L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deleted engineering bacterium and construction method and application thereof
A technology of lactate dehydrogenase and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of D-lactic acid, L-lactate dehydrogenase gene deletion mutants and their construction, can solve the problems of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene deletion and other problems, and achieve broad application Foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
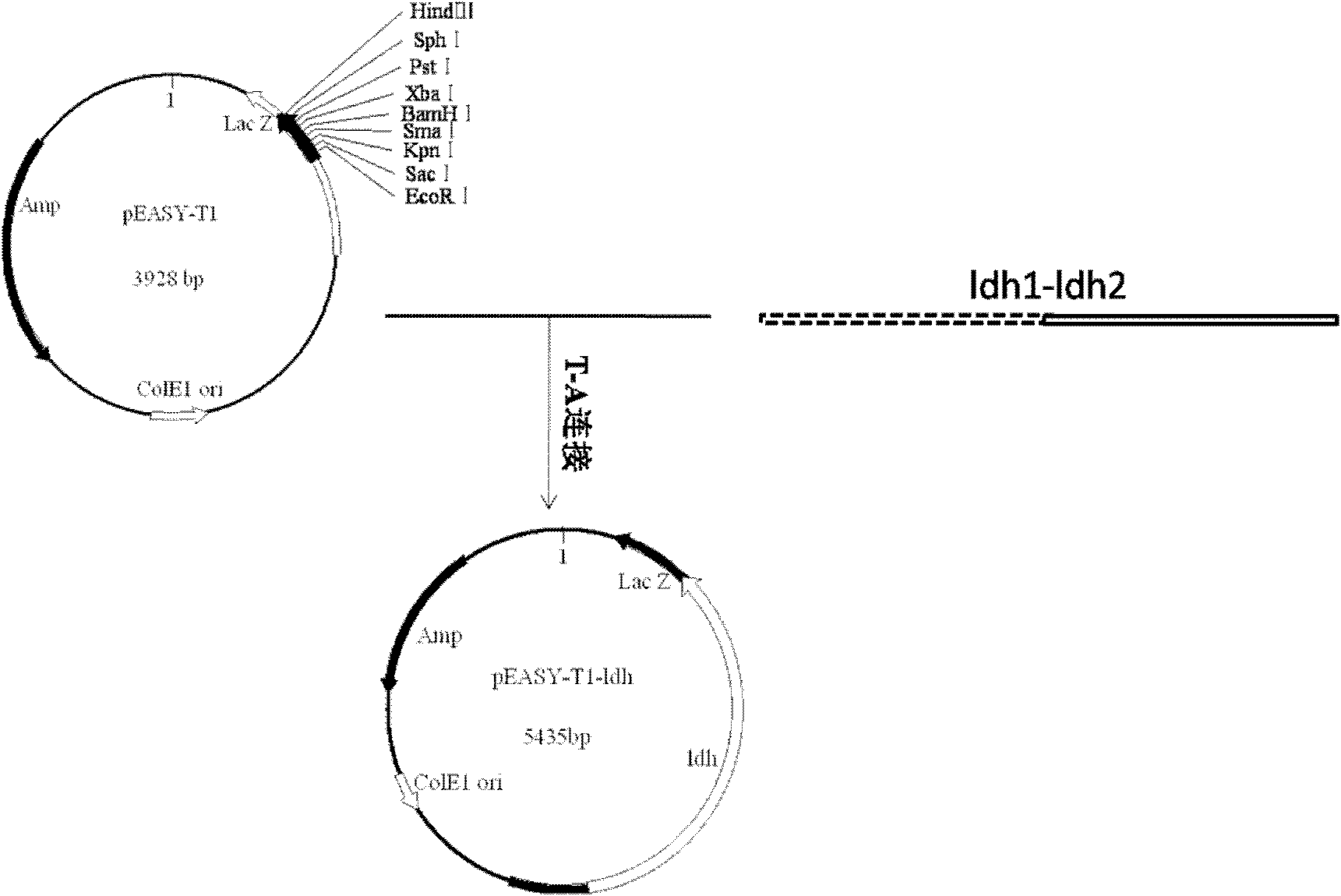
[0032] Embodiment 1: Construction of gene knockout vector:
[0033] 1. Splicing of upstream and downstream sequences of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene
[0034](1) According to the upstream and downstream DNA sequences of the ldh gene (NCBI-GI: 58036263) in Corynebacterium glutamicum, design primers to amplify its upstream and downstream sequences by PCR. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0035] uldh1: 5′-CCAAGGTGCCGACACTAAT-3′
[0036] dldh1: 5′-CGGTGATTTCGCAACTCCAACATCTCCTG-3′
[0037] uldh2: 5′-TTGGAGTTGCGAAATCACCGACCACGAGA-3′
[0038] dldh2: 5′-GCTTCCAGACGGTTTCATC-3′
[0039] Using the genomic DNA of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 as a template, under the guidance of primers uldh1, dldh1 and uldh2, dldh2, the upstream and downstream homology arm sequences of the ldh gene were cloned by PCR. The PCR amplification conditions and system were as follows:
[0040] Reaction system Amplification conditions
[0041] Composition Volume Temperature Time
[0042] uldh1(...
