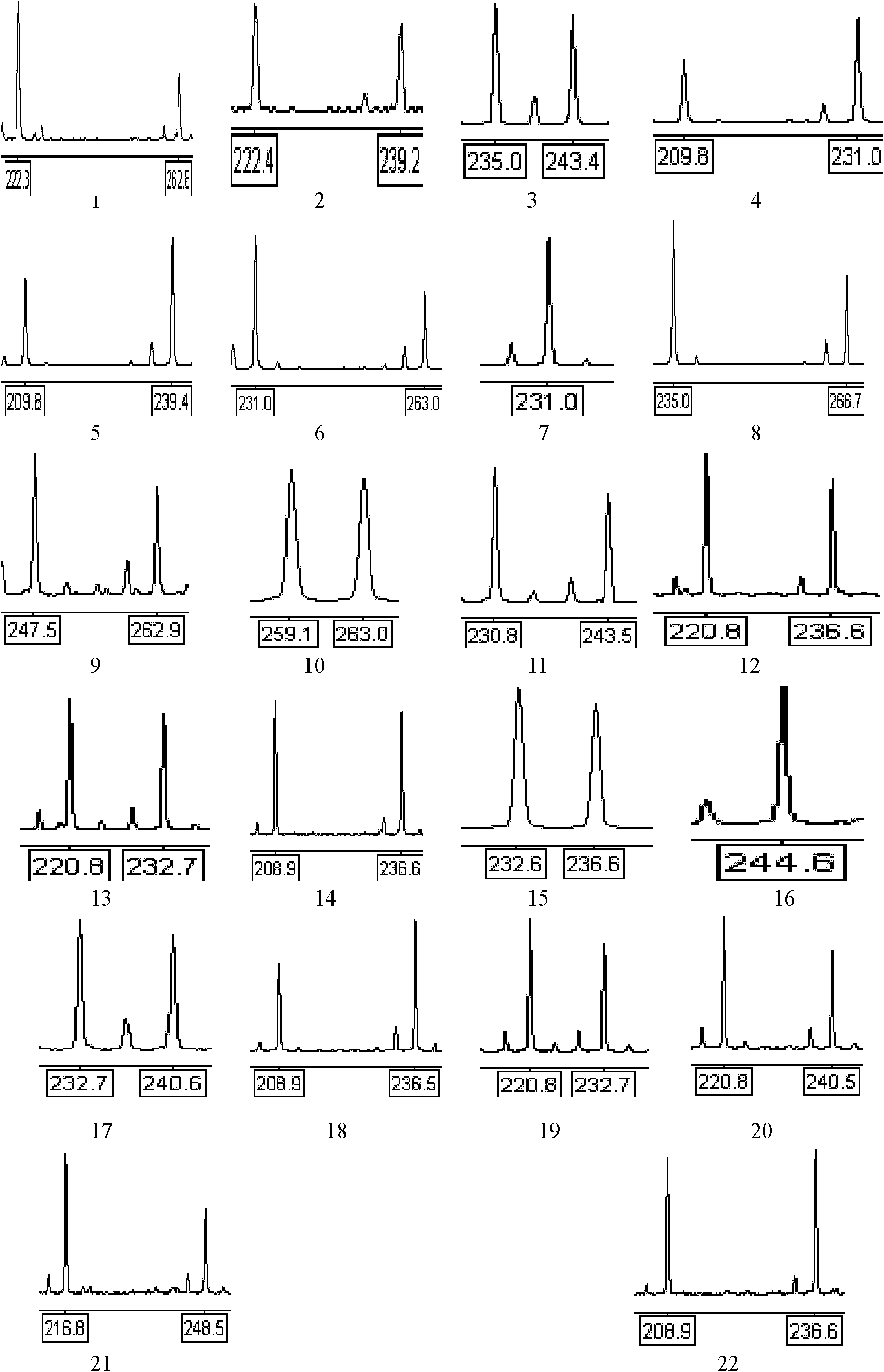
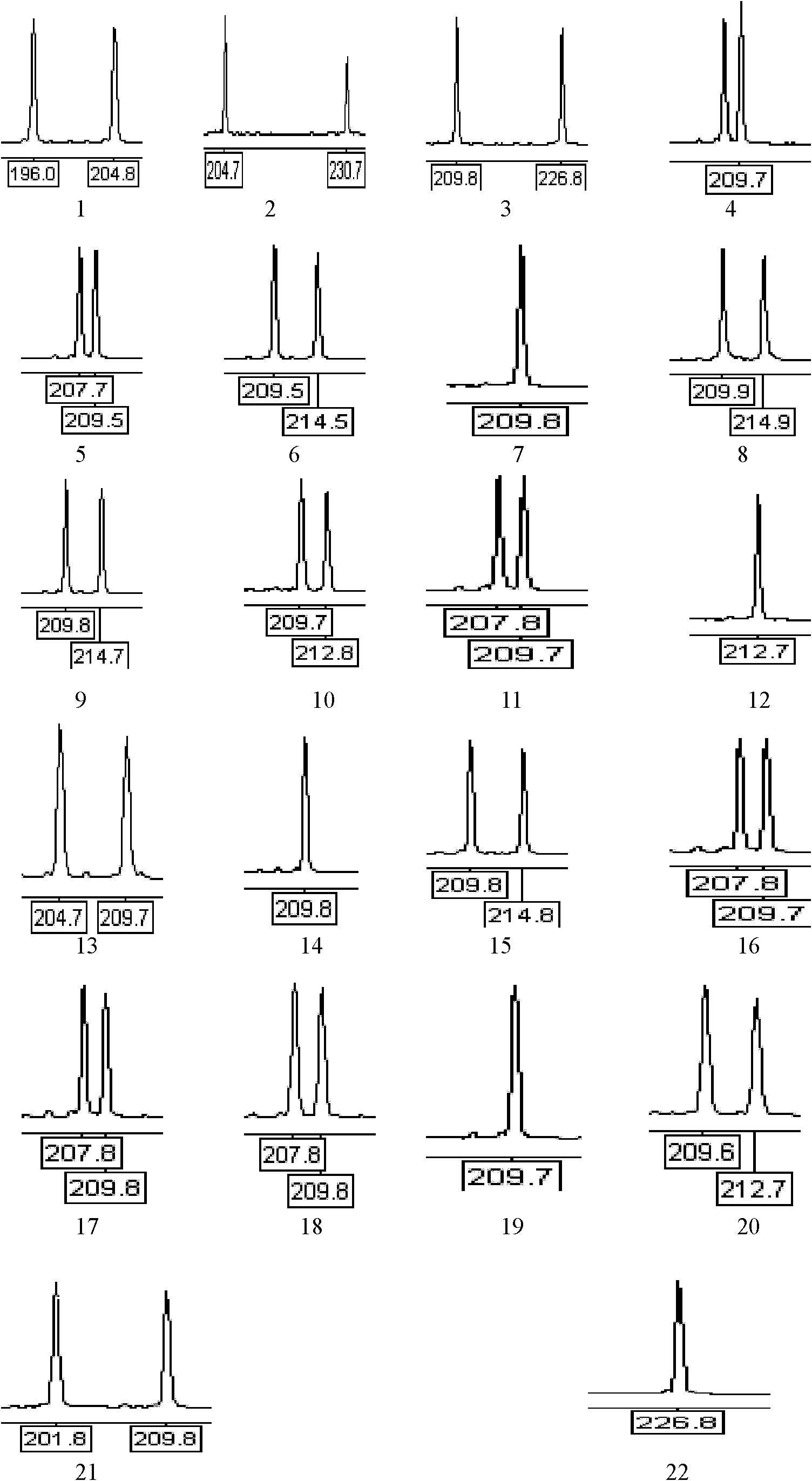
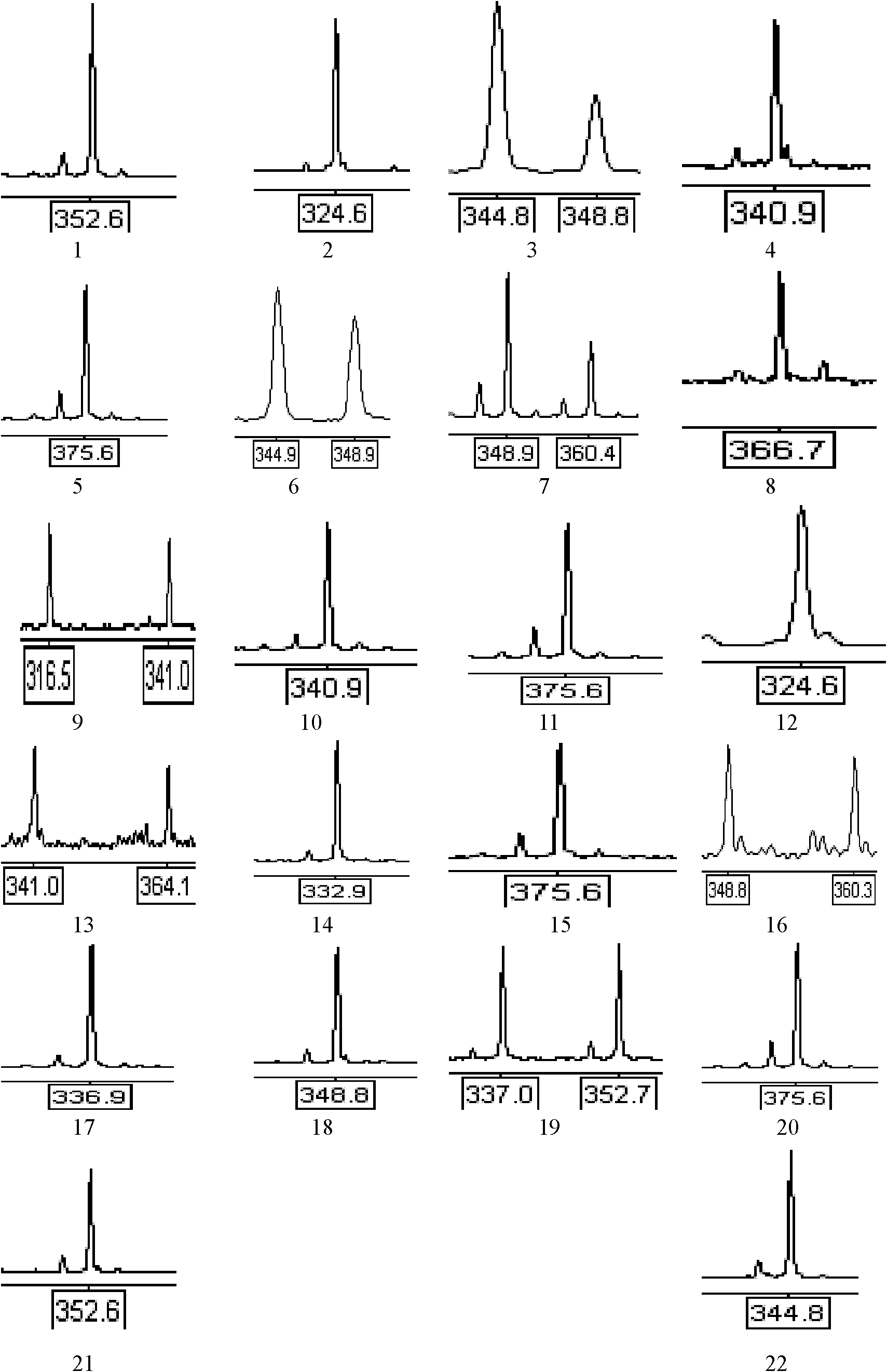
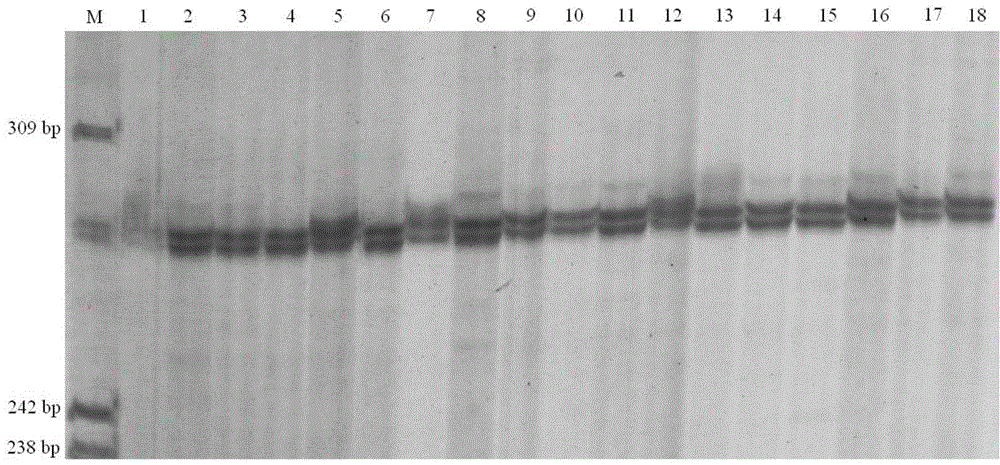
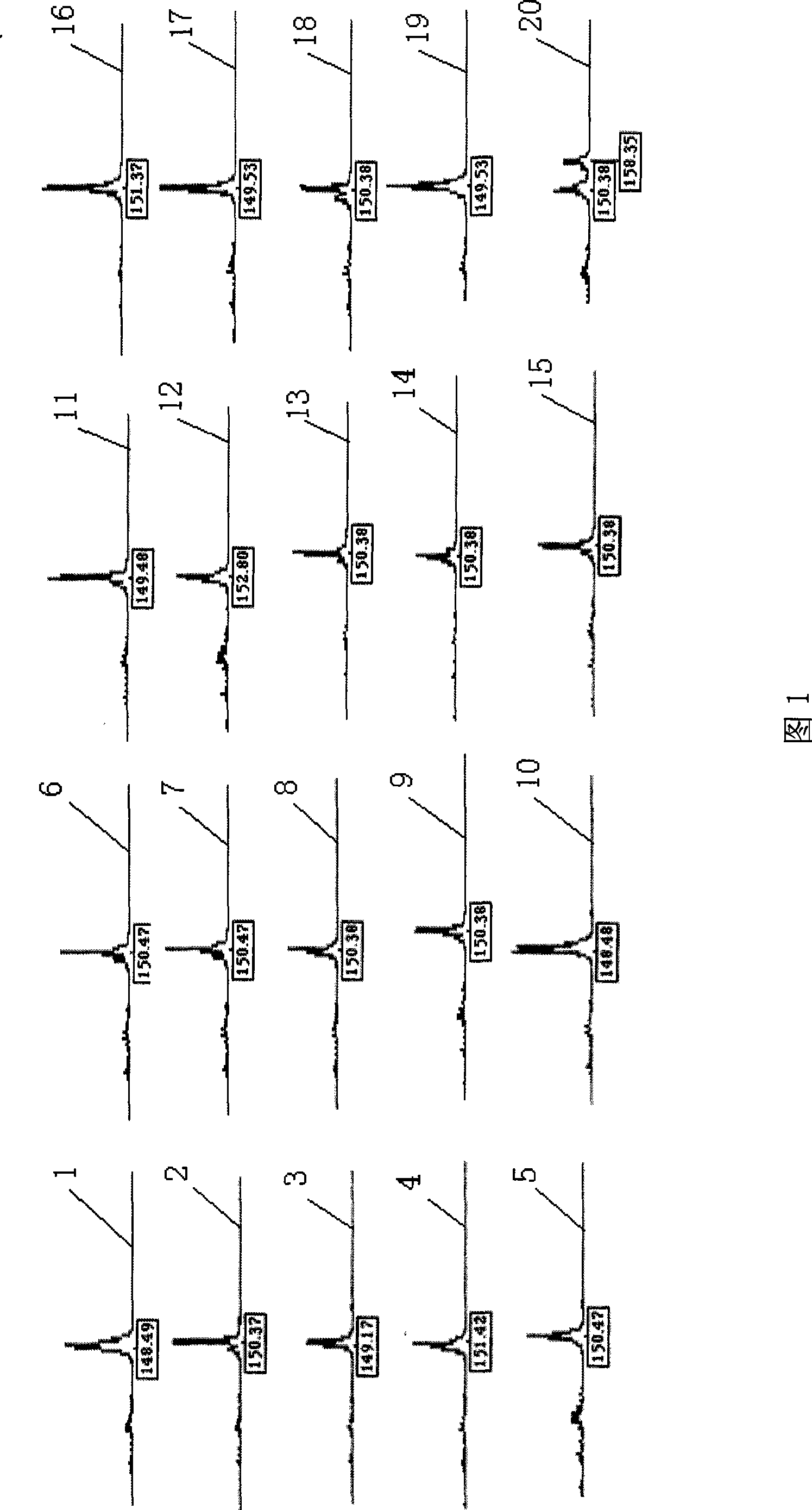
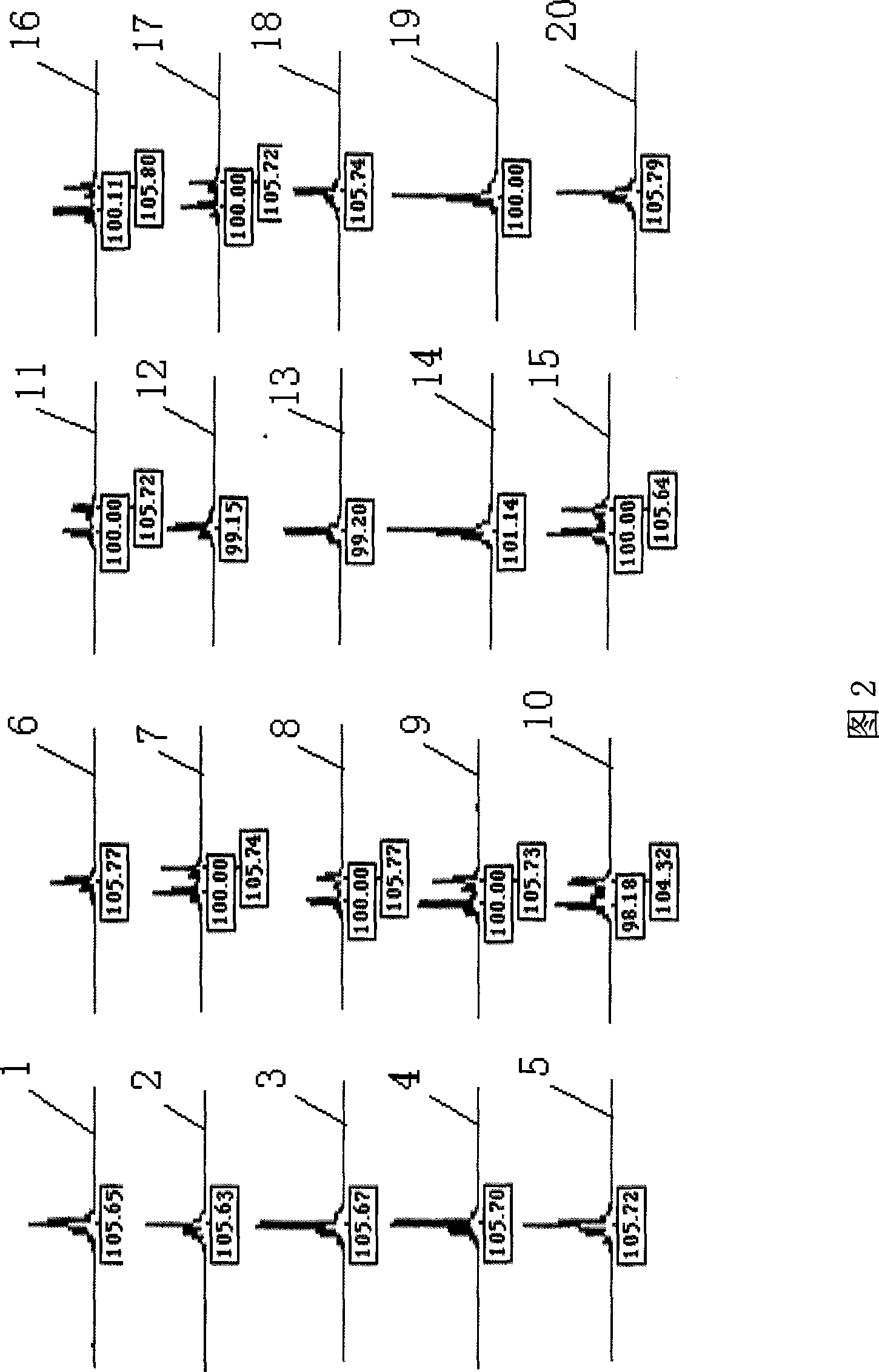
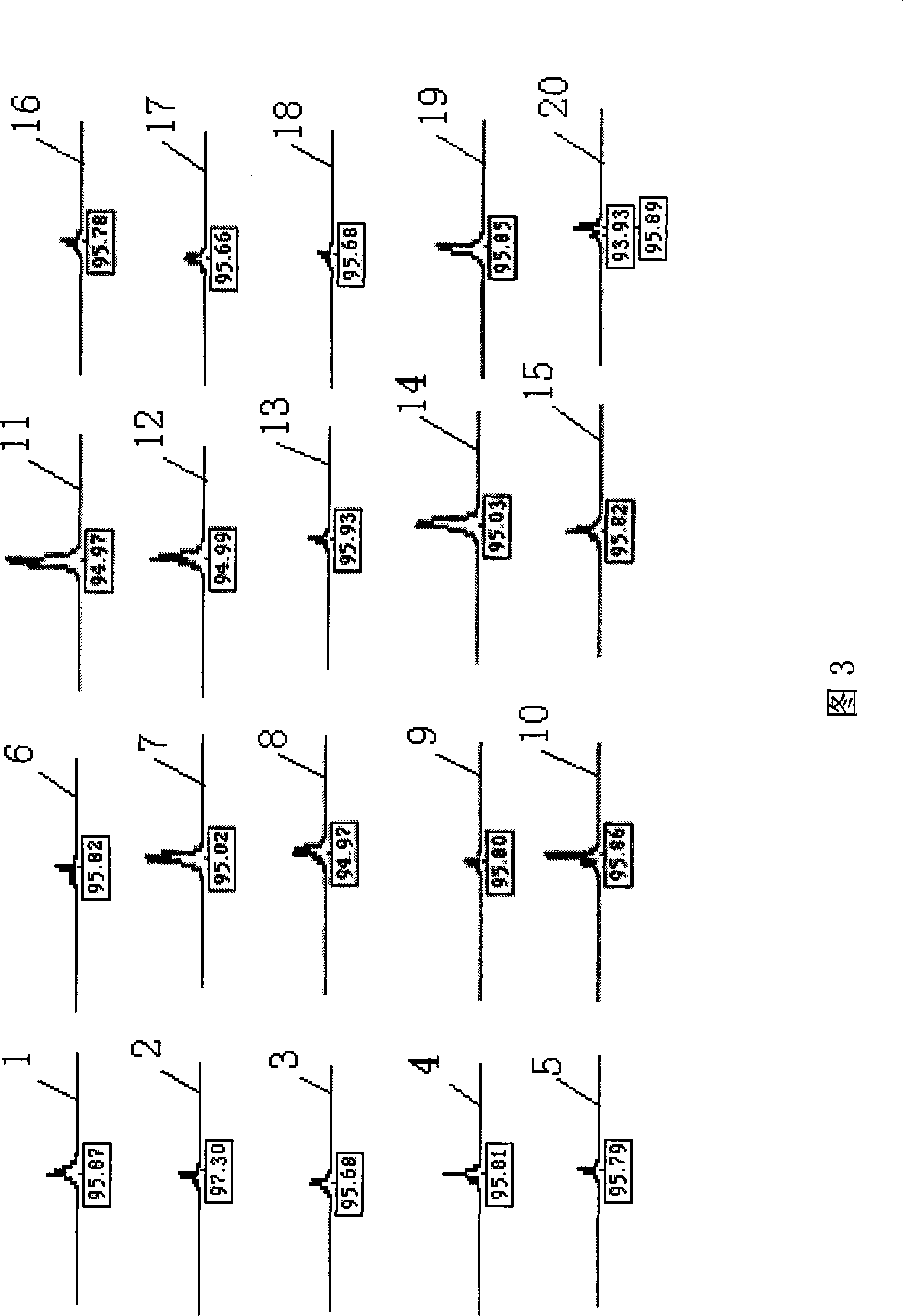
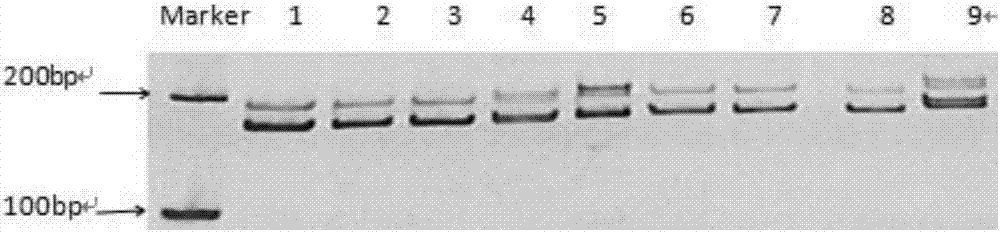
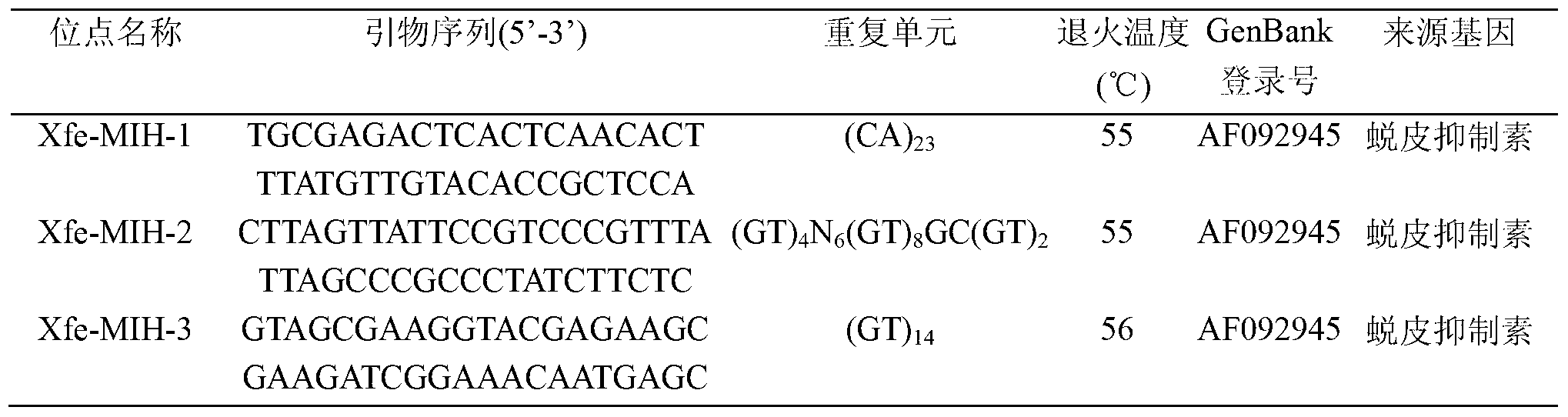
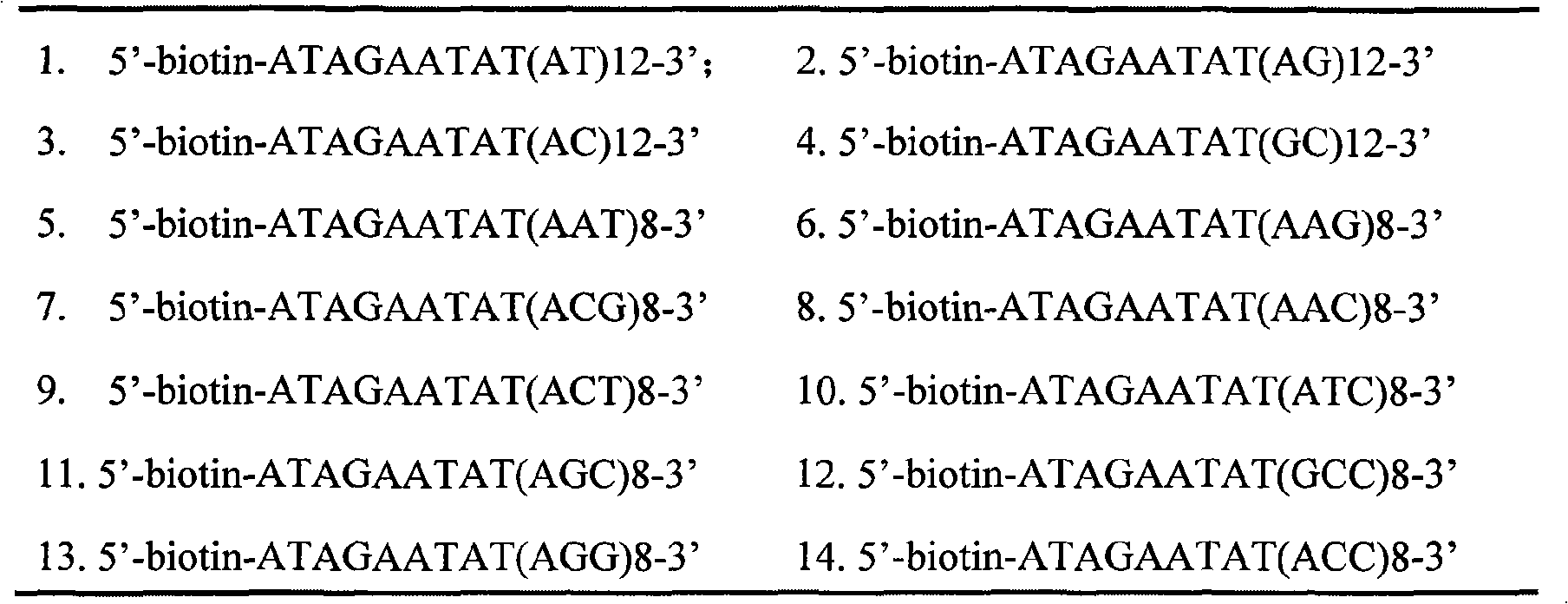
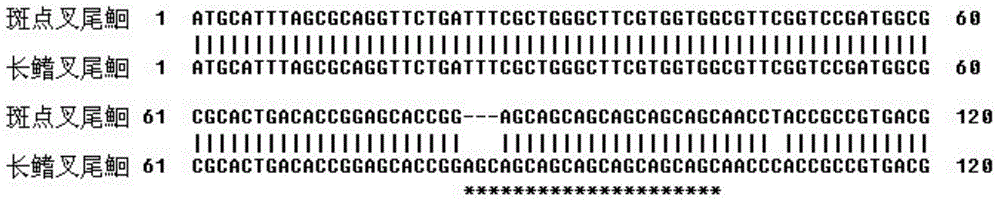
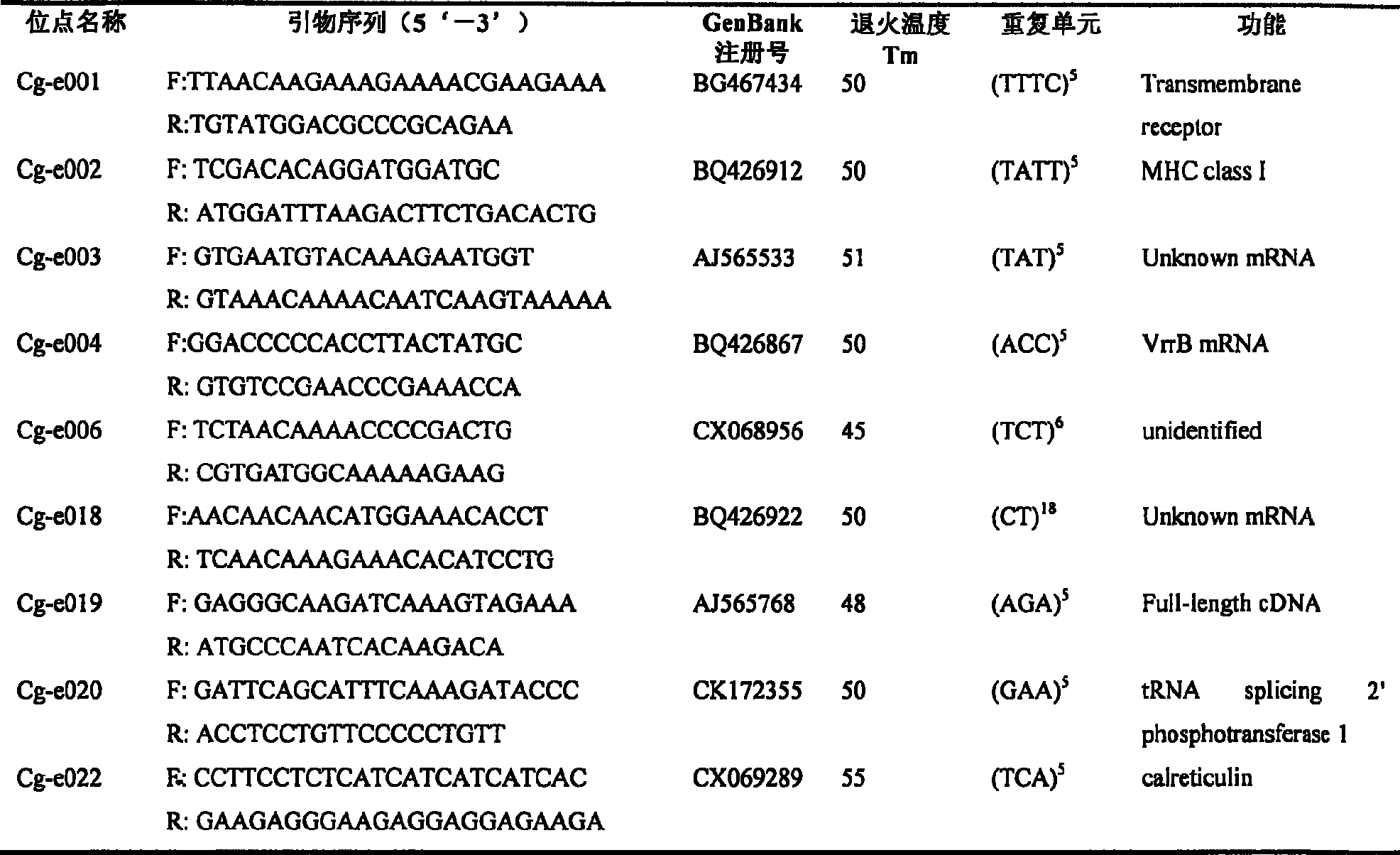
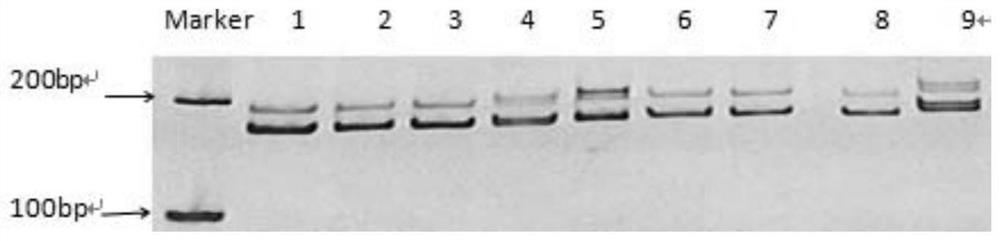
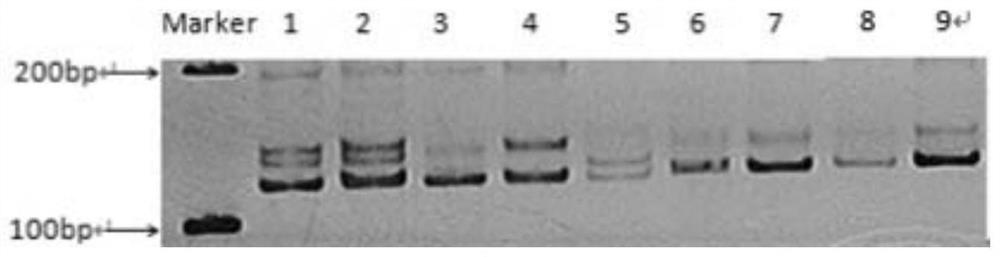
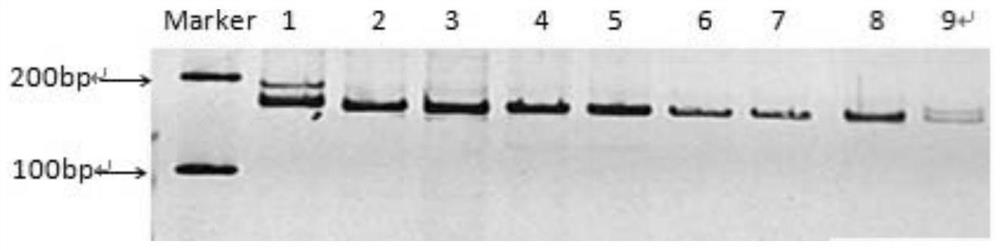
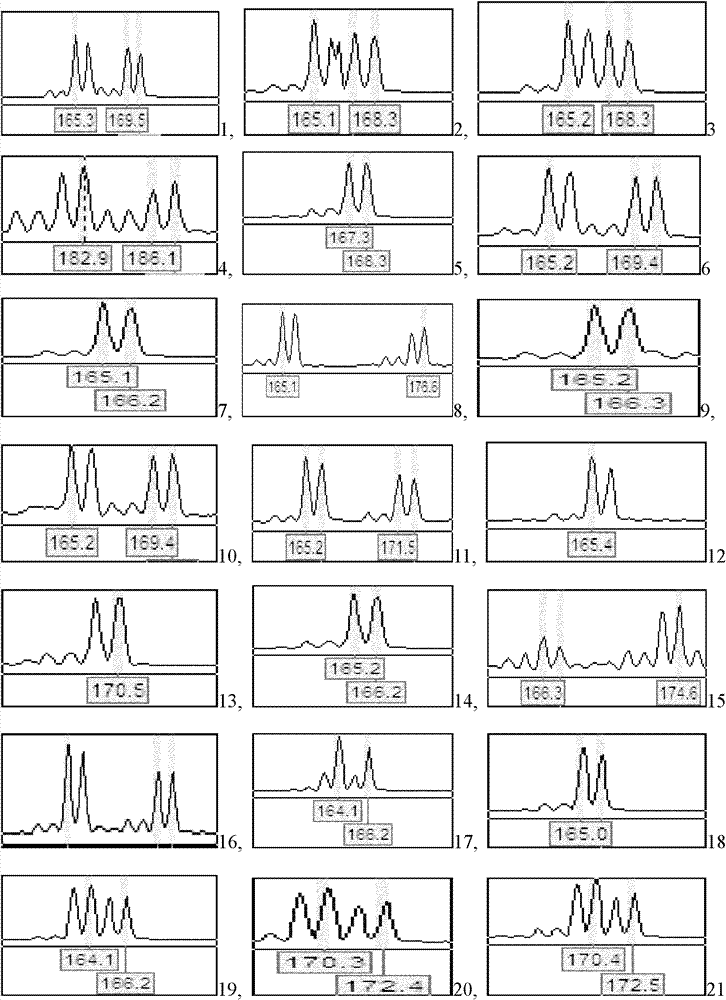
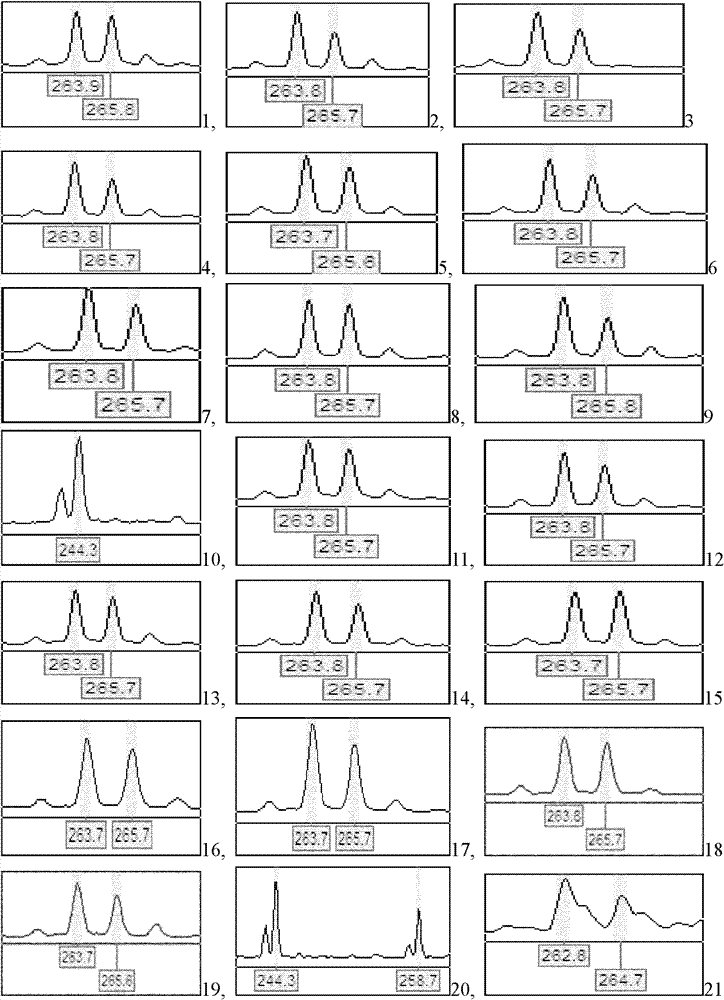
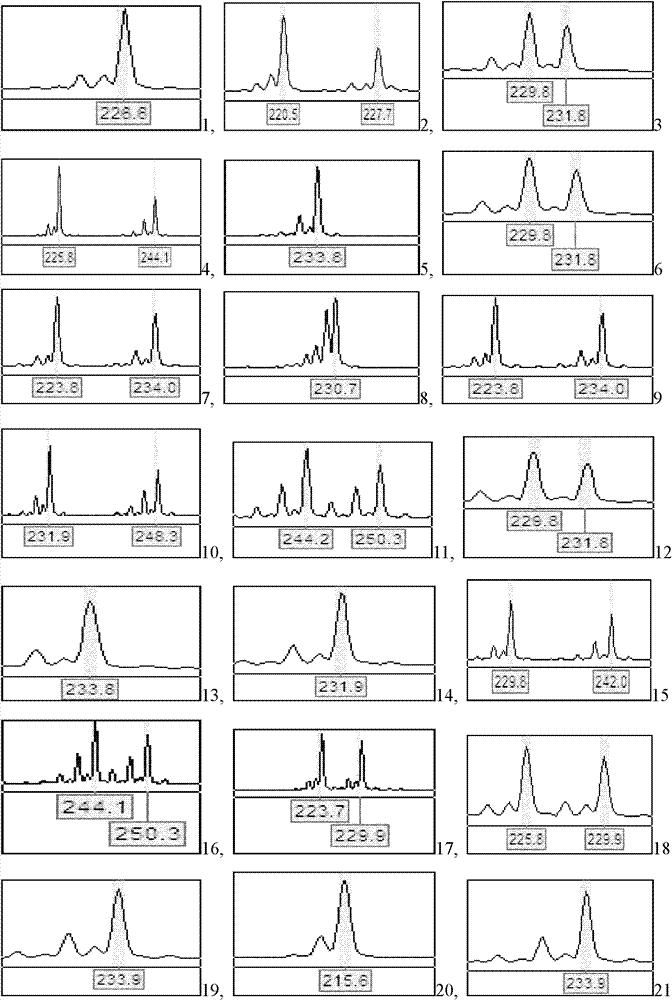
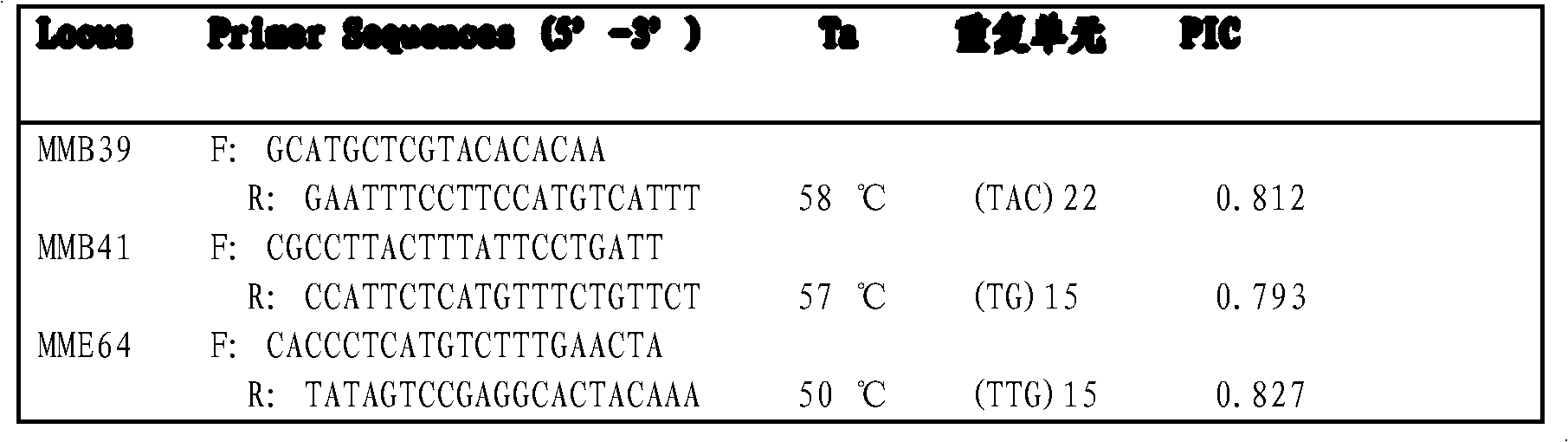
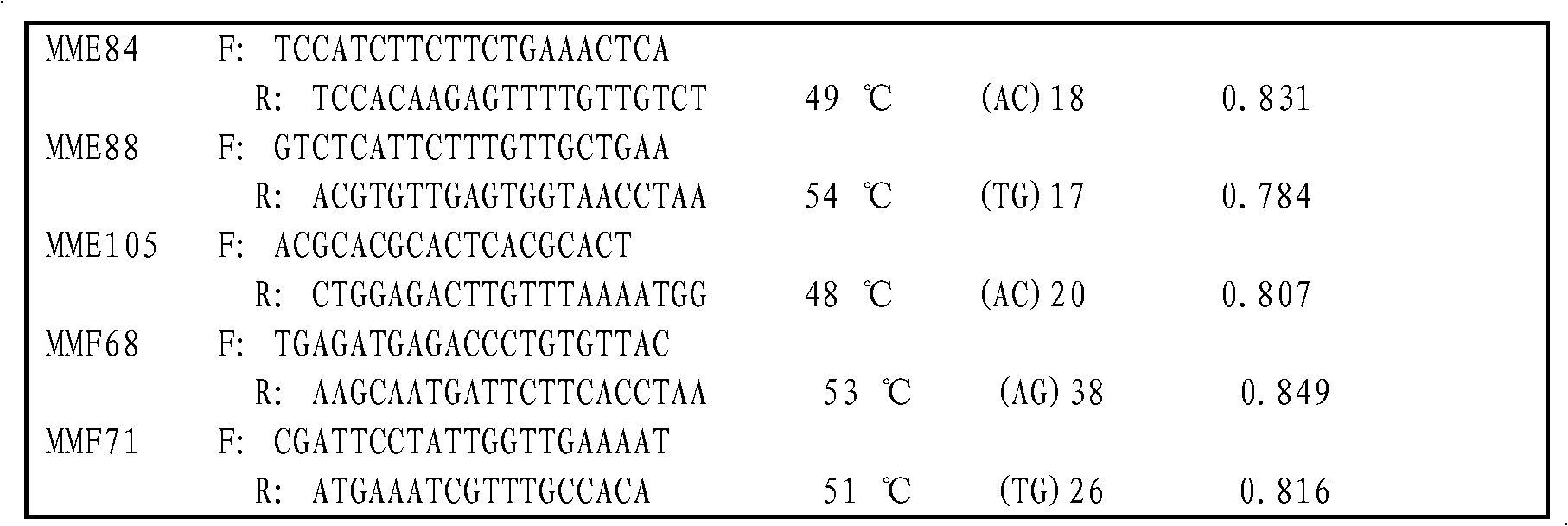
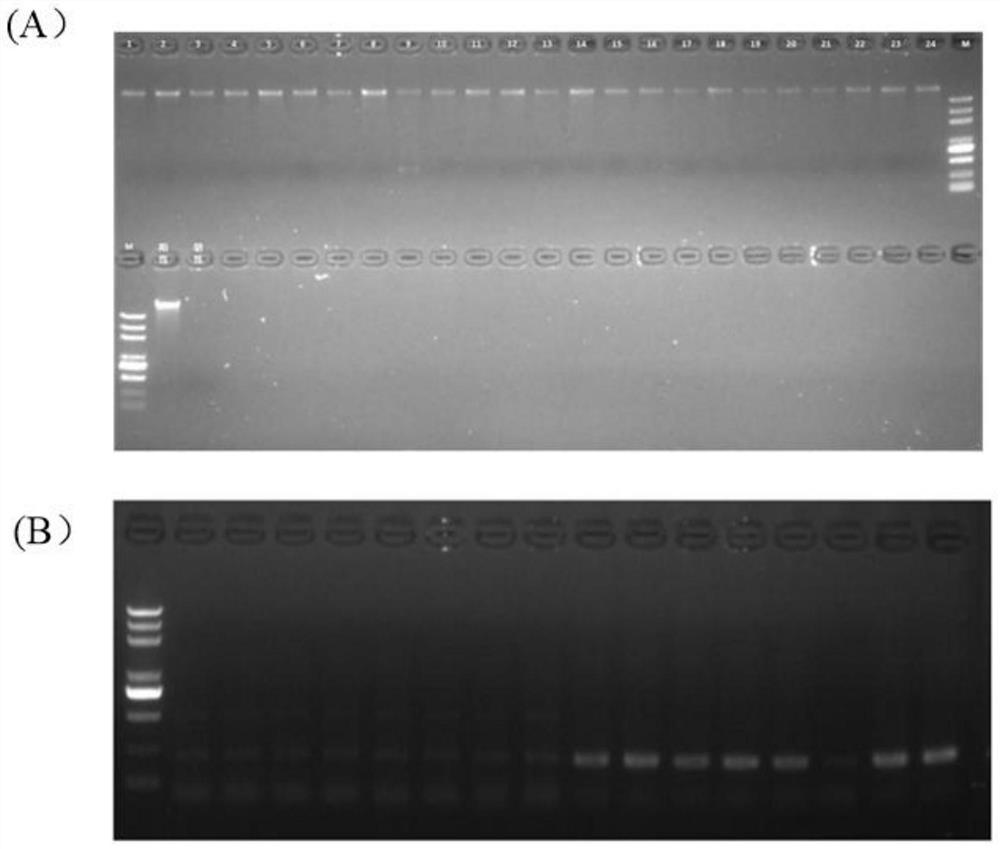
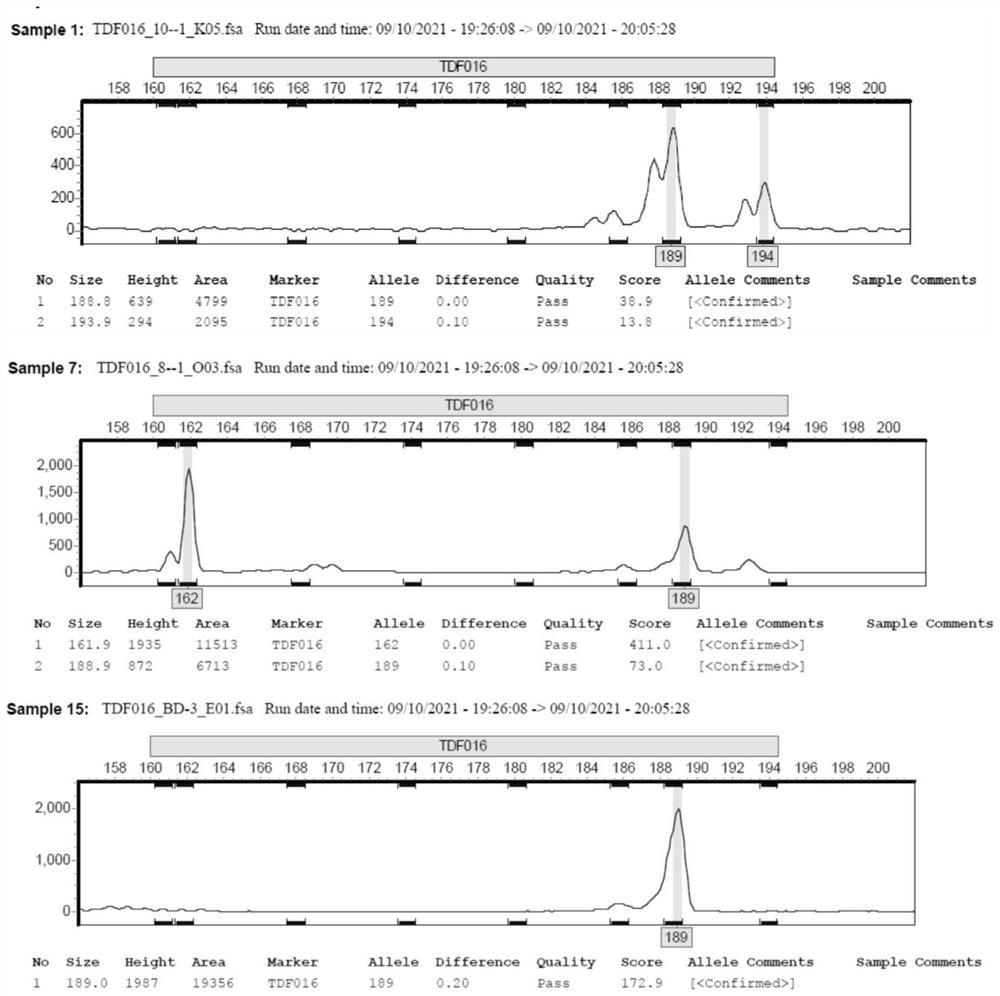
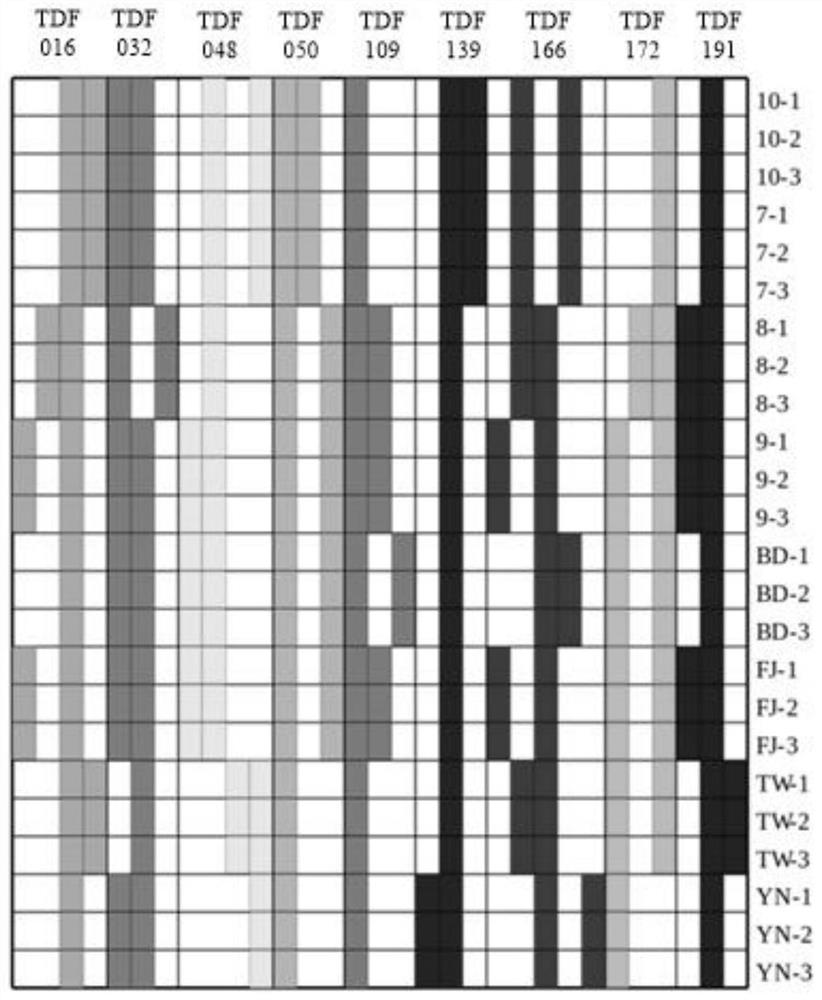
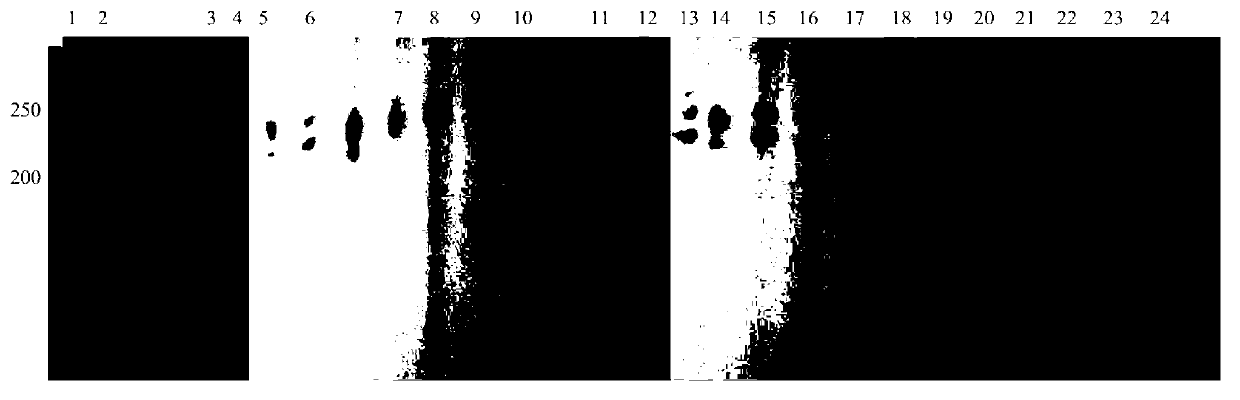
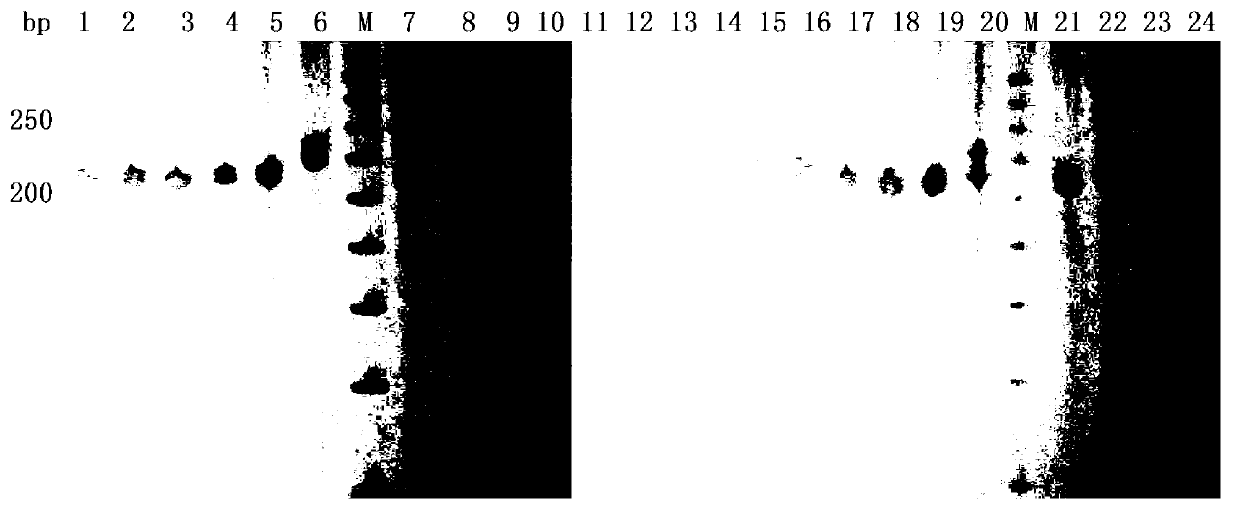
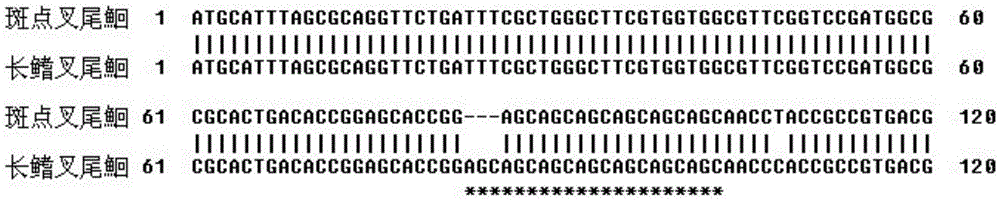
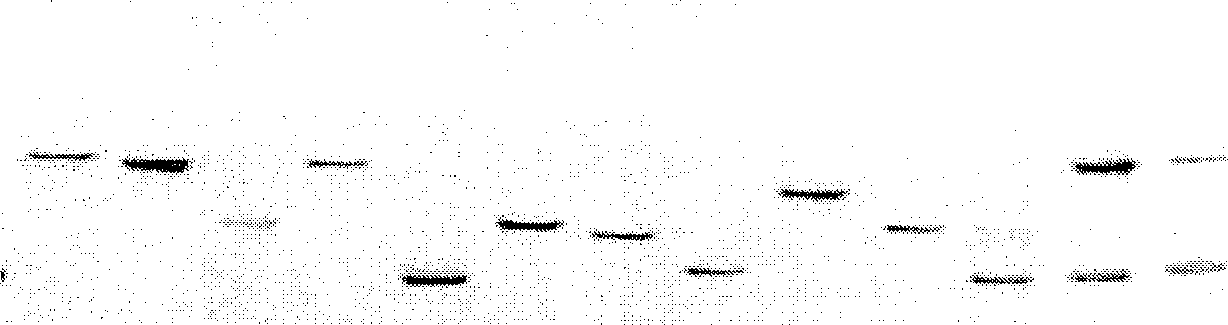Patents
Literature
40 results about "Microsatellite Repeat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A short sequence of DNA, usually 1 to 4 basepairs (a unit of DNA), that is repeated together in a row along the DNA molecule. There is variation from person to person in the number of repeats. There are hundreds of places in human DNA that contain microsatellites.
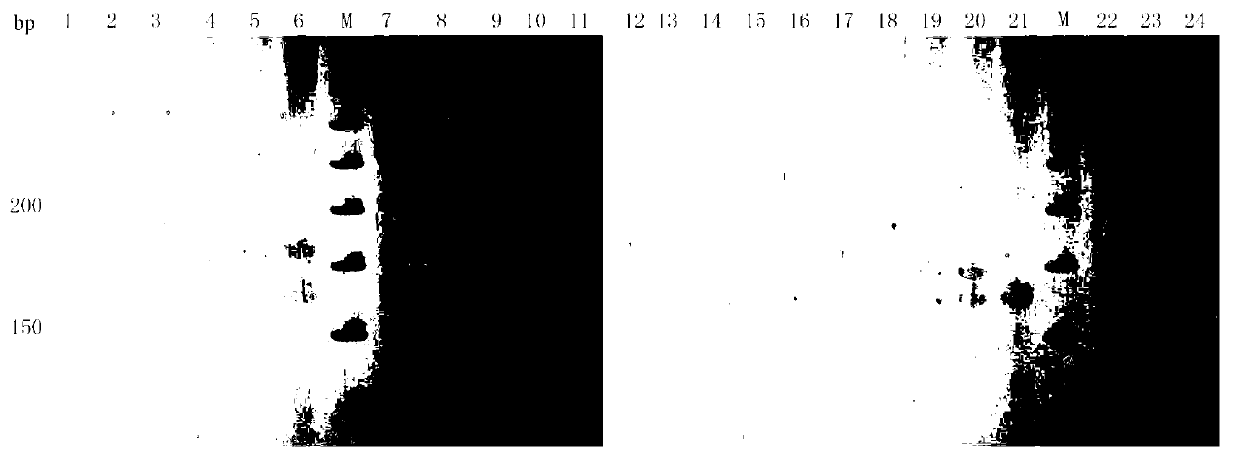
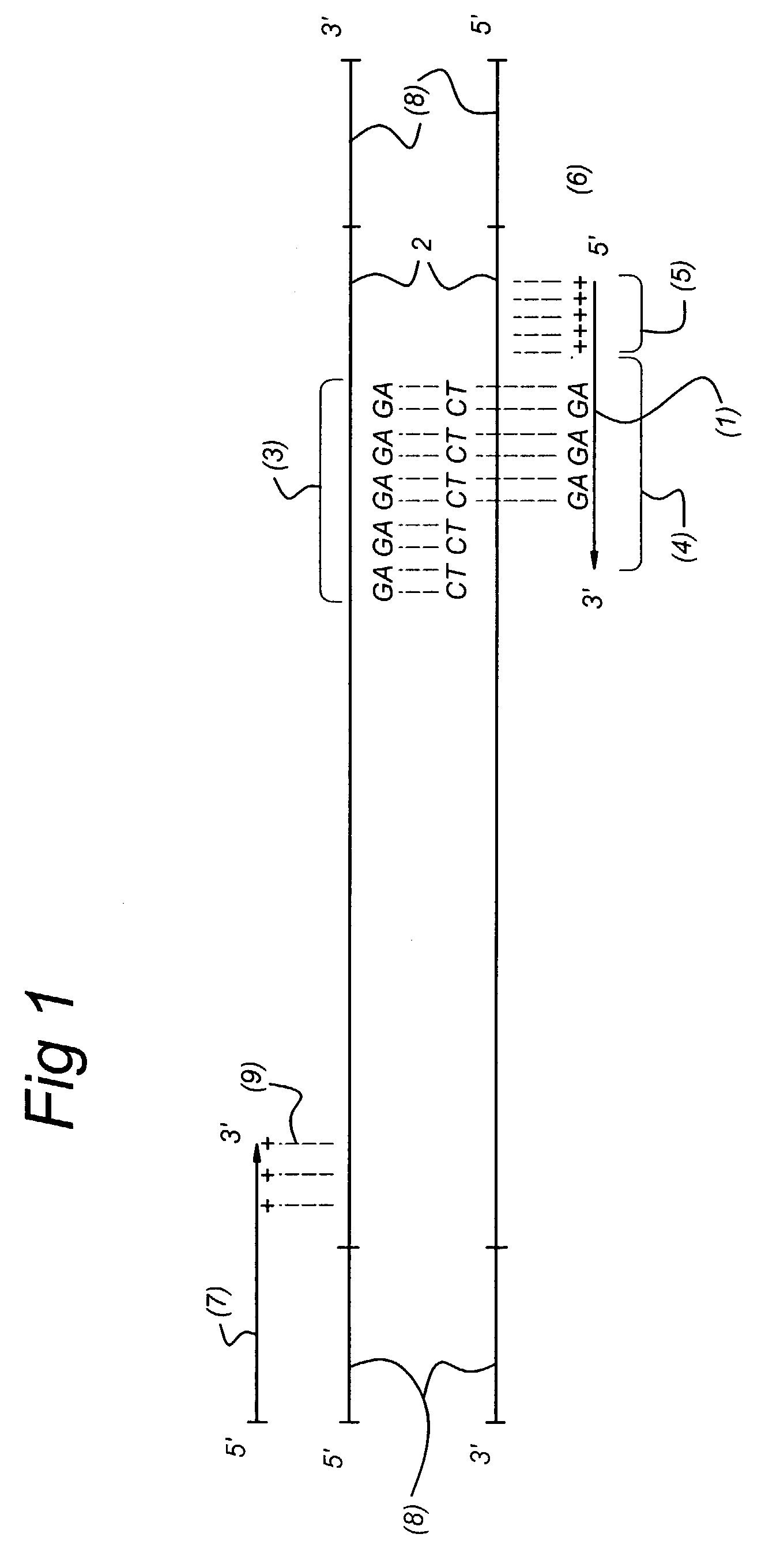
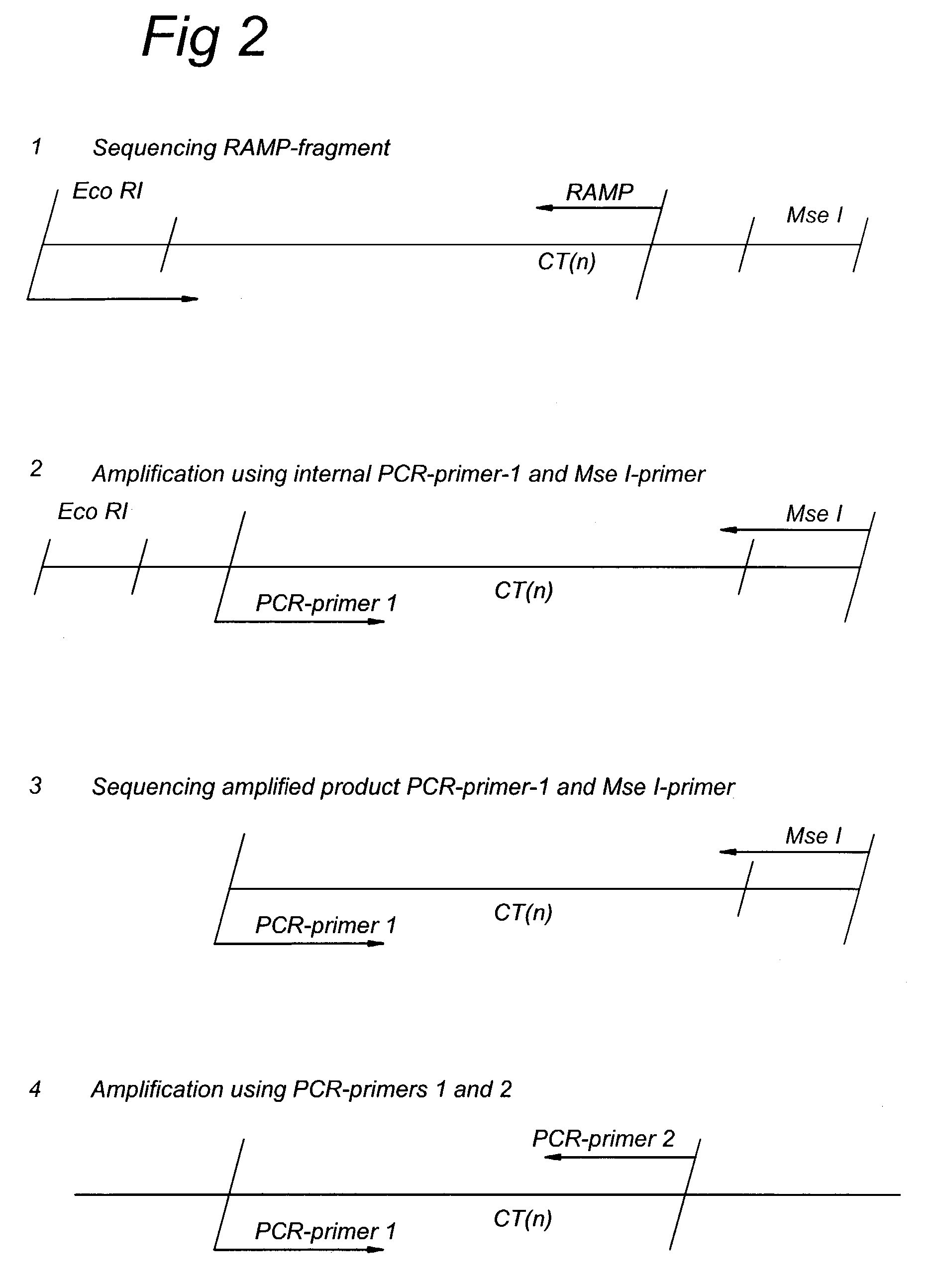
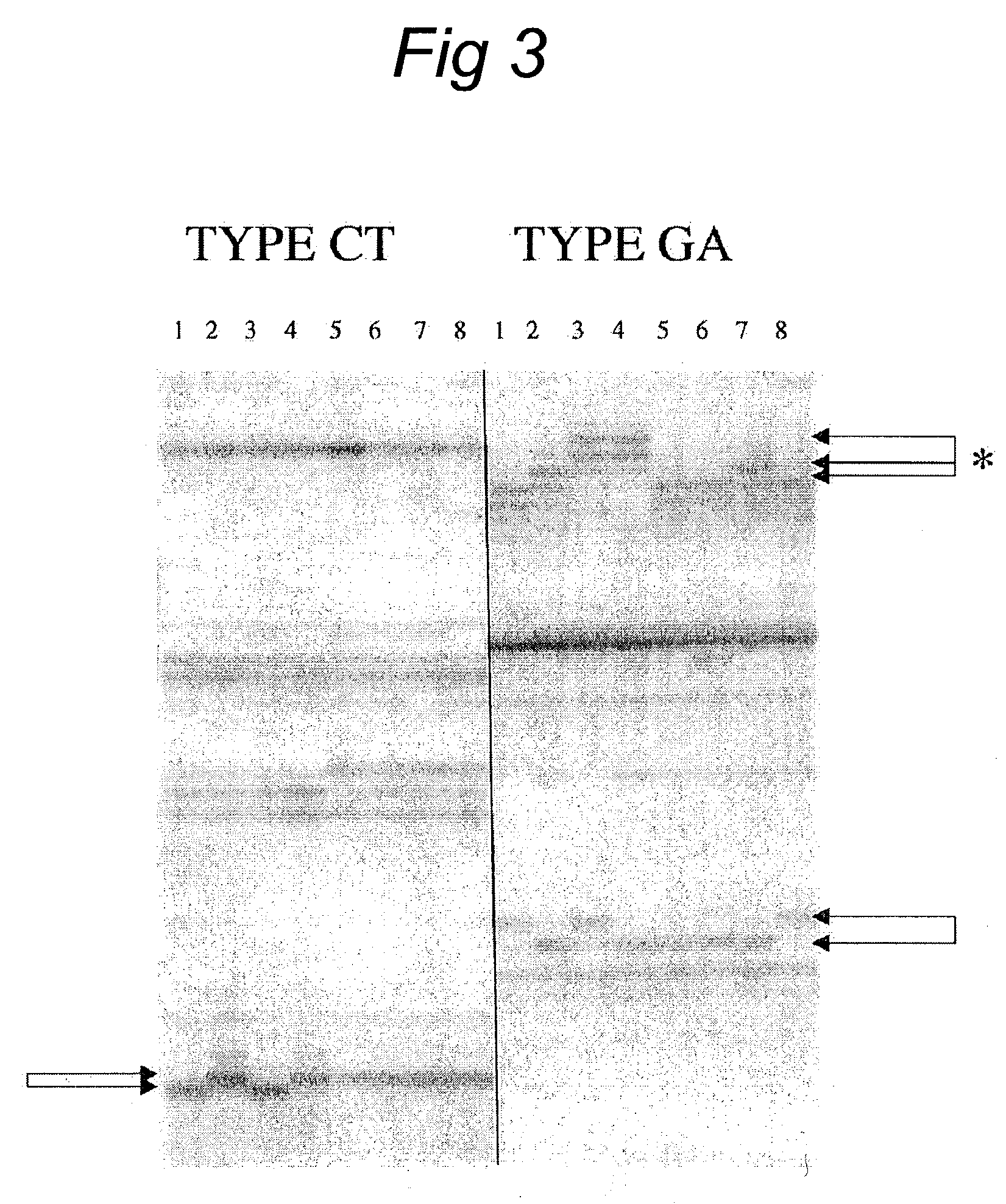
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method of screening pacific oyster EST micro-satellite mark
The invention discloses a screening method of Pacific oyster EST micro satellite label, which comprises the following steps: finding micro satellite site with Pacific oyster EST sequence announced by GeneBank and micro satellite searching software SSRhunter; screening and separating 2-6 base repeat unit micro satellite fragment (repeat times >5); getting repeat ESTs sequence with micro satellite; designing primer at two sides flank sequence of micro satellite repeat sequence; detecting optimization primer as the micro satellite label further; proceeding overall merit for micro satellite repeatability, stability, polymorphism; getting micro satellite label. The invention can be used for Pacific oyster species resource and genetic heterogeneity, molecular population genetics, species resource determination, genetic atlas construct, functional gene research, Pacific oyster breeding and cultivation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microsatellite DNA markers for Trionyx sinensis
The invention discloses microsatellite DNA markers for Trionyx sinensis, which is characterized in that an enriched library of microsatellites (CA)n, (AAC)n, (ACAG)n and (GATA)n from the Trionyx sinensis is constructed, and positive clones of microsatellite sequences are screened and sequenced to obtain 63 clones containing microsatellite repetitive sequences, thus determining 15 microsatellite markers with rich polymorphism, namely, PSW01, PSW02, PSW03, PSW04, PSW05, PSW06, PSW07, PSW08, PSW09, PSW10, PSW11, PSW12, PSW13, PSW14 and PSW15. The microsatellite DNA markers for the Trionyx sinensis of the invention can be applied to researching genetic diversity and paternity test for the Trionyx sinensis in different geographical populations, have the advantage of good repeatability, and are reliable and effective molecular markers.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting microsatellite markers of Charybdis feriatus
