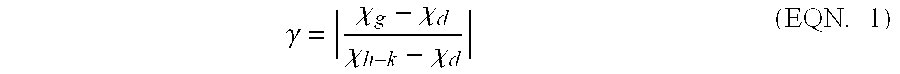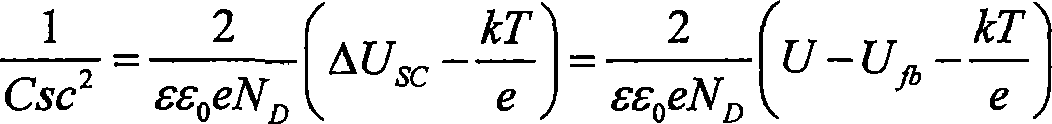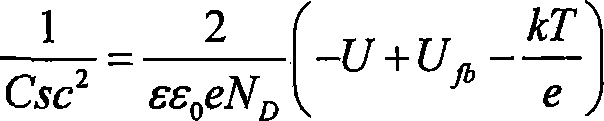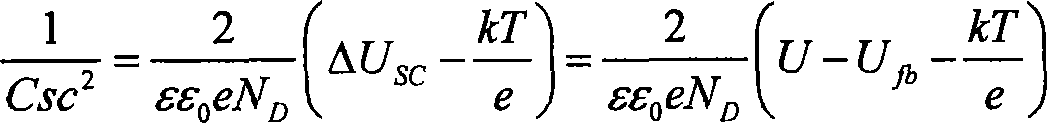Patents
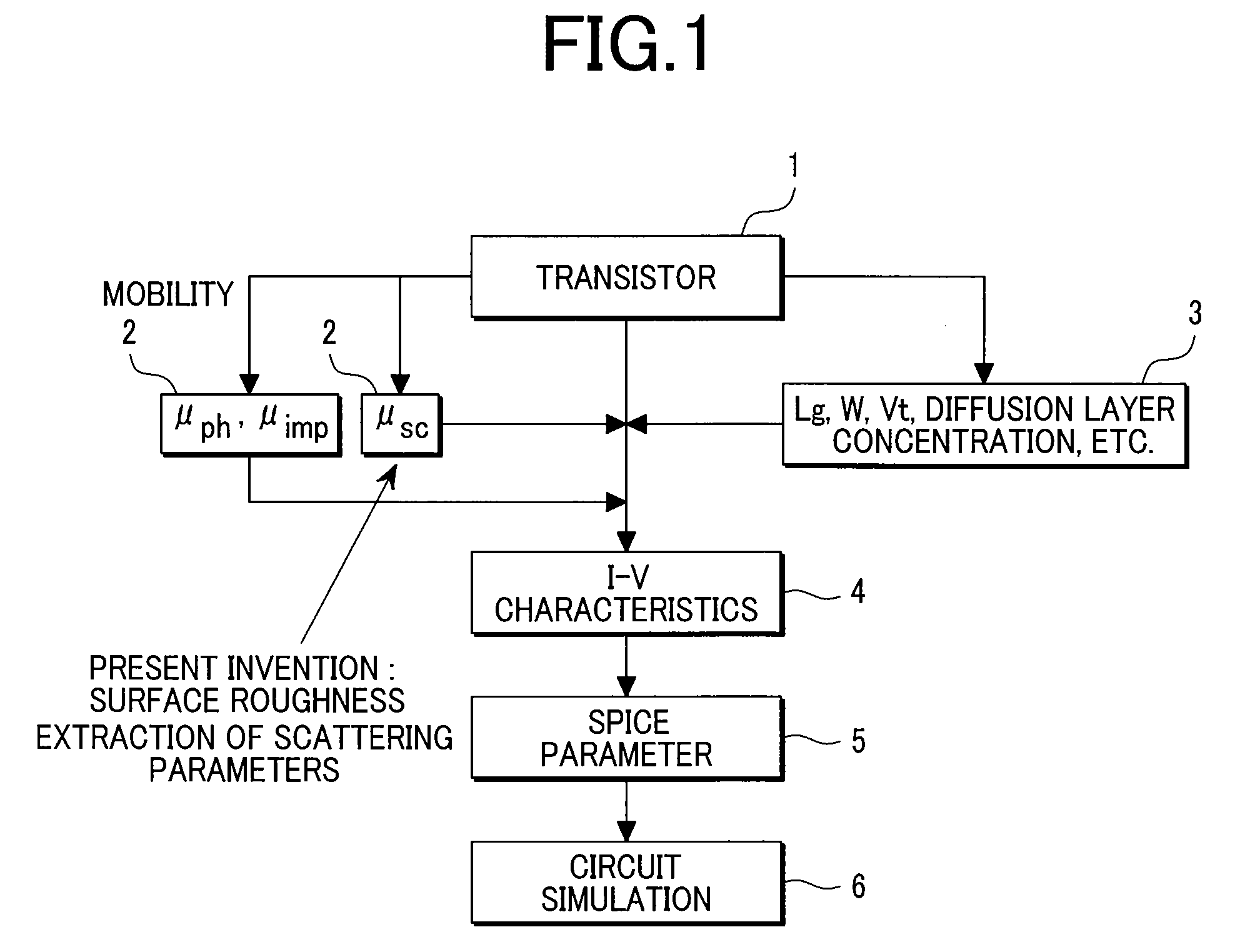
Literature
146 results about "Flat band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
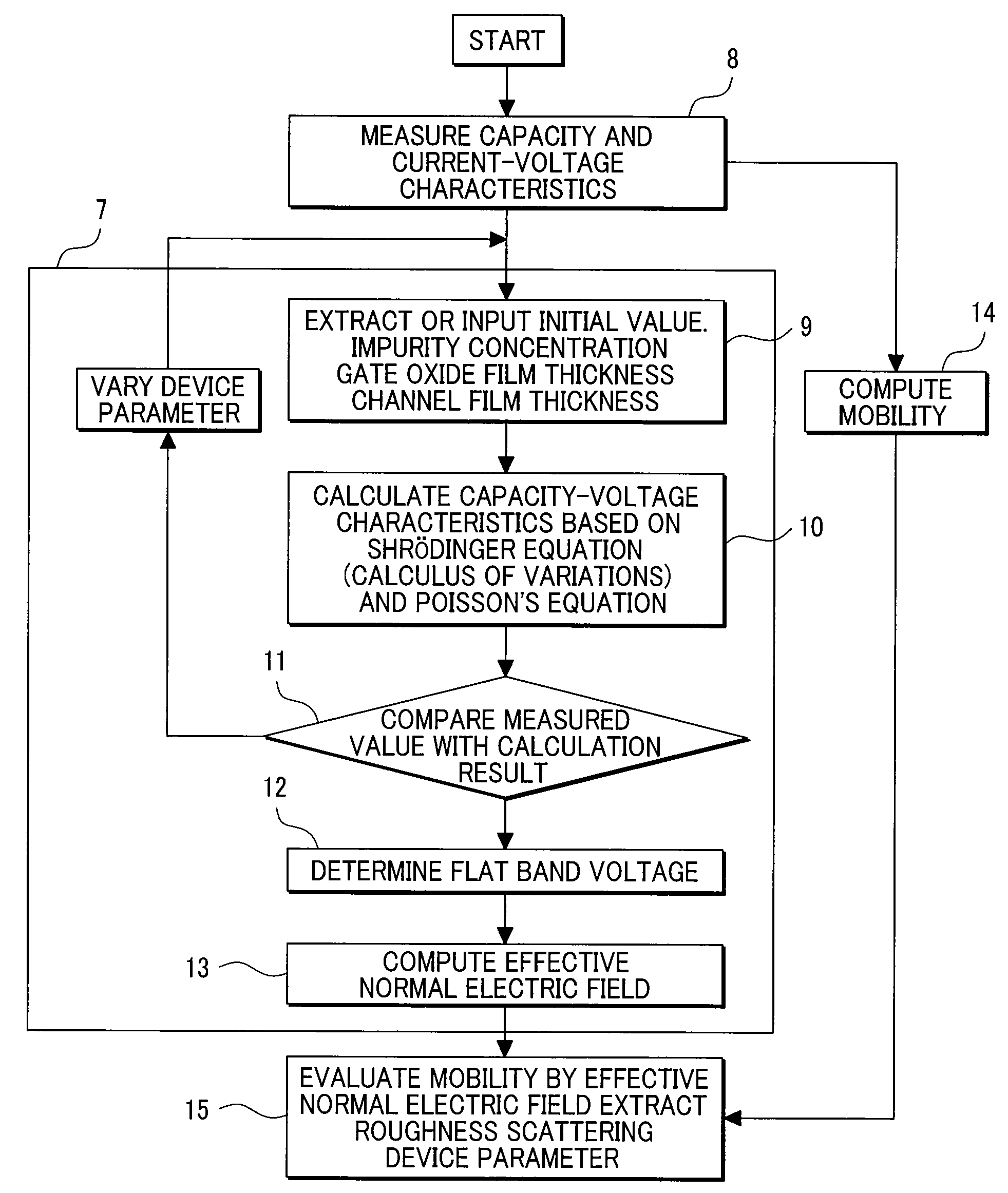
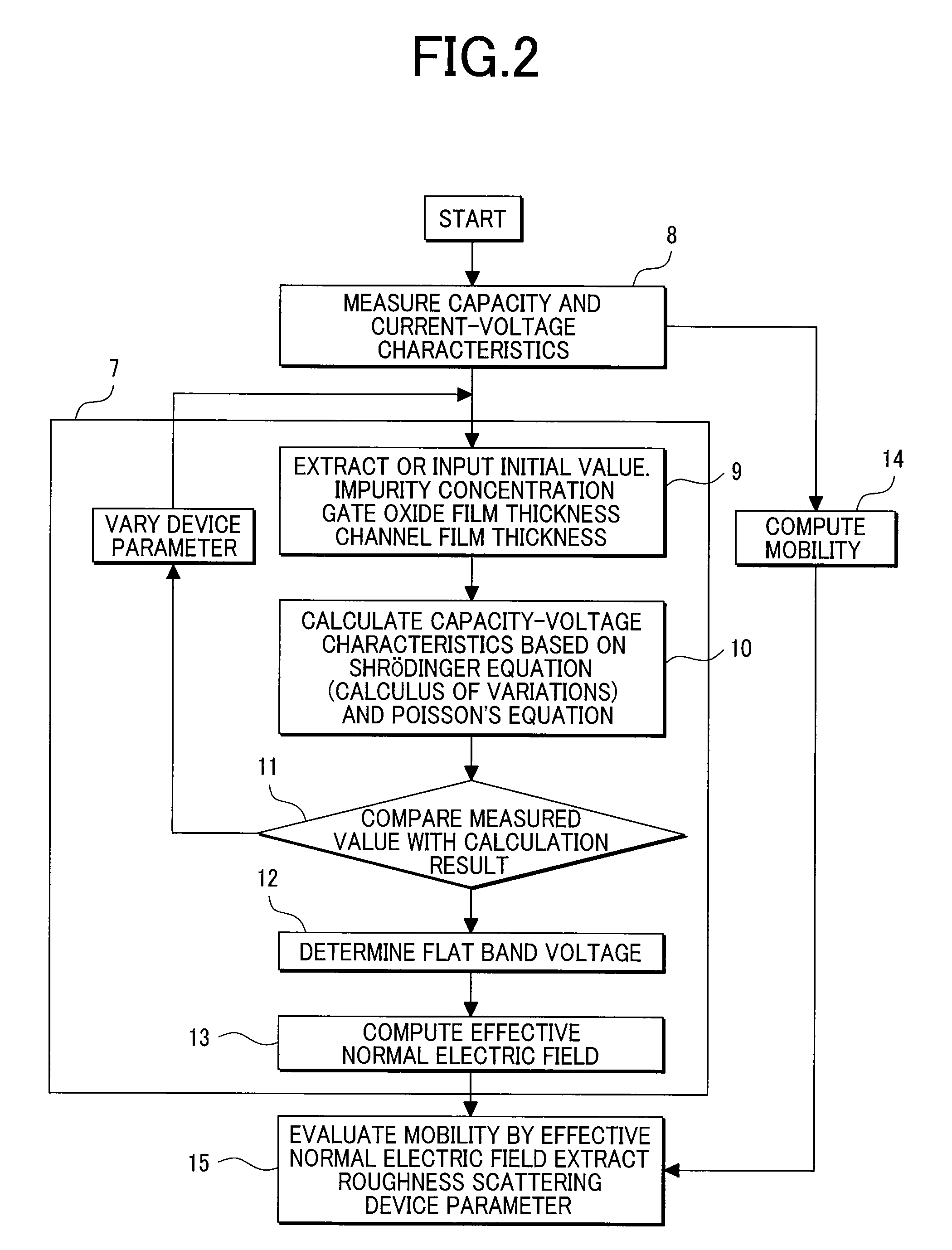
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
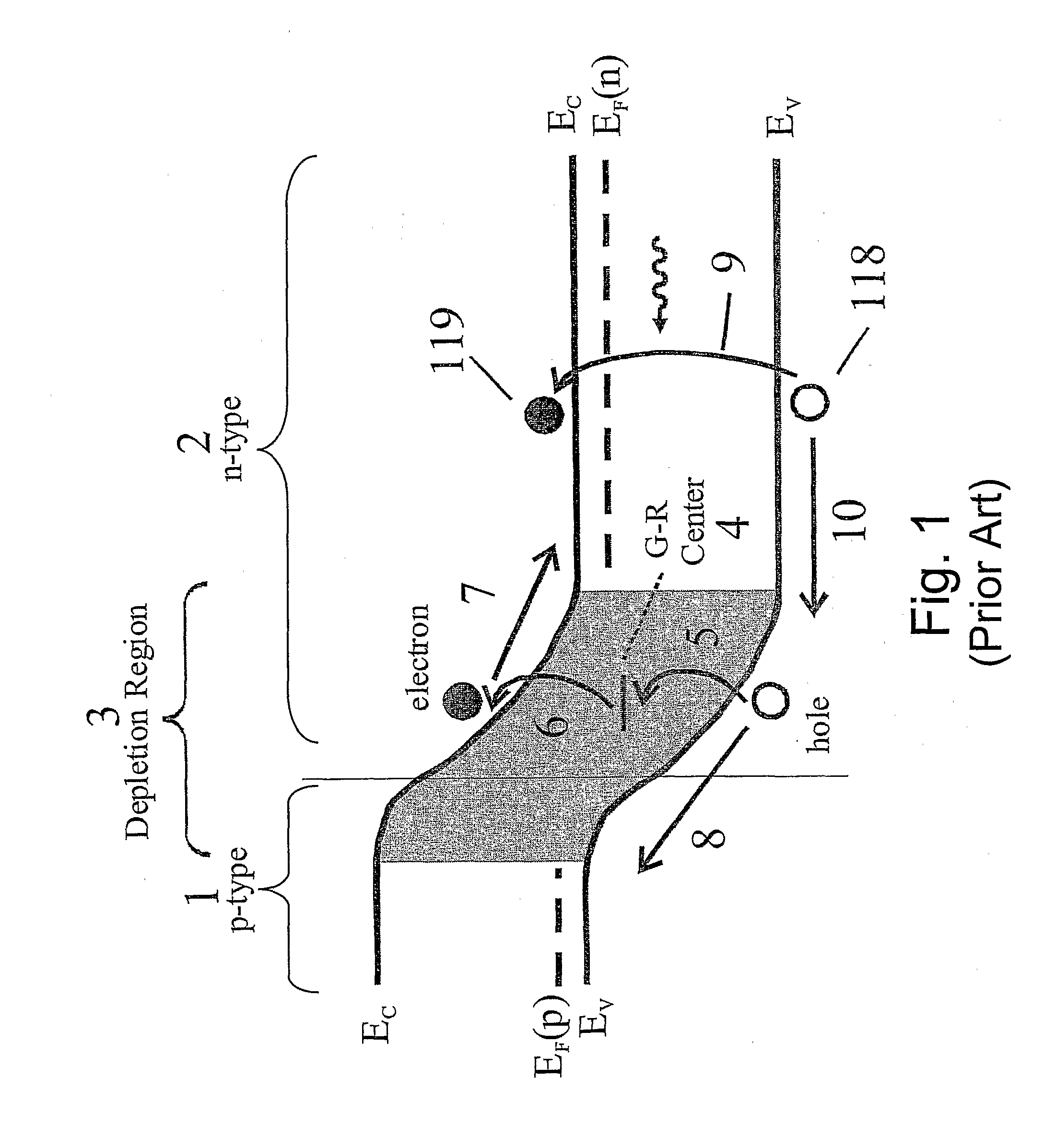
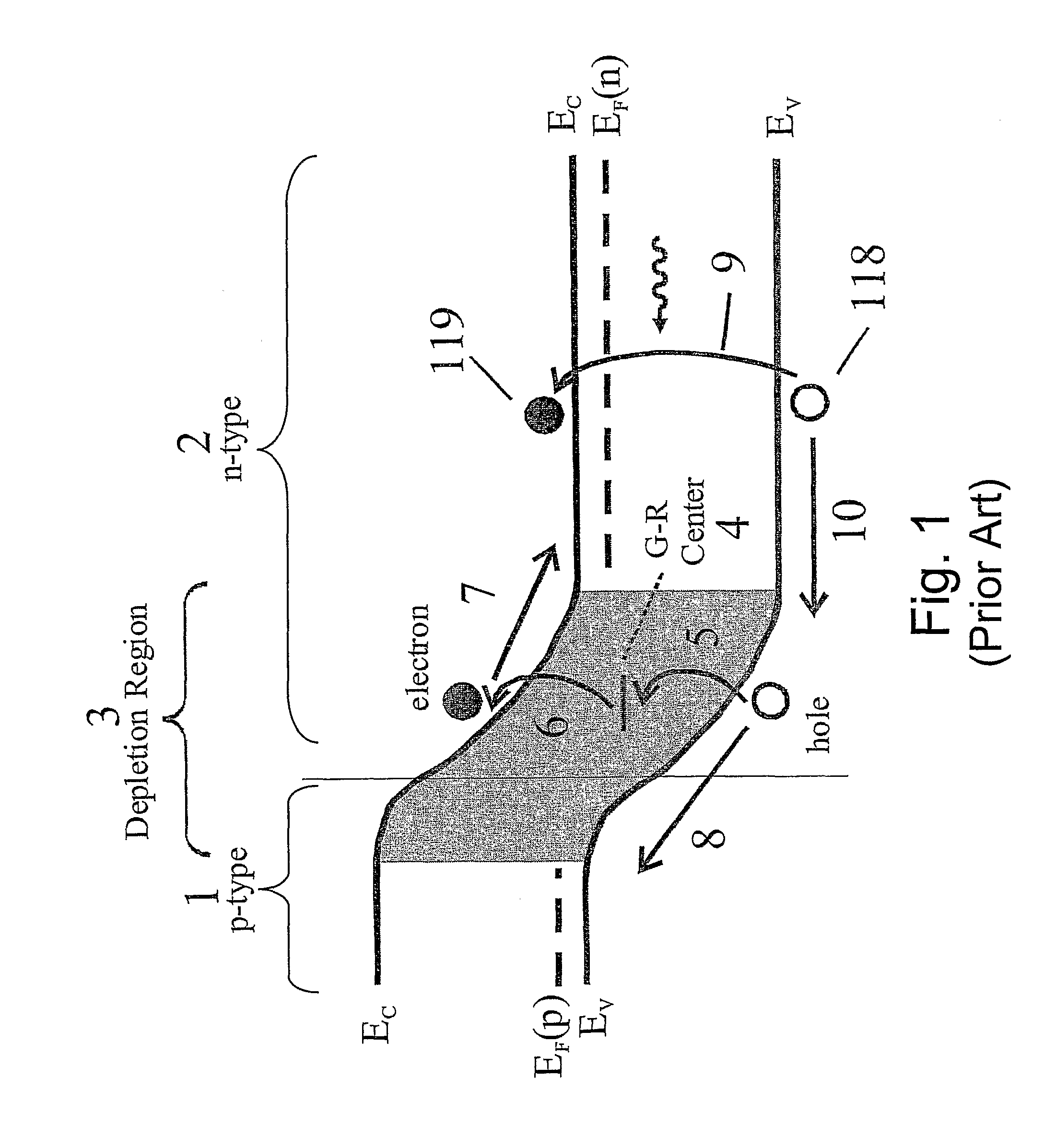
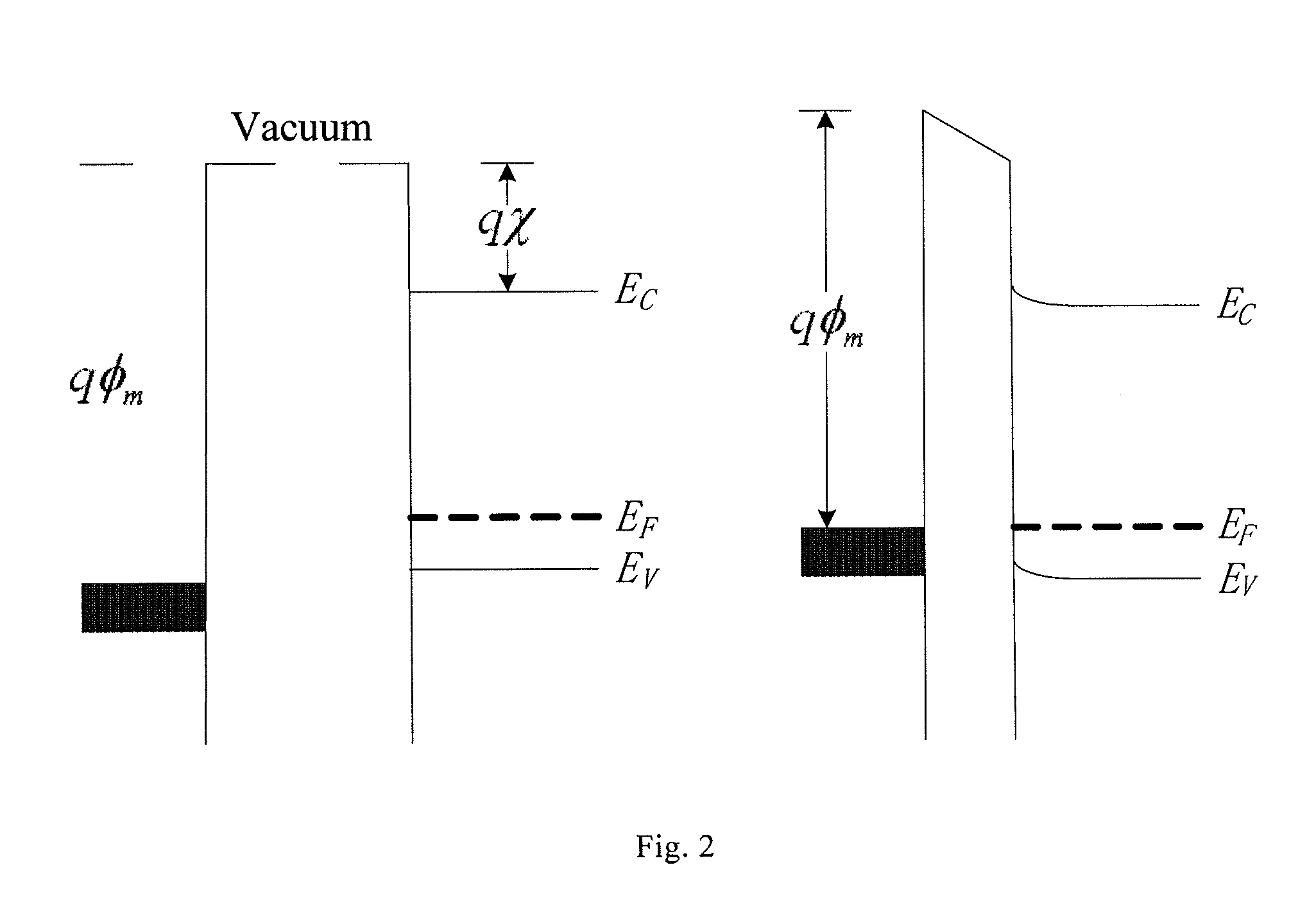
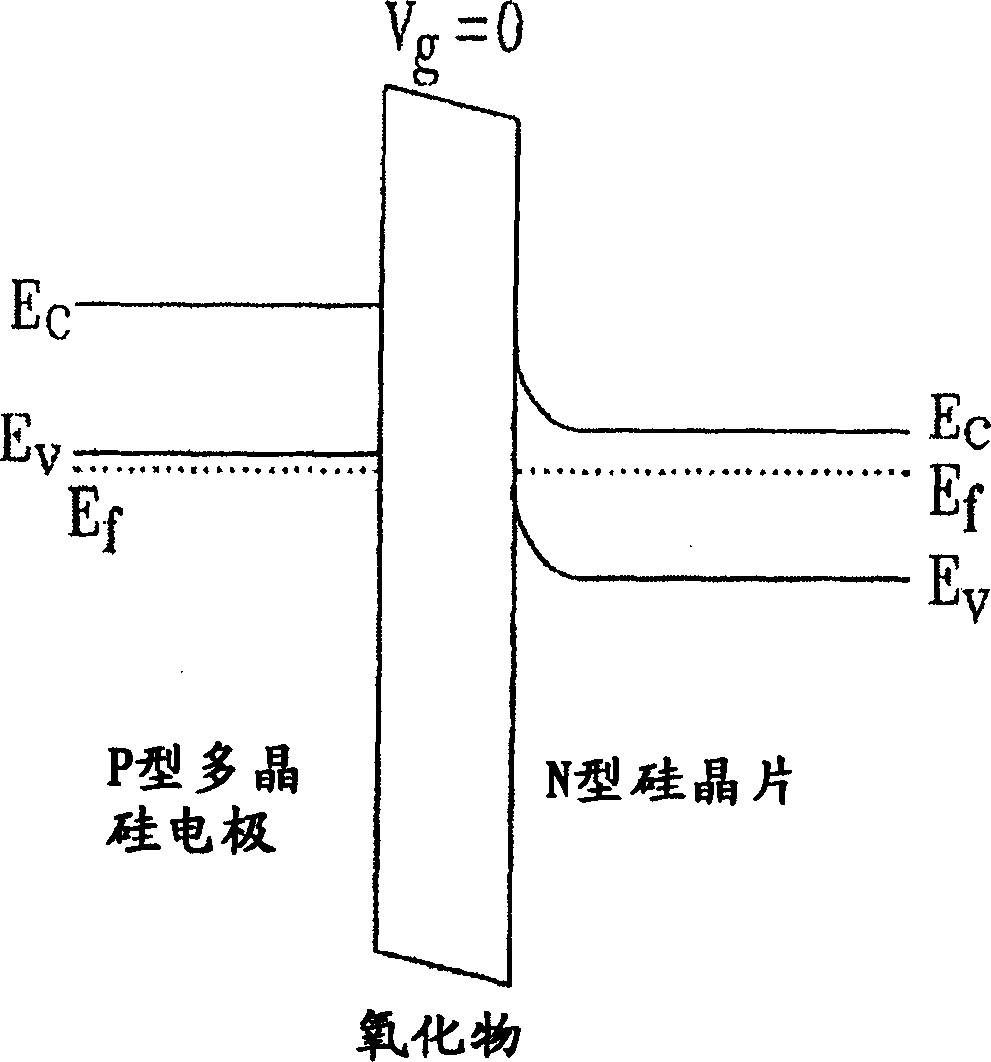
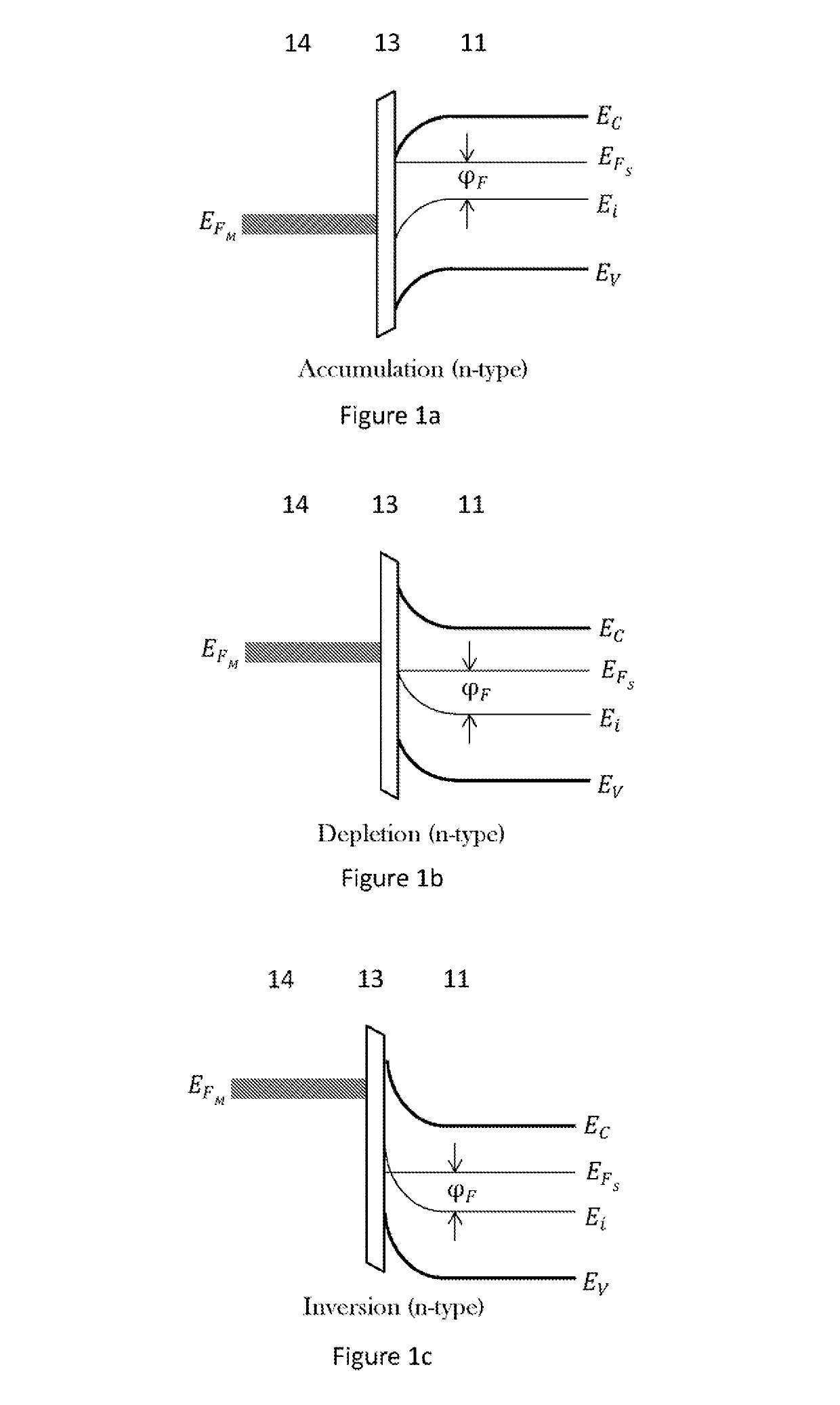
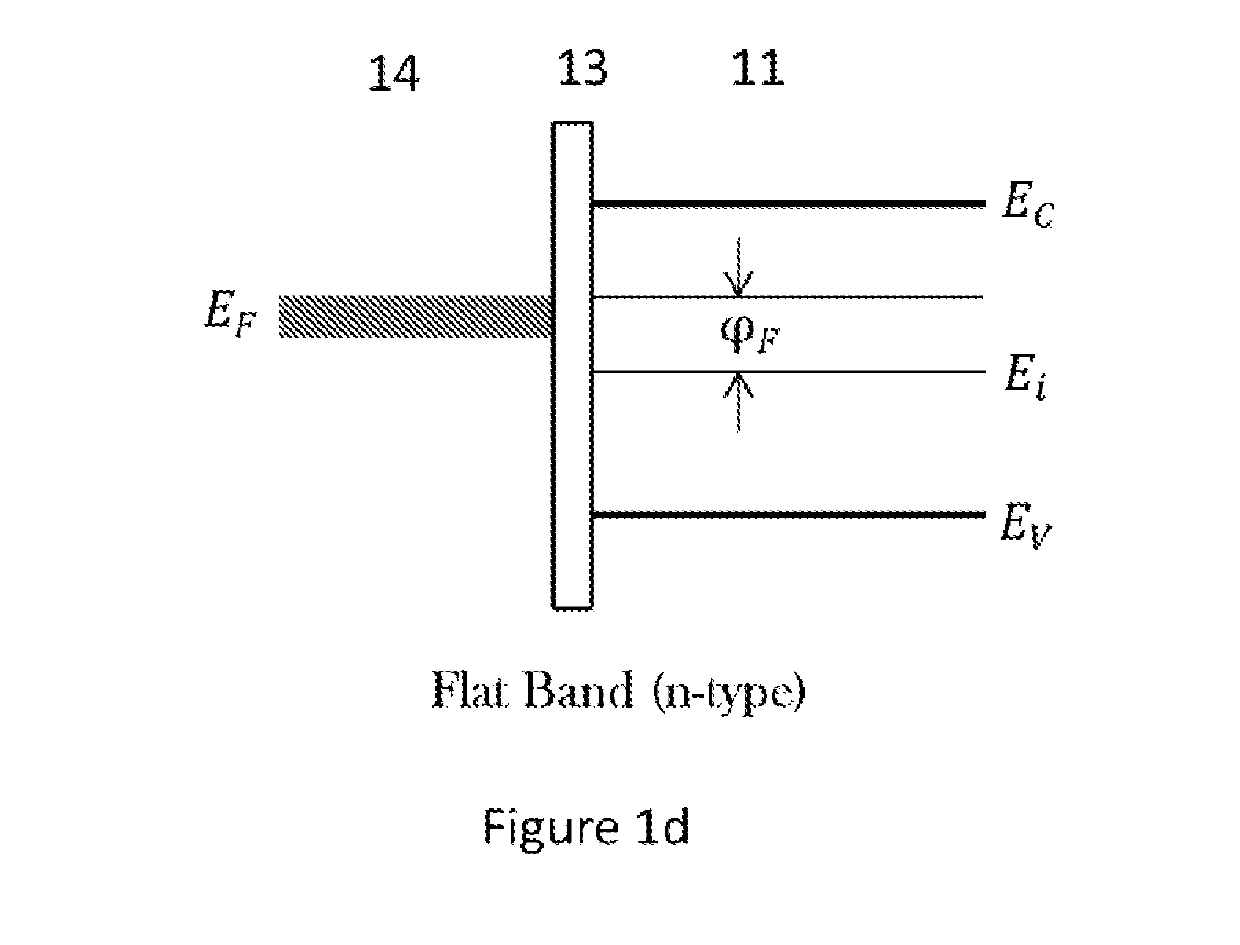