Embodiment 2
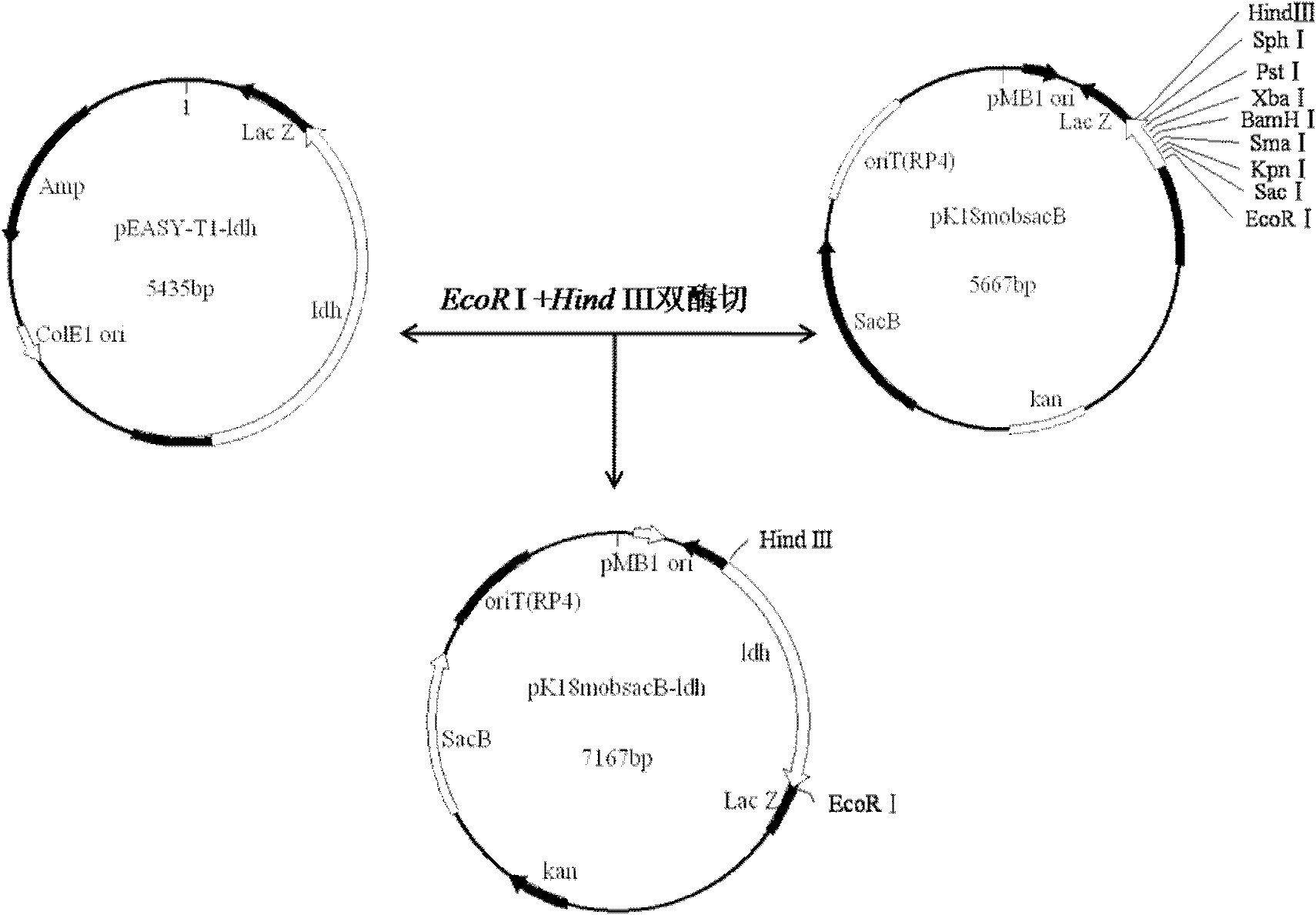
[0054] Example 2: Screening of single exchange strains after homologous recombination
[0055] The constructed L-lactate dehydrogenase gene knockout vector pK18mobsacB-ldh was electrotransformed into competent cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032, and the transformation conditions were: 25μF, 600Ω, 2.5kV electric shock, pulse time 10-12ms, Spread the bacterial solution on a BHIS plate with 25 μg / ml kanamycin and culture it for 24 to 48 hours, select positive colonies, and use 10% sucrose plates containing 25 μg / ml kanamycin to replicate the transformed colonies that were initially screened. To confirm by screening, pick the colonies that can grow on the kanamycin-resistant plate but cannot grow on the kanamycin-resistant plate containing 10% sucrose, extract the genomic DNA of the positive colony after re-screening, and amplify ldh1 - The upstream and downstream primers dldh1 and uldh2 of ldh2 were used for PCR amplification. In addition, primers s1 and s2 for amplif...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: Screening of ldh gene knockout strain
[0057] Insert the strain C.glutamicum Res167L with single exchange into the liquid LB medium without antibiotics for overnight culture, then collect the bacterial liquid, concentrate it by centrifugation, spread it on the LB medium containing 10% sucrose, and pick out the outgrowth Positive strains were placed on solid LB plates containing kanamycin and kanamycin, respectively, and the colonies that could grow on the plate without antibiotics but could not grow on the plate containing antibiotics were picked and shaken. Colony PCR was further performed with upstream and downstream primers dldh1 and uldh2 for amplifying ldh1-ldh2. Additional PCR amplification was performed with primers for amplifying ldh and internal amplification primers up1 and down1 for the ldh1-ldh-ldh2 fragment. The amplification results of the three pairs of PCR primers were consistent with the expected values, indicating that the screened stra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com