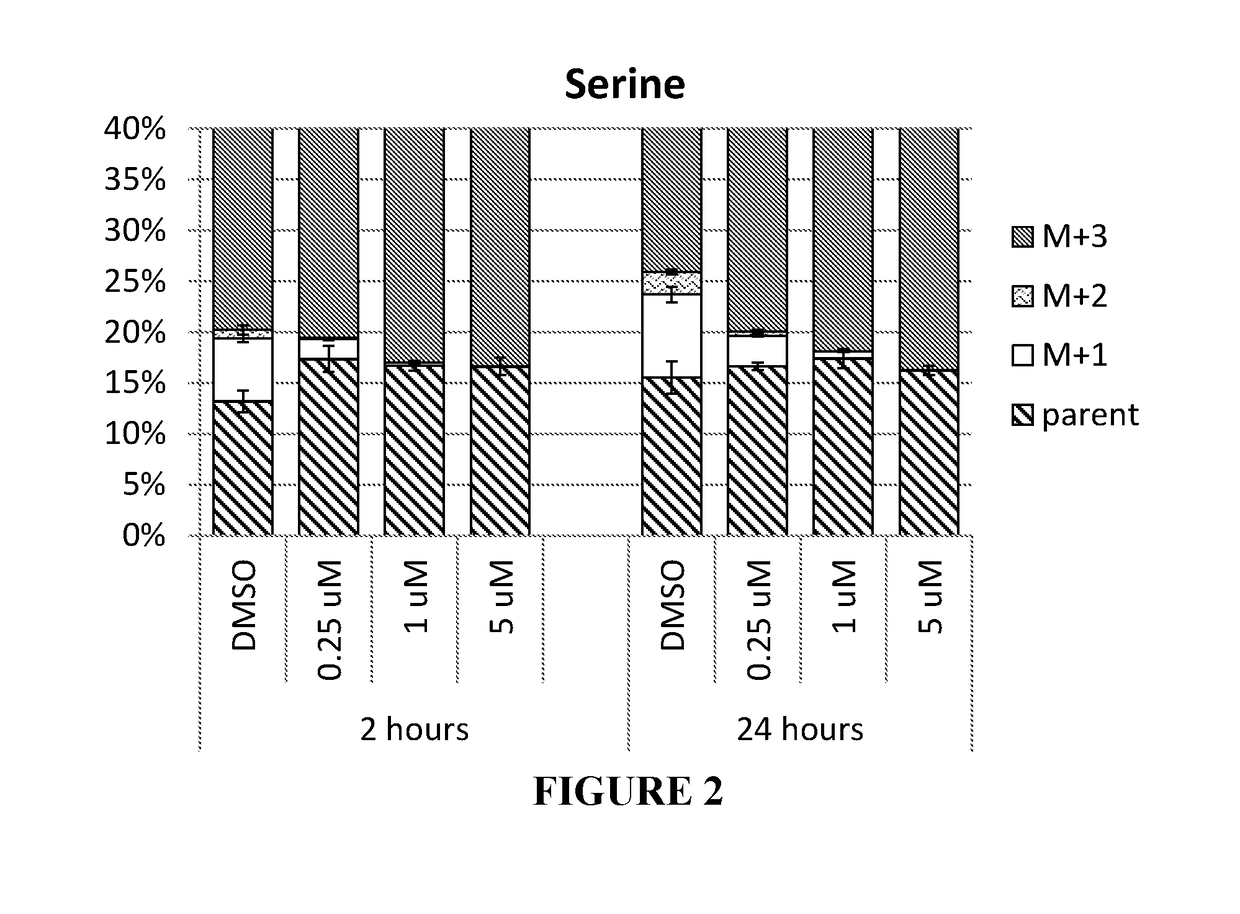
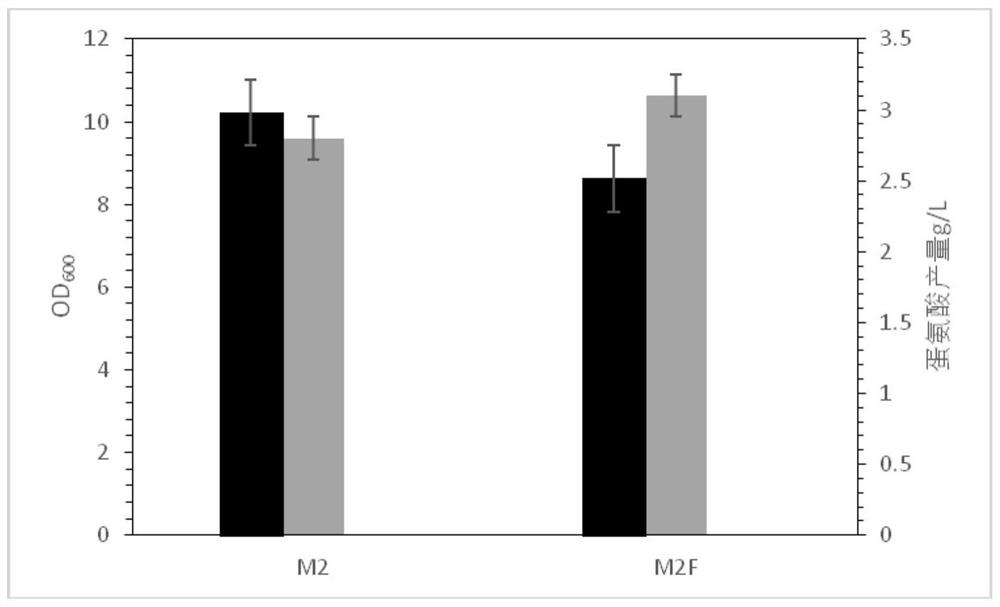
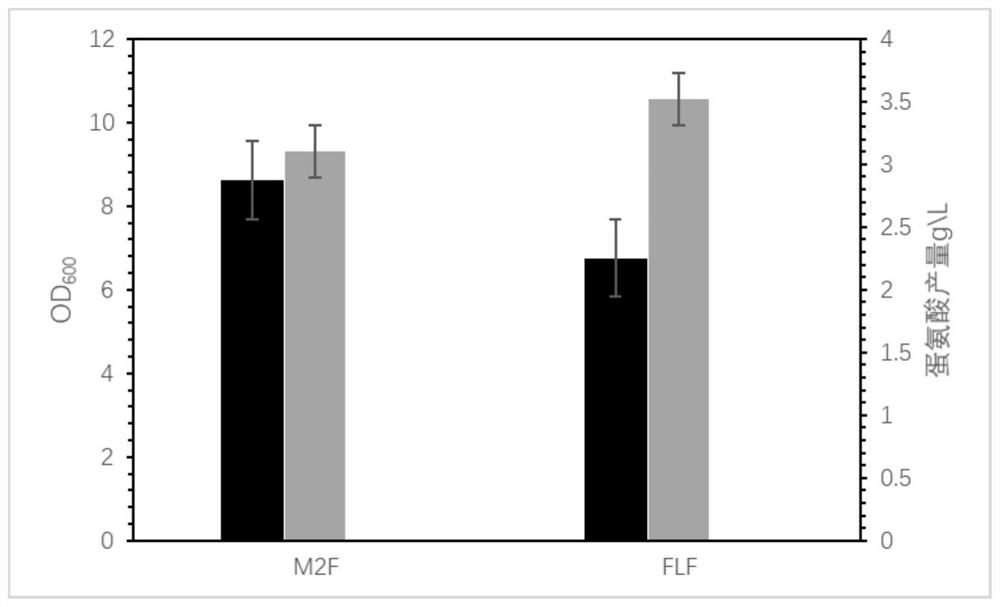
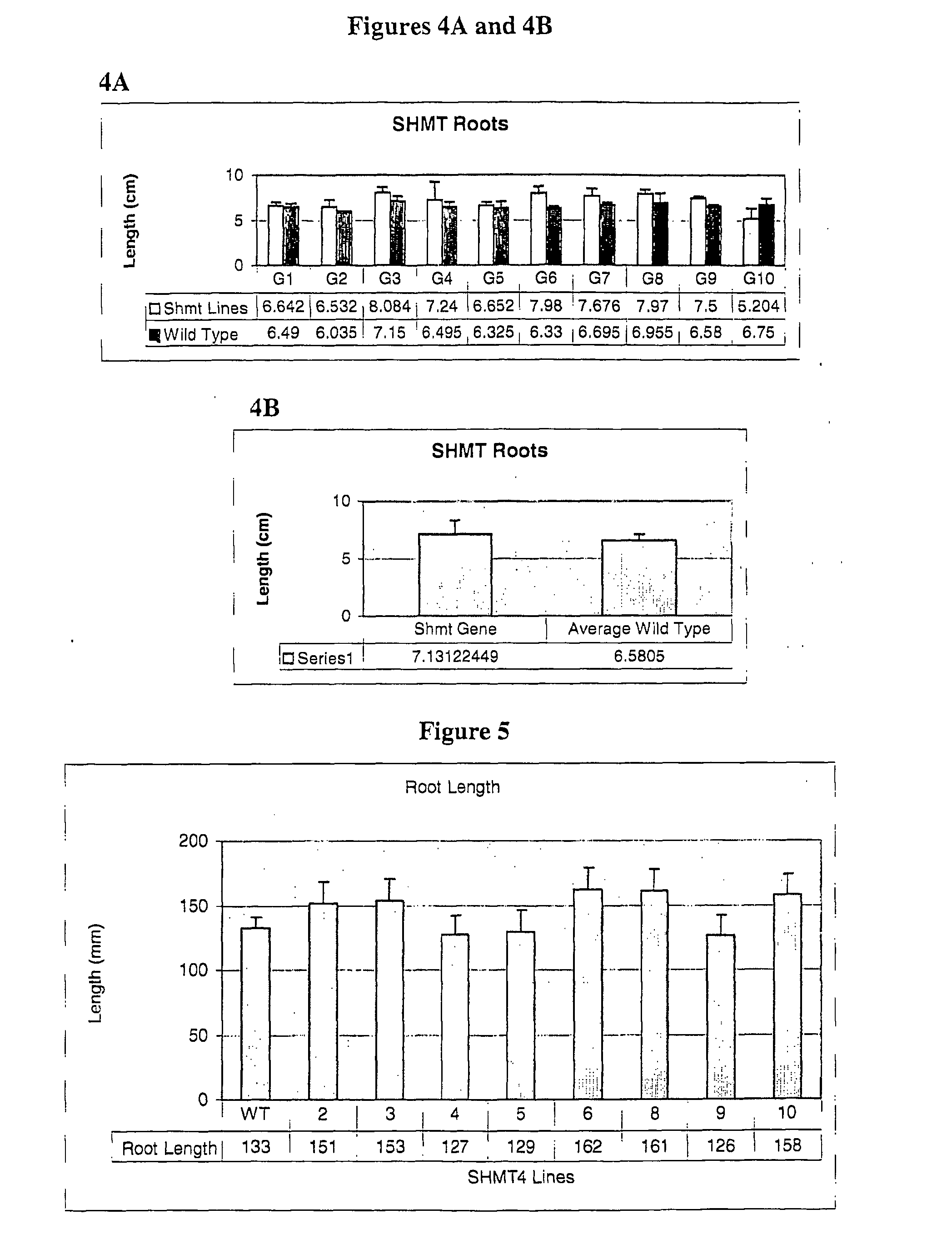
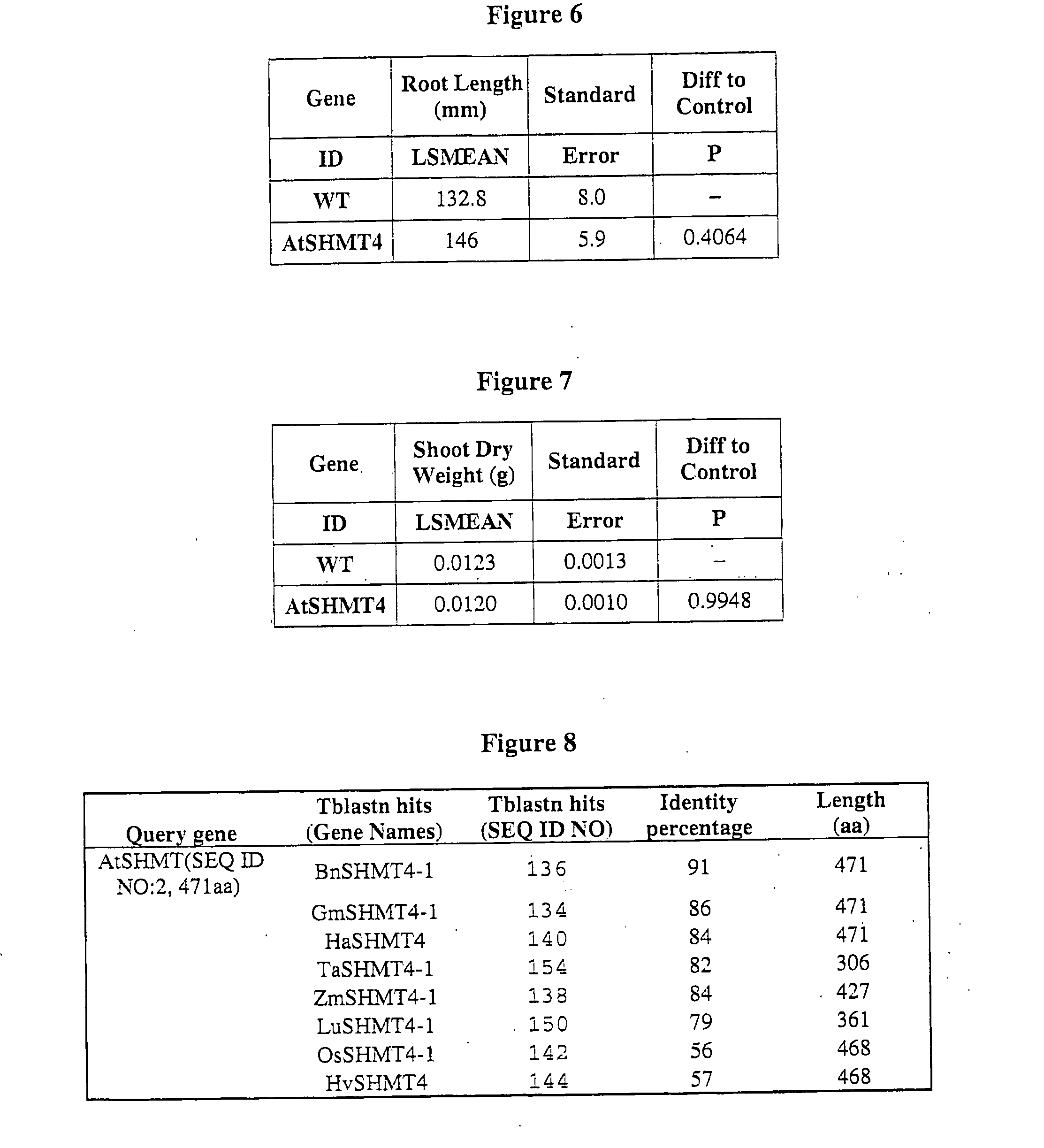
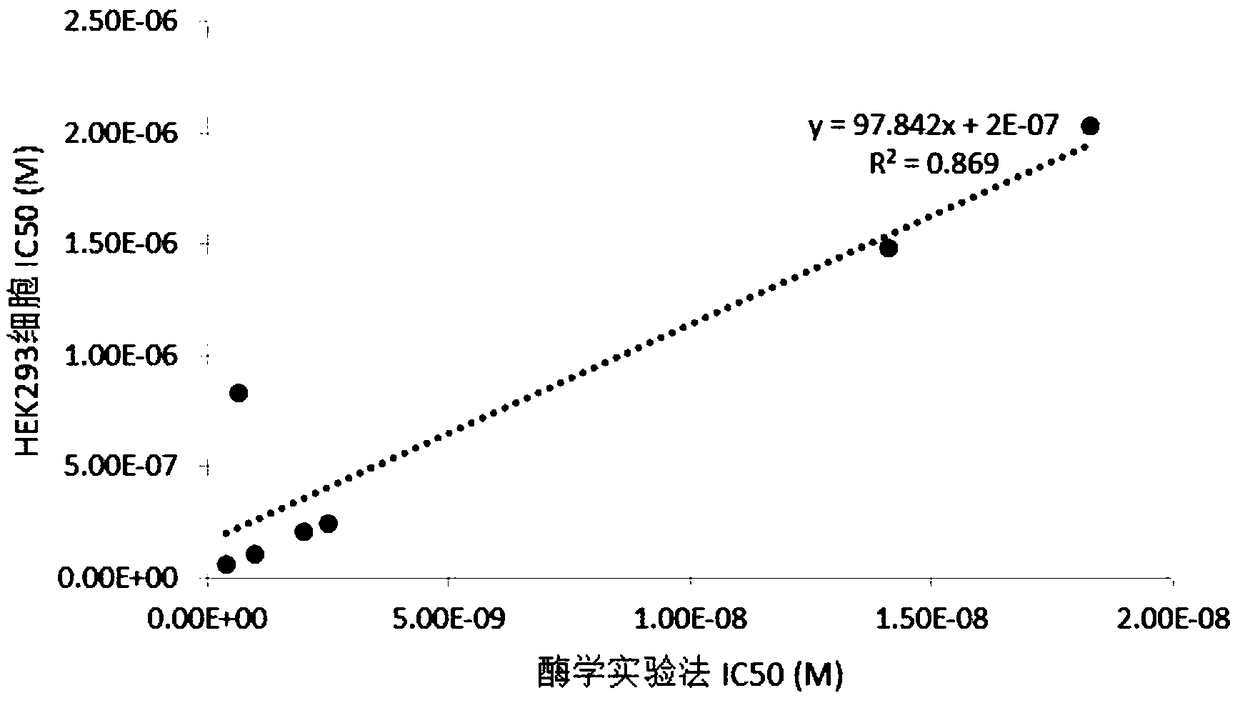
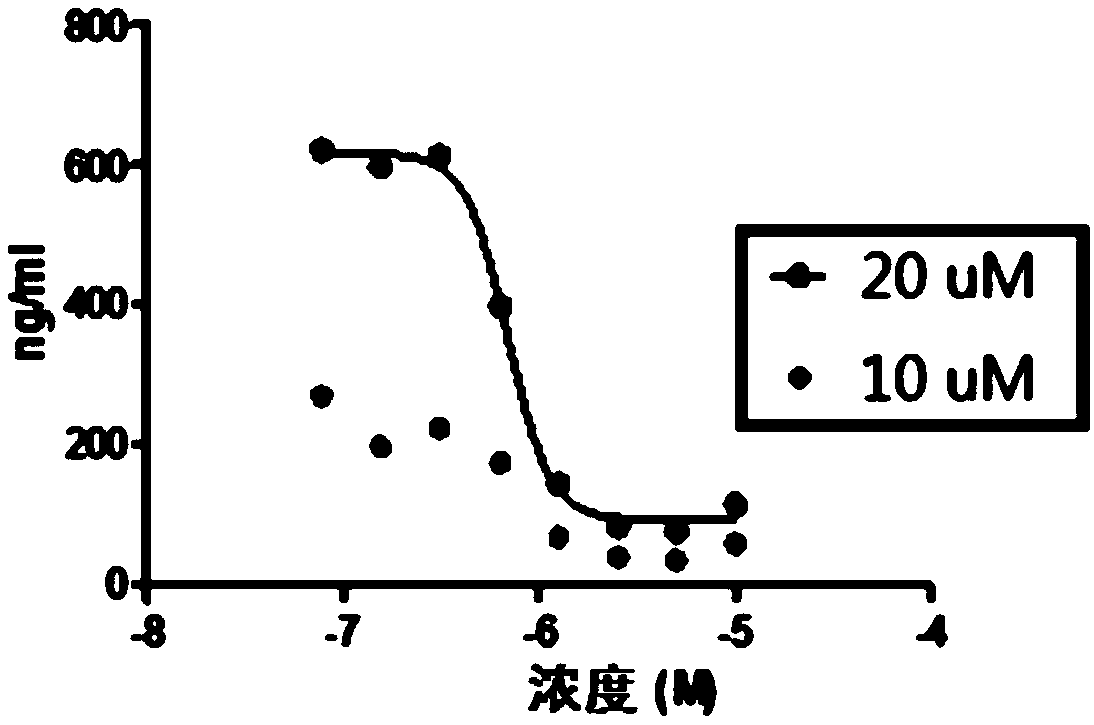
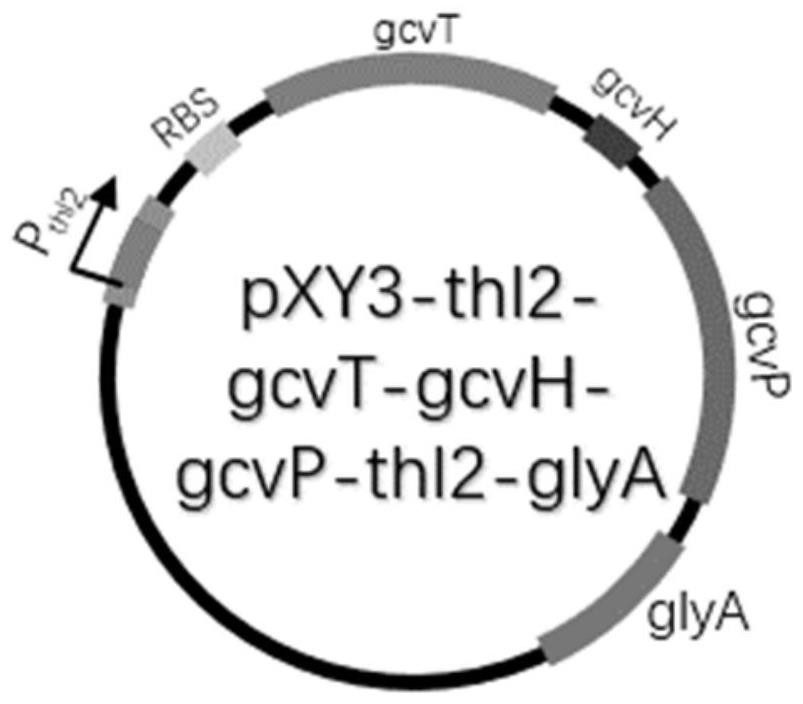
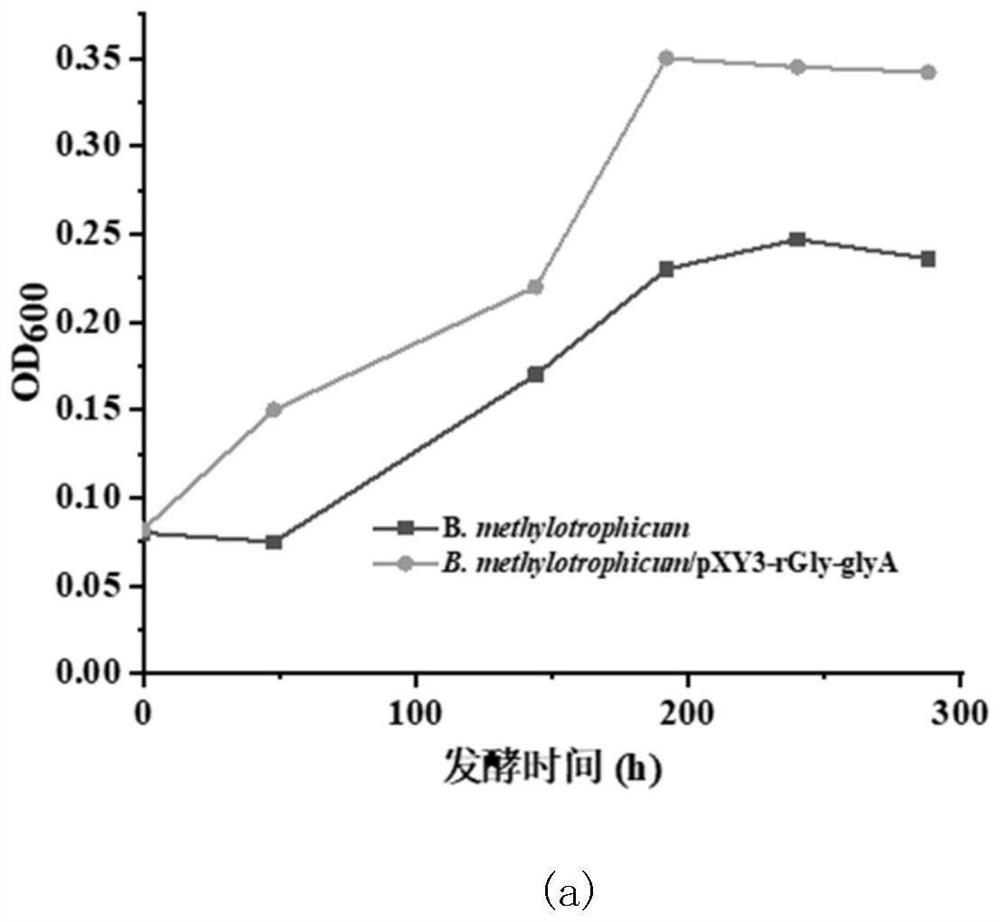
