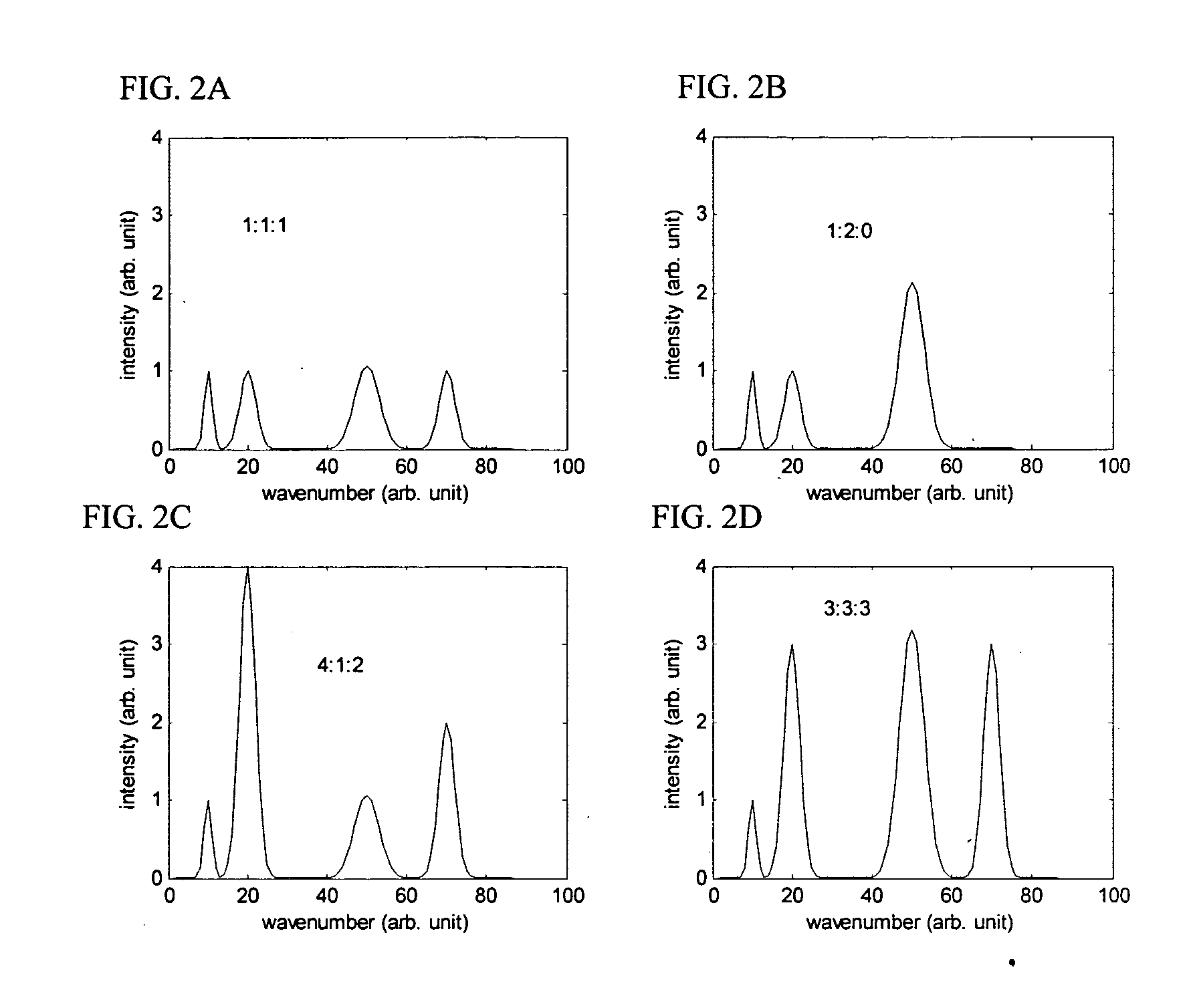
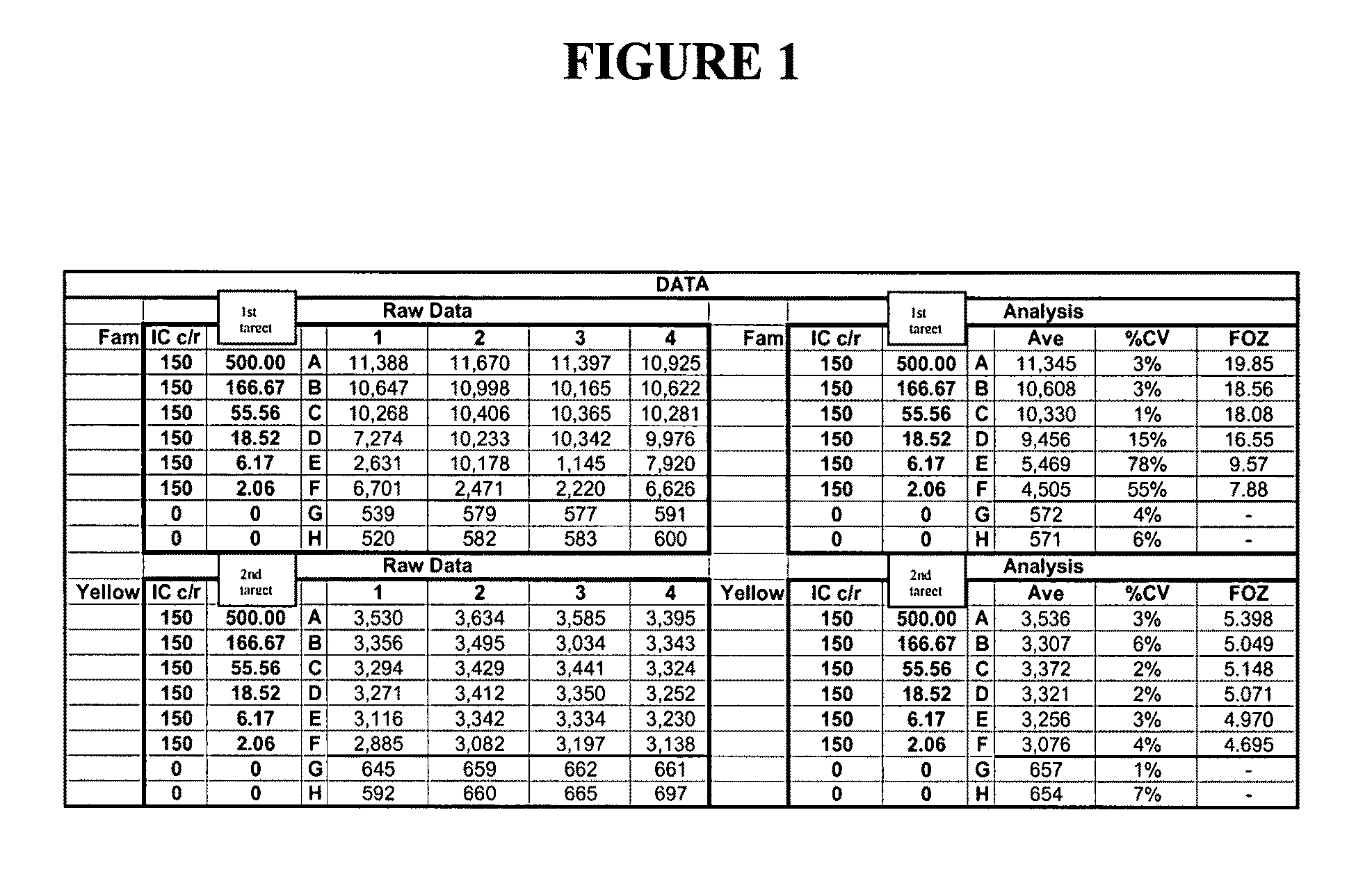
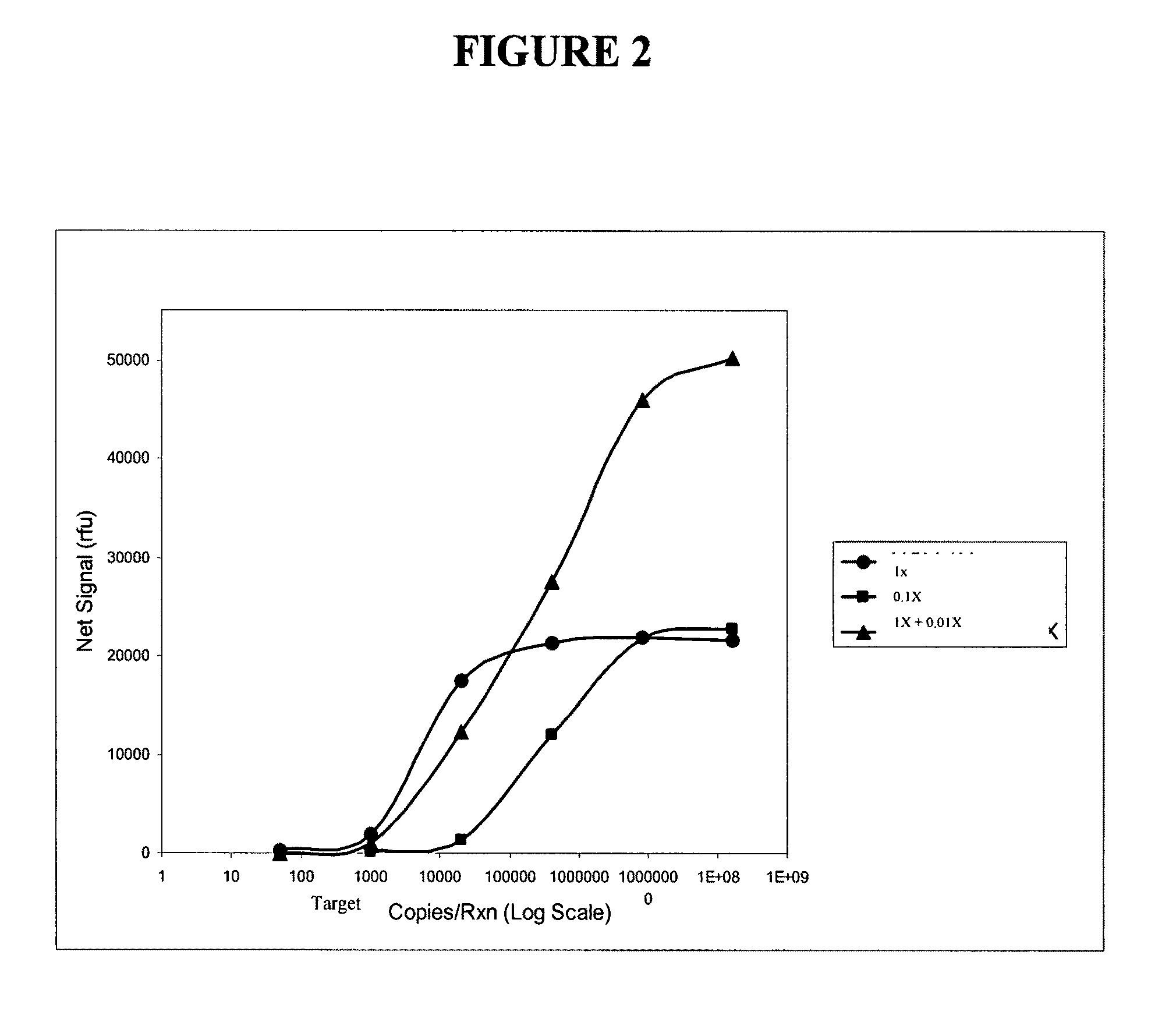
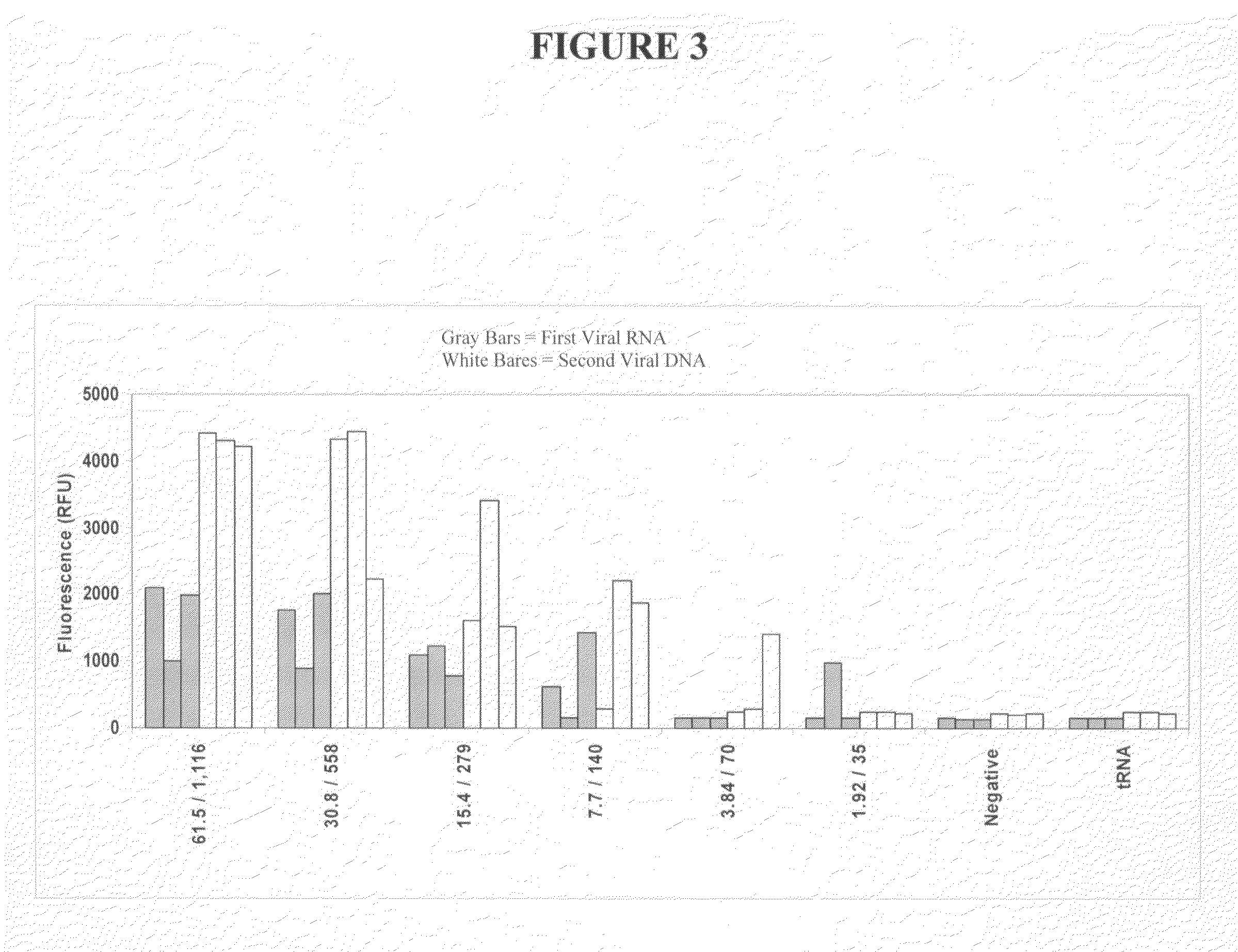
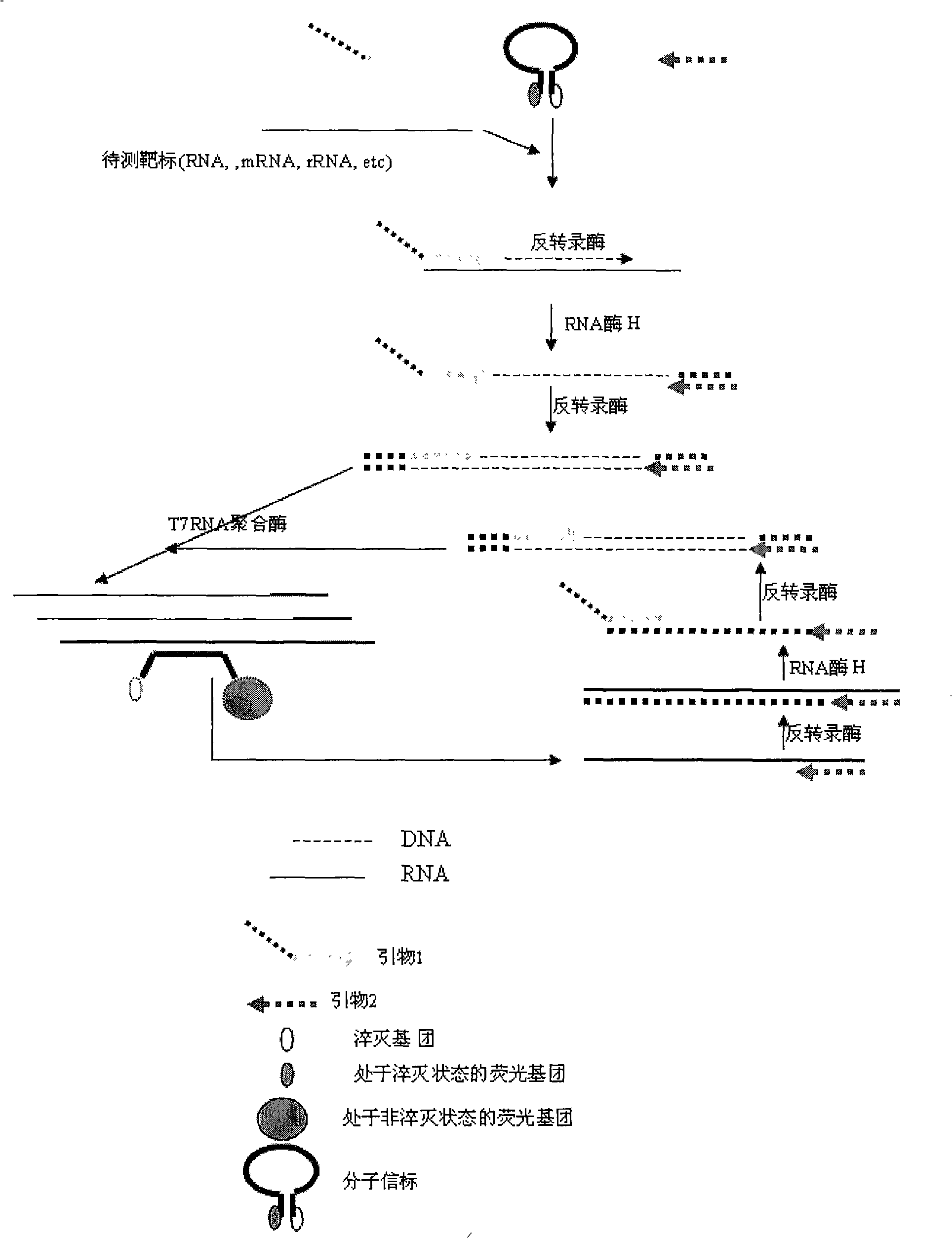
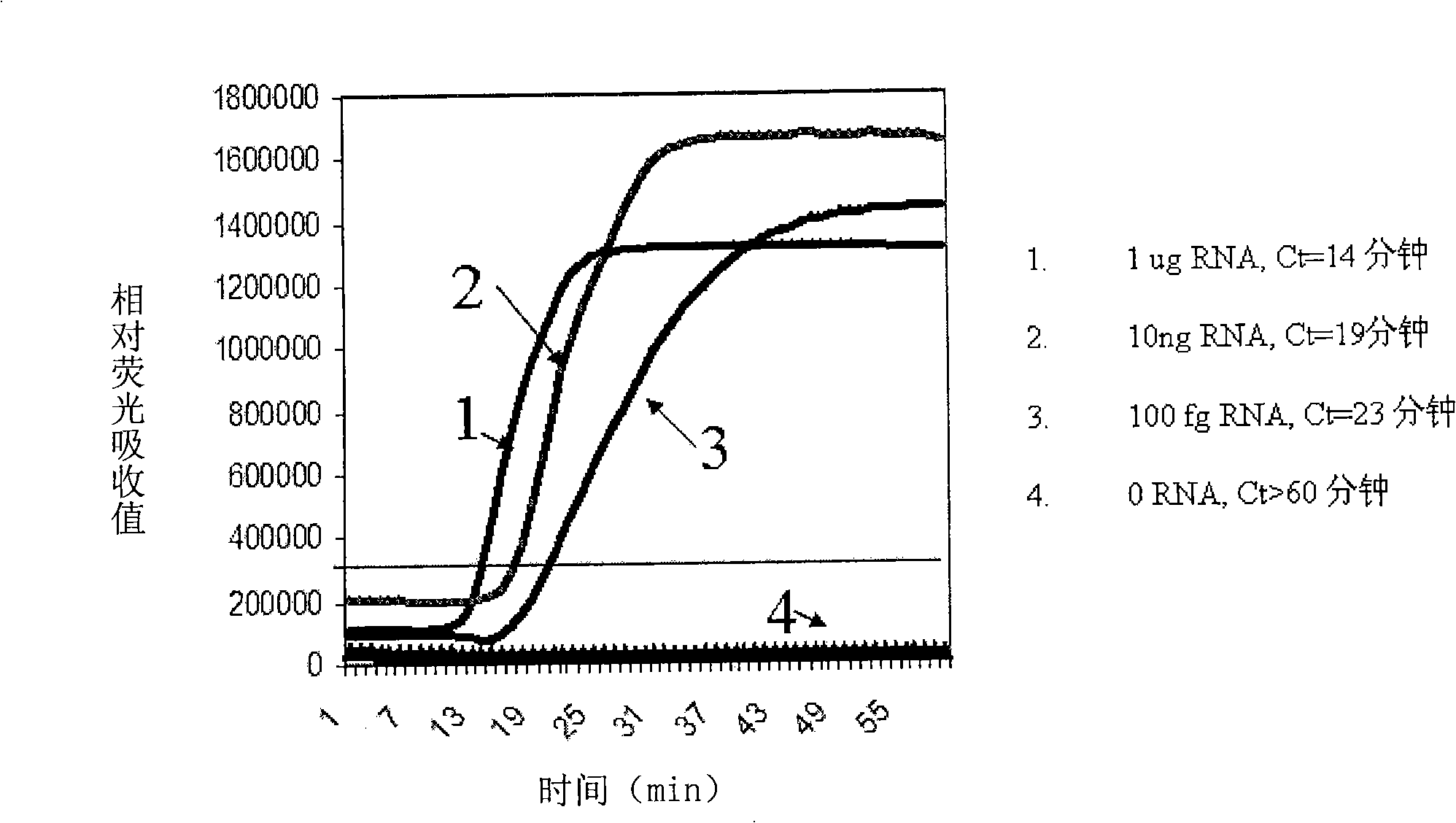
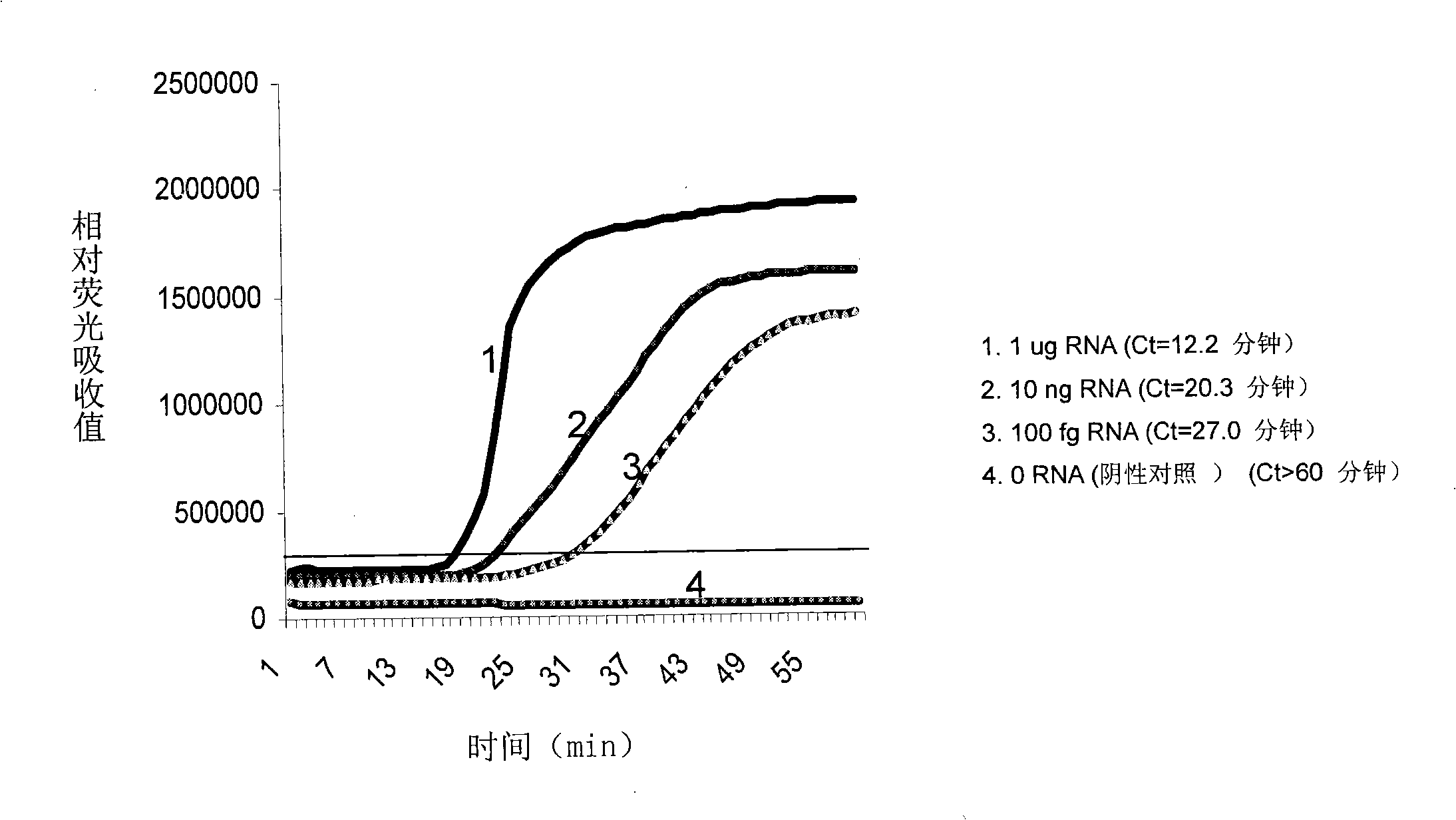
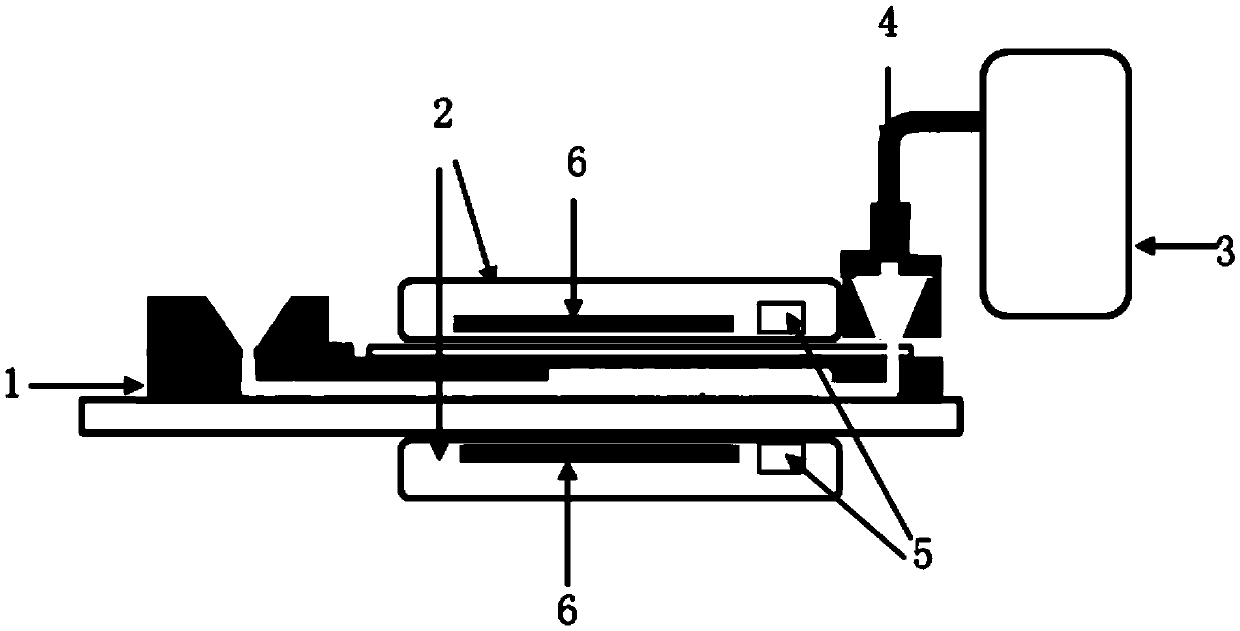
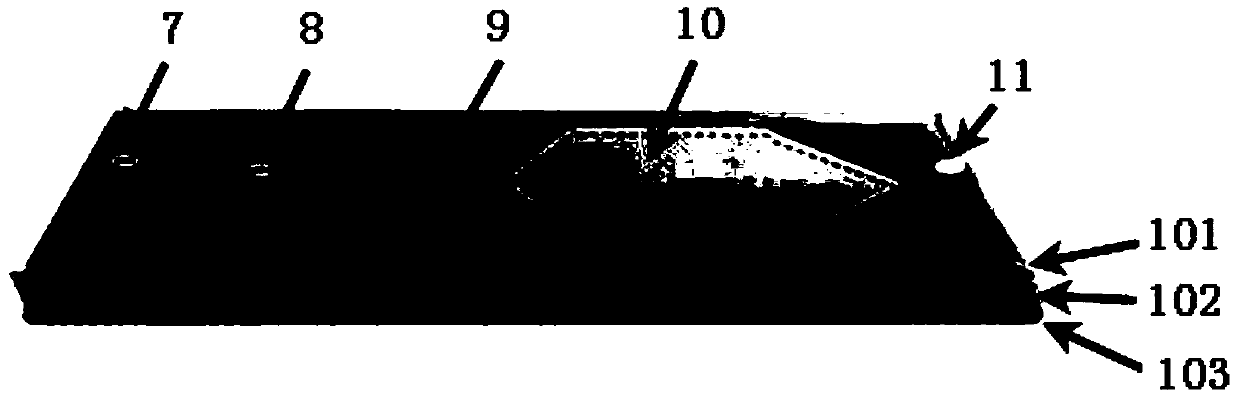
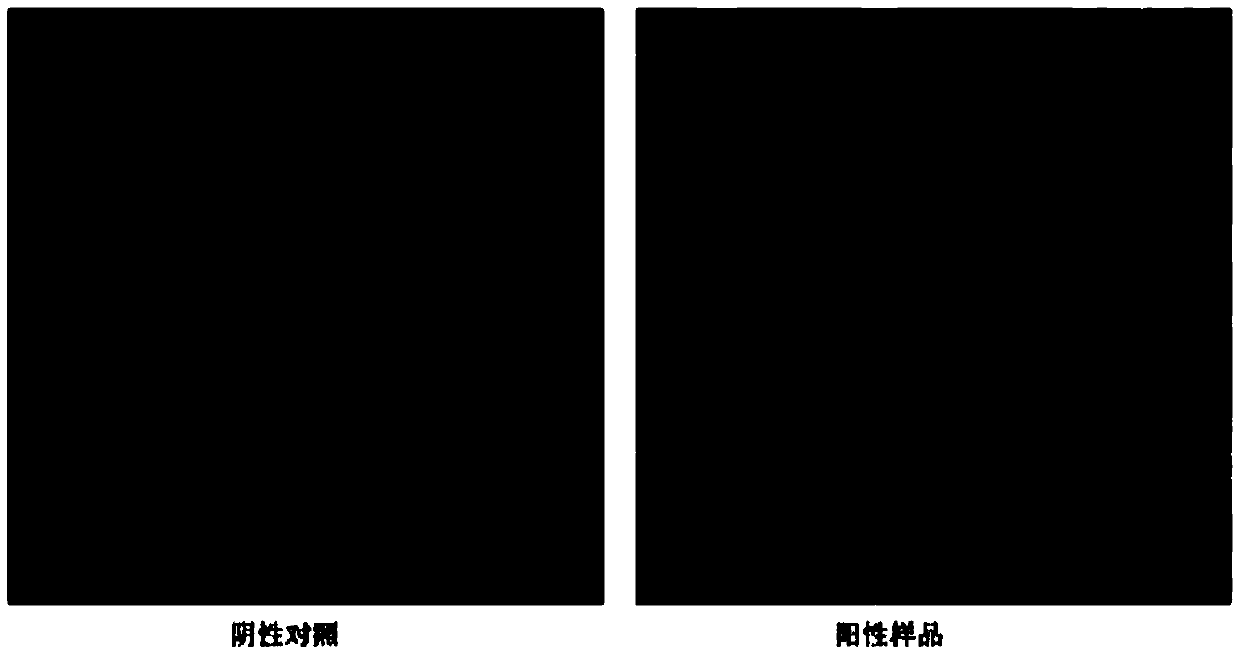
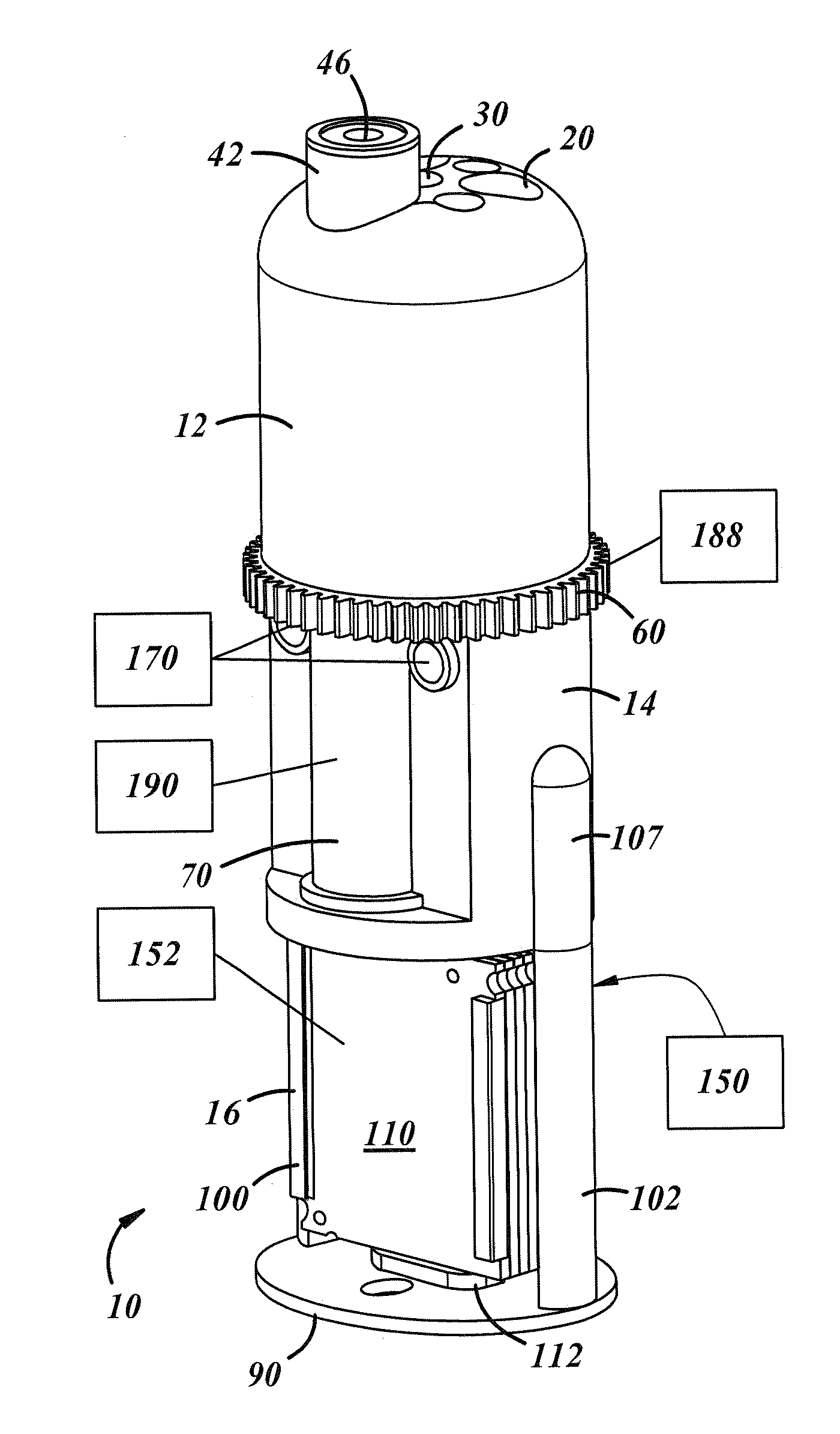
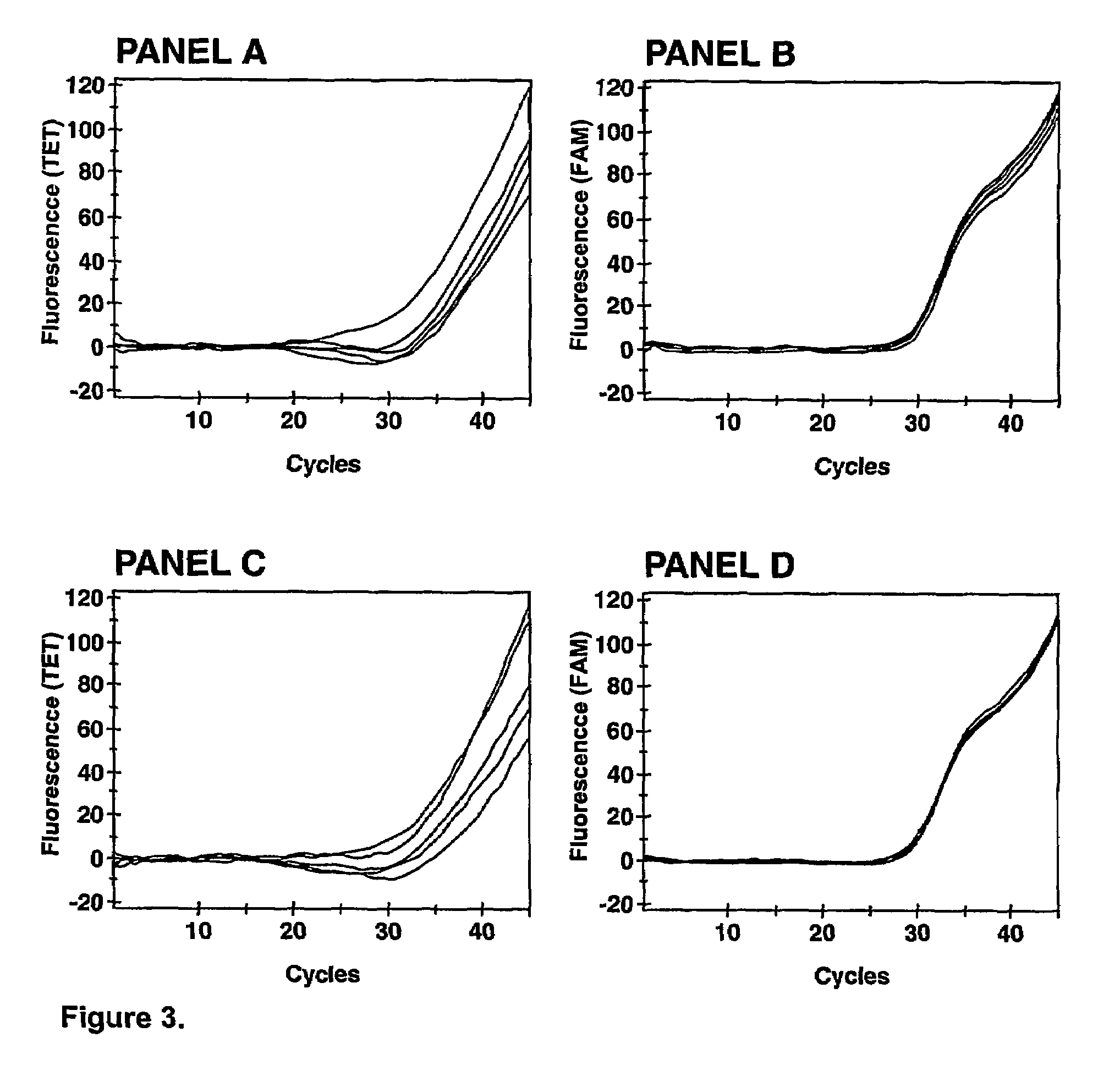
