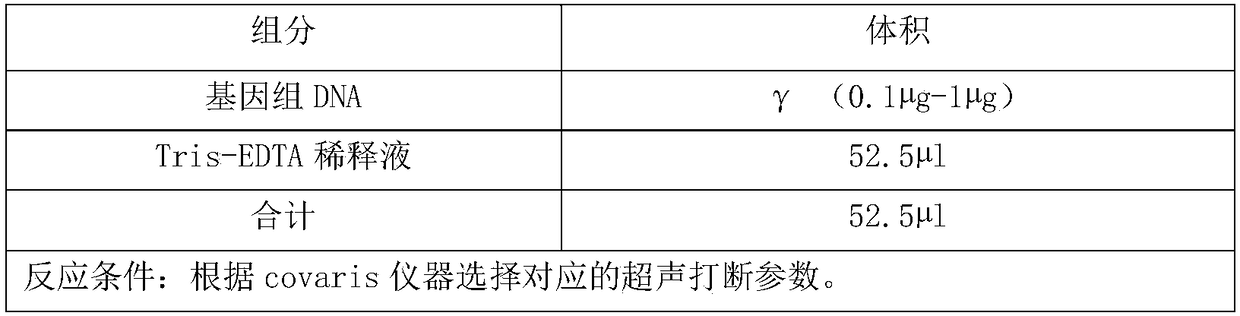
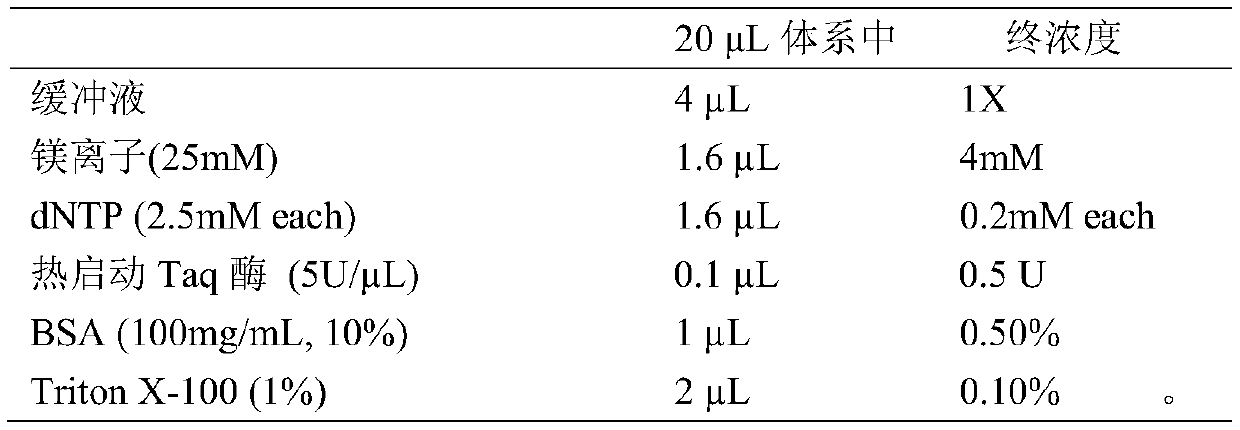
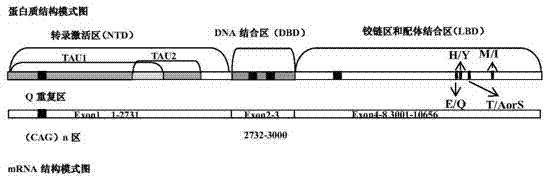
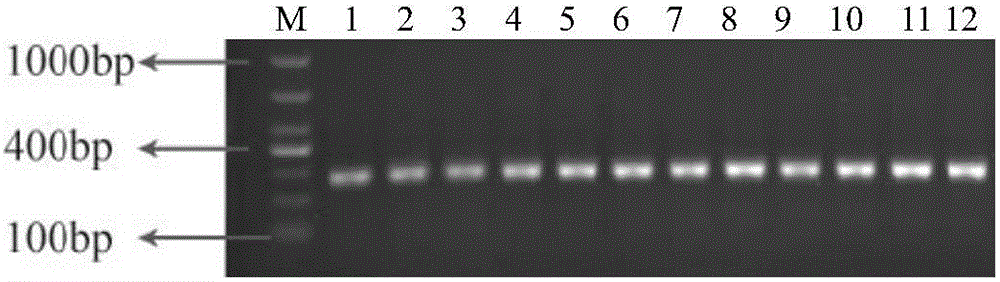
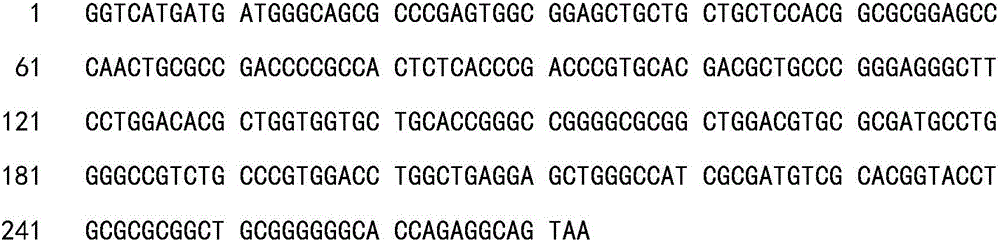
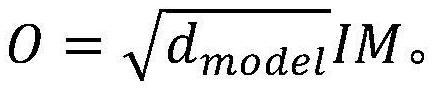Patents
Literature
132 results about "Upstream and downstream (DNA)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
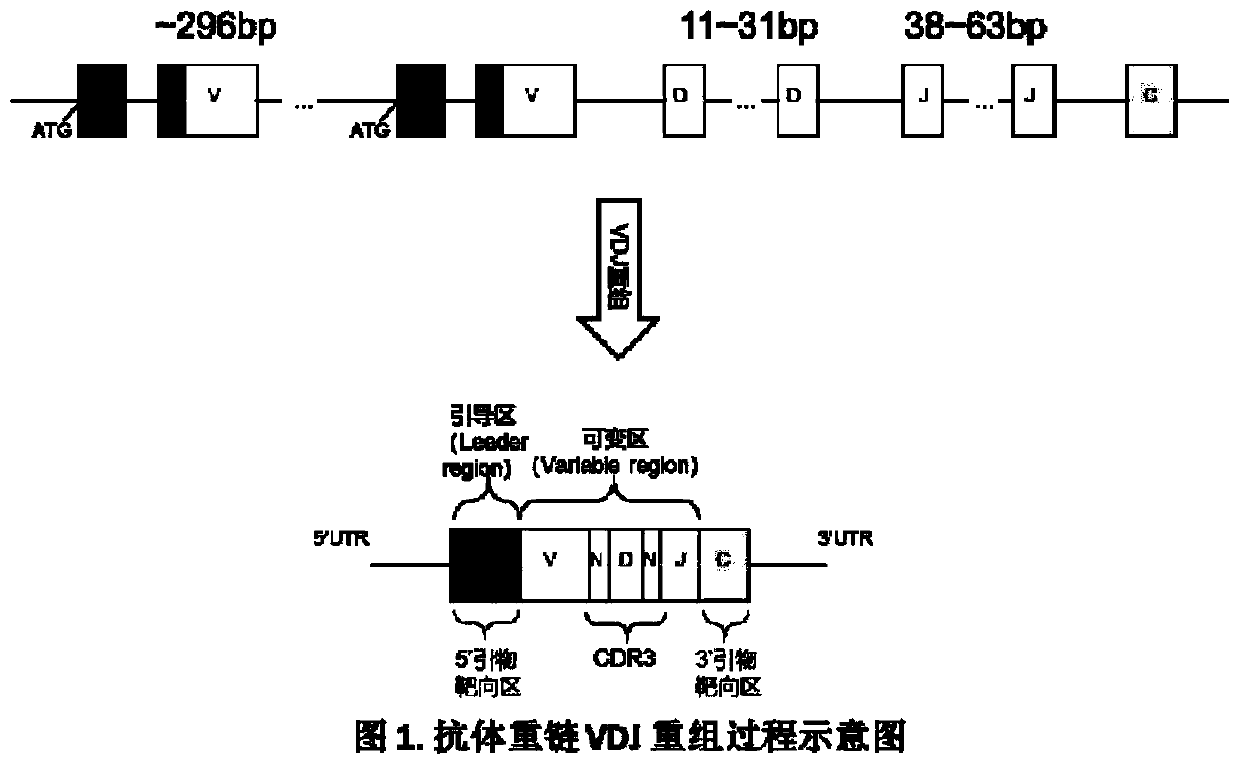
In molecular biology and genetics, upstream and downstream both refer to relative positions of genetic code in DNA or RNA. Each strand of DNA or RNA has a 5' end and a 3' end, so named for the carbon position on the deoxyribose (or ribose) ring. By convention, upstream and downstream relate to the 5' to 3' direction respectively in which RNA transcription takes place. Upstream is toward the 5' end of the RNA molecule and downstream is toward the 3' end. When considering double-stranded DNA, upstream is toward the 5' end of the coding strand for the gene in question and downstream is toward the 3' end. Due to the anti-parallel nature of DNA, this means the 3' end of the template strand is upstream of the gene and the 5' end is downstream.
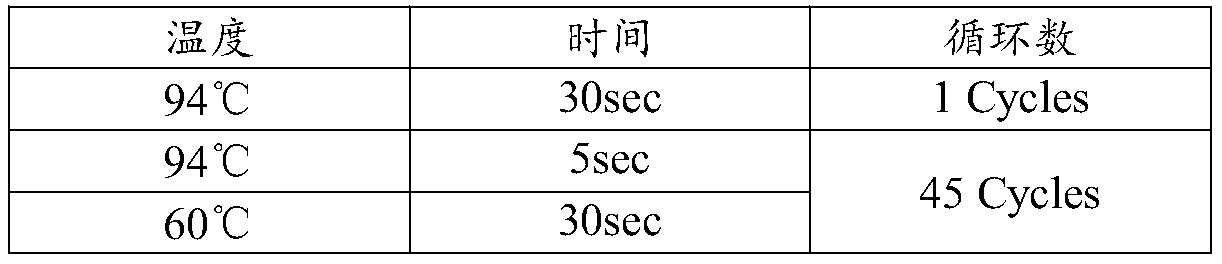
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20110123991A1Easy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationStrand invasionOligonucleotide
An isothermal process for amplifying a nucleic acid target molecule that relies on an upstream primer, a downstream primer, a strand invasion system and an oligonucleotide, wherein the upstream and downstream primers are not substrates for the strand invasion system during the amplification process and do not amplify the target molecule independently of the strand invasion system, wherein the oligonucleotide is a substrate for the strand invasion system.
Owner:GENEFORM TECH LTD
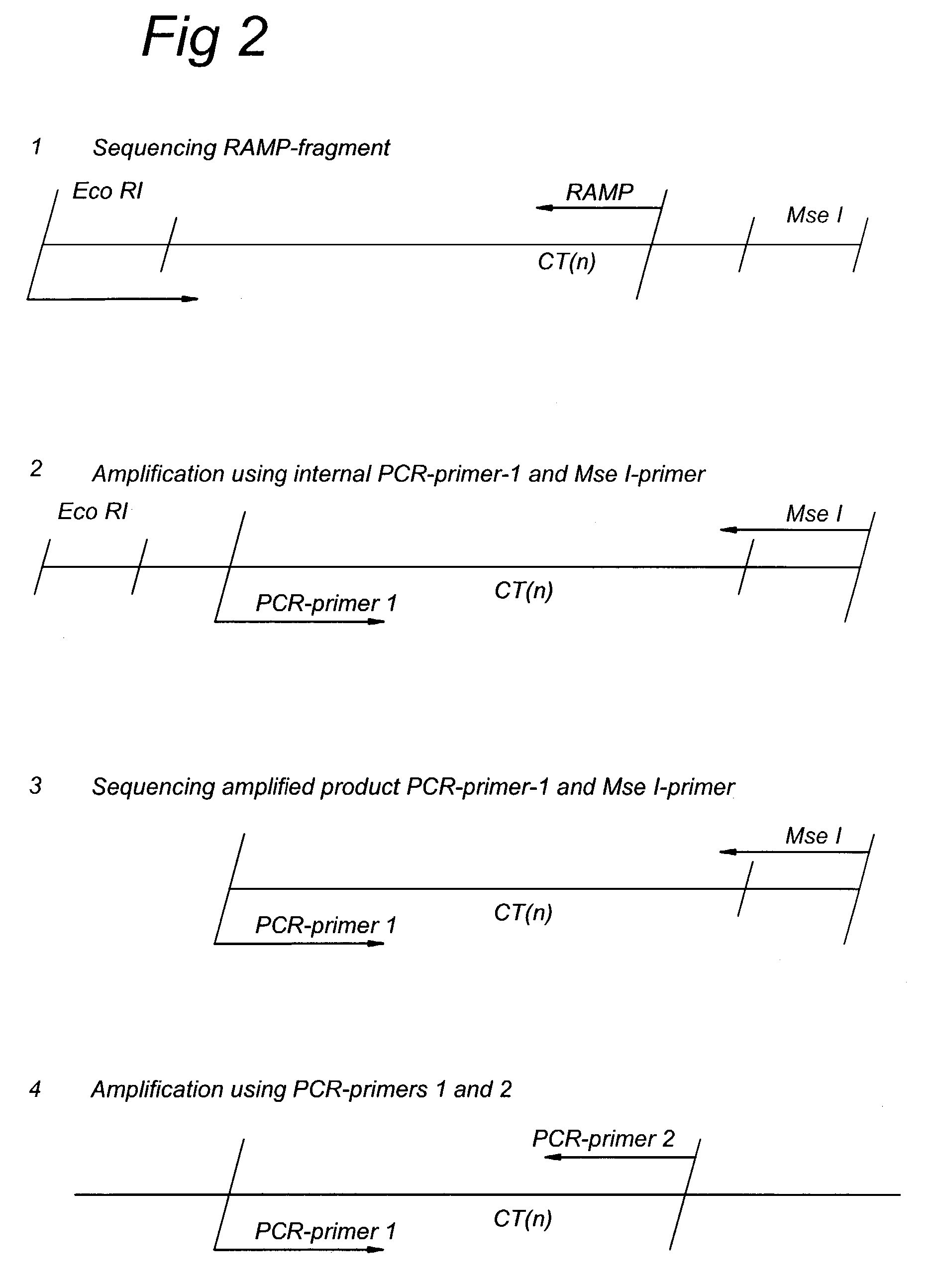
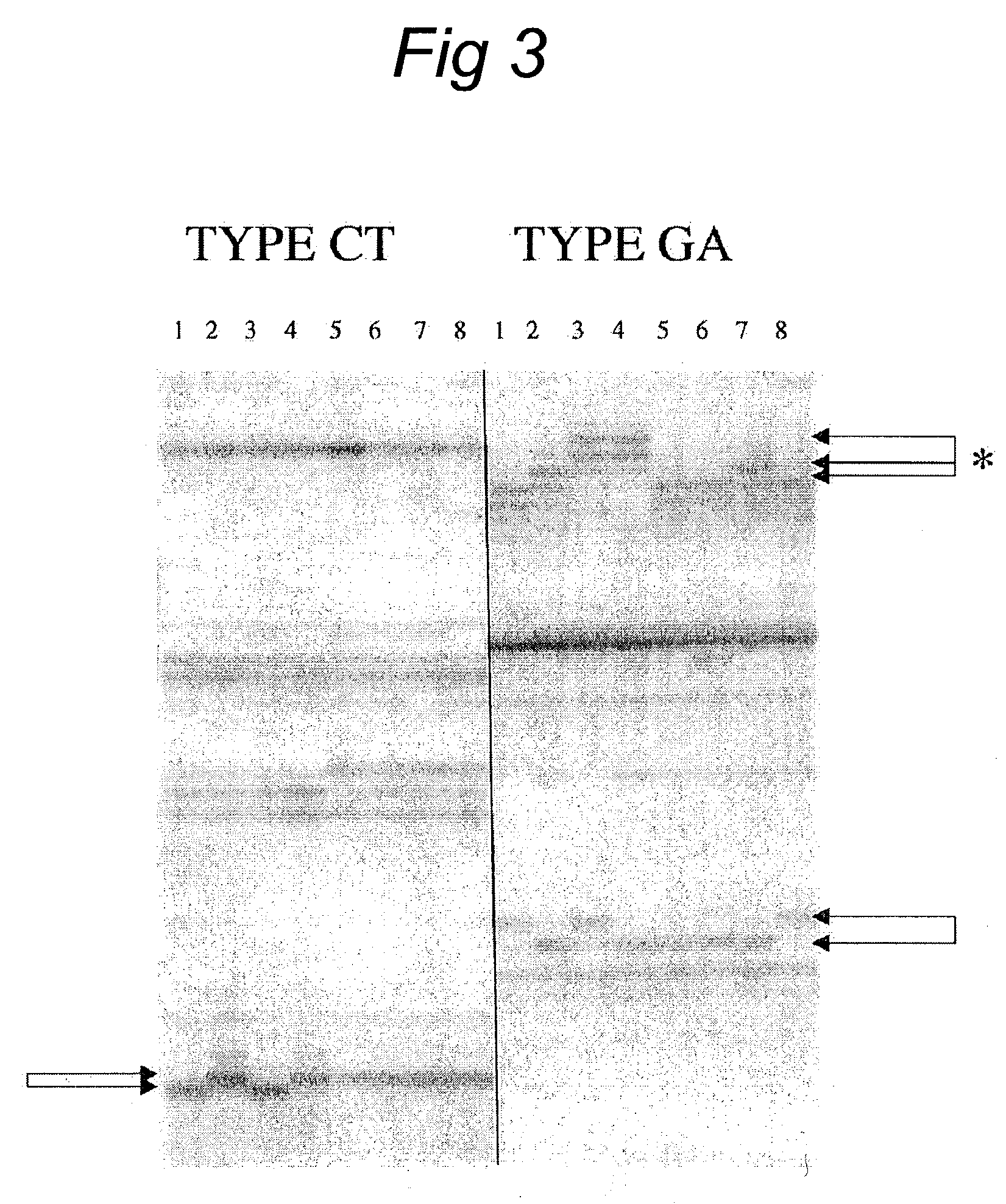
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Detection and application of new molecular marker hsa-circ-0001017 of gastric cancer
ActiveCN106591428AReduce yieldHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHousekeeping geneFluorescence
The invention relates to a cyclic RNA molecular marker for diagnosis of gastric cancer, the cyclic RNA molecular marker is characterized in that the cyclic RNA is hsa-circ-0001017, the invention also provides a method for detection of the cyclic RNA molecular marker in plasma, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting blood, and extracting total RNA in the plasma; (2) performing reverse transcription of the total RNA into cDNA; (3) performing droplet digital PCR detection of a cDNA solution of the step (2) by use of specific amplification back-to-back primers and amplification upstream and downstream primers of housekeeping gene GAPDH, after the completion of the reaction, detecting fluorescence signal values of all droplets, setting a threshold, and determining whether the droplets include the cyclic RNA or the housekeeping gene GAPDH, wherein the droplets higher than the threshold are positive droplets, and the droplets below the threshold are negative droplets; and (4) counting the number of the positive droplets, and calculating the copy number of the hsa-circ-0001017 and the housekeeping gene GAPDH in the plasma for quantitative detection of the hsa-circ-0001017 and the housekeeping gene GAPDH in the plasma. Compared with the prior art, the advantages are that the hsa-circ-0001017 can be specifically expressed in plasma in patients with gastric cancer, and can be used as a new molecular marker for diagnosis of the gastric cancer.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Probes, method and chip for detecting alpha and/or beta-thalassemia mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such probes, such method and such chip
ActiveCN106591441AEnables detection of deletions in large regionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBeta thalassemiaNew mutation