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Serine hydroxymethyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
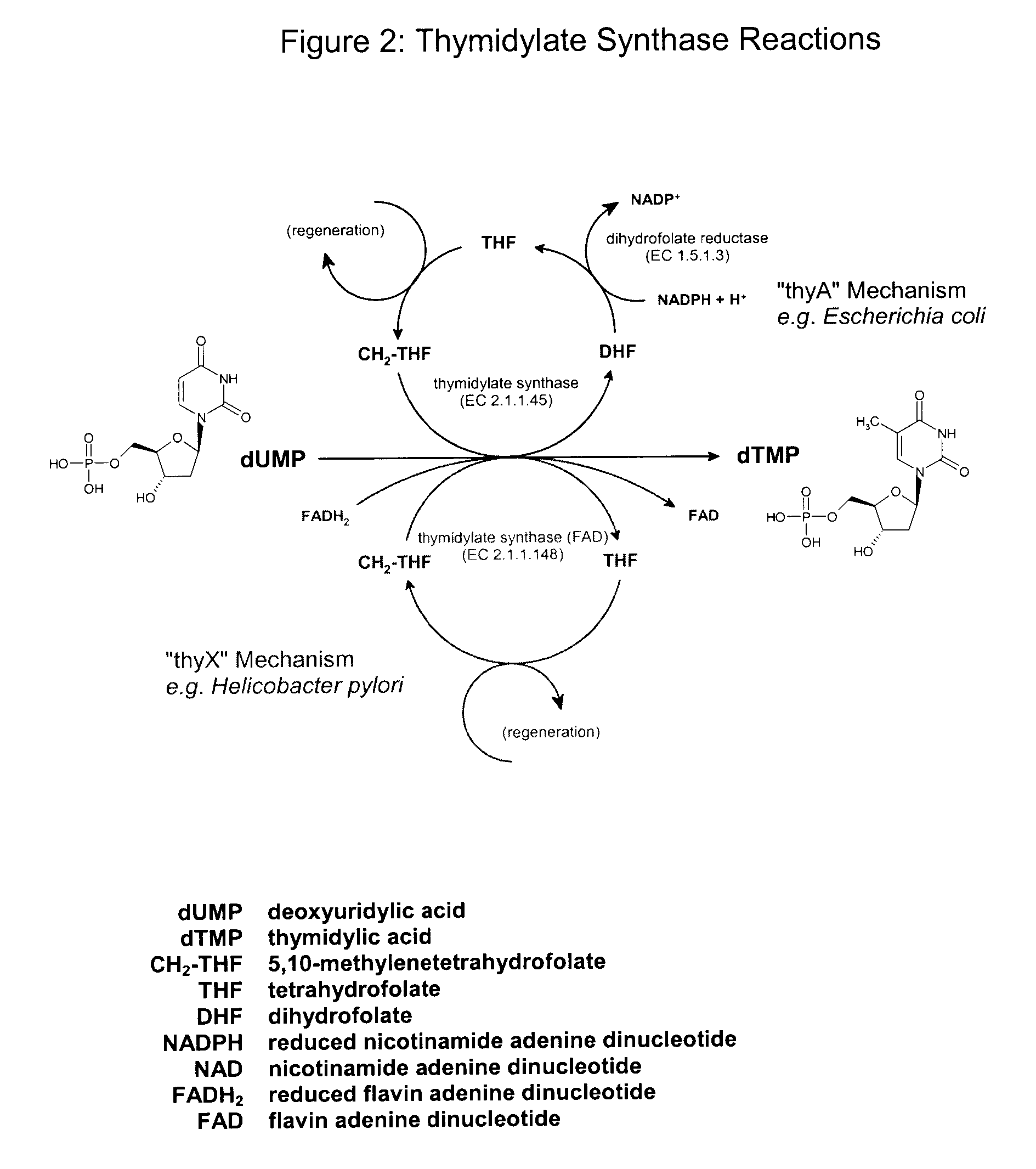
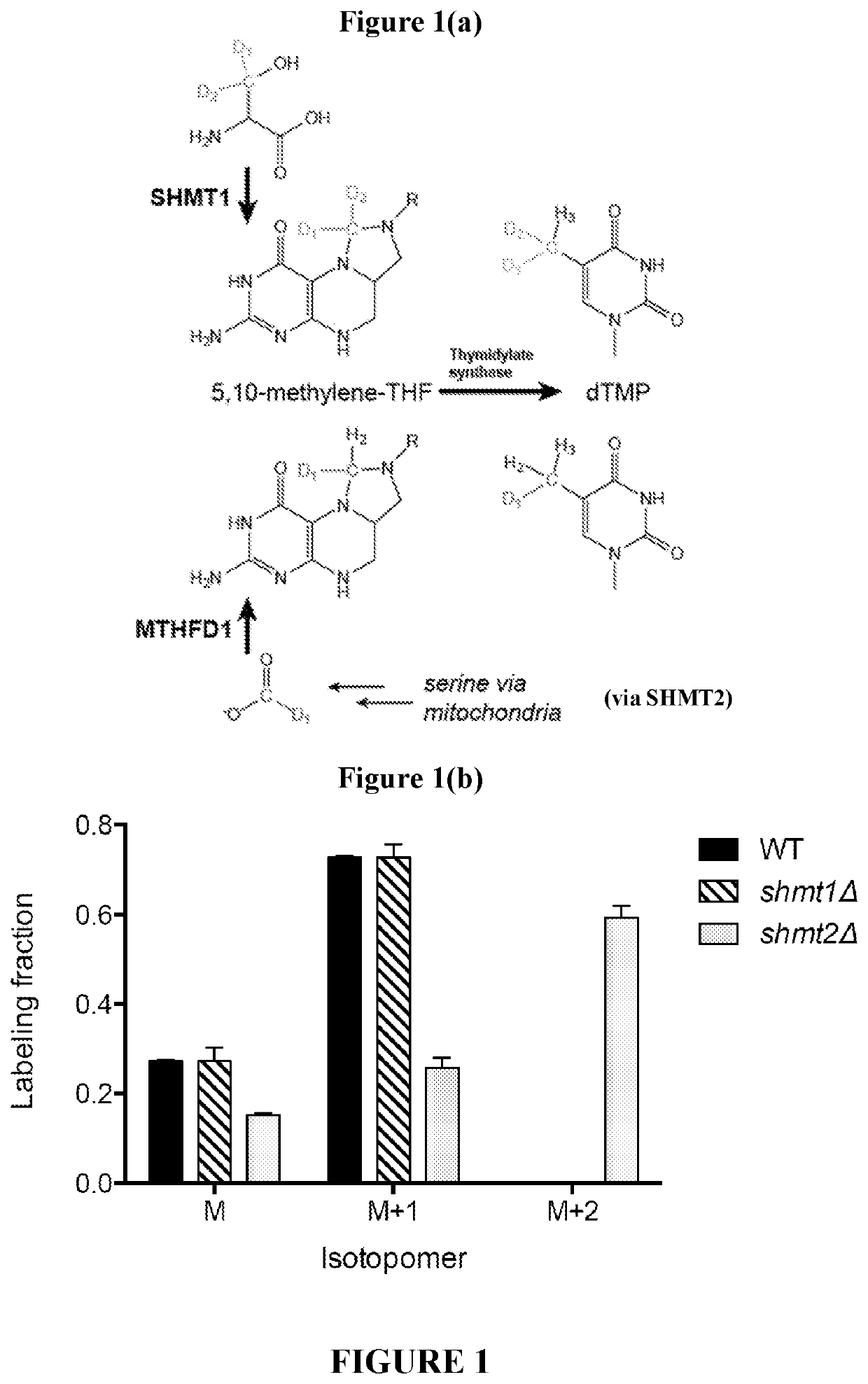
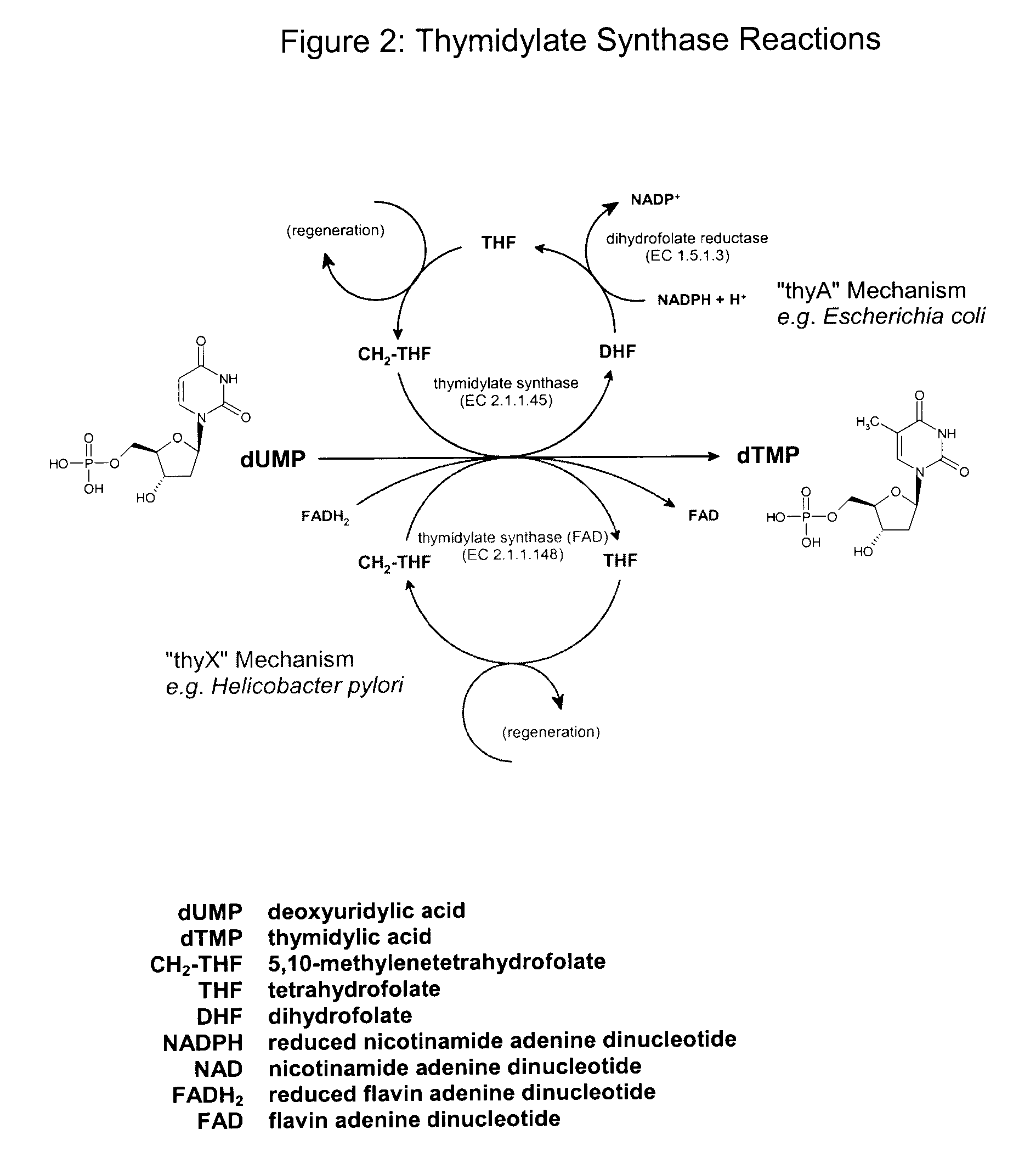
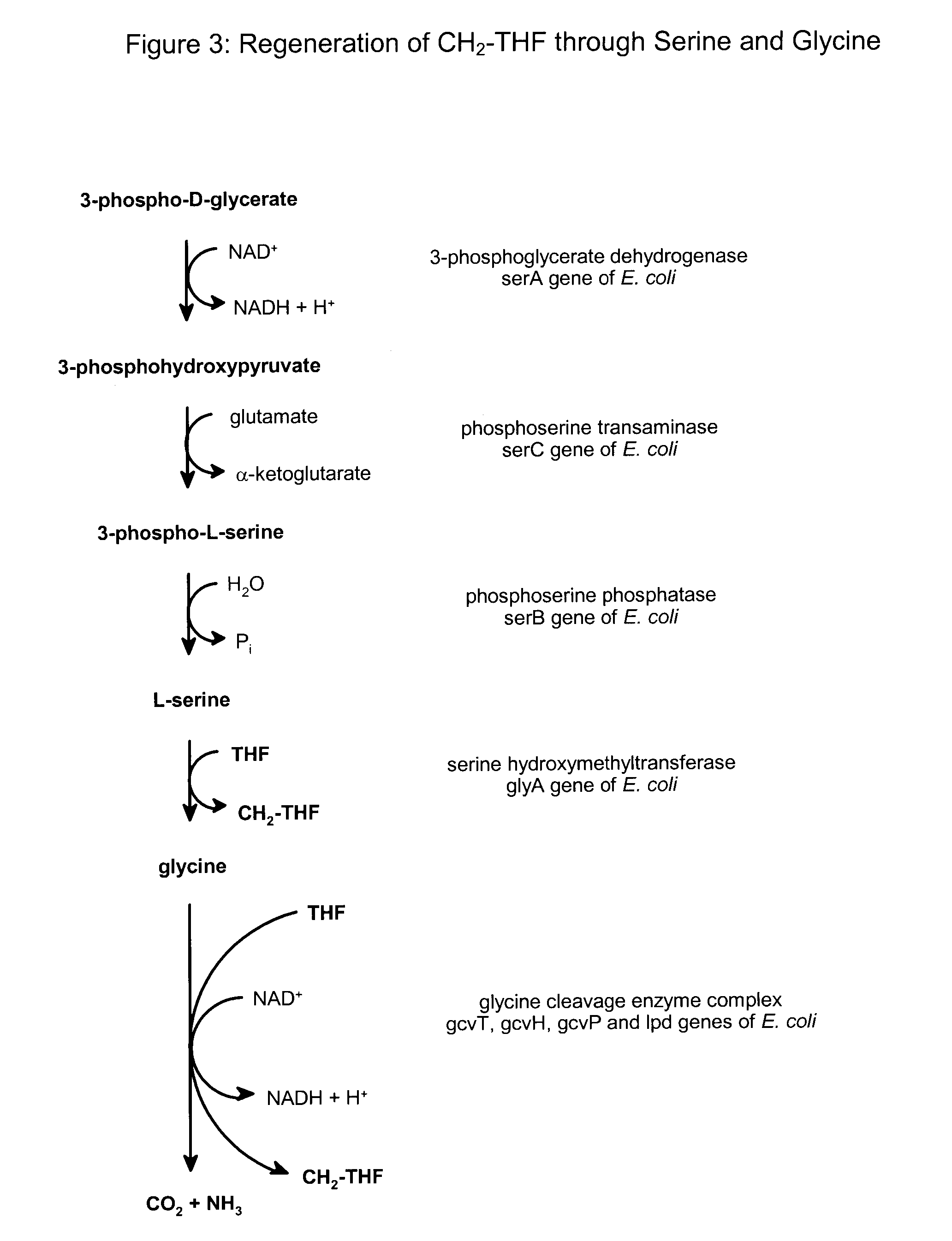
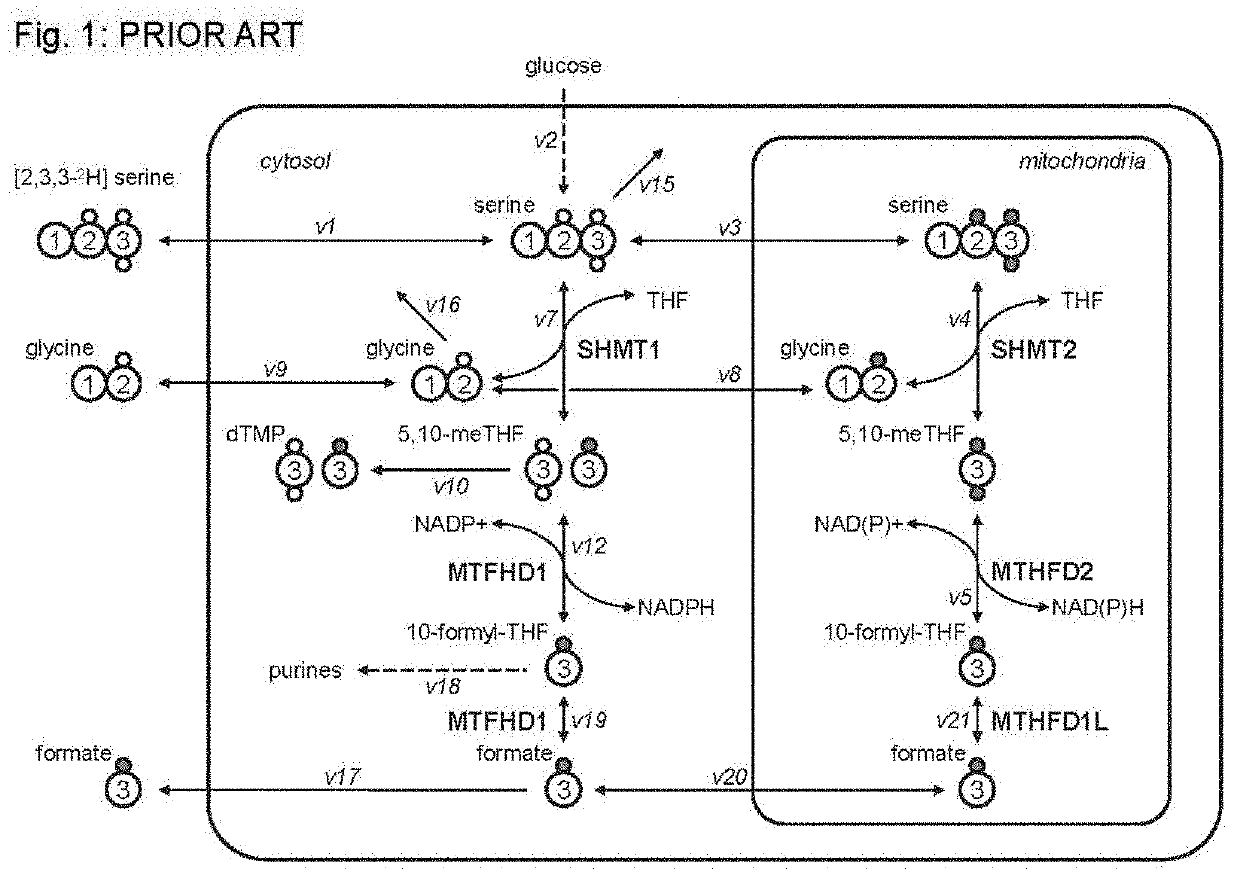
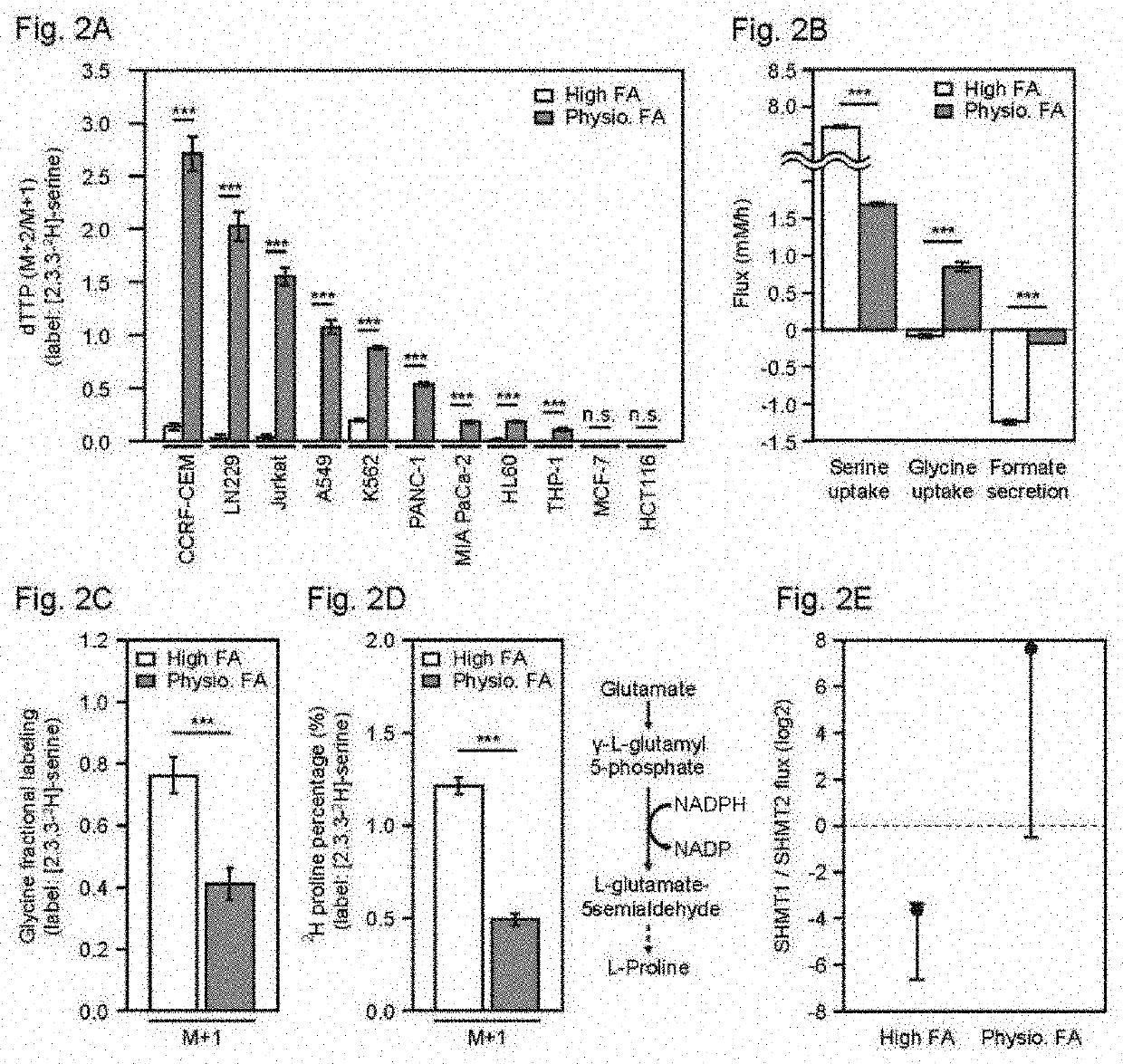
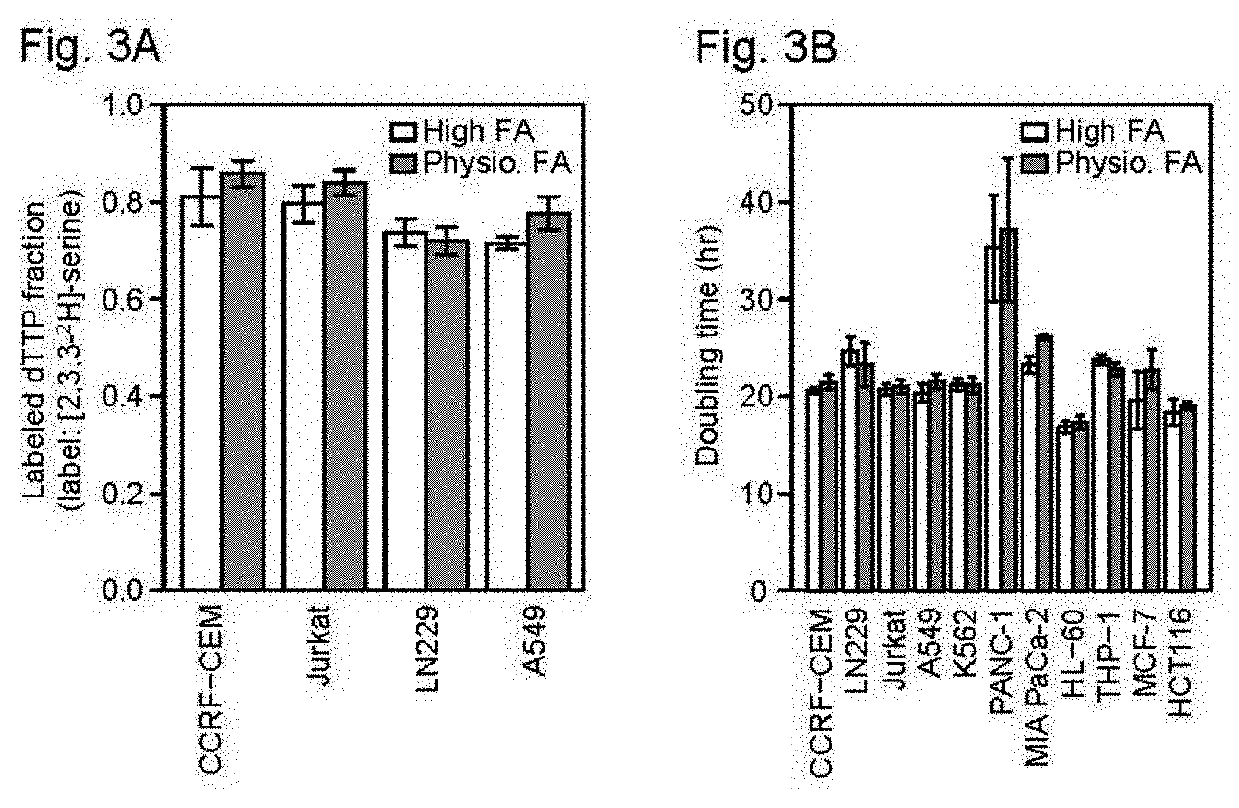
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) (Vitamin B₆) dependent enzyme (EC 2.1.2.1) which plays an important role in cellular one-carbon pathways by catalyzing the reversible, simultaneous conversions of L-serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH₂-THF). This reaction provides the largest part of the one-carbon units available to the cell.
