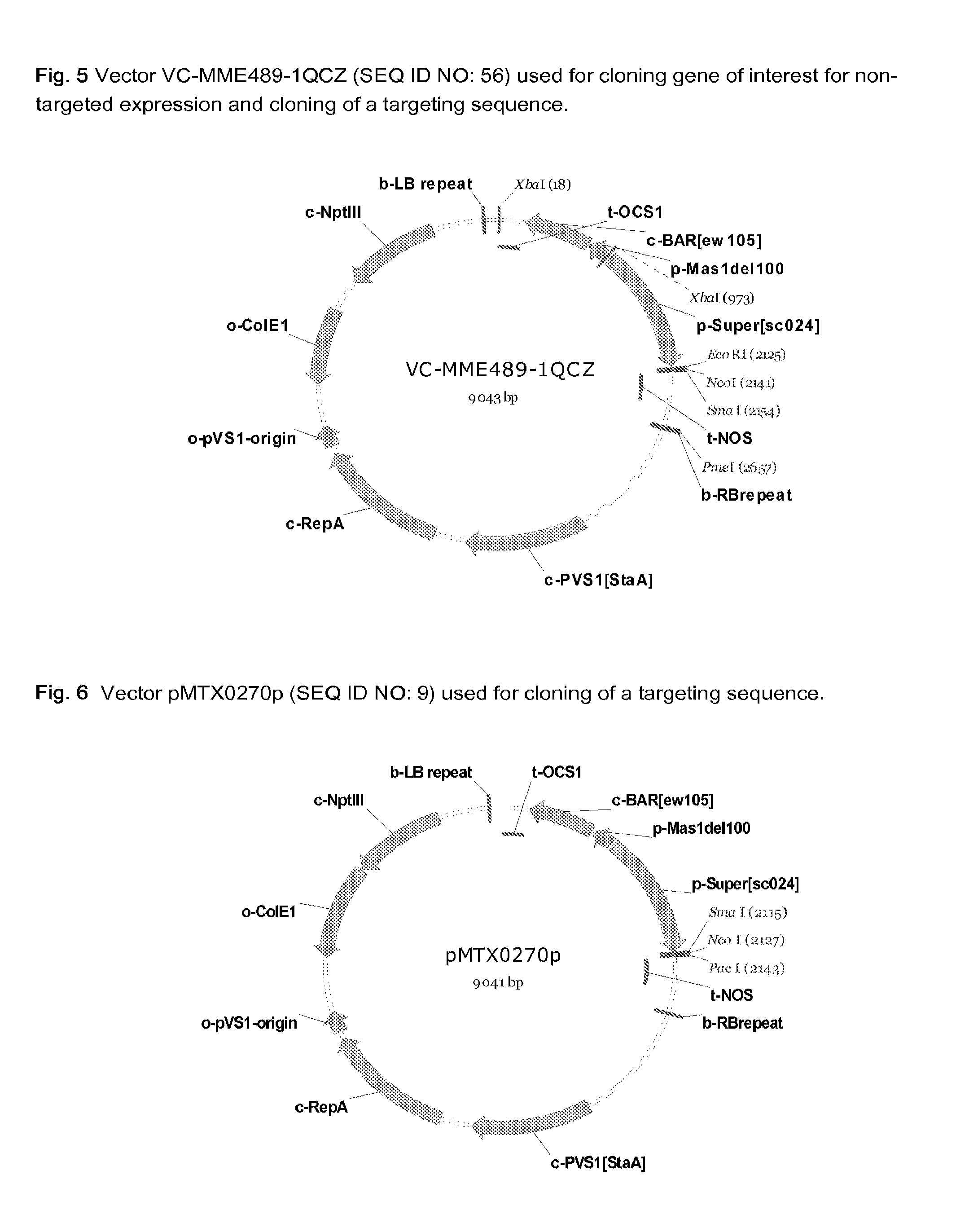
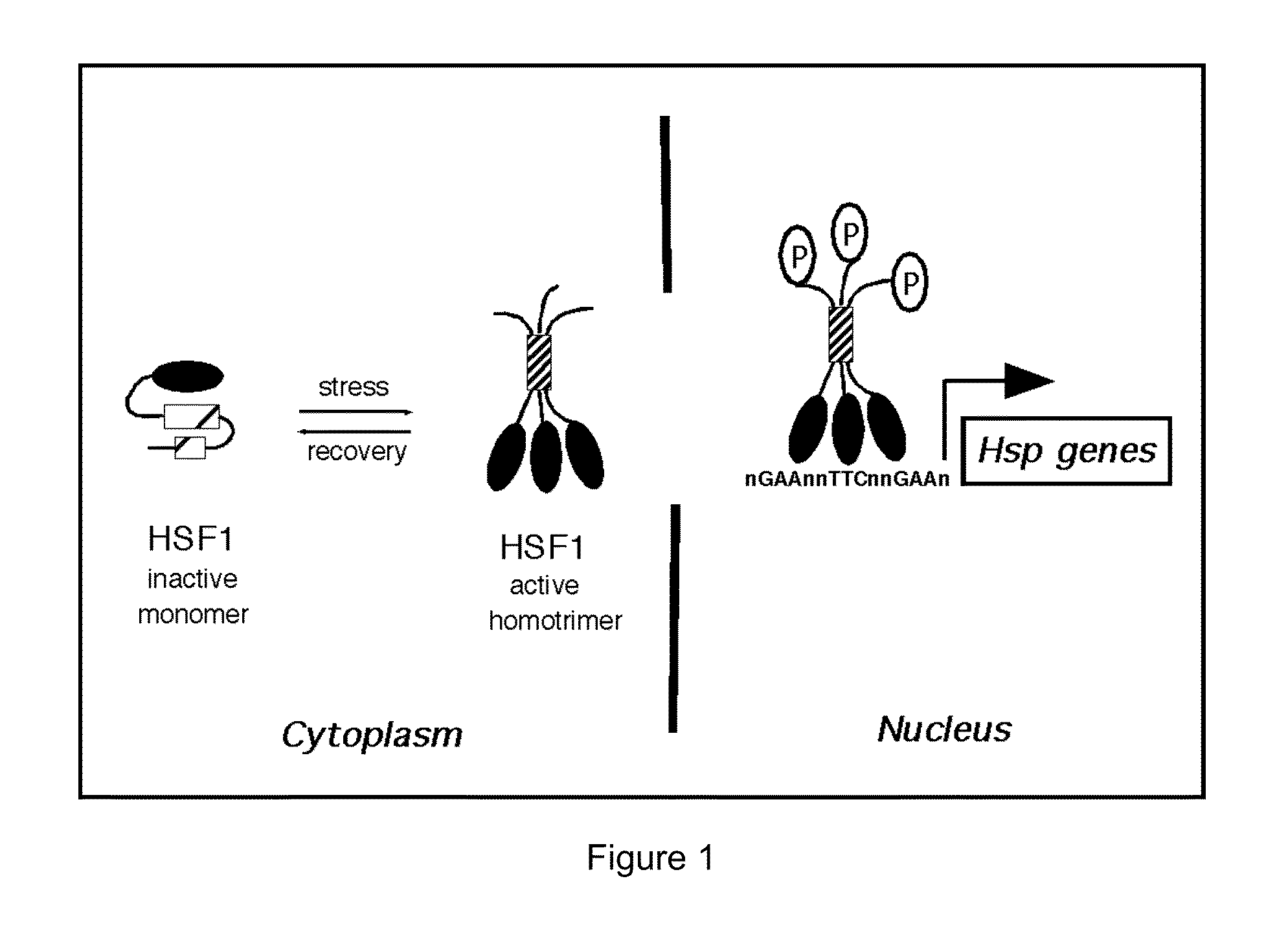
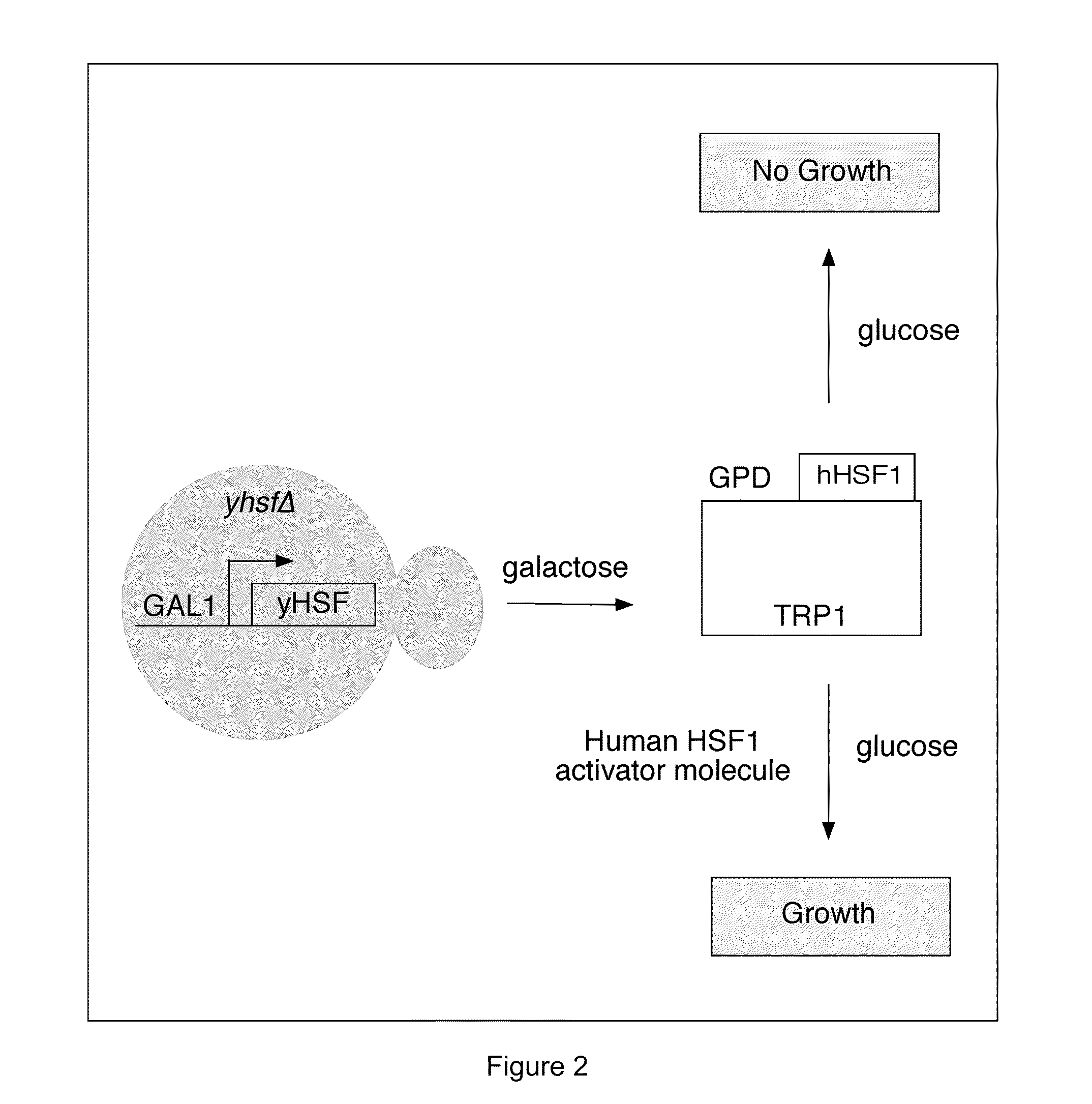
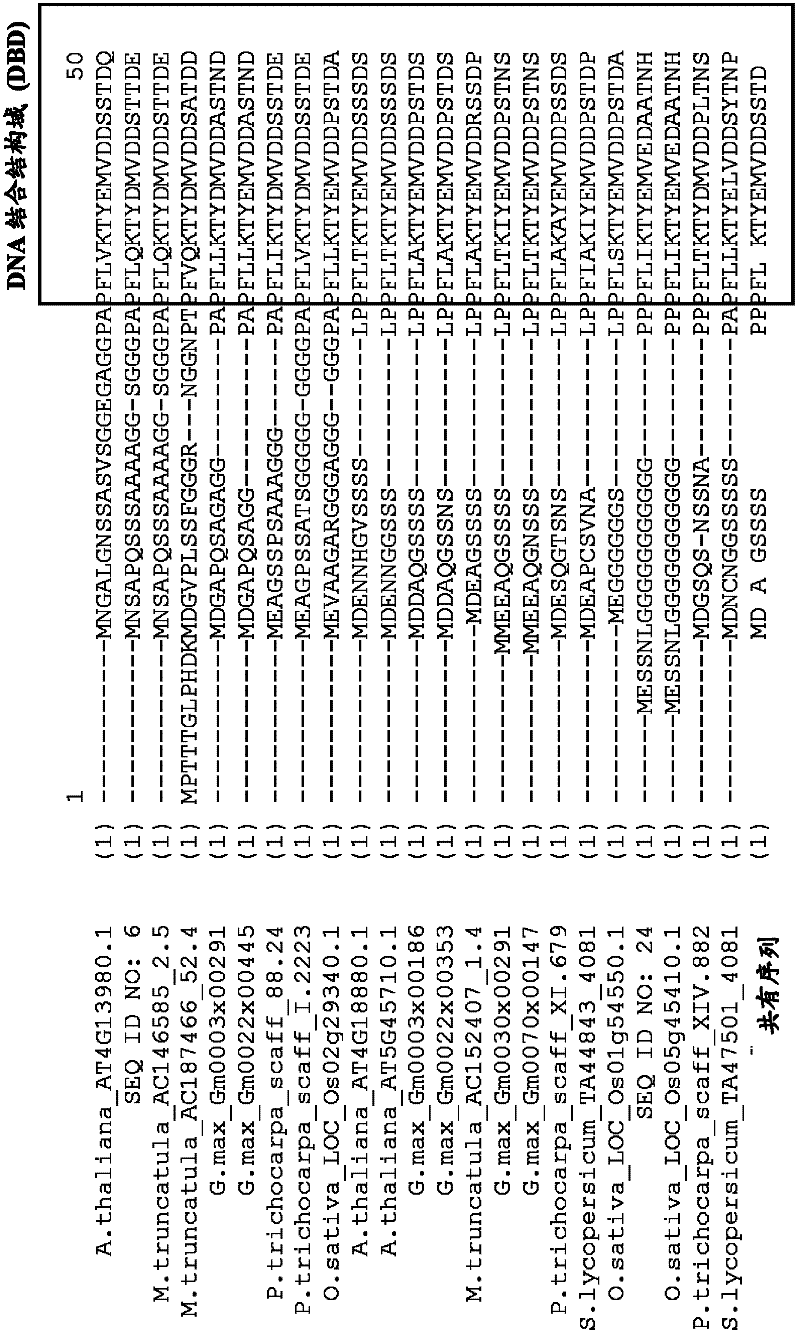
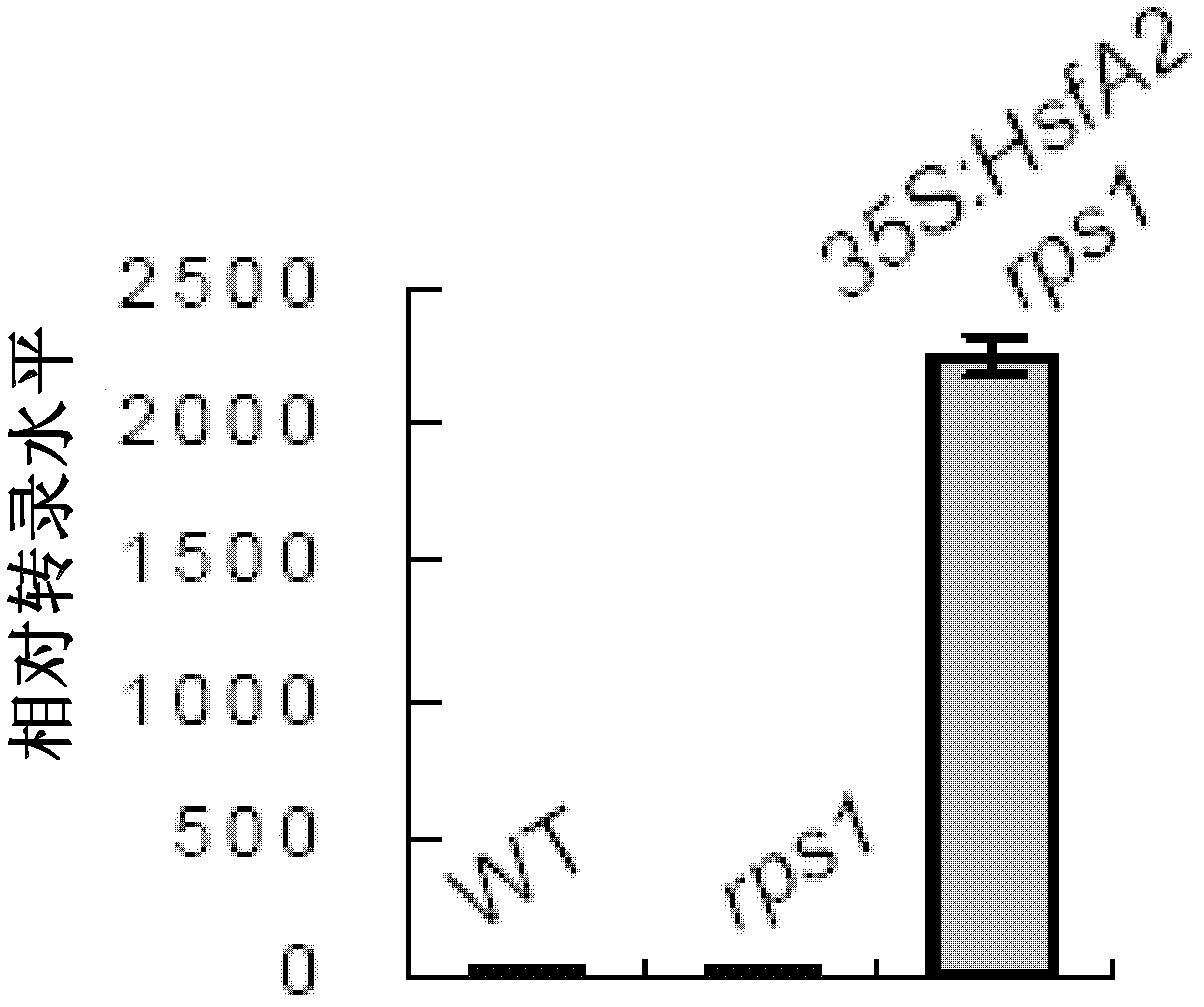
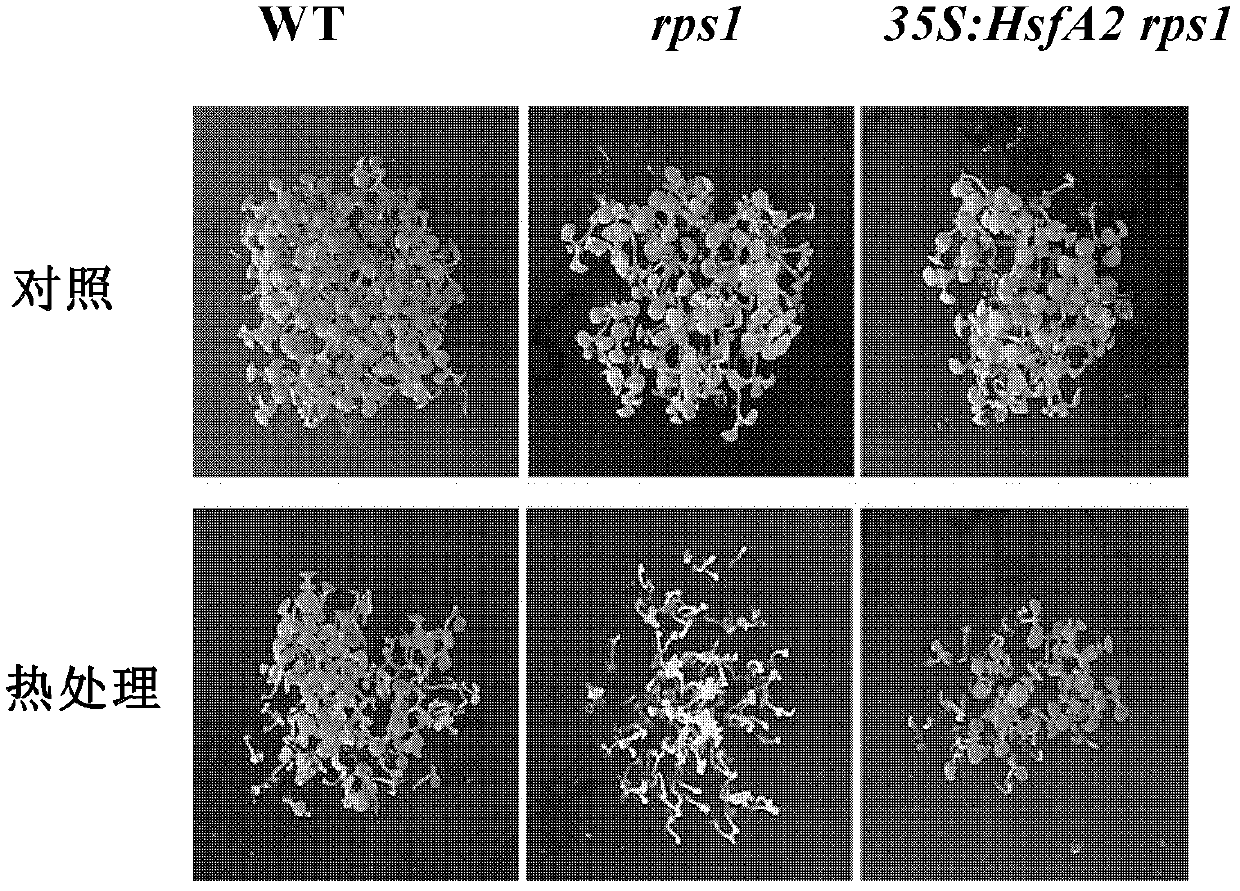
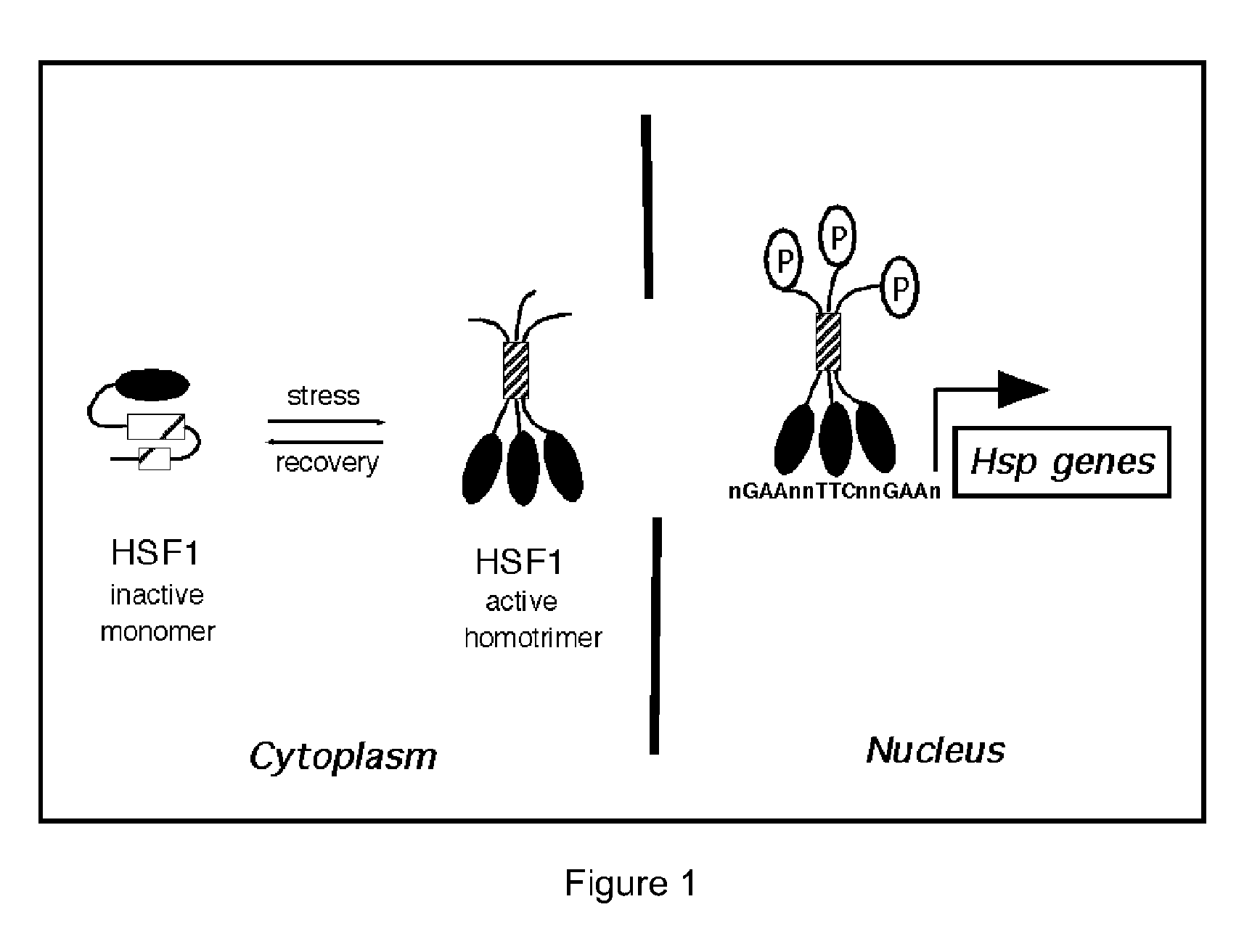
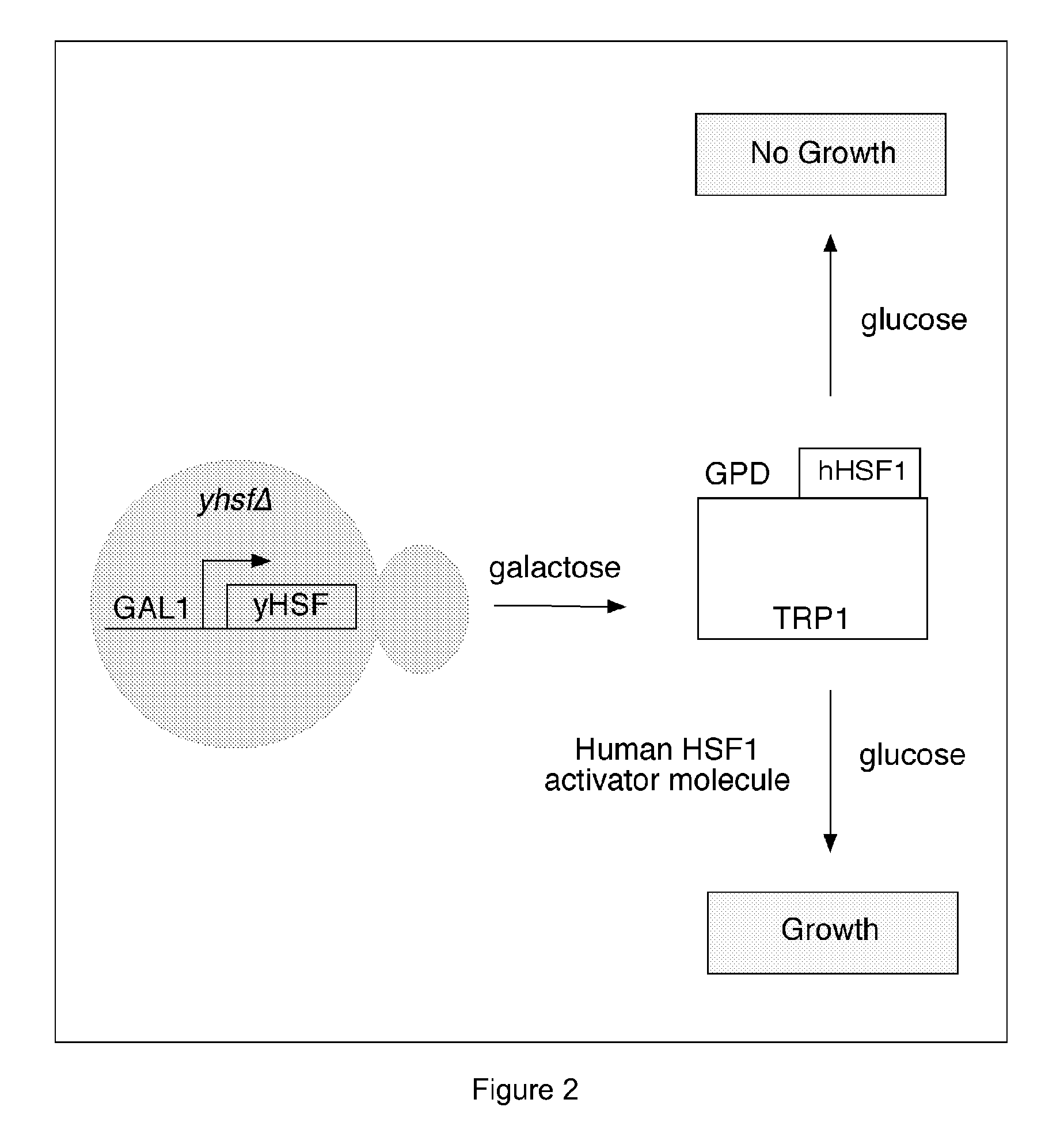
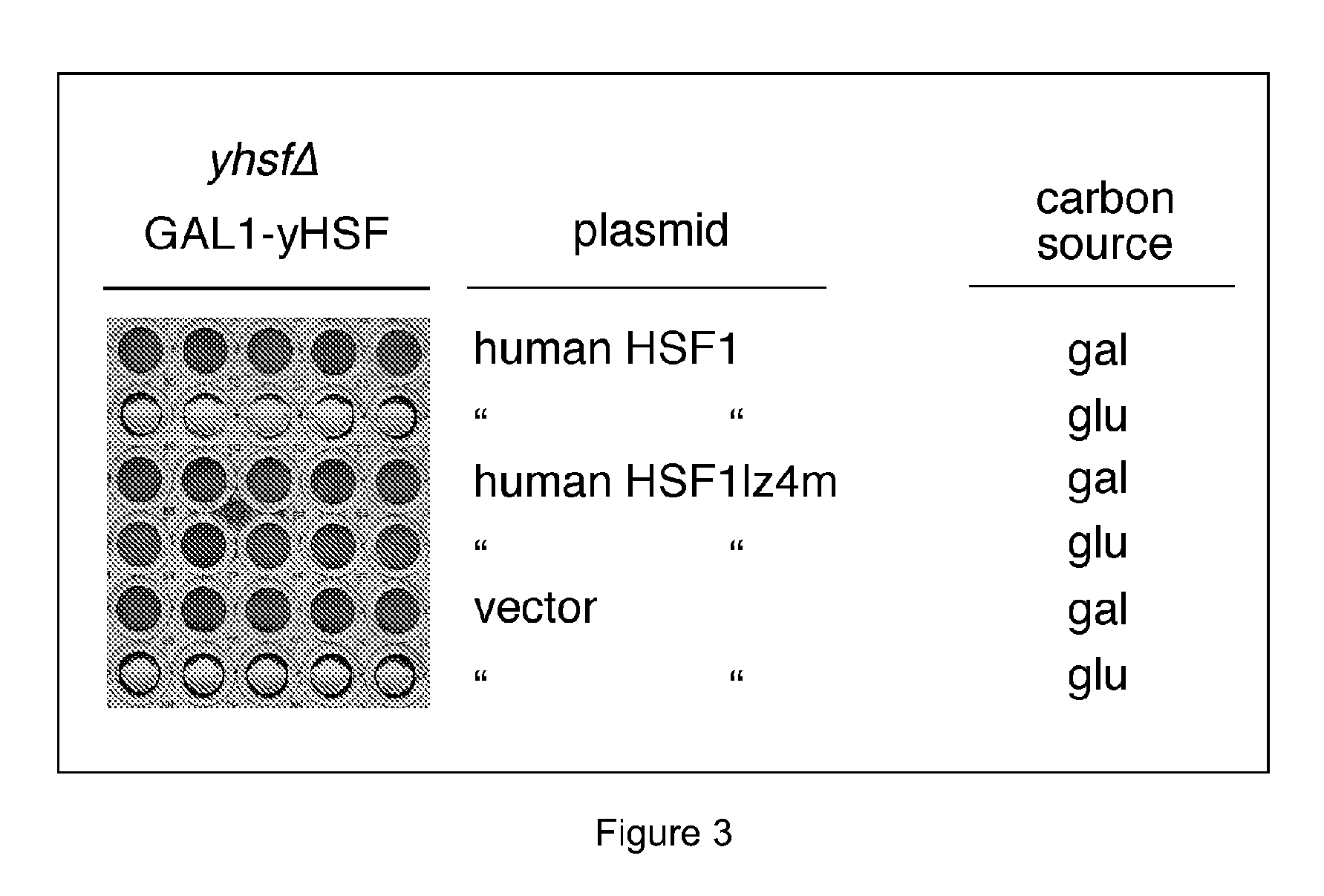
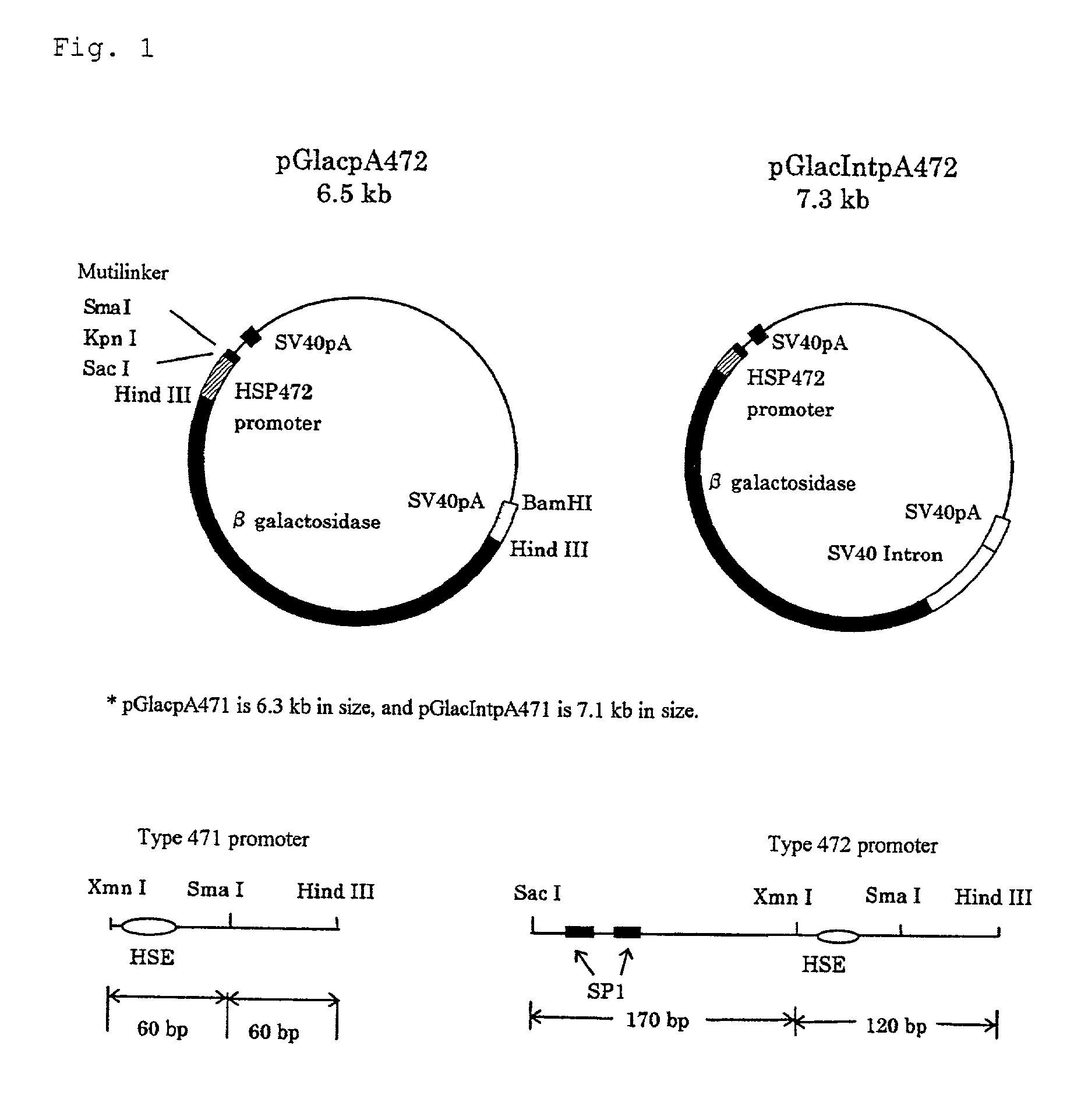
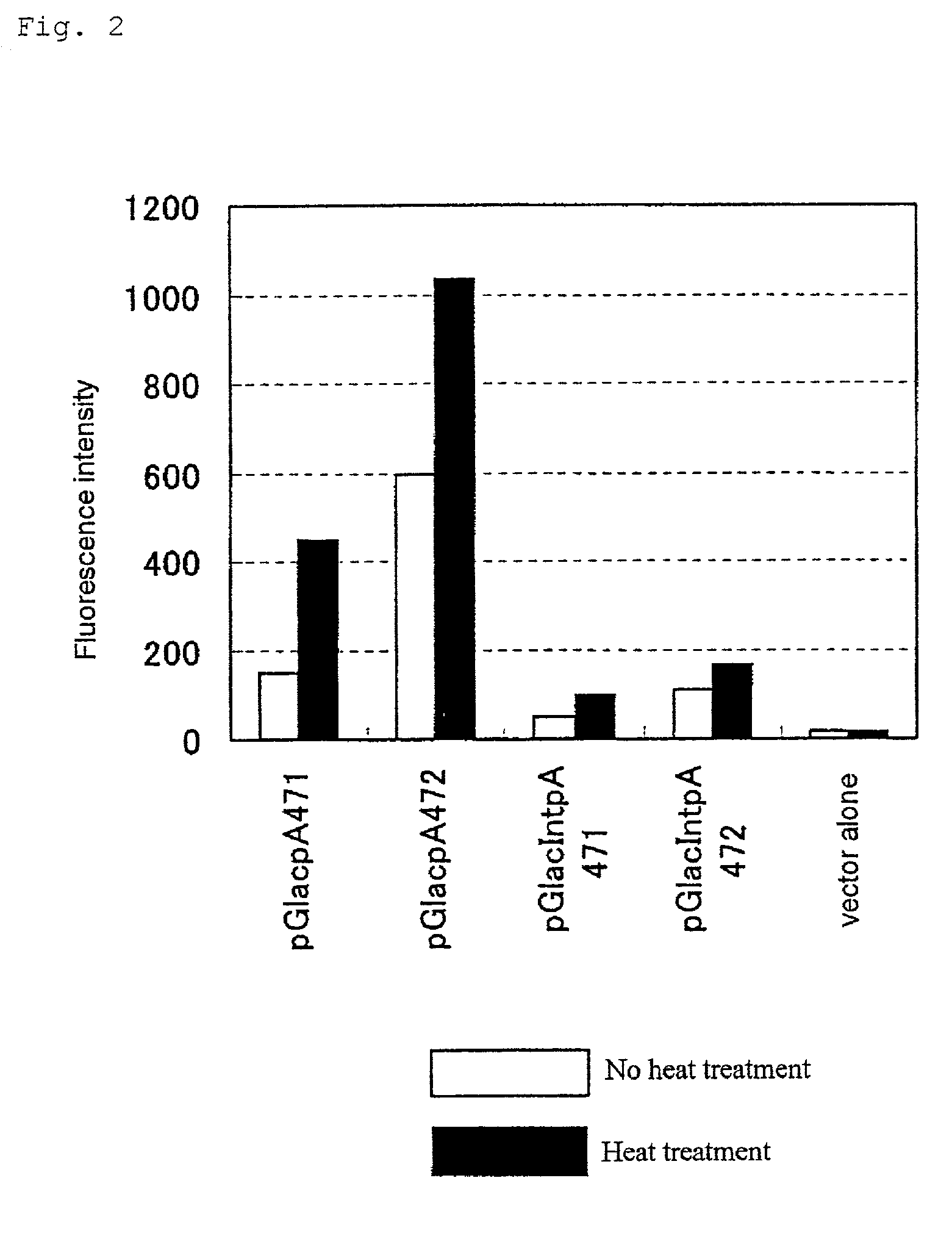
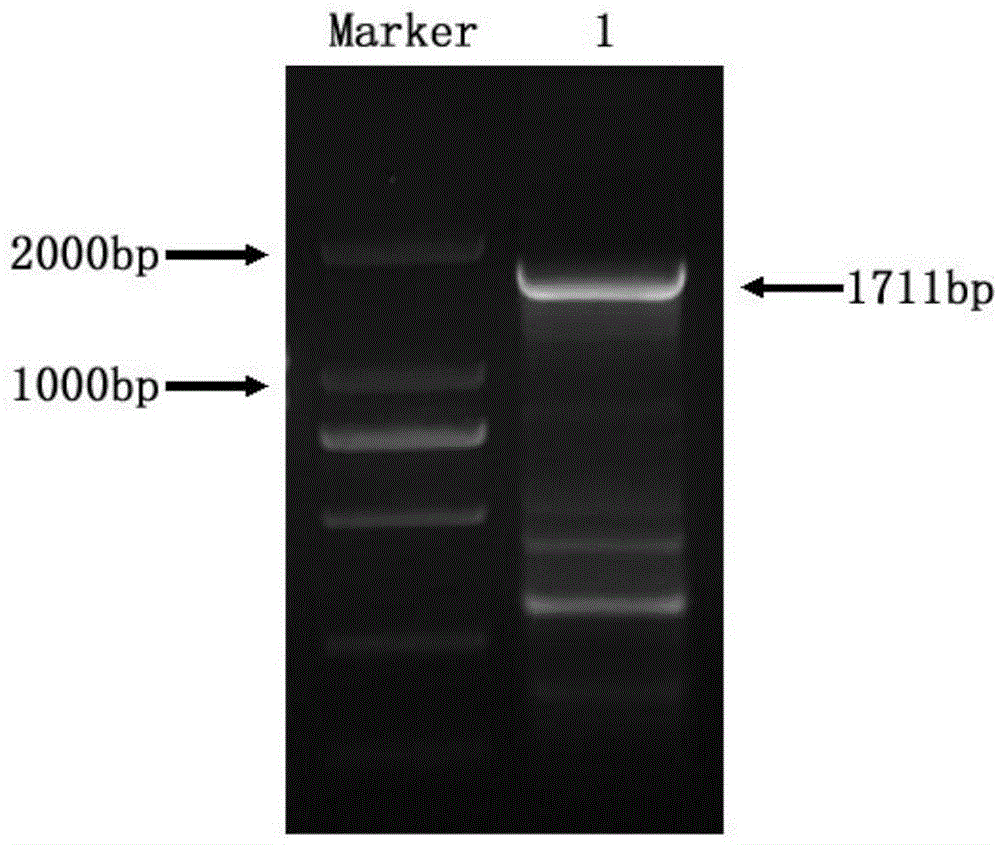
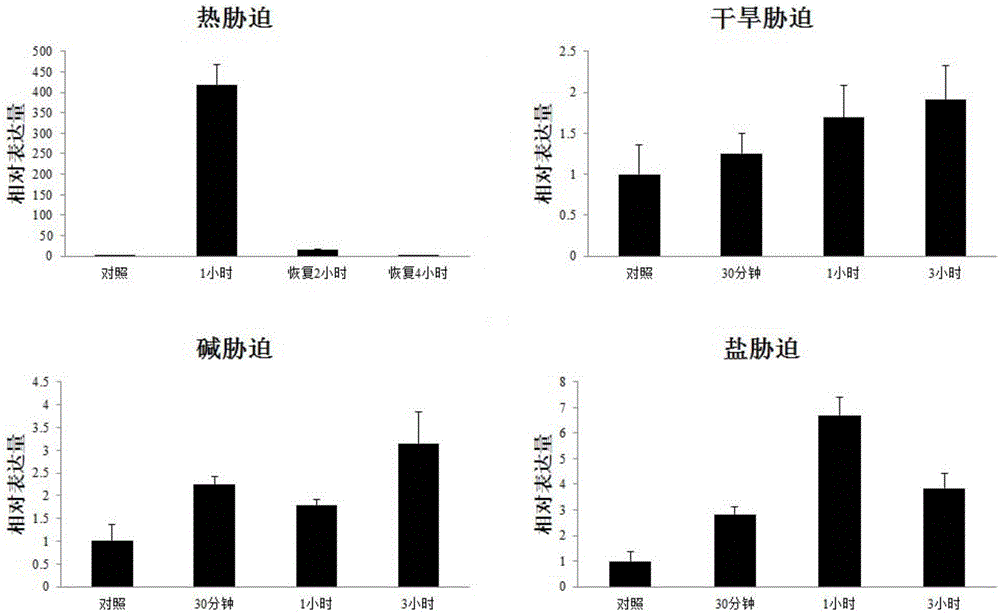
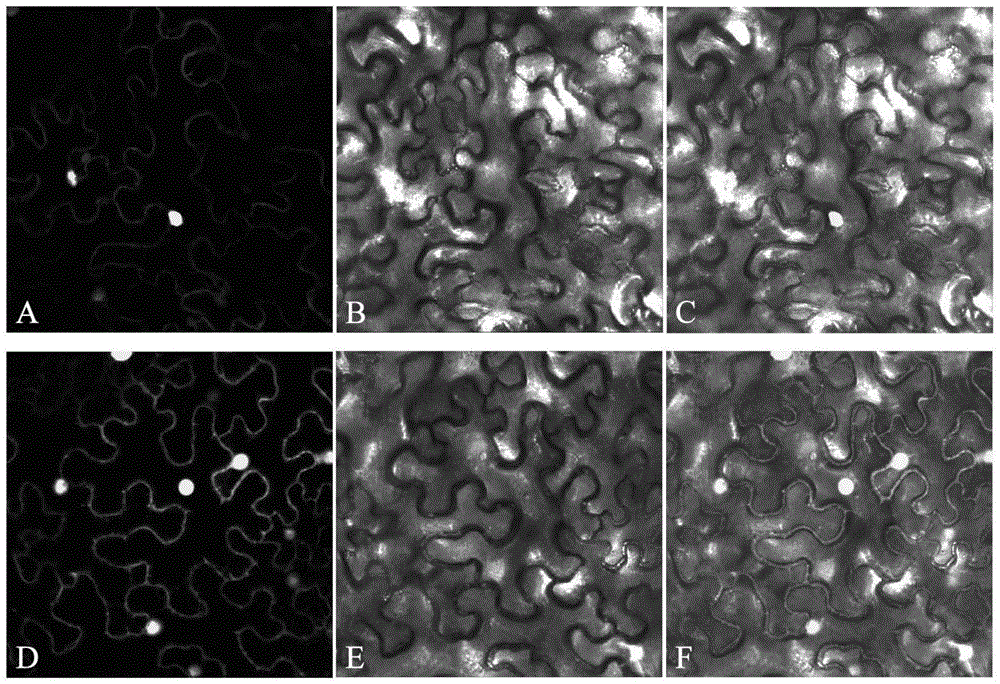
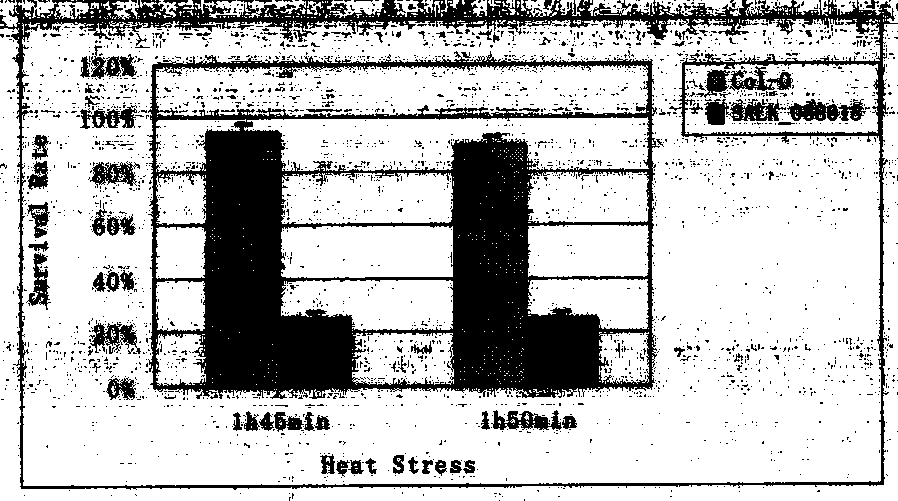Patents
Literature
