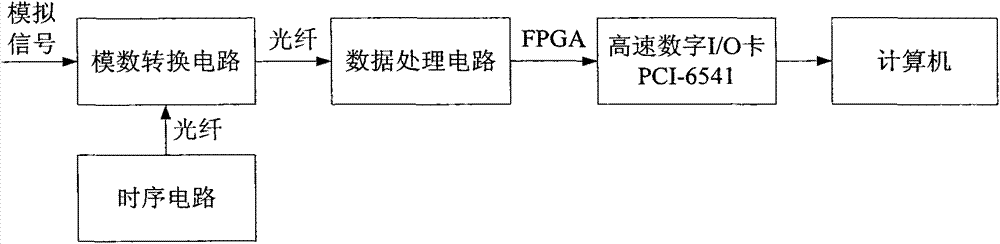
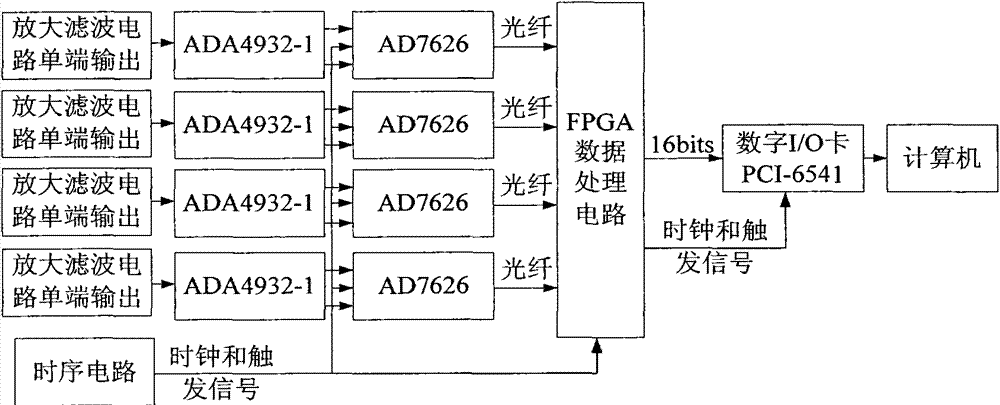
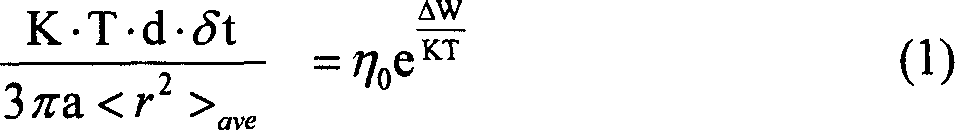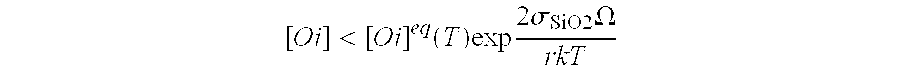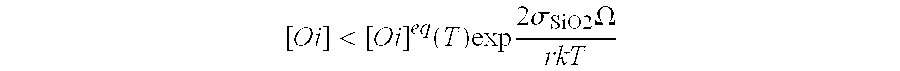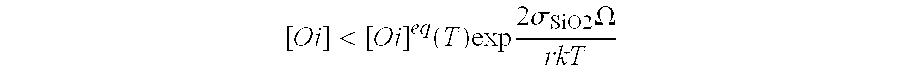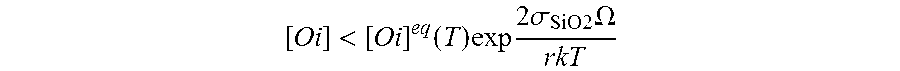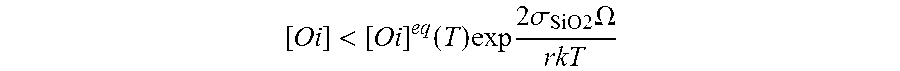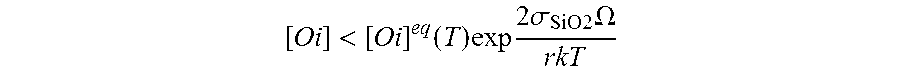Patents
Literature
47 results about "Boltzmann constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
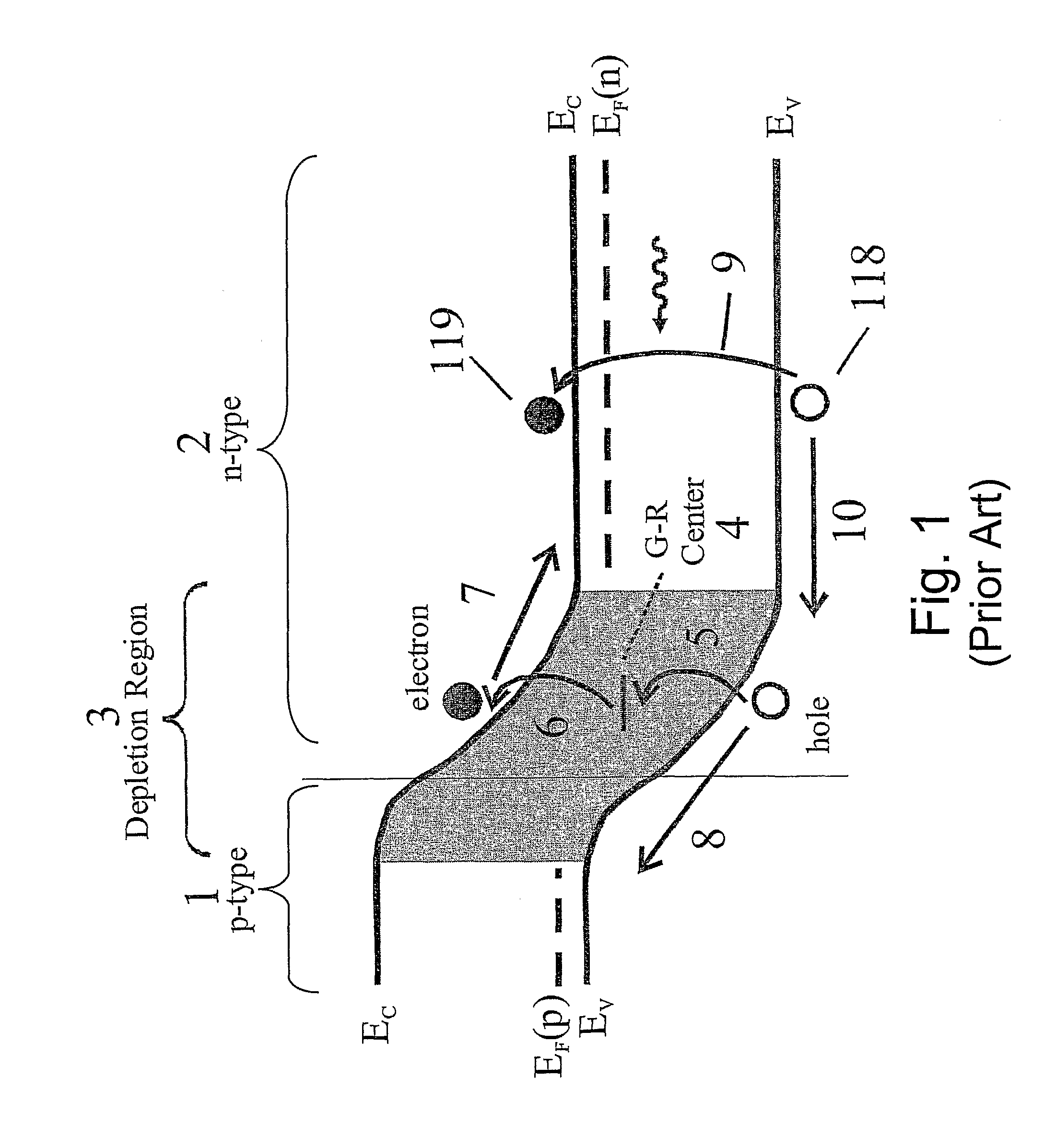
The Boltzmann constant (kB or k), named after its discoverer, Ludwig Boltzmann, is a physical constant that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula. The Boltzmann constant has the dimension energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy.
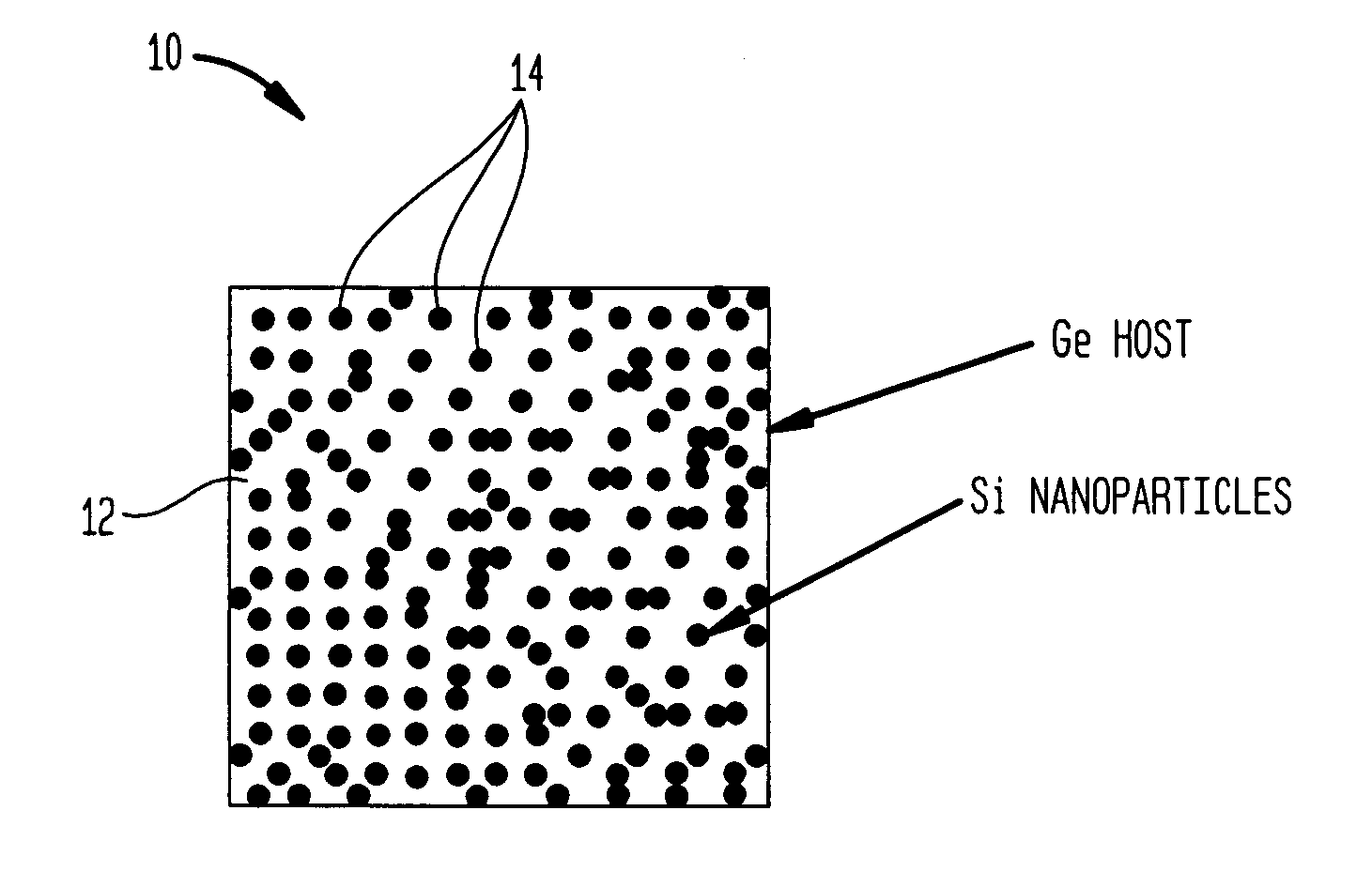
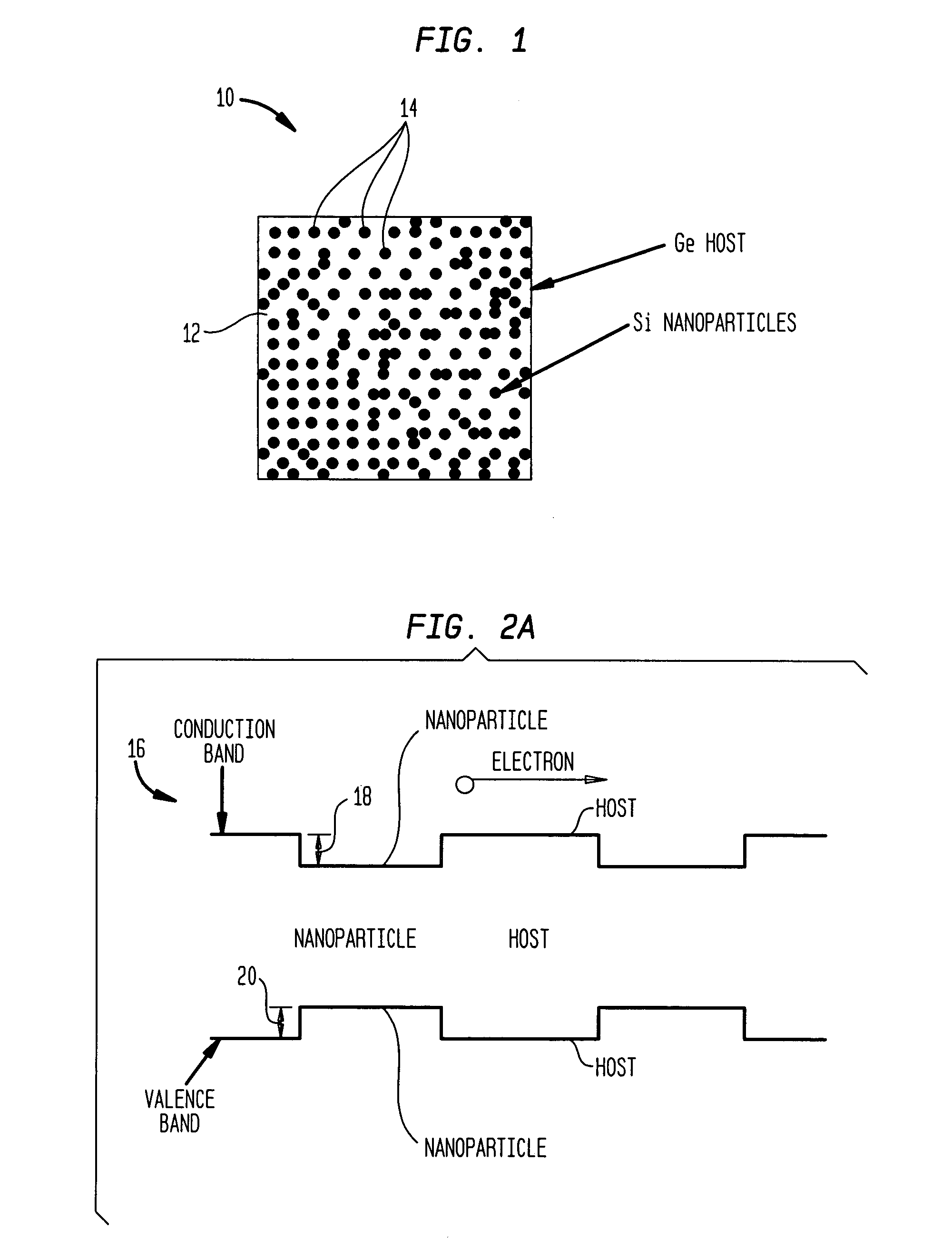
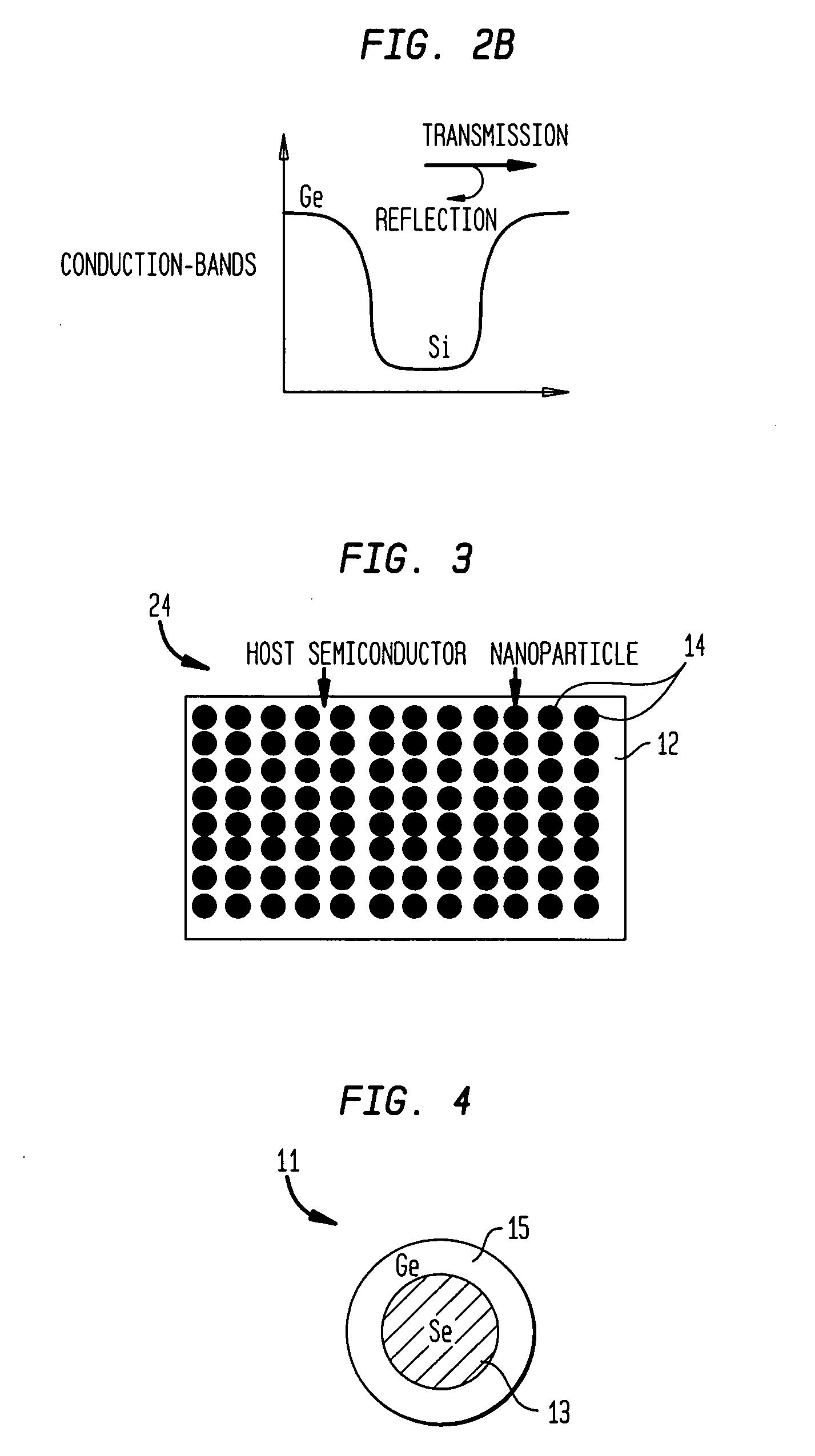
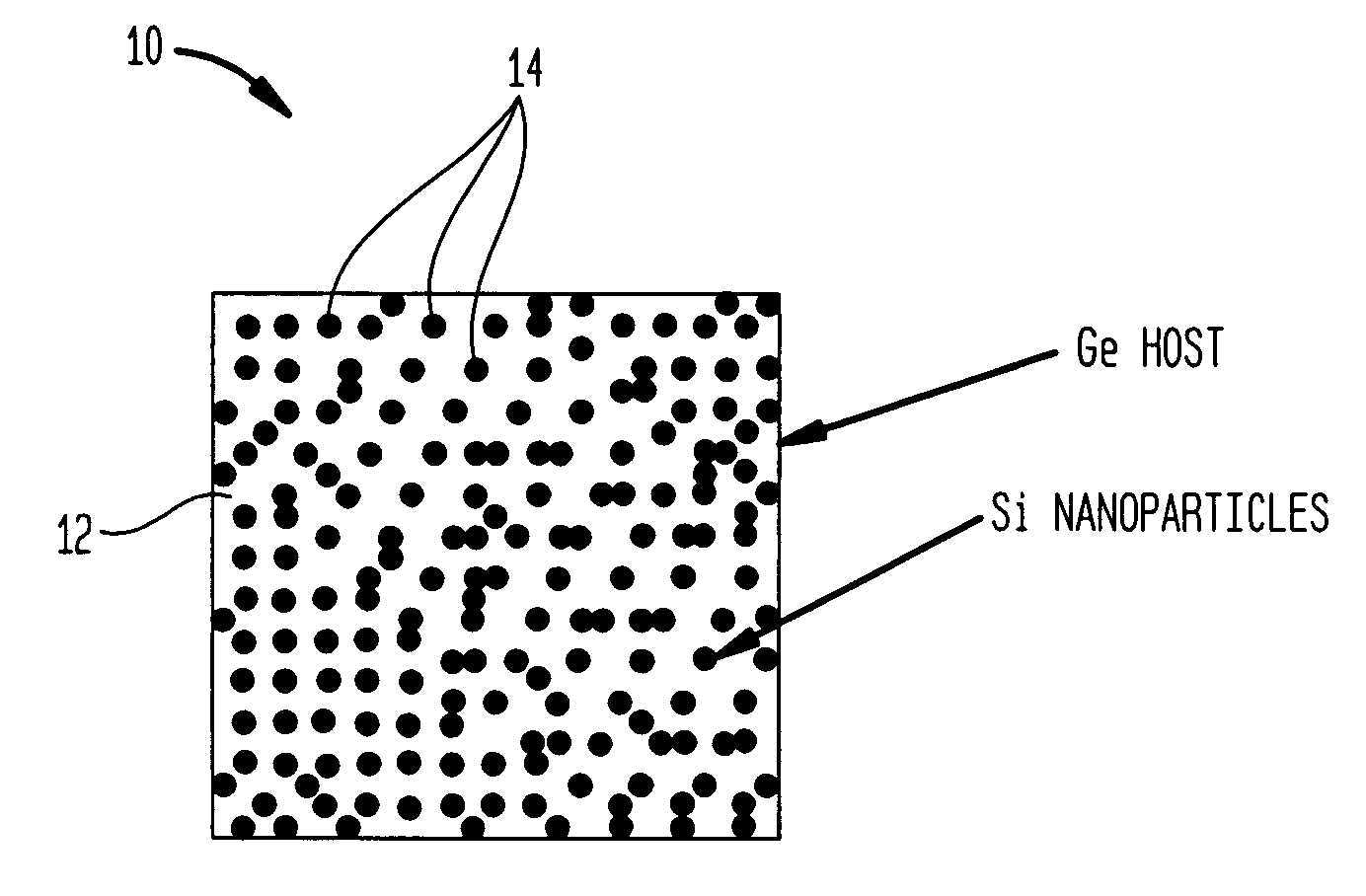
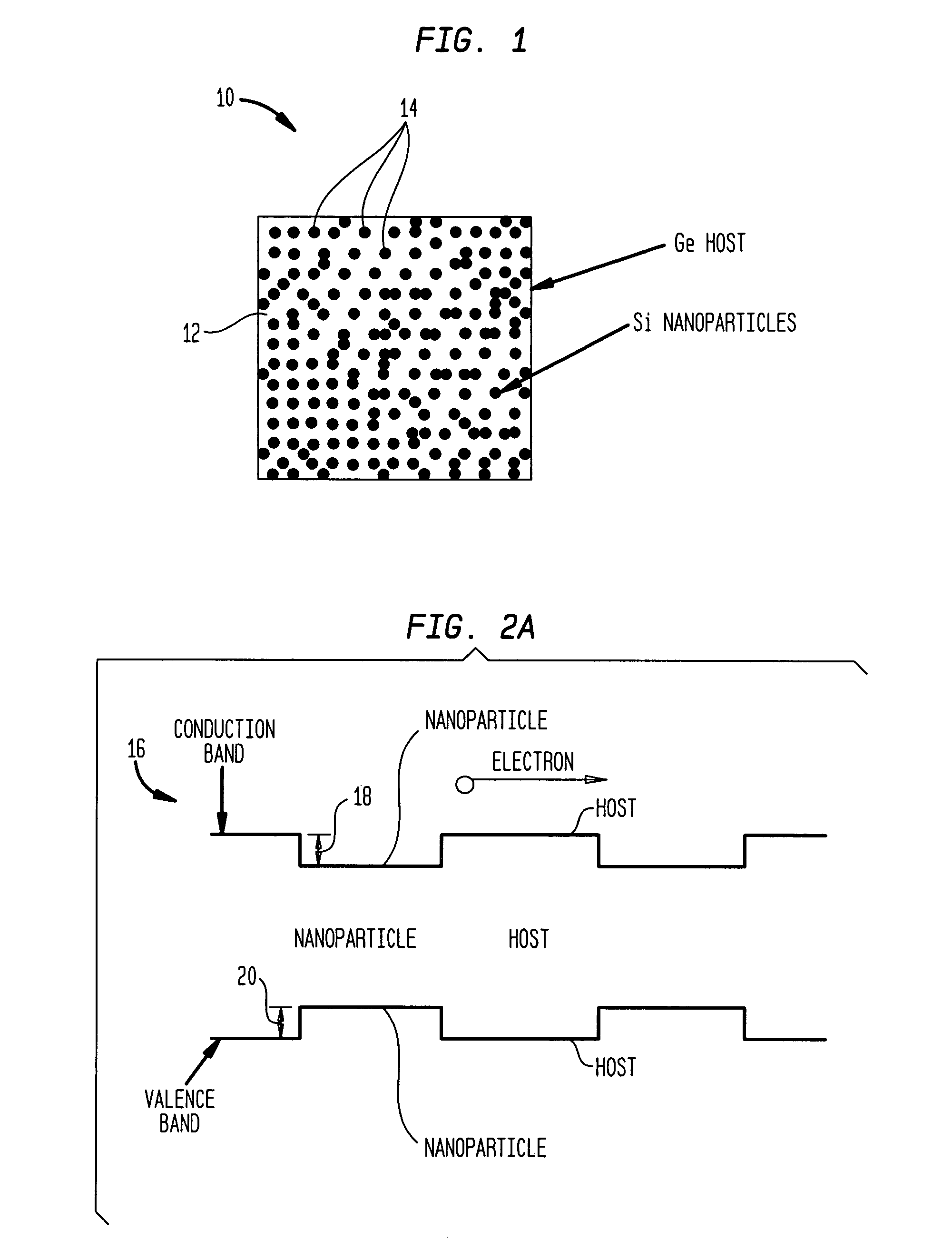
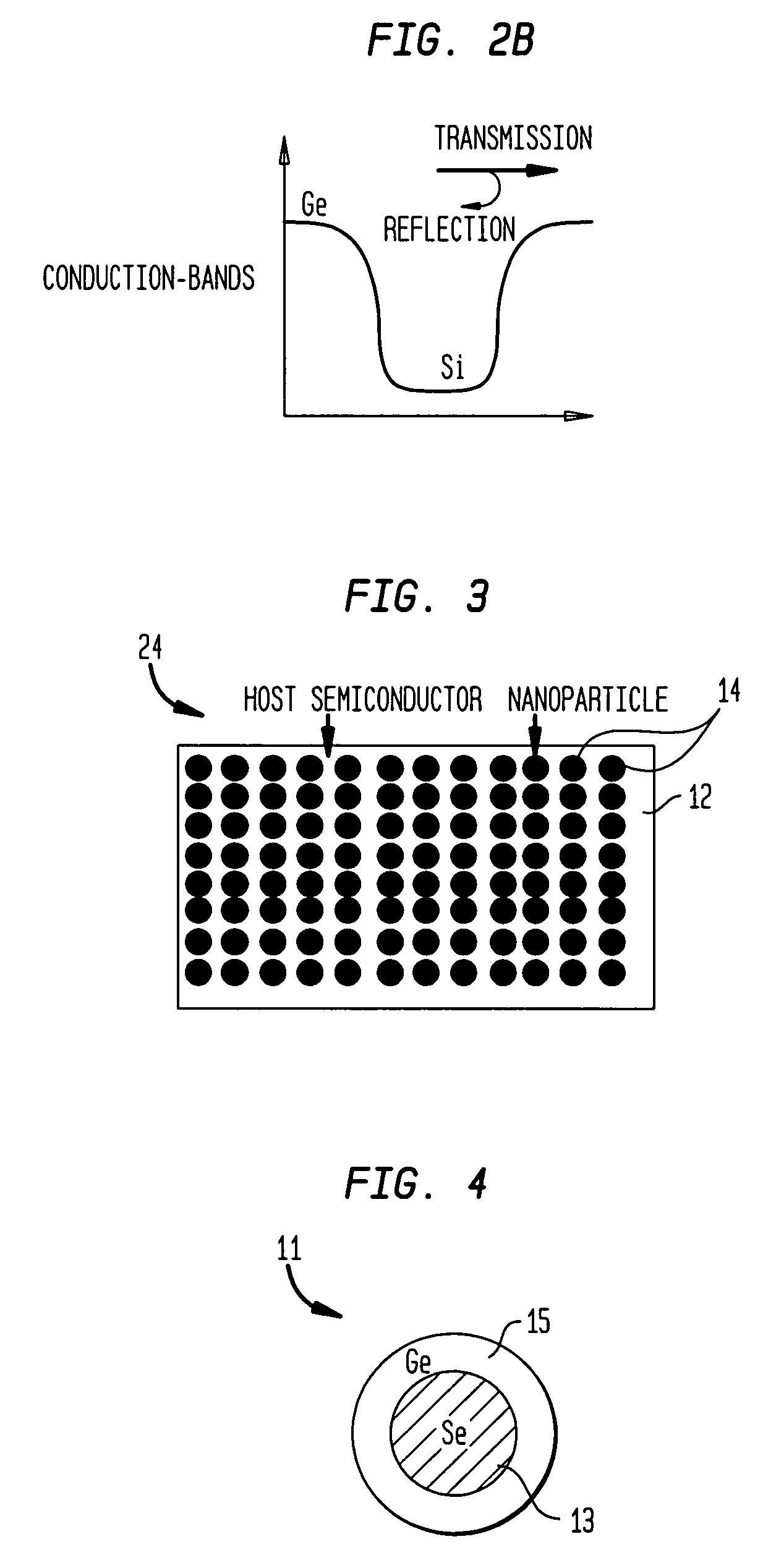
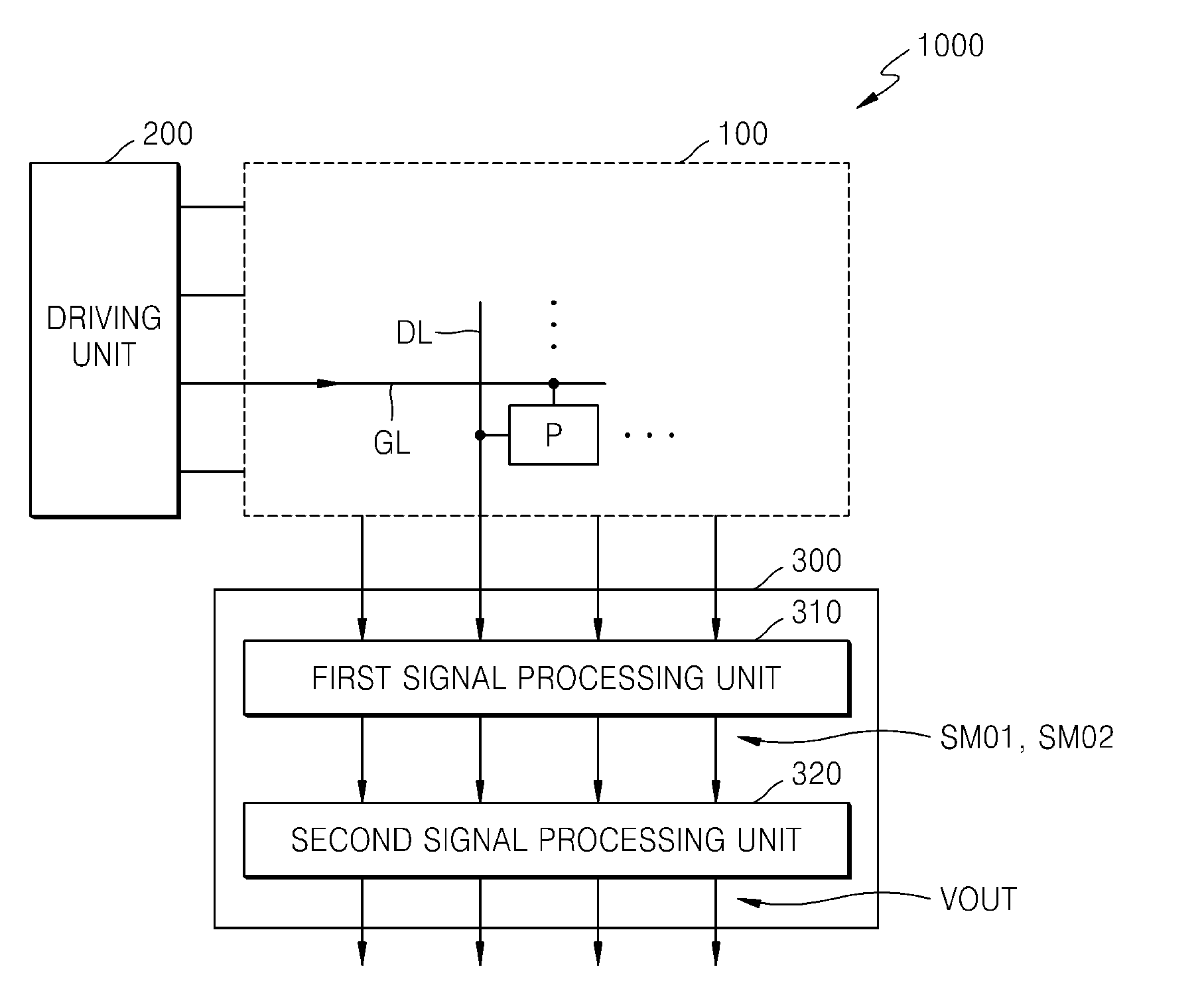
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
InactiveUS20060102224A1Improve thermoelectric performanceLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectValence bandConduction band
The present invention is generally directed to nanocomposite thermoelectric materials that exhibit enhanced thermoelectric properties. The nanocomposite materials include two or more components, with at least one of the components forming nano-sized structures within the composite material. The components are chosen such that thermal conductivity of the composite is decreased without substantially diminishing the composite's electrical conductivity. Suitable component materials exhibit similar electronic band structures. For example, a band-edge gap between at least one of a conduction band or a valence band of one component material and a corresponding band of the other component material at interfaces between the components can be less than about 5 kBT, wherein kB is the Boltzman constant and T is an average temperature of said nanocomposite composition.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
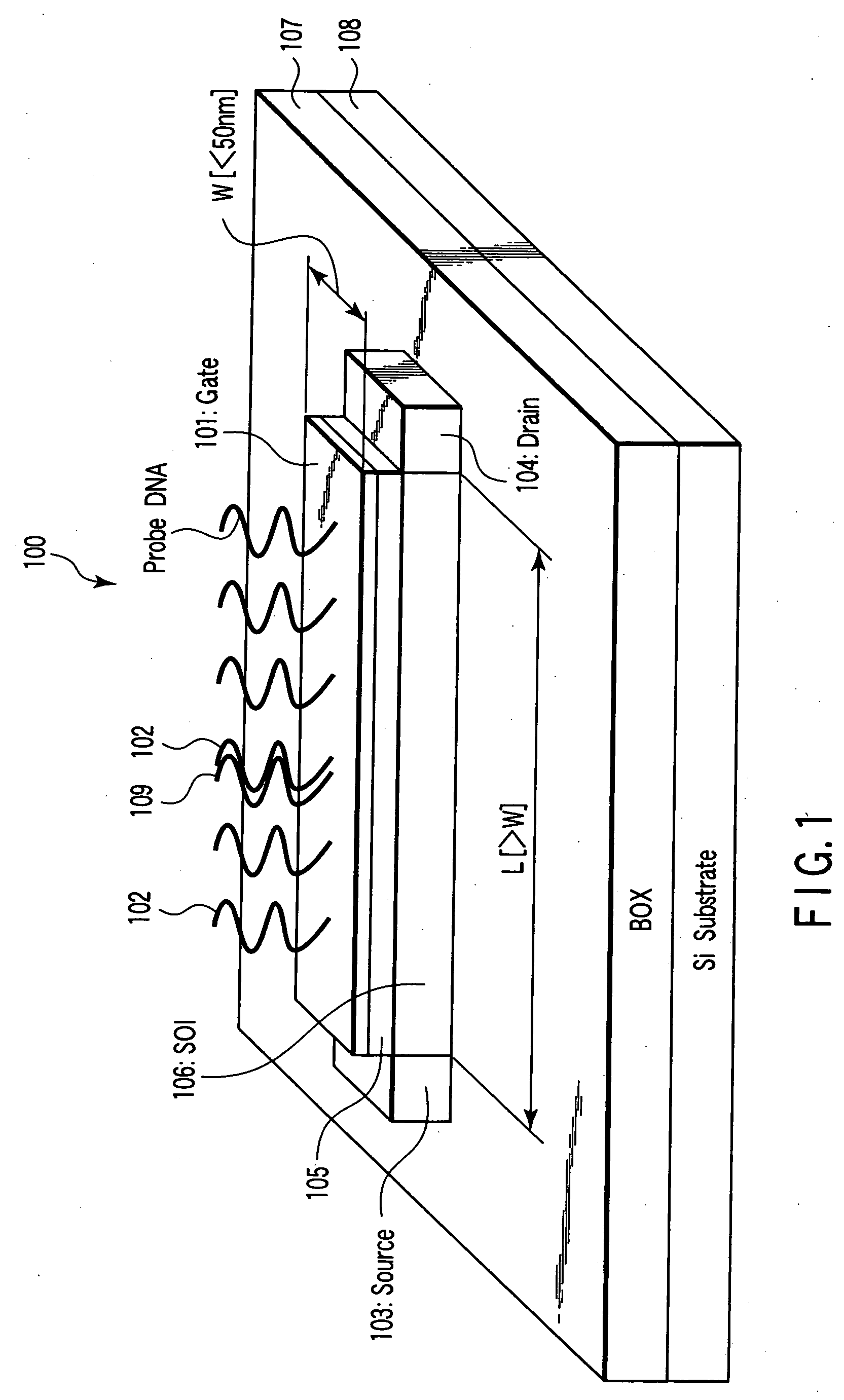
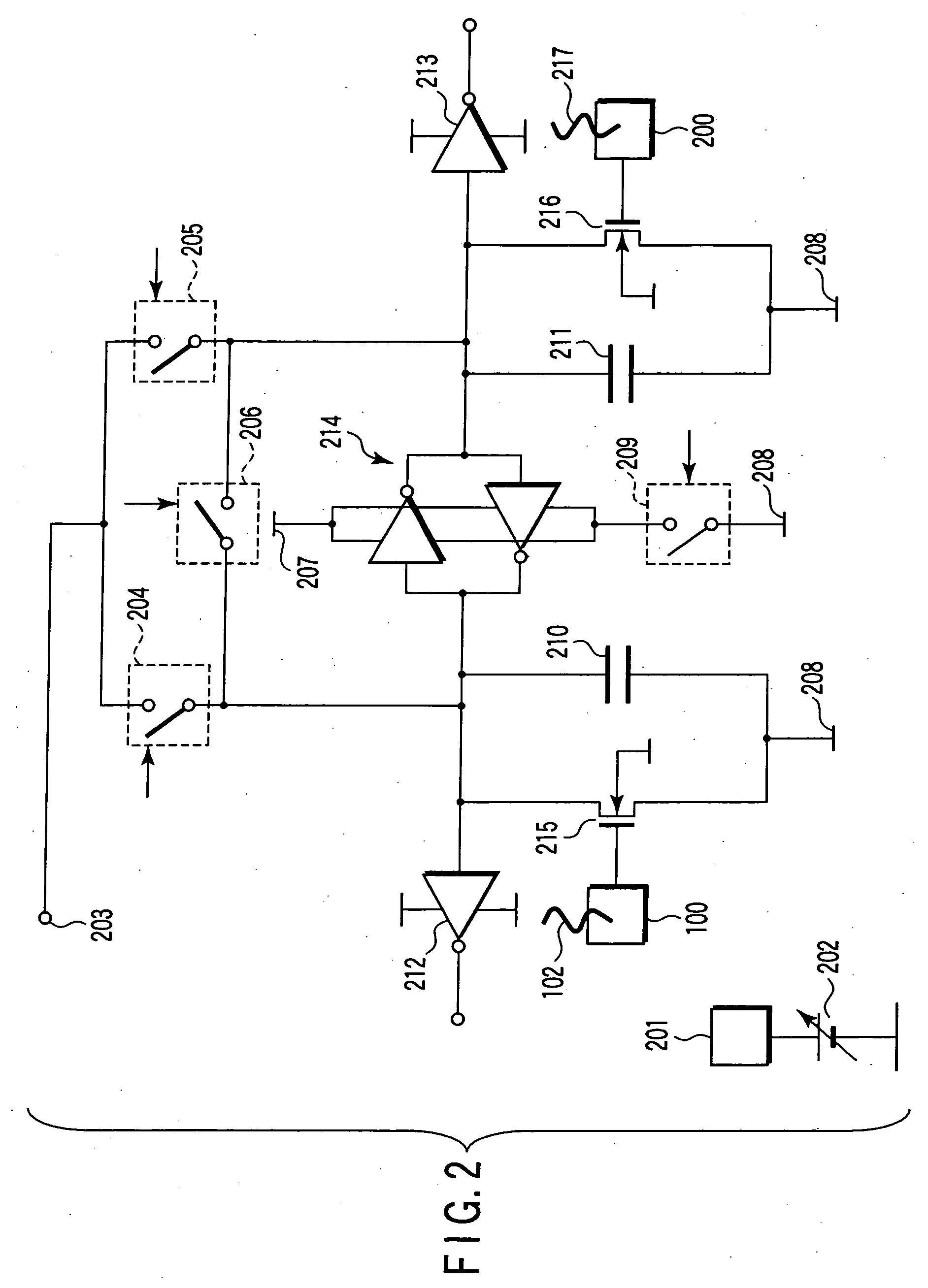
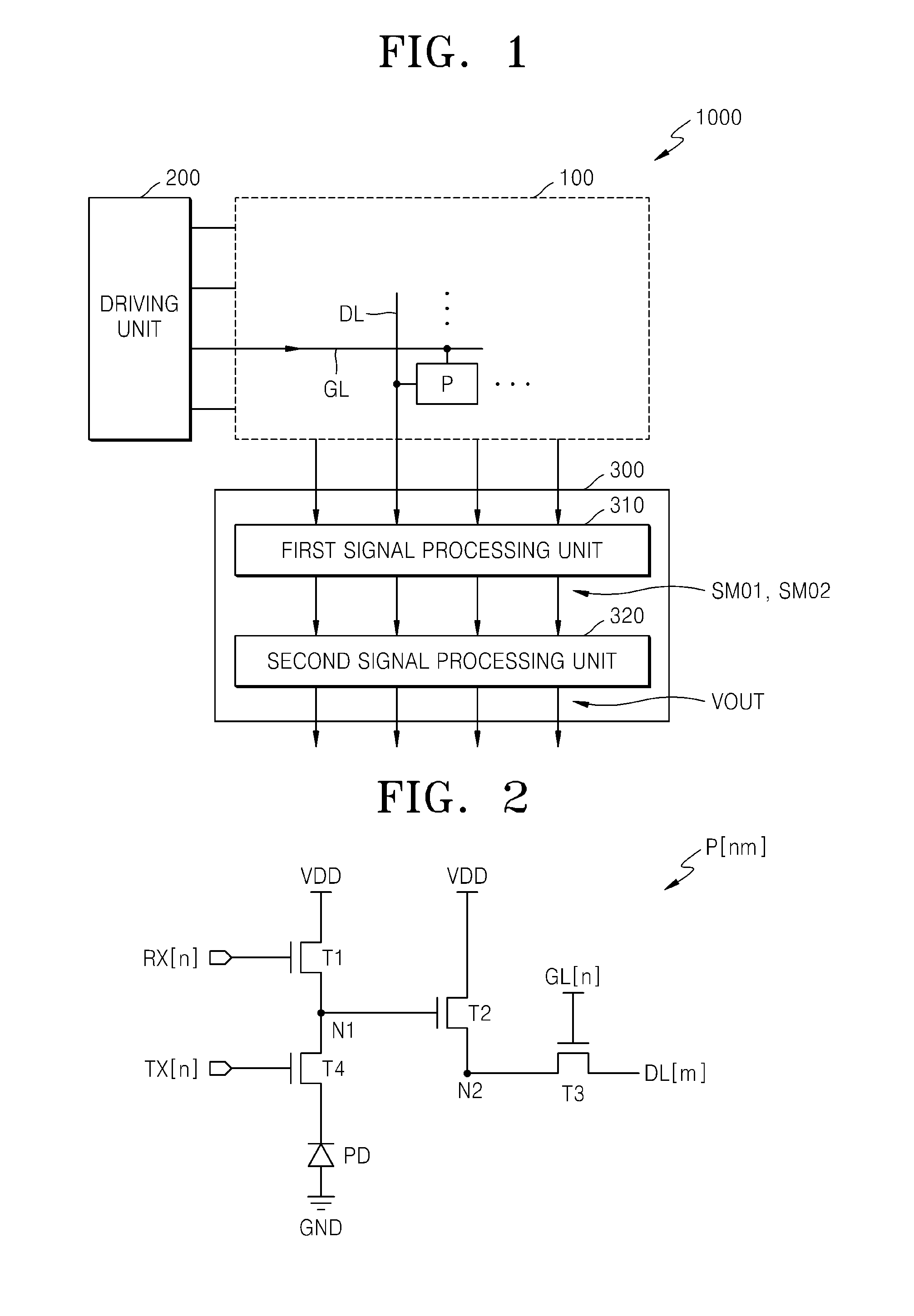
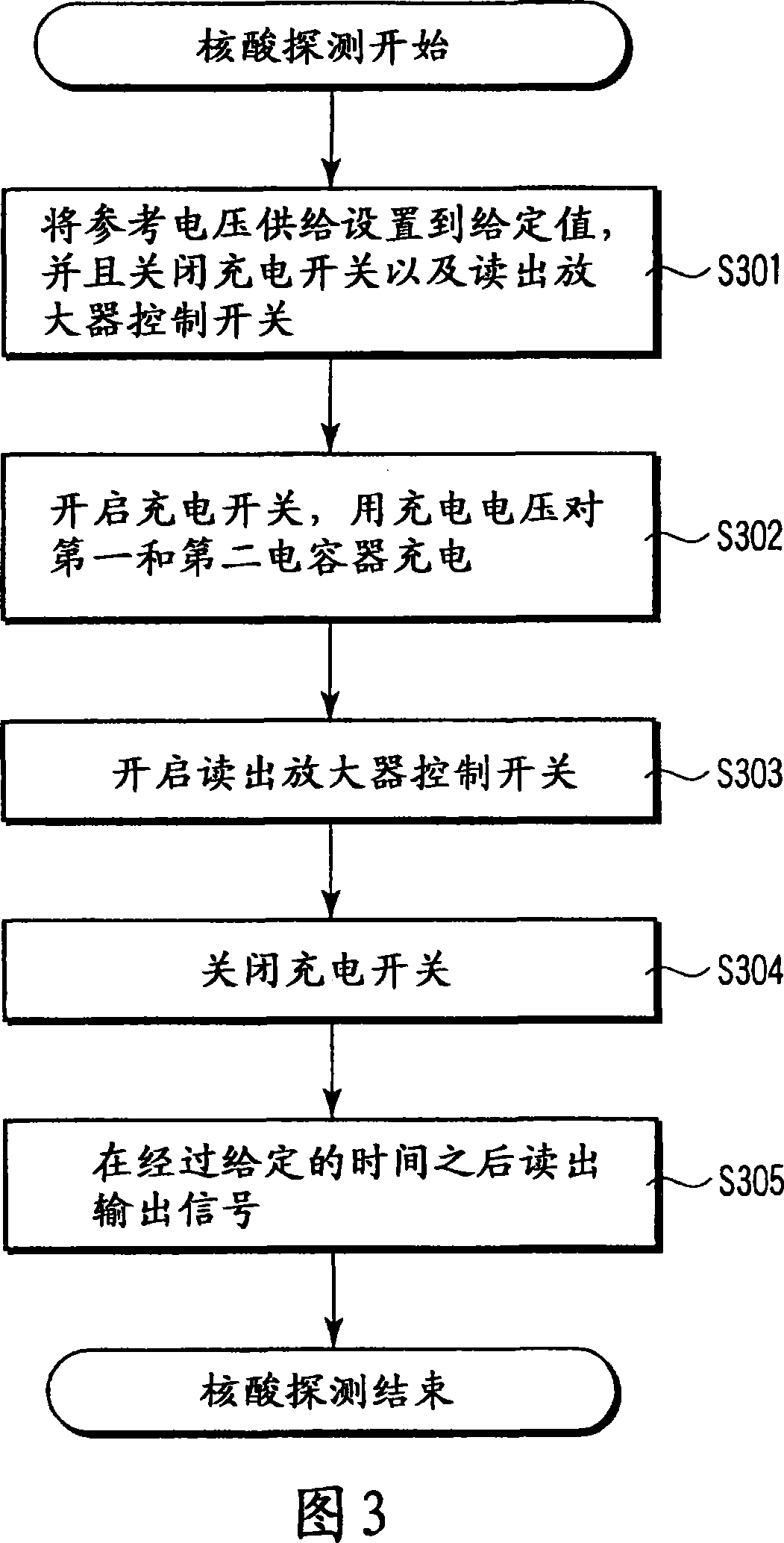
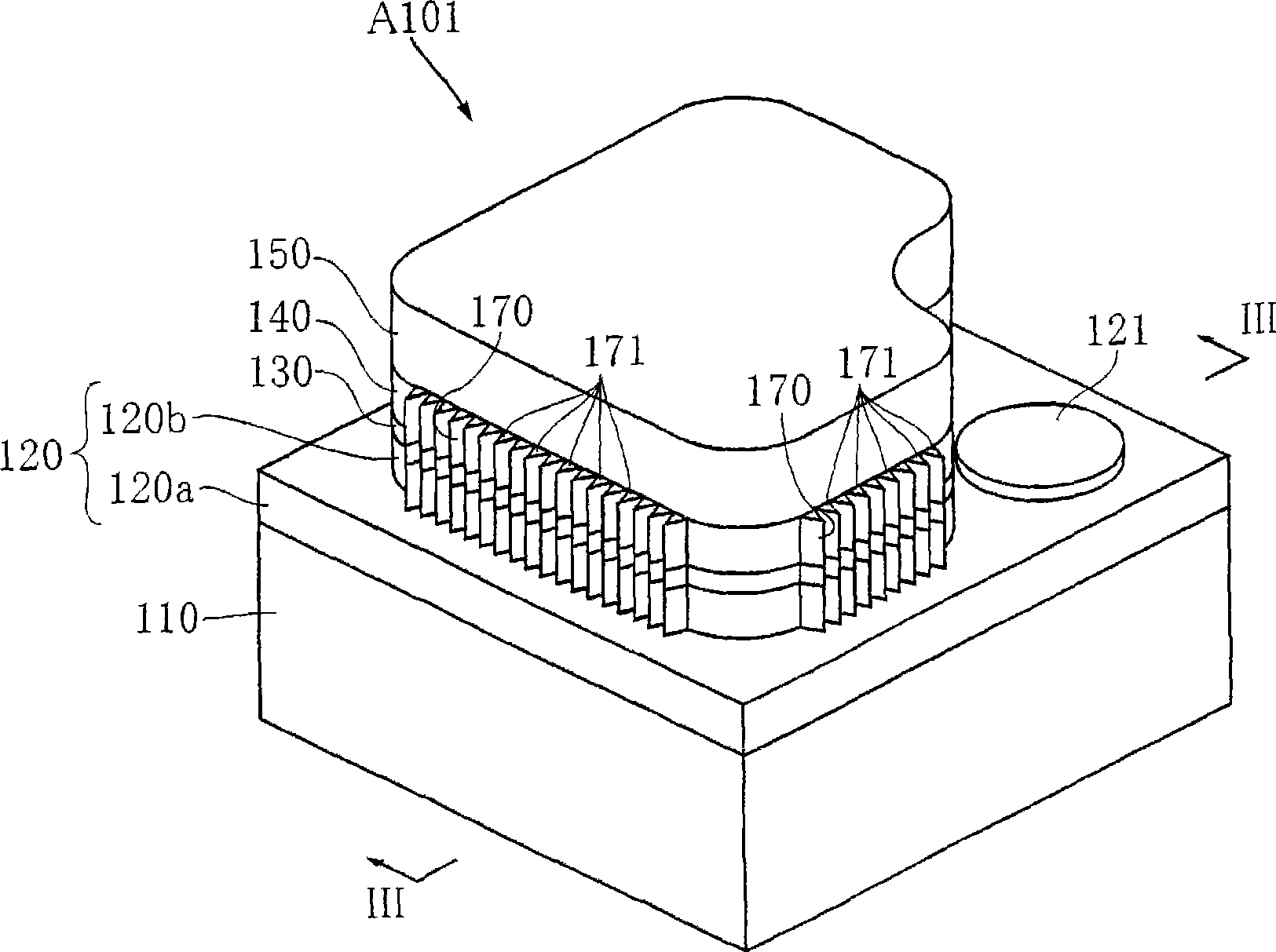
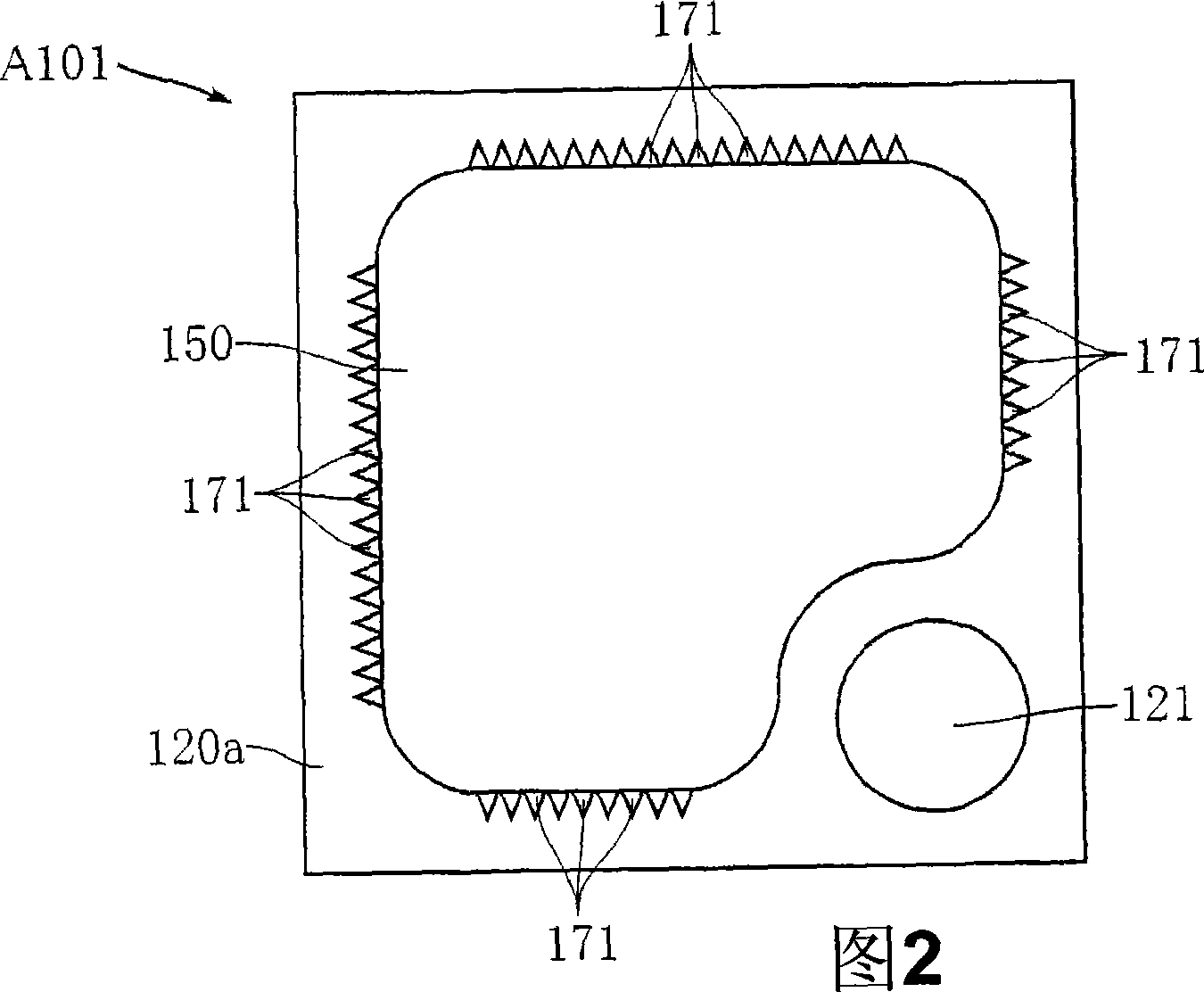
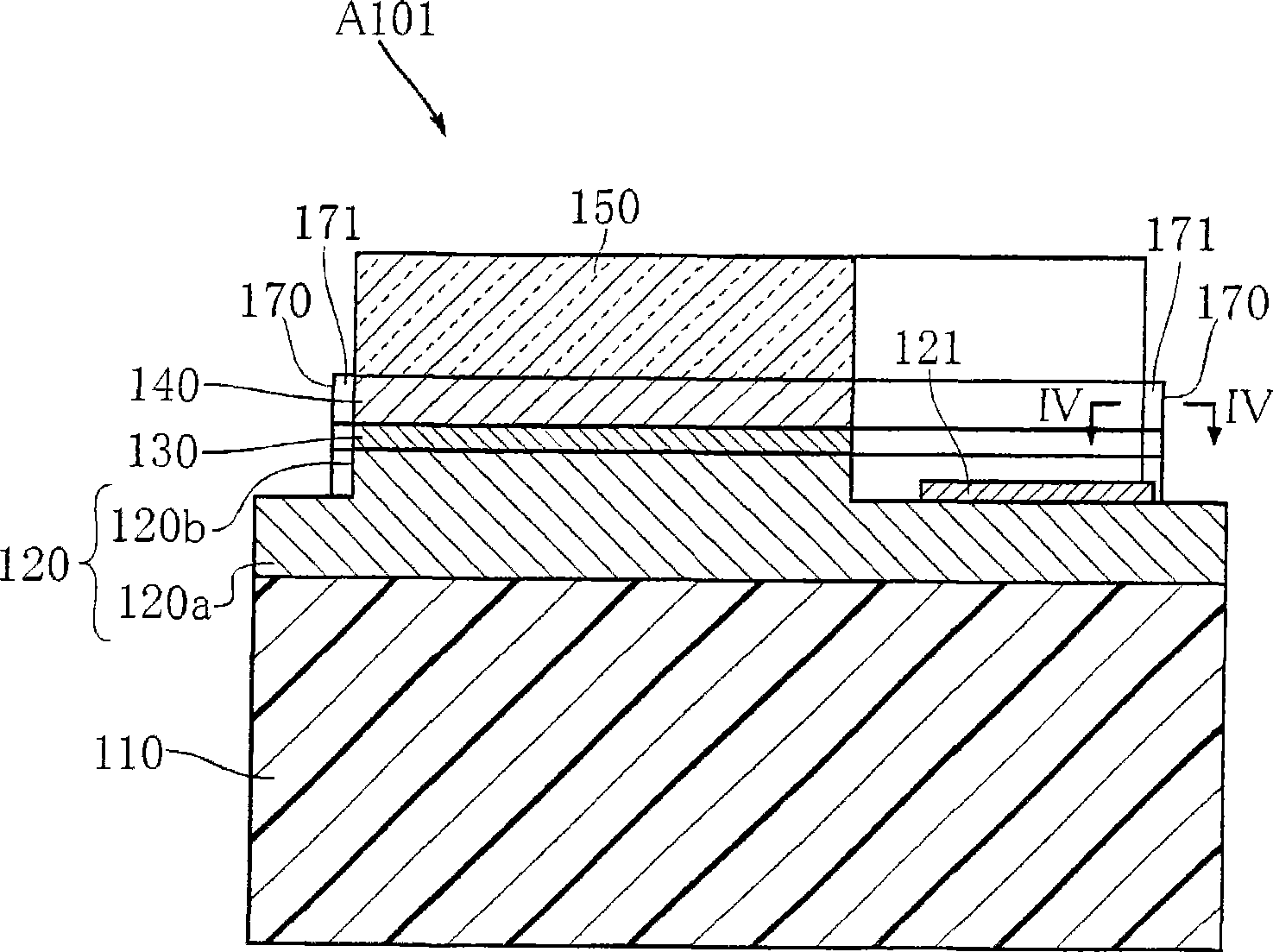
Nucleic acid detecting sensor, nucleic acid detecting chip, and nucleic acid detecting circuit
InactiveUS20060147983A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDielectricNucleic Acid Probes
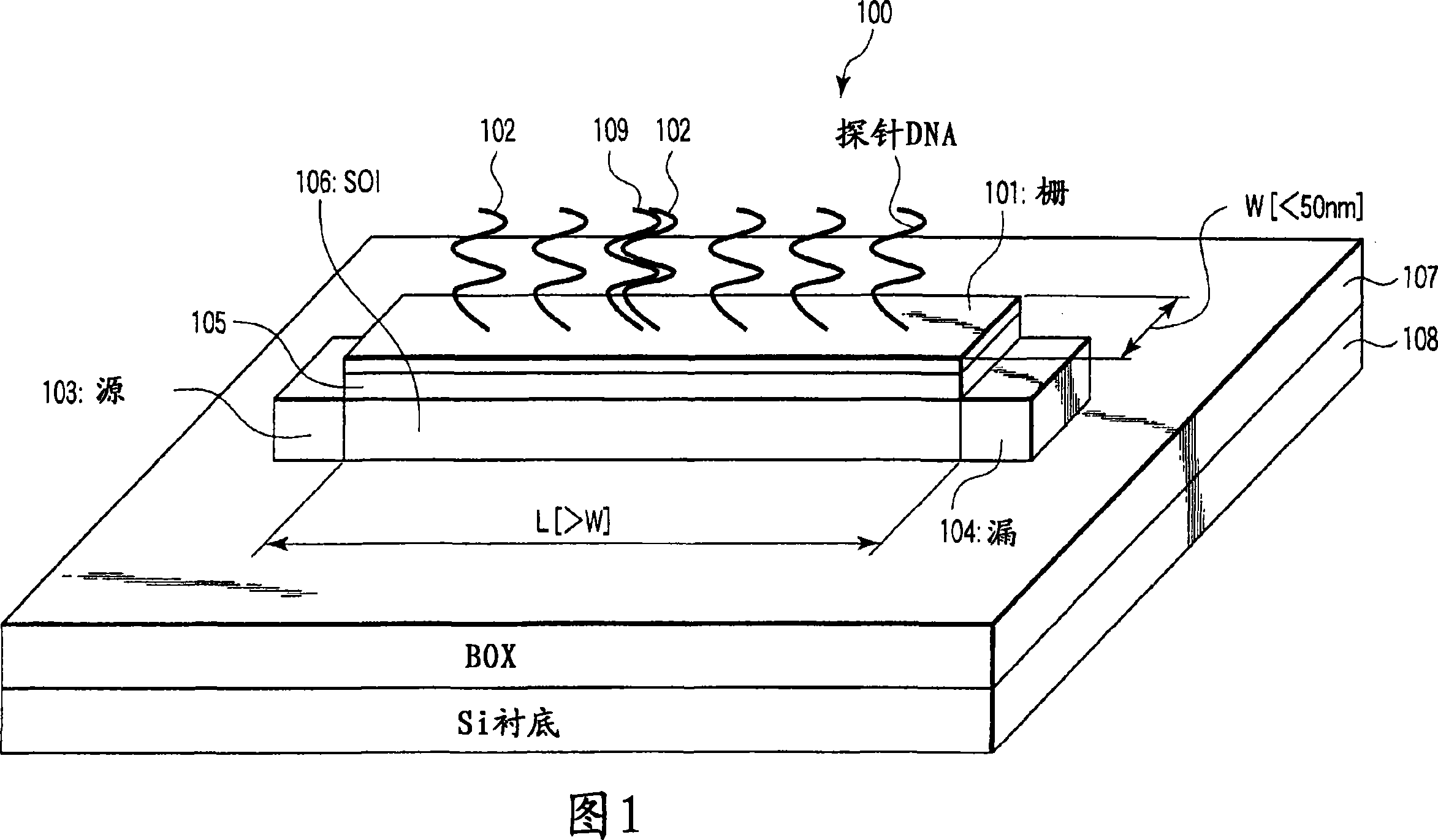
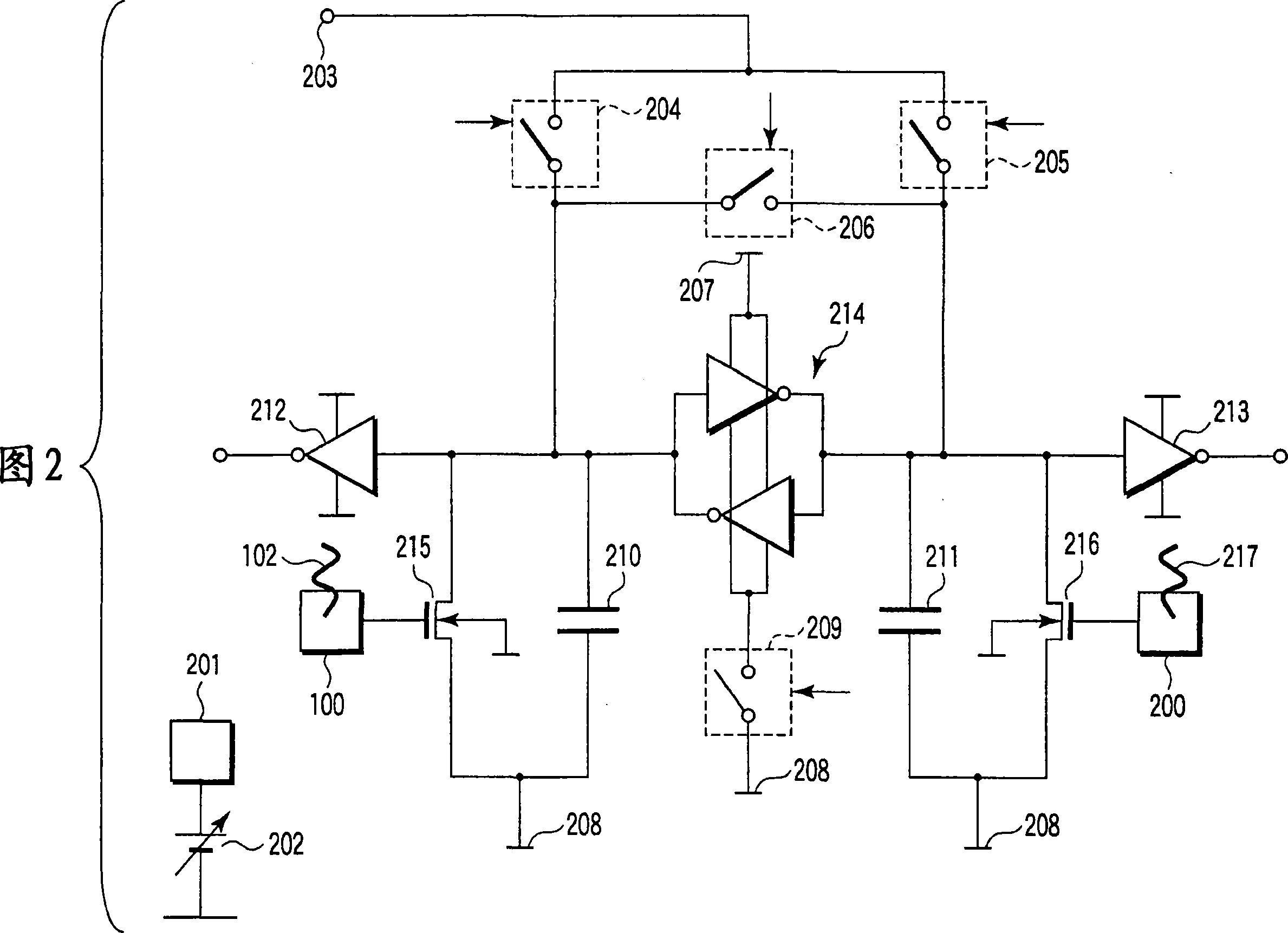
