Polypeptide having d-lactate dehydrogenase activity, polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide, and process for production of d-lactic acid
A lactate dehydrogenase and polynucleotide technology, applied in the field of D-lactic acid production, can solve problems such as problems in the yield of D-lactic acid, and achieve the effect of high-purity production, high efficiency and production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
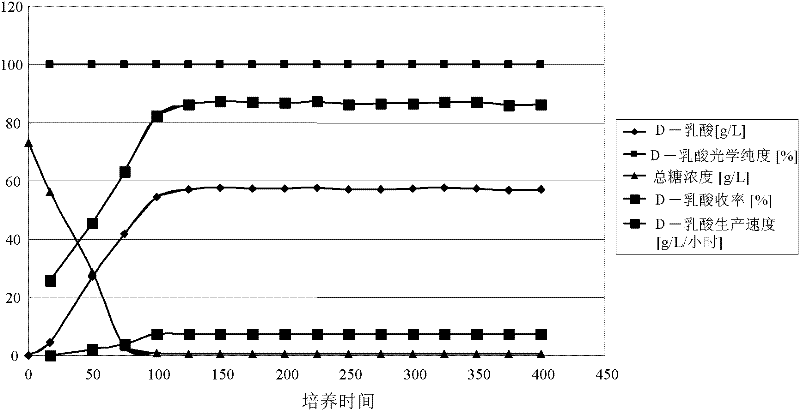
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] (Example 1) Determination of the base sequence of a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide having D-LDH activity derived from Limulus americana (hereinafter referred to as the D-LDH gene derived from Limulus americana)
[0102] In order to prepare cDNA of Limulus americana, polyA(+) RNA was purified. polyA(+) RNA isolated from hemocytes of Limulus americana. Total RNA was isolated from blood cells of Limulus americana (purchased from Marine Biological Laboratory (USA)) using the AGPC method (see Experimental Medicine Vol. 9 (1991), pp. 1937-1940). Using the isolated total RNA, polyA(+) RNA was isolated using "Oligotex-dT30 Super Kit" (manufactured by Takara Bio Co., Ltd.). Next, cDNA was synthesized using "SuperScript II Reverse Transcriptase" (manufactured by Invitrogen Co., Ltd.) with Oligo d(T) as a primer. Next, using this reaction solution as a template, PCR was performed using the oligomeric DNAs described in SEQ ID NO: 8 and SEQ ID NO: 9, which were designed wit...
Embodiment 2
[0106] (Example 2) Construction of D-LDH Gene Expression Plasmid Derived from American Limulus
[0107] The D-LDH1 gene and the D-LDH2 gene (hereinafter respectively referred to as Lp. ) on the ORF5' side and ORF3' side of the oligomeric DNA described in SEQ ID NO: 20 and SEQ ID NO: 21, or the oligomeric DNA described in SEQ ID NO: 22 and SEQ ID NO: 23 as a primer set, using the polyA (+) RNA of Limulus americana The synthesized cDNA was used as a template for PCR to clone the gene. The resulting DNA fragment was cut with restriction enzymes XhoI and NotI, and introduced into the yeast expression vector pTRS11 (with a TDH3 promoter and a selection marker URA3 gene, which was similarly cut with restriction enzymes XhoI and NotI, referring to Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2006-280368 No. bulletin. Wherein, the TDH3 promoter and the terminator are expressed as the GAPDH promoter and the terminator.) Cutting site, making a DNA construct comprising the TDH3 promoter, Lp.D-LDH1 gen...
Embodiment 3
[0108] (Example 3) Introduction of D-LDH gene expression plasmid derived from Limulus americana into yeast
[0109] The pTRS205 and pTRS206 obtained in Example 2 were introduced into Saccharomyces cerevisiae SW029-1B strain (genotype: MATa ura TRP(Δpdc1::TRP1) his ade lys leu) (hereinafter referred to as SW029-1B strain) as a yeast. The introduction of the plasmid was carried out by the lithium acetate method using "YEASTMAKER Yeast Transformation System" (manufactured by Crontec Corporation) (see the attached protocol for details). The SW029-1B strain used as the host is a strain lacking the ability to synthesize uracil. Due to the function of the selection marker URA3 gene contained in pTRS205 and 206, the transformed yeast introduced with pTRS205 and 206 can be selected on a uracil-free medium. The confirmation of the introduction of the D-LDH gene expression vector into the thus obtained transformant can be confirmed by using the genomic DNA extraction kit "Gentoru Kun" (T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com