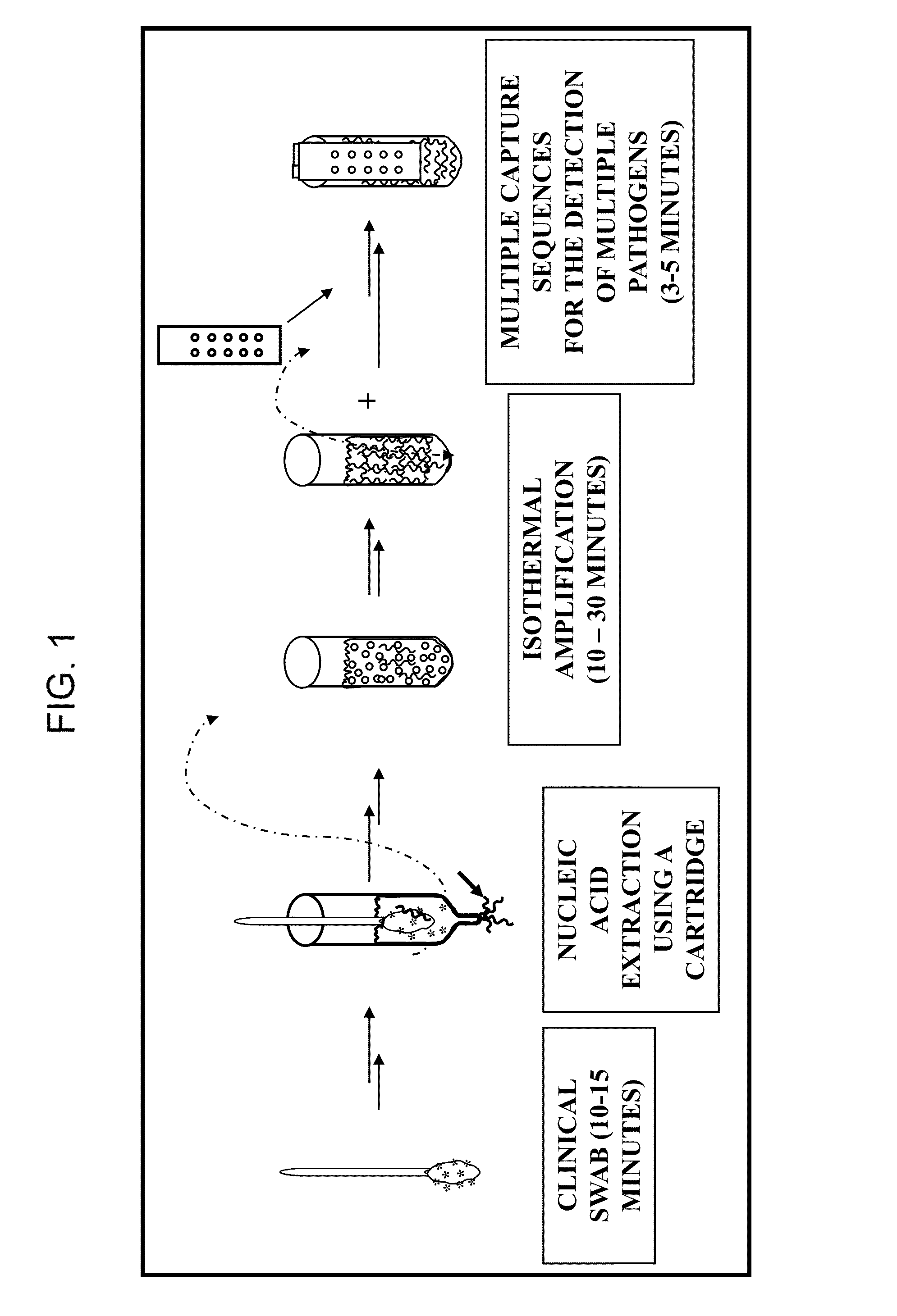
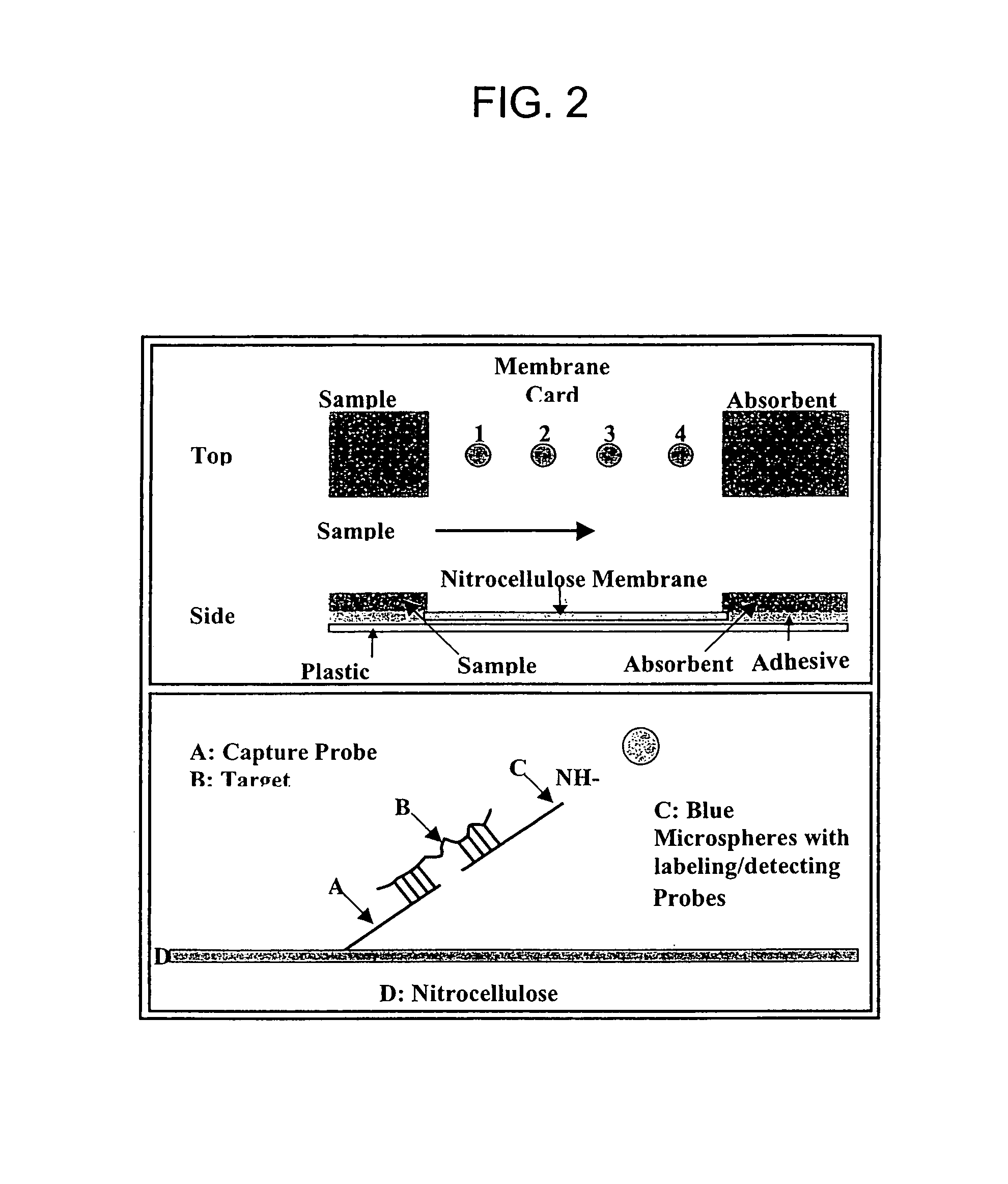
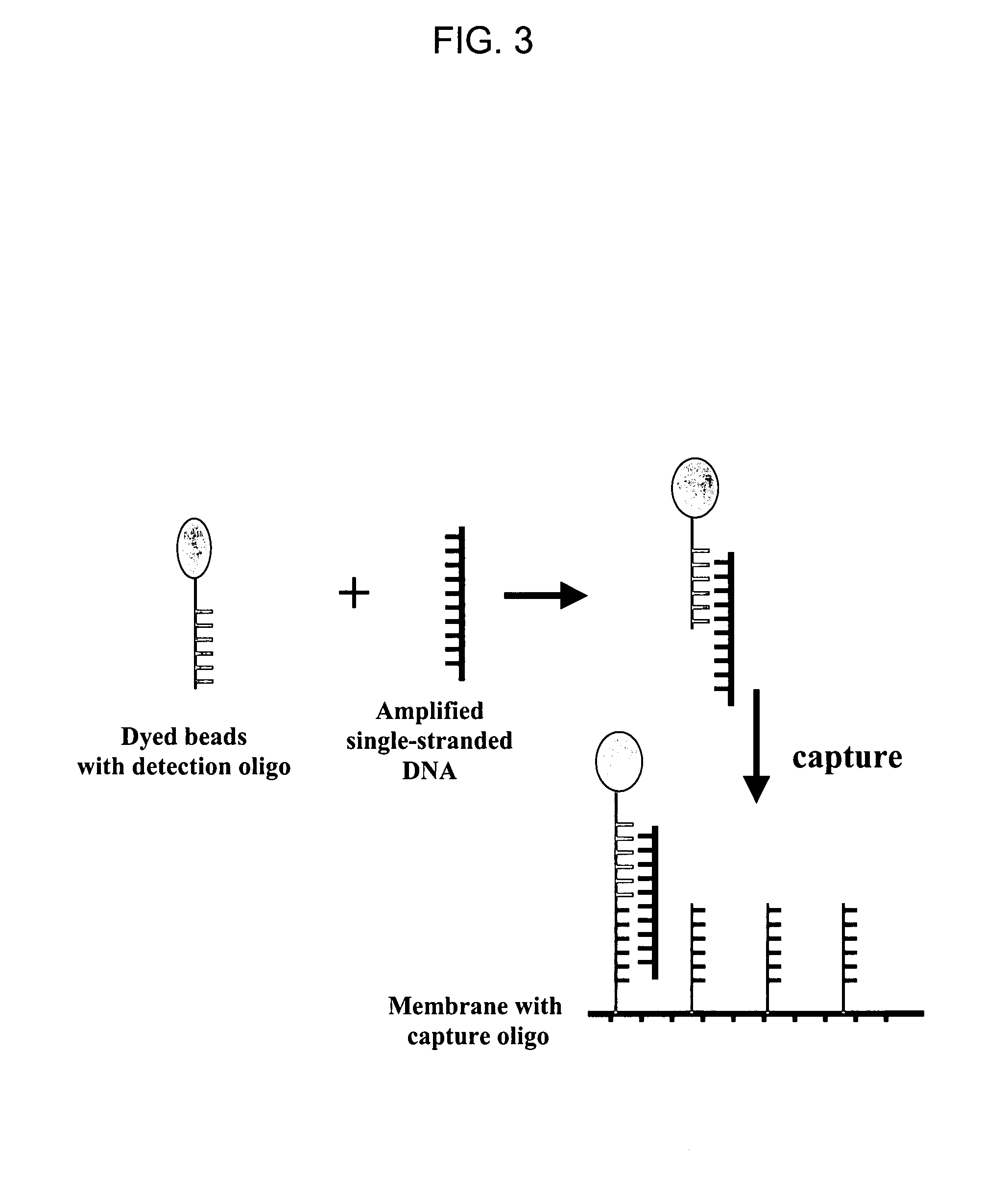
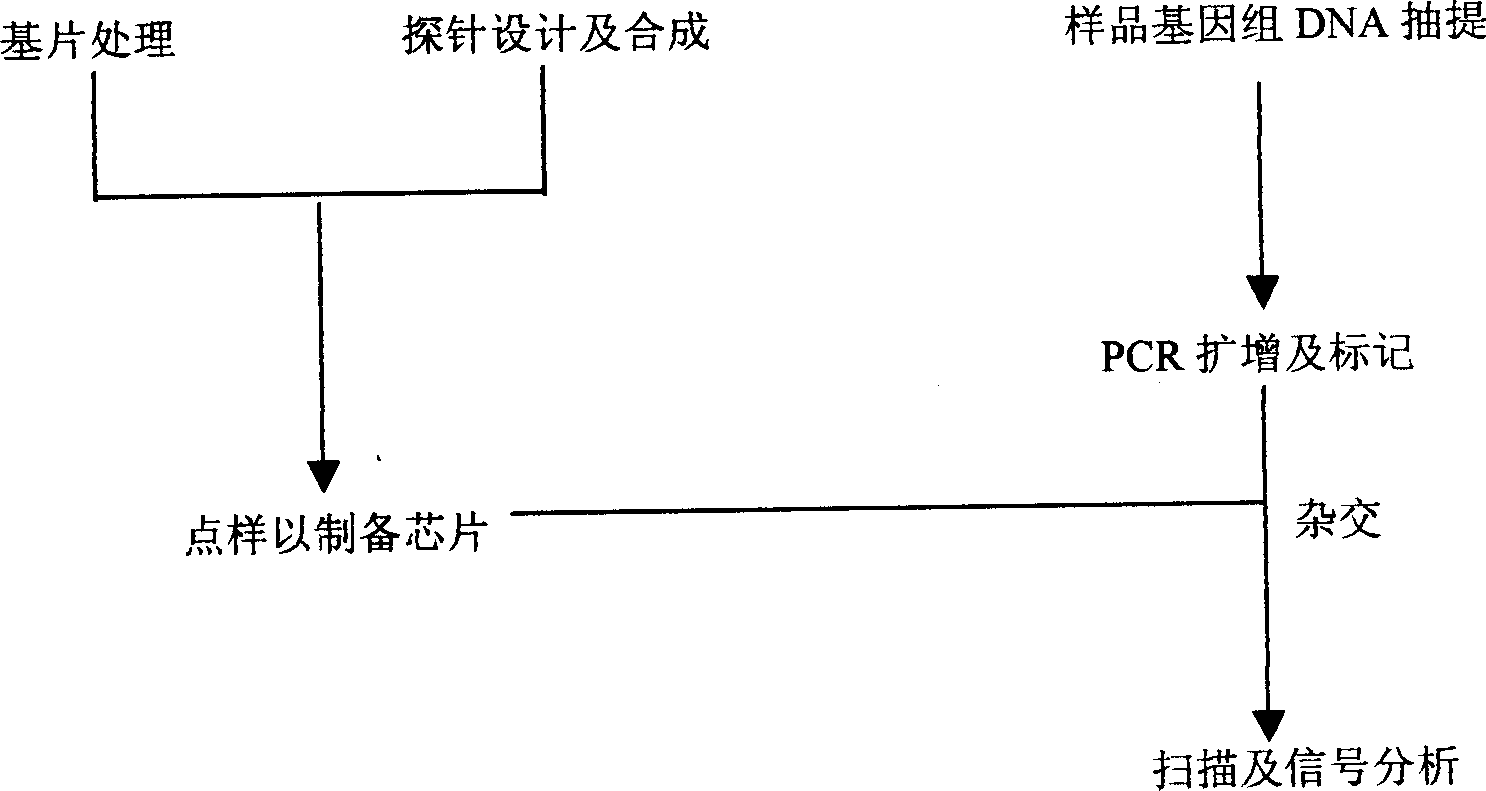
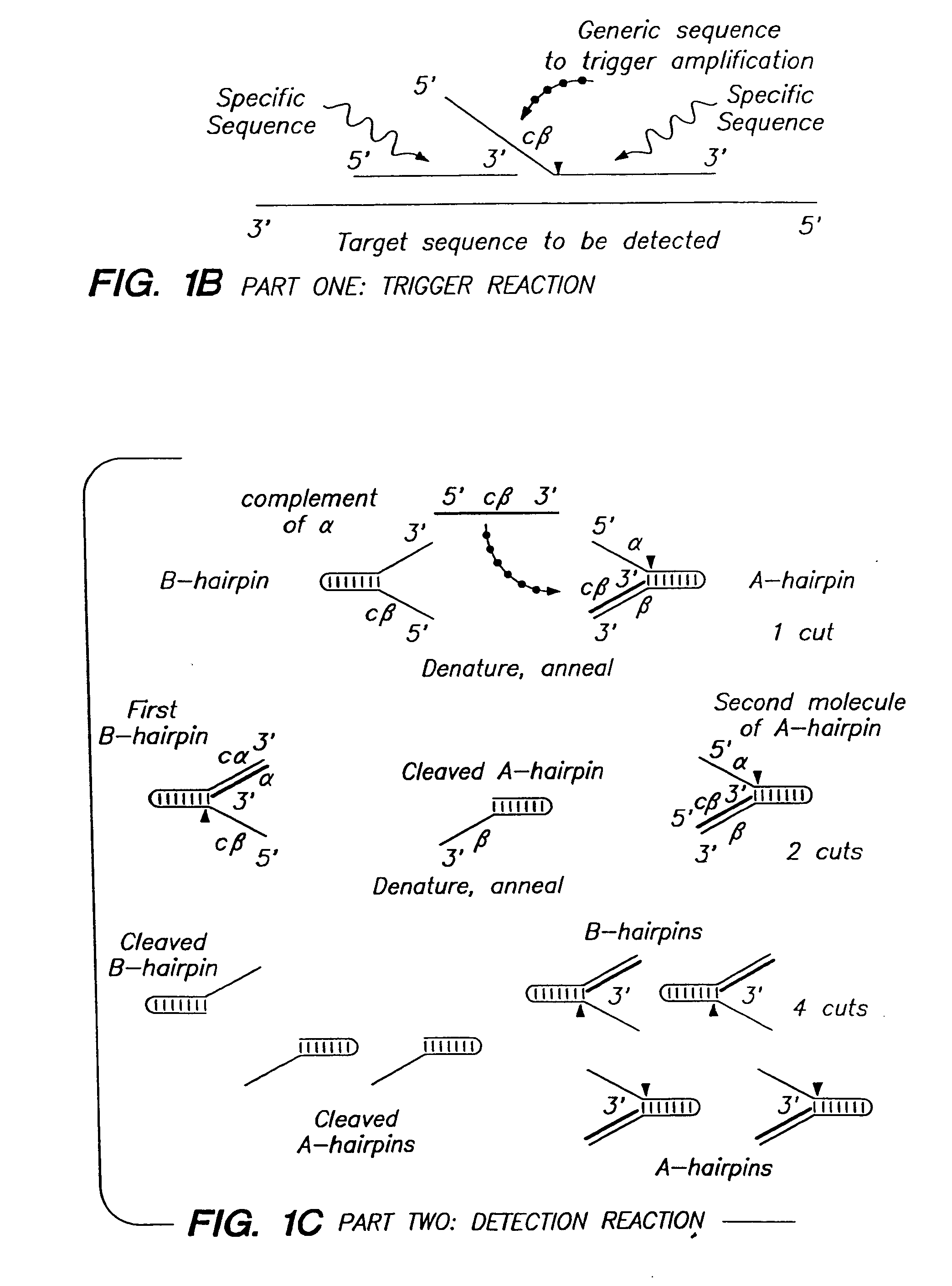
Patents
Literature
192 results about "Nucleic Acid Testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid testing (NAT) is a molecular technique for screening blood donations to reduce the risk of transfusion transmitted infections (TTIs) in the recipients, thus providing an additional layer of blood safety.