Nucleic acid detecting sensor includes field-effect transistor, detector which detects target nucleic acid molecules having sequences from sample based on degree of a variation in threshold voltage of field-effect transistor, and at least one nucleic acid probe molecule which is hybridized with corresponding one of target nucleic acid molecules, and is immobilized on gate of field-effect transistor, wherein gate width of field-effect transistor is of order of length obtained by expression given below (ε0εrkBT / e2n)1 / 2 where ε0 is dielectric constant of vacuum, εr is relative dielectric constant of channel region, kB is Boltzmann constant, T is absolute temperature of the channel region, e is elementary charge, and n is equilibrium carrier density in the channel region in field-effect transistor where channel is formed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
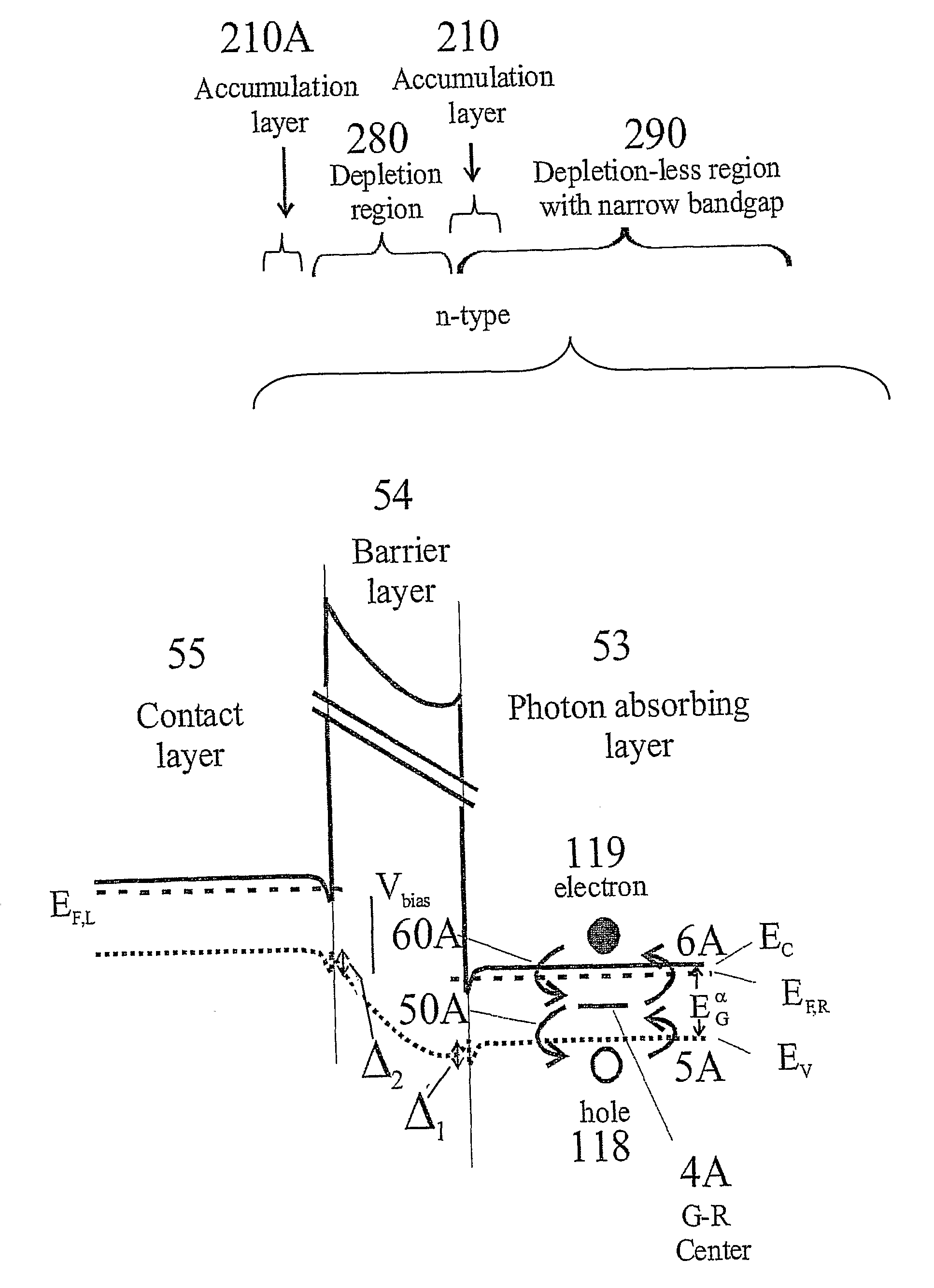
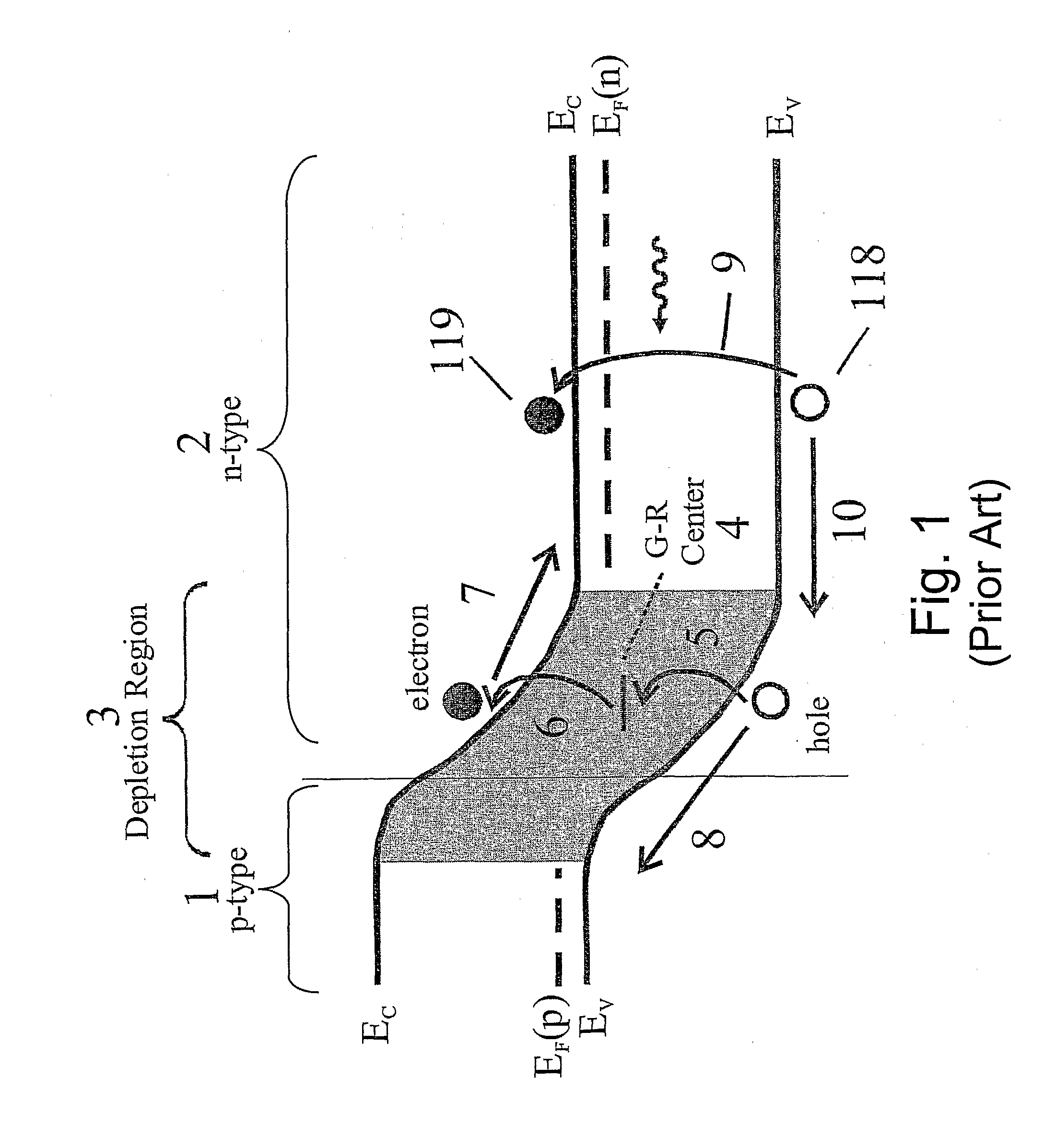
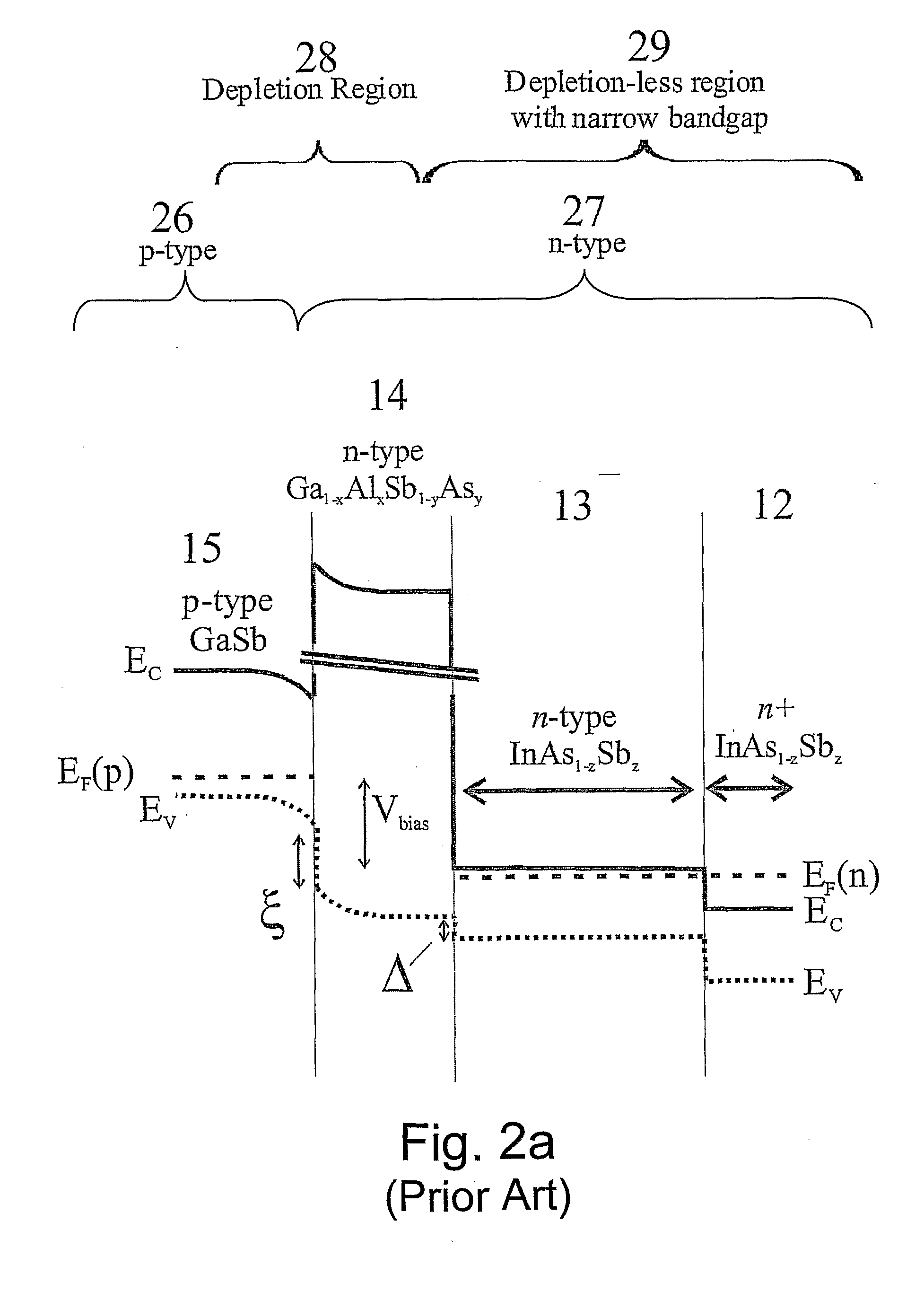
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090256231A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal biasPhotodetector
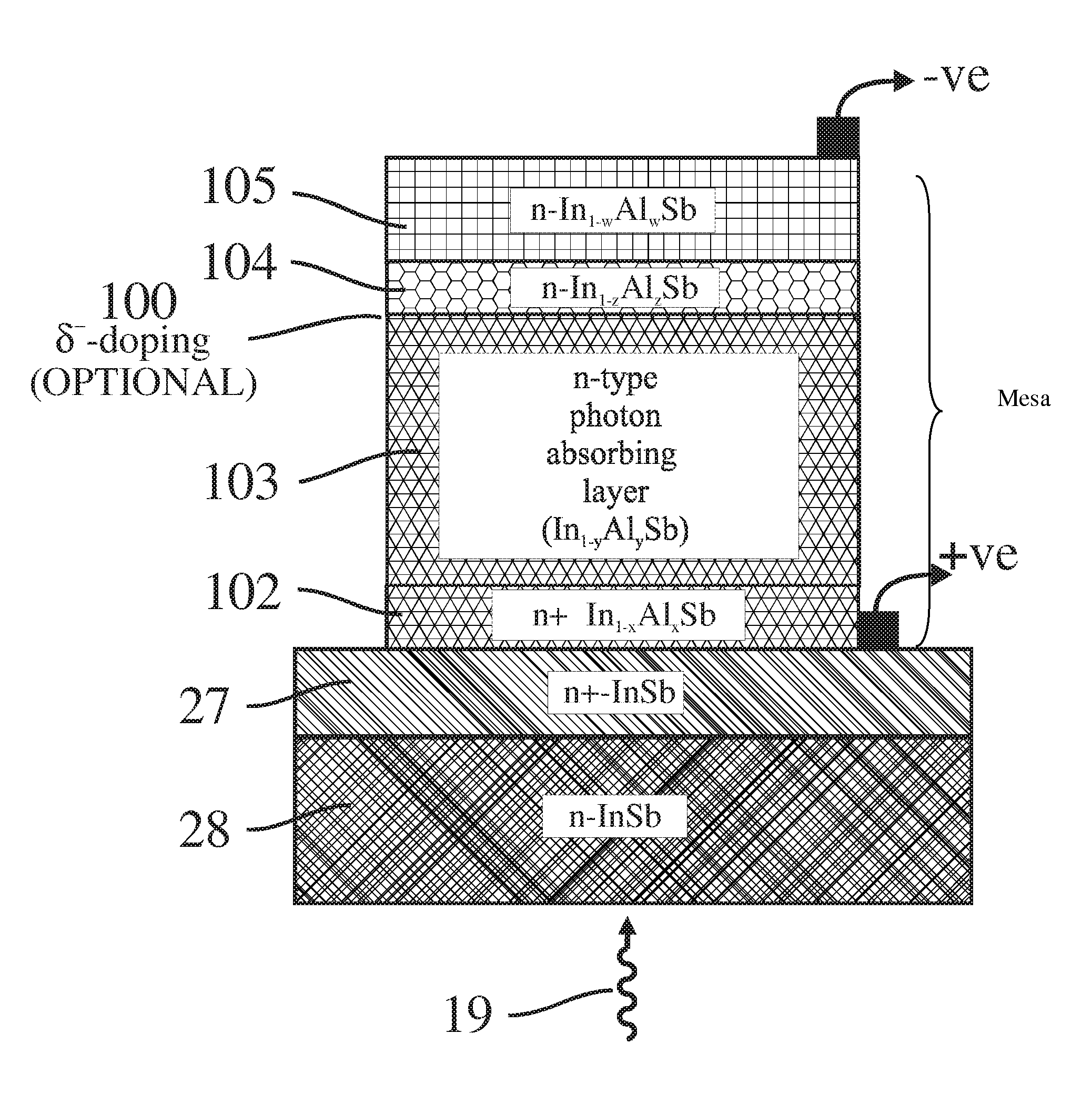
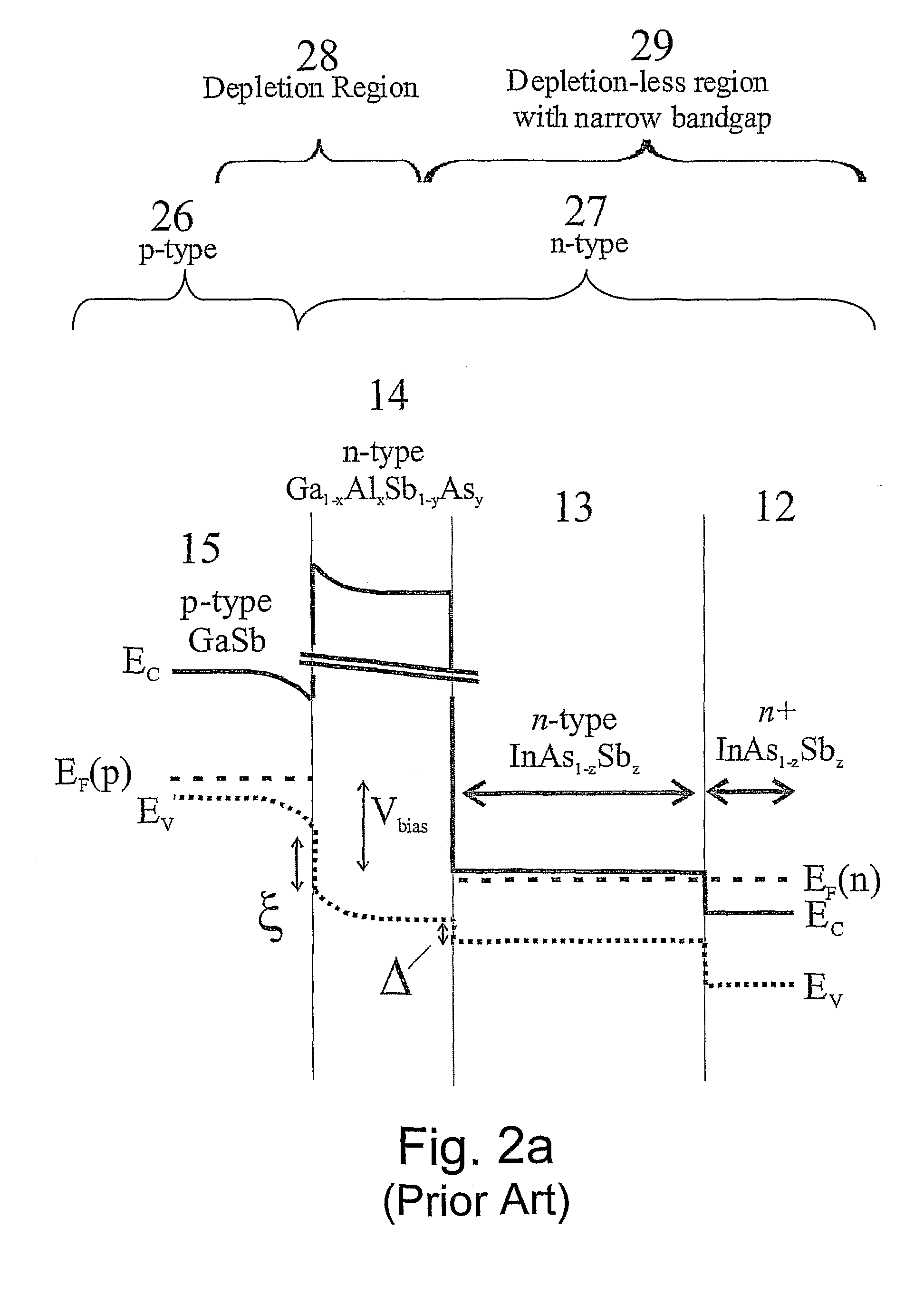
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Semiconductor Light Emitting Element
InactiveUS20090026468A1Increase brightnessIncrease the amount of lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexLength wave
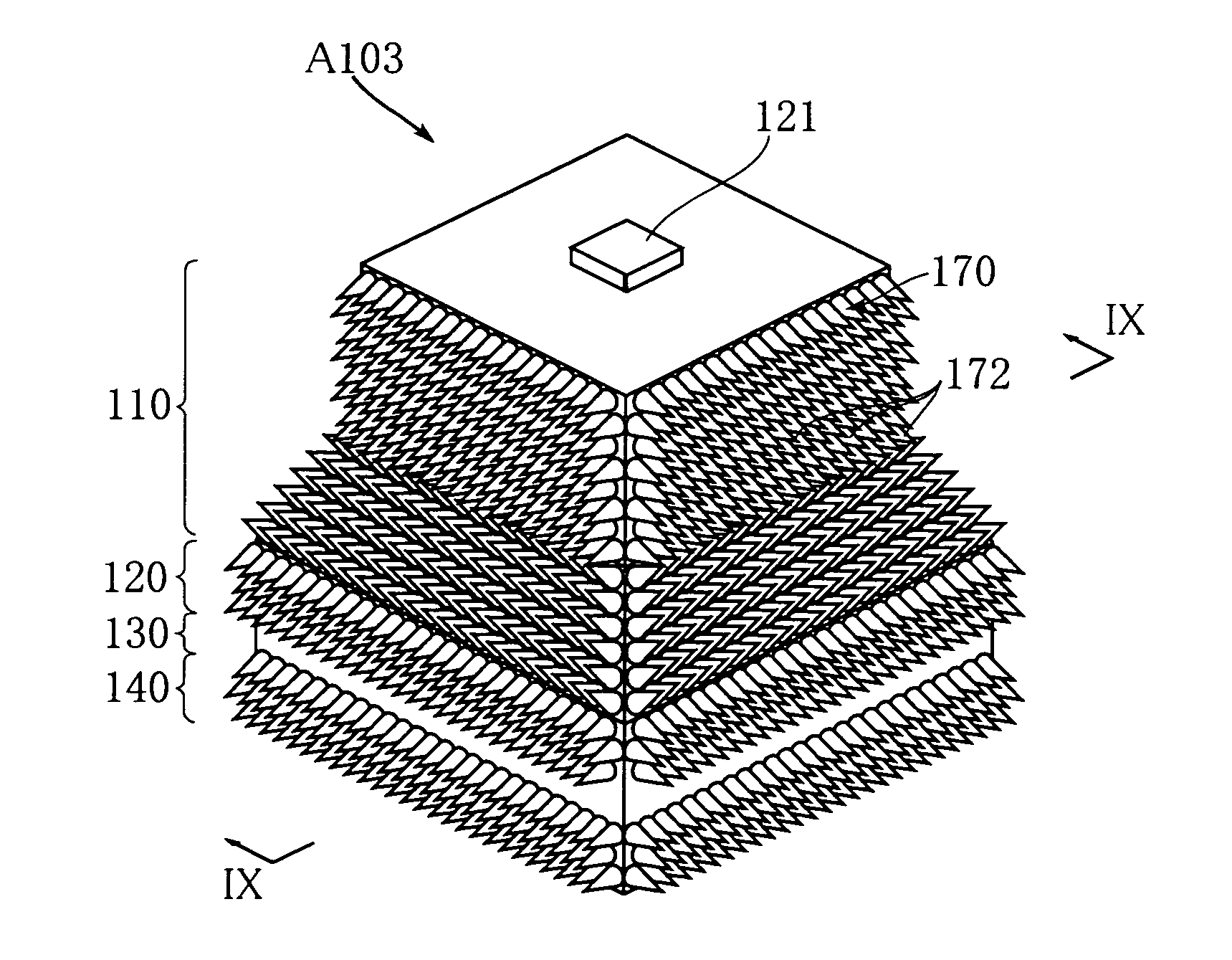
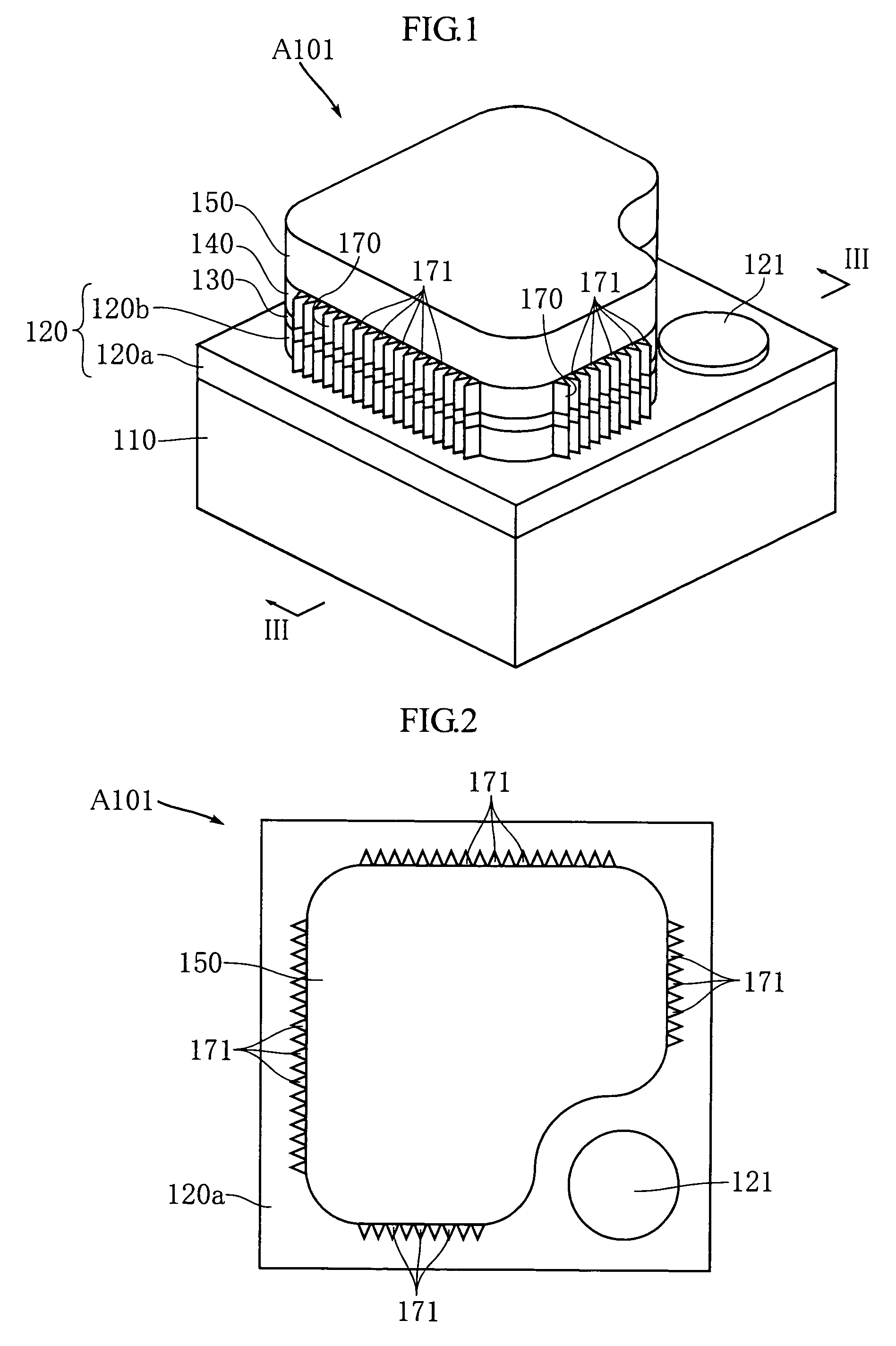
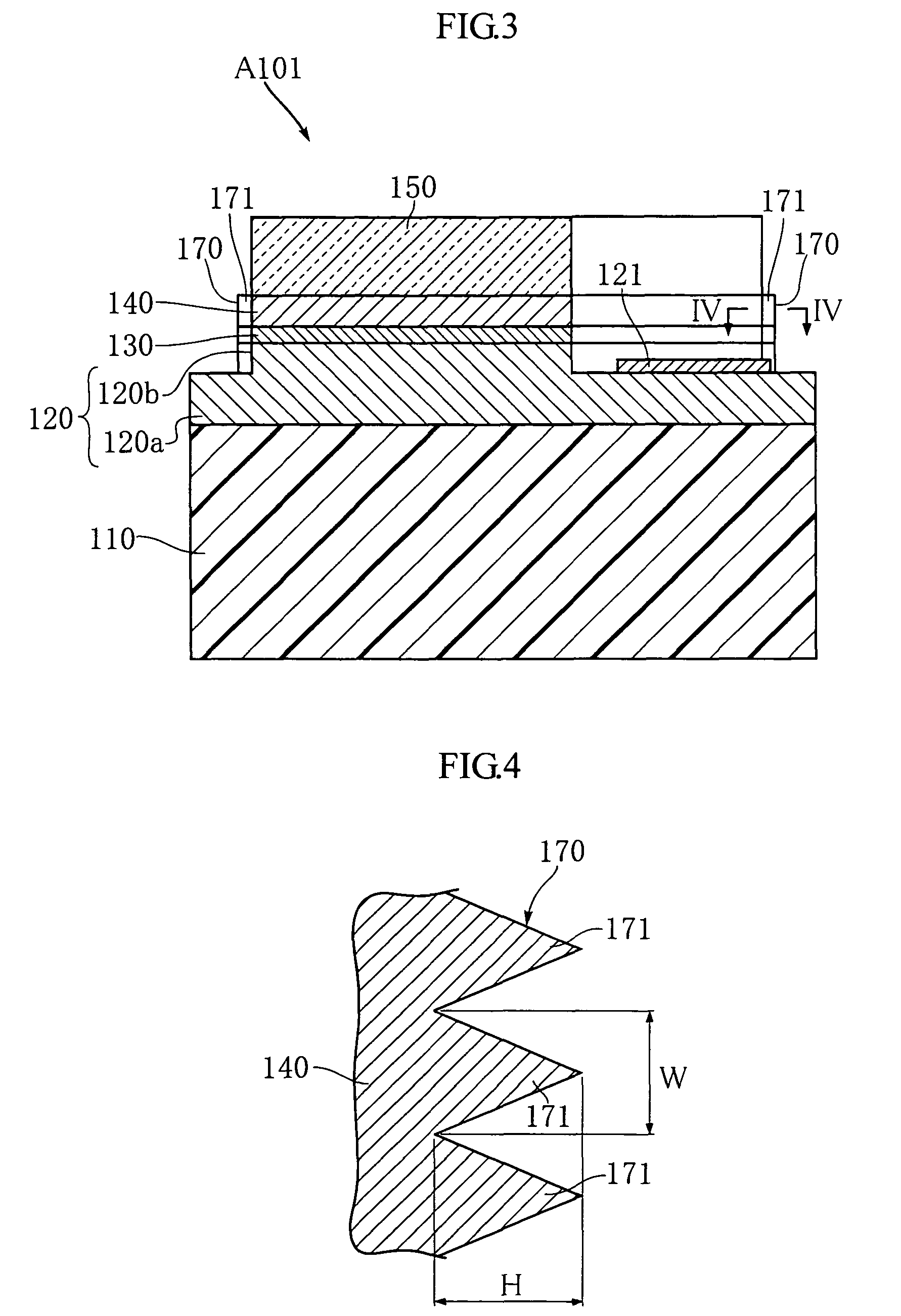
In a semiconductor light emitting element, a p-type layer (220), an active layer (230) and an n-type layer (240) are laminated on a substrate in this order. The n-type layer (240) is formed with a rectangular n-side electrode (241) whose width in one direction is equal to that of the n-type layer (240). The thickness t of the n-type layer (240) satisfies Formula 1 below. The semiconductor light emitting element includes a side surface (270) extending in the lamination direction and formed with a plurality of projections (271). Supposing that the wavelength of the light from the active-layer (230) is λ and the index of refraction of the n-type layer (240) or the p-type layer (220) is n, the average WA of widths at bottoms of the projections is set to satisfy WA≧λ / n.t≥ρJ0e4γκBT·W(L-W)Formula1where L is width of the n-type layer in a direction different from the one direction,T is absolute temperature,W is width of the n-side electrode in a direction different from the one direction,J0 is current density at the contact portion between the n-side electrode and the n-type layer,e is elementary charge,γ is diode ideality factor,κB is Boltzmann constant,ρ is specific resistance of the n-type semiconductor layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
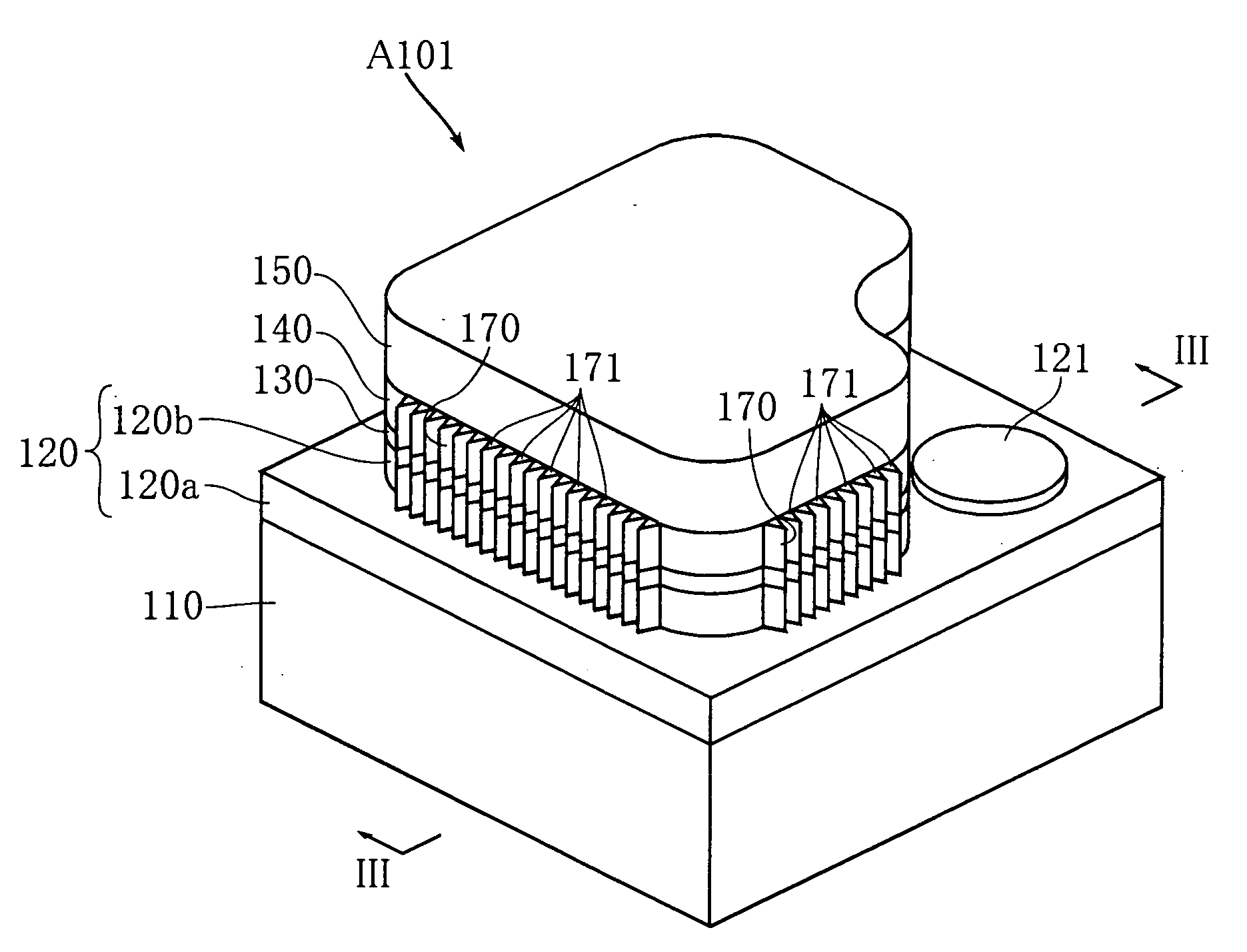
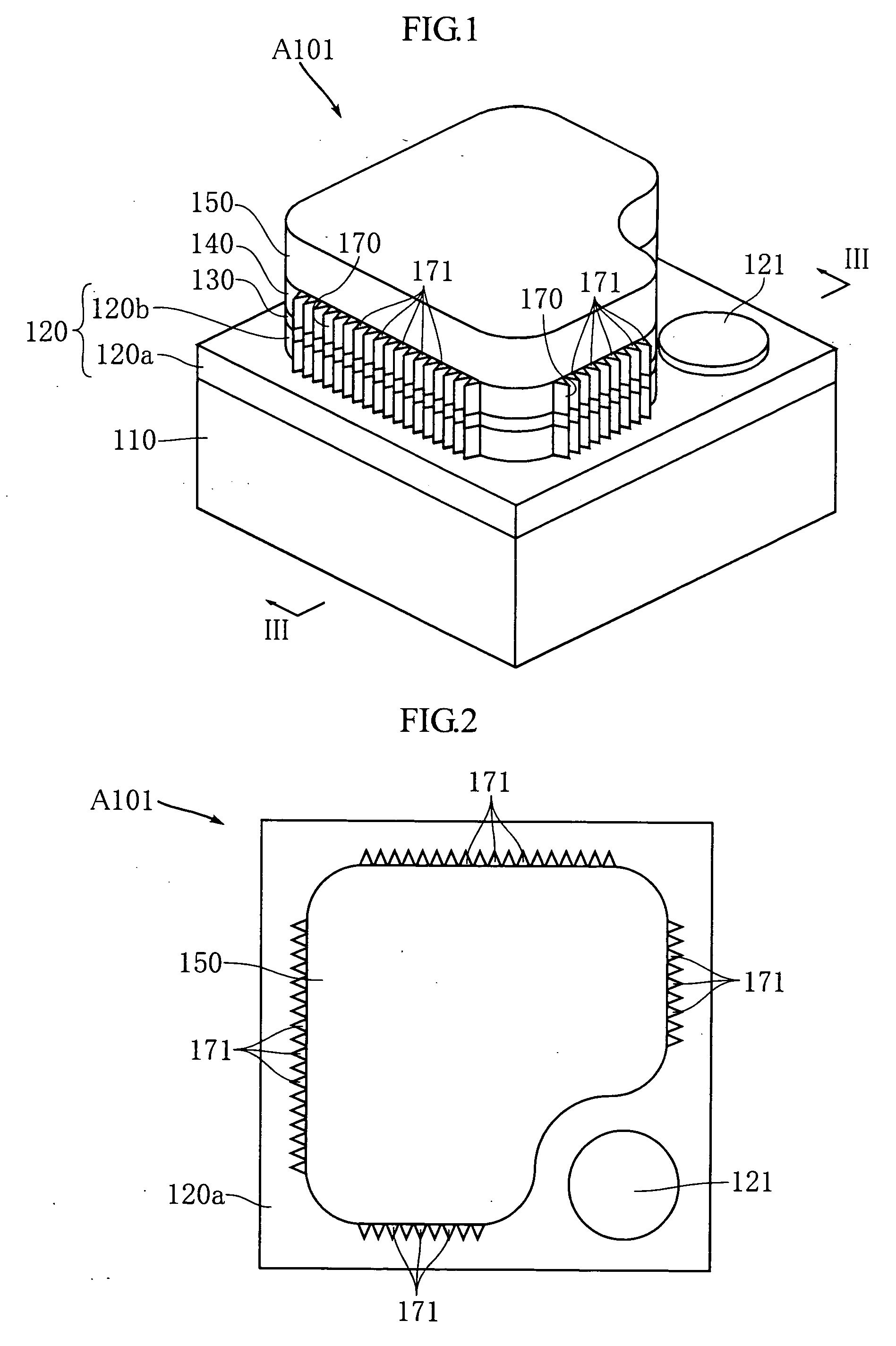
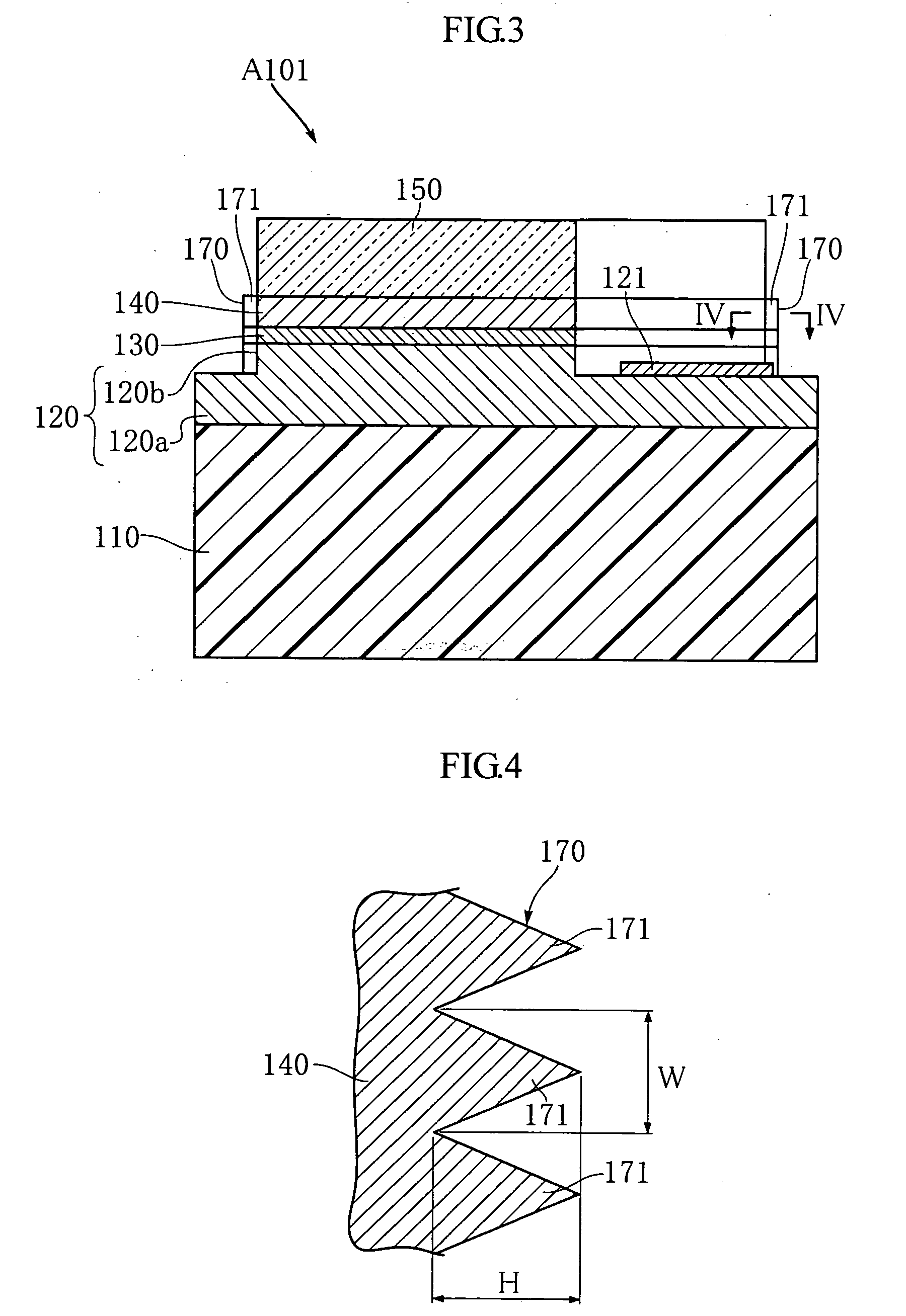
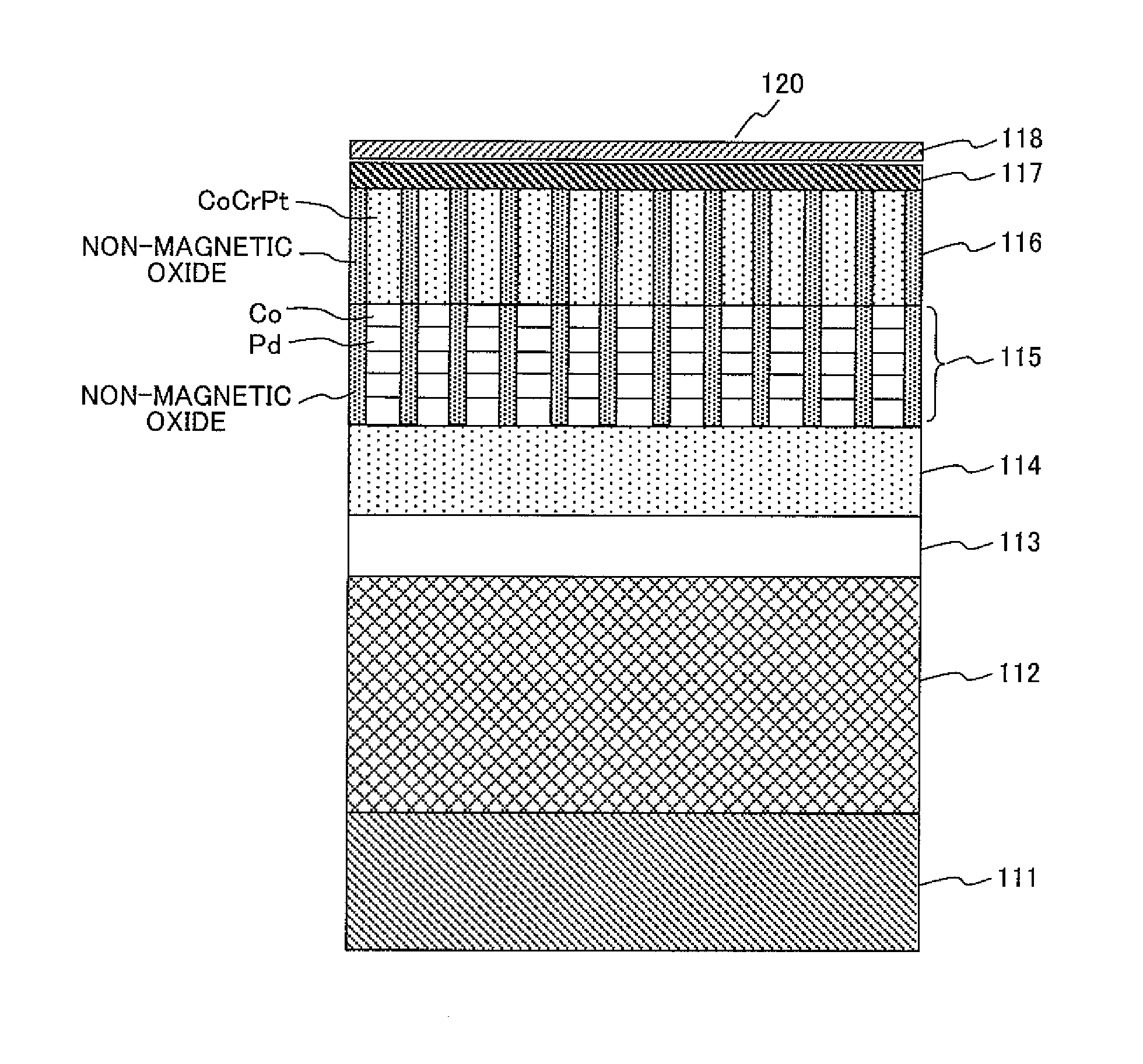
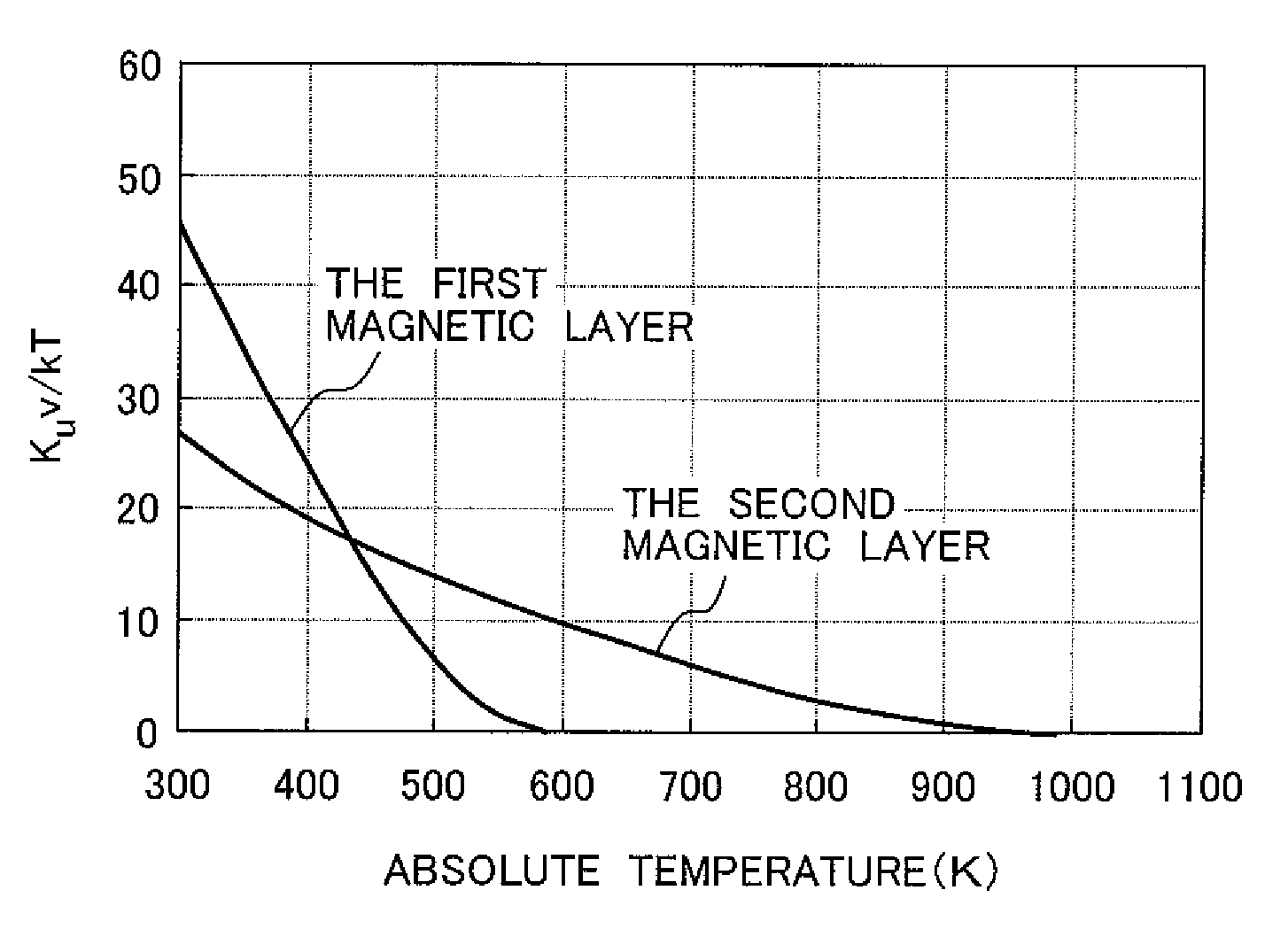
Thermally assisted recording media and system
InactiveUS20100110576A1Ultra-high densityCombination recordingPatterned record carriersMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
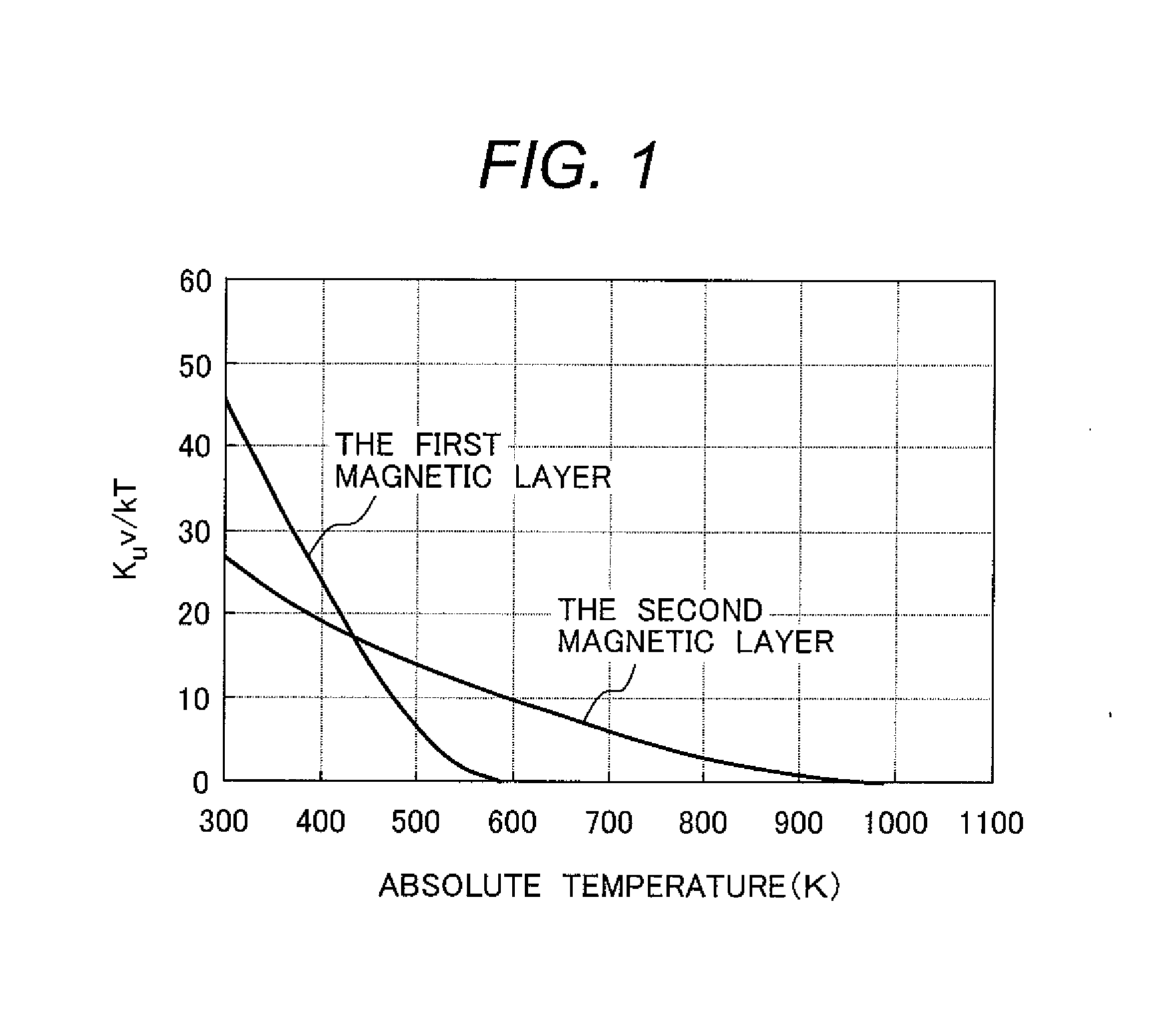
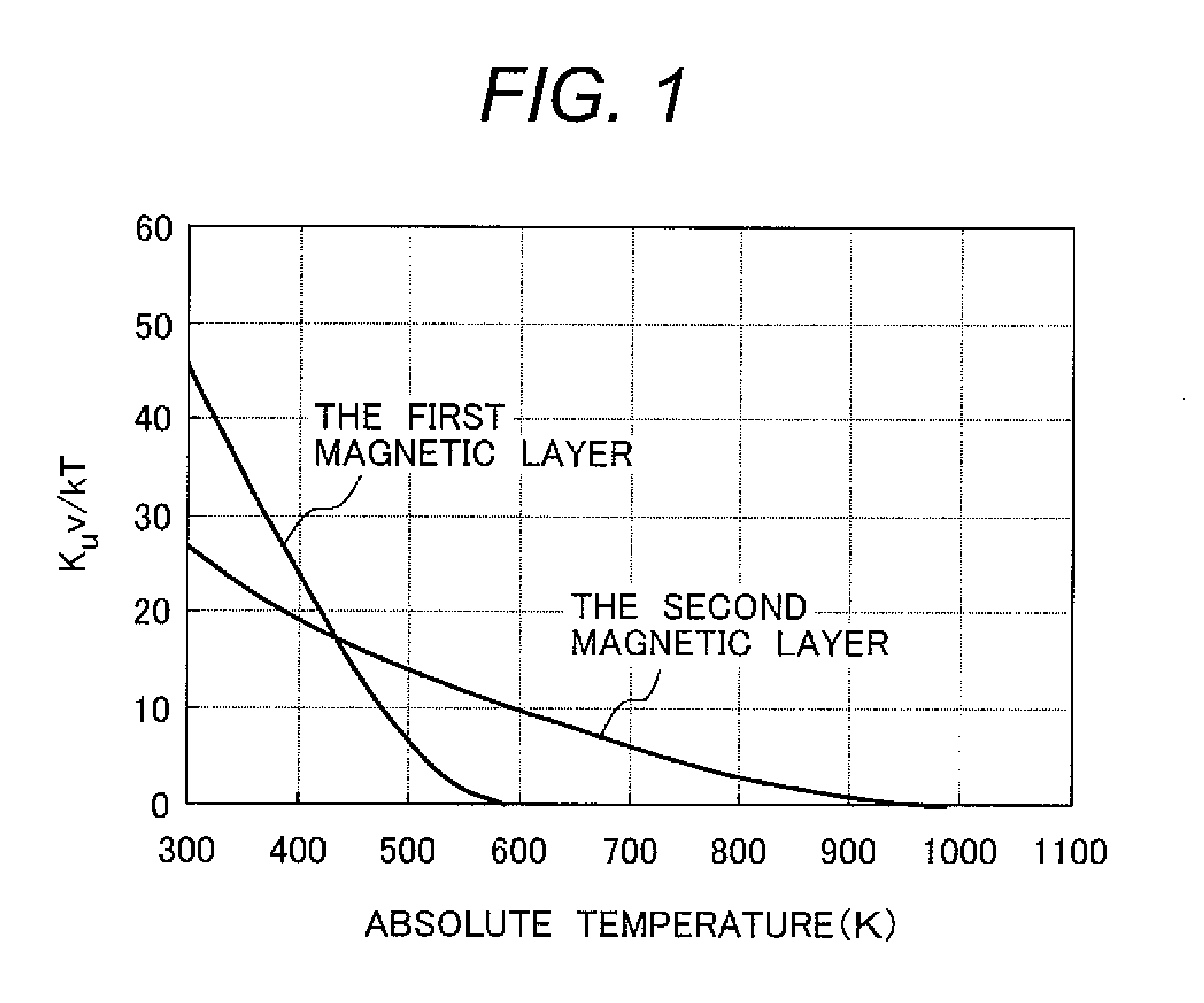