Plants with Increased Yield
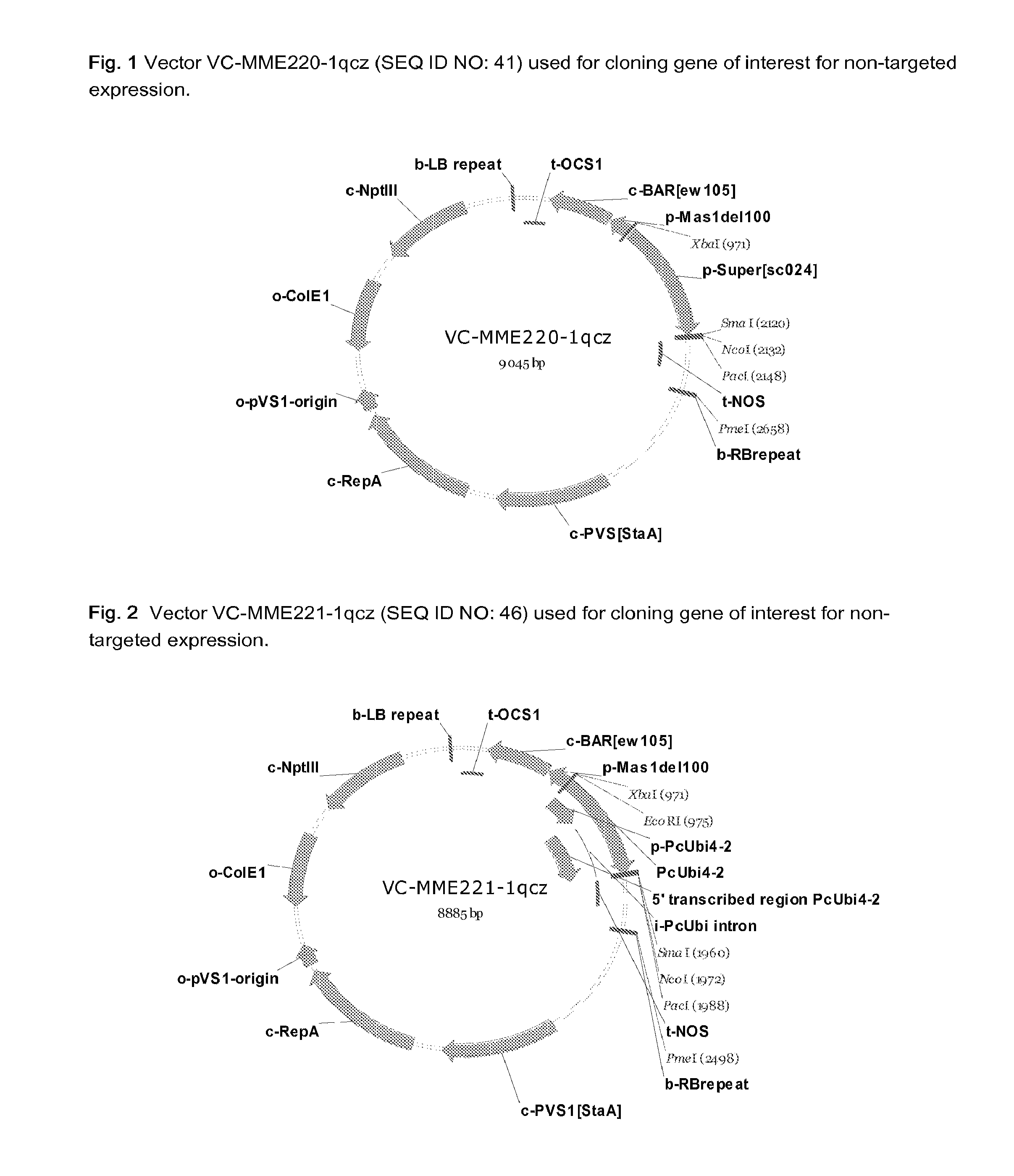
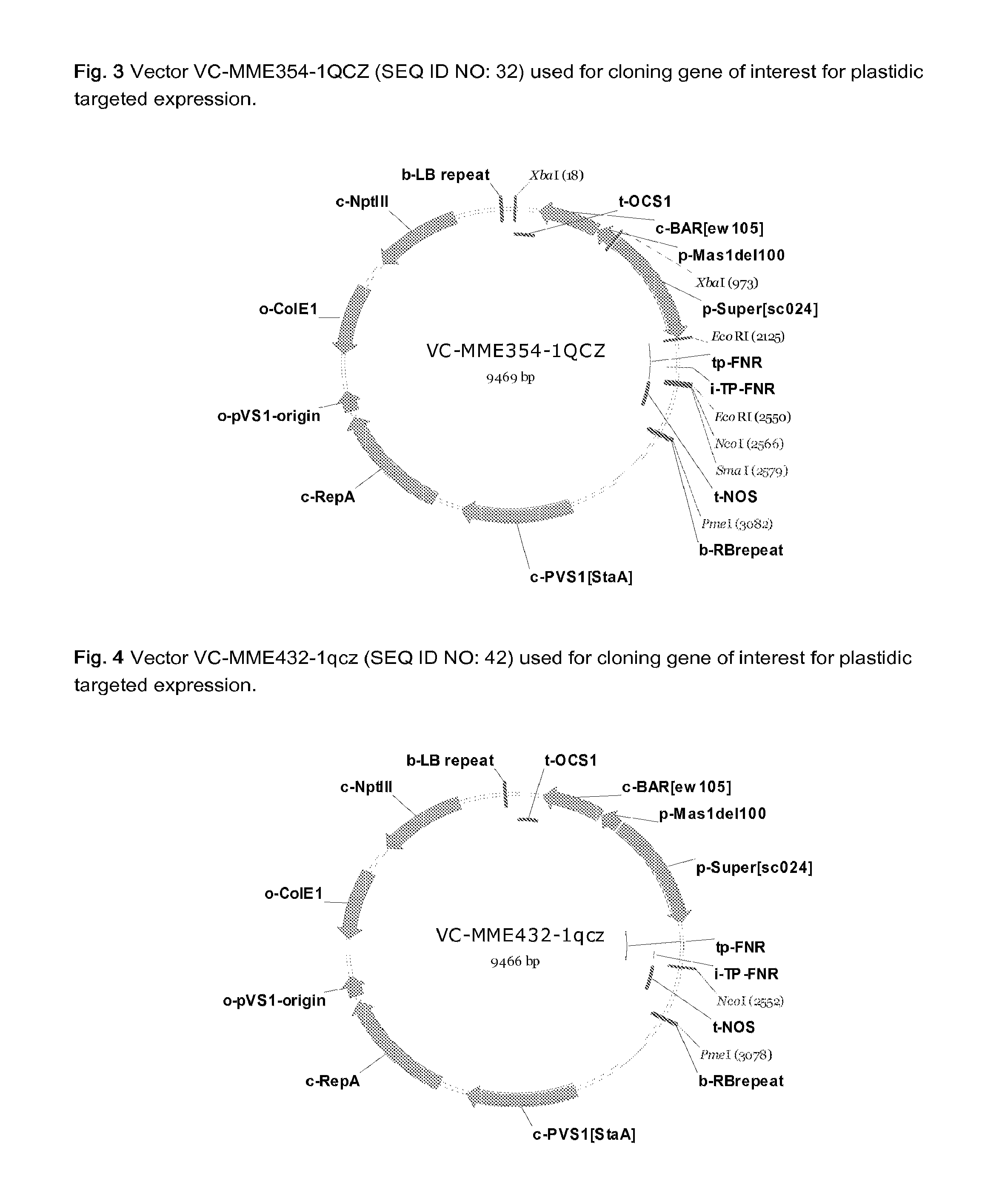
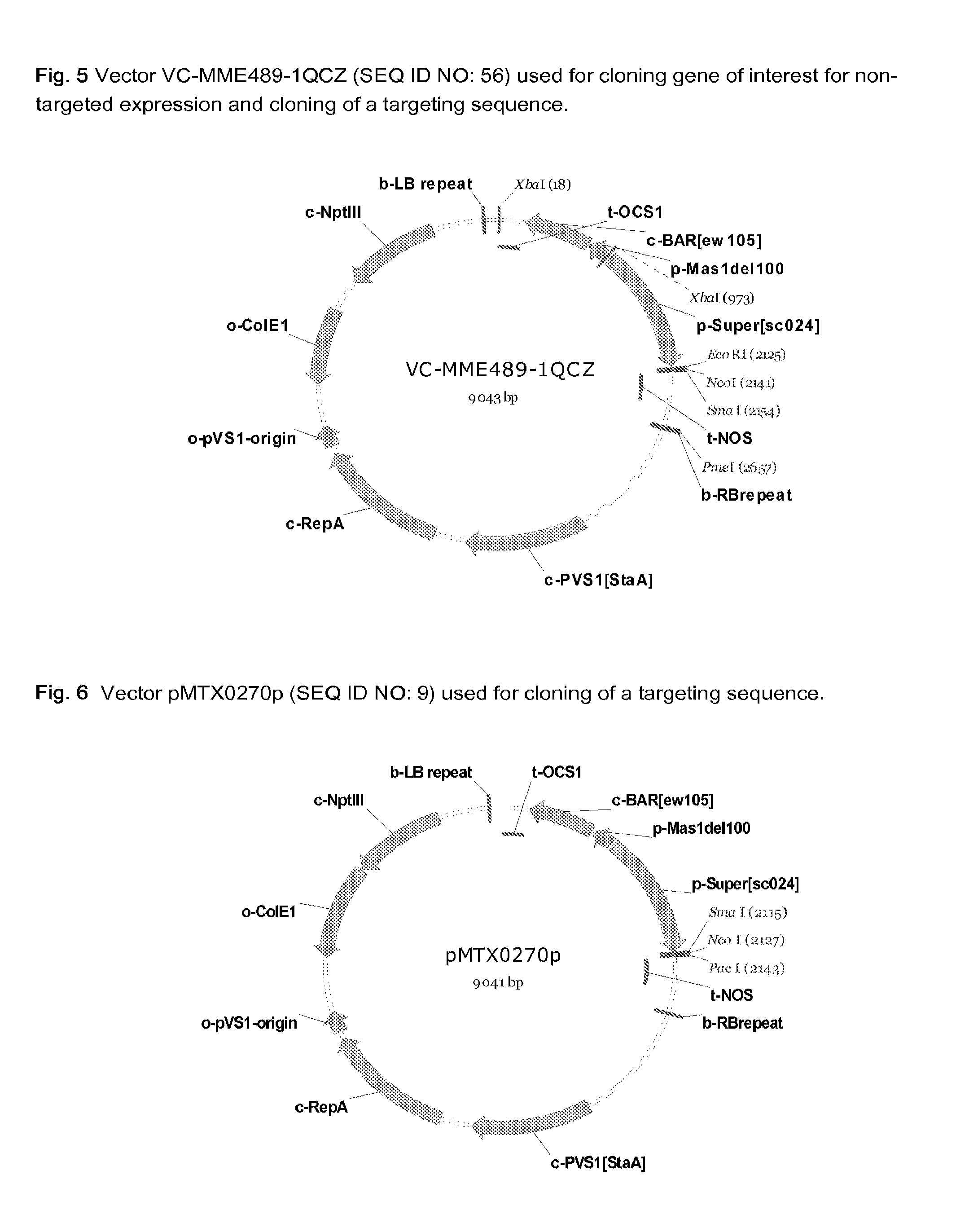
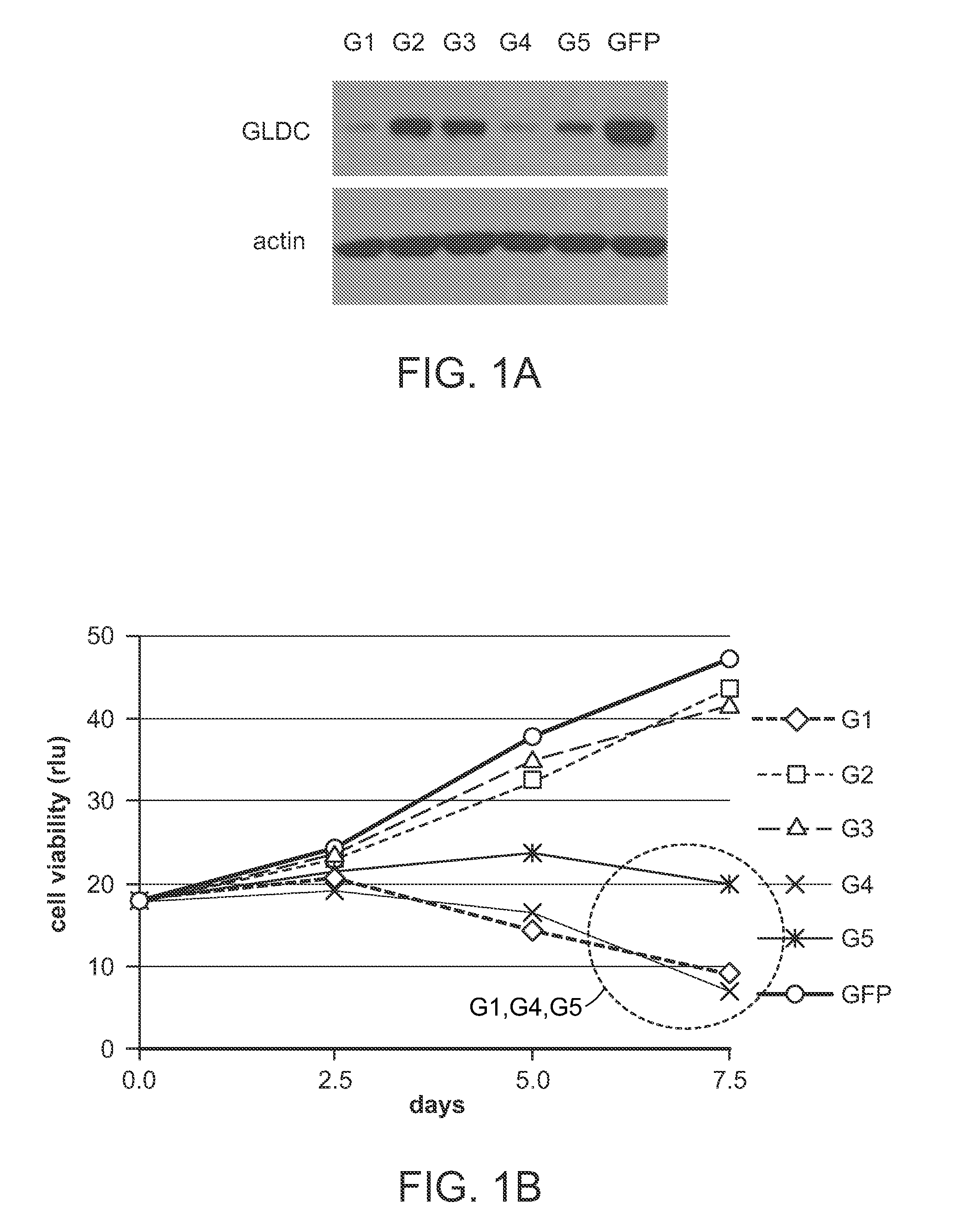
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Inhibition of the glycine cleavage system for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20150011611A1Prevent proliferationAvoid survivalBiocideCompound screeningGlycine cleavage systemAnticarcinogen
In some aspects, methods of inhibiting survival or proliferation of a tumor cell are provided, the methods comprising inhibiting the glycine cleavage system (GCS) of the tumor cell. In some aspects, methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a tumor, the method comprising inhibiting the GCS in the tumor. In some embodiments, the methods comprise contacting a tumor cell or tumor with a GCS inhibitor. In some embodiments, the tumor cell or tumor has elevated expression of serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SH1VIT2). In some aspects, methods of identifying a tumor cell or tumor that is sensitive to inhibiting the GCS are provided, the methods comprising determining whether the tumor cell or tumor overexpresses SHMT2. In some aspects, methods of identifying a candidate anti-cancer agent are provided, the methods comprising identifying or modifying a GCS inhibitor.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Synthetic method of L-serine
InactiveCN102220389AHigh yieldShort processOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationL serineUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a synthetic method of L-serine, which comprises the following steps: A) transforming the concentration of a substrate: adding the substrate, namely glycine and serine hydroxymethyltransferase accounting for 3%-8% by weight into a biological reactor; feeding 37% of formaldehyde water solution when the temperature is 40-50 DEG C and getting L-serine transformation liquid by transformation; B) purifying through an ultrafiltration membrane: purifying the L-serine transformation liquid in the A) step through the ultrafiltration membrane under the conditions that the temperature is 25-35 DEG C, the pressure at an inlet is 0.4-0.8MPa and the pressure at an outlet is 0.1-0.3MPa; C) performing adsorption and elution through ion-exchange resin: regulating the pH value of penetrating fluid in the B) step to 4.5-5.5, then exchanging the L-serine transformation liquid onto resin through the ion-exchange resin and further eluting with 0.8-1.5mol / L of hydrochloric acid; D) concentrating through a nanofiltration membrane: concentrating L-serine eluent in the step C) through the nanofiltration membrane under the conditions that the temperature is 25-35 DEG C, the pressure at the inlet is 0.4-0.8MPa and the pressure at the outlet is 0.1-0.3MPa; and getting an L-serine finished product after concentration. The synthetic method of the L-serine is simple in operation, short in production period, low in cost, high in yield and low in environmental protection pressure, and suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP JIAYUAN CHEM +1
Recombination methyl nourishment bacillus and application thereof
The present invention discloses one kind of recombinant methylotrophic bacillus and its application. The recombinant methylotrophic bacillus MB202 is obtained through inserting glyA into the polyclonal site of pLAFR3 to obtain recombinant vector pLAFRg, and the subsequent three parent crossbreeding to introduce pLAFRg into methylotrophic bacillus MB200 to obtain the recombinant methylotrophic bacillus MB202. Through shaking table culture of MB202 at 32 deg.c in 50mM Tris-HCl culture medium with glycine in 10 mg / ml, methanol in 50 mg / ml, and biomass of 10<8>-10<9> CFU / ml, in pH 8.5 for 48 hr, L-serine yield may reach 11.5mg / ml; and through fermentation culture of MB202 at 32 deg.c for 12 hr, the activity of serine hydroxymethlase may reach 115 U. The recombinant methylotrophic bacillus MB202 has broad application foreground in producing L-serine and treating methanol waste water.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