The invention provides primers, a method and a chip for detecting alpha and / or beta-thalassemia point mutation and deletion mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such primers, such method and such chip. The primers, the method, the chip and application thereof have the advantages that through designing of capture probes, relevant genes involved in alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia are enriched and all mutation information including SNP and indel in full-length sequences of genes is detected; through addition of autosome, X-chromosome and Y-chromosome regions as well as upstream and downstream regions of coded genes as references, structure variations such as SNV and CNV are detected; compared with existing various hotspot mutation site detection technologies, the method is capable of detecting hotspot mutation information as well as some rare mutations and undiscovered new mutation types to detect and analyze full-length sequence specificity of target genes, fully covers the mutation types and makes up the defect that a conventional detection method easily causes missing detection of low-frequency mutations and rare mutations greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN E GENE TECH
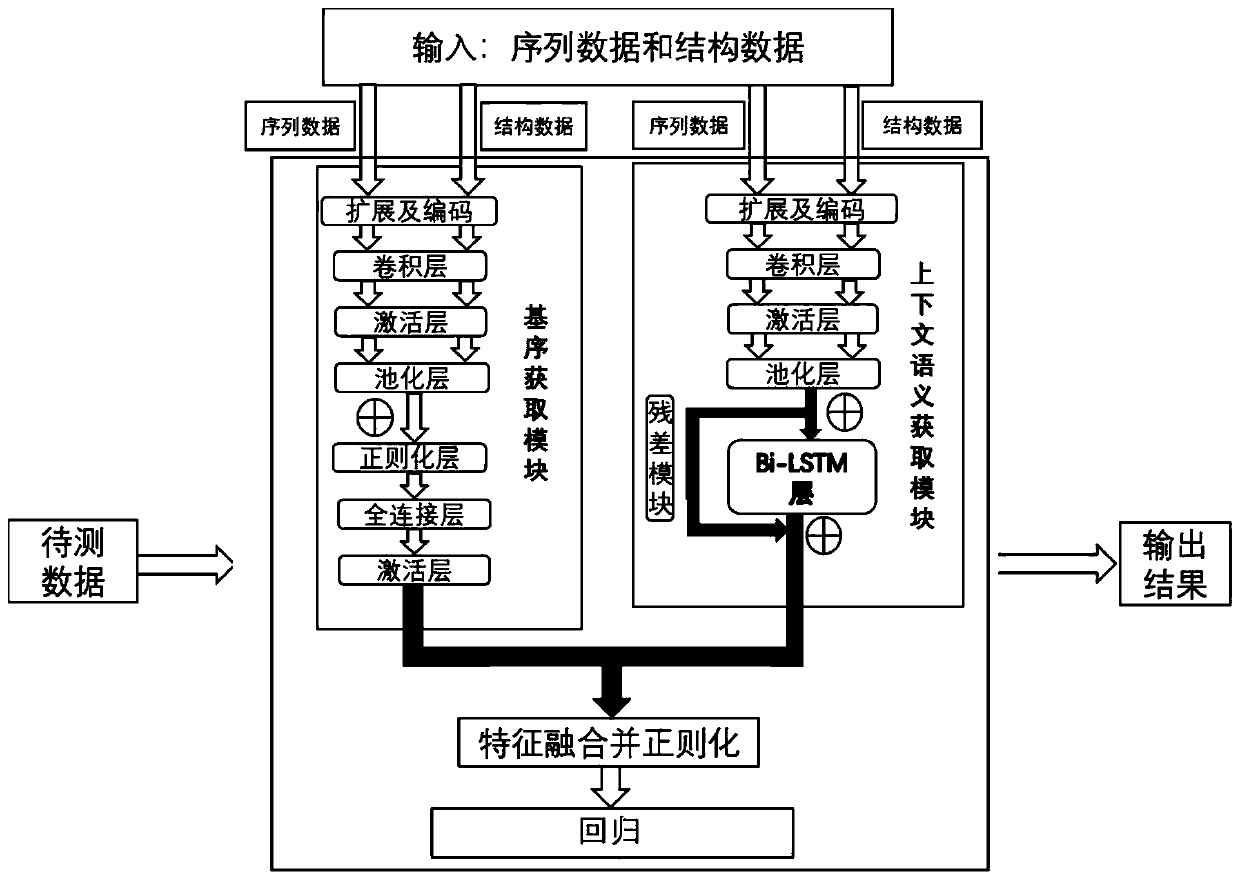
Method and system for constructing models for predicting protein-RNA interaction binding sites
ActiveCN111192631AImprove forecast accuracyGood time complexityProteomicsGenomicsBinding siteData mining
The invention provides a method and a system for constructing a model for predicting protein-RNA interaction binding sites. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a method and a system for predicting the protein-RNA interaction binding sites by using the method. A deep learning model is trained using sequence characteristics at and upstream and downstream of an RNA and protein binding site and measured RNA structure characteristics, and the model is used to predict a protein-RNA interaction binding site. In the feature extraction process, a motif acquisition module constructed based on aconvolutional neural network and a context semantic acquisition module constructed based on a recurrent neural network are used. Compared with the prior art, the trained model has remarkable progressin the aspects of judgment accuracy, calculation time and universality of an application platform.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
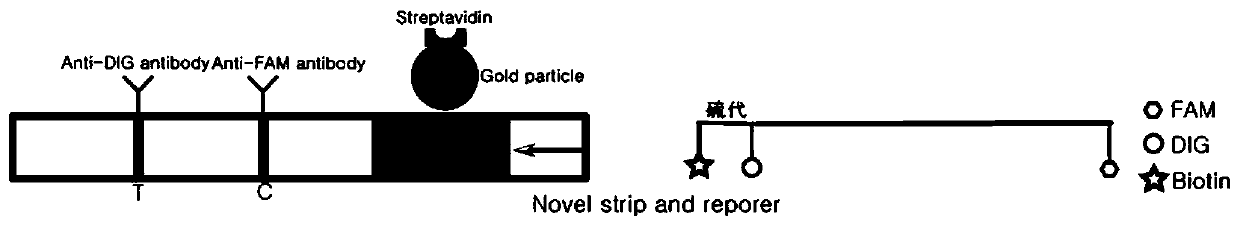
Detection method based on CRISPR/Cas and nucleic acid test paper and human papilloma virus detection kit
PendingCN111560482AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid testSingle strand
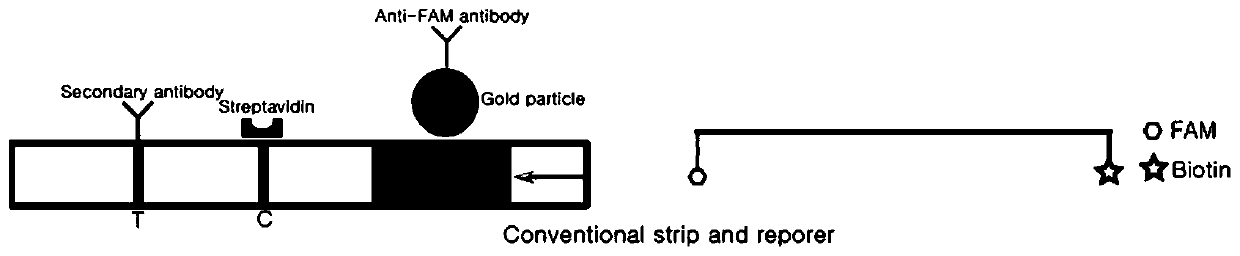
The invention relates to the technical field of gene detection, in particular to a nucleic acid detection method based on CRISPR / Cas and nucleic acid test paper and a human papilloma virus rapid detection kit. The human papilloma virus detection kit comprises crRNA, Cas12, RPA upstream and downstream primers, a buffer system and a single-stranded DNA reporter molecule, the sequence of the reportermolecule is 5 '-NNN......-3', the length of the reporter molecule is 3-30 basic groups, FAM, DIG and Biotin labeling is carried out, and meanwhile modification for preventing DNA enzyme or cas12 degradation after activation is carried out on nucleic acid molecules. The CRISPR / Cas and nucleic acid test paper-based nucleic acid detection method and the human papilloma virus rapid detection kit havethe advantages that innovative reporter molecule design and modification are adopted, and corresponding test paper strips are combined, so that non-specific color development is completely eradicated, and the kit has remarkable significance in clinical practical application.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
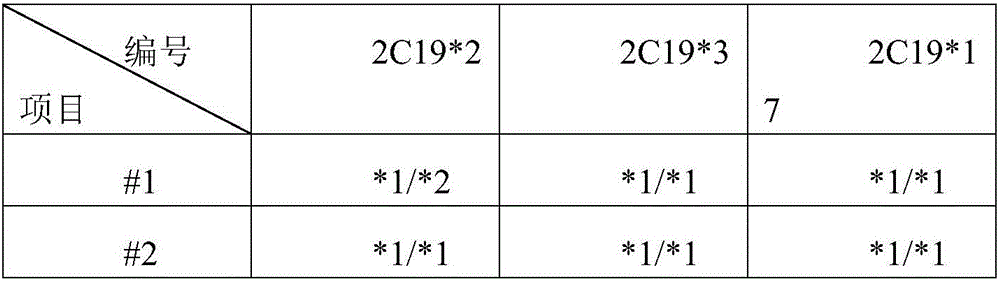
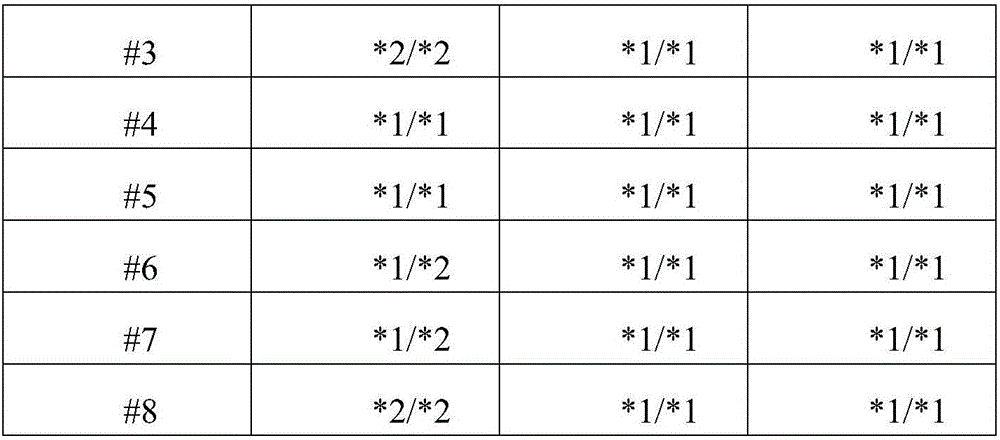
Detection probe for SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) of human CYP2C19 gene and application of detection probe
InactiveCN106702019AIncreased sensitivityHigh Primer Match RateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluoProbesMedicine
The invention provides a detection probe for an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) of a human CYP2C19 gene. A detection primer consists of a specific upstream and downstream primer pair of the gene and a specific Taqman double fluorescent probe which are respectively used for correspondingly detecting SNPs at CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3 and CYP2C19*17 sites. The detection probe has the characteristics of quick detection and high specificity; furthermore, the detection method is simple; positive contrast and negative contrast which are necessary to conventional fluorescent quantitation PCR are eliminated, so that the operation steps and the experimental cost are reduced; the subsequent clinical treatment strategy can be guided more quickly and better.
