Recombinant Pichia pastoris engineering strain and its application in synthesizing levodopa
A technology of Pichia pastoris and levodopa, applied in application, genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as bacterial infection, increased process steps and energy consumption, fermentation failure, etc., to save production costs and reduce process treatment degree, the effect of continuous culture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1 Construction of Pichia pastoris recombinant strain YZ001
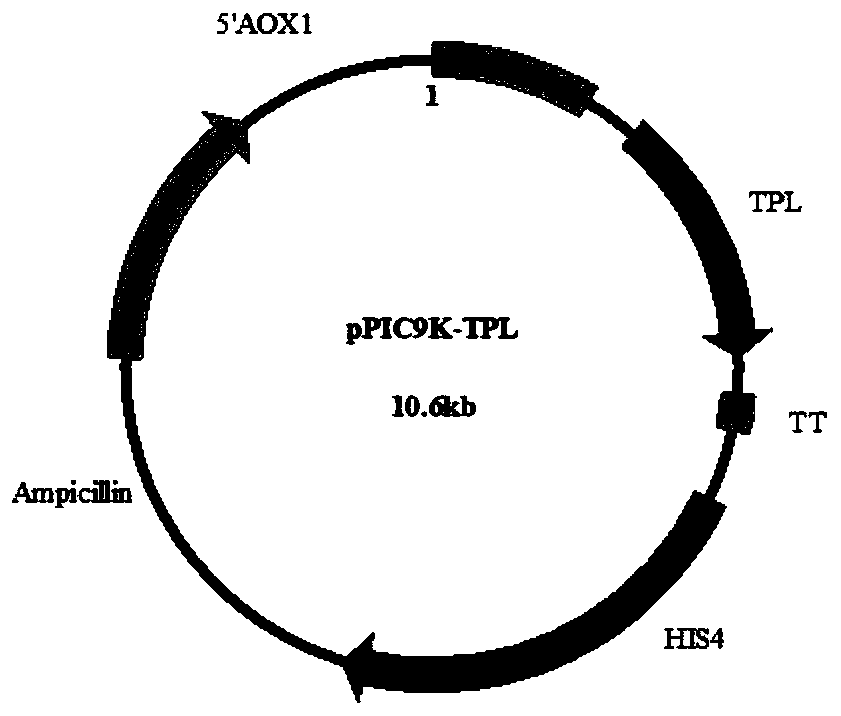
[0027] This example is based on the amino acid sequence of Kluyvera intermedia tyrosine phenol lyase shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The DNA sequence of tyrosine phenol lyase (TPL) shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is optimized according to the codon preference of Pichia pastoris to obtain the TPL gene after codon optimization, and its optimized sequence is as SEQ ID NO. 3 shown. The whole gene synthesis was carried out by a biotechnology company (Jinweizhi Biotechnology Company), and the synthesized gene was cloned on the pETDuet-1 vector to obtain the plasmid pETDuet-TPL. By designing primers YW500 and YW504, the plasmid pETDuet-TPL was used as a template to amplify TPL by PCR. The amplification system is 50 μL (2x PrimeSTAR Max DNA polymerase (purchased from Beijing Baoriyi Biological Co., Ltd.) 25 μL, 1 μL YW500+1 μL YW504, 0.5 μL pETDuet-TPL plasmid, distilled water to 22.5 μL), pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 minut...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The construction of embodiment 2 Pichia pastoris recombinant strain YZ002
[0031] Using the genome of Pichia pastoris GS115 as a template, PCR amplification of HAC1 (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4) was performed by designing primers YW507 and YW508. The amplification system is 50 μL (2×PrimeSTAR Max DNA polymerase 25 μL, 1 μL YW507+1 μL YW508, 0.5 μL GS115 genome, distilled water to 22.5 μL), pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 minutes, denaturation at 98°C for 10 seconds, annealing at 58°C for 15 seconds, Extend at 72°C for 2 minutes (30 cycles), and extend again at 72°C for 10 minutes.