A thermally assisted magnetic recording medium includes a substrate and at least two, i.e., first and second magnetic recording layers. These layers are hard magnetic layers and contain magnetic grains and a non-magnetic substance magnetically segregating the magnetic grains at grain boundaries. The first magnetic recording layer has a magnetic anisotropy energy Ku1, a grain volume v1, and energy for maintaining its recording magnetization Ku1v1; the second magnetic recording layer has a magnetic anisotropy energy Ku2, a grain volume v2, and energy for maintaining its recording magnetization Ku2v2; and the ratio Ku1v1 / kBT of Ku1v1 to a thermal fluctuation energy kBT, where kB represents a Boltzmann constant and T represents an absolute temperature, and the ratio Ku2v2 / kBT of Ku2v2 to kBT satisfy the following conditions: Ku1v1 / kBT is larger than Ku2v2 / kBT at room temperature, but is smaller than Ku2v2 / kBT at temperatures around the Curie temperature of the first magnetic recording layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8004012B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesValence bandExternal bias
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Semiconductor light emitting element
InactiveUS7781791B2Accurate emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexLength wave
In a semiconductor light emitting element, a p-type layer (220), an active layer (230) and an n-type layer (240) are laminated on a substrate in this order. The n-type layer (240) is formed with a rectangular n-side electrode (241) whose width in one direction is equal to that of the n-type layer (240). The thickness t of the n-type layer (240) satisfies Formula 1 below. The semiconductor light emitting element includes a side surface (270) extending in the lamination direction and formed with a plurality of projections (271). Supposing that the wavelength of the light from the active-layer (230) is λ and the index of refraction of the n-type layer (240) or the p-type layer (220) is n, the average WA of widths at bottoms of the projections is set to satisfy WA≧λ / n.t≥ρJ0e4γκBT·W(L-W)Formula1whereL is width of the n-type layer in a direction different from the one direction,T is absolute temperature,W is width of the n-side electrode in a direction different from the one direction,J0 is current density at the contact portion between the n-side electrode and the n-type layer,e is elementary charge,γ is diode ideality factor,κB is Boltzmann constant,ρ is specific resistance of the n-type semiconductor layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for reducing thermal noise
ActiveUS7298151B2Electric signal transmission systemsProduction of permanent recordsCapacitanceEngineering
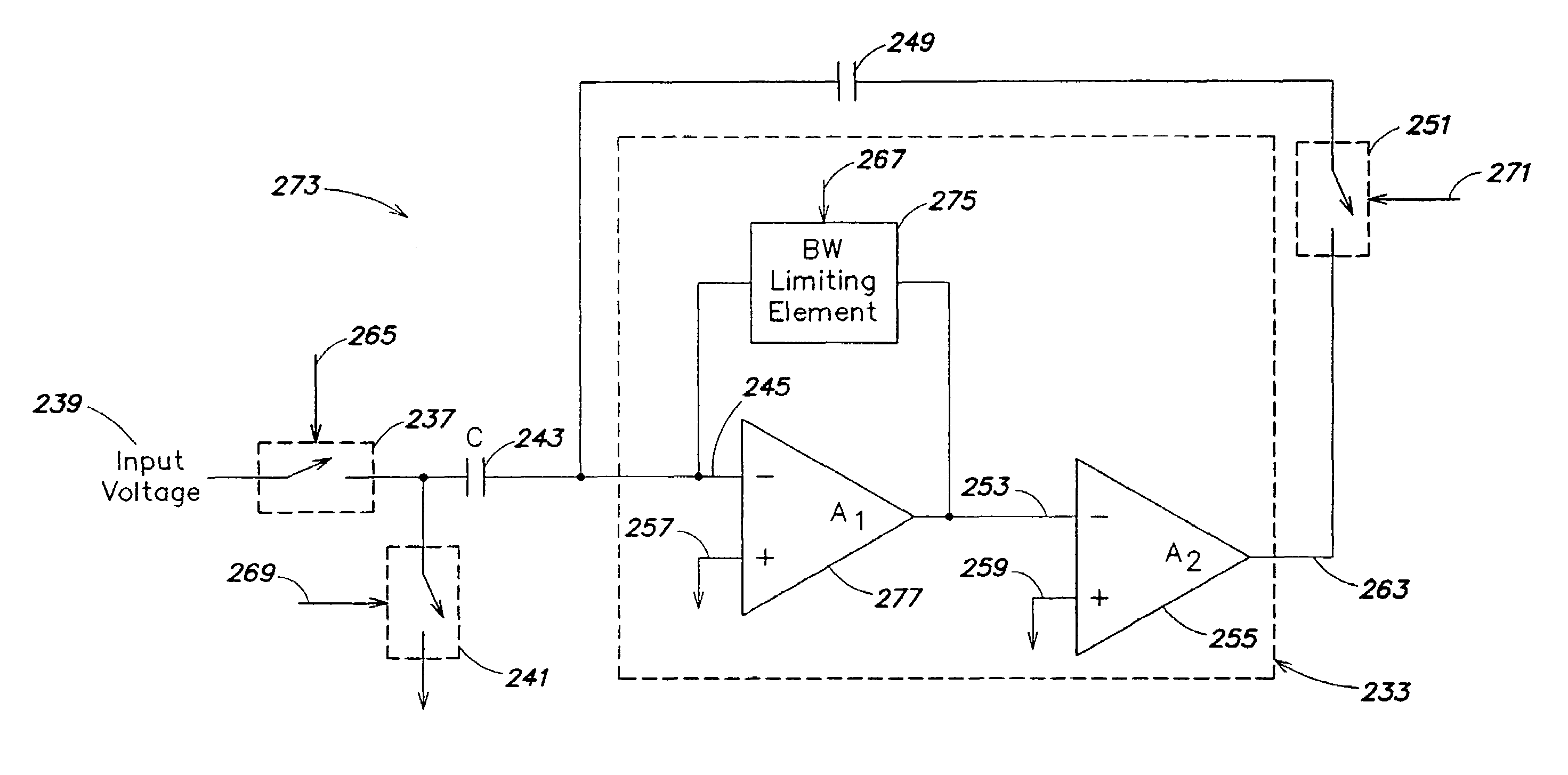
Methods and apparatus for reducing the thermal noise integrated on a storage element are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention is directed to a sampling circuit comprising a sampling capacitor to store a charge, the sampling capacitor being exposed to an ambient temperature. The sampling circuit further comprises circuitry to sample the charge onto the capacitor, wherein thermal noise is also sampled onto the capacitor, and wherein the circuitry is constructed such that the power of the thermal noise sampled onto the capacitor is less than the product of the ambient temperature and Boltzmann's constant divided by a capacitance of the sampling capacitor. Another embodiment of the invention is directed to a method of controlling thermal noise sampled onto a capacitor. The method comprises an act of independently controlling the spectral density of the thermal noise and / or the bandwidth of the thermal noise.