Isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and molecular modification method
A genome-scale, metabolic network technology, applied in the field of metabolic engineering molecular transformation of microbial synthetic bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Based on the metabolic network model of the Bacillus subtilis type strain, the characteristic reactions of isobutanol biosynthesis were added. The model uses glucose as the sole carbon source, and other subsystems except central carbon metabolism (glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway and tricarboxylic acid cycle), such as amino acid synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, lipid synthesis, energy and coenzyme synthesis, And the linear pathways in cell wall synthesis were combined, and the related transport reactions of substrate absorption and product secretion were added. A total of 130-150 reactions were included to obtain the metabolic network model of isobutanol synthesizing bacteria.
Embodiment 2
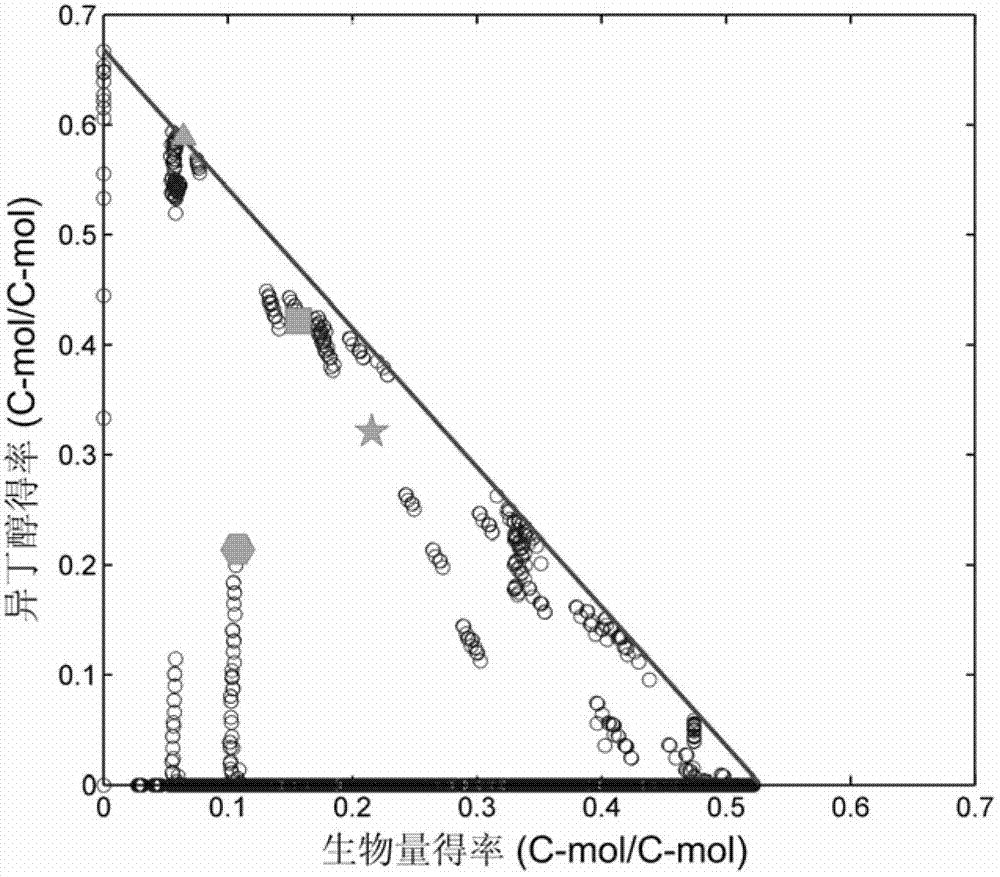
[0033] Transform the metabolic network model of isobutanol-synthesizing bacteria into a recognizable mathematical matrix model, and use the elementary pattern analysis algorithm with the help of the METATOOL tool (version 5.1, 2008) to obtain all relevant patterns that can exist independently in the strain. In EXCEL, from 10000-12000 models, it is determined that there is a model for isobutanol synthesis, of which the maximum theoretical yield of isobutanol is 0.6-0.7C-mol / C-mol, and the maximum theoretical value of bacterial cell yield is 0.5-0.6 C-mol / C-mol (eg figure 1 ). After screening for these modes, the linear correlation of each reaction with the target reaction in these modes was calculated. A linear correlation coefficient of 65-80% indicates that the reaction is related to isobutanol synthesis, and a positive correlation indicates that the gene encoding the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction has a positive effect on isobutanol, and vice versa. The standard deviat...
Embodiment 3
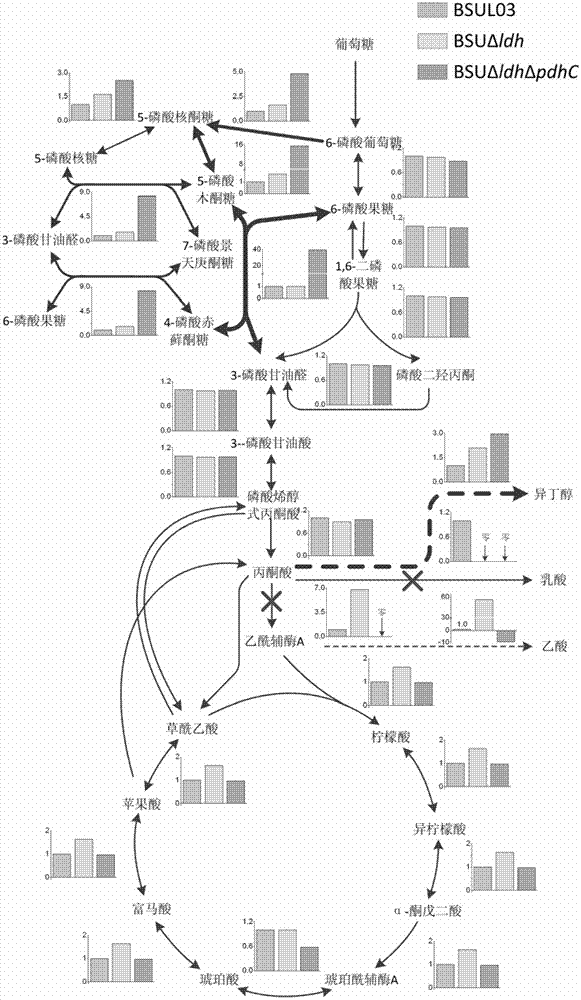
[0036] From the two most important key genes obtained in Example 2, calculate the average value, variance and standard deviation coefficient of the relative flux of carbon flow in these modes for each reaction. The relative flux of carbon flow in each reaction is based on the glucose absorption rate. By simulating the genes ldh and pdhC that have the greatest impact on the synthesis of isobutanol, the effect of gene knockout on the flux of each reaction in the central carbon metabolism of the whole cell is determined. influence, such as figure 2 . Compared with the wild strain BSUL03, the central metabolic pathway simulated by the single-gene modification BSUΔldh, including the pentose phosphate pathway and the citric acid cycle pathway, was 40%-70% larger, and the glycolysis pathway was not changed much, only reduced by 4 %, the flux of isobutanol synthesis pathway increased by 1-1.5 times. For the flux distribution simulated by double gene knockout, the pentose phosphate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com