Patents
Literature
128 results about "Facultative anaerobic organism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A facultative anaerobe is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent. Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Listeria spp., Shewanella oneidensis and Yersinia pestis. Certain eukaryotes are also facultative anaerobes, including fungi such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and many aquatic invertebrates such as Nereid (worm) polychaetes.
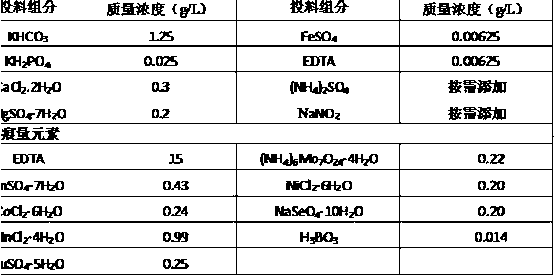
Compositions for removing hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons from contaminated environments
InactiveCN1668535AReduce concentrationLow costOther chemical processesWater treatment compoundsSorbentSulfate
The invention provides a bioremediation composition for in situ bioremediation of soil and / or groundwater contaminated with hydrocarbons, comprising an adsorbent capable of adsorbing said hydrocarbons, a mixture of facultative anaerobes capable of metabolizing said hydrocarbon under sulfate-reduction conditions, a sulfate-containing compound that releases sulfate over a period of time, and a nutrient system for promoting growth of said anaerobes, wherein said nutrient system includes a sulfide scavenging agent.
Owner:REMEDIATION PROD INC
Method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria from common activated sludge
InactiveCN103159325AShorten the timeHigh activityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeActivated carbon
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, and particularly relates to a method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria by performing nitration treatment on common activated sludge. The method is characterized in that nitration treatment is performed on the common activated sludge, thus increasing the quantity of aerobiotic ammonium oxidation bacteria (AOB) in the sludge; some AOB are facultative anaerobes and capable of performing similar anaerobic ammonium oxidation in an oxygen-free condition; additionally, AOB generate hydroxylamine oxidoreductase which is beneficial to enrichment for the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria; and activated carbon is poured in an activity enhancement phase to improve the attachment environment for the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, and the competitions of other bacteria and Anammox bacteria for the attachment environment of activated carbon can also be reduced. The invention provides a time-saving and efficient method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Seedling raising substrate for machine-transplanted seedling tray for hybrid rice
InactiveCN104322311AHigh degree of fitReduce mechanical damageGrowth substratesCulture mediaPhosphoric acidFacultative anaerobic organism
The invention provides a seedling raising substrate for a machine-transplanted seedling tray for hybrid rice. The seedling raising substrate is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 50 to 60 parts of crop stalk with lower than 10 percent of water content, 21 to 30 parts of animal waste with lower than 10 percent of water content, 13 to 20 parts of substrate carrier and 1 to 2 parts of substrate synergist, wherein the substrate synergist consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 65 to 75 percent of calcium cyanamide, 15 to 25 percent of calcium superphosphate, 7 to 9 percent of sodium silicate, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of boron and zinc and 0.5 to 1.5 percent of bioactive fungicide; the bioactive fungicide is one or several of bacillus subtilis, facultative anaerobe and agricultural photosynthetic bacteria; the raw materials are composted and fermented for three times to form the seedling raising substrate for the machine-transplanted seedling tray for hybrid rice. The seedling raising substrate is comprehensive in nutrition, is suitable for mechanized seedling raising for the hybrid rice, and ensures that germination and rooting of rice seeds are quick, the planting percent is high and seedlings are robust.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Facultative anaerobe of degrading polychlorinated diphenyl and obtainding process
InactiveCN1793311AAvoid secondary pollutionSolve problems that cannot be effectively biodegradedMicroorganismsContaminated soil reclamationSucrosePolychlorinated biphenyl
The invention relates to degrading polychlorinated biphenyl facultative anaerobe and gaining method in environment bioengineering field. It includes the following steps: sampling; screening; separating; purifying; screening and domesticating PCBs degrading strain. The new strain raoultella terrigena LY402 is grained. The strain is facultative anaerobe, and utilizes sucrose fat as carbon source to degrade 2,3,4,4-quadri-chlordiphenyl. The degrading rate of the aroclor1242 is 98.02-99.15% in 70h under oxygen; but aroclor1260 is 96.55% in 8 days under the opposite condition. Its advantages are that it can degrade different sits PCBs; and it can utilize sucrose fat to high effectively degrade PCBs and has no secondary pollution.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for treating electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN102010102AAdded secondary physical and chemical treatmentImprove water qualityWaste water treatment from metallurgical processMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandRetention time
