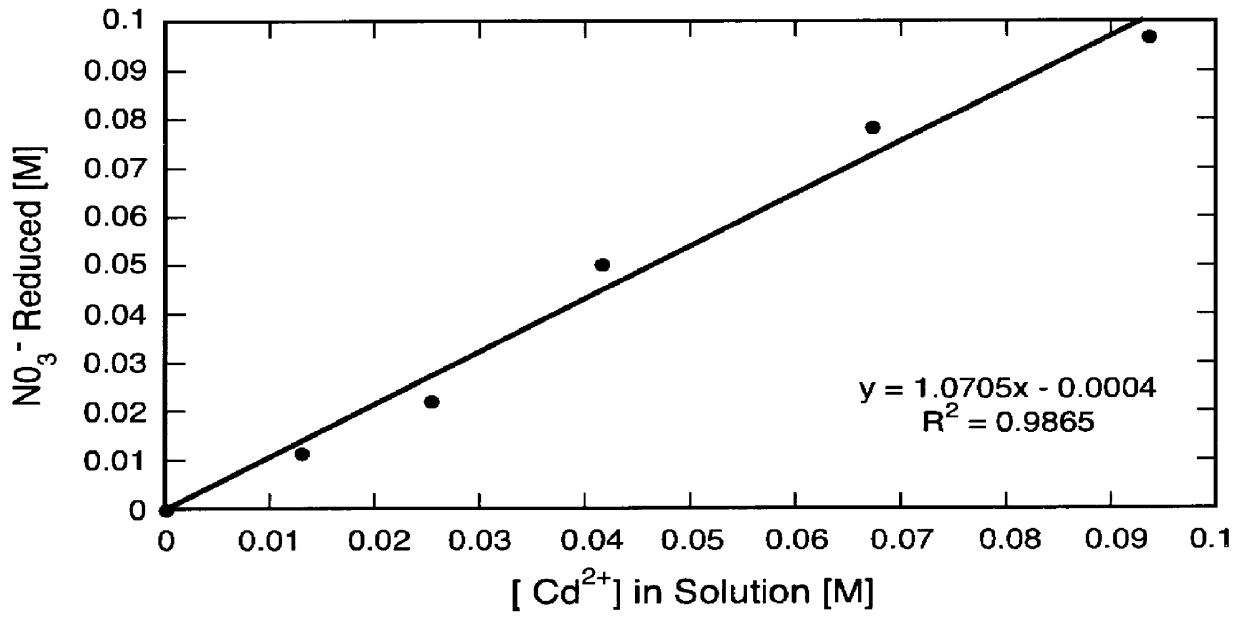
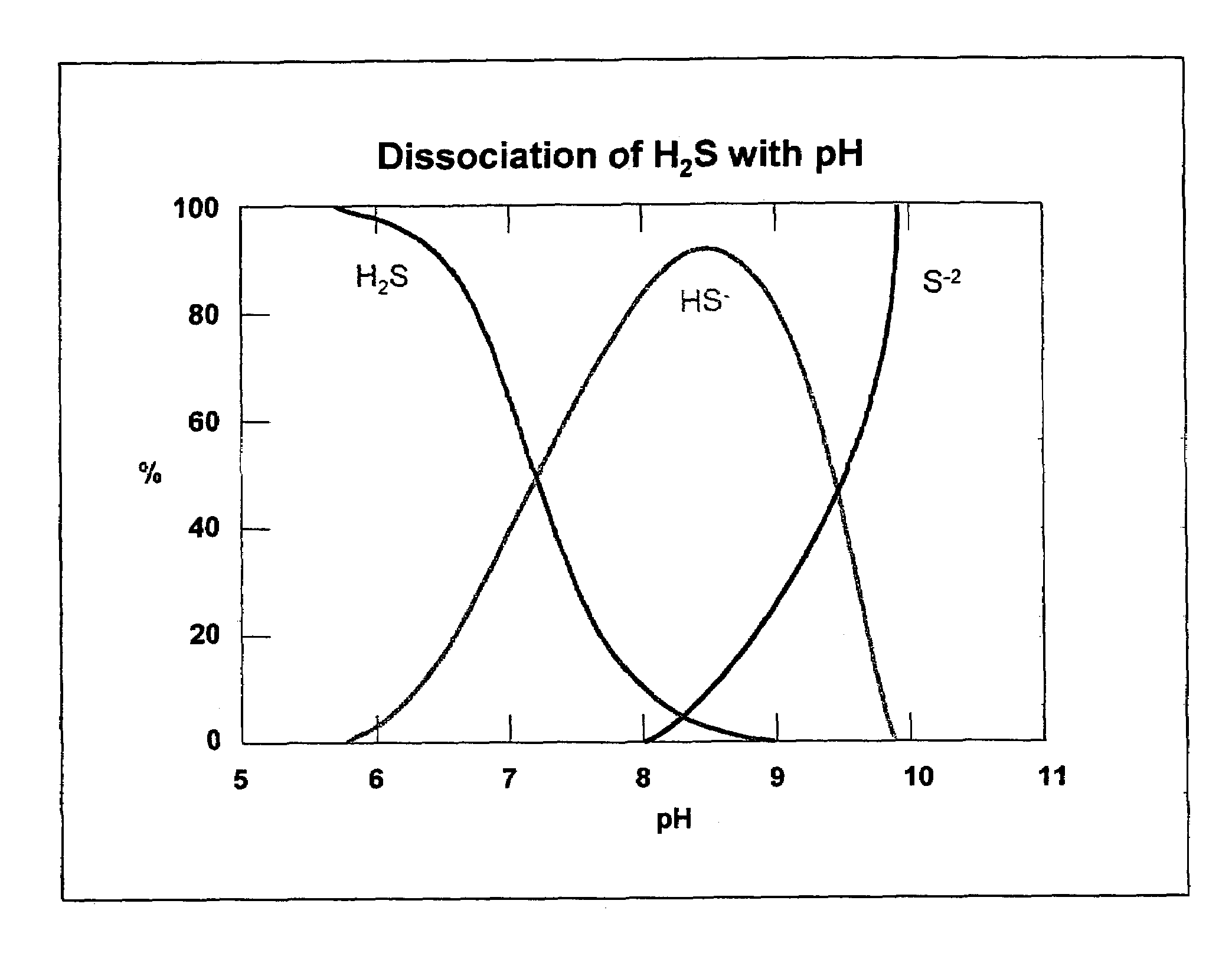
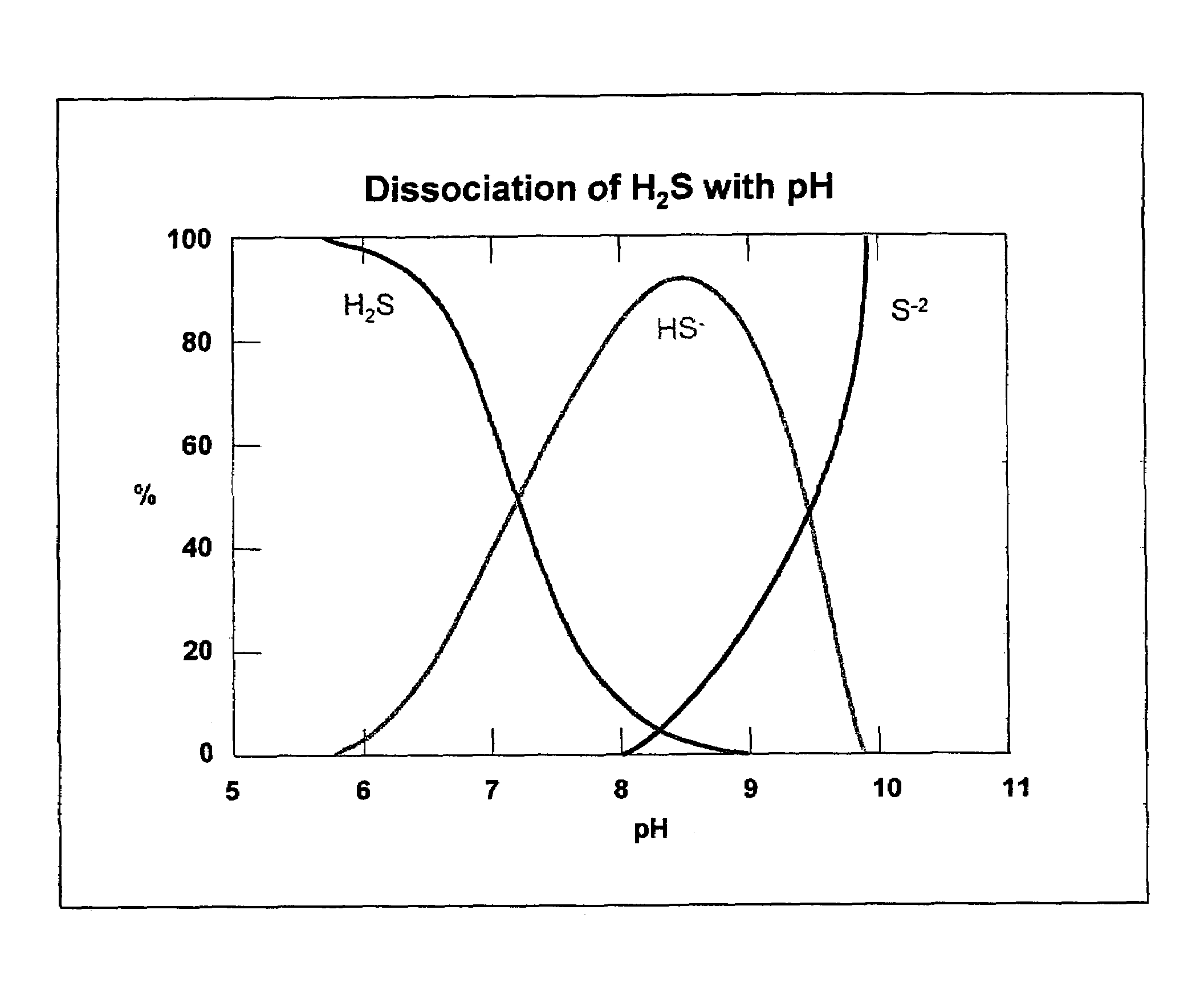
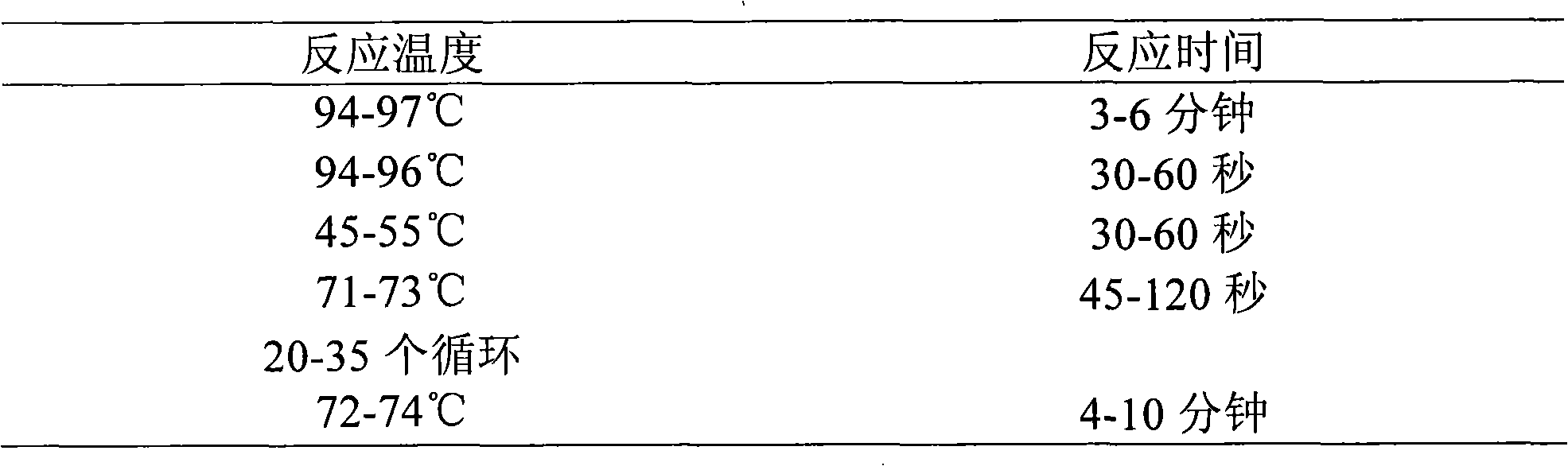
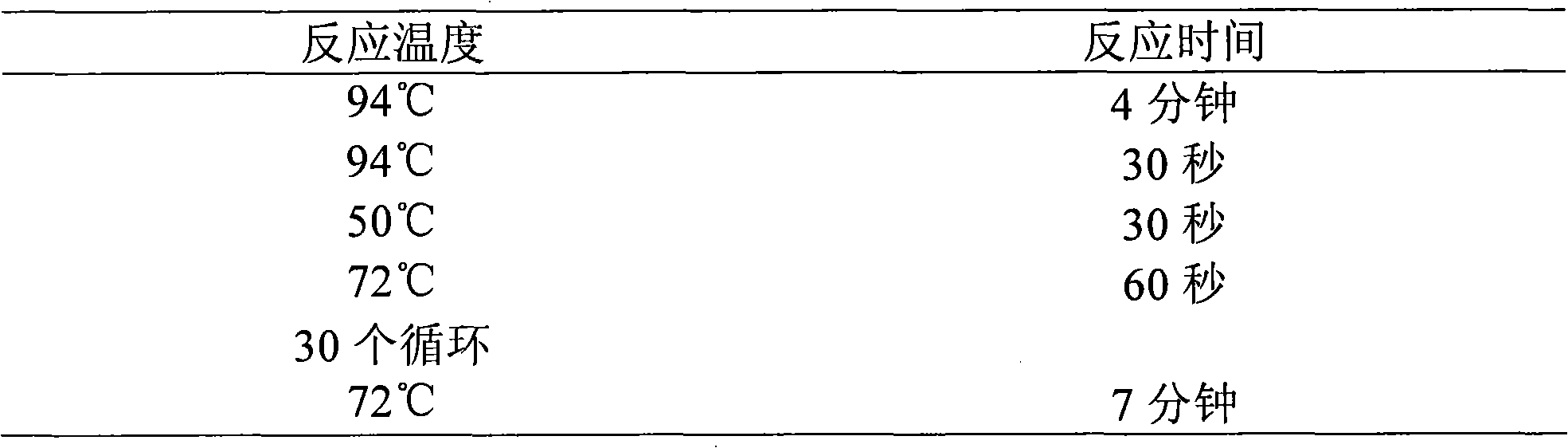
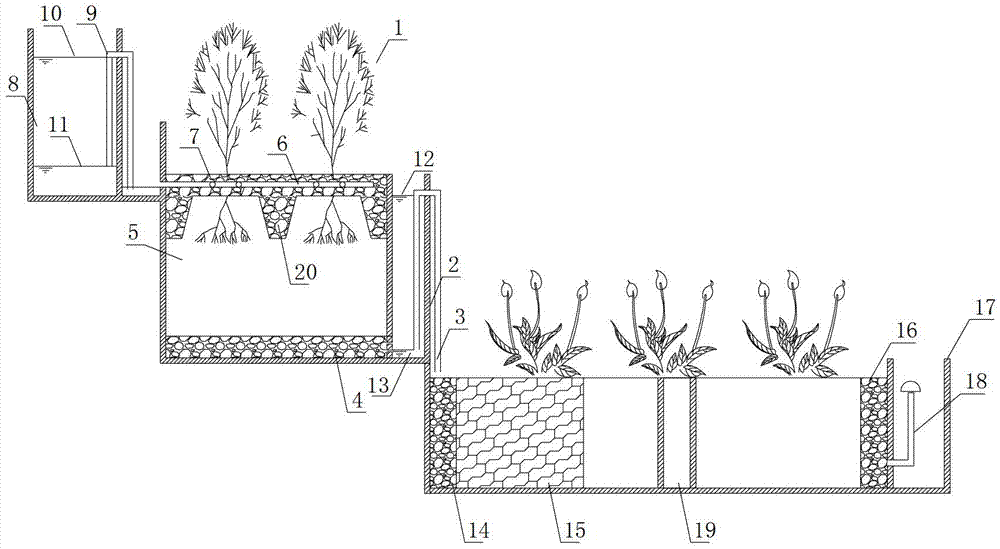
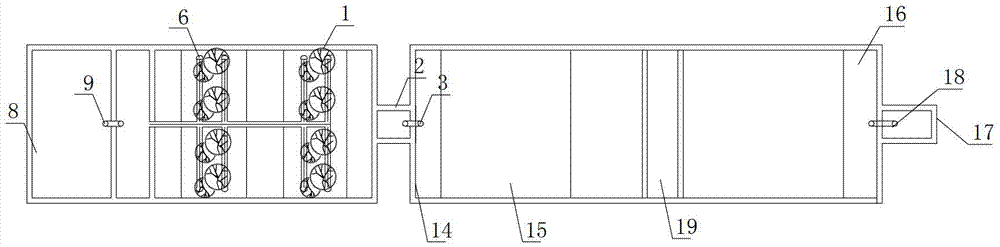
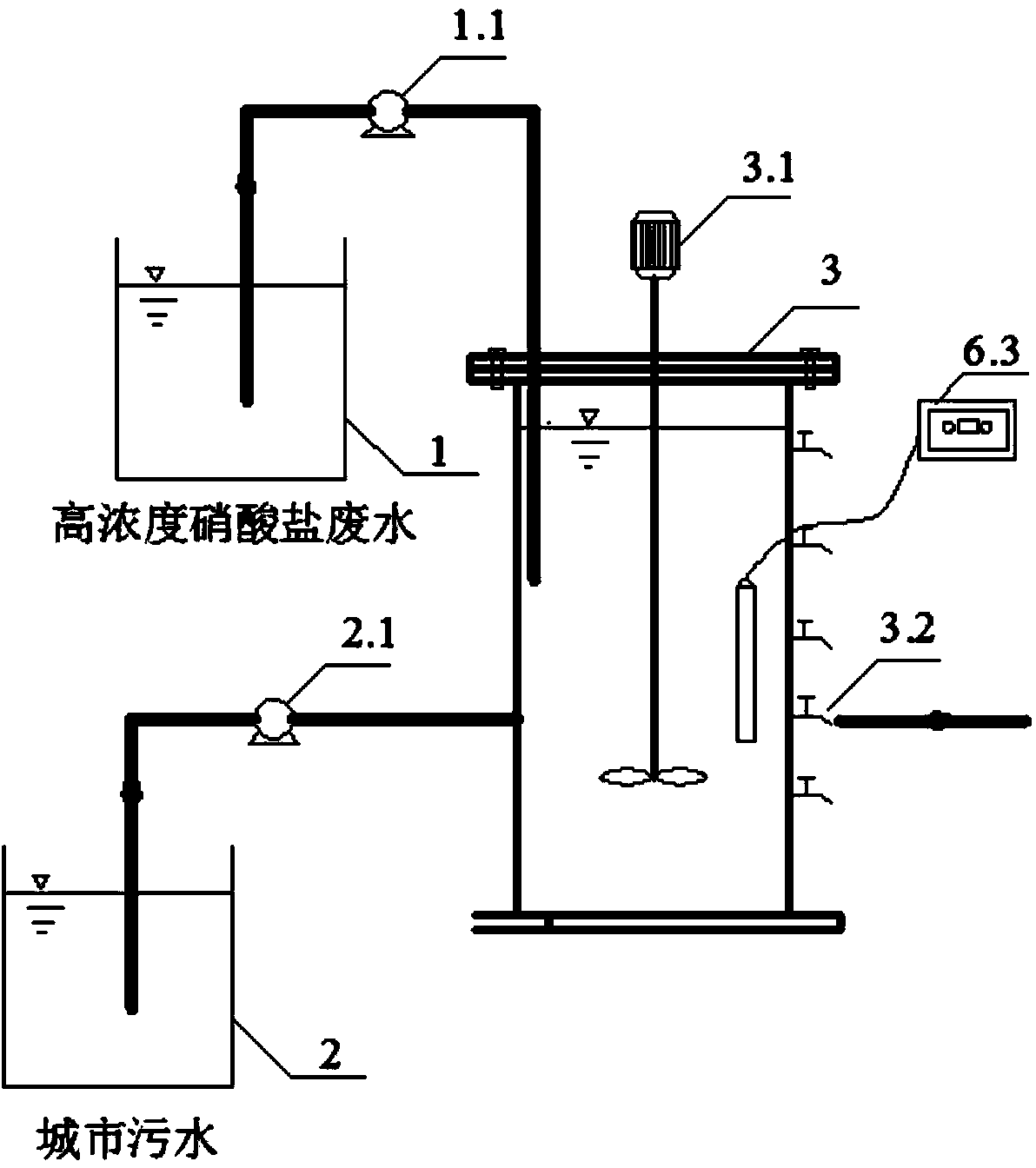
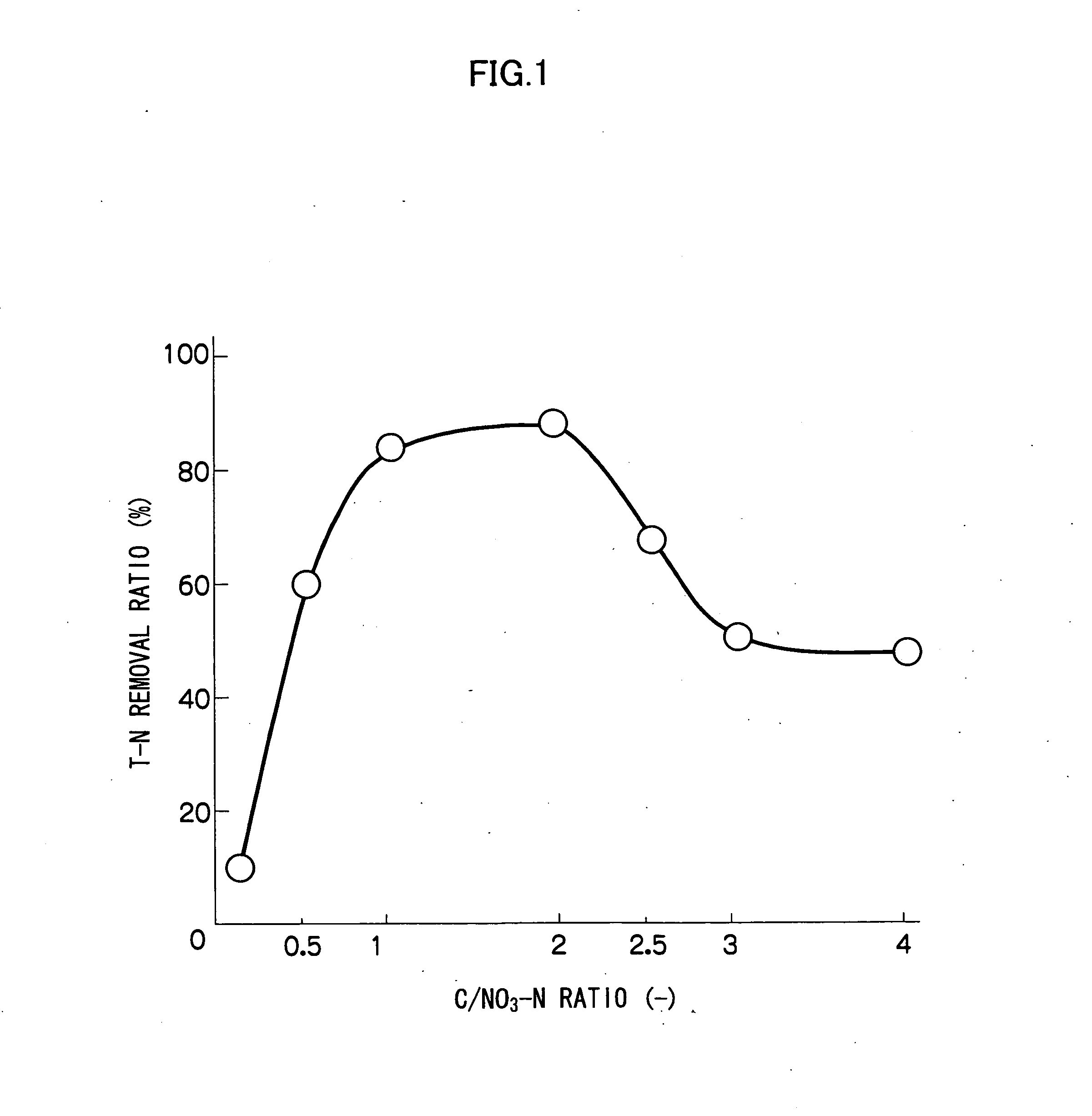
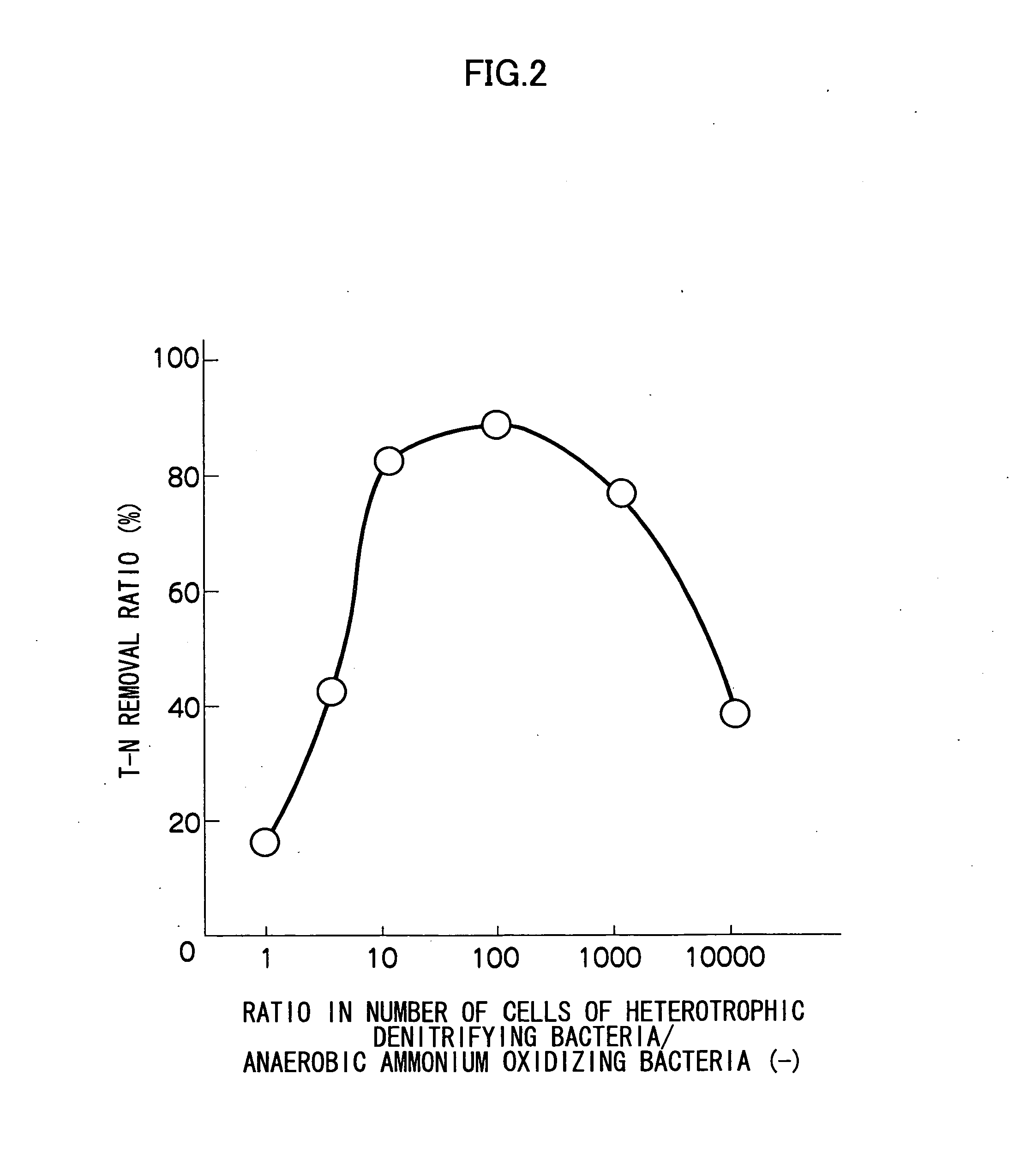
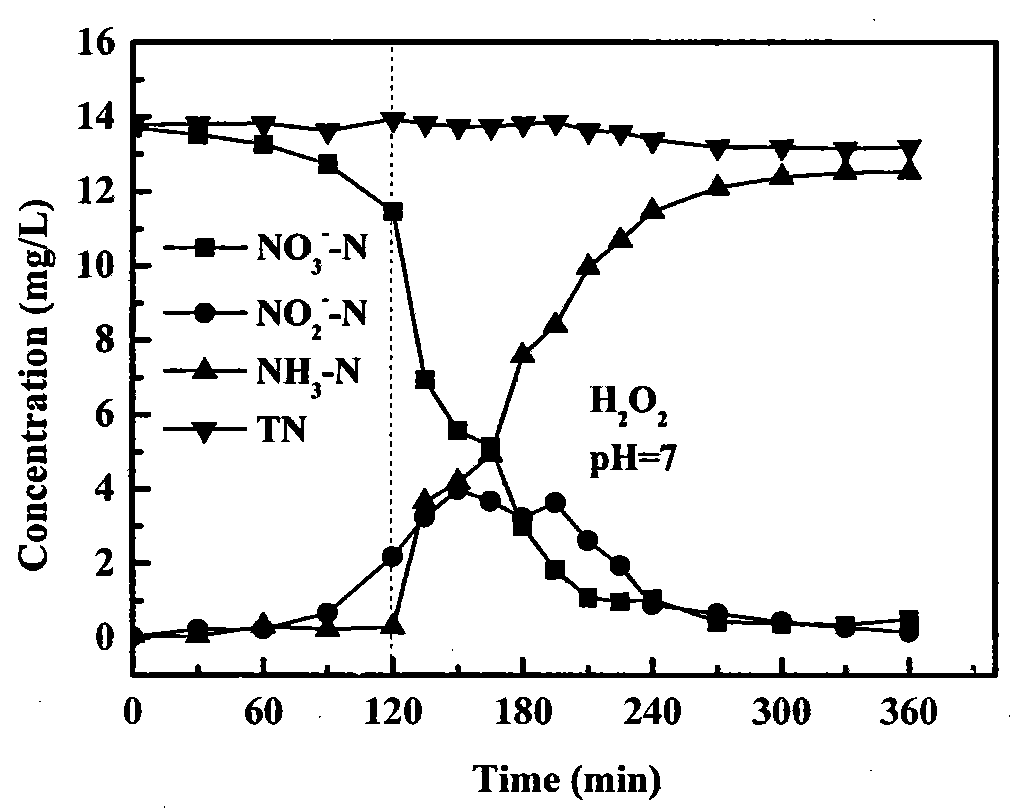
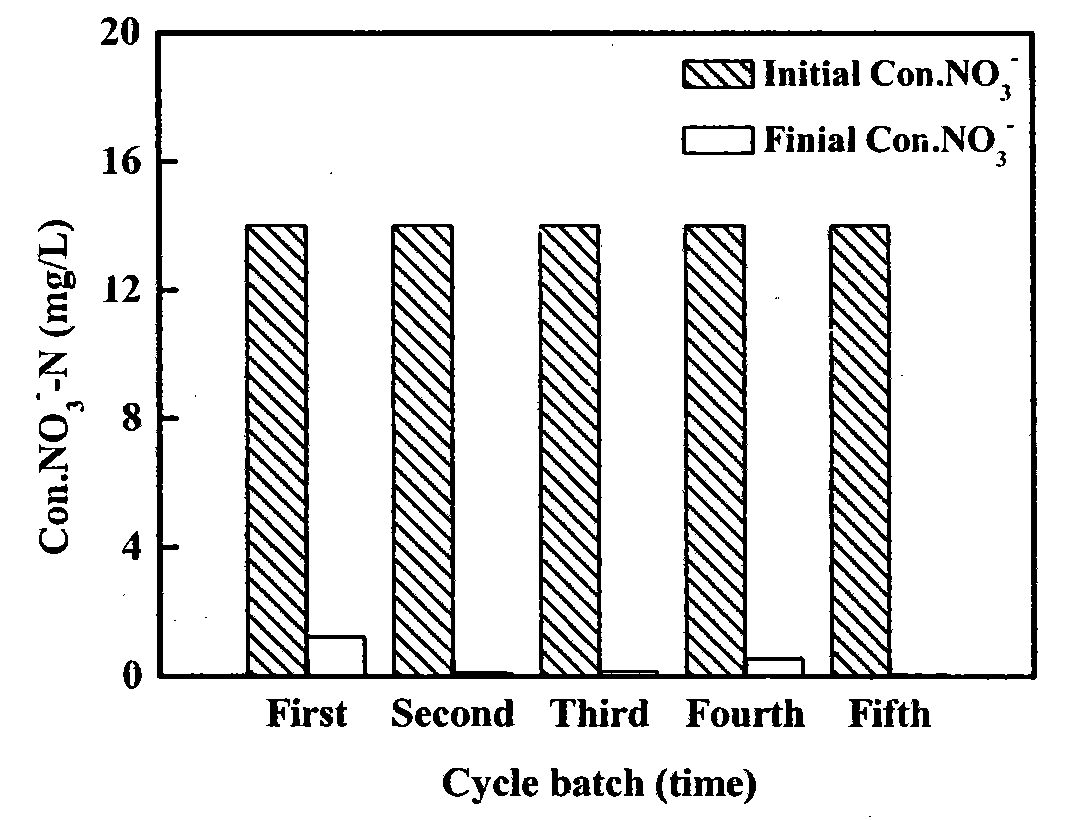
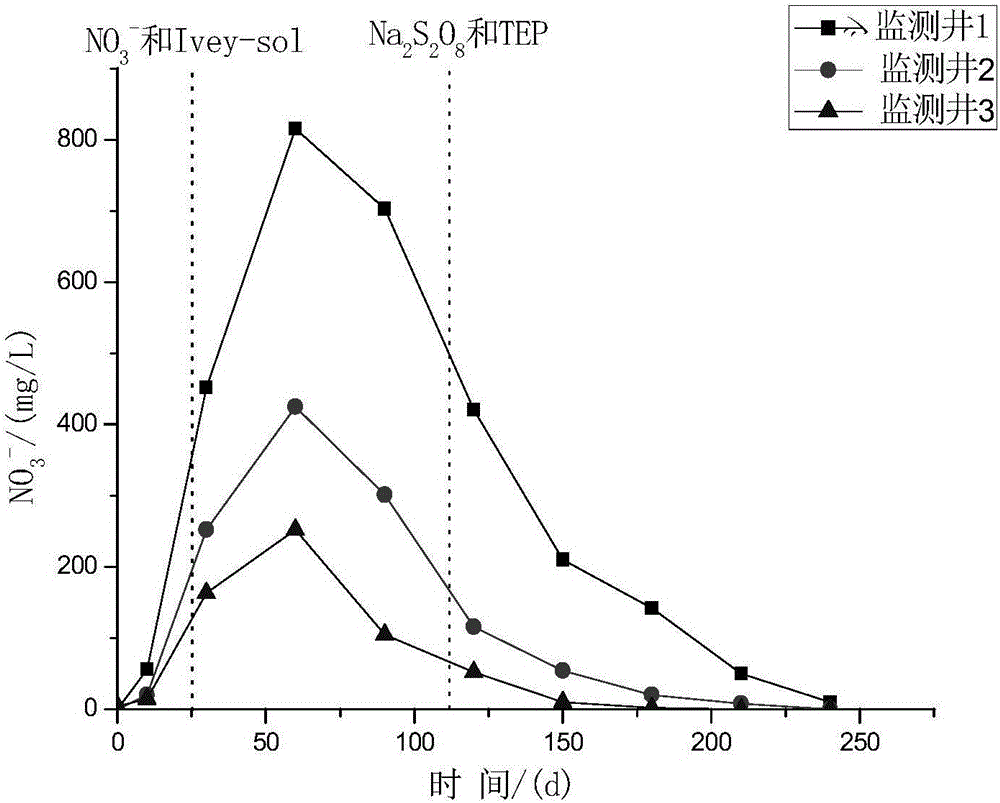
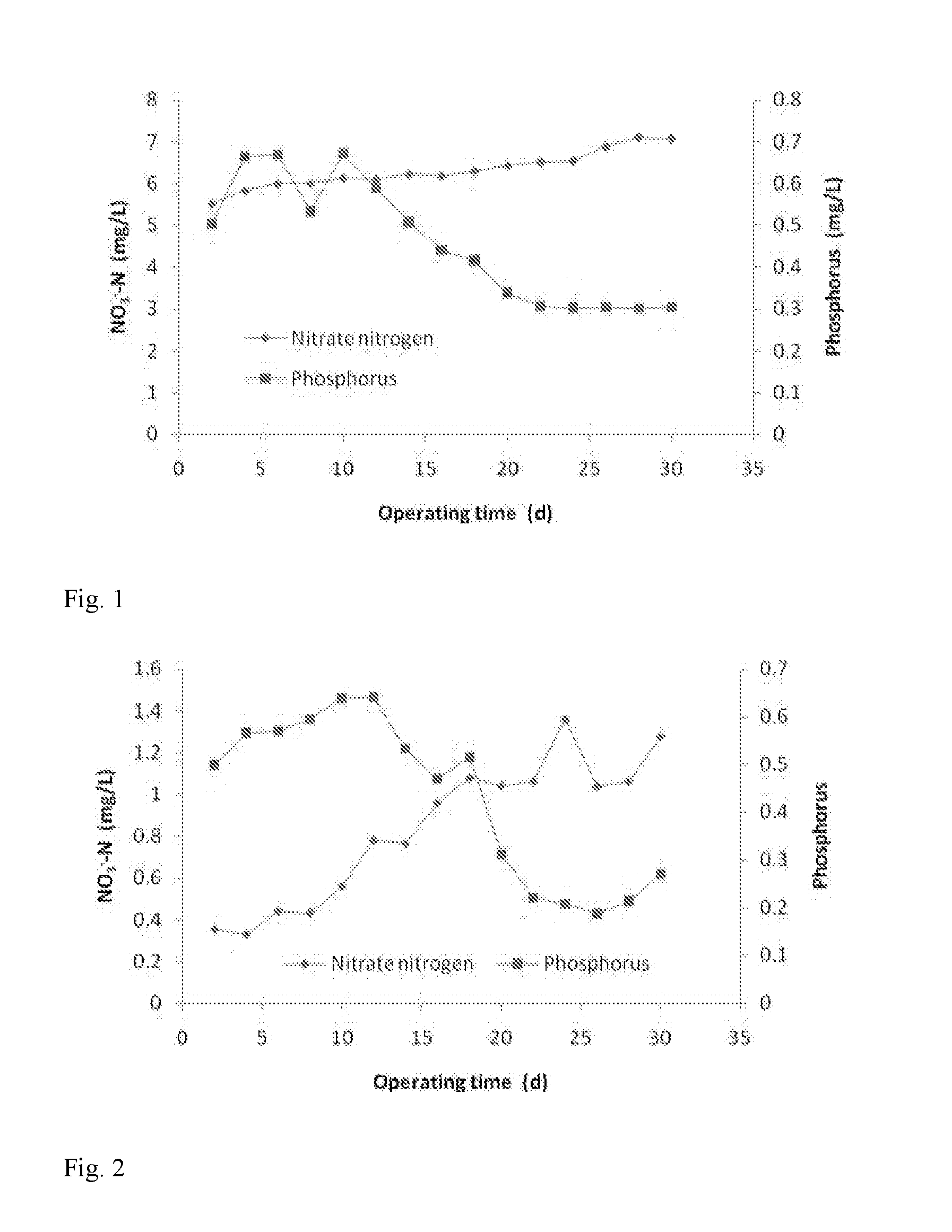
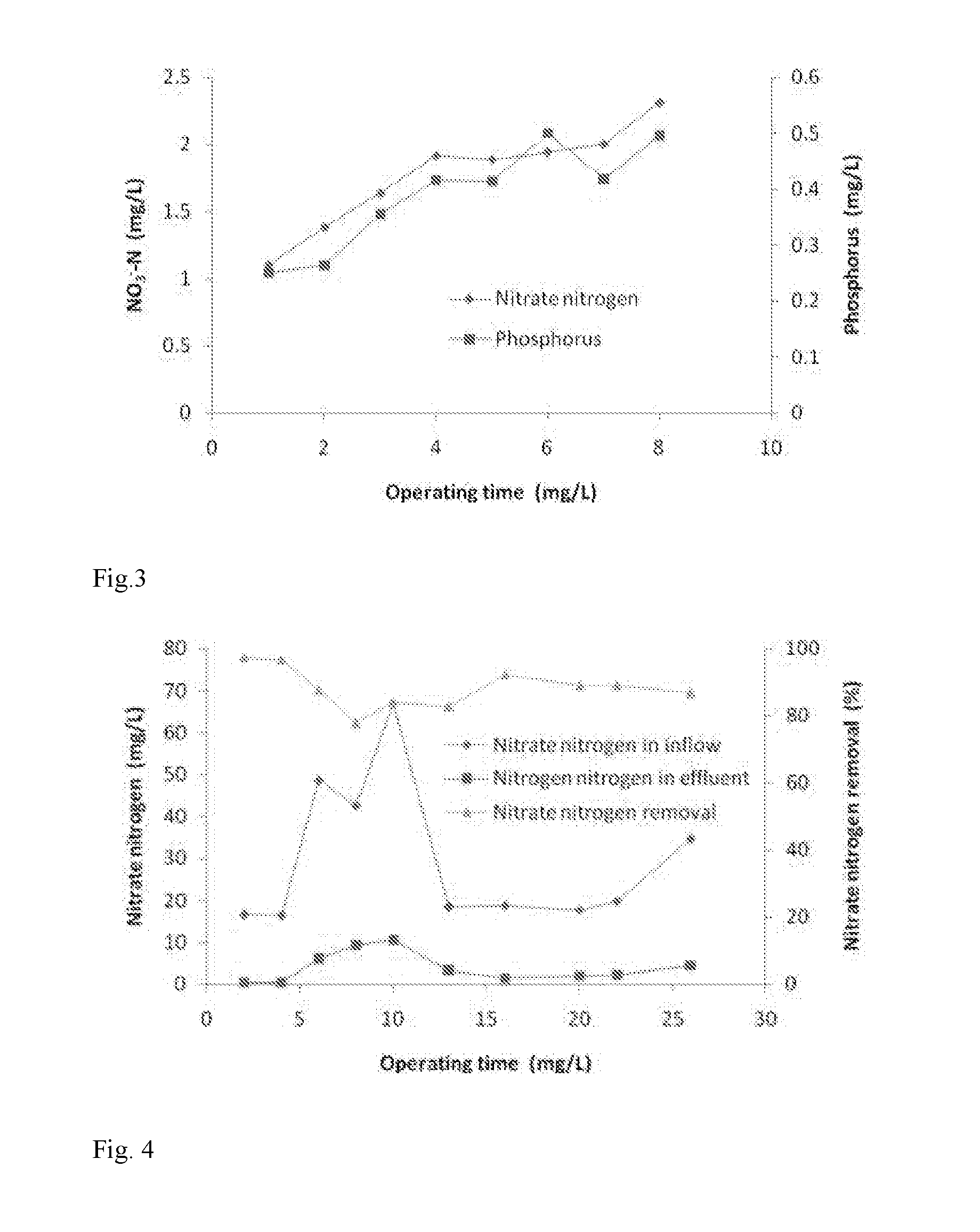
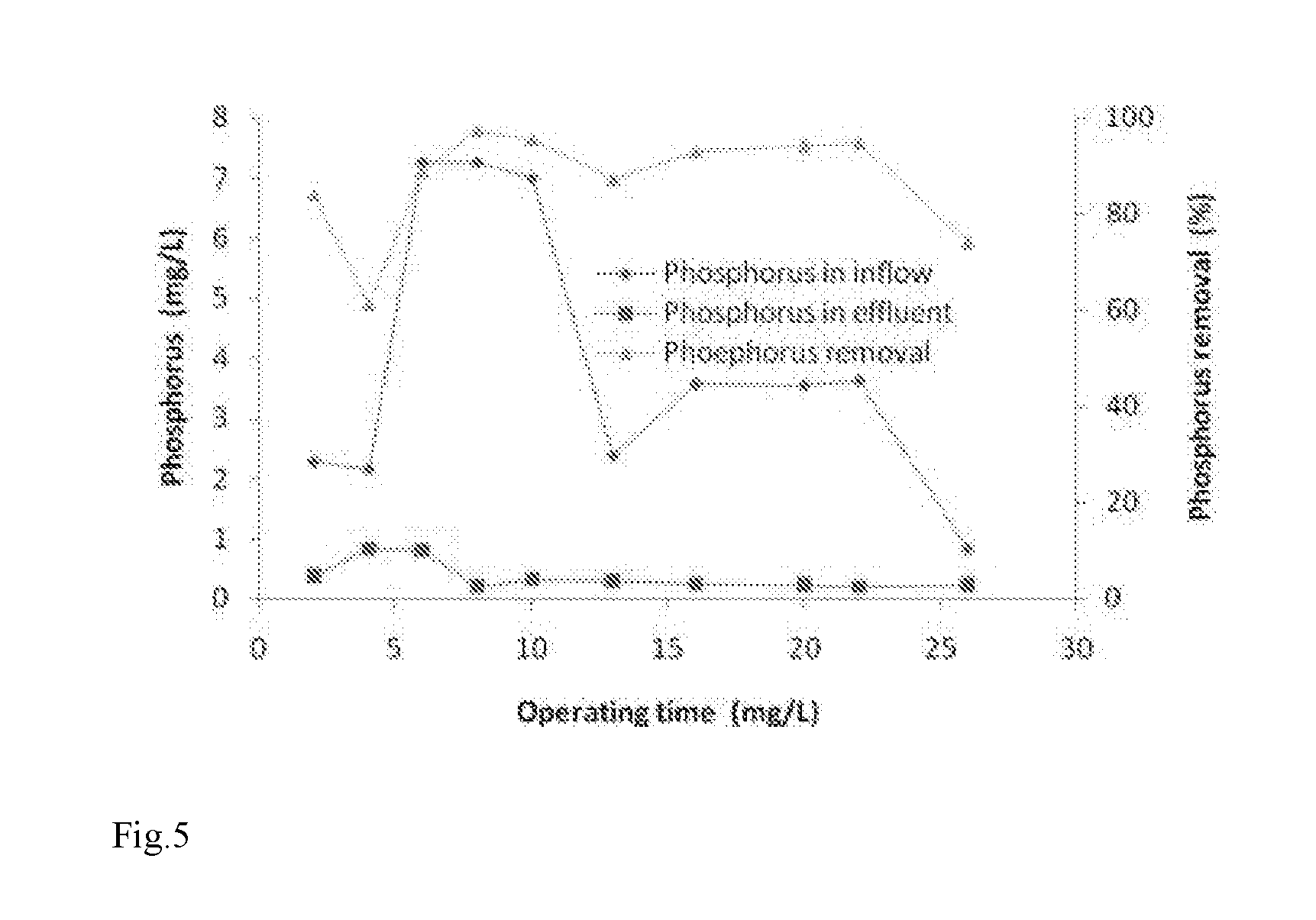
Patents
Literature
219 results about "Nitrate reducing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrate reduction test is a test that determines the production of an enzyme called nitrate reductase, which results in the reduction of nitrate (NO3). Bacterial species may be differentiated on the basis of their ability to reduce nitrate to nitrite or nitrogenous gases. To determine the ability of an organism to reduce nitrate to nitrite.
Composition for odor control
ActiveUS20050115895A1Promote growthInhibition productionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsSpecific enzymeWaste stream
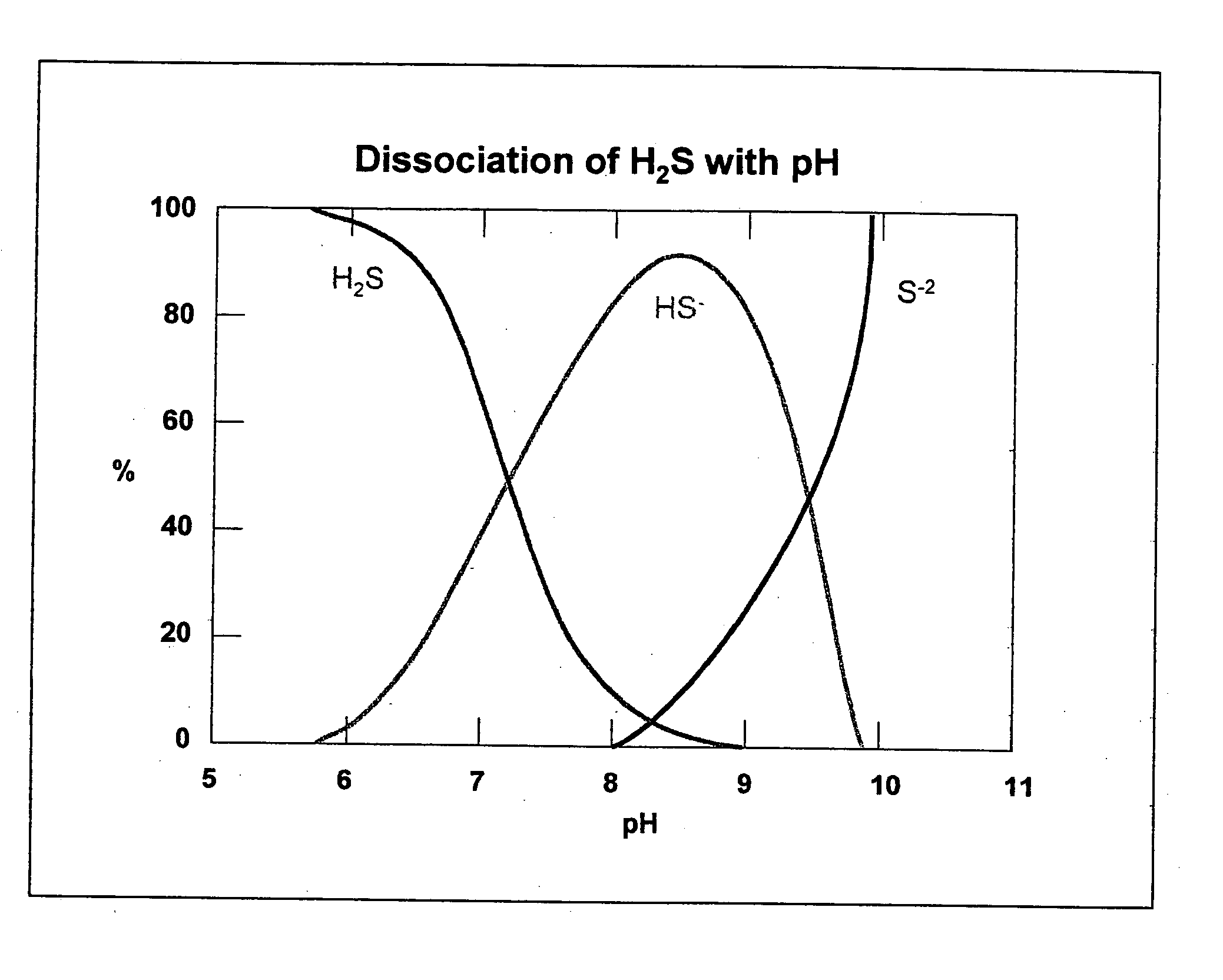
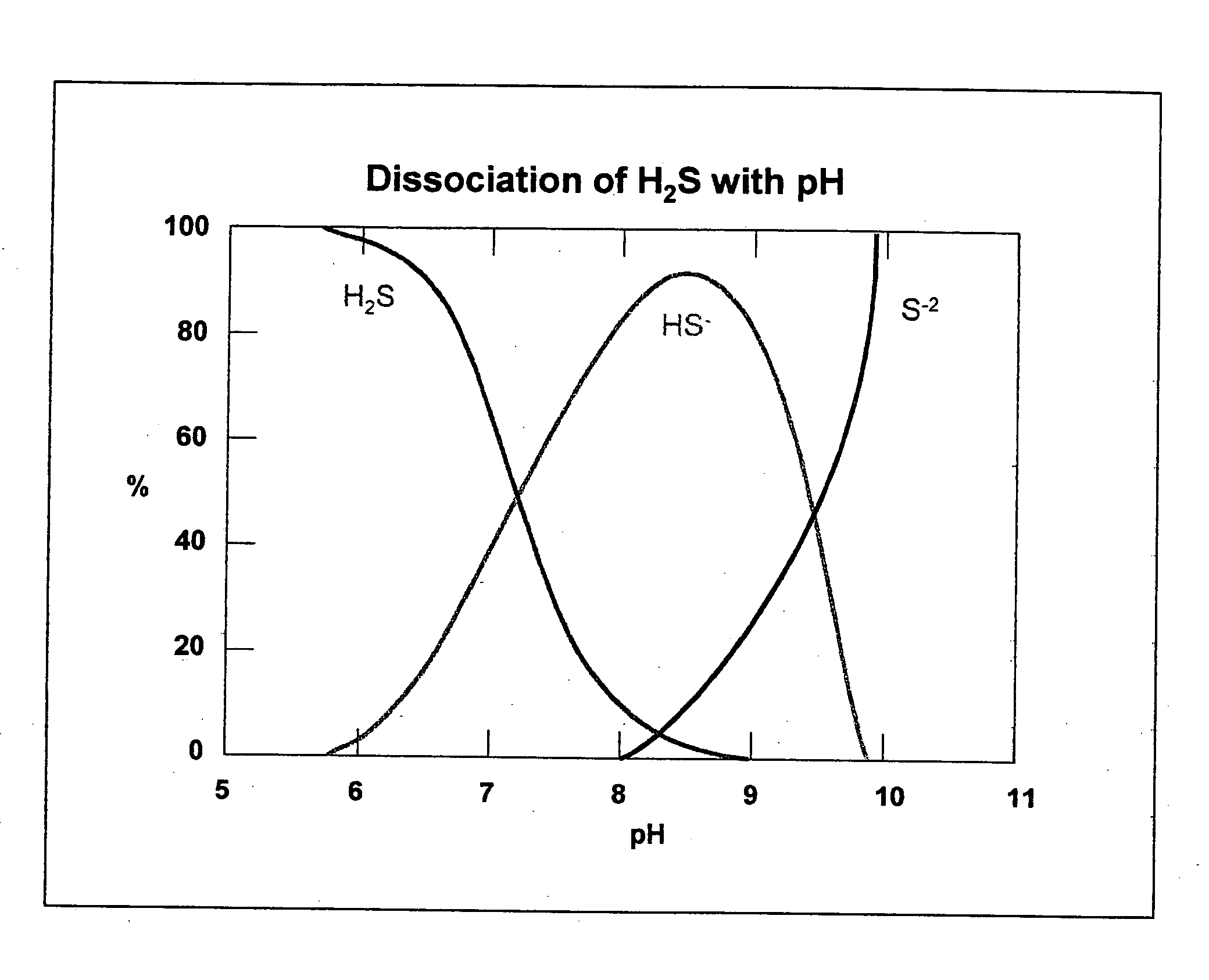
A synergistic composition is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of nitrate salt, sulfide-consuming compound, pH-elevating compound, sulfide-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria, and sulfide-oxidizing enzyme. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating compound, which both decreases the amount of gaseous H2S and puts the aqueous phase into a pH range where naturally occurring bacteria can more easily metabolize the sulfide. The composition also includes one or more nitrate salts which will accomplish longer term prevention of odors. Specific bacteria are incorporated into the formulation to insure that the nitrate has the right type and amount of bacteria present to prevent formation of and / or consume sulfide. Specific enzymes are incorporated into the formulation to promote oxidation of sulfide.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Metal modified active carbon fiber electrode and method for removing nitrate thereby
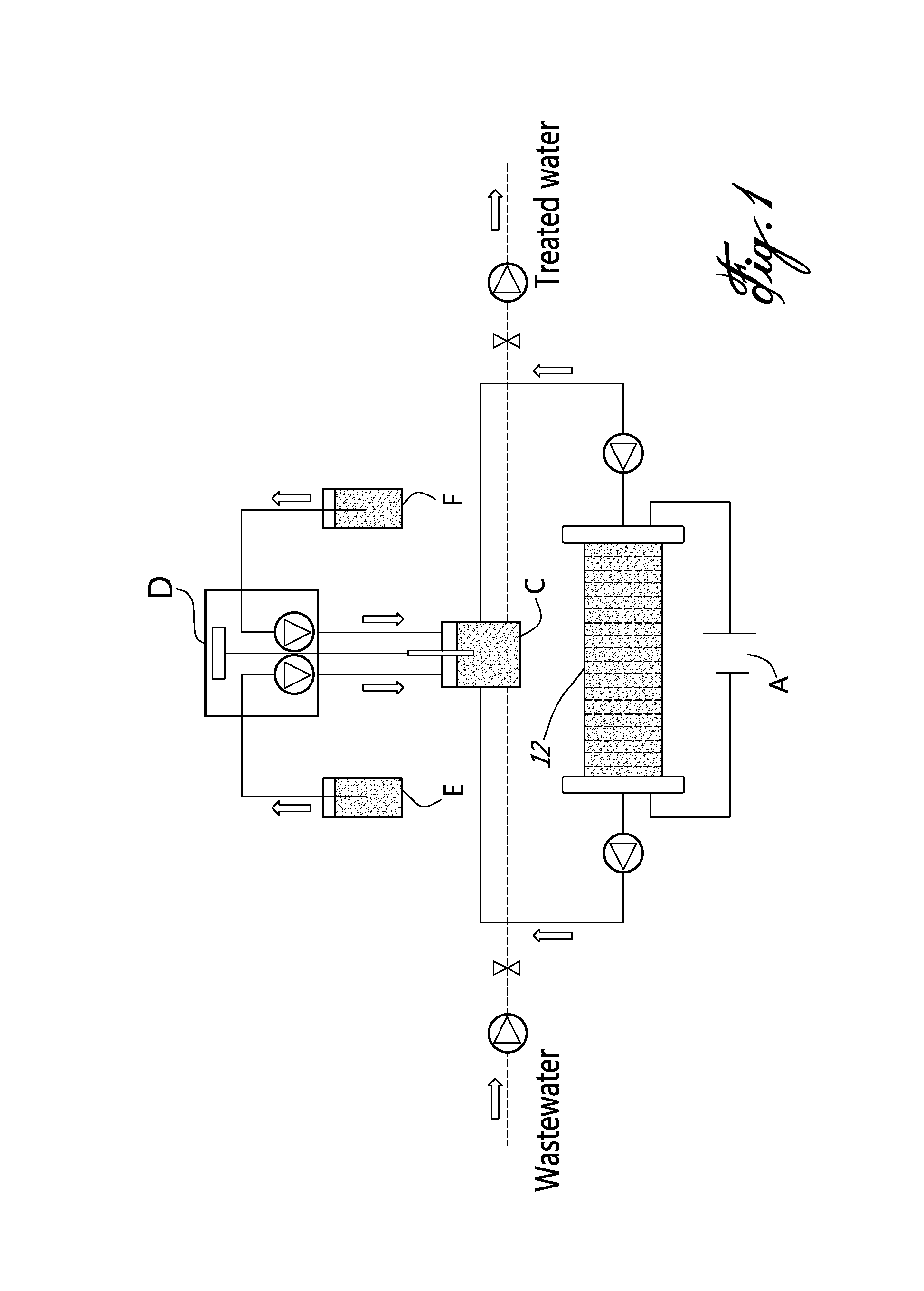
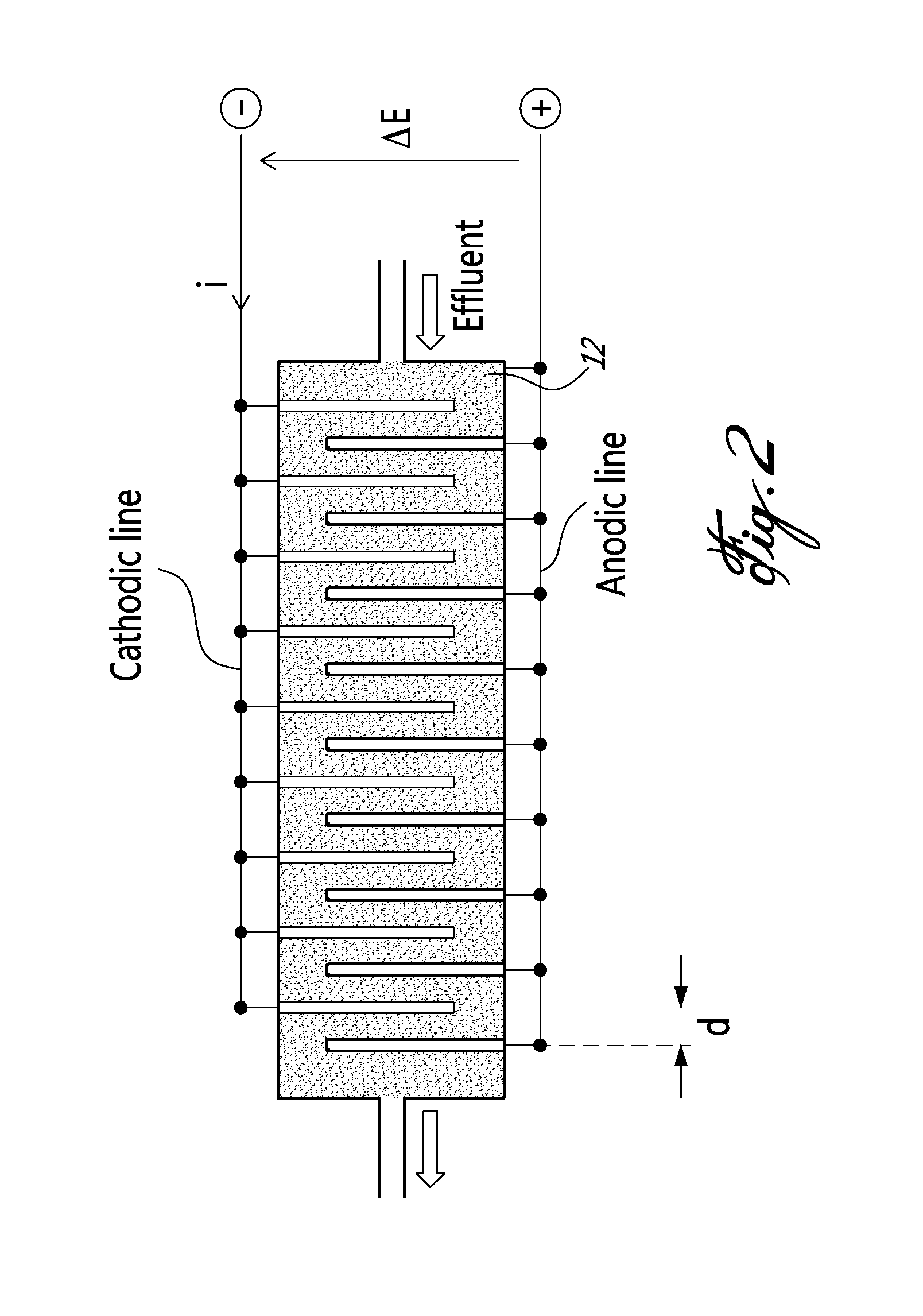
The invention, belonging to water treatment technical field, discloses the electric pole used for removing nitrate in water. The invention uses one of noble metals (palladium, platinum, gold, rhodium, and ruthenium) and one of non noble metals (copper, tin, indium, zinc and silver) to modify the activated carbon fiber and make the electric pole. The method uses the said electric pole as negative pole, and uses graphite and lead oxide as anode, deoxidizing the nitrate at the condition of energisation. The electric pole is cheap and high activity, and the invention is simple operation, convenient management and suits for small-scale decentralized feedwater treatment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of reducing nitrosamine content in tobacco leaves
InactiveUS7549425B2Inhibit productionReduce contentTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Nitrate reduction
InactiveUS6030520APhotography auxillary processesFrom normal temperature solutionsNitriteMetal catalyst
