Engineering bacteria for knocking out pyruvate formate-lyase genes and application of engineering bacteria
A technology of pyruvate formic acid and engineering bacteria, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of reduced 1,3-propanediol production, waste of substrate glycerol, inhibition of cell growth, etc., and achieve the effects of reduced toxicity, reduced formic acid production, and increased rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Construction of a Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strain in which the key gene of the formate metabolic pathway—pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene is inactivated.
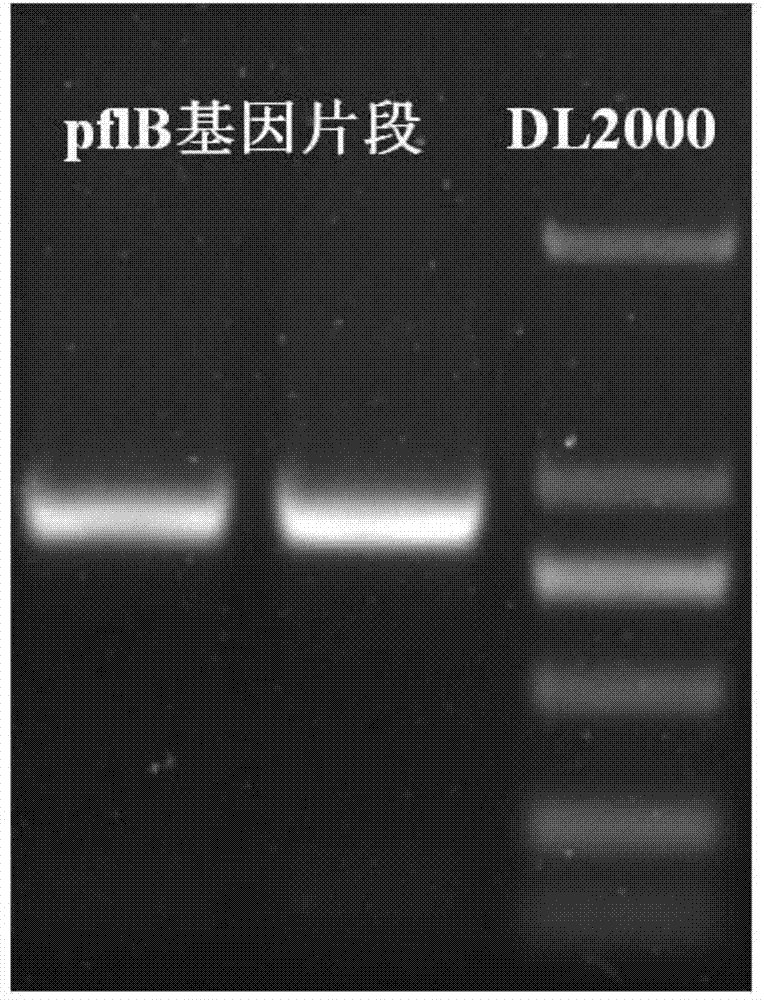
[0023] (l), cloning the partial sequence of pyruvate formate lyase gene pflB
[0024] Design primers for PCR amplification of part of the gene sequence of pyruvate formate lyase flpB. The primer sequences are as follows: upstream primer pflB-F: taggtacctgaaagacaaattcgcccag and downstream primer pflB-R: gagagctccatgcgatccattacttcgt. Using the genomic DNA of wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae (preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, preservation number: CCTCC M 2011075) as a template, under the guidance of primers pflB-F and pflB-R, pyruvate was amplified by PCR For the partial sequence of formate lyase pflB, PCR amplification conditions are: first 95°C for 3 minutes; then 94°C for 1 minute, 50°C for 1 minute, 72°C for 1 minute, a total of 32 cycles; finally 72°C for 10 minutes. After th...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Detection of activity of pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene in an insertionally inactivated Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strain.
[0030] Carry out the activity detection of pyruvate formate lyase to the Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strain whose flpB gene of pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene of embodiment 1 is inserted inactivated, with wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae as a control, the specific method comprises The following steps:
[0031] (1) The Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strain whose pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene is inactivated is inoculated in 100 mL of medium (every liter of water contains 20 g of glycerol, 10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast powder, 5 g of NaCl, pH 7.0, Sterilize at 120°C for 20 minutes), shake and culture at 37°C for 6-12 hours, and collect bacteria by sampling and centrifuging every 2 hours;
[0032] (2) Suspend and wash the bacteria twice with 100mL phosphate buffer (0.1M, pH7.5);
[0033] (3) Suspend the bacteria with 2.5mL phosphat...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Fermentative production of 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strain with knockout pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene
[0038] (1) culture medium
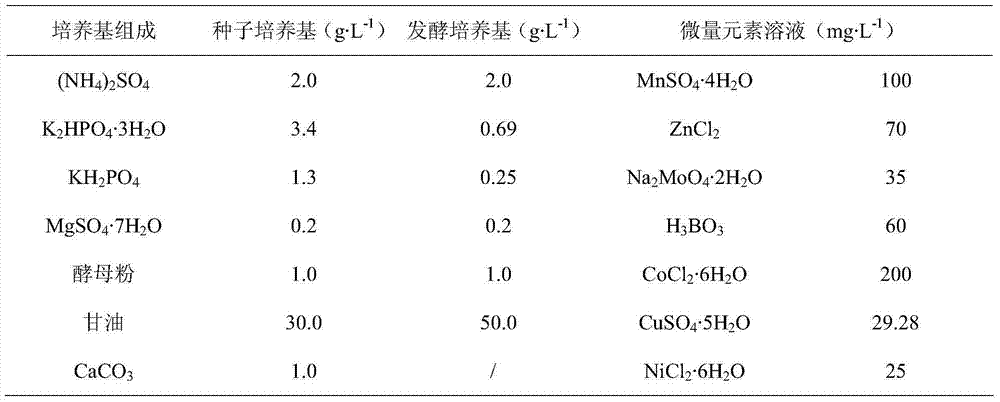
[0039] LB medium (g·L -1 ): yeast powder 5, peptone 10, NaCl 10, agar 10, adjusted to pH 7.0, for short-term preservation and activation of Klebsiella species. The composition of seeds and fermentation medium is shown in Table 1:
[0040] Table 1: Medium Composition
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] (2) Training method
[0044] (i) Seed activation: Klebsiella pneumoniae mutant strains and wild bacteria with knockout of the pyruvate formate lyase flpB gene preserved in glycerol tubes in Example 1 were respectively inoculated into LB medium for slant activation, at a temperature of 37° C. Incubate for 12 hours to activate the seeds.
[0045] (ii) Seed culture: 250mL triangular flask sealed with 9 layers of gauze, filled with 100mL of seed culture medium, inserted into the slant lawn (activated seeds o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com