InactiveCN103305611BFast detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenotype
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting microsatellite markers of Charybdis feriatus. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting a genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of the Charybdis feriatus; (2) obtaining a gene sequence containing microsatellite repeats according to the functional gene sequence of the Charybdis feriatus in a GeneBank database; (3) designing a microsatellite marker primer; (4) implementing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the genomic DNA of different individuals of the Charybdis feriatus; and (5) detecting denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of PCR products. The method has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, sensitivity and the like, and can intuitively detect the genotype of different individuals of the Charybdis feriatus, so that a polymorphism map of genetic variation of the Charybdis feriatus on a functional gene microsatellite site is obtained quickly; the microsatellite markers can be applied to the fields of analysis on genetic variation and population genetic diversity of the Charybdis feriatus.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam
InactiveCN102719527AThe design principle is feasibleEasy to markMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadGenetics
The invention relates to a molecular assisted technology for genetic breeding, in particular to a microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam. The microsatellite marking method comprises four steps of obtaining microsatellite loci source, designing a primer, optimizing the primer and establishing a microsatellite marker parentage determination system, and the specific process is as follows: firstly using a bead enriching library method to screen microsatellite sequences, and using a microsatellite retrieval software to carry out rapid separation of microsatellite fragments; designing a primer on a microsatellite repeated flanking sequence, optimizing the primer and leading the primer to become a microsatellite marker; then carrying out a comprehensive evaluation on repeatability, stability and polymorphism information content value during the amplification process of the microsatellite marker, and determining the microsatellite markers therein as the microsatellite parentage determination system of the hard clam for differentiation among different parentages of the hard clam or identification and determination among individuals. According to the invention, a molecular marking method for genetic breeding of the hard clam is provided.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chinese alligator microsatellite DNA mark
InactiveCN101368205AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationChinese alligatorGenetic diversity
The invention discloses an alligator sinensis microsatellite DNA mark which includes the construction of the enriched libraries of (CT / AG)n, (AC / GT)n and (GATA)n of an alligator sinensis microsatellite, the screening and sequencing of the positive clones of a microsatellite sequence, obtaining 25 clones which comprise the repeated sequence of the microsatellite and conforming 10 microsatellite marks of Asiu1, Asiu2, Asiu4, Asiu20, Asiu44, Asiu45, Asiu84, Asiu96, Asiu122 and Asiu234 of abundant polymorphism. The alligator sinensis microsatellite DNA mark can be used for the studies on genetic diversity of different geographic populations of the alligator sinensis, has good repetitiveness and is a reliable and effective molecule mark.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Specific primers and screening method for EST-SSR (Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat) marker of torreya grandis transcriptome sequence