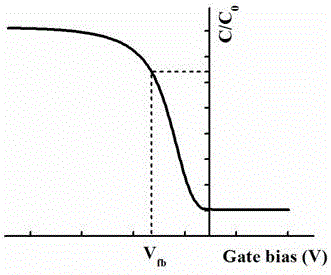
The flat band voltage still corresponds to the voltage which when applied to the gate electrode yields a flat energy band in the semiconductor. The charge in the oxide or at the interface changes this flatband voltage.
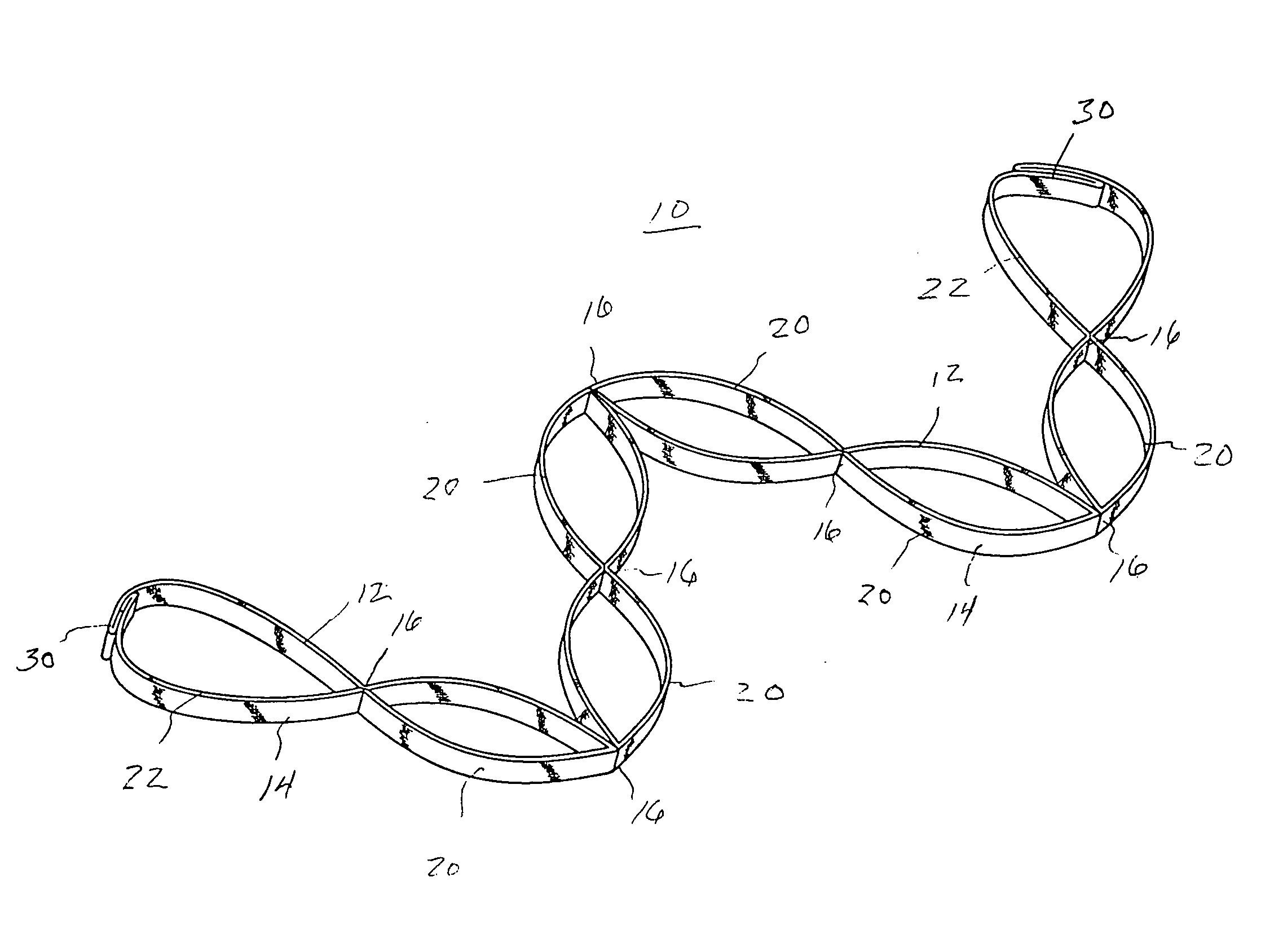
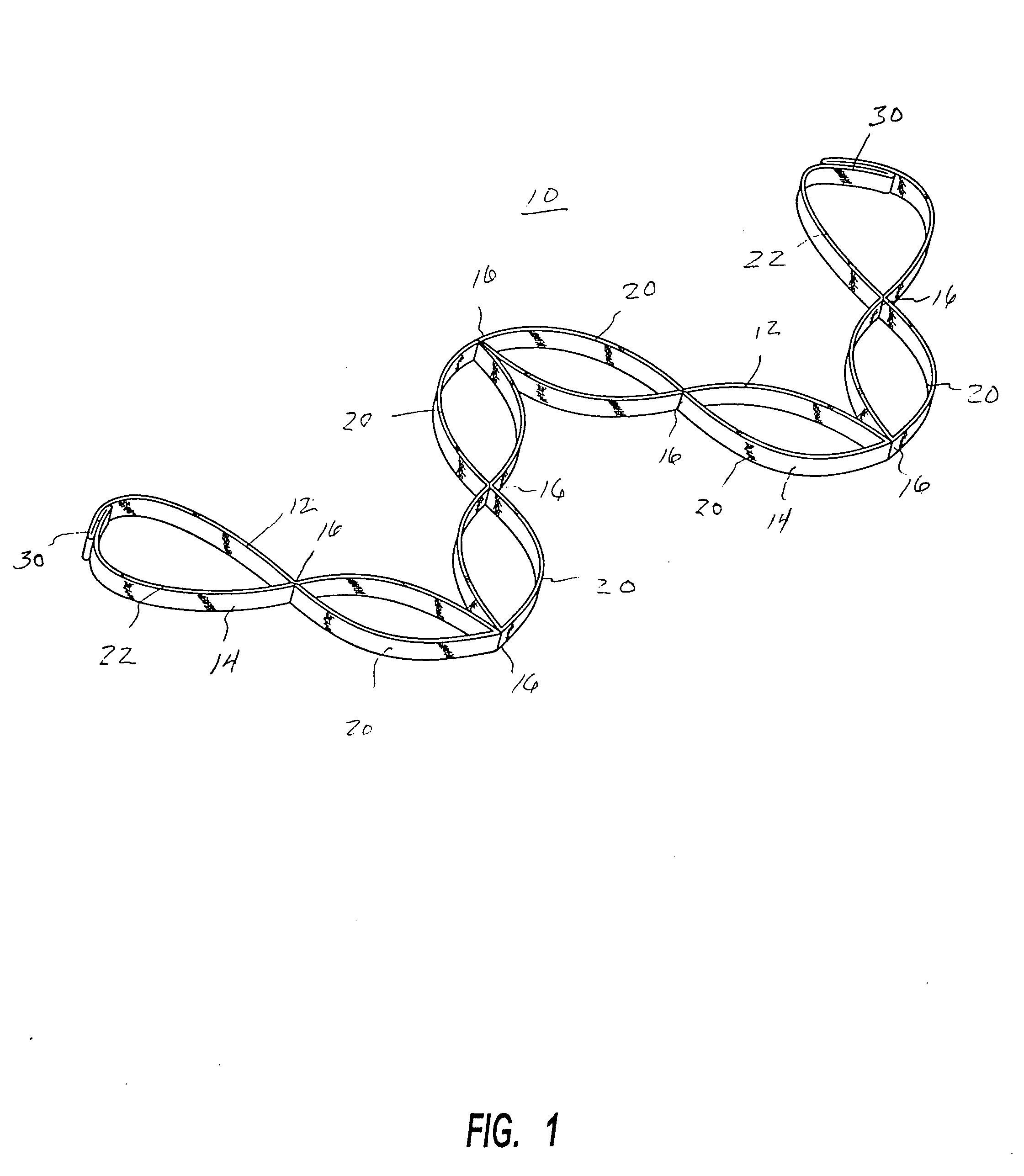
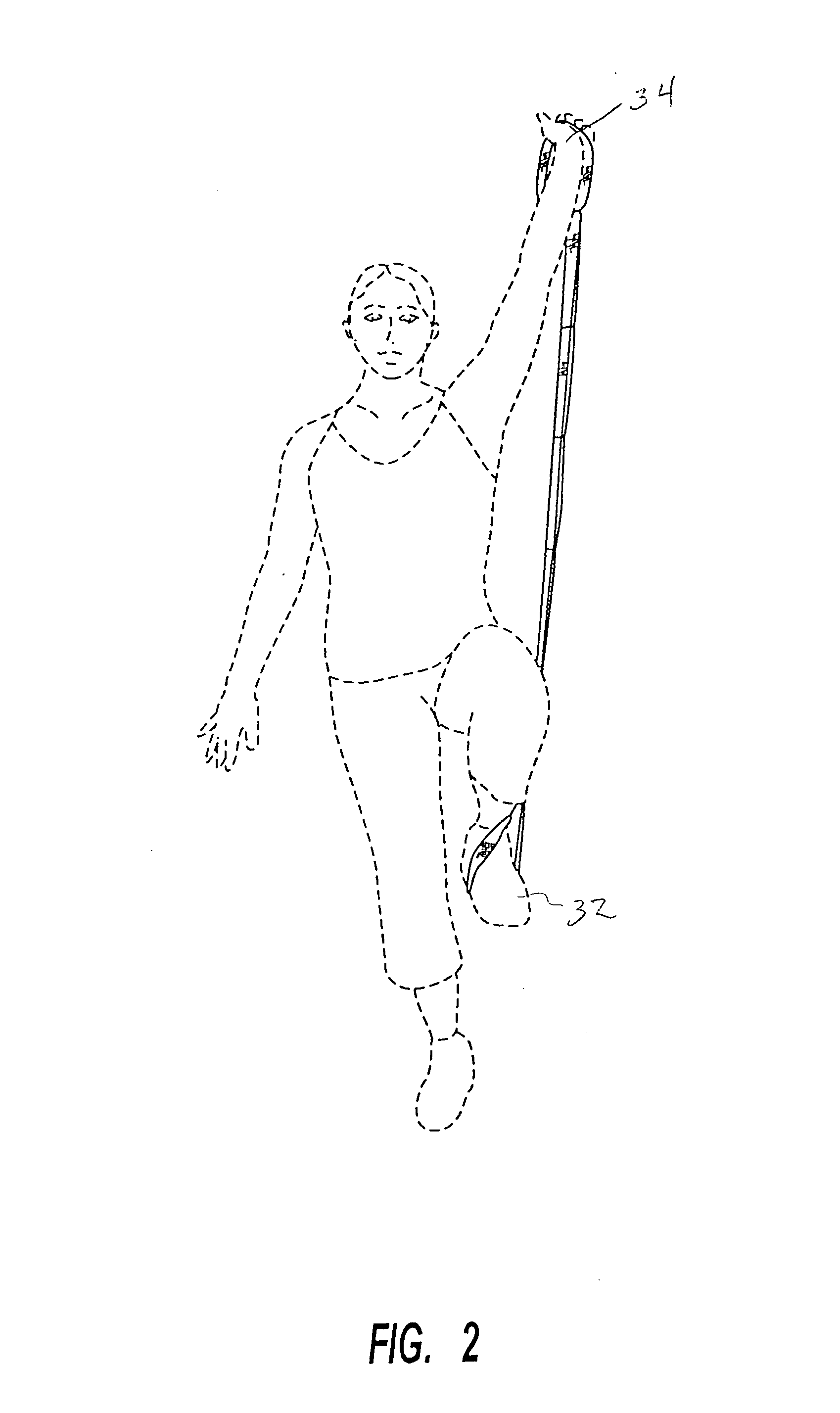
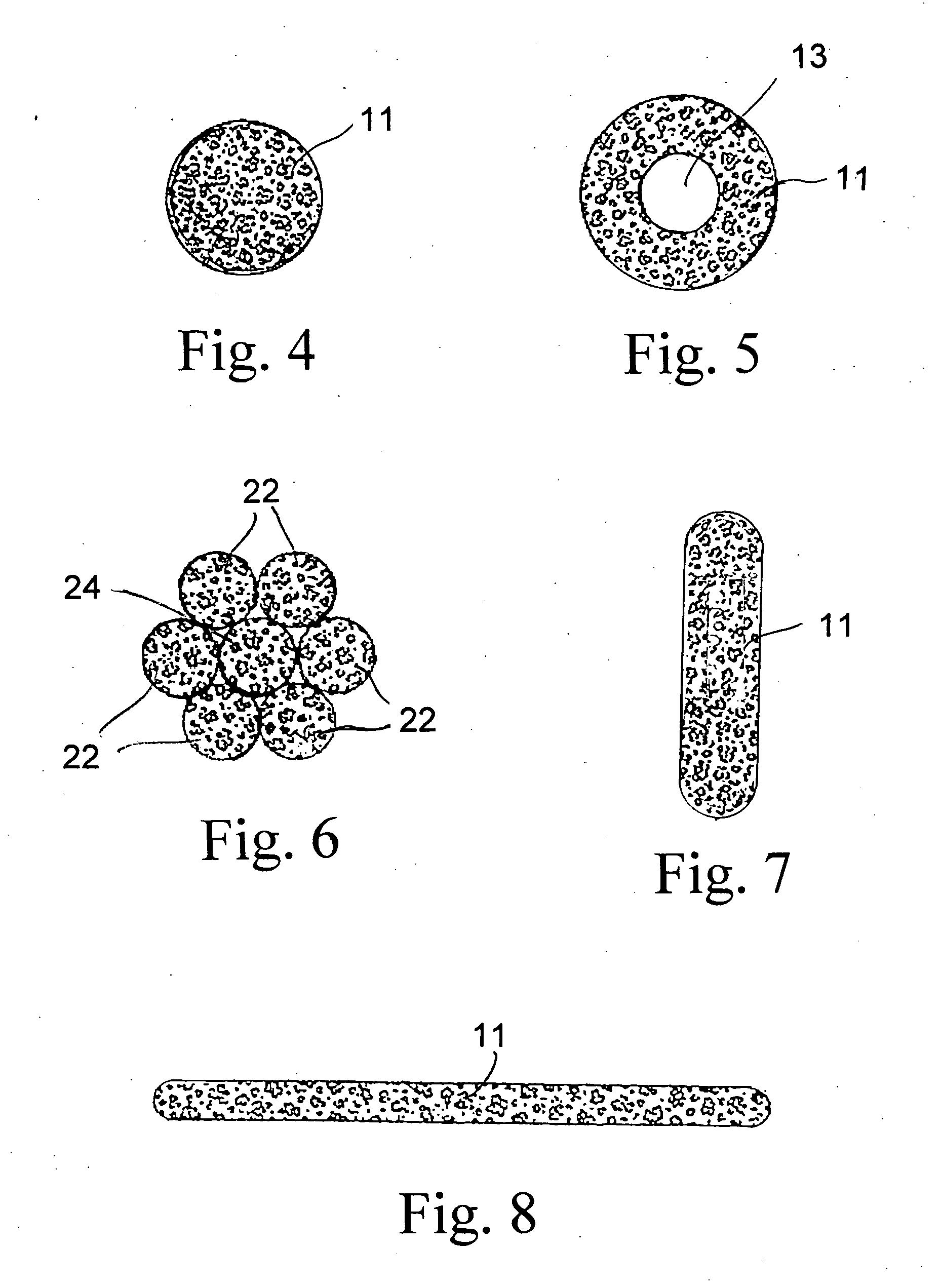
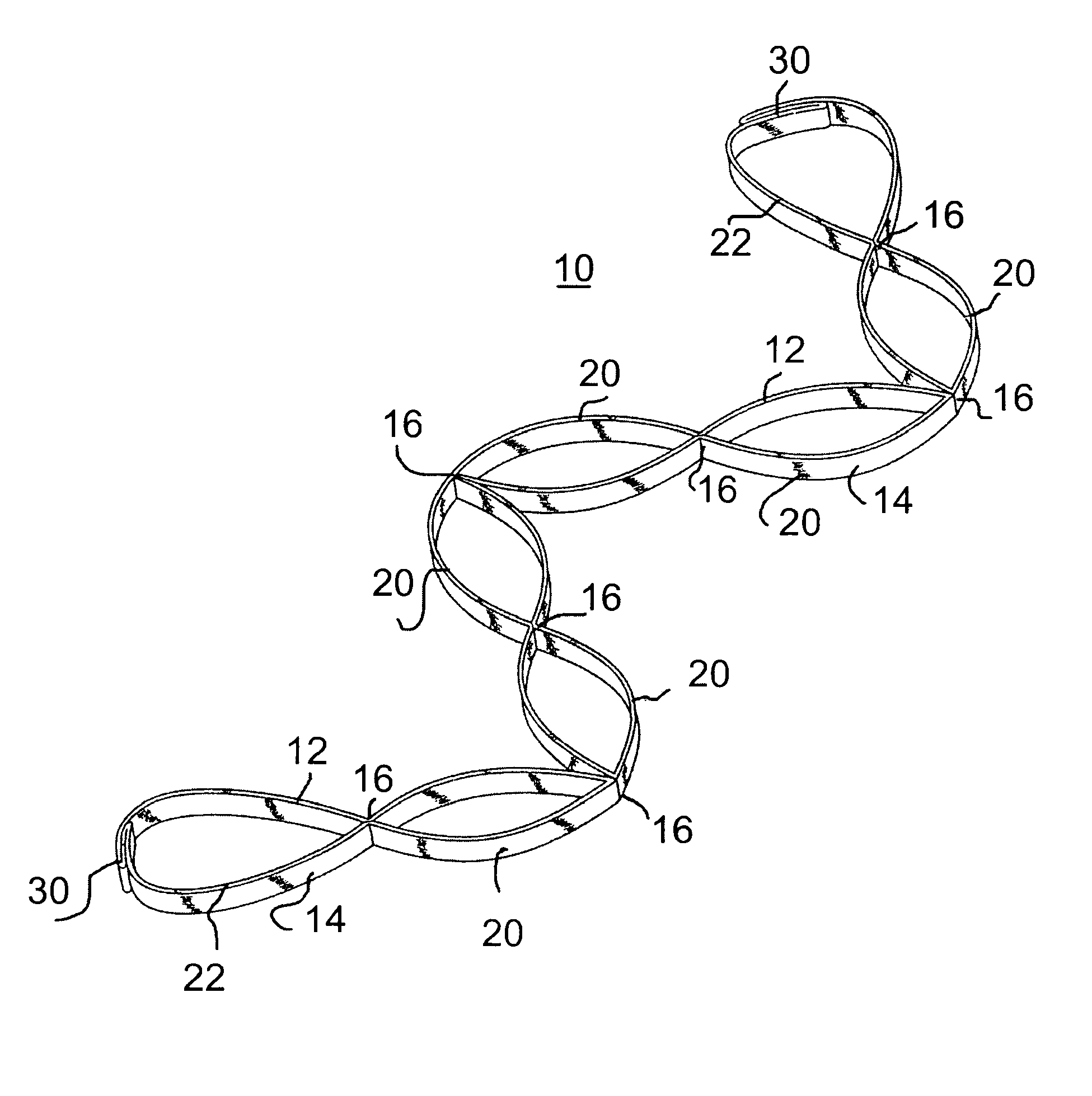
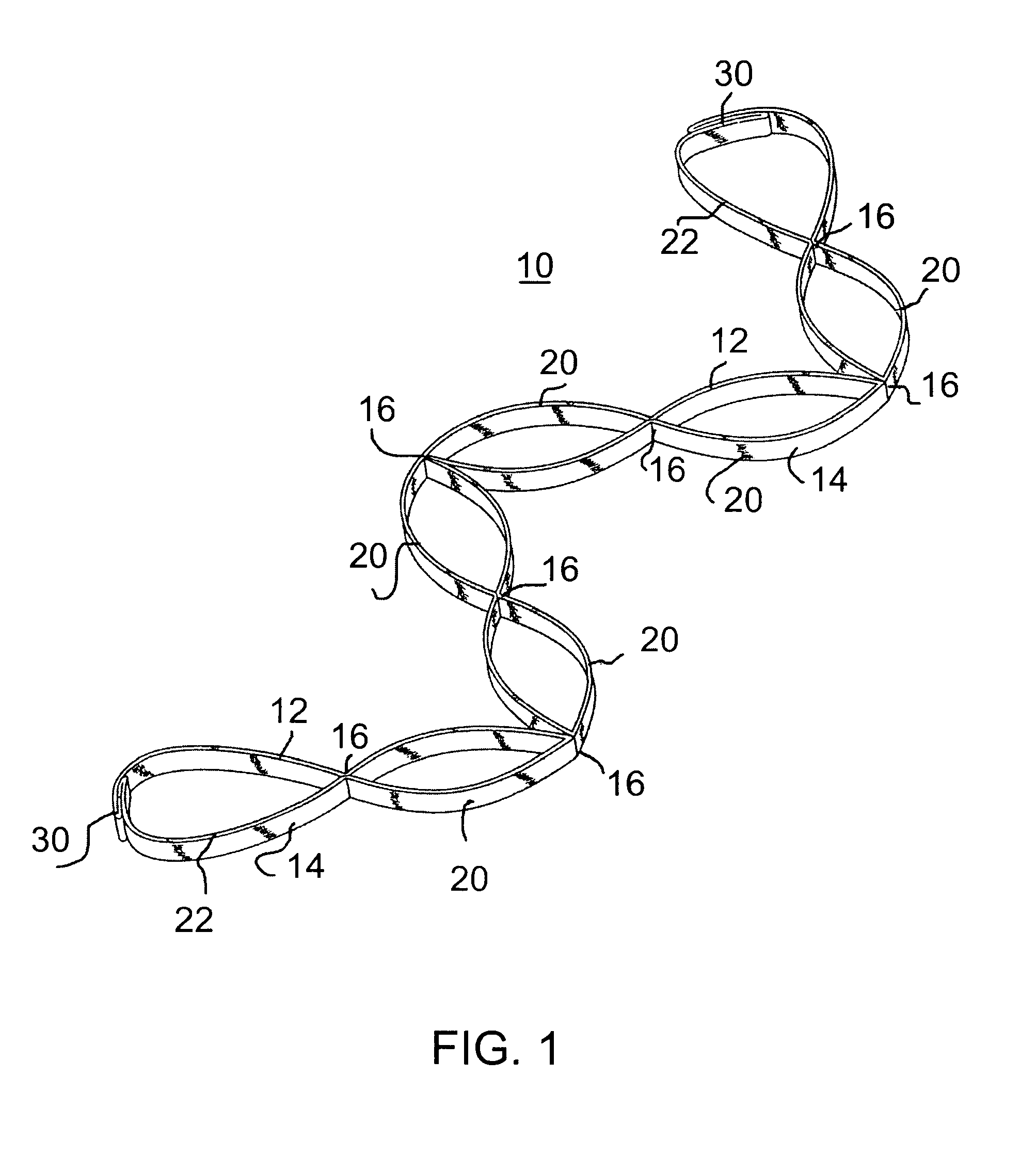
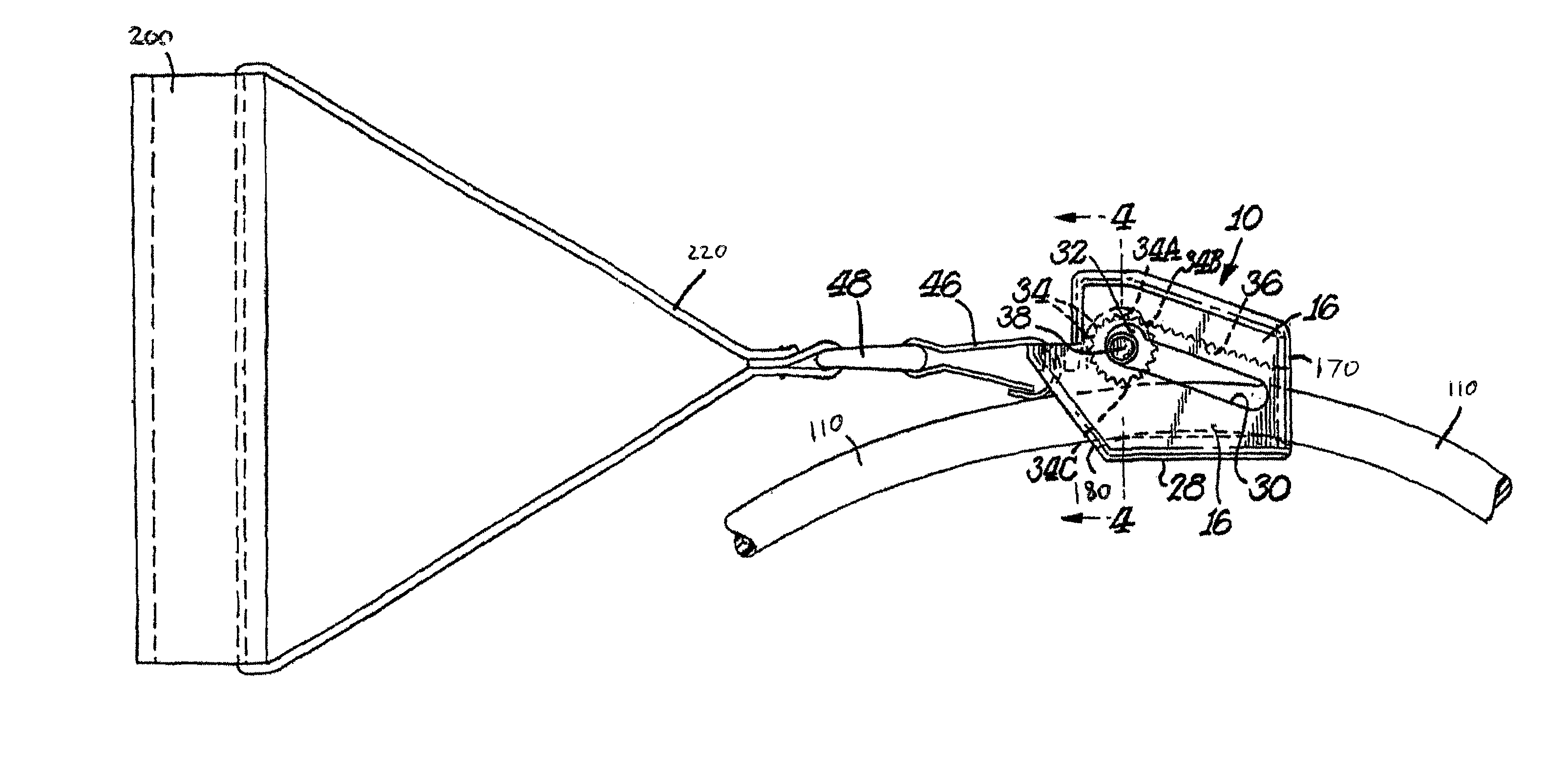
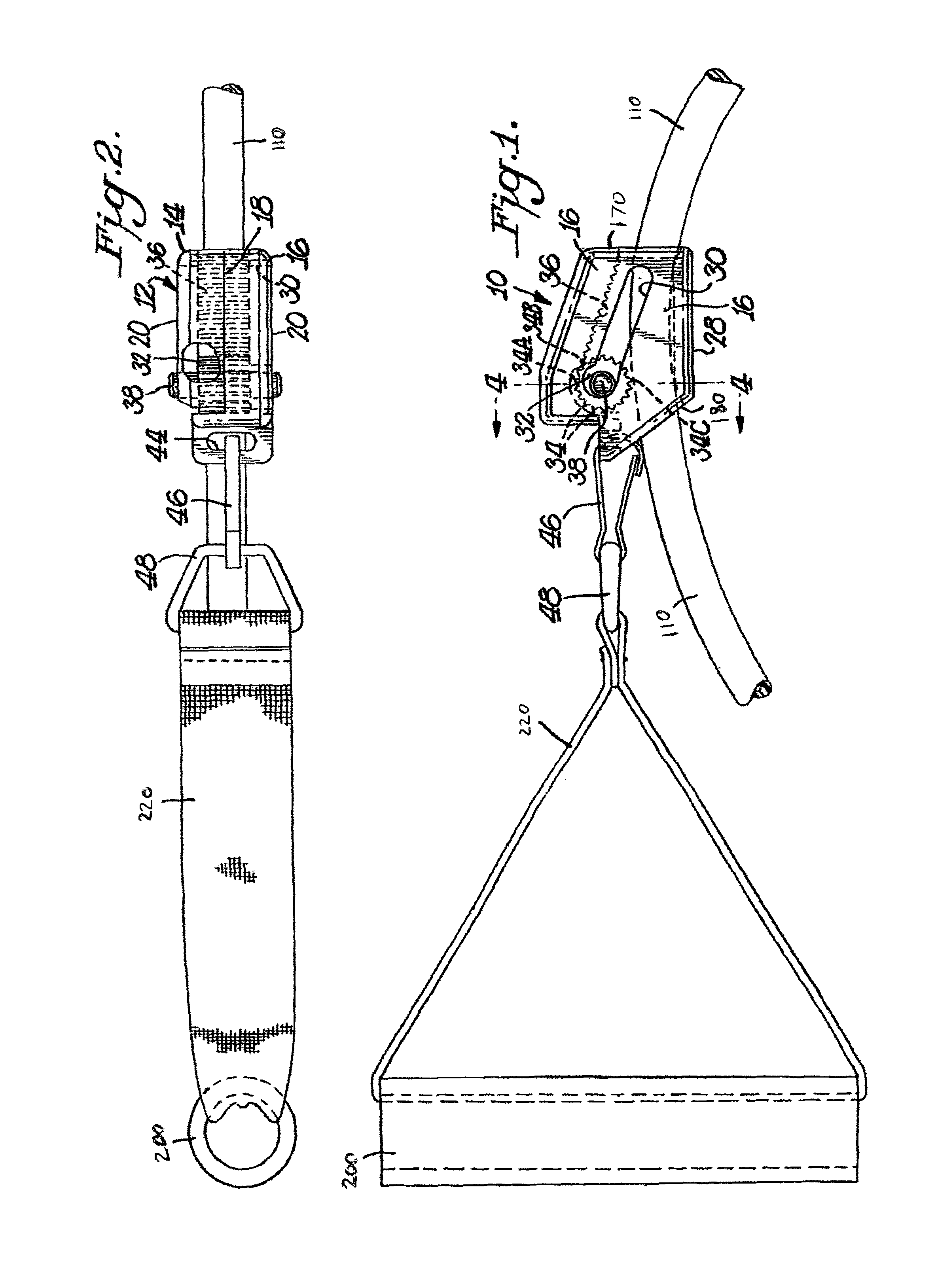
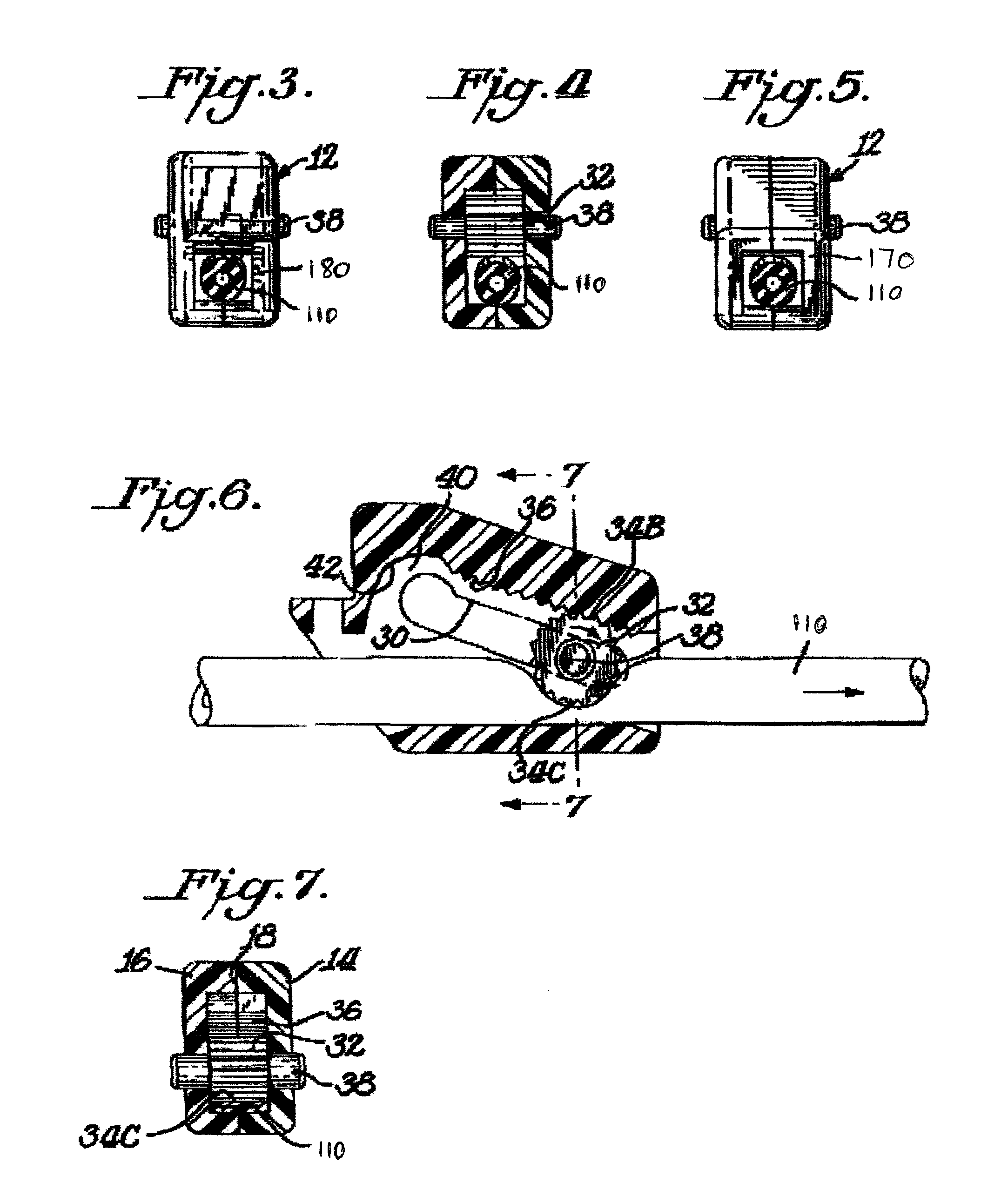
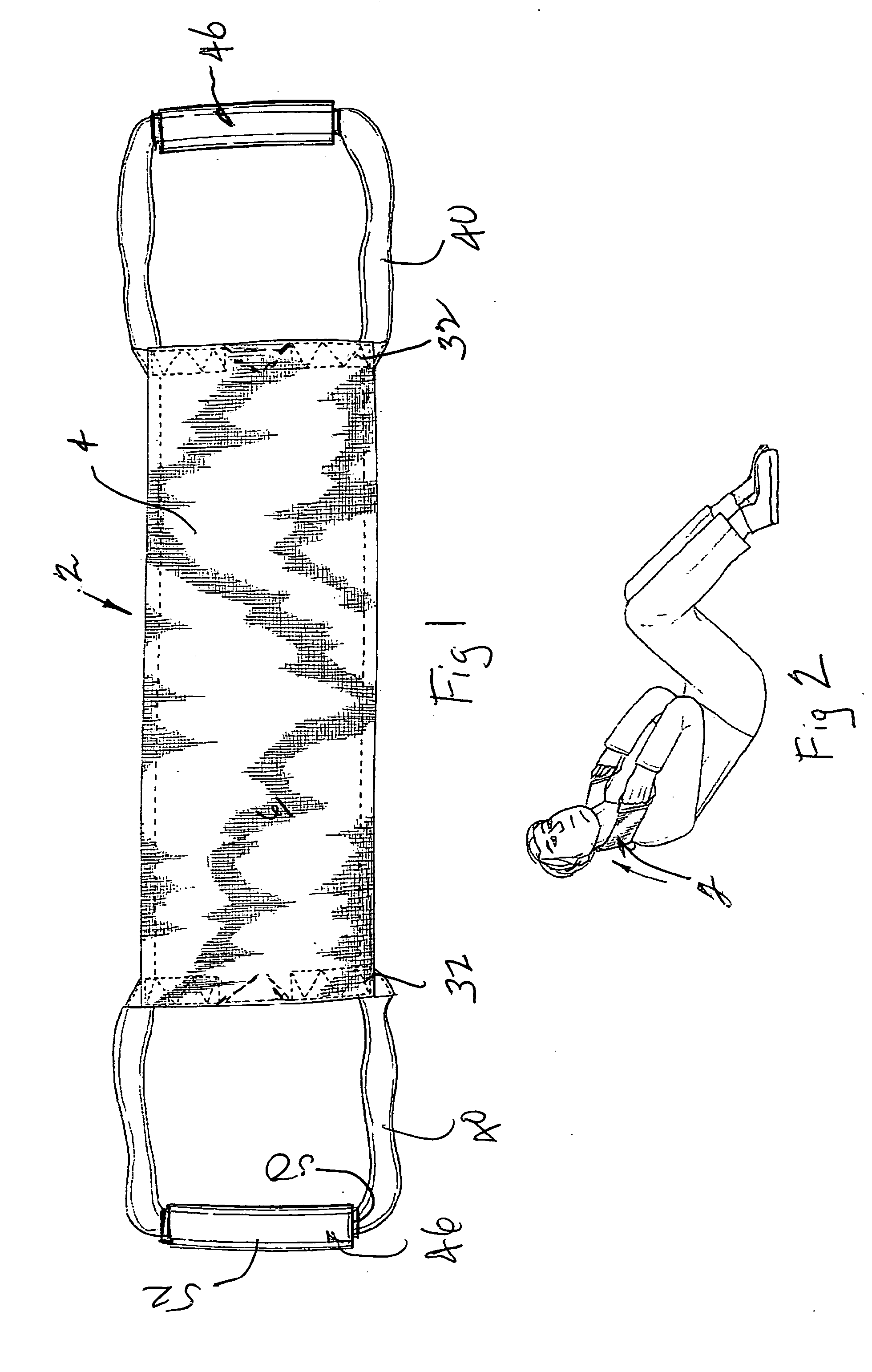
Muscle tension strap
InactiveUS20080132392A1Improve muscle tensionFunctionalResilient force resistorsEngineeringFlat band
A muscle tension strap including a pair of elongated flat bands each formed of substantially non-resilient material. The pair of flat bands are affixed together at a plurality of intermediate points therealong to form a plurality of tandem loops. The plurality of intermediate points at which the pair of elongated flat bands are affixed together are in a range of four to seven. Portions of each flat band adjacent each end are affixed together in overlying relationship to form a final loop with a handle therein and the pair of flat bands have a length in a range of five feet to seven feet.