Owner:北京一立科技发展有限公司
Method for constructing high-throughput sequencing library of immune group library for screening cross-reaction between samples
PendingCN110257476ASolve the problem of preferenceSolve the problem of cross-reactivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeReceptor for activated C kinase 1
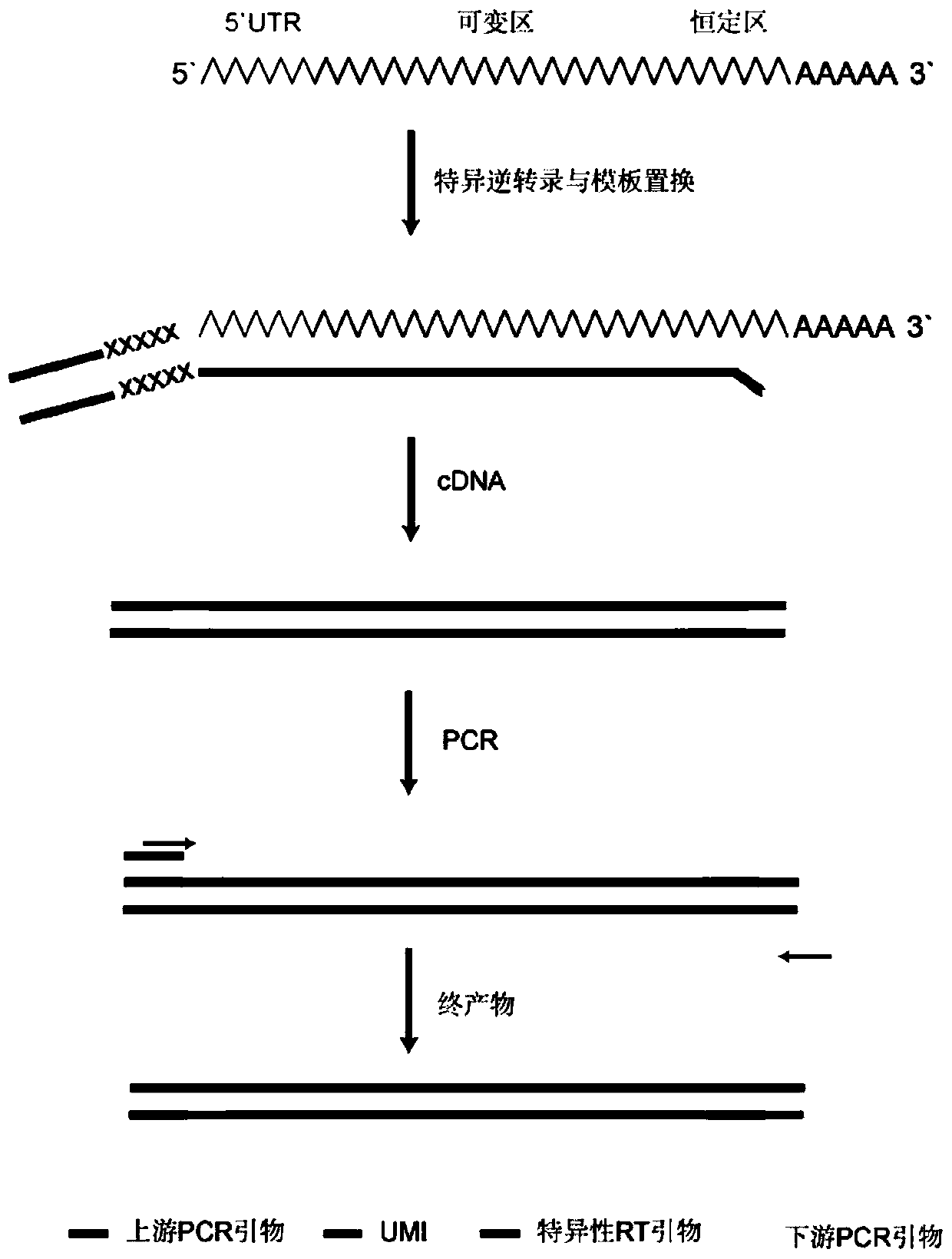
The invention relates to a method for constructing a high-throughput sequencing library of an immune group library for screening a cross-reaction between samples. The method is characterized in that: RNA of more than 10 ng is taken as a starting amount, a principle of RACE is used to make the template conversion when the RNA is reversely transcribed into cDNA, a known sequence is added to the 5' ends of all cDNAs, a product with the known sequence is used as a template, PCR amplification is performed by using a double-ended Barcode primer, the resulting product is purified and ligated to a sequencing linker sequence to obtain the final sequencing library, which can be used for samples of different receptor sources, during PCR amplification, PCR amplification can be performed using only one pair of primers to achieve equivalent amplification, and the primer preference problem caused by multiplex primer amplification is solved, and the upstream and downstream primers used in PCR amplification are designed to be labeled with Barcode composed of 4 to 12 different bases, which avoids the problem of cross-reaction between samples when multiple samples are simultaneously constructed.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Primer probe for detecting mutation of KRAS gene and kit thereof
InactiveCN107022619AStrong specificityTo achieve the purpose of specific bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTrue positive rateMultiplex pcrs
The invention relates to a primer probe for detecting mutation of a KRAS gene and a kit thereof. The kit comprises digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction) premix liquid, a liquid droplet stabilizer and primer probe mixing liquid, wherein the digital PCR premix liquid is used for preparing digital PCR reaction liquid; the primer probe mixing liquid comprises upstream and downstream primers A for detecting a 12th codon, a mutation probe A for a G12R site of the 12th codon, a mutation probe B for a G12V site of the 12th codon, a mutation probe C for a G12D site of the 12th codon, a mutation probe D for a G12A site of the 12th codon, a mutation probe E for a G12S site of the 12th codon, and a mutation probe F for a G12C site of the 12th codon; upstream and downstream primers B for detecting a 13th codon, and a mutation probe G for a G13D site of the 13th codon; upstream and downstream primers C for detecting a 61st codon, and a mutation probe H for a Q61L site of the 61st codon. The kit for detecting the mutation of the KRAS gene has the advantages that the sensitivity and specificity are high, the sample demand amount is small, and multiplex PCR detection can be rapidly and accurately performed.
Owner:上海赛安生物医药科技股份有限公司
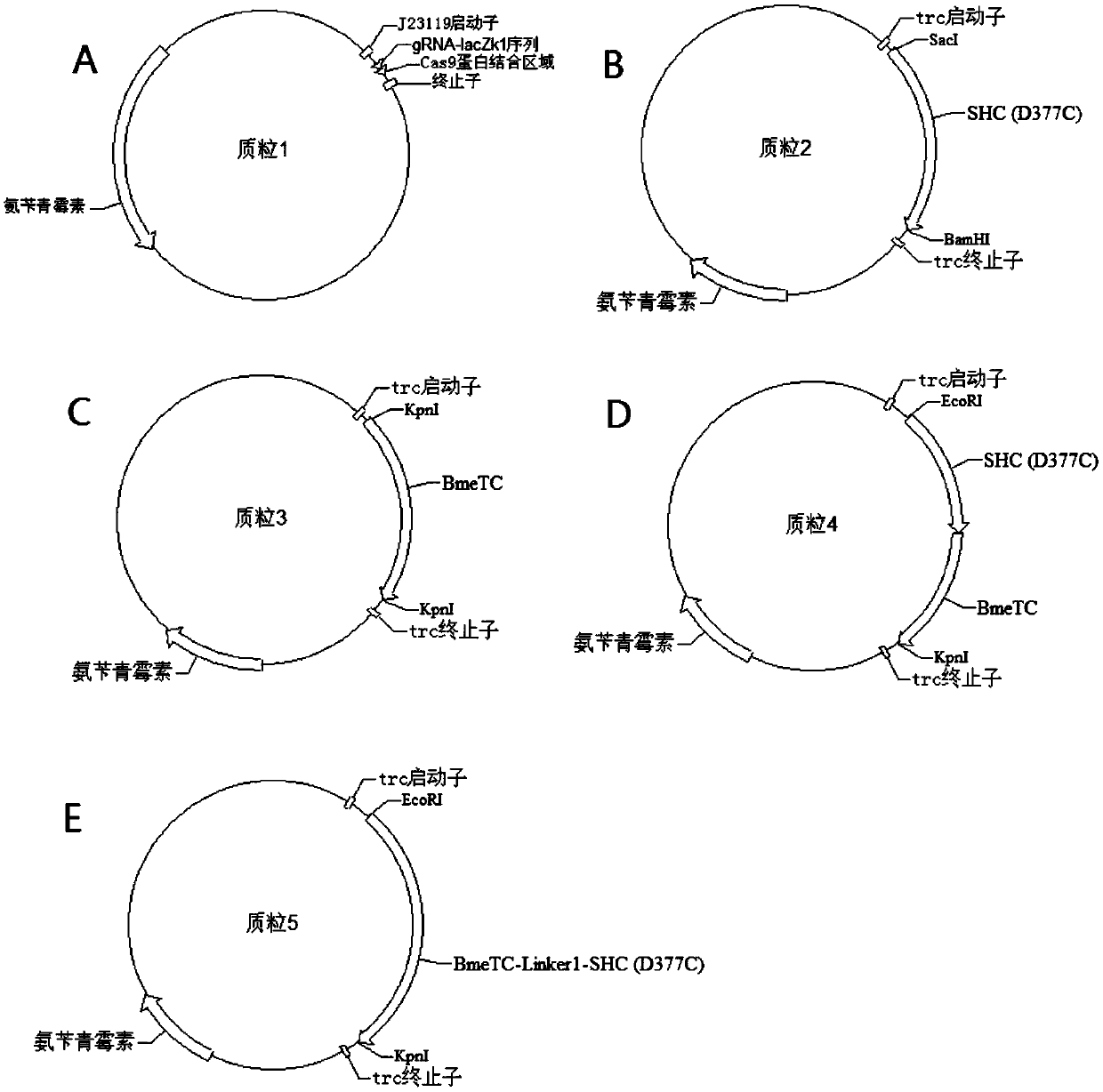
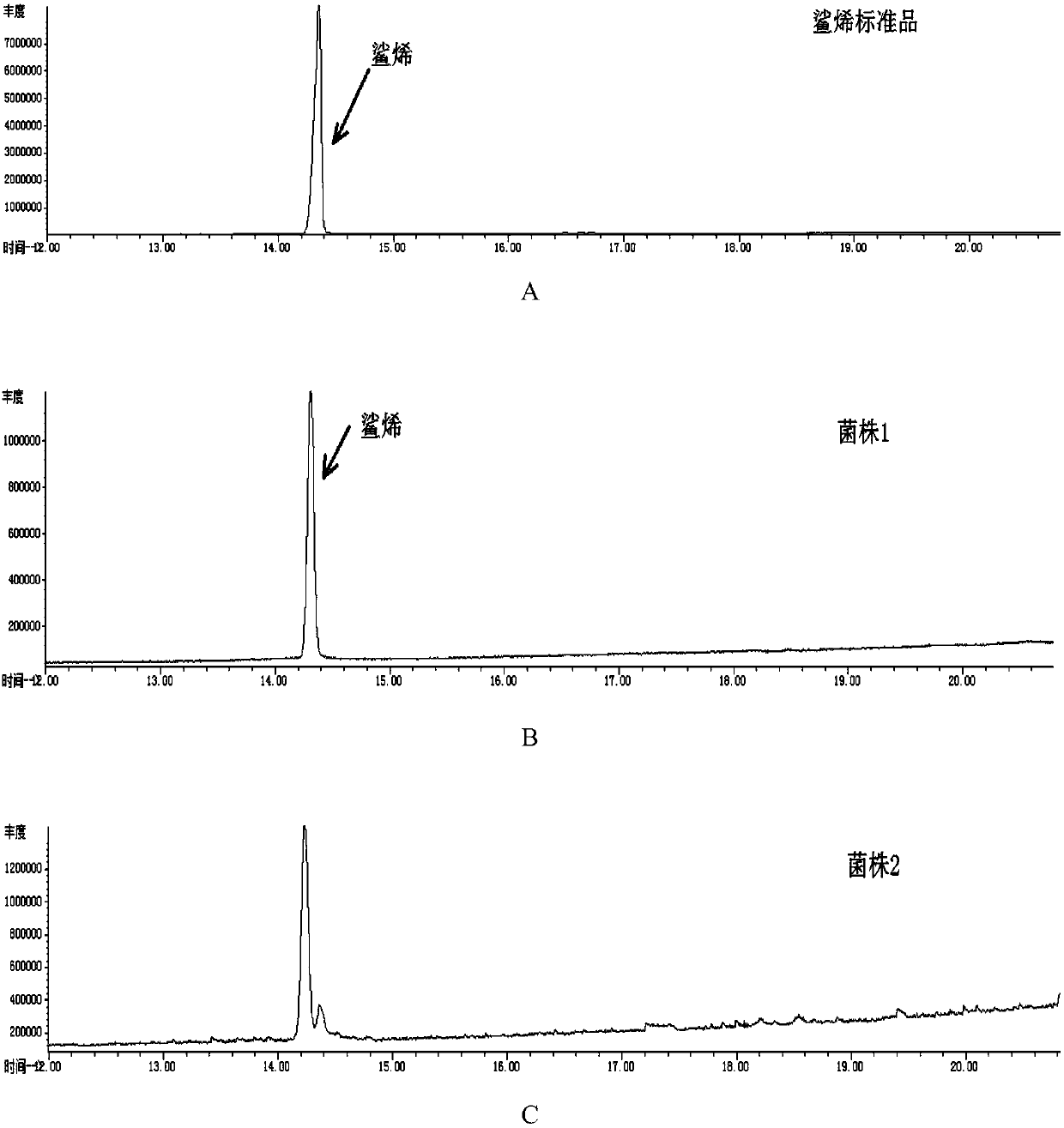
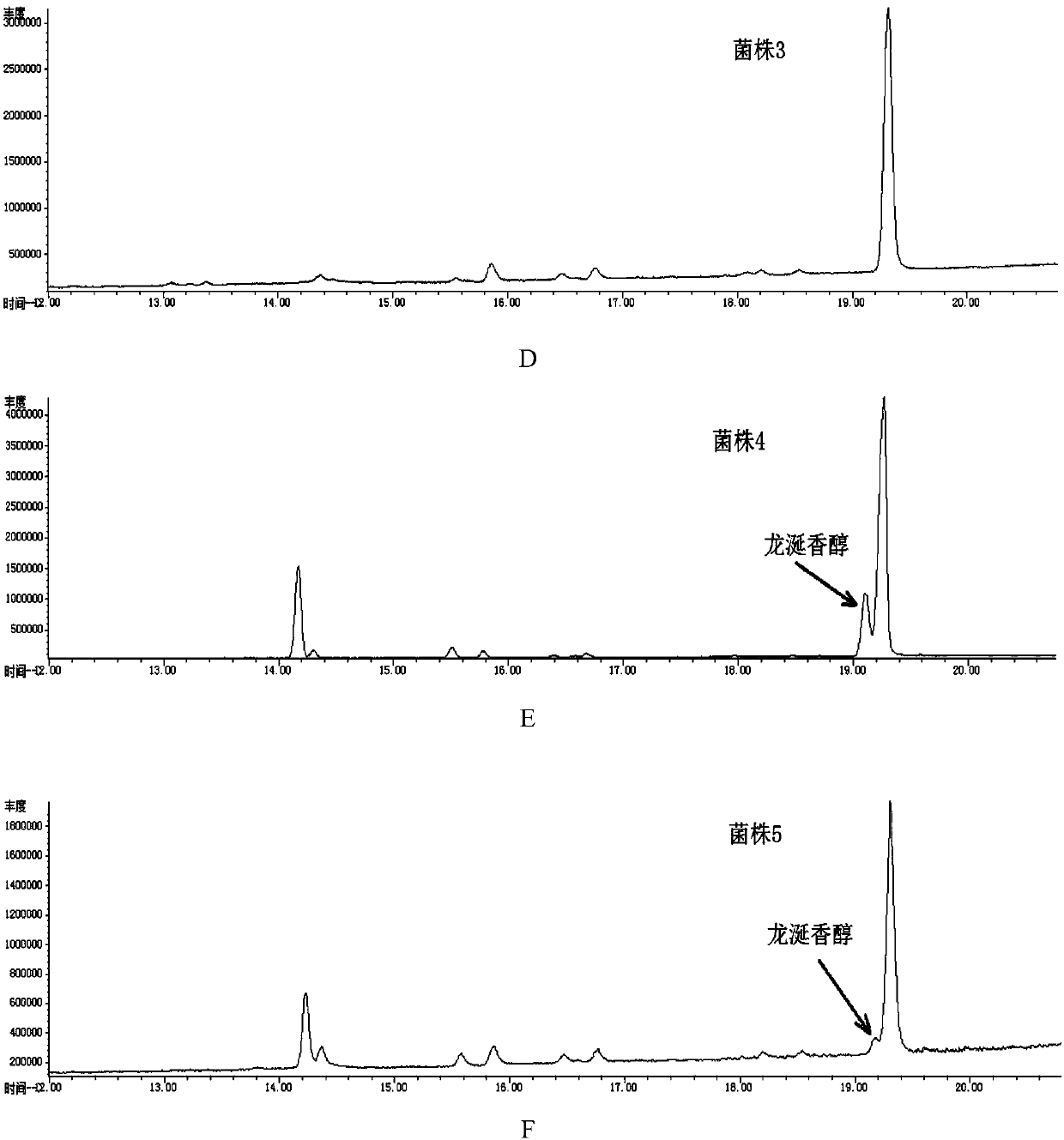
Recombinant escherichia coli for heterologously synthesizing ambrein and construction method thereof
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for heterologously synthesizing ambrein and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps of: (1) fusing saccharomyces-cerevisiae squalene synthase gene ERG9 with truncation of 26 amino acid residues at a C end and homologous arms at the upstream and downstream of a lacZ site of the escherichia coli into adonor DNA; constructing plasmid 1; transforming the donor DNA and the plasmid 1 together into the escherichia coli, eliminating the plasmid 1, obtaining the recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing squalene, and naming the recombinant escherichia coli as a strain 1; (2) connecting alicyclobacillus-acidocardarius squalene-hopene cyclase gene D377C SHC with mutation from the 377th amino acid residue into cysteine residue and bacillus-megaterium cyclase gene BmeTC into one segment, then inserting the segment into escherichia-coli expression plasmid p5C to obtain plasmid 4; (3) transforming the plasmid 4 into the strain 1 to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli for heterologously synthesizing the ambrein, and naming the recombinant escherichia coli as a strain 4. Proved by experiments,the recombinant escherichia coli for heterologously synthesizing the ambrein is fermented to obtain the ambrein.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Molecular identification method of HMGR gene mRNA in pear stock-scion transfer
ActiveCN107460200ASolve the problem that RT-PCR identification cannot be carried out by designing specific primersIt is difficult to solve the technology and takes a long timeMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesMolecular identificationEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a molecular identification method of HMGR gene mRNA in pear stock-scion transfer. The molecular identification method comprises the following steps: (1) by taking pyrus bretschneideri rehd as scion and pyrus betulifolia bunge as stock, carrying out micro grafting of test-tube seedlings; (2) extracting total RNA of pyrus bretschneideri rehd, pyrus betulifolia bunge and grafted stock and scion, carrying out reverse transcription to obtain cDNA, carrying out PCR amplification on the total length of the HMGR gene, and carrying out second-time PCR by adopting the amplification result as a template, thus obtaining respective HMGR gene fragments, wherein the sequences of upstream and downstream primers obtained through two times of PCR are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1-4; and (3) carrying out enzyme digestion on the PCR product obtained for the second time by adopting restriction endonuclease, and comparing enzyme digestion spectrograms before and after grafting for identifying the transfer condition. The method provided by the invention is rapid and sensitive, is high in accuracy, is simple and convenient, and can be applied to other pear plants.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Vector for knocking out L-lactic dehydrogenase 1 gene and construction method of vector
InactiveCN104673819AUse lessAvoid joiningMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Construction method of gene detection library of hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and kit