ActiveCN107287288AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGerm plasmGenetic diversity
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) marker technology and application, and particularly relates to specific primers and a screening method for an EST-SSR (Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat) marker of a torreya grandis transcriptome sequence. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly, assembling fine torreya grandis seed kernel and circular torreya grandis seed kernel transcriptome data by adopting Trinity software to obtain a transcript sequence; secondly, carrying out SSR site research on Unigene with 1kb or above obtained by screening by using an MISA (MIcroSAtellite identification tool) program, and carrying out screening and separating on 2 to 6 base repeat units and repeat times according to microsatellite fragments with repeat times of 9, 8, 5, 5 and 5 in sequence, thereby obtaining an ESTs sequence with microsatellite repeat; thirdly, designing the primers by using a Primer 3 program; finally, comprehensively evaluating repeatability, stability and polymorphism of the EST-SSR marker to obtain the EST-SSR marker. The specific primers disclosed by the invention can be used for conveniently and quickly analyzing germ plasm resources of different types and genetic diversity of interspecific and intraspecific torreya grandis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Polygonatum cyrtonema microsatellite markers
InactiveCN101654707AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityGenetics
The invention discloses polygonatum cyrtonema microsatellite markers. A method for realizing the technical scheme of the invention comprises the following steps: constructing an enriched library of apolygonatum cyrtonema microsatellite (CT)n; screening and sequencing positive clones containing microsatellite sequences to obtain 55 clones containing microsatellite repetitive sequences; and screening the 55 clones to obtain the following 14 high-polymorphism microsatellite molecular markers: Pc1, Pc2, Pc3, Pc4, Pc5, Pc6, Pc7, Pc8, Pc9, Pc10, Pc11, Pc12, Pc13 and Pc14. The 14 microsatellite markers can be used for researching the genetic diversity of polygonatum cyrtonema, variable and evolutionary relationships among species and populations of polygonatum plants and the authentication of polygonatum cyrtonema varieties, have the characteristic of good repetitiveness, and are reliable and effective molecular markers.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting microsatellite markers of Charybdis feriatus
InactiveCN103305611AFast detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenotype
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting microsatellite markers of Charybdis feriatus. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting a genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of the Charybdis feriatus; (2) obtaining a gene sequence containing microsatellite repeats according to the functional gene sequence of the Charybdis feriatus in a GeneBank database; (3) designing a microsatellite marker primer; (4) implementing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the genomic DNA of different individuals of the Charybdis feriatus; and (5) detecting denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of PCR products. The method has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, sensitivity and the like, and can intuitively detect the genotype of different individuals of the Charybdis feriatus, so that a polymorphism map of genetic variation of the Charybdis feriatus on a functional gene microsatellite site is obtained quickly; the microsatellite markers can be applied to the fields of analysis on genetic variation and population genetic diversity of the Charybdis feriatus.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Construction method of Plectropomus microsatellite DNA molecular markers
