Microsatellite marking method applicable to parentage determination of hard clam
A technology of microsatellite markers and microsatellites, which is applied in the field of molecular assistance in genetic breeding, can solve problems such as few reports of successful applications, and achieve the effect of feasible design principles, good practicability, and simple marking methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
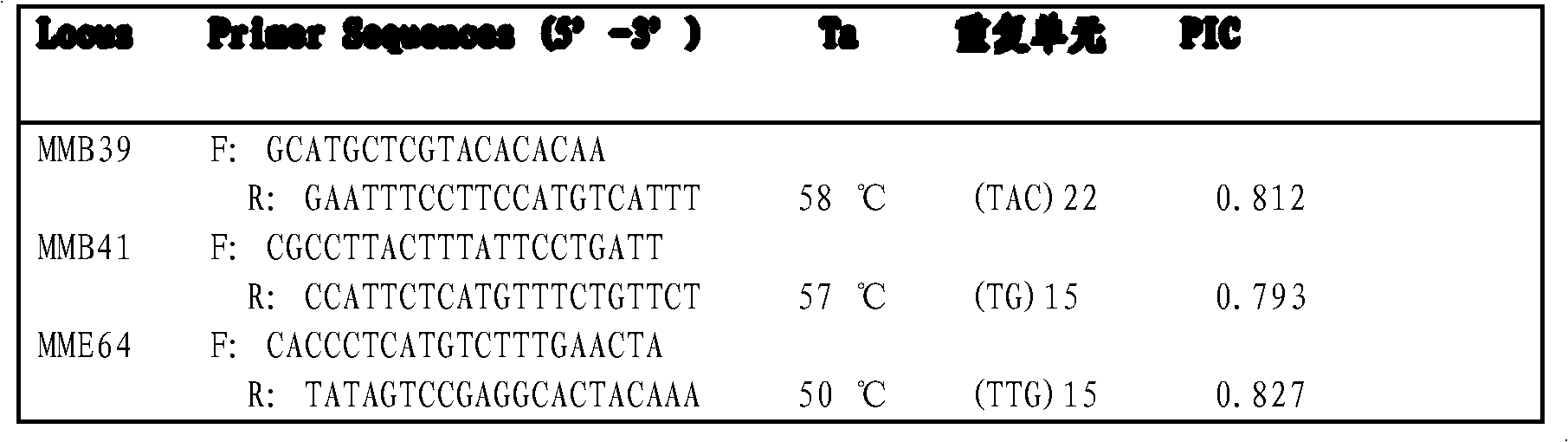
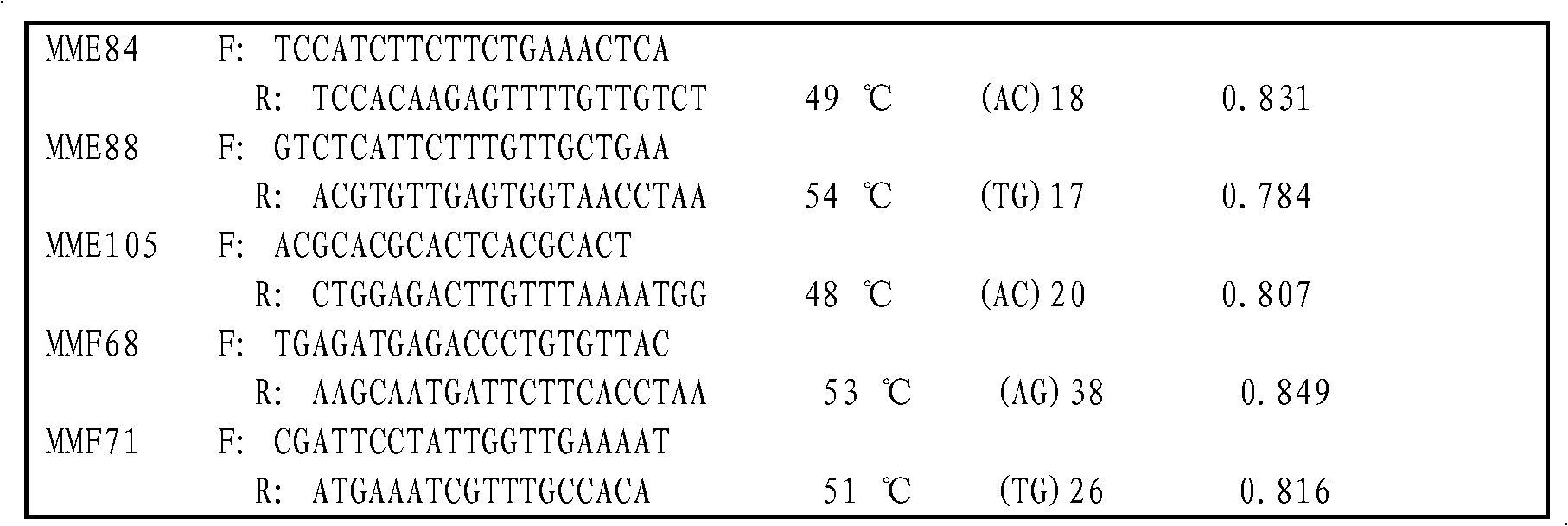
[0039] 1) The source of microsatellite loci: extract the genomic DNA of Meretrix meretrix, the extraction method is as follows:
[0040]Take a tissue less than 30mg, cut it into as small pieces as possible, add it to a 1.5ml Eppendorf tube, then add 500μL of cell lysate and 5μL of 20mg / ml proteinase K, shake gently, and lyse at 65°C for 4h. Then, 600 μL of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (volume ratio 25:24:1) mixture was added to the lysed sample, shaken for 20 minutes, centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken. Then add phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol mixture, repeat the above operation 2 times. Then take the supernatant, add 2 times the volume of cooled absolute ethanol and 1 / 10 of the supernatant volume of 3mmol / L sodium acetate, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, keep the DNA precipitate, and wash twice with 70% ethanol After the ethanol evaporated completely, the DNA was dissolved in TE buffer and stored in a re...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment is divided into three steps of extracting clam genomic DNA, PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection of PCR products:
[0049] Extract clam DNA: select clam X 7 S 27 Take 30 mg of fresh tissue from each individual of the family’s parents and 30 offspring, cut it into pieces and add it to a 1.5ml Eppendorf tube, then add 500 μL of cell lysate and 5 μL of 20 mg / ml proteinase K, shake gently, and leave overnight at 37°C . Then add 600 μL of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (volume ratio 25:24:1) mixture to the lysed sample, shake for 20 minutes, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 10 minutes, and take the supernatant. Then add phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol mixture, repeat the above operation 2 times. Then take the supernatant, add 2 times the volume of cooled absolute ethanol and 1 / 10 volume of 3mmol / L sodium acetate, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, keep the DNA precipitate, wash twice with 70% ethanol, and wait After th...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Using the microsatellite marking method of the present invention to carry out microsatellite marking site MMF68 in clam X 7 S 27 Types in the parents and their 5 offspring in the family, offspring numbers 1, 3, 17, 29, 56 (see figure 1 ):
[0057] (1) Source of microsatellite loci: Genomic DNA of clams was extracted, genomic DNA fragments of clams were obtained by restriction endonuclease method, microsatellite magnetic bead enrichment library was constructed, positive clones were detected, and microsatellite repeats were obtained by sequencing the DNA sequence;
[0058](2) Primer design: Use the software Primer Premier 5.0 to design primers at the flanking sequences of the microsatellite repeats. The primer design conditions are: the primer length is 19-25mer; the GC content is 40%-60%; the annealing temperature is 45-65°C; The expected PCR product length is 100-400bp; the MMF68 primer is F: TGAGATGAGACCCTGTGTTAC; R: AAGCAATGATTCTTCACCTAA.
[0059] (3) Primer optim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com