Patents
Literature
694 results about "Pseudomonas cruciviae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pseudomonas cruciviae is a Gram-negative, rod bacterium. It may be reclassified as Comamonas testosteroni. The type strain is IFO 12047.
rPA optimization
An optimized synthetic polynucleotide encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen and an anthrax vaccine based on the encoded protective antigen. Furthermore, heterologous expression in a host Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteria of an optimized polynucleotide sequence encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Methods for production of plants resistant to HPPD herbicides
Methods for making transgenic plants that are resistant to HPPD herbicides are presented. Polynucleotides other than those from Pseudomonas fluorescens that encode resistant HPPD enzymes are enclosed for use in the process of making transgenic plants that are tolerant to HPPD-inhibiting herbicides.
Owner:SYNGENTA LTD
Fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain as well as acquisition method and application thereof
InactiveCN102002468AHigh enzyme productionEnzyme richBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentFlax fiberUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain has pectase and hemicellulase producing capacity and flax degumming activity. The fluorescent pseudomonad strain screened by the invention has fast propagation, high antipollution capacity and good heat and alkali resistance; since a composite degumming enzyme solution is used for flax degumming, the degumming period is shortened greatly, and the system and the culturing process is safe for operation without toxicity or environmental pollution; the invention can shorten the flax degumming period, enhance the flax yield and the strength of flax fibers, improve the quality of the flax fibers by adopting the composite degumming enzyme solution for flax microbial degumming, thereby being beneficial to popularization; in addition, the invention can not only be used for flax raw stem degumming, roving scouring and the biological pretreatment of flax fabrics, but also can be used for the degumming and the biological pretreatment of hemp bast fibers, i.e. ramie, jute, hemps, and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Over-expression of extremozyme genes in pseudomonads and closely related bacteria
InactiveUS20050130160A1Increase cell densityImprove the level ofSugar derivativesBacteriaPseudomonasOver expression
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Enzyme and microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101560488AImprove degradation rateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroides xylanisolvensFlavobacterium aquatile
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose and application thereof. The active component of the microbial inoculum consists of Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Clostridium xylanolyticum, Clostridium lentocellum, Flavobacterium aquatile, and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Experiments prove that the microbial inoculum has high degradation rate to the lignocellulose, and the degradation rate can reach between 60 and 70 percent. The microbial inoculum has low cost and simple preparation, breaks through the limitation that a purification bacterium and a clastic enzyme thereof cannot decompose the lignocellulose efficiently, provides a key technique for decomposing, saccharifying biomass containing cellulose and converting the biomass into an energy source, and has extensive application prospect in the field of decomposing the lignocellulose.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of pseudomonas and its use and method for removing cadmium pollution in environment
ActiveCN102286405ASolve pollutionAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates pseudomonas, use thereof and a method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment. The pseudomonas class is named pseudomonas putidaHN103 and the collection number in a collection center is CCTCCNo.M2011184; and the shape and characteristics of the pseudomonas putidaHN103 comprise: 1) on a culture medium, a bacterial colony which used to be colorless and transparent turns white, smooth and convex-like with irregular edges; and 2) according to the result of bacterial microscopic examination, pseudomonas belongs to brevibacterium and is gram negative. The use of the bacteria is the use of the bacteria as a biological repair material for removing cadmium pollution. The method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment comprises the following steps: 1) regulating the cadmium ion concentration in sewage to a range in which pseudomonas can grow normally; 2) placing pseudomonas; 3) keeping the pseudomonas in the sewage for a certain time period; and 4) removing bacterial absorbing cadmium ions. The pseudomonas requires small investment, is low in cost, high in adaptability and capable of effectively removing cadmium, can quickly and obviously lower the concentration of cadmium ions in the environment and is suitable for biological remediation environments polluted by cadmium.