ActiveCN104357547AEfficient methodSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscriptome SequencingMetapopulation
The invention discloses a construction method of Plectropomus microsatellite DNA molecular markers. According to the method, Unigene containing Plectropomus microsatellite repeat sequences is firstly screened out by transcriptome sequencing. Then microsatellite sites are detected in the Unigene sequences. Specific primers of microsatellite markers are designed according to the sequences of both ends of the microsatellite sites and are used for detecting polymorphism of the microsatellite sites. The microsatellite markers with abundant polymorphism of Plectropomus are exploited, and seven microsatellite DNA molecular markers of Plectropomus are verified further. The Plectropomus microsatellite DNA molecular markers provided by the invention can be applied to population genetic structure and genetic breeding study of Plectropomus population.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Polygonatum filipes microsatellite markers
InactiveCN101654708AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPolygonatum filipesGenetic diversity
The invention discloses polygonatum filipes microsatellite markers. A method for realizing the technical scheme of the invention comprises the following steps: constructing an enriched library of a polygonatum filipes microsatellite (CT)n; screening and sequencing positive clones containing microsatellite sequences to obtain 84 clones containing microsatellite repetitive sequences; and screening the 84 clones to obtain the following 11 high-polymorphism microsatellite molecular markers: Pt1, Pt2, Pt3, Pt4, Pt5, Pt6, Pt7, Pt8, Pt9, Pt10 and Pt11. The 11 microsatellite markers can be used for researching the genetic diversity of polygonatum filipes and variable and evolutionary relationships among species and populations of polygonatum plants, have good repetitiveness and are reliable and effective molecular markers.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
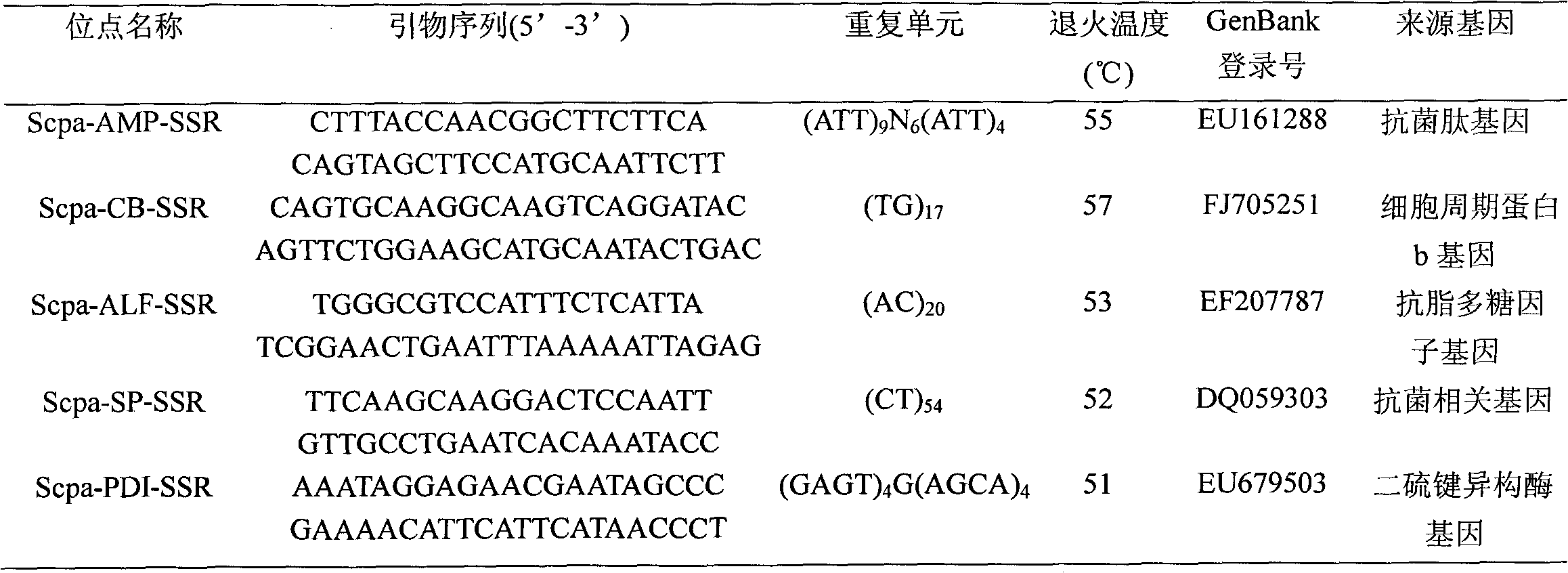
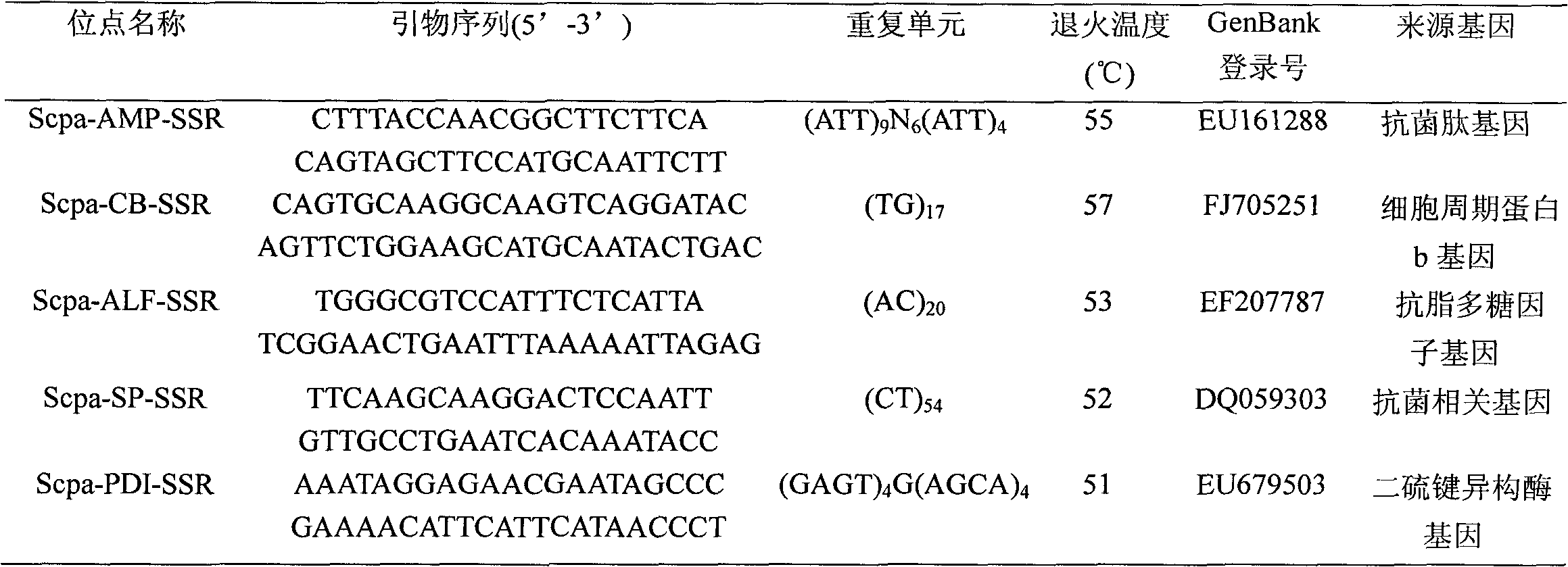
Quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes
InactiveCN101787395AFast detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmScylla paramamosain
The invention relates to a quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomic DNA of the Scylla paramamosain; (2) acquiring a gene sequence containing microsatellite repeats according to a functional gene sequence of the Scylla paramamosain in a GeneBank database; (3) designing microsatellite marker primers; (4) performing PCR amplification on the genomic DNA of different geographic population or different individuals in the population of the Scylla paramamosain; and (5) detecting a PCR product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The detection method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy, sensitivity and the like, and can intuitively detect genotypes of different individuals of the Scylla paramamosain so as to quickly acquire a polymorphic map for hereditary variation at functional gene microsatellite loci of the Scylla paramamosain; and the microsatellite markers can be applied to the fields such as hereditary variation analysis of the Scylla paramamosain, germ plasm resource protection and management, genetic linkage map construction and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Chinese hamster microsatellite genetic marker and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101328500AImprove standardizationImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRestriction enzyme digestionScreening method