Nucleic acid detection system
InactiveUS20050227275A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesHaptenReagent
The present application discloses a system for detecting target nucleic acid comprising: a container comprising a nucleic acid amplification mix comprising a primer labeled with different haptens at its 5′ and 3′ ends, and optionally dNTP labeled with a hapten to form a nucleic acid complex; and a lateral flow test device comprising a reservoir area comprising reagent conditions suitable for binding of a specific binding partner with the nucleic acid complex; a dye area comprising a specific binding partner to the nucleic acid complex, wherein the specific binding partner is linked or conjugated to a reporter dye or another hapten; and a test area comprising a different specific binding partner specific to a different aspect of the nucleic acid complex.
Owner:ACCESS BIO
Nucleic acid detection cassette and nucleic acid detection device
InactiveUS7482153B2Prevent leakageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesProcess region
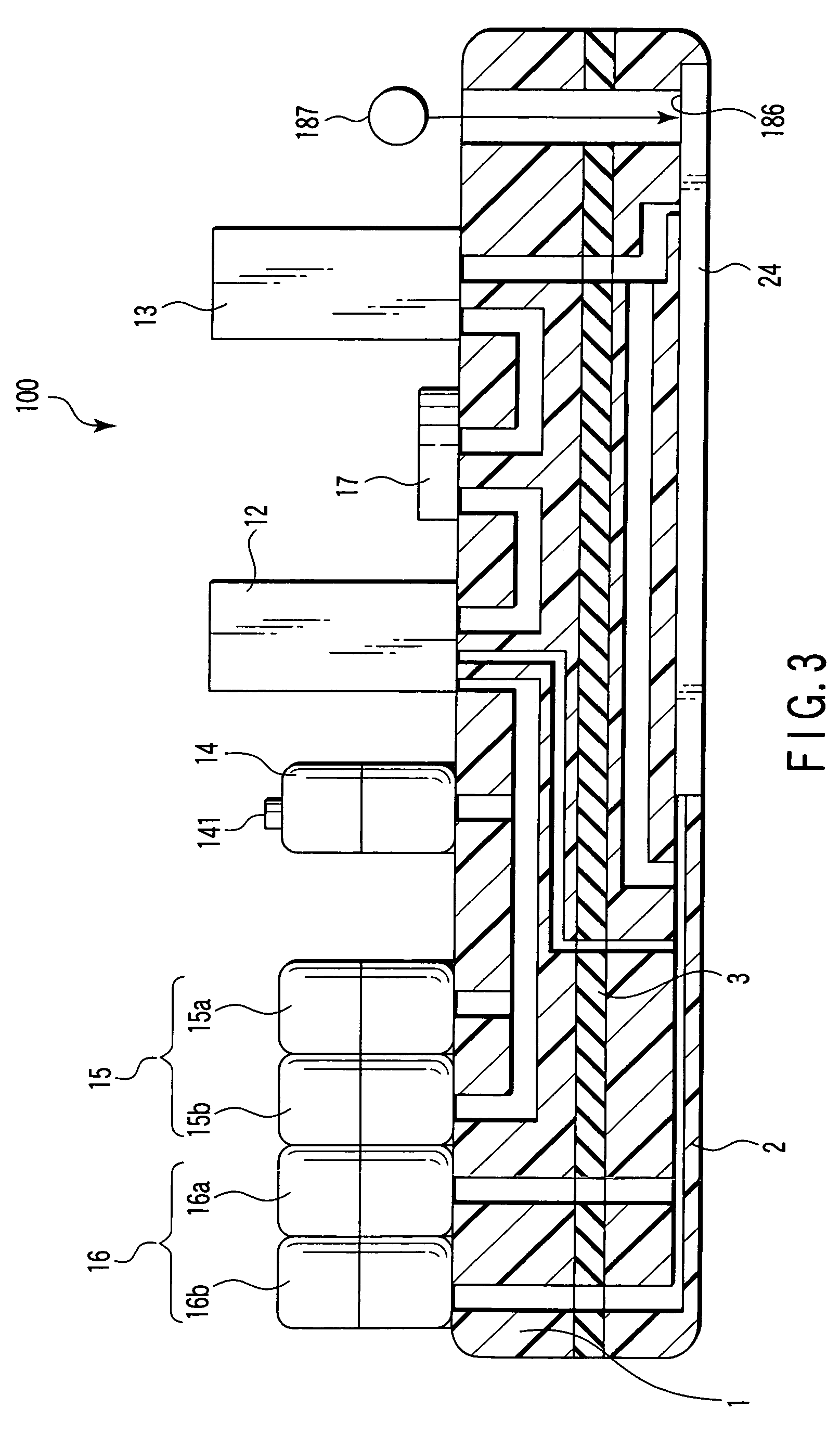
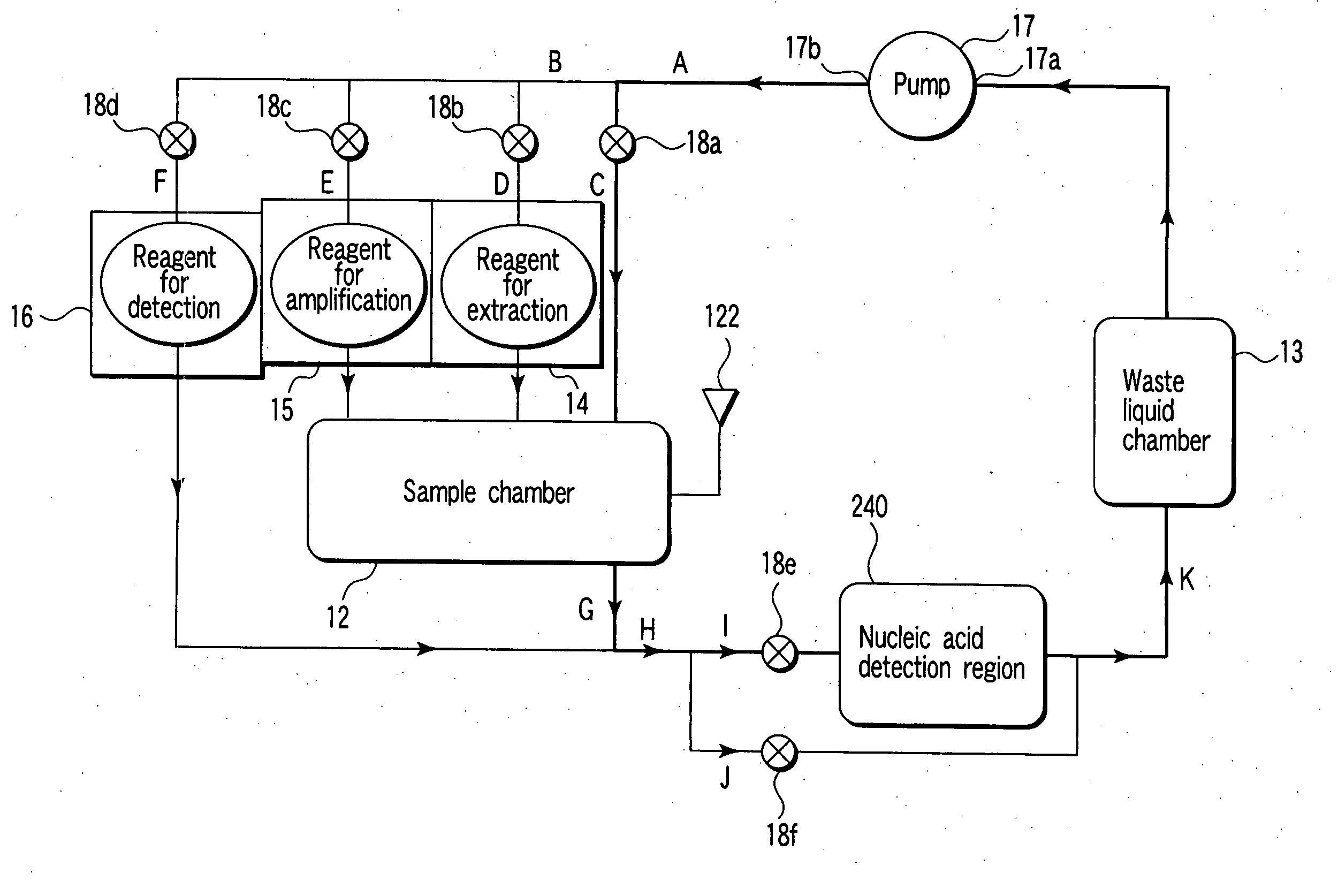
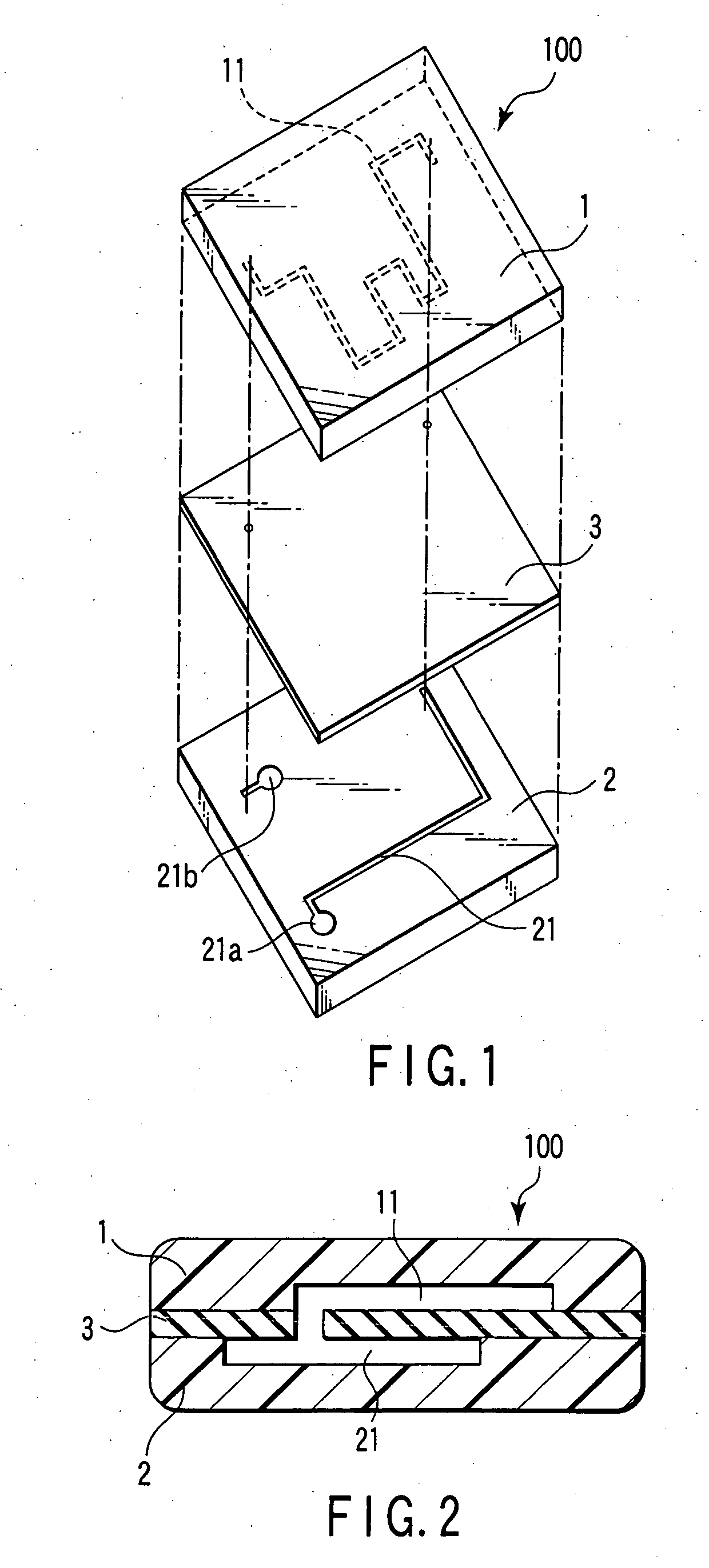
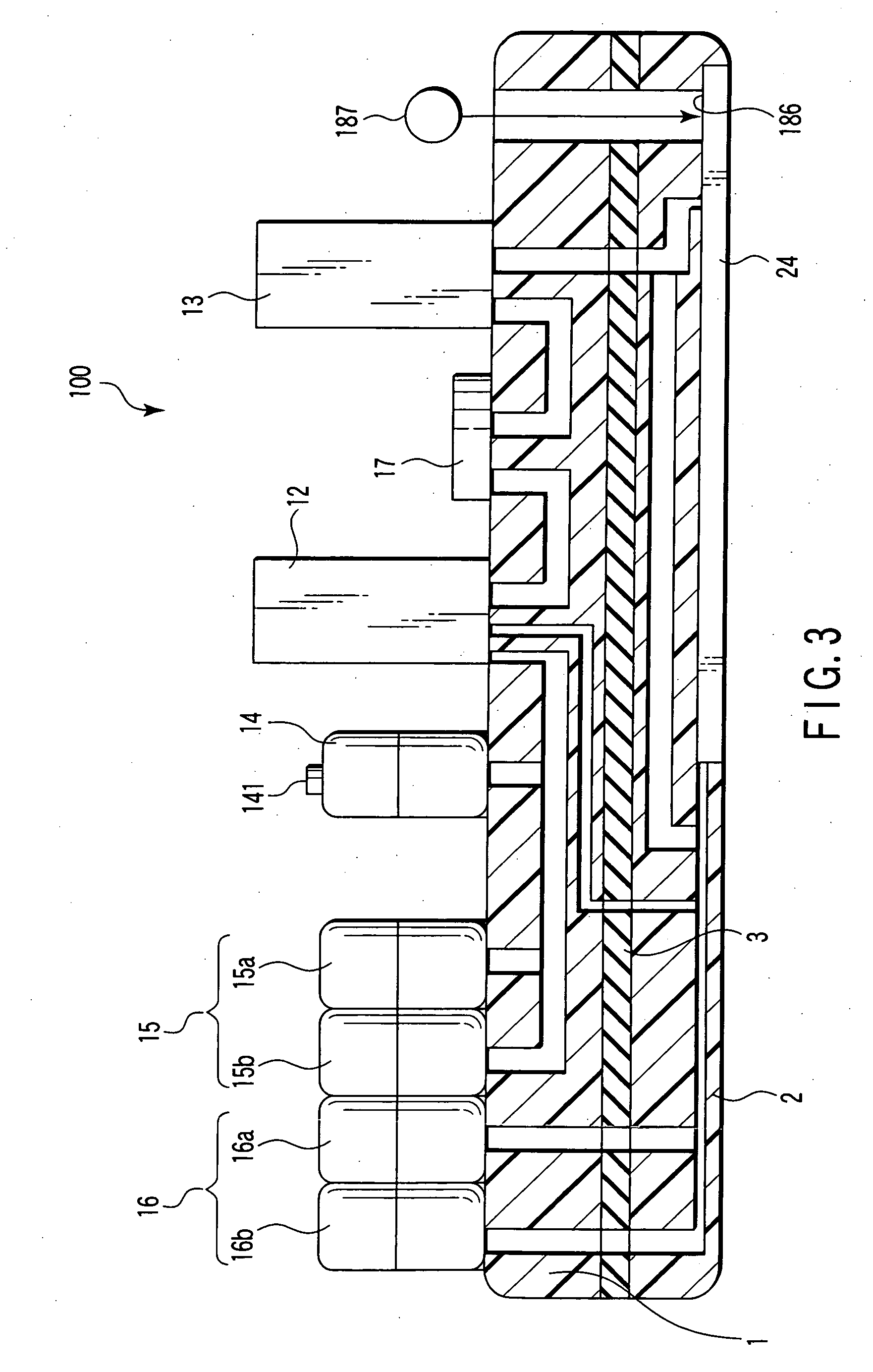
A nucleic acid detection cassette includes a cassette body, a nucleic acid detection region disposed in the cassette body, a first channel disposed in the cassette body, a second channel disposed in the cassette body. The nucleic acid detection region, in which a nucleic acid probe is immobilized, has a reagent inflow port, to which the first channel is connected, and a reagent outflow port, to which the second channel is connected. The nucleic acid detection cassette further includes a reagent injection portion which injects a reagent into the first channel, and a nucleic acid pretreatment region which is disposed in the first channel and which performs pretreatment for the detection of a nucleic acid. The first channel, the second channel, the nucleic acid detection region, the nucleic acid pretreatment region, and the reagent injection portion are sealed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nucleic acid detection cassette and nucleic acid detection device
InactiveUS20060216812A1Prevent leakageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesProcess region
A nucleic acid detection cassette includes a cassette body, a nucleic acid detection region disposed in the cassette body, a first channel disposed in the cassette body, a second channel disposed in the cassette body. The nucleic acid detection region, in which a nucleic acid probe is immobilized, has a reagent inflow port, to which the first channel is connected, and a reagent outflow port, to which the second channel is connected. The nucleic acid detection cassette further includes a reagent injection portion which injects a reagent into the first channel, and a nucleic acid pretreatment region which is disposed in the first channel and which performs pretreatment for the detection of a nucleic acid. The first channel, the second channel, the nucleic acid detection region, the nucleic acid pretreatment region, and the reagent injection portion are sealed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nucleic acid detecting sensor, nucleic acid detecting chip, and nucleic acid detecting circuit
InactiveUS20060147983A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDielectricNucleic Acid Probes
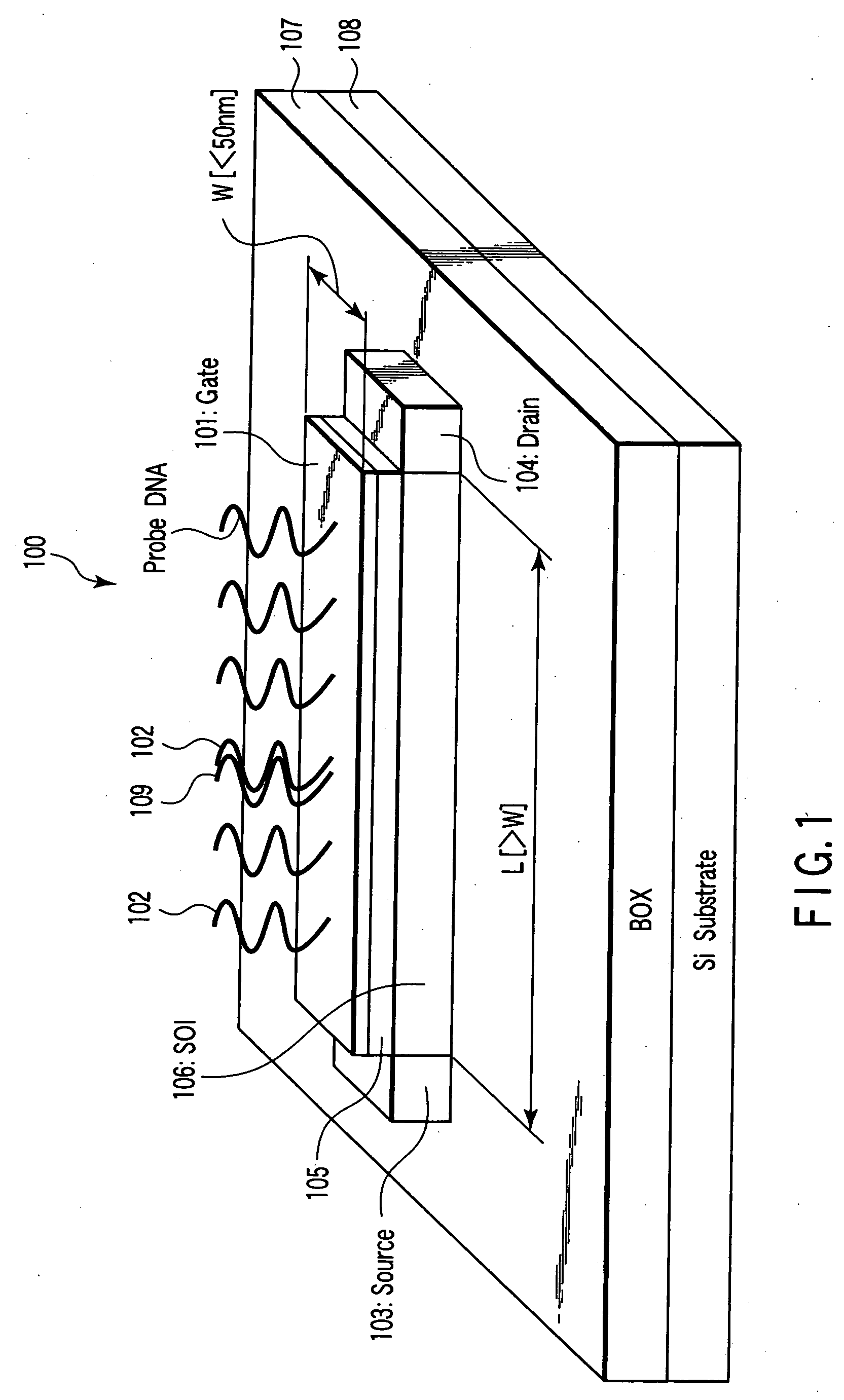
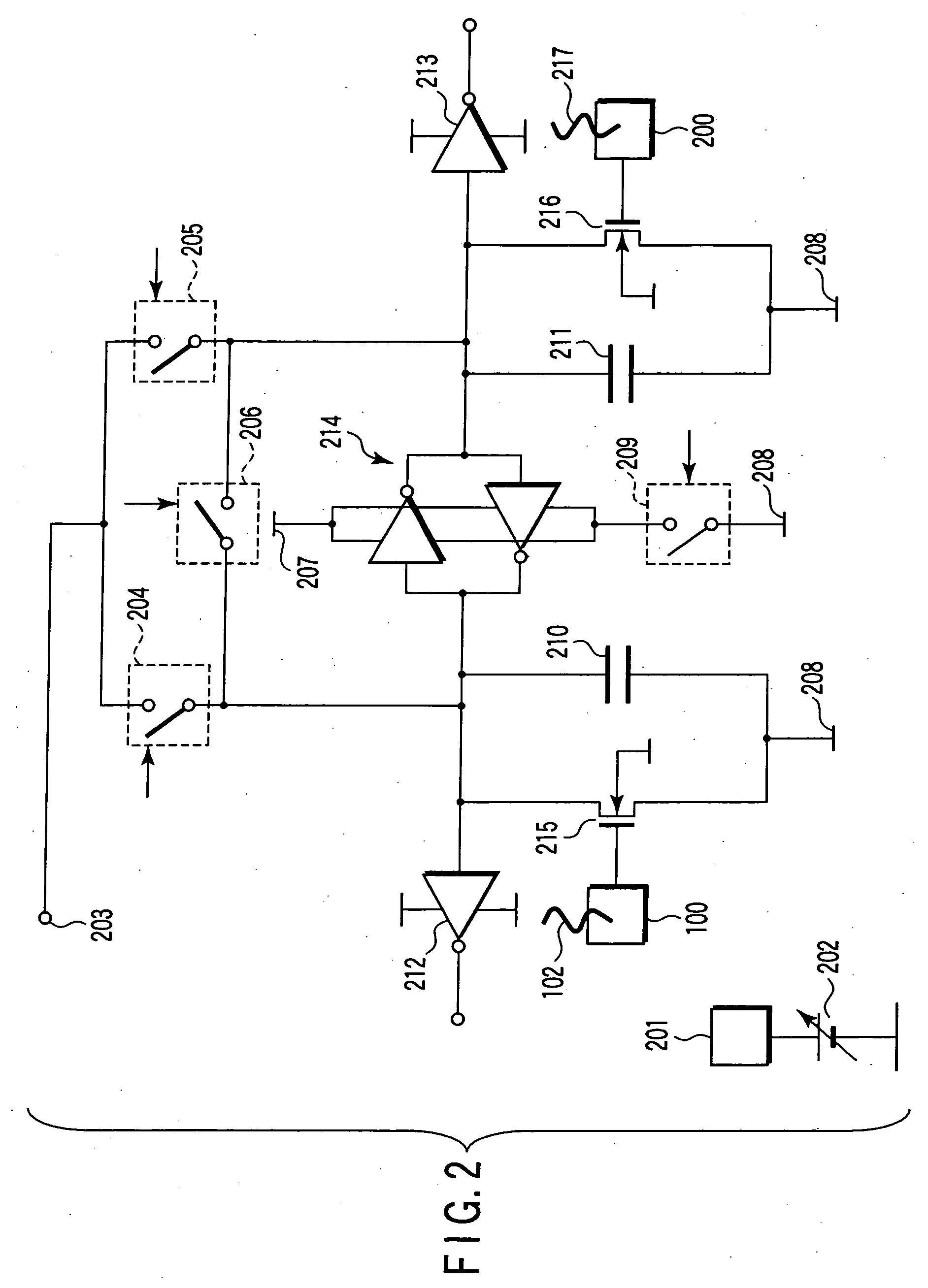
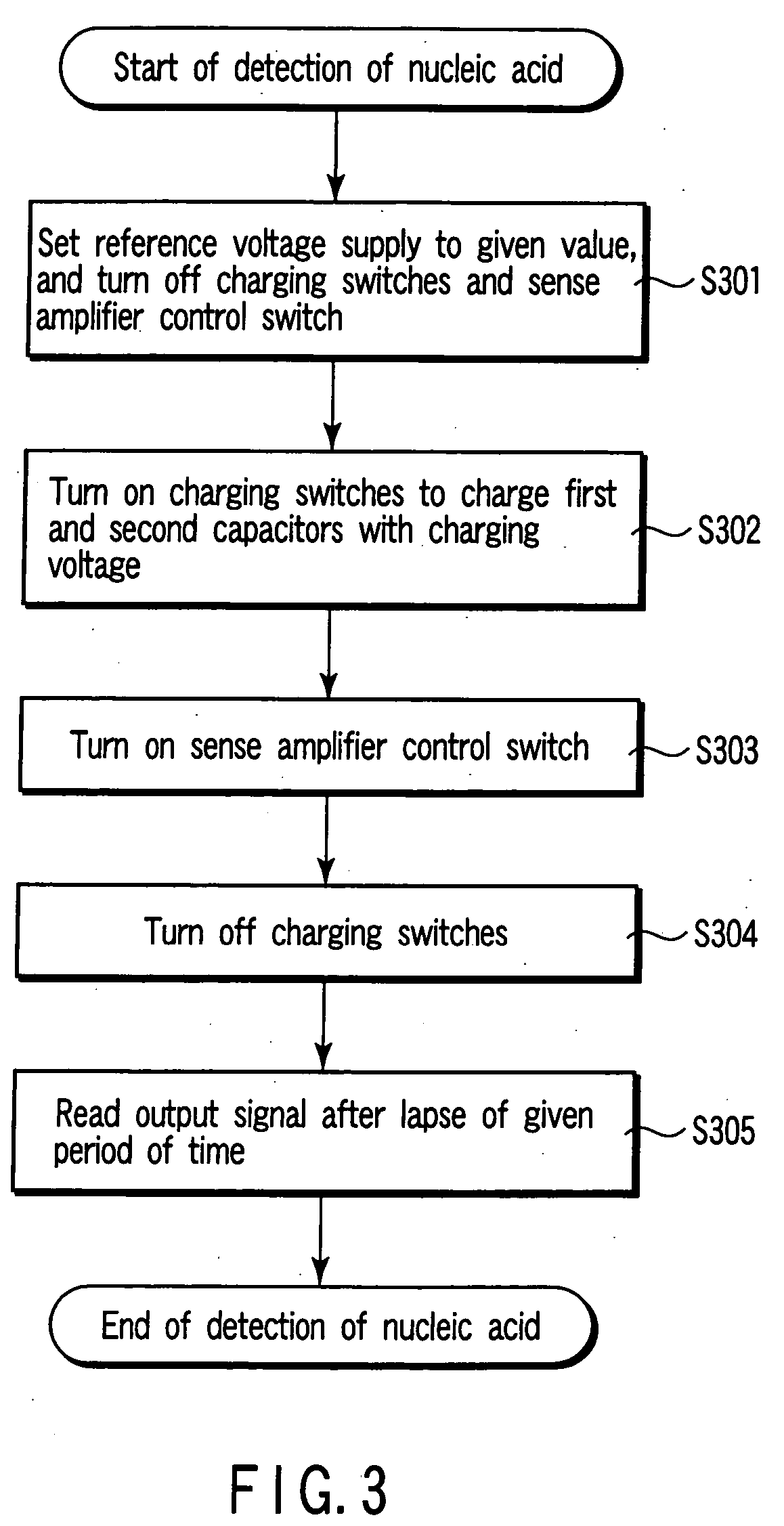
Nucleic acid detecting sensor includes field-effect transistor, detector which detects target nucleic acid molecules having sequences from sample based on degree of a variation in threshold voltage of field-effect transistor, and at least one nucleic acid probe molecule which is hybridized with corresponding one of target nucleic acid molecules, and is immobilized on gate of field-effect transistor, wherein gate width of field-effect transistor is of order of length obtained by expression given below (ε0εrkBT / e2n)1 / 2 where ε0 is dielectric constant of vacuum, εr is relative dielectric constant of channel region, kB is Boltzmann constant, T is absolute temperature of the channel region, e is elementary charge, and n is equilibrium carrier density in the channel region in field-effect transistor where channel is formed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nucleic acid detecting cassette and nucleic acid detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20090023201A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalytical chemistryNucleic Acid Testing
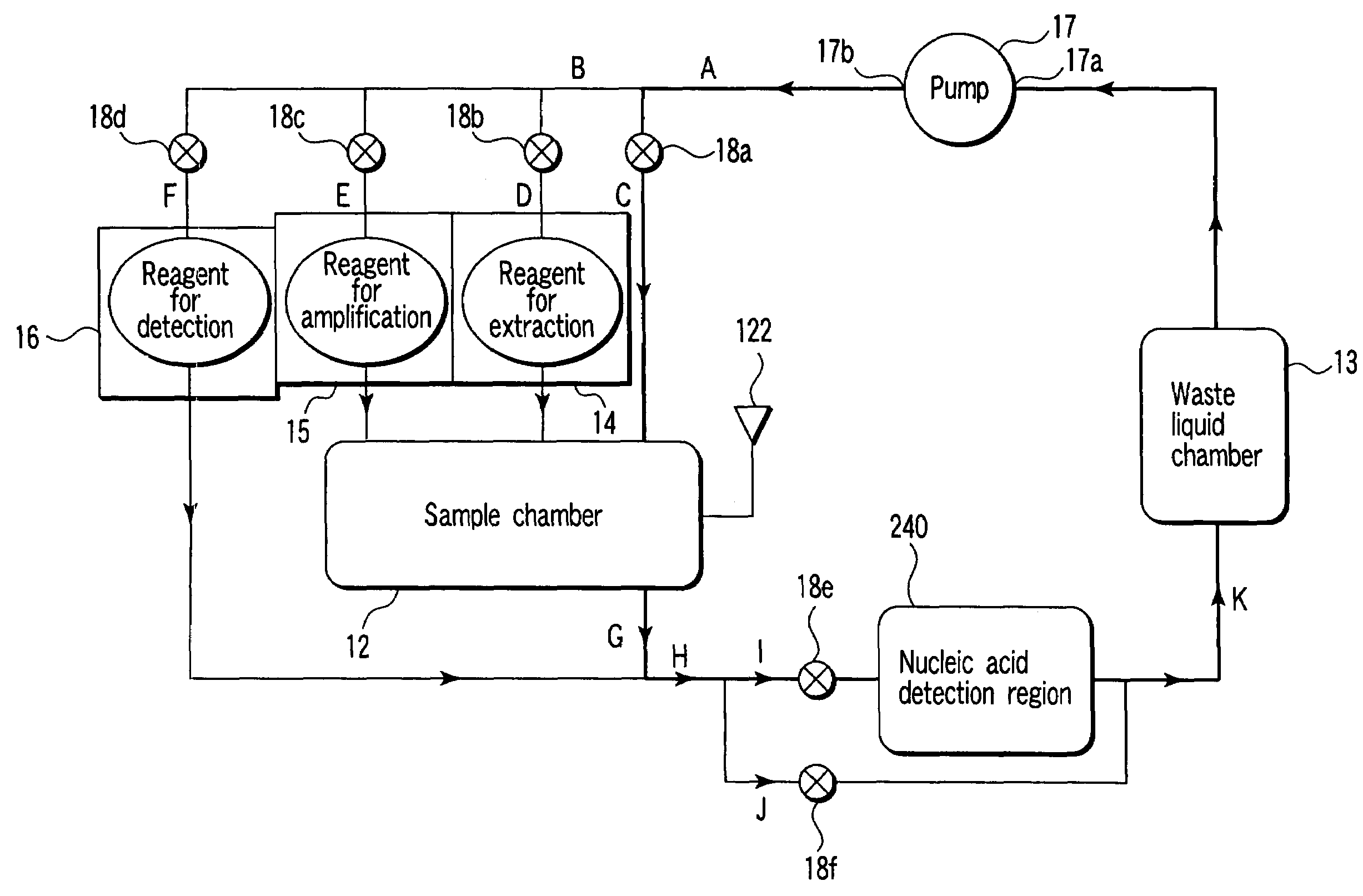
In a nucleic acid detecting cassette in which a heating treatment chamber and a liquid delivery channel are constituted of a stationary member and flexible members, the heating treatment chamber is held by convex heating sections from both sides, whereby the heat treatment chamber and the liquid delivery channel are spatially separated from each other. Thus, it is possible to automatically execute a consistent process including nucleic acid amplification and other required treatments of the object sample as well as detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for amplifying target nucleic acid sequence by using cross primer and kit for amplifying target nucleic acid sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN101638685AAmplification is fast and efficientLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseGenetics human
The invention relates to a novel technique for amplifying a nucleic acid sequence, in particular to a method for amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence at a constant temperature by using a cross primer. The invention also relates to a method for marking the amplified target nucleic acid sequence in an amplified reaction and a method for quickly detecting the target nucleic acid sequence. The invention also relates to a kit used in quick nucleic acid diagnosis, the application of the kit in the aspect of detecting the nucleic acid of pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria, viruses andthe like, and the application of the kit in gene diagnoses correlative with human genetic diseases.
