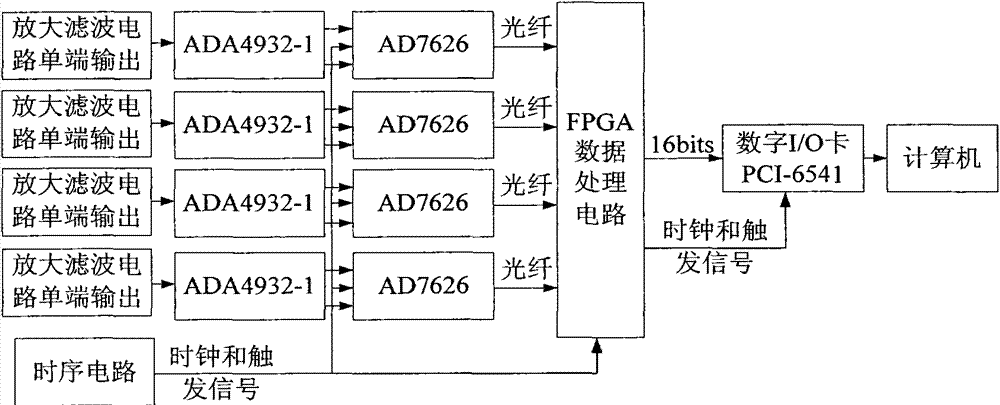
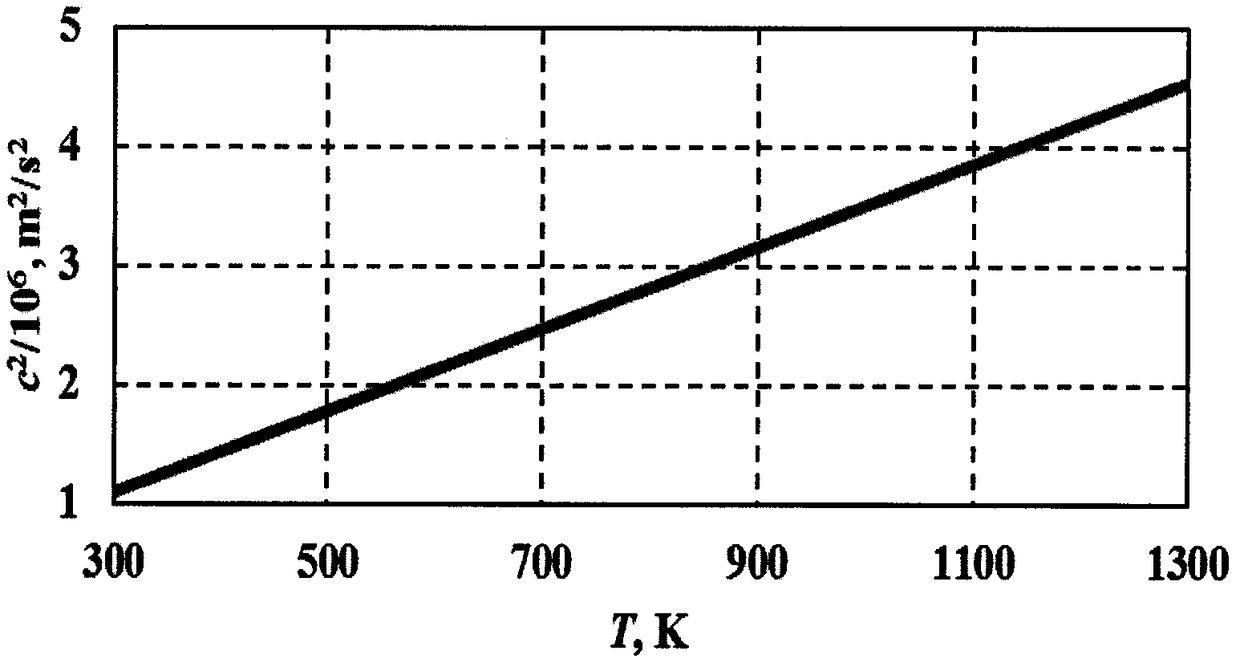
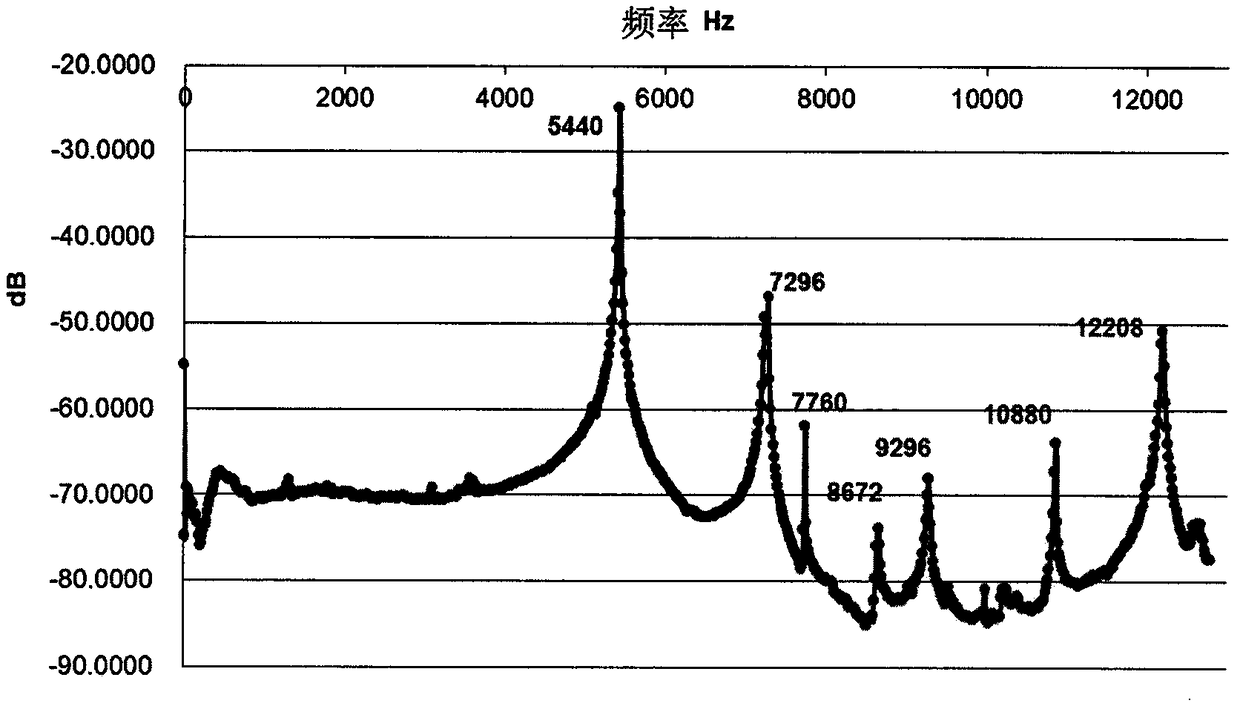
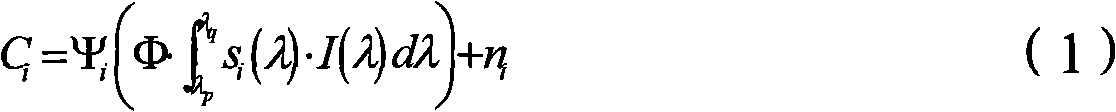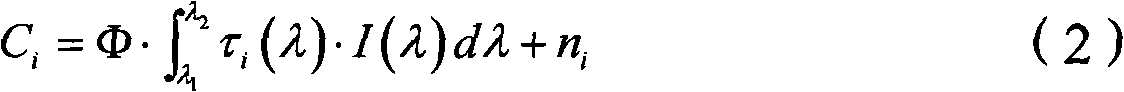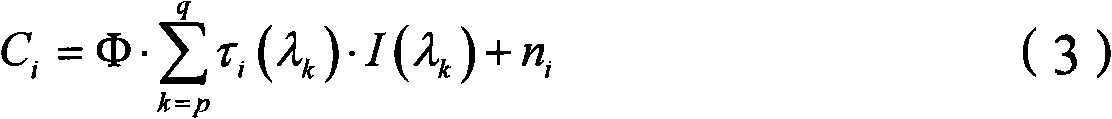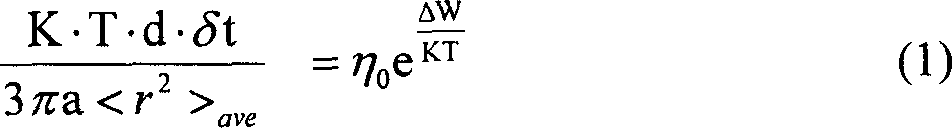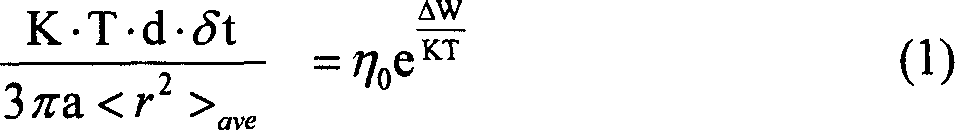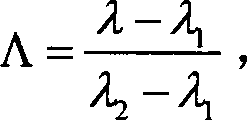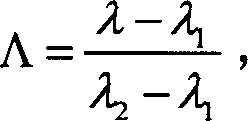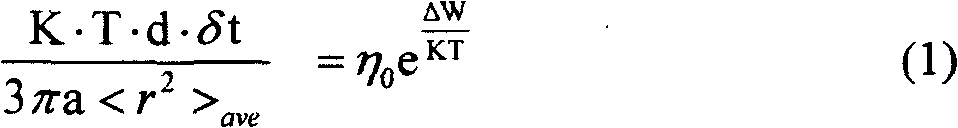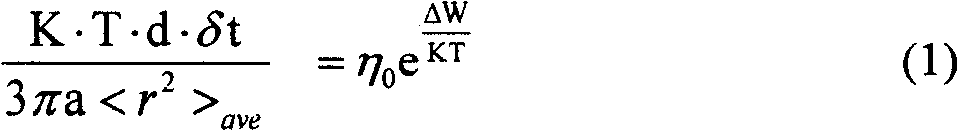Patents
Literature
48 results about "Thermodynamic temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermodynamic temperature is the absolute measure of temperature and is one of the principal parameters of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic temperature is defined by the third law of thermodynamics in which the theoretically lowest temperature is the null or zero point. At this point, absolute zero, the particle constituents of matter have minimal motion and can become no colder. In the quantum-mechanical description, matter at absolute zero is in its ground state, which is its state of lowest energy.
Fluid heating system
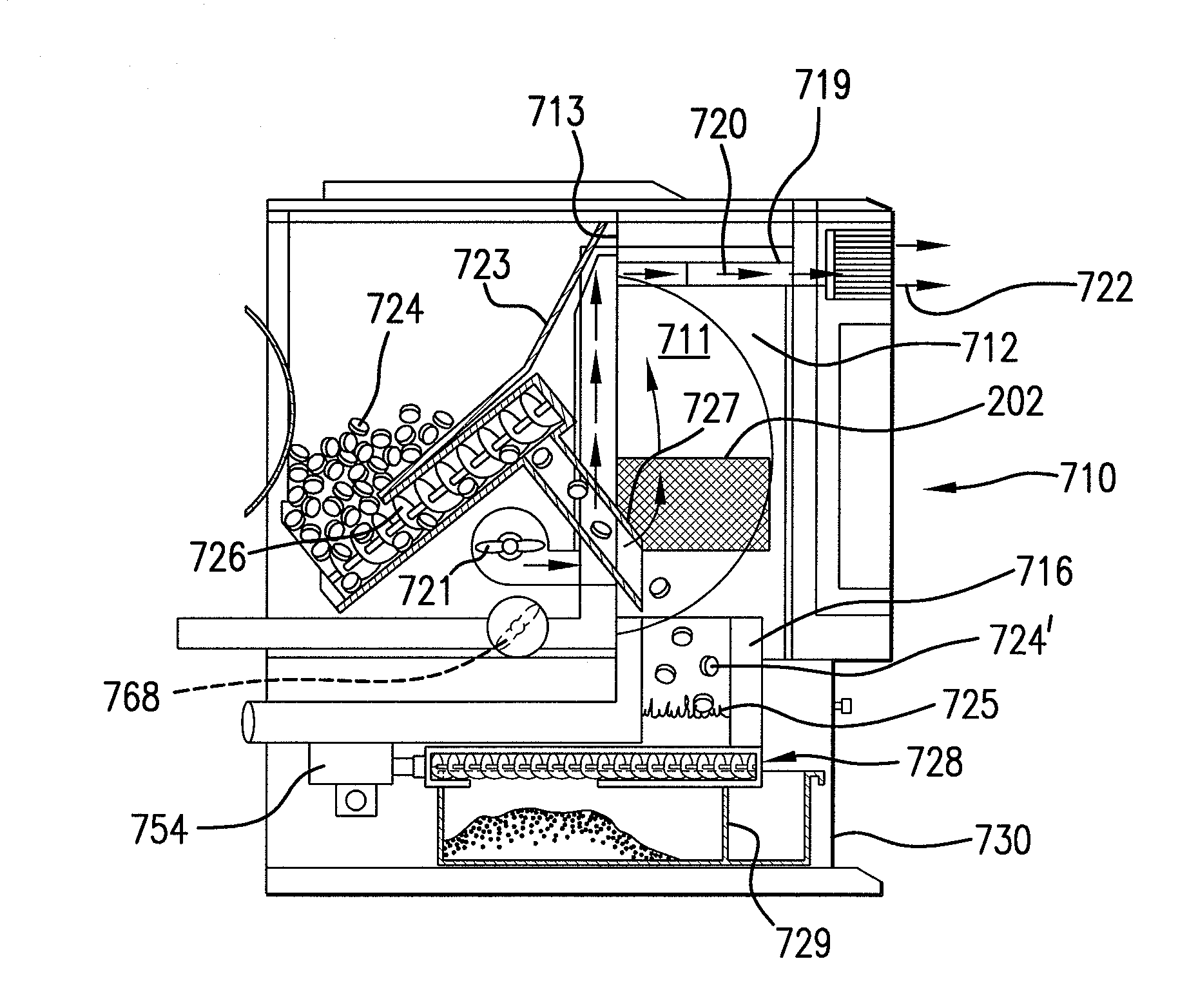
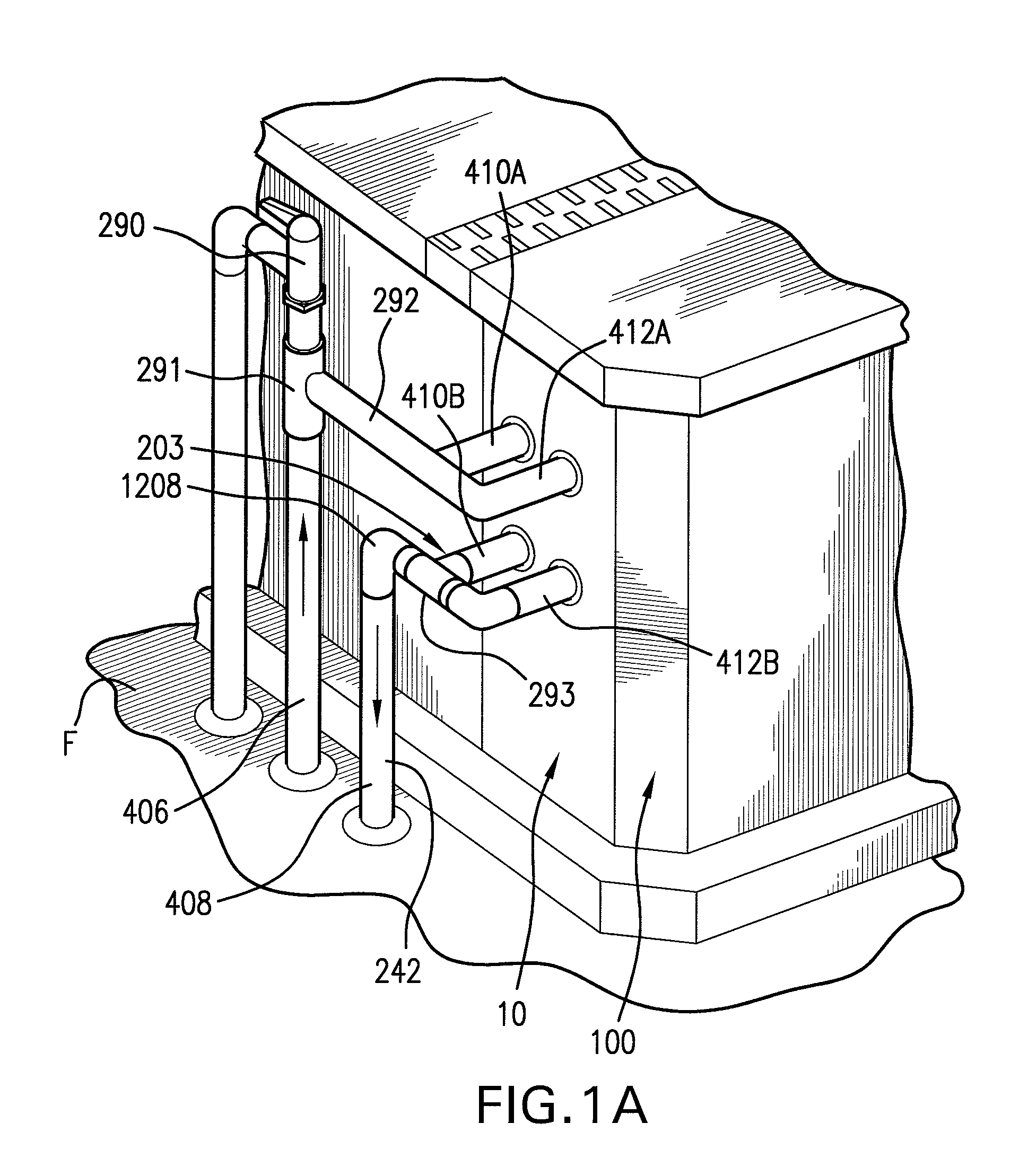
ActiveUS20100251973A1Facilitate control of fluid flowAvoid the needMechanical apparatusDomestic stoves or rangesEngineeringBiological activation
A fluid heat exchange system with a fluid flow circuit having a heat exchange fluid flow loop, a heat absorption component (as in a domestic hot water tank inclusive of small commercial use tanks as in tanks of 20 to 120 gallons), a heat exchanger and preferably also a pump. A controlled and automated fuel supply source based heater (as in a pellet stove) is in heat passage communication with the said heat exchanger. A control unit triggers activation of the pump upon fluid in the heat absorption component reaching or dropping below a preset temperature, and the fluid flow circuit is arranged such that, during times of non-activation of the pump, fluid is free to flow in a unidirectional flow within the fluid circuit based on thermodynamic temperature differentials alone. A retrofitting of a domestic hot water tank is also featured preferably making use of preexisting drain and safety vent porting for in-feed and out-feed porting in the exchange loop side. Also, the flow circuit preferably is free of check valves and steam accommodation equipment.