The invention relates to an animal DNA molecule heredity mark technique, in particular to a Chinese hamster microsatellite heredity mark and a selecting method thereof to solve the problems that the report on the Chinese hamster microsatellite mark is not presented and the method for selecting the microsatellite mark that the DNA genome is broken down by the restriction enzyme digestion has a plurality of problems. The Chinese hamster genome DNA is extracted and is broken down by ultrasonic, and the DNA segment is reclaimed by electrophoresis. A Chinese hamster genome microsatellite enriched library is established, positive cloning vectors are selected from the library for sequencing. 17 microsatellite marks are obtained by selection. According to the microsatellite repetitive sequence, a primer is designed and 17 pairs of primers are selected for the heredity detection. When the method is used, the PCR amplification is performed on genome DNA of different individuals in a colony or of different colonies of Chinese hamster by using the 17 pairs of the primers. The electrophoresis detection is performed on the amplification product. According to the detection data and a map, the gene of each individual is determined. The method has good stability, high repetitiveness, strong comparability and simple operation.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Molecular genetics identification method for channel catfishes and flathead catfishes
ActiveCN104419758ARapid identificationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMyostatinIctalurus catus
The invention belongs to the genetics field and relates to a molecular genetics identification method for channel catfishes and flathead catfishes. The molecular genetics identification method for channel catfishes and flathead catfishes comprises the following steps: respectively extracting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of to-be-identified channel catfishes and flathead catfishes; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on amicine genes of the channel catfishes and flathead catfishes; sequencing and comparing; if AGC microsatellites, starting from the 83th locus, of the MSTN (myostatin) gene are repeated for six times, identifying the catfishes as channel catfishes, and if the microsatellites are repeated for seven times, judging the catfishes as flathead catfishes. The molecular genetics identification method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly, simply and conveniently, accurately and effectively identifying the channel catfishes and the flathead catfishes, is good in result stability and high in repetitive rate, so that the blank of identifying channel catfishes and flathead catfishes according to the existing domestic molecular biologic criteria is filled up.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE +1
Microsatellite marker of homatula fish as well as amplification primer and application of microsatellite marker
ActiveCN113373241AHigh polymorphismImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationRepetitive SequencesGenetics