The invention discloses a method for treating electroplating wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) primary physical-chemical treatment; (2) secondary physical-chemical treatment: after the discharged water generated in step (1) is subject to homogenizing treatment, adding sodium hypochlorite into the homogenized water, then adding sodium pyrosulfite into the obtained product to remove residual chlorine, and adding aluminum chlorhydroxide into the obtained product; and (3) biochemical system treatment: adding appropriate biochemical sewage into the product obtained in step (2), mixing the biochemical sewage and the product, then feeding the obtained mixture into a biological hydrolysis pool; controlling the mixture under appropriate conditions and within an appropriate retention time; carrying out reduction on the obtained mixture by utilizing facultative anaerobes; and hydrolyzing the obtained discharged water subjected to reduction, feeding the discharged water into an aerobic biological oxidation pond, and then carrying out mass propagation of engineering bacterias under an appropriate condition by using organic pollutants in wastewater. By using the method provided by the invention, the total treatment rates of a system are as follows: the treatment rate of heavy metal is greater than or equal to 99.7 percent, the treatment rate of ammonia nitrogen is greater than or equal to 90 percent, and the treatment rate of chemical oxygen demand (COD) is greater than or equal to 88 percent, therefore, the electroplating wastewater treated by using the method comprehensively meets the requirements of the Discharge Standard for Pollutants from Electroplating Industry (GB21900-2008).
Owner:兰溪市卓越电子有限公司
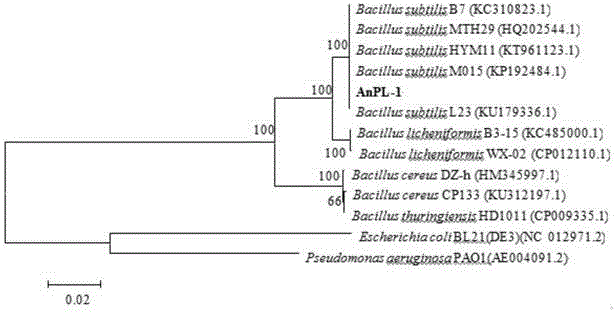
Bacillus subtilis for anaerobic production of lipopeptid surfactant and application of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN106754539AEnhanced overall recoveryHigh surface activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial oilFacultative anaerobic organism
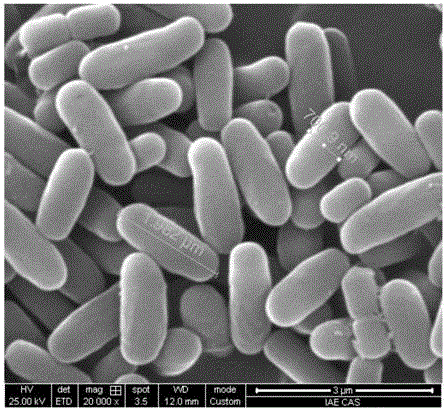
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis AnPL-1 capable of generating a lipopeptid surfactant under an anaerobic condition, with a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 13461. The strain AnPL-1 is a facultative anaerobe; a temperature range for efficient production of lipopeptid under the anaerobic condition is 30-40 DEG C; a pH (potential of hydrogen) value range is 6.0-7.5; a tolerance range of NaCl is 0-5%. An emulsion coefficient of an anaerobic fermentation solution of the strain for crude oil is equal to or greater than 56%; the diameter of an oil drainage circle is equal to or greater than 15mm; the lipopeptid surfactant produced by the strain AnPL-1 in situ in a physical simulation rock core increases a crude oil recovery factor by 9.9%. The strain has important popularization and application values in the field of microbial oil recovery and environmental pollution remediation.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
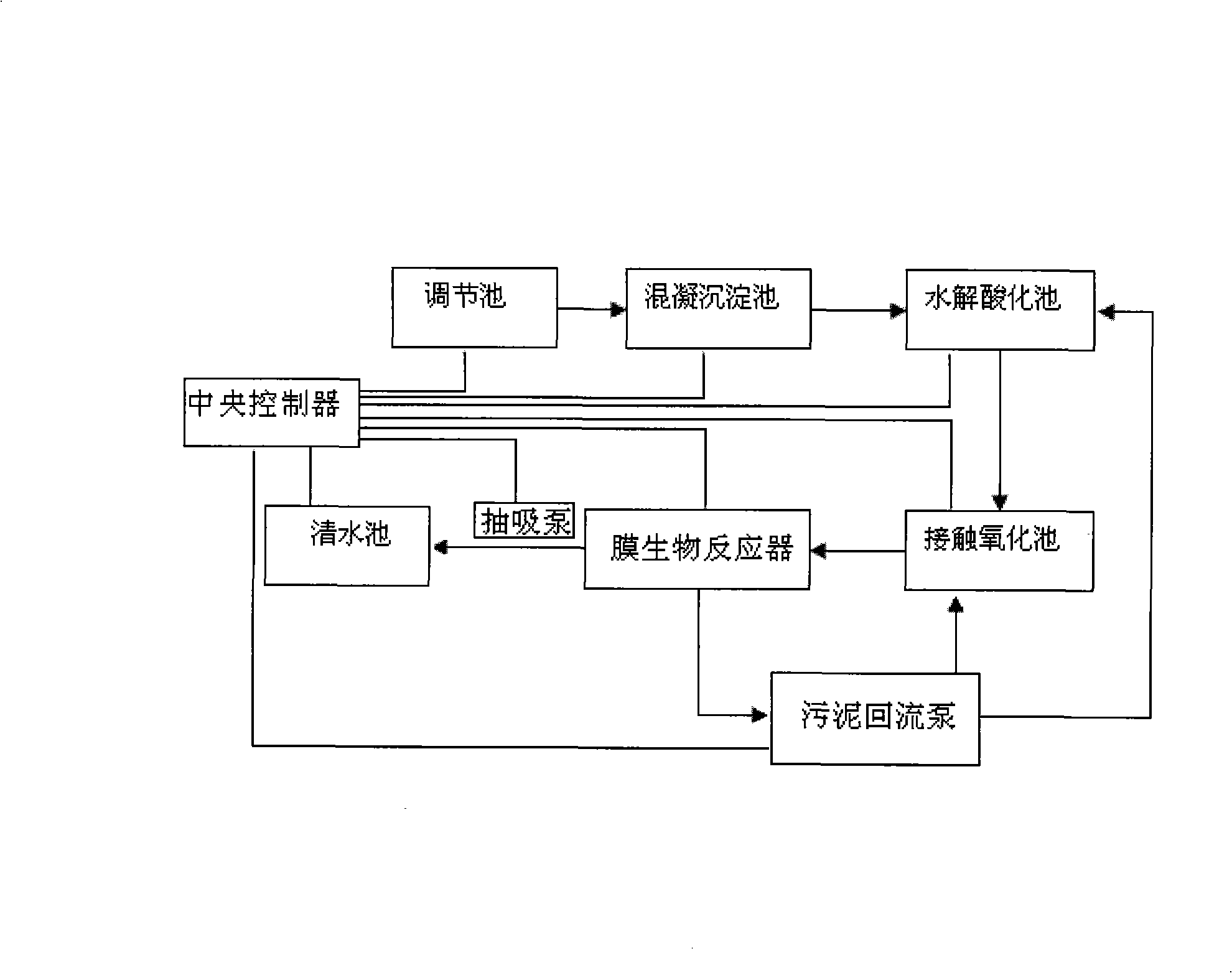
Method for treating dyeing wastewater and dedicated device
InactiveCN101538100ASimple processLow costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAutomatic controlSlag
The invention provides a method for treating dyeing wastewater and a dedicated device. The method comprises the following steps of treatment under the automatic control of a central control unit: A, discharging the dyeing wastewater which is uniform quality and uniform quantity into a flocculation precipitating tank, and adding coagulating agent and flocculating agent to the flocculation precipitating tank so as to precipitate the suspended substance and part of organic substances; B, discharging the clear liquid of the wastewater in step A into a hydrolytic acidification tank, and decomposing the macromolecular organic substances in the wastewater into micro molecular substances under the action of facultative anaerobe; C, discharging the wastewater in step B into a contact oxidation tank, feeding air into the contact oxidation tank and decomposing the organic substances in the wastewater under the action of aerobe; D, discharging the wastewater in step C into a membrane bioreactor, and entrapping and decomposing the stale biological membrane slag and the residual organic substances by the membrane bioreactor; and E, sucking the clear water in step D into a clean water tank and discharging the sludge in the membrane bioreactor into the hydrolytic acidification tank or the contact oxidation tank respectively through a return sludge pump by the concentration of the sludge. The invention has the advantages that the treatment cost is low and the treated water is recyclable, thereby helping enterprises to achieve the purposes of energy conservation and emission reduction.
Owner:惠州市雄越保环科技有限公司
Vaginitis test kit and preparation method thereof
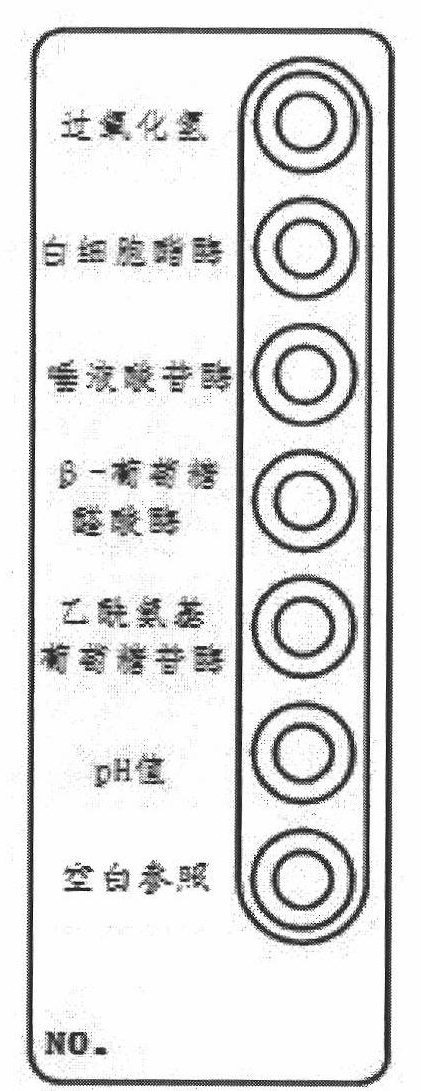
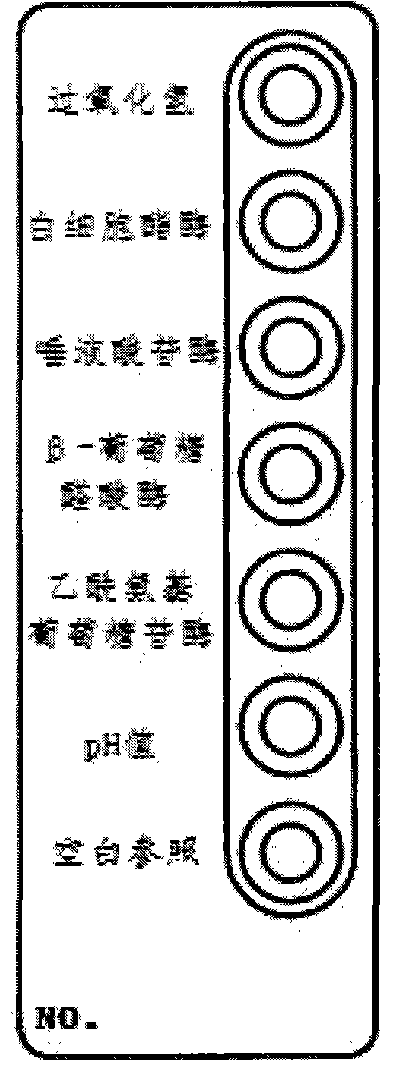
ActiveCN102321731AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterial vaginosisFacultative anaerobic organism
The invention discloses a vaginitis test kit which comprises a reaction device, a sampling test tube, a straw, joint test diluent, joint test chromogenic reagent, joint test stop solution, a user manual and a joint test colourimetric card, wherein a hydrogen peroxide reaction hole, a leukocyte esterase reaction hole, a sialic acid glucoside enzyme reaction hole, a beta- glucuronic acid enzyme reaction hole, a P glucosidase reation hole and a pH value hole; relevant reaction bases are arranged in the reaction holes; reach reaction base comprises a corresponding reaction substrate curing layer,a chromogenic promotional layer and a chemical inert carrier layer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the test kit and the preparation method of a novel chemical carrier. The test kit can be used for distinguishing bacterial vaginosis and vaginitis, and can further identify aerobic / anaerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria and other flora in vaginal secretion. The method is simple and quick to operate, has high accuracy, and is applicable to clinical practice, particularly hospital outpatient practice.