Owner:USTAR BIOTECHNOLOGIES (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Methods and compositions for nucleic acid detection and sequence analysis
InactiveUS20050147977A1Easy to distinguishSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSignalling molecules
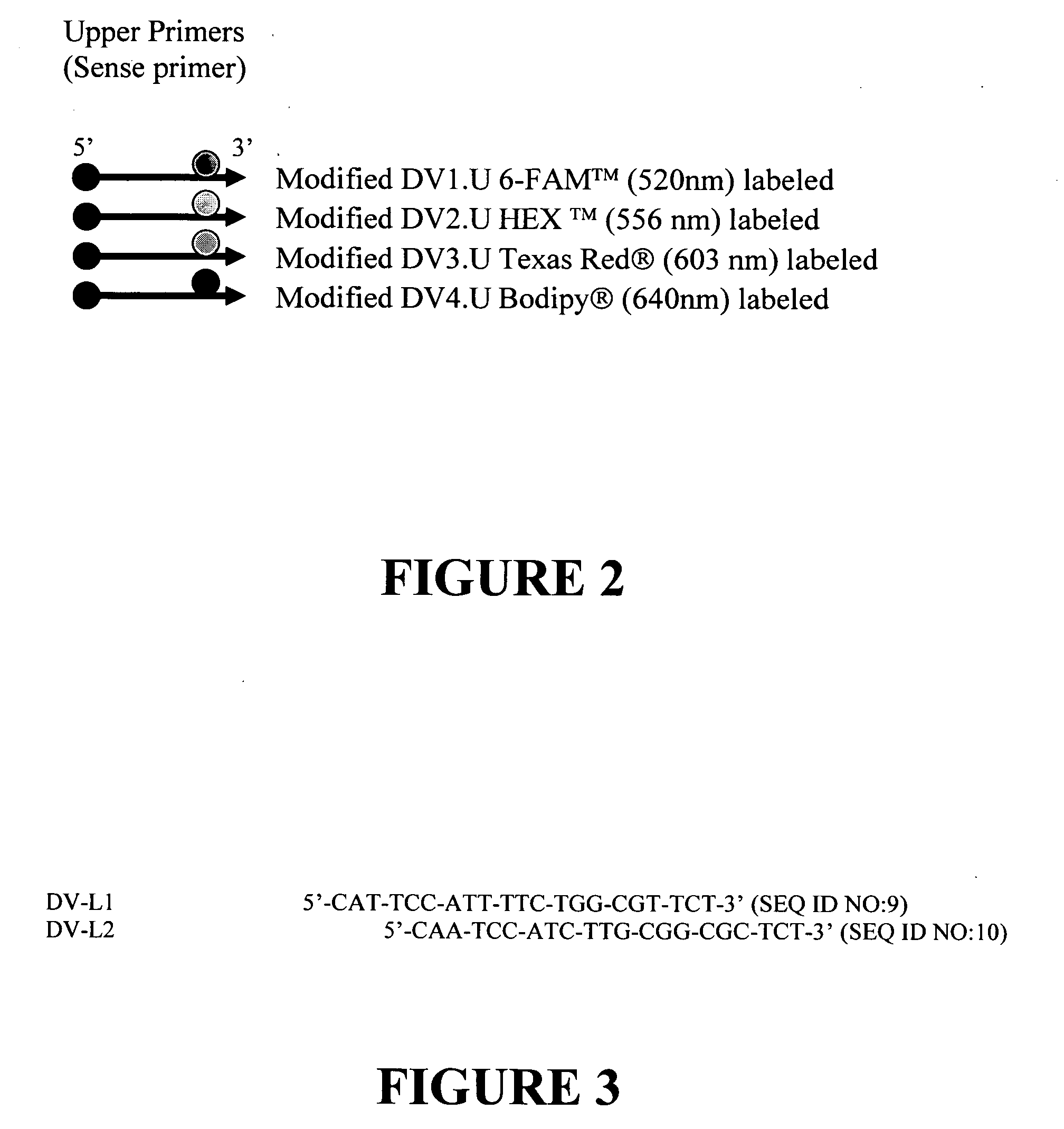
A population of labeled probes is provided that utilize an encoding system in which both the intensity and specific characteristics of a signal molecule are utilized to reduce the number of signal molecules necessary to identify each member of the population of probes. In the population of labeled probes, each labeled probe includes a probe associated with a series of detectably distinguishable signal molecules. The number and type of signal molecules identifies the associated probe, and the number of probes in the population exceeds the number of unique signal molecules. The population of probes are used in methods of the invention and reaction mixtures of the invention, for identifying a target molecule and for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule, for example.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Universal method and composition for the rapid lysis of cells for the release of nucleic acids and their detection
InactiveUS7494771B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid testSolid particle
This invention describes a rapid (10 to 15 minutes), simple, flexible and efficient method of nucleic acids extraction for nucleic acid testing assays. This method has the following basic steps: i) mechanical cell lysis using solid particles in the presence of a chelating agent, followed by ii) controlling the presence and / or activity of NAT assays inhibitors. This method is applicable to various biological samples and universal for microorganisms, as one can use it to extract nucleic acids from test samples containing target viruses, bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, parasites or other eukaryotic cells, including animal and human cells.
Owner:ART RECH & TECH AVANCEES INC ART ADVANCED RES TECH INC +1
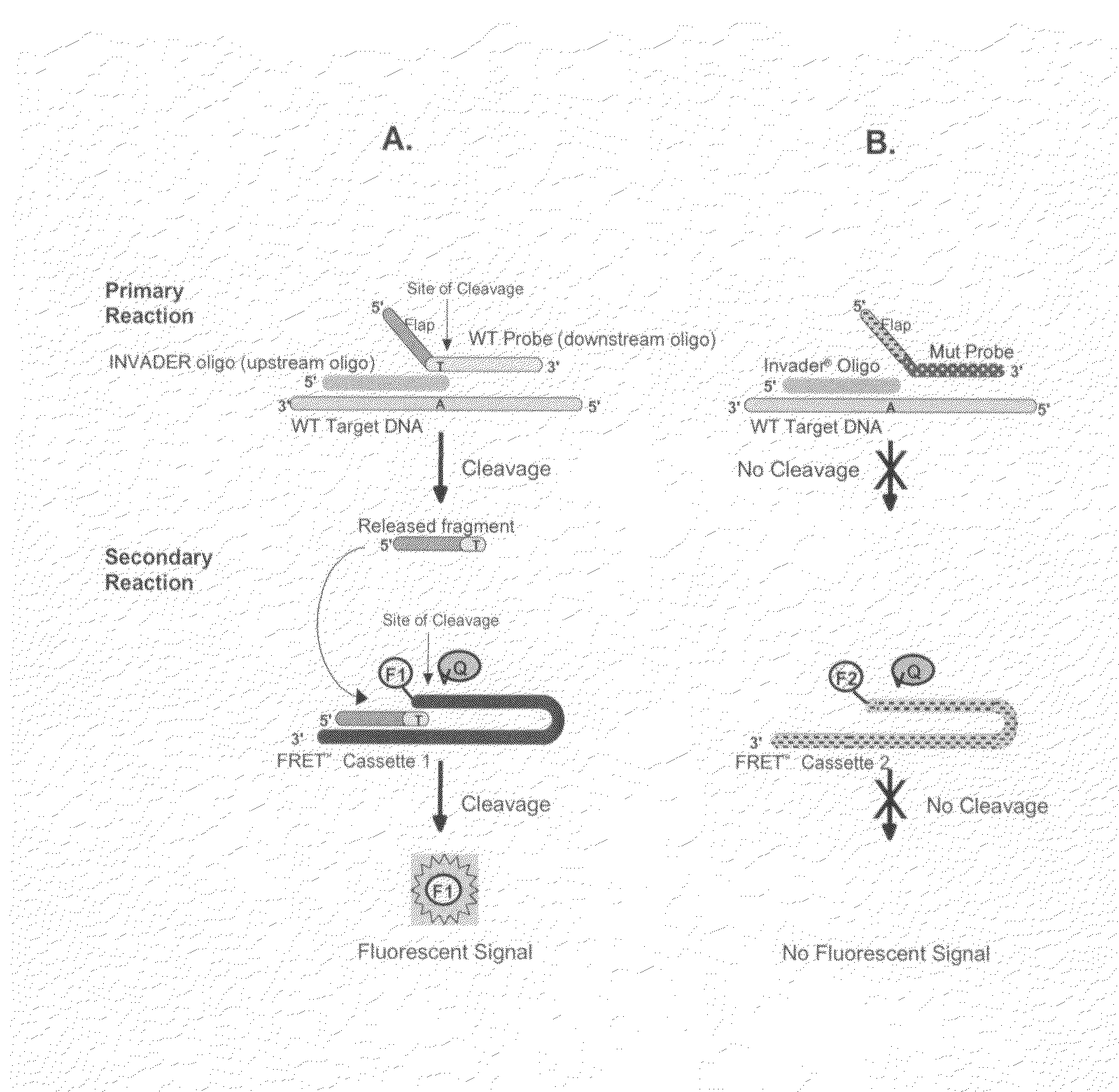
T-structure invasive cleavage assays, consistent nucleic acid dispensing, and low level target nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS7759062B2Improve dynamic rangeRaise the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNon targetedNon target
The present invention relates to systems, methods and kits for low-level detection of nucleic acids, detecting at least two different viral sequences in a single reaction vessel, and increasing the dynamic range of detection of a viral target nucleic acid in a sample. The present invention also relates to T-structure invasive cleavage assays, as well as T-structure related target dependent non-target amplification methods and compositions. The present invention further relates to methods, compositions, devices and systems for consistent nucleic acid dispensing onto surfaces.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Constant temperature synchronous amplification detecting process for nucleic acid and use thereof
ActiveCN101333565AAvoid pollutionShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNegative strandFluorescence
Owner:SHANGHAI RENDU BIOTECH
Digital isothermal nucleic acid detecting device and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN105505761AOvercome accuracyOvercoming Absolute Quantification ProblemsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlMicrosphere
The invention provides a digital isothermal nucleic acid detecting device which comprises a micro-fluidic chip, a temperature control system and a pressure driving system. A microfluidic channel for microsphere forming and a reaction section for nucleic acid amplification are formed by the micro-fluidic chip through sequential laminating of a substrate layer, a channel layer arranged on the substrate layer and a cover plate layer arranged on the channel layer. The temperature control system comprises a lower press plate for applying pressure to the substrate from bottom to top and an upper press plate for applying pressure to the cover plate layer from top to bottom, and temperature sensing chips and temperature control heating elements for heating the reaction section are arranged in the upper press plate and the lower press plate. The pressure driving system is connected to the micro-fluidic chip and used for applying pressure to the channel layer in the micro-fluidic chip so that liquid to be detected can flow into the reaction section from the inflow end. According to the scheme, microsphere preparation and nucleic acid amplification and detection are integrated through the digital isothermal nucleic acid detecting device and the detection method, and the advantages of being high in sensitivity and the like are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Nucleic acid testing device and method
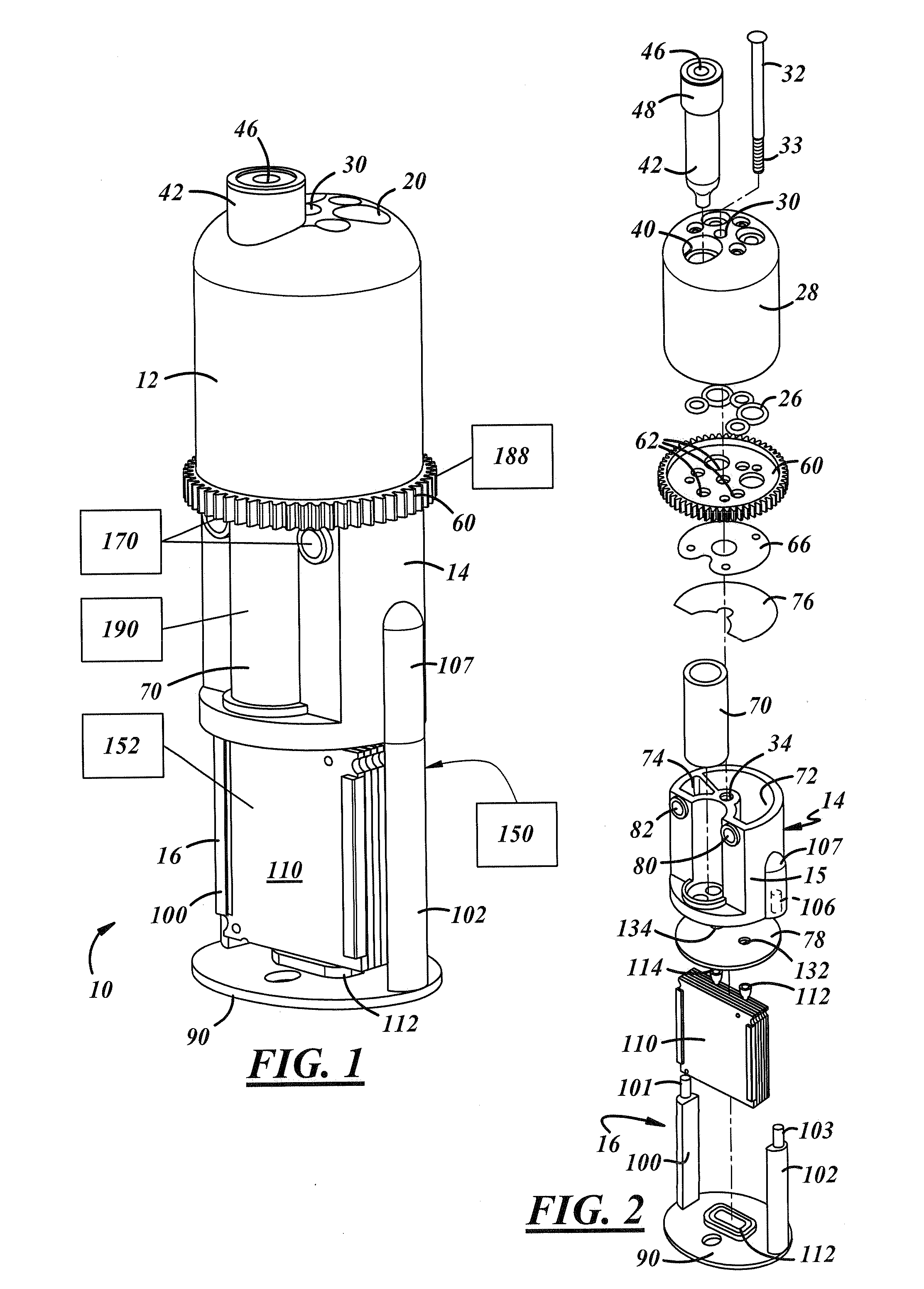
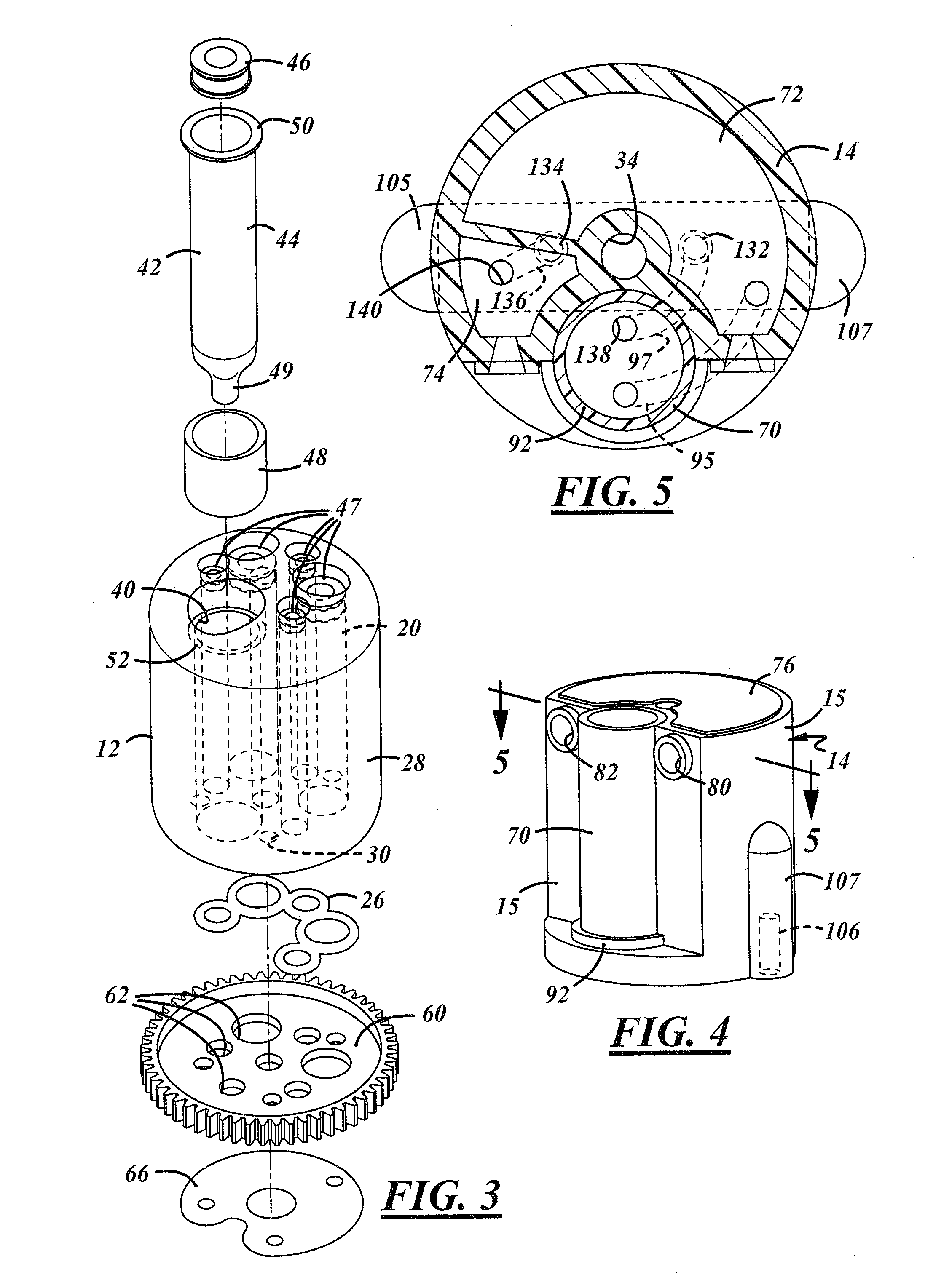
InactiveUS20110244466A1Small and inexpensiveEasy to assembleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusFlow cellSpecimen collection
Devices and systems for extracting, purifying and amplifying nucleic acids, and methods for use of such devices and systems. The devices have top sections which include a plurality of syringe vessels with applicable reagent materials, as well as a channel for a specimen collection dropper. Plungers force the materials sequentially into reaction chambers in the middle sections. Once the samples are extracted and purified, they are drawn by a vacuum into PCR devices where they are subjected to denaturing, annealing and extension steps and amplified. Interrogation of flow cells provide real-time quantitative detection.