InactiveCN109486937AEfficient captureImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationHybridization probeHypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The invention discloses a construction method of a gene detection library of hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and a kit and relates to mutation of ACTC1, ACTN2, MYBPC3, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, TNNI3,TNNT2 and TPM1 genes. Target regions comprise an exon region of coding amino acid of the 9 genes and 20 basic group regions at the upstream and downstream of an exon; in order to ensure that all the target regions are covered, a target region library is obtained through a hybridization probe capturing method after the library is prepared; then an LMPCR (Ligation-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reaction)method is adopted to amplify the library; and after the library is purified, a sample library for sequencing is obtained. The library construction method has simple steps and a rapid speed and the cost of constructing the library is effectively reduced; related genes of the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are covered; an illumina high-throughput sequencing machine is combined and related gene mutation can be rapidly and accurately obtained; and the construction method has great significance on the hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Owner:ANNGEEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Application of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) sites of yak whole genome, primer set for detecting and kit
ActiveCN108251540AImprove measurement accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMolecular breeding
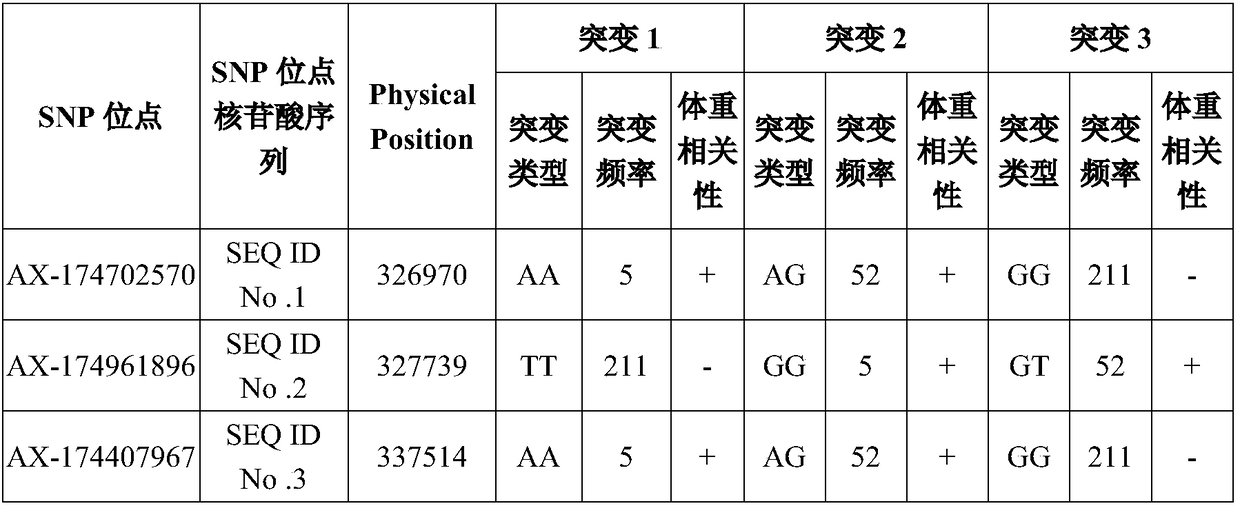
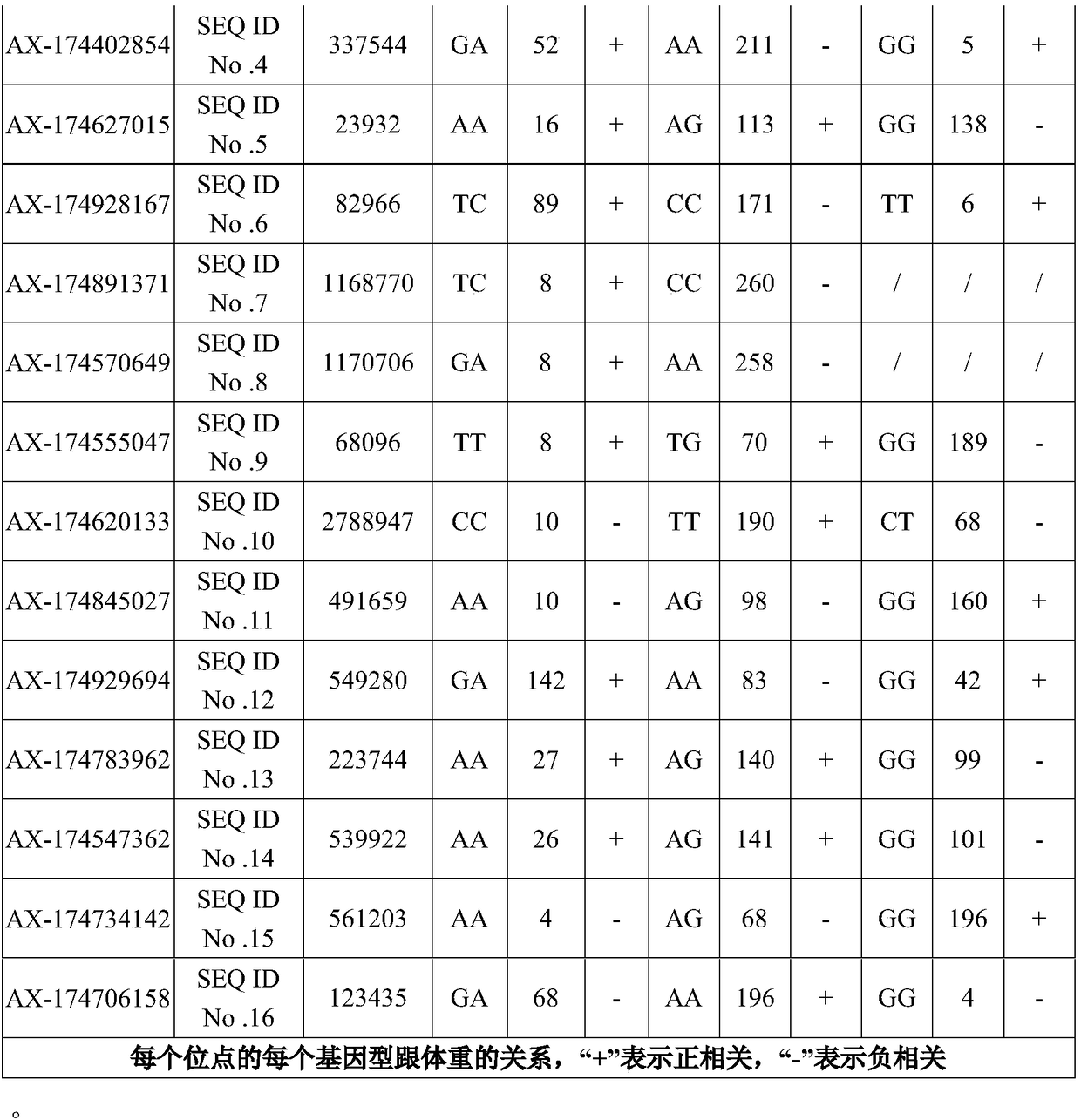
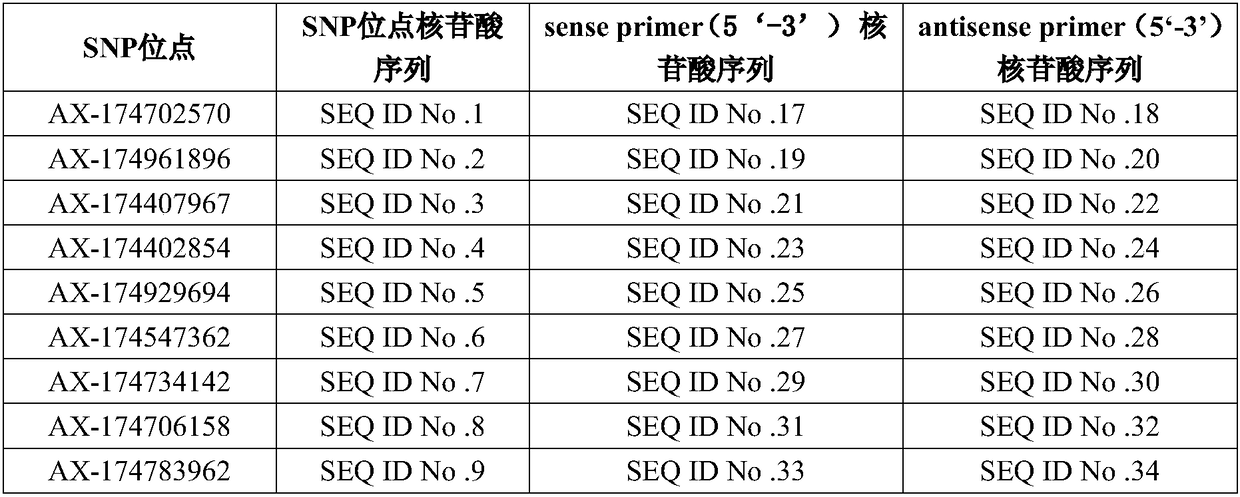
The invention discloses application of 16 SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) sites of a yak whole genome in yak phenotypic character or molecular breeding analysis, aiming at solving the problem inthe prior art that the yak phenotypic character or molecular breeding analysis is not carried out by adopting the SNP sites. Nucleotide sequences of the 16 SNP sites provided by the invention are shown as SEQ ID No. 1 to SEQ ID No. 16. The invention further discloses a primer set for detecting the 16 SNP sites and a kit comprising the primer set. The invention further discloses a yak phenotypic character or molecular breeding analysis method. The 16 SNP sites provided by the invention can provide supports for an upstream and downstream breeding process and have the advantages of high determination accuracy, easiness for realizing standard and automatic detection and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY TIBET ACADEMY OF AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI +2
Novel coronavirus detection kit
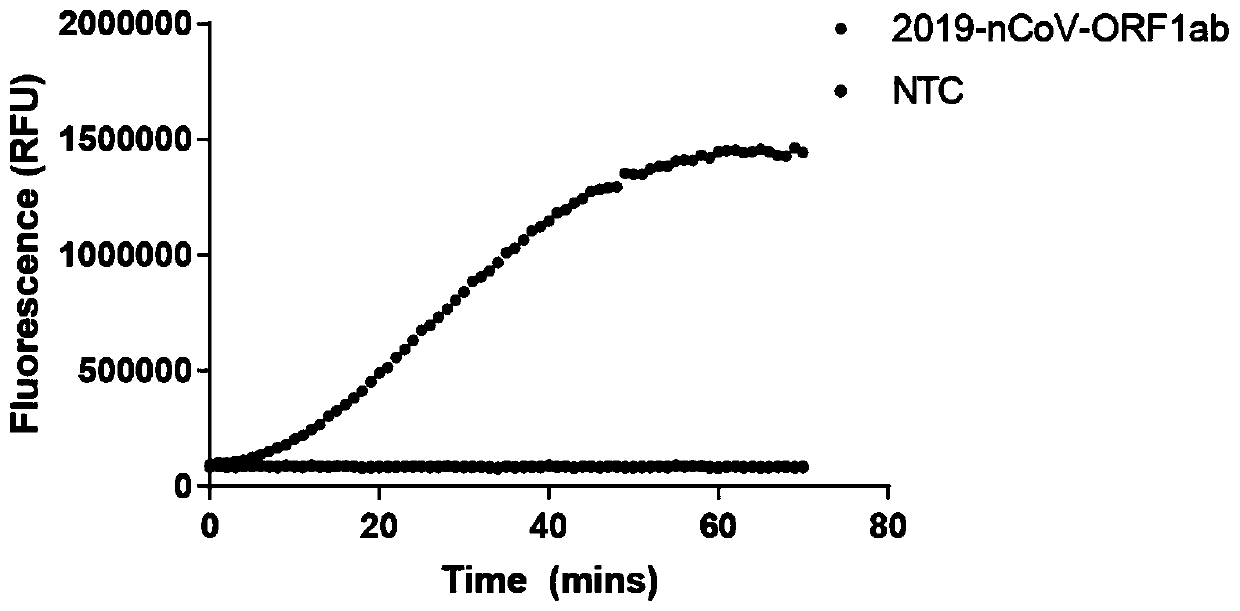
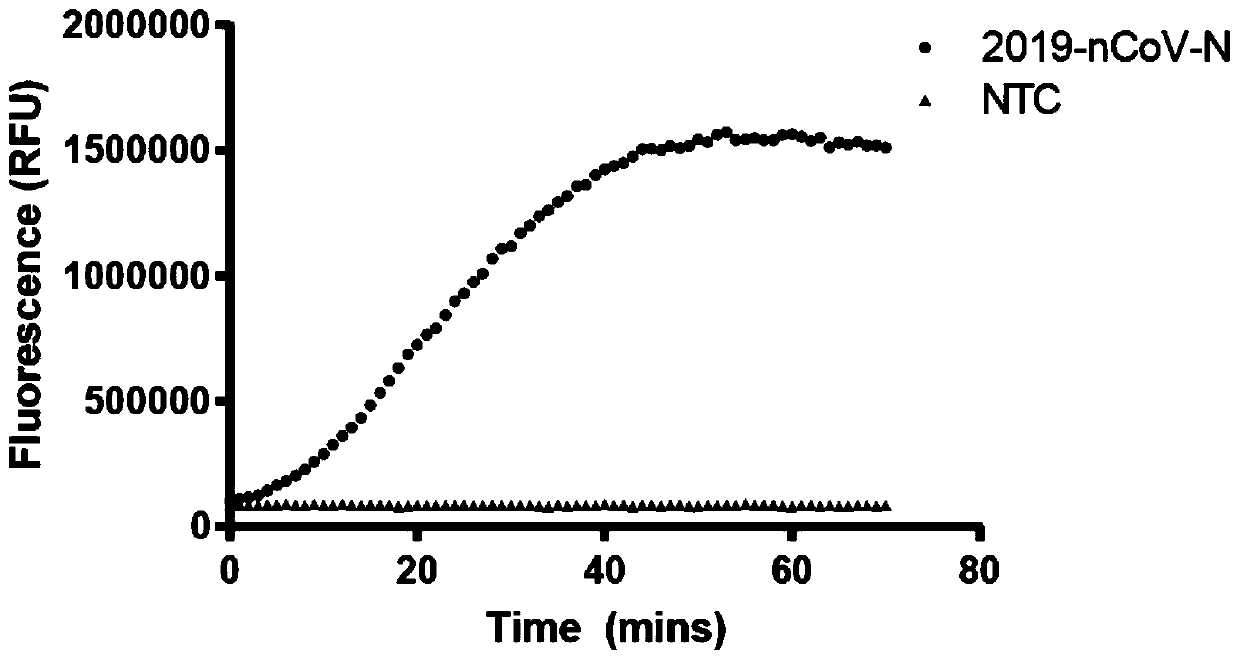
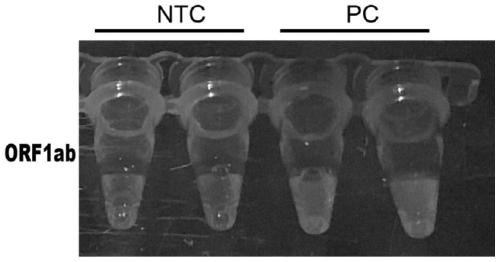
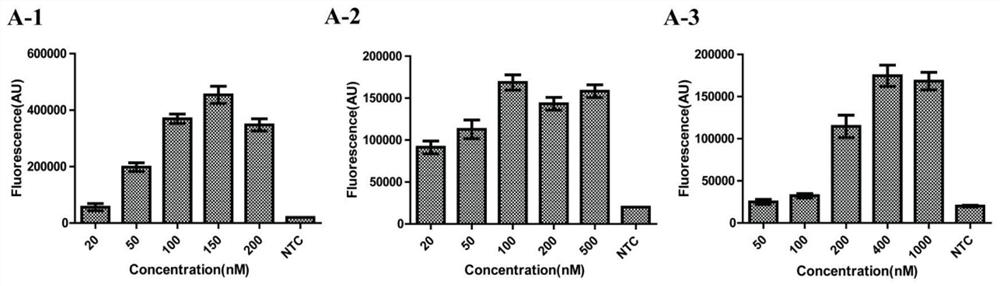
PendingCN111500792AFast, accurate and convenient detectionGet rid of dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerSimple sample
The invention relates to the technical field of gene detection, in particular to a novel coronavirus detection kit which comprises crRNA, Cas12 protein, RPA upstream and downstream primers, a buffer system and a single-stranded DNA reporter molecule. The crRNA is crRNA which is designed to be specific for a target gene; the upstream and downstream primers of the RPA are as follows: a 5'-TTTN-3' sequence is searched for aiming at a conserved region ORF1ab and an N gene region of the novel coronavirus, a forward primer is designed within 0-200 bp nearby the 5'-region of the novel coronavirus, and a reverse primer is designed within 25-200 bp nearby the near 3'-region of the novel coronavirus. The method has the advantages that due to the fact that RPA isothermal amplification has low requirements for samples, a rapid and simple sample treatment mode can be adopted, RPA-mediated DNA amplification can be conducted at the temperature of 30-42 DEG C, and dependence on a precise PCR instrument is avoided.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
Salmonella detection primer group, method and kit based on RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system
InactiveCN113186313AChanging binding energyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideSalmonella
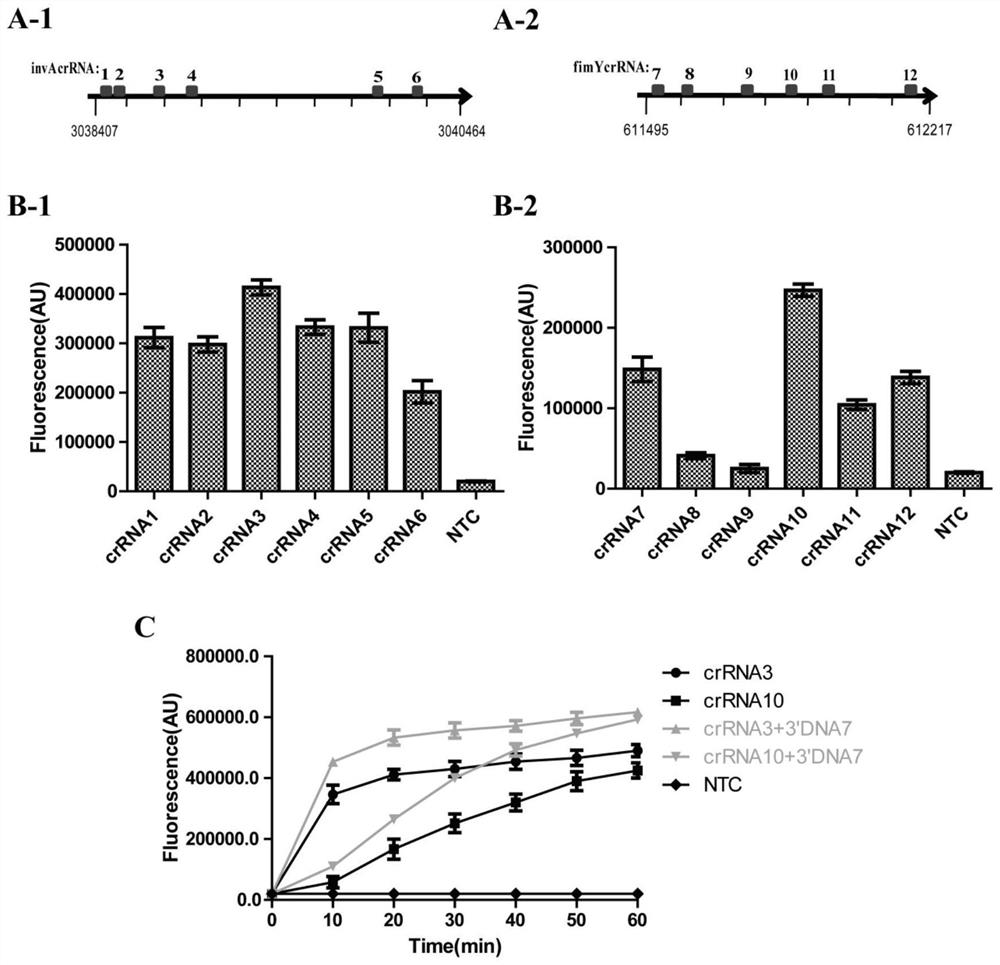
The invention provides a salmonella detection primer group, a salmonella detection method and a salmonella detection kit based on an RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system, and relates to the field of salmonella detection. Based on the combination of a recombinase polymerase amplification technology and a CRISPR gene detection technology, salmonella is detected through an optimized and modified crRNA double-target gene combination, crRNA is screened and optimized aiming at an invA gene and a fimY gene of the salmonella respectively, and upstream and downstream primers for RPA reaction are designed according to nucleotide sequences at two ends of a matched sequence of the crRNA, so that the primer group is obtained. According to the primer group and the crRNA, the RPA-LbCas12a-TTECDS system is designed, and t hesalmonella detection method and kit are established according to the system. The detection method and the kit provided by the invention are used for detecting actual samples, and have the advantages of strong specificity, rapid detection, high sensitivity and high precision.
Owner:常州市疾病预防控制中心
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method and kit for quickly diagnosing bovine parainfluenza virus 3 (BPIV-3)
InactiveCN102212622AShorten the timeReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBovine parainfluenza virusMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method and a kit for quickly diagnosing bovine parainfluenza virus 3 (BPIV-3), and belongs to the field of biomedical detection. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the method comprises acquisition of a sample, extraction of virus RNA, design optimization of a specific primer, RT-PCR amplification, agarose gel electrophoresis and result judgment; the specific primer is designed for a specific fragment of BPIV-3 nucleoprotein (NP) genes, and the upstream and downstream sequences of the specific primer are respectively P1: 5'-GGATGTTTGGGAGTGATCTTGAGTA-3' and P2: 5'-TGTGTTGAAAAATGAAGCAAGACCT-3'; the quick RT-PCR diagnosing kit for detecting the BPIV-3 comprises a sample virus RNA extracting reagent, a reverse transcription reagent, a PCR reagent, a positive reference substance and a negative reference substance; and by verifying, the method is sensitive and specific and has applicationprospect.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Kit for detecting HER2 gene amplification by digital PCR