Owner:武汉华中农大资产经营有限公司
Antibodies to the PcrV Antigen of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
InactiveUS20090191186A1Avoid cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsPseudomona aeruginosaHigh affinity antibody
The current invention provides high-affinity antibodies to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV protein that have reduced immunogenicity when administered to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Phage therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
This invention relates to a bacteriophage MPK6 (deposit number: KCCM 11044P) having a lytic activity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or a progeny bacteriophage thereof having a RFLP (Restriction fragment length polymorphism) DNA profile substantially equivalent to the bacteriophage MPK6. The present invention provides a bacteriophage MPK6 or a progeny bacteriophage thereof capable of treating a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection disease, and suggests an anti-bacterial activity of MPK6 and its progeny bacteriophage using a mammalian and non-mammalian infection model. According to the present invention, the present bacteriophage MPK6 or progeny bacteriophage thereof represents very effective efficacy on treatment of P. aeruginosa-induced peritonitis-sepsis.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
Biological-Based Catalyst to Delay Plant Development Processes
ActiveUS20080236038A1Extended shelf lifeFacilitating longer-distance transportationBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBrevibacterium ketoglutamicum
The present invention is directed to methods for delaying a plant development process comprising exposing a plant or plant part to one or more bacteria or enzymes. In specific embodiments, the one or more bacteria are selected from the group consisting of Rhodococcus spp., Pseudomonas chloroaphis, Brevibacterium ketoglutamicum, and a mixture comprising any combination of these bacteria. Apparatuses for delaying a plant development process comprising a catalyst that comprises one or more of the above bacteria.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Composite bacterial preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102199562AImprove decomposition abilityPromote degradationBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyDecomposition
The invention discloses a composite bacterial preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of agricultural biochemistry. The composite bacterial preparation comprises the following components in parts by volume: 10-40 parts of brevibacillus brives fermentation bacterial liquid, 10-40 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation bacterial liquid and 15-45 parts of sugarcane thermophilic actinomyces, wherein the bacterial count in each mol of fermentation liquid is 0.4-0.7 billion. The strains of brevibacillus brives, pseudomonas fluorescens and sugarcane thermophilic actinomyce are separated from rabbit dung and fungi residues; and fermentation bacterial liquids of the separated strains are mixed according to a proper proportion to form the composite bacterial preparation. The composite bacterial preparation disclosed by the invention can be used for accelerating the degradation of organic materials and reducing the conversion of organic nitrogen into gaseous nitrogen, so that the composite bacterial preparation can present stronger ammonia-suppressing and decomposing capabilities in the fermentation process of pig manurecompost; and a smaller amount of ammonia gas is released while thorough decomposition of pig manure is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Plant bacteriostatic composition and application thereof in cosmetics
ActiveCN102669191AGood antibacterial effectAdd lessCosmetic preparationsBiocideEscherichia coliOfficinalis
The invention provides a plant bacteriostatic composition and application thereof in cosmetics. The plant bacteriostatic composition is obtained by compounding a licorice extract, a honeysuckle extract and a Mangnolia officinalis extract. The plant bacteriostatic composition has good bacteriostatic effect and particularly has a synergistic effect of inhibiting escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, candida albicans and aspergillus niger. The plant bacteriostatic composition can be applied to skin-care and washing cosmetics, reduces the adding amount of original preservatives and enables a product to have both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Owner:TIANJIN YU MEI JING GRP