Owner:THERMAL GRADIENT
Nucleic acid testing method for point-of-care diagnostics and genetic self-monitoring
InactiveUS20080050735A1The testing process is simpleSpecial trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careGenomic DNA
This invention describes a nucleic acid testing procedure in a form of portable device or a test kit for the purposes of clinical genetic testing, infectious disease diagnostics, biodefense, forensic analysis, paternity testing, pet and cattle breeding, food testing, etc. This testing does not include toxic chemicals and is simple enough to be used by an average individual without any special laboratory training. The procedure includes collecting the sample, potential isothermal amplification of the whole genomic DNA or a fragment of genomic DNA, denaturing double-stranded DNA into single-stranded form, hybridizing the denatured sample DNA to single-stranded allele-specific tester oligonucleotides complementary to the analyzed DNA sequence of interest, selective removal of single-stranded DNA from DNA hybrids, and finally detecting the label in double-stranded hybrids to determine the presence or absence of a particular sequence in the initial sample.
Owner:PUSHNOVA ELENA
Biological reagents and methods to verify the efficiency of sample preparation and nucleic acid amplification and/or detection
ActiveUS7718402B2Affects the efficiency of the release of the nucleic acid contentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisTest sampleNucleic acid sequencing
This invention relates to reagent comprising: any one of cells, viral particles, organelles, parasites, cells comprising organelles, cells comprising viral particles, cells comprising parasites, cells comprising bacterial cells and any combination thereof, the cells, viral particles, organelles or parasites comprising at least one nucleic acid sequence serving as an internal control (IC) target for nucleic acid testing (NAT) assay; wherein the reagent is suitable to be added to a test sample undergoing sample preparation to release, concentrate and / or purify nucleic acids and amplification and / or detection of nucleic acids so as to be used to verify: (i) the efficiency of sample preparation; and (ii) the efficiency of nucleic acid amplification and / or detection. The present invention also relates to a method to verify or validate the preparation and amplification and / or detection of a nucleic acid target sequence in a sample spiked with a reagent of the present invention.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Nucleic acid detection system and method for detecting influenza
ActiveUS8980561B1Minimize extentUnprecedented assay speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationSingle strand dna
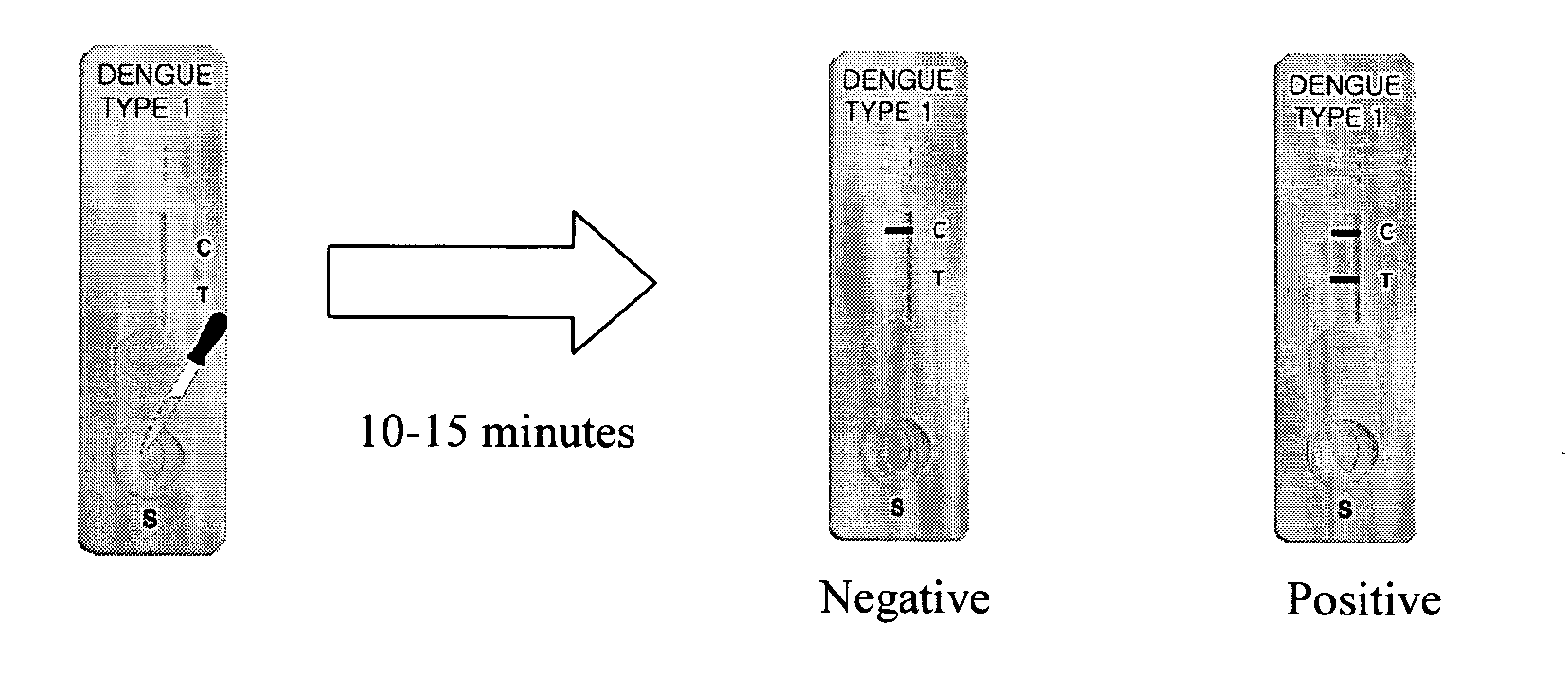
The invention provides a rapid, sensitive and specific nucleic acid detection system which utilizes isothermal nucleic acid amplification in combination with a lateral flow chromatographic device, or DNA dipstick, for DNA-hybridization detection. The system of the invention requires no complex instrumentation or electronic hardware, and provides a low cost nucleic acid detection system suitable for highly sensitive pathogen detection. Hybridization to single-stranded DNA amplification products using the system of the invention provides a sensitive and specific means by which assays can be multiplexed for the detection of multiple target sequences.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Preparing method for tr-gene products detecting oligonucleotides chip and use thereof
InactiveCN1584049AGuaranteed specificityTo achieve the purpose of mutual verificationMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousOligonucleotide chip
A method for preparing oligonucleotide chip for transgene product detection and use are disclosed. It includes: designing specific oligonucleotide probe and related primer by heterogeneric inserting gene, species internal standard gene, specific boundary sequence in transgene product gene set, fixing probe on glass slide to form transgene product detecting chip, amplifying DNA of plant to be tested by related primmer, marking by fluorescence, and hybridizing with chip. It can be use to acquire variable information.
Owner:国家质量监督检验检疫总局动植物检疫实验所 +2
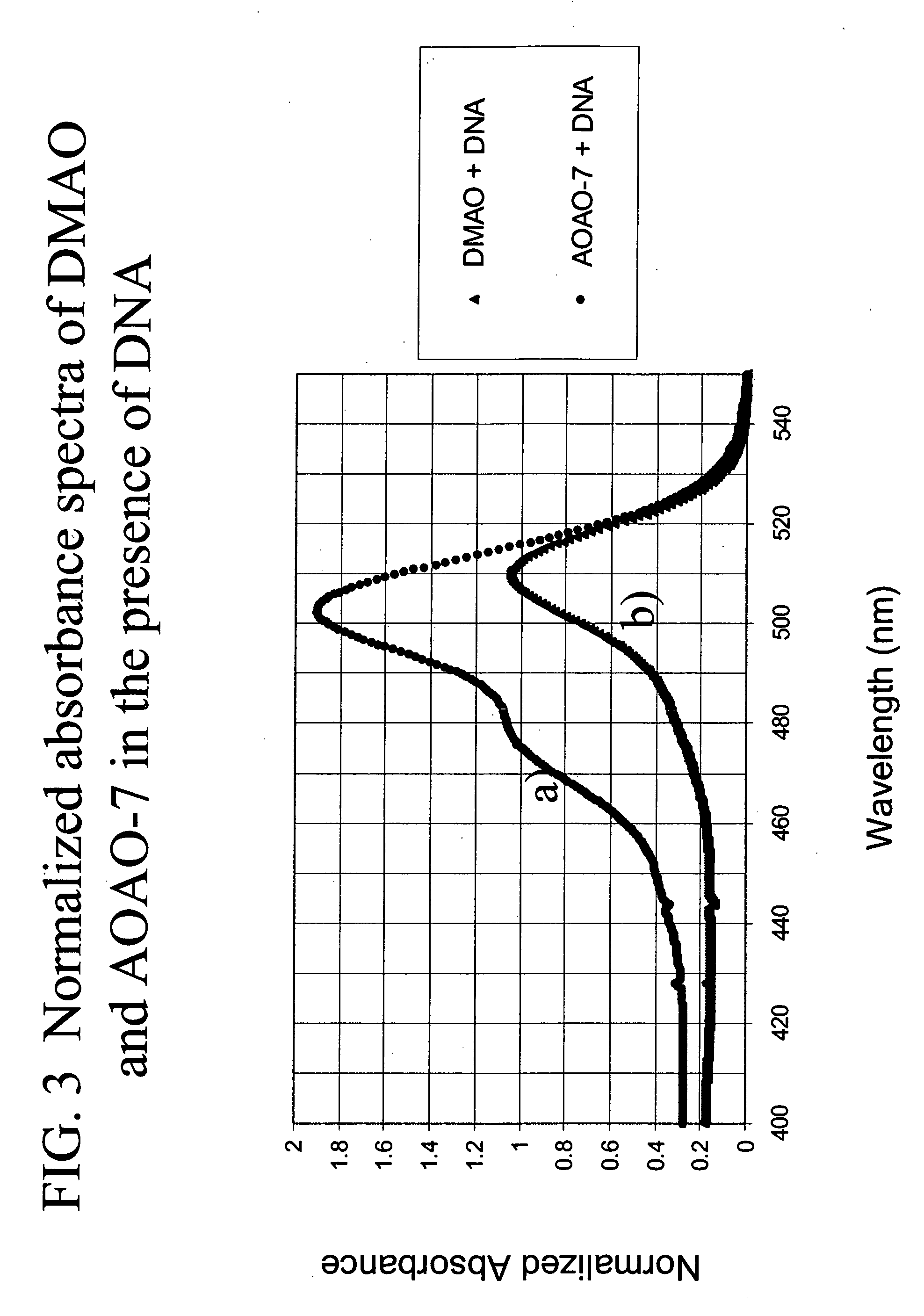
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS20060211029A1Increase DNA detection sensitivity“effective dye concentrationMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesStainingStrong acids
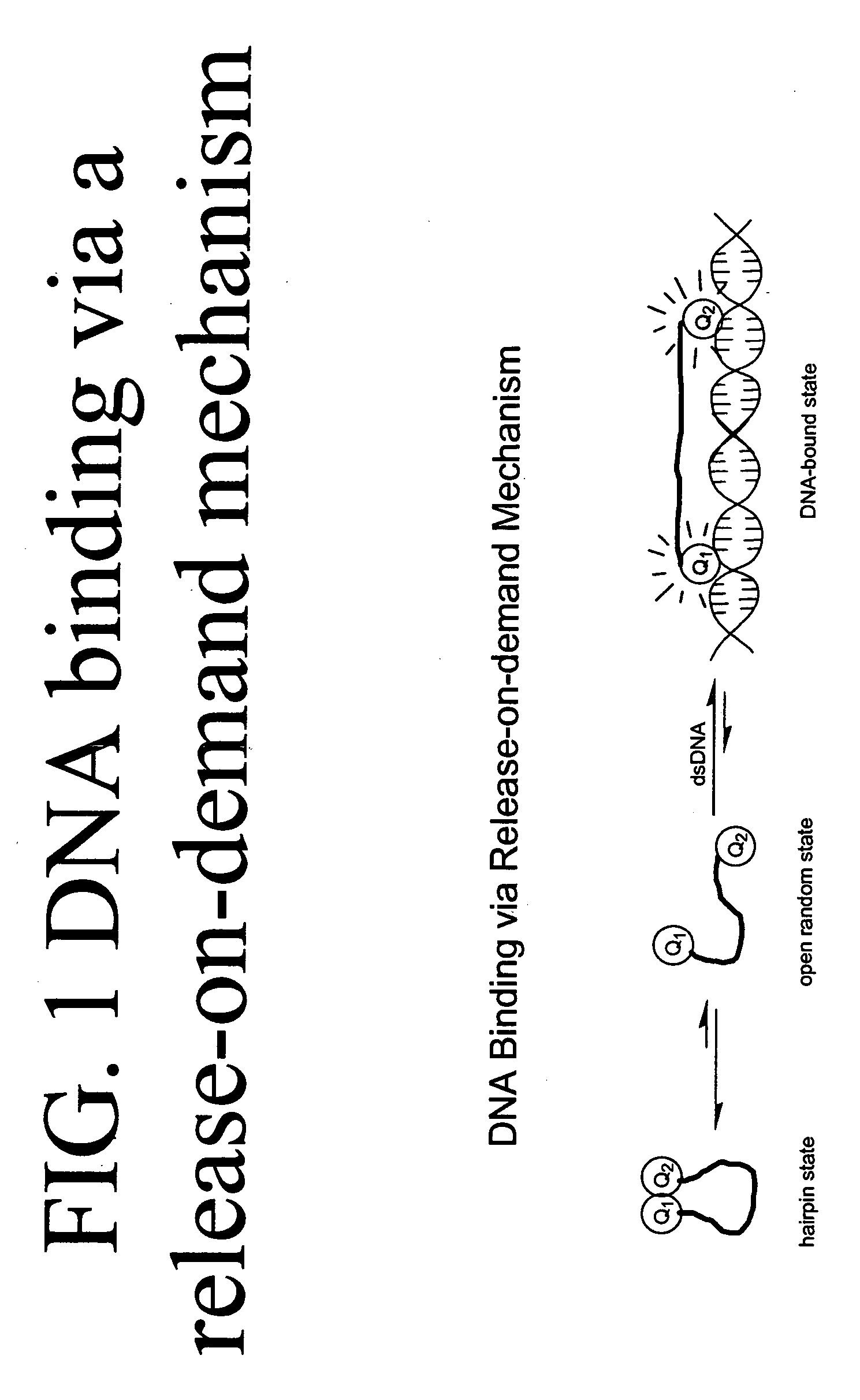
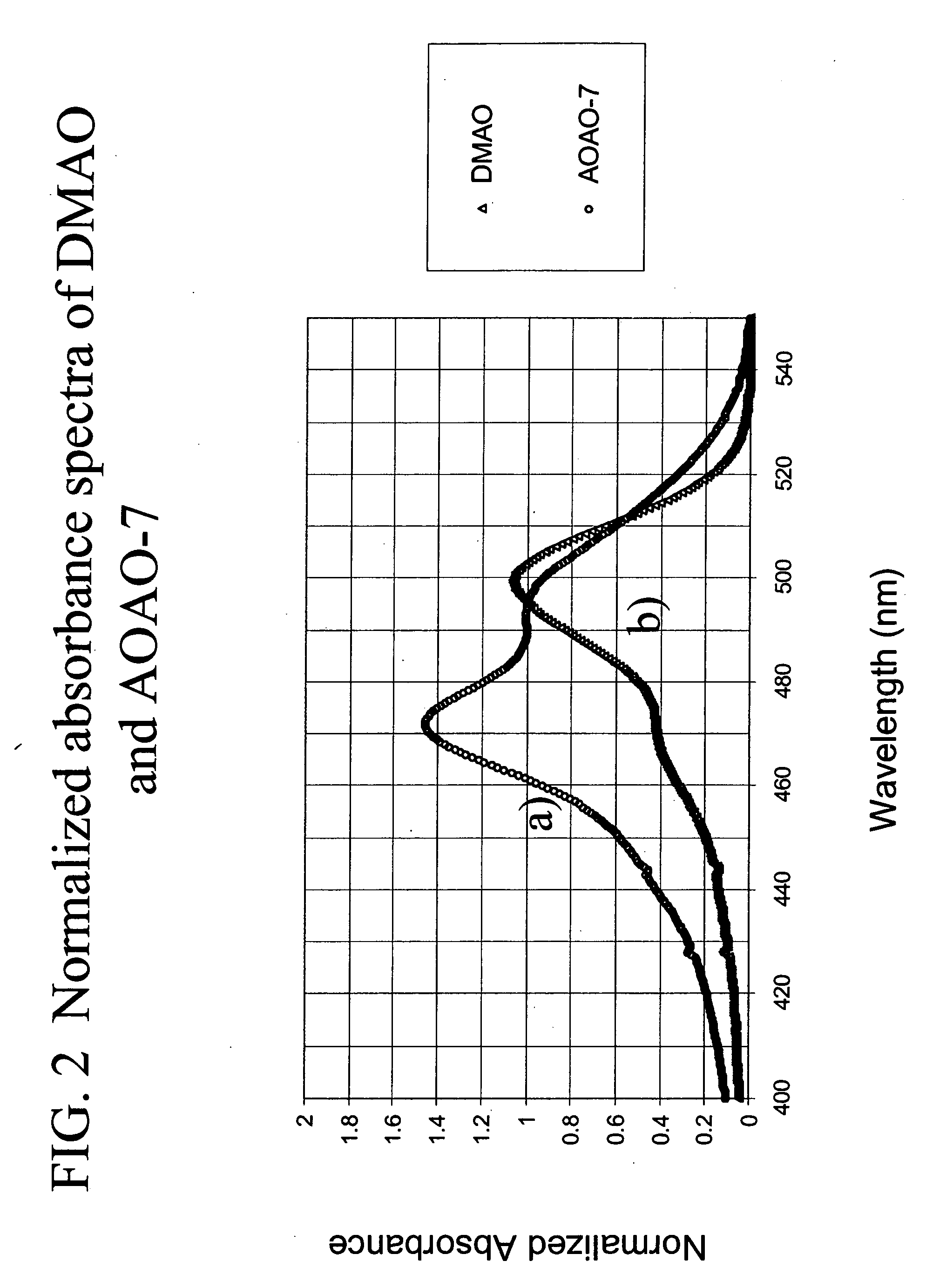
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
crRNA (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat-Derived Ribonucleic Acid) for specifically detecting exon mutation of human KRAS genes #2 and #3 based on CRISPR technique
InactiveCN108893529AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementTemperature controlKRAS
The invention discloses crRNA (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat-Derived Ribonucleic Acid) for specifically detecting exon mutation of human KRAS genes #2 and #3 based on a CRISPR technique. The crRNA is characterized by comprising a CRISPR-Cas13a system as well as crRNA, wherein the crRNA can be combined with the CRISPR-Cas13a system; and the crRNA has a sequence format of5'-Cas13a protein anchoring sequence-crRNA guide sequence-3'. The crRNA has the advantages that according to detection results, whether the human KRAS gene have mutation or not can be judged intuitively through fluorescent reading, high-flux sequencing can be avoided, and the crRNA has the advantages of being low in cost, possible in multi-time detection, high in detection speed, possible in direct result analysis, and the like, and is applicable to large-scale clinical sample detection; the nucleic acid testing technique disclosed by the invention is different from a conventional detection technique which is based on PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) techniques, and no complex temperature control instrument or system is needed in a whole reaction process; and three steps of reactions are carried out in a same reaction system, so that operation procedures can be further simplified, and nucleic acid fragments with specific sequences can be detected within two hours.