Owner:MOULTON KELLY J
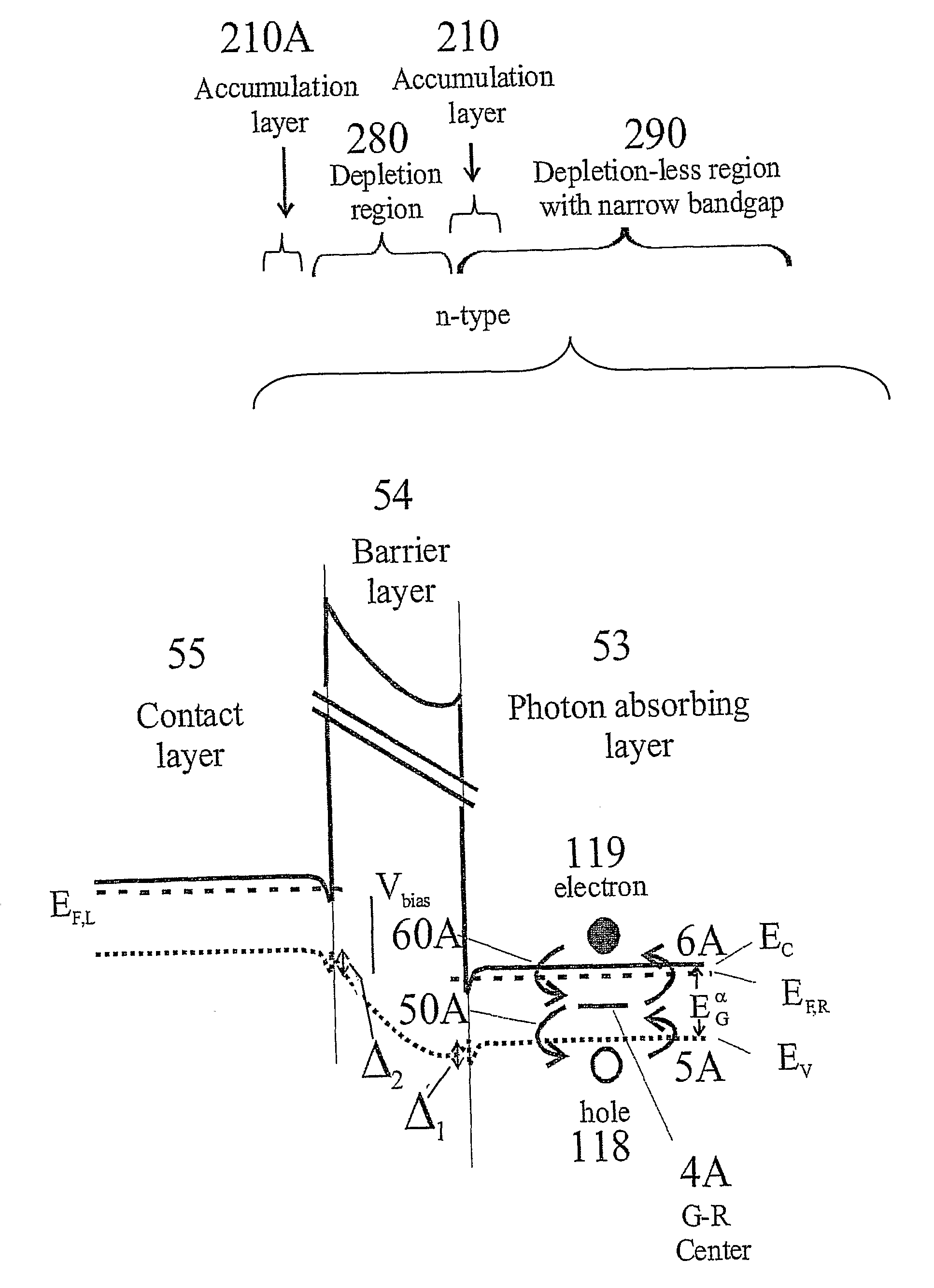
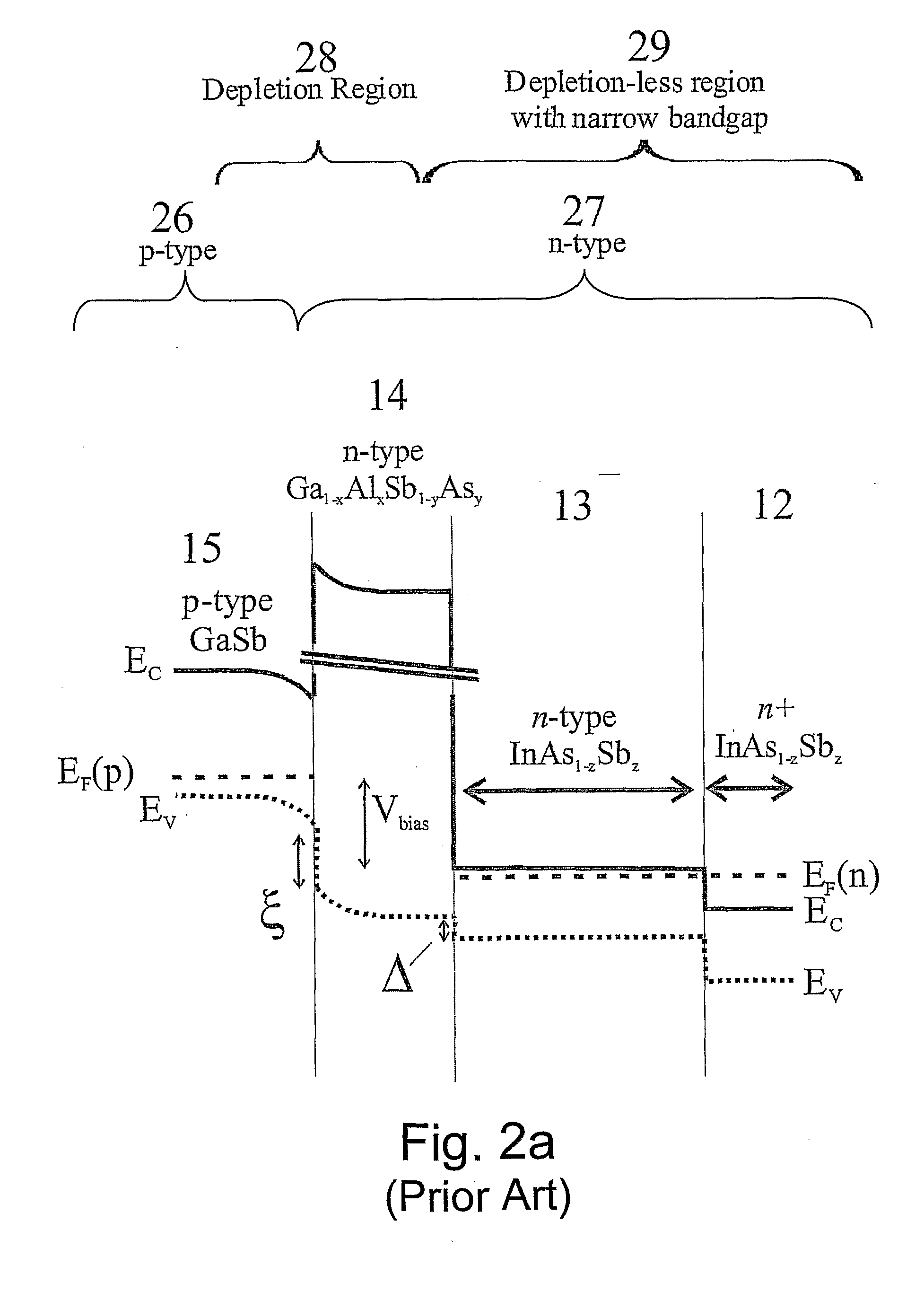
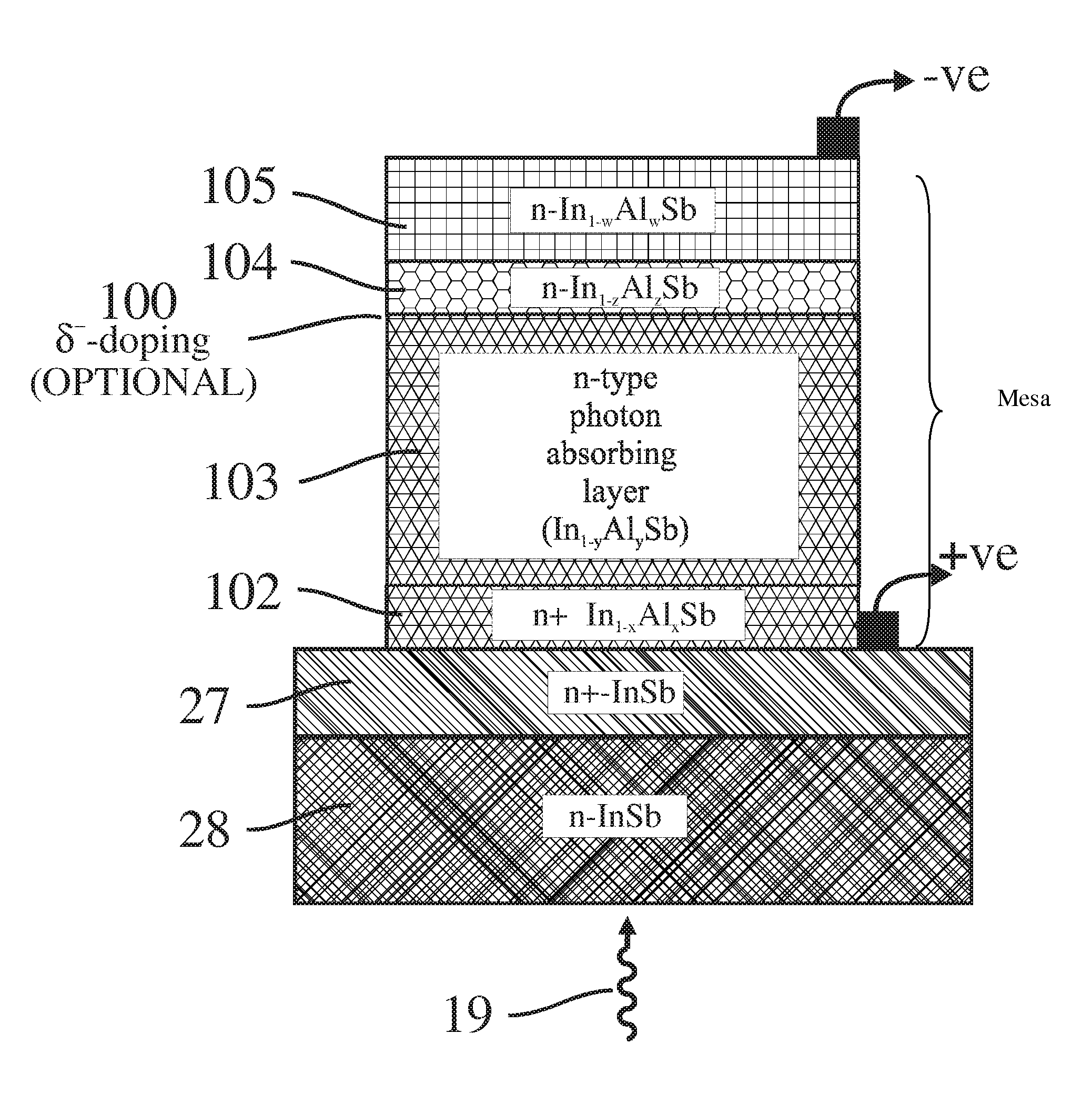
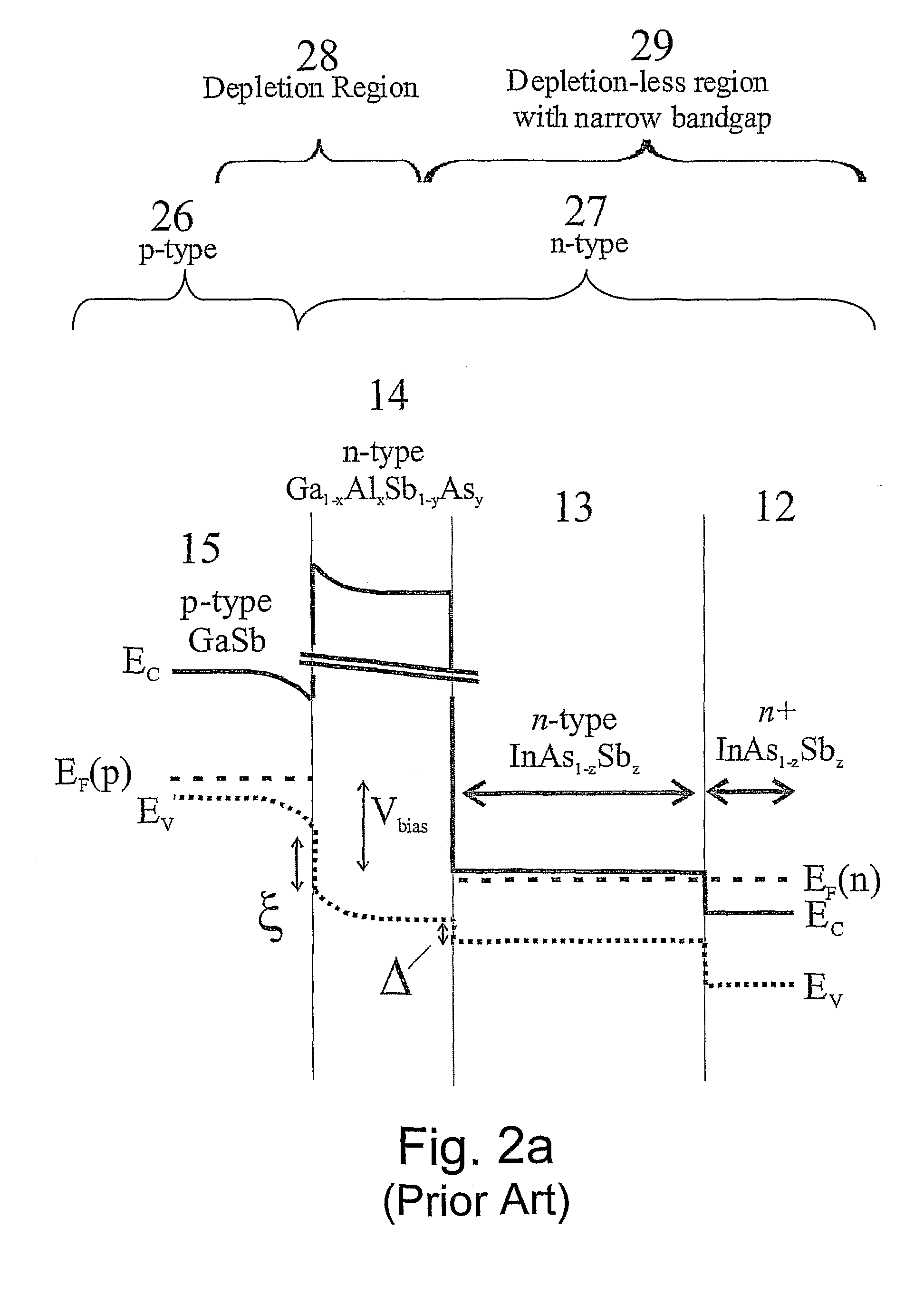
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090256231A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal biasPhotodetector
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Elastic exercise device
InactiveUS20070207903A1Reduce disadvantagesSimple and safe processResilient force resistorsElastomerNeoprene
An elastic exercise device is provided, which is made of an expanded elastomer that has the strength and elasticity suitable for performing tension-type exercises. The device preferably consists of a single elongated piece or of an endless loop of desired size and shape. The device can have various cross-sectional profiles, such as a fully filled cylindrical configuration, a tubular configuration, an oval or flat band configuration or a multistrand configuration. The device can be made from elastomer materials such as neoprene or polyethylene by extrusion, casting or injection molding.
Owner:CSABAI JULIUS S
Muscle tension strap
Owner:MOULTON KELLY J
Exercise resistance system
InactiveUS8403818B1Quickly securedEasy to implementResilient force resistorsRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyDumbbellRange of motion
The present invention provides for an improved exercise resistance system to conduct numerous total body exercises. An adjustable elastic resistance cord or flat band may be combined with weights, or each type of resistance may be used alone, in order to vary the means of creating resistance during exercise. The length of the elastic resistance cord or flat band may be adjusted by means of a slip free, length quick adjustment device. The elastic resistance cord or flat band may be passed through the length quick adjustment device which may be secured at various points along the length of the elastic resistance cord or flat band, to change its effective usable length and thus change the level of strength, and range of motion. The length quick adjustment device may be secured by pulling an elastic resistance cord or flat band in one direction, and released by pulling the elastic resistance cord or flat band in the opposite direction.One end of the elastic resistance cord or flat band is attached to any hand engagement structure, preferably a cord handle / grip, a dumbbell handle / grip, a bar, or a glove. The other end of the elastic resistance cord or flat band is secured to any anchor structure, preferably a movable structure, such as a flat board, pad, aerobic step, workout bench, or TV interactive exercise structure.
Owner:WILKINSON WILLIAM T +3
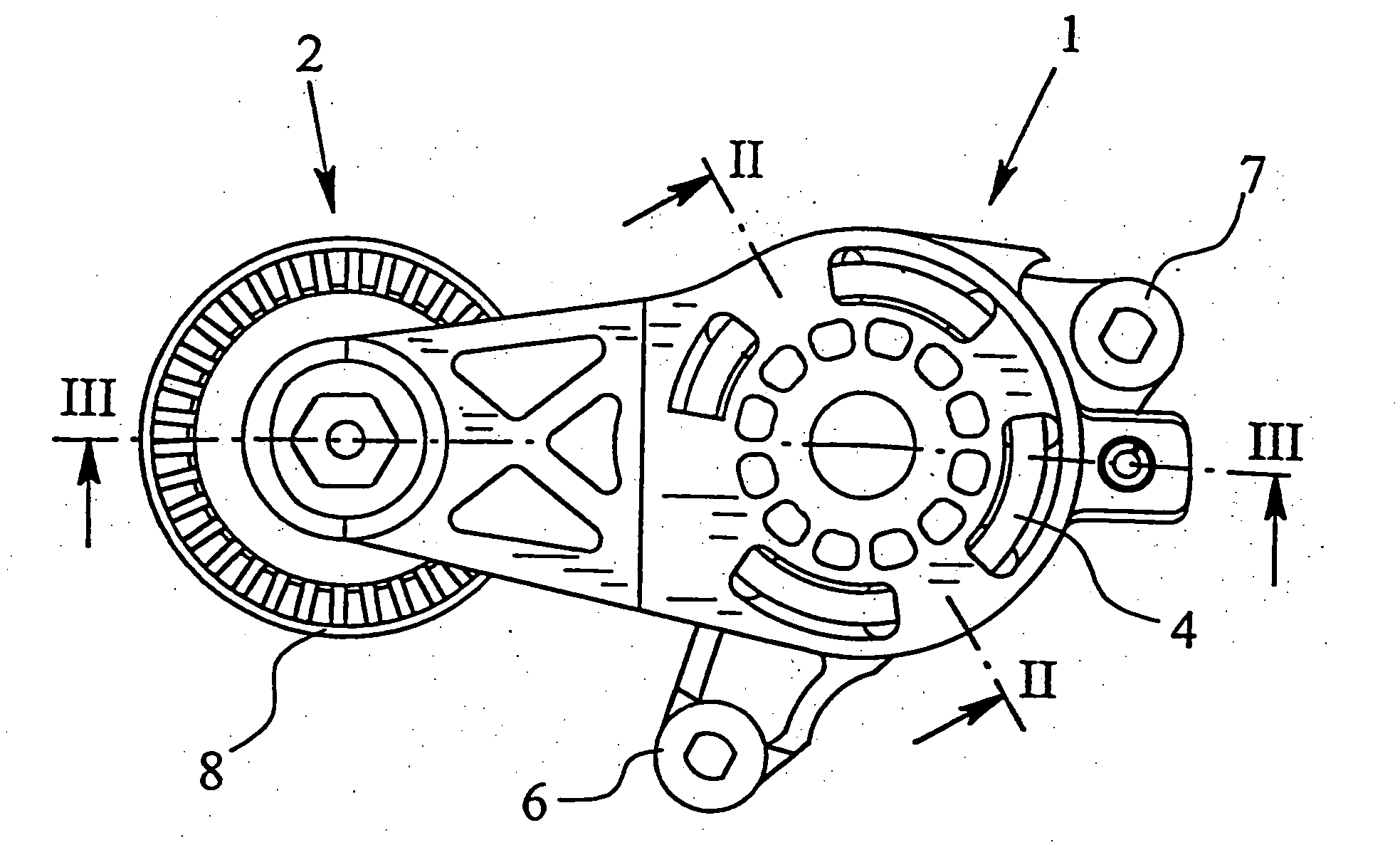
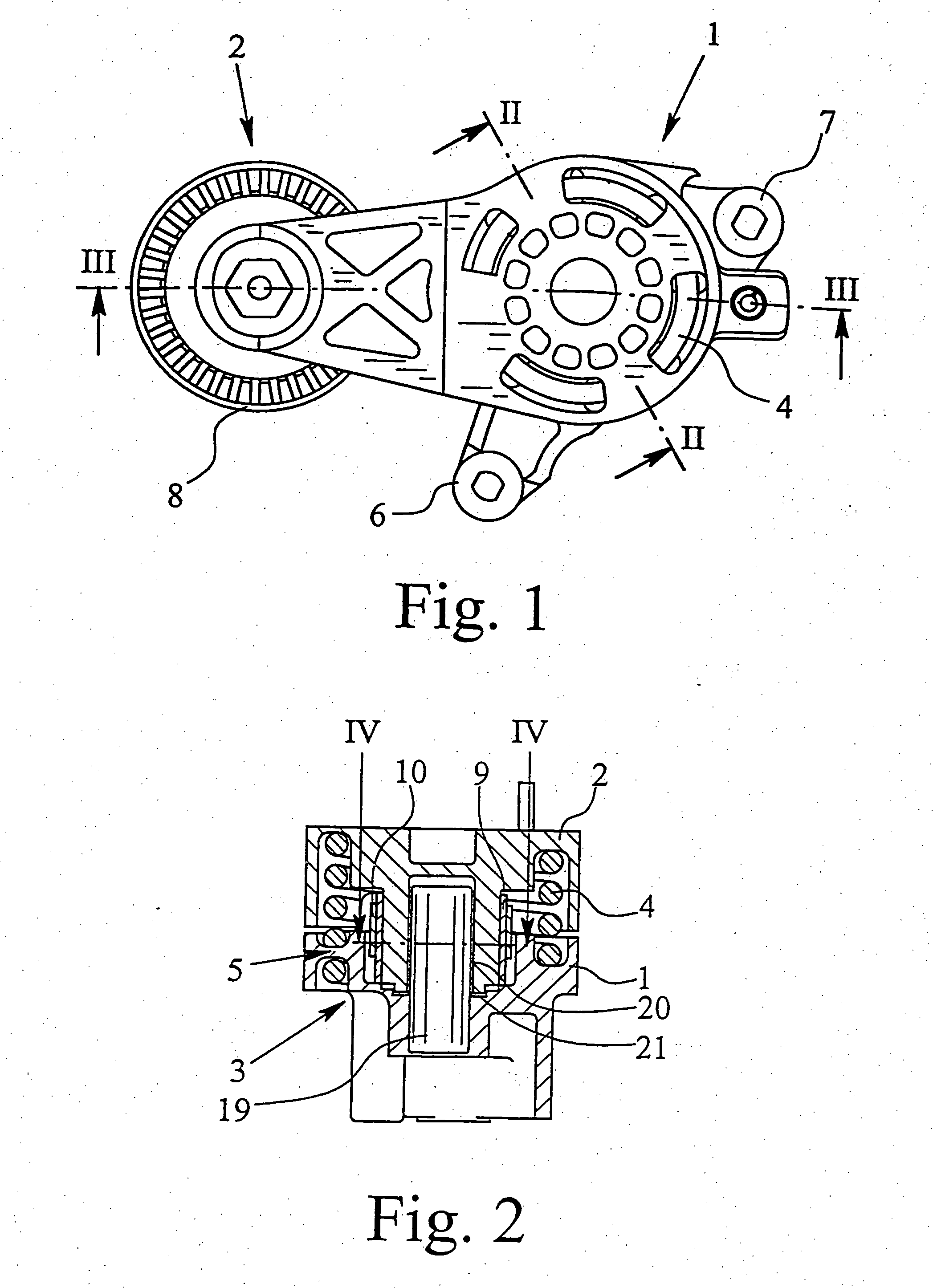
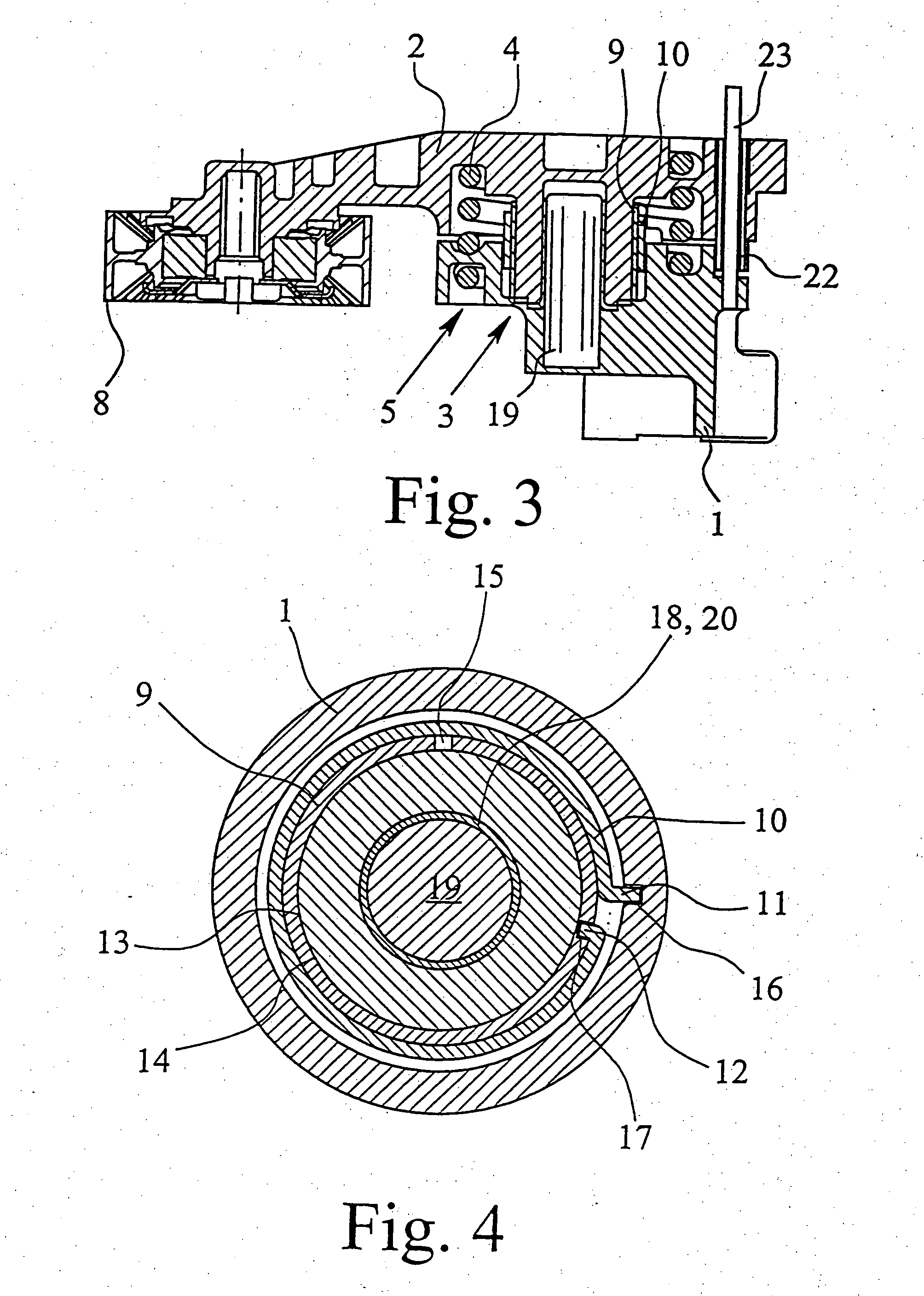
Belt tensioning device
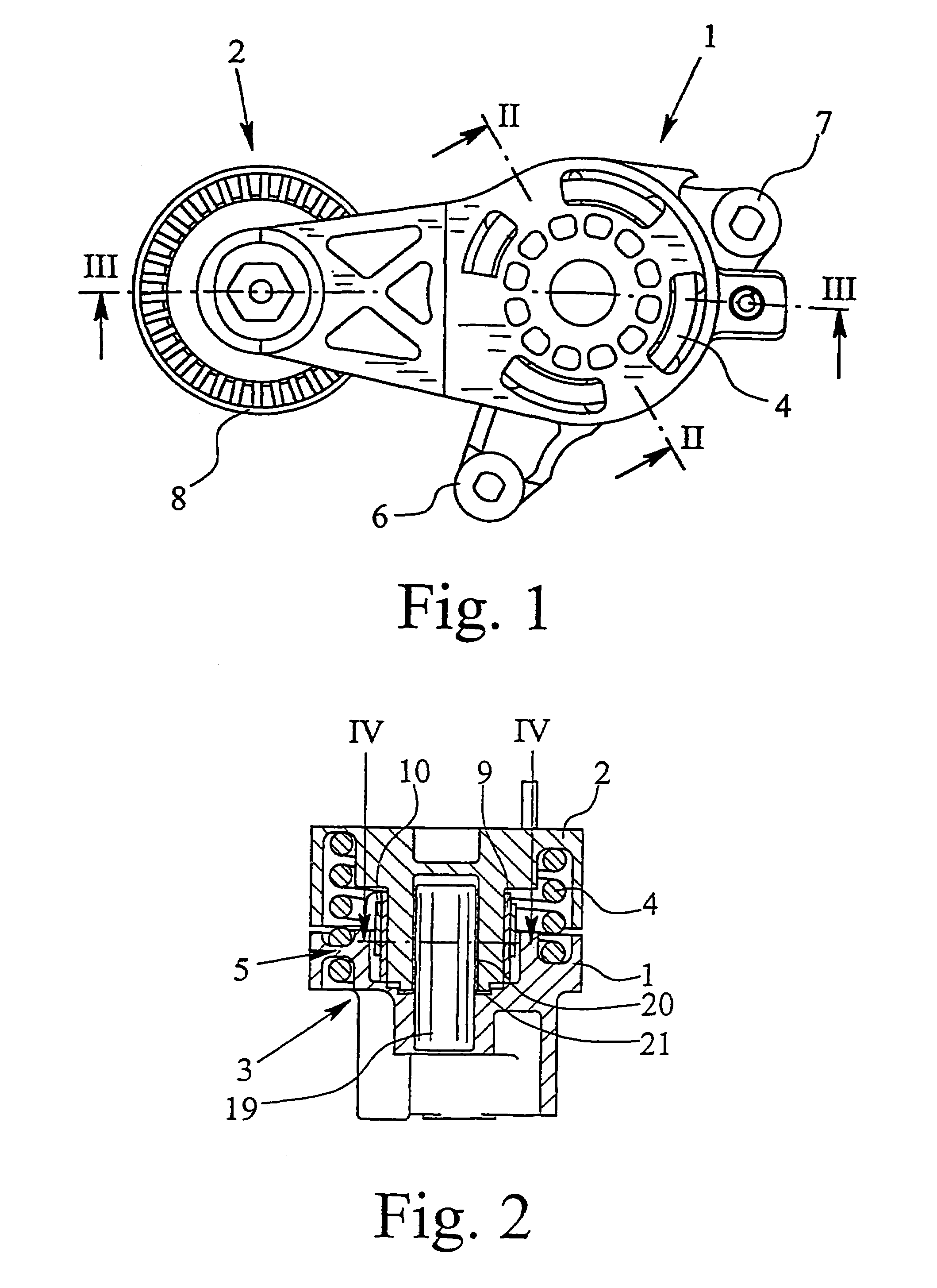
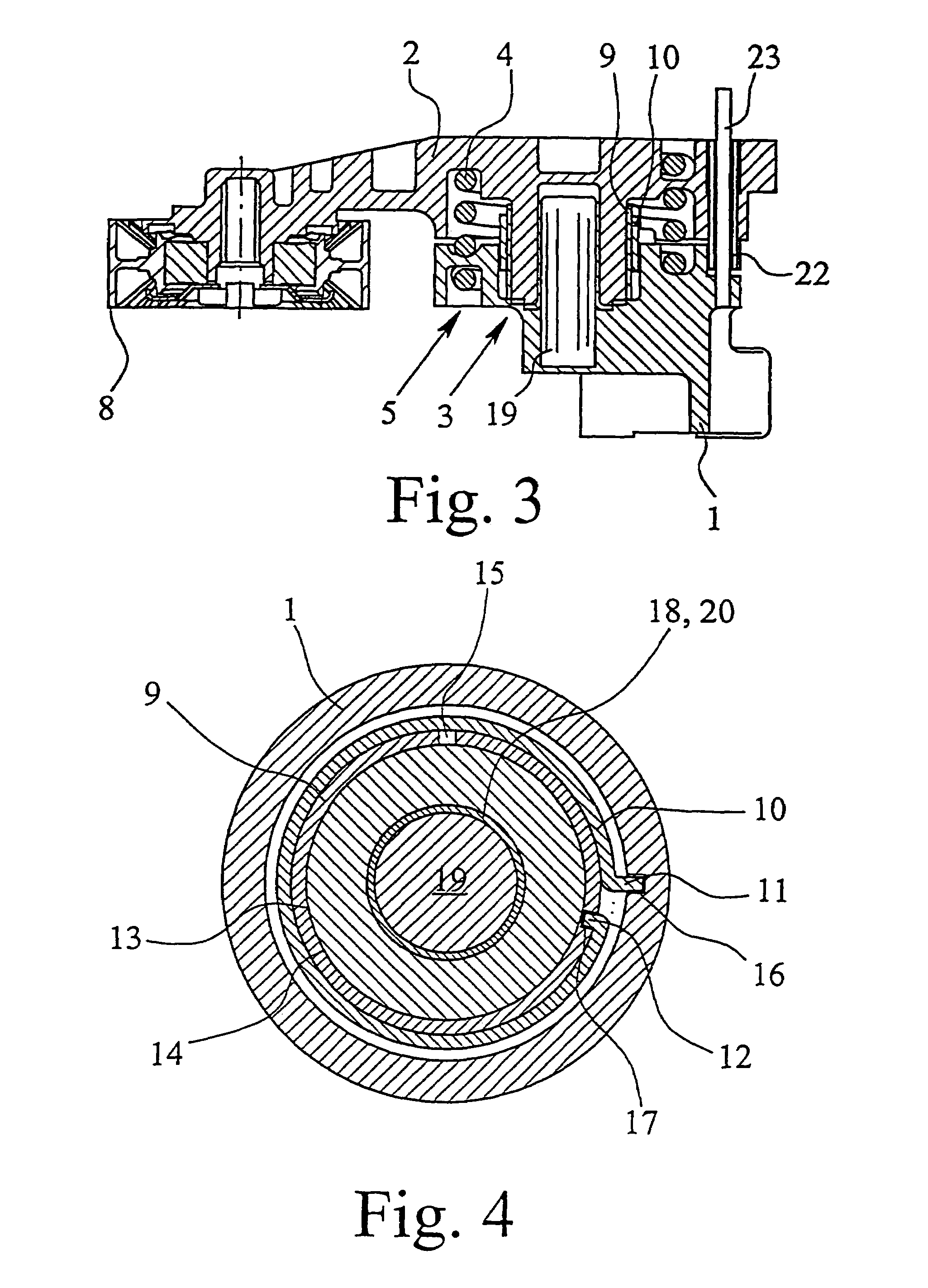
InactiveUS7104909B2Simplify design and production technologyProduced cost-effectivelyGearingFlat bandEngineering
A tensioning device for attraction mechanism including a receiving and mounting housing, a roller carrier pivotably connected to the mounting housing, a bearing which radially supports the roller carrier relative to the mounting housing, a spring between the roller carrier and the mounting housing for applying a tensioning force, and a damping device. The damping device includes a damping bush which, by friction, dampens any movement between the roller carrier and the mounting housing in such a way that damping is greater in the direction of an increasing tension force than in the direction of decreasing tension force. A flat band spring applies the friction force to the damping bush. The flat band spring is secured, at a first end, to the receiving and mounting housing in a rotationally fast way, and at a second end to the damping bush in a rotationally fast way.