The invention discloses a microsatellite marker of homatula fish as well as an amplification primer and application of the microsatellite marker. According to the microsatellite marker, 17 microsatellite markers are screened from genomic DNAs of three types of fishes (homatula red-tail, homatula brachysome and homatula bainite) of homatula, specific primers are designed in flanking areas at two ends of a microsatellite repetitive sequence for amplification, the obtained amplification product has high polymorphism and good stability, the microsatellite marker can be used in the fields of population genetic diversity, genetic structure, genetic resource protection and the like of three types of fishes of the homatula.
Owner:WATER ENG ECOLOGICAL INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecular marker
InactiveCN102703444AHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityOfficinalis
The invention discloses a radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA molecular marker, comprising the steps of constructing a radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite (CT) n enrichment library; screening and sequencing microsatellite sequence positive clone; obtaining 55 clones containing the microsatellite repeated sequence; and screening to obtain 9 high polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers Po1, Po2, Po3, Po4, Po5, Po6, Po7, Po8 and Po9. The radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA molecular marker can be used for researching genetic diversity of the radix polygonati officinalis, variation and evolutionary relationship between polygonatum plants and population, has good repeatability and is a reliable and efficient molecular marker.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Rattus losea microsatellite DNA marker and amplification primer thereof and a detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN108300793AGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetic diversity
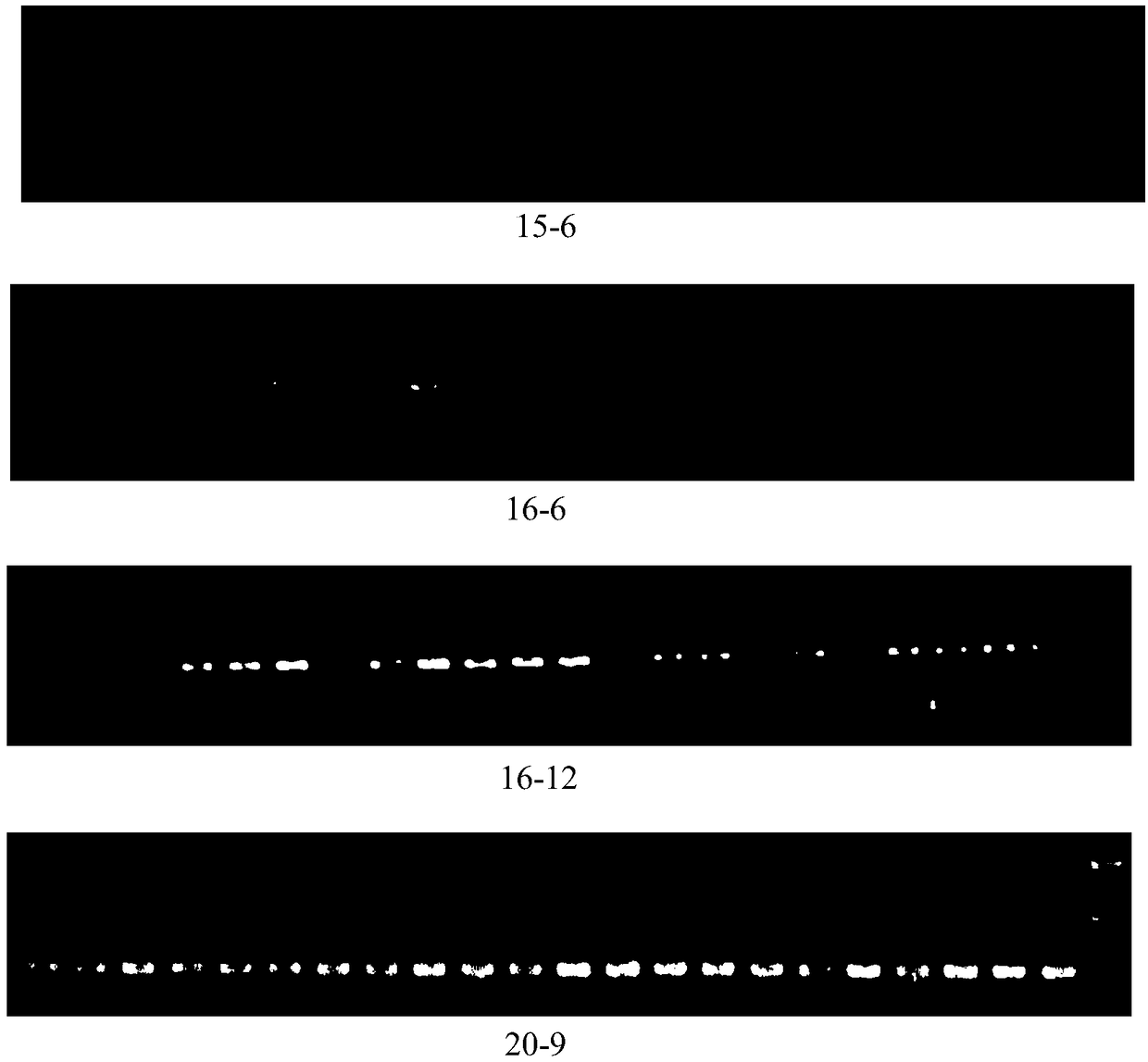
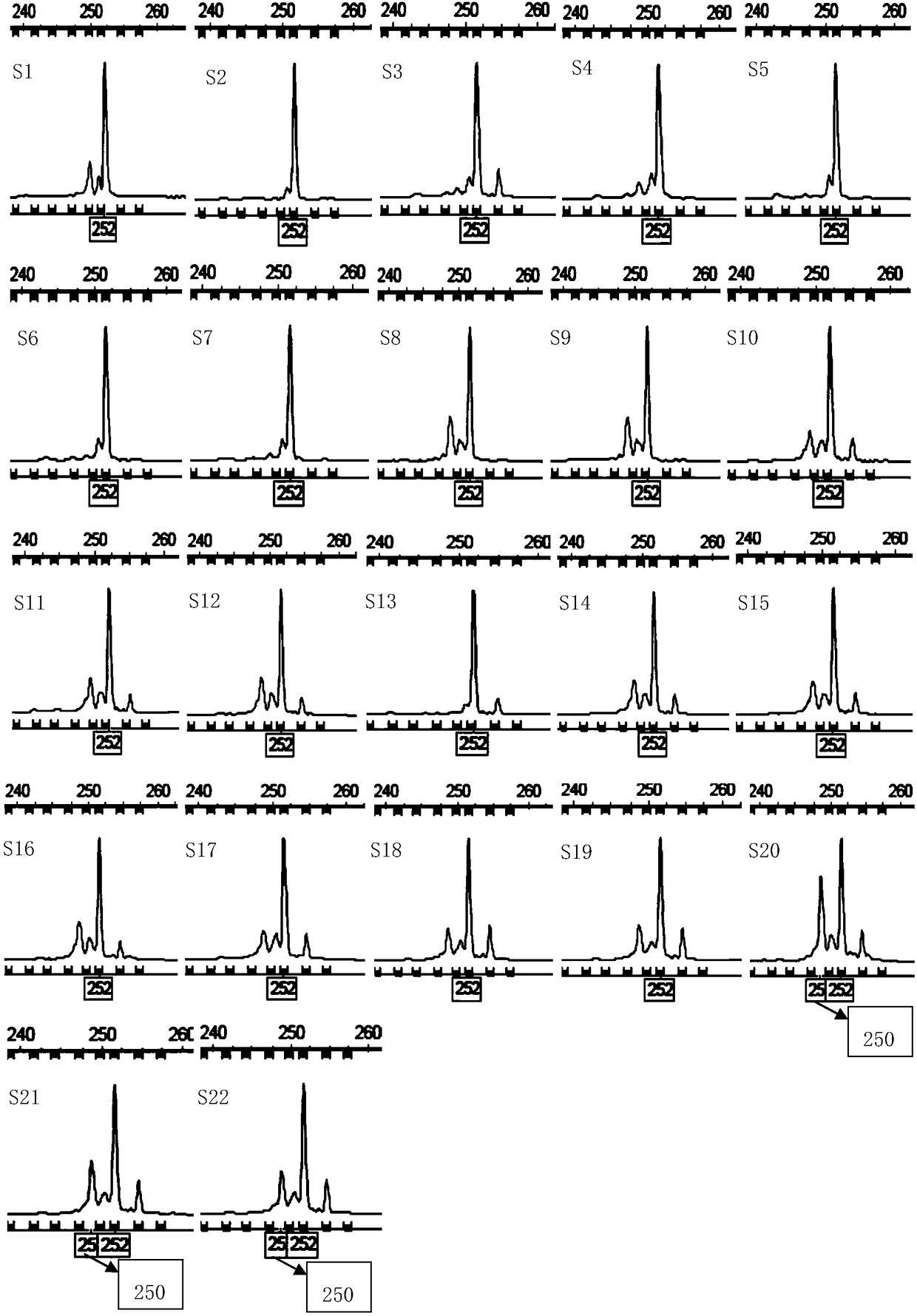
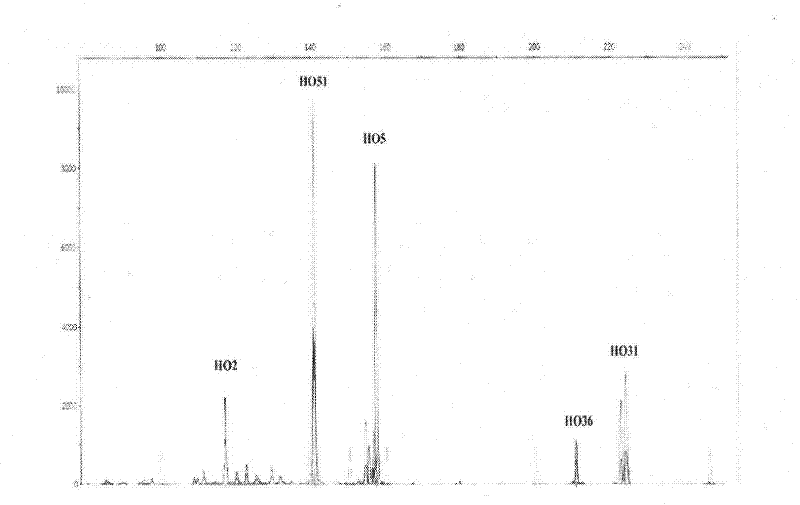
The invention discloses a rattus losea microsatellite DNA marker and an amplification primer thereof and a detection method and application thereof. Through the construction of rattus losea microsatellite (CT) n, (AG) n, (TG) n and (AC) n enriched libraries, screening and sequencing of positive clones containing microsatellite sequences and the cloning containing a microsatellite repeated sequence, eight microsatellite markers chrom1-26, chrom2-2, chrom15-6, chrom16-6, chrom16-12, chrom20-9, chrom20-37 and chrom-16 rich in polymorphism are obtained, and nucleotide sequences thereof are respectively as shown in SEQ ID No. 1-8. The rattus losea microsatellite DNA marker can be applied to researches of study of genetic diversity and the identification of parental relationship of different populations of rattus losea, is good in repeatability and is a reliable and effective molecular marker.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Micro-satellite DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) method for identifying reproductive mode of termite nest group
InactiveCN102559896AImprove targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesGenotype
The invention relates to a micro-satellite DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) method for identifying a reproductive mode of a termite nest group, which comprises the following steps of: collecting above 20 termite samples from a same nest group in the open air, extracting a sample genome DNA and diluting; searching a micro-satellite site related to a termite reproductive mode on GenBank, designing a primer on the side wing of a micro-satellite repetitive sequence by utilizing software Primer Premier 5.0, carrying out electrophoresis on an automatic analyzer after the termite samples DNA are subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by selecting a micro-satellite primer