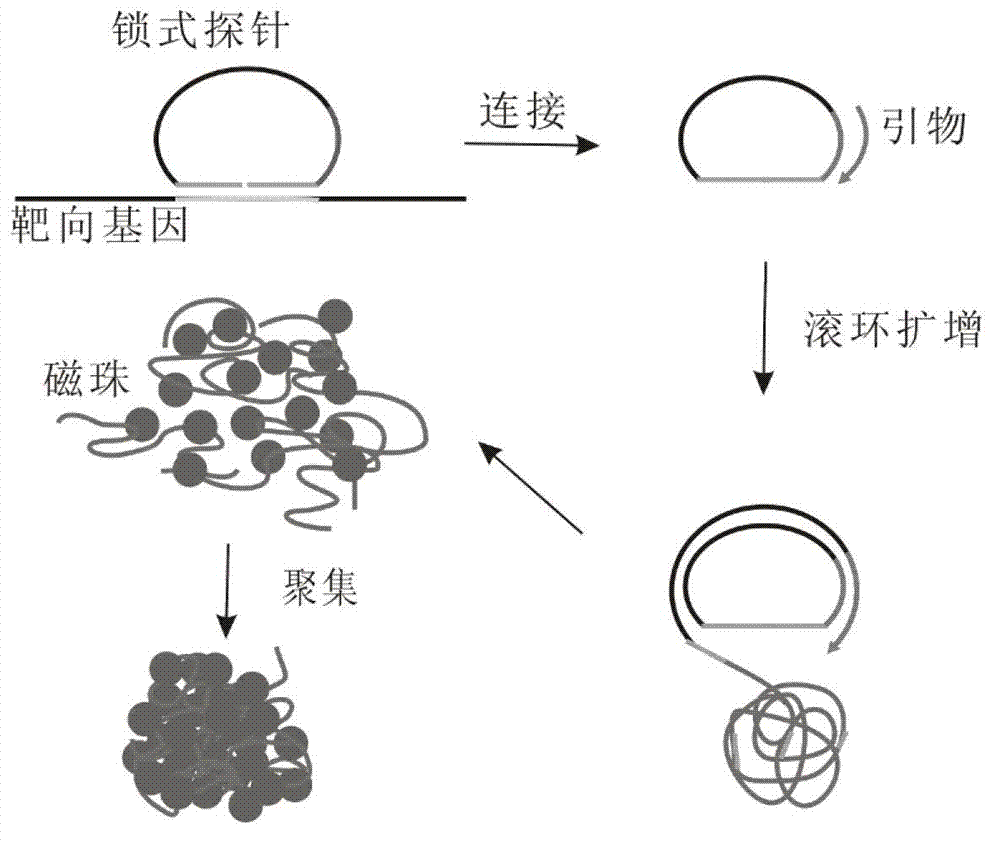
Method for detecting nucleic acid
A detection method and nucleic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as complicated operation, and achieve the effect of simple experimental device, convenient operation, and low professional technical requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Ligase Selection
[0040] Target molecule: ACTCAGAGGAAGAAAACGATGAAATAGATGGAG.
[0041] 1. Design the following padlocks and amplification primers according to the above target molecules.
[0042] Padlock probes (with a phosphate group at the 5' end):
[0043] PO 3 -GTTTTTCTTCCTCGCTAAGTCTAAGAAAGTAGGATAGGACAGATAGCCATCTATTTCATC.
[0044] Primer: TTTCTTAGACTTAGCG.
[0045] 2. Add the padlock probe, target nucleic acid molecule, ligase and reaction buffer to 10 μL of the ligation system, and react at the corresponding temperature for 1 hour.
[0046] In this example, three kinds of ligases were used respectively, and the formulation of the connection system and the conditions of the connection reaction are as follows:
[0047] 1) Taq DNA ligase
[0048] 10μL ligation system containing 20mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), 25mM KAc, 10mMMg(Ac) 2 , 10mM DTT, 1mM NAD, 0.1% Triton X-100, 20U thermophilicTaq DNA ligase (New England BioLabs, Jitai Bio, China), 500nM phosphoryla...