Owner:DONGO KENNETH A +1
Calibration method and system for relative spectral-response characteristic of CCD imaging device
InactiveCN101294867ACalibration method is simpleThe calibration method is validSpectrum investigationTesting optical propertiesRadiative transferSpectral response
The invention relates to a method for calibrating the relative spectral response characteristic of a CCD imaging device. The method comprises the following steps: A. taking a light source with known spectral radiation distribution as a measurement object, utilizing the CCD imaging device to be calibrated for the imaging of the measurement object, and acquiring and analyzing the image to obtain a measured value; B. changing the spectral radiation flux entering the CCD imaging device through adjusting the thermodynamic temperature of the light source and / or adopting a color filter; C. constructing an equation set of mathematical physics for describing the corresponding relation between the measured value and the relative spectral response characteristic according to the known equation of mathematical physics of radiative transfer of the CCD imaging device; D. taking the measured value of the CCD imaging device under different spectral radiation flux as known quantity and solving the equation of mathematical physics, so as to calibrate the relative spectral response characteristic of the CCD imaging device. The invention further discloses a system for calibrating the relative spectral response characteristic of the CCD imaging device. The method is simple and efficient, and can avoid the introduction of instrument measurement transfer errors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Direct isobutene aminating process to prepare tert-butyl amine
InactiveCN1436768AReduce manufacturing costImprove conversion rateAmino preparation by hydrogen substitutionMolecular sieveReaction temperature
In the direct isobutene aminating process, isobutylene and ammonia are directly reacted to prepare tert-butyl amine in the presence of catalyst the reaction temperature of 150-280 deg.c, normal temperature or reaction pressure of 0.05-0.5 MPa, isobutylene and ammonia feeding molar ratio of 0.5-2 and isobutylene space velocity of 260-409 / hr(-1). The catalyst has aluminosilicate molecular sieve as mother body with Si / Al ratio of 30-300, specific surface area of 100-800 sq m / g and pore volume of 0.1-0.4 mg / g, and the molecular sieve is first denatured into H-molecular sieve and then denatured with one or more denaturing elements Ce, La and Ga in the weight content of 1-10 wt%. The present invention adopts catalyst with relatively low cost, and the direct aminating is in relatively low temperature or the favorable thermodynamic temperature range.
Owner:SINOPEC SHANGHAI PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD +1
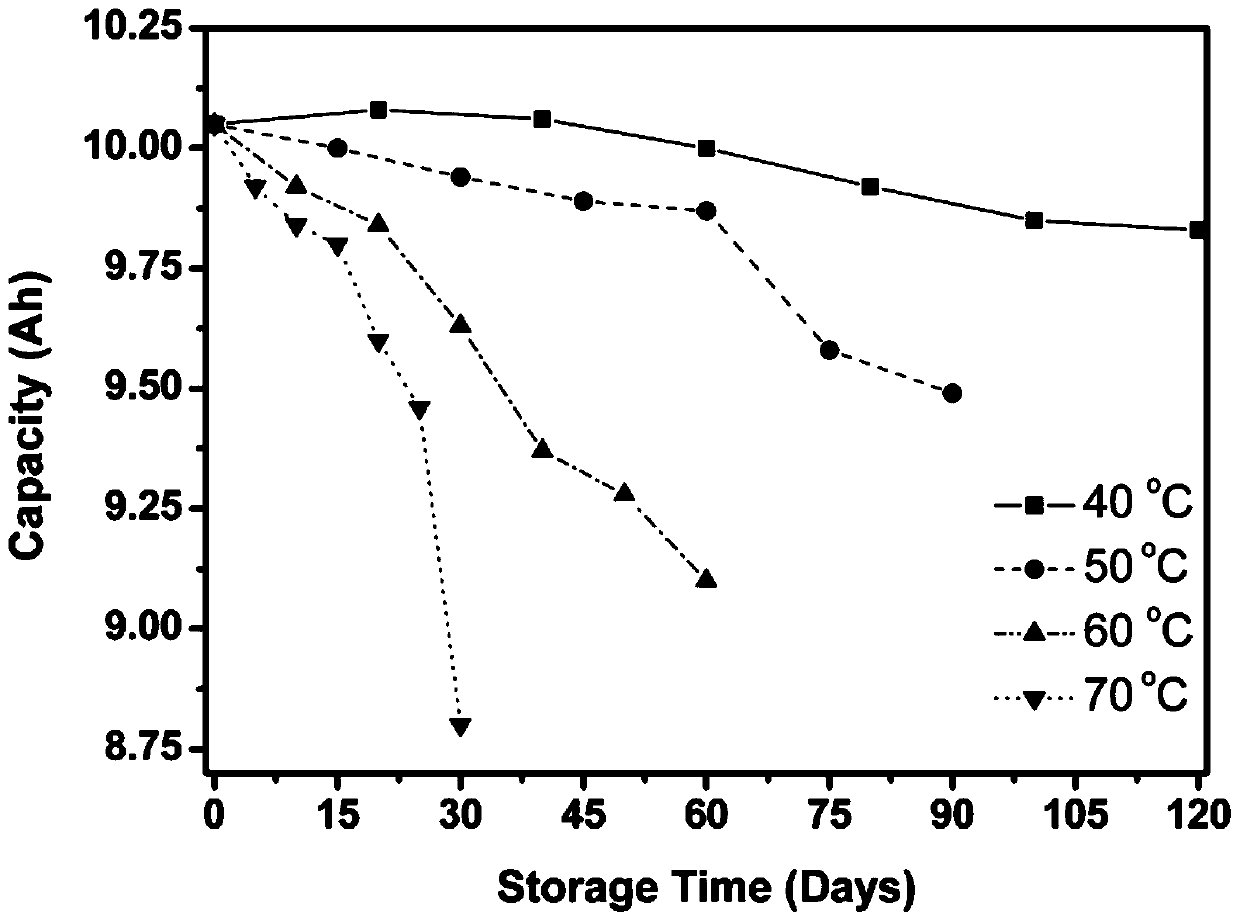
High-temperature accelerated storage test method for zinc-silver battery
ActiveCN104991195AThe experimental method is simpleEfficient experimental methodElectrical testingUltrasound attenuationZinc
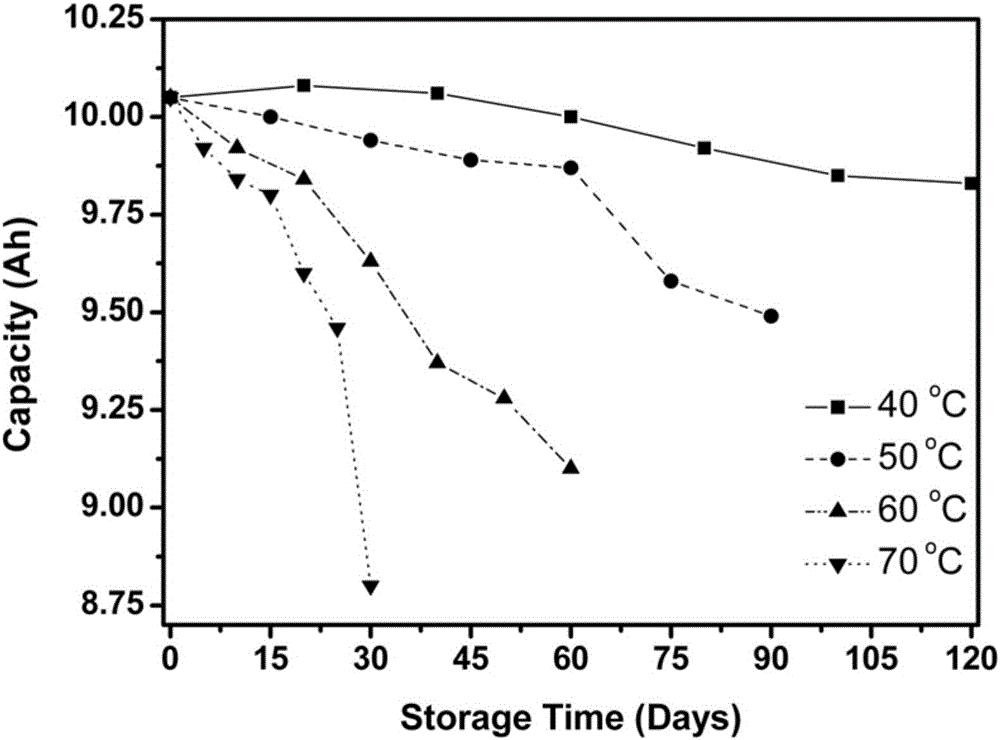
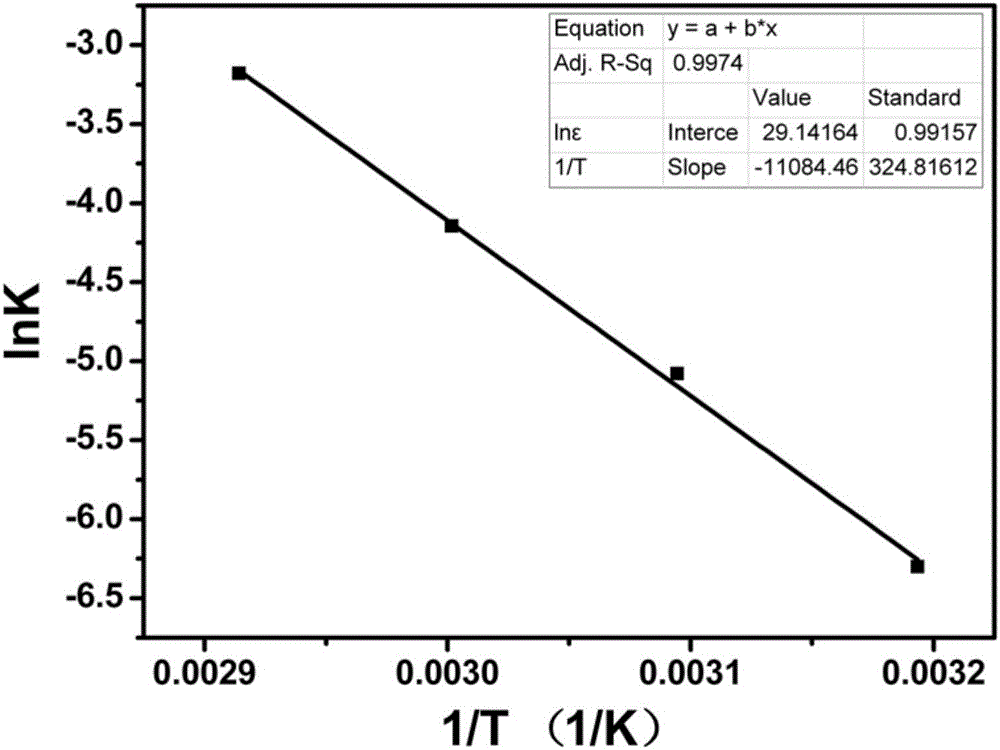
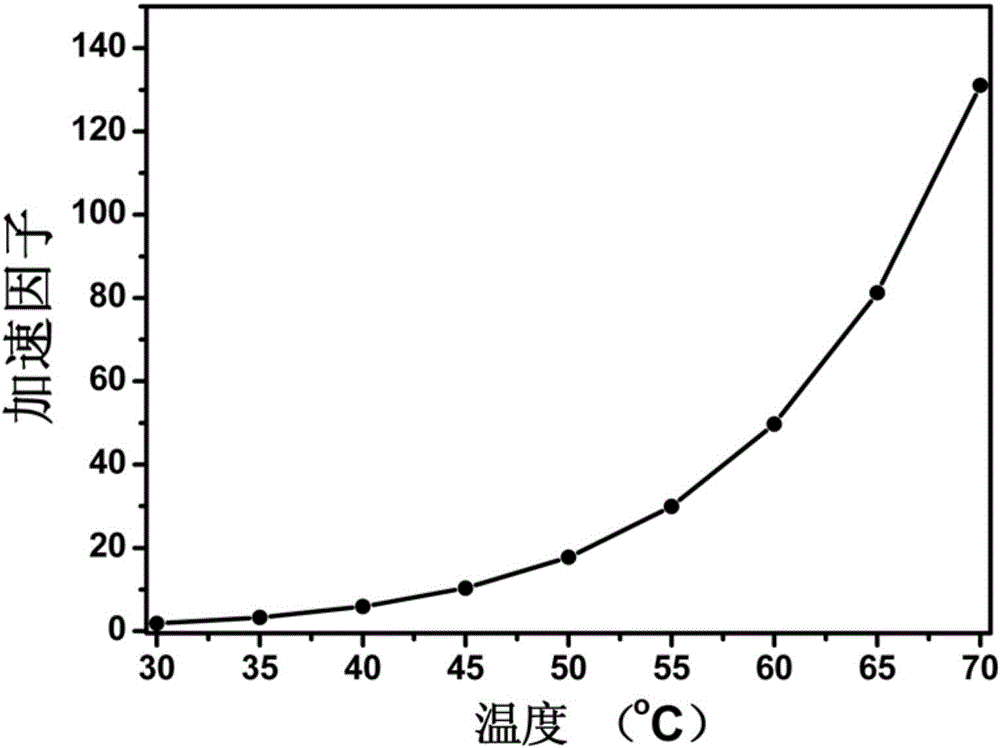
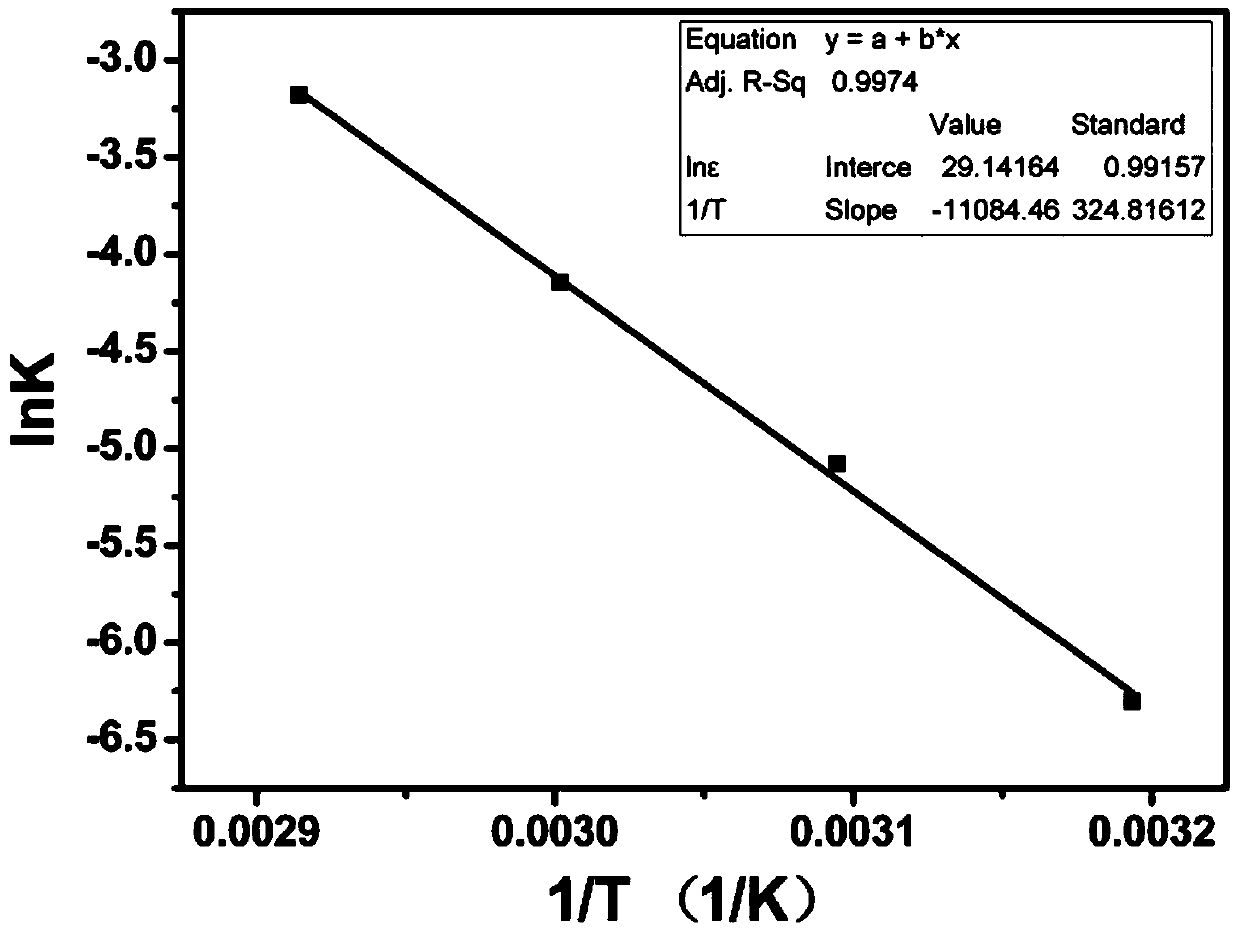
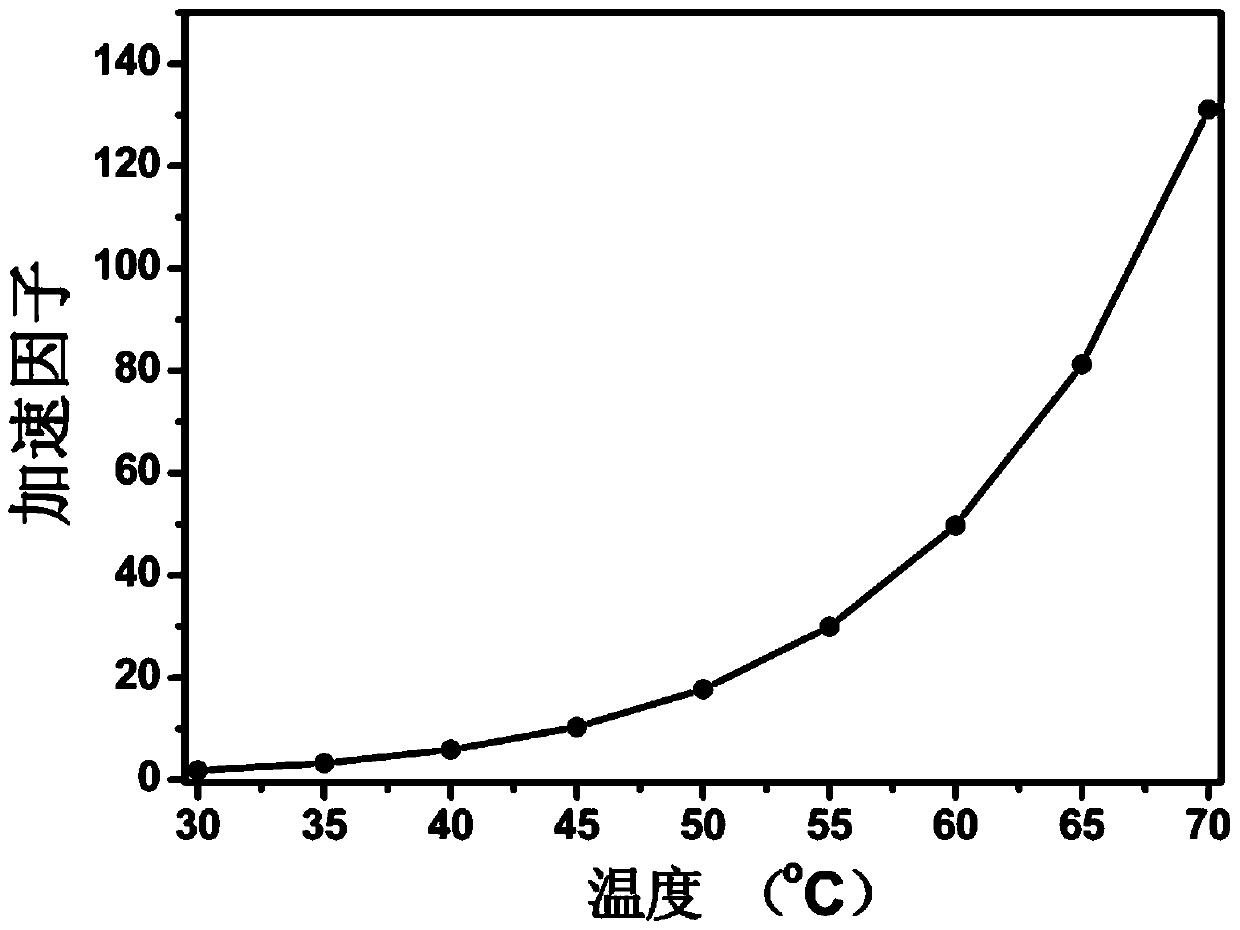
The present invention discloses a high-temperature accelerated storage test method for a zinc-silver battery, comprising: a step 101 of dividing N zinc-silver batteries into four groups according to high-temperature accelerated storage temperatures and respectively putting the four groups of zinc-silver batteries into constant temperature ovens at the temperatures of 40 DEG C, 50 DEG C, 60DEG C, and 70 DEG C; taking out the zinc-silver batteries for performing discharge at intervals of time T, and drawing a diagram about an average discharge capacity of the zinc-silver batteries changing over time at different storage temperatures; calculating an attenuation rate of the average discharge capacity of the zinc-silver batteries at different storage temperatures; a step 102 of taking the attenuation rate of the average discharge capacity of the zinc-silver batteries at different storage temperatures as a life characteristic K to fit a linear function about logarithm of the life characteristic K relative to reciprocal of thermodynamic temperature; a step 103 of calculating an accelerated factor of different storage temperatures of the zinc-silver batteries relative to a normal temperature; and a step 104 of calculating high-temperature accelerated storage time corresponding to normal-temperature storage time, and simulating the state of the zinc-silver battery after normal-temperature long-time storage through high-temperature short-time storage of the zinc-silver battery.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Thermodynamic temperature measurement method in nuclear radiation environment
