Unmarked gene knock-out method of pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 based on homologous recombination
A technology of Pediococcus lactis and marker-free genes, applied in the field of marker-free gene knockout of Pediococcus lactis DQ2 based on homologous recombination, to achieve the effect of safe large-scale industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
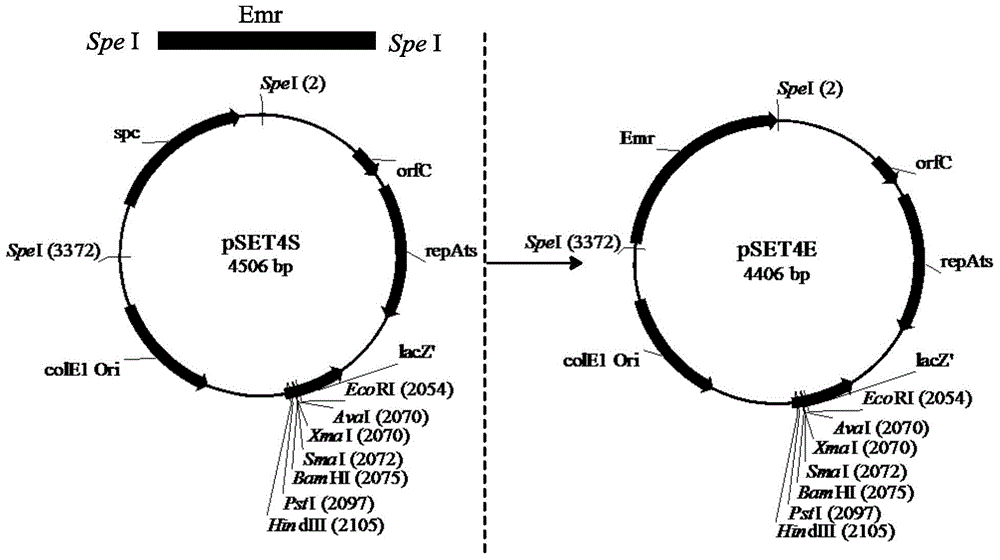
[0046] Embodiment 1: Construction of pSET4E plasmid
[0047]The thermosensitive suicide plasmid pSET4S is an Escherichia coli-Gram-positive bacterial wide host range shuttle plasmid. The source of this plasmid is found in DaisuKeTaKamatsu, MaKotoOsaKi, and TsutomuSeKizaKi, ThermosensitiveSuicideVectorsforGeneReplacementinStreptococcussuis, Plasmid, 2001, 46(2): 140-148. The plasmid can replicate when the culture temperature is 37°C in Escherichia coli, so as to facilitate the cloning of homologous fragments, but cannot replicate when the culture temperature is 37°C in Streptococcus suis. This plasmid can be used not only for gene knockout of Streptococcus suis, but also for gene knockout of some other Gram-positive bacteria, so consider using this plasmid as an initial plasmid to construct a suitable knockout plasmid for gene knockout of P.acidilactici remove.
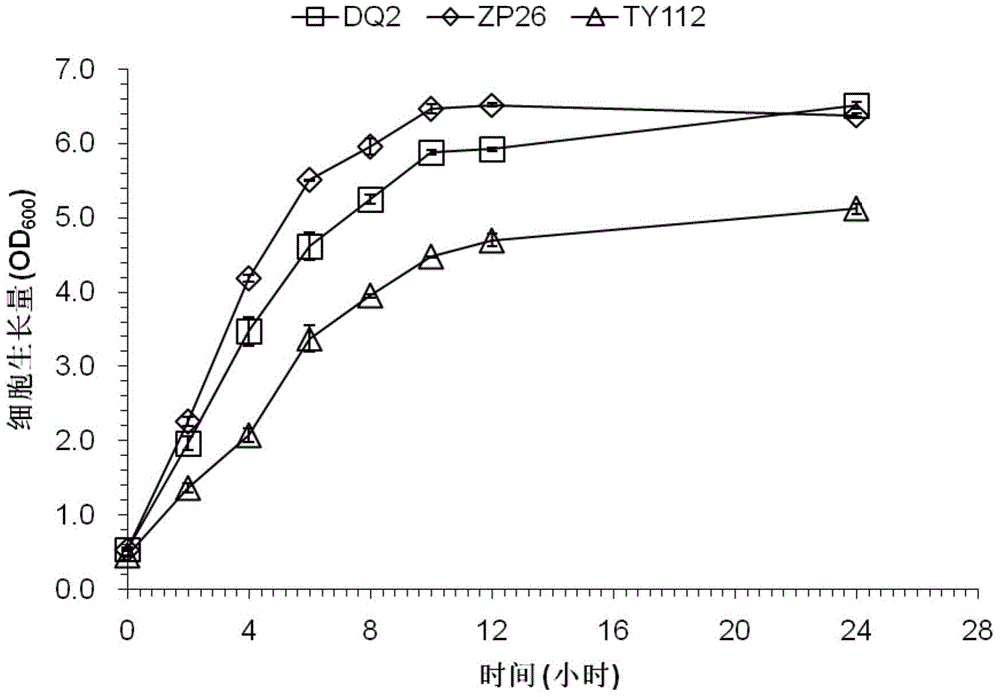
[0048] It was found that P.acidilacticiDQ2 was highly resistant to spectinomycin (>150μg / mL), but sensitive to eryt...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Unmarked Knockout of P.acidilacticiDQ2ldh Gene
[0057] (1) Construction of ldh gene knockout plasmid pSET4E-Δldh
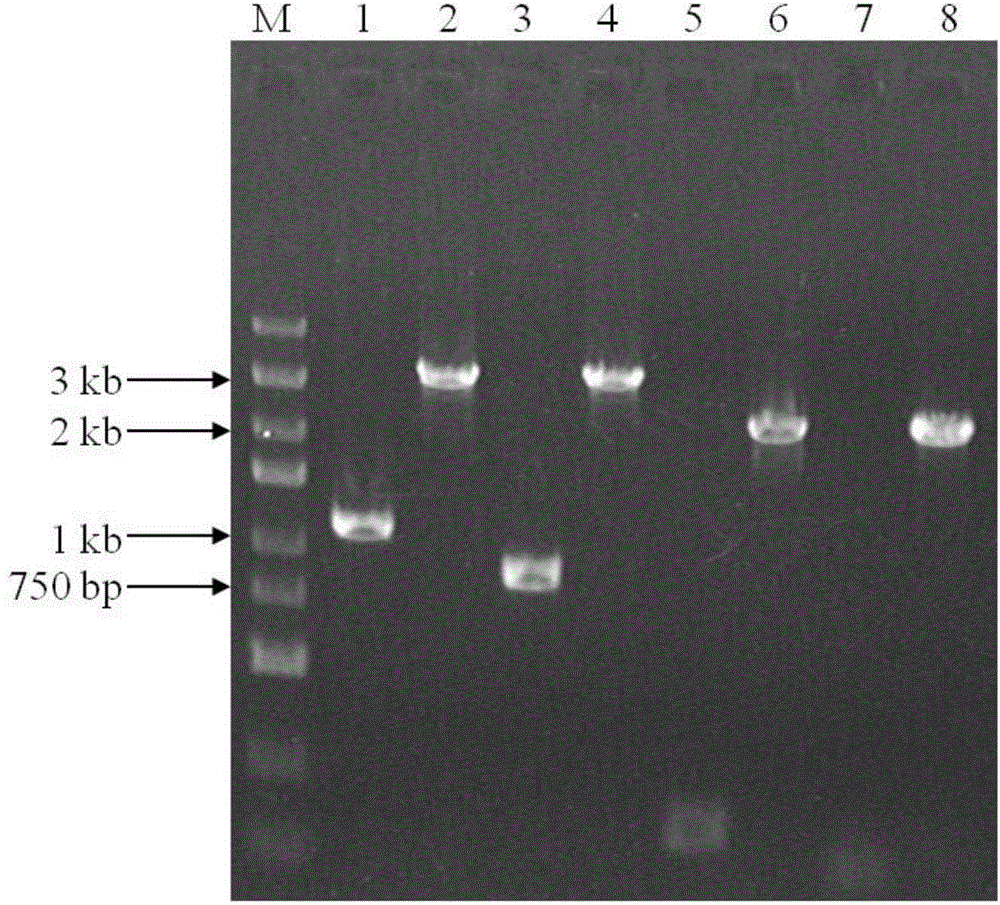