and determining the genotype of each strip corresponding sample in a electrophoretic diagram by using SAGAGT software; and carrying out chi-square test on observed genotype frequencies and expected genotype frequencies of the termite samples based on a Mendel's law and judging the reproductive mode of the termite nest group. The micro-satellite DNA identification for reproductive modes of ten reticulitermes chinensis nest groups in Changsha by adopting the micro-satellite DNA method shows that the reticulitermes chinensis nest groups include seven simple nest groups, two amplified nest groups and one mixed nest group. The micro-satellite DNA method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the results are reliable, the reproductive modes of the termite group can be accurately judged, and the important reference value is provided for the formulation of a termite prevention strategy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
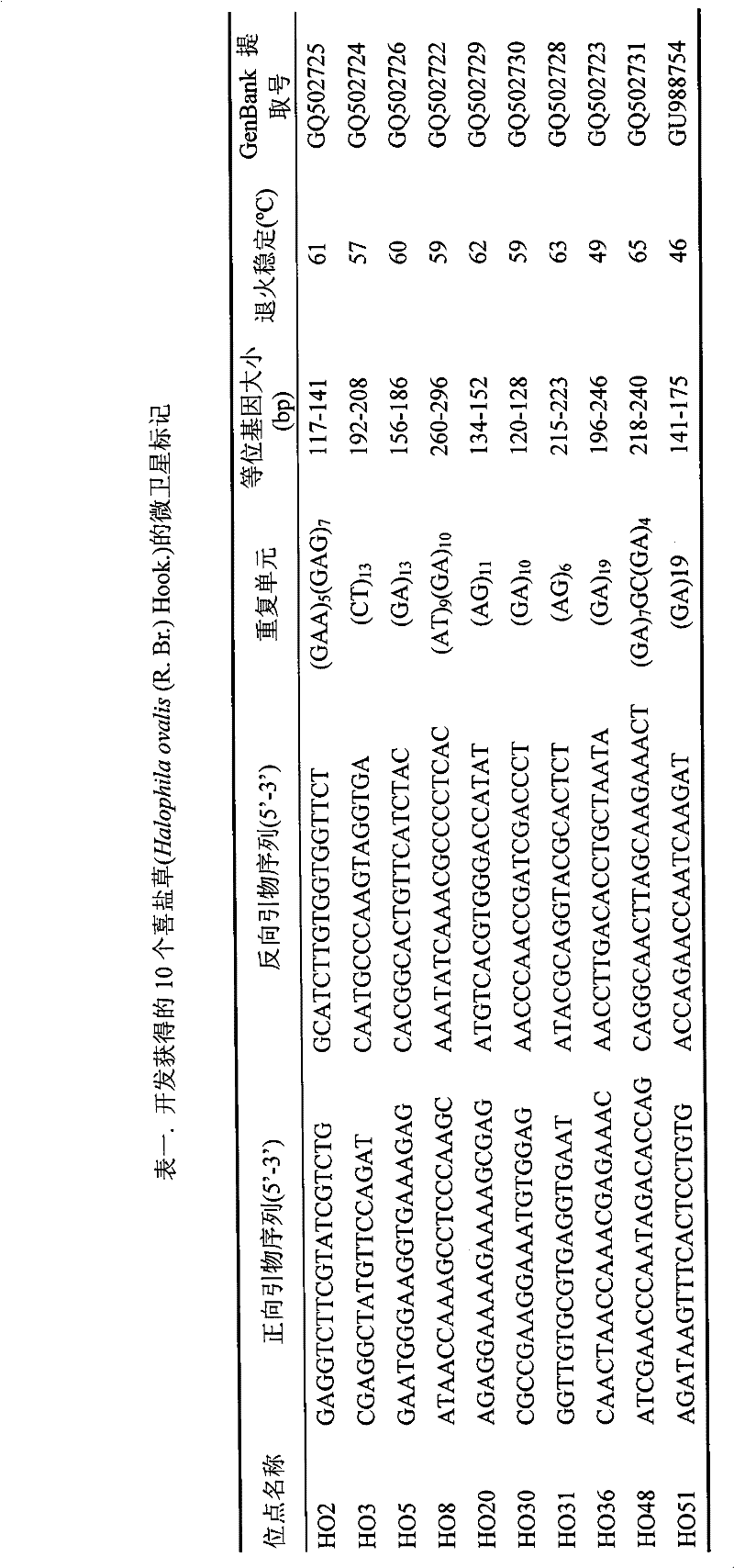
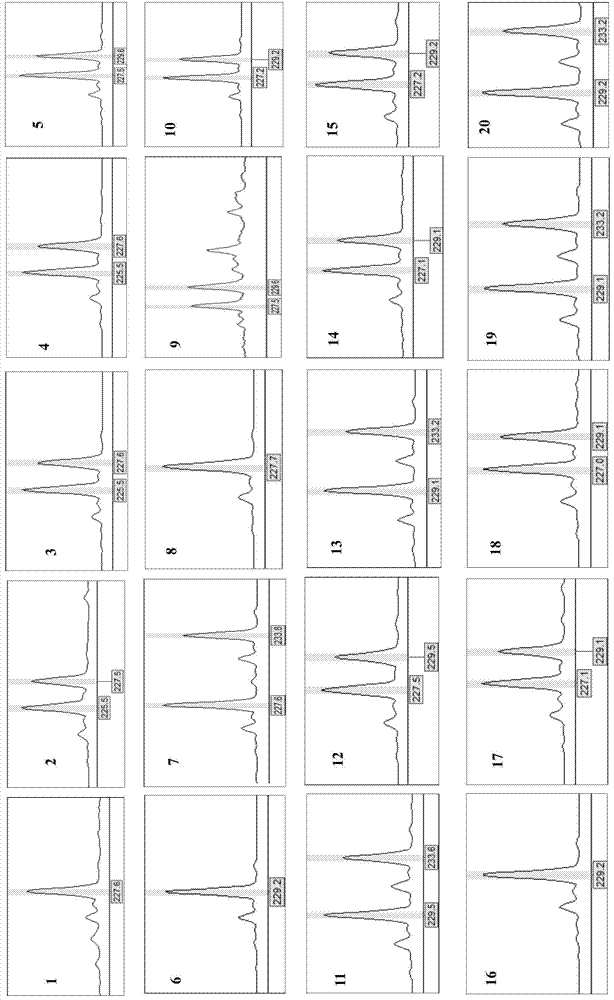
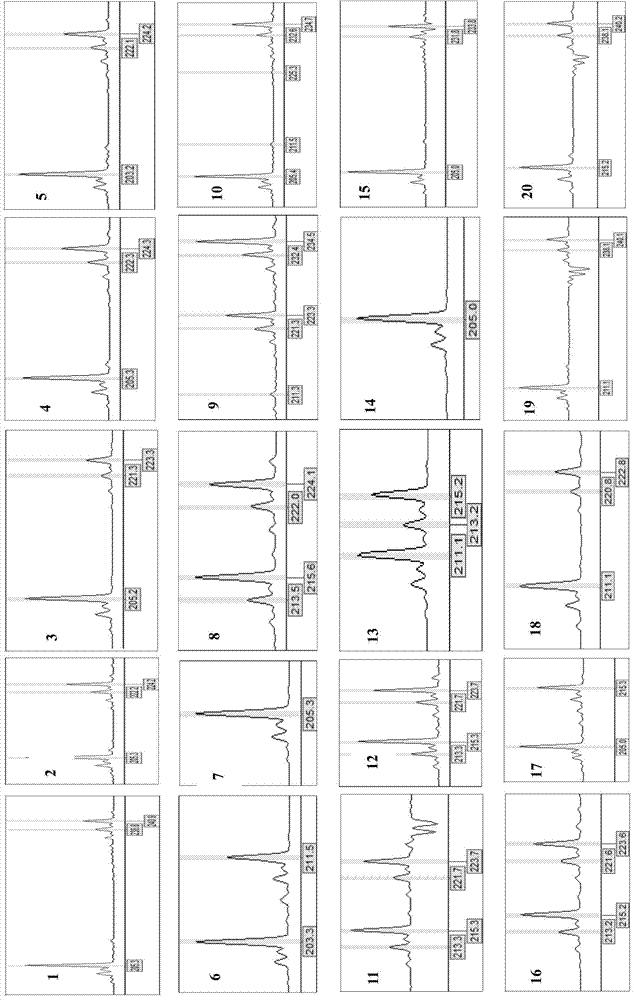
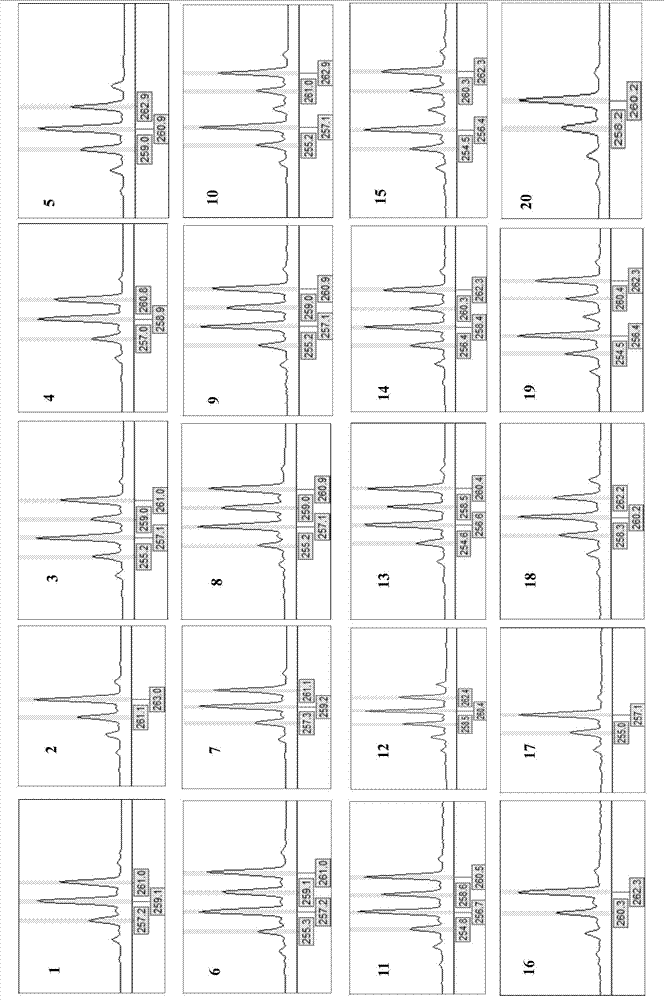
Screening Method of Microsatellite Markers in Seagrass Saltophila
InactiveCN102286457AImprove stabilityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotin-streptavidin complexGenetic diversity
The invention discloses a method for screening microsatellite markers of seagrass halophila. Firstly, the improved CTAB method is used to extract genomic DNA of the leaf tissue of halophila; , and the DNA fragments were sequenced, and DNA sequences with more than 5 base repeats (2-6) units were screened; then specific primers were designed at the flanking sequences at both ends of the microsatellite repeat sequence, and different geographical distribution groups The individual genome DNA of Salina philodendron was amplified by PCR to detect and optimize primers; finally, the fragment size of the PCR product was analyzed to determine the genotype of each individual, obtain the genetic polymorphism map of Salina philodendron, and determine the repeatability, Microsatellite markers with high stability and polymorphism. The invention can be used for the identification of germplasm resources, genetic diversity analysis, genetic map construction and other researches of the halophobia, and can be further used for the management, protection and restoration of the halophobia seagrass bed.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Pteroceltis tatarinowii microsatellite DNA molecular marker and isolation and screening method thereof
The invention discloses a microsatellite DNA molecular marker for an economic useful tree variety pteroceltis tatarinowii endemic to China. An isolation and screening method of the microsatellite DNA molecular marker comprises the following steps: constructing a pteroceltis tatarinowii (AG)n and (AC)n-enriched library, screening and sequencing microsatellite sequence positive clones, obtaining 72 positive clones containing microsatellite repetitive sequences, and screening to obtain 12 microsatellite markers which have high polymorphism and can be stably amplified, namely Pt1, Pt2, Pt3, Pt4, Pt5, Pt6, Pt7, Pt8, Pt9, Pt10, Pt11 and Pt12 respectively. The microsatellite DNA molecular marker has the advantages that a pteroceltis tatarinowii microsatellite DNA molecular marker technical system is established, reestablishment of genetic diversity analysis and specie evolution history of pteroceltis tatarinowii can be realized by utilizing the markers, a genetic basis is also provided for pteroceltis tatarinowii forest seedling breeding, and the repeatability is good, so that the microsatellite DNA molecular marker is reliable and effective.