InactiveCN105157844AMeet practical requirementsReduce technical complexityRadiation pyrometryNuclear radiationEnvironment effect
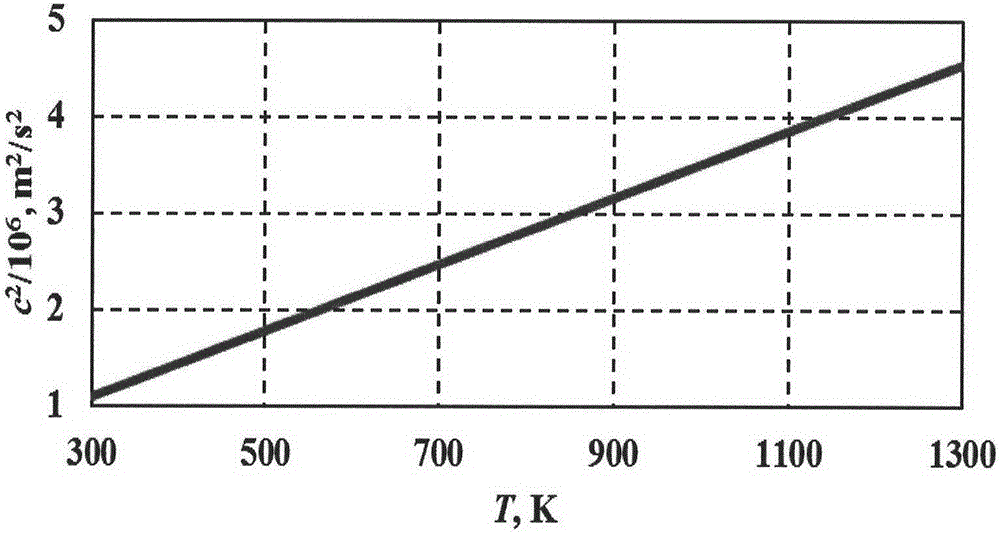
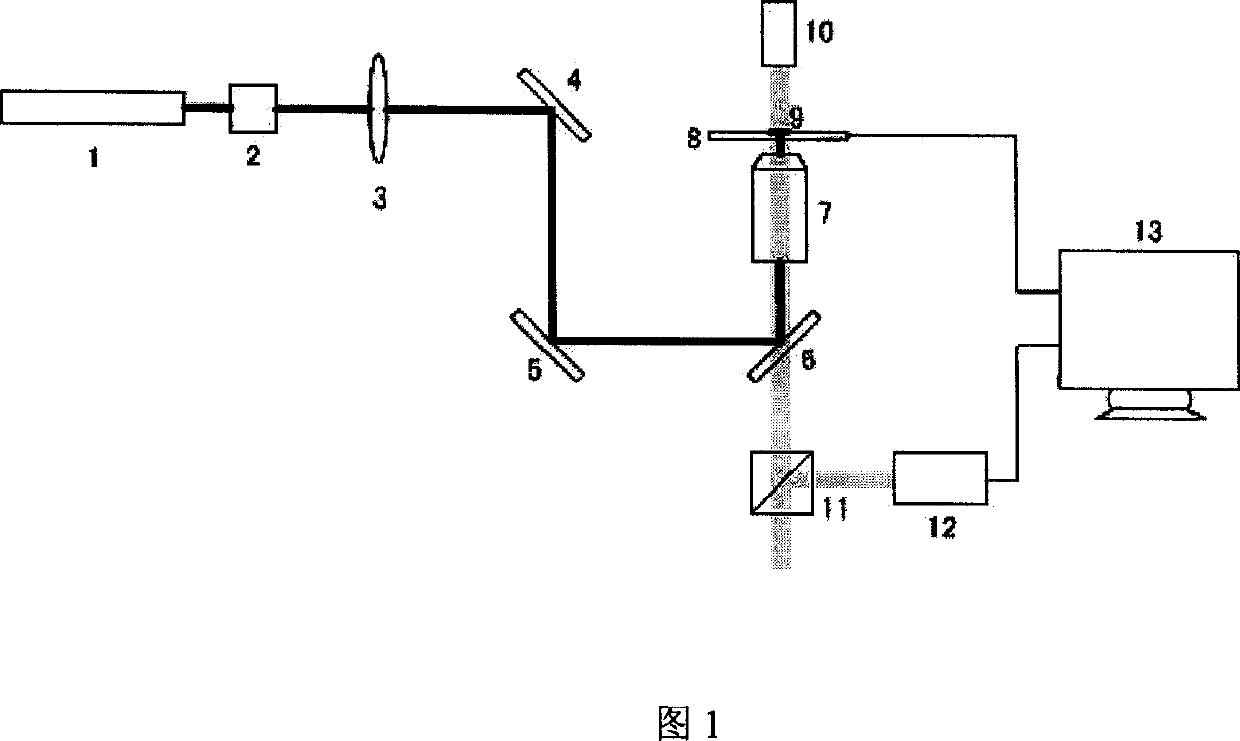
The invention relates to a thermodynamic temperature measurement method in a nuclear radiation environment. The thermodynamic temperature measurement method is characterized by comprising the steps of providing a graphite tube having a predetermined length; filling the graphite tube with helium; inserting the graphite tube vertically from the top of a reactor to the bottom of the reactor; and providing an acoustic signal for the graphite tube, calculating the average acoustic velocity of the helium in the graphite tube, and obtaining the corresponding thermodynamic temperature based on the relationship between the average acoustic velocity and temperature of the helium. The invention achieves the application of the acoustic resonance thermodynamic temperature measurement to the temperature measurement in the nuclear radiation environment, and reduces the complexity of the absolute temperature method temperature measurement technology and the difficulty in operation for practical requirements. According to the invention, the acoustic resonance thermodynamic temperature measurement method in the nuclear radiation environment is applicable to nuclear radiation environment thermodynamic temperature measurement and also to systems that require no harsh environmental influence and a stable operation status.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
A method for measuring liquid phase micro-area temperature
InactiveCN1963420ASolve the problem that the temperature measurement range is limited by the temperature measurement probeLow temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesTemperature measurement of flowing materialsSilicon dioxideMicro-needle
This invention relates to one liquid phase micro part temperature method, which is characterized by adopting light tamper or micro needle to transfer polyphenylacetylene or earth silicon emulsion or powder to test probe head into micro test area to discharge test probe by use of image.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Directional solidification casting method of continuous cold crucible
ActiveCN103008624ASolve the problem of forming complex castingsProcess parameters are easy to controlSteady state temperatureThermal insulation
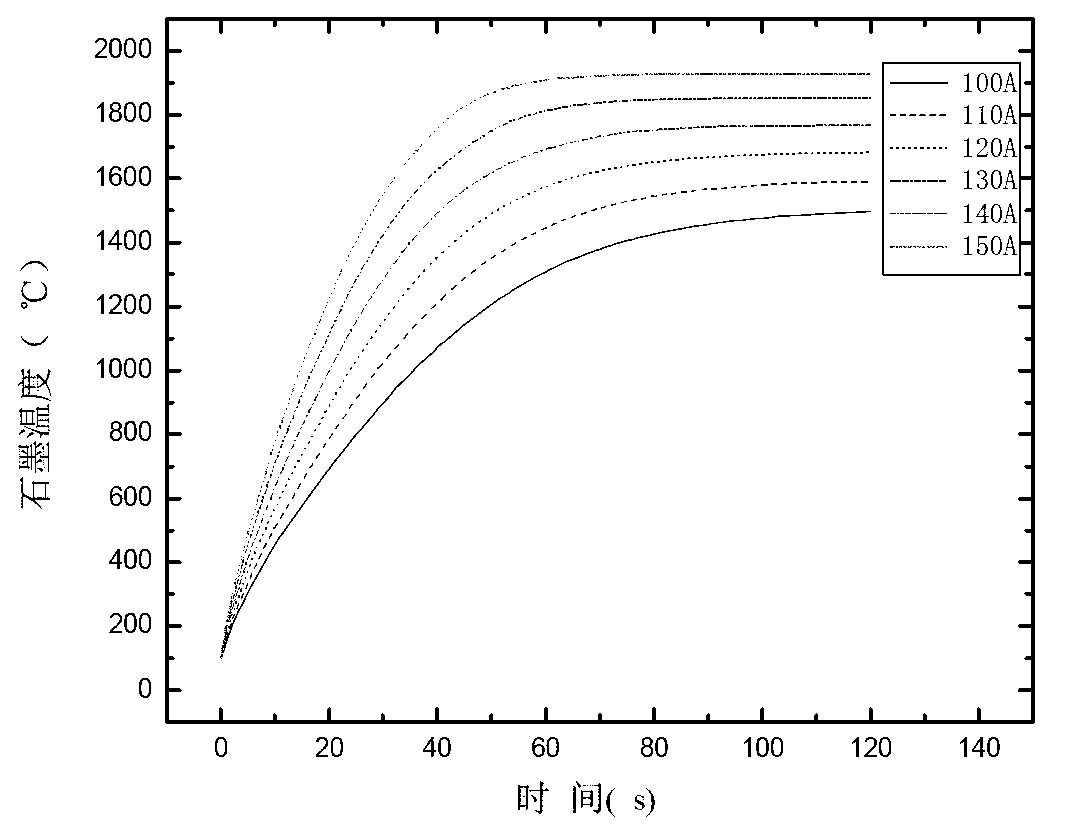
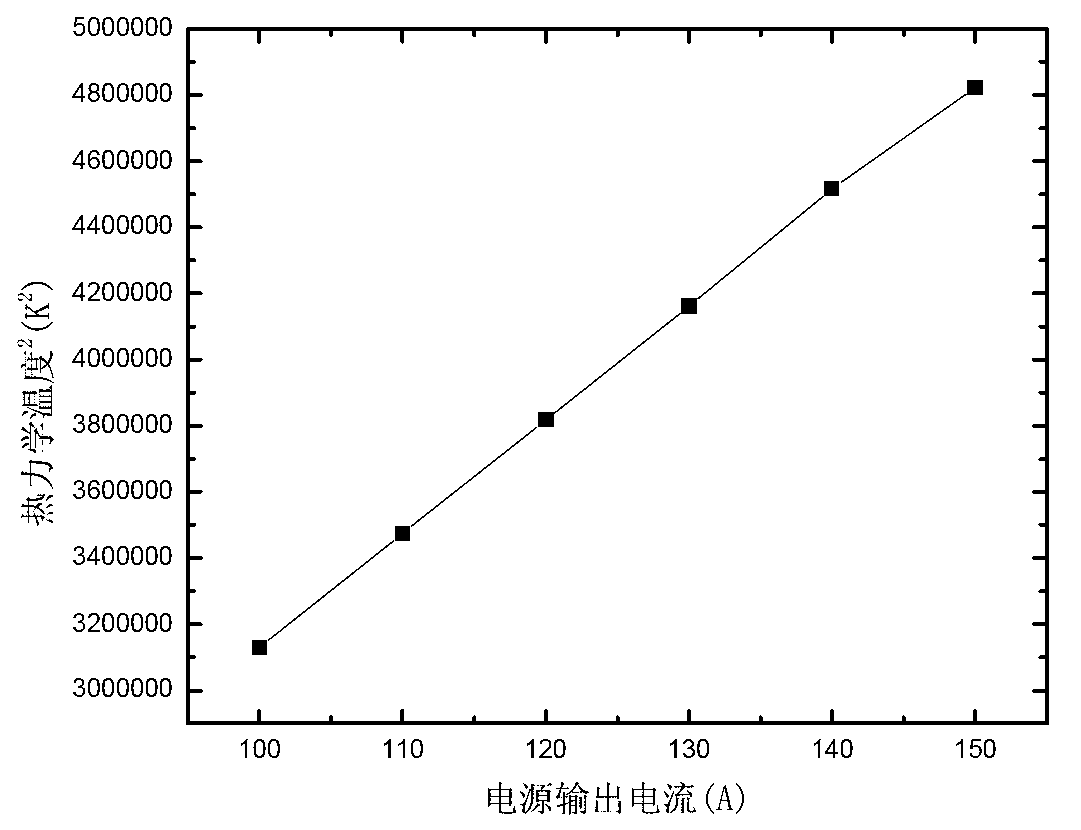
The invention discloses a directional solidification casting method of a continuous cold crucible. According to the directional solidification casting method, a water-cooled copper crucible in a directional solidification device of an electromagnetic cold crucible is arranged in a closed furnace body, wherein an electromagnetic induction coil is arranged outside the water-cooled copper crucible; the lower end of a bar extends into the water-cooled copper crucible; a crystallizer filled with a coolant material is arranged under the water-cooled copper crucible; a pull-down rod is arranged in the crystallizer; a formwork is fixed at the upper end of the pull-down rod; a circular graphite heating element, having a height of 55-65mm, an outer diameter of 55-65mm and an inner diameter of 40-50mm, is arranged outside the formwork; a thermal insulation layer is covered outside the graphite heating element; an induction coil is arranged outside the thermal insulation layer; and a graphite induction heating steady-state temperature is determined by the formula (refer to the Specification), wherein I represents an input current, r represents the radius of a coil, epsilon is 0.9, and a is an empirical parameter 2816681. According to the directional solidification casting method of a continuous cold crucible, the relation between the output current and the thermodynamic temperature of the graphite is provided, and the basis for conveniently controlling the process parameters in actual use is provided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for measuring temperature in vacuum environment based on wavelength modulation spectrum technology