METHOD FOR PRODUCING MONOCLONAL IgA ANTIBODY
InactiveUS20160039944A1Improving and optimizing intestinal environmentSuppressing alternationAntibacterial agentsAnimal cellsMonoclonal IgAIntestinal microorganisms
The present invention provides a component having effects in vivo of improving or optimizing the intestinal environment, suppressing intestinal putrefaction, or suppressing alternation of intestinal bacterial growth and / or pathological changes of intestinal bacterial growth in gut microbiota. The invention also provides an active ingredient suitably used for treating intestinal diseases. The invention provides a monoclonal IgA antibody that binds to amino acids 11 to 333 of serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
Owner:CURED INC
SHMT Inhibitors
ActiveUS20180117010A1Low toxicityImmunological disordersAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
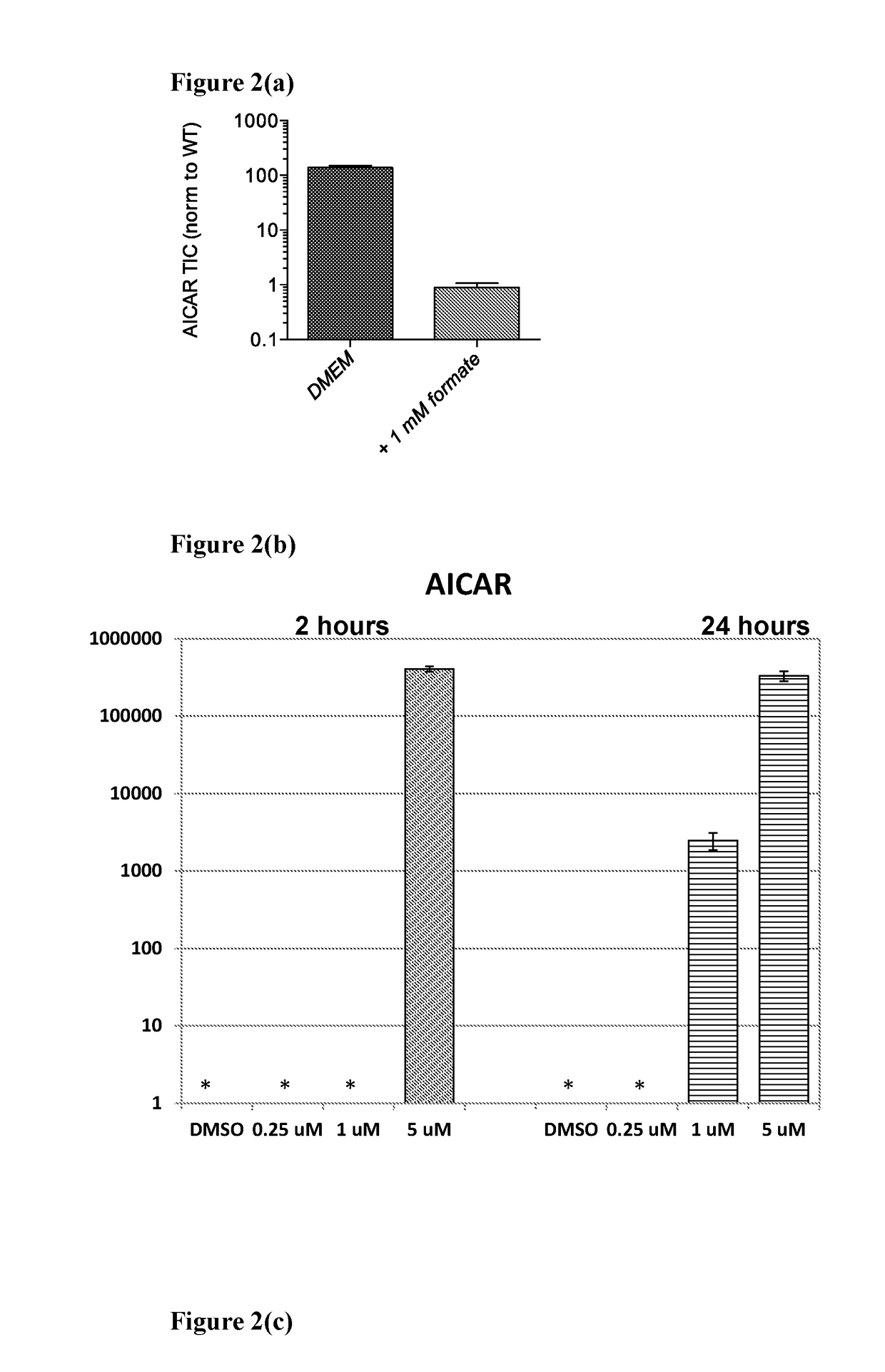
The present invention relates to a method for the treatment of cancer or an autoimmune disorder, comprising the administration of a serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) inhibitor, and in particular the administration of pyrazolopyran compounds of Formula (VI) as presently described, wherein the compounds are capable of inhibiting a mammalian SHMT, such as human SHMT1 and / or SHMT2. The treatment method further comprises the optional administration of an additional agent as a rescue therapy to reduce toxicity, wherein said agent may be chosen from formate, a formate salt, folinic acid, formate ester, or leucovorin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Biological method for improving yield of L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate by virtue of two-plasmid engineering bacteria
InactiveCN105861534AIncrease cumulativeIncrease profitTransferasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologySynthesis methods
The invention provides a biological synthesis method for increasing the accumulation of L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate, an L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate synthetase system co-expressed recombinant plasmid and a construction method and application thereof. The L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate synthetase system co-expressed recombinant plasmid comprises serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) gene GlyA and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene MetF sequences. The biological synthesis method for increasing the accumulation of the L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate comprises the following steps: converting for accumulating an original strain of the L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate to obtain a recombinant strain by virtue of the L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate synthetase system co-expressed recombinant plasmid, and fermenting the recombinant strain. The accumulation of the L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate in the recombinant strain in a final fermentation product is remarkably higher than that of the original strain, the utilization rate of the raw material is increased, and production cost and energy consumption are reduced.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase mutant and application thereof
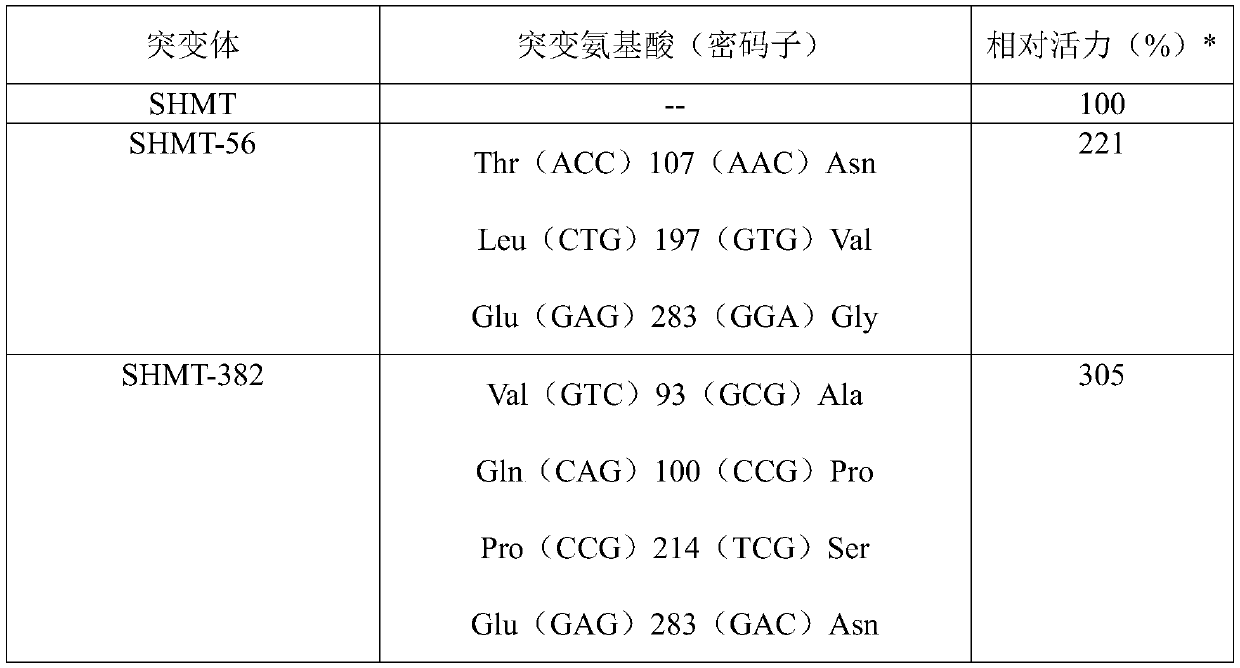
ActiveCN110872593AIncrease enzyme activityHas the prospect of industrial development and applicationBacteriaTransferasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferaseHydroxymethyl
The invention discloses a serine hydroxymethyltransferase mutant with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO: 3. Compared with wild serine hydroxymethyltransferase, the serine hydroxymethyltransferase mutant has the advantages that the enzyme activity of catalyzing glycine and formaldehyde to react to produce serine is improved, and the serine hydroxymethyltransferase mutant hasindustrial development and application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Nucleoside high-yielding strain as well as construction method and application thereof