Owner:武汉八颗星生物科技有限公司
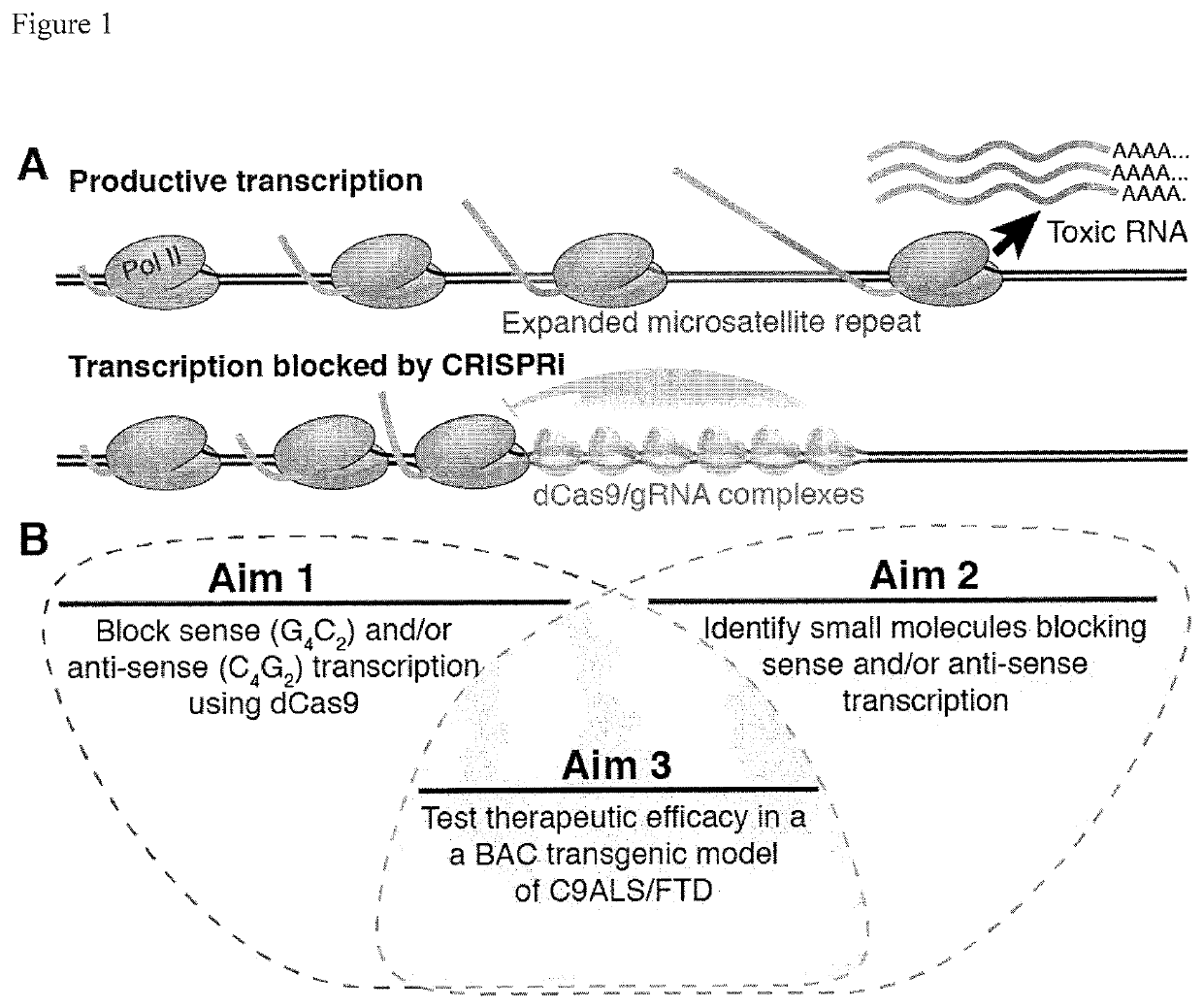
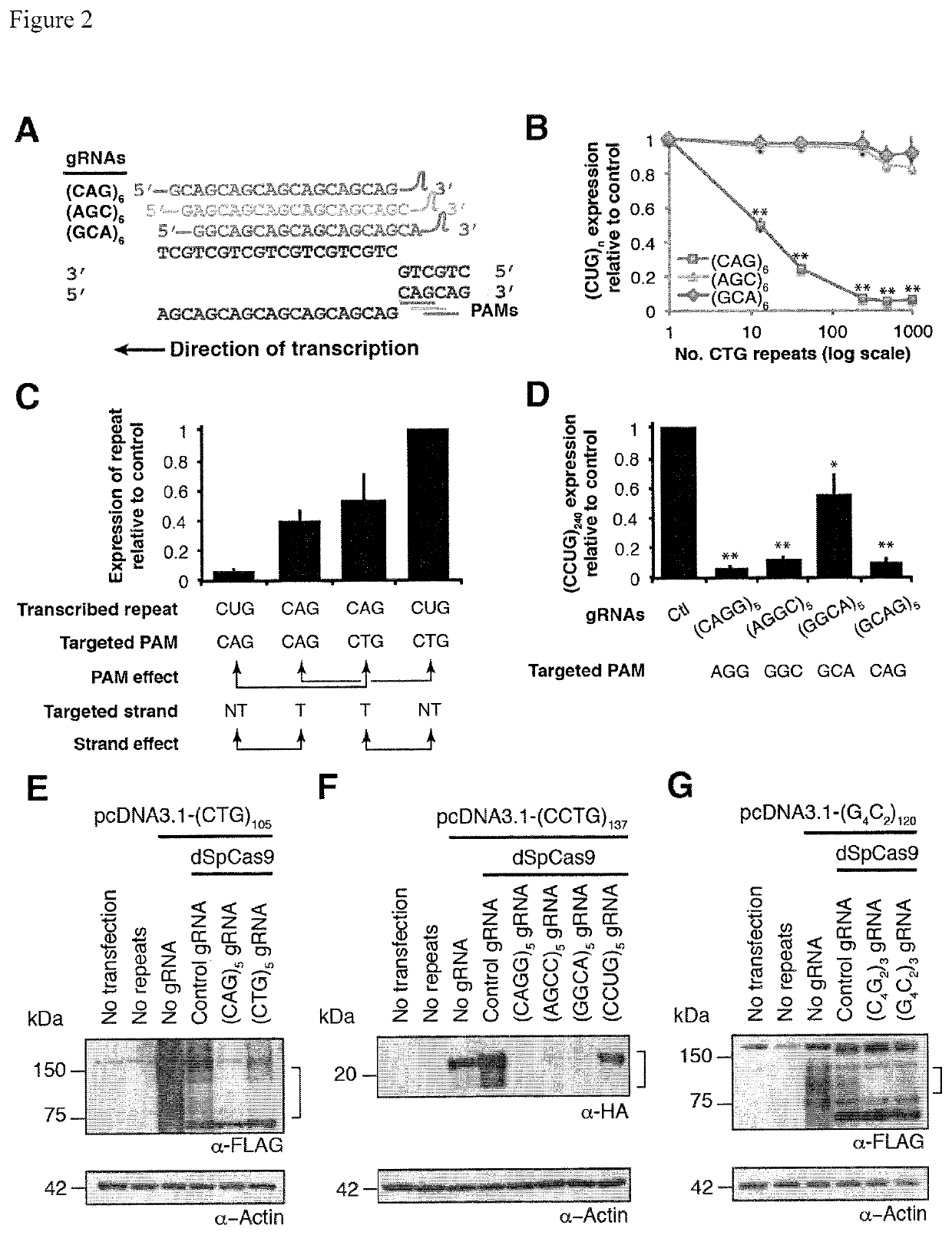
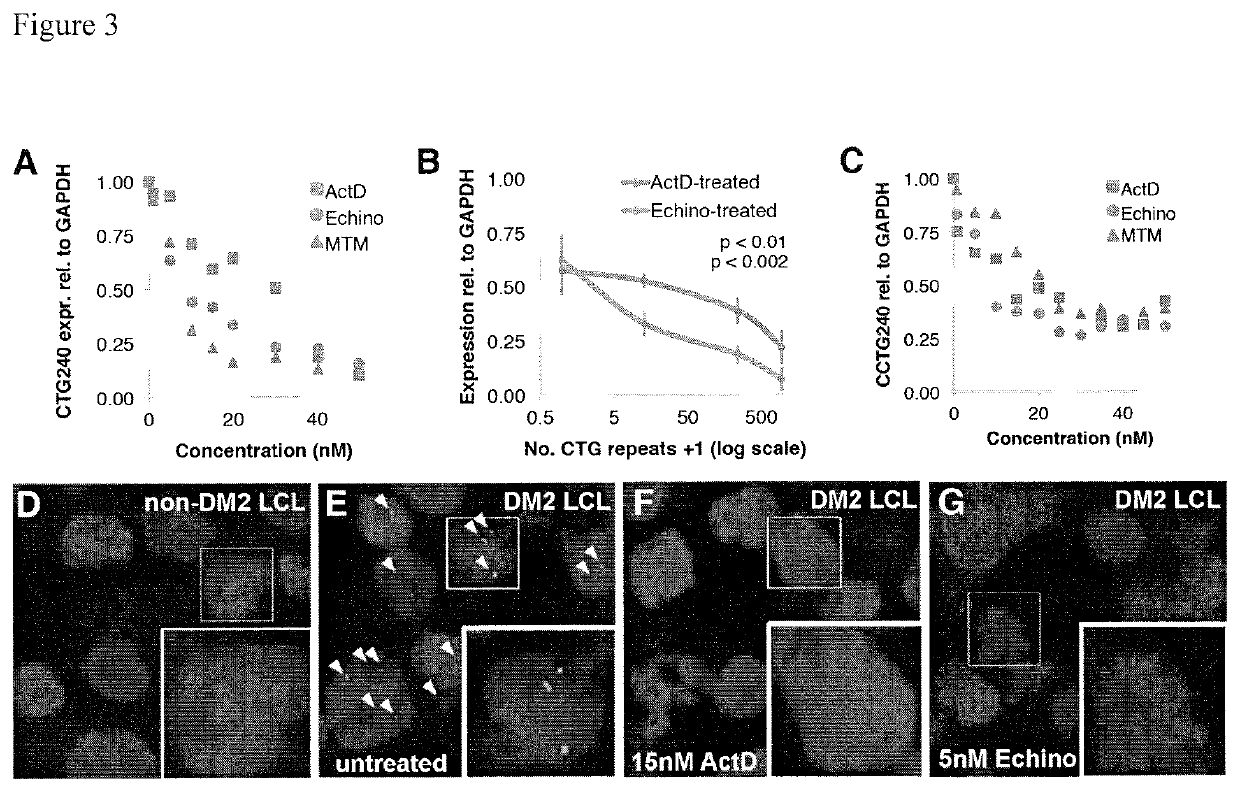
Compositions and methods for impeding transcription of expanded microsatellite repeats
PendingUS20210285010A1Reduce decreaseDecreased myotoniaOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseGenetics
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for treating diseases characterized by expanded microsatellite repeats by impeding or inhibiting transcription of expanded microsatellite repeats.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method of screening pacific oyster EST micro-satellite mark
InactiveCN100532573CMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenetic diversityPacific ocean
The invention discloses a screening method of Pacific oyster EST micro satellite label, which comprises the following steps: finding micro satellite site with Pacific oyster EST sequence announced by GeneBank and micro satellite searching software SSRhunter; screening and separating 2-6 base repeat unit micro satellite fragment (repeat times >5); getting repeat ESTs sequence with micro satellite; designing primer at two sides flank sequence of micro satellite repeat sequence; detecting optimization primer as the micro satellite label further; proceeding overall merit for micro satellite repeatability, stability, polymorphism; getting micro satellite label. The invention can be used for Pacific oyster species resource and genetic heterogeneity, molecular population genetics, species resource determination, genetic atlas construct, functional gene research, Pacific oyster breeding and cultivation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
SSR molecular marking method of wheat grain hardness gene
ActiveCN103757096AIncrease diversityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a SSR molecular marking method of a wheat grain hardness gene and relates to the technical field of wheat molecular marker-assistant breeding. The SSR molecular marking method is characterized in that a PCR primer containing a microsatellite repetition section is designed in a microsatellite-feature nucleotide sequence tightly linked with a hardness gene; the target specie is subjected to PCR amplification; and then allelic variation of Pina and Pinb genes of different species is determined by polyacrylamide electrophoresis. The SSR molecular marking method has the advantages of simpleness, high speed, high stability and high allele diversity and realizes molecular marking only by common polyacrylamide electrophoresis.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
A kind of est-ssr marker specific primer and screening method for the transcriptome sequence of Torreya torreya
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) marker technology and application, and particularly relates to specific primers and a screening method for an EST-SSR (Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat) marker of a torreya grandis transcriptome sequence. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly, assembling fine torreya grandis seed kernel and circular torreya grandis seed kernel transcriptome data by adopting Trinity software to obtain a transcript sequence; secondly, carrying out SSR site research on Unigene with 1kb or above obtained by screening by using an MISA (MIcroSAtellite identification tool) program, and carrying out screening and separating on 2 to 6 base repeat units and repeat times according to microsatellite fragments with repeat times of 9, 8, 5, 5 and 5 in sequence, thereby obtaining an ESTs sequence with microsatellite repeat; thirdly, designing the primers by using a Primer 3 program; finally, comprehensively evaluating repeatability, stability and polymorphism of the EST-SSR marker to obtain the EST-SSR marker. The specific primers disclosed by the invention can be used for conveniently and quickly analyzing germ plasm resources of different types and genetic diversity of interspecific and intraspecific torreya grandis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Microsatellite DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) markers of Chinese three-keeled pond turtle
The invention discloses a microsatellite DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) markers of a Chinese three-keeled pond turtle, which are determined by comprising the steps of constructing a library rich in tortoise microsatellites (CA)n (Carbonic Anhydrase)n and (GATA)n, screening and sequencing positive clones containing microsatellite sequences to obtain 59 clones containing microsatellite repetitive sequences, and determining 10 microsatellite markers with rich polymorphisms, wherein the 10 microstaellite markers are Mclw01, Mclw02, Mclw03, Mclw04, Mclw05, Mclw06, Mclw07, Mclw08, Mclw09 and Mclw10. The invention provides 10 new microsatellite loci of the Chinese three-keeled pond turtle and primer sequences and amplification methods for amplifying the 10 microsatellite loci, can be applied to a study on genetic diversity of different geographical populations of the Chinese three-keeled pond turtles and a study on paternity identification, and the molecular markers are reliable and effective with good repeatability.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam
InactiveCN102719527BThe design principle is feasibleEasy to markMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsRepeatability
The invention relates to a molecular assisted technology for genetic breeding, in particular to a microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam. The microsatellite marking method comprises four steps of obtaining microsatellite loci source, designing a primer, optimizing the primer and establishing a microsatellite marker parentage determination system, and the specific process is as follows: firstly using a bead enriching library method to screen microsatellite sequences, and using a microsatellite retrieval software to carry out rapid separation of microsatellite fragments; designing a primer on a microsatellite repeated flanking sequence, optimizing the primer and leading the primer to become a microsatellite marker; then carrying out a comprehensive evaluation on repeatability, stability and polymorphism information content value during the amplification process of the microsatellite marker, and determining the microsatellite markers therein as the microsatellite parentage determination system of the hard clam for differentiation among different parentages of the hard clam or identification and determination among individuals. According to the invention, a molecular marking method for genetic breeding of the hard clam is provided.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
EST-SSR (expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat) molecular marker, kit and identification method for identifying mesona chinensis variety
PendingCN114507748AGood design specificityImprove versatilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRepetitive SequencesSequence analysis
According to the EST-SSR molecular marker, the kit and the identification method for identifying the mesona chinensis benth variety, EST sequences in transcriptome data are used for analyzing composition and characteristics of microsatellite repetitive sequences contained in the mesona chinensis benth, mesona chinensis benth EST-SSR primers are developed, the effectiveness of the mesona chinensis benth EST-SSR primers and the universality of the mesona chinensis benth EST-SSR primers in mesona chinensis benth are verified, and the mesona chinensis benth variety is identified. The method is expected to provide important tools and valuable information for researches such as genetic relationship identification, phyloevolution, genetic variation and genetic map construction of mesona chinensis and related species thereof.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecular marker
InactiveCN102703444BHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityOfficinalis
The invention discloses a radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA molecular marker, comprising the steps of constructing a radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite (CT) n enrichment library; screening and sequencing microsatellite sequence positive clone; obtaining 55 clones containing the microsatellite repeated sequence; and screening to obtain 9 high polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers Po1, Po2, Po3, Po4, Po5, Po6, Po7, Po8 and Po9. The radix polygonati officinalis microsatellite DNA molecular marker can be used for researching genetic diversity of the radix polygonati officinalis, variation and evolutionary relationship between polygonatum plants and population, has good repeatability and is a reliable and efficient molecular marker.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
A molecular genetic identification method for channel catfish and longfin catfish
ActiveCN104419758BRapid identificationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMyostatinIctalurus catus
The invention belongs to the genetics field and relates to a molecular genetics identification method for channel catfishes and flathead catfishes. The molecular genetics identification method for channel catfishes and flathead catfishes comprises the following steps: respectively extracting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of to-be-identified channel catfishes and flathead catfishes; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on amicine genes of the channel catfishes and flathead catfishes; sequencing and comparing; if AGC microsatellites, starting from the 83th locus, of the MSTN (myostatin) gene are repeated for six times, identifying the catfishes as channel catfishes, and if the microsatellites are repeated for seven times, judging the catfishes as flathead catfishes. The molecular genetics identification method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly, simply and conveniently, accurately and effectively identifying the channel catfishes and the flathead catfishes, is good in result stability and high in repetitive rate, so that the blank of identifying channel catfishes and flathead catfishes according to the existing domestic molecular biologic criteria is filled up.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE +1
A Construction Method of Microsatellite DNA Molecular Marker
ActiveCN104357547BEfficient methodSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscriptome SequencingMetapopulation
The invention discloses a construction method of Plectropomus microsatellite DNA molecular markers. According to the method, Unigene containing Plectropomus microsatellite repeat sequences is firstly screened out by transcriptome sequencing. Then microsatellite sites are detected in the Unigene sequences. Specific primers of microsatellite markers are designed according to the sequences of both ends of the microsatellite sites and are used for detecting polymorphism of the microsatellite sites. The microsatellite markers with abundant polymorphism of Plectropomus are exploited, and seven microsatellite DNA molecular markers of Plectropomus are verified further. The Plectropomus microsatellite DNA molecular markers provided by the invention can be applied to population genetic structure and genetic breeding study of Plectropomus population.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com