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Potential amplified nonequilibrium thermal electric device (PANTEC)
InactiveUS20050155642A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSemiconductor devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
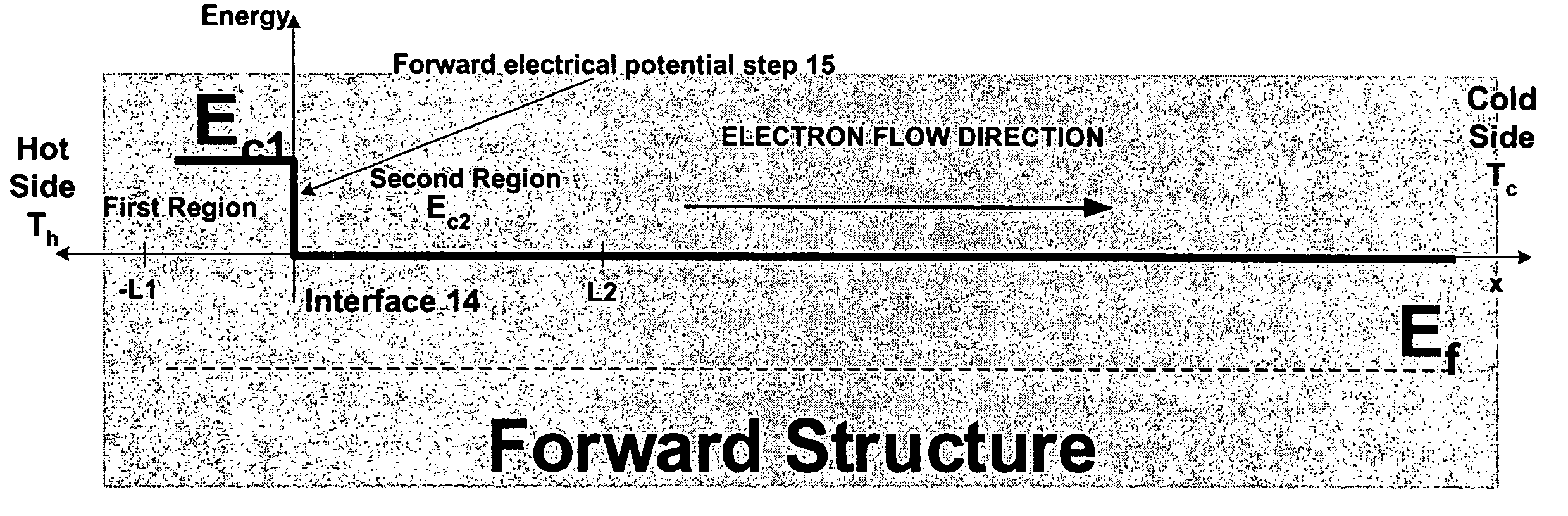
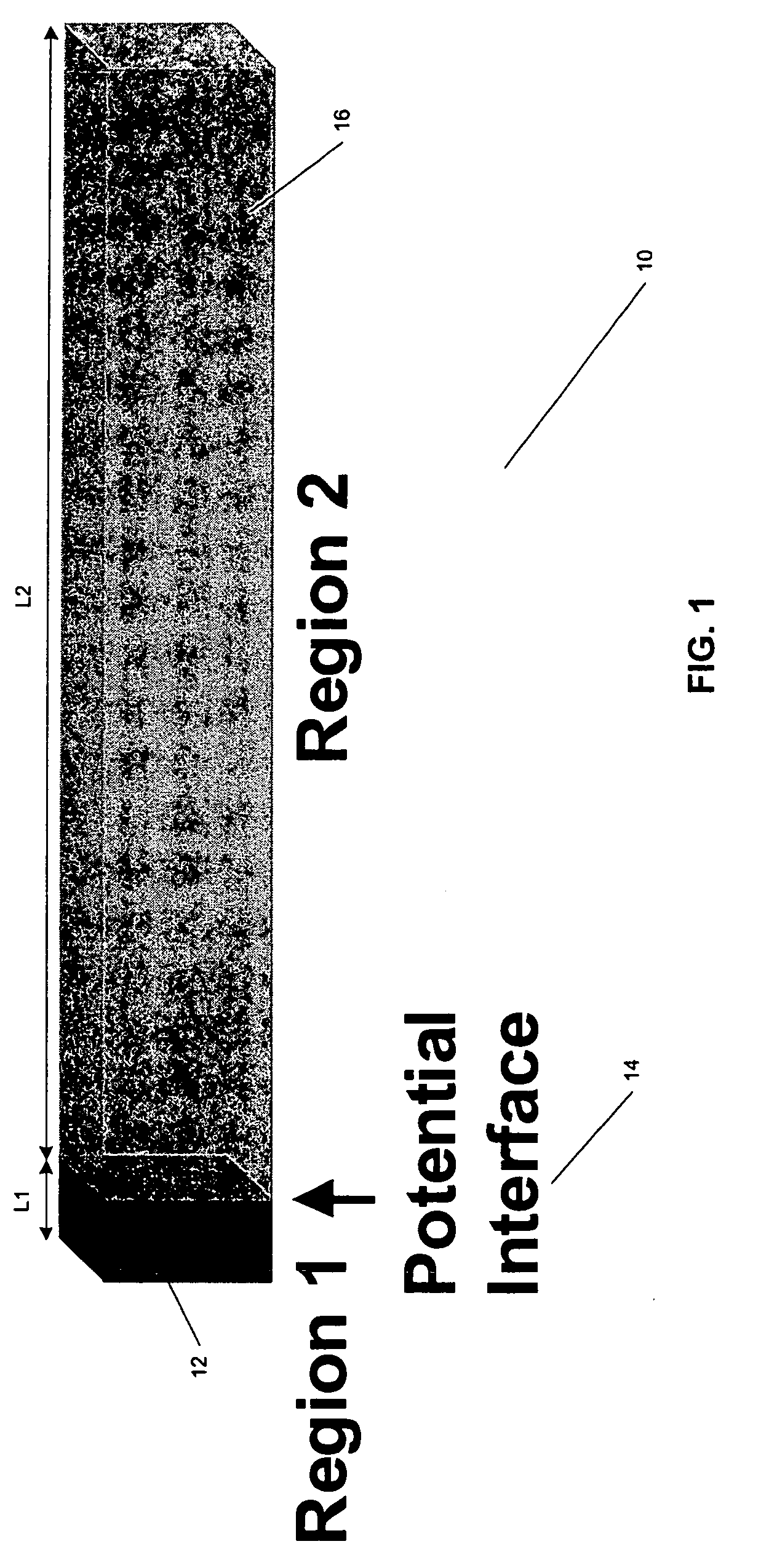
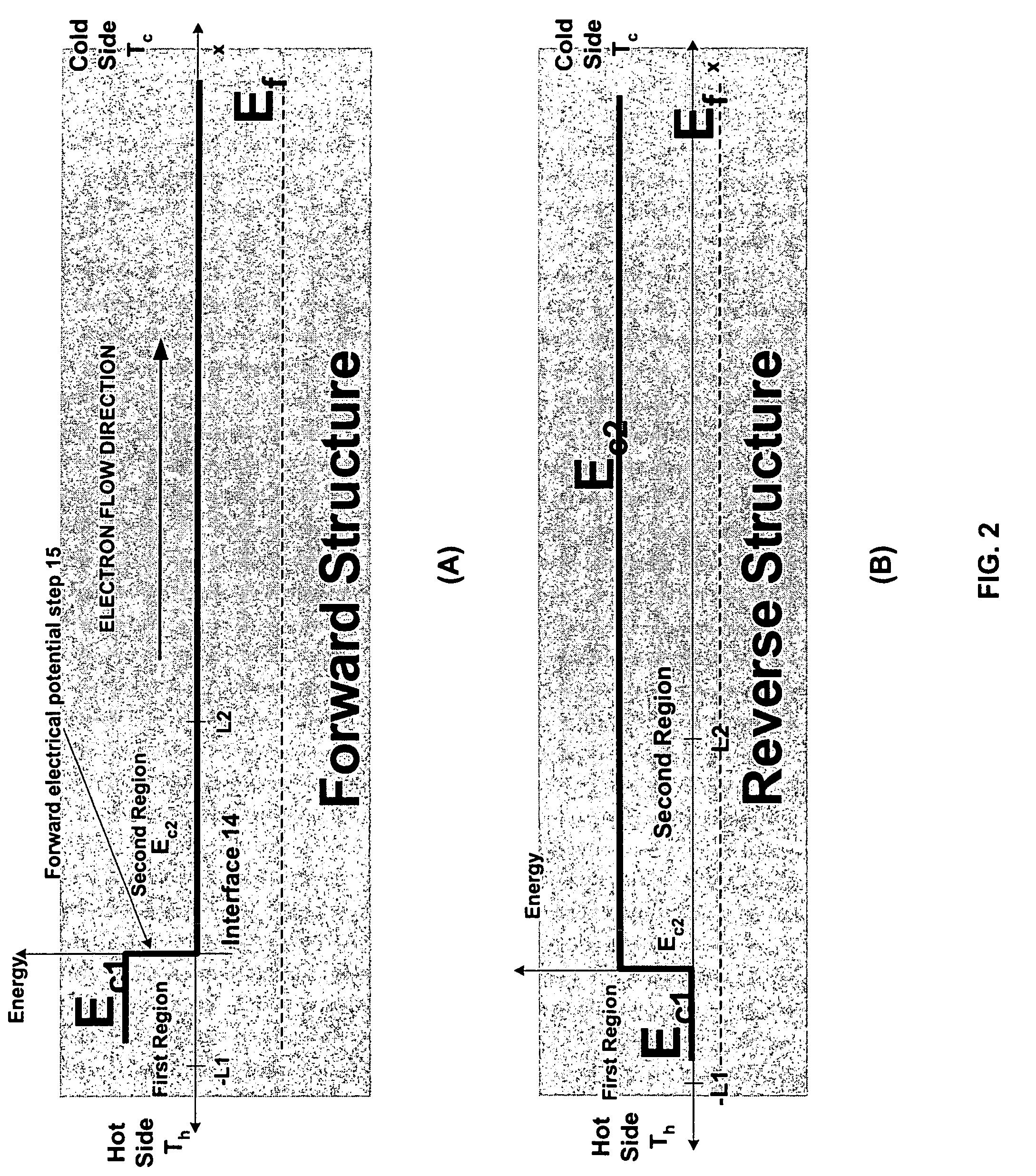
A semiconductor structure is provided that can be used for cooling, heating, and power generation. A first region of the semiconductor structure has a first length and comprises a first semiconductor material doped at a first concentration with a first dopant. A second region is disposed adjacent to the first region so as to define a first interface, has a second length which is longer than the first length, and comprises a second semiconductor material doped at a second concentration with a second dopant. At least one of the first material, second material, first concentration, second concentration, first length, second length, first dopant, and second dopant is selected to create, at the first interface, a forward electrical potential step having a barrier height dependent at least in part on an average temperature (T) of the semiconductor structure, e.g., a range of approximately 3-10 κBT, where κB is the Boltzmann constant.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
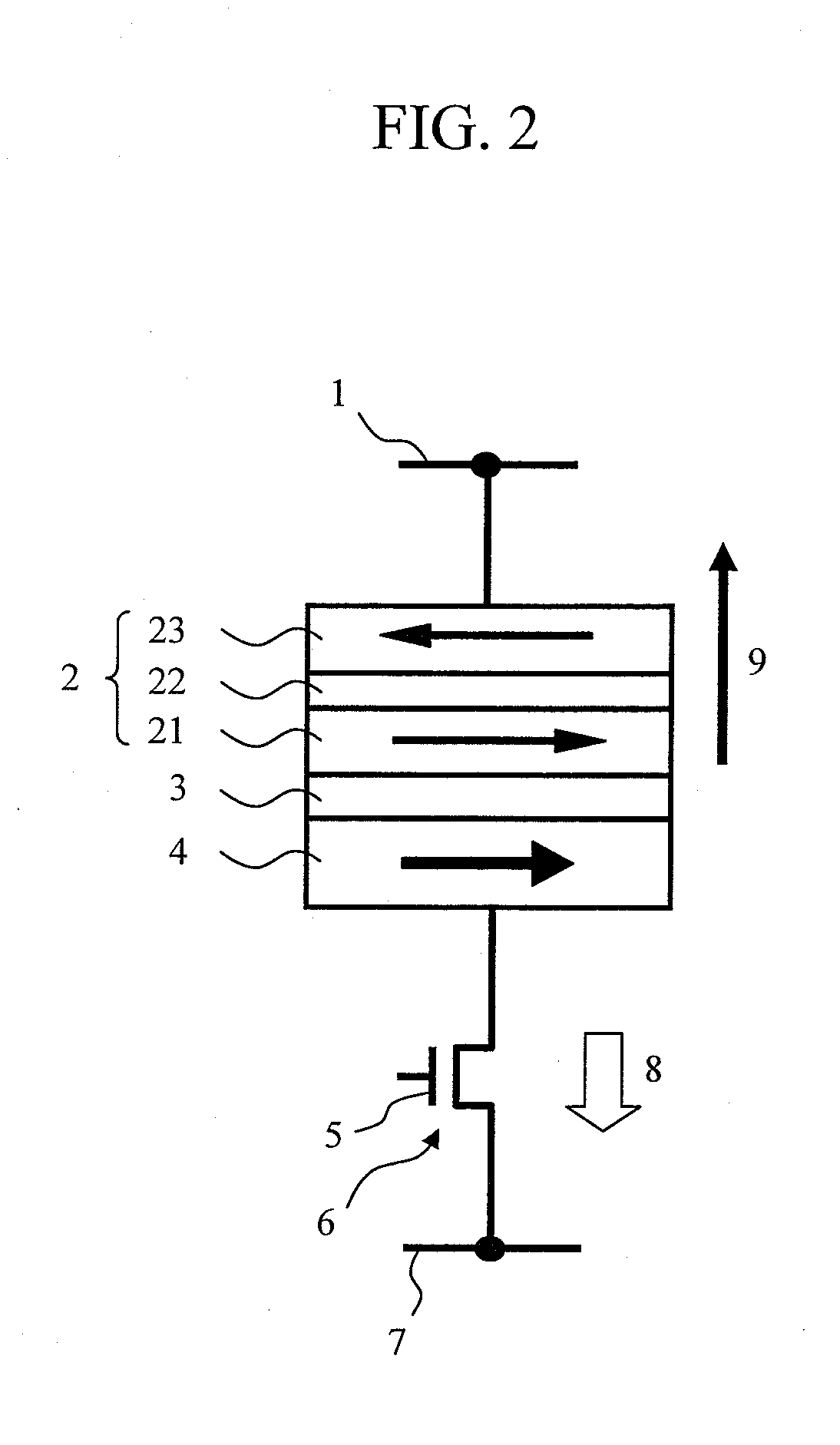
Magnetic memory
InactiveUS20120012955A1Total current dropMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMagnetic memory
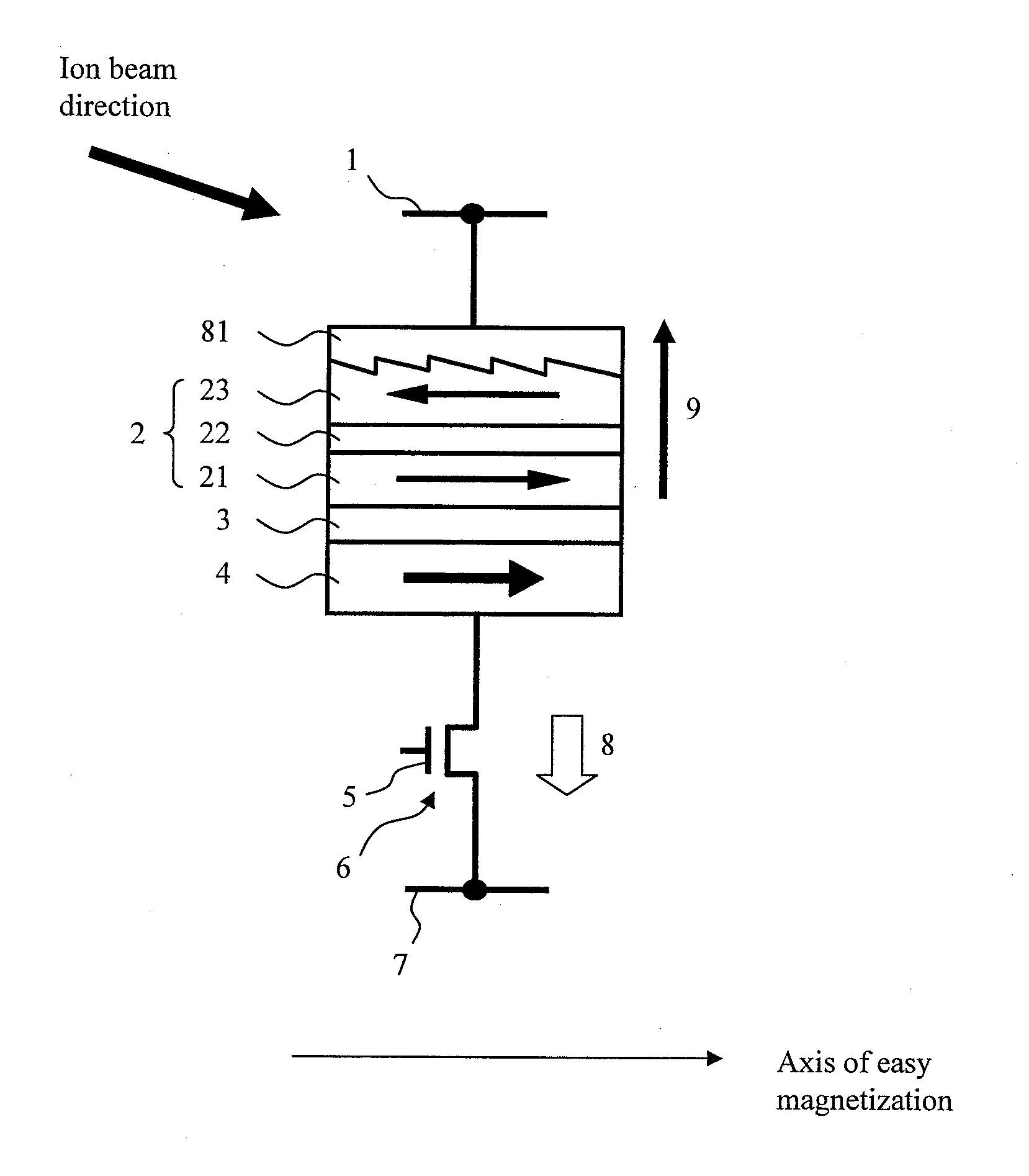
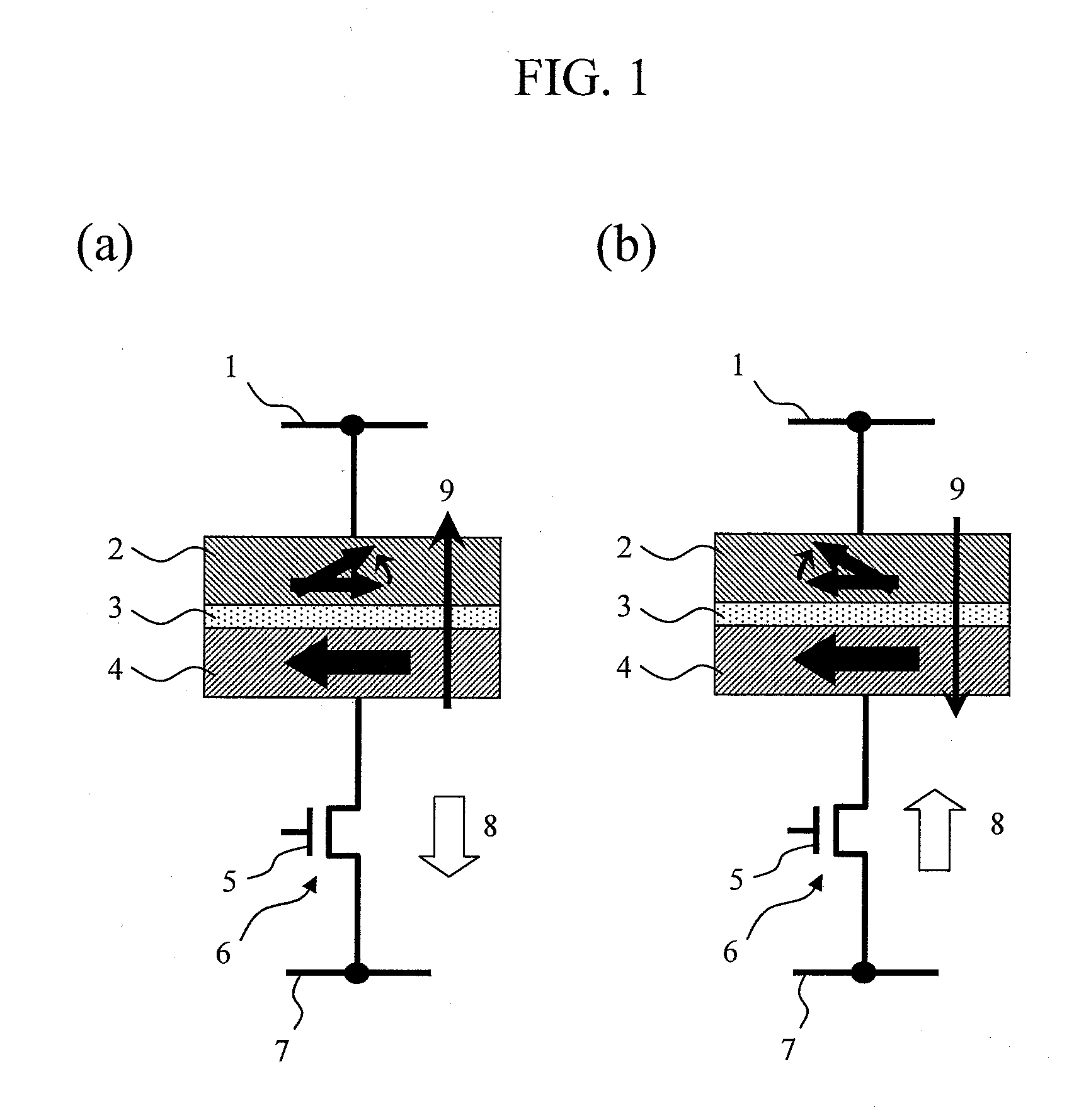
Provided is a magnetic random access memory to which spin torque magnetization reversal is applied, the magnetic random access memory being thermal stable in a reading operation and also being capable of reducing a current in a wiring operation. A magnetoresistive effect element formed by sequentially stacking a fixed layer, a nonmagnetic barrier layer, and a recording layer is used as a memory element. The recording layer adopts a laminated ferrimagnetic structure. The magnetic memory satisfies the expression Ms2(t / w)>|Jex|>(2kBTΔ) / S, in which kB is a Boltzmann constant, T is an operating temperature of the magnetic memory, S is an area parallel to a film surface of the magnetoresistive effect element, t and Ms are respectively a film thickness and a saturated magnetization of the ferromagnetic layer having a smaller film thickness among two ferromagnetic layers which are constituent members of the laminated ferrimagnetic structure, w is a length of a short side of the recording layer, Δ is a thermal stability index of the magnetic memory, and Jex is exchange coupling energy acting between the two ferromagnetic layers of the recording layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