62 results about "Heat Shock Transcription Factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
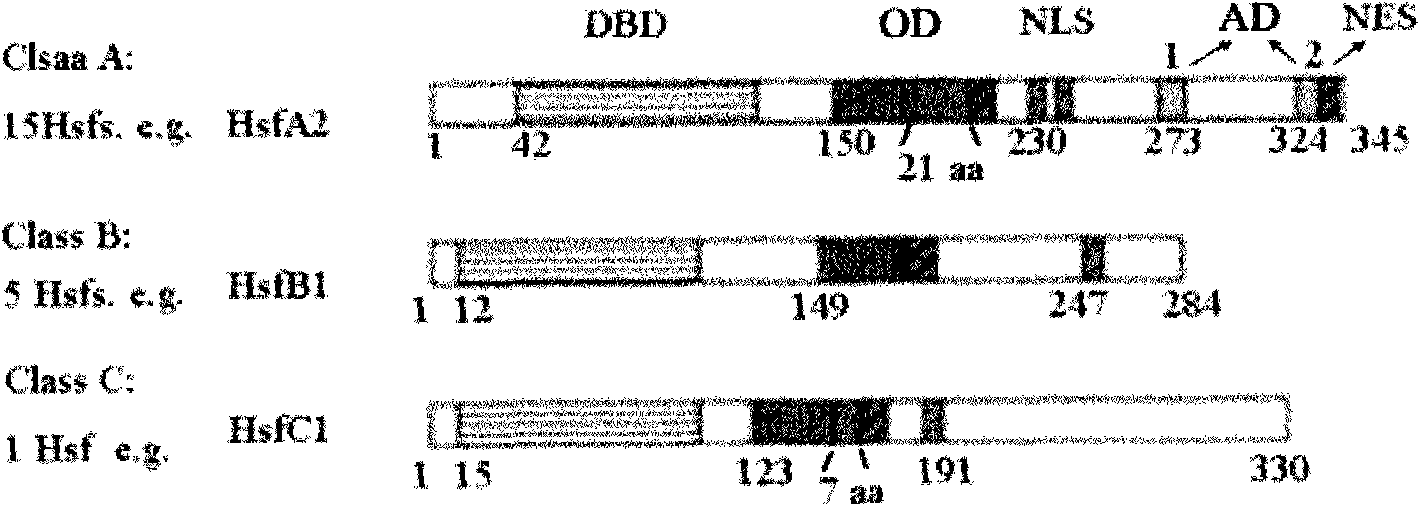
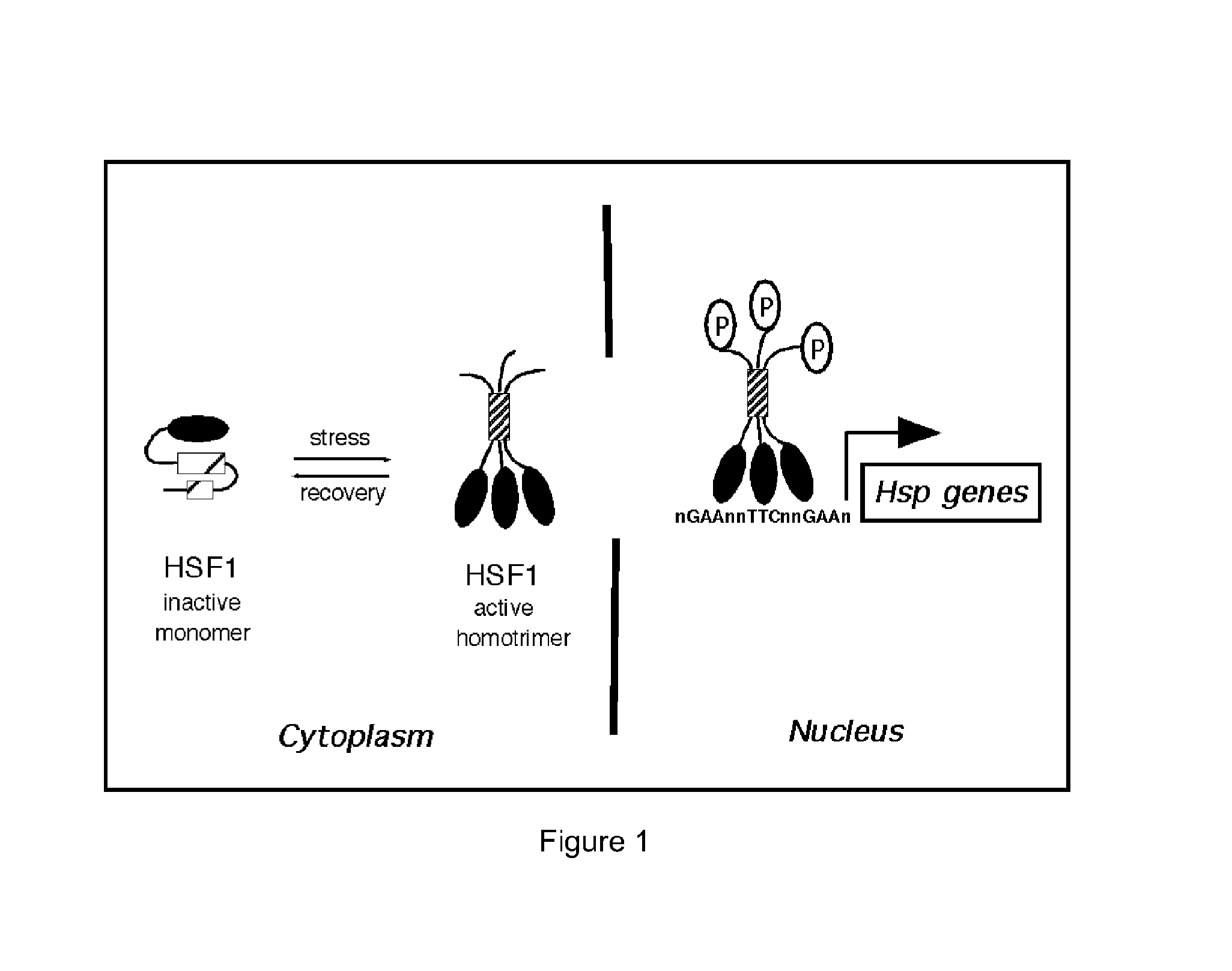
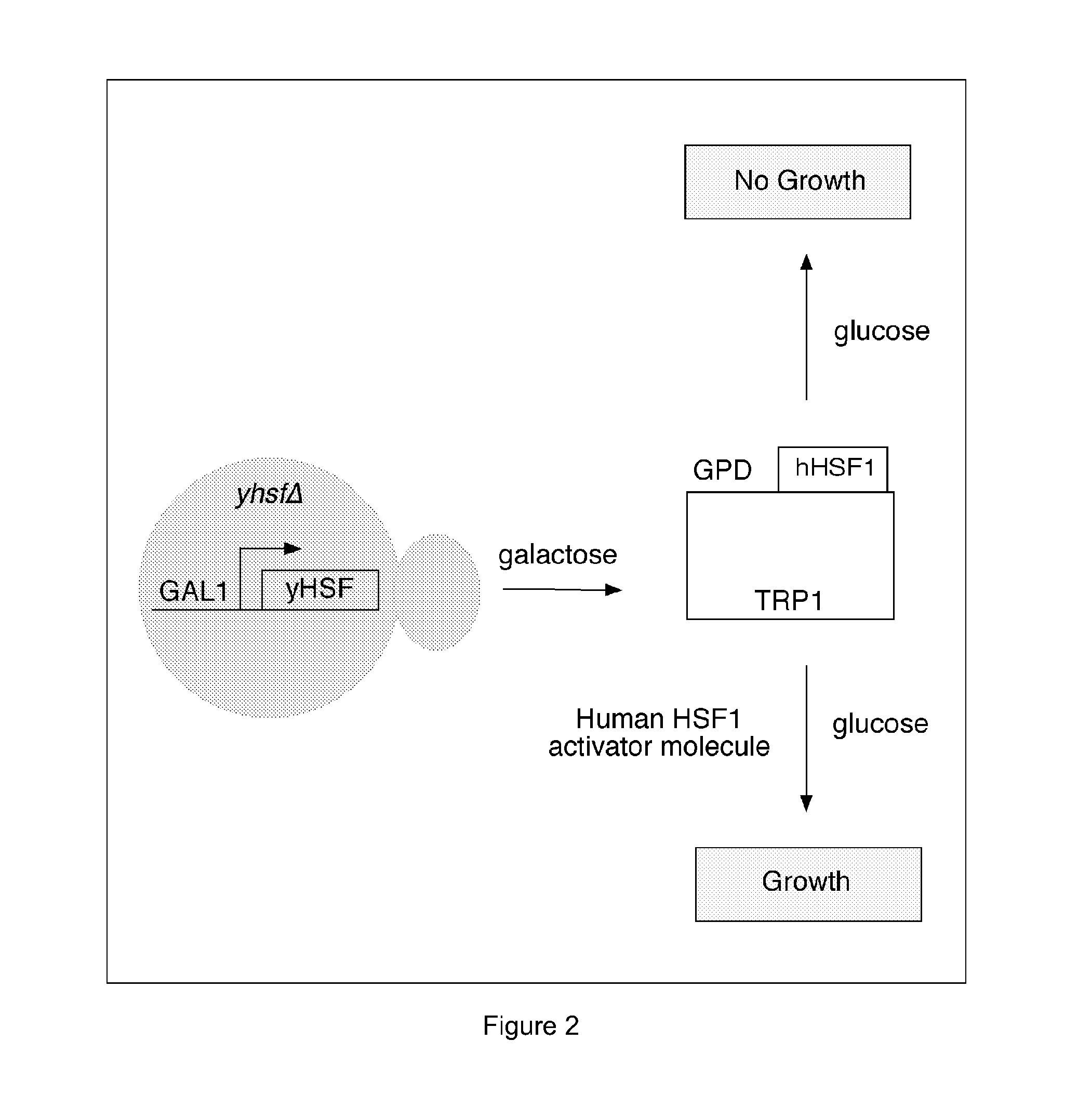
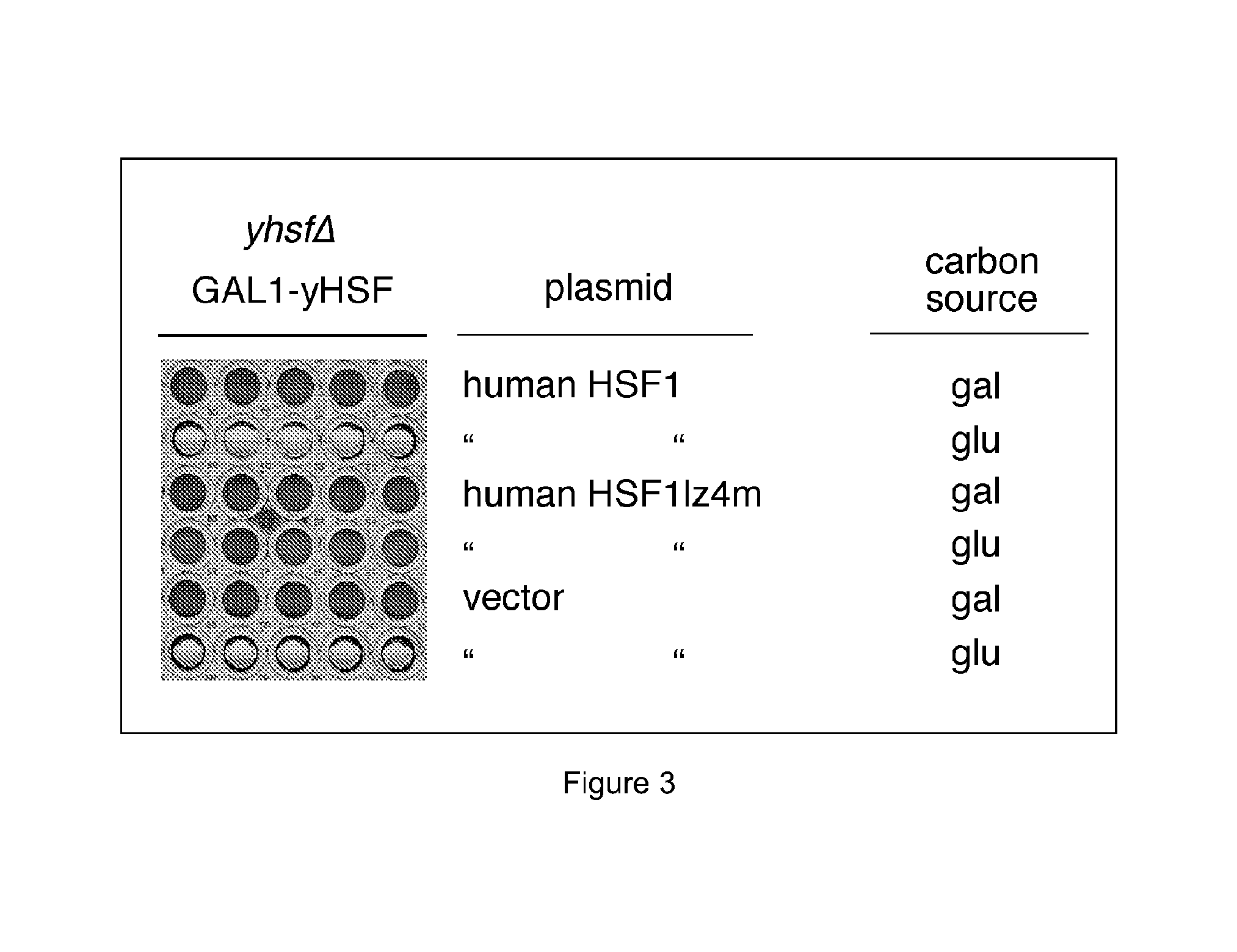
In molecular biology, heat shock factors (HSF), are the transcription factors that regulate the expression of the heat shock proteins. A typical example is the heat shock factor of Drosophila melanogaster.
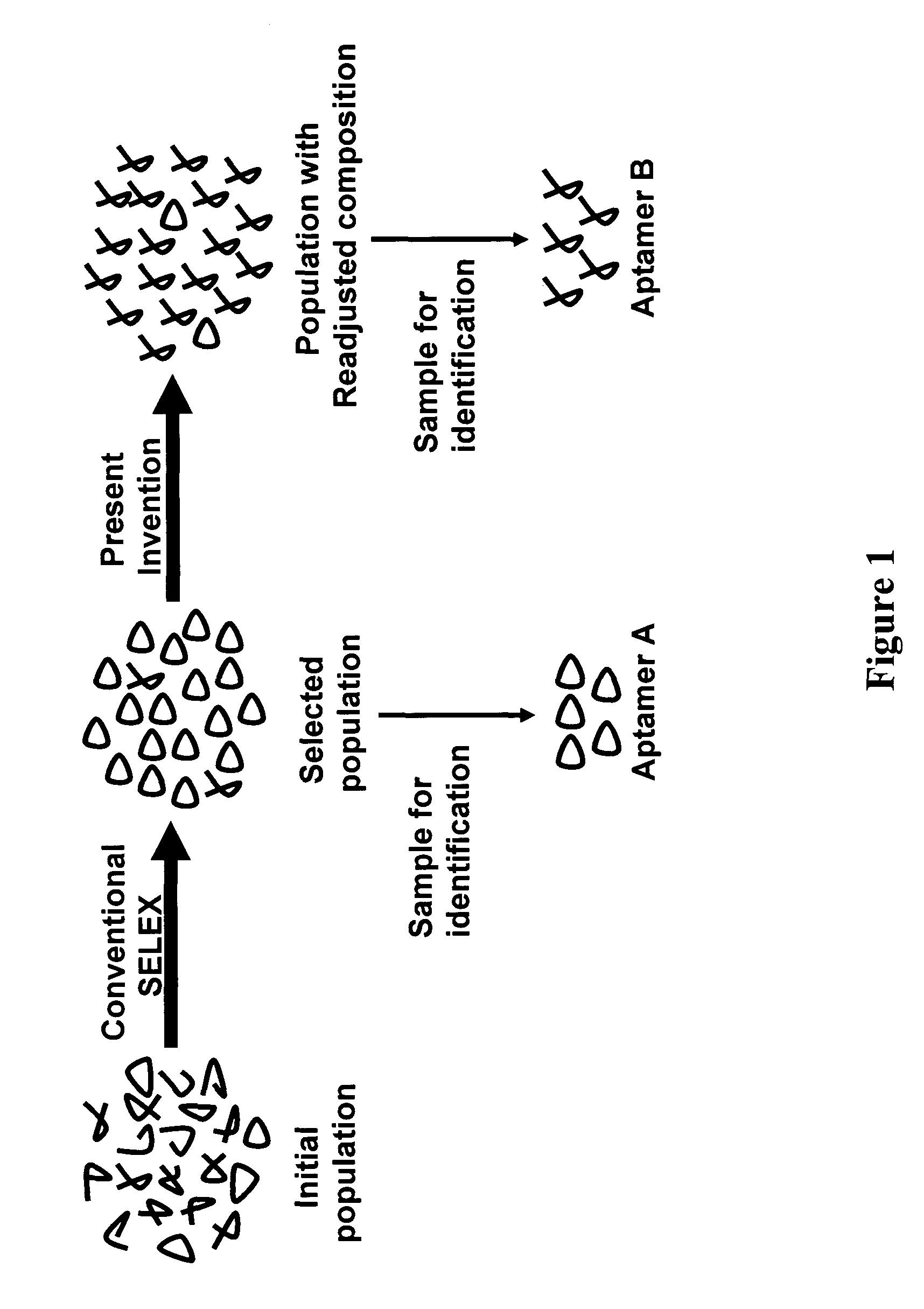
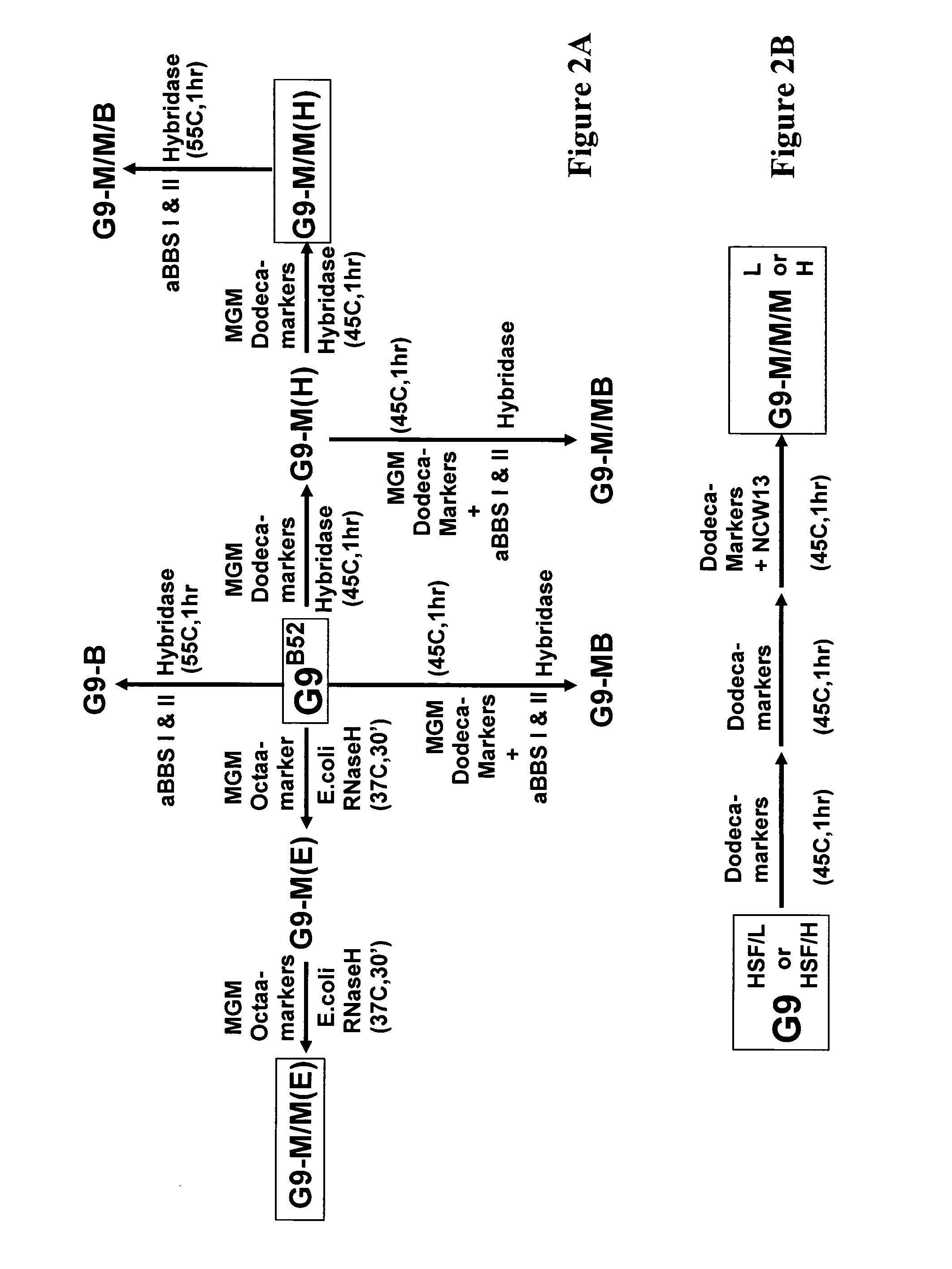
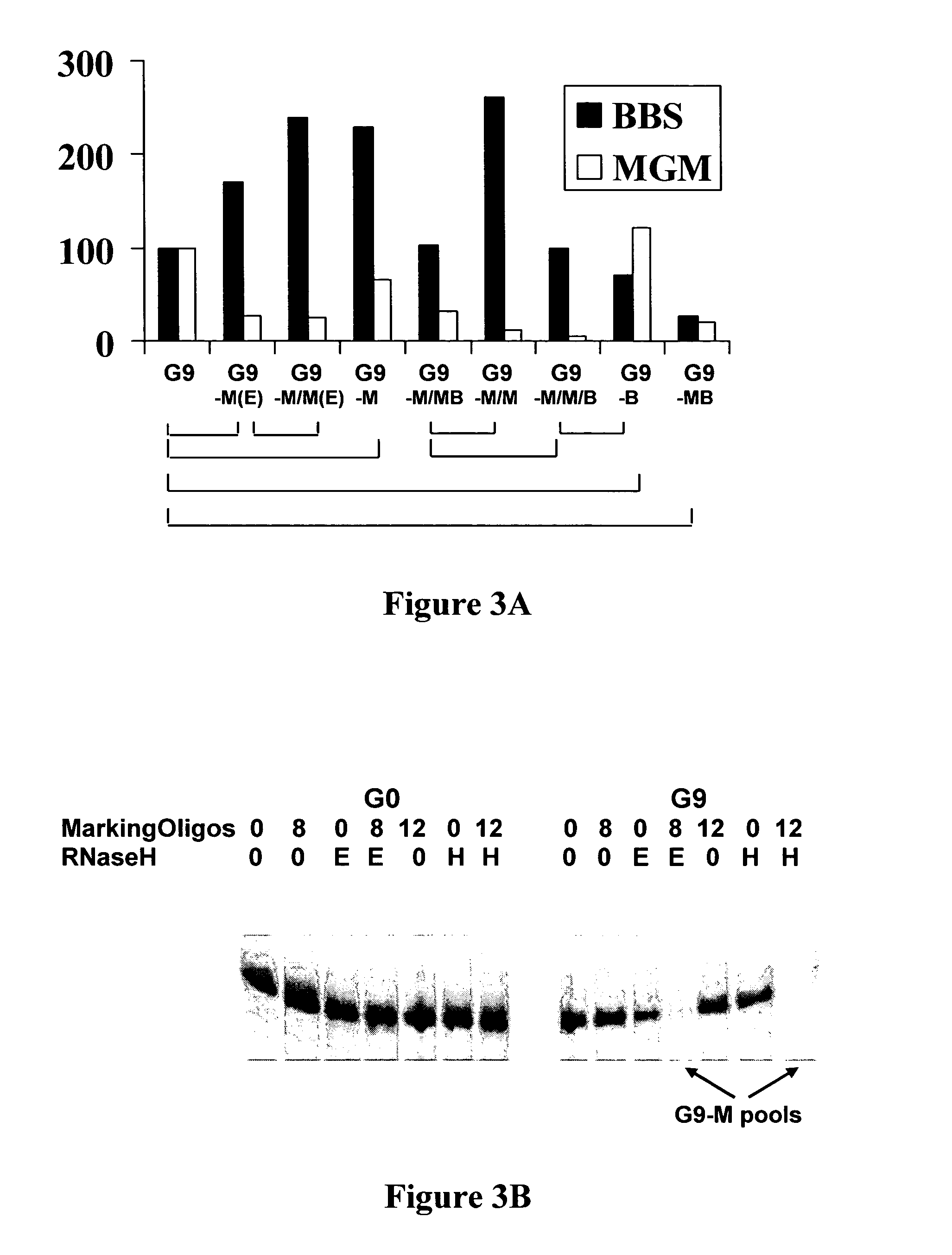
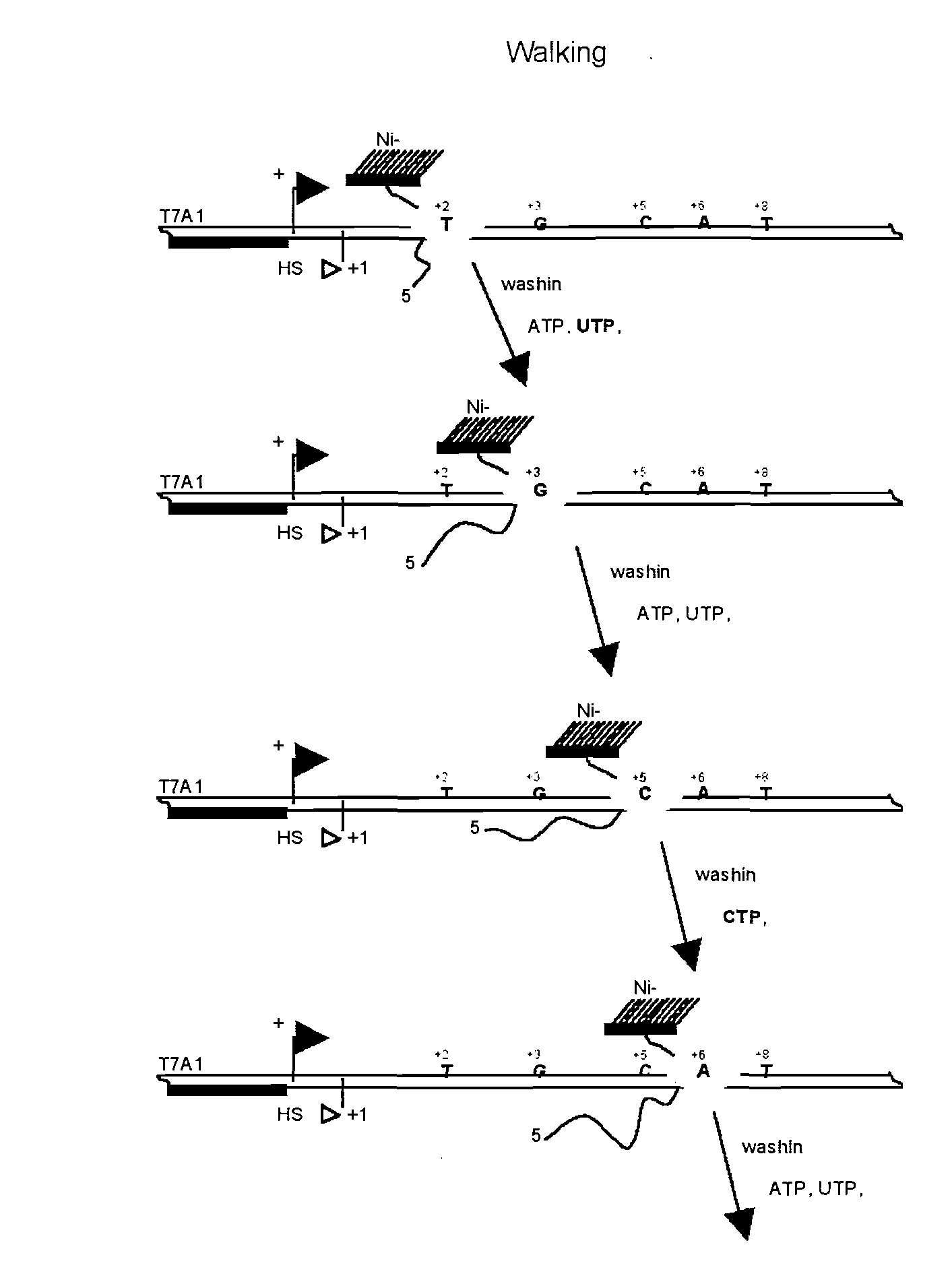
Exhaustive selection of RNA aptamers against complex targets