InactiveCN103308186AReduce the effects of stressReduce measurement errorRadiation pyrometryTwo temperatureWavelength modulation
The invention discloses a method for measuring a temperature in a vacuum environment based on a wavelength modulation spectrum technology, and belongs to the technical field of tunable laser diode absorption spectroscopy. According to the method, a laser is modulated by utilizing a high-frequency sine wave, a low-frequency triangular wave and a low-frequency square wave based on the wavelength modulation spectrum technology, so that selected two temperature measurement spectral lines appear at a high level position and a low level position respectively; spectral line scanning is realized by the triangular wave; the second harmonic signal ratio of the two spectral lines is obtained by experimental measurement; the rotational temperature of gas molecules is determined by comparing the second harmonic signal ratio with a theoretical calculating value; and the rotational temperature and a translational temperature (the classical thermodynamic temperature) are kept balance all the time, so that the temperature of gas can be measured. By the method, the problems of surface material analysis and temperature traceability of a current contact temperature sensor applied in the vacuum environment are solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for measuring clay dispersion average binding free energy and adsorption free energy to cation
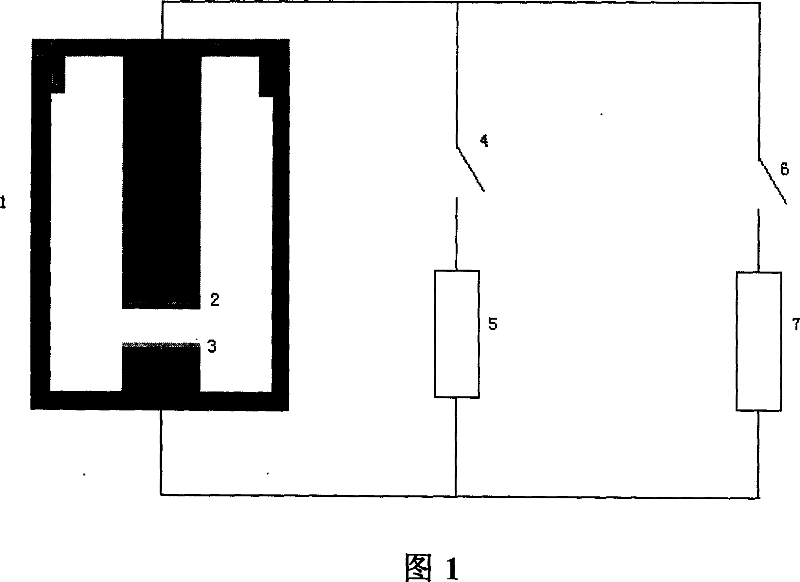
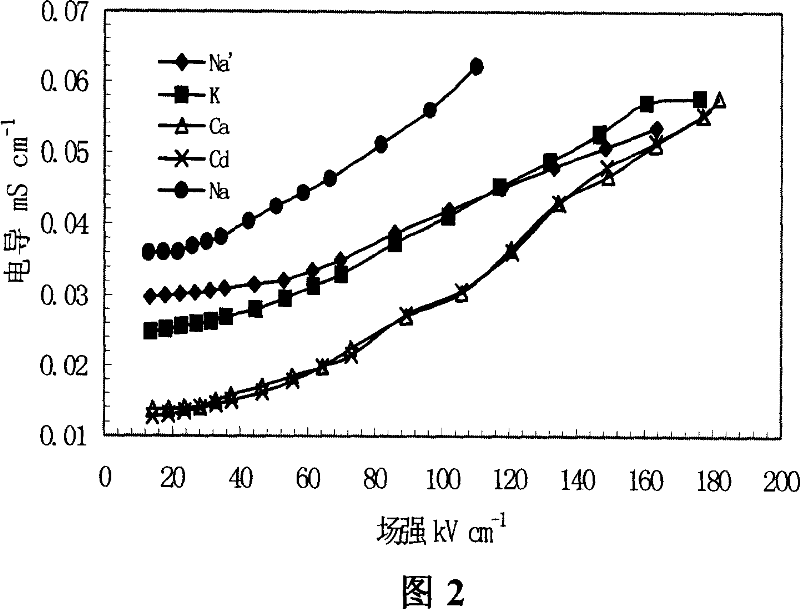
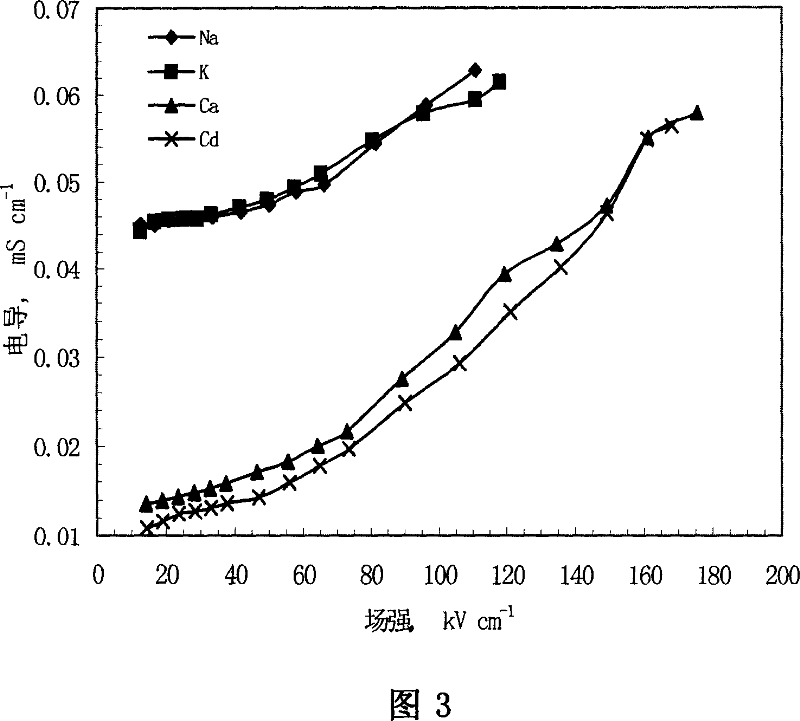
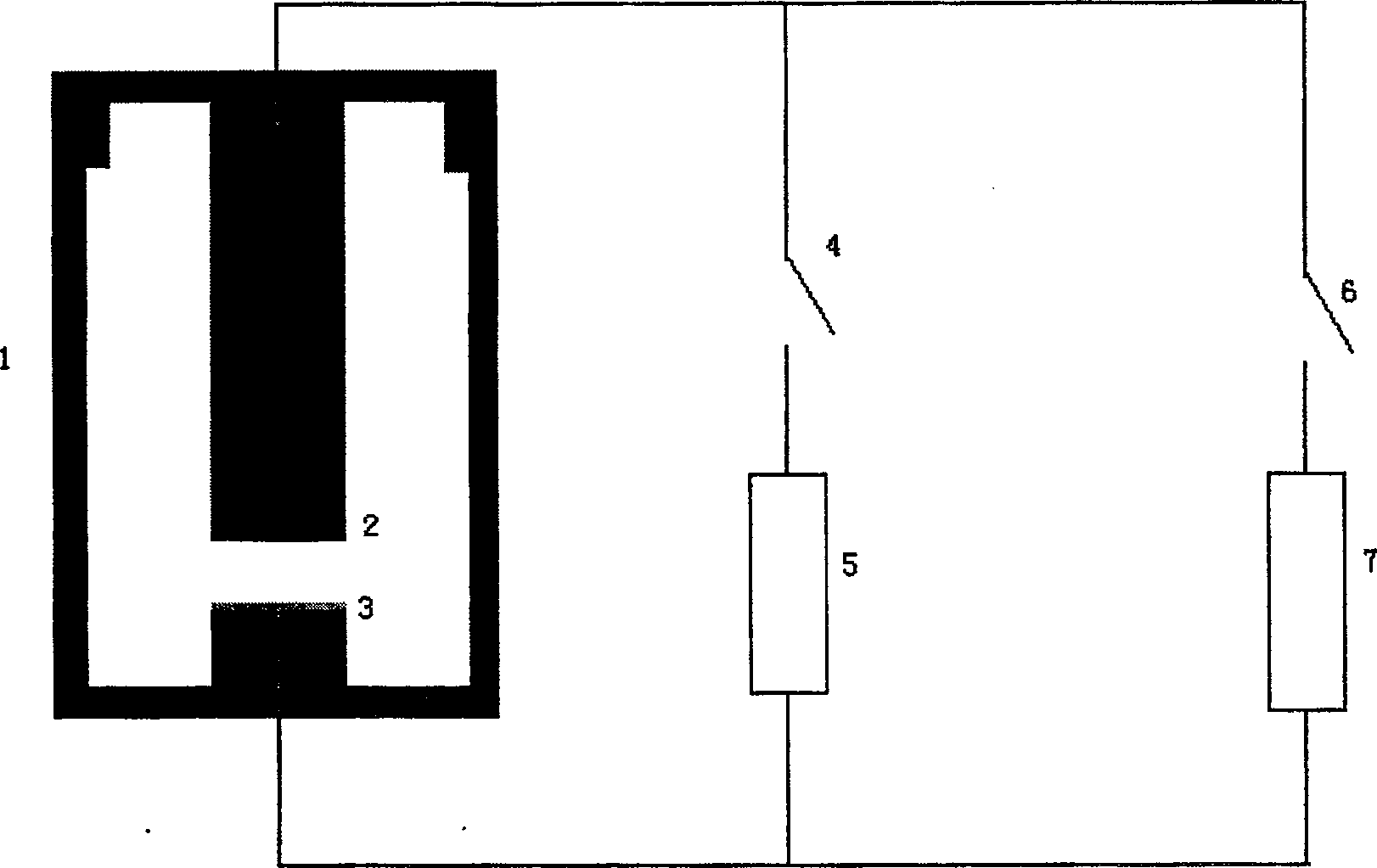
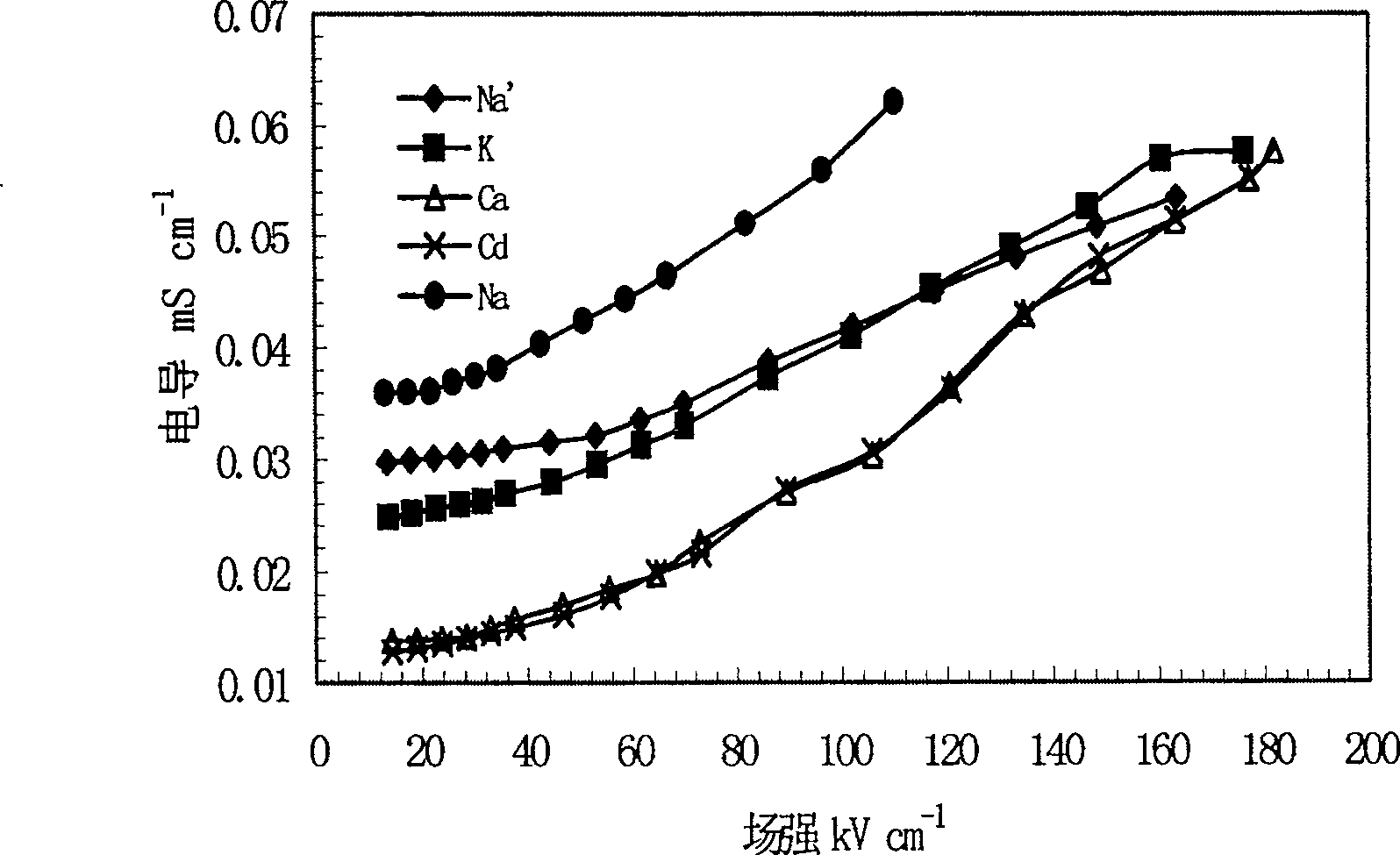
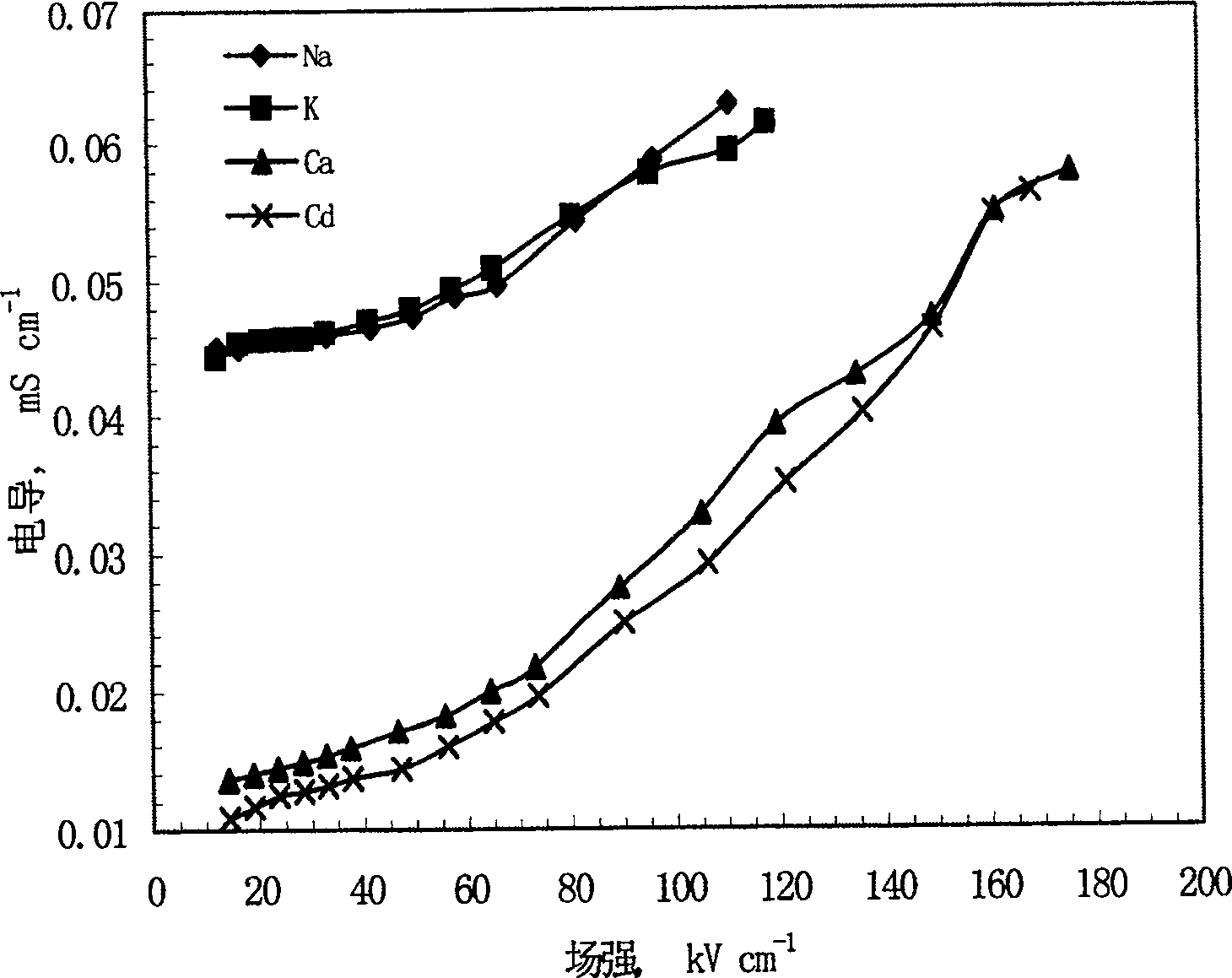
This invention relates to one method to test earth anode ion even combination free energy and absorptive free energy, which comprises the following steps: a, processing the anode saturation earth adhesive particles with radium less than 2 mu m and then using ion remove water or stilled water to match earth hanging liquid; b, putting the earth hanging liquid into field less than 15kV.cm<-1> to gradually form field intensity to test each conductivity rate to get the relation ship curve between earth hanging liquid and field intensity; c, according to math formula to compute particles anode ion even combination free energy and absorptive free energy, wherein, Delta G=RTln(2CEC.Cp.lambada / EC0) (4); Delta G=RTln(EC / EC0) with R for gas constant; T for thermal temperature and CEC for anode ion exchange volume and Cp for particle concentration.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite metal material, preparation method thereof and metal material product
ActiveCN106676339ARaise the thermodynamic temperatureIncrease temperatureMetal rolling arrangementsMetal layered productsDeep drawingMetal
The invention discloses a composite metal material, a preparation method thereof and a metal material product. The composite metal material comprises a first alloy layer, a second alloy layer and a third alloy layer which is made from 4A60 aluminum alloy and located between the first alloy layer and the second alloy layer. The preparation method of the composite metal material comprises the following steps that step one, one face of the first alloy layer and one face of the third alloy layer are subjected to hot rolling bonding; step two, the other face of the third alloy layer and one face of the second alloy layer are subjected to hot rolling bonding at 200-400 DEG C; and step three, a finished product obtained through hot rolling bonding is annealed to obtain the composite metal material. According to the composite metal material, the preparation method thereof and the metal material product, by adoption of the 4A60 aluminum alloy of the third alloy layer, the thermodynamic temperature generated from the middle brittle phase of aluminum and iron is increased, and therefore, by adoption of the preparation method of the composite metal composite, on the premise that the product percent of pass is ensured, the temperature in the deep drawing process of the aluminum and the 430 stainless iron is increased, and the machining efficiency of the product is improved.