InactiveCN110669843AReduce human interferenceThe result is stableMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoProbesAbsolute quantification
The invention belongs to the technical field of HER2 gene amplification detection reagents, and particularly relates to a kit for detecting HER2 gene amplification by digital PCR. The kit comprises aprimer probe premixed solution, the primer probe premixed solution comprises (1) upstream and downstream primers for detecting an HER2 gene and a fluorescent probe for detecting the HER2 gene; (2) upstream and downstream primers for detecting a human FAS gene, and a fluorescent probe for detecting the human FAS gene; and (3) upstream and downstream primers for detecting a human ACTB gene, and a fluorescence probe for detecting the human ACTB gene. The kit for detecting the HER2 gene amplification provided by the invention can conduct absolute quantification compared with real-time fluorescentquantification PCR, and a detection lower limit is obviously lower than the fluorescent quantification PCR. Moreover, a primer probe combination of the kit has high specificity and better detection effect.
Owner:宁波胤瑞生物医学仪器有限责任公司
TALEN and pMD18 vector-based site-directed mutagenesis system and its application
InactiveCN104212778AStable passageAccurate passagingHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionDouble strandTarget gene
The invention relates to a TALEN and pMD18 vector-based site-directed mutagenesis system and its application. The system is composed of nuclease TALEN and a pMD18 vector, the nuclease TALEN is a transcription activator-like effect factor shearing a target gene target sequence, and the TALEN is composed of nuclease TALEN-L identifying the 5'-terminal of the target sequence and nuclease TALEN-R identifying the 3'-terminal of the target sequence; and the pMD18 vector is a pMD18 homologous recombinant template plasmid inserted into human AR site-directed mutagenesis gene, and the pMD18 vector is composed of corresponding upstream and downstream sequence of the target gene, and a puromycin screening marker. The system allows genome to be efficiently and accurately edited by using the homologous sequence provided by the Pmd18 vector during the cut-out of a double strand DNA molecule by the TALEN; and puromycin resistant gene is carried out when the introduced homologous sequence is adopted to edit the DNA sequence, so manual labor in the screening process is substantially reduced.
Owner:SHAOXING PEOPLES HOSPITAL
CDKN2A gene fragment and application of primers of CDKN2A gene fragment in diagnosing tumors
InactiveCN105779465AEasy to operateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDNA methylationNormal people
The invention discloses a CDKN2A gene fragment and application of the primers of CDKN2A gene fragment in diagnosing tumors.By designing an upstream and downstream primer pair, the specific CDKN2A gene fragment is determined, the gene fragment shows remarkable high DNA methylation in tumor patients while showing low DNA methylation in normal people, and statistic differences exist between DNA methylation of tumor patients and that in normal people.Occurrence and development of tumors are tracked with the level changes of DNA methylation of the gene fragment, and thus a novel biomarker is provided for diagnosis, treatment effect monitoring and prognosis improvement judgment of tumors.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
DNA template for modifying primary cells by gene editing and fixed-point insertion method
PendingCN112210573ASimple production processAvoid tumor pathogenicityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorDiseaseA-DNA
The invention mainly discloses a DNA template for modifying primary cells by gene editing and a fixed-point insertion method. The DNA template comprises a plasmid, a target gene which is constructed on the plasmid and needs to be introduced, homologous sequences (homologous arms) at the upstream and downstream of a target sequence, and a DNA sequence recognized by Guide RNA; then, an RNP complex of a gene editing protein and the Guide RNA, and the DNA template are delivered to a cell line or a primary cell by utilizing an electroporation technology, so that a target gene is inserted into a genome of the cell line or the primary cell at a fixed point, and the cell line or the primary cell is modified. One practical application of the DNA template is that a chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell inserted at a fixed point can be produced without depending on viruses, and therefore, the DNA template has better safety and effectiveness in the application of immune cells for treating diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
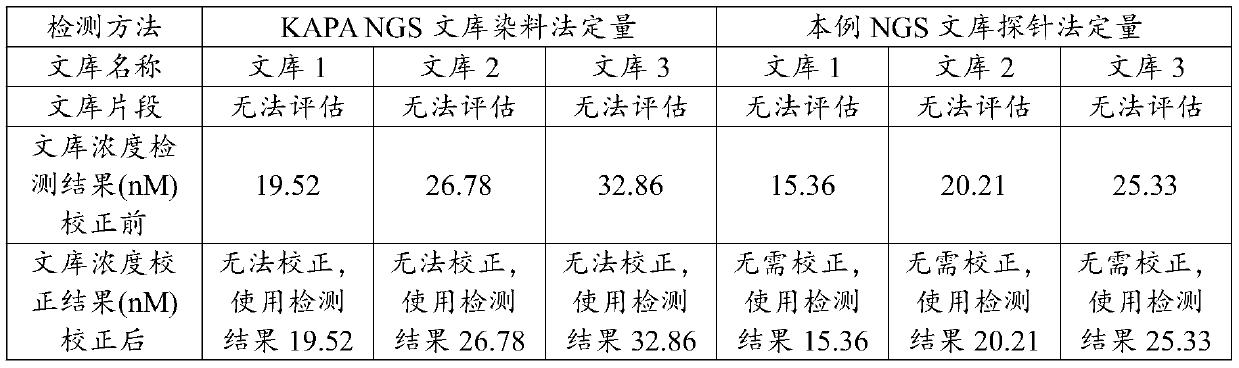
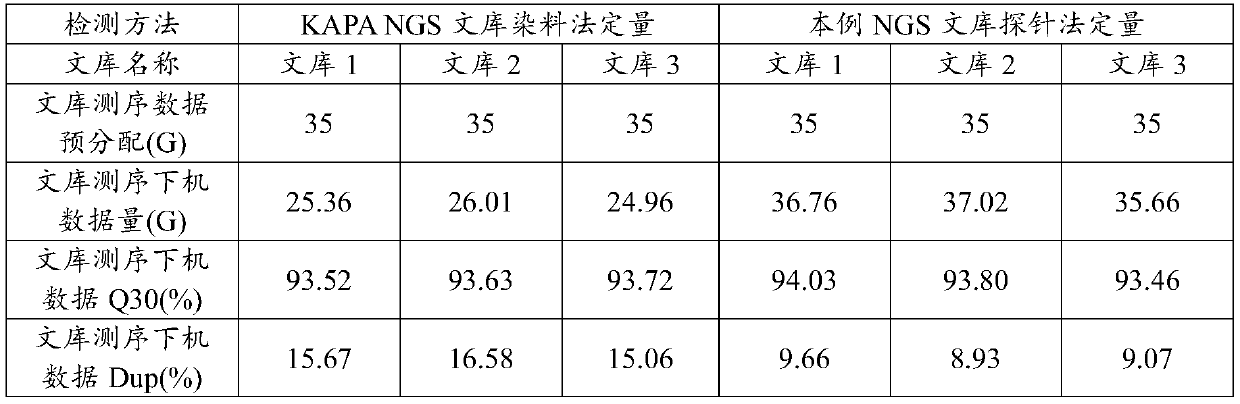
Test kit and detection method for quantitative detection of high-throughput sequencing library
PendingCN111088328AAchieving absolute quantificationGet the actual concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorophoreA-DNA
The invention discloses a test kit and a detection method for quantitative detection of a high-throughput sequencing library. The test kit comprises a detection primer and a detection probe which aredesigned for the joint sequence of a to-be-detected high-throughput sequencing library, wherein upstream and downstream primers of the detection primer have sequences shown as Seq ID No.1 and Seq ID No.2; the detection probe has a sequence shown as Seq ID No.3; the 5'end of the detection probe is modified by a fluorophore; and the 3'end of the detection probe is modified by a fluorescence quenching group. According to the test kit, an NGS library is quantitatively detected through a TaqMan probe method, and absolute quantification of the NGS library can be achieved; and compared with a conventional dye method for QPCR quantitative detection, the test kit can obtain the actual concentration of the NGS library more accurately; the size of a DNA fragment based on the NGS library does not needto be corrected, which is of great significance to high-throughput sequencing; and the sequencing quality can be improved, so an optimal sequencing data result is obtained.