Owner:JIANGSU BIOPERFECTUS TECH CO LTD
Organic fermentation fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106478167AImprove conversion rateReduce incidenceBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersInsect diseaseLivestock manure
The invention relates to the field of an organic fertilizer, and concretely relates to an organic fermentation fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) aerobic fermentation: mixing livestock manure and anaerobic bacteria, fermenting a mixture for 8-15 days at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C to form a primary fermentation fertilizer; 2) facultative anaerobic fermentation: mixing the primary fermentation fertilizer and facultative anaerobe, fermenting a mixture for 10-20 days at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C to form a secondary fermentation fertilizer; and 3) anaerobic fermentation: mixing the secondary fermentation fertilizer and anacerobe, and fermenting a mixture at the temperature of no higher than 45 DEG C for more than 3 months to form the organic fermentation fertilizer. The method has the advantages of rapid fermentation and deodorizing, high nutrient conversion rate, high organic matter conversion rate and effective inhibition of insect disease.
Owner:南充禾香生物科技有限公司 +1
Preparation method and application of microbial inoculant for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil
InactiveCN103333823ASimple preparation processLow costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationQuinoneHalohydrocarbon
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a microbial inoculant for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil, belonging to the technical field of soil remediation in environmental engineering. The invention is characterized in that the microbial inoculant containing the quinone-reducing facultative anaerobe Shewanella sp. and poly-halohydrocarbon dehalogenated product facultative aerobic degrading bacterium is prepared by surplus sludge lysis solution preparation and culture medium optimization, and is used for remediating poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil. The microbial inoculant has the advantages of wide raw material sources, simple preparation technique and no secondary pollution during soil remediation, can effectively overcome the defect that the high operating cost of the biologically reinforced remediation of poly-halohydrocarbon-polluted soil limits the large-scale application, and has wide application prospects in remediation of soil polluted by poly-chlorine organic substances, poly-bromine aromatic hydrocarbons and poly-fluorine organic substances.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Freshwater compound microorganism substrate modifier
ActiveCN104176834AImprove water qualityAvoid secondary pollutionBiological water/sewage treatmentAnaerobic bacteriaFresh water organism
The invention discloses a freshwater compound microorganism substrate modifier, and belongs to the field of biotechnology in freshwater aquaculture. The substrate modifier is formed by mixing and uniformly stirring bacillus natto powder, lactic acid bacteria powder, clostridia butyricum powder, a biological flocculant and an oxygen producer. According to the substrate modifier disclosed by the invention, after organic pollutants in aquatic water are flocculated to form bottom mud by virtue of flocculating effects of the biological flocculant, organic flocculate in the bottom mud is decomposed by virtue of strong decomposition of aerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobe and strict anaerobe, so that the quality of the bottom mud of the freshwater aquatic water is improved; and the freshwater compound microorganism substrate modifier has the characteristics of biodegradability, safety, efficiency, no toxicity and no secondary pollution.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Screening method and application of strain for producing 1,3-propanediol
ActiveCN102965323AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSequence analysisWater baths
The invention discloses a screening method and application of a strain for producing 1,3-propanediol, relating to 1,3-propanediol. A screening method and application of clostridium butyricum Gen160 and the strain screening method for producing 1,3-propanediol with waste glycerol are provided. The screening method comprises the steps as follows: adding collected samples to cabbage juice, putting the samples into a water bath after an enrichment culture to kill nonsporeforms, transferring the samples to a clostridium multiplication liquid medium, carrying out an anaerobic culture and then putting the samples into the water bath again, transferring the samples to a fermentation medium, carrying out a high performance liquid chromatograph to analyze fermentation products after the anaerobic selective enrichment culture and selecting positive strains capable of producing 1,3-propanediol; separating out single colonies by a high layer agar column method; carrying out an aerobiotic culture and the anaerobic culture to remove facultative anaerobes and to obtain strict anaerobes, analyzing the fermentation products and selecting the strains to carry out 16S rDNA (ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence analysis and identification, wherein the strains are capable of producing 1,3-propanediol and the cultural characteristics and the colonial morphologies confirm to the cultural characteristics of the clostridium butyricum consistently.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