Owner:YINBANG CLAD MATERIAL
Hybrid iteration method for gas energy inversion thermodynamic temperature
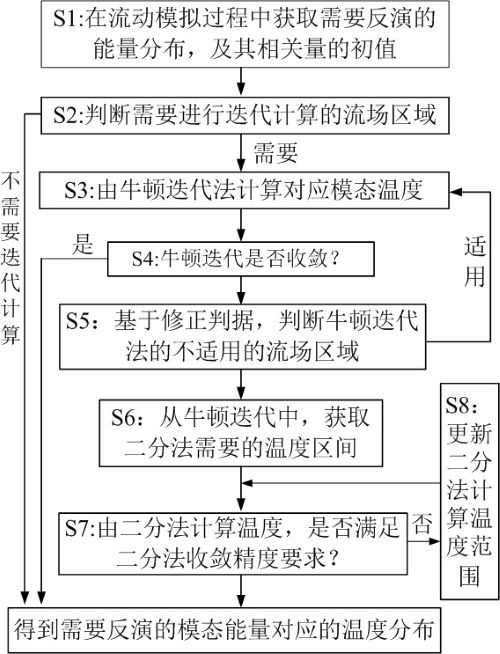
ActiveCN112417743AImprove computing efficiencyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringTranslational energy
The invention discloses a hybrid iteration method for gas energy inversion thermodynamic temperature. The method is mainly used for a sub-iterative inversion calculation process of gas modal energy (translational energy, rotational energy, vibration energy, electron energy and combination of the translational energy, the rotational energy, the vibration energy and the electron energy) to corresponding gas thermodynamic temperature in a hypersonic non-equilibrium flow numerical simulation process. According to the method, on the basis of a Newton iteration method, gas energy inversion characteristics are combined, a local dichotomy is introduced to correct a calculation criterion, and the Newton iteration method and the dichotomy are combined to form a hybrid iterative calculation method. According to the method, the advantage that convergence is fast when an iteration initial value approaches a true value of a Newton iteration method is reserved, the calculation efficiency is high, theadvantage that a dichotomy has high stability for a monotonic function is absorbed, and the divergence problem of the Newton iteration method under extreme conditions is avoided.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Fluid heating system
ActiveUS9182115B2Facilitate control of fluid flowAvoid the needMechanical apparatusDomestic stoves or rangesEngineeringRetrofitting
Owner:DONGO KENNETH A +1
Method for evaluating lightning protection effective size coefficients of horizontal grounding body at different temperatures
ActiveCN111985109AImprove accuracyPrecise temperature regulationDesign optimisation/simulationTemperature control using electric meansTemperature controlEngineering
The invention discloses a method for evaluating lightning protection effective size coefficients of a horizontal grounding body at different temperatures, and the method comprises the steps of building a horizontal grounding body lightning protection effective size coefficient temperature control test device according to the evaluation method; according to the evaluation step, setting the test thermodynamic temperature through a test upper computer, and performing temperature adjustment on homogeneous soil around the horizontal grounding body through a temperature control test device; injecting transient voltage into the horizontal grounding body through a transient voltage generation device, and measuring wave head time of the injected transient voltage; and calculating and evaluating thelightning protection effective size coefficient of the horizontal grounding body according to the wave head time of the injected transient voltage and the test thermodynamic temperature. According tothe invention, the diffusion process of the transient current along the horizontal grounding body at different soil temperatures can be effectively simulated, the test precision is improved through real-time temperature control, and the lightning protection effective size coefficient of the horizontal grounding body can be accurately and effectively evaluated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Wide-temperature-range high-precision temperature calibration device
PendingCN108225618ASolve temperature problemsAddress limitationsThermometer testing/calibrationResonant cavityRefractive index
The invention relates to a wide-temperature-range high-precision temperature calibration device which comprises a thermal switch gold barrel, a pressure cabin and a refrigerating machine. The pressurecabin is positioned inside the thermal switch gold barrel; cold flow can be provided by the refrigerating machine, so that the internal temperature of the pressure cabin can be reduced to reach target temperatures. The wide-temperature-range high-precision temperature calibration device is characterized in that a resonant cavity is arranged in the pressure cabin, a plurality of protruded hollow cylindrical bosses are arranged on the side surfaces of the resonant cavity, and thermometers are arranged on the surfaces of the protruded hollow cylindrical bosses. The wide-temperature-range high-precision temperature calibration device has the advantages that the thermodynamic temperatures of very low temperature zones at the temperatures of 5K-25K in wide temperature ranges of 5K-300K can be measured by the aid of advanced constant-pressure gas refractive index temperature measuring methods in a high-precision manner, and accordingly reference-level thermometers and standard-level thermometers can be calibrated by the aid of the wide-temperature-range high-precision temperature calibration device.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving electric conductivity of carbon nano tube network
The invention discloses a method for improving electric conductivity of a carbon nano tube network, which comprises the following steps of: (1) uniformly distributing carbon nano tubes on the surface of a substrate to form a sample; (2) placing the distributed carbon nano tube sample in a target chamber of an ion beam irradiation device, and heating the sample; (3) after the carbon nano tube sample is heated to a thermodynamic temperature of between 700 and 1,000 DEG C, irradiating the sample by using ion beams; and (4) after the irradiation is finished, stopping heating, and cooling the sample to room temperature, and taking the sample out of the target chamber. Compared with the prior art, the method can effectively improve the electric conductivity of the carbon nano tube network under the condition of avoiding chemical pollution, can be compatible with the conventional semiconductor process, and can be used for promoting the performance of carbon nano tube related devices and used for manufacturing flexible transparent conductive films of the carbon nano tubes.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