Owner:深圳海普洛斯医学检验实验室 +1
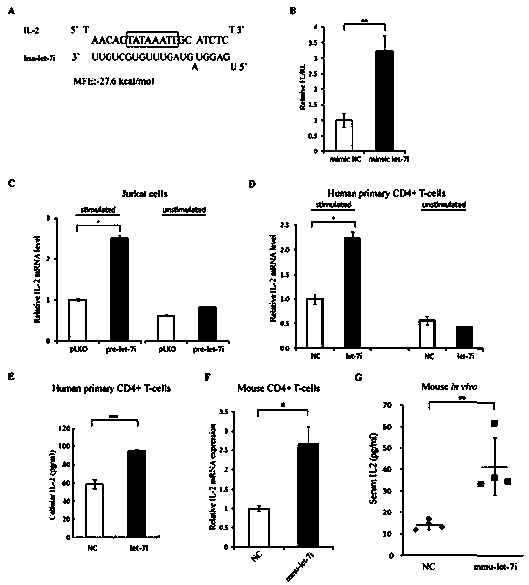
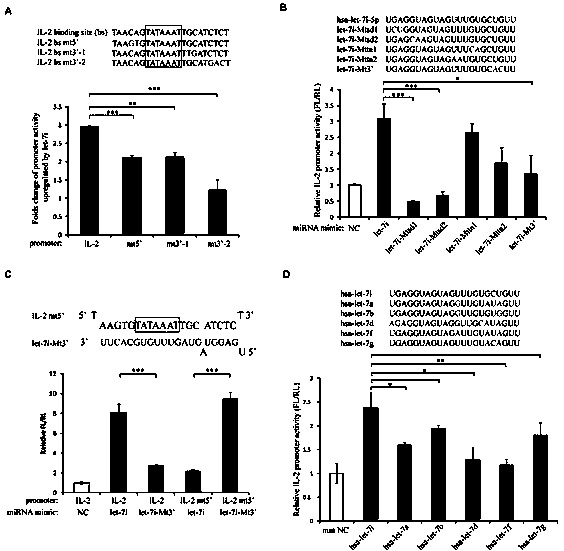
Small molecule RNA, preparation method thereof and application in pharmaceuticals for transcriptional activity of specificity up-regulated genes
ActiveCN103509797AHigh expressionUpregulates gene transcription activityGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyTranscription initiation siteBase J
The invention discloses a method for specificity up-regulated gene expression through a targeting core promoter utilizing small molecule RNAs (including micro-RNAs and small interfering RNAs) and a series of regulation target genes. According to the invention, when a TATAbox sequence is contained in the promoter, a target site is in the range of expanding 20 basic groups from the upstream and downstream sides respectively by taking the TATAbox sequence as the center; when no TATAbox sequence is contained in the promoter, the target site is a 1-50 sequences on the upstream side of the genetic transcription initiation site. The micro-RNAs hsa-let-7i, hsa-miR-138, hsa-miR-92a, hsa-let-7c and hsa-miR-181d specifically regulate up the expression of interleukin-2, insulin, thyrocalcitonin, histone and c-myc gene respectively. Besides, aiming to the randomly-selected 19 gene promoters, the artificially-synthesized small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can enhance the transcriptional activities of 78.9% of the genes. The invention aims to provide the method for specificity up-regulated gene expression utilizing micro-RNAs and has higher application values and broad application prospects in the biotechnology and the biomedicine field.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QIANYANG BIO-TECH PHARM CO LTD
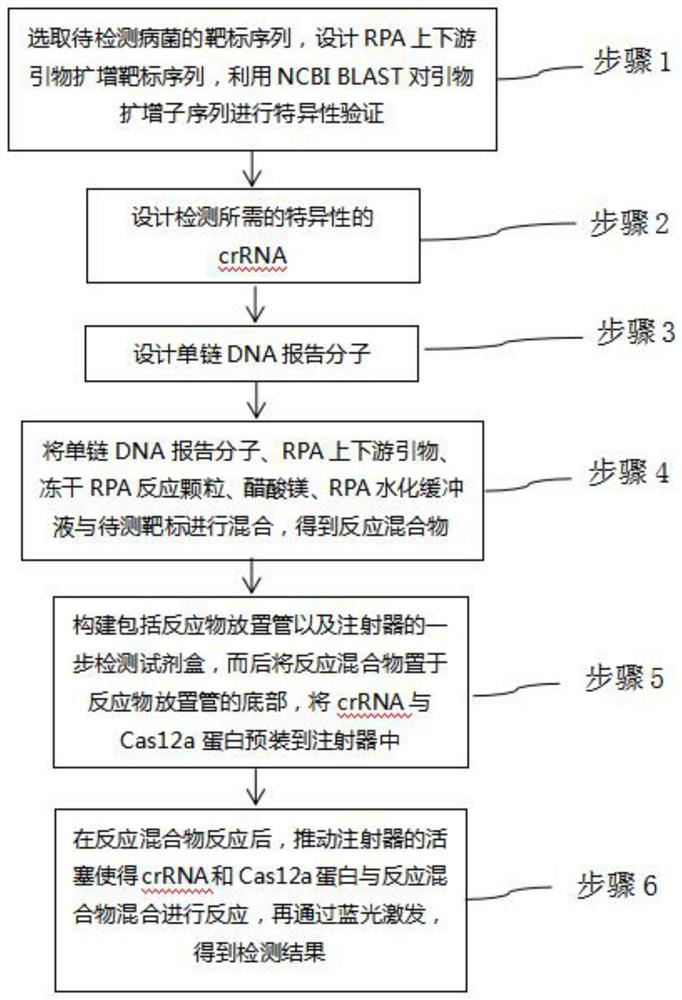
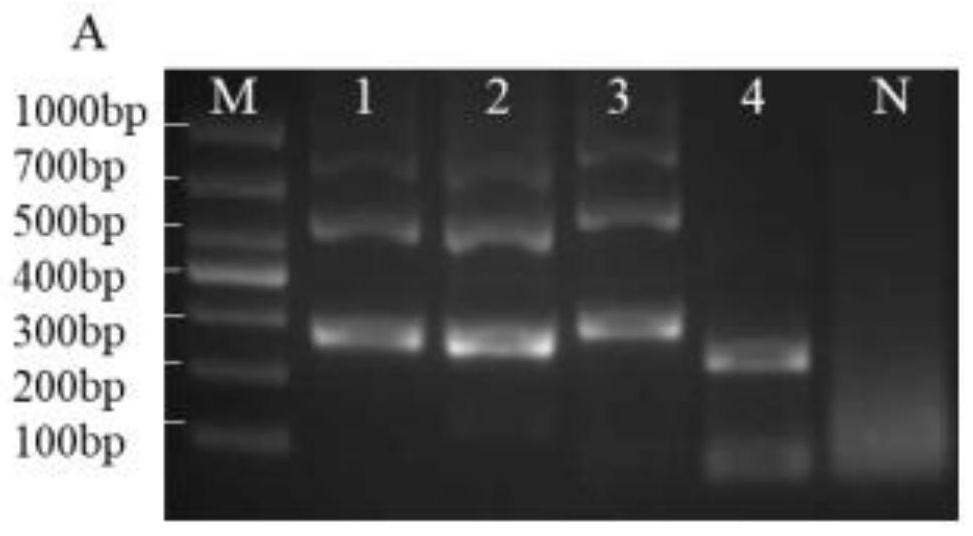
CRISPR/Cas12a one-step nucleic acid detection method
PendingCN112695073ANo pollutionEfficient use ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionEthylic acid
The invention provides a CRISPR / Cas12a one-step nucleic acid detection method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting a target sequence of bacteria to be detected, designing upstream and downstream primers of RPA, performing specific screening, amplifying the target sequence to obtain a primer amplicon sequence, and performing specific verification on the primer amplicon sequence by utilizing NCBI BLAST; 2, designing specific crRNA; 3, designing a single-stranded DNA reporter molecule; 4, mixing the single-stranded DNA reporter molecule, the RPA upstream and downstream primers, freeze-dried RPA reaction particles, magnesium acetate, an RPA hydration buffer solution, NEB buffer 2.1, RNase Inhibitor and a target to be detected to obtain a reaction mixture; 5, constructing a one-step detection kit comprising a reactant placing tube and an injector, placing the reaction mixture at the bottom of the reactant placing tube, and preloading crRNA and Cas12a protein into the injector; and 6, after the reaction mixture reacts, pushing a piston of the injector to enable the crRNA and the Cas12a protein to be mixed with the reaction mixture for a reaction, and performing blue light excitation to obtain a detection result.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for multicopy integration of target gene to saccharomyces cerevisiae genome
InactiveCN110699383AAchieving multi-copy integrationShort timeHydrolasesStable introduction of DNANucleaseGene expression
