Pseudomonas putida gene knockout and genome simplification system
A Pseudomonas putida gene knockout technology, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, can solve the problems of high economic cost, troublesome knockout screening, low accuracy rate, etc., achieve simple and efficient operation, increase the probability of correct mutation, and correct rate-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
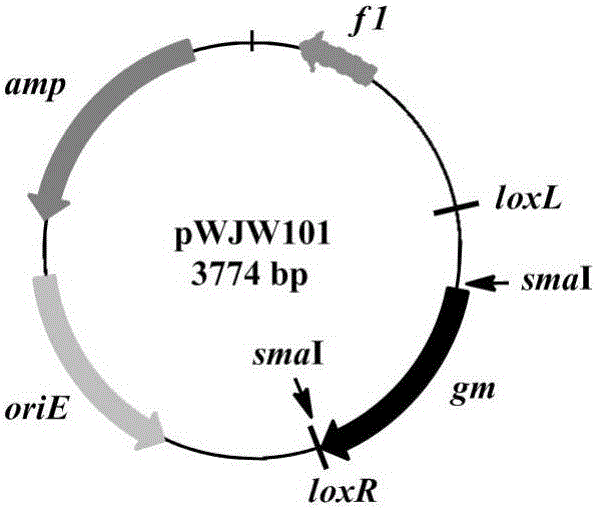
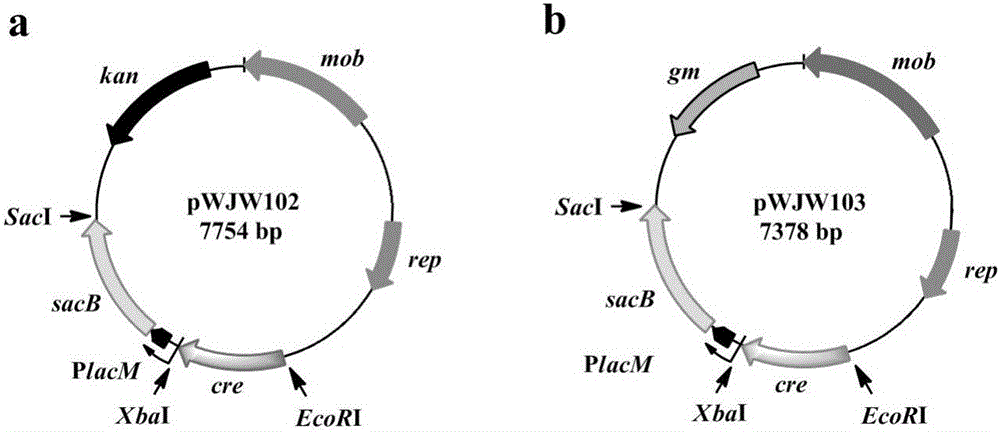
[0030] Example 1 Construction of template plasmid pWJW101 and expression plasmids pWJW102 and pWJW103
[0031] (1) Construction of the template plasmid pWJW101 for amplifying the Gm-resistant fragment with loxL / R sites in the same direction at both ends: the first step: using pBBR1MCS-5 (Kovach, M.E. et al. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS,carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes.Gene 166,175-176(1995).) as a template, gm-F / gm-R primer pair as a template, PCR amplification to obtain the gm gene, and in its SmaI restriction sites were introduced at both ends, after enzyme digestion and purification, it was ready for use; pDTW202 (Hu J, TanY, LiY, Hu X, Xu D, Wang X. Construction and application of an efficient multiple-gene-deletion system in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Plasmid, 2013,70 (3): 303-313) plasmid as template, with pBSloxL-F and pBSloxR-R primers as template, PCR amplification obtains the linear pBSloxL / R plasmid fragment ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Knockout of PP5288 in Pseudomonas putida KT2442
[0044] 1. Obtaining the knockout plasmid pWJW201
[0045] Using the genome of Pseudomonas putidaKT2442 as a template, the upstream and downstream fragments of the PP5288 gene were amplified with corresponding primers, respectively. EcoRI and XbaI were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the upstream fragment, respectively, and BamHI and HindIII restriction sites were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the downstream fragment, respectively. Using pWJW101 as a template and primers
[0046] gm-lox-XbaI(+)acctctagaAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCG,
[0047] gm-lox-BamHI(-)cgggatccGCGCAATTAACCCTCACTAAAG,
[0048] The gm cassette containing loxL / R sites at both ends was amplified, and XbaI and BamHI restriction sites were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends, respectively. The upstream fragment of PP5288 was purified by EcoRI and XbaI digestion, the downstream fragment was purified by BamHI and HindIII digestion, the gm box fra...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Knockout of gene cluster PP3126-PP3142 in Pseudomonas putida KT2442 in embodiment 3
[0083] 1. Obtaining the knockout plasmid pWJW202
[0084] Using the P.putidaKT2442 genome as a template, the upstream and downstream fragments of the PP3126-PP3142 gene cluster were amplified with corresponding primers. SacI and XbaI were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the upstream fragment, respectively, and BamHI and SacI restriction sites were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the downstream fragment, respectively. Using pDTW202 as a template, with primers
[0085] kan-lox-XbaI(+)acctctagaAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCG,
[0086] Kan-lox-BamHI(-)cgggatccGCGCAATTAACCCTCACTAAAG,
[0087] The kan cassette containing loxL / R sites at both ends was amplified, and XbaI and BamHI restriction sites were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends, respectively. The upstream fragment of the PP3126-PP3142 gene cluster was purified by SacI and XbaI digestion, the downstream fragment was purified by BamHI...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com