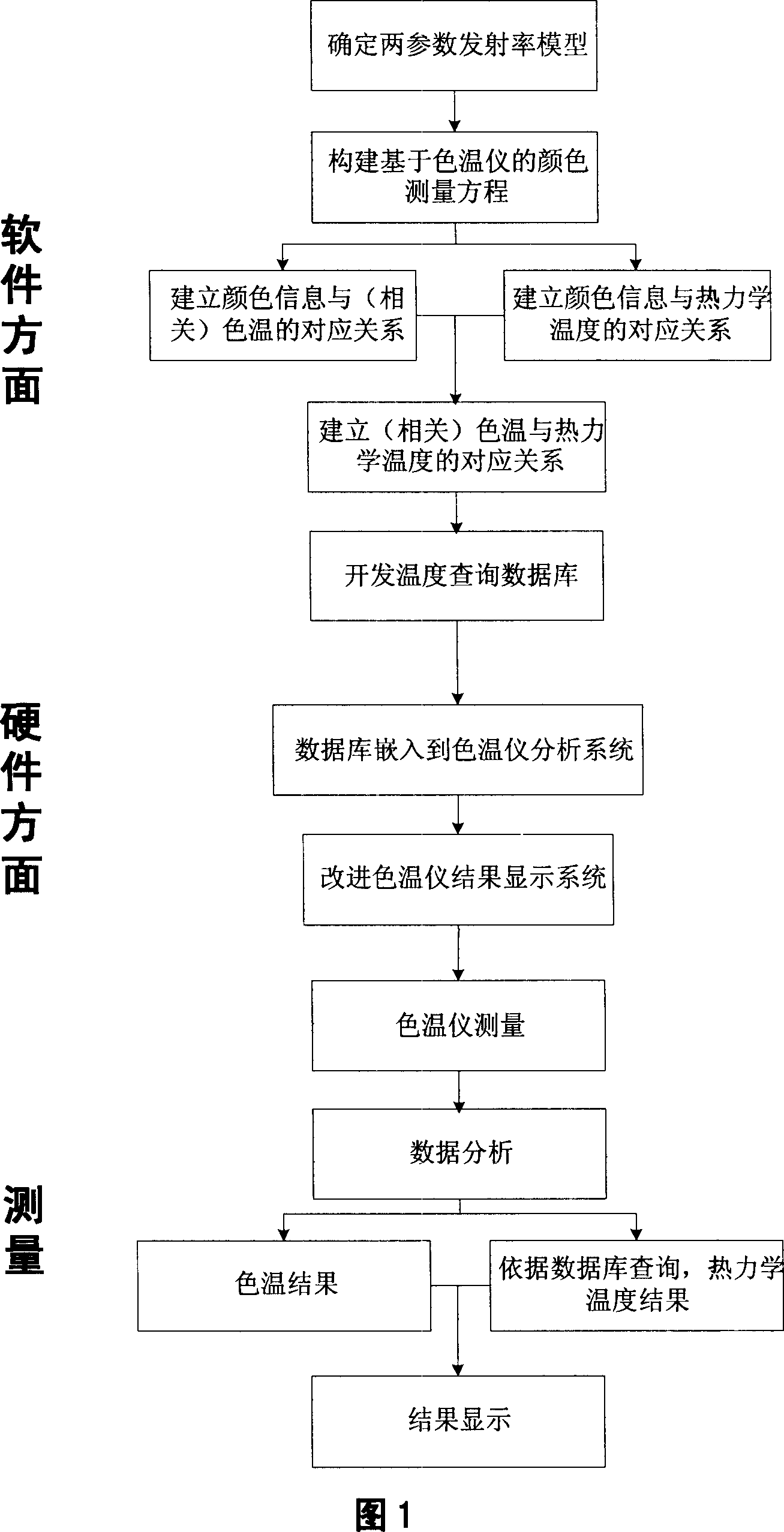
Method for implementing thermodynamic temperature measurement based on color temperature meter
ActiveCN1928518AEliminate measurement effectsInnovativeRadiation pyrometryEmissivityMeasuring instrument
The thermodynamic temperature radiation measurement method based on color temperature meter comprises: based on dual-parameter emissivity function in special wave band, creating a closed radiation pyrometry equation to ensure the measurement without emissivity data and scaled thermodynamic temperature; with color temperature meter and former equation, selecting color information as the study cross-point to build the mathematical correlation database; using the database and meter for measurement. This invention overcomes defects in prior art, and expands meter application range.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SAFETY SCI & TECH
Four-channel noise thermometer with quantum voltage as reference
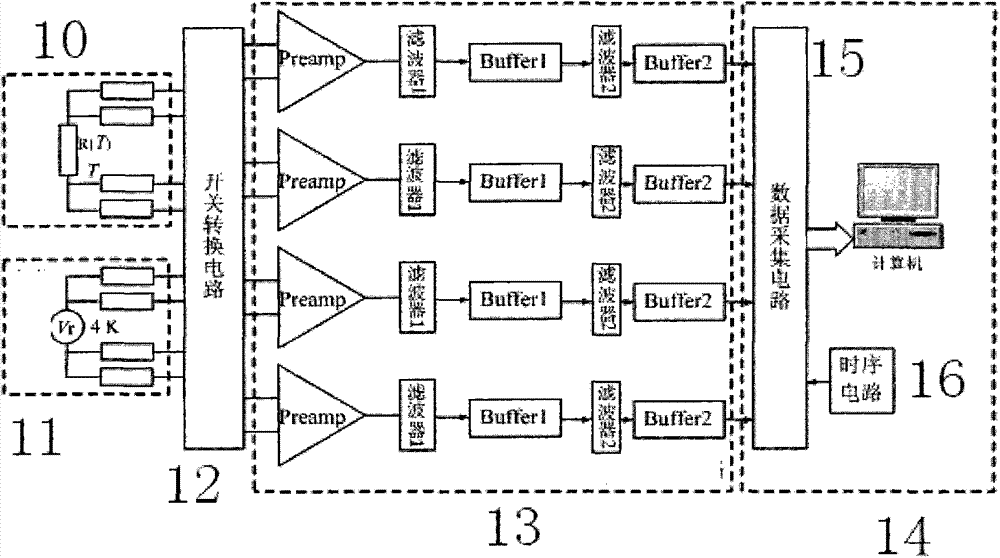
InactiveCN103674315AMeasurement integration time reductionShort integration timeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansData acquisitionMeasurement study
The invention relates to a four-channel noise thermometer with a quantum voltage as reference. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference comprises a noise source to be measured, a reference quantum voltage pseudo noise source, and a switch change-over circuit which is connected with the noise source to the measured and the reference quantum voltage pseudo noise source. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference is characterized in that a four-channel amplifying and filtering circuit is connected with a switch connecting circuit, and the four-channel amplifying and filtering circuit is correspondingly connected with a four-channel acquisition channel of a data acquisition and processing portion. The four-channel noise thermometer with the quantum voltage as the reference can effectively reduce integral time required by measurement, reduces system deviations and can play an enormous role in thermodynamic temperature and Boltzmann constant measurement studies.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
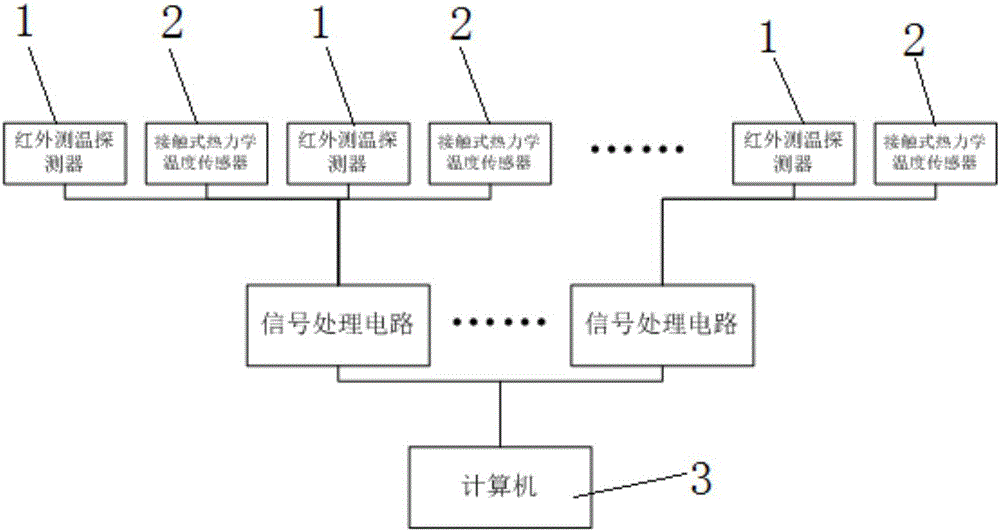
Surface emissivity measurement system
InactiveCN105890773ASimple structureEasy to installRadiation pyrometryData displaySignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a surface emissivity measurement system, and relates to the technical field of emissivity measurement. The surface emissivity measurement system comprises an infrared temperature measurement detector, a contact-type thermodynamic temperature sensor, a signal processing circuit and a computer; the contact-type thermodynamic temperature sensor is arranged on the surface of a target object to be measured, and transmits a surface thermodynamic temperature signal of the target object to be measured to the signal processing circuit; the infrared temperature measurement detector is arranged on the upper side of the target object to be measured, and transmits a radiation temperature signal of the surface of the target object to be measured to the signal processing circuit after the radiation temperature signal is processed; the signal processing circuit conditions the received signal, and then transmits the conditioned signal to the computer; the computer is used for performing calculating processing, data display and storage on the emissivity of the surface of the target object to the measured. The surface emissivity measurement system has the beneficial effects that the system is simple in structure and easy to install and maintain; a target material does not need to be sampled; the measurement precision is high.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
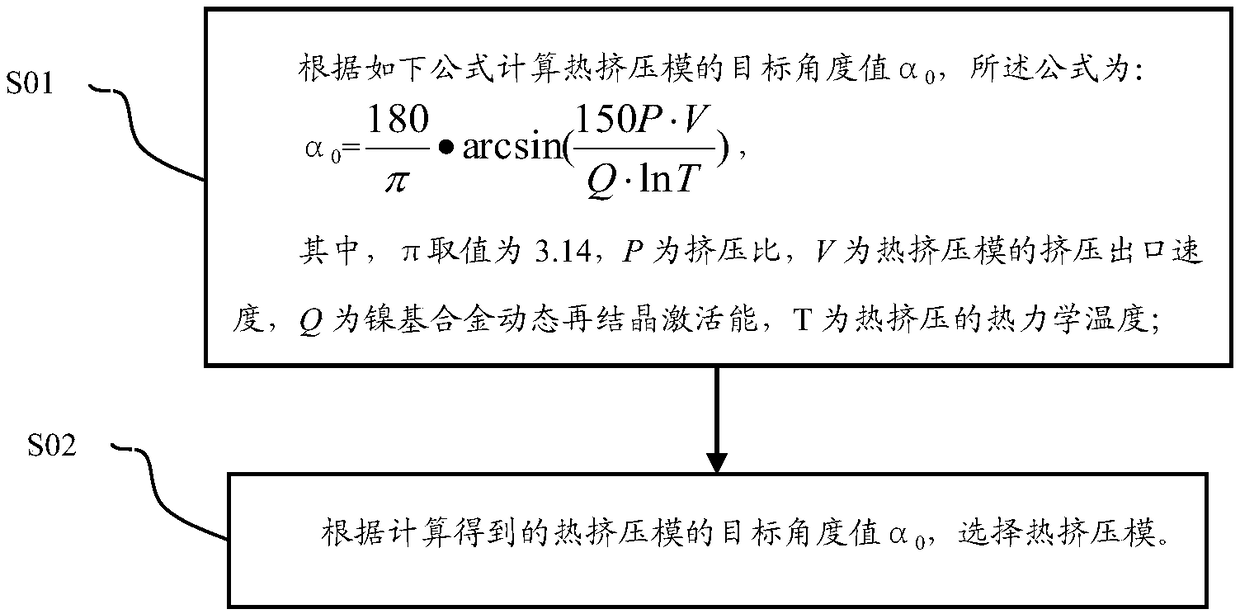
Hot Extrusion Process of Nickel-based Alloy Rods
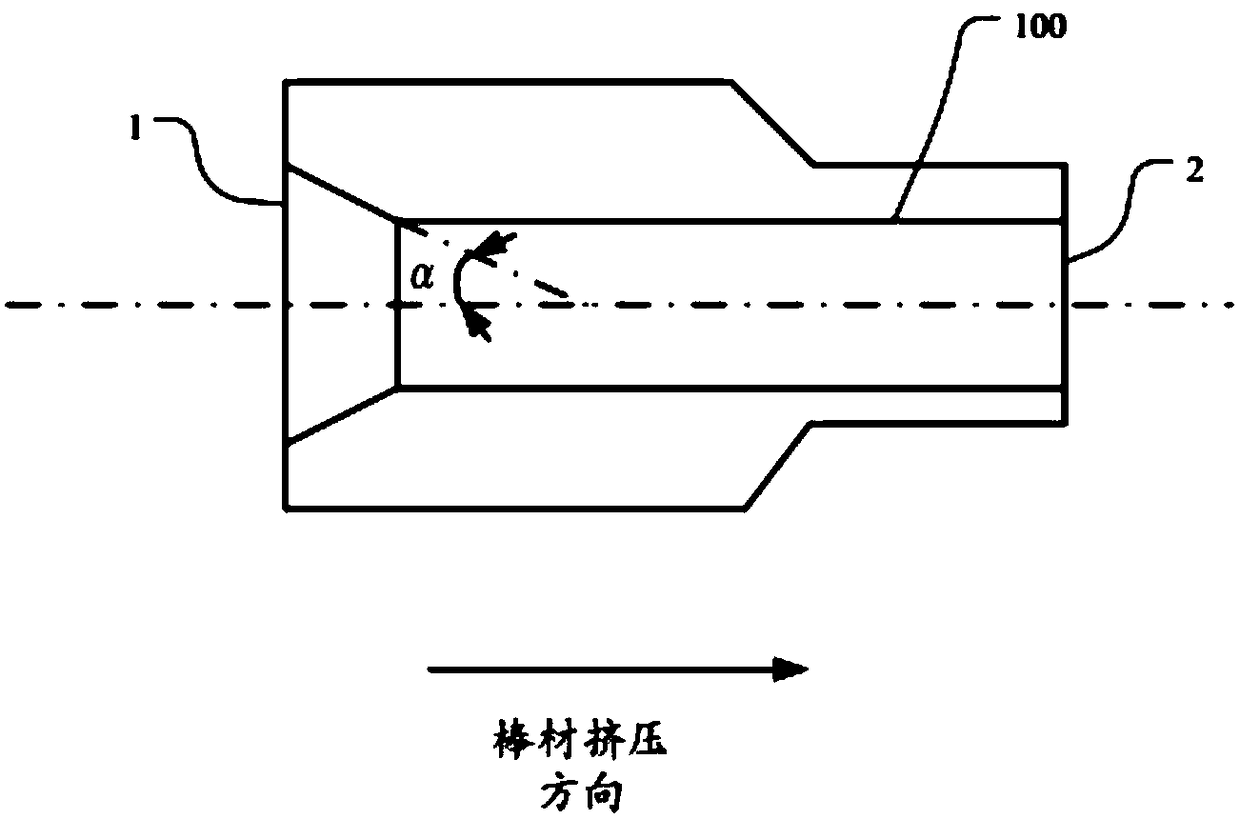
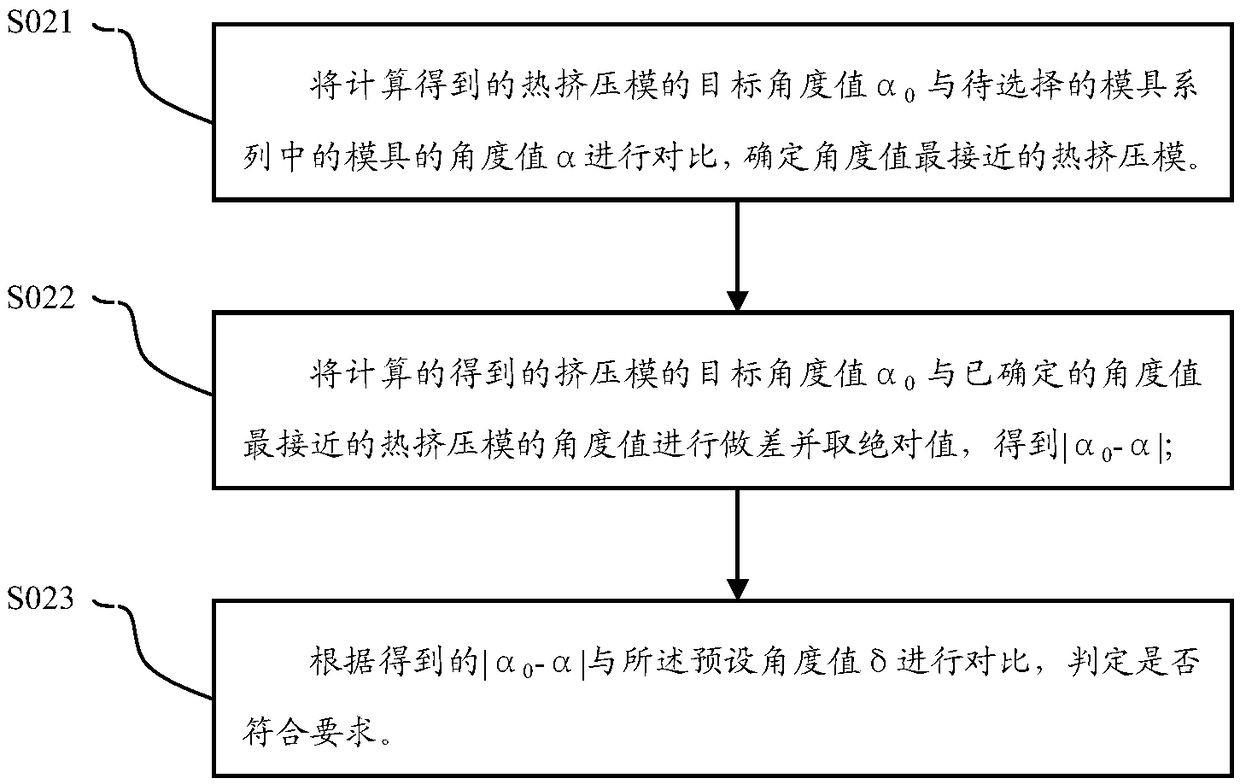
ActiveCN106984661BFormulate fast and efficientLow experience requirementExtrusion diesExtrusion control devicesActivation energyAlloy
The invention discloses a nickel base alloy bar hot extrusion technology. The nickel base alloy bar hot extrusion technology comprises following steps: a, according to the following formula, the target angle value alpha0 of a heat extrusion die is calculated, the formula is shown in the specification, the value of pion is 3.14, P is the extrusion ratio, V is the extrusion outlet speed of the hot extrusion die, Q is nickel base alloy dynamic recrystallization activation energy, and T is the thermodynamics temperature of hot extrusion; b, according to the calculated target angle value alpha0 of the hot extrusion die, the hot extrusion die is selected. Through the hot extrusion technology, the specific bar heat extrusion process flow is rapidly and efficiently formulated, the manufactured bar is free of surface scale cracks, warping and other defects, the bar size approaches to the finished product size, and the surface can meet the requirement through the simple grinding and polishing; in the machining process, heat extrusion blocking run does not exist.