InactiveUS7435542B2Reduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processHigh concentrationHeat Shock Transcription Factor
A method of identifying RNA ligands which bind to a target molecule by treating a first pool of RNA ligands that collectively bind more than one target under conditions effective to reduce the concentration or eliminate the presence of one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands from the first pool of RNA ligands; amplifying the RNA ligands in the treated first pool, thereby forming a second pool of RNA ligands that is enriched in one or more non-predominate target-binding RNA ligands of the first pool but not the one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands thereof; and identifying one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands that are present in the second pool at a higher concentration than other target-binding RNA ligands. Oligonucleotides and kits which can be used in practicing the present invention are also disclosed, as are aptamers that bind to a heat shock factor protein and their use.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Heat shock RNA and its use in activation of heat shock transcription factor and treatment of cancer, inflammation, ischemia, neurodegeneration, age-related diseases, HIV infection, deafness, and related disorders
InactiveUS20070238682A1Good effectHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTotal DeafnessAge related disease
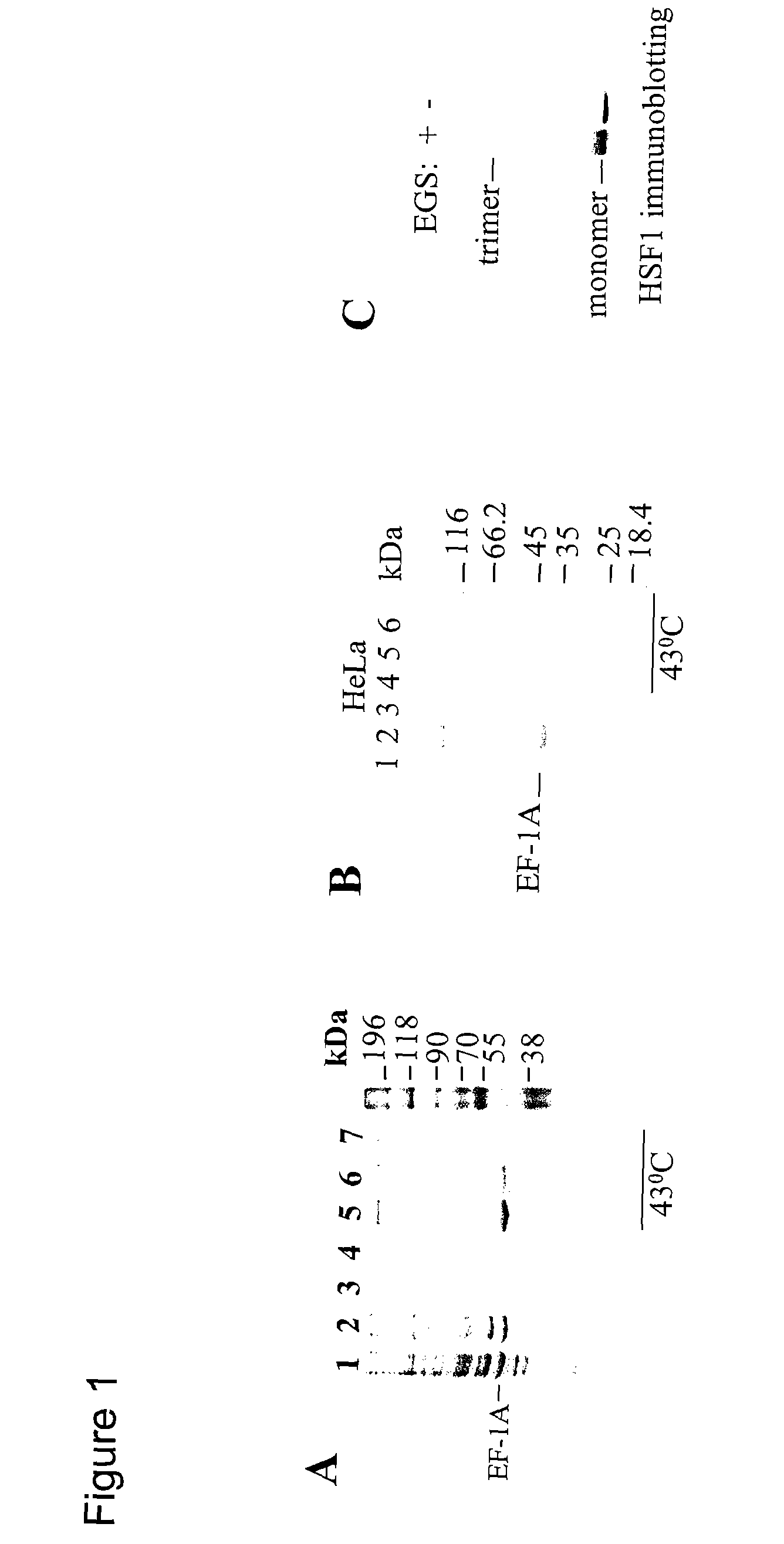
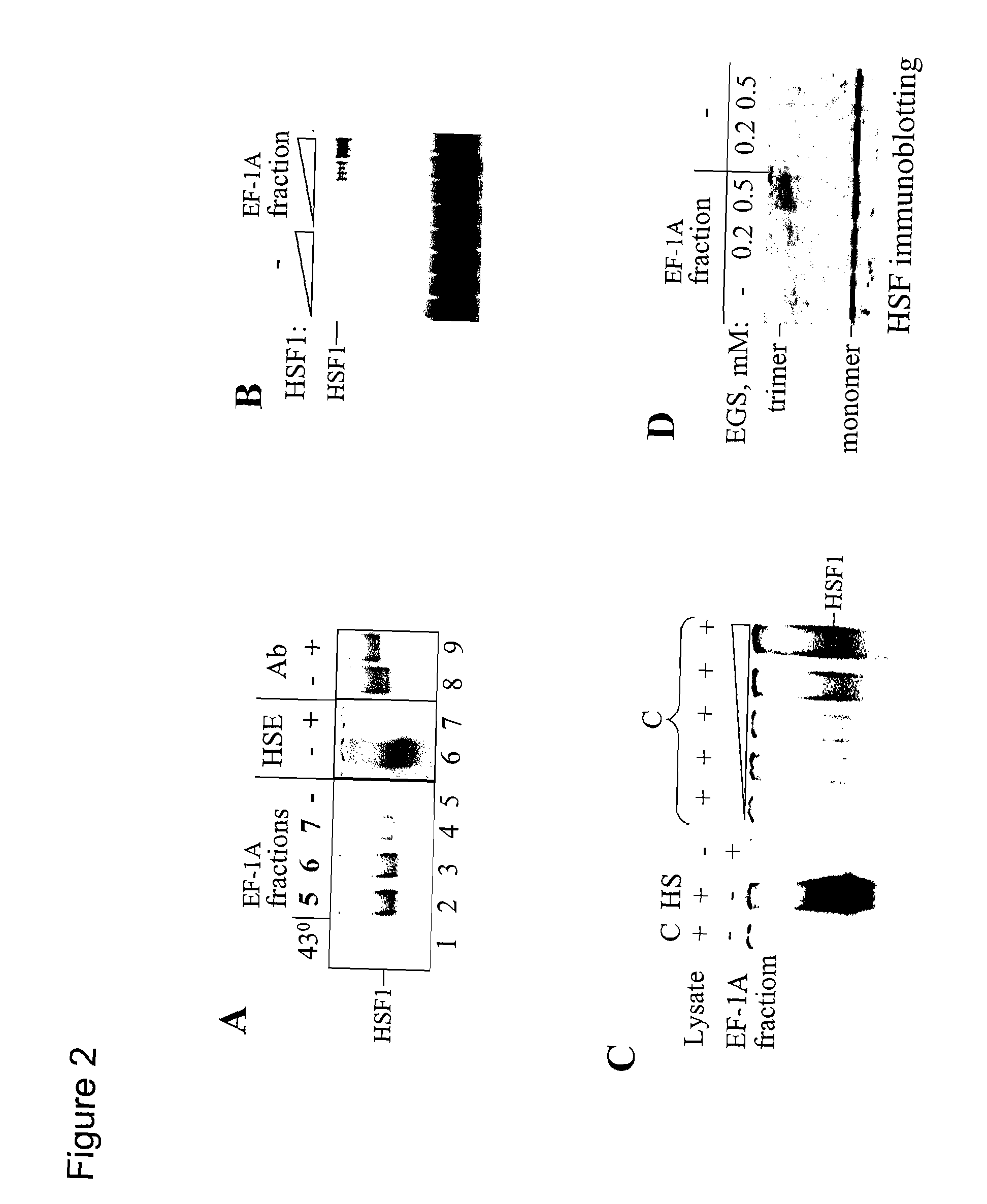
The present invention provides a novel RNA, designated herein as the “HSR1” (Heat Shock RNA), and its use together with translation elongation factor eEF1A in activation of heat shock transcription factor HSF. The invention further provides the use of HSR1 for generation of novel therapeutics for the treatment of cancer, inflammation, ischemia, neurodegeneration, age-related diseases, HIV infection, deafness, and related disorders.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