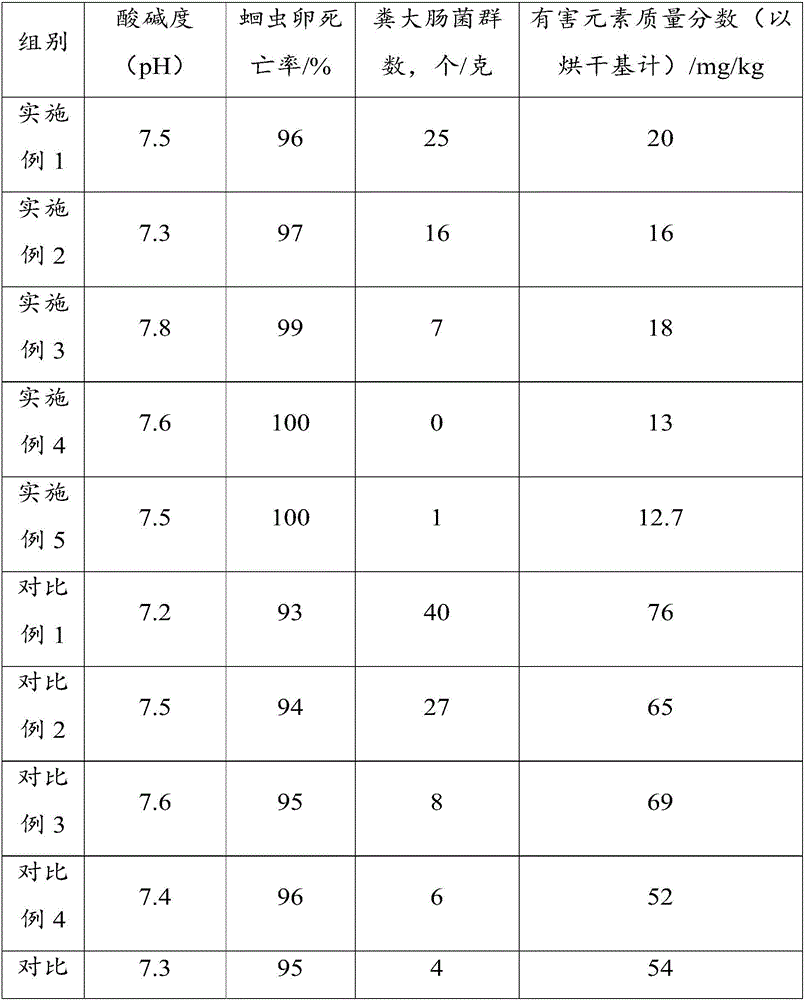
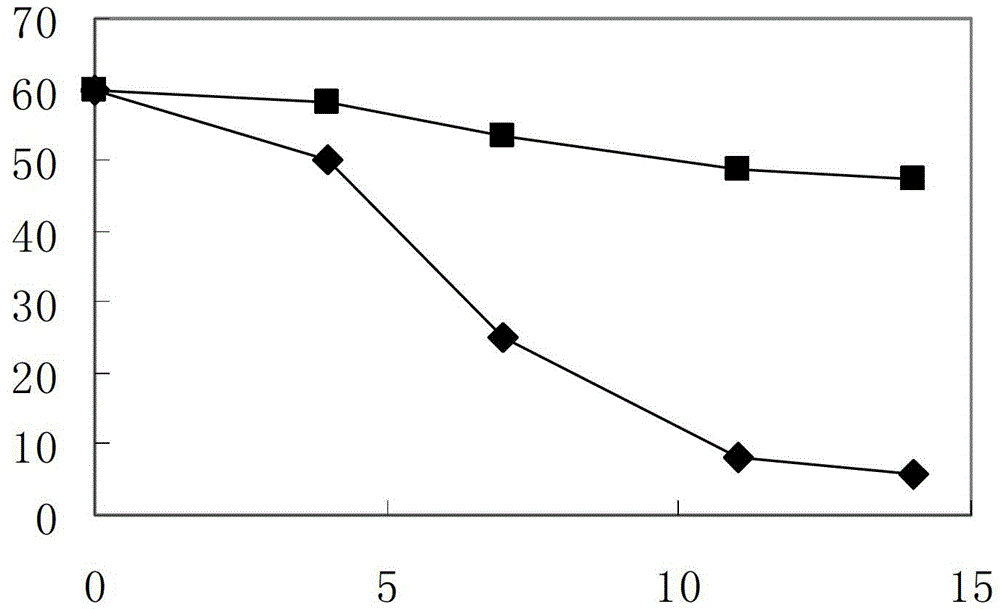
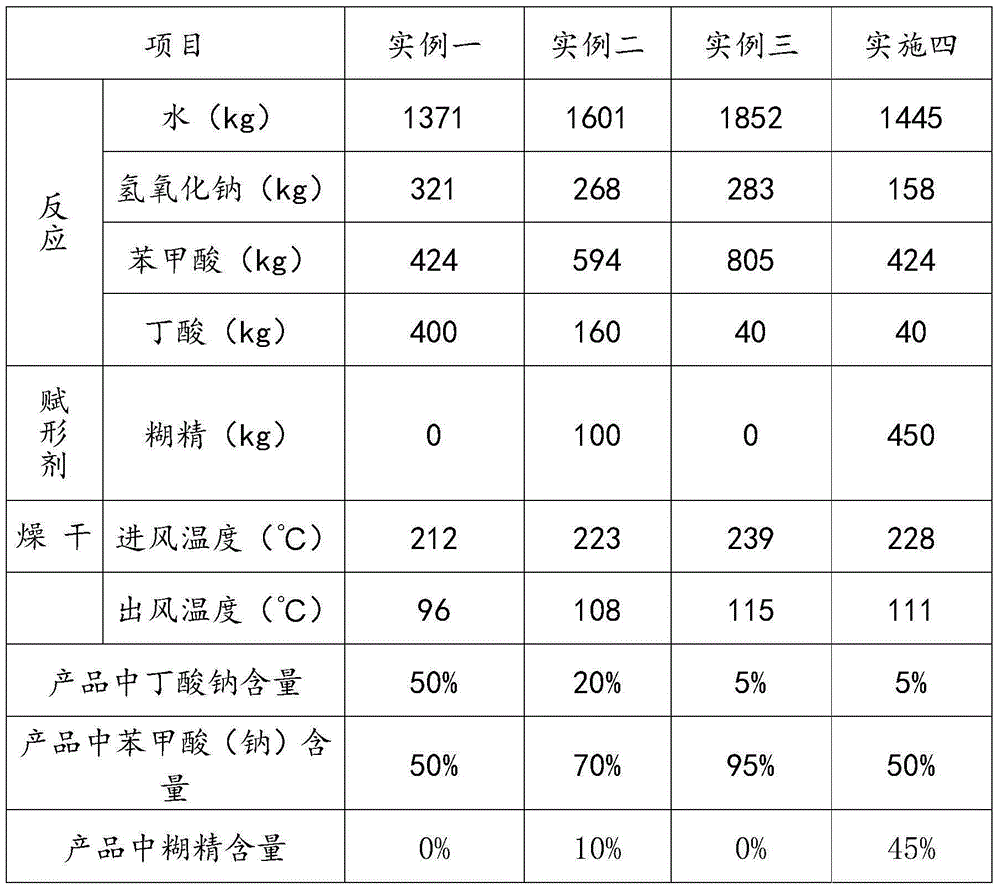
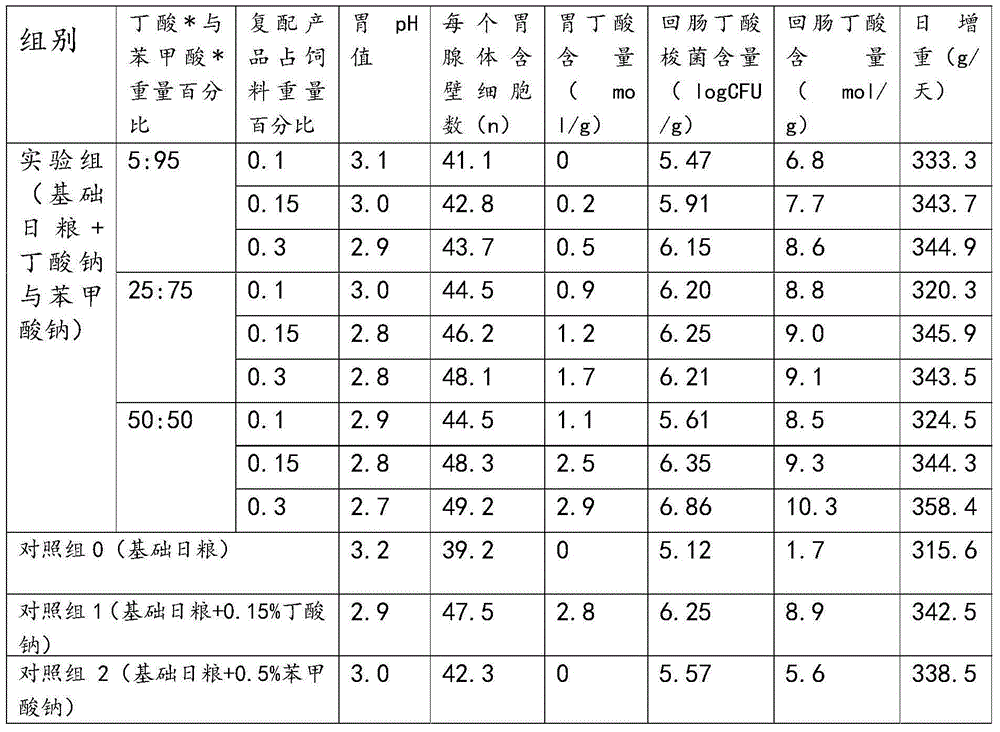
Butyrate, butyrate derivative and benzoic acid compound formula, preparation method and application of butyrate, butyrate derivative and benzoic acid compound product as feed additive
The invention discloses a butyrate, butyrate derivative and benzoic acid compound formula, a preparation method and an application of the butyrate, butyrate derivative and benzoic acid compound product as a feed additive. The weight ratio of butyrate or a butyrate derivative and benzoic acid or benzoate is 5%-50% and 50%-95%. With the adoption of the scheme, benzoate and butyrate enter an animal body and are dissociated into acidic molecules, butyric acid stimulates growth of parietal cells, parietal cells produce hydrochloric acid reducing pH value in the stomach, benzoic acid in the stomach inhibits facultative anaerobes such as lactobacillus and anaerobes producing butyric acid, and the two groups of bacterial communities become dominant bacterial communities, generate more endogenous organic acid such as lactic acid and butyric acid and are beneficial to gastrointestinal tract health and animal growth, so that the superimposed effect of benefits of the two components is realized.
Owner:SINGAO
Transformant capable of producing isopropanol
ActiveUS20100203604A1Efficient productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyltransferase activityFacultative anaerobic organism
A transformant capable of producing isopropanol which is constructed by transferring the following genes (a) to (d) into an aerobic bacterium or a facultative anaerobic bacterium:(a) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase activity;(b) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetoacetyl CoA:acetate CoA-transferase activity;(c) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetoacetate decarboxylase activity; and(d) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having isopropanol dehydrogenase activity.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Proteus mirabilis strain and method for producing S-equol through daidzein conversion by using the same
InactiveCN102925378ASolve processing problemsSuitable for industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention discloses a Proteus mirabilis strain and a method for producing S-equol through daidzein conversion by using the Proteus mirabilis strain, wherein the strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 13, 2011, and a preservation number is CCTCC M 2011390. In the prior art, the existing technology is difficult to prepare the S-equol through conversion. With the present invention, the problem in the prior art is solved, and a single function microorganism strain for directly converting a prochiral compound daidzein into a chiral compound S-equol and a preparation method thereof are provided; and compared with the strictly anaerobic equol conversion strains and the mixing bacteria conversion in the previous reports, the Proteus mirabilis LH-52 strain of the present invention is a facultative anaerobe, and is more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis bacterial strains and application thereof in microbial power generation
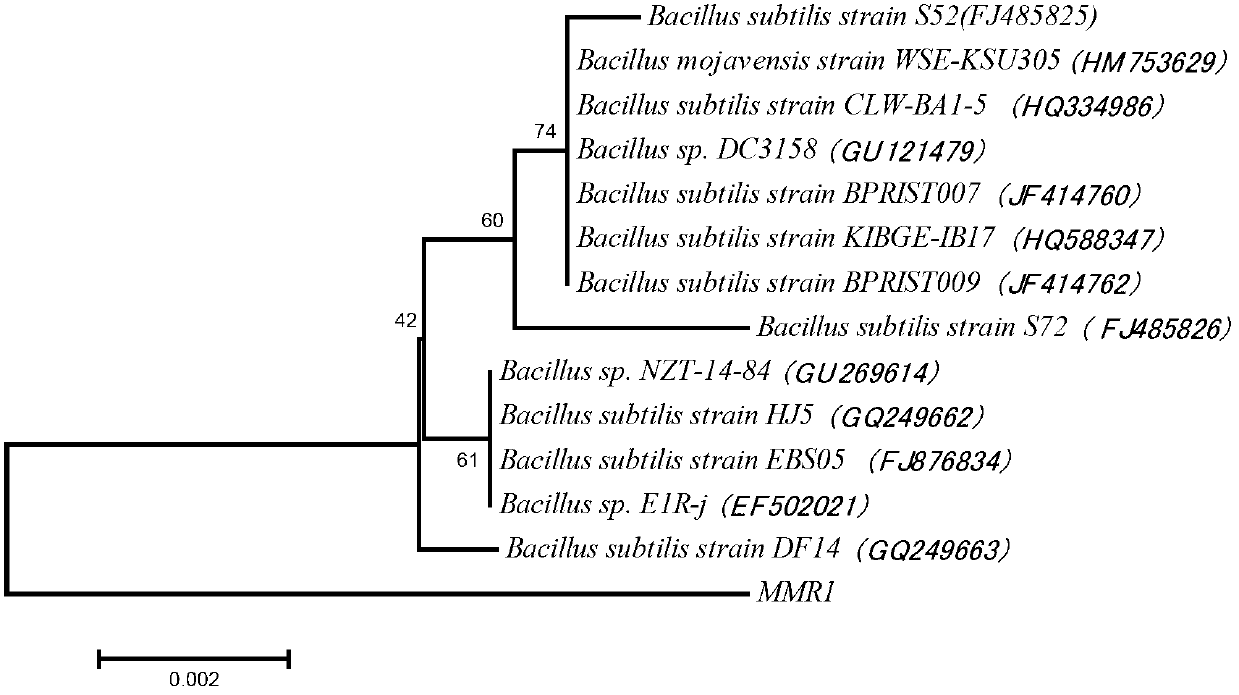
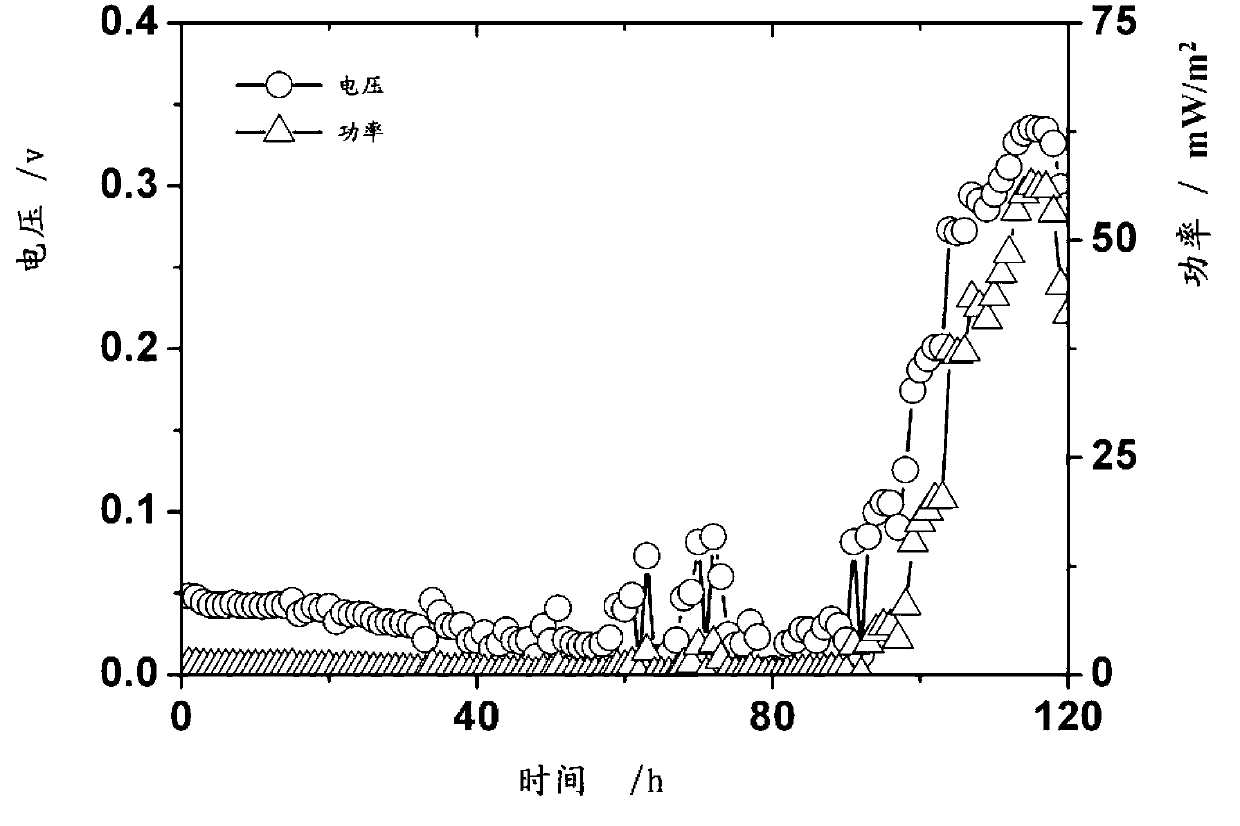
InactiveCN103131651AWith power generation performanceRealize purificationBacteriaFinal product manufactureMicroorganismMicrobial fuel cell
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology, in particular to bacillus subtilis bacterial strains. The bacterial strain is MMR-1, and the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No.6871. The invention further provides a microbial fuel cell which comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, and an external circuit, wherein the anode chamber comprises anode solutions, an anode, and electricity generating microbes, and the electricity generating microbes are biological pure cultures of the bacillus subtilis bacterial strains or biological pure cultures which have all the identifying characteristics of the bacillus subtilis bacterial strains. The bacillus subtilis bacterial strains are facultative anaerobes and have a function of generating electricity, so that the rang of electricity generating microbes is expanded, and anaerobic experiment conditions can be improved through the preparation of the microbial fuel cell by using the bacillus subtilis bacterial strains.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method of utilizing aquatic product viscera and oyster shells to prepare organic fertilizer