Owner:太原钢铁(集团)有限公司
Method for improving electric conductivity of carbon nano tube network
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring clay dispersion average binding free energy and adsorption free energy to cation
InactiveCN100510727CPreparing sample for investigationMaterial resistanceCation-exchange capacityElectric field
The method for measuring the average binding free energy and average adsorption free energy of soil clay particles to cations includes: a. preparing soil clay particles with a particle size of <2 μm and saturated with cations, and then preparing a soil suspension with deionized water or distilled water; b. Place the soil suspension under an electric field with an initial field strength ≤ 15kV cm-1, and gradually increase the field strength, measure the conductivity of the soil suspension under each field strength, and obtain the conductivity and field strength of the soil suspension c. Calculate the average binding free energy and adsorption free energy of soil clay particles to cations according to the following mathematical formulas: ΔGbo=RTln(2CEC Cp λ / EC0) (4); ΔGad=RTln(EC / EC0 ) (8); in the formula, R is the gas constant; T is the thermodynamic temperature; CEC is the cation exchange capacity, Cp is the concentration of soil clay particles in the suspension; λ is the equivalent conductance of dissociated cations; EC0 is the field strength ≤ 15kV Conductivity of the suspension under an electric field of cm-1; EC is the conductivity of the suspension under an electric field of field strength >15kV·cm-1.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
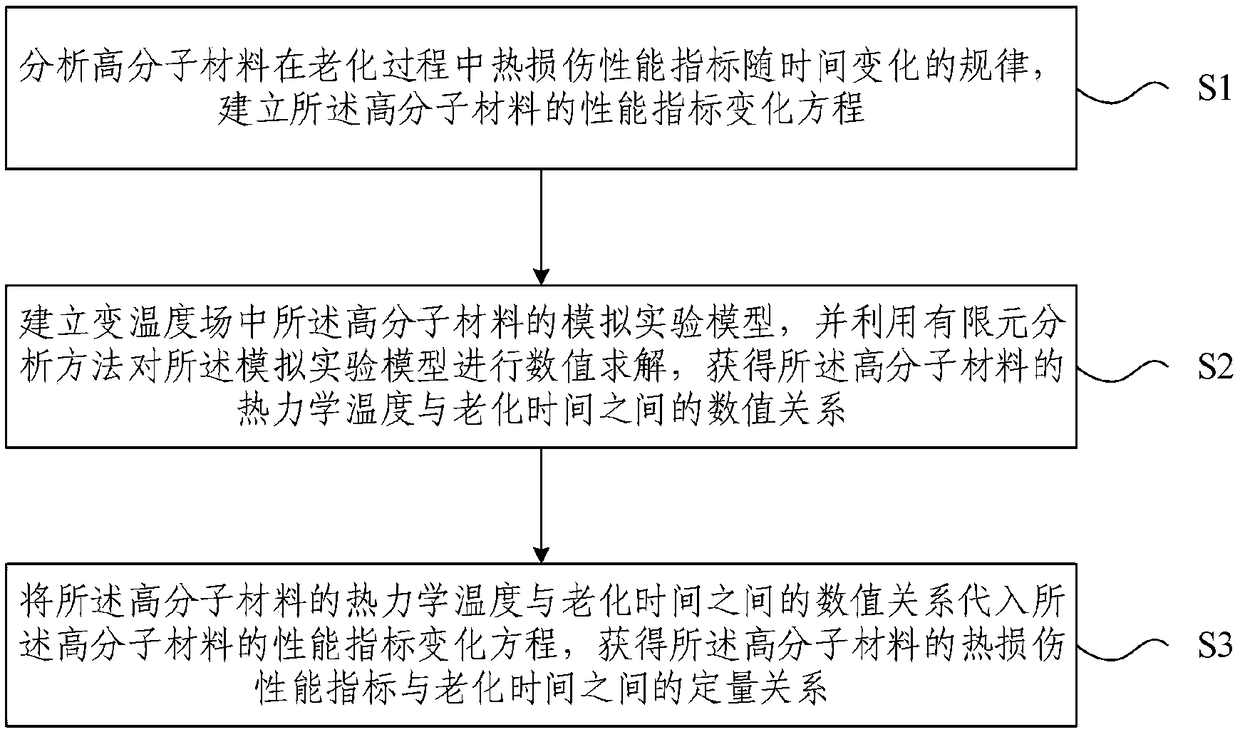
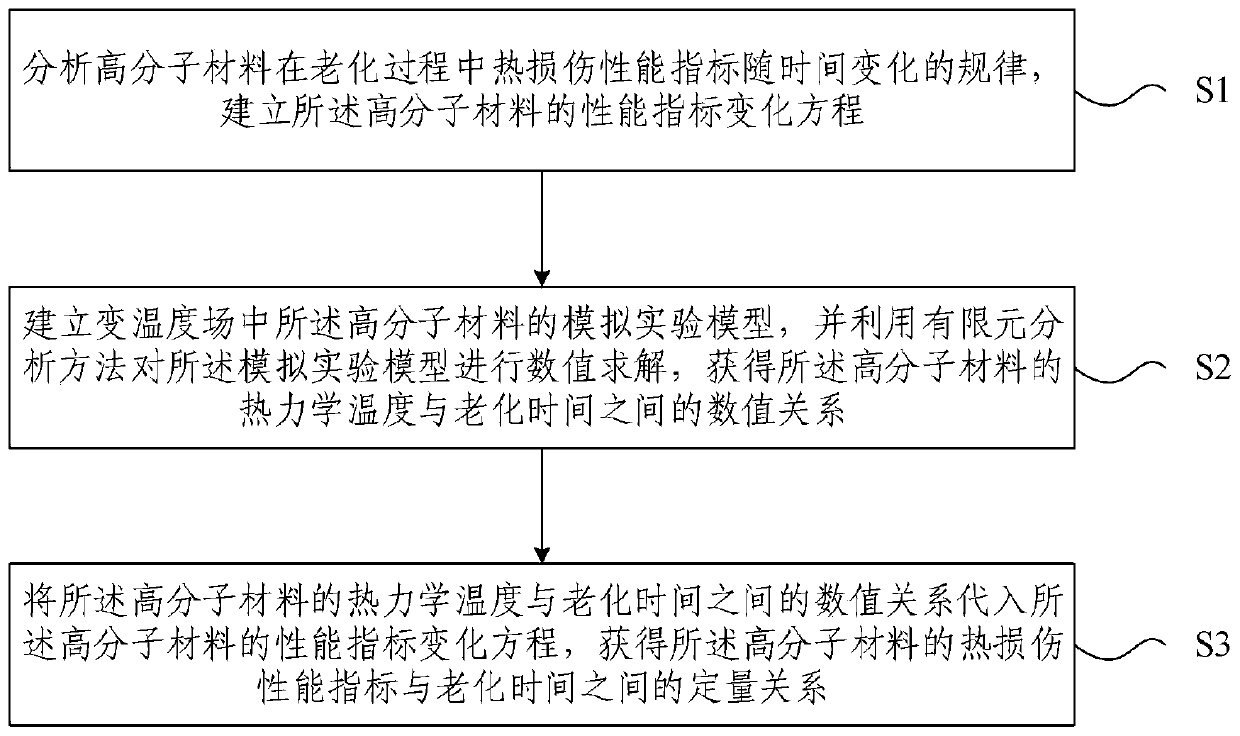
Thermal analytical calculating method and device for high molecular material in variable temperature field
ActiveCN109192253ARealize aging experimental researchHas reference valueMolecular entity identificationTemporal changeChemical physics
The invention provides a thermal analytical calculating method and device for a high molecular material in a variable temperature field. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing the rule ofa time-dependent heat injury performance index of the high molecular material in an aging process and establishing a performance index change equation of the high molecular material; establishing a simulation experiment model of the high molecular material in the variable temperature field and solving the numerical value of the simulation experiment model by means of a finite element method to obtain a numerical value relationship between thermodynamic temperature and aging time of the high molecular material; and introducing the numerical value relationship between thermodynamic temperatureand aging time of the high molecular material into the performance index change equation of the high molecular material to obtain a quantitative relationship between the heat injury performance indexand the aging time of the high molecular material. According to the invention, an aging experiment research of the high molecular material in a slow variable temperature condition can be achieved, theobtained data is of reference value, and the integral operation is feasible.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
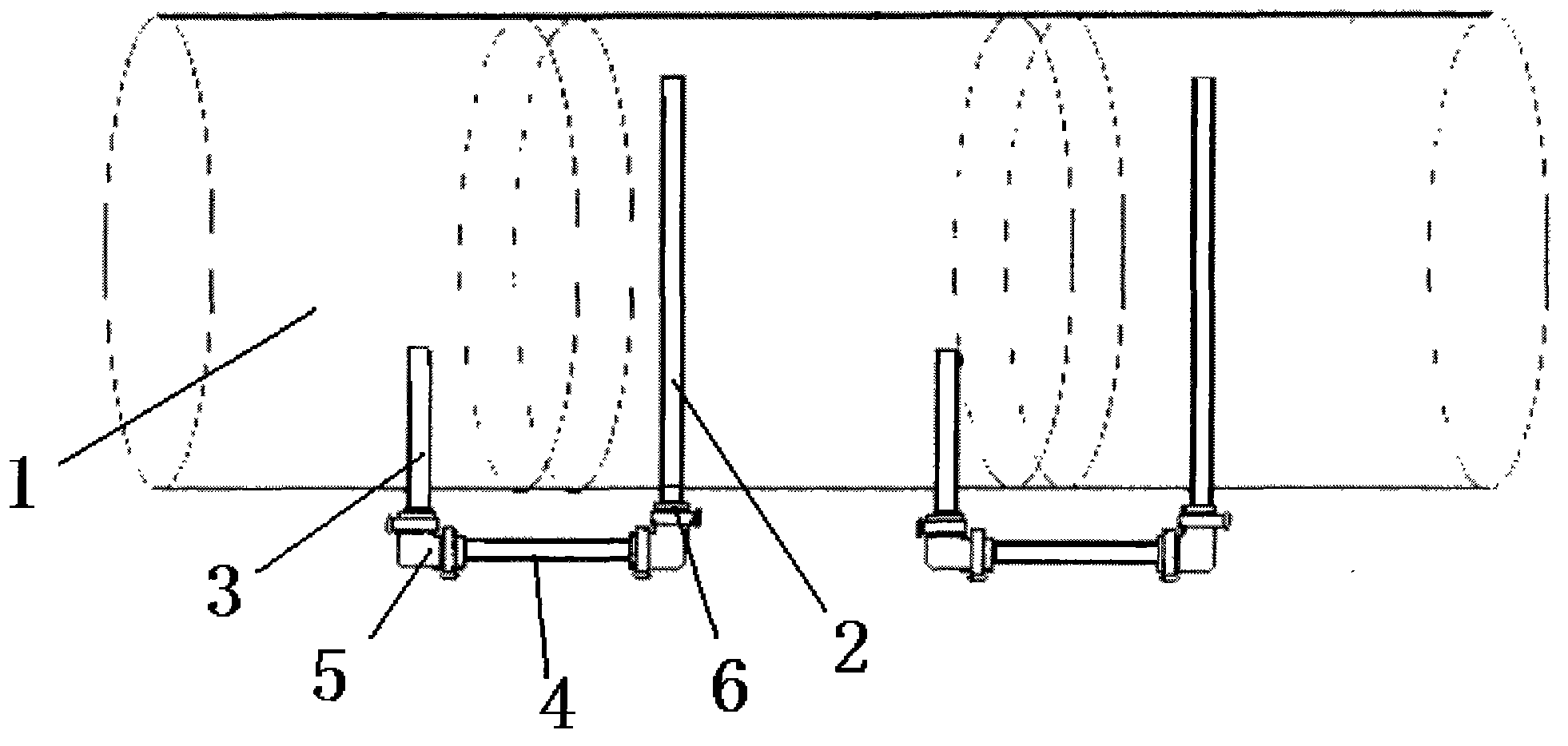
Solar hot water temperature gradient manifold
InactiveCN103629833AIncrease water temperatureFree disassemblySolar heat devicesSolar thermal energy generationSolar waterWater quality
The invention relates to a solar hot water temperature gradient manifold. The solar hot water temperature gradient manifold is designed according to the fluid thermodynamic temperature gradient principle. The solar hot water temperature gradient manifold is used for enabling hot water to carry out flow division according to a certain gradient temperature, and is arranged between two solar water tanks with the temperature grade difference. The solar hot water temperature gradient manifold comprises a long pipe, a short pipe and a connecting pipe, wherein the long pipe is arranged in the solar water tank with the lower water temperature, and the tail end of the long pipe is arranged on the upper portion of the solar water tank; the short pipe is arranged in the solar water tank with the higher water temperature, and the tail end of the short pipe is arranged on the lower portion of the solar water tank; the long pipe is connected with the short pipe through the connecting pipe. The solar hot water temperature gradient manifold has the advantages that hot water on the upper layer of the solar water tank with the lower water temperature can be conveyed to the solar water tank with the higher water temperature, and conveying flow of the hot water, with the higher temperature, between multi-level heating water tanks is quickened. The solar hot water temperature gradient manifold is simple in structure, snap rings and silica gel elbows can be freely disassembled, and cleaning is convenient; due to the fact that anti-bacterial layers are arranged on the inner wall of the long pipe, the inner wall of the short pipe and the inner wall of the connecting pipe respectively, bacteria breeding is reduced, and water quality is ensured.
Owner:GUANGXI JIKUAN SOLAR ENERGY EQUIP
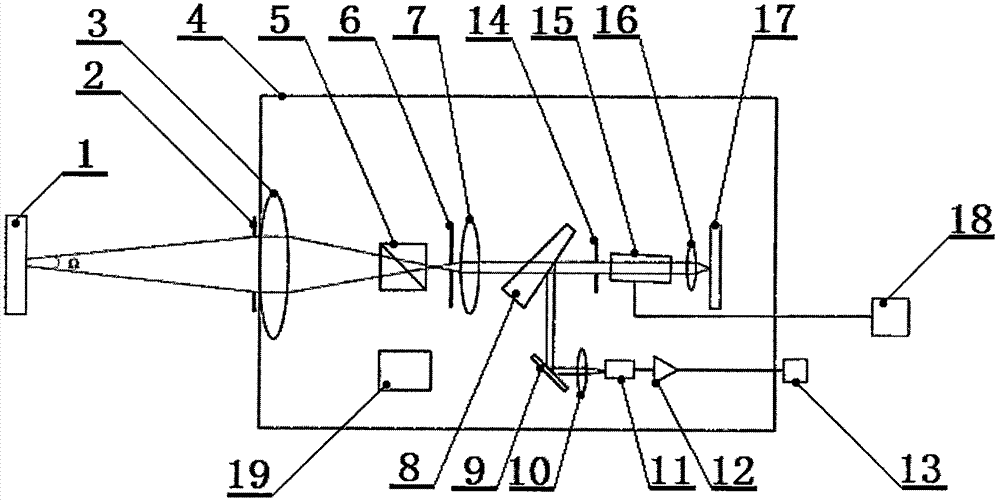
Method of measuring black body thermodynamic temperature
PendingCN107024283AReduce lossWide tunable wavelength rangeRadiation pyrometryAction spectrumBlack body
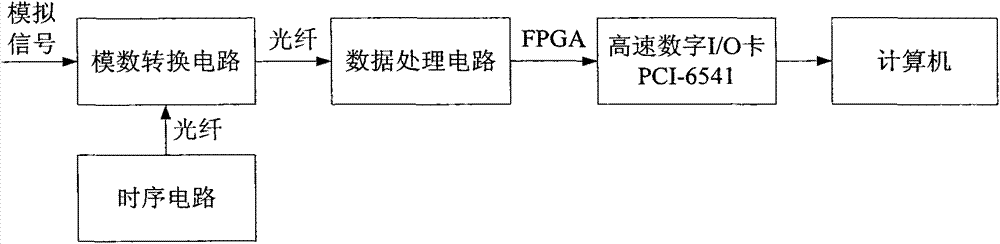
The present invention relates to the radioactivity detection technology field. A method of measuring a black body thermodynamic temperature is characterized in that a radiation spectrometer is placed at a specific position, so that the distance between an aperture diaphragm and a to-be-measured object is about 900 millimeters; a CCD camera is used to observe an image of a detected area on the to-be-measured object; the radiation spectrometer is moved to detect the different areas on the to-be-measured object; the light entering the radiation spectrometer passes an acousto-optic tunable filter two times, then enters a photodiode and is transformed into a voltage signal, the voltage signal is amplified by a transimpedance amplifier, and then a narrow-band output signal is outputted, a voltage is outputted, the acousto-optic tunable filter filters the light in a light beam and within a narrow band frequency range, a microwave frequency outputted by a microwave generator is changed in a scanning manner to regulate and control the acousto-optic tunable filter to scan and filter the narrow band light, and a radiation spectrum of the to-be-measured object within a wavelength range of 650-1000 nanometers is obtained, so that the thermodynamic temperature of the to-be-measured object is analyzed.