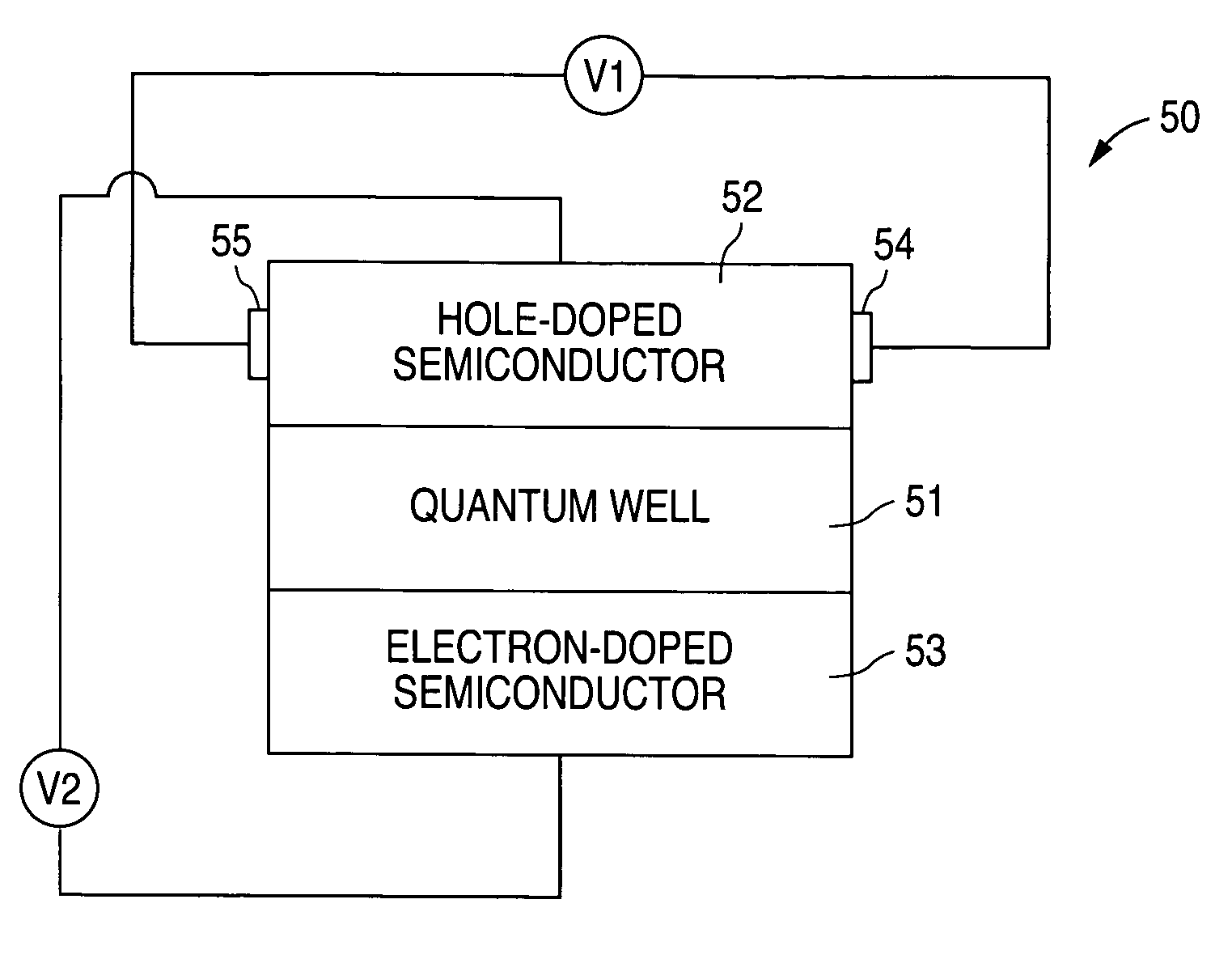
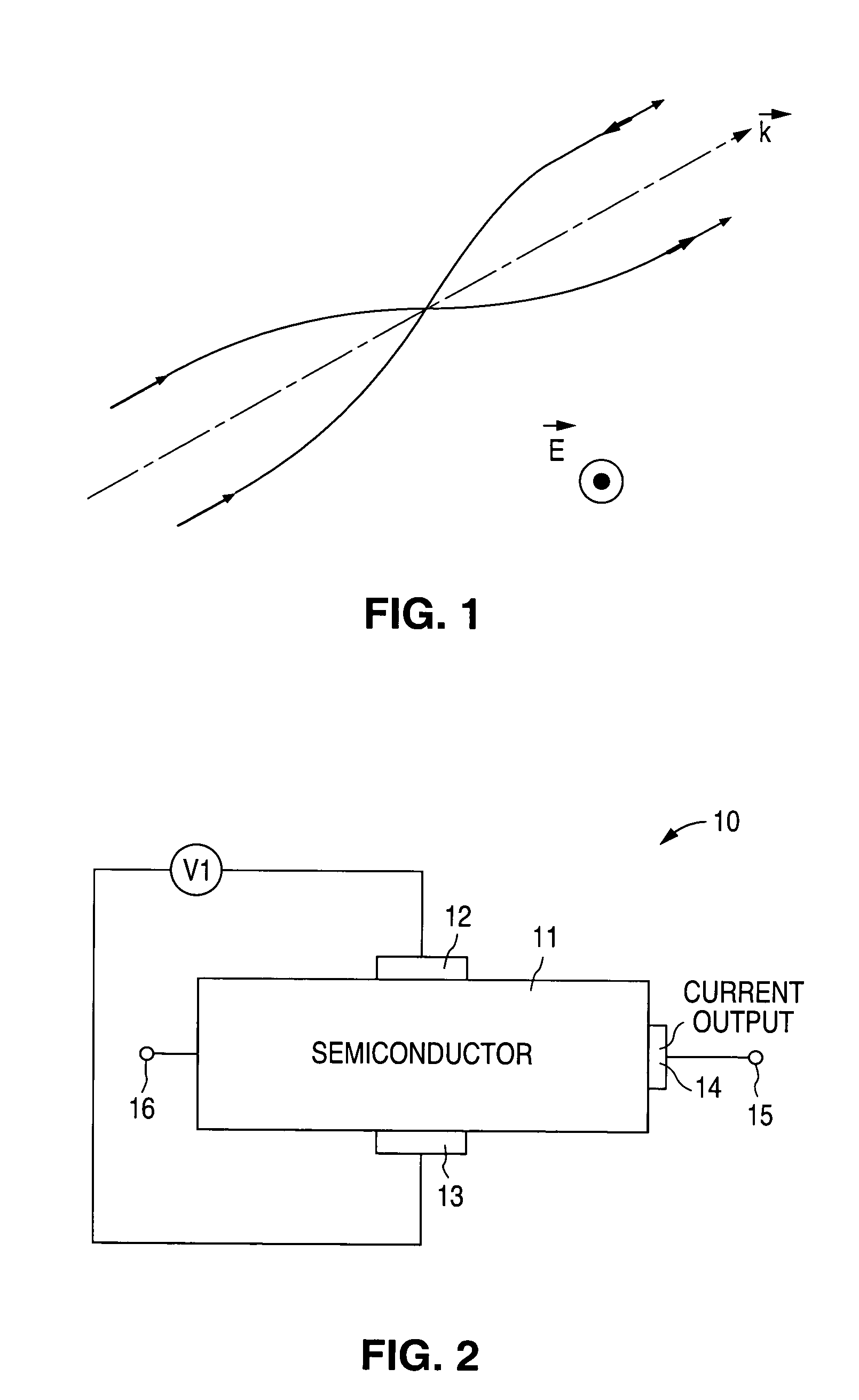
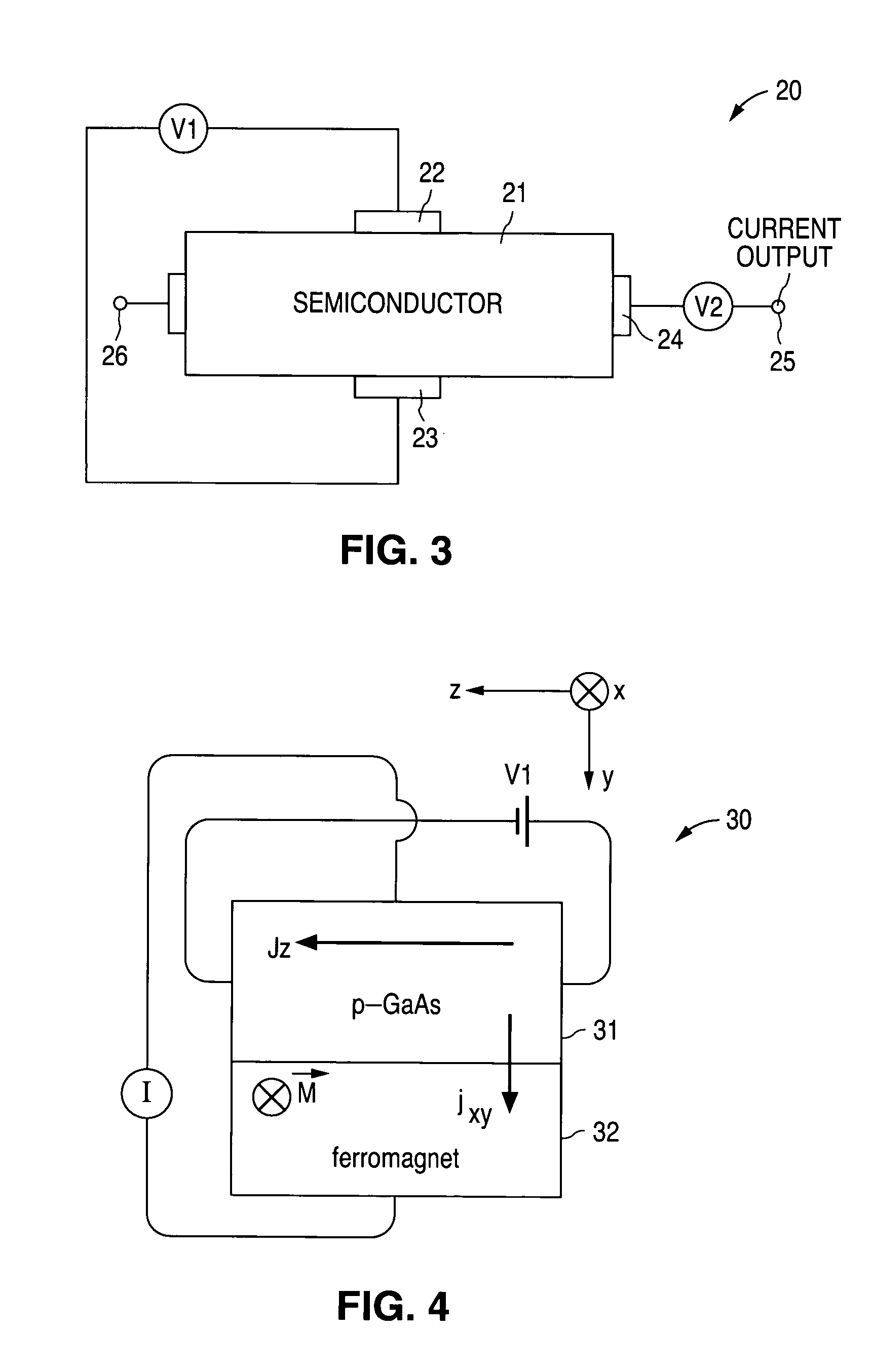
Electric field induced spin-polarized current
InactiveUS7037807B1Current provideOvercomes shortcomingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
A device and a method for generating an electric-field-induced spin current are disclosed. A highly spin-polarized electric current is generated using a semiconductor structure and an applied electric field across the semiconductor structure. The semiconductor structure can be a hole-doped semiconductor having finite or zero bandgap or an undoped semiconductor of zero bandgap. In one embodiment, a device for injecting spin-polarized current into a current output terminal includes a semiconductor structure including first and second electrodes, along a first axis, receiving an applied electric field and a third electrode, along a direction perpendicular to the first axis, providing the spin-polarized current. The semiconductor structure includes a semiconductor material whose spin orbit coupling energy is greater than room temperature (300 Kelvin) times the Boltzmann constant. In one embodiment, the semiconductor structure is a hole-doped semiconductor structure, such as a p-type GaAs semiconductor layer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
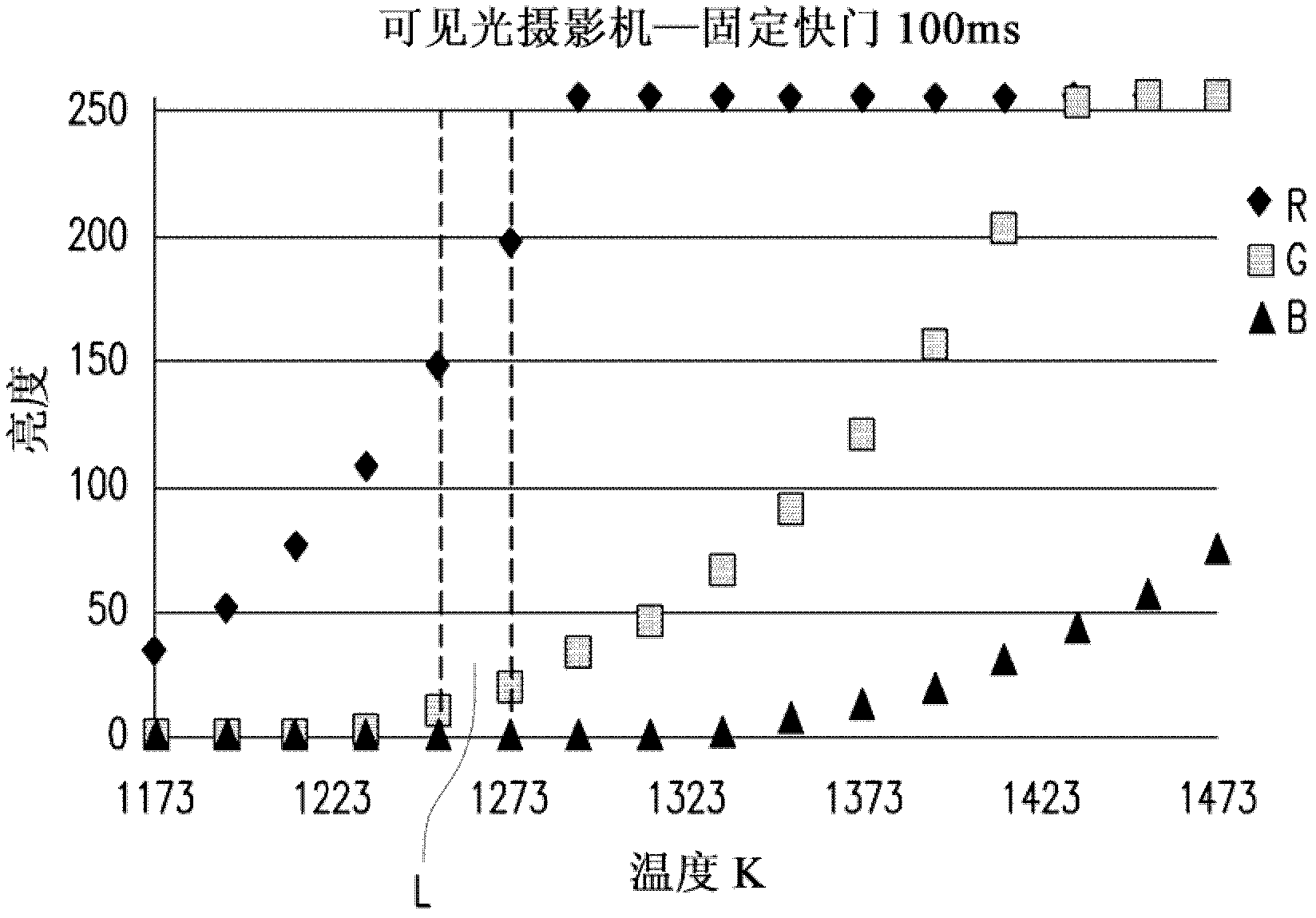
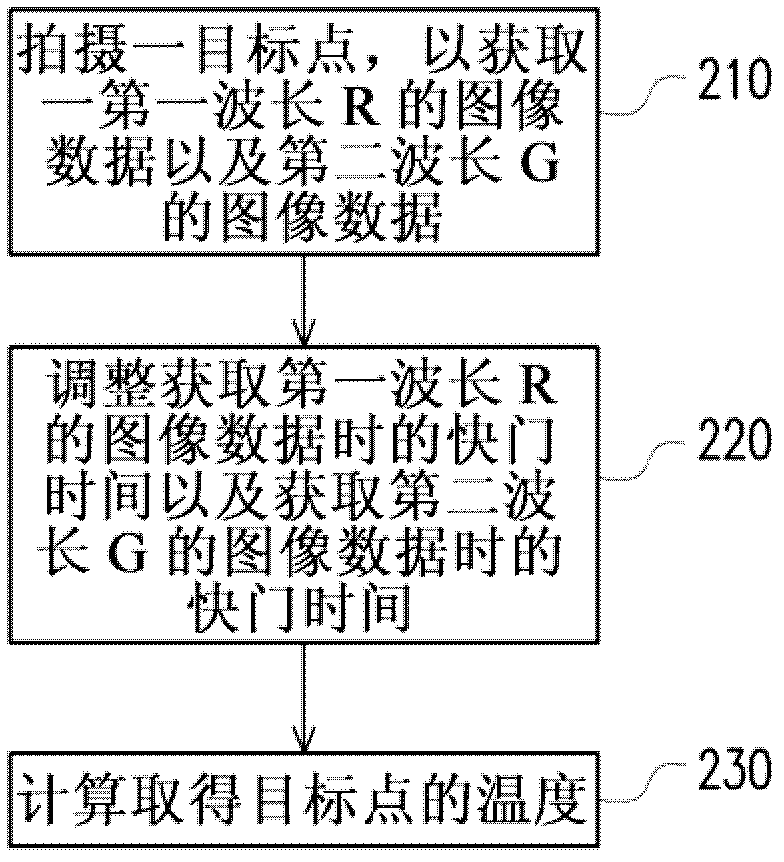
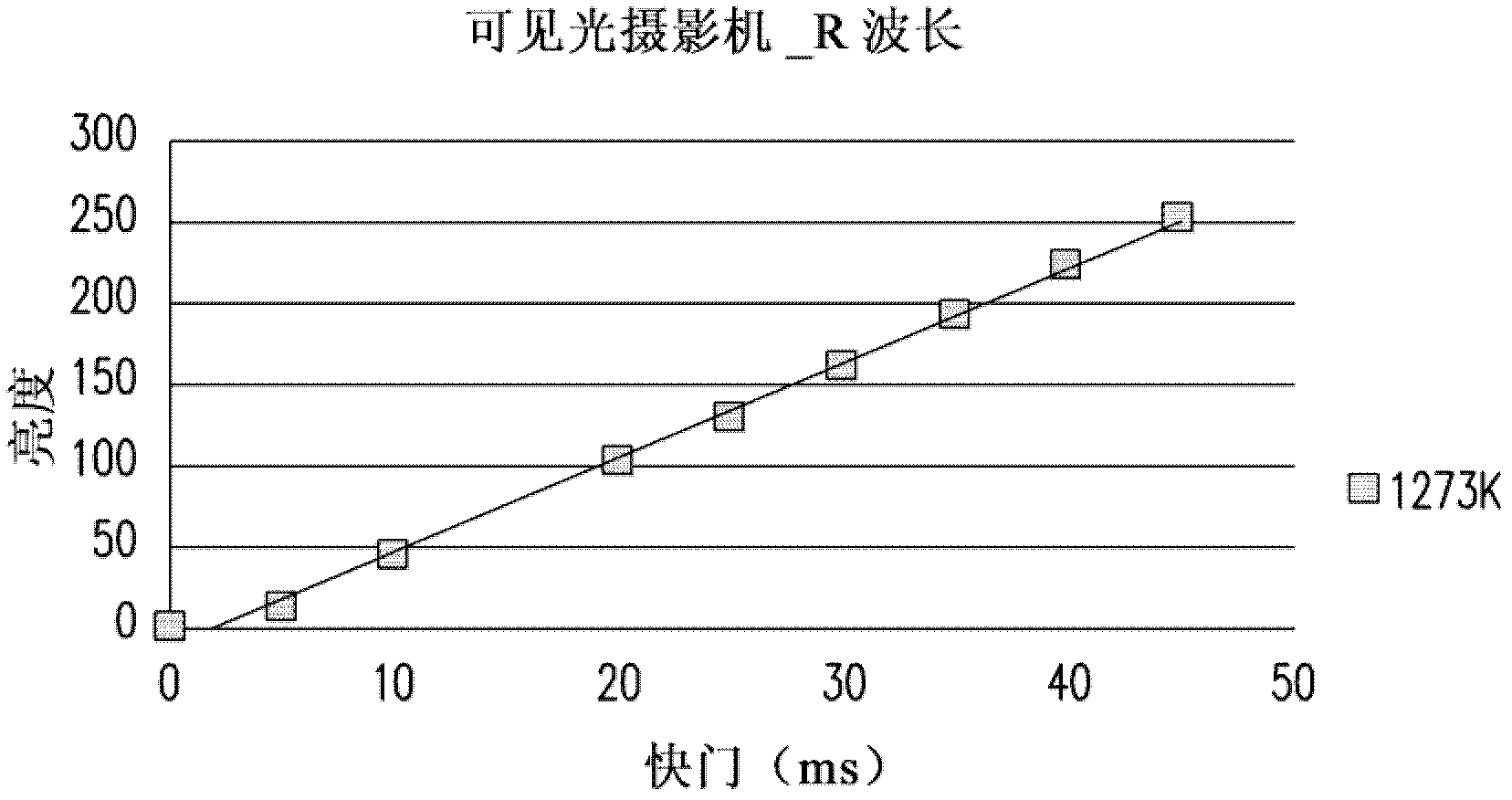
Non-contact temperature measuring method
A non-contact temperature measuring method comprises the steps of shooting a target point to obtain the image data of a first wavelength and the image data of a second wavelength; when the target point is shot, adjusting the shutter time for obtaining the image data of the first wavelength and the shutter time for obtaining the image data of the second wavelength to obtain a first brightness corresponding to the first wavelength and a second brightness corresponding to the second wavelength; and computing the temperature of the target point according to the following formula (1), wherein lambda 1 is the first wavelength, lambda 2 is the second wavelength, L lambda 1 (T) is the first brightness, L lambda 2 (T) is the second brightness, A is a correction coefficient, S1 is the shutter time for obtaining the image data of the first wavelength, and S2 is the shutter time for obtaining the image data of the second wavelength. In the formula: constant C=hc / k, k is a Planck constant, c is light velocity, and h is a Boltzmann constant.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
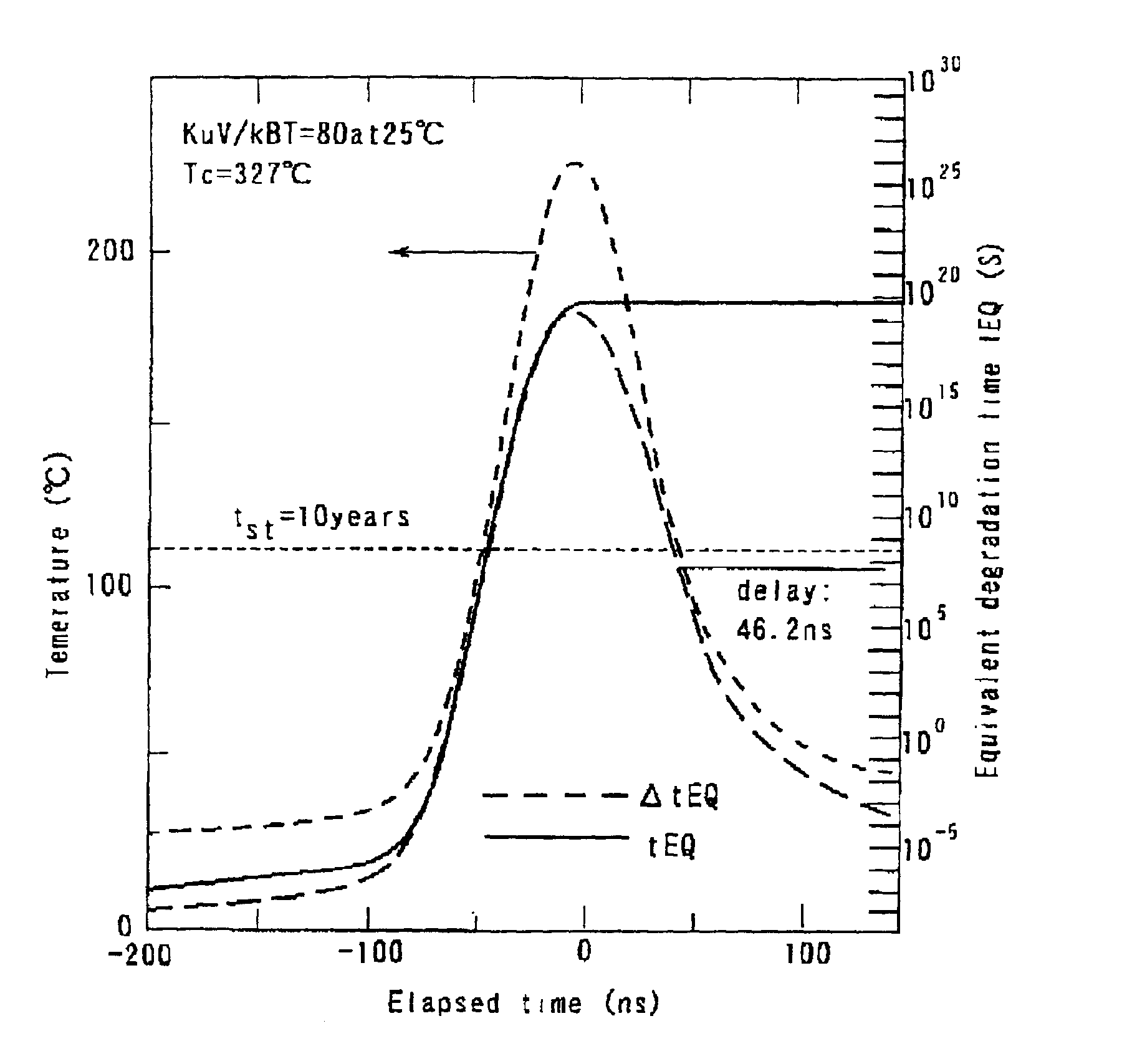
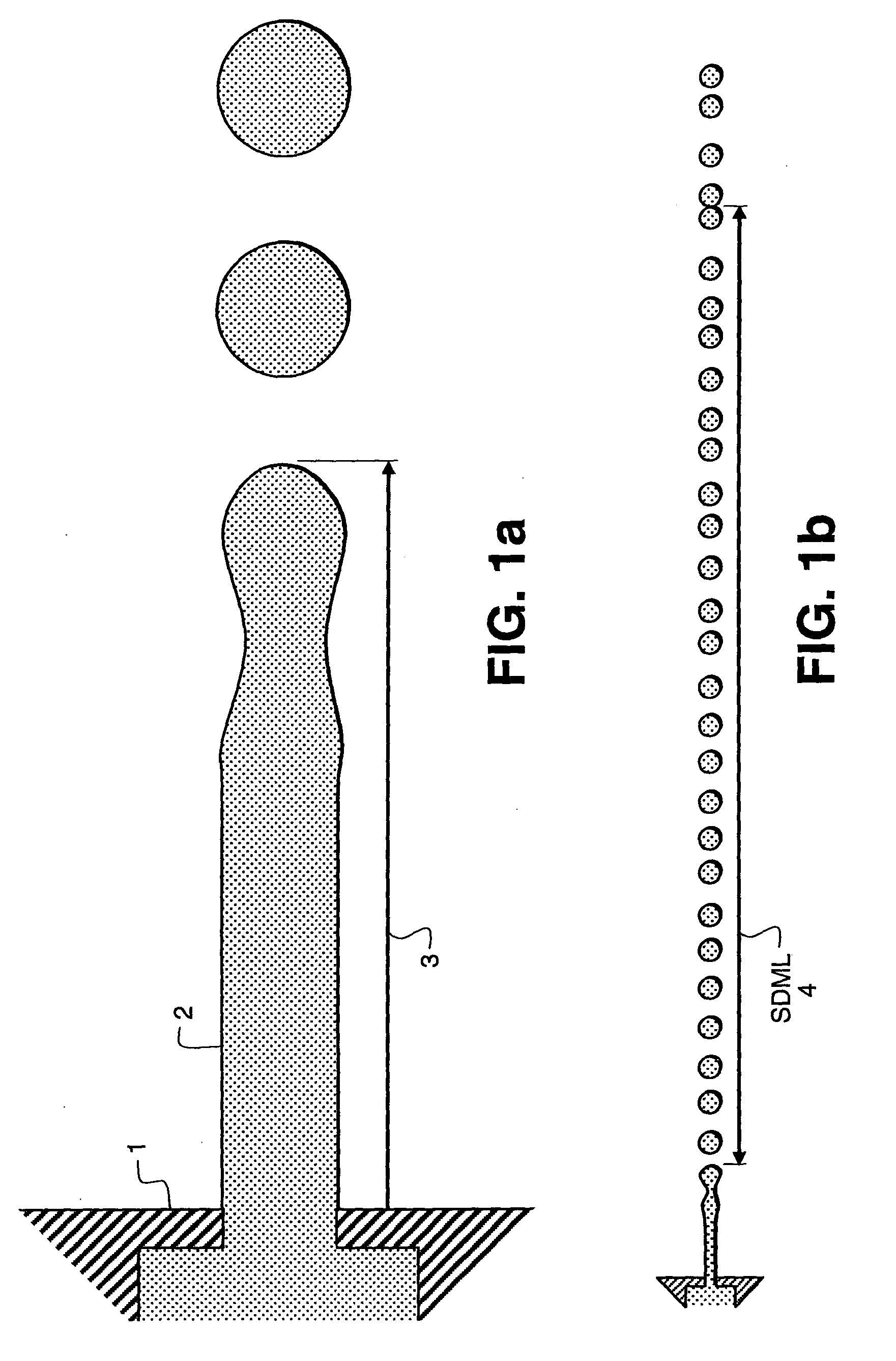
Magnetic recording apparatus and method of designing the same
InactiveUS6894857B2Simple designControl fluctuationsCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
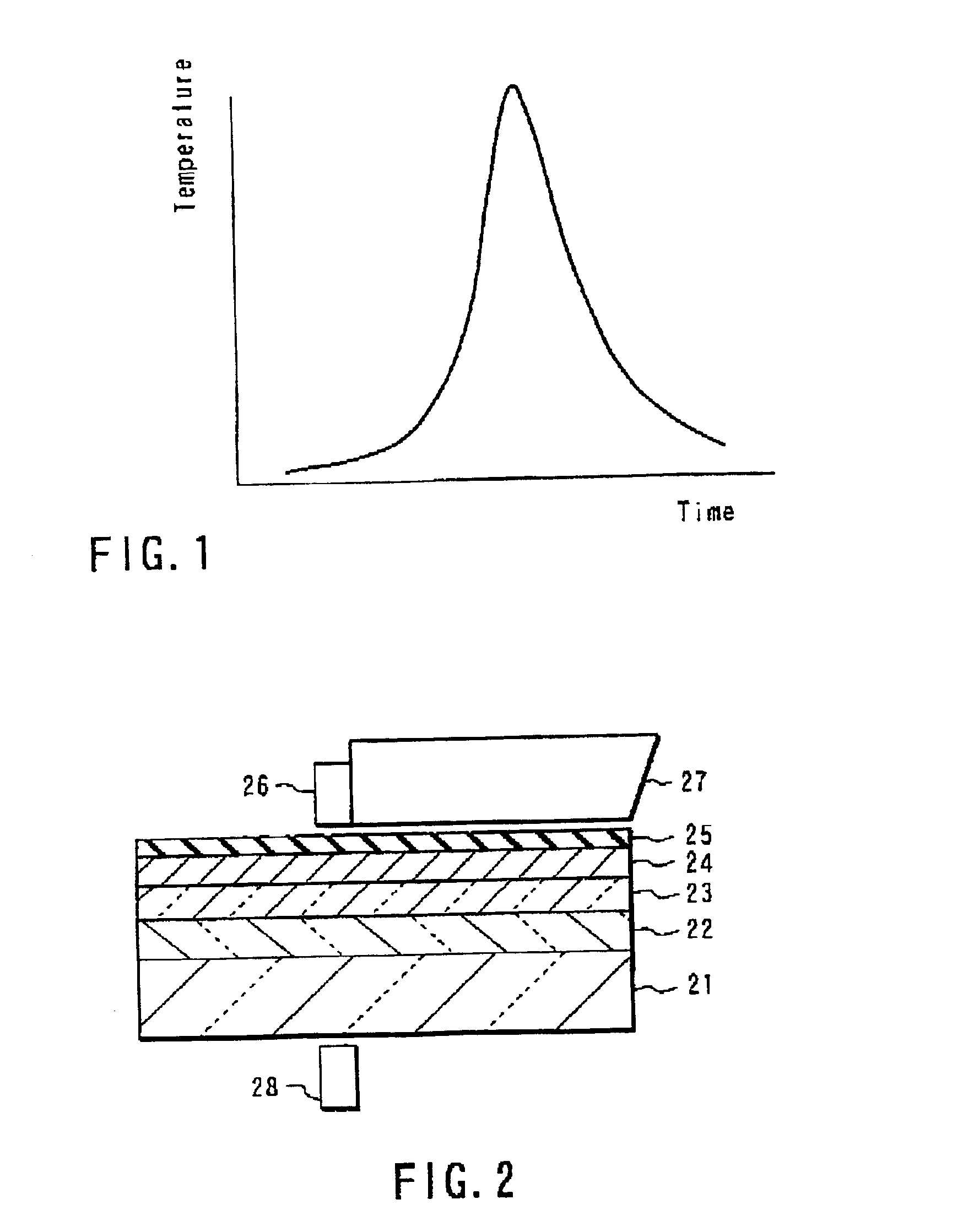
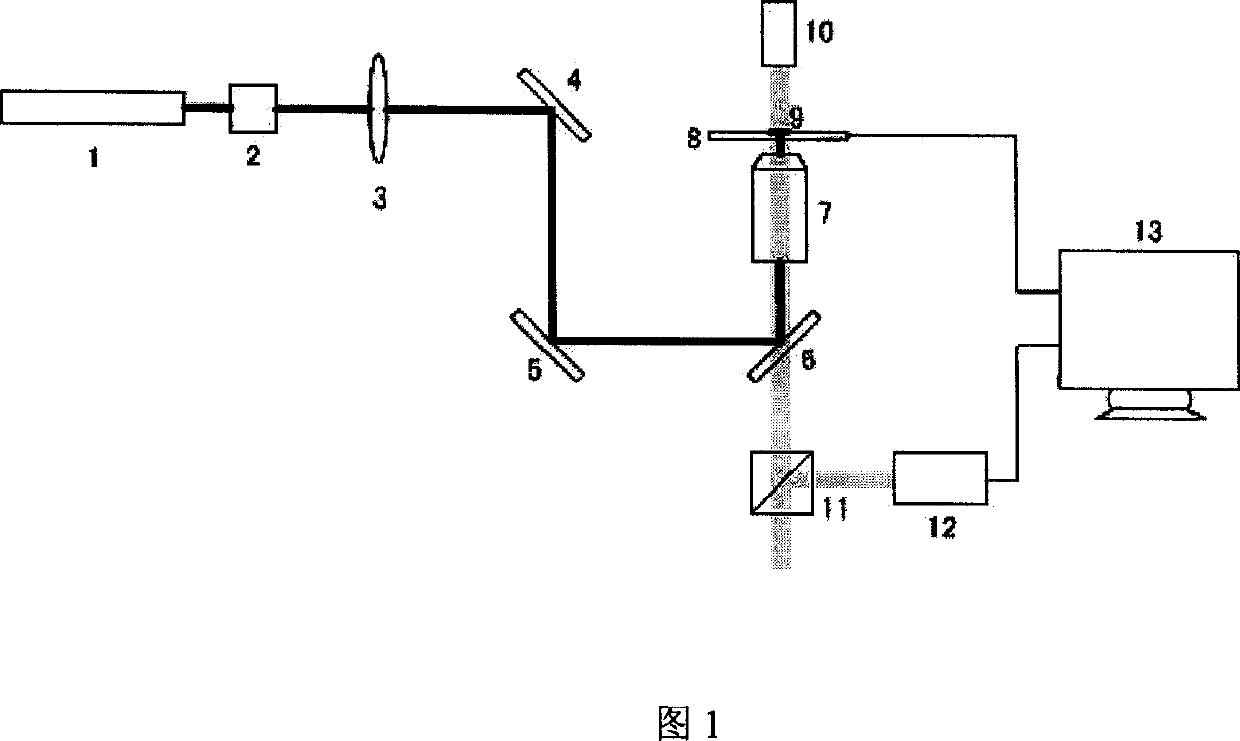
