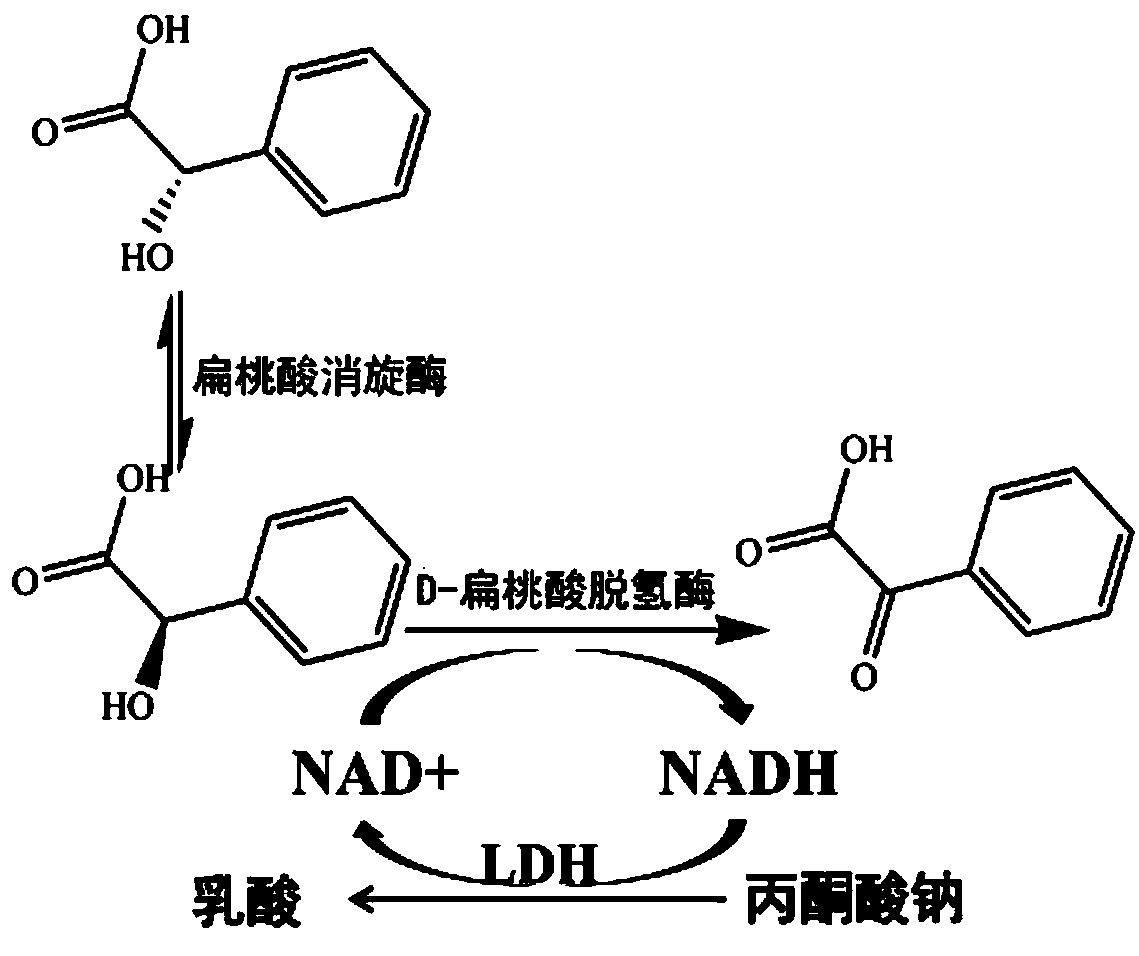
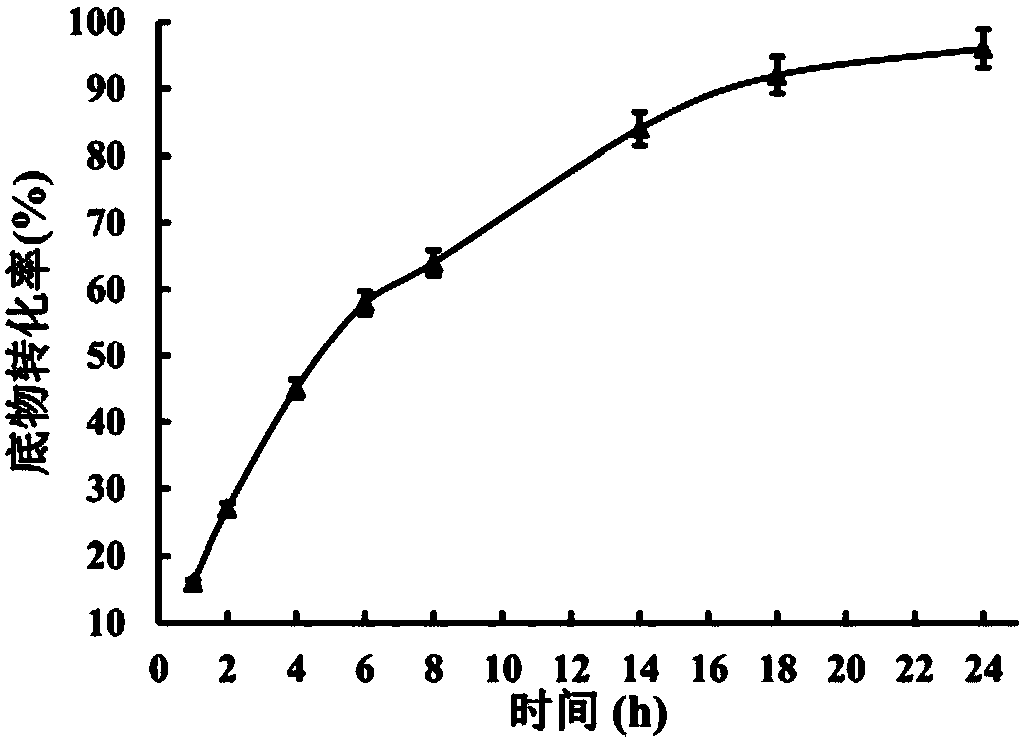
Genetic engineering compound bacteria and application thereof in biosynthesis of PGA (phenylglyoxylic acid)
A technology for acetophenone acid and biosynthesis, which is applied in the directions of genetic engineering, application, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of increasing separation cost and high cost of mandelic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Gene mining of genes encoding L-lactate dehydrogenase:
[0053] Using the highly active L-LDH (OJF74586) derived from Lactobacillus casei as a probe, BLAST analysis was performed based on the non-redundant database, and a series of genome information sources without expression identification and putative genes were found from the query results. L-lactate dehydrogenase sequence. Construct and analyze the phylogenetic tree of these sequences, and then select 1 to 2 representative gene sequences from each branch. For the target gene that is easy to obtain from the strain, the target gene can be obtained by PCR amplification using the genome as a template. The obtained gene was codon-optimized for whole-gene synthesis. After comparative analysis, the Lactobacillus helveticus genome was selected as a potential L-lactate dehydrogenase for further research.
[0054] Taking the codon usage frequency of E.coli K12 strain as a reference, the OPTIMIZER server was used to optimize...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Gene mining of the gene encoding mandelate racemase:
[0057]Using the highly active PpMR derived from Pseudomonas putida as a probe, BLAST analysis was performed based on the non-redundant database, and a series of putative racemases that were not expressed and identified and were found from the query results were found sequence. Construct and analyze the phylogenetic tree of these sequences, and then select 1 to 2 representative gene sequences from each branch. For the target gene that is easy to obtain from the strain, the target gene can be obtained by PCR amplification using the genome as a template. The obtained gene was codon-optimized for whole gene synthesis, and Herbaspirillum rubrisubalbicans genome source was selected as a potential mandelate racemase for further research after comparative analysis.
[0058] Taking the codon usage frequency of E.coli K12 strain as a reference, the OPTIMIZER server was used to optimize the codon of the potential HrMR gene se...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Construction and expression analysis of genetic engineering bacteria producing D-mandelate dehydrogenase (LhDMDH) and L-lactate dehydrogenase (LhLDH):
[0061] Step 1. Construction of a recombinant plasmid: link the coding genes of D-mandelate dehydrogenase (LhDMDH) and L-lactate dehydrogenase (LhLDH) to the pETDuet1 plasmid respectively to obtain the recombinant plasmid pETDuet1-LhDMDH-LhLMDH;
[0062] Step 2: Transform the recombinant plasmid into host cells: transform the recombinant plasmid pETDuet1-LhDMDH-LhLMDH into Escherichia coli BL21 (purchased from Invitrogen) competent cells by heat shock, add 0.4mL LB liquid medium, and heat at 37°C, 220rpm After incubation for 1 hour under high temperature, spread on LB solid plates containing 50 μg / mL ampicillin, and incubate at 37°C for 12-16 hours to obtain monoclonal colonies;
[0063] Step 3. Screening and identification of recombinant bacteria: Pick single-clonal colonies into 4 mL of LB liquid medium containing 50 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com