Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for performing alcohol fermentation by using xylose, and preparation method and application thereof
A kind of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ethanol fermentation technology, applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
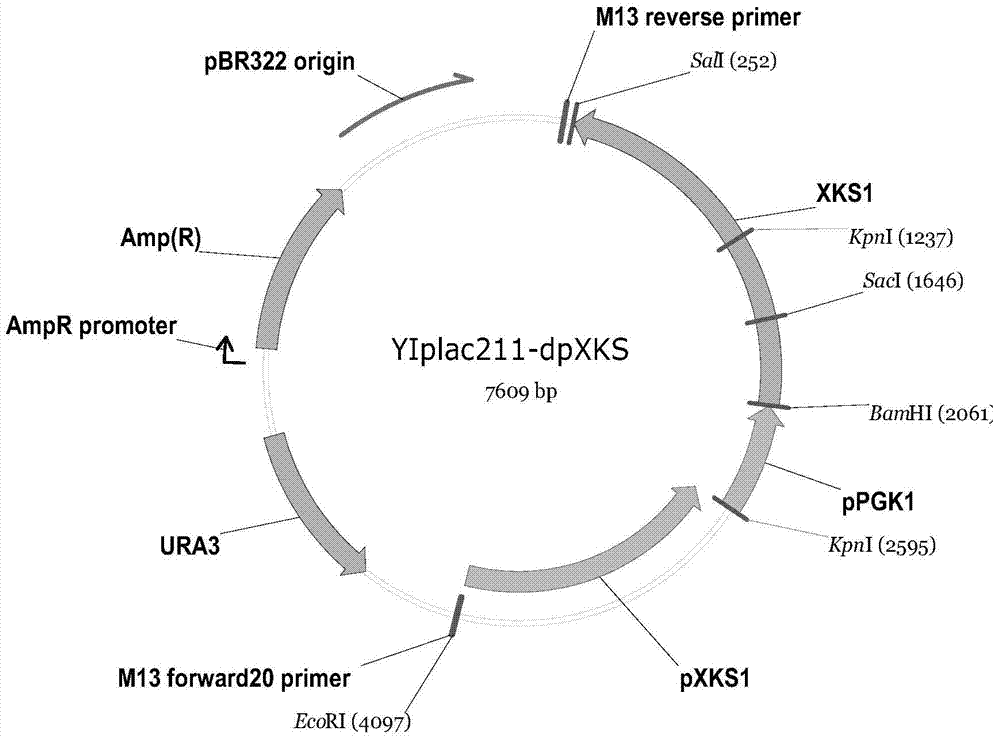
[0066] Embodiment 1 utilizes xylose to carry out the preparation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered bacterium of ethanol fermentation
[0067] (1) The primers designed to realize the present invention were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. as shown in Table 1 above.
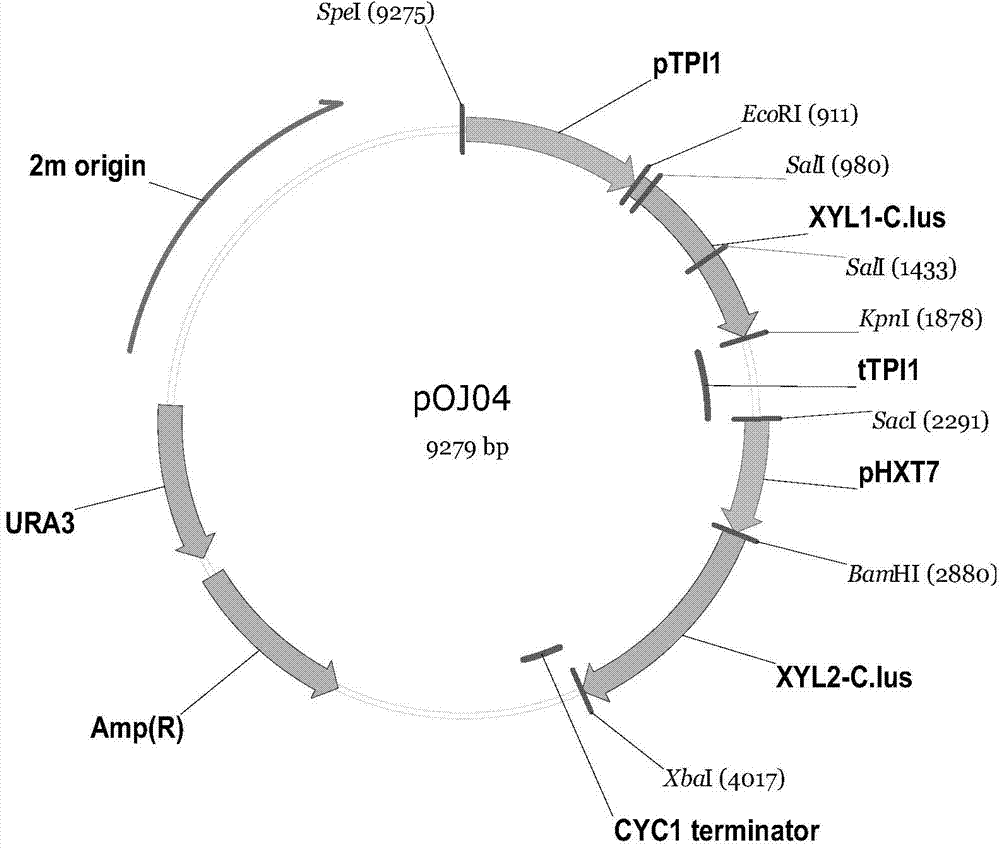
[0068] (2) Obtaining xylose reductase gene (xyl1) and xylitol dehydrogenase gene (xyl2)
[0069] Candida lusitaniae CICC 1461 of Portugal (China Industrial Microbial Culture Collection Management Center) was inoculated on YPX plate medium (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, xylose 20g / L, agar 15g / L, pH Naturally) at 30°C for activation. The activated yeast was inoculated into (1% (v / v) inoculum amount) YPX liquid medium, and cultured at 30° C. and 200 rpm for 18 hours to obtain cells in logarithmic phase. Add 400 μL of AE buffer (pH 5.2, 50 mM NaAc, 10 mM EDTA), 50 μL of 10% (w / v) SDS and 600 μL of phenol / chloroform mixture into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube (phenol and chloroform ar...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2 Enzyme Activity Determination of Xylose Reductase and Xylitol Dehydrogenase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0118] (1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0119] Insert yeast strain 004-PGK and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain 1917 into 5mL YPX liquid