InactiveCN105753606APromote fermentationReduce investmentBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersFecesMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a method of utilizing aquatic product viscera and oyster shells to prepare organic fertilizer.The method mainly includes following steps: culturing high-temperature-resistant facultative anaerobe methyl nutritional bacillus (Bacillus methylotrophicus) HL-4 to obtain a microbial agent for standby use; well mixing the microbial agent with enzyme to obtain a fermentation agent for standby use; well mixing the aquatic product viscera, oyster shell powder, animal excrement and excipients to obtain an organic fertilizer fermentation medium; adding the fermentation agent into the organic fertilizer fermentation medium for heap building fermentation in a natural standing manner for 7-40 days; drying, smashing and packaging a product after fermentation to obtain the organic fertilizer.The aquatic product viscera and the oyster shells are utilized in a high-value manner, and heap turning is not needed in the whole preparation process of the organic fertilizer, so that equipment investment and labor cost are saved and the method has good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Method for producing organic fertilizer without pile turning
InactiveCN105732143APromote fermentationReached maturityBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersMicrobial agentOrganic fertilizer
The invention discloses a method for producing organic fertilizer without pile turning. The method comprises the following main steps: culturing high-temperature-resistant facultative anaerobe bacillus methylotrophicus HL-4 to obtain a microbial agent for standby; mixing bacillus methylotrophicus bacteria and enzyme, and preparing a fermenting agent after uniform mixing for later use; adding the fermenting agent into organic fertilizer fermenting raw materials, and conducting pile construction and fermentation, wherein the fermentation is adopted as the natural standing fermentation, and the fermentation time is 7-40 d; drying, smashing and packaging the fermented product to prepare the finished organic fertilizer. The method for producing the organic fertilizer without pile turning is provided, so that not only can the input of pile turning equipment be reduced, but also the labor and energy costs can be reduced, and good application prospects are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Bacillus coagulans and its use in preparation of L-lactic acid
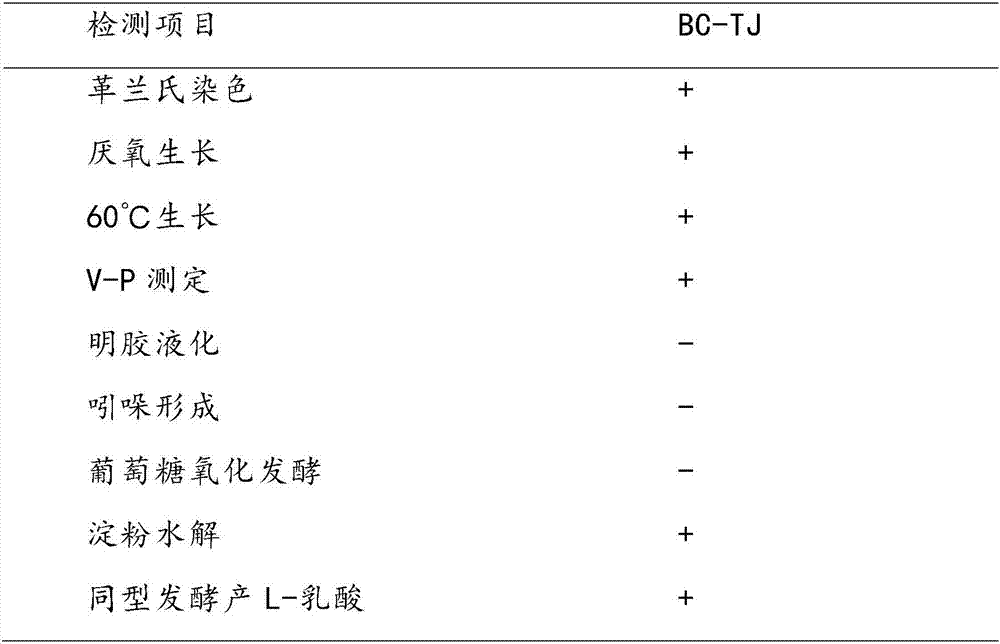
PendingCN107227273AReduced Chances of ContaminationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseMicrobiology
The invention provides Bacillus coagulans BC-TJ or its passage product Bacillus. The Bacillus coagulans BC-TJ has a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 14044. The Bacillus coagulans BC-TJ is a facultative anaerobic strain, can grow under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, has a high fermentation temperature, reduces contaminative microbe pollution probability during the fermentation process, is free of sterilization of the equipment, realizes open fermentation and reduces energy and the labor cost. The Bacillus coagulans BC-TJ utilizes lignocellulose hydrolyzate as a raw material to produce L-lactic acid, realizes a yield of 160+ / -1.5 g / l and optical purity of 100% or more and has a fermentation production capacity of 2.2 g / l / h. In the fermentation process, reductive sugar supply is avoided and a production cost is further reduced. The Bacillus coagulans BC-TJ has the great potential in large-scale industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Drop oxygen enrichment type micro-aerobic-sludge-bed process and wastewater treatment method thereof
ActiveCN106630150ACost effective removalReduce processing costsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAnaerobic respirationSludge
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment, and particularly relates to a micro-aerobic biological treatment process and a method thereof for treating sewage. The micro-aerobic biological treatment process and the method thereof for treating the sewage aim at solving the problems that an existing wastewater treatment technique is not complete enough, high in energy consumption, high in running expense and complicated in process, and the like. In the process, a micro-aerobic sludge bed, a filling material, a drop flow guiding groove, an oxygen-enriched water refluxing tank, a refluxing pipe, a refluxing pump, a check valve, a water inlet pipe, a settling tank, a water outlet pipe and a residual sludge discharging pipe are provided. According to the method, a micro-aerobic environment is beneficial to the mutualism among an aerobic bacterium, an anaerobic bacterium and a facultative anaerobic bacterium; these cultures metabolize a pollutant in a synergistic manner; additionally, as oxygen participates in a biochemical reaction, the oxidizing action and the reducing action in a system can occur at the same time; the anaerobic respiration, the aerobic respiration, the nitrification and the denitrification are enabled to coexist in a treatment system; the system is subjected to oxygen enrichment by a drop procedure, so as to maintain an oxygen source in the sludge bed. The process and the method are compact in layout, and have a favorable application prospect in aspects of treating wastewater; the running space and the running expense are saved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Bagged fermented feed package for livestock and poultry without antibiotics and high live bacteria