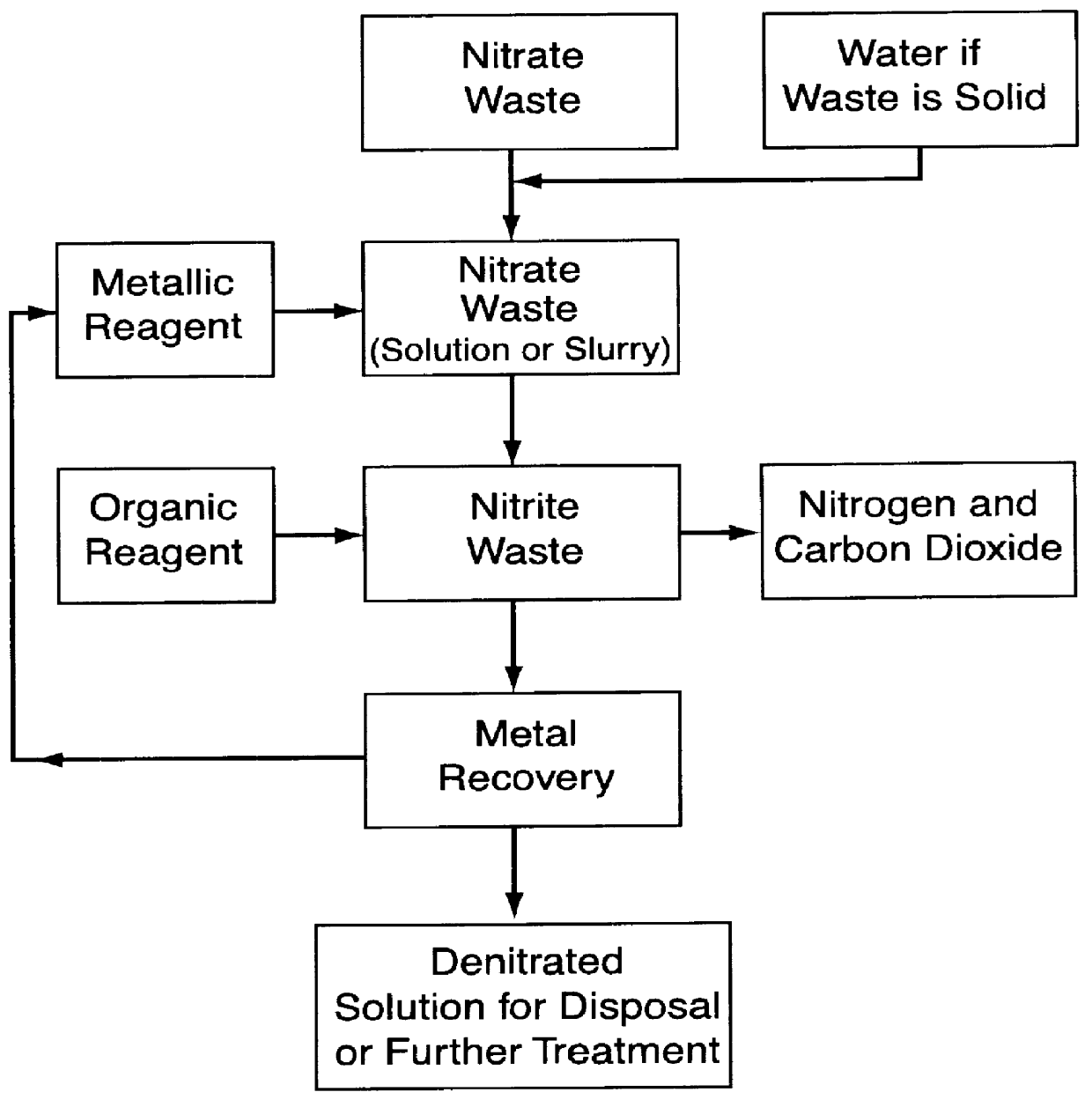
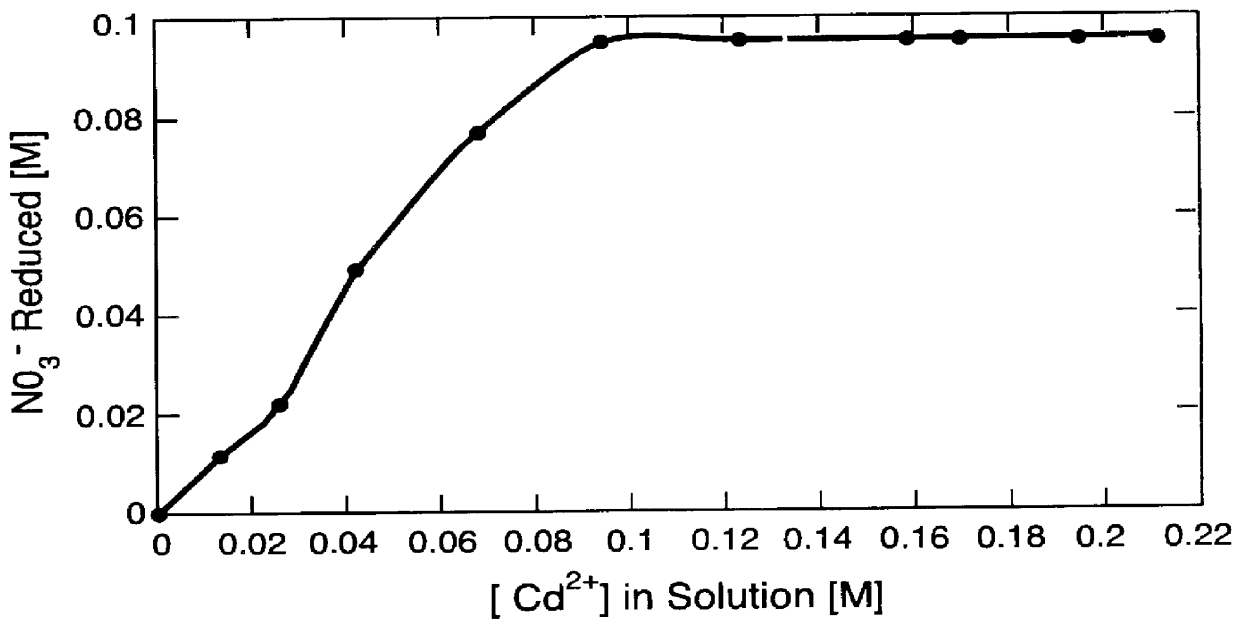
Nitrates are reduced to nitrogen gas by contacting the nitrates with a metal to reduce the nitrates to nitrites which are then contacted with an amide to produce nitrogen and carbon dioxide or acid anions which can be released to the atmosphere. Minor amounts of metal catalysts can be useful in the reduction of the nitrates to nitrites. Metal salts which are formed can be treated electrochemically to recover the metals.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Removing odoriferous sulfides from wastewater
ActiveUS7285217B2Promote growthInhibition productionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsSpecific enzymeWaste stream
A synergistic composition is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of nitrate salt, sulfide-consuming compound, pH-elevating compound, sulfide-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria, and sulfide-oxidizing enzyme. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating compound, which both decreases the amount of gaseous H2S and puts the aqueous phase into a pH range where naturally occurring bacteria can more easily metabolize the sulfide. The composition also includes one or more nitrate salts which will accomplish longer term prevention of odors. Specific bacteria are incorporated into the formulation to insure that the nitrate has the right type and amount of bacteria present to prevent formation of and / or consume sulfide. Specific enzymes are incorporated into the formulation to promote oxidation of sulfide.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method for strengthening indigenous microbes and improving oil recovery by improving microbial florae in oil deposit
The invention provides a method for strengthening indigenous microbes and improving oil recovery by improving microbial florae in an oil deposit. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) analyzing composition of microbial florae in the oil deposit; and (2) introducing exogenous microbes into the oil deposit according to an analysis result, so that the oil deposit with the introduced exogenous microbes contains the following microbes: hydrocarbon-oxiding bacteria, fermentative bacteria, heterotrophic bacteria, methanogenic bacteria, sulphate-reducing bacteria, and nitrate-reducing bacteria. Due to the adoption of the method provided by the invention, by adding the exogenous microbes into the oil deposit, the structure of the microbial florae in the oil deposit is improved, the function of the microbial florae in the oil deposit is strengthened, as a result, the oil displacement effect is improved, and the application range of microbial oil recovery technology is enlarged.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
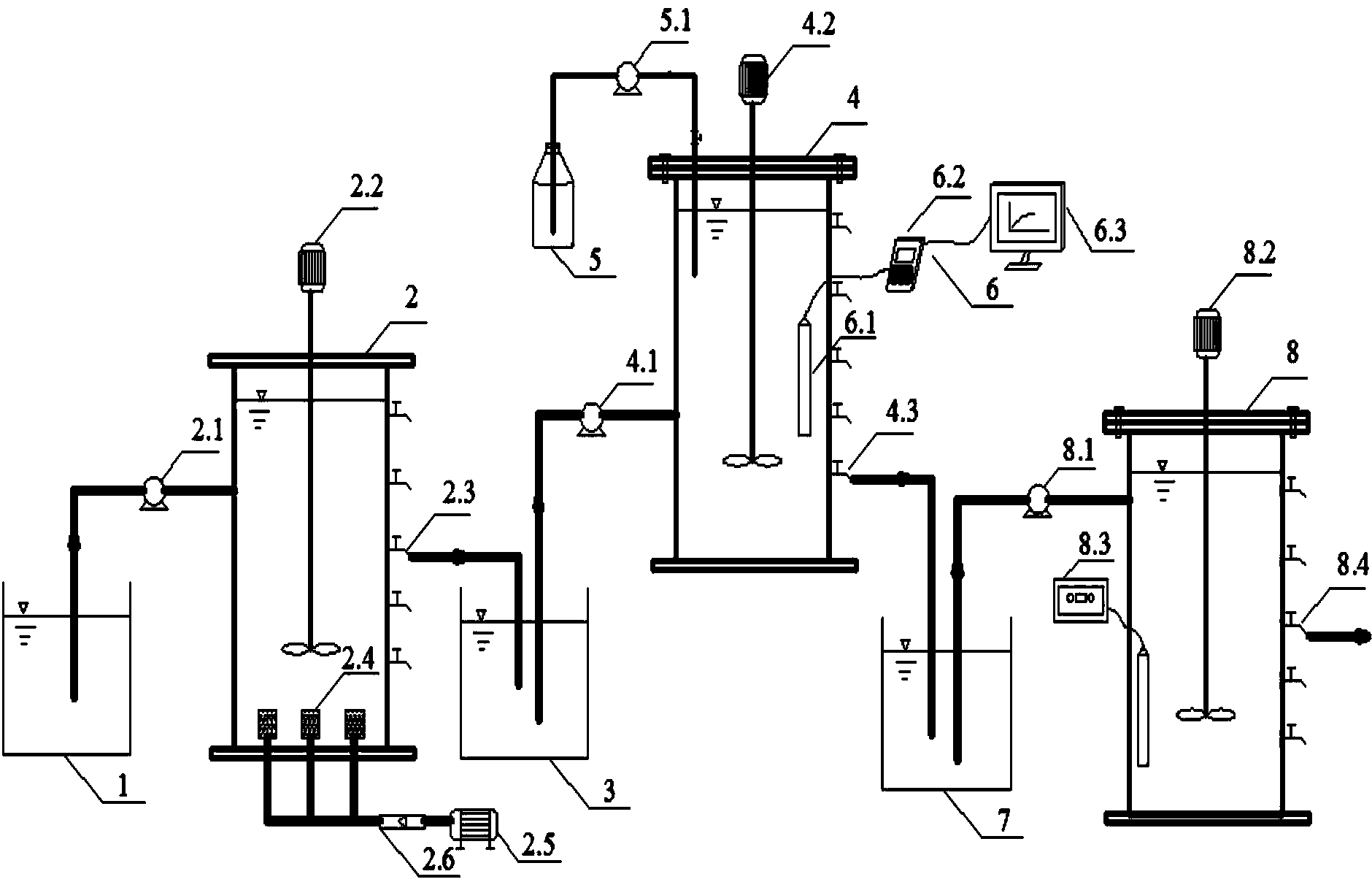
Method for enhanced nitrogen removal of tidal flow-horizontal subsurface flow hybrid constructed wetland and system thereof
InactiveCN102923860AStrong reductionAvoid secondary pollutionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentConstructed wetlandNitration