Pseudomonas fluorescens strain, microbial inoculum and use thereof as seedling culture medium for controlling tomato bacterial wilt
The invention provides a strain namely a pseudomonas fluorescens strain (2)-16' for controlling tomato bacterial wilt by using pathogenic bacteria antagonistic microbes, wherein the preservation serial number of the strain is CGMCC NO.3330. The invention also provides a microbial inoculum prepared from the pseudomonas fluorescens train (2)-16'. The invention further provides use of the pseudomonas fluorescens strain (2)-16' for controlling the tomato bacterial wilt, particularly as a seedling culture medium for controlling the tomato bacterial wilt. The pseudomonas fluorescens strain (2)-16' is directionally separated and selectively cultured, is cultured for propagation first, and then is prepared into a product of the microbial inoculum; mushroom residues after culturing edible fungi are fermented and thoroughly decomposed and then are used for preparing the seedling culture medium together with other base materials in certain proportion; and a raw anti-microbial agent is organically combined with the seedling culture medium directly. The pseudomonas fluorescens strain (2)-16' has a large number of advantages of abundant available resources, low cost and capacity of avoiding secondary pollutions, and provides an effective way for solving a soil-borne disease namely the tomato bacterial wilt.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Novel nitrile hydratase
ActiveUS20070009985A1Impairing the enzyme's original activityImpairment of activityFungiBacteriaNovel mutationMutant
The amino acid sequence of a mutant which is obtained by introducing a novel mutation into a Pseudonocardia thermophila JCM3095-derived nitrile hydratase consisting of two types of heterogeneous subunits, and the base sequence of the gene are provided. The nitrile hydratase is modified by specifying the region to be modified in the stereostructure / amino acid sequence of the nitrile hydratase, and applying alteration such as substitution, insertion, deletion or the like, to the amino acids in the amino acid sequence which are corresponding to the amino acid residues forming the region. Also provided is a method for modifying an enzyme having a nitrile hydratase activity.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Sodium alginate compound immobilized microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105754984APromote degradationWide range of media typesWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationInorganic saltsMicrobial agent
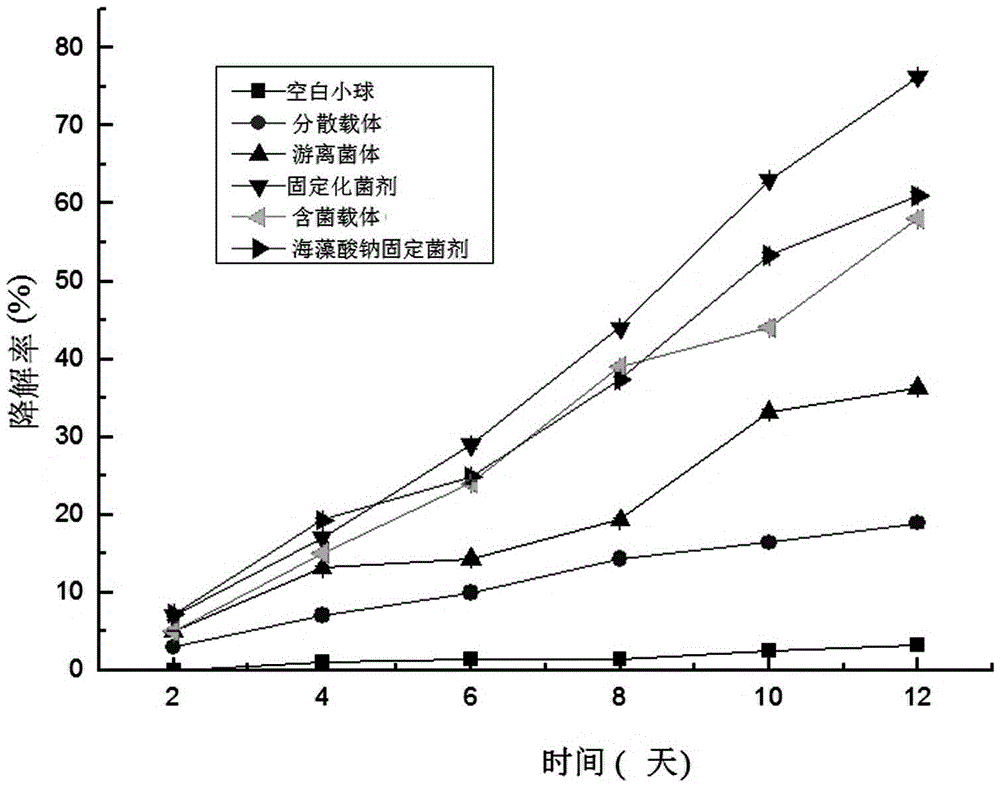
The invention discloses a sodium alginate compound immobilized microbial agent and a preparation method thereof, and the sodium alginate compound immobilized microbial agent solves the problem that an immobilization way of pseudomonas suitable for di-chlorine quinoline acid degradation in the prior art is absent. A carrier culture medium with the pseudomonas and sodium alginate are mixed to obtain a mixture, and the mixture is dropwise added into calcium chloride with concentration being 1-4% to stand for 2-4 hours to prepare a granule; the mass concentration of the sodium alginate is 2-6%; the carrier culture medium comprises an adsorption carrier and an inorganic salt liquid culture medium; a weight ratio of the adsorption carrier to the sodium alginate is (1-3) to 1; and the adsorption carrier consists of corn cob, bamboo charcoal and oil cake in a weight ratio being 1:(1-2):1. According to the invention, the degradation efficiency of bacteria is effectively improved, and the degradation rate of the immobilized microbial agent is much higher than the sum of the physical absorption efficiency of blank spheres and biological degradation efficiency of a free bacterial strain, so that the effect of mutual promotion can be achieved.