InactiveCN102293321ASmall footprintComplete antigen degradationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention belongs to the field of feed packaging, in particular to a bagged fermented feed package for livestock and poultry without antibiotics and high live bacteria. Bagged fermented feed package for livestock and poultry without antibiotics and high live bacteria. The fermented feed package is composed of a packaging bag and a feed base material packed in the packaging bag to inoculate the bacteria. A mixed bacterial solution with a bacterial count greater than 108cfu / g, the mixed bacterial solution is composed of aerobic bacteria and facultative anaerobic bacteria; the packaging bag is equipped with a one-way air outlet valve device. The fermented feed prepared by using the fermented feed package has comprehensive nutrition of the mixture, is fermented, has biological activity, does not remain, and does not produce drug resistance.
Owner:浙江德清博诚生物科技有限公司
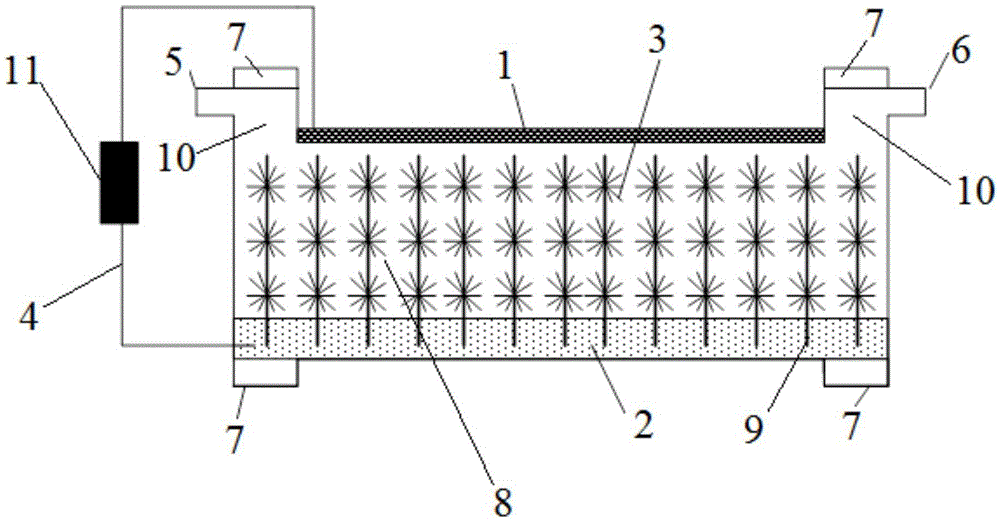
Green desert ground surface windproof structure
ActiveCN106759248AWill not polluteImprove survival rateOther chemical processesClimate change adaptationMicroorganismEcological environment
The invention discloses a green desert ground surface windproof structure. A windproof layer covers the desert ground surface, and the windproof layer is obtained through microorganism seepage-proofing and strengthening fluid treatment; the content of sandy soil in desert with the particle size being 0.075-60 mm is larger than 50%, and microorganisms in strengthening fluid are aerobiotic type bacteria; or the content of sandy soil in desert with the particle size being smaller than or equal to 0.075 is larger than or equal to 50%, the microorganisms in strengthening fluid are facultative anaerobic bacteria, and the windproof layer cannot be blown and scattered at the maximum wind speed of 20 m / s. The microorganism reaction process depended by the green desert ground surface windproof structure is the process existing in the soil ecological environment, and the environment cannot be polluted; a microorganism-plant combined sand treatment technology is adopted, and the survival rate is higher compared with pure planting of plants; the green desert ground surface windproof structure mainly depends on the biocement technology, the effect is high in speed compared with biological crust generated by utilizing other bacteria, fungi, blue-green algae and the like, and basically no requirement exists for the environment.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device and application thereof
ActiveCN105565473ATo make up for the inability to continue to use photosynthesis to generate electron acceptors for sewage treatmentImplement multi-level processingTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesCarbon feltFacultative anaerobic organism
The invention relates to a bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device and application thereof. The bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device which is a system comprises module reaction cavities, air cathodes, carbon felt and carbon brushes. The air cathodes are arranged on the tops of the module reaction cavities, the carbon felt is arranged at the bottoms of the module reaction cavities and is used as an anode, the carbon brushes are arranged between the air cathodes and the carbon felt, a water inlet and a water outlet are respectively formed in two ends of the top of each module reaction cavity, the air cathodes are opposite to the carbon felt, facultative anaerobes grow on the carbon felt in an attached manner, algae plants grow on the carbon brushes in an attached manner, the air cathodes are connected with the carbon felt by external circuits, and the bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device is used for treating organic sewage. Compared with the prior art, the bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device has the advantages that the bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device is simple and compact in integral structure, and components of the bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device can be modularly combined with one another; synergistic effects can be realized on the basis of algae, the facultative anaerobes and the air cathodes, ion exchange membranes can be omitted, and accordingly the bacteria and algae combined biological electrochemical device is low in economic cost and stable in configuration, can run stably and has an excellent application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Microbial culture medium and use thereof
InactiveCN1746289AQuality assuranceColony morphology is goodBacteriaMicrobiology processesBiotechnologyFacultative anaerobic organism
A microbial medium and its use are disclosed. The medium consists of pancreatic casein peptolysis 5-30 proportion, yeast extractive powder 0.5-20 proportion, grape sugar 0.5-20 proportion, sodium chloride 1-15 proportion, L-cystine 0.1-5 proportion and sulfur sodium ethylate or sulfur glycolic acid 0.1-8 proportion. It is characterized by adding agar into medium with content=50-500g / cm2. It can be used for CFU count of anaerobe or facultative anaerobe.