A method of designing a thermally-assisted magnetic recording apparatus having a magnetic recording medium, a heater and a magnetic head includes, determining a stable retention time tst for recorded magnetization and a thermal-fluctuation stability coefficient βst calculated from β(T)=KuV / kBT, where Ku is a magnetic anisotropy energy density, V is an activation volume, and kB is Boltzmann's constant, obtaining an equivalent degradation time tEQ calculated from tEQ=Σ(ΔtEQ), that sums values of ΔtEQ within a period of time Δt for a time span during which the medium is substantially degraded, where ΔtEQ=exp(ln(Δt)−β−βst) and β is a thermal-fluctuation stability coefficient for a medium temperature T in Δt, and determining specifications of the medium, the heater and the magnetic head in a manner to meet the relationship of tEQ<tst.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
A method for measuring liquid phase micro-area temperature
InactiveCN1963420ASolve the problem that the temperature measurement range is limited by the temperature measurement probeLow temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesTemperature measurement of flowing materialsSilicon dioxideMicro-needle
This invention relates to one liquid phase micro part temperature method, which is characterized by adopting light tamper or micro needle to transfer polyphenylacetylene or earth silicon emulsion or powder to test probe head into micro test area to discharge test probe by use of image.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for calibrating surface temperature of metal flat plate
InactiveCN102620836AAccurately measure emissivityEasy maintenanceRadiation pyrometryStefan–Boltzmann lawTest object
The invention relates to a method for calibrating surface temperature of a metal flat plate, which comprises the following steps: heating one surface of a measured metal flat plate by taking a constant temperature bath medium as a heating source, and installing a plurality of direct contact type thermal sensors on the surface to measure the temperature of the measured metal flat plate; measuring the surface temperature of the measured metal flat plate on the other surface of the to-be-measured metal flat plate with a non-contact type temperature-measuring apparatus; and calculating the surface emissivity of the measured metal flat plate according to the temperature measurement principle Stefan-Boltzmann law of an infrared temperature-measuring apparatus, wherein the Stefan-Boltzmann law is that the relationship between the radiant energy of a black body and the temperature T of the black body is as follows: W is equal to epsilon*alpha*T4, where Boltzmann constant alpha is equal to 5.67*10<-8>W / m<2>.K<4>, T is the absolute temperature of a tested object and has a unit of K, and epsilon is the surface emissivity of the tested object. The method provided by the invention is simple and easy to implement, and can accurately measure the surface emissivity of the measured metal flat plate so as to ensure accurate surface temperature measurement of the measured metal flat plate.