Owner:MUHR UND BENNDER KG
Flat Belt Clamping System and Method
A belt clamping system including an open-ended, flat belt with an end portion having a number of teeth projecting therefrom and a clamping plate with matching tooth profile for use in connecting the belt end to another structure. The flat belt may be reinforced with longitudinally extending cords. The toothed profile may be a standard timing belt profile and may be unreinforced. A length of timing belt profile material may be welded to the flat surface of the open-ended flat belt at or near an end. The length of timing belt profile may include at least 7 tooth pitches. The end portion may be clamped between a flat surface of a flat plate and a grooved surface of a grooved plate having grooves complementary to the timing belt teeth.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
Method for semiconductor circuit
InactiveUS20090132974A1Mobility can be measuredDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designMOSFETCurrent voltage
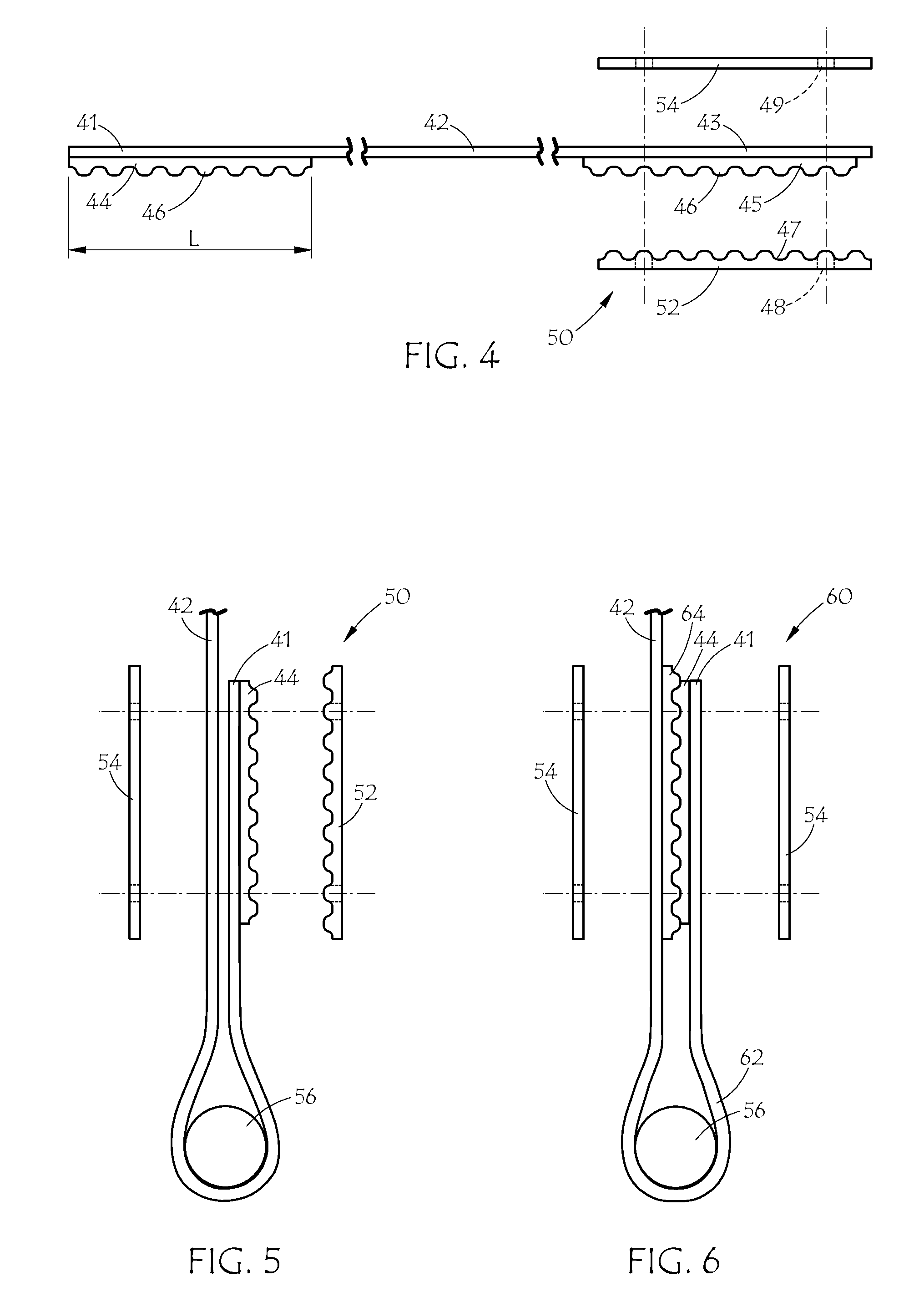
Capacity-gate voltage characteristics of a field-effect transistor having plural gates are measured against a voltage change in each one of the gates for an inverted MOSFET and for an accumulated MOSFET, respectively. These measurements together with numerical simulations provided from a model for quantum effects are used to determine flat band voltages between the plural gates and a channel. Next, an effective normal electric field is calculated as a vector line integral by using a set of flat band voltages for the measured capacity as a lower integration limit. Lastly, mobility depending on the effective normal electric field is calculated from current-gate voltage characteristic measurements and capacity measurements in a source-drain path, and the calculated mobility is substituted into an equation for a current-voltage curve between source and drain.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
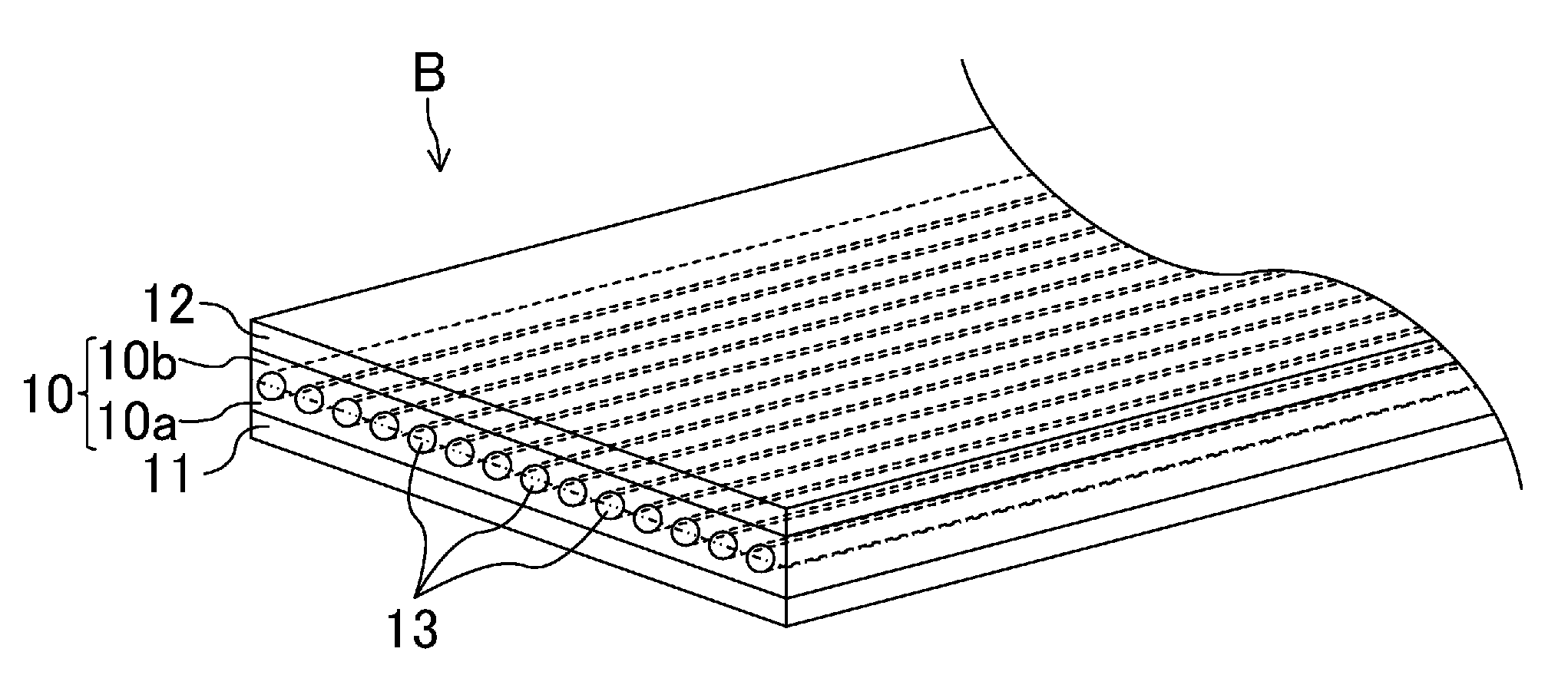
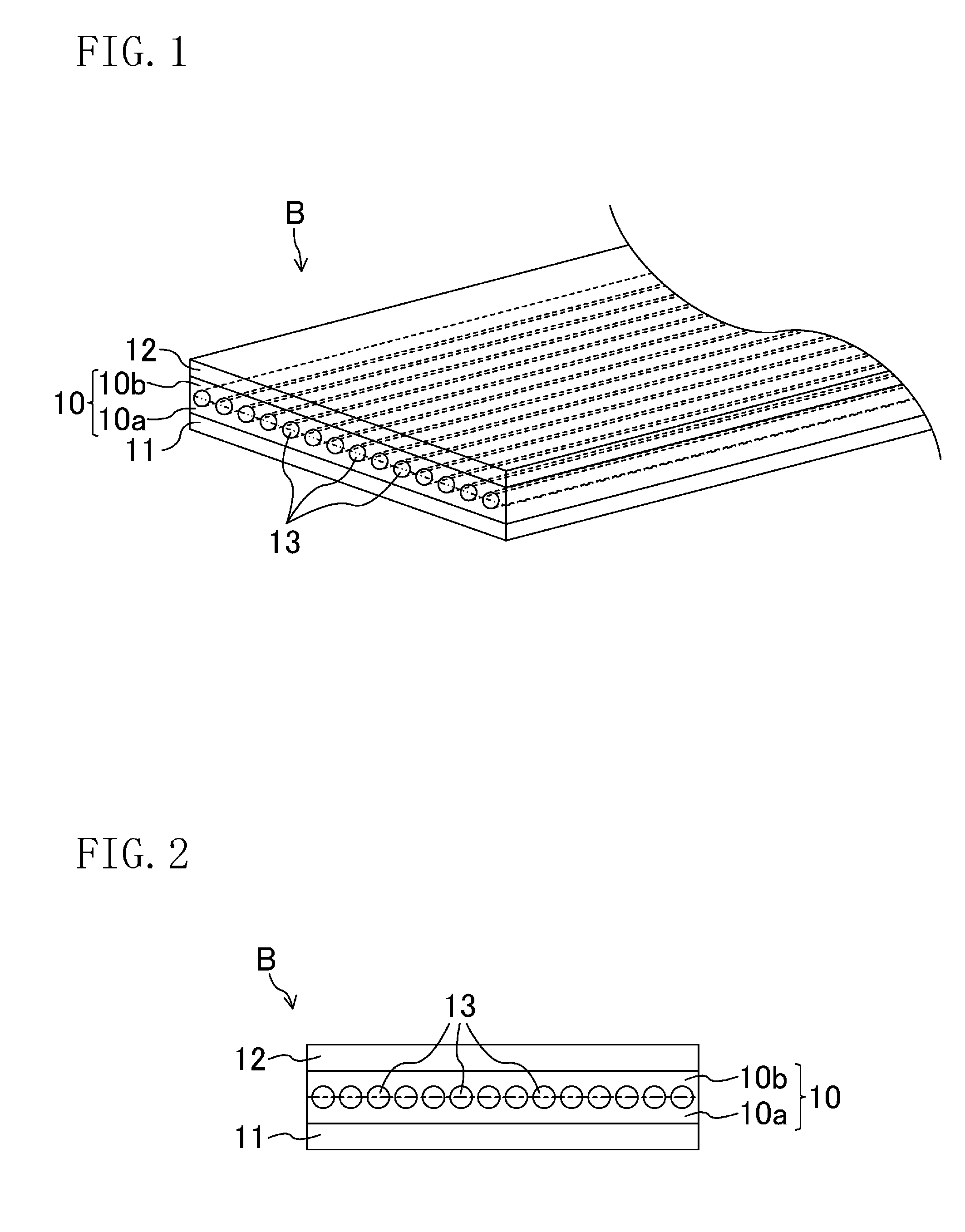
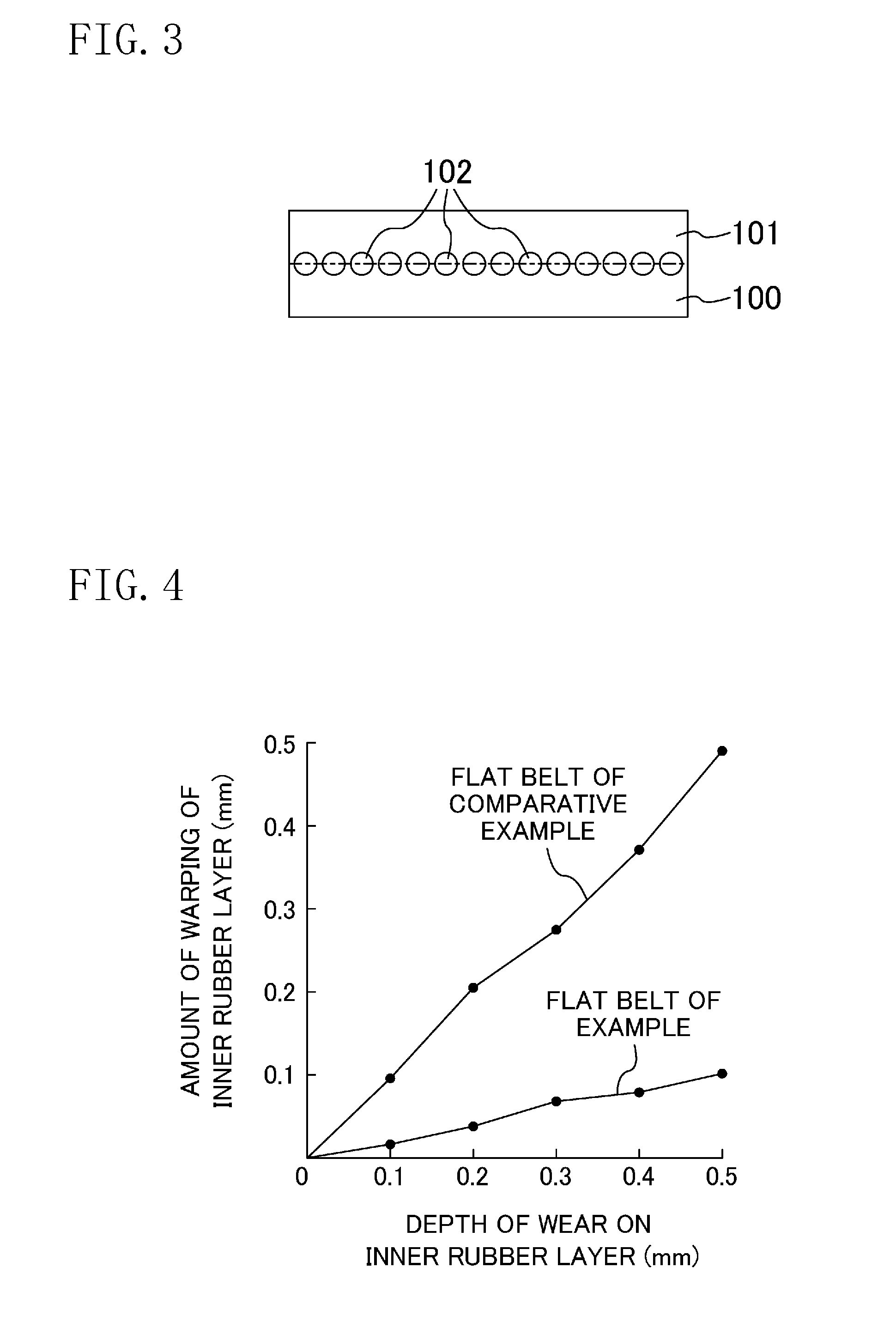
Flat belt
A flat belt includes an adhesive rubber layer formed in an endless ring shape and having a tensile member embedded therein, a first rubber layer provided on a surface of the adhesive rubber layer, and a second rubber layer provided on the other surface of the adhesive rubber layer, in which an elastic modulus in a belt width direction of the adhesive rubber layer is higher than the elastic modulus in the belt width direction of each of the first rubber layer and the second rubber layer.
Owner:BANDO CHEM IND LTD
Semiconductor, functional device, electrochromic device, optical device, and image-taking unit
A semiconductor comprises a compound (A) adsorbed on a surface of the semiconductor, the compound (A) having at least one lone electron pair and substantially not undergoing in oxidation-reduction reactions, wherein the presence of the compound (A) negatively changes a flat band potential of the semiconductor with reference to that when the compound is absent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8004012B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesValence bandExternal bias
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
Belt tensioning device
A tensioning device for attraction mechanism including a receiving and mounting housing, a roller carrier pivotably connected to the mounting housing, a bearing which radially supports the roller carrier relative to the mounting housing, a spring between the roller carrier and the mounting housing for applying a tensioning force, and a damping device. The damping device includes a damping bush which, by friction, dampens any movement between the roller carrier and the mounting housing in such a way that damping is greater in the direction of an increasing tension force than in the direction of decreasing tension force. A flat band spring applies the friction force to the damping bush. The flat band spring is secured, at a first end, to the receiving and mounting housing in a rotationally fast way, and at a second end to the damping bush in a rotationally fast way.
Owner:MUHR UND BENNDER KG
Flat strap structure
InactiveUS20050278901A1High strengthIncreased shear strengthFlexible elementsHose connectionsPlastic materialsEngineering
A flat strap structure including at least one metal reinforcing wire and a strap made of plastic material by molding. The metal reinforcing wire is integrally embedded in the plastic strap. The metal reinforcing wire is formed of flexible metal wire or steel cable or is composed of electrically conductive wires enclosed by a layer of cable. The metal reinforcing wire serves to enhance the shear strength and tension strength of the flat strap to ensure safety in use of the flat strap. In addition, the electrically conductive wires can conduct current to transmit electric signal.
Owner:HUANG WEN SHENG
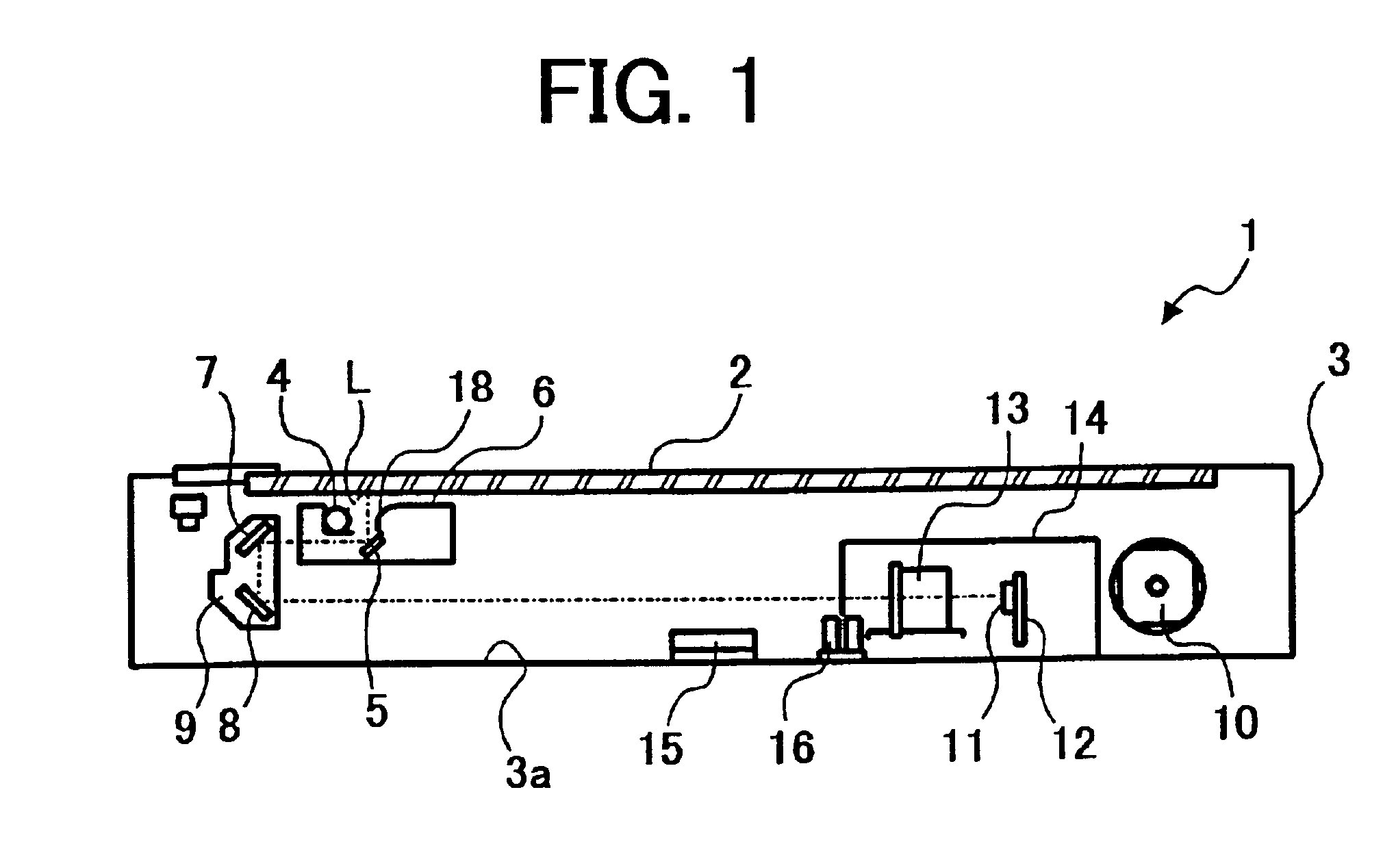
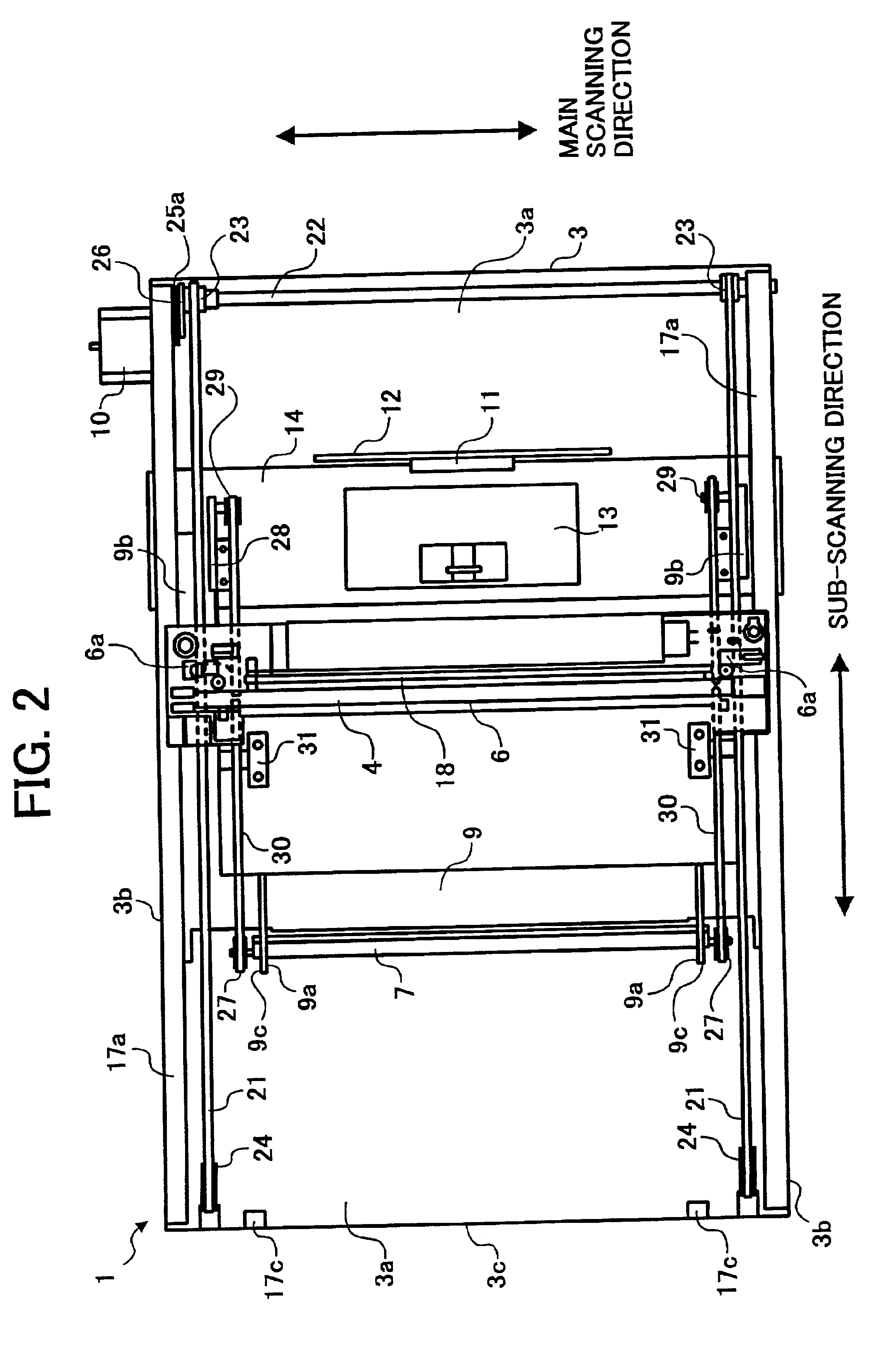
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus including the optical scanning device
InactiveUS6836633B2Electrographic process apparatusPictoral communicationReciprocating motionFlat band
An optical scanning device including a housing, a first carriage carrying a light source and a first mirror, a second carriage carrying second and third mirrors, the second carriage cofigured to move in a sub-scanning direction at one-half of a speed of the first carriage, first and second timing pulleys spaced apart in the sub-scanning direction, a timing belt spanned around the first and second timing pulleys to reciprocate the first carriage in the sub-scanning direction, a drive device to drive the first timing pulley, flat pulleys supported by the second carriage and spaced apart in the sub-scanning direction by a moving distance of the second carriage, a flat belt spanned around the flat pulleys to reciprocate the second carriage in the sub-scanning direction, an engaging member engaging the timing and flat belts to the first carriage, and a fixing member fixing the flat belt to the housing.