Owner:NAT INST FOR THE CONTROL OF PHARMA & BIOLOGICAL PROD
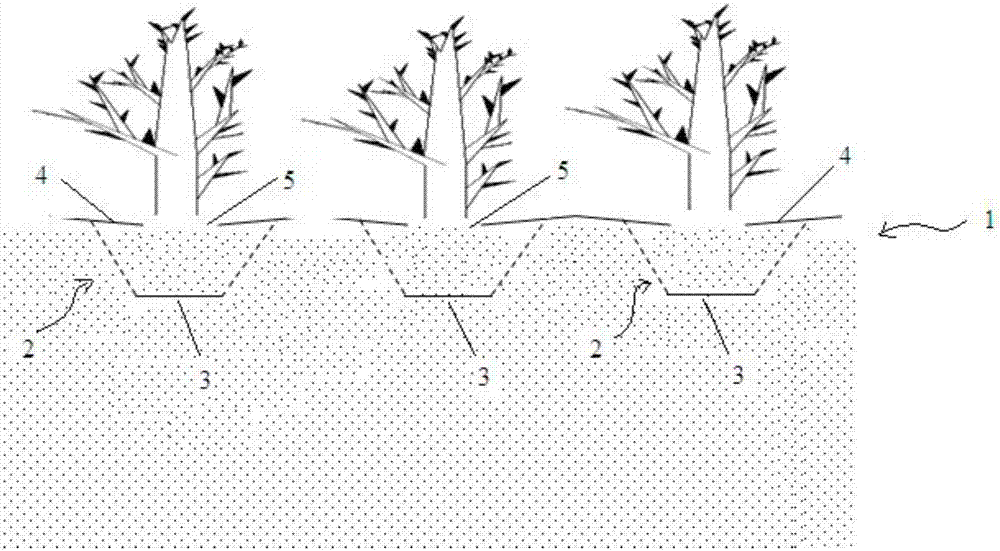
Desert planting structure and method for planting plant in desert
ActiveCN106856700APromote growthWill not polluteClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMicroorganismEcological environment
The invention discloses a desert planting structure and a method for planting a plant in a desert. A planting pit is formed in the planting structure downwards from a desert surface; an impervious layer is arranged on one part of surface of the planting pit; a plant is planted in the planting pit and then desert soil is backfilled, and an earth surface windproof layer is arranged on the surface of the planting pit, wherein content of sandy soil of which the particle sizes are smaller than or equal to 0.075mm in the desert is greater than or equal to 50%; the impervious layer and the earth surface windproof layer are obtained through treatment of an anti-seepage reinforcement solution of microorganisms; the microorganisms are facultative anaerobe; the ratio of the permeability coefficients of the impervious layer to the desert free of the impervious layer is smaller than 5%; the earth surface windproof layer is not blown away under the condition that the maximal wind speed is 20m / s. The dependent microbial reaction process is a process existing in a soil ecological environment and the environment is not polluted; by adopting a microorganism-plant combined with sand control technology, the survival rate is higher than that of a pure plant planting method.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for performing mixed fermentation on lactobacillus acidophilus and clostridium butyricum as well as fermentation equipment thereof
InactiveCN108004191AGrowth inhibitionRelease the ability to grow and reproduceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFacultative anaerobic organismOrganism
The invention relates to the field of biology and provides a method for performing mixed fermentation on lactobacillus acidophilus and clostridium butyricum. The method comprises the following steps:inoculating the lactobacillus acidophilus on an unsterilized solid culture medium to perform fermentation, and then inoculating clostridium butyricum liquid to perform fermentation. The synergistic inhibition effect on infectious microbes by the lactobacillus acidophilus and the clostridium butyricum can be utilized, the growth of the infectious microbes can be effectively inhibited and the infectious microbes in the production process can be effectively controlled; furthermore, under the condition of not sterilizing the raw materials, the lactobacillus acidophilus and the clostridium butyricum are fermented, so that the cost is reduced and the practicability is high. In addition, the invention also provides fermentation equipment. The fermentation equipment can be applied to solid fermentation production of anaerobic bacteria or facultative anaerobic bacteria such as the clostridium butyricum and the lactobacillus acidophilus; and the fermentation equipment discharges volatile metabolic products such as hydrogen and carbon dioxide to the external air through a gas outlet pipe, relieves metabolic inhibition, and can release viable bacteria to improve the growth and reproduction capacity and increase the number of the fermented viable bacteria.
Owner:湖北华扬科技发展有限公司
Sewage treatment system and sewage treatment method thereof
InactiveCN107417040AEasy to handleHigh degree of integrationMultistage water/sewage treatmentTreatment involving sedimentationAutomatic controlWater quality
The invention relates to a sewage treatment system and a sewage treatment method thereof. The sewage treatment system comprises an adjusting tank, a sludge tank, reaction integral equipment and assistant integral equipment, wherein the reaction integral equipment consists of a BBE (Biomedical Biological Engineering) biological efficient treatment tank, a secondary sedimentation tank, a coagulation-flocculation reaction tank and a third sedimentation tank; the assistant integral equipment consists of a dosing room, a warehouse, an air blower machine room and a control room; a plurality of aeration hoses are arranged in the BBE biological efficient treatment tank; the aeration hoses are connected with air inlet tubes and air blowers; efficient active suspended packing for culturing facultative anaerobe is arranged in the BBE biological efficient treatment tank; air blowers are arranged in the air blower machine room; a main control mechanism is arranged inside the control room; and the dosing room is connected with the adjusting tank, the secondary sedimentation tank, the third sedimentation tank and the coagulation-flocculation reaction tank through dosing pipelines respectively. By adopting the sewage treatment system, nitration and denitrification can be synchronized, meanwhile sludge treatment can be achieved rapidly, the whole process is high in integration degree, automatic control is achieved, and a remarkable water quality improvement effect is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI PUSHI ECOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT ENG
