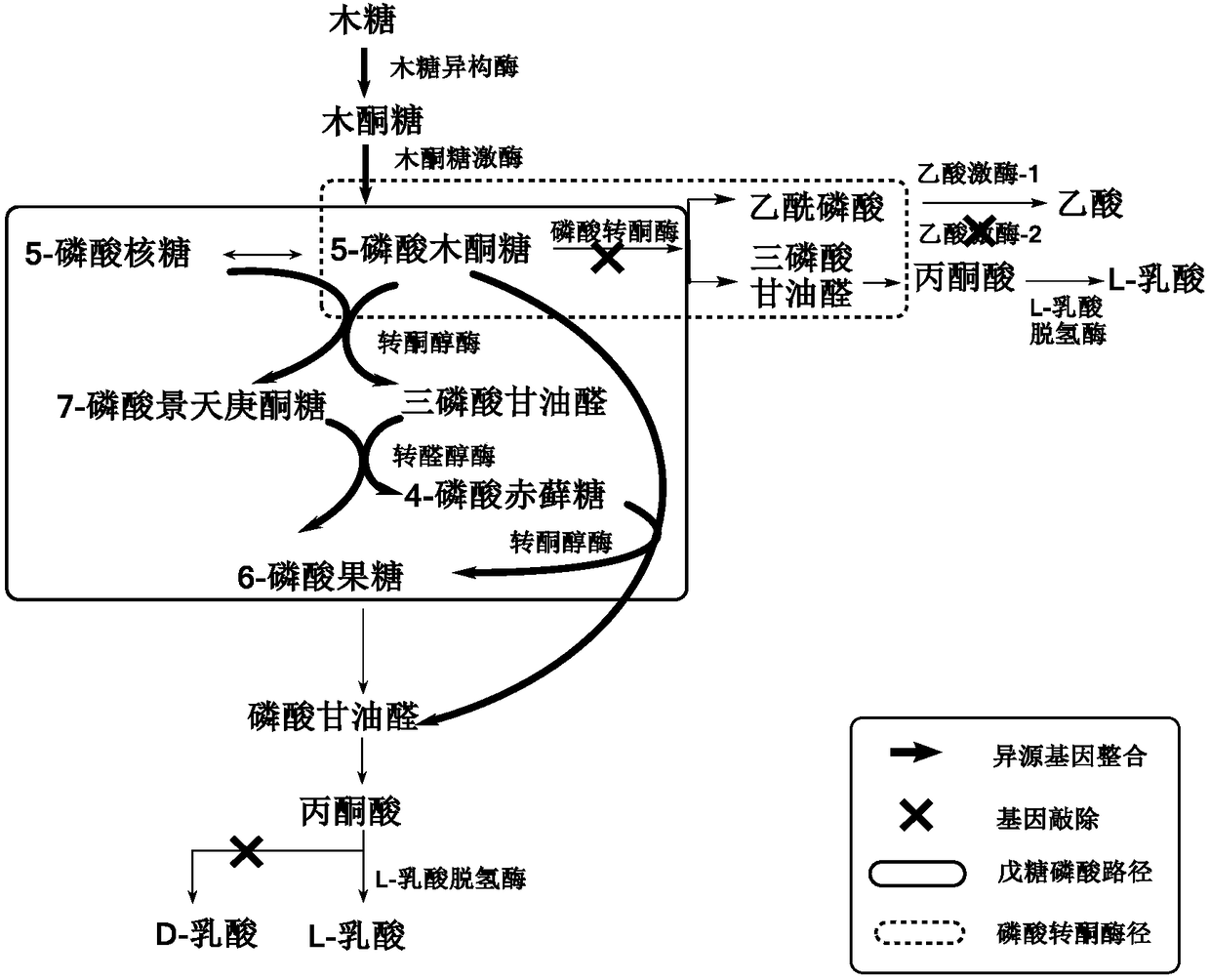
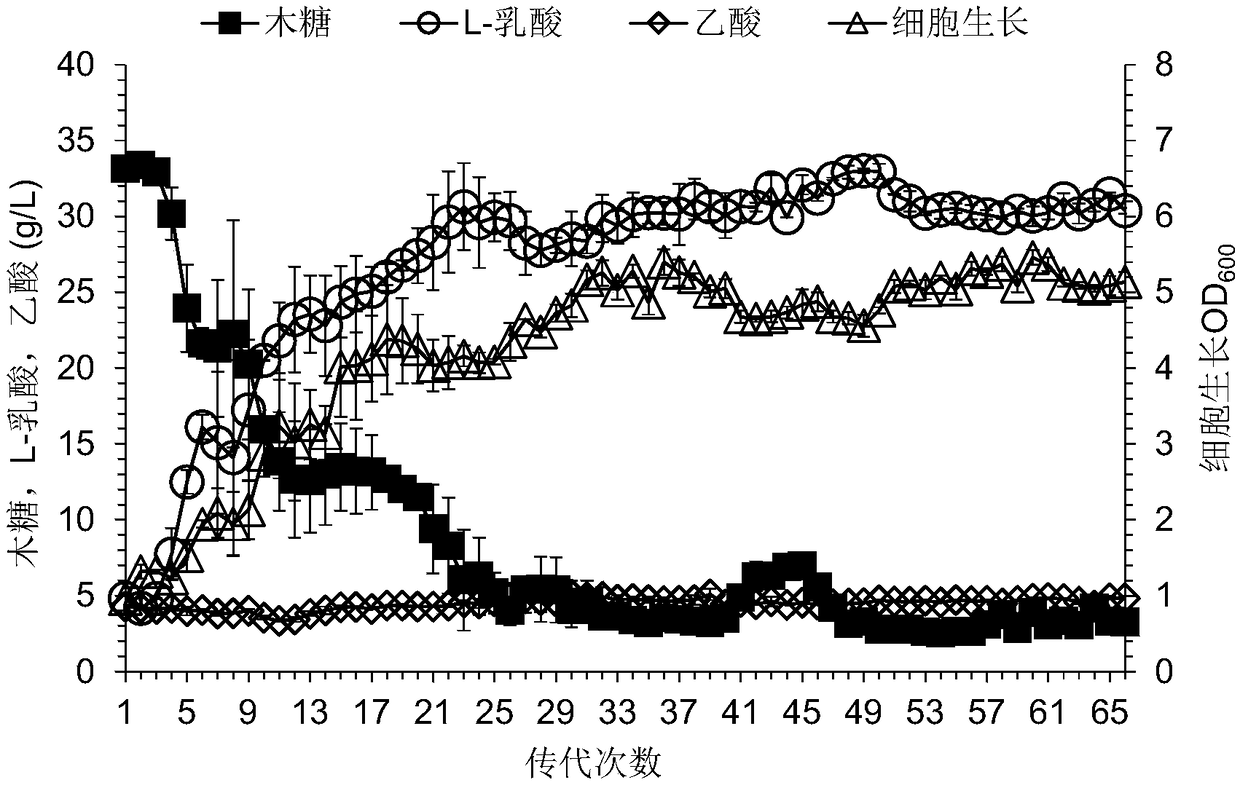
Construction method of pediococcus acidilactici for producing L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose
The invention discloses a construction method of pediococcus acidilactici for producing L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The construction method comprises the following construction steps: integrating heterogenous xylose isomerase, xylulokinase, transketolase and transaldolase coding genes on a genome of a strain pediococcus acidilactici TY112 (with the accession number of CGMCC NO.8664) for producing L-lactic acid by utilizing a thermosensitive knockout system; knocking out phosphoketolase and acetokinase coding genes; and carrying out adaptive evolution for improving the capacity of co-fermentation of glucose and xylose. With the construction method, an engineering strain capable of efficiently producingoptically pure L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose is successfully obtained, the engineering strain is named P.acidilactici ZY271, and the accession number is CGMCC NO.13611.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
InactiveUS20130295620A1Promote conversionReduce productionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementXylose fermentationXylitol
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com