[0058] According to the upstream and downstream DNA sequences of the ldh gene (NCBI-GI=304328039) in the model strain DSM20284 of Pediococcus acidilactici, design corresponding primers up-F-ldh, up-R-ldh, down-F-ldh, down-R-ldh (SEQ ID NO : 7-10) PCR amplification ldh gene upstream and downstream sequences up-ldh (the sequence of about 1 kb size upstream of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene initiation codon) (SEQ ID NO: 11), down-ldh (L-lactate dehydrogenase A sequence of about 1 kb in size downstream of the stop codon of the hydrogenase gene) (SEQ ID NO: 12).
[0059] Using the genomic DNA of P.acidilacticiDQ2 as a template, the upstream and downstream homologous sequences of the ldh gene up-ldh, up-ldh, Down-ldh, the PCR amplification system is the same as before.
[0060] The PCR amplification conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Unmarked Knockout of the P.acidilacticiDQ2ldhD Gene
[0069] (1) Construction of ldhD gene knockout plasmid pSET4E-ΔldhD
[0070] According to the upstream and downstream DNA sequences of the ldhD gene (NCBI-GI=304329050) in Pediococcus acidilacticiDSM20284, design corresponding primers up-F-ldhD, up-R-ldhD, down-F-ldhD, down-R-ldhD (SEQ ID NO: 20-23) PCR amplification of its upstream and downstream sequences up-ldhD (the sequence of about 1 kb size upstream of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene start codon) (SEQ ID NO: 24), down-ldhD (D-lactate dehydrogenase gene stop codon downstream approximately 1 kb sequence) (SEQ ID NO: 25).
[0071] Using the genomic DNA of P.acidilacticiDQ2 as a template, PCR cloned the upstream and downstream homologous sequences of the ldhD gene up-ldhD and For down-ldhD, the PCR amplification system remains the same as before.
[0072]The PCR amplification conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, denaturatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com