Endophytic bacteria capable of producing ACCD, its soil renovation bacterium agent and its application
A plant endophytic bacteria and bioremediation technology, applied in the fields of agriculture and environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of small biomass, slow growth of hyperaccumulating plants, affecting the efficiency of phytoremediation, etc., to improve the restoration efficiency and improve plant stress resistance. Sex, the effect of promoting plant growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The plant endophytic bacteria Jp3-3 bacterial strain of high-yield ACCD in the present invention is obtained from the separation and purification of the stem of Comnyza canadensis growing in a certain copper tailing area in Jiangxi Province, China, and the separation method is as follows:
[0027] First clean the surface of the stems of the small fly with tap water, then wash it again with sterile water, then soak it in 75% ethanol for 5 minutes, rinse it with sterile water, then immerse it in 2.5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5 minutes, rinse it several times with sterile water . Put the surface-sterilized stems in a mortar and grind until homogenized, take 0.1ml of the homogenate and spread it on an LB plate (10g of peptone, 5g of yeast extract, 10g of NaCl, 1000mL of water, 20g of agar, pH 7.0), and incubate at 28°C for 3 days , Pick a single colony, streak it on an LB plate and save it after purification. The strains were inoculated in LB culture medium, shaken...
Embodiment 2
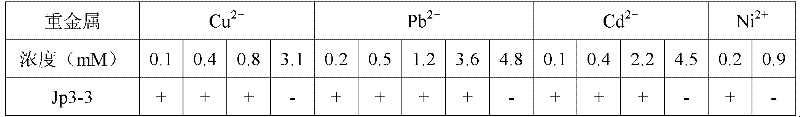
[0029] Streak inoculation of Jp3-3 (CCTCC NO: M 2011250) in LB medium containing different concentrations of heavy metals, culture at 30°C for 3 days, and observe its growth and growth conditions. The results are shown in Table 1. Jp3-3 strain can tolerate a variety of heavy metals (minimum inhibitory concentrations of Cu, Pb, Cd, Ni are 3.1, 4.8, 4.5, 0.9mM, respectively).
[0030] Table 1 The growth of bacterial strains on LB medium containing different concentrations of heavy metals
[0031]
[0032] In the above table, "+" indicates good growth, and "-" indicates no growth.
Embodiment 3
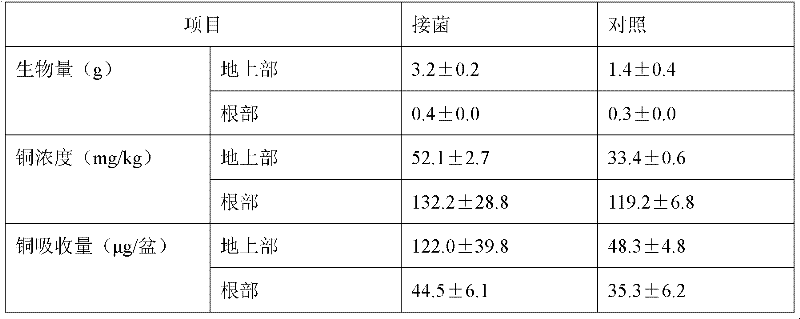
[0034] Jp3-3 (CCTCC NO: M 2011250) was inoculated in LB culture medium and cultured on a shaking table for 20 h, collected by centrifugation at 4°C, and was mixed with SM culture medium (glucose 1.0 g, sucrose 1.0 g, sodium citrate 1.0 g, apple Acid 1.0g, Mannitol 1.0g, Sodium Acetate 1.0g, KH 2 PO 4 0.4g, K 2 HPO 4 2.0g, MgSO 4 0.2g, CaCl 2 0.1g, CuSO 4 1mg, NiSO 4 1mg, ZnSO 4 5mg, FeSO 4 5mg, MnSO 4 3 mg, CoSO 4 1 mg, Na 2 MoO 4 1 mg, H 3 BO 3 2mg, biotin 2 (VB 6 ) 10mg, thiamine (VB 1 ) 2mg, cyanocobalamin (VB 12 )0.1mg, pantothenic acid (VB 3) 5mg, folic acid 2mg, riboflavin 5mg, niacin 5mg, distilled water 1000mL, pH 6.4. Vitamins were added after filter sterilisation. ) was washed and centrifuged twice, the bacteria were suspended in SM culture medium, and inoculated in SMA culture medium according to the inoculum size of 5% (v / v) [Add filter-sterilized ACC (1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylic acid deaminase) to a final concentration of 3 mM. ], cultur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com