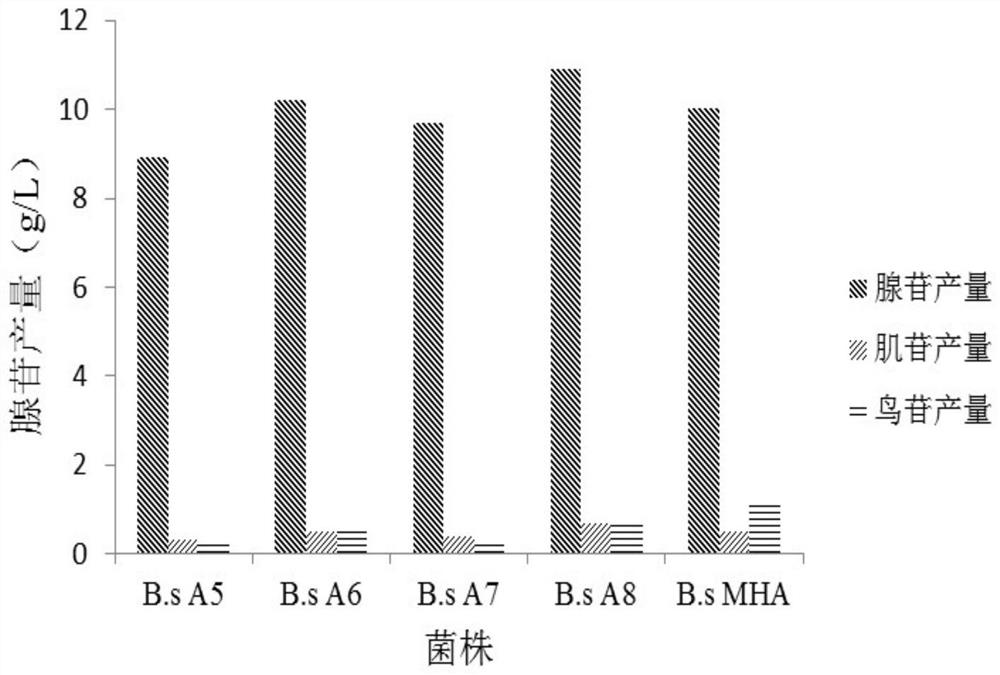
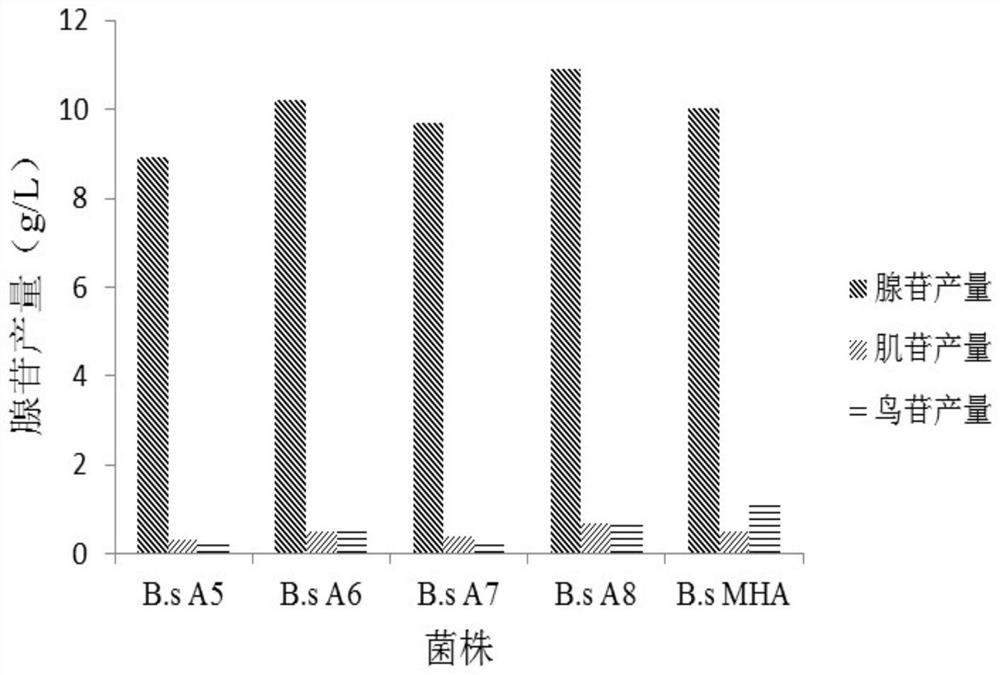
ActiveCN112126666AEfficient accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferaseBacilli
The invention provides a nucleoside high-yielding strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention also provides a method for producing nucleoside by fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of (1) enhancing a serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene glyA, as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, of bacillus subtilis; and / or (2) weakening a 2,3-diphosphoglyceric acid independent phosphoglyceric acid mutant enzyme gene pgm of a coded NCBI reference sequence WP_003228330.1 on a chromosome of the bacillus subtilis; and (3) applying the strain obtained in the step (1) and / or the step (2) to fermentation production of the nucleoside. The engineered strain bacillus subtilis provided by the invention is the nucleoside high-yielding strain, can effectively accumulate the nucleoside, improves the yield of the nucleoside, and lays a foundation for industrial production of the nucleoside.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Novel process
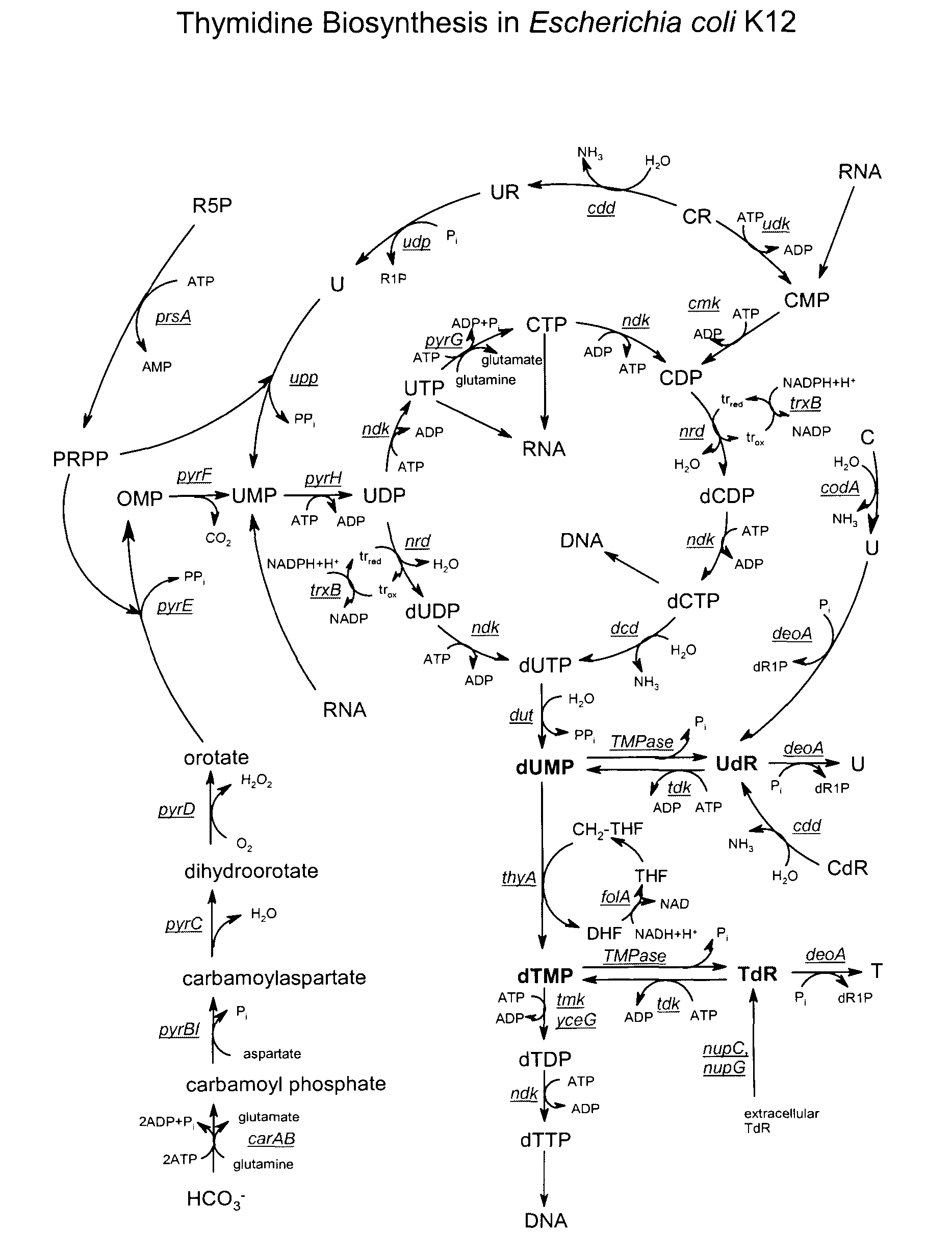
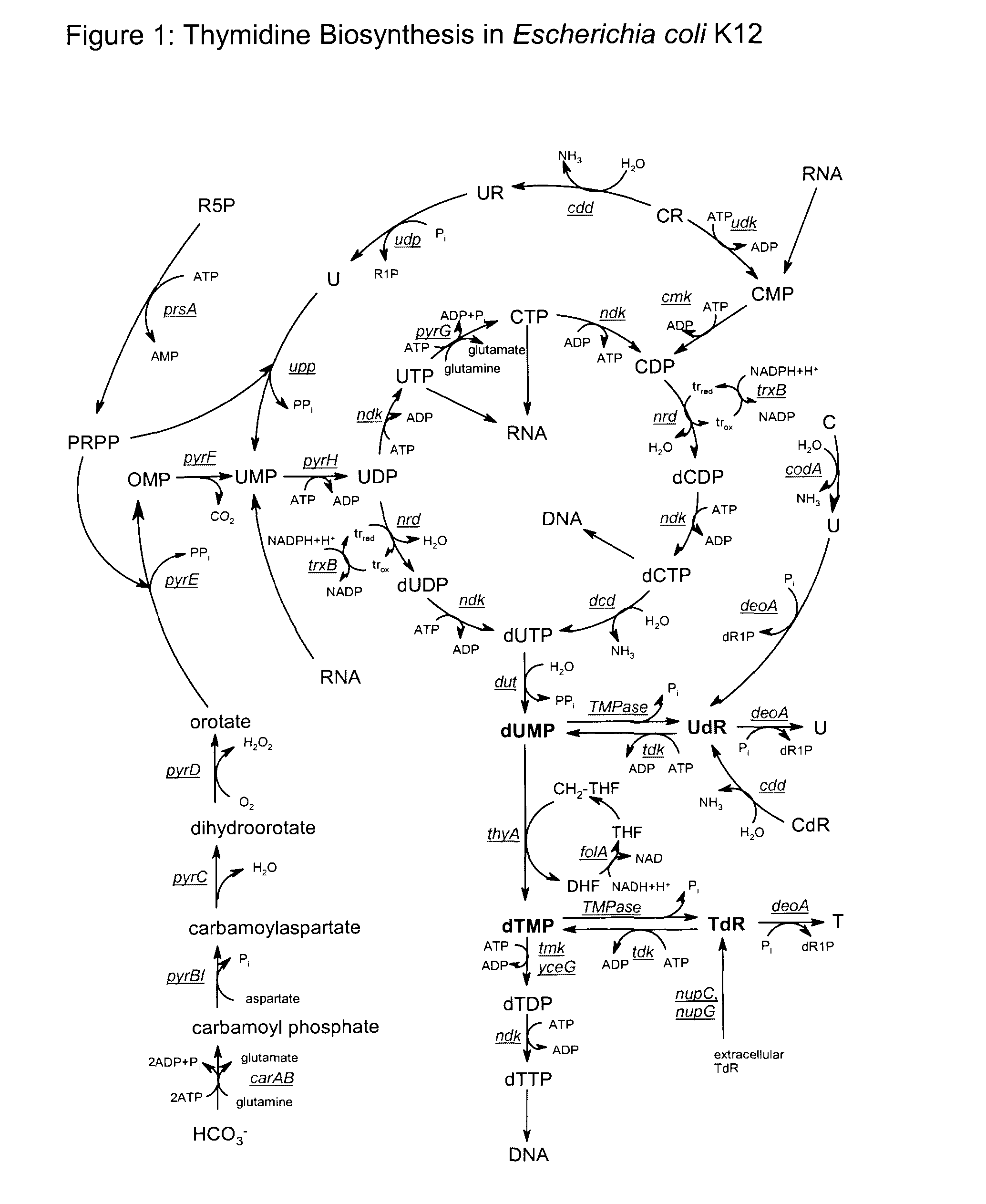
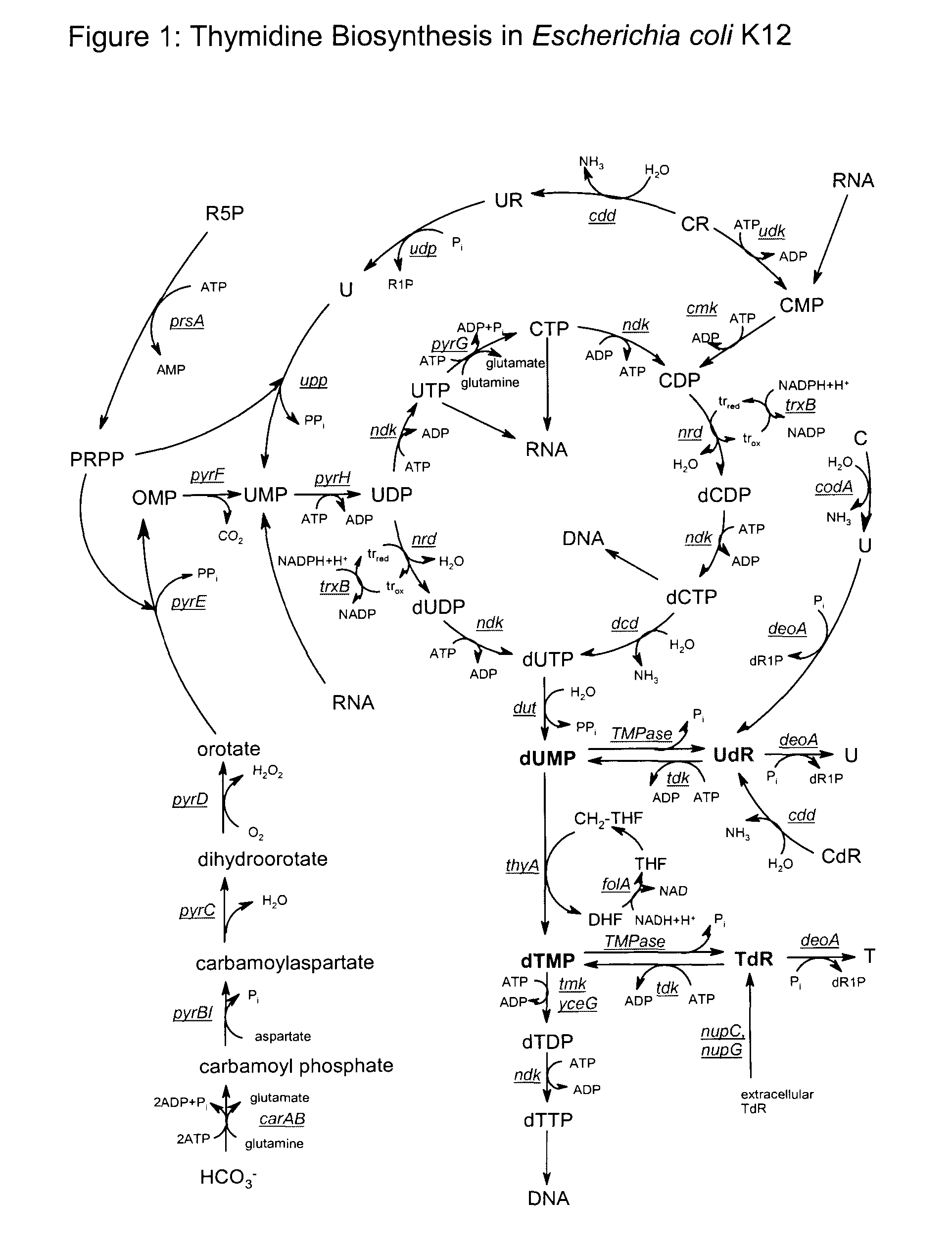
Novel organisms, including DNA construct host cell combinations, are disclosed. The organisms comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for enzymes which promote the supply of single carbon units for the conversion of dUMP to dTMP. Examples include: dihydrofolate reductase genes e.g. T4 frd; Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase genes e.g. glyA; 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase genes e.g. serA; and THF synthase genes e.g. ADE3. The organisms are used in a biological method of producing thymidine with significantly reduced levels of uridine.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
SHMT inhibitors
ActiveUS10646475B2Low toxicityImmunological disordersAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to a method for the treatment of cancer or an autoimmune disorder, comprising the administration of a serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) inhibitor, and in particular the administration of pyrazolopyran compounds of Formula (VI) as presently described, wherein the compounds are capable of inhibiting a mammalian SHMT, such as human SHMT1 and / or SHMT2. The treatment method further comprises the optional administration of an additional agent as a rescue therapy to reduce toxicity, wherein said agent may be chosen from formate, a formate salt, folinic acid, formate ester, or leucovorin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
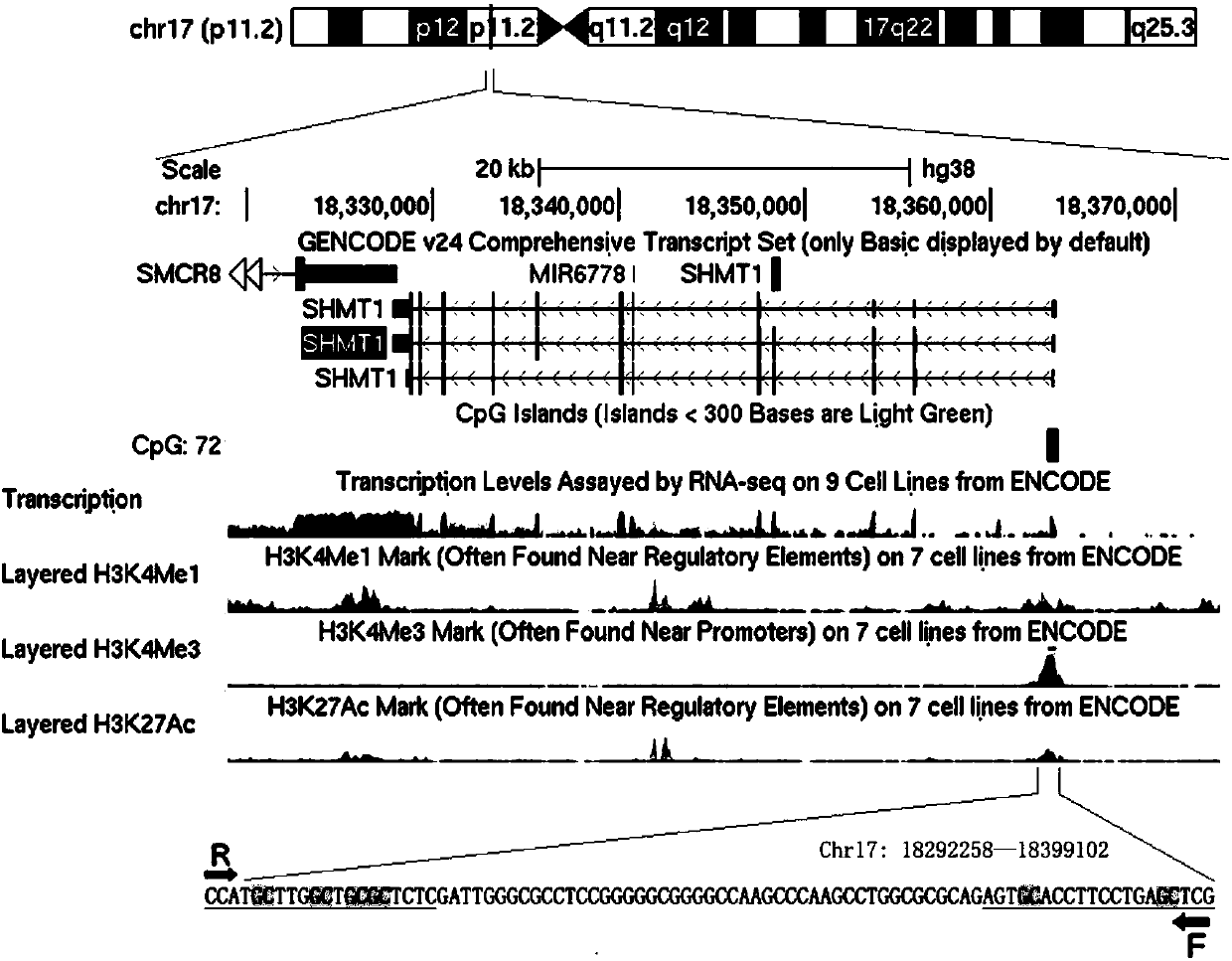
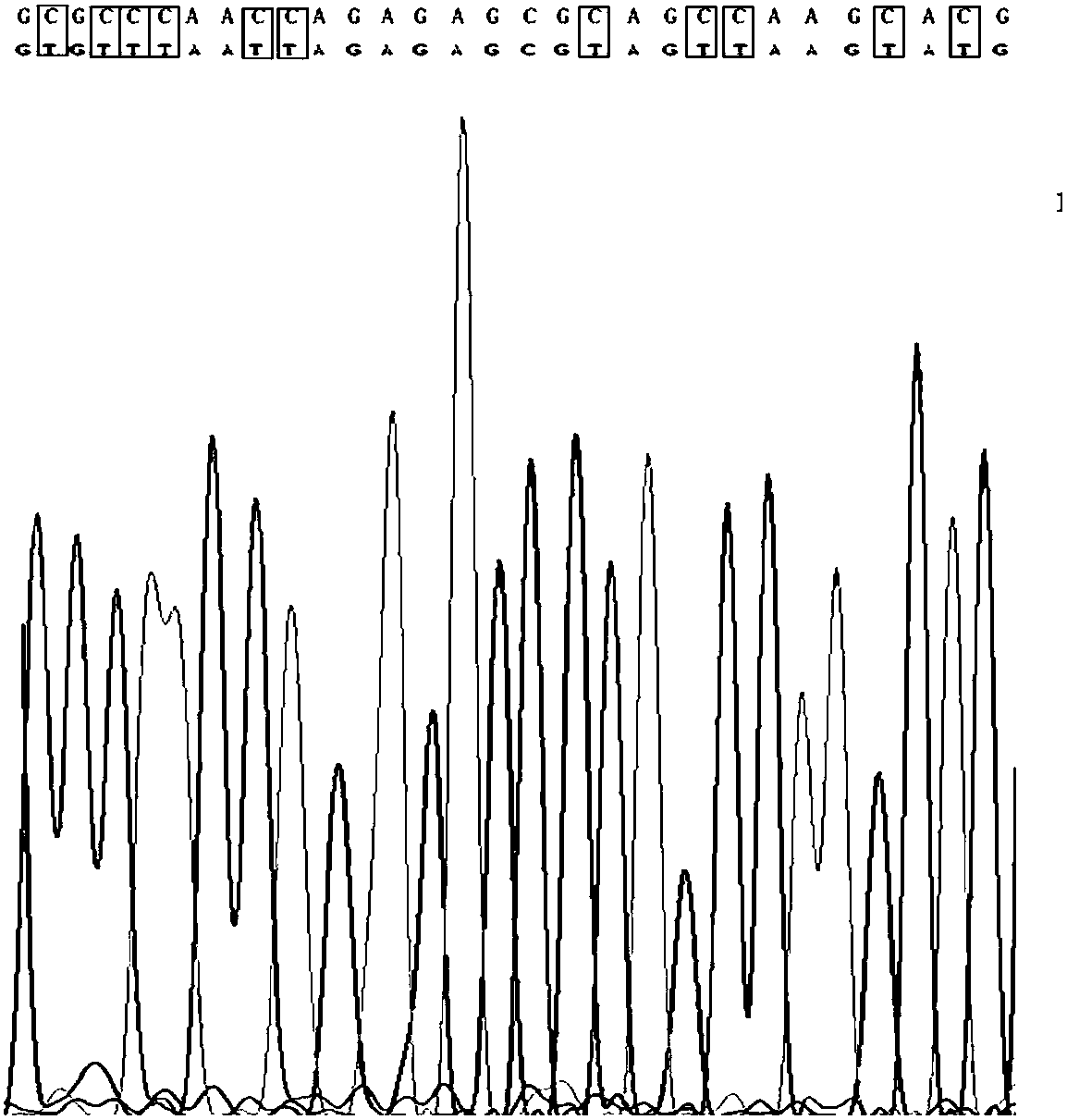
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene promoter region methylation degree detection kit and method
InactiveCN107841549AWith real-time monitoringStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlFluorescence
The invention discloses a serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene promoter region methylation degree detection kit. The detection kit comprises DNA extract, a fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction solution, a positive control, a negative control and a plurality of seal pipes with covers. The fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction solution comprises a pair of serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene promoter region methylation specific amplification primers shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses a method for detecting a serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene promoter region methylation degree. The kit utilizes a fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, has the advantages of real-time monitoring, strong specificity and accurate quantification and ensures the accuracy of the diagnosis result.