Owner:四川润林肆汇中药材有限公司
Hydrogen oxidizing bacteria wmq-7 and its isolation method and application
The invention relates to Pseudomonasputida WMQ-7, which has been collected in China Typical Model Cultivation Center (CCTCC) of Wuhan University on March 8, 2011 with the collection number of CCTCC M 2011060, and also relates to a method for separating and culturing the Pseudomonasputida WMQ-7 in hydrogen-absorbing enzyme-free soil of the rhizosphere of a leguminous plant. The method comprises the following steps of: enriching, separating and culturing the Pseudomonasputida WMQ-7 by using a culture device for continuously introducing H2 and a mineral salt culture medium, and screening strains with higher H2 oxidizing capacity by using gas chromatography. A hydrogen bacterium preparation is prepared from the optimal strains through fermented in a laboratory. The biological preparation can promote plant growth and improve yield, fertilizer efficiency and stress resistance of plants when used for agricultural production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Deletions in domain ii of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS20100215656A1Maintain immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Modified bacteriocins and methods for their use
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Foam dressing containing composite silver-zinc antibacterial material and preparation method of foam dressing
The invention provides a foam dressing containing a composite silver-zinc antibacterial material and a preparation method of the foam dressing. The foam dressing containing the composite silver-zinc antibacterial material comprises polyurethane foaming plastic and the composite silver-zinc antibacterial material, wherein the composite silver-zinc antibacterial material is adhered to the inside of the polyurethane foaming plastic, comprises the following raw materials in content: nano silver, nano zinc and a nano inorganic carrier; and the composite silver-zinc antibacterial material contains the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 10%-20% of silver and 20%-40% of zinc. The composite silver-zinc antibacterial material is dispersed into the foam dressing in a manner of foam molding or ultrasonic dipping together with foam. The foam dressing containing the composite silver-zinc antibacterial material is capable of effectively absorbing diffusate of the wound surface, and effectively inhibiting growth and breeding of staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa and candida albicans.
Owner:SHENZHEN TSINGHUA YUANXING NANO MATERIAL CO LTD
Tool for the transfer and production of proteins using the pseudomonas type III secretion system
ActiveUS7939319B2Easy to retouchPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaNucleotidePseudomonas
The present invention provides a vector for expression of a chimeric protein which is the result of the fusion between the N-terminal end of ExoS of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and an amino acid sequence of interest, the N-terminal end of ExoS corresponding to the N-terminal end of the chimeric protein. The vector contains the following from 5′ to 3′:a promoter,a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding at least the 48 (SEQ ID 4) and at the most the 96 (SEQ ID 6) amino acids of the N-terminal end of ExoS; or any sequence of the same size that is at least 70% identical thereto and that has a secretion activity at the same level as that of ExoS,a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence of interest.