Owner:江苏博嘉生物医学科技有限公司
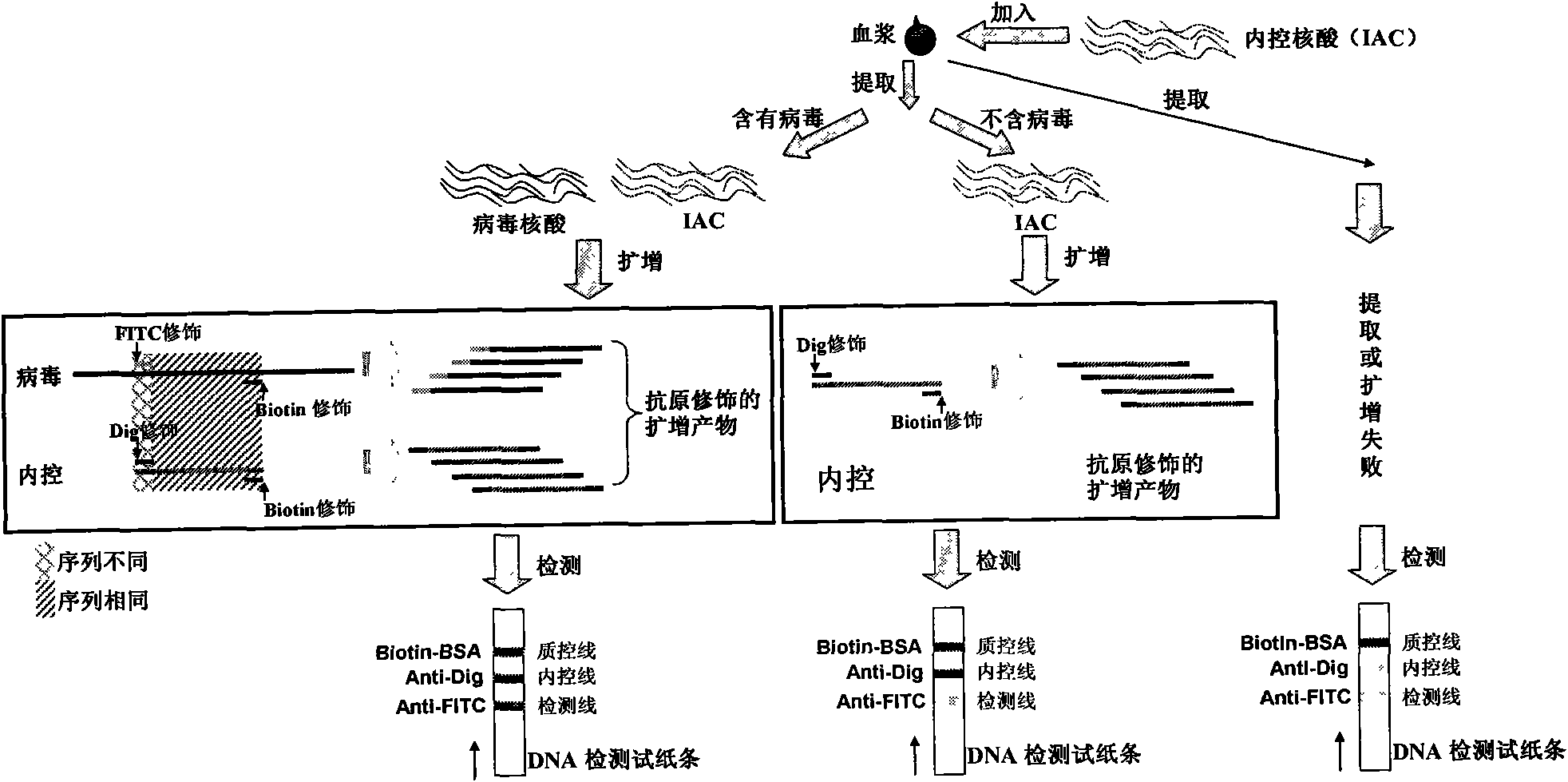
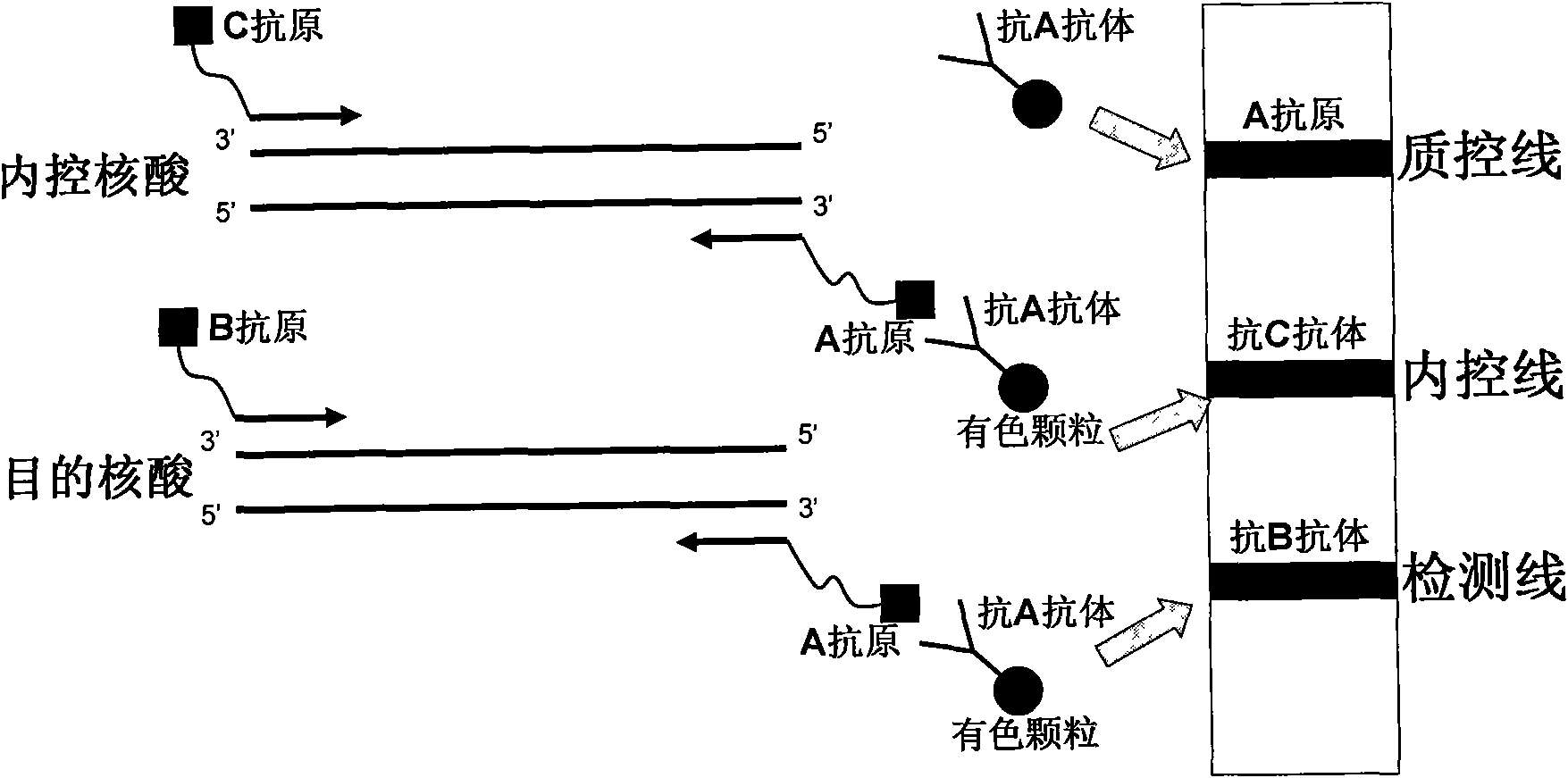
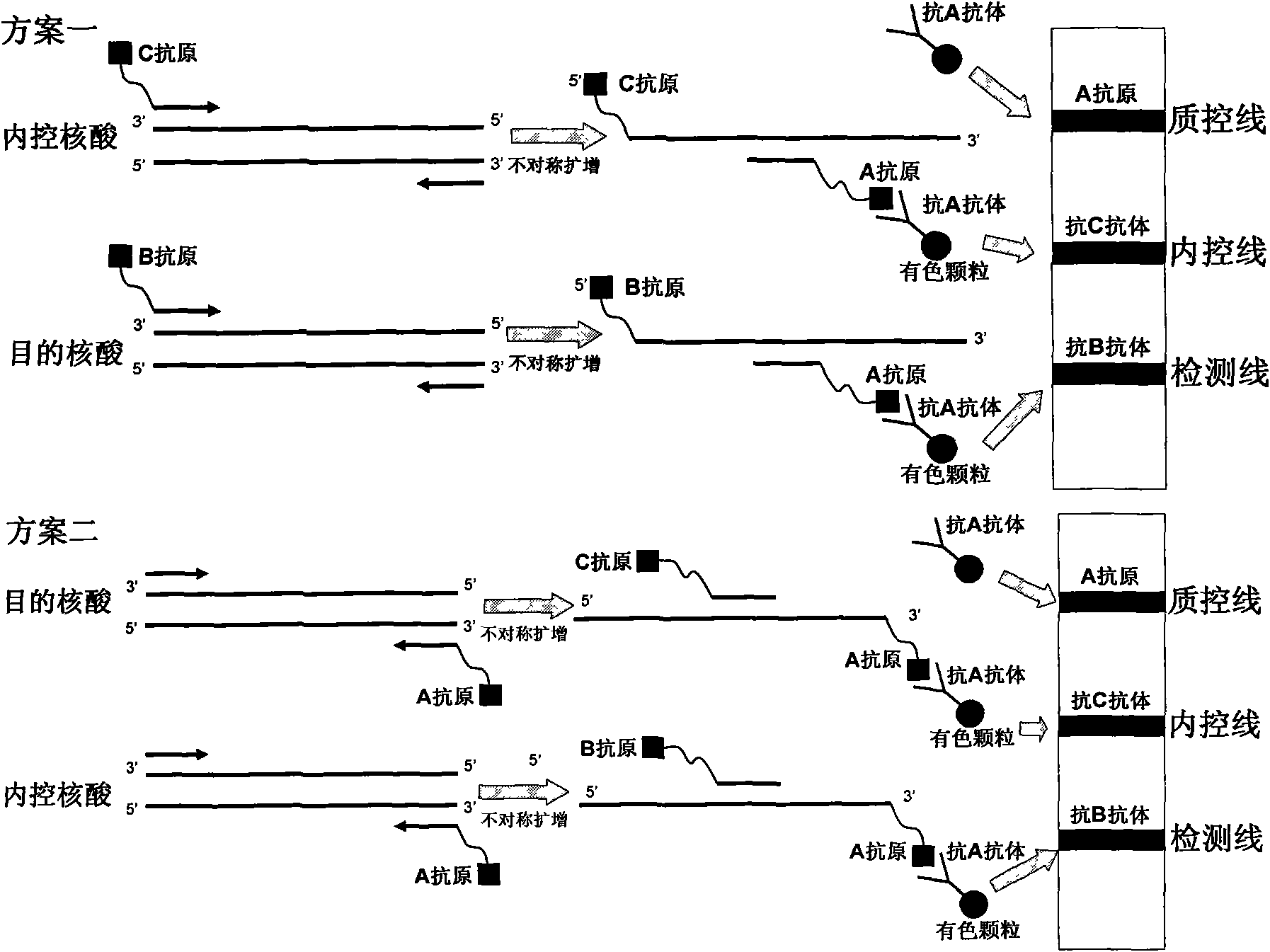
Method for semi-quantitatively detecting pathogenic nucleic acid by adding internal control nucleic acid
InactiveCN101957373AAvoid diagnostic problems that are prone to false negativesAvoid problems prone to false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTest sampleQuality control
The invention belongs to the field of nucleic acid detection and discloses a method for semi-quantitatively detecting pathogenic nucleic acid by adding internal control nucleic acid. Corresponding internal control is added in the whole process of extracting and amplifying target nucleic acid and testing by using a test paper, so that the internal control and a target segment are parallelly operated, and the semi-quantitative detection is performed finally through color development and intensity contrast of three strips, namely a detection line, an internal control line and a quality control line on the test paper. In the method, in the whole process of processing the target nucleic acid, the corresponding internal control is taken as a positive contrast, and false negative results due to links such as extraction, amplification or sample application errors are avoided in the processing of detecting by using the test paper. Meanwhile, by comparing color development intensity of the internal control line and a sample line and introducing the semi-quantitative function on the basis of the qualitative function of the immunochromatographic test paper to estimate the copy number of tested samples, the detection results are more detailed, accurate and reliable. The method has the advantages of convenient and quick operation and capacity of meeting the actual clinical requirement.
Owner:HUADONG RES INST FOR MEDICINE & BIOTECHNICS
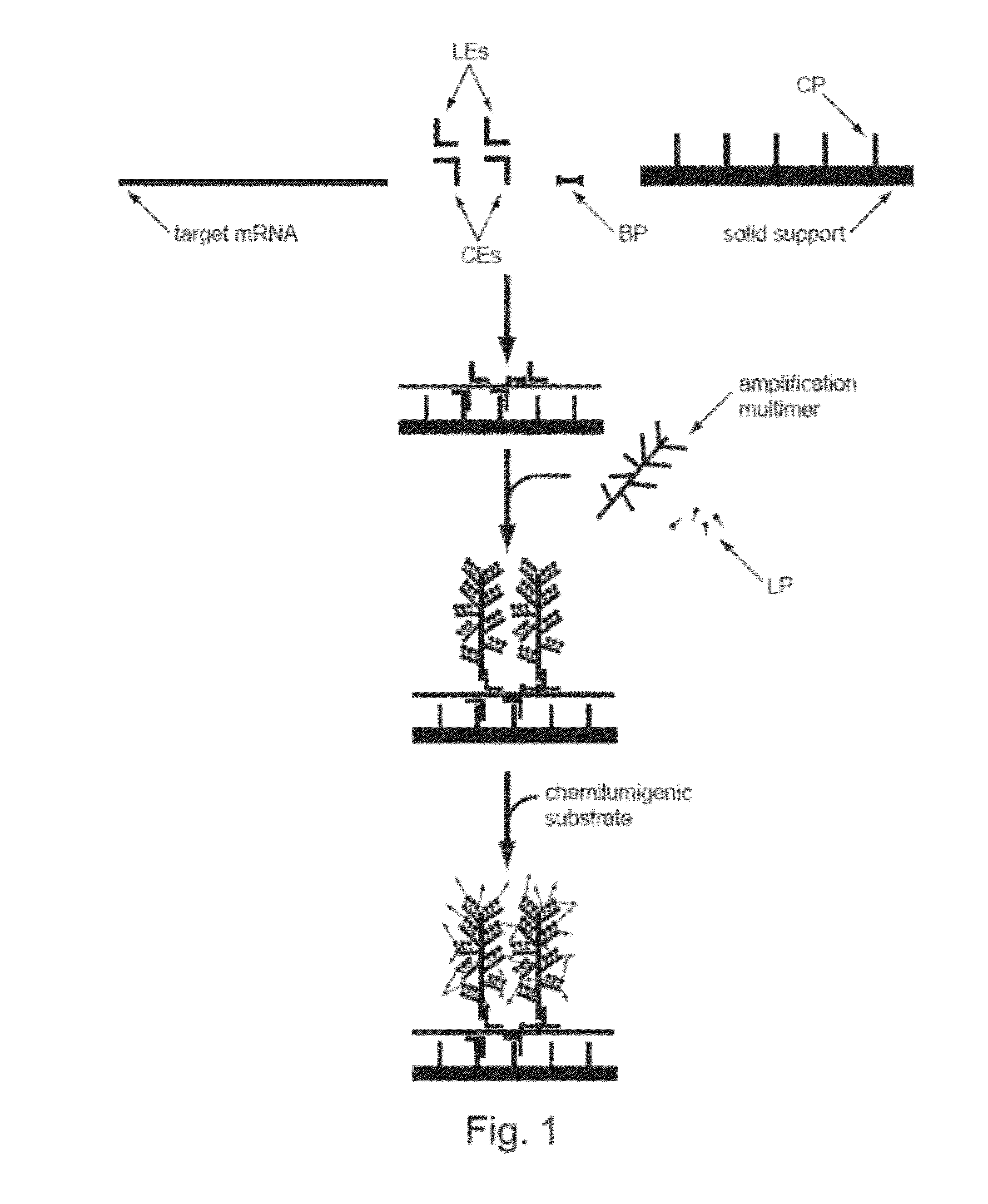
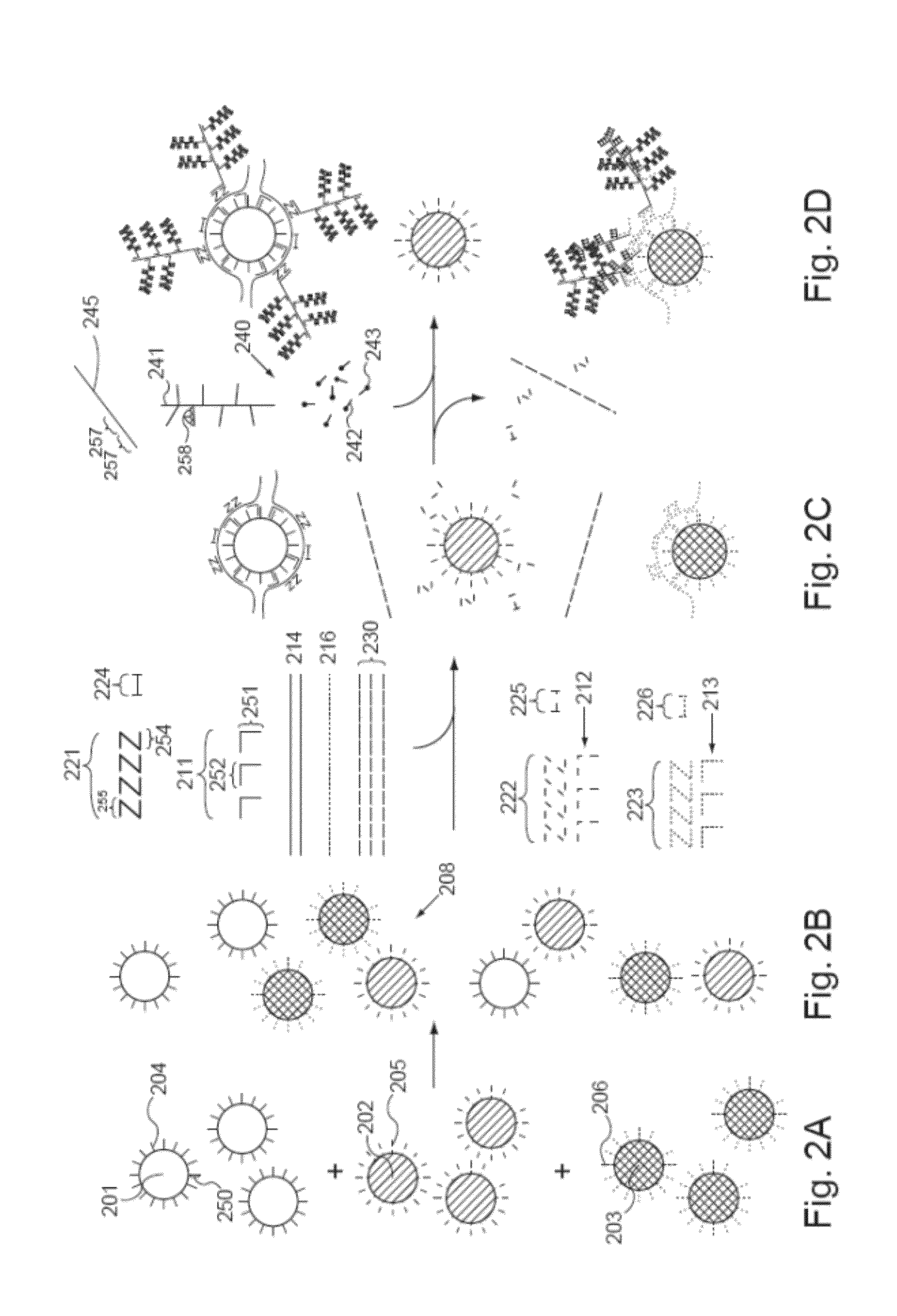
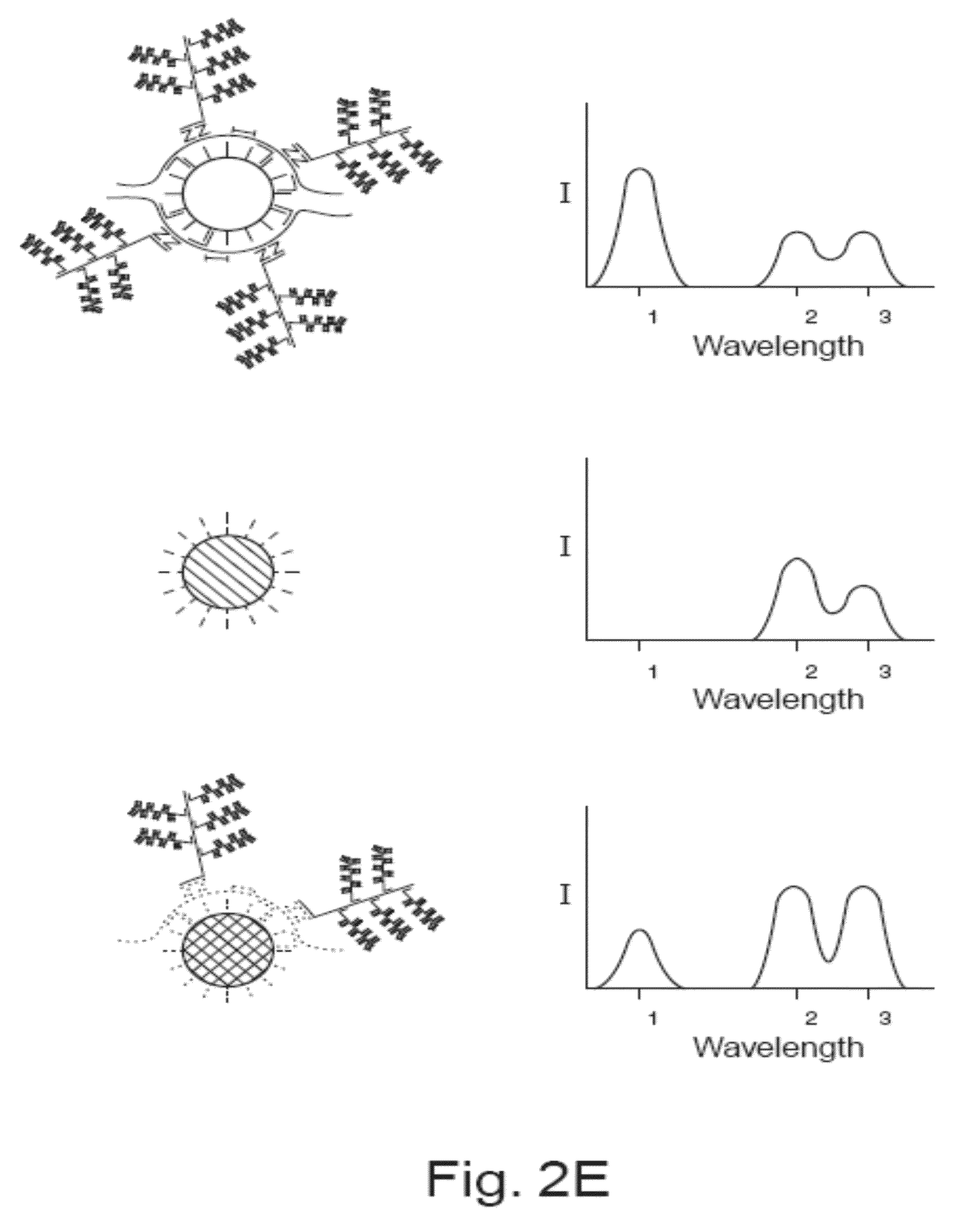
Detection of Nucleic Acids
Methods of detecting various types of nucleic acids, including methods of detecting two or more nucleic acids in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Detection assays may be conducted at least in vitro, in cellulo, and in situ. Nucleic acids which are optionally captured on a solid support are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label probe system with the nucleic acids. Various label probe system embodiments are provided. Compositions, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acid detection assay
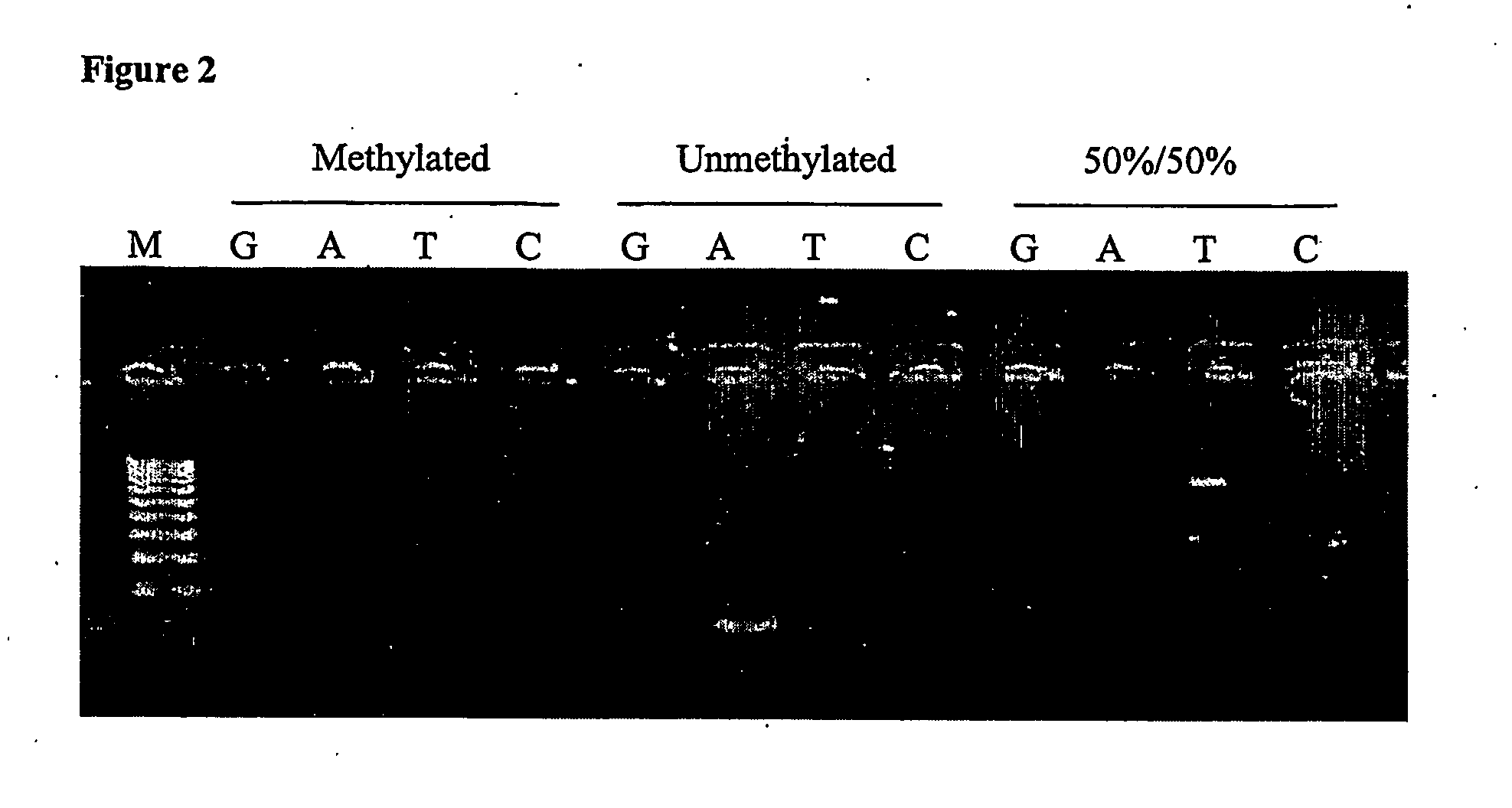
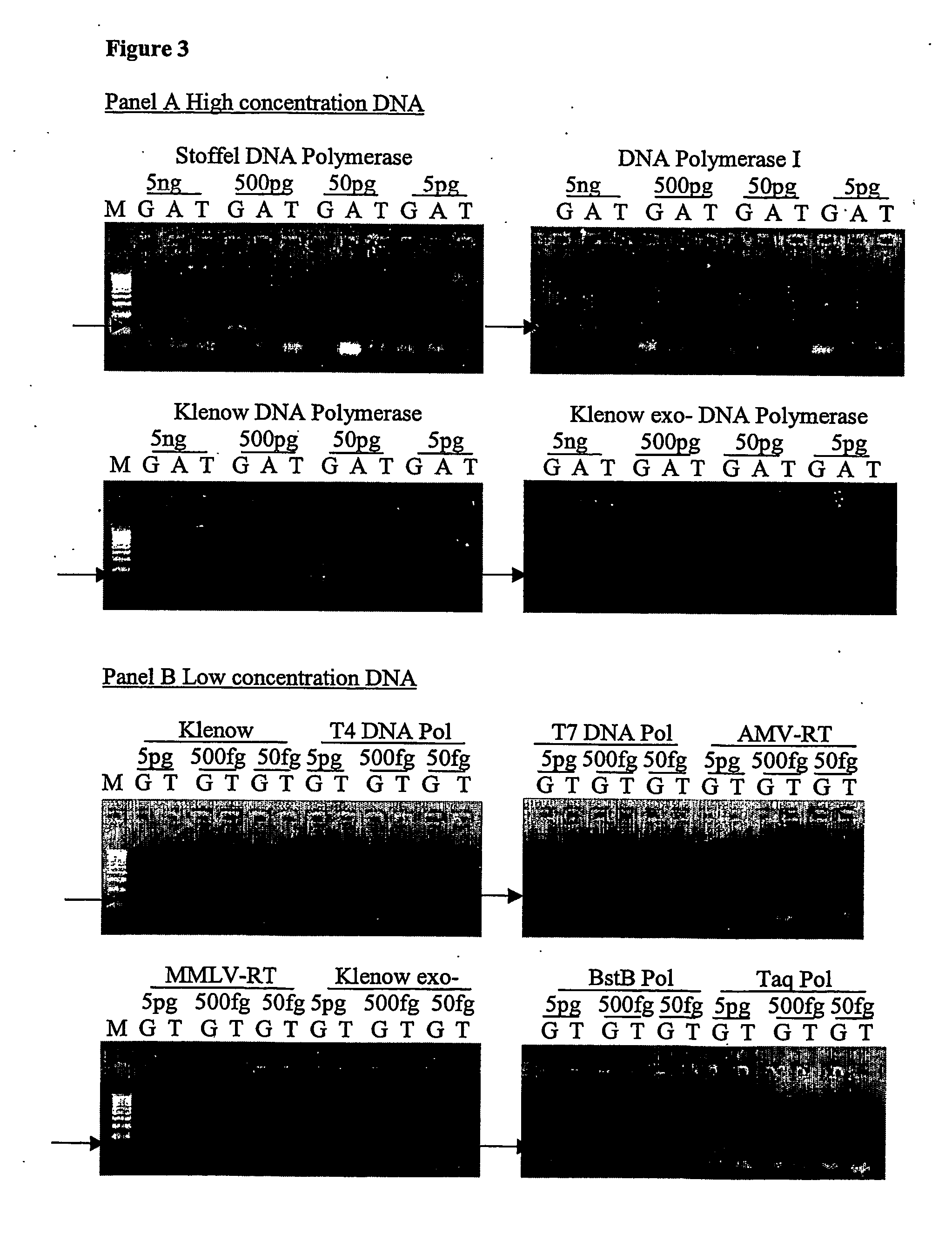
A method for determining the methylation status of a potential methylation site in genomic nucleic acid comprising treating genomic nucleic acid with an agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form a. modified nucleic acid template containing a potential methylation site; providing a first clamp containing a first capture sequence complementary to a region flanking one side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template, providing a second clamp containing a second capture sequence complementary to a region flanking the other side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; allowing the first clamp and the second clamp to hybridise to the modified nucleic acid template; ligating the hybridised first and second clamps to form a probe spanning the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; digesting the modified nucleic acid template to obtain the probe; and detecting the probe and determining the methylation status of the potential methylation site in the modified genomic nucleic acid.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Nucleic acid detection combining amplification with fragmentation
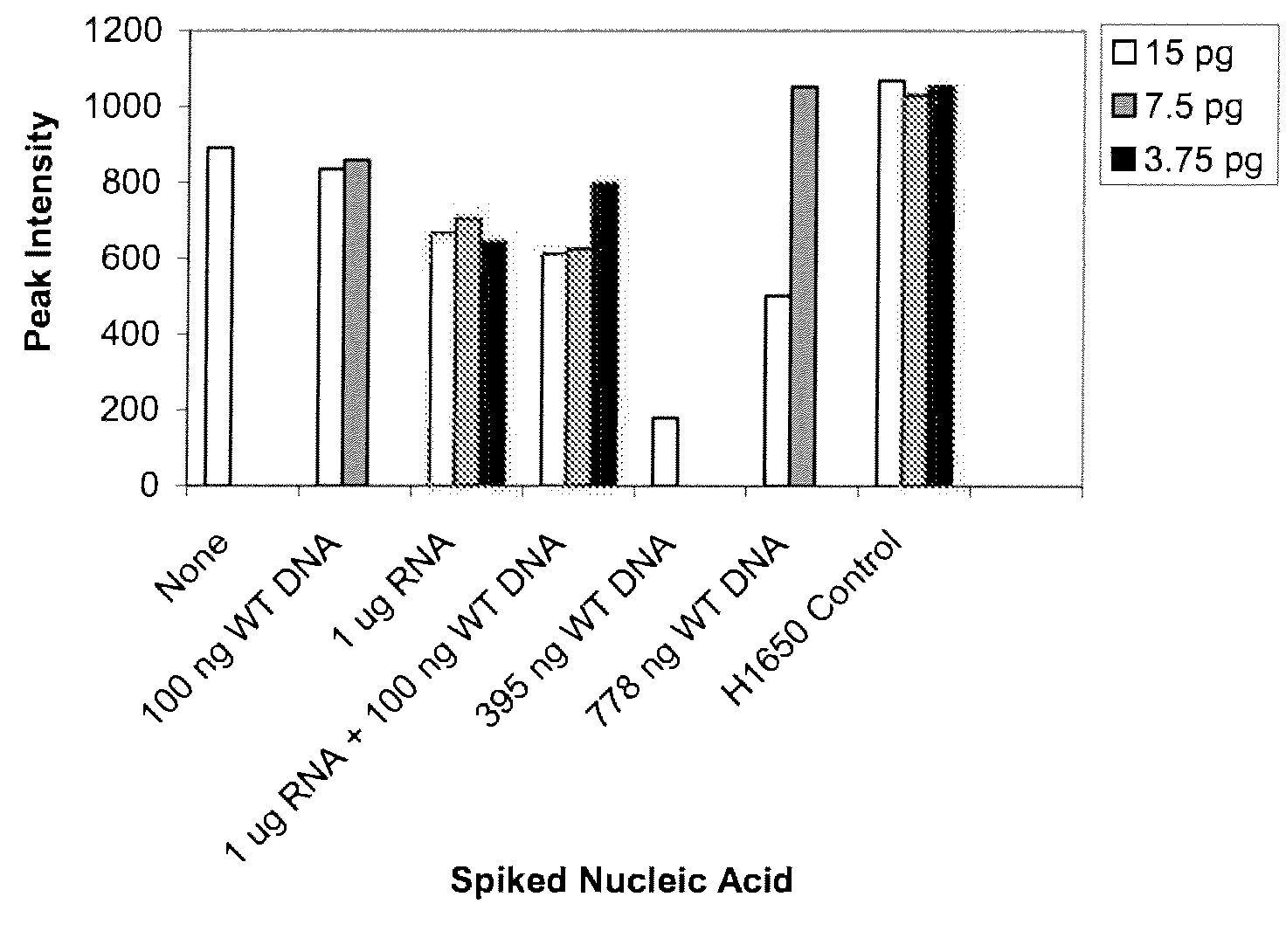
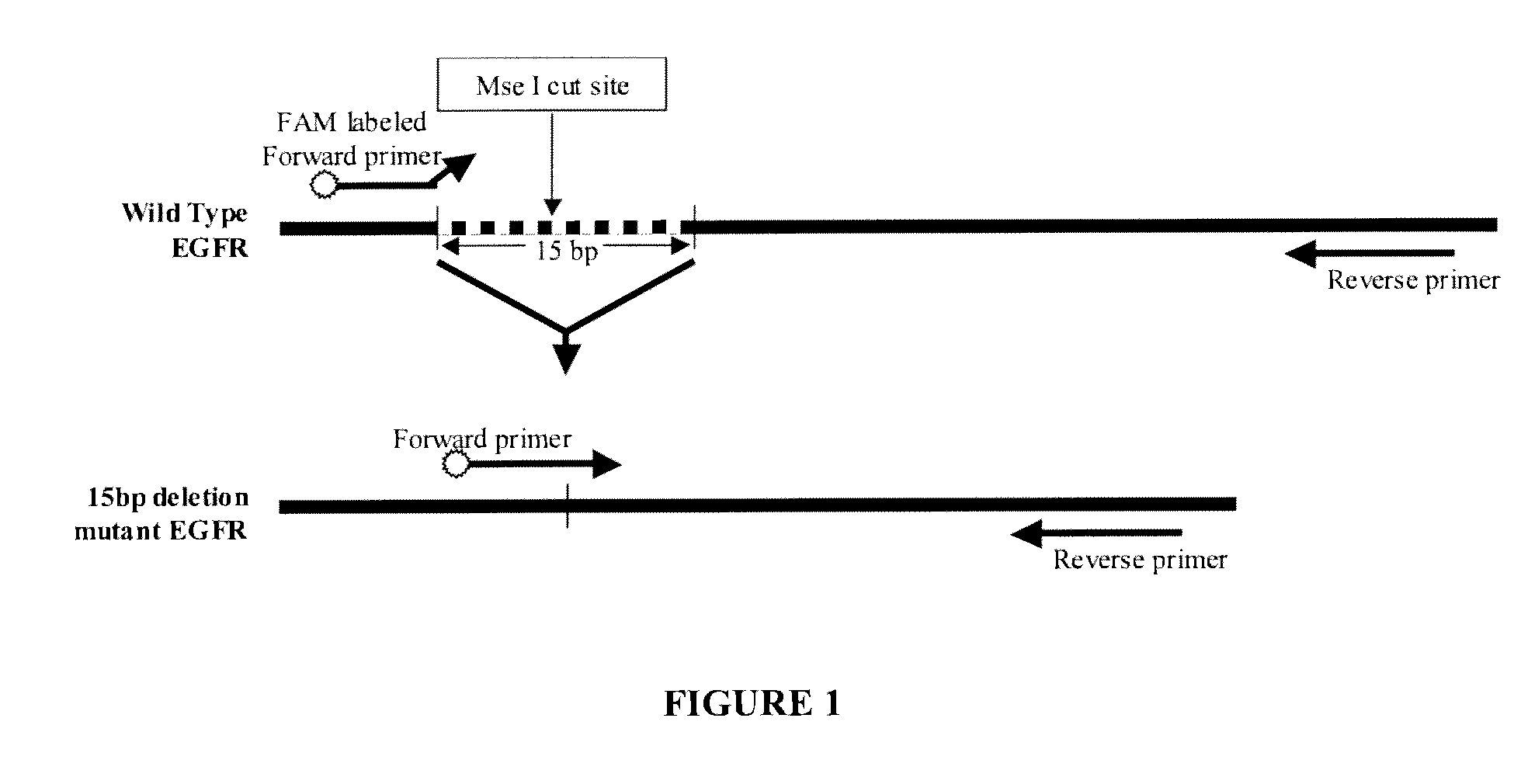
Provided herein are methods and compositions for detection of a nucleic acid target in a sample. The methods and compositions use primer directed amplification in conjunction with nucleic acid fragmentation. The methods have high sensitivity even in the presence of a large amount of non-target nucleic acid. Also provided are oligonucleotides and kits useful in the method. Exemplary nucleic acid targets are those with mutant gene sequence such as mutant sequence of the EGFR, APC, TMPRSS2, ERG and ETV1 genes.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
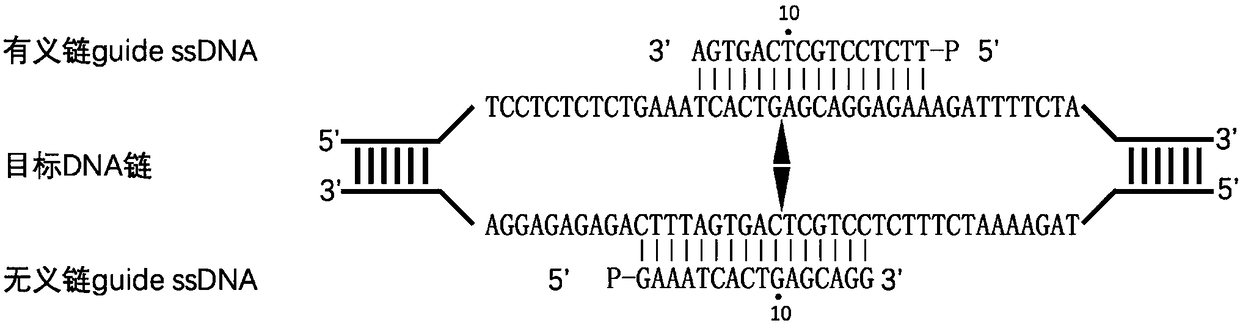
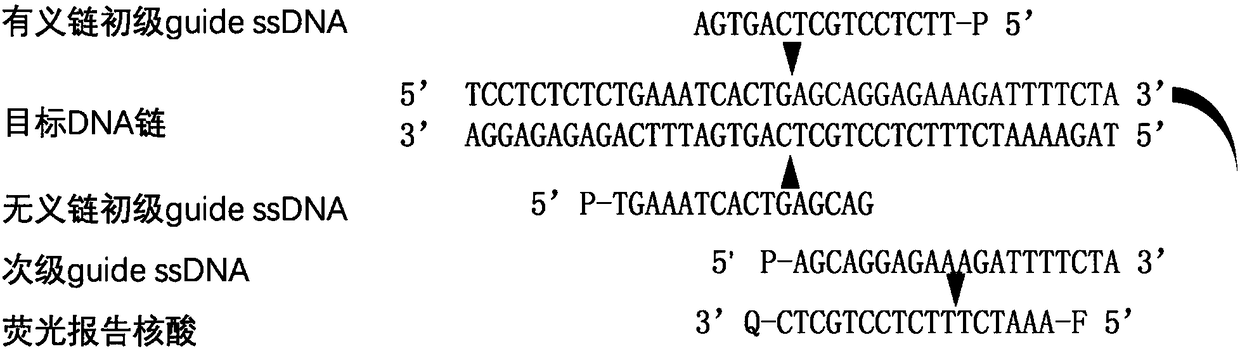