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment and specifically relates to a method for enhanced nitrogen removal of a tidal flow-horizontal subsurface flow hybrid constructed wetland and a system thereof. The system orderly comprises a non-powered automatic water intake device (8), a tidal-flow constructed wetland bed, a non-powered automatic water drainage device (2) and a horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland bed. The tidal-flow constructed wetland which is high in ammonia nitrogen oxidation effect and the horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland which is excellent in nitrate reduction capability are rationally combined into one system by thoroughly utilizing the characteristics of the aerobic environment of the former and the anaerobic environment of the latter; therefore, conditions are created for thorough nitration / denitrification; and simultaneously, a horizontal subsurface-flow wetland slow-release carbon source enhanced region (15) and a backflow well (19) are arranged in the horizontal subsurface-flow wetland bed, so that enhanced removal of total nitrogen in the sewage can be realized and secondary pollution on the carbon source is avoided at the same time.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
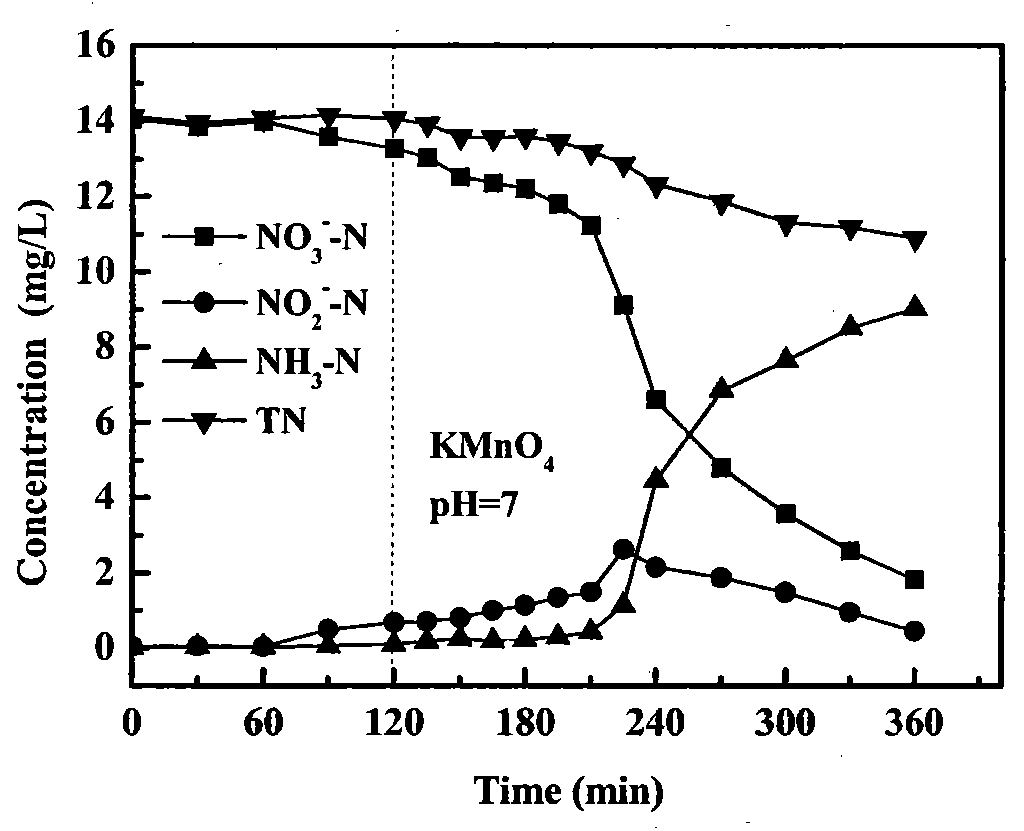
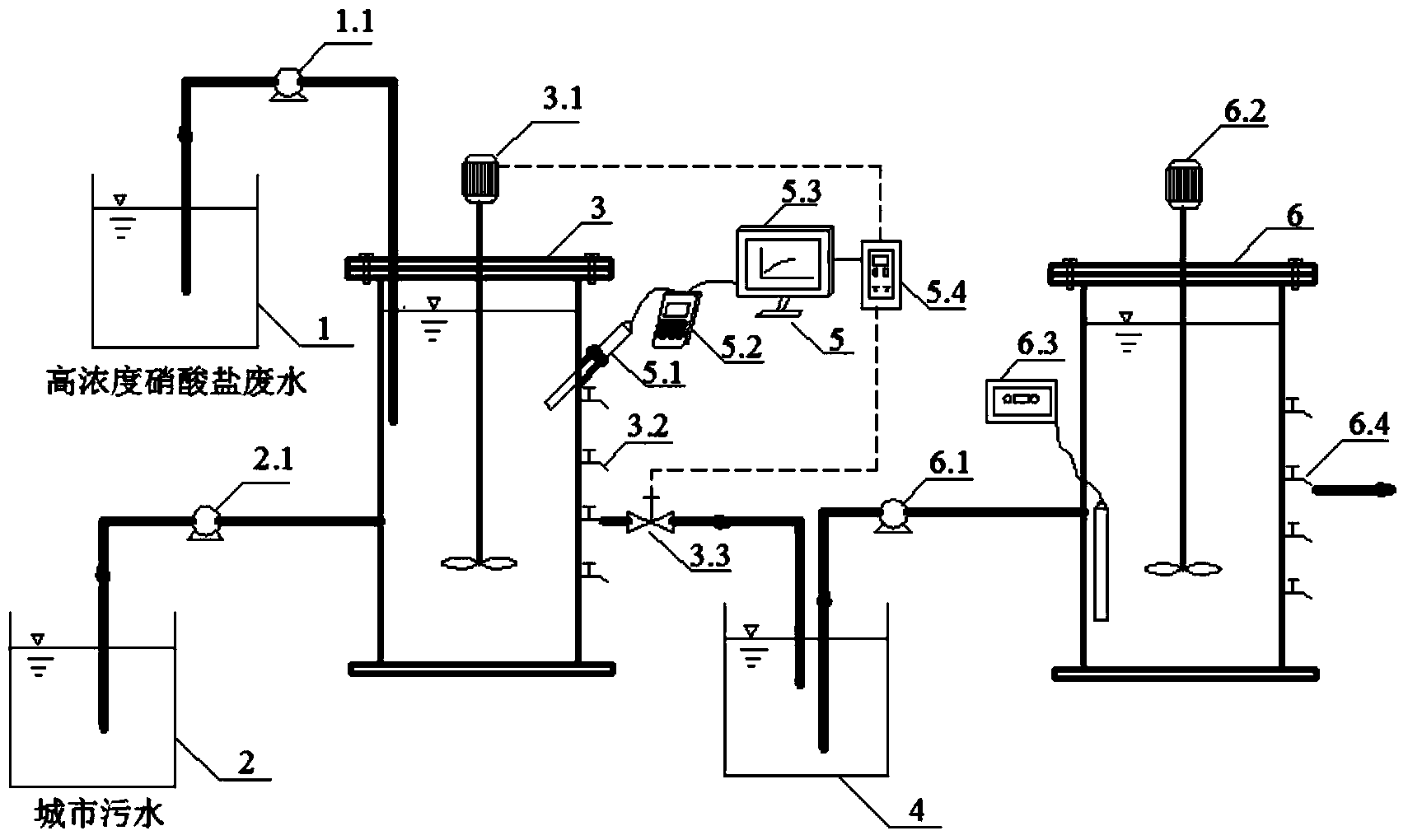
Method for treating high-concentration nitrate waste water and municipal sewage through denitrification anaerobic ammonium oxidation SBR
ActiveCN104276656AStable reaction matrixImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyWater contaminantsBiological treatment apparatusHigh concentrationLead nitrate
The invention provides a method for treating high-concentration nitrate waste water and municipal sewage through denitrification anaerobic ammonium oxidation SBR, belonging to the field of sewage biotreatment. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, culturing and acclimating denitrifying bacteria population and anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria population which have inadequate denitrification characteristic, then inoculating anaerobic ammonium oxidation sludge and denitrifying sludge with high nitrite accumulation rate in the same reactor, leading nitrate waste water and municipal sewage to flow in denitrification anaerobic ammonium oxidation SBR reactor at a certain ratio, performing anaerobic ammonium oxidation to nitrite accumulated during reduction of nitrite and ammonium nitrogen in the municipal sewage to generate nitrogen gas and synchronously removing. According to the method, nitrate generated during anaerobic ammonium oxidation can be reduced through denitrifying bacteria without the condition of adding a carbon source, the nitrogen removal efficiency of a system can be improved, and the effective route for realizing sewage nitrogen removal with high efficiency and low energy consumption can be provided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Laterosporo short bacillus, and its fermentating process and use
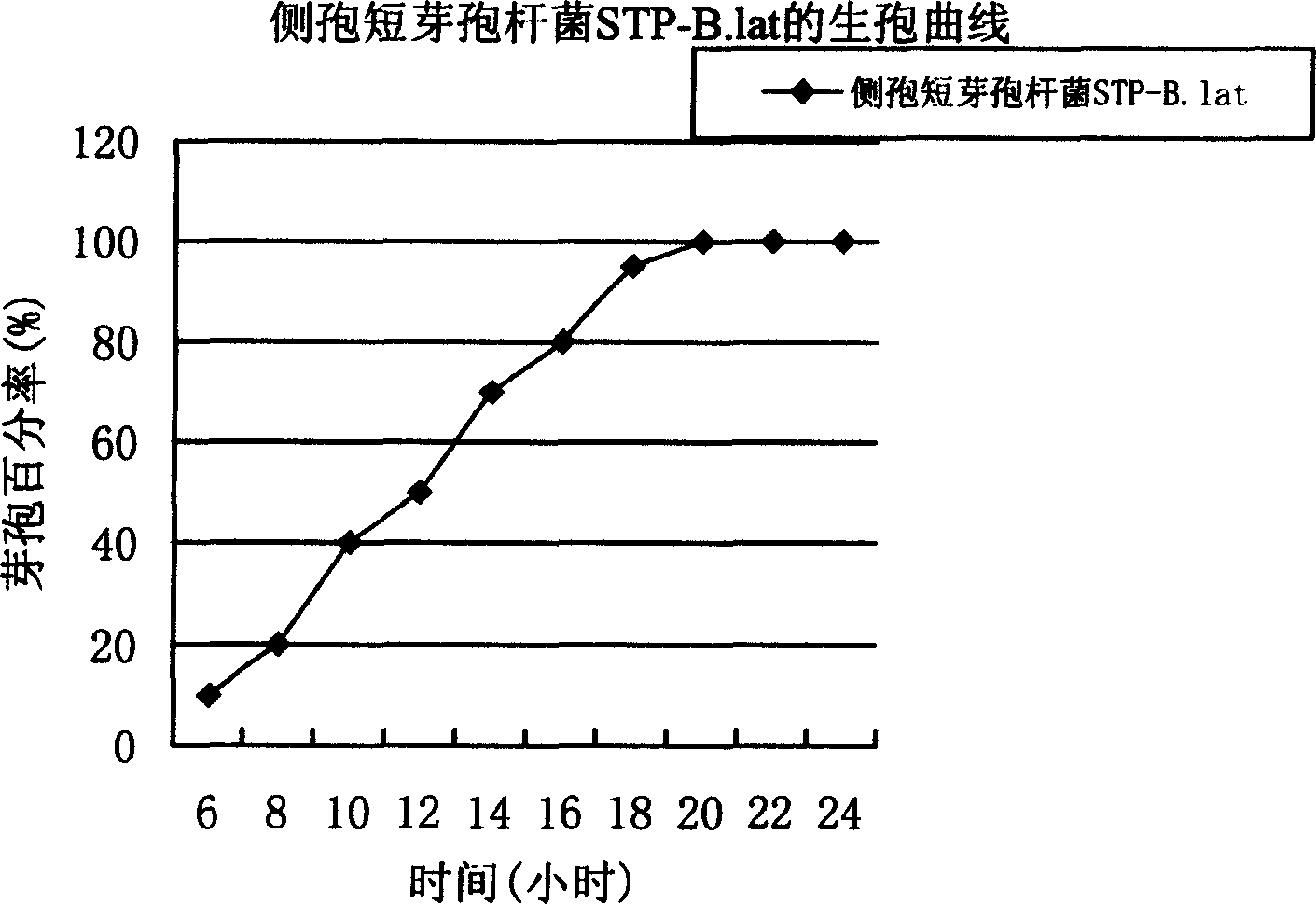
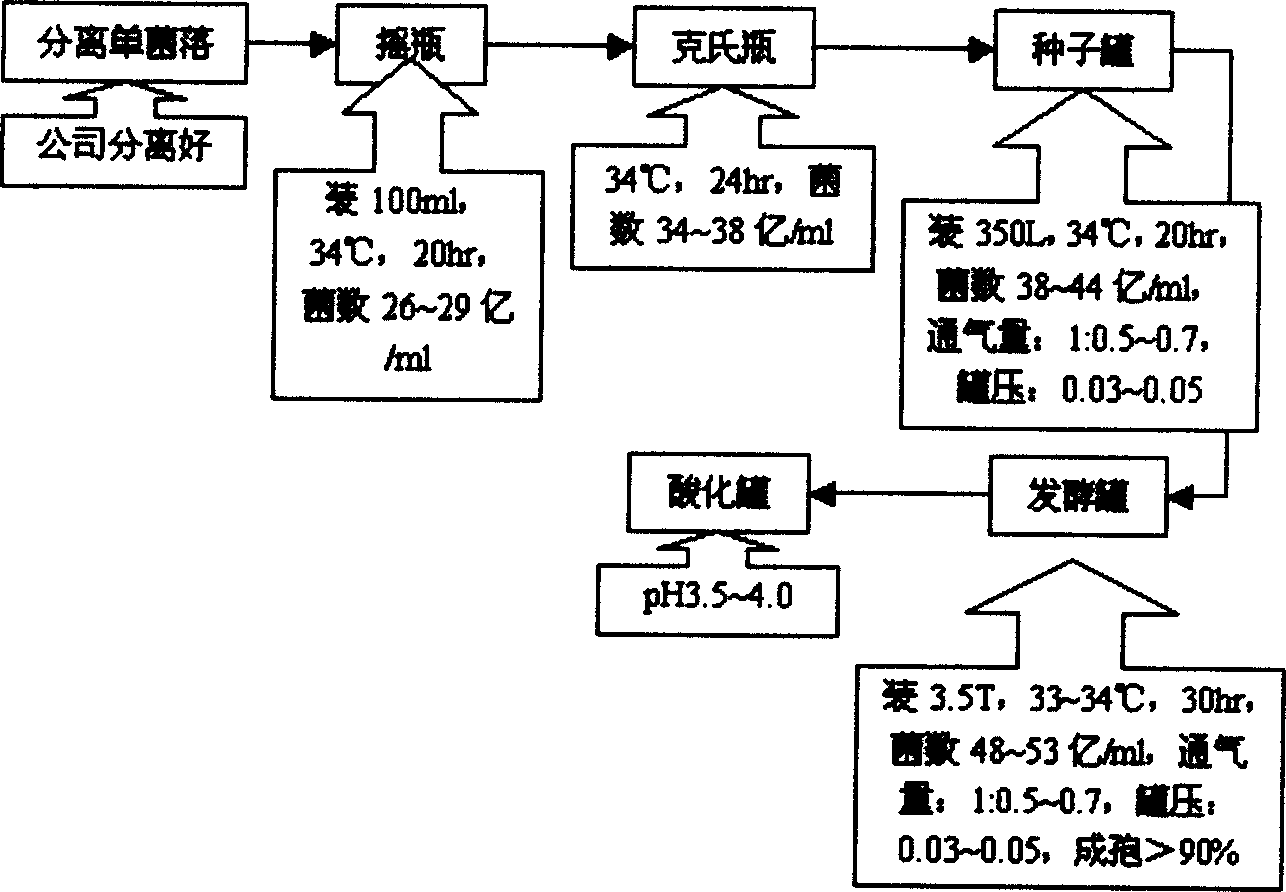
The invention provides a kind of Brevibacillus laterosporus (STP-B.latCGMCCNo.1119), the character follows this. G+, haulm shape, the shape is (0.4-0.5)*(2-2.5)mu. The spore adnation is from neutrality to sub-neutrality. The spore bursa will enlarge. Most of the spore is vertebra aitch, the remainder is disciform. VP-, ph value of culture fluid is 7.2, amylolysis-, gelatin dispergation-, decomposition casein+, katalase+, oxidase-, cirate -, dextrose aerogenesis-, dextrose acidgenesis+, L-arabinose acidgenesis-, xylose acidgenesis-, mannit acidgenesis+, azotate deocidisation+, methyl red+, pH5.7 growth+.