Owner:RICOH KK
Multi-working voltages CMOS device with single gate oxide layer thickness and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20130049119A1Reduce manufacturing costSuitableTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricManufacturing technology
The present invention provides a multi-working voltages CMOS device with single gate oxide layer thickness, gate work functions of CMOS transistors are regulated by implanting ions with different work functions into metal oxide dielectric material layers of the CMOS transistors, thus to realize different flat-band voltages under the condition of single dielectric layer thickness, and realize a multi-working voltages CMOS structure under the condition of single dielectric layer thickness. The present invention overcomes the process complexity of multiple kinds of gate dielectric layer thicknesses needed by traditional multi-working voltages CMOS, simplifies the CMOS process, makes the manufacturing procedure simple and easy to execute, reduces the preparation cost and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
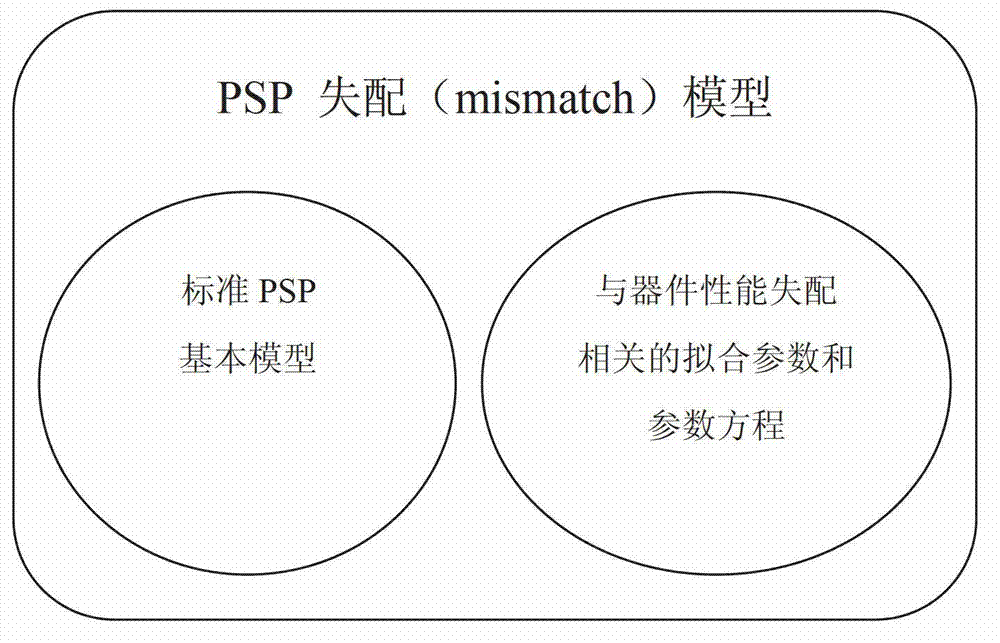
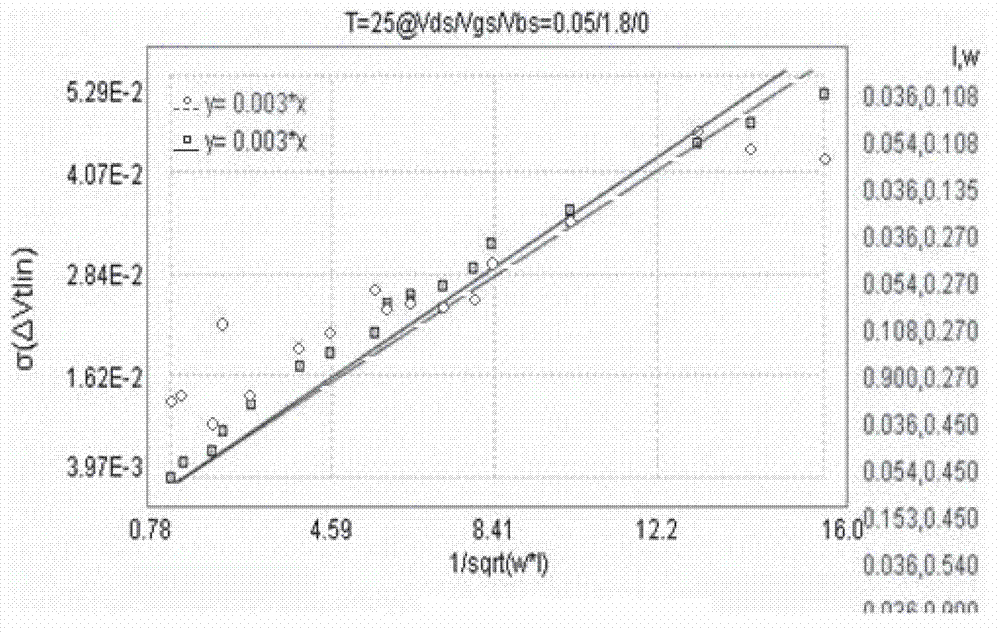
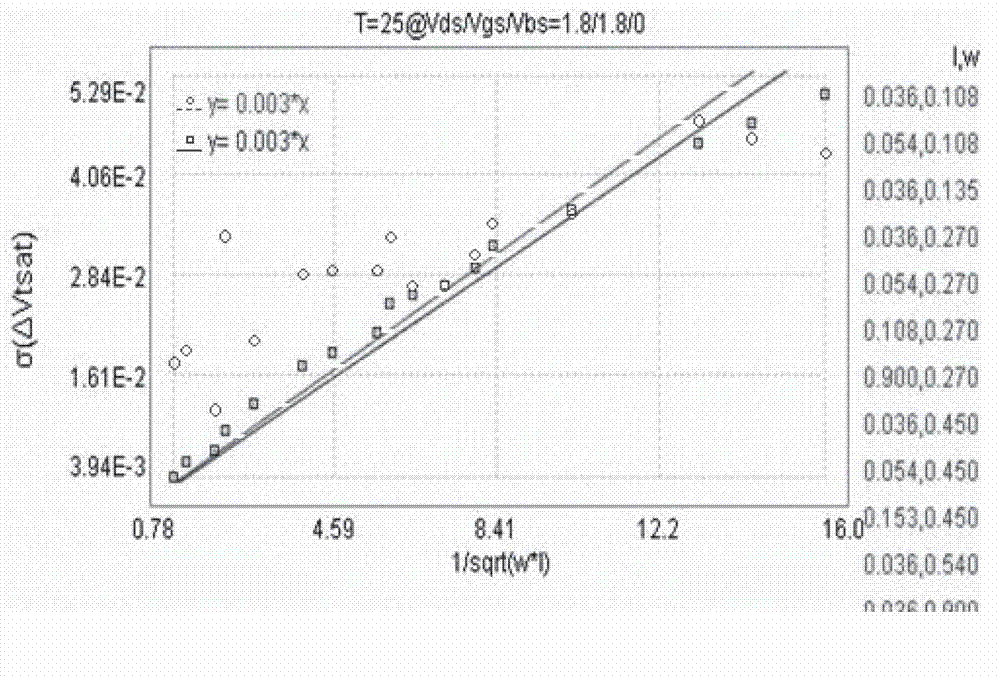
Modeling method for PSP mismatch model of MOS transistor
ActiveCN102968538AClear physical meaningHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionModel method
The invention discloses a modeling method for a PSP mismatch model of an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor. The modeling method comprises the steps that a device performance mismatch submodule is added to a standard PSP model and comprises fitting parameters and parametric equations relevant to device performance mismatch; the fitting parameters are influence coefficients of influence degrees of the device performance mismatch on essential parameters, namely toxo, vfbo and wot of the PSP model; the device performance mismatch submodule affects variation characteristics of linear threshold voltage Vtlin, saturation threshold voltage Vtsat, linear drain current Idlin and saturation drain current Idsat of the transistor through the influence coefficients; the effects of the device performance mismatch on the gate-oxide thickness toxo, the size-irrelevant flat-band voltage vfbo and the effective trench width variation wot caused by trench blocking doped transverse diffusion are determined; and the gate-oxide thickness toxo, the size-irrelevant flat-band voltage vfbo and the effective trench width variation wot due to the trench blocking doped transverse diffusion are redefined.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Broadband programmable gain amplifier with precise gain step size
InactiveCN101924527AAccuracy meetsFulfil requirementsGain controlUltrasound attenuationCommunications system
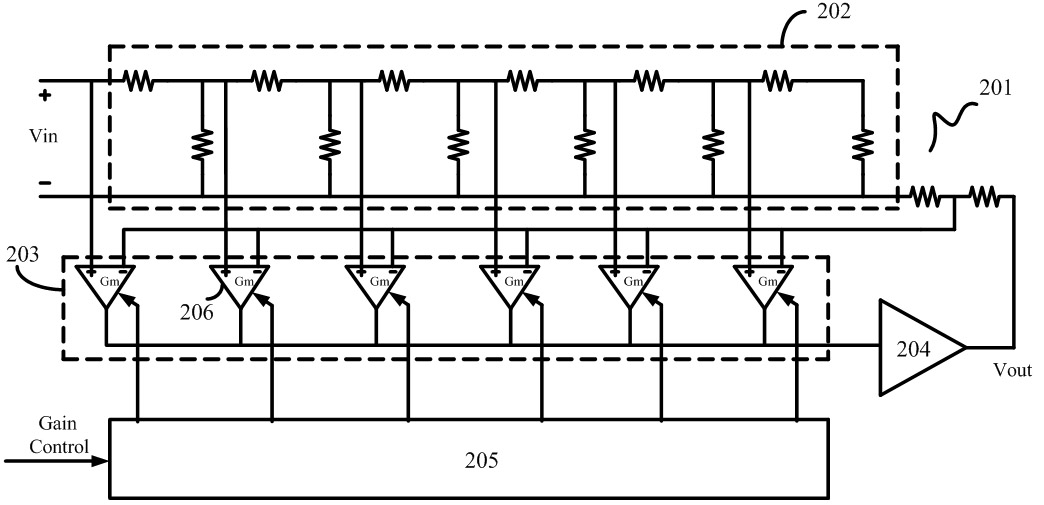
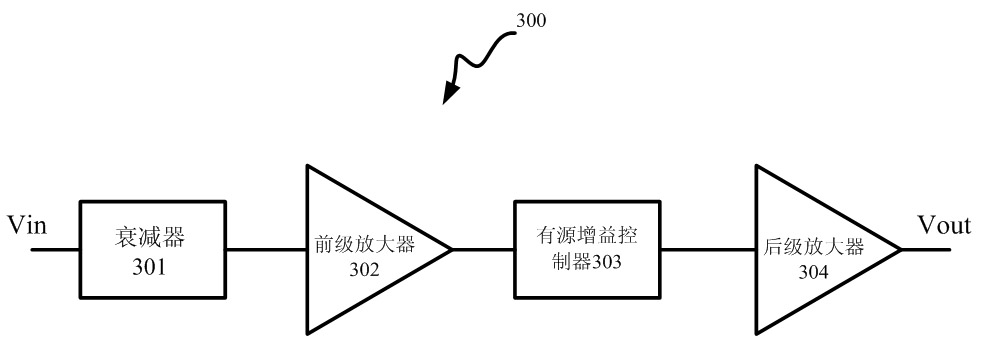
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits, in particular to a broadband programmable gain amplifier with precise gain step size. The broadband programmable gain amplifier comprises a passive attenuation network, an active gain controller and two fixed gain amplifiers. Firstly, a signal passes through the attenuation network, and the corresponding attenuation intensity isselected according to the size of an input signal to acquire a signal with moderate amplitude; the signal is amplified through a first-level fixed gain amplifier to enter the active gain controller to acquire a precise gain; and the signal is amplified through a second-level fixed gain amplifier to acquire a final signal. The active gain controller mainly consists of two connected feedback loops,and the precise gain step size is acquired through controlling the relative intensity of the two feedback loops. The invention can meet the requirements on continuous improvement of VGA gain precision and flat band width in systems, such as communication systems, disc reading systems and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
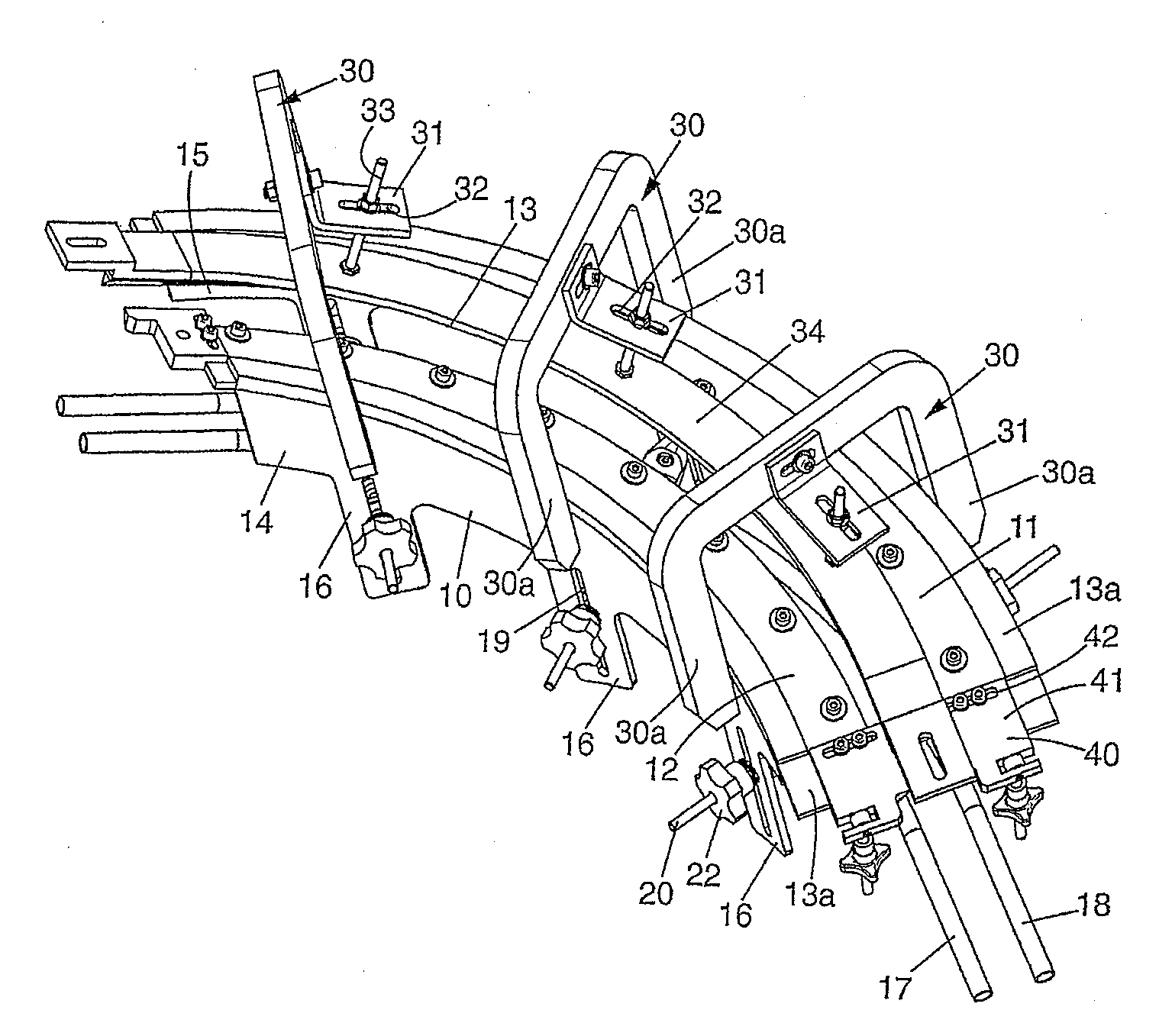
Rail Element For Conveying Suspended Objects, Preform-Supply Device Comprising One Such Element And Curved Flat Band Which Can Be Fixed To One Such Element
InactiveUS20080196998A1High trafficLimit lateral swingingCharge manipulationConveyor partsEngineeringFlat band
The invention relates to a rail element for conveying suspended objects, such as bottles or preforms. The inventive element comprises two guide rails (11, 12) which are separated by a pre-defined distance and which form lateral support surfaces for the objects being conveyed along a conveyor passageway (13), such as preform sub-neck guides. The invention is characterised in that it defines a helically-curved conveyor section and consists of a frame (10) on which the guide rails (11, 12) are helically arranged, whereby at least one guide rail (11, 12) comprises a flat band that can be removed from the frame (10).