Owner:UNIV GRENOBLE ALPES
Pseudomonad ZCJ bacterial strain applied to nicotine degradation of tobacco and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN101525579AShorten aging cycleImprove biological activityTobacco preparationFungiScreening methodMicrobiology
The invention relates to a technology of biological degradation of nicotine in tobacco, in particular to a pseudomonad ZCJ bacterial strain applied to nicotine degradation of tobacco and a screening method and an application thereof. The pseudomonad ZCJ bacterial strain (Pseudomonas sp. ZCJ) was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on March, 30th, 2009 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO. M209064. The invention also discloses screening and application of the bacterial strain. In the invention, nicotine degradation bacterial strain screened from tobacco materials has relatively high biological activity and is applicable to degradation of nicotine in tobacco in a solid state, thus achieving the purpose of the degradation of the nicotine in tobacco.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND +1
Fusion protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus as PRRS vaccine
A fusion protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) for PRRSV vaccine. The fusion protein includes: (a) a Pseudomoitas Exoloxin A (PE) peptide that comprises a binding domain and a translocating domain; (b) a peptide fragment that contains a N-terminal portion of PRRSV ORF6 protein; (c) a peptide fragment that has a N-terminal portion of PRRSV ORF5 protein; and (d) a carboxyl terminal domain that comprises an amino acid seciuence KDEL. The PE peptide is located at the N-terminus of the fusion protein, and the peptide fraament containinC the N-terminal portion of PRRSV ORF5 protein is located between the peptide fragment containing the N-terminal portion of PRRSV ORF6 protein and the carboxyl terminal domain.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Method for preparing environment-friendly and high-efficiency biological organic fertilizer by using distilled spirit vinasse
ActiveCN102992915ARelease fullyEffective activityClimate change adaptationBioloigcal waste fertilisersWater contentAmmonium sulfate
The invention provides a method for preparing environment-friendly and high-efficiency biological organic fertilizer by using distilled spirit vinasse, comprising the following steps of: puffing fermentation substrate by a threaded rod type puffing machine; transporting into a wet material mixing machine, cooling and adding microelement mineral salt, and inoculating bacterium liquid in proportion when the temperature is reduced to 30-35DEG C, completely mixing; and filling the inoculated and mixed fermentation substrate into a novel silica gel breathable membrane fermentation bag, packaging and sealing by an automatic metering and packing system, and fermenting for 5-7 at constant temperature in a fermentation room to obtain a finished product. The fermentation substrate is prepared by evenly mixing 50-60 parts by weight of distilled spirit vinasse, 5-10 parts by weight of humic acid, 5-15 parts by weight of sunflower husk powder, 5-10 parts by weight of ammonium sulfate, 5-10 parts by weight of potassium chloride and 5-10 parts by weight of corn steep liquor, wherein the water content of the fermentation substrate is 30-40 wt%; and the mixed bacterium liquid comprises bacterium liquid of streptomyces jingyangensis, clostridium butyricum, pseudomonas mendocina, azotobacter chroococcum and rhizopus oryzae.
Owner:张有聪
Manganese-oxidized pseudomonas T34, method for preparing biogenic manganese oxide and application of pseudomonas or biogenic manganese oxide in degrading ciprofloxacin
ActiveCN105331551AEasy to getImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCatalytic oxidationMacromolecular Substances
The invention discloses manganese-oxidized pseudomonas T34, a method for preparing biogenic manganese oxide and application of the pseudomonas or the biogenic manganese oxide in degrading ciprofloxacin, and discloses a pseudomonas strain pseudomonassp. T34 which is capable of generating a manganese oxide, wherein the strain is preserved with preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2014168. The strain, in an environment with presence of low-valence manganese ions, can be used for oxidizing the low-valence manganese ions in the environment, so that a manganese dioxide compound is formed and the formed manganese dioxide compound is coated on the surfaces of bacteria. The biogenic manganese oxide generated from the strain, which is quite strong in catalytic oxidation capacity, is capable of degrading organic macro-molecular substances into micro-substances which can be absorbed and utilized by the bacteria with efficiency much higher than that of chemically synthesized manganese oxide. The manganese oxide generated from the strain has the advantages of being strong in catalysis capacity, environment-friendly, easy for production and the like, so that a new way is created for solving the current antibiotic pollution status in the environment.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Monoamine oxidase and gene and application thereof
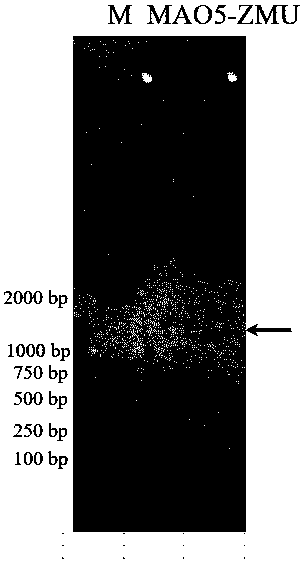