Owner:SHENGTAIPING BIOLOGICAL ENG TECH BEIJING
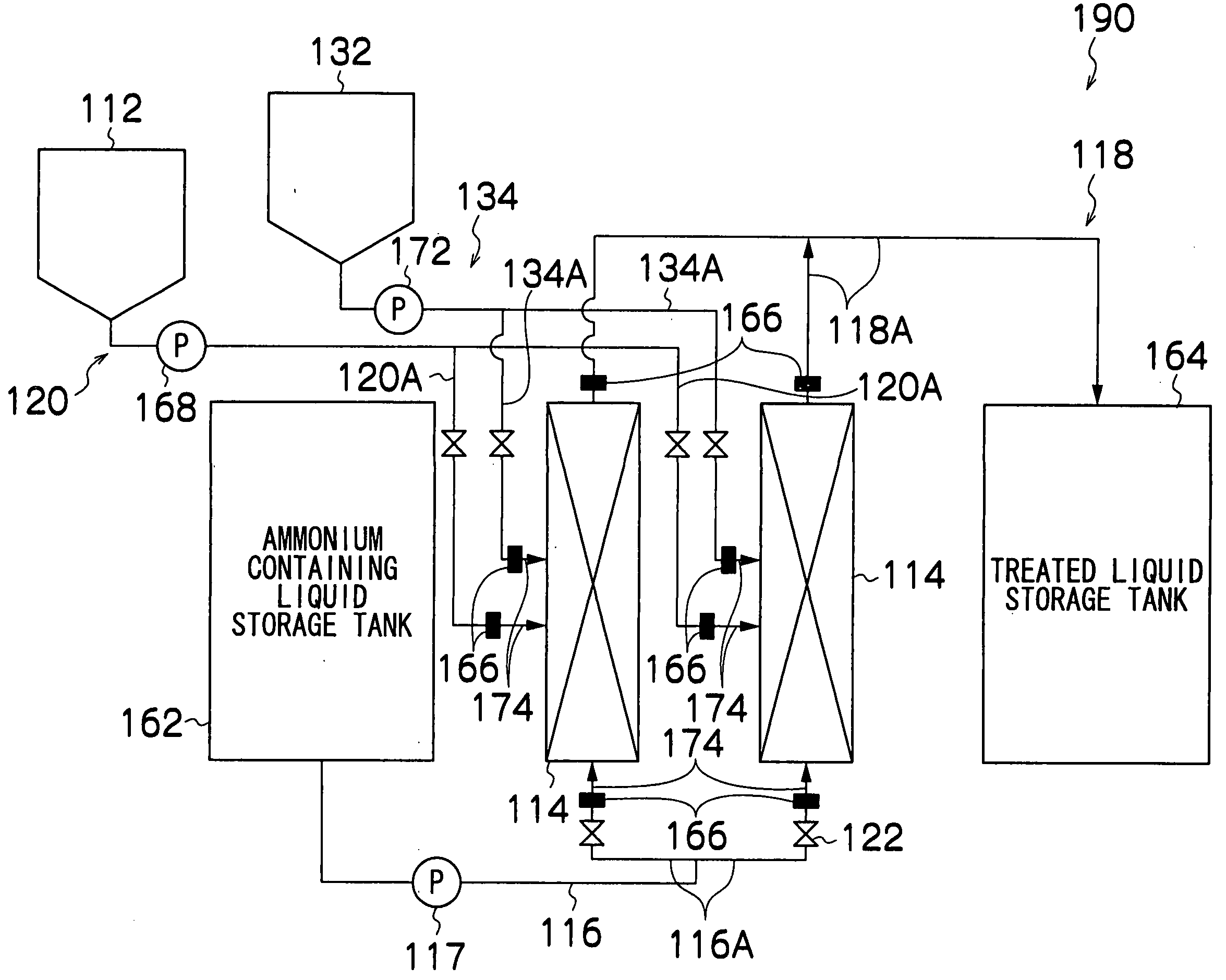
Process and equipment for treating ammonium containing liquid
ActiveUS20060191846A1Low costConstantly stableOther chemical processesWater contaminantsReduction treatmentNitrite concentration
The process for treating an ammonium containing liquid by denitrification treatment of an ammonium containing liquid containing at least ammonium comprises carrying out nitrate reduction treatment of reducing nitrate contained in or added to the ammonium containing liquid to nitrite, and carrying out anaerobic ammonium oxidation treatment of simultaneously anaerobically denitrifying nitrite produced in the nitrate reduction treatment and ammonium contained in the ammonium containing liquid by anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
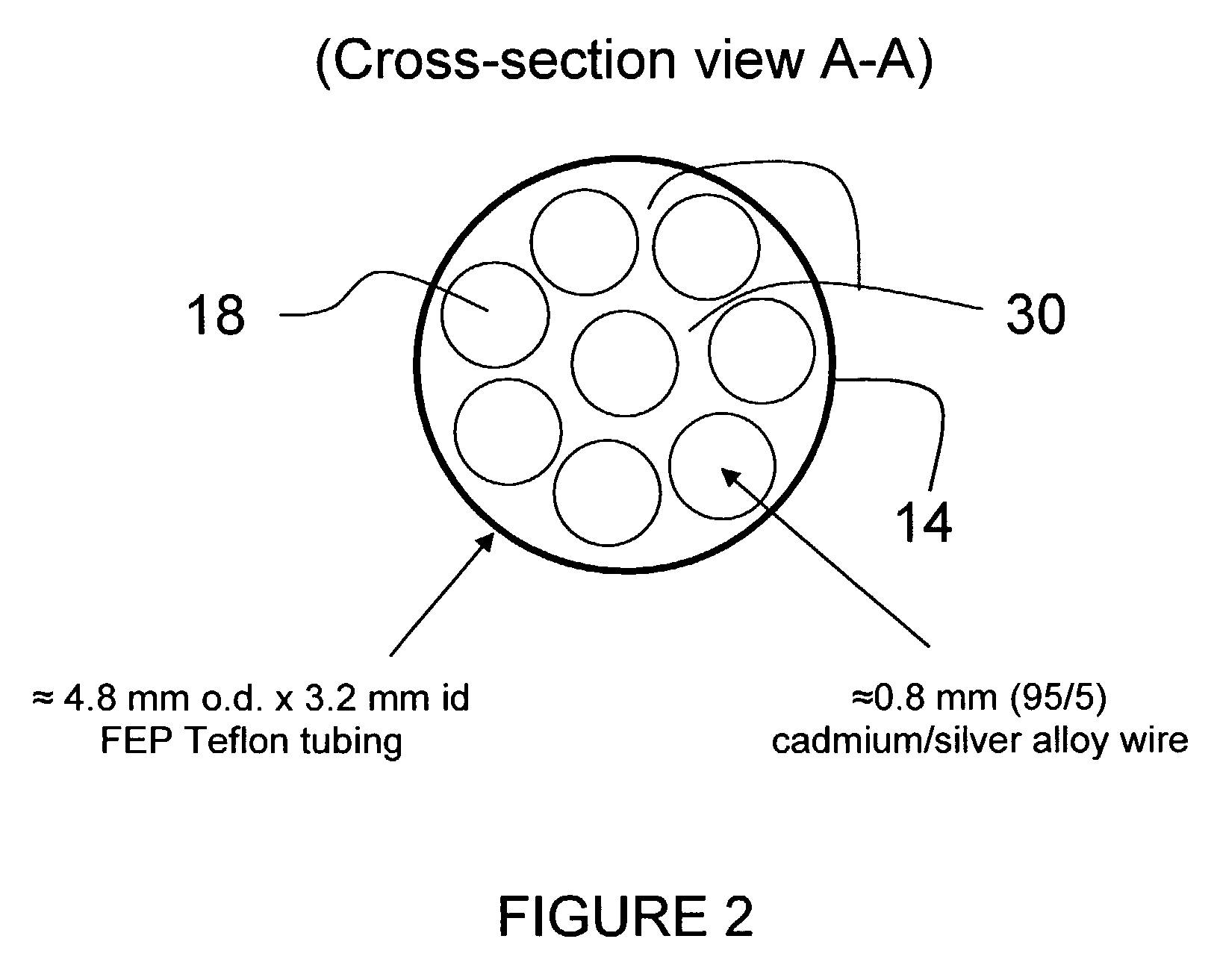
Reduction device for nitrate determination
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Device and method for treating low-carbon-nitrogen-ratio urban sewage by virtue of half nitrification/partial denitrification/anaerobic ammonium oxidation
ActiveCN104291443AReduce energy consumptionAccumulation and stabilityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrationOxidative treatment
The invention discloses a device and method for treating low-carbon-nitrogen-ratio urban sewage by virtue of half nitrification / partial denitrification / anaerobic ammonium oxidation, belonging to the field of sewage treatment. The device comprises an urban domestic sewage tank, a half nitrification reactor, a first intermediate water tank, a partial denitrification reactor, an external carbon source storage tank, a partial denitrification online monitoring and control system, a second intermediate water tank and an anaerobic ammonium oxidation reactor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly introducing domestic sewage into the half nitrification reactor, oxidizing part of ammonia nitrogen in the domestic sewage into nitrate nitrogen by virtue of aeration, introducing effluent into the partial denitrification reactor, reducing nitrate into nitrite by using a small amount of an external carbon source, and introducing the effluent into the anaerobic ammonium oxidation reactor for denitrification. By adopting the device and the method disclosed by the invention, stable and efficient denitrification of the low-carbon-nitrogen-ratio urban sewage can be achieved, and the problems that the existing short-cut nitrification nitrite accumulation of the urban domestic sewage is unstable and an existing anaerobic ammonium oxidation process is low in denitrification efficiency can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nitrate and nitrite rapid testing paper and use thereof
InactiveCN1645114AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical methods analysisNitriteReducer
A test paper for fast measuring out nitrate and nitrite is composed of colour display test paper soaked with mixture in the same volume of diazotization reagent and coupling reagent, and reaction test paper coated with nitrate reducer, the test paper can provide quick detection of nitrate and nitrite contained in food or vegetables.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
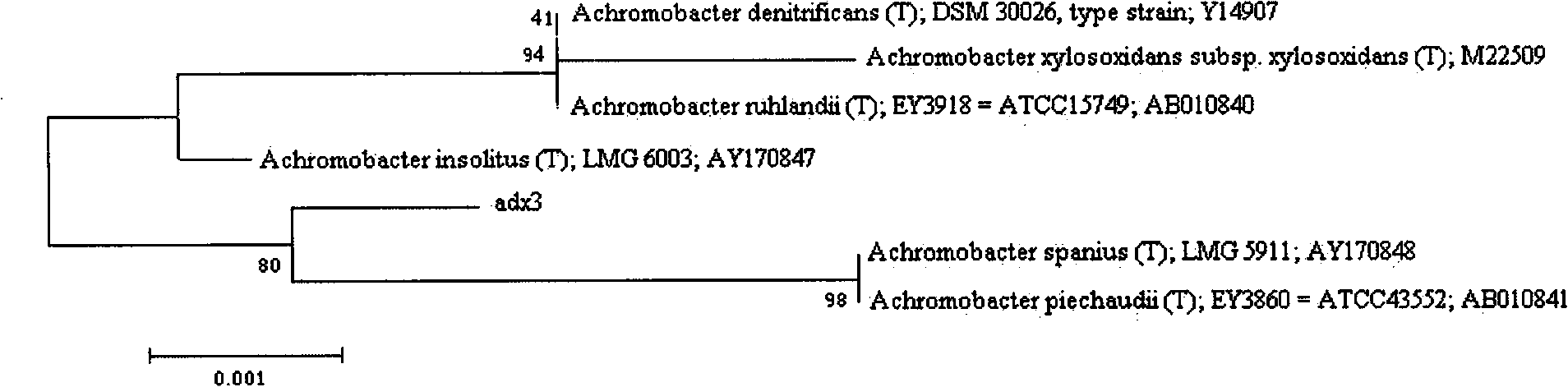