Owner:SIDEL PARTICIPATIONS SAS
Multi-band-pass terahertz band-pass filter based on frequency selective surface structure
InactiveCN104681899ASolve only single-frequency filteringSolve the lack of polarization sensitivityOptical filtersWaveguide type devicesElectromagnetic wave transmissionDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a multi-band-pass terahertz band-pass filter based on a frequency selective surface structure, and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic wave transmission function devices. The multi-band-pass terahertz band-pass filter is composed of an underlay dielectric substrate through which terahertz waves can be transmitted and two frequency selective surface layers which are arranged on upper surface and the lower surface of the underlay dielectric substrate; the two frequency selective surface layers are arranged oppositely and are the same in structure; each frequency selective surface layer comprises a plurality of resonance units arranged in a matrix. The multi-band-pass terahertz band-pass filter has the characteristics of three-band-pass filtering, polarization insensitivity, small insertion loss, flat band-pass ripple, remarkable out-of-band rejection, simple structure, small size and the like, and is convenient to adjust and control and easy to process.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
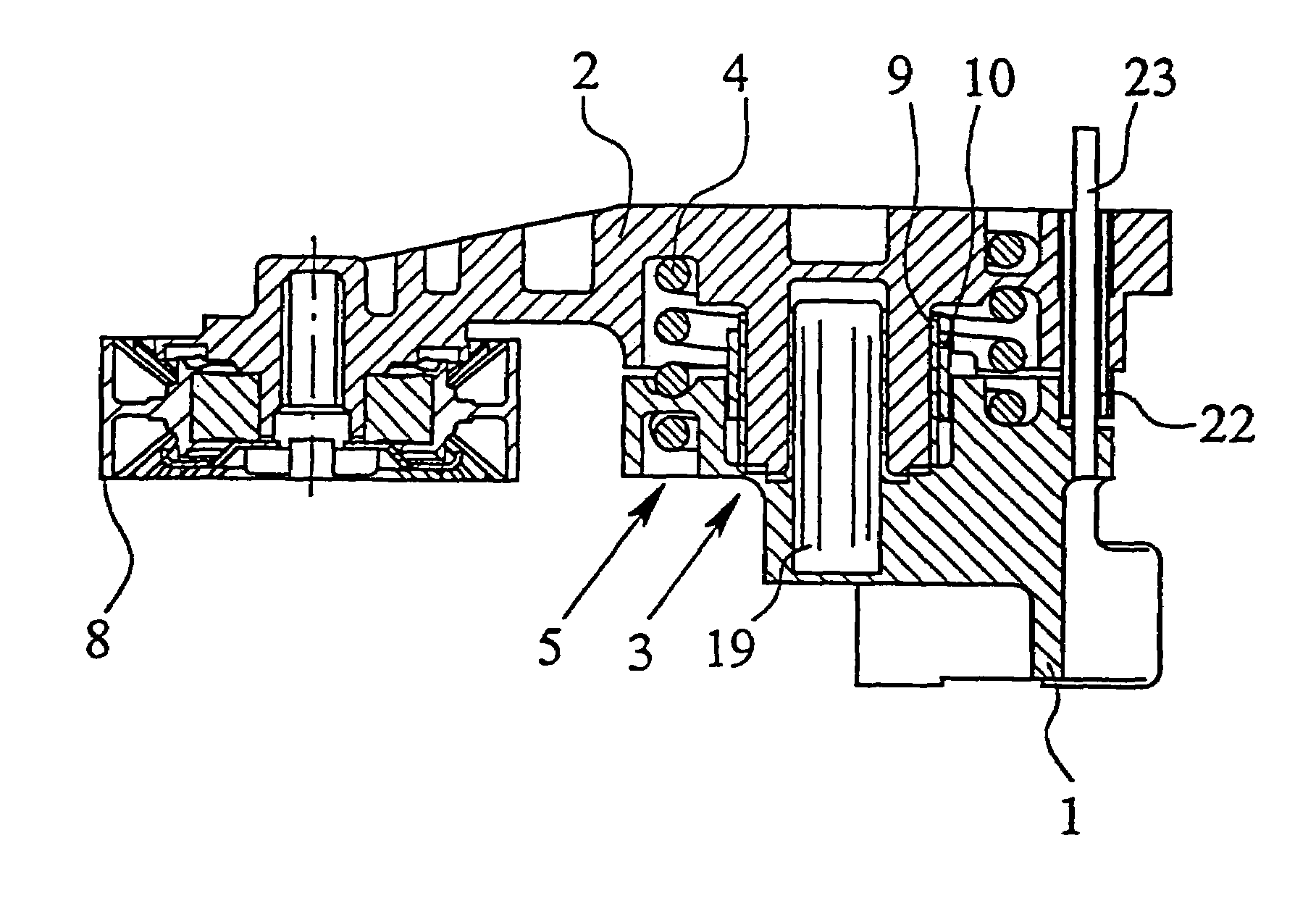
Mutual compensating metals-oxides-semiconductor structure and its mfg. method
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) structure including an intermediate layer between a Si-containing gate electrode and a high-k gate dielectric, so that a threshold voltage and a flat-band voltage of the structure are stabilized.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
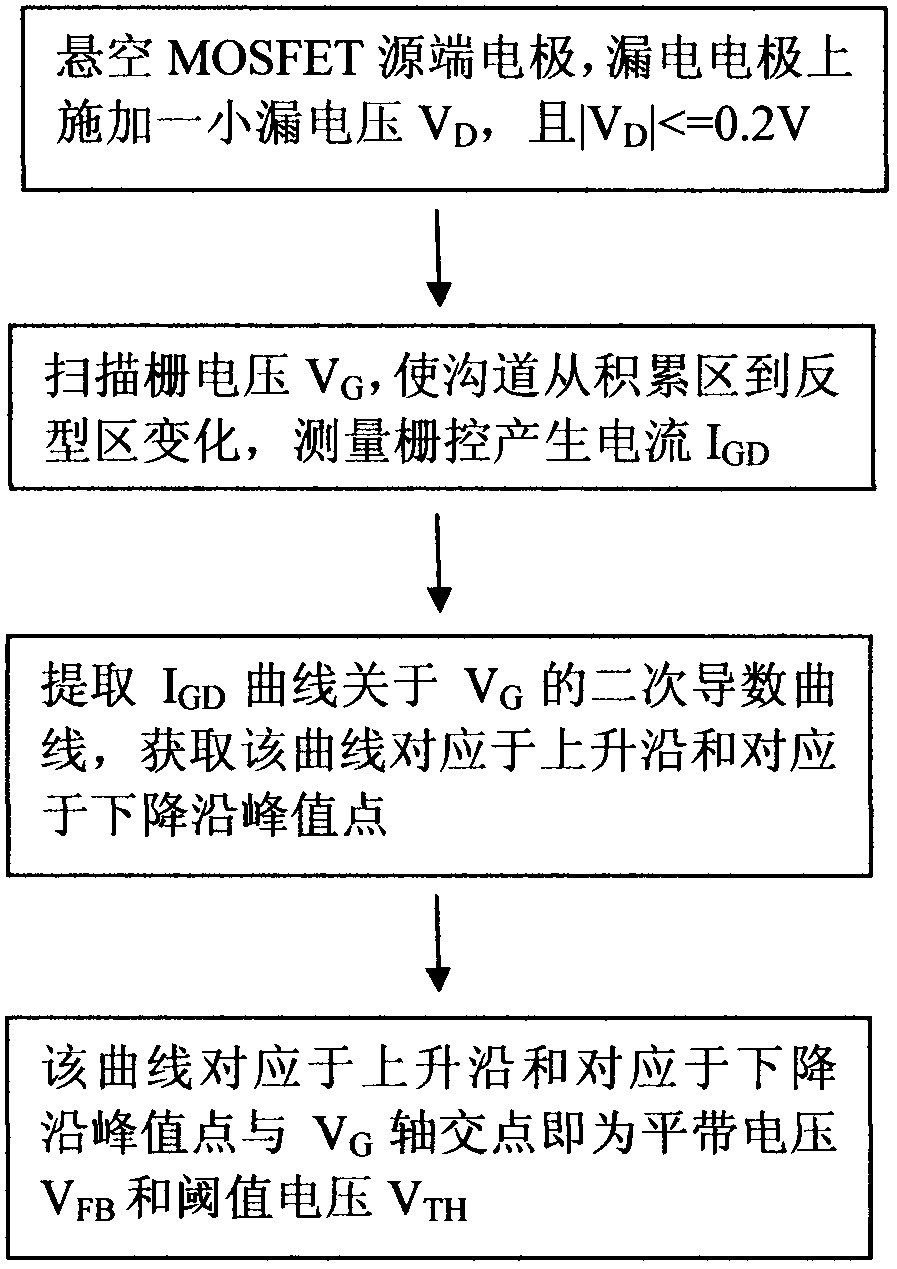
Method for extracting flat-band voltage and threshold voltage of MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) based on current generation of grid-control drain electrode
ActiveCN102692543AEliminate sources of inaccuracyAccurate extractionCurrent/voltage measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingMOSFETEngineering
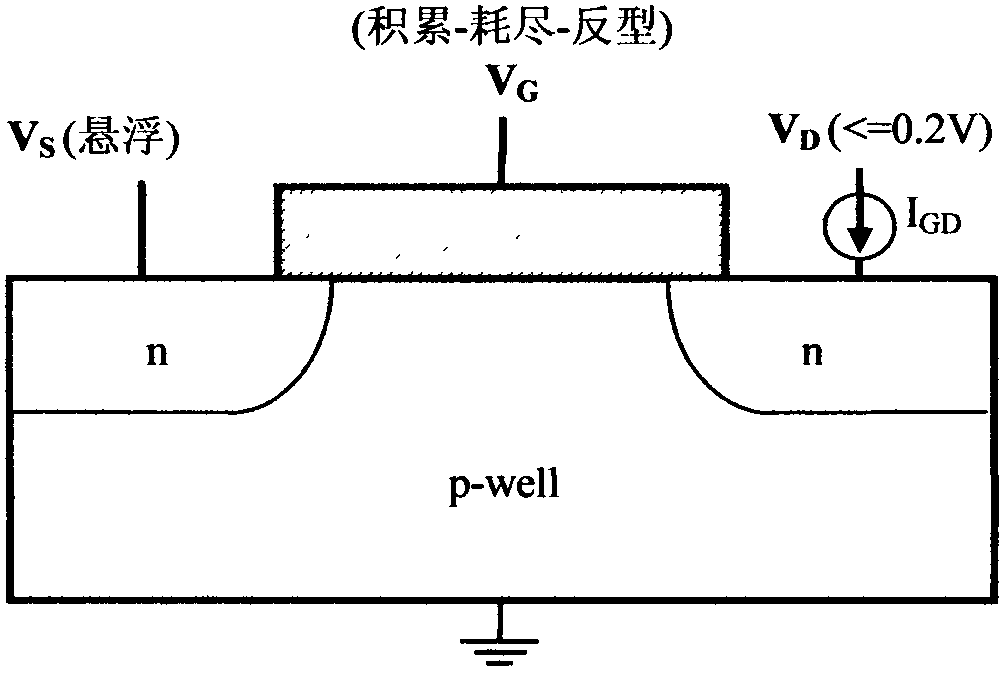
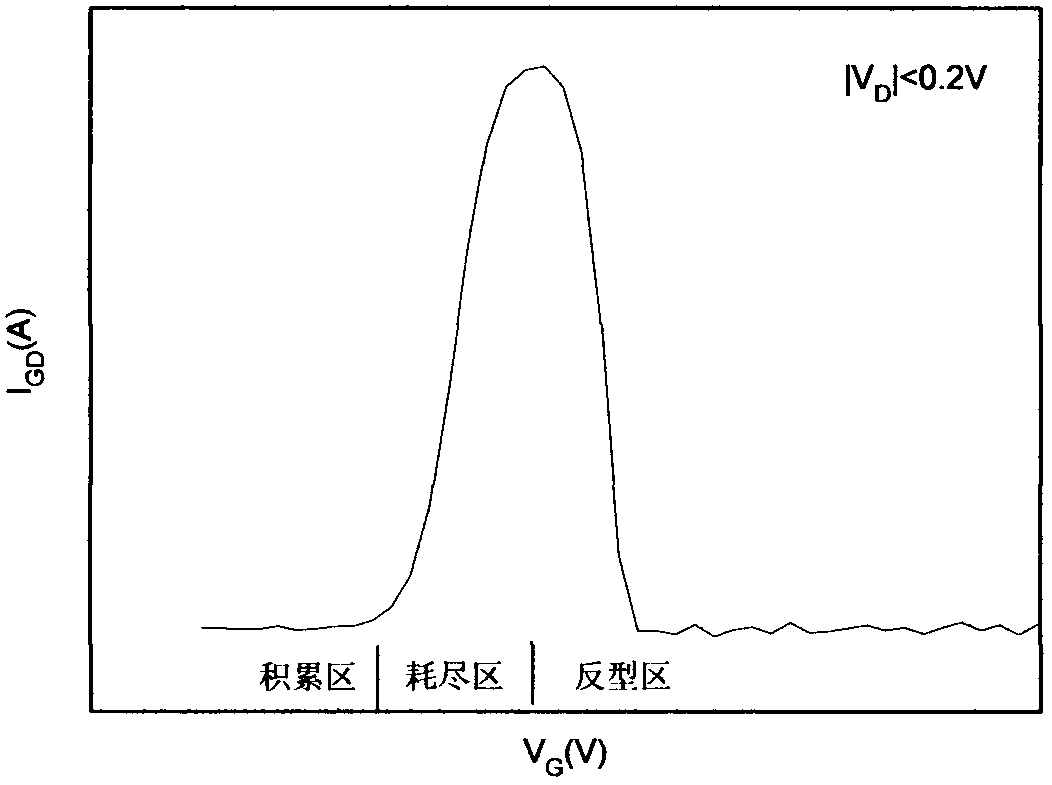
A method for extracting flat-band voltage and threshold voltage of an MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) based on current generation of a grid-control drain electrode belongs to the filed of micro electronic technique, is used for extracting VFB and VTH through the variation of grid-control generated current caused by the fact that a channel of the MOSFET changes from an accumulation region, an exhaustion region to a transoid region, and includes the following steps: an electrode at the source end of the MOSFET is hung in the air, a small drain voltage VD is exerted on the drain electrode, and the absolute valve of the VD is smaller than or equals to 0.2 V; the gate voltage VG is scanned, the channel changes from the accumulation region to the transoid region, and the grid-control generated current is measured under the drain bias VD; secondary partial differentiation operation for the obtained grid-control generated current curve IGD is performed to obtain the relation curve of the secondary derivative and the VG; the curve forms three peak value points, so as to obtain the peak value point corresponding to the rise edge and the peak value corresponding to the decline edge; the flat-band voltage VFB can be obtained through forming a vertical at the peak value point corresponding to the rise edge and enabling the vertical to be intersected with a grid voltage shaft; and the threshold voltage VTH can be obtained through forming a vertical at the peak value point corresponding to the decline edge and enabling the vertical to be intersected with the grid voltage shaft.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
Linear actuator with releasably interlocking bands
The linear actuator comprises an elongated first band wound in helical form about a central axis and capable of taking a retracted position and an extended position with its turns spaced from one another in the direction of the central axis, and first fasteners carried by the first band and longitudinally disposed therealong. The linear actuator also comprises an elongated second substantially flat band wound on itself, with its turns substantially transversely parallel to the central axis, and capable of taking a retracted, spiral position with its turns nested within one another and an extended position with its turns forming a helix around the central axis and generally equally radially spaced therefrom to form a telescopic column, the first and second bands, when in retracted position, in respective locations so as to clear each other. Second fasteners are carried by the second band and longitudinally disposed therealong, the second fasteners capable of cooperating with the first fasteners to releasably interlock the first and second bands. A spacer successively spaces the turns of the first band. A powered drive causes relative rotation on one hand of the first and second bands and on the other hand of the spacer about the central axis. Guide means guide the turns of the second band towards the turns of the first band to releasably interlock the first and second fasteners. A retaining member retains the first and second fasteners in interlocked fashion in the telescopic column.
Owner:TION LAFOREST
Photosensitive device with electric shutter
ActiveUS20190296178A1Fast neutralizationEasy to usePhotometry electrical circuitsSemiconductor devicesElectronic shutterSemiconductor materials
A photosensitive transistor or voltage-mode device which comprises a gate electrode, a layer of ambipolar two-dimensional material such as graphene and a layer of photoactive semiconducting material forms a junction with the ambipolar two-dimensional material. The photoactive semiconducting material and the ambipolar two-dimensional material are configured so that there is a non-screening gate voltage interval where an interface voltage at the junction between the photoactive semiconducting layer and the ambipolar two-dimensional material can be changed by applying to the gate electrode a gate voltage which falls within the non-screening gate voltage interval. The non-screening gate voltage interval comprises a flat-band gate voltage at which the interface voltage is zero. An electrical shutter can be operated at this gate voltage.
Owner:EMBERION OY
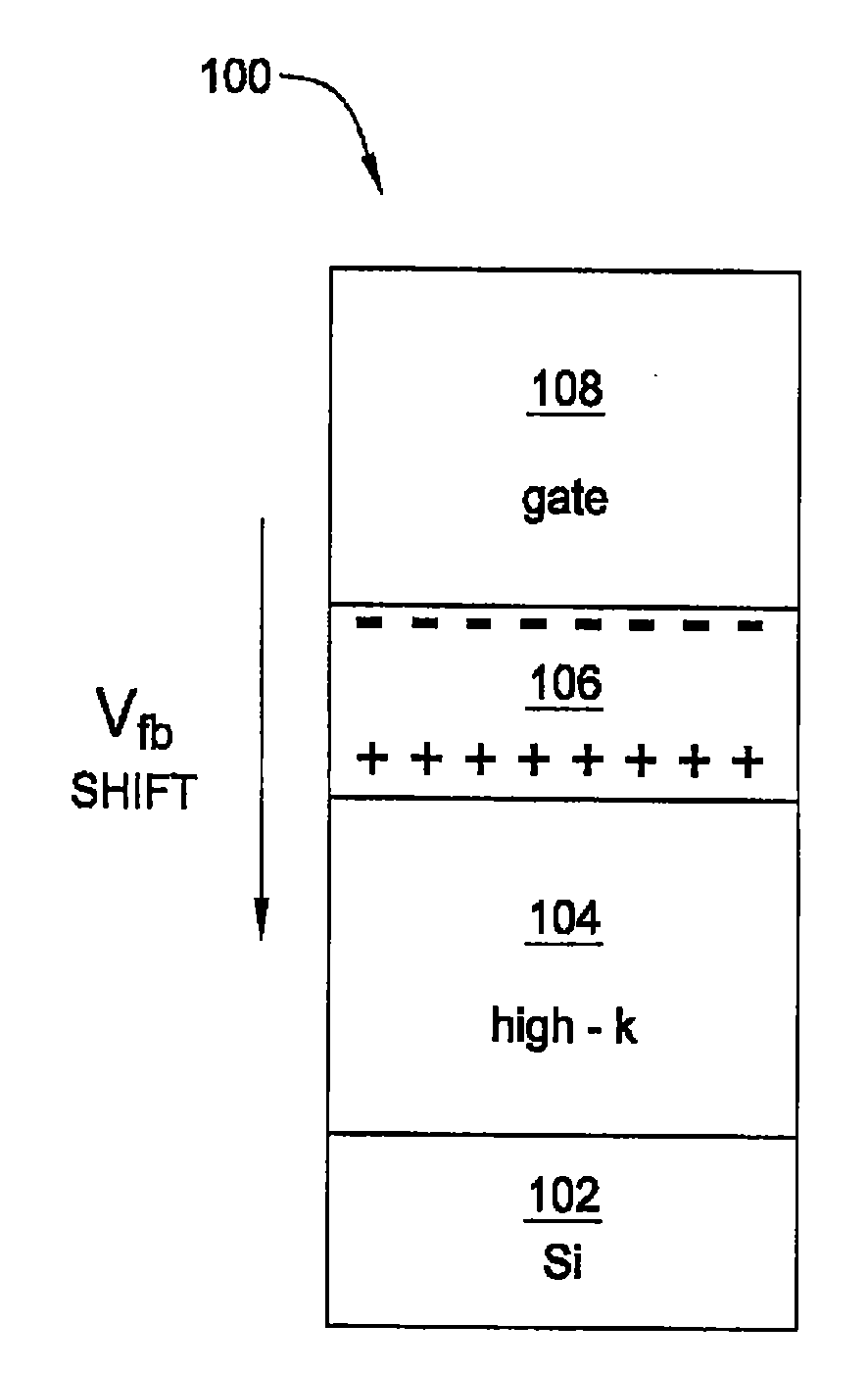
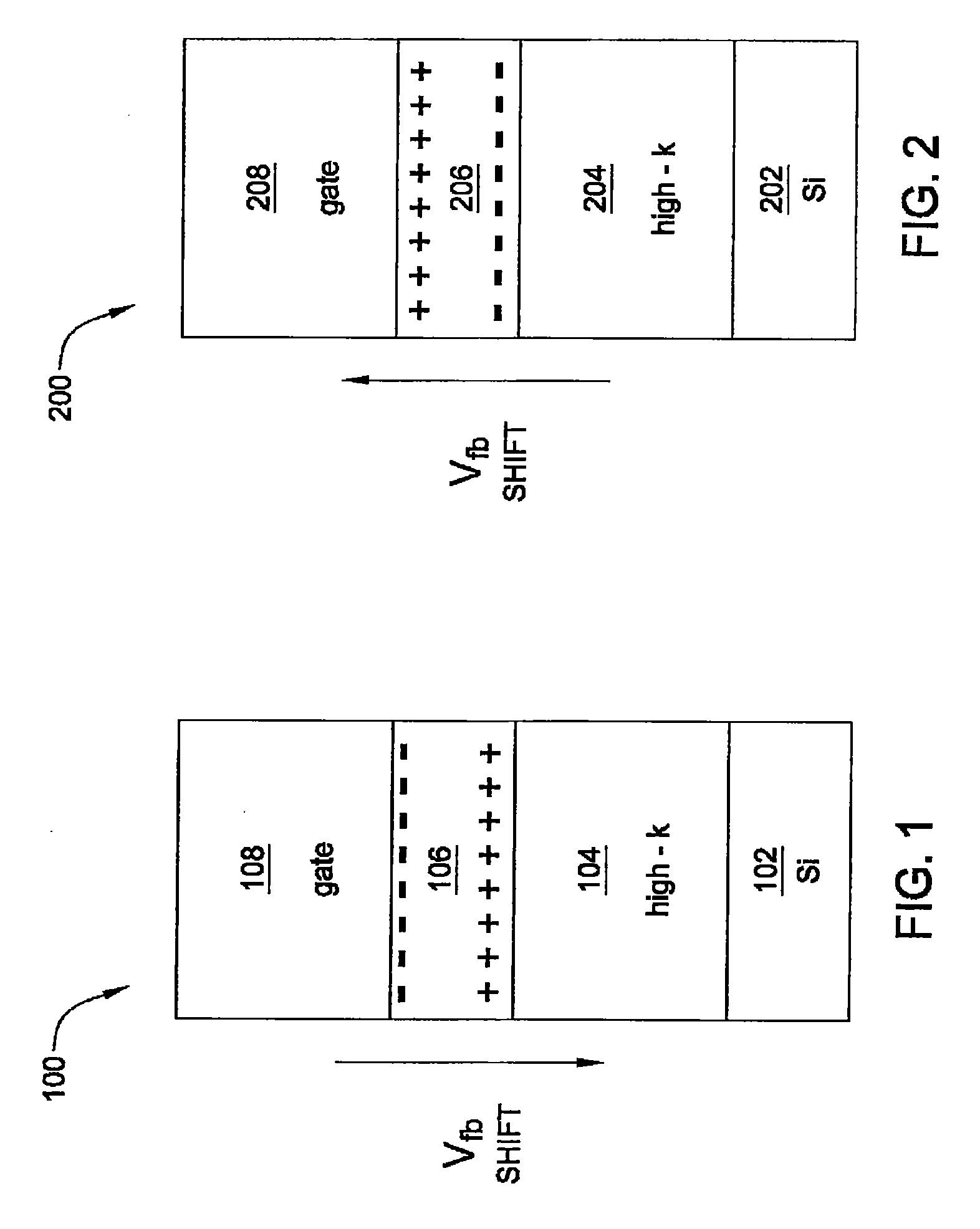
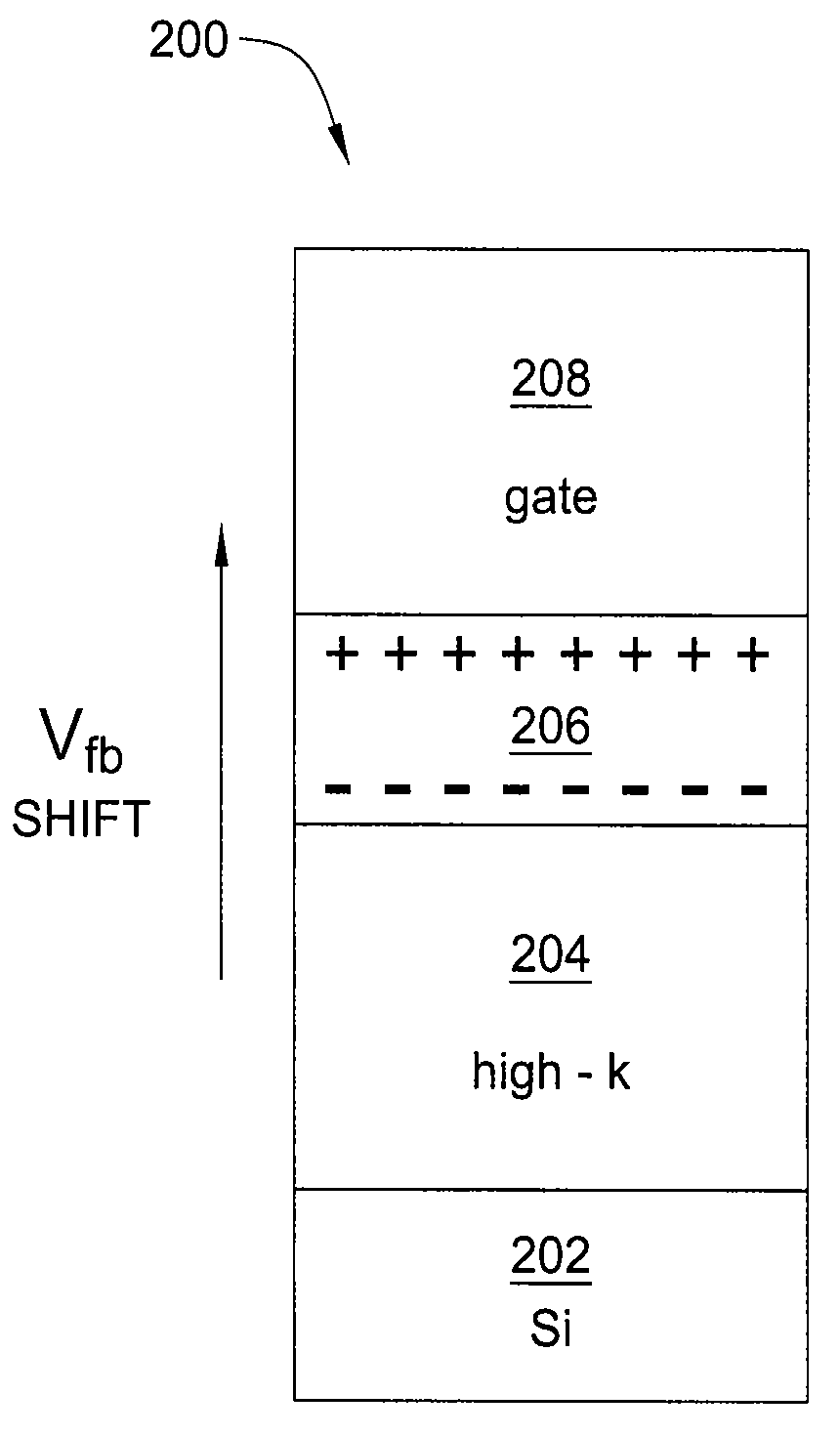
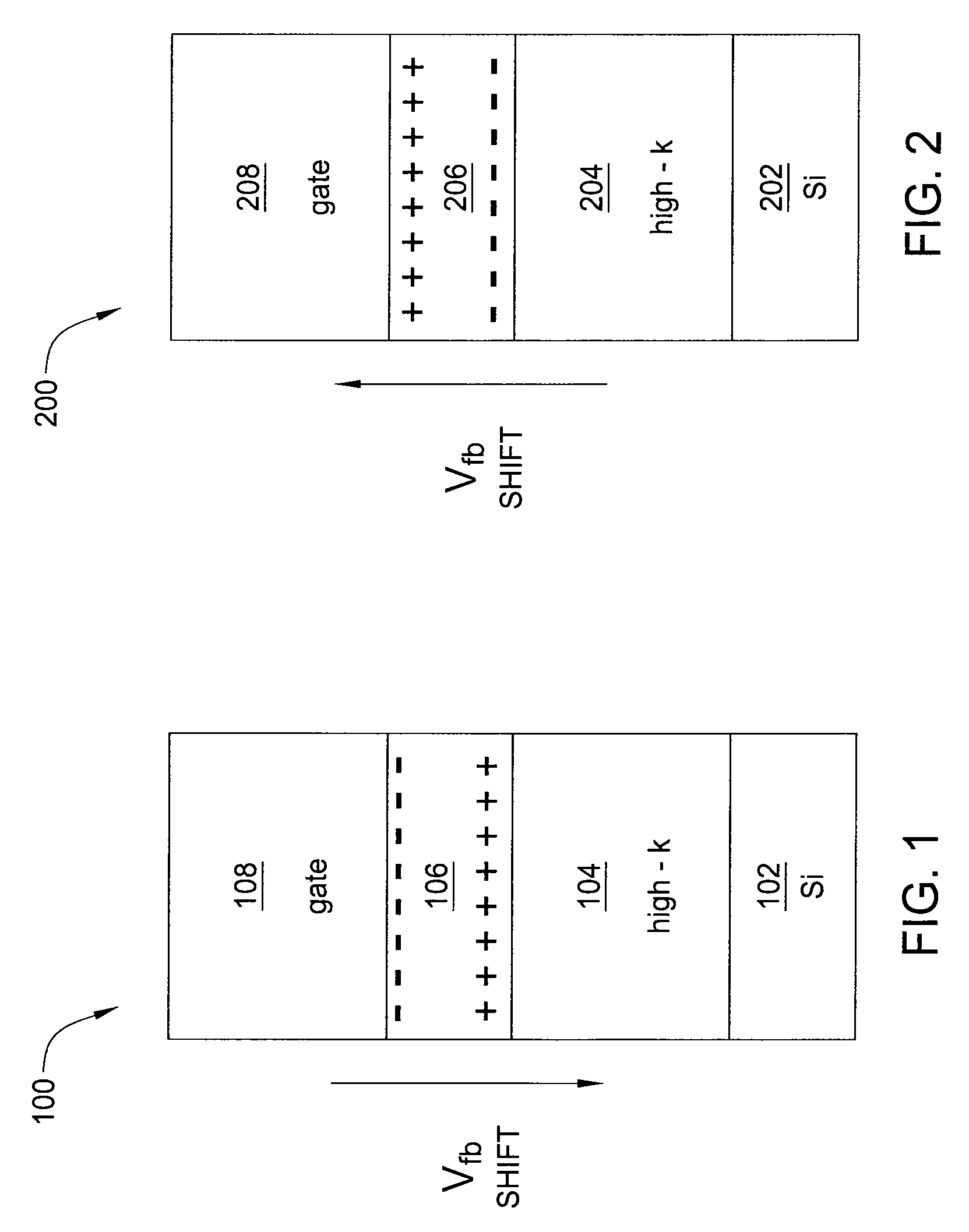
Method and apparatus for flatband voltage tuning of high-k field effect transistors
ActiveUS20090302370A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorDielectric layer
In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for flatband voltage tuning of high-k field effect transistors. One embodiment of a field effect transistor includes a substrate, a high-k dielectric layer deposited on the substrate, a gate electrode deposited on the high-k dielectric layer, and a dipole layer positioned between the substrate and the gate electrode, for shifting the threshold voltage of the field effect transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
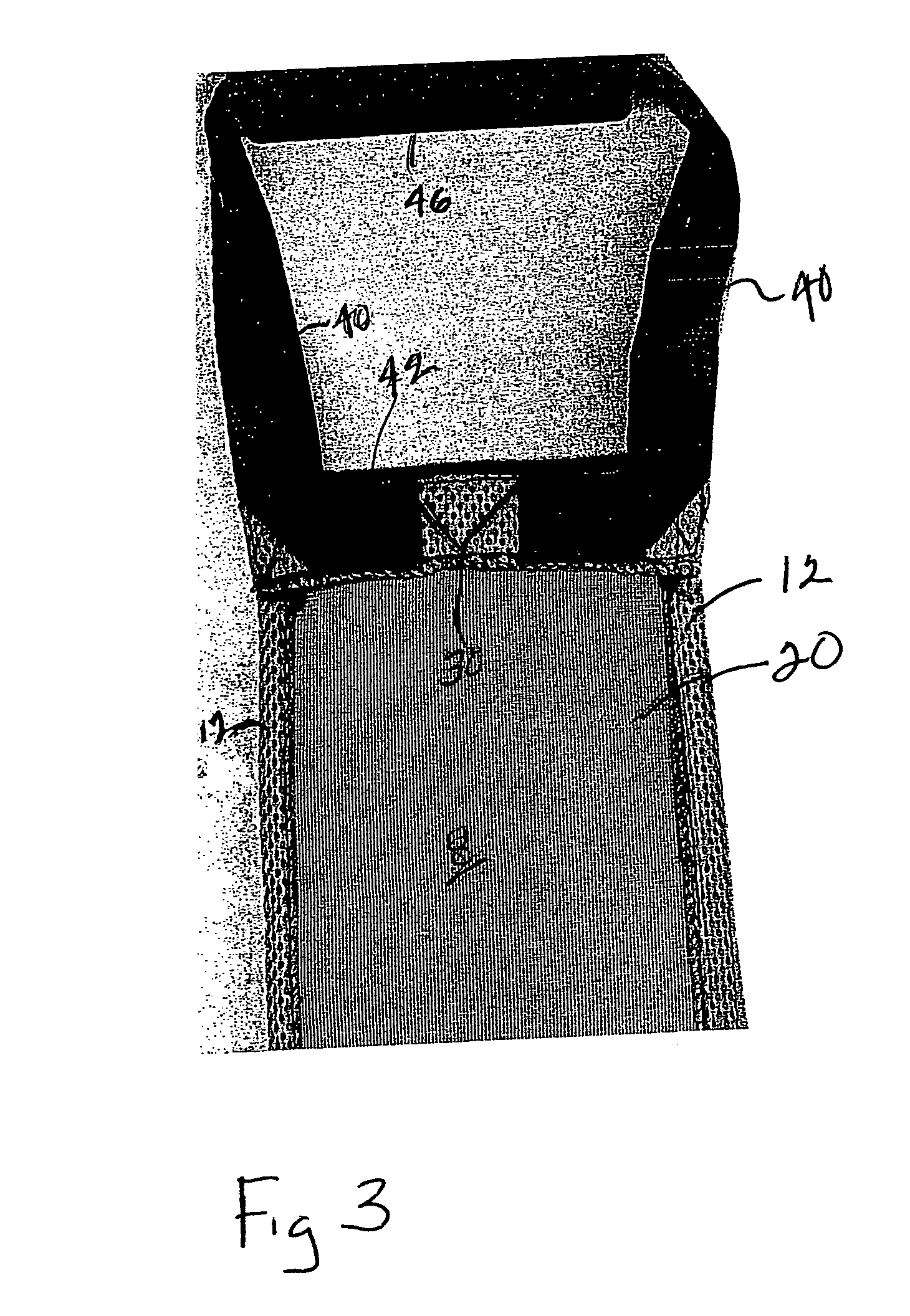
Abdominal exercise device
InactiveUS20060234844A1Economical to useCheap manufacturingResilient force resistorsStiltsFlat bandPhysical therapy
An abdominal exercise device having a flat band formed by a double layer of mesh material. A pair of straps are retained on each end of the band. A pair of cushioned handles are respectively retained on the straps.