The invention discloses a monoamine oxidase from Pseudomonas sp., a coding gene, a recombinant expression vector, a recombination expression transformant, and the synthesis application of the monoamine oxidase in tetrahydroquinoline chiral amine compounds. The coding gene of the monoamine oxidase MAO5-ZMU is from Pseudomonas sp. ZMU-T01. The amino acid sequence of monoamine oxidase protein is shown in SEQID No.1, and the corresponding coding gen nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQIDNo.2; the monoamine oxidase gene can be connected with an expression carrier to construct to obtain a recombination expression plasmid; the recombination expression plasmid is converted to escherichia coli to obtain genetically engineered bacteria with monoamine oxidase activity. The genetically engineered bacteria with monoamine oxidase activity can be used for effectively catalyzing 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline compounds for oxidation splitting, has the characteristics of high selectivity, moderatereaction condition, environment protection and the like and can be used for the biosynthesis of the chiral tetrahydroquinoline compounds.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-bacterial carboxy apatite composite coating, its preparing method and use
InactiveCN101070441AImprove biological activityImprove antibacterial propertiesAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesApatiteAdditive ingredient
This invention relates to one kind of the antibacterial hydroxyl apatite compound coat, the preparation method and the application, its characteristic is the related compound coat is composed of the metal silver powder and the hydroxyl apatite powder, the metal silver powder is treated as the antibacterial increase ingredient, the silver powder' quality accounts for 1-5% of the compound coat, the particle size of the silver powder is 20-100mum, the particle size of the hydroxyl apatite powder is 10-100mum. This invention making the compound coat is realized by using the spray technics of the vacuum plasma. The provided compound coat has an above 95% excellent antibacterial effect on the coliform, the green pus pseudomonad and the golden yellow staphylococcus, and the cytotoxic rank in vitro of the compound coat is zero, has no cytotoxicity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase and application
ActiveCN107058265ABroad antibacterial spectrumImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaFood preservationBacteroidesBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase and application. The artificial pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase has nucleic acid sequences 1 and 2 and amino acid sequences 3 and 4; a gene engineering technology is utilized and polycation nonapeptide and hydrophobic pentapeptide are added at an N end of previous Gram-negative bacterium phage lyase and are developed to obtain artificial lyase capable of efficiently killing pseudomonas aeruginosa, pseudomonas putida, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus subtilis. The lyase and a derivative thereof can be independently used or can be coordinated with a surfactant and can be used for specifically deactivating the pseudomonas aeruginosa and bacillus; the lyase can be used for removing and inhibiting a biological coating film formed by microorganisms, and an enzyme preparation source which is safe and has no toxic or side effect is provided for preventing and controlling infection of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, the bacillus licheniformis and the bacillus subtilis at present and controlling biological coating film pollution caused by bacteria including the bacillus licheniformis and the bacillus subtilis and the like in foods.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Endophytic azotobacter of wheat producing ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase and application thereof
InactiveCN102250808AIncrease nitrogenase activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismPseudomonas cichorii
The invention discloses endophytic azotobacter of wheat producing ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase and application thereof. The endophytic azotobacter of wheat is pseudomonas sp. GDXM114, and is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the collection number of CGMCC No.5040. The pseudomonas sp. GDXM114 with the collection number of CGMCC No.5040 has the advantages of higher nitrogenase activity, ACC deaminase activity and wide application prospect in producing nitrogenase microorganism inoculants and microbial organic fertilizers.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A genetically engineered bacteria, its constructing method and use thereof
The present invention relates to one kind of genetic engineering bacteria, one kind of soybean disease causing variety of clove pseudomonads with preservation number of CGMCC 1276, and its construction process and use. The genetic engineering bacteria is obtained through inserting Tn5 transposon S17-1 into the genome of the initial strain to deactivate its temperature controlling gene. The strain may be used in industrial fermentation production of crown bacterin at 26-28 deg.c, in the yield near the initial bacteria and up to 35-40 mg / L.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWSUN CROPSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com