Owner:WISDRI WUHAN WIS IND FURNACE
Photo detecting pixels and x-ray detector including the same
ActiveUS20110278465A1Reducing kTC switching noiseReduce switching noiseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceControl signal
An X-ray detector including photo detecting pixels capable of reducing kTC switching noise (k: Boltzmann's constant; T: temperature; C: capacitance) by accurately performing correlated double sampling (CDS). Each of the pixels includes a first transistor comprising a first electrode connected to a first power line, a second electrode connected to a first node, and a gate electrode receiving the reset signal; a second transistor comprising a first electrode connected to the first power line, a second electrode connected to a second node, and a gate electrode connected to the first node; a third transistor comprising a first electrode connected to the second node, a second electrode connected to a data line, and a gate electrode connected to a gate line; a fourth transistor comprising a first electrode connected to the first node, a second electrode connected to a photo detecting diode, and a gate electrode receiving the control signal; and the photo detecting diode comprising a first electrode connected to the fourth transistor, and a second electrode connected to ground.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Thermally assisted recording media and system
InactiveUS8089829B2Combination recordingPatterned record carriersMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
Owner:HITACHI LTD
FET based nucleic acid detecting sensor
Nucleic acid detecting sensor includes field-effect transistor, detector which detects target nucleic acid molecules having sequences from sample based on degree of a variation in threshold voltage of field-effect transistor, and at least one nucleic acid probe molecule which is hybridized with corresponding one of target nucleic acid molecules, and is immobilized on gate of field-effect transistor, wherein gate width of field-effect transistor is of order of length obtained by expression given below (([epsilon]0[epsilon]rkBT / e<2>n)<1 / 2>, where [epsilon]0is the dielectric constant of vacuum, [epsilon]rthe relative permittivity of channel domain, kBthe Boltzmann constant, T the absolute temperature of the channel domain of FET, e the elementary charge, and n an equilibrium carrier density in the channel region in the field-effect transistor where a channel is formed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor light emitting element
In a semiconductor light emitting element, a p-type layer (220), an active layer (230) and an n-type layer (240) are laminated on a substrate in this order. The n-type layer (240) is formed with a rectangular n-side electrode (241) whose width in one direction is equal to that of the n-type layer (240). The thickness t of the n-type layer (240) satisfies Formula 1 below. The semiconductor light emitting element includes a side surface (270) extending in the lamination direction and formed with a plurality of projections (271). Supposing that the wavelength of the light from the active layer (230) is lambada, and the index of refraction of the n-type layer (240) or the p-type layer (220) is n, the average WA of widths at bottoms of the projections is set to satisfy WA >= lambada / n. In formula 1, L is width of the n-type layer in a direction different from the one direction, T is absolute temperature, W is width of the n-side electrode in a direction different from the one direction, J 0 is current density at the contact portion between the n-side electrode and the n-type layer, e is elementary charge, gamma is diode ideality factor, kappa is Boltzmann constant, rho is specific resistance of the n-type semiconductor layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Film-forming material and method for predicting film-forming material
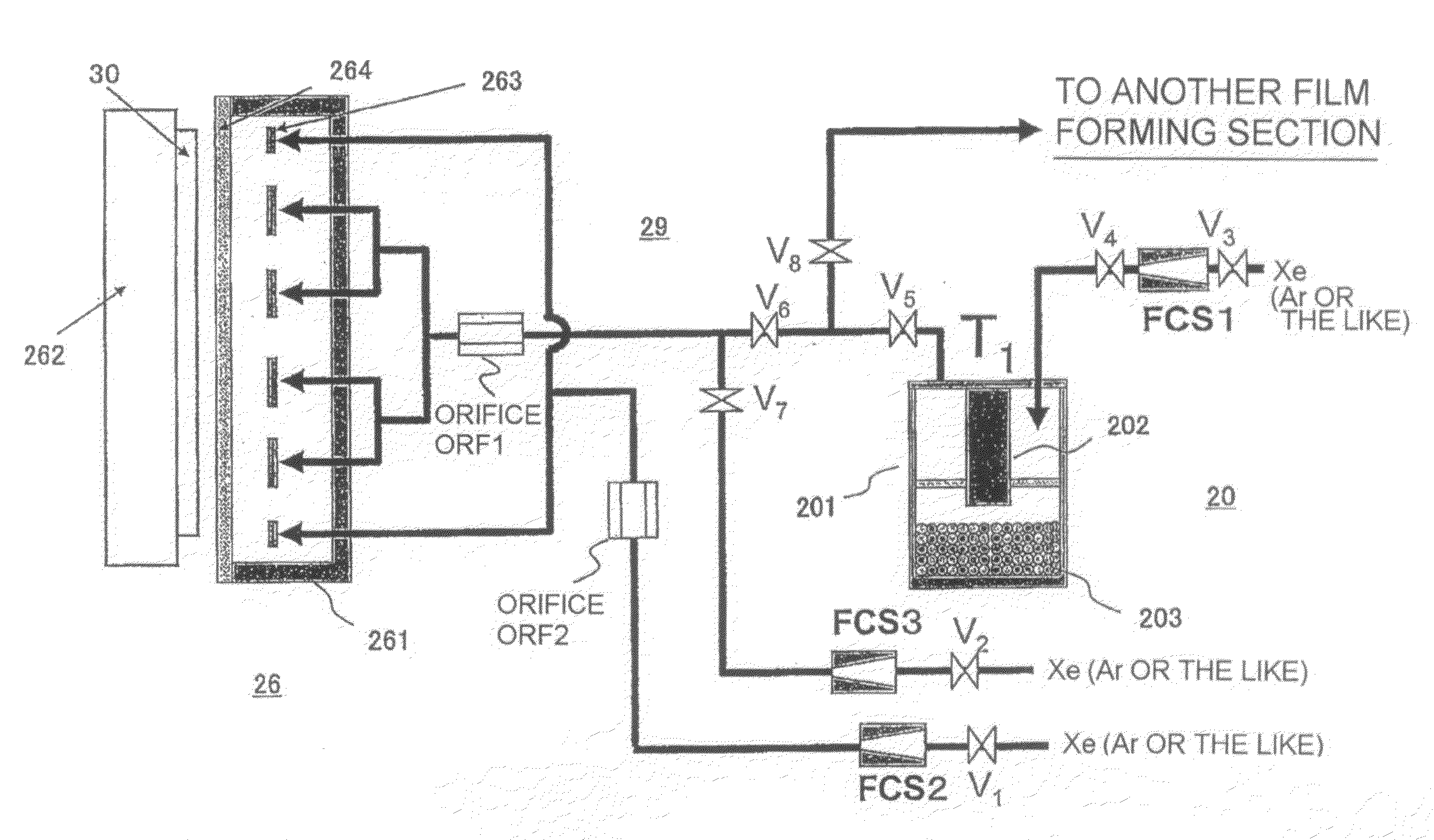
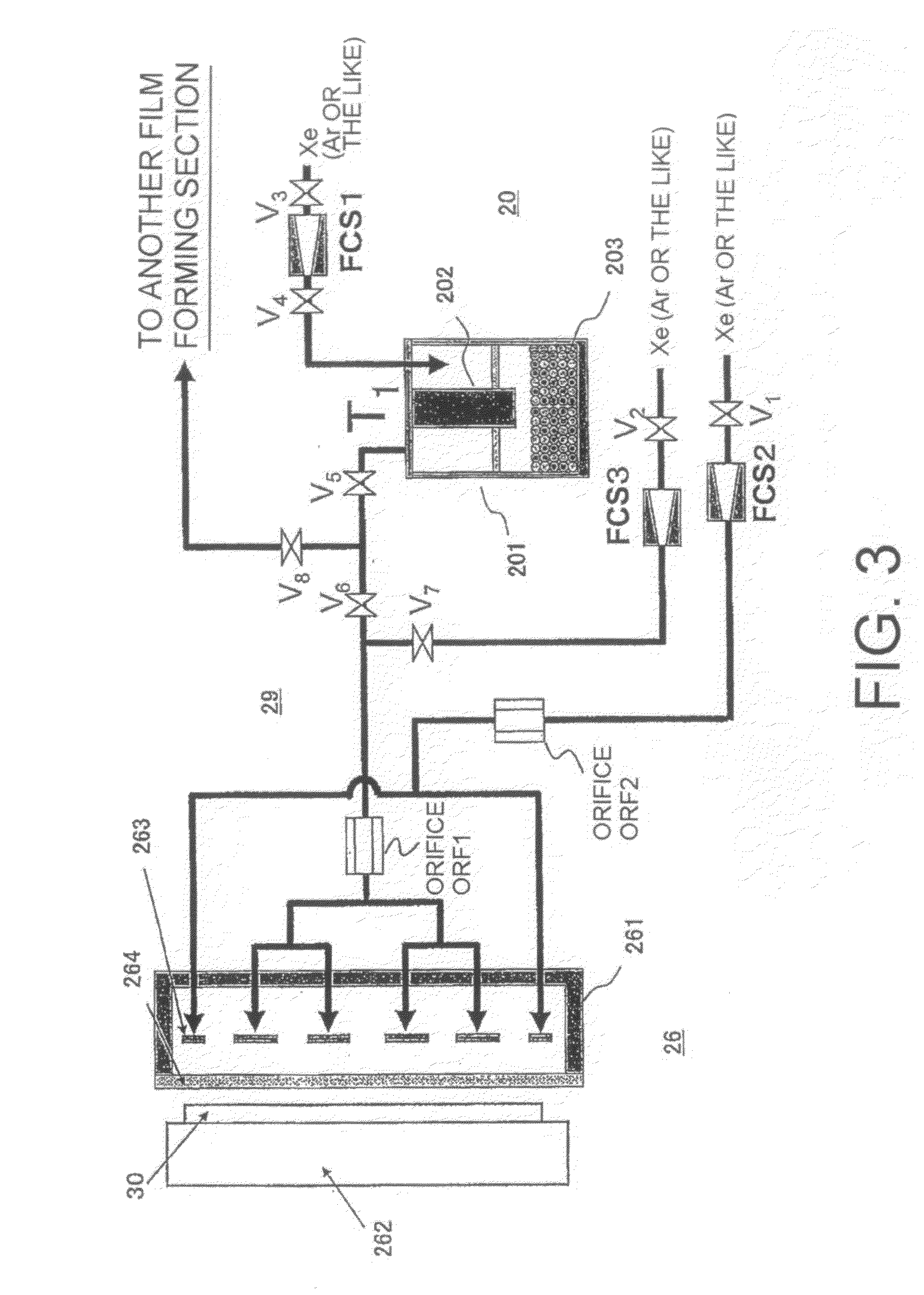
InactiveUS20090110823A1Solid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingActivation energyBoltzmann constant
Disclosed is a method for prediction of a film material such as a raw material for organic EL. In the method, a film material having an evaporation rate (V(%)) represented by the formula below can be predicted based on the values of the constant (Ko) and the activation energy (Ea). V=(Ko / P)×e−Ea / kT wherein Ko represents a constant (%·Torr), P represents a pressure (Torr), Ea represents an activation energy (eV), k represents a Boltzmann constant, and T represents an absolute temperature.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Silicon wafer and process for producing it
ActiveUS20050032376A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh yieldPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityOxygen
A process for producing a single-crystal silicon wafer, comprises the following steps: producing a layer on the front surface of the silicon wafer by epitaxial deposition or production of a layer whose electrical resistance differs from the electrical resistance of the remainder of the silicon wafer on the front surface of the silicon wafer, or production of an external getter layer on the back surface of the silicon wafer, and heat treating the silicon wafer at a temperature which is selected to be such that an inequality (1) [O i]<[O i]eq(T)exp 2σSiO2Ωr k Tis satisfied, where [Oi] is an oxygen concentration in the silicon wafer, [Oi]eq(T) is a limit solubility of oxygen in silicon at a temperature T, σSiO2 is the surface energy of silicon dioxide, Ω is a volume of a precipitated oxygen atom, r is a mean COP radius and k the Boltzmann constant, with the silicon wafer, during the heat treatment, at least part of the time being exposed to an oxygen-containing atmosphere.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Silicon wafer and process for producing it
InactiveUS20060278157A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh yieldAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthOxygenSilicon dioxide
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Magnetic memory
InactiveUS8957486B2Total current dropSolid-state devicesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryMagnetic memory
Provided is a magnetic random access memory to which spin torque magnetization reversal is applied, the magnetic random access memory being thermal stable in a reading operation and also being capable of reducing a current in a wiring operation. A magnetoresistive effect element formed by sequentially stacking a fixed layer, a nonmagnetic barrier layer, and a recording layer is used as a memory element. The recording layer adopts a laminated ferrimagnetic structure. The magnetic memory satisfies the expression Ms2(t / w)>|Jex|>(2kBTΔ) / S, in which kB is a Boltzmann constant, T is an operating temperature of the magnetic memory, S is an area parallel to a film surface of the magnetoresistive effect element, t and Ms are respectively a film thickness and a saturated magnetization of the ferromagnetic layer having a smaller film thickness among two ferromagnetic layers which are constituent members of the laminated ferrimagnetic structure, w is a length of a short side of the recording layer, Δ is a thermal stability index of the magnetic memory, and Jex is exchange coupling energy acting between the two ferromagnetic layers of the recording layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
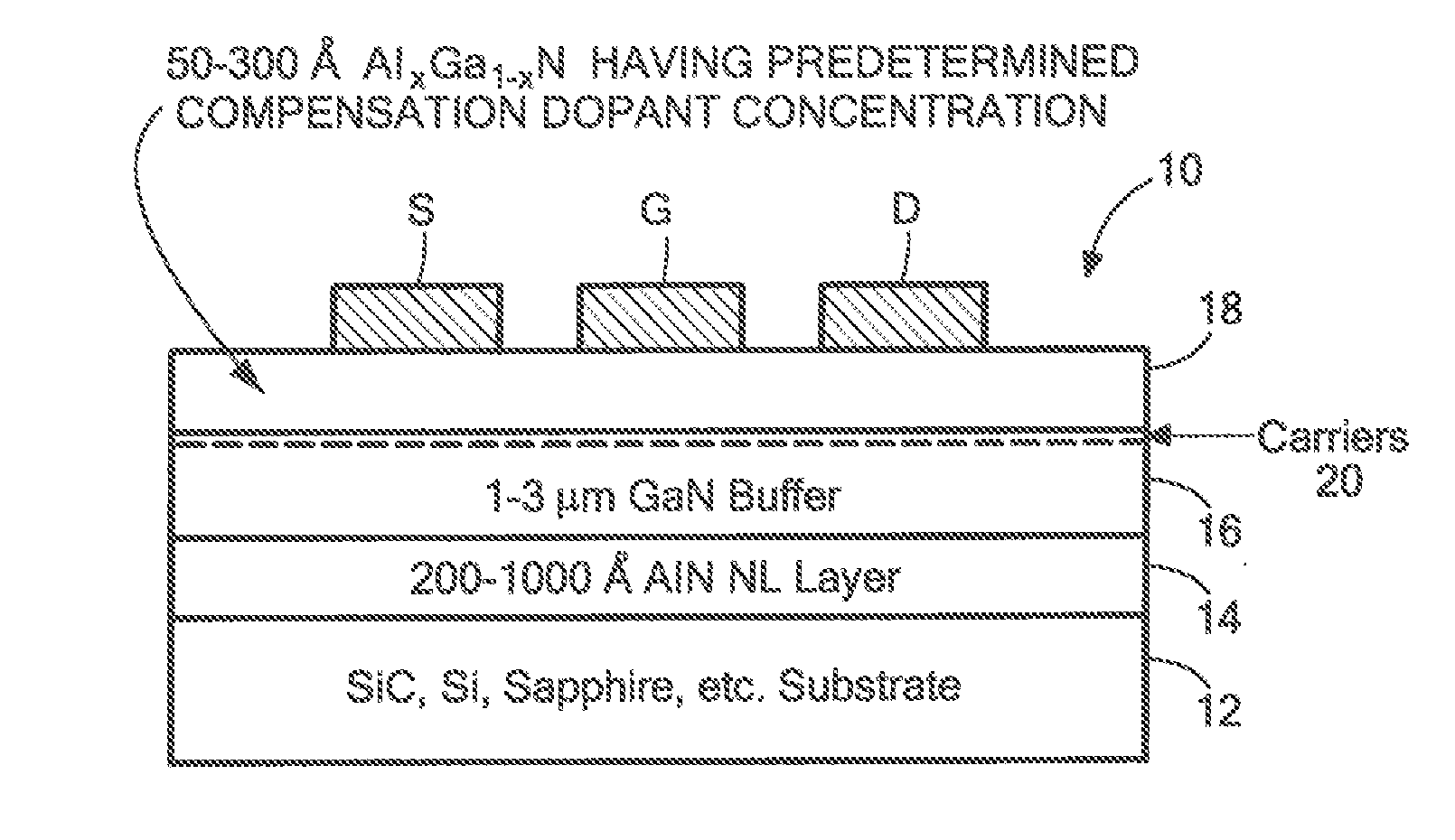
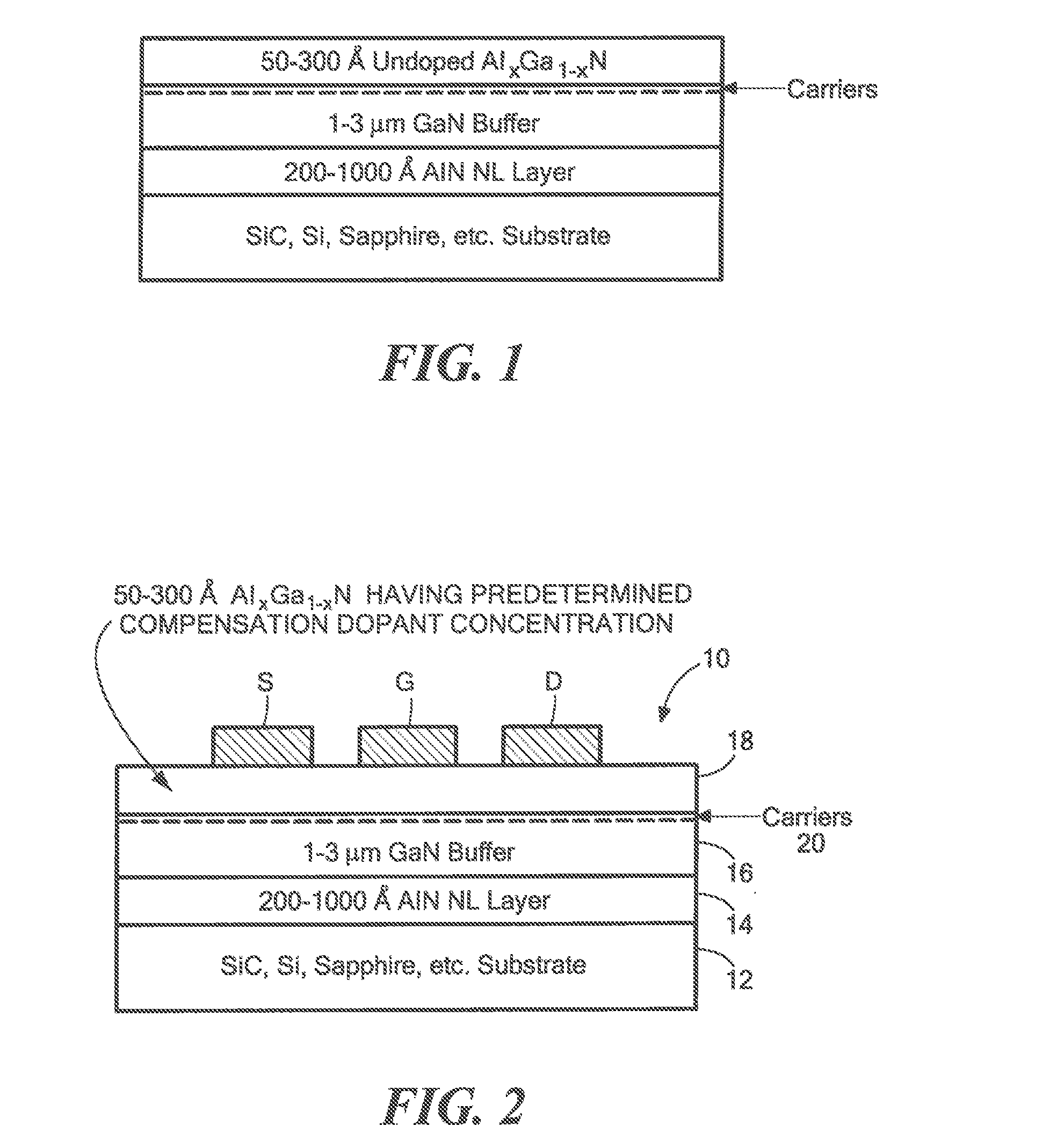
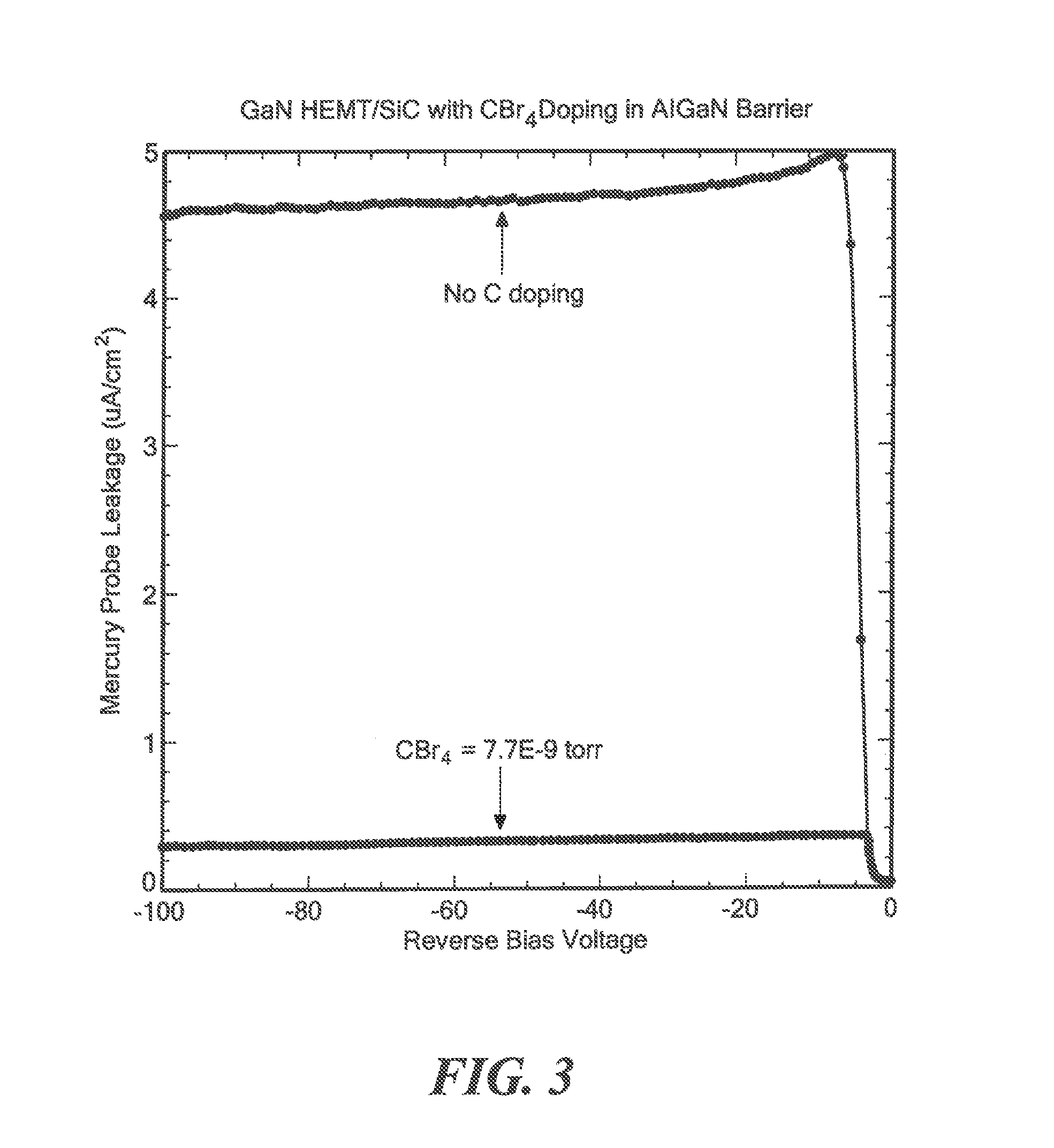
Polarization effect carrier generating device structures having compensation doping to reduce leakage current
InactiveUS20140183545A1Reduce leakage currentLeakage entreatsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantValence band