ActiveUS20110112073A1Improve intracellular quality controlImprove quality controlBiocideSenses disorderHeat Shock Transcription FactorPharmaceutical formulation
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Methods of treating cancer using a heat shock factor activity inhibitor
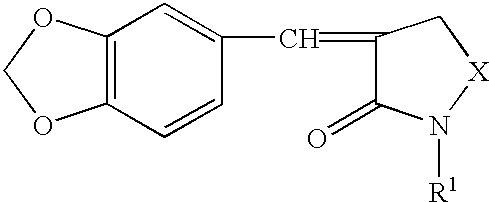
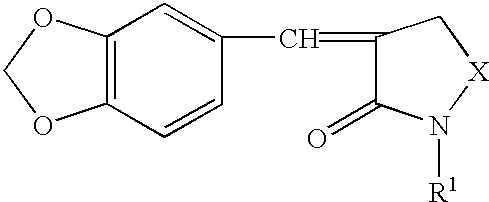
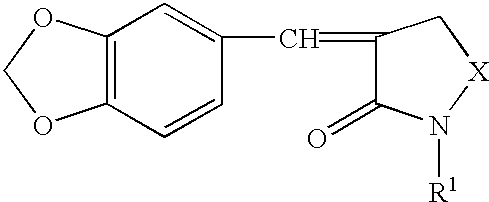
A disease treatment is provided by controlling the expression of a protein induced by a heat shock factor.The novel compound benzo-1,3-dioxole provides an inhibitor of HSF activity or an inhibitor of inducing the production of a protein regulated by HSF, which inhibits the activity of a heat shock factor, a transcriptional regulatory factor, thereby in turn inhibiting transcription of a structural gene having a heat shock element sequenc in the gene region for transcriptional regulation into RNA, and thus inhibiting translation of the gene into a protein, and resulting in inhibition of inducing production of RNA or protein encoded by the gene. It also provides a drug for treating or preventing cancer through thermotherapy and a drug for treating or preventing stress diseases such as depression.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a HSFA4 or HSFA5 (Heat Shock Factor of the class A4 or A5) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a HSFA4 or a HSFA5 polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various yield-related traits by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an oligopeptide transporter protein (OPT4-like) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an OPT4-like polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Heat shock transcription factor-binding protein
InactiveUS6485936B1Rule out the possibilityImprove purification effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesA-DNAHsp70