Owner:深圳市南山区慢性病防治院
Biological production of thymidine
Novel organisms, including DNA construct host cell combinations, are disclosed. The organisms comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for enzymes which promote the supply of single carbon units for the conversion of dUMP to dTMP. Examples include: dihydrofolate reductase genes e.g. T4 frd; Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase genes e.g. glyA; 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase genes e.g. serA; and THF synthase genes e.g. ADE3. The organisms are used in a biological method of producing thymidine with significantly reduced levels of uridine.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
A method based on enzymatic modification to improve the dyeing performance of silk fibers
ActiveCN109281209BHigh electronegativityImprove dyeing effectDyeing processPolymer sciencePhosphorylation
The invention discloses a method for improving dyeing performance of a real silk fabric based on enzymatic modification; serine hydroxymethyltransferase is used for catalyzing glycine in protein fibermacromolecules to be converted into serine, the number of the serine in real silk fiber is increased, phosphorylation of the serine and threonine residues in the real silk fiber is catalyzed by protein kinase A, the cationic dye binding effect is enhanced, and the dyeing performance of the real silk fabric is improved. The method specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymaticconversion of amino acids in real silk; and (2) catalyzing the phosphorylation by the protein kinase A. Compared with the modification and improvement of the electronegativity of the surface of the real silk fiber by applying a chemical method, the method has the advantages of being high in enzyme catalysis efficiency, mild in reaction conditions and obvious in dyeing performance improvement.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Silk antibacterial finishing method based on enzyme-catalyzed conversion and grafting
ActiveCN109267357AIncrease the number ofIncrease the amount of graftingBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsAnimal fibresCross-linkCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a silk antibacterial finishing method based on enzyme-catalyzed conversion and grafting. Glycine in protein fiber macromolecules is catalyzed by utilizing serine hydroxymethyltransferase to be converted into serine, the number of serine in silk fibers can be increased, then the serine in the silk fibers is catalytically oxidized by utilizing laccase and a 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl pyridine-nitrogen-oxide (TEMPO) system to generate an aldehyde group, the aldehyde group is cross-linked with polylysine to perform the silk antibacterial finishing treatment. The silk antibacterial finishing method comprises the following steps: (1) enzymatically converting amino acid in silk; and (2) catalytically oxidizing silk grafted polylysine by virtue of laccase-TEMPO. Compared with thetraditional chemical cross-linking method antibacterial finishing treatment, the silk treated in the method of the invention has good antibacterial performance, mild enzyme treatment condition, and higher physical and mechanical properties compared with an un-treated sample.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method and system for treating cancer
PendingUS20210077462A1Organic active ingredientsDisease diagnosisCancer cellFOLYLPOLYGLUTAMATE SYNTHETASE
The invention provides a method for treating cancer in which a level of reduced folate carrier (RFC) or folylpolyglutamate synthetase (FPGS) in cancer cells of the biopsy is determined. If the level of RFC or FPGS in the cancer cells is below a threshold value, the cancer is treated with an inhibitor of serine-hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT)1. If the level of RFC or FPGS in the cancer cells is above the threshold value, the cancer is treated with an inhibitor of SHMT2
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
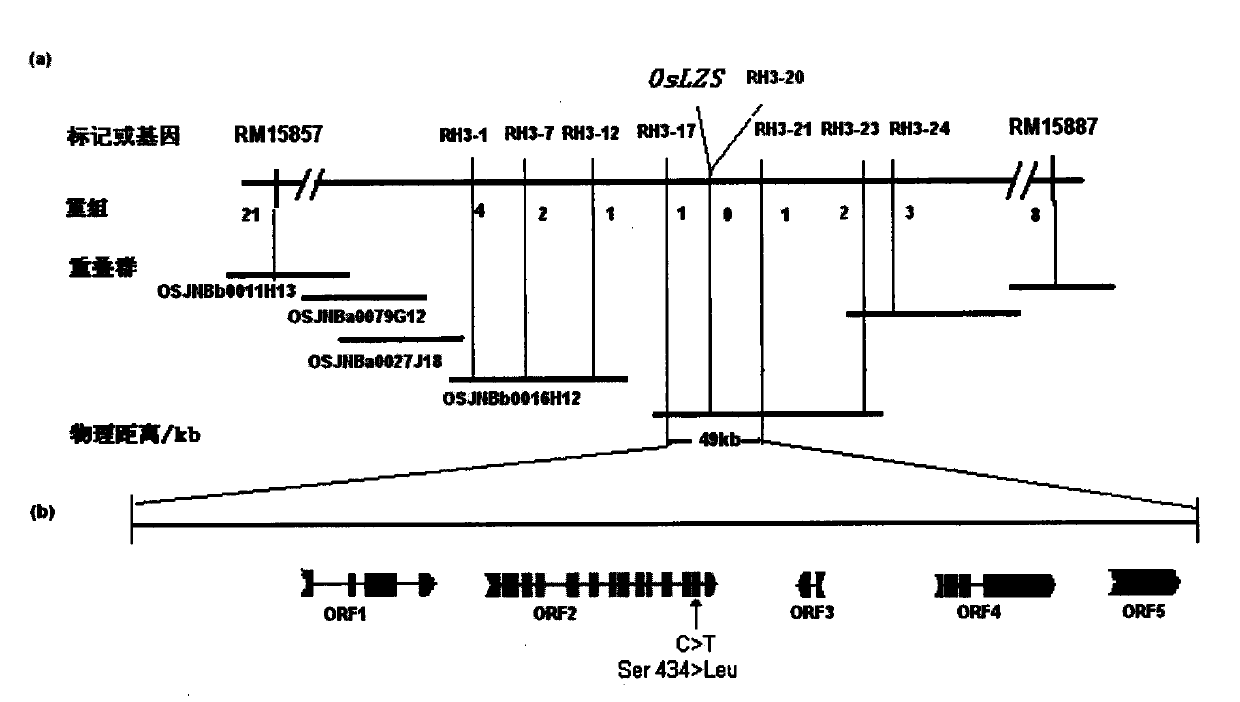
Rice serine hydroxymethyl transferase protein and function of coding gene thereof
The invention relates to a rice serine hydroxymethyl transferase protein and a function of a coding gene thereof, wherein the protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and the gene for coding the protein has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a plasmid containing the gene, a plant expression vector and a host cell. The invention also discloses a lethal method for the seedling stage of cultivars. The plant expression vector is used for converting plant cells, and the converted plant cells are cultured into plants. In the invention, the site of a new gene cloned in a mottle leaf lethal mutant in the seedling stage can be mutated to obtain a seedling-stage lethal phenotype. The invention has broad application prospects in hybrid seed production and purification as well as seed intellectual property protection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating cancer
PendingUS20210213020A1Reduced activityPoor pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLPOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSerine hydroxymethyltransferaseHigh dosage
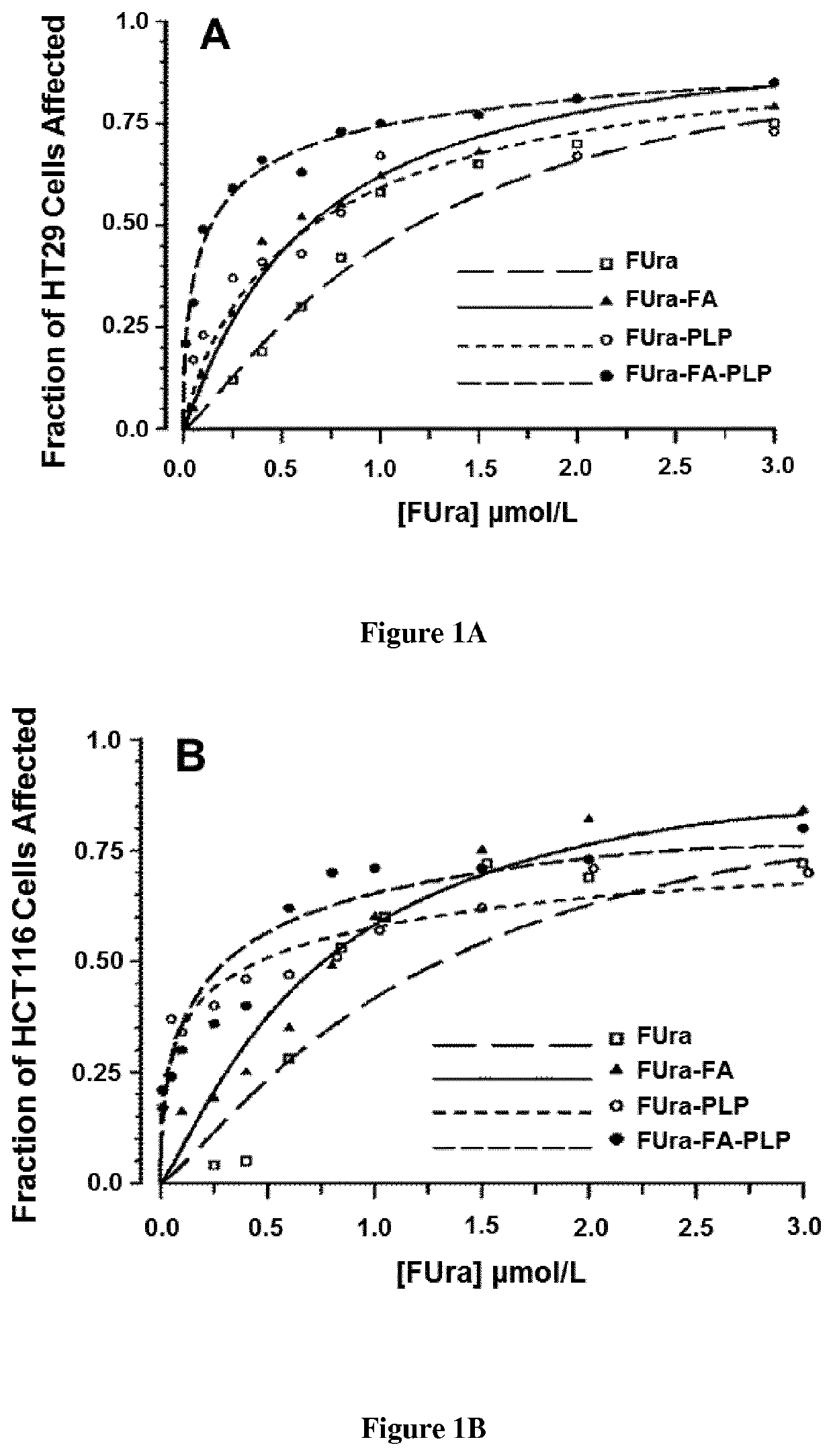
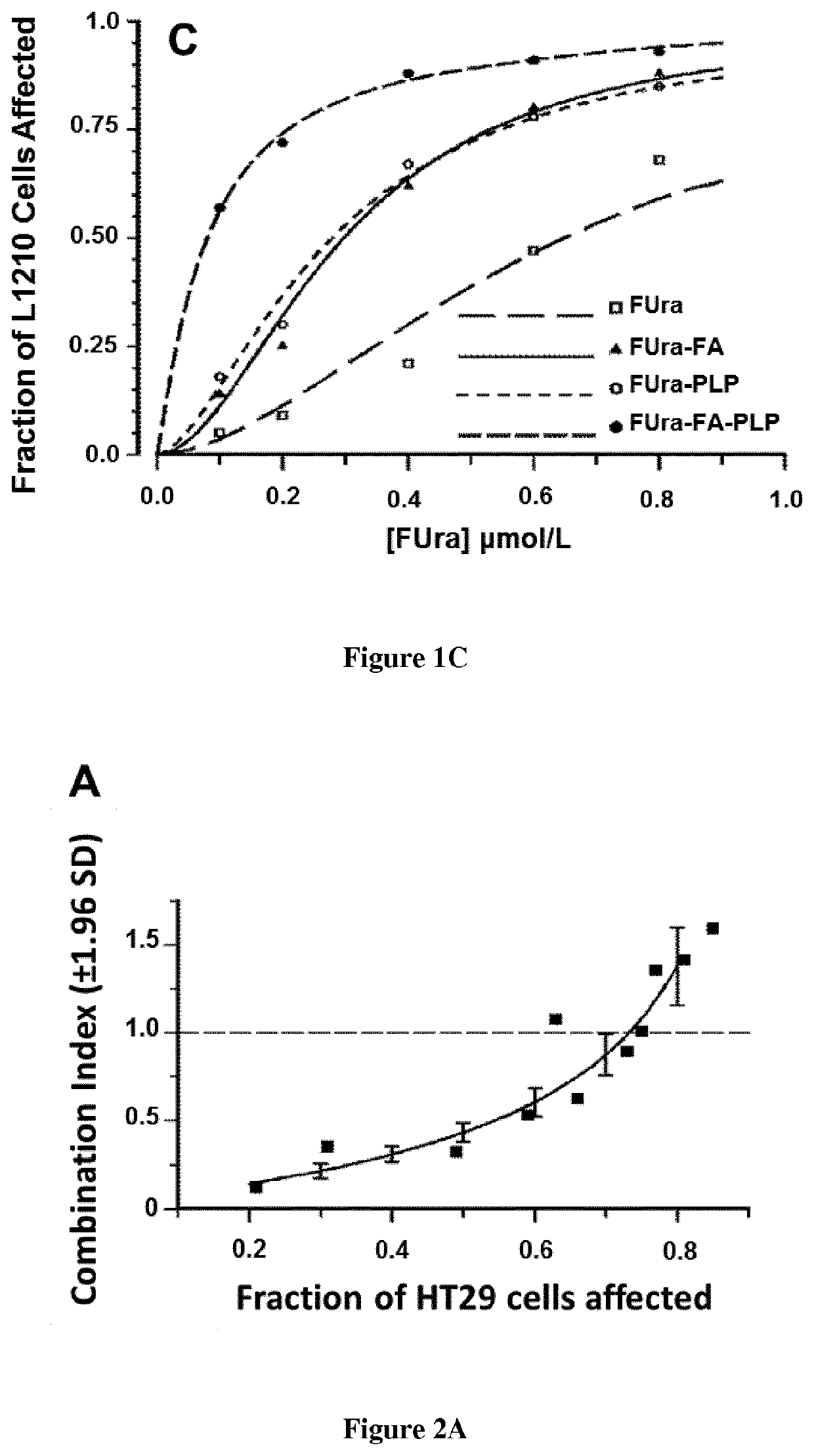
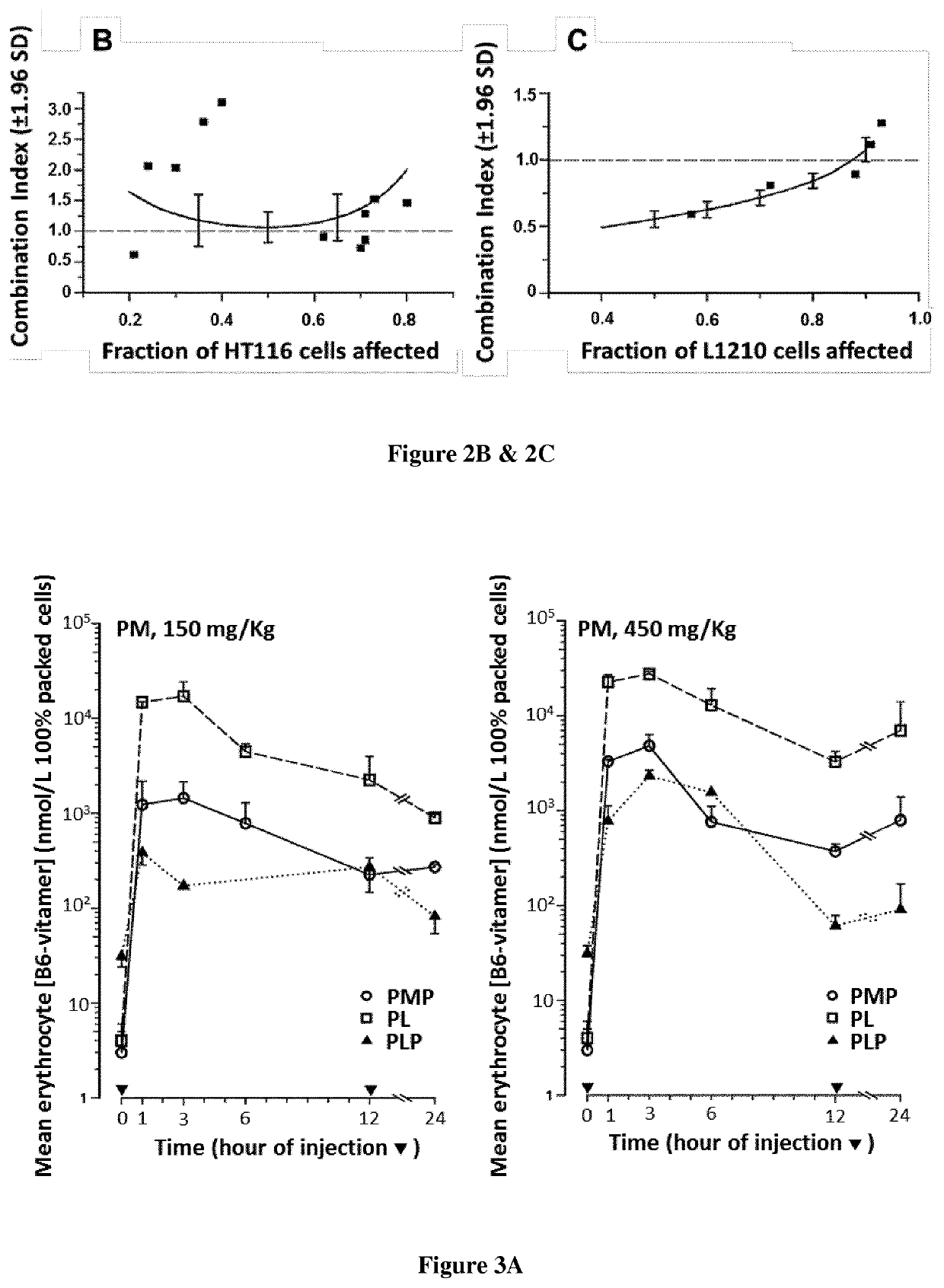
Disclosed are methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating cancer. It was hypothesized that low activity of serine hydroxymethyl transferase (SHMT) due to poor pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) availability within cancer cells would result in insufficient growth inhibition in cancer cells exposed to 5-fluorouracil (FUra), as well as to FUra in combination with N5-formyl tetra hydro pteroylglutamate (5-HCO—H4PteGlu; folinic acid). Cancer cell lines were exposed to FUra as a single agent and to FUra with folinic acid, in combination with high concentration PLP. There was demonstrated synergistic and additive interactions upon cytotoxicity of FUra by folinic acid and PLP combined in HT29, HCT116, and L1210 cancer cells. Murine studies of parenteral administration of pyridoxamine or pyridoxine in high doses showed that intracellular PLP is augmented to levels close or greater than the Kd reported for binding of cofactor to SHMT, suggesting modulation of the fluoropyrimidines by vitamin B6 was possible.