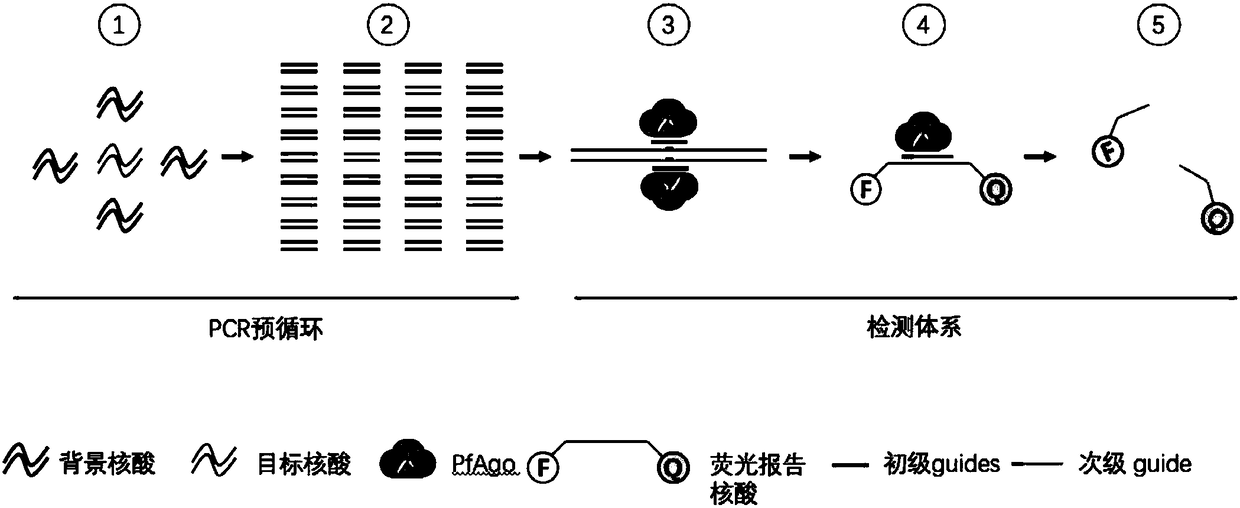
Nucleic acid testing method based on prokaryotic Argonaute protein and application of nucleic acid testing method
ActiveCN108796036AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMedical diagnosis
The invention provides a nucleic acid testing method based on a prokaryotic Argonaute protein and an application of the nucleic acid testing method, and particularly provides a system for detecting atarget nucleic acid molecule. The system comprises guide ssDNAs, gene editing enzyme Pyrococcus furiosus Argonaute (PfAgo) and a fluorescence reporter nucleic acid. The nucleic acid testing method ishigh in sensitivity, good in specificity and high in flux and can be widely applied to the fields of molecular medical diagnosis, food safety testing, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
T-structure invasive cleavage assays, consistent nucleic acid dispensing, and low level target nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS20080131870A1Improve dynamic rangeRaise the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNon targetedNon target
The present invention relates to systems, methods and kits for low-level detection of nucleic acids, detecting at least two different viral sequences in a single reaction vessel, and increasing the dynamic range of detection of a viral target nucleic acid in a sample. The present invention also relates to T-structure invasive cleavage assays, as well as T-structure related target dependent non-target amplification methods and compositions. The present invention further relates to methods, compositions, devices and systems for consistent nucleic acid dispensing onto surfaces.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Nucleic acid detection compositions
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Biological reagents and methods to verify the efficiency of sample preparation and nucleic acid amplification and/or detection
ActiveUS20070015139A1Affects the efficiency of the release of the nucleic acid contentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisGranular cellTest sample
This invention relates to reagent comprising: any one of cells, viral particles, organelles, parasites, cells comprising organelles, cells comprising viral particles, cells comprising parasites, cells comprising bacterial cells and any combination thereof, the cells, viral particles, organelles or parasites comprising at least one nucleic acid sequence serving as an internal control (IC) target for nucleic acid testing (NAT) assay; wherein the reagent is suitable to be added to a test sample undergoing sample preparation to release, concentrate and / or purify nucleic acids and amplification and / or detection of nucleic acids so as to be used to verify: (i) the efficiency of sample preparation; and (ii) the efficiency of nucleic acid amplification and / or detection. The present invention also relates to a method to verify or validate the preparation and amplification and / or detection of a nucleic acid target sequence in a sample spiked with a reagent of the present invention.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
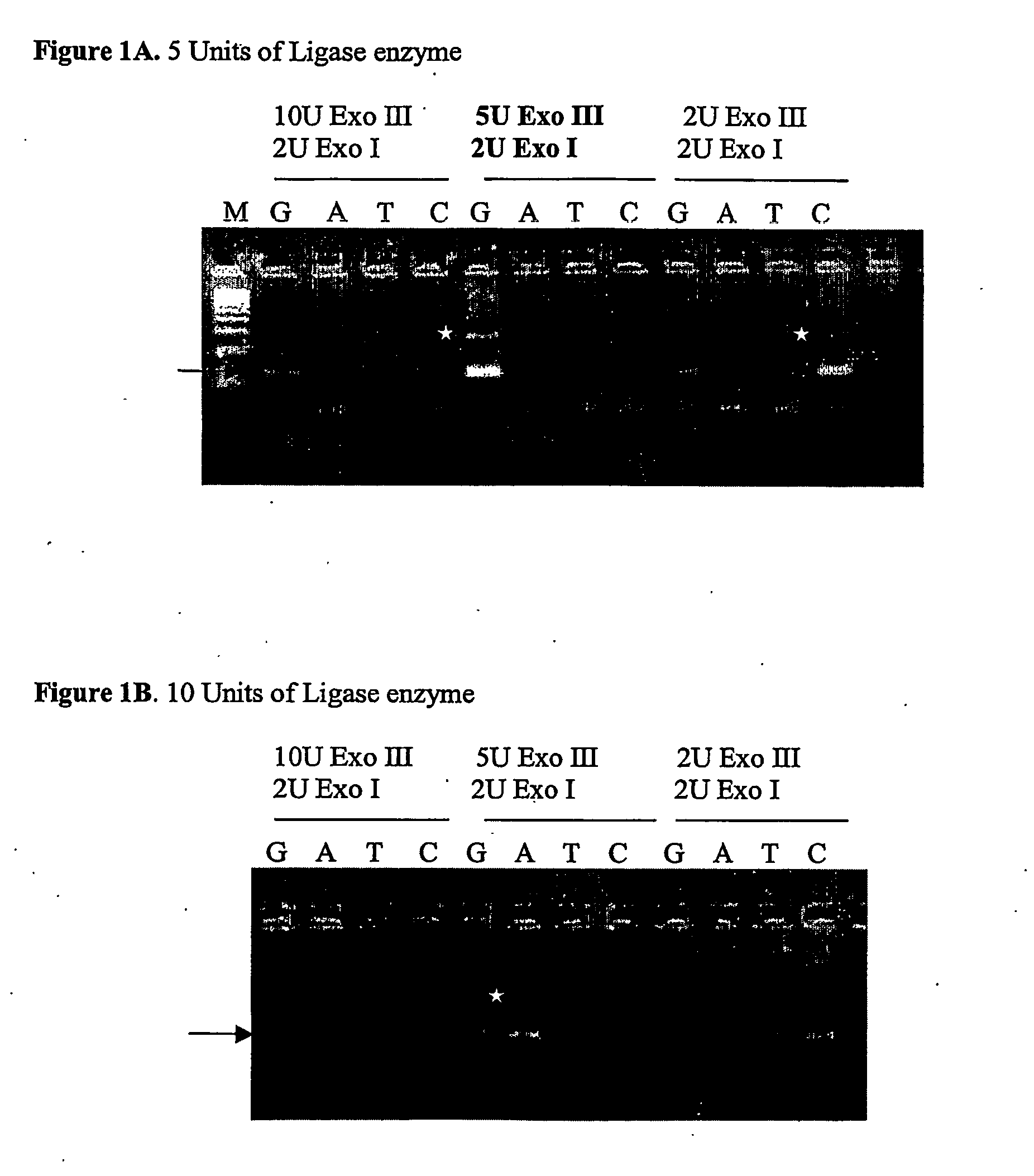
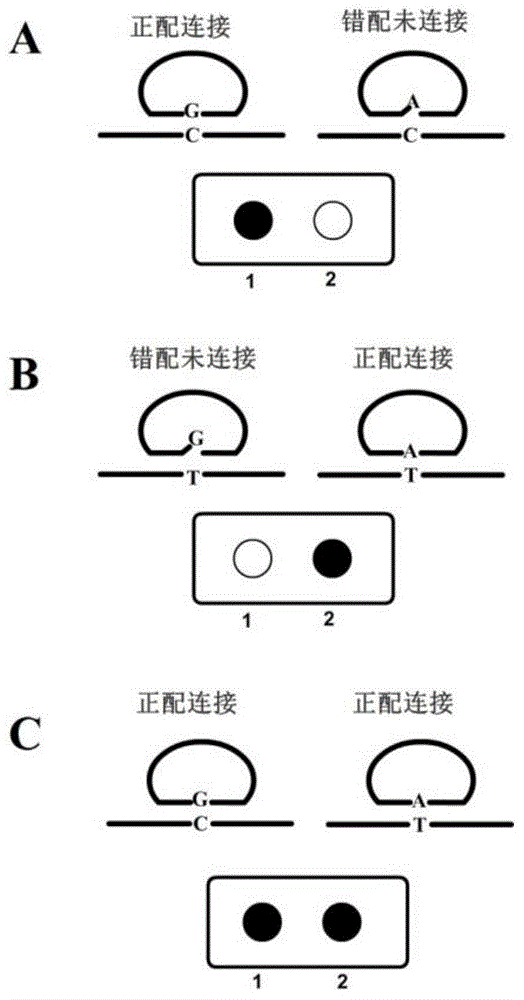
Method for detecting nucleic acid
ActiveCN102827929ALow costReduce the need for technical expertiseMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadA-DNA
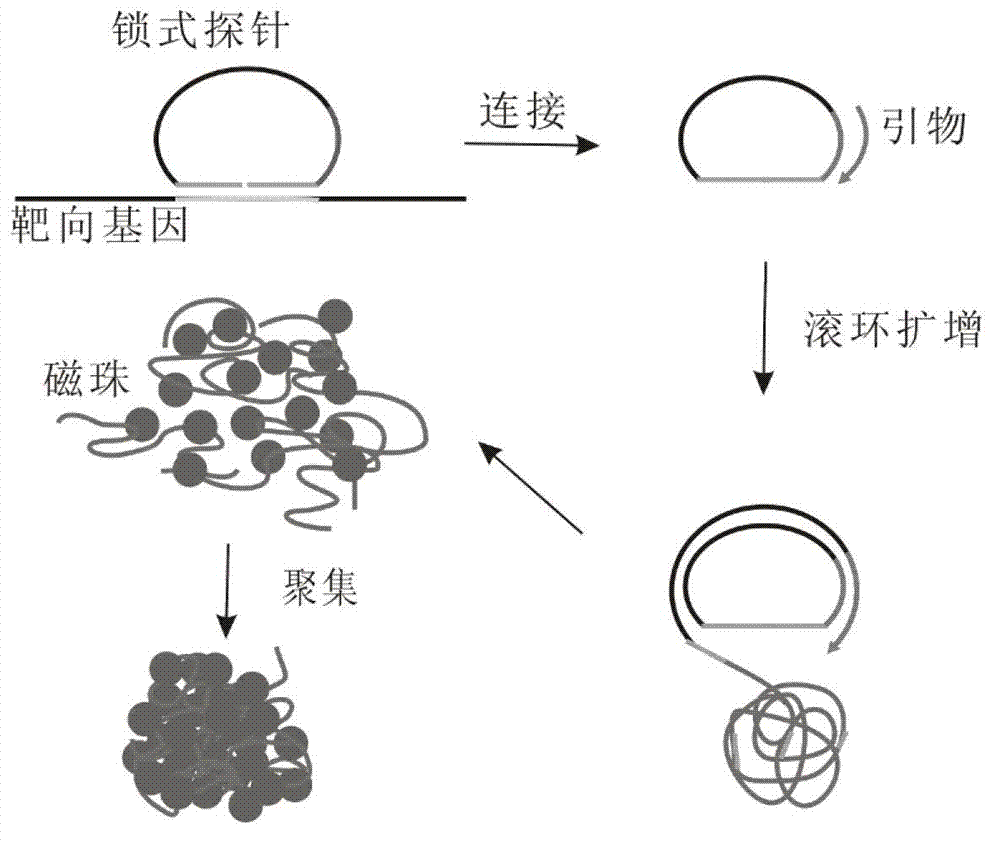
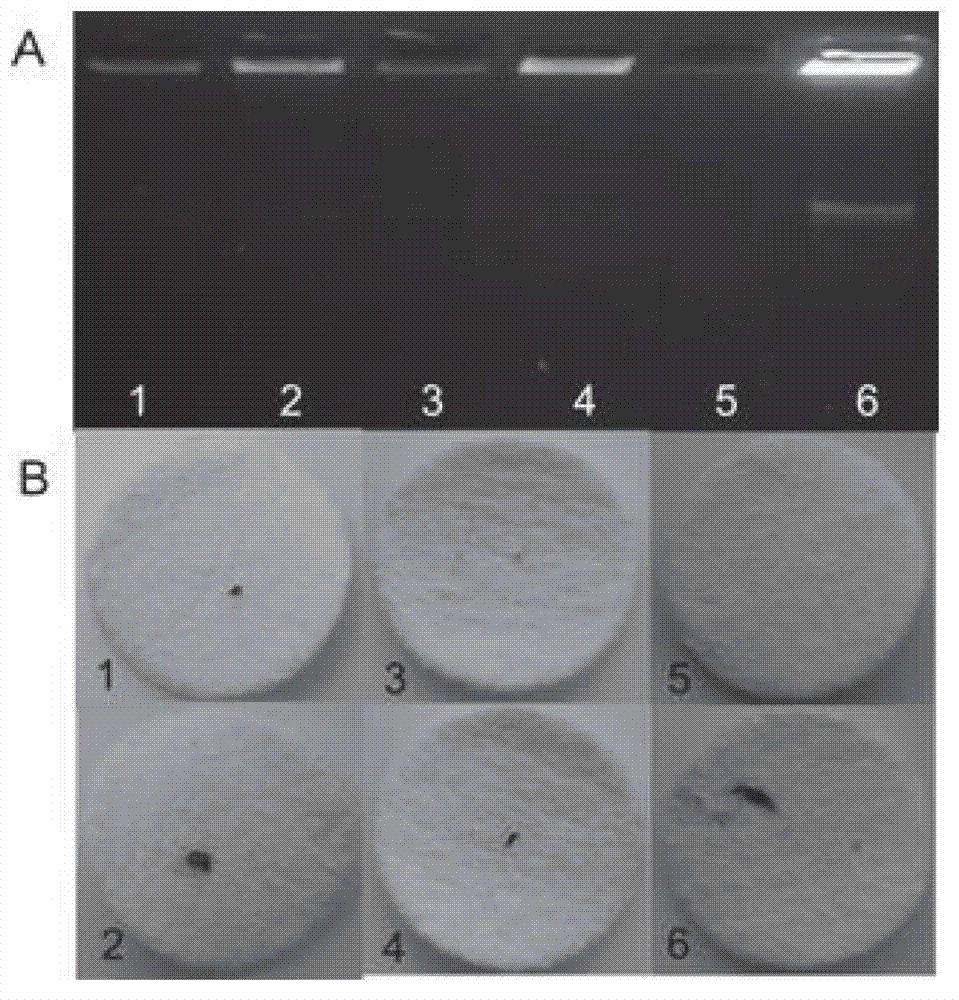
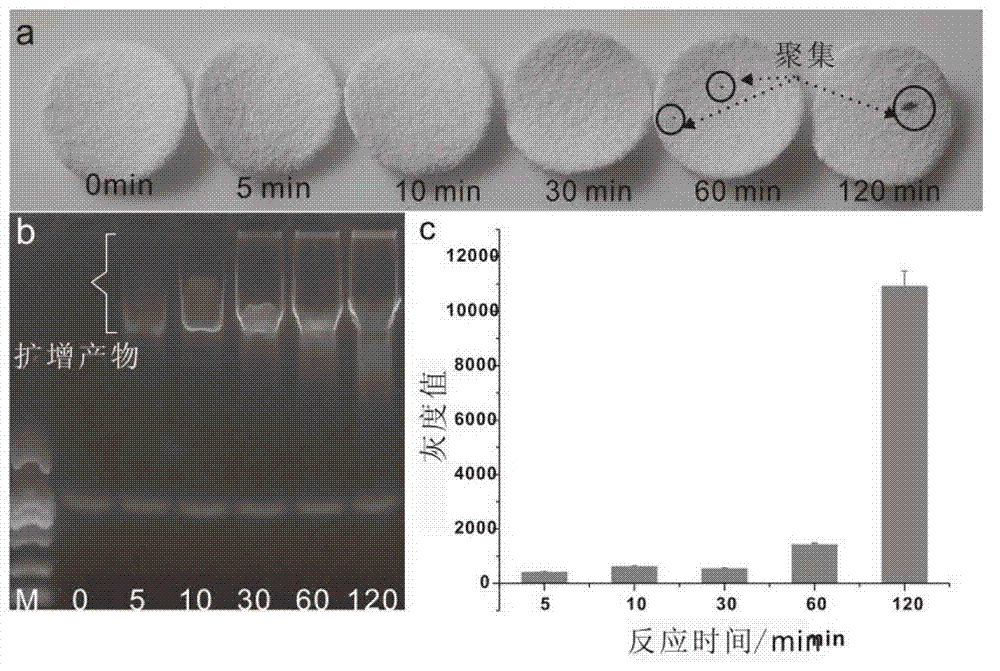
The invention discloses a method for detecting nucleic acid, which comprises the following steps that: (1) a lock type probe and an amplification primer are designed and synthesized according to the sequence of a target nucleic acid molecule; (2) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) reverse transcription product is treated in advance, and then is mixed with the lock type probe, ligase and buffer solution, and heating is carried out to inactivate the ligase after the ligation; (3) a ligation product is taken as a template, and the amplification primer is utilized for roll loop amplification; (4) after the roll loop amplification is completed, magnetic beads are added into a roll loop amplification system to gather the amplification products, and the whole material is transferred to filter paper to be aired; and (5) the surface of the filter paper is observed by naked eyes to judge whether the DNA or RNA contains the target nucleic acid molecule or not. The method requires simple experimental devices, only needs a pipettor and a constant temperature heater to complete the whole detection process, and is very low in cost compared with the conventional method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