Owner:JINHUA VOCATIONAL TECH COLLEGE
High temperature accelerated storage test method for zinc-silver battery
ActiveCN104991195BThe experimental method is simpleEfficient experimental methodElectrical testingHigh temperature storageRoom temperature
The invention discloses a high-temperature accelerated storage test method for zinc-silver batteries. In step 101, N pieces of zinc-silver battery cells are divided into four groups according to the high-temperature accelerated storage temperature, and put into 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, and 70°C respectively. In a constant temperature oven; take out the zinc-silver battery monomer for discharge after every time T, and draw the graph of the average discharge capacity of the zinc-silver battery monomer with time at different storage temperatures; calculate the attenuation of the discharge capacity of the monomer under different storage temperatures rate; step 102, with the attenuation rate of the average discharge capacity of the zinc-silver battery cell under different storage temperatures, the life characteristic K, fitting the linear function of the logarithm of the life characteristic K for the reciprocal of the thermodynamic temperature; step 103, calculating this type of zinc-silver battery The acceleration factors of different storage temperatures of the battery relative to normal temperature; step 104, calculate the high-temperature accelerated storage time corresponding to the storage time at normal temperature, and simulate the state after long-term storage at normal temperature by storing the zinc-silver battery at high temperature for a short time.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
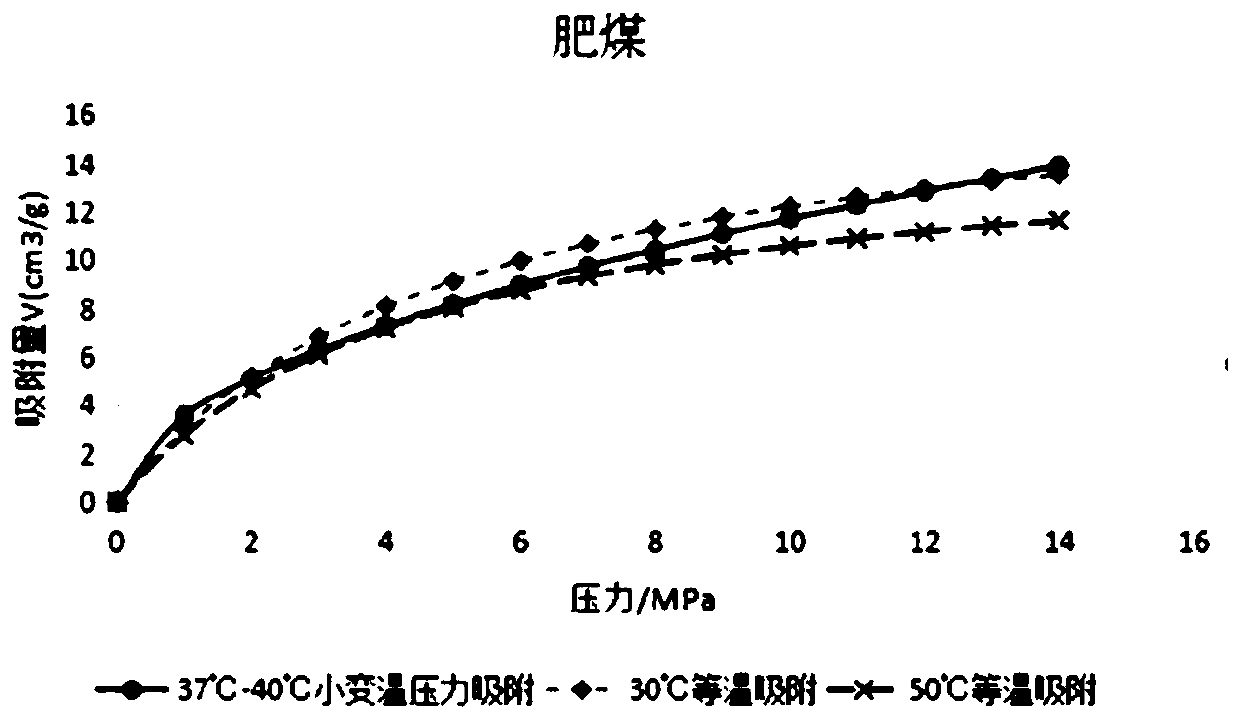
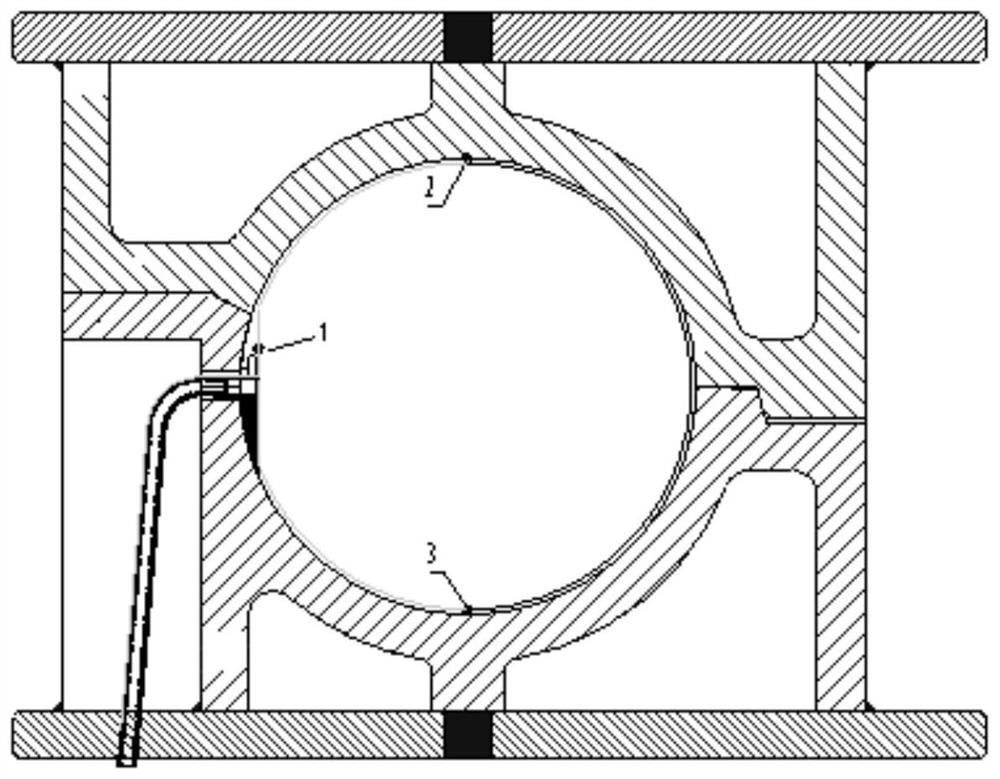
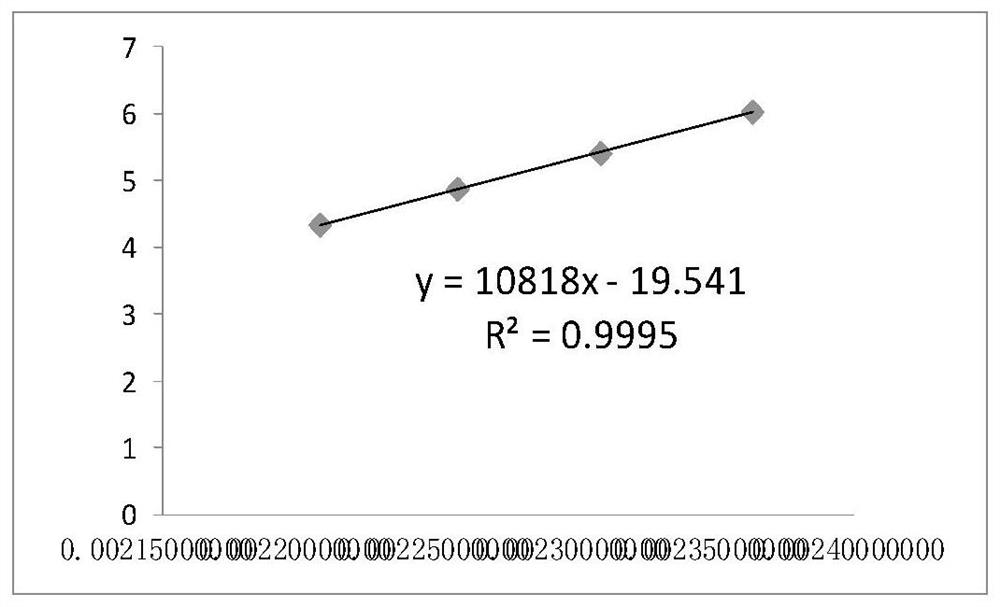
Method for making small temperature swing adsorption curve for coalbed methane drainage
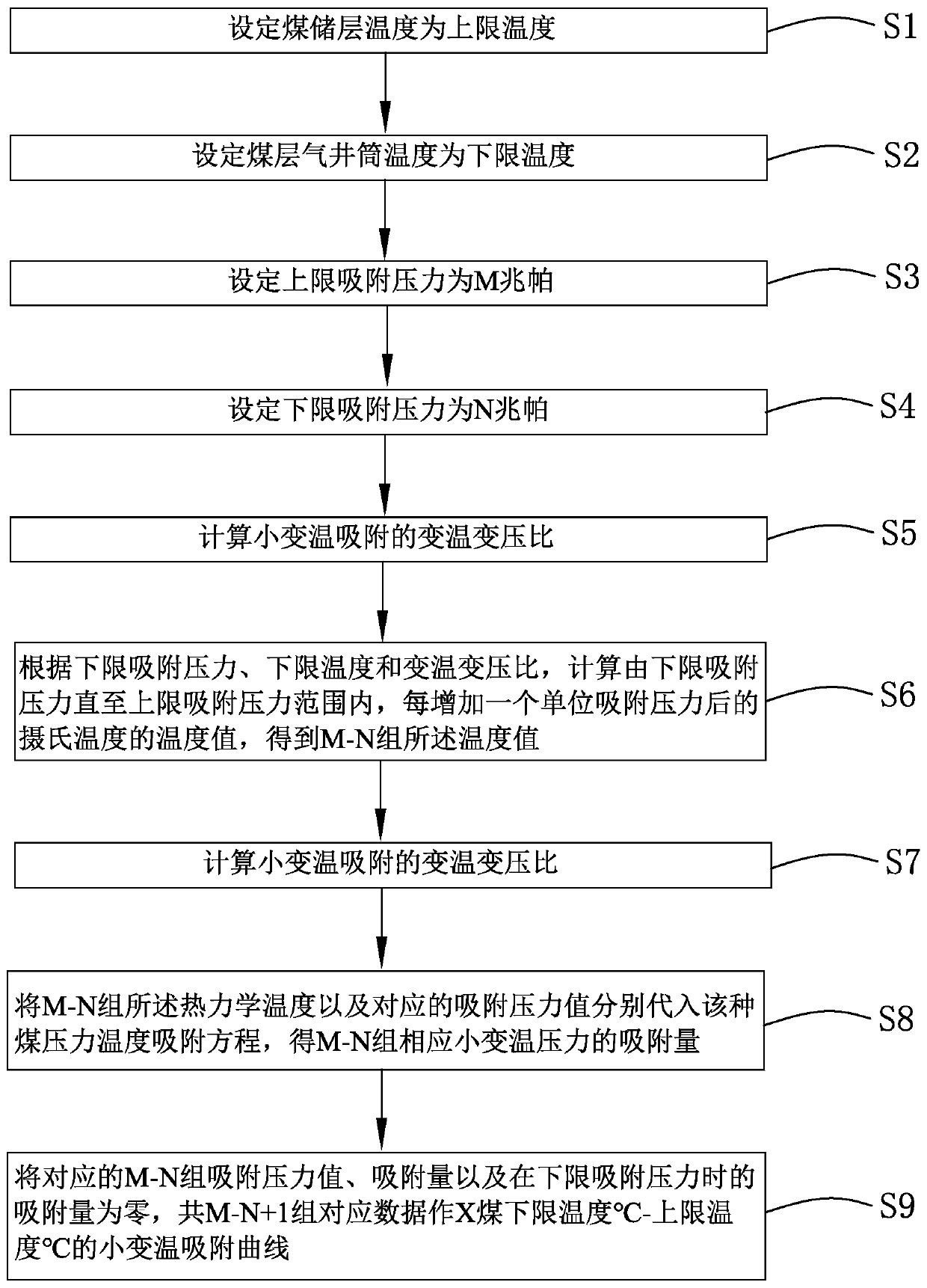
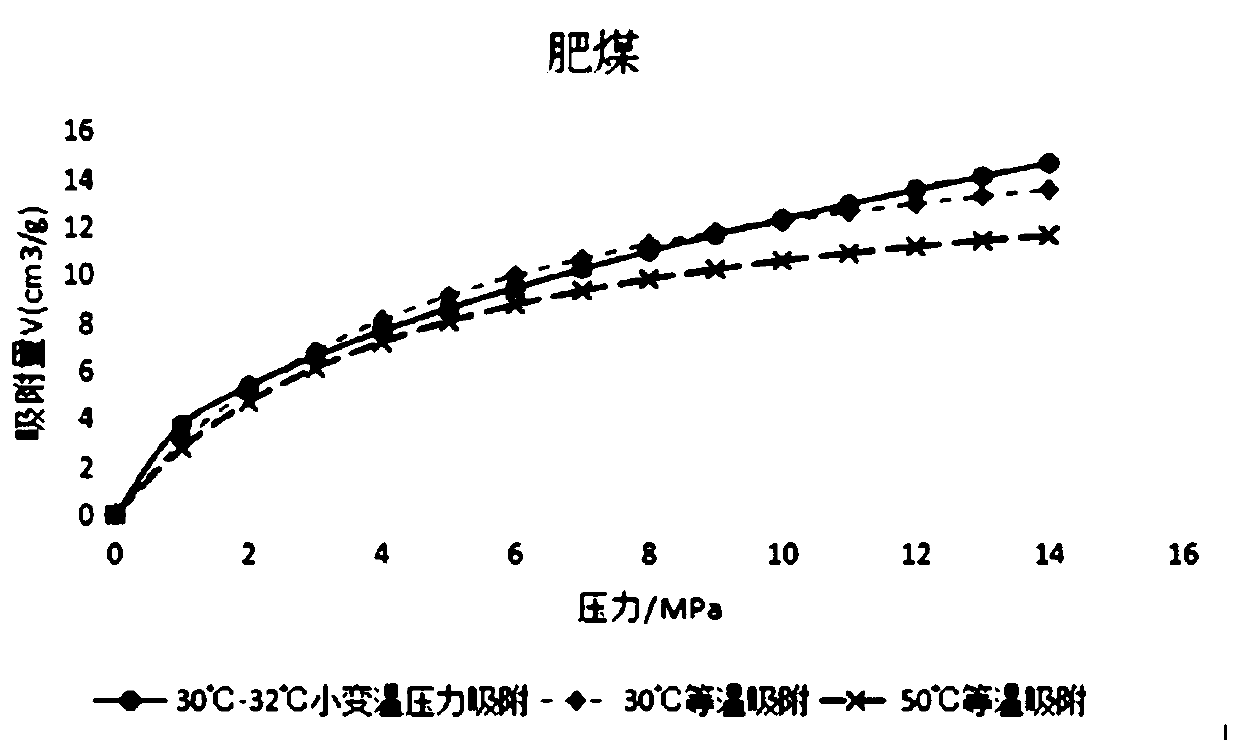
The invention provides a method for making a small temperature swing adsorption curve for coalbed methane drainage. The method comprises the steps: the coal reservoir temperature is set as the upper limit temperature; the coalbed methane shaft temperature is set as the lower limit temperature; the upper limit adsorption pressure is set to be M MPa; the lower limit absorption pressure is set to beN MPa; the temperature and pressure swing ratio of small temperature swing adsorption is calculated; according to the lower limit absorption pressure, the lower limit temperature and the temperature and pressure swing ratio, temperature values of centigrade temperatures after the adsorption pressure of one unit is increased each time are calculated, and the M-N sets of temperature values are obtained; the calculated temperature values are converted into thermodynamic temperatures (K) from the centigrade temperatures (DEG C); and the M-N sets of thermodynamic temperatures and corresponding adsorption pressure values are substituted into a coal pressure temperature adsorption equation, and the adsorption quantity is obtained; and the small temperature swing adsorption curve is made. Comparedwith relevant technologies, coalbed methane represented by the small temperature swing adsorption curve made by the method for making the small temperature swing adsorption curve for coalbed methanedrainage corresponds with the actual situation better, practicability is high, and the accuracy degree is high.
Owner:XIAN SIYUAN UNIV
Determination method for vulcanization degree of inner tube
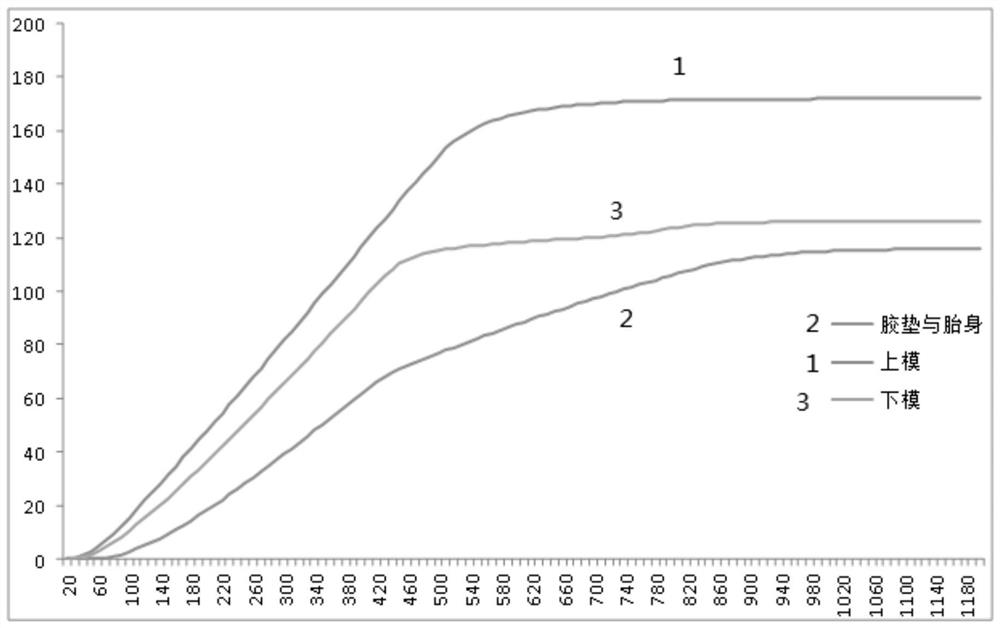
PendingCN112986326AAccurately record real-time temperaturePracticalMaterial heat developmentPolymer scienceVulcanization
Owner:山东玲珑橡胶科技有限公司
Calculation method and device for thermal analysis of polymer materials in variable temperature field
ActiveCN109192253BRealize aging experimental researchHas reference valueMolecular entity identificationMolecular materialsHeat injury
The invention provides a thermal analytical calculating method and device for a high molecular material in a variable temperature field. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing the rule ofa time-dependent heat injury performance index of the high molecular material in an aging process and establishing a performance index change equation of the high molecular material; establishing a simulation experiment model of the high molecular material in the variable temperature field and solving the numerical value of the simulation experiment model by means of a finite element method to obtain a numerical value relationship between thermodynamic temperature and aging time of the high molecular material; and introducing the numerical value relationship between thermodynamic temperatureand aging time of the high molecular material into the performance index change equation of the high molecular material to obtain a quantitative relationship between the heat injury performance indexand the aging time of the high molecular material. According to the invention, an aging experiment research of the high molecular material in a slow variable temperature condition can be achieved, theobtained data is of reference value, and the integral operation is feasible.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
A method for measuring liquid phase micro-area temperature
InactiveCN100437059CSolve the problem that the temperature measurement range is limited by the temperature measurement probeLow temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesTemperature measurement of flowing materialsSilicon dioxideMicro-needle
This invention relates to one liquid phase micro part temperature method, which is characterized by adopting light tamper or micro needle to transfer polyphenylacetylene or earth silicon emulsion or powder to test probe head into micro test area to discharge test probe by use of image.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A thermodynamic temperature measurement method for nuclear radiation environment
InactiveCN105157844BMeet practical requirementsReduce technical complexityRadiation pyrometryNuclear radiationEnvironment effect
The invention relates to a thermodynamic temperature measurement method in a nuclear radiation environment. The thermodynamic temperature measurement method is characterized by comprising the steps of providing a graphite tube having a predetermined length; filling the graphite tube with helium; inserting the graphite tube vertically from the top of a reactor to the bottom of the reactor; and providing an acoustic signal for the graphite tube, calculating the average acoustic velocity of the helium in the graphite tube, and obtaining the corresponding thermodynamic temperature based on the relationship between the average acoustic velocity and temperature of the helium. The invention achieves the application of the acoustic resonance thermodynamic temperature measurement to the temperature measurement in the nuclear radiation environment, and reduces the complexity of the absolute temperature method temperature measurement technology and the difficulty in operation for practical requirements. According to the invention, the acoustic resonance thermodynamic temperature measurement method in the nuclear radiation environment is applicable to nuclear radiation environment thermodynamic temperature measurement and also to systems that require no harsh environmental influence and a stable operation status.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com