A semiconductor structure having: a first semiconductor layer; and an electric carrier generating layer disposed on the first semiconductor layer to generate electric carriers within the first semiconductor layer by polarization effects, the electric carrier generating layer having a predetermined conduction band and a predetermined valance band, the electric carrier generating layer having a concentration of non-carrier generating contaminants having an energy level, the difference in the energy level of the non-carrier type contaminants and the energy level of either the conduction band or the valence band being greater than 10 kT, where k is Boltzmann's constant and T is the temperature of the electric carrier generating semiconductor layer, the electric carrier generating semiconductor layer being doped with a dopant having an energy level, the difference in the energy level of the dopant and the energy level of either the conduction band or the valence band being greater than 10 kT, the dopant having a concentration equal to or greater than the concentration of the non-carrier generating contaminants.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Continuous inkjet printing
ActiveUS20100321449A1Reduction tendencyReduce wearOther printing apparatusPrintingParticulatesLiquid density
A continuous inkjet method in which liquid passes through a nozzle, the liquid being jetted comprising one or more dispersed or particulate components and where the particle Peclet number, Pe, defined byPe=1.25φT·deff3μSkTρU3xis less than 500 and where the effective particle diameter, deff, is calculated asdeff=(∫0∞d3φ(d)d∫0∞φ(d)d)1 / 3where Φ(d) is the volume fraction of the particles or components of diameter d (m) and where ΦT is the total volume fraction of dispersed or particulate components, μS is the viscosity of the liquid without particles (Pa.s), ρ is the liquid density (kg / m3), U is the jet velocity (m / s), x is the length of the nozzle in the direction of flow (m), k is Boltzmann's constant (J / K) and T is temperature (K). The present invention limits the magnitude of flow induced noise generated by particulate components in the ink to maximise the efficiency of drop formation and to minimise adverse interactions with the nozzle.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
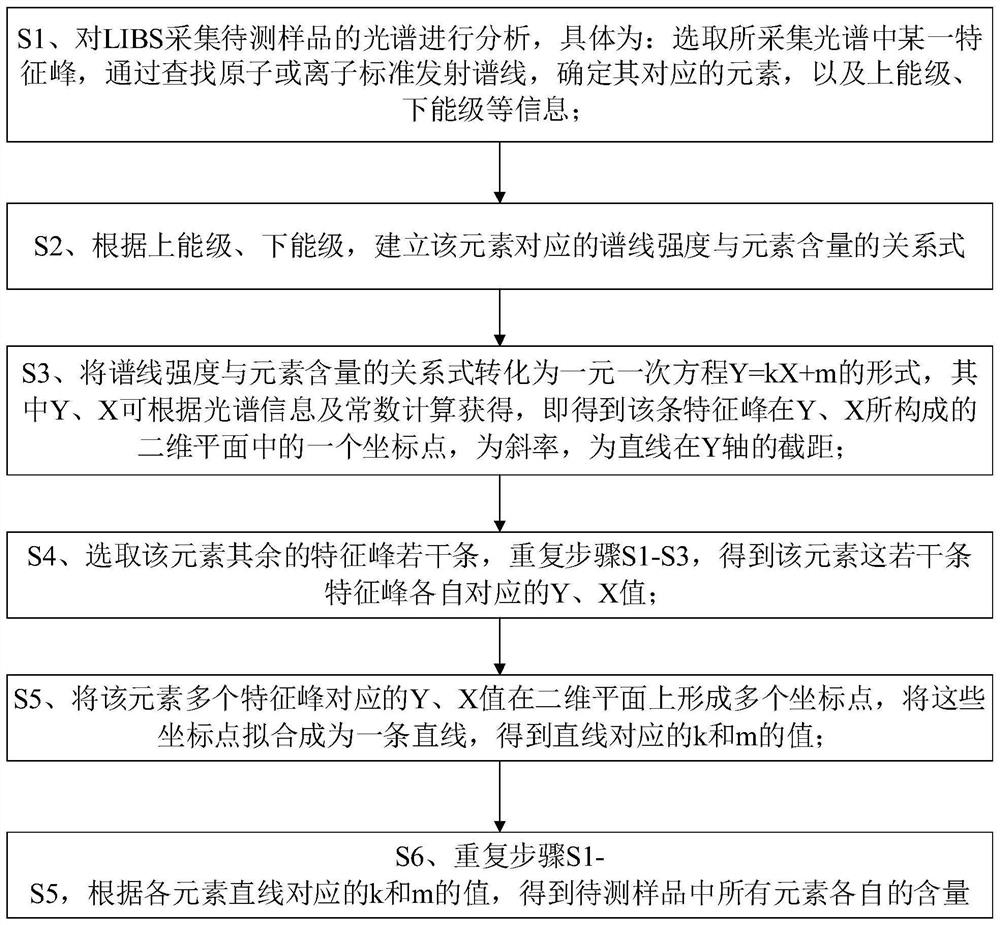
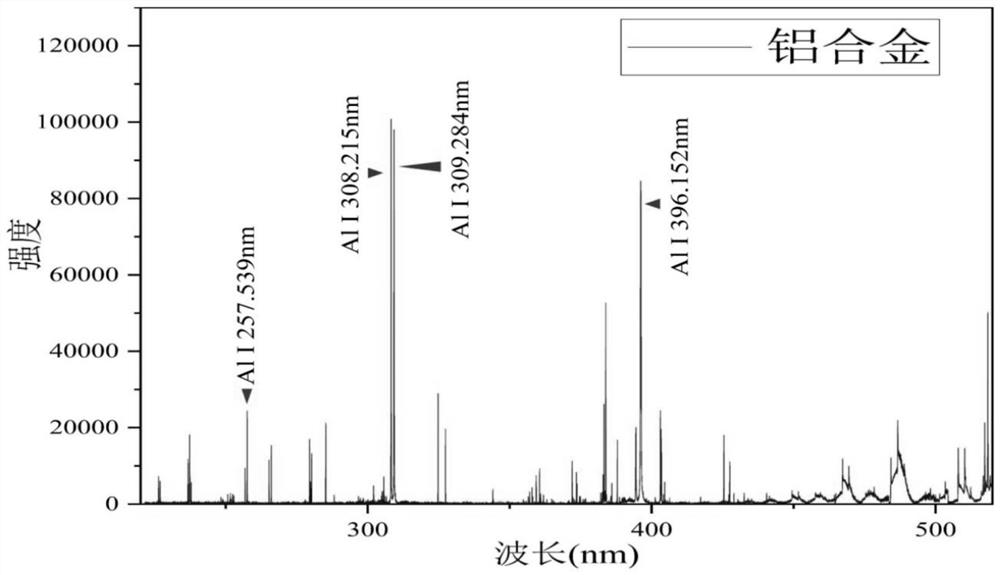
Non-calibration method for quantitative analysis of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy elements
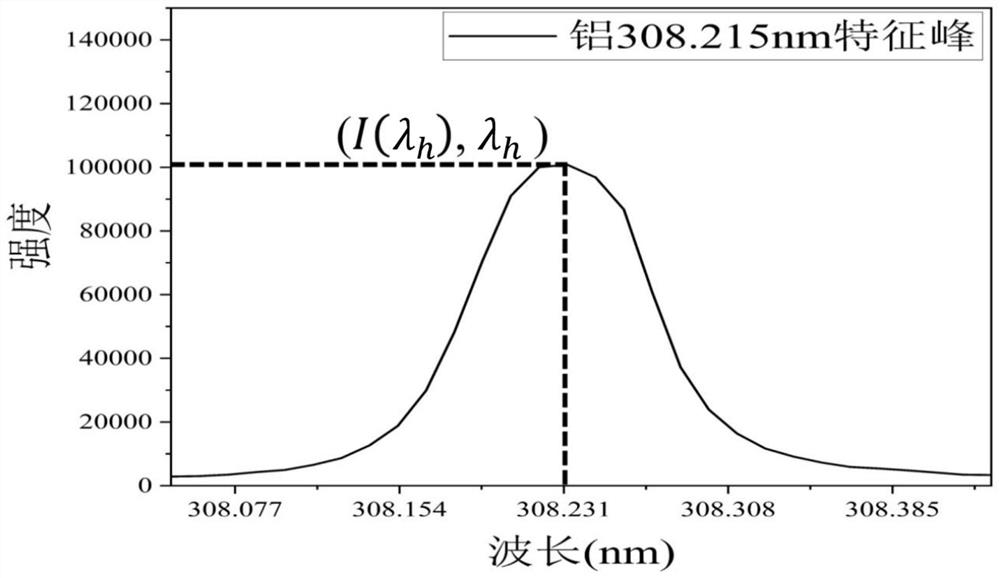
ActiveCN112834485AOvercoming matrix effectAccurate Elemental Quantification ResultsAnalysis by thermal excitationElement analysisLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention discloses a non-calibration method for quantitative analysis of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy elements, which is applied to the field of spectral element analysis and aims to solve the technical problems that in the prior art, a to-be-detected sample needs to have certain priori knowledge, and the sample to be detected with unknown elements cannot be quickly and accurately quantitatively analyzed. The method is based on a Maxwell rate distribution law and a Doppler effect; a quantitative relation between the intensity of a spectrum peak and the like and physical quantities such as characteristic light wavelength, element content, instrument parameters, atomic mass, light velocity, upper and lower energy levels, a Boltzmann constant and a Planck constant is given; meanwhile, quantitative analysis of elements of the to-be-detected sample is realized according to a normalization method and the like; and the method provided by the invention can overcome the matrix effect to a great extent, and is suitable for solid, liquid and gas samples and various types of LIBS (Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) equipment.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
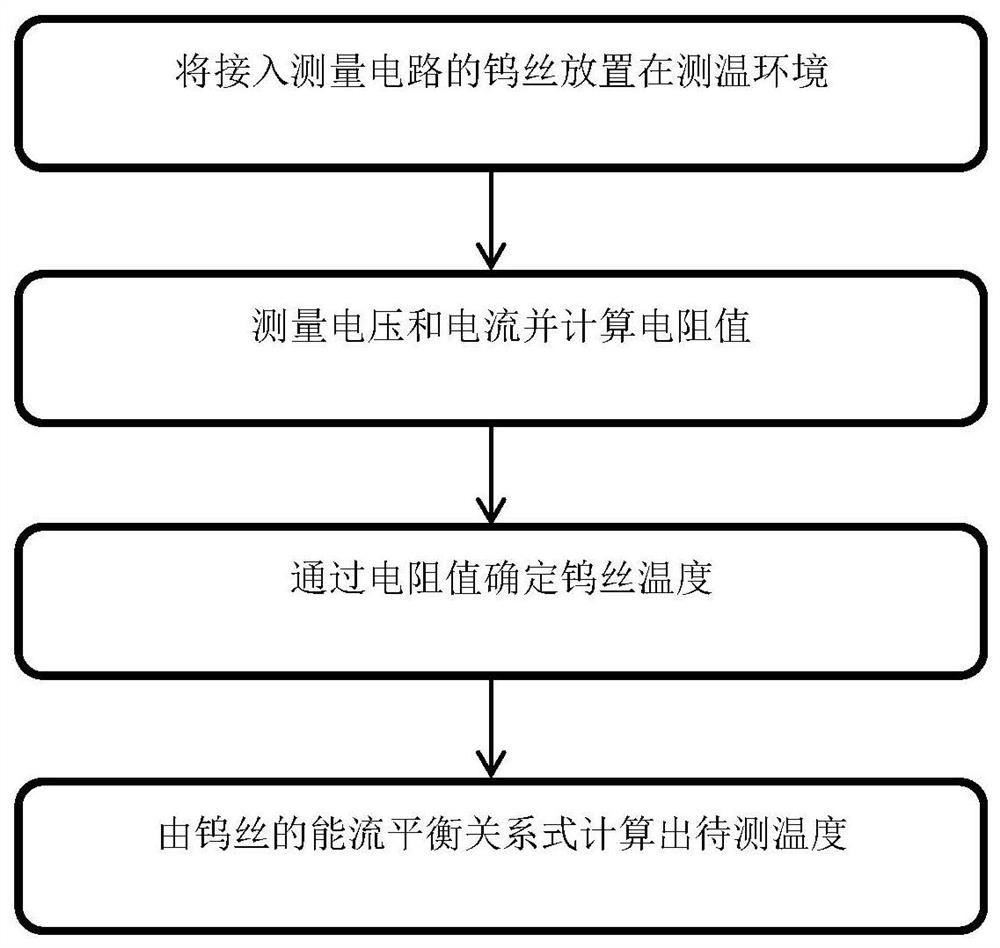
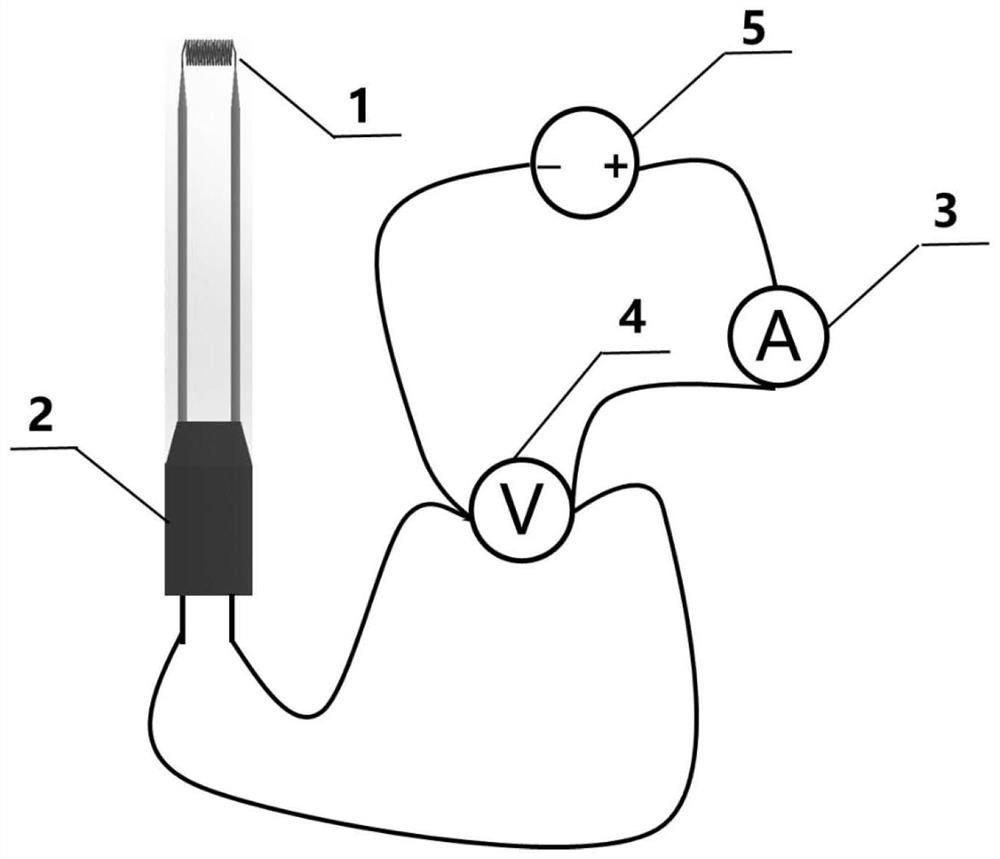
Contact measurement method for temperature of high-temperature gas based on steady-state energy flow balance relation
PendingCN113654689AExpand the temperature measurement rangeLow costThermometer applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
The invention belongs to the technical field of temperature measurement instruments, discloses a contact measurement method for the temperature of high-temperature gas based on a steady-state energy flow balance relation and aims to solve the problems existing in measurement of the temperature of a high-temperature heat source in an open state. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a steady-state equation of a probe tungsten filament and the surrounding environment, measuring a voltage value V at the two ends of the probe tungsten filament and a current value I flowing through the probe tungsten filament through an ampere meter and a voltmeter of a measuring device, thereby calculating the probe tungsten filament resistance R and the probe tungsten filament temperature TW; and substituting the voltage value V, the current value I, the probe tungsten filament temperature TW, the probe tungsten filament superficial area S1 obtained through direct measurement, the total radiation area S2 of the probe tungsten filament, the known heat transfer coefficient beta of the environment and the probe tungsten filament, and Stefan-Boltzmann constant sigma into the established steady-state equation to obtain the temperature TS of the environment gas. The method is easy to operate and low in cost, contact measurement can be carried out on the temperature of 2000-6000 K, and the temperature measurement range of contact measurement is greatly widened.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
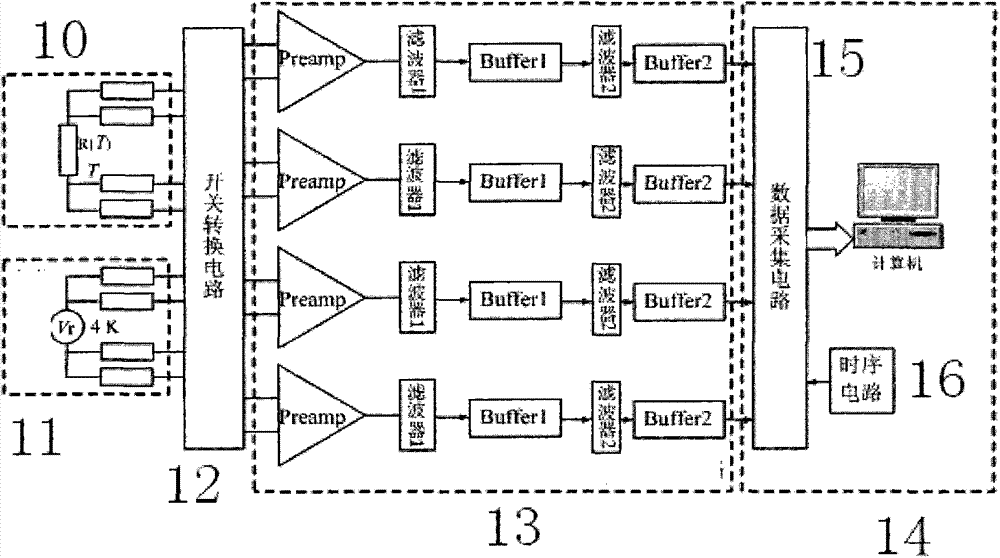
Four-channel noise thermometer with quantum voltage as reference
InactiveCN103674315AMeasurement integration time reductionShort integration timeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansData acquisitionMeasurement study
The invention relates to a four-channel noise thermometer with a quantum voltage as reference. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference comprises a noise source to be measured, a reference quantum voltage pseudo noise source, and a switch change-over circuit which is connected with the noise source to the measured and the reference quantum voltage pseudo noise source. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference is characterized in that a four-channel amplifying and filtering circuit is connected with a switch connecting circuit, and the four-channel amplifying and filtering circuit is correspondingly connected with a four-channel acquisition channel of a data acquisition and processing portion. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference can effectively reduce integral time required by measurement, reduces system deviations and can play an enormous role in thermodynamic temperature and Boltzmann constant measurement studies.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Method of measuring impurity activation energy in semiconductor
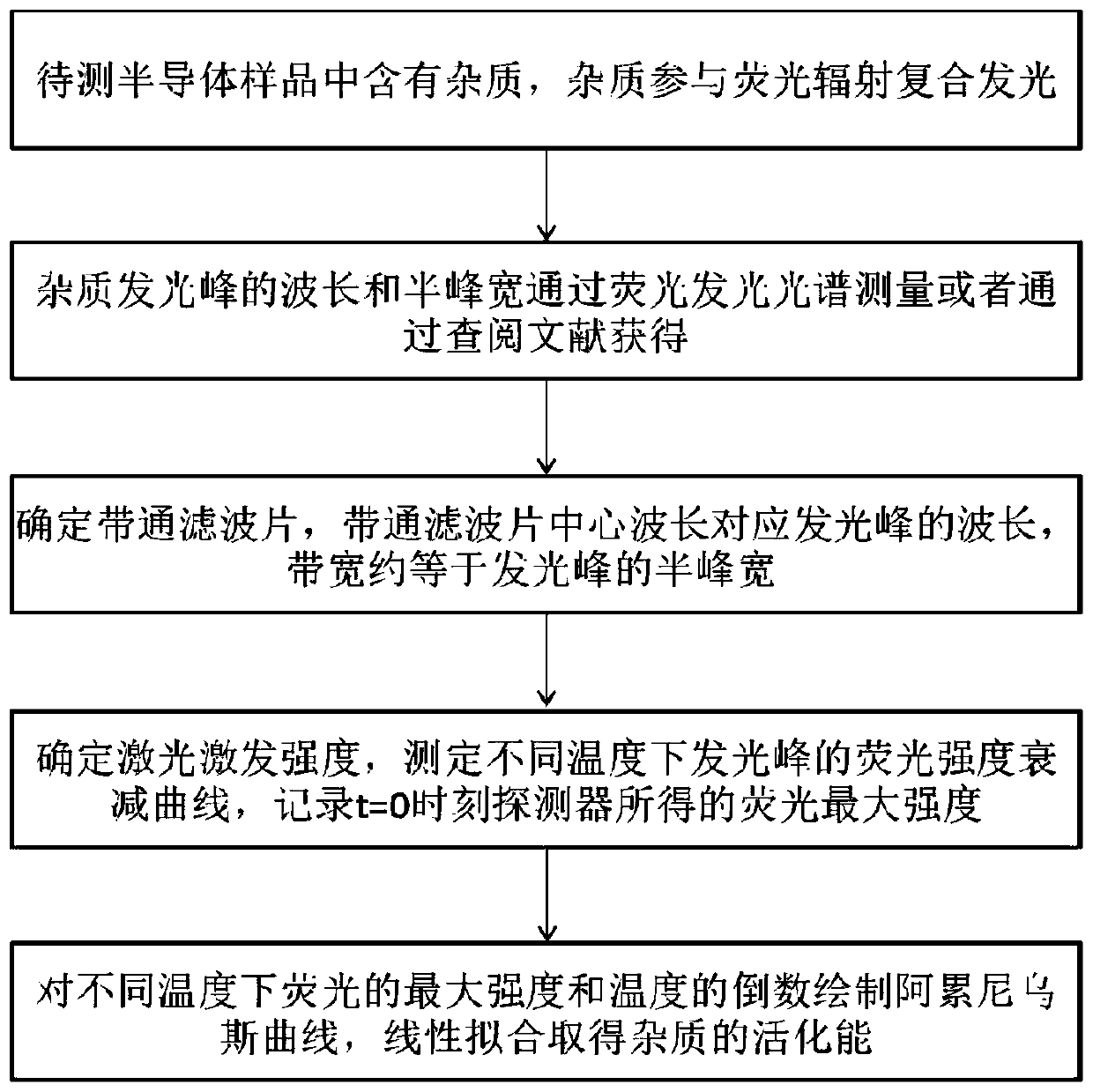
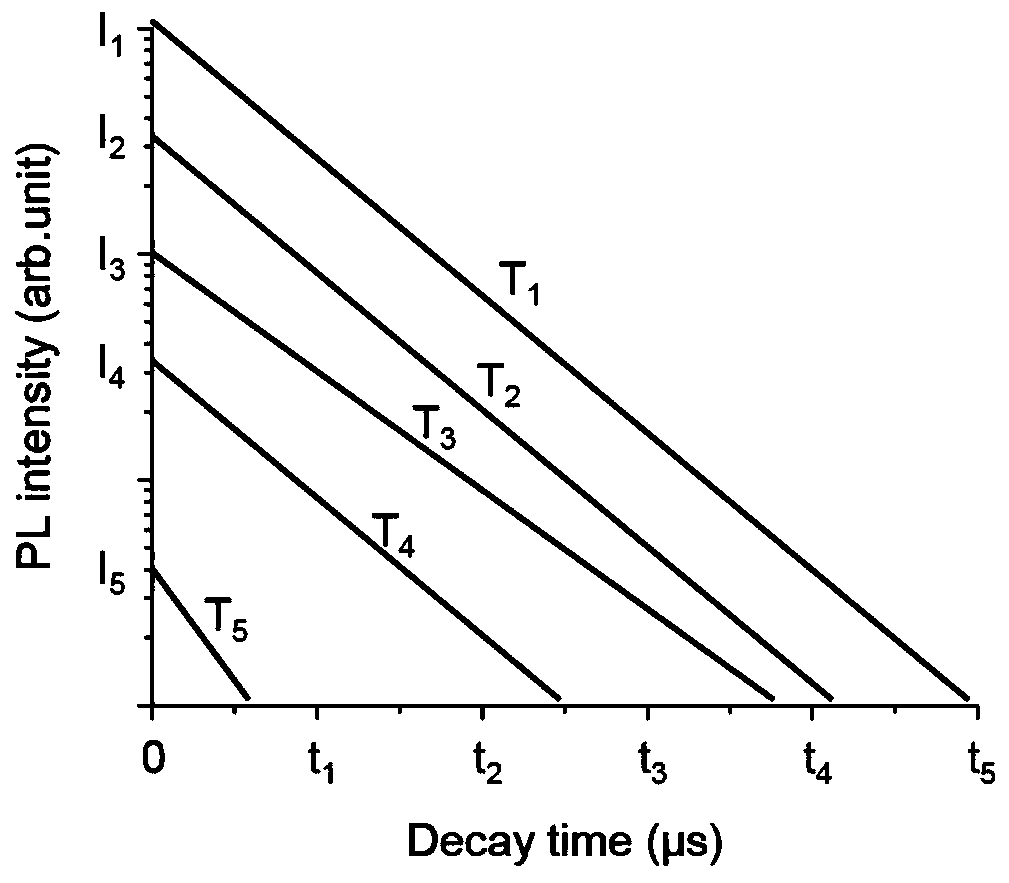
ActiveCN111366833ASimple processEasy to operateContactless testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceBandpass filteringSemiconductor materials
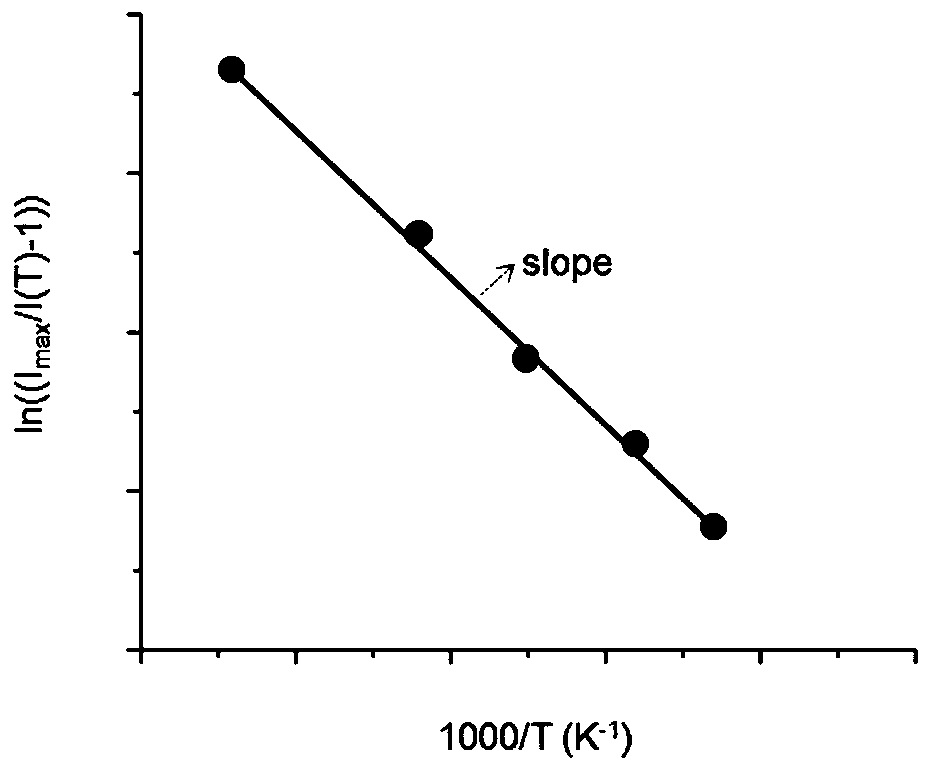
The embodiment of the invention relates to a semiconductor material analysis and detection technology, discloses a method for measuring activation energy of impurities in a semiconductor, and expandsapplication occasions of a time-resolved fluorescence spectrum. The method comprises the following steps of impurities in the semiconductor participating in fluorescence radiation composite luminescence; obtaining the wavelength and the half-peak width of an impurity luminescence peak; determining a band-pass filter, determining laser excitation intensity, determining fluorescence intensity attenuation curves of corresponding light-emitting peaks at different temperatures, and recording the maximum fluorescence intensity obtained by the detector at the moment t=0; drawing an Arrhenius curve according to the fluorescence maximum intensity and the reciprocal of the temperature measured by the detector at different temperatures, carrying out linear fitting to obtain a slope, and multiplying the slope by a Boltzmann constant to obtain the activation energy of the impurities. The method is advantaged in that the temperature-dependent carrier lifetime information can be obtained by using thevariable-temperature time-resolved fluorescence spectrum, the activation energy of an impurity introduction energy level can be obtained, the method is simple, convenient and easy to operate, experiment cost is greatly reduced, and operation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com