medium, shake culture overnight at 30°C, 200rpm, transfer into 50mL fresh YPX medium, and make the initial OD 600 0.1, 30°C, 200rpm shake flask culture, to OD 600 about 1. Use a pre-frozen 50mL centrifuge tube to centrifuge at 4°C and 3000rpm for 15min, collect the cells, discard the supernatant, resuspend the bacteria with an equal amount of pre-cooled triethanolamine buffer (100mM, pH 7.0), wash the cells, centrifuge and discard Supernatant; then resuspend the cells with 10 mL ice-cold triethanolamine buffer, transfer 1.5 mL to a pre-frozen cell disruption tube containing 750 mg glass beads, add 15 μL PMSF (1 mmol) and 7.5 μL DTT (0.5 mmol). Put the cell disruption tube containing the glass beads and cells i...
Embodiment 3
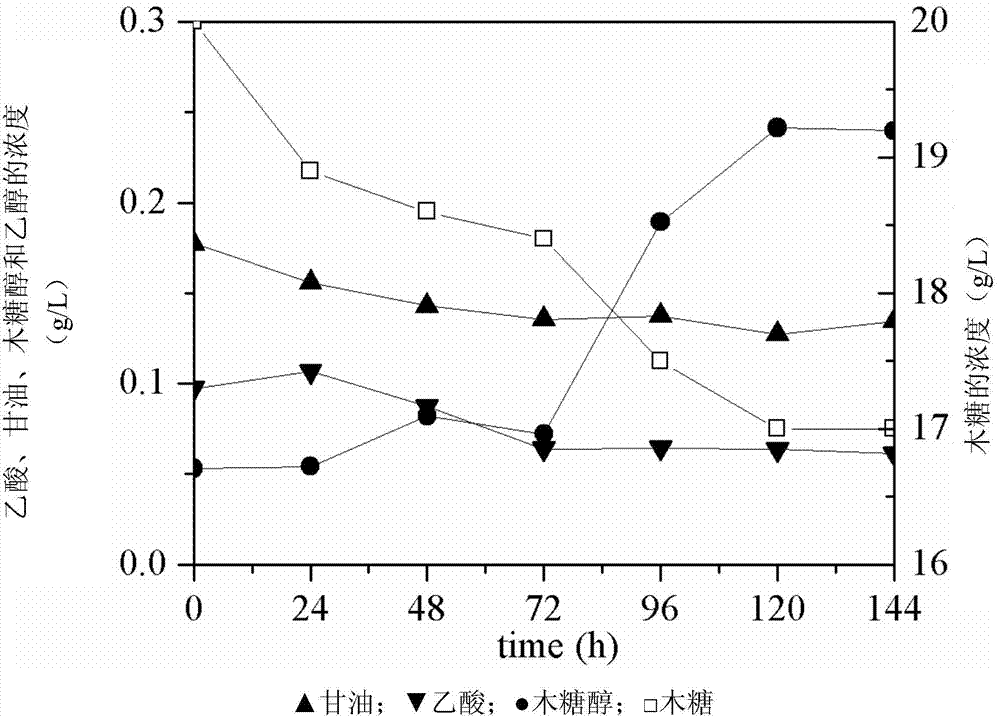
[0128] Example 3 Metabolite Detection of Engineering Bacteria in Xylose as the Only Carbon Source Medium
[0129] (1) Fermentation method
[0130] The fermentation temperature was controlled at 30°C, the optimum growth temperature of yeast, and YPX medium was used. The aerobic fermentation is as follows: use a 250mL conical flask with a liquid volume of 50mL, seal it with gauze, and select a rotation speed of 200rpm. The anaerobic fermentation is as follows: use a 100mL serum bottle with a liquid volume of 50mL, use an anaerobic pumping system to vacuumize the serum bottle and fill it with nitrogen to form anaerobic conditions. The yeast to be tested was streaked on the YPX plate to isolate a single colony, and the bacteria were picked and inoculated into 50mL liquid YPX medium, and cultured at 30°C and 200rpm to OD 600 between 1.0-1.5, centrifuged to collect the bacteria, inoculated into the corresponding fermentation medium, so that the initial OD 600 is 0.1. After sampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com