Owner:INSERM INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHIRCHE MEDICALE +2
Inhibition of the glycine cleavage system for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS9493775B2Organic active ingredientsCompound screeningAbnormal tissue growthGlycine cleavage system
In some aspects, methods of inhibiting survival or proliferation of a tumor cell are provided, the methods comprising inhibiting the glycine cleavage system (GCS) of the tumor cell. In some aspects, methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a tumor, the method comprising inhibiting the GCS in the tumor. In some embodiments, the methods comprise contacting a tumor cell or tumor with a GCS inhibitor. In some embodiments, the tumor cell or tumor has elevated expression of serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SH1VIT2). In some aspects, methods of identifying a tumor cell or tumor that is sensitive to inhibiting the GCS are provided, the methods comprising determining whether the tumor cell or tumor overexpresses SHMT2. In some aspects, methods of identifying a candidate anti-cancer agent are provided, the methods comprising identifying or modifying a GCS inhibitor.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Artemisia annua absorbing formaldehyde and its cultivation method
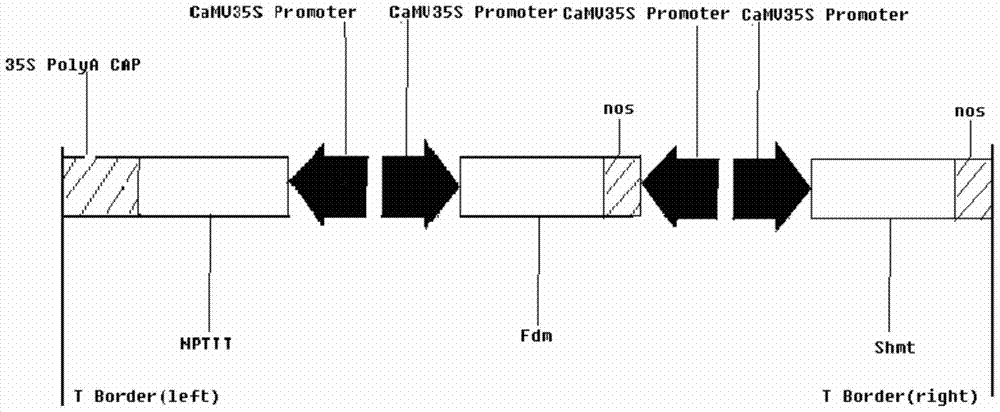
InactiveCN104531759BTall plantIncrease contentFermentationGenetic engineeringSerine hydroxymethyltransferaseGenetic engineering
The invention provides artemisia apiacea absorbing formaldehyde and a cultivation method of the artemisia apiacea. The artemisia apiacea absorbing formaldehyde contains a Shmt gene and an Fdm gene. The sequence of the Shmt gene is SEQ ID NO: 1 and the sequence of the Fdm gene is SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the invention, a serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene Shmt of pseudomonas putida and the Fdm gene of a formaldehyde dismutase gene are cloned and converted into artemisia apiacea so as to improve synthesis of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and formaldehyde dismutase in artemisia apiacea, so that a genetic engineering artemisia apiacea variety with high content of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and formaldehyde dismutase is obtained, thereby greatly improving the capacity of artemisia apiacea absorbing formaldehyde. Therefore, the artemisia apiacea becomes a plant of eliminating formaldehyde released in home decoration.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL & PHARMA COLLEGE
Nucleoside high-yielding bacteria and its construction method and application
ActiveCN112126666BEfficient accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesMicrobiologyPhosphoglycerate mutase
The invention provides nucleoside high-yielding bacteria and its construction method and application. The present invention also provides a method for fermentatively producing nucleosides, comprising: (1) enhancing the serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene glyA of Bacillus subtilis as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; and / or (2) weakening the Bacillus subtilis chromosome 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase gene pgm encoding NCBI reference sequence WP_003228330.1; and (3) using the strain obtained in step (1) and / or step (2) for nucleoside fermentation production. The bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a high-yield nucleoside strain, which can effectively accumulate nucleosides, increase the yield of nucleosides, and lay a foundation for the industrial production of nucleosides.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Double expression application of Arabidopis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene and formate dehydrogenase gene
ActiveCN104774866AIncrease absorption rateIncrease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGeneticsSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
The invention discloses a double expression application of Arabidopis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene and formate dehydrogenase gene. The cDNA of Arabidopis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT gene is used to construct a plant expression vector, the plant expression vector constructed by the cDNA of Arabidopis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT gene is transferred to tobacco through Agrobacterium mediation, and a plant expression vector constructed by the cDNA of Arabidopis thaliana formate dehydrogenase FDH gene is transferred to the tobacco through Agrobacterium mediation after detection correctness to obtain two exogenous genes SHMT / FDH inserted double expression transgenic tobacco capable of improving the formaldehyde absorption and tolerance ability of plants. Experiment results show that the double expression transgenic tobacco can change the content of chlorophyll and soluble sugar in tobacco to effectively reduce the toxicity of HCHO to plants in order to make the transgenic tobacco leaf maintain good HCHO absorption ability under the stress of high concentration HCHO; and the double expression transgenic tobacco can effectively reduce the oxidation stress and has a substantially better oxidation stress reduction effect than single expression transgenic tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing monoclonal IgA antibody
Owner:CURED INC
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-methionine at high yield as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112779200AIncrease productionStrengthen internal transportationBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliLarge intestine
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Yield Increase in Plants Overexpressing the SHSRP Genes
InactiveUS20100162434A1Increased root growthIncrease productionSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyIncreased tolerance
A transgenic crop plant transformed by a Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase-Like Stress-Related Polypeptide (SHSRP) coding nucleic acid, wherein expression of the nucleic acid sequence in the crop plant results in the plant's increased root growth, and / or increased yield, and / or increased tolerance to environmental stress as compared to a wild type variety of the plant Also provided are agricultural products, including seeds, produced by the transgenic crop plants. Also provided are isolated novel SHSRPs, and isolated novel nucleic acids encoding SHSRPs, and vectors and transgenic plant containing the same.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method for improving dyeing performance of real silk fiber based on enzymatic modification
The invention discloses a method for improving dyeing performance of a real silk fabric based on enzymatic modification; serine hydroxymethyltransferase is used for catalyzing glycine in protein fibermacromolecules to be converted into serine, the number of the serine in real silk fiber is increased, phosphorylation of the serine and threonine residues in the real silk fiber is catalyzed by protein kinase A, the cationic dye binding effect is enhanced, and the dyeing performance of the real silk fabric is improved. The method specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymaticconversion of amino acids in real silk; and (2) catalyzing the phosphorylation by the protein kinase A. Compared with the modification and improvement of the electronegativity of the surface of the real silk fiber by applying a chemical method, the method has the advantages of being high in enzyme catalysis efficiency, mild in reaction conditions and obvious in dyeing performance improvement.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
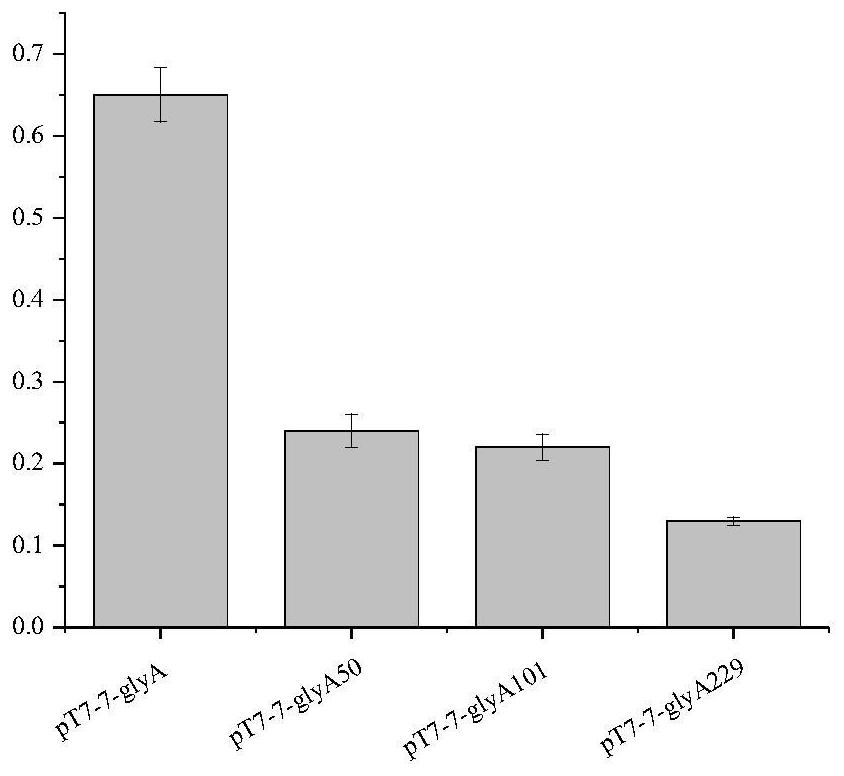
A kind of mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and use thereof
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and use thereof. The present invention provides a mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase. The amino acid sequence of the mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase is relative to the amino acid sequence of wild-type serine hydroxymethyltransferase. The amino acid residue at position 229, or the amino acid residue at position 229, is replaced by other amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence of the wild-type serine hydroxymethyltransferase includes the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.24. The mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and related genetic engineering bacteria provided by the invention can effectively improve the ability of Escherichia coli to produce L-serine.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A method for screening folic acid metabolism related drug
ActiveCN109207551ALittle side effectsEffectiveComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementStable Isotope LabelingSide effect
The invention discloses a method for screening a folic acid metabolism related drug. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a cell line with stable physiological state and a compound tobe detected at different concentrations respectively, wherein the cell line has a serine hydroxymethyltransferase expression function; (2) adding stable isotope labeled serine and incubating until thereaction is complete; 3, obtaining the supernatant of the cell culture solution and detecting the content of glycine label by the stable isotope; (4) judging the activity of the compound to be detected by using the glycine content and the corresponding concentration of the compound to be detected. The screening success rate of the detection method is high, and the screened compounds have strongerefficacy and less side effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEMPARTNER CO LTD
Reconstructed butyric acid bacillus methylophilus for synergistically assimilating methanol by utilizing WLP (White Like Prescription) pathway and reducing glycine pathway and application of reconstructed butyric acid bacillus methylophilus
PendingCN114480239AAchieving assimilative efficiencyIncreased assimilation efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
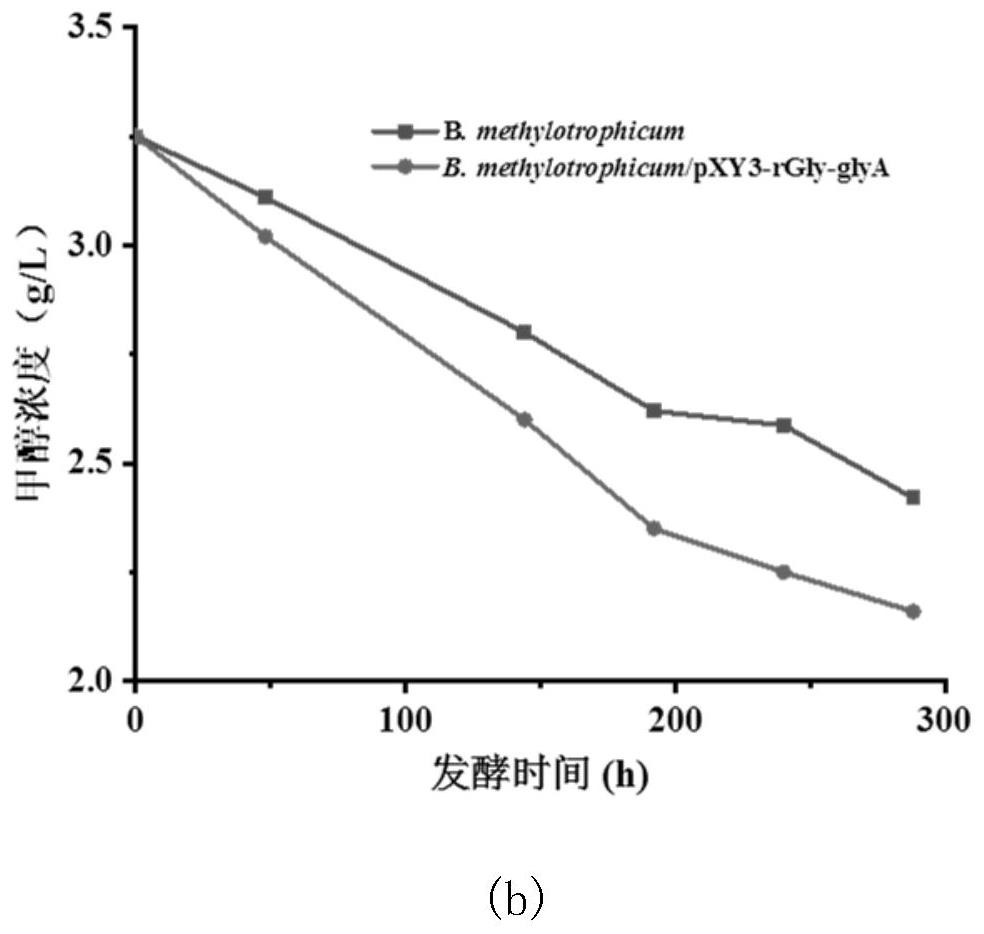
The invention relates to reconstructed butyric acid bacillus methylophilus for assimilating methanol by utilizing a WLP (White Like Prescription) pathway and a reductive glycine pathway and application thereof. The step of reconstructing the methyl butyric acid bacillus comprises assimilating methanol through a natural WLP way; gene introduced into the reconstructed butyric acid methyl bacillus comprises glycine splitting system aminomethyltransferase (GcvT), glycine splitting system H protein (GcvH), glycine decarboxylase (GcvP) and over-expression endogenous serine hydroxymethyltransferase (glyA) which are derived from escherichia coli. Fermentation verification shows that compared with an original strain, the reconstructed bacillus methylophilus has the advantages that the maximum biomass is increased by 55.26%, the methanol assimilation amount is increased by 34.47%, fermentation conditions for fermentation production and synthesis of butyric acid by the reconstructed strain are optimized, the final maximum biomass is increased by 55.26%, the methanol assimilation amount is increased by 57.14%, and the butyric acid synthesis amount is increased by 77.78%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
An Antibacterial Finishing Method of Silk Based on Enzymatic Conversion and Grafting
ActiveCN109267357BIncrease the number ofIncrease the amount of graftingBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsAnimal fibresPolymer scienceSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
The invention discloses a silk antibacterial finishing method based on enzyme-catalyzed conversion and grafting. Glycine in protein fiber macromolecules is catalyzed by utilizing serine hydroxymethyltransferase to be converted into serine, the number of serine in silk fibers can be increased, then the serine in the silk fibers is catalytically oxidized by utilizing laccase and a 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl pyridine-nitrogen-oxide (TEMPO) system to generate an aldehyde group, the aldehyde group is cross-linked with polylysine to perform the silk antibacterial finishing treatment. The silk antibacterial finishing method comprises the following steps: (1) enzymatically converting amino acid in silk; and (2) catalytically oxidizing silk grafted polylysine by virtue of laccase-TEMPO. Compared with thetraditional chemical cross-linking method antibacterial finishing treatment, the silk treated in the method of the invention has good antibacterial performance, mild enzyme treatment condition, and higher physical and mechanical properties compared with an un-treated sample.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com