A method for multicopy integration of a target gene to a saccharomyces cerevisiae genome includes: selecting target sequences, designing homologous arm primers in length of 15-90bp on two sides of each cleavage site in the corresponding target sequences to primer front ends of amplification target gene cassettes to synthesize homologous arm loaded primers, and amplifying the target gene cassettesto obtain donor DNA fragments; subjecting transcribed gRNA vectors in corresponding target sequences and the donor DNA fragments to co-transformation into Cas9 nuclease expressing saccharomyces cerevisiae to realize gene integration; removing Cas9 nuclease expression vectors and the transcribed gRNA vectors by a non-resistant flat plate. The method has advantages that the homologous arm primers ontwo sides of each cleavage site is in sequence length of 15-90bp, and by respective adding of the homologous arm primers to upstream and downstream primers of the target gene cassettes, an integratorgene template can be obtained directly through once PCR, so that multi-copy integration of target genes is realized. Compared with an existing method, the method has advantages of low time consumption and simplicity in operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Capture probes for large genomic rearrangement detection based on capture sequencing, kit and detection method
PendingCN111534579AEasy to detectLow purity requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBase JNucleotide
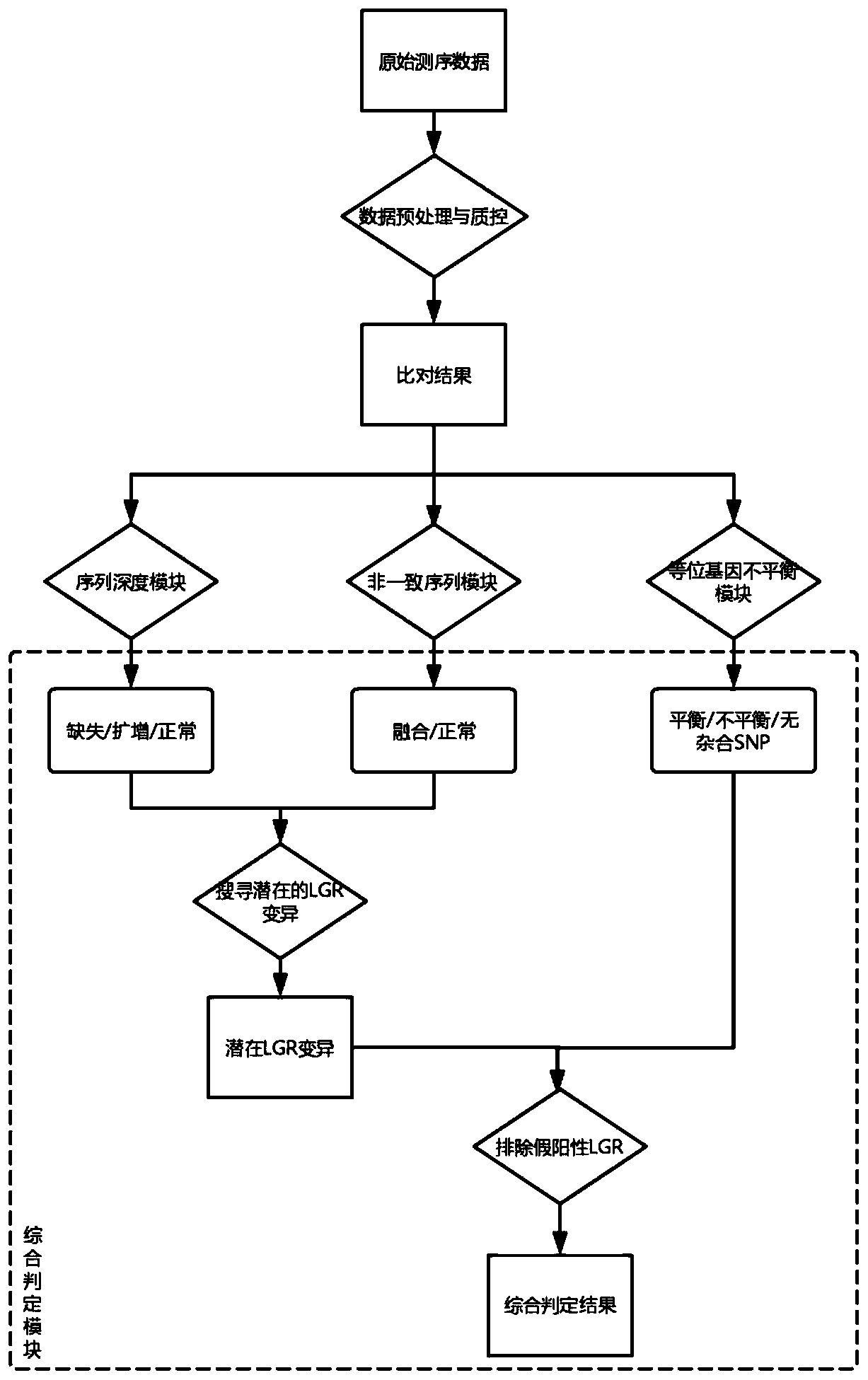
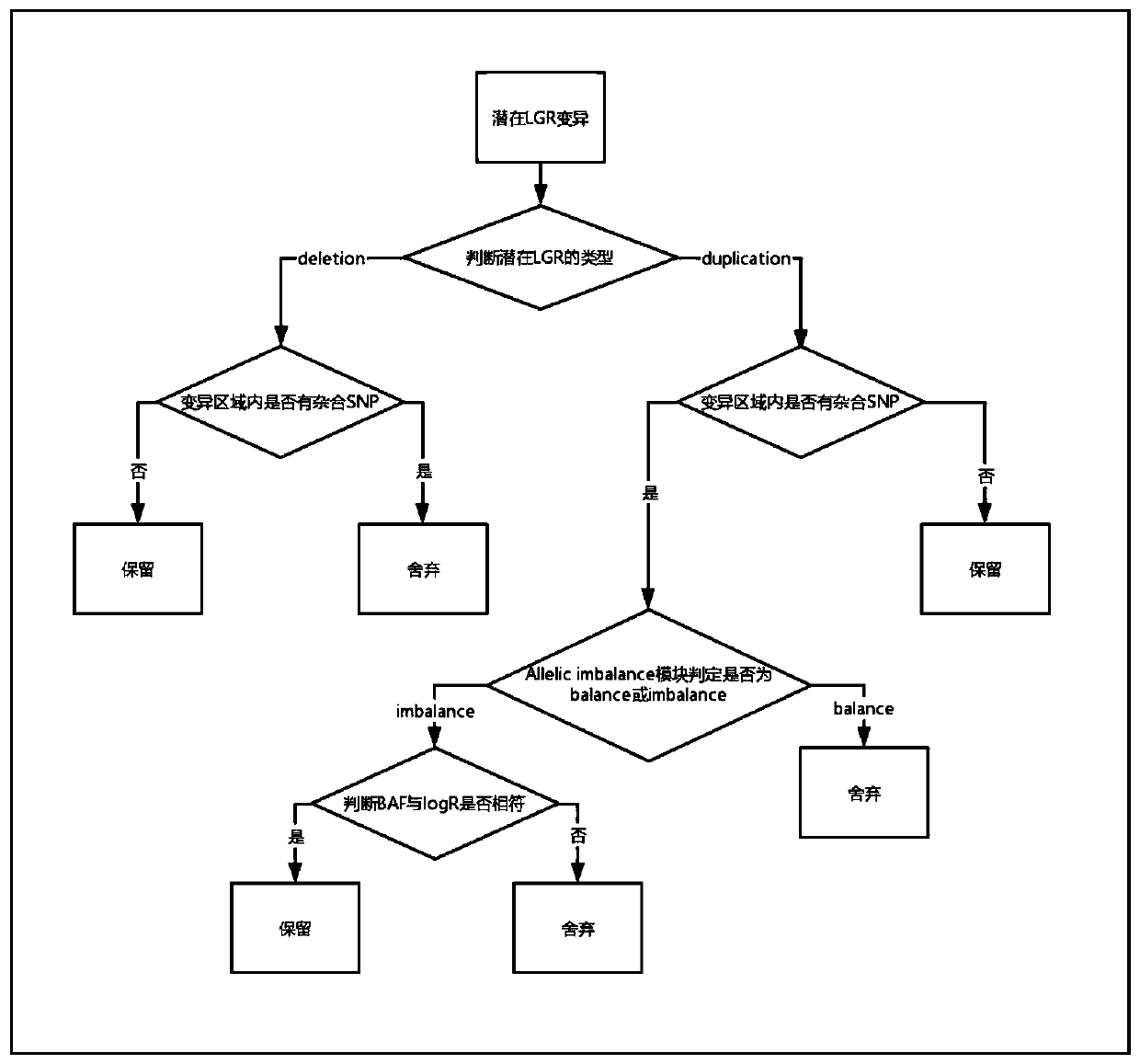
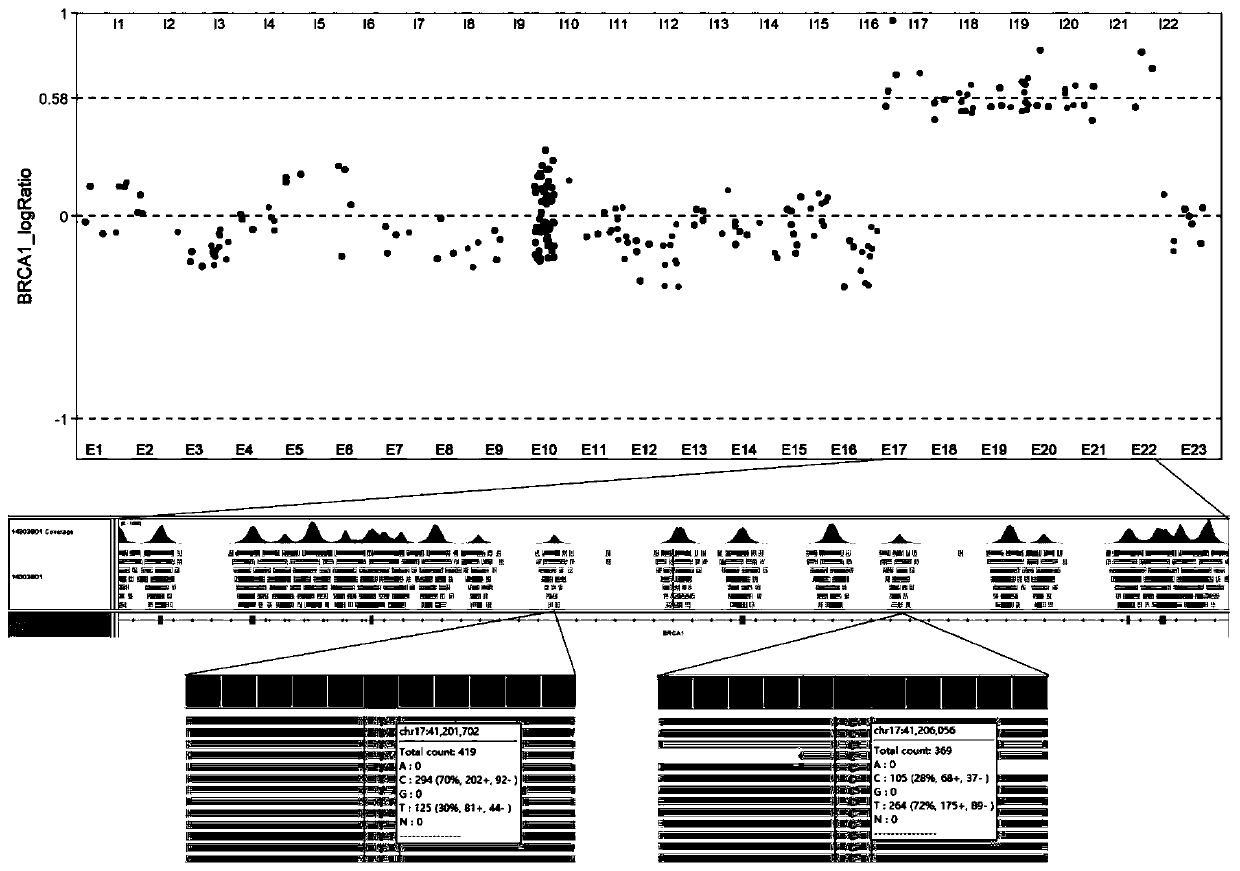
The invention discloses a large genomic rearrangement (LGR) detection method based on capture sequencing. The capture probes of the invention comprise exon probes and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) probes. The exon probes comprise at least three probes aiming at each exon of the gene and 60bp regions at two ends of the exon, and can achieve 2X complete coverage for the exon and the 60bp regions at two ends of the exon. The SNP probes comprise SNP loci with the population occurrence frequency of 30%-70% in the gene intron region and the upstream and downstream within the 5000bp ranges ofthe gene. Meanwhile, the invention further provides an algorithm formed by integrating a reads depth algorithm module, an allelic imbalance algorithm module and a discordant sequence algorithm module,and the algorithm is used for carrying out large genomic rearrangement analysis on the NGS sequencing data. By adoption of the method, the LGR can be effectively detected, the requirement for the purity of a nucleic acid sample is lowered, false positive caused by single-base variation is reduced, and high detection performance is achieved for exon amplification.
Owner:上海思路迪医学检验所有限公司
Design method of nucleic acid capture probe for HLA typing
ActiveCN110853708AEfficient captureImprove the effect of hybrid captureSequence analysisHybridisationRepresentative sequencesGene probe
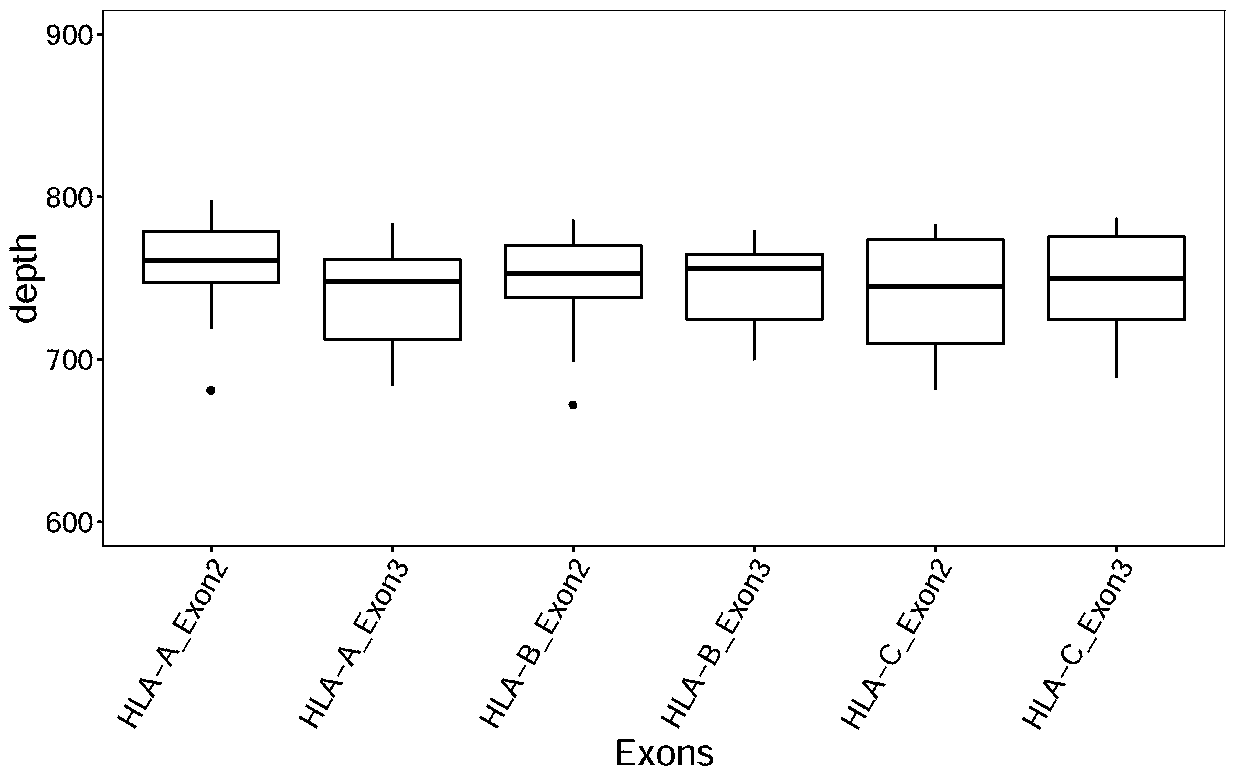
The invention discloses a design method of a nucleic acid capture probe for HLA typing. The design method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C sequence libraries; 2) performing multiple sequence alignment, and searching SNP sites on each gene Exon2 and Exon3 and upstream and downstream SNP sites; 3) selecting an area covering a set number of SNP sites as a probe design candidate area by using a sliding window separation algorithm; 4) performing clustering analysis to obtain a representative sequence of each probe design candidate region as a candidate probe; 5)repeating all the candidate probes to obtain capture probes of the three genes. The invention also discloses the probe designed by the method, and the sequence of the probe is shown as SEQ ID NO: 9-88. The nucleic acid capture probe is designed for all polymorphic sites of Exon2 and Exon3 regions with the GC proportion of 60% or above in the HLA gene, and the hybrid capture effect of the HLA geneprobe is improved.