Achromobacter capable of degrading aniline and application thereof
InactiveCN101514330AGood self-flocculation propertiesImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsGram stain negativeWastewater
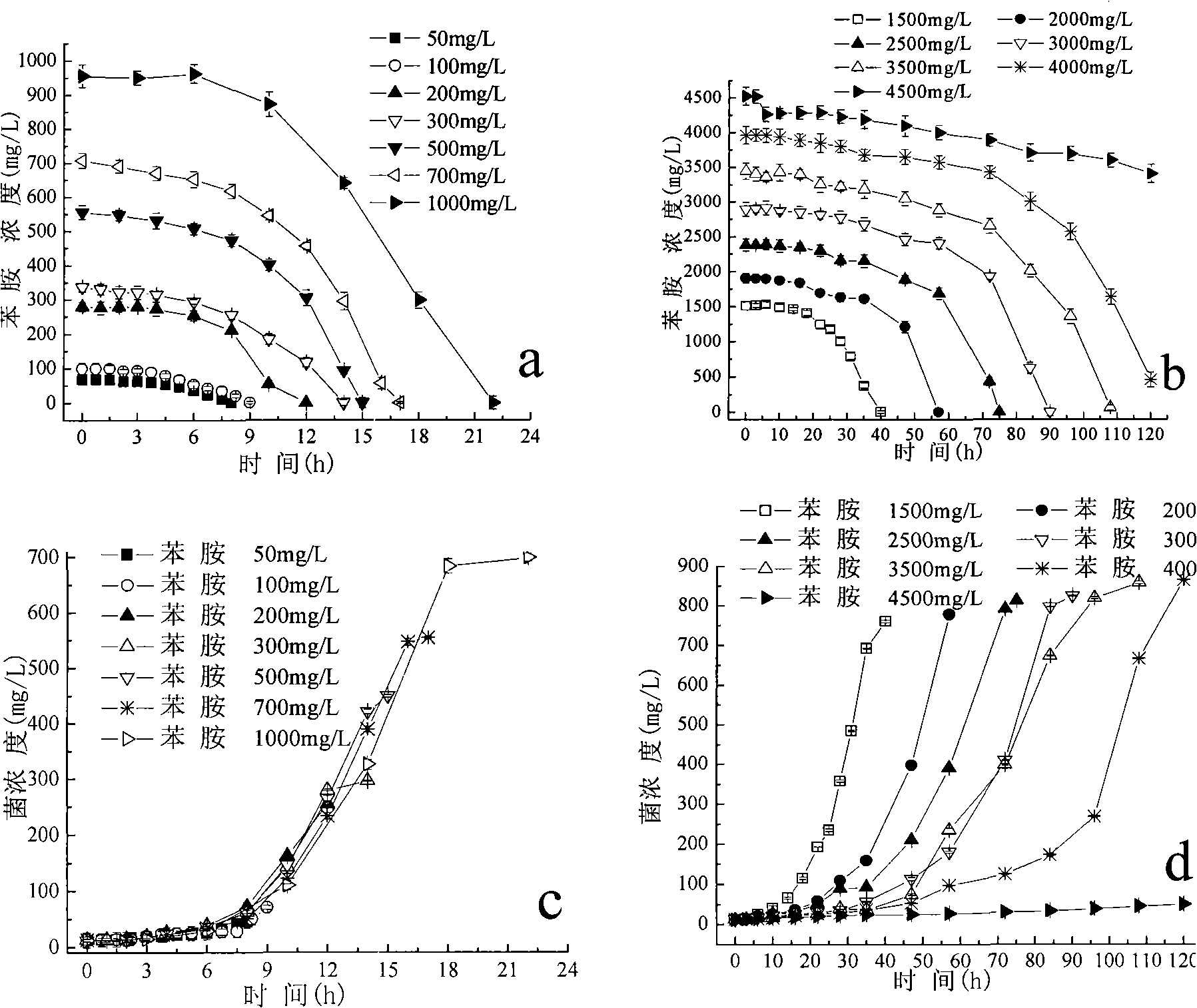
The invention discloses an achromobacter capable of degrading aniline, wherein the 16S rDNA of the achromobacter has a sequence of SEQ ID No.1. Colonies are yellow, round, smooth and humid with neat edges and convex bulges. Through electron microscope observation, the achromobacter does not have flagellum and spore bacteria; and under the observation of the electron microscope, the form of the achromobacter is a thicker bacillus which is gram staining negative and oxidase and catalase negative, and is reduced by nitrate to generate gas. The achromobacter can achieve the efficient degradation of aniline pollutants under an aerobic condition, the maximum tolerance concentration to the aniline is up to 4,500 milligrams per liter, the aniline of which the concentration is less than or equal to 4,000 milligrams per liter can be completely removed, thus the achromobacter plays an important role in the controlling practice of aniline industrial wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
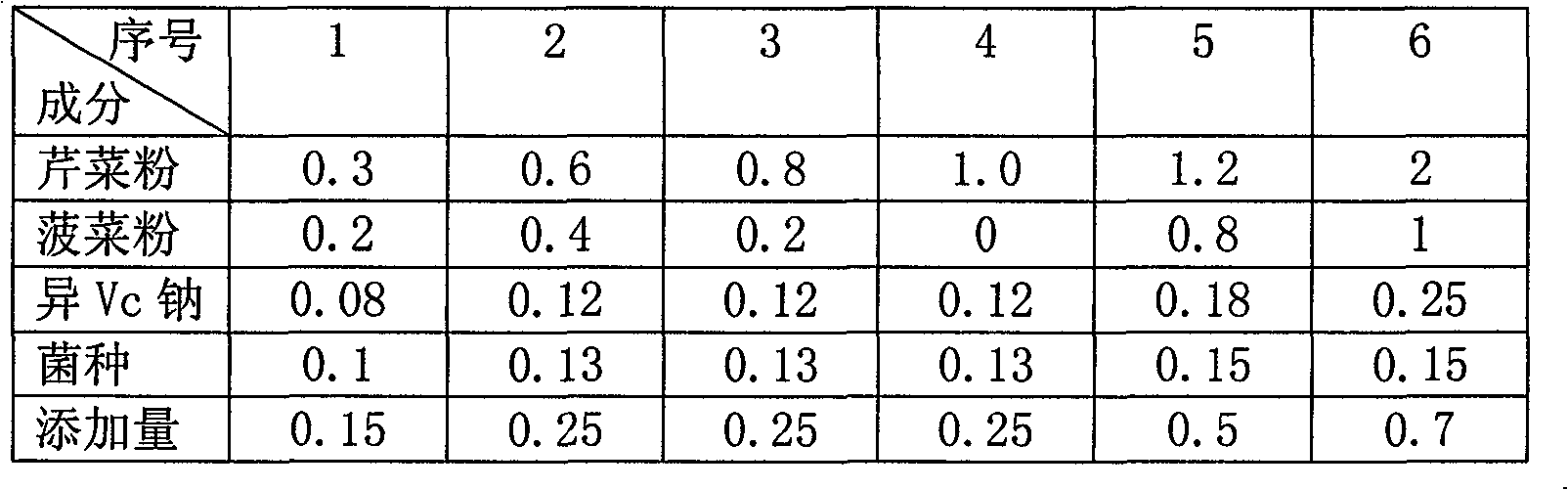
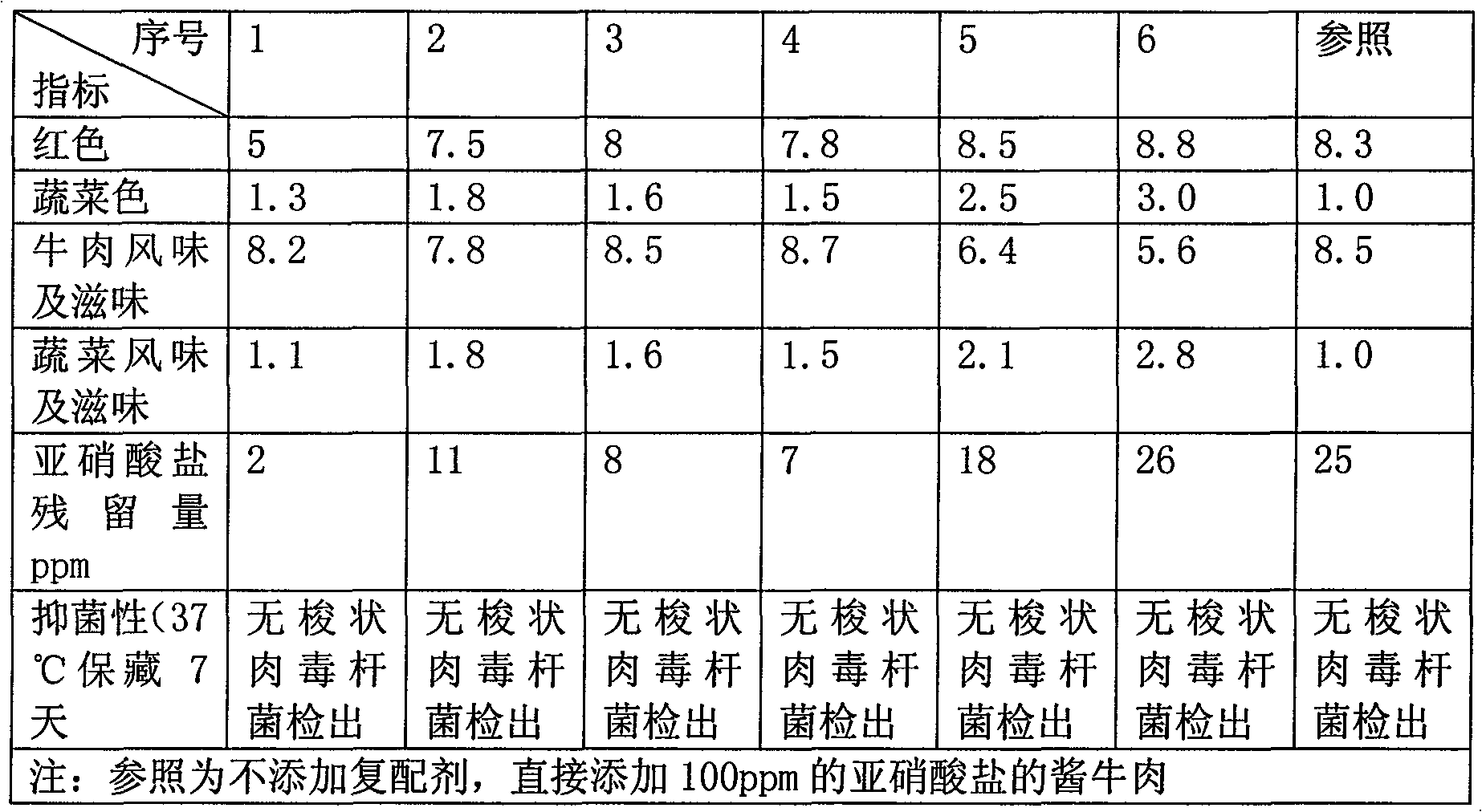
Green composite additive agent for sauced beef
InactiveCN101406296AExcellent color developmentImprove antioxidant capacityFood preparationSodium lactateEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a green composite additive for sauced beef, which is characterized in that the green composite additive is prepared by a composite curing agent and a composite spraying agent, wherein the composite curing agent contains 0.6 to 1.2 weight portions of celery powder, 0 to 0.4 weight portion of spinach powder, 0.08 to 0.15 weight portion of nitrate reducing bacteria and 0.08 to 0.015 weight portion of abnormal VC sodium; and the composite spraying agent contains 0.05 to 0.15 percent of tea polyphenol and 0.7 to 2 percent of sodium lactate aqueous solution. The composite additive is nutritious, healthy and widely applied, and not only can be applied to the sauced beef but also can be applied to meat products such as smoked sausages, smoked hams, fermented sausages, and so on. Moreover, the green composite additive accords with the requirements of consumers on safe and green foodstuffs, has larger realistic meaning in industrial production, provides a novel concept for production of the green meat products, and simultaneously creates good economic benefit for enterprises.
Owner:江苏迈斯克食品有限公司
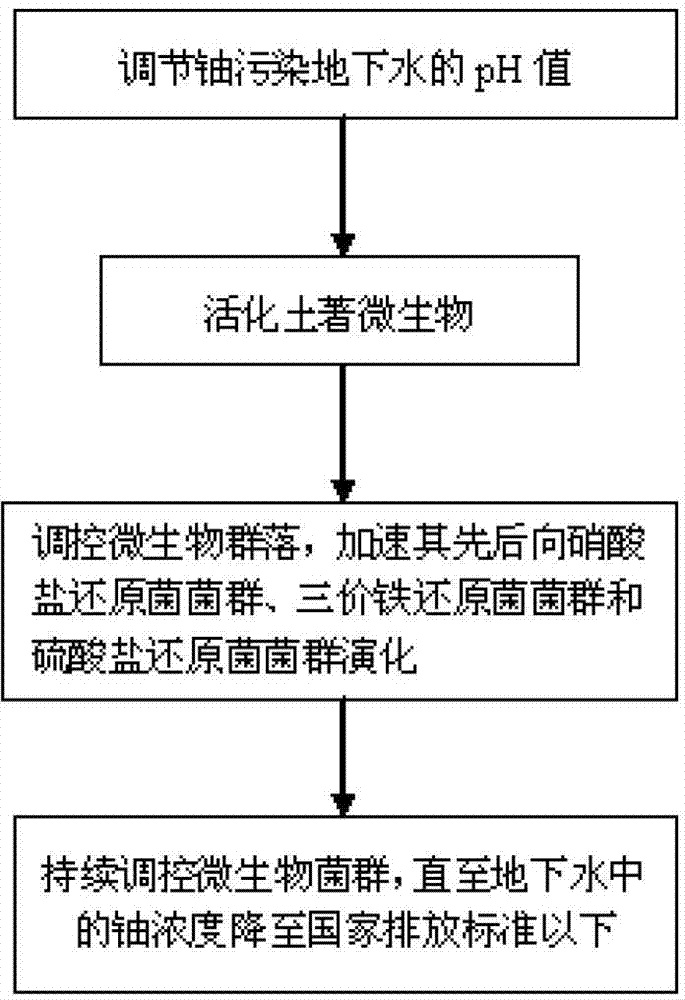
Method of using native function microflora to in-situ purify ground water polluted by uranium
ActiveCN103093847AEasy to operateIn situ repairRadioactive decontaminationSulfate-reducing bacteriaEmission standard
The invention relates to a method of using native function microflora to in-situ purify ground water polluted by uranium. The method translates transferable hexavalent uranium into nontransferable uranous uranium in the ground water through nitrate reducing bacteria flora, ferric iron reducing bacteria flora and sulfate reducing bacteria flora which are formed under the anaerobic condition by microorganism, and therefore the purpose of purifying the ground water polluted by the uranium is achieved. The specific implementation method comprises: (1) adjusting a potential of hydrogen (Ph) value of the ground water polluted by the uranium; (2) activating the microorganism in sediments; (3) regulating and controlling variation of the microflora, accelerating evolution of the nitrate reducing bacteria flora, the ferric iron reducing bacteria flora and the sulfate reducing bacteria flora by means of adding a carbon source, regulating oxidation reduction potential of the water polluted by the uranium and the like; (4) continuously regulating and controlling the microbial flora until uranium concentration in the ground water polluted by the uranium is reduced below the national emission standard and the purpose of purifying the groundwater polluted by the uranium is achieved. The method of using the native function microflora to in-situ purify the ground water polluted by the uranium solves in-situ purifying problem of the ground water polluted by the uranium, and has the advantages of being high in purifying efficient, short in period, simple in equipment, short in process procedure, low in purifying cost, strong in operability, free of secondary pollution, good in purifying effect and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
A method of removing nitrates from water by utilization of a zero-valent iron/oxidizing agent/zeolite synergetic system
ActiveCN104341055AHigh removal rateLow costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentReduction ActivityIron powder
A method of removing nitrates from water by utilization of a zero-valent iron / oxidizing agent / zeolite synergetic system is provided. The zero-valent iron is common iron powder. The oxidizing agent is a common oxidizing agent used in water treatment. The zeolite is natural zeolite or artificial zeolite. The method is characterized in that: the oxidizing agent in the system oxidizes and strips a passivation layer formed on the surface of the zero-valent iron to allow electrons in the zero-valent iron to be transferred continuously to the outside, so that the zero-valent iron maintains high reduction activity to reduce the nitrates into ammonia nitrogen. Then efficient selective absorption of the zeolite to the ammonia nitrogen is utilized to remove the ammonia nitrogen in the water body. The method is environmental friendly, simple, feasible, low in cost, and capable of being efficiently used for treatment of waste water containing nitrates of industrial enterprises and nitrate restoration and removal for underground water.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Single stage denitration
InactiveUS7011800B1Reduce needImprove processing efficiencyNitrogen compoundsDispersed particle separationSimple Organic CompoundsSingle stage
A system and method using superheated steam optionally augmented by oxygen for the reduction of nitrogen oxides present for reducing nitrogen oxides present in a wide variety of organic compounds. The system includes a single reaction vessel, or optionally, multiple reaction vessels in operational communication. Reduction takes place quickly when a steam / oxygen mixture is injected into the reaction vessel or vessels. Reducing additives are metered into the reaction vessel or vessels and / or provide energy input to reduce nitrates to nitrogen. The oxygen, when used, allows for some oxidation of waste by-products and provides an additional offset for thermal requirements of operation.