Embodiment 2
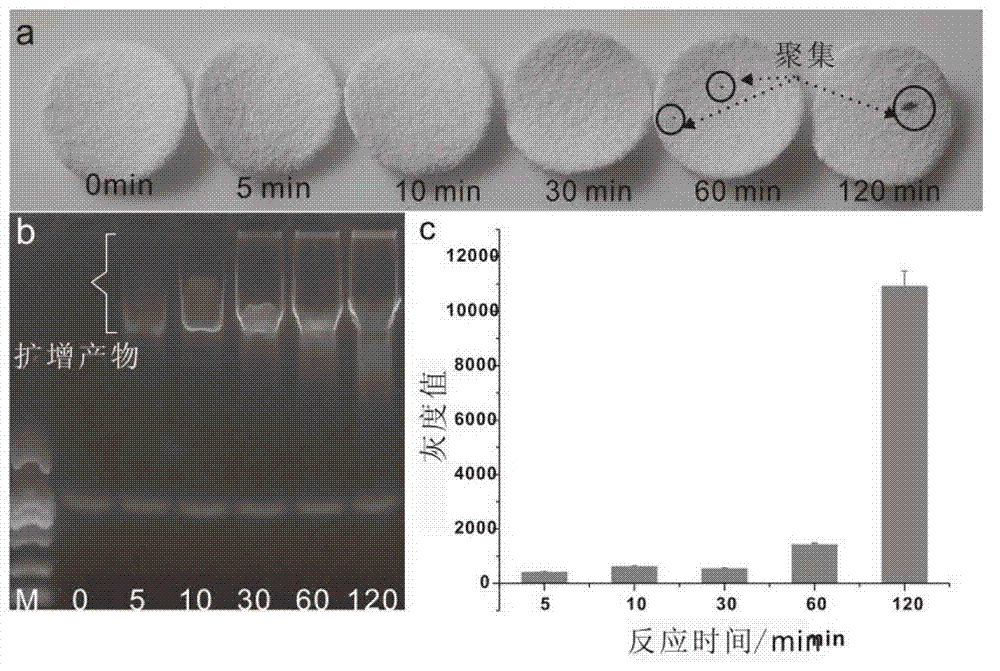
[0058] The ligation efficiency and sequence recognition ability of DNA ligase directly affect the sensitivity and specificity of the detection method. The ligation efficiency of T4 DNA ligase is relatively high, and the cost is low, but because its reaction temperature is only 16°C, at this temperature Under certain conditions, incompletely matched sequences (such as mutant sequences) tend to hybridize with padlock probes to form double strands. If the mutation site happens not to be at the ligation site, it will also be ligated, resulting in non-specific ligation and high background . The reaction temperature of Taq DNA ligase is relatively high (higher than 45°C), which is higher than the hybridization Tm of the mutant sequence. Under this condition, the mutant sequence will not hybridize with the padlock probe to form a double strand, so the background is relatively low. Example 2 Rolling Circle Amplification Time Optimization
[0059] Target molecule: ACTCAGAGGAAGAAAACGAT...
Embodiment 3
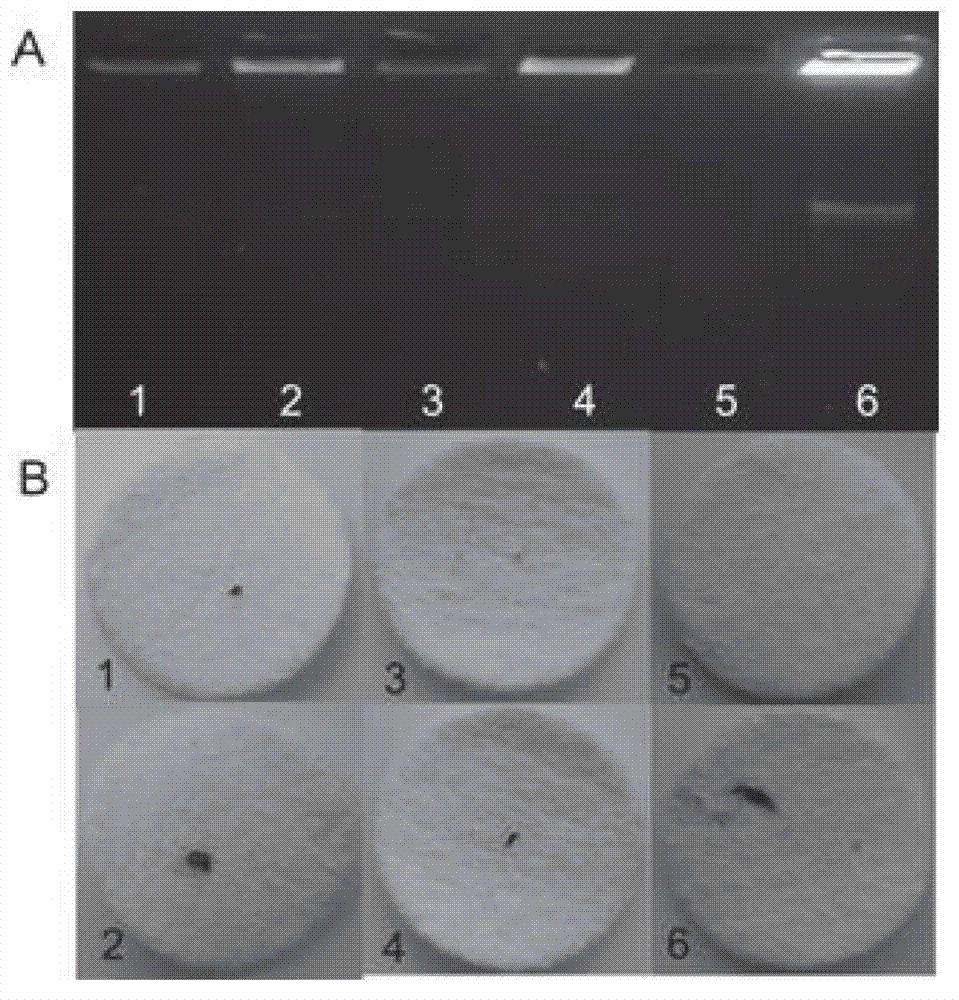
[0072] Embodiment 3 sensitivity analysis
[0073] The operation method of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 2, and the reaction time is selected as 4 hours, the difference is that the copy number of the target molecule is 10 respectively. 6 ~10 10 , the result is as Figure 4 As shown, it can be seen that this method can detect at least 10 7 Copies (equivalent to 17 amol) of the target molecule. In addition, it was also found that the copy number of the target molecule is within a certain range, and there is a linear relationship with the aggregation amount of the magnetic beads, and there are obvious differences in the aggregation and dispersion results of the magnetic beads, which is very easy to judge.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com