Owner:上海仁东医学检验所有限公司
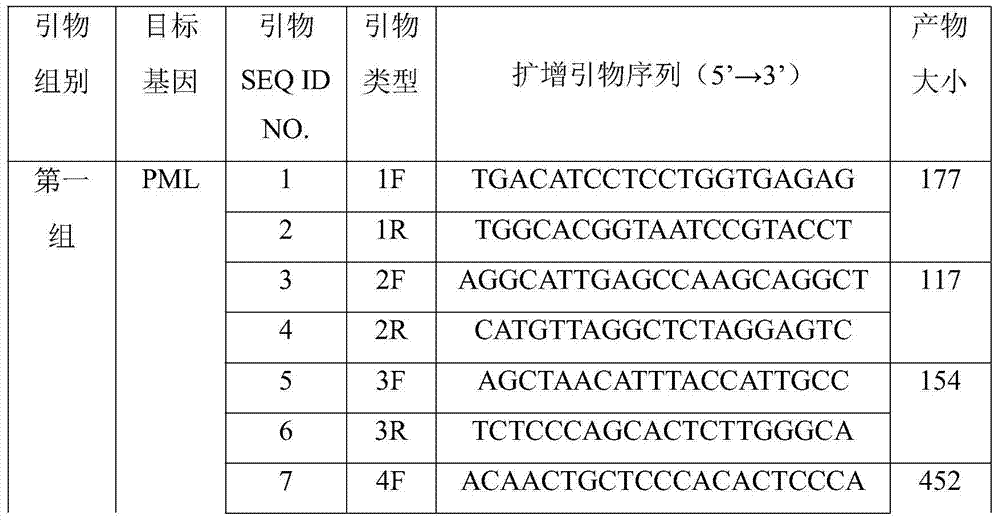
PML/RAR alpha fusion gene detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN107083418AStrong specificityReduce background noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenome
The invention discloses a PML-RAR alpha fusion gene detection kit and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises a first group of probes for detecting upstream and downstream sequences of a PML gene and a second group of probes for detecting upstream and downstream sequences of a RAR alpha gene. Each one of the probes is labeled with a dye. The dyes labeling the two groups of probes are in different colors. The two groups of probes are amplification products obtained by amplification based on a human genomic DNA as a template and amplification primers. The length of the probes is designed according to a lot of experiments. Through experiment result comparison and statistic analysis, the optimal length is obtained and the optimal balance between the detection specificity and hybridization time is realized. The PML-RAR alpha fusion gene detection kit guarantees result specificity and sensitivity, shortens hybridization time, has detection time of 7-8h and improves detection efficiency.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
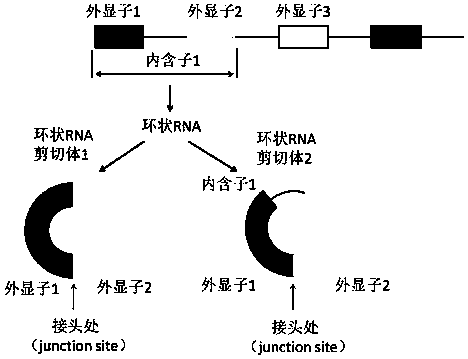
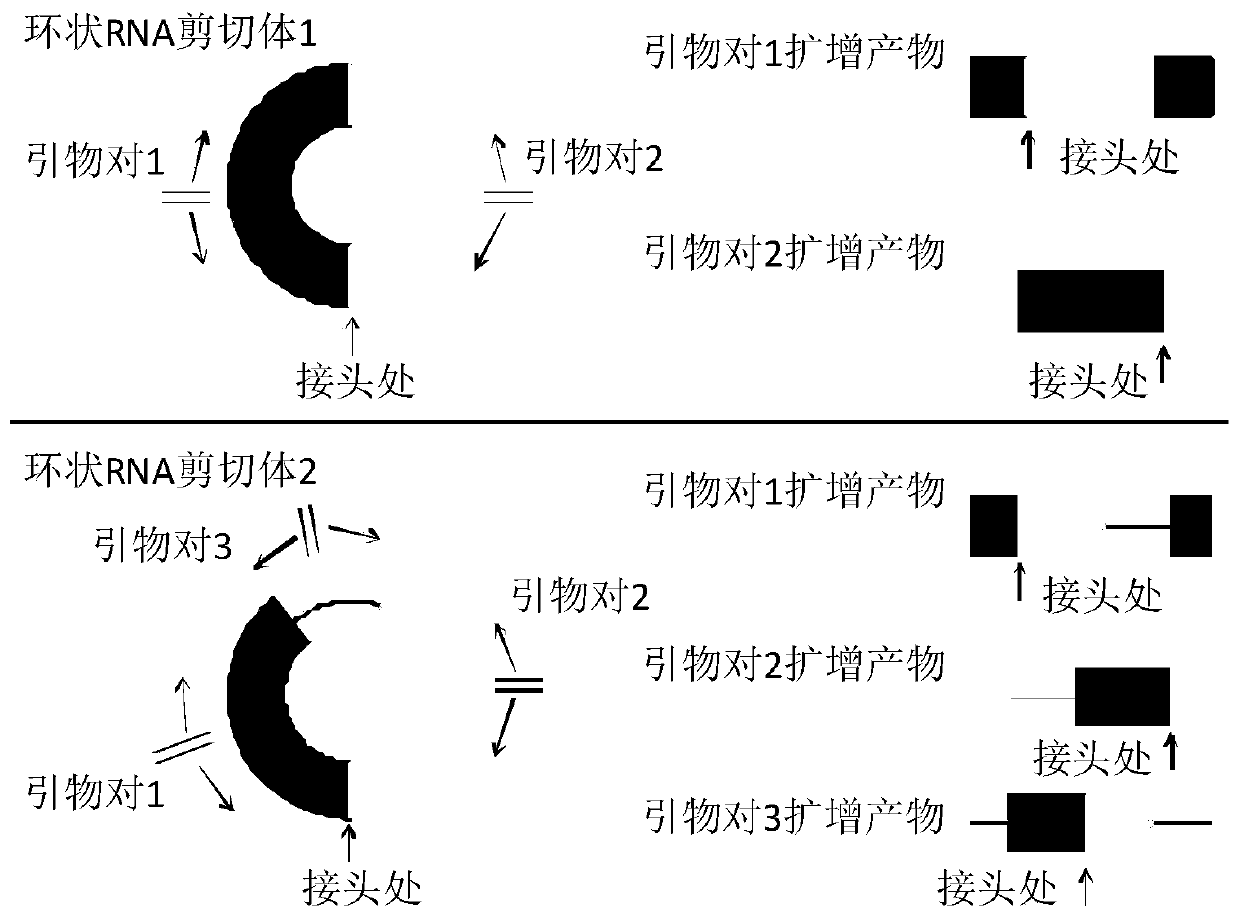
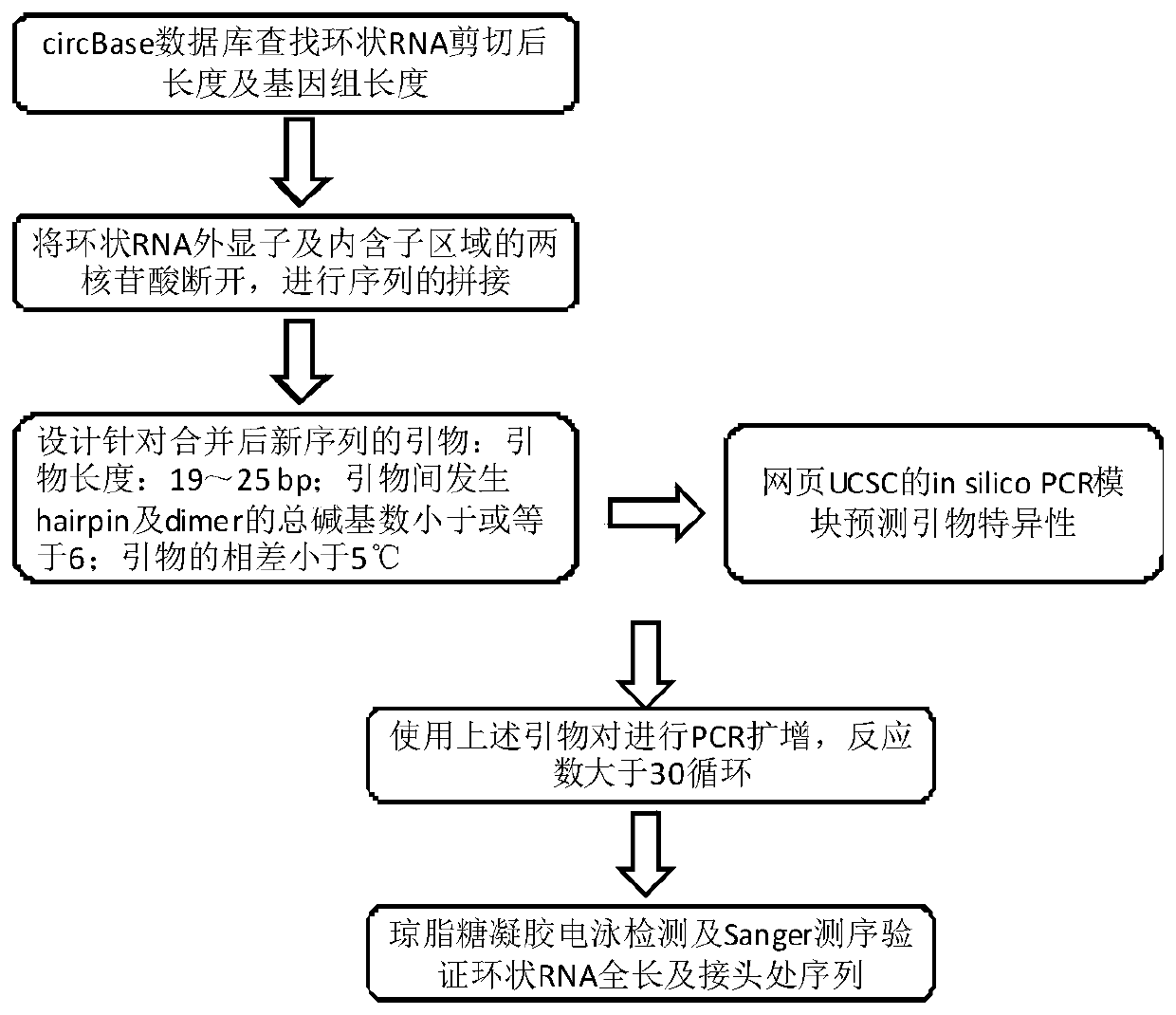
Method for detecting full-length sequence of circular RNA
The invention discloses a detection method of a full-length sequence of circular RNA, which comprises the steps of: (1) searching for a DNA sequence of a target circular RNA in a database; (2) randomly taking the middle of two nucleotides, corresponding to exons and / or intron regions of the DNA sequence, of the circular RNA as a disconnection point to disconnect the circular RNA into two DNAs, andconnecting the 3' end of one DNA sequence with the 5' end of the other sequence to form a new DNA sequence; (3) designing upstream and downstream primers of the novel DNA full-length sequence; (4) verifying the upstream and downstream primers designed in the step (3) to ensure that the upstream and downstream primers cannot amplify linear RNA molecules to obtain a final primer pair; (5) carryingout PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on cDNA corresponding to the circular RNA via the final prime pair; and (6) carrying out agarose electrophoresis detection and Sanger sequencing on the PCR product in the step (5) to obtain the full-length sequence of the circular RNA. The detection method is suitable for acquiring the full-length sequence of the circular RNA more easily and simply.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
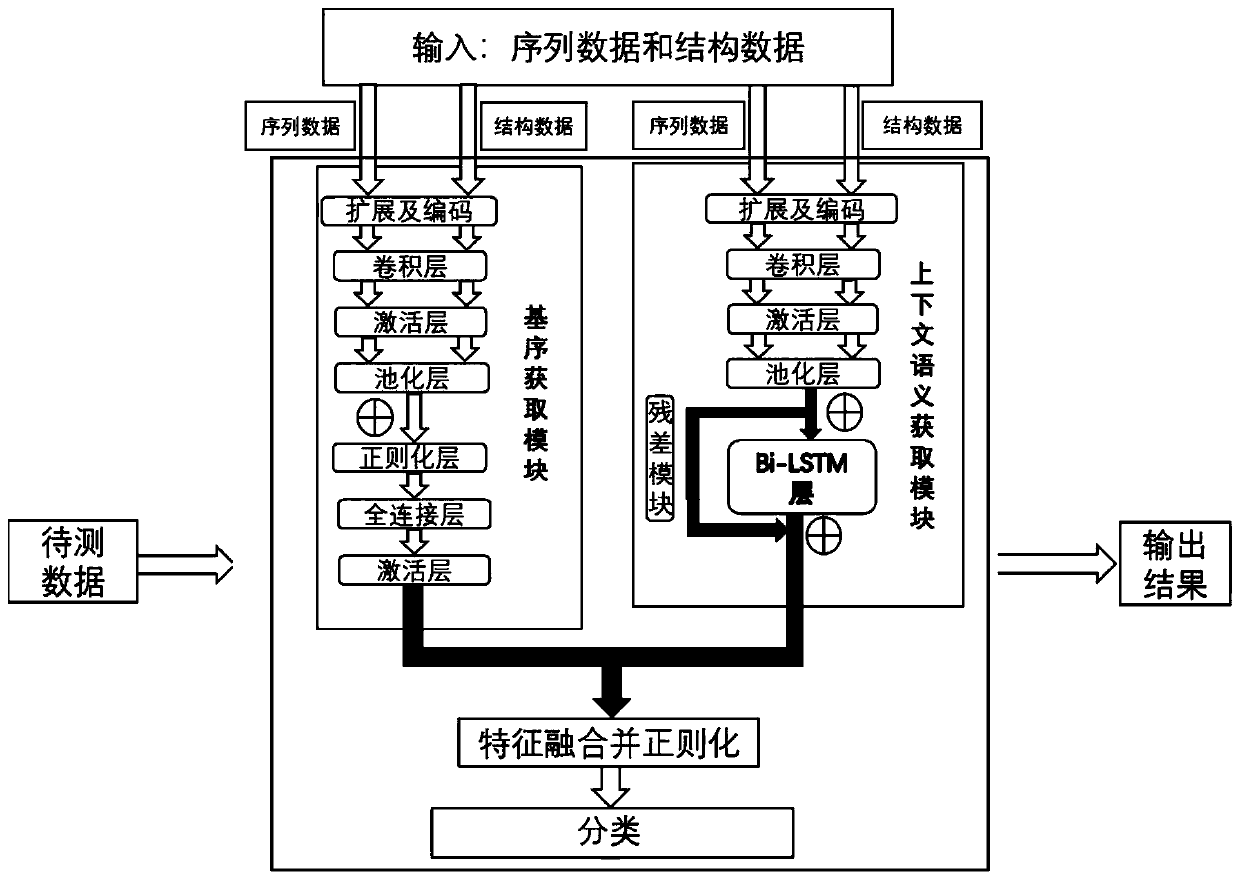
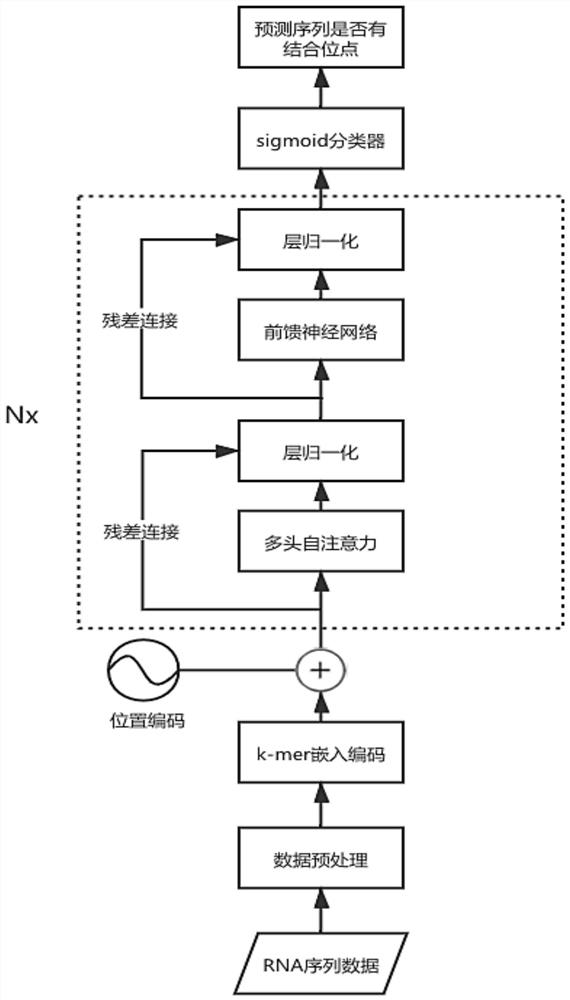
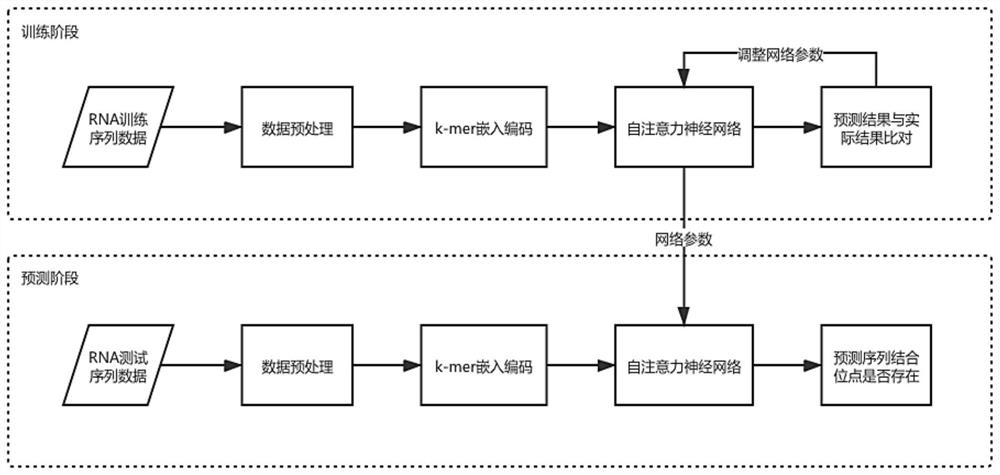
RNA-protein binding site prediction method and system based on self-attention mechanism
ActiveCN114023376AEffective sequence featuresImprove forecast accuracyBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setBinding site
The invention discloses an RNA-protein binding site prediction method and system based on a self-attention mechanism. According to the method, a deep learning model is trained through employing the sequence features of an RNA and protein binding site and upstream and downstream, and an RNA-protein interaction binding site is predicted through employing the model; in the coding process of the sequence features, a k-mer embedded coding mode is introduced, the context relationship between adjacent nucleotides is coded, and more effective features are provided for the model; in the feature extraction process, a prediction model is constructed by using a self-attention mechanism, RNA sequence features are focused from the global perspective, and key subsequences are endowed with higher weights so that the network can fully learn key features, and then the model prediction accuracy is improved; and finally, the method provided by the invention is evaluated on a reference data set, and the method is superior to the prior art in the aspect of prediction precision.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com