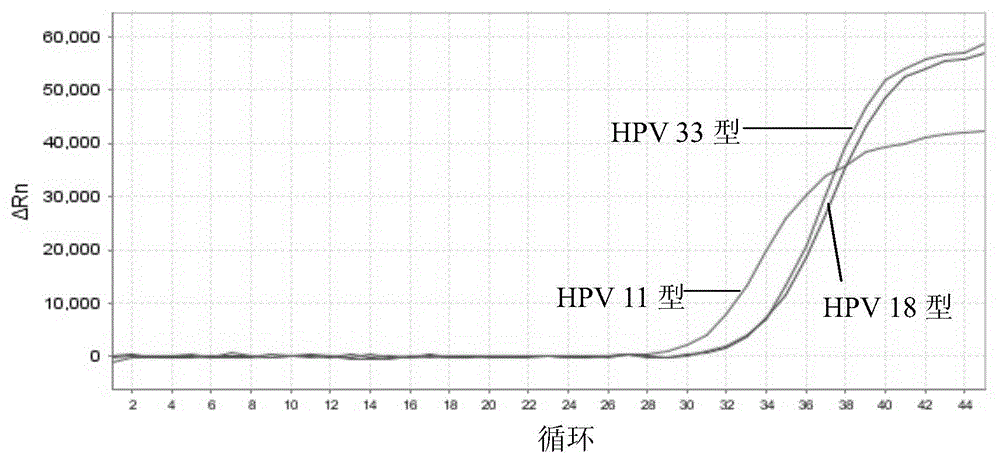
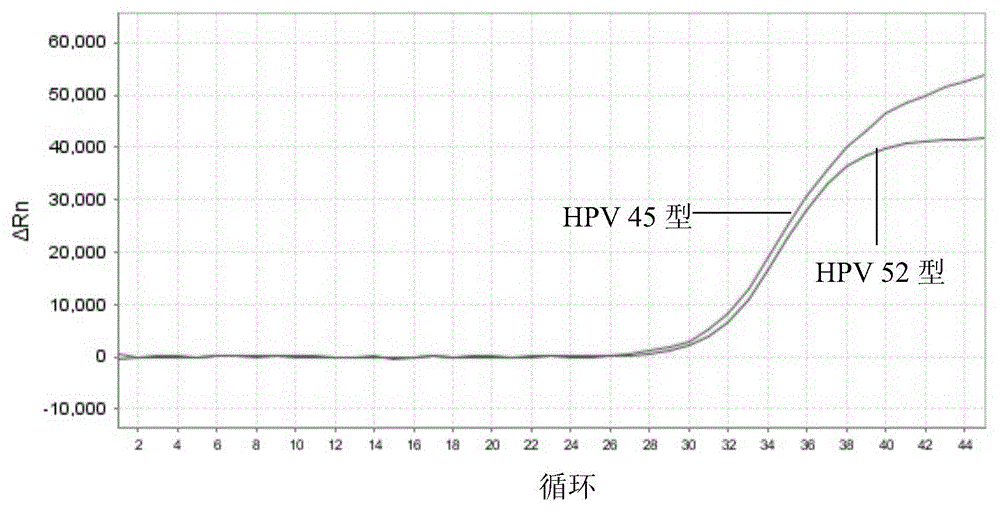
Nucleic acid detection kit for human papilloma virus, use method and application thereof
ActiveCN105506173AAvoid false negativesIncrease throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesLower riskFluorescence
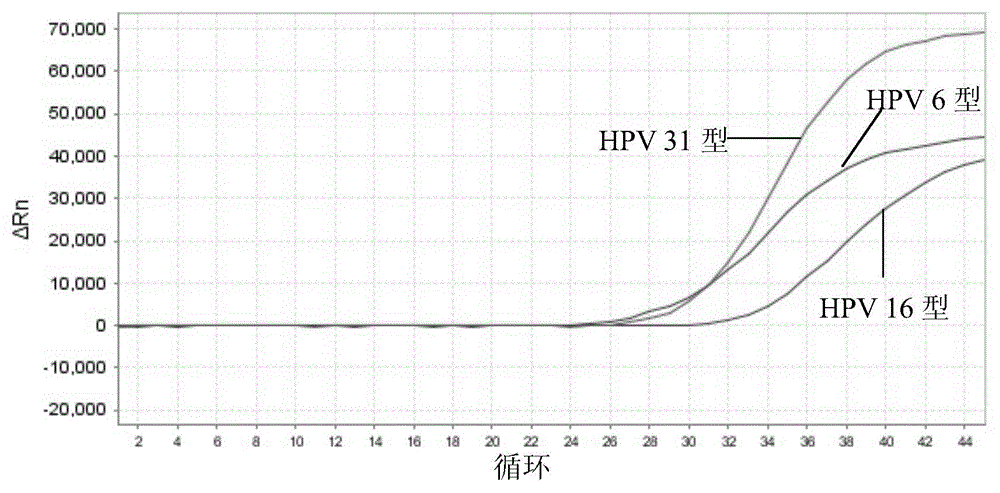
The invention discloses a nucleic acid detection kit for human papilloma virus, a use method and an application thereof. The kit includes a nucleic acid amplification reagent comprising a primer pair and a probe corresponding to the primer pair. The use method of the kit includes the following steps: 1) extracting nucleic acids from a sample; 2) preparing the reagent; 3) performing PCR amplification; and 4) performing fluorescent detection to a PCR amplification reaction product at 65-72 DEG C, and determining infection type of the HPV according to the changes on the Ct value of a target amplification curve and the Ct value of an internal standard amplification curve. The kit can be used for detecting low-risk and high-risk human papilloma virus and for typing the human papilloma virus. The kit can be used for calculating relative viral load of the HPV, can avoid pollution, can increase treatment throughput of samples, and can avoid missing detection.
Owner:SUZHOU SYM BIO LIFESCI CO LTD
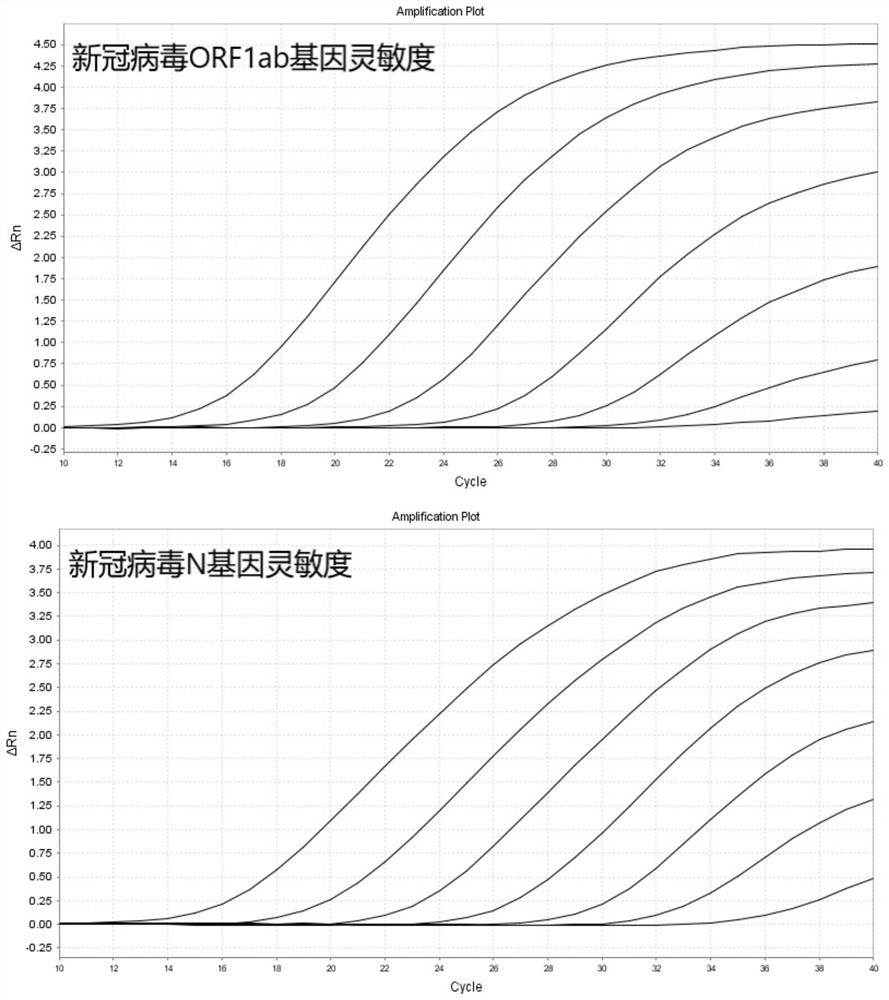
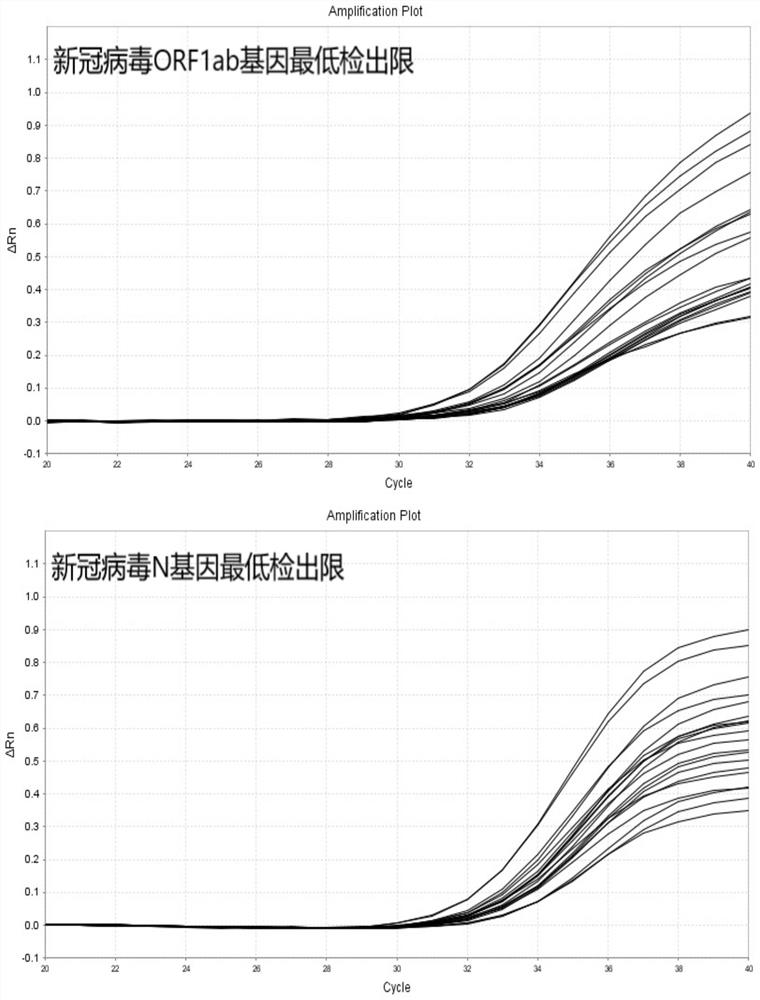
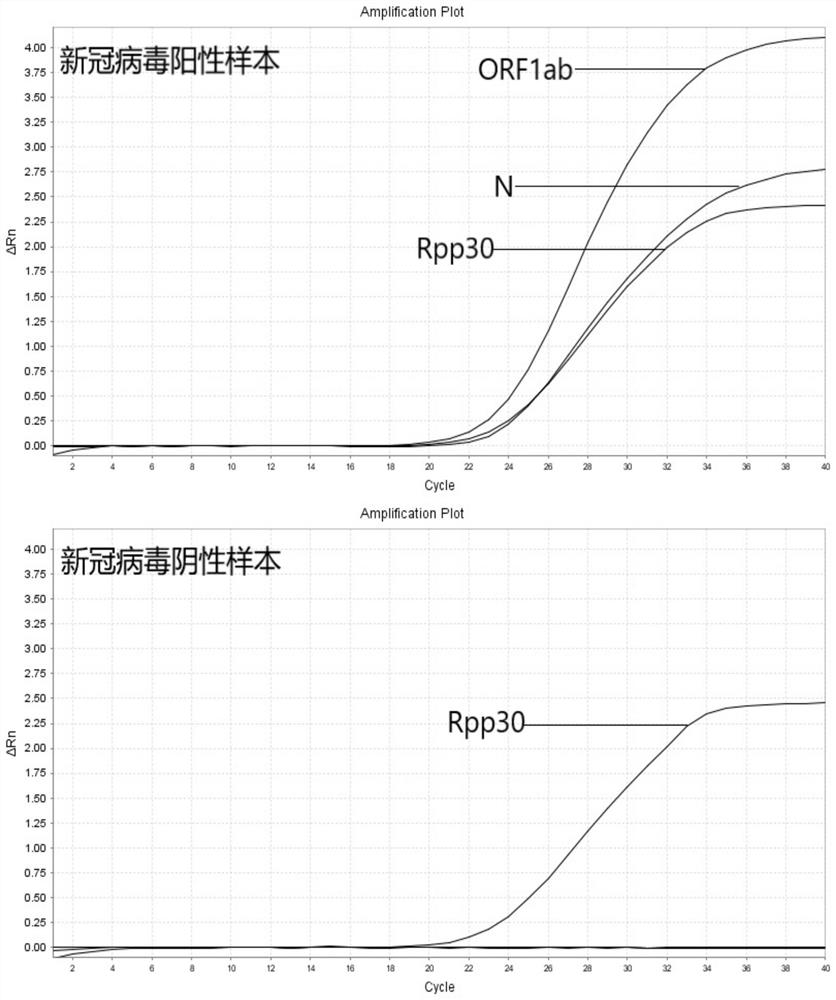
COVID-19 nucleic acid testing primer probe composition, COVID-19 nucleic acid testing kit and COVID-19 nucleic acid testing method
PendingCN111621604AAvoid mutual interferenceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesForward primerViral nucleic acid
The invention relates to the field of the biological technology and the medical examination technology, and provides a COVID-19 nucleic acid testing primer probe composition, a COVID-19 nucleic acid testing kit and a COVID-19 nucleic acid testing method for solving the problems of low accuracy, poor specificity and low sensitivity of a traditional virus nucleic acid testing method. The COVID-19 nucleic acid testing primer probe composition comprises a first primer probe group, a second primer probe group and a third primer probe group, wherein the first primer probe group comprises a forward primer ORF1ab-F, a probe ORF1ab-P and a reverse primer ORF1ab-R; the second primer probe group comprises a forward primer N-F, a probe N-P and a reverse primer N-R; and the third primer probe group comprises a forward primer Rpp30-F, a probe Rpp30-P and a reverse primer Rpp30-R. According to the primer probe composition disclosed by the invention, through artful design of an amplification primer pair and a detection probe, mutual interference between a plurality of primer pairs and corresponding detection probes is avoided. The kit has a simple structure, an interior label is used for monitoring a collection, transportation and extraction process of a sample to be detected, and the false negative of a detection result is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHROMYSKY MEDICAL RES +1
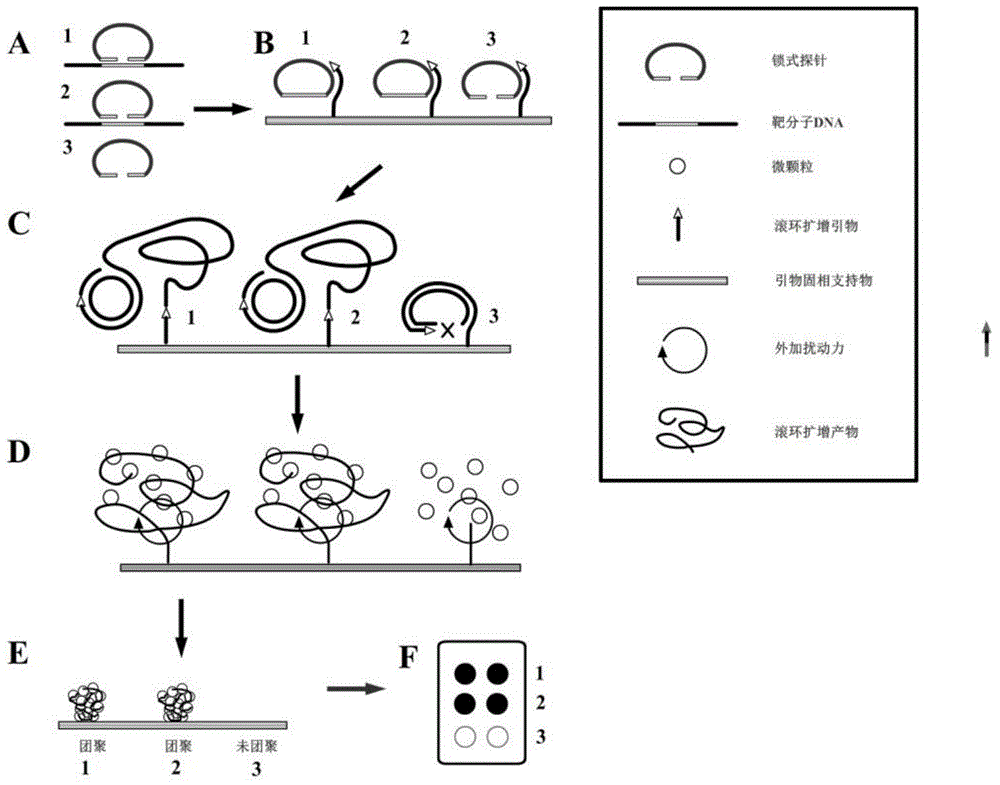
Multiplex nucleic acid visualization detection method and kit based on solid phase rolling circle amplification and particle aggregation
InactiveCN104830985AHigh detection throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMedical department
The invention discloses a multiplex nucleic acid visualization detection method and kit based on solid phase rolling circle amplification and particle aggregation. The provided method utilizes the technologies of solid phase rolling circle amplification on a sheet and magnetic particle aggregation to achieve the visualization detection on multiplex nucleic acid characteristic sequences of a sample. The provided method has the characteristics of high detection flux, high sensitivity, quick detection speed, and simple operation. Furthermore, the method does not need expensive thermal amplification cycler or fluorescence detection system, can be used in medical service platforms in different levels, and are especially suitable for different medical departments in remote areas or developing areas.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com