Cellulose decomposing strain CX10 from termite gut and application thereof
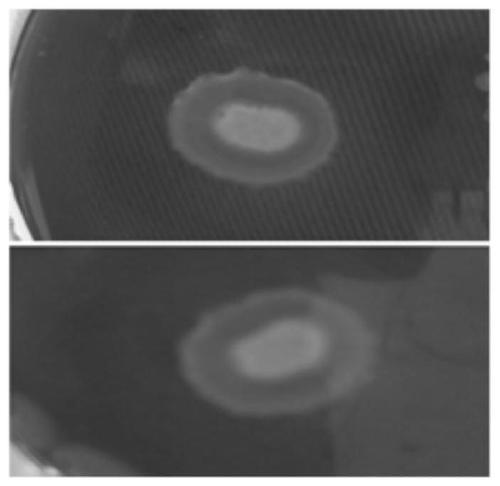
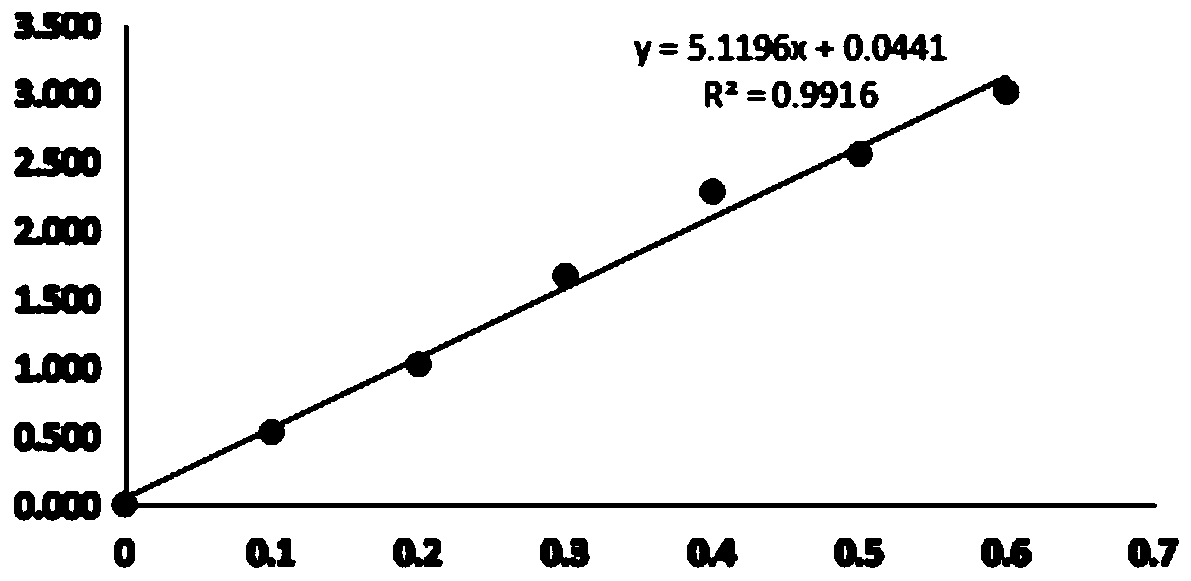
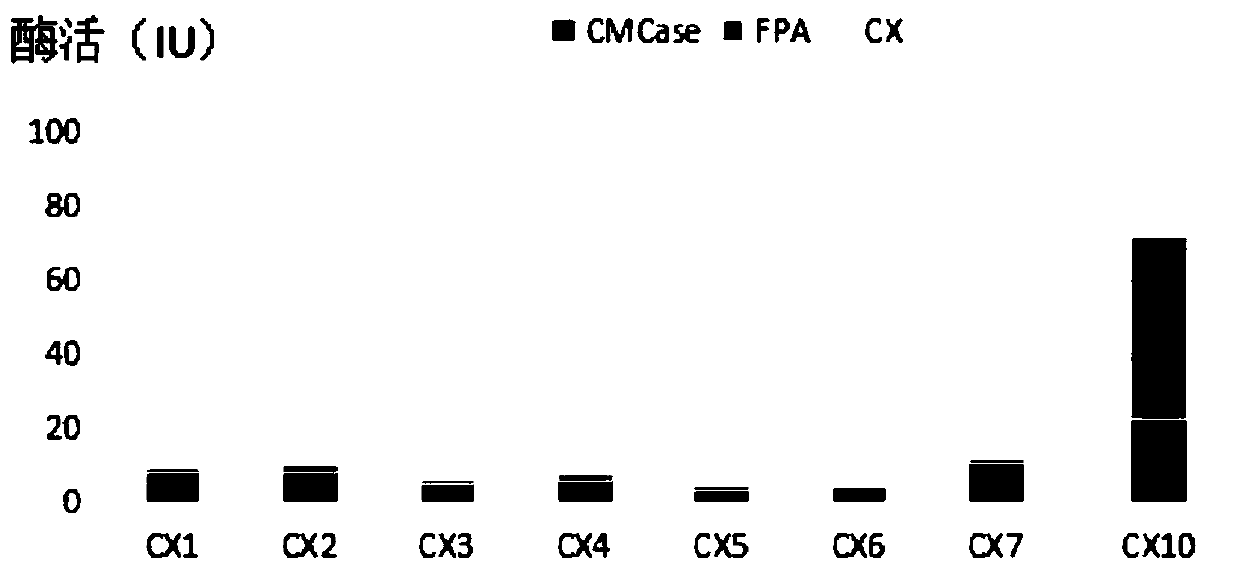
The invention discloses a cellulose decomposing strain CX10 from a termite gut and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the General Microbiological Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms at the No.3, first yard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang district, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16344. The strain is a gram-positive bacillus and free of capsules, endogenous spores can be seen after spore staining, the bacterial colony is a single one and in a cracked shape, the bacterial colony is white, and the edge of the bacterial colony is complete.The strain is a facultative anaerobic strain for producing cellulase; within 48 hours, the FPA enzyme activity of the strain is 49.5 U / mL, the CMCase enzyme activity is 95.0 IU / mL, and the CX enzyme activity is 23.26 IU / mL. The strain is very high in biodiversity value, and has a scientific value of further research on cellulose-enriched crops and development and application of a traditional Chinese medicine fermentation recycling.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Membrane aerated biofilm micro-aerobic sludge bed process and wastewater treatment method thereof
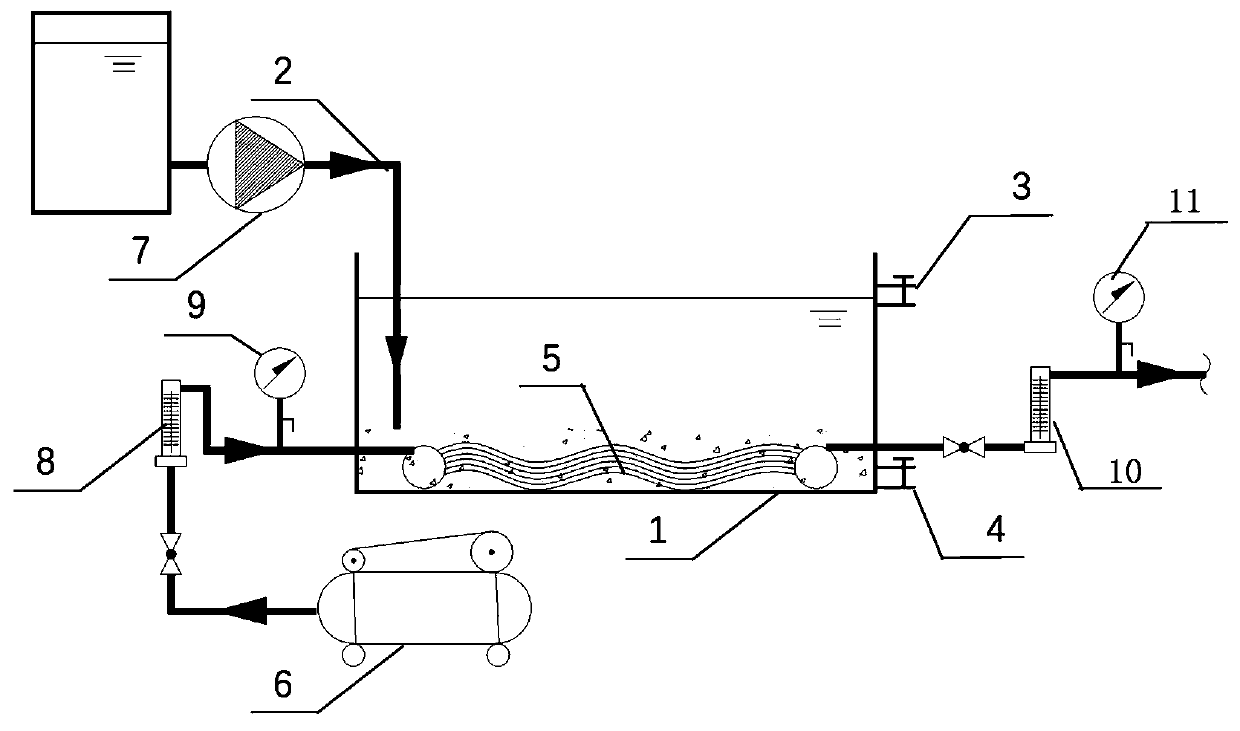
InactiveCN110342634AHigh oxygen mass transfer efficiencyReduce energy consumptionWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentPeristaltic pumpIndustrial waste water
Belonging to the field of sewage denitrification treatment, the invention discloses a membrane aerated biofilm micro-aerobic sludge bed process and a wastewater treatment method thereof. The membraneaerated biofilm micro-aerobic sludge bed process adopts a biofilm micro-aerobic sludge bed, a sludge bed water inlet pipe, a sludge bed water outlet pipe, a sludge discharge pipe, a biofilm aeration component, an air pump, a circulating pump, a peristaltic pump, air flow meters and pressure gauges. The treatment method realizes the mutualism and collaborative metabolism of aerobic bacteria, anaerobic bacteria and facultative anaerobes in a micro-aerobic environment, at the same time utilizes the efficient oxygen mass transfer efficiency of the membrane aeration component and enables wastewaterto flow on the outer surface of the biofilm to form back diffusion of oxygen and pollutants, and can realize effective removal of pollutants in a bioreactor. The process and the treatment method provided by the invention are suitable for denitrification treatment of urban sewage and industrial wastewater, and have the advantages of high treatment efficiency, high energy utilization rate, stable effluent effect, fast start-up speed, etc.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing antibiotic-free high-live bacterium fermented feed for livestock and poultry
ActiveCN102326667ASmall footprintComplete antigen degradationAnimal feeding stuffWorking-up animal fodderBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention belongs to the field of processing of feeds, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a livestock and poultry fermented feed for producing high-quality livestock and poultry meat. A method for preparing an antibiotic-free high-live bacterium fermented feed for livestock and poultry comprises the following steps of: 1) crushing a feed base stock and a strain culture mediuminto 10 to 100-mesh powder; inoculating mixed bacterial liquid in an amount which is 10 to 40 percent of the total weight of the feed base stock, and mixing uniformly, wherein the total bacterial count is more than 108 colony-forming units / gram, the mixed bacterial liquid consists of aerobic bacteria and facultative anaerobe; and 2) loading the mixed materials into a packaging bag with a one-way air outlet valve device, packaging in a sealing way, standing, performing solid state fermentation for more than 5 days, and thus obtaining the antibiotic-free high-live bacterium fermented feed for the livestock and the poultry. The fermented feed prepared by the method has comprehensive mixture nutrition, is formed by fermentation, has bioactivity, cannot be left over and cannot generate medicine resistance.
Owner:DEQING BOSHIJIA BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com