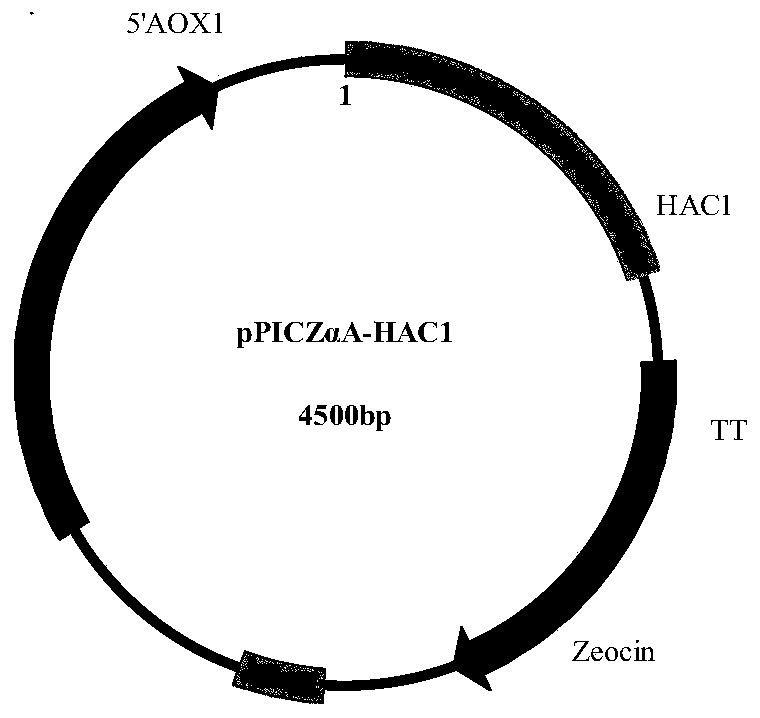
[0032]After recovering the HAC1 fragment gel obtained above, digest it with restriction endonucleases EcoR I and Not I, and connect it to the pPICZαA vector that was also digested with EcoR I and Not I to construct the pPICZαA-HAC1 plasmid, such as figure 2 shown. The cloning system is 20 μL (2 μL 10x T4 ligase buffer, 6 μL digested TPL fragment, 2 μL digested pPICZαA ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The SDS-PAGE analysis of embodiment 3 Pichia pastoris recombinant strain YZ002
[0038] BMGY medium: 1% yeast powder, 2% peptone, 1.34% YND, 0.1mol / L pH 6.0 phosphate buffer, 1% glycerol, 4×10-5% biotin.
[0039] BMMY medium: 1% yeast powder, 2% peptone, 1.34% YND, 0.1mol / L pH 6.0 phosphate buffer, 2% methanol, 4×10-5% biotin.
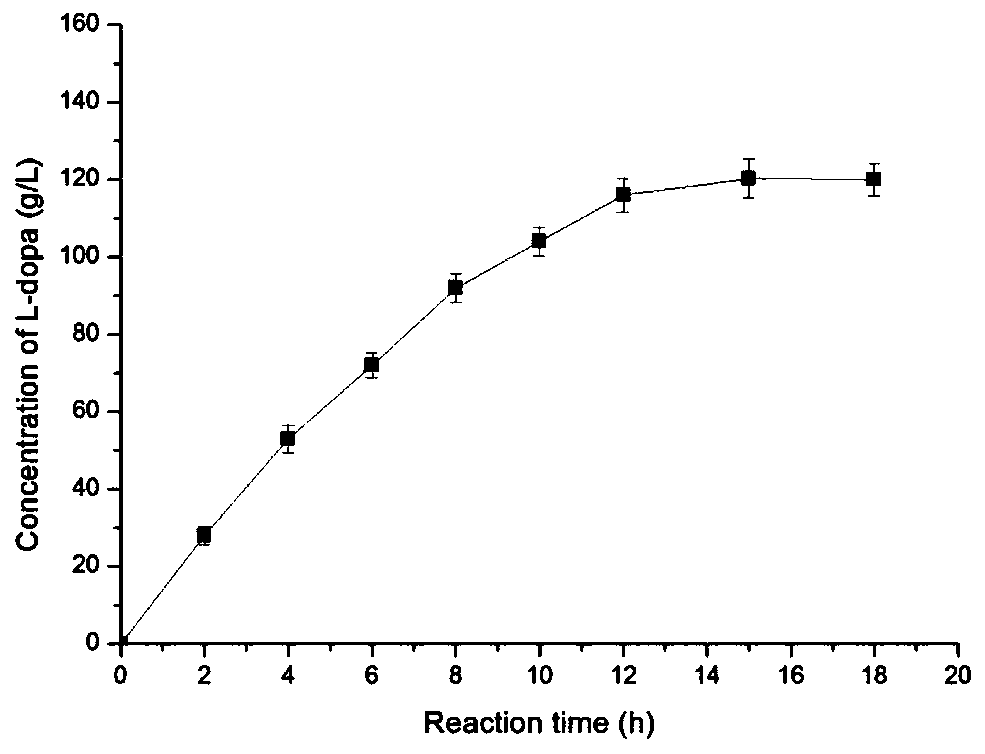
[0040] The SDS-PAGE analysis of Pichia recombinant bacteria is as follows: inoculate Pichia recombinant bacteria in BMGY medium and culture overnight at 30°C, then transfer to 50mL fresh BMGY medium to make the initial OD600 0.1, and cultivate to OD600 at 30°C 6.0, centrifuged at 4000rpm for 10min, collected bacteria, resuspended with 50mL BMMY medium to OD600 of 1.0 for culture, and added 100% methanol to the medium every 24h to a final concentration of 1%. After induction of expression for 72 hours, the supernatant was taken to analyze the protein expression by SDS-PAGE. Gel preparation and electrophoresis are as follows, use 10% gel formula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com