Owner:KATES MICHAEL P +1
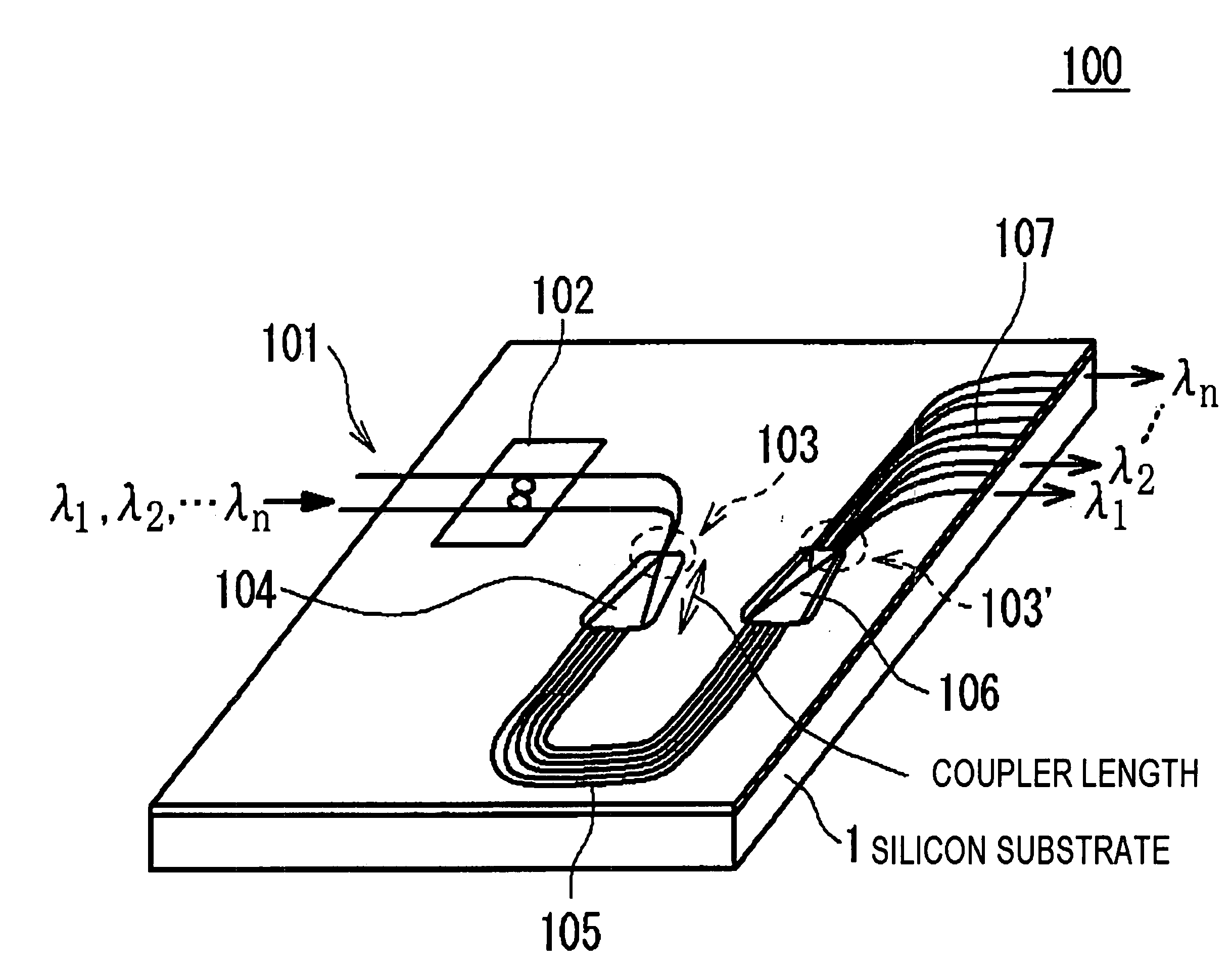
Optical wavelength division multiplexer
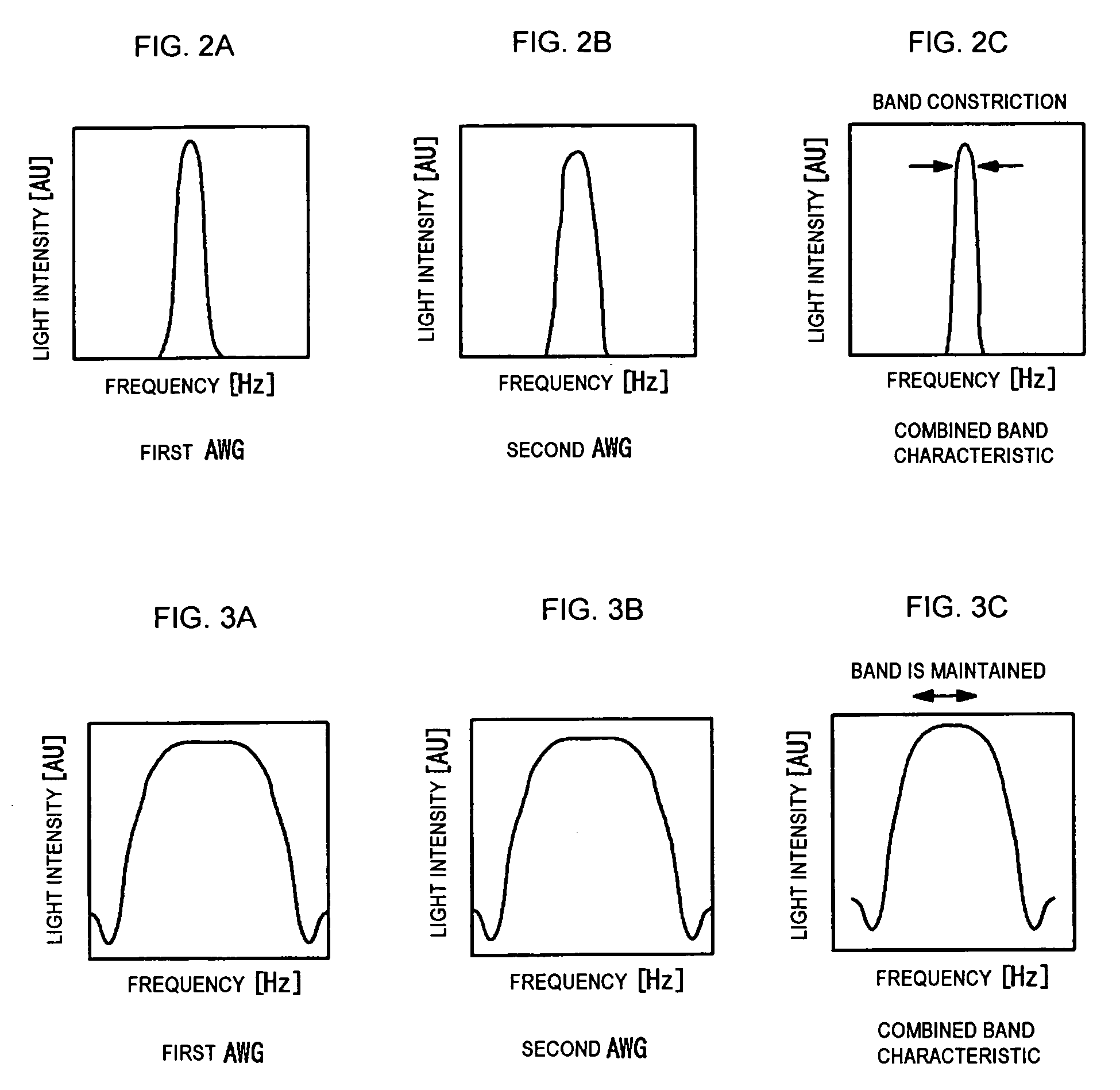
InactiveUS20060222296A1Reducing excessive lossReducing the excessive lossCoupling light guidesGratingMultiplexer
In an optical wavelength division multiplexer, flattening of band characteristic can be realized while reducing excessive loss due to the flattening of band characteristic in an arrayed waveguide grating. Further, the flat band of the band characteristic can be made broader. The optical wavelength division multiplexer according to the invention includes: a first coupler optical waveguide 104 and a second coupler optical waveguide 106; one or more input side connecting part waveguide(s) 103 with one end connected to an input optical waveguide 101 and the other end connected to an optical input end face of the first coupler optical waveguide 104; one or more output side connecting part waveguide(s) 103′ with one end connected to an output optical waveguide 107 and the other end connected to an optical output end face of the second coupler optical waveguide 106; and an arrayed optical waveguide 105 connected between the first coupler optical waveguide 104 and the second coupler optical waveguide 106 and having plural channel waveguides with different lengths from one another, and further includes an optical interferometer connected to at least two optical waveguides between the input side connecting part waveguide 103 and the input optical waveguide 101. The optical interferometer includes a ring structure 202 that feeds back an input light, and is provided so that an interference period of the optical interferometer may become equal to a difference between frequencies of light output from adjacent optical waveguides of the output side connecting part waveguide 107.
Owner:NEC CORP
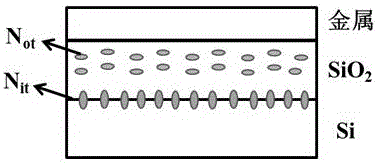
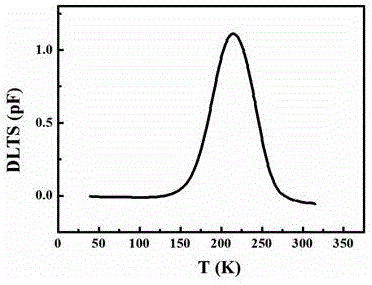
Separation test method of charge in SiO2 and SiO2/Si interface state
InactiveCN106684012AImplement separation testingSimple manufacturing processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementFlat bandDeep level
The invention provides a separation test method of the charge in SiO2and a SiO2 / Si interface state. The separation test method specifically includes the steps of (1) after a SiO2 thin film is grown on the surface of a silicon wafer, growing a metal thin film on the surface of SiO2 to obtain an MIS device; (2) conducting a C / V test of the MIS device to obtain a flat band voltage Vfb, and then calculating the total charge density Ntot; (3) conducting a deep-level transient spectrum test of the MIS device to obtain the distribution of the energy density of the interface state with the energy level, and after integrating, obtaining the total interface state Nit; and (4) subtracting Ntot from Nit to obtain Not, and then achieving the separation test of Not and Nit. The preparation method of the test structure (MIS) used in the invention is simple and quick, has low requirements for equipment, and is conducive to the promotion in science and industry.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for flatband voltage tuning of high-k field effect transistors
In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for flatband voltage tuning of high-k field effect transistors. One embodiment of a field effect transistor includes a substrate, a high-k dielectric layer deposited on the substrate, a gate electrode deposited on the high-k dielectric layer, and a dipole layer positioned between the substrate and the gate electrode, for shifting the threshold voltage of the field effect transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
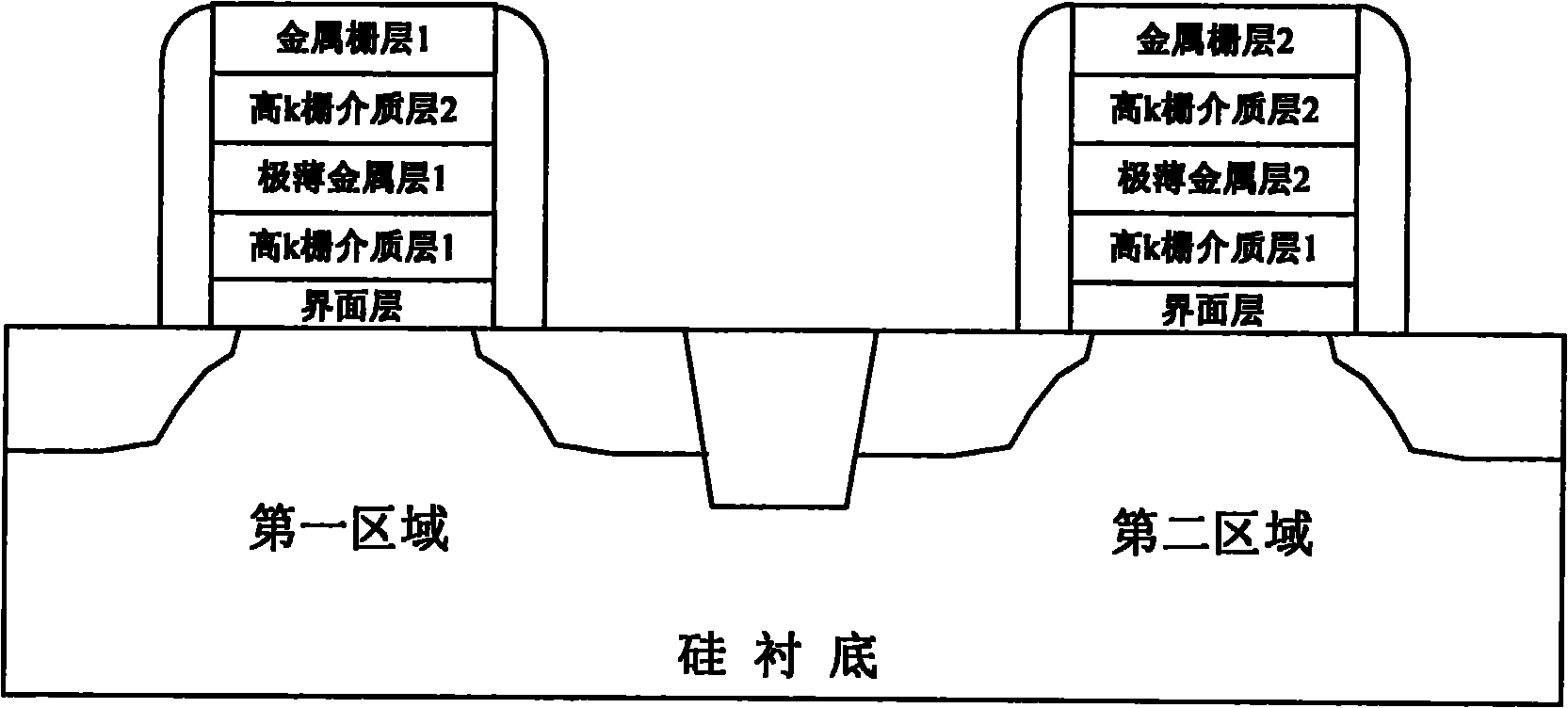
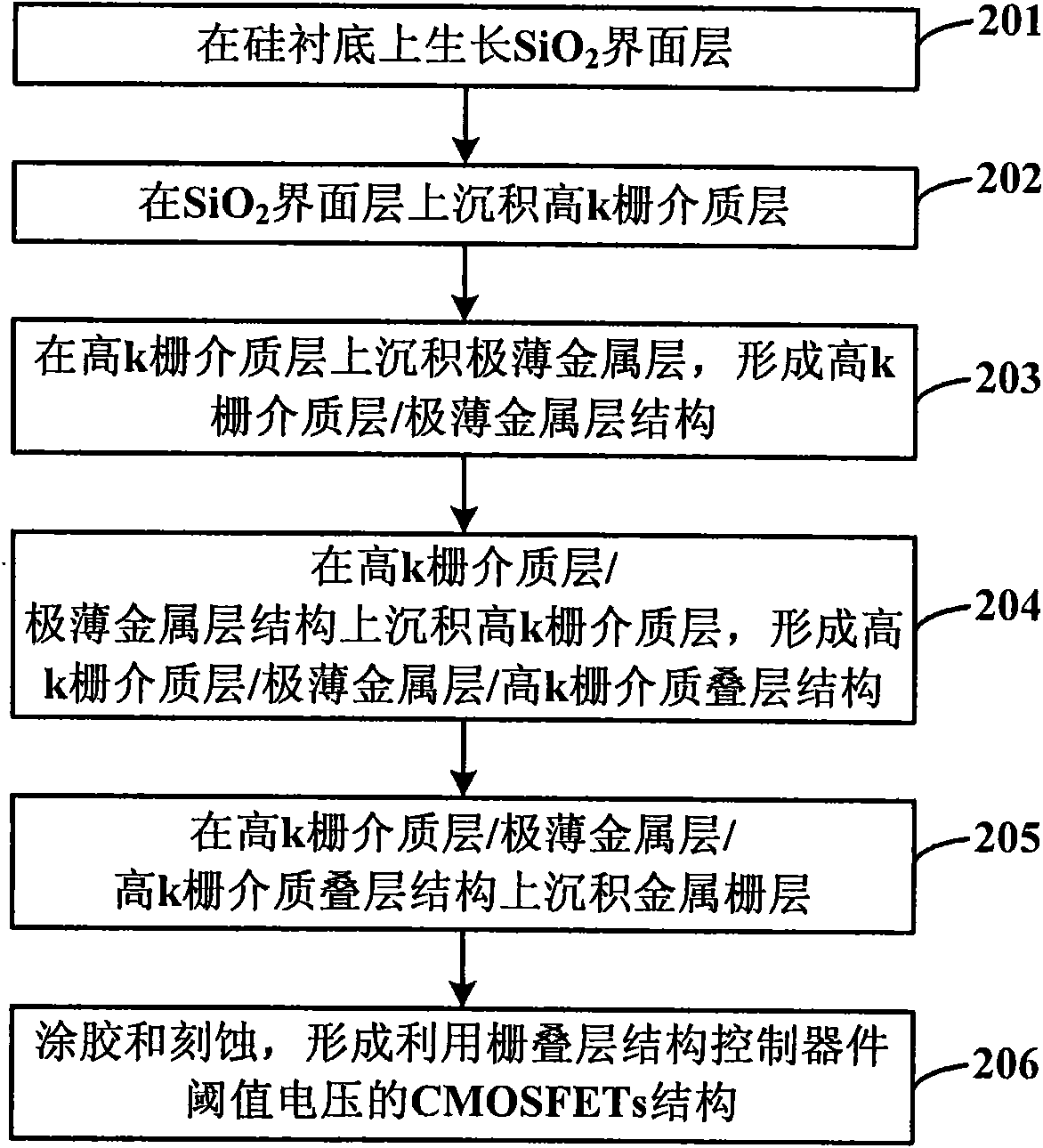
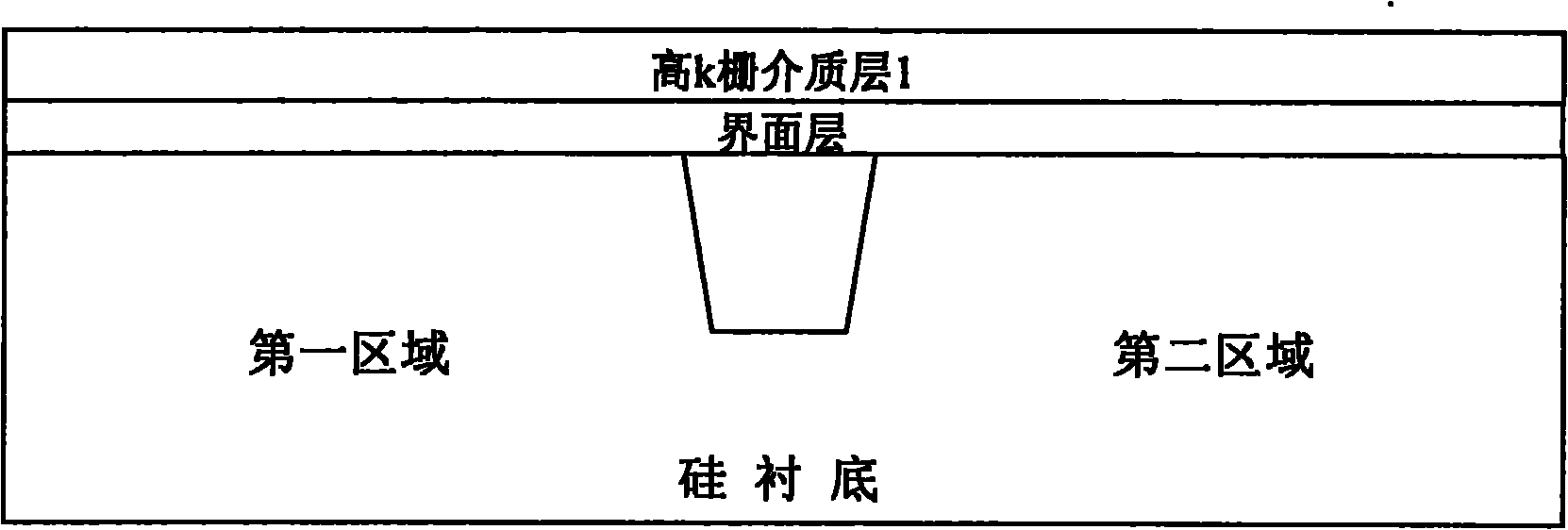
CMOSFETs structure for controlling threshold voltage of device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101930979AControl Threshold VoltageControl quantityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricGate stack
The invention discloses a CMOSFETs structure for controlling the threshold voltage of a device by using a gate stack structure and a manufacturing method thereof. The structure comprises a silicon substrate, a SiO2 boundary layer growing on the silicon substrate, a high k gate dielectric layer deposited on the SiO2 boundary layer, an ultra thin metal layer deposited on the high k gate dielectric layer, a high k gate dielectric layer deposited on the ultra thin metal layer structure and a metal gate layer deposited on the high k gate dielectric stack structure. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: respectively depositing the ultra thin metal layers in the high k gate dielectric layers in the regions of NMOS and PMOS devices, and regulating the flat band voltage of the devices by using positive or negative charges formed by the ultra thin metal layers in the high k gate dielectric layers, thereby controlling the threshold voltage of the devices. The invention not only can enhance the interface dipole between the high k gate dielectric layer and the SiO2 boundary layer in the CMOS device, but also can well control the type and the number of permanent charges in the high k gate dielectric layer, thereby effectively controlling the threshold voltage of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Monitoring method for organic coating material carrier density
InactiveCN101246188AHigh densityMonitorableWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCurrent density measurementsCapacitanceEpoxy
The invention discloses a method for monitoring organic coating material carrier density. The invention includes the following steps: measure electrode base material is stainless steel stick which is sealed with epoxy resin, after the working surface is polished, cleaned and dried, the working surface is painted with organic coating material, the thickness of the painted film is controlled at 25 microns plus or minus 2 microns, and the working surface is constant temperature dried at 35 DEG C, then the membrane coated electrode is obtained; the membrane coated electrode is dipped in 5% sodium salt solution at room temperature, the saturated calomel is used as the assistant electrode, the platinum electrode is the reference electrode, the membrane coated electrode potential U and the capacitance Csc are measured; the relationship curve between the Csc-2 and U is drawn, and the Mott-Schottky relation schema is obtained; according to the Mott-Schottky relational expression, the Mott-Schottky relation schema is extrapolated to the crossing point of the potential axis, then the flat-band potential Ufb is obtained, at the same time the space charge density ND is calculated by slope, which is the carrier density.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com