Owner:STUDSVIK INC
Method and process for synchronously removing perchlorate and nitrate in drinking water
InactiveCN103613210ASolve the problem of low pHSolve SO
<sub>4</sub>
<sup>2-</sup>
The problem of exceeding the standardWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentElectron donorNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method and process for synchronously removing perchlorate and nitrate in drinking water. In the method, perchlorate and nitrate in water are synchronously reduced through sulfur autotrophy and electrochemical hydrogen autotrophy coupling. The wastewater containing perchlorate and nitrate goes through a bio-membrane reactor taking sulfur particles as filler, and perchlorate and nitrate are partially reduced into chloride ions and nitrogen by taking elemental sulfur as an electron donor while H<+> and SO4<2-> are generated. A complex three-dimensional electrode-bio-membrane reactor taking a carbon medium as filler reduces H<+1> into H2 by use of an electrochemical process between a carbonaceous material and an electrode, and the rest perchlorate and nitrate are reduced into chloride ions and nitrogen by taking hydrogen as an electron donor. The method and process for synchronously removing perchlorate and nitrate in drinking water, provided by the invention, are economical and efficient and simple to operate.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method and system for electrochemical removal of nitrate and ammonia
InactiveUS20130168262A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove electrical activityCellsMachining electric circuitsAlloyElectrochemistry
An electrochemical method and system for removing nitrate and ammonia in effluents, using an undivided flow-through electrolyzer, said electrolyzer comprising at least one cell, each cell comprising at least one anode and one cathode, the cathode being in a copper / nickel based alloy of a high corrosion resistance and a high electroactivity for nitrate reduction to ammonia and the anode being a DSA electrode of a high corrosion resistance and a high electroactivity for ammonia oxidation to nitrogen in presence of chloride.
Owner:TRANSFERT PLUS S E C +1
Anaerobic molysite biological nitrogen removal process
InactiveCN103420480AIncrease concentrationAchieve removalTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesFerrous saltsElectron donor
The invention discloses an anaerobic molysite biological nitrogen removal process which is characterized in that denitrifying bacterium enrichment culture is taken as a biocatalyst, under the anaerobic condition, nitrate is taken as an electron acceptor, ferrous salt is taken as an electron donor, the nitrate is reduced into N2 in the same reactor, and the ferrous salt is oxygenized into ferric iron, wherein the molar ratio of the nitrate to the ferrous salt is 1.0 to 5.0, the reaction temperature is 20 to 35 DEG C, the pH value is 7.0 to 9.0, and the hydraulic retention time is 0.5 to 2.0 d. The process has the following advantages: 1, ferrous salt is taken as the electron donor, nitrate is taken as the electron acceptor, and waste is treated with waste, so that the purposes of removing nitrate-nitrogen pollutant and utilizing ferrous salt waste can be achieved; 2, no organic matter is required, so that the problem that the carbon source is not enough relatively during waste water biological nitrogen removal can be relieved effectively; 3, ferric iron, which is a ferrous salt oxidation product and has high values, can be reclaimed; 4, the concentrations of nitrate and ferrous salt, which can be treated, can reach 1500 mgN / L and 30000 mgFe / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device and method for treating high-concentration nitrate wastewater and urban sewage by partial denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation
ActiveCN104291529ASave organic carbon sourcesLow running costWater treatment parameter controlMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationNitrogen gas
The invention provides a device and a method for treating high-concentration nitrate wastewater and urban sewage by partial denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and belongs to the field of sewage bio-treatment. Nitrate wastewater and urban sewage enter a partial denitrification reactor, nitrate is reduced into nitrite through heterotrophic denitrification strains by using biodegradable organic carbon sources in the urban sewage, effluent enters an anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, and ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in the urban sewage are subjected to anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction to generate nitrogen. By adopting the device and the method, synchronous nitrogen removal of the high-concentration nitrate wastewater and the urban sewage is realized, additional carbon sources are not needed, the operational management is convenient, the operating cost is reduced, the consumption of energy is reduced, and the denitrification efficiency is high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
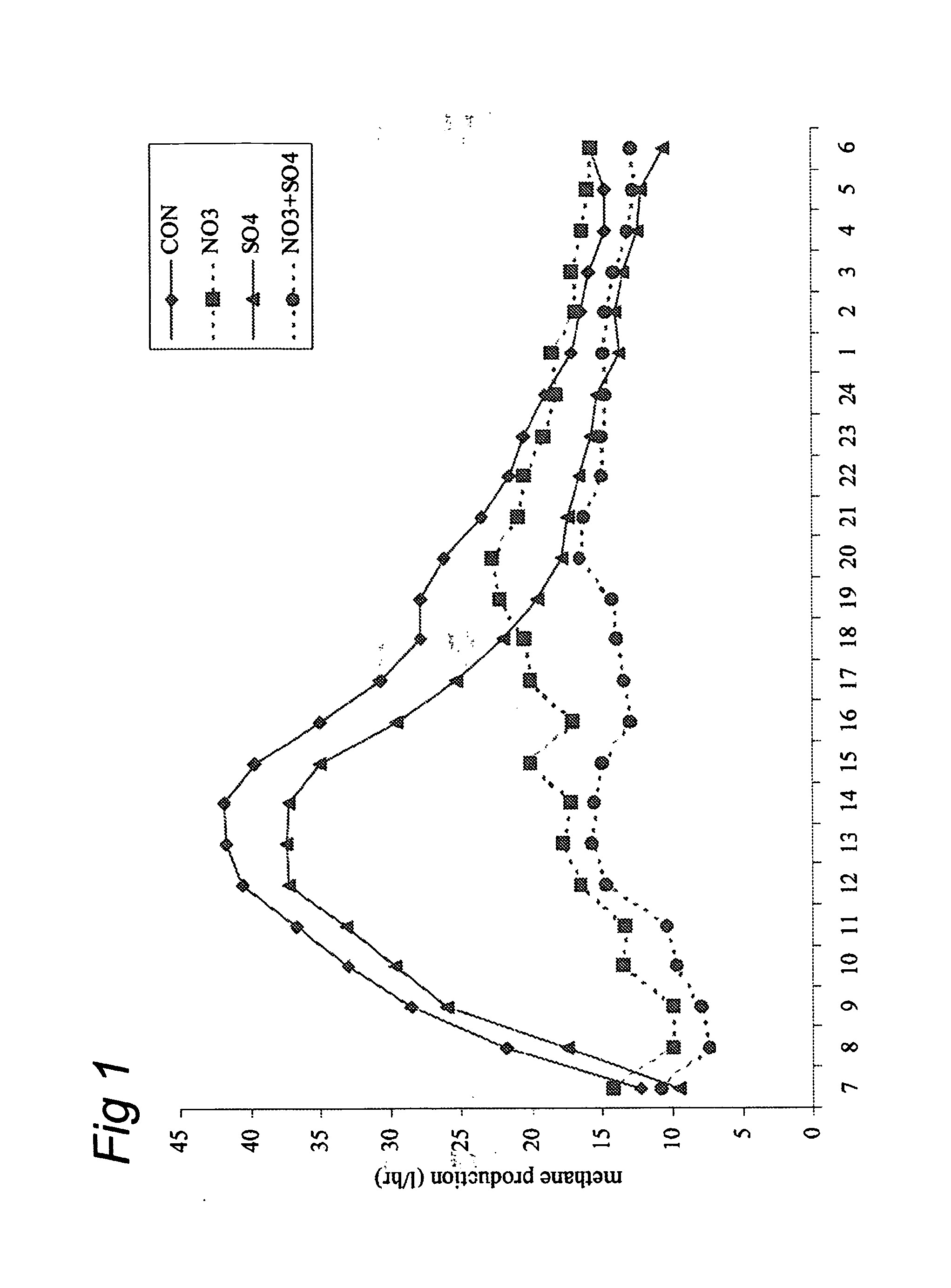
Compositions for reducing gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants
ActiveUS20120219527A1More energyEmission reductionBiocideMetabolism disorderNitrite poisoningFermentation
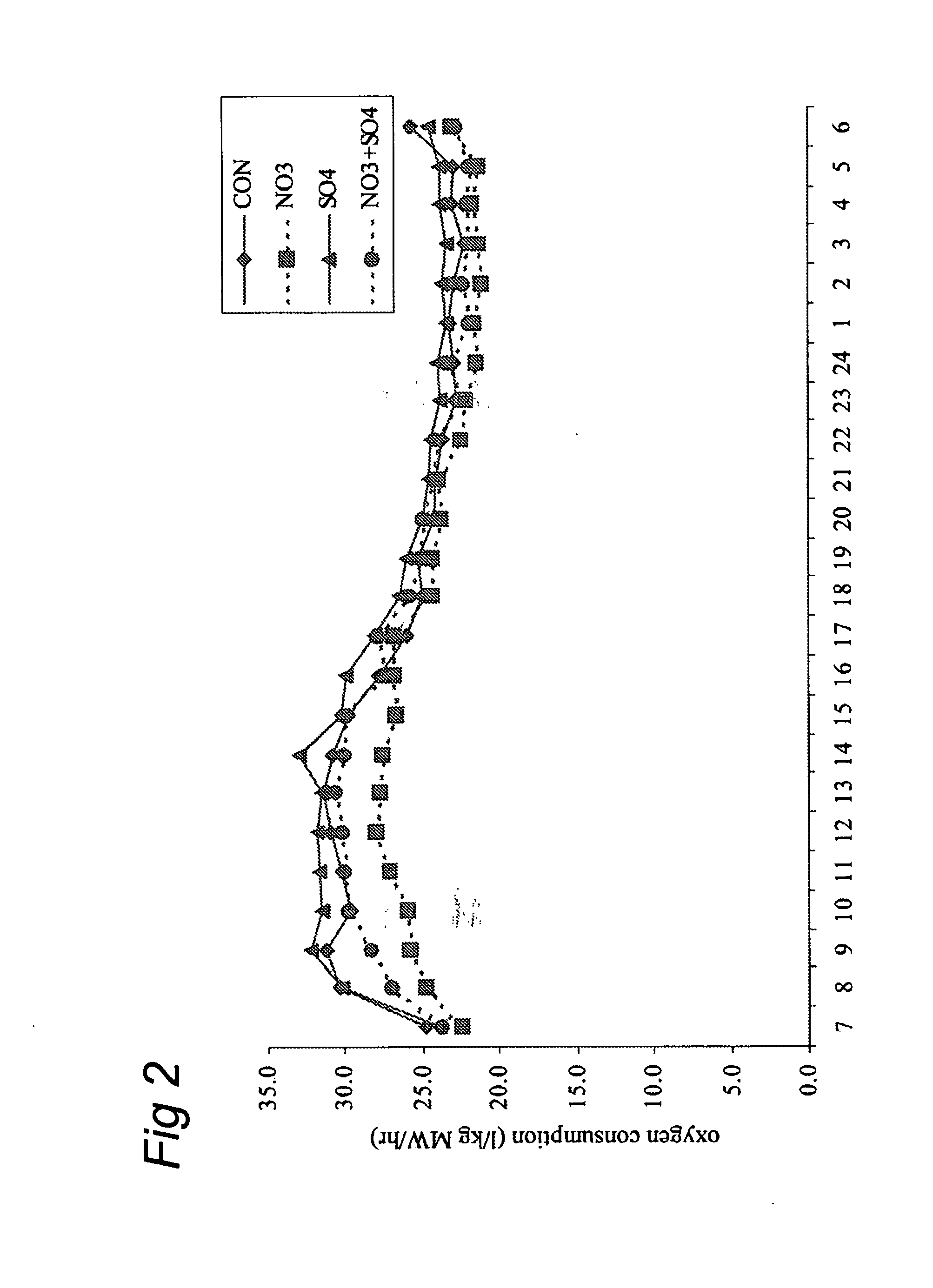
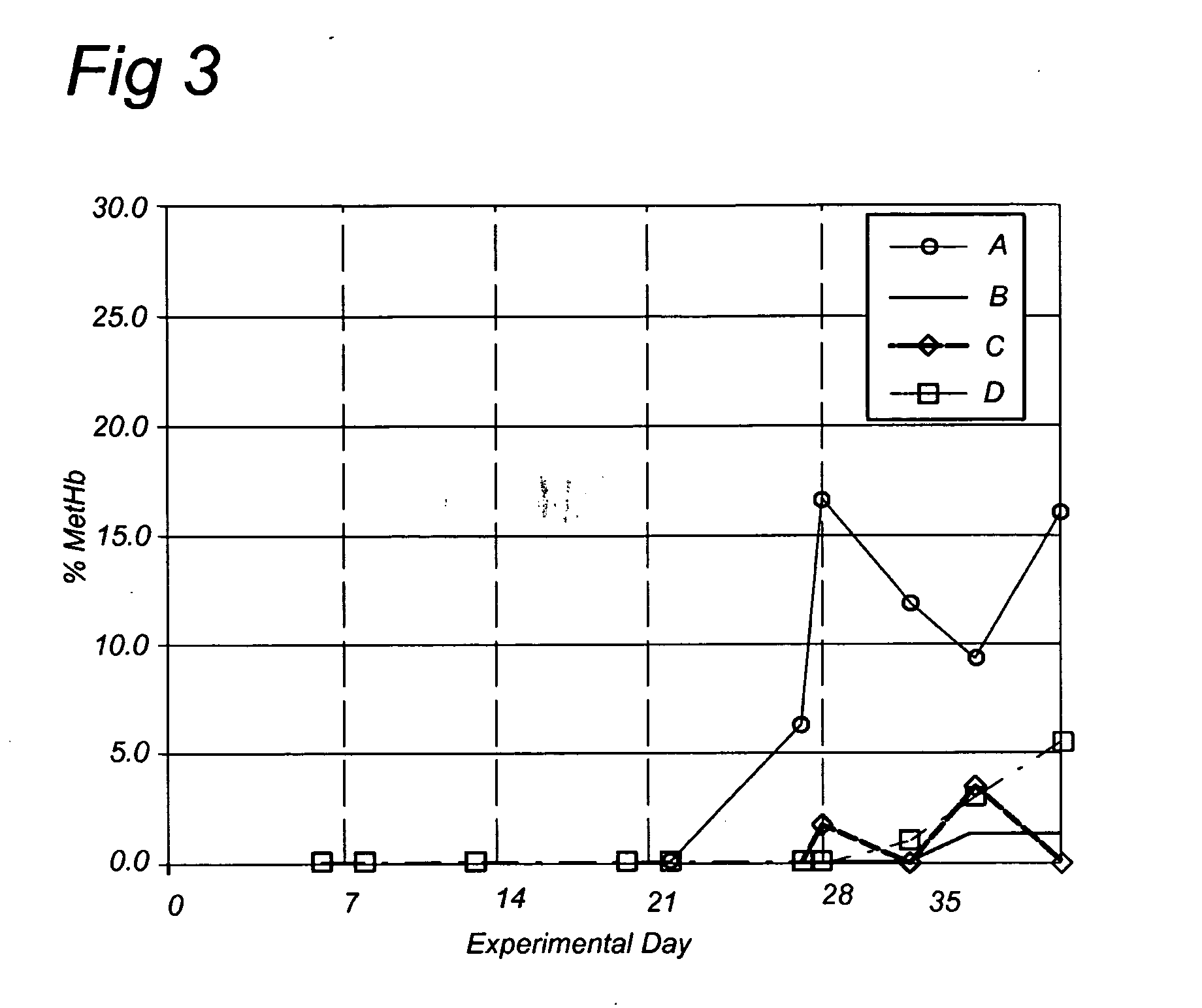
The present invention concerns the reduction of gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants with the aid of agents that compete for the hydrogen atoms required by methanogens during normal fermentation of ingested feed. The invention in one aspect resides in the findings that both nitrate reductive pathways as well as sulphate reductive pathways outcompete gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants and, that the methanogenesis reducing effects of nitrate and sulphate are completely additive. At the same time the combined administration of nitrate and sulphate was found to be fully effective to avoid or mitigate the potential problems of nitrite intoxication normally encountered when using nitrate alone, which effect is further enhanced, where necessary, by the addition of a nitrite reducing probiotic micoroorganism. Hence, products are provided comprising high amounts of a combination of a nitrate compound and a sulphate compound and optionally a nitrite reducing probiotic microorganism, as well as methods of reducing gastro-intestinal methanogenesis in ruminants using such compositions.
Owner:CARGILL THE NETHERLANDS HLDG
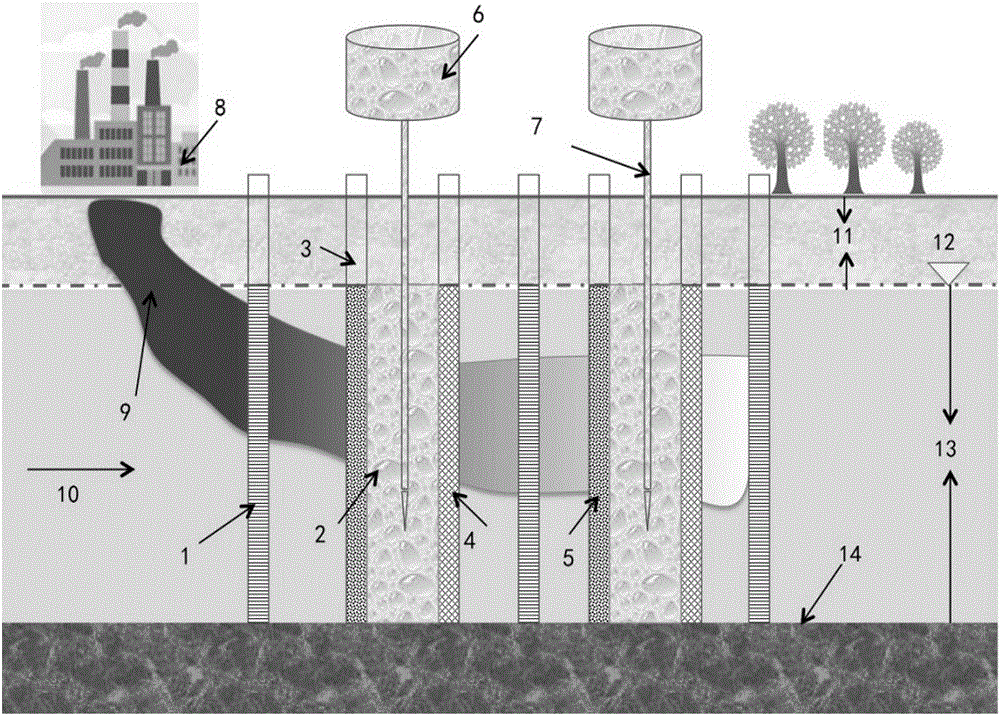
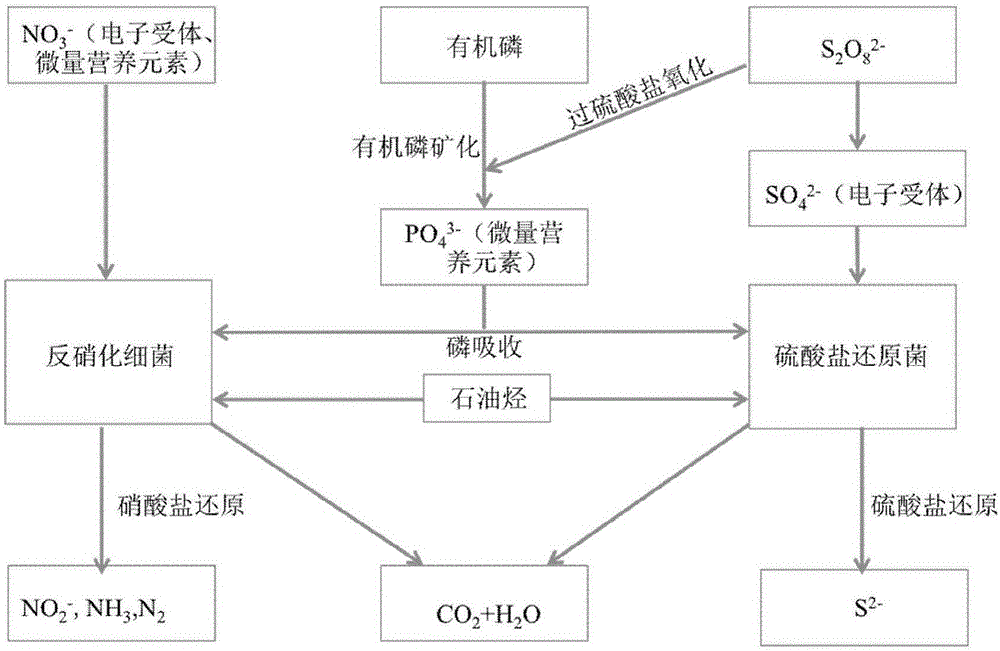
Permeable reactive barrier system and method for in-situ remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon in groundwater by enhanced anaerobic biotechnology
ActiveCN106495318AIncreasing the thicknessControl migrationWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsIn situ remediationSulfate-reducing bacteria
The invention discloses a permeable reactive barrier system and a method for in-situ remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon in groundwater by an enhanced anaerobic biotechnology, and belongs to the field of groundwater remediation. Groundwater containing the petroleum hydrocarbon flows through a permeable reactive barrier along the water flow direction, nitrate-reducing bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria formed by microorganisms under anaerobic conditions are utilized to degrade the petroleum hydrocarbon in groundwater, and accordingly the purpose of remediation of the petroleum hydrocarbon polluted groundwater is achieved. The permeable reactive barrier system and the method effectively solve the problems of low efficiency and high power consumption in a method for in-situ remediation of the petroleum hydrocarbon in the groundwater with the aid of indigenous microbial flora, and have the advantages of low acting time, high remediation efficiency, strong operability and good remediation effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Streptococcus thermophilus separated from tibetan kefirs as well as separation method and applications thereof
The invention discloses streptococcus thermophilus separated from tibetan kefirs as well as a separation method and applications thereof, belonging to the field of microbial technology. The separation method is characterized in that an operation of streaking separation is performed on a M17 culture medium plate, an operation of culturing is performed 48 hours at a temperature of 42 DEG C, a bacterial colony is circular and raised, neat in edge and milk white in color, bacterial colonies which are non-transparent, contain spherical bacteria, can be subjected to wiredrawing, provided with wet and smooth surface, and mostly arranged in chains with different lengths are selected, and no spore is produced; the streptococcus thermophilus is negative in a catalase test, positive in gram stain, negative in a nitrate reduction test, and has no motility and aerobic and facultative anaerobic growth, gelatin is not liquefied, hydrogen sulfide is not produced, and the streptococcus thermophilus is negative in an indole test; the streptococcus thermophilus does not grow at a temperature of 15 DEG C; the growth temperature is 37-45 DEG C; the highest and lowest initial growth pH values are respectively 9.0 and 4.0, and the growth initial pH value is 6.5-7.0. The streptococcus thermophilus aas well as separation method and applications thereof disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that the maximum quantity of exopolysaccharides produced when the streptococcus thermophilus is fermented 30 hours by using a M17 culture solution under the condition of 42 DEG C is 111 mg / L; and when a fermented yoghurt is prepared by using strains provided by the invention, the amounts of a thickener and a stabilizer can be reduced.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Natural pyrrhotite biological filter and method for utilizing same to synchronously remove nitrate-nitrogen and phosphorus from water
InactiveUS20160311712A1Cheap and easily availableLow C/N ratioWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsElectron donorBiological filter
The field of advanced wastewater treatment, and more specifically, to a natural pyrrhotite biofilter and a method for utilizing same to synchronously remove nitrate-nitrogen and phosphorus from water is provided. The method includes the following steps: (1) preparation of the packing material and construction of the biofilter; (2) start-up of the biofilter; (3) operation of the biofilter. The method disclosed in the present invention on the one hand takes pyrrhotite as the electron donor to help sulfur-based autotrophic denitrifying bacteria reduce nitrates into nitrogen gas, and on the other hand utilizes pyrrhotite and its oxidates to eliminate phosphorus through adsorption and chemical precipitation. Therefore, this method realizes synchronous removal of nitrate-nitrogen and phosphorus in water.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
High-bile salt resistance strain and bile salt hydrolase genes
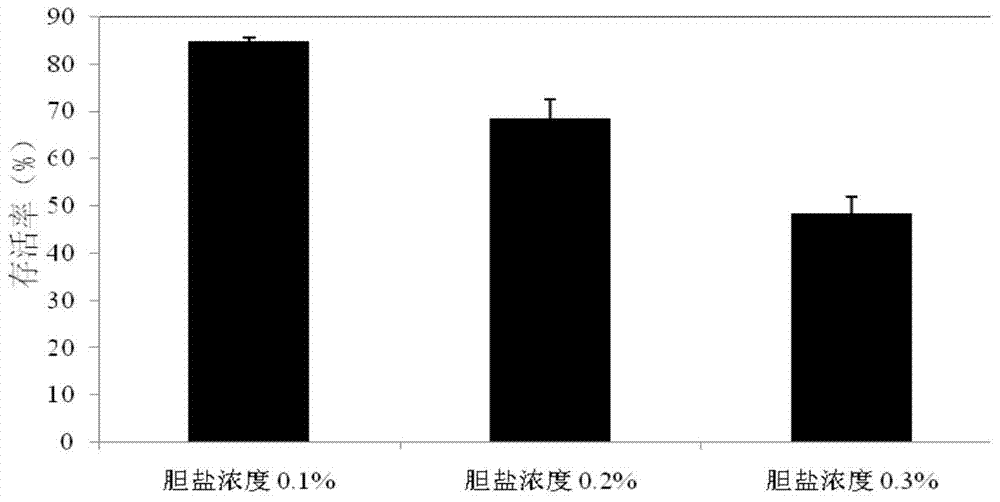
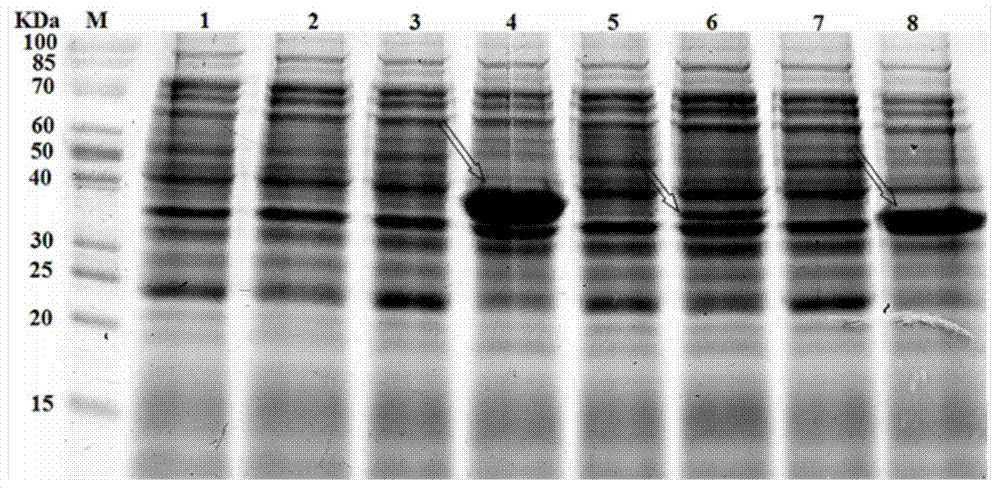
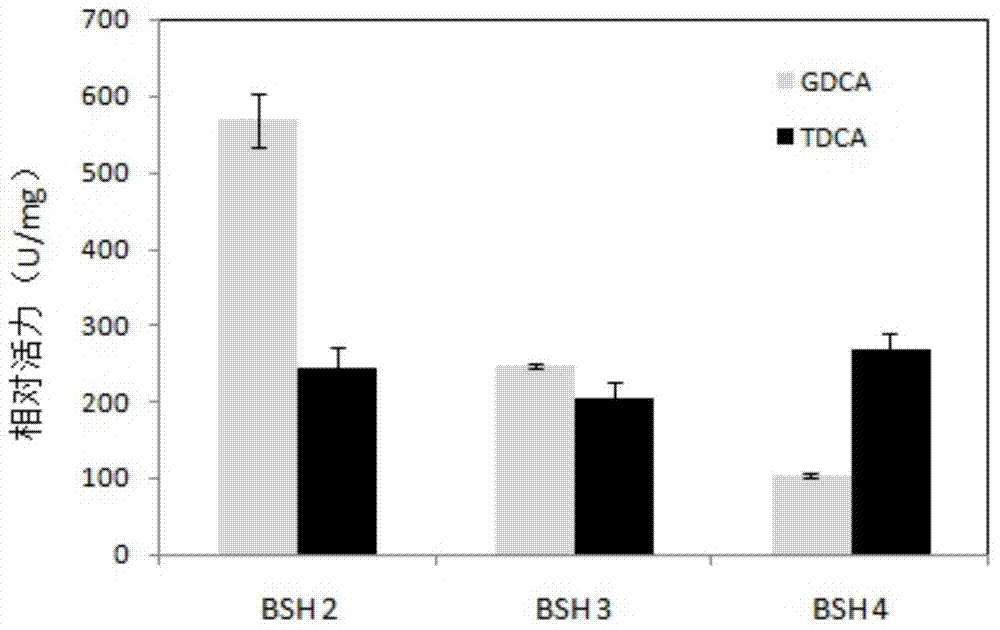
ActiveCN103571776AHigh bile salt toleranceStrong nitrate reducing abilityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyBile salt hydrolase
The invention discloses a high-bile salt resistance strain and bile salt hydrolase genes. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCCNo.8198. The strain has high acid resistance, high bile salt resistance, high nitrate reducing capability and the like. Three types of bile salt hydrolase genes of the strain are amplified, and are cloned, sequenced and heterogeneously expressed, so that generated bile salt hydrolases have high activity. The strain and the bile salt hydrolases can be used in the fields of food, medicine, agriculture and the like as food and feed leavening agents, microecological preparations, medicament expression carriers, feed additives and the like; the bile salt hydrolases can be developed into recombinant protein products, and can also be used for the molecular modification of lactic acid bacteria strains as selection markers of lactic acid bacteria gene engineering expression systems.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
Special filler for nitrate nitrogen removal using sulfur-iron coupling technology, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109879419ASmall volumeTake advantage ofWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesElectron donorCoupling
The invention discloses a special filler for nitrate nitrogen removal using a sulfur-iron coupling technology, and a preparation method thereof. The filler comprises, by mass, 40-60% of elemental sulfur, 10-15% of limestone, 15-25% of pyrite and 30-40% of denitrifying bacteria immobilized particles. Autotrophic denitrifying bacteria utilize the limestone to synthesize cells, the pyrite is used asan electron donor for nitrate reduction to complete the denitrification process, the denitrifying bacteria immobilized particles provide denitrifying bacteria to complete removal of nitrogen from thewastewater, and all the above components are designed to be granular to make the filler sufficiently stirred in order to ensure the full utilization of the filler.
Owner:SUZHOU FANGZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Highly effective phosphorus removal bacteria and its produced bacteria formulation
InactiveCN1807585AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological propertyPseudomonas putida
The bacterium agent in this invention is used to biologically strenghen dephosphor- ization process in urban sewage treatment plant. It has mainly two uses: quickly start the biodephosphorization ability of new sewage treatment plant; resume the strong biodephosphorization ability of exasperate dephosphorization system. It is made from high efficient ployphospher bacterial strain GM6, and it is odor Pseudomonas putida from appraising result. Its main biocharacteristic is G-. Its thalli is rhabditiform with the size of 0. 7í‡2. 5ª–m, and it is facultative anaero-bic; it is positive in indole reaction, oxidase and sulfate reduction reaction; while negative in methyl red test, V-P reaction, citrate test and hydrogen sulfide reaction; the number of the strain 16S rDNA is DQ133506. The strain can be used to sewage dephosphorization.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
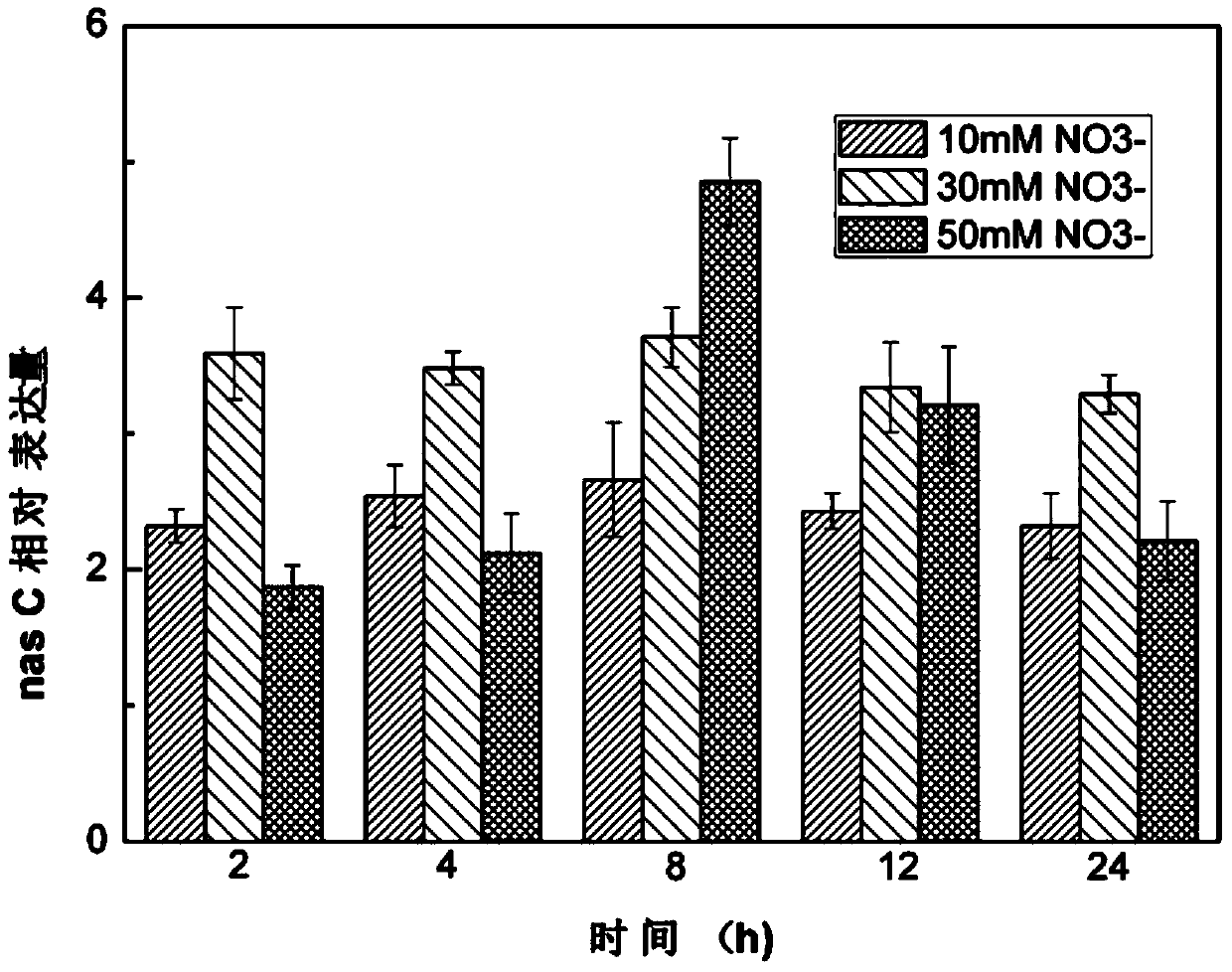
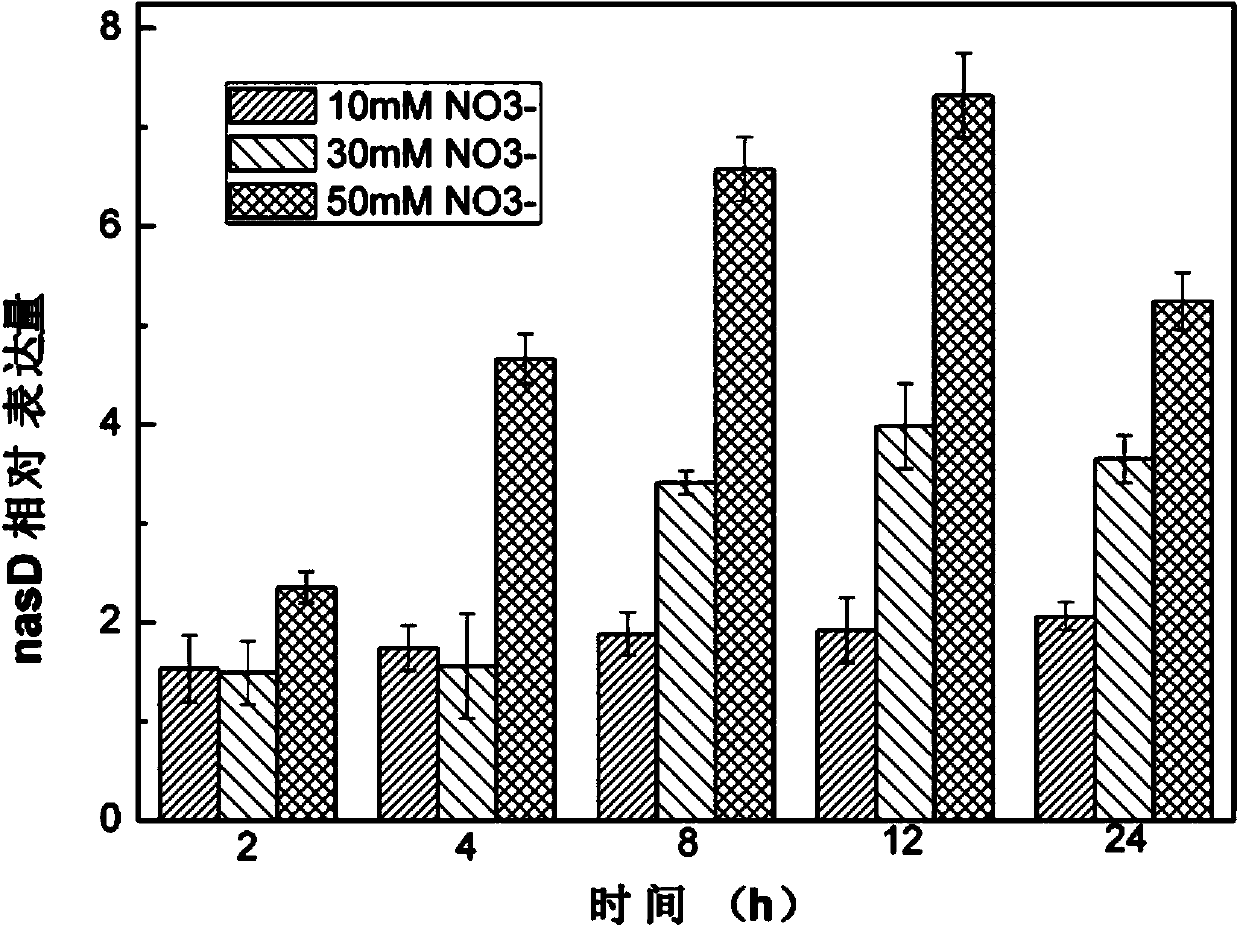
Assimilation nitrate reductase gene and assimilation nitrite reductase gene both extracted from bacillus megaterium as well as applications of assimilation nitrate reductase gene and assimilation nitrite reductase gene
InactiveCN103725654ASolve the removal problemMicrobiological testing/measurementContaminated soil reclamationBacillus megateriumTotal rna
The invention discloses an assimilation nitrate reductase gene and an assimilation nitrite reductase gene both extracted from bacillus megaterium as well as applications of the assimilation nitrate reductase gene and the assimilation nitrite reductase gene, and relates to the field of the biotechnology. The assimilation nitrate reductase gene is catalytic subunit nasC (Seq ID No.1) which codes assimilation nitrate reductase Nas; the assimilation nitrite reductase gene is large subunit nasD (Seq ID No.2) which codes assimilation nitrite reductase NiR. According to the invention, total RNA is extracted from the bacillus megaterium NCT-2, then cDNA synthesis is conducted to obtain a cDNA template, and function representation is realized through fluorogenic quantitative PCR. The assimilation nitrate reductase gene and the nitrite reductase gene can be further applied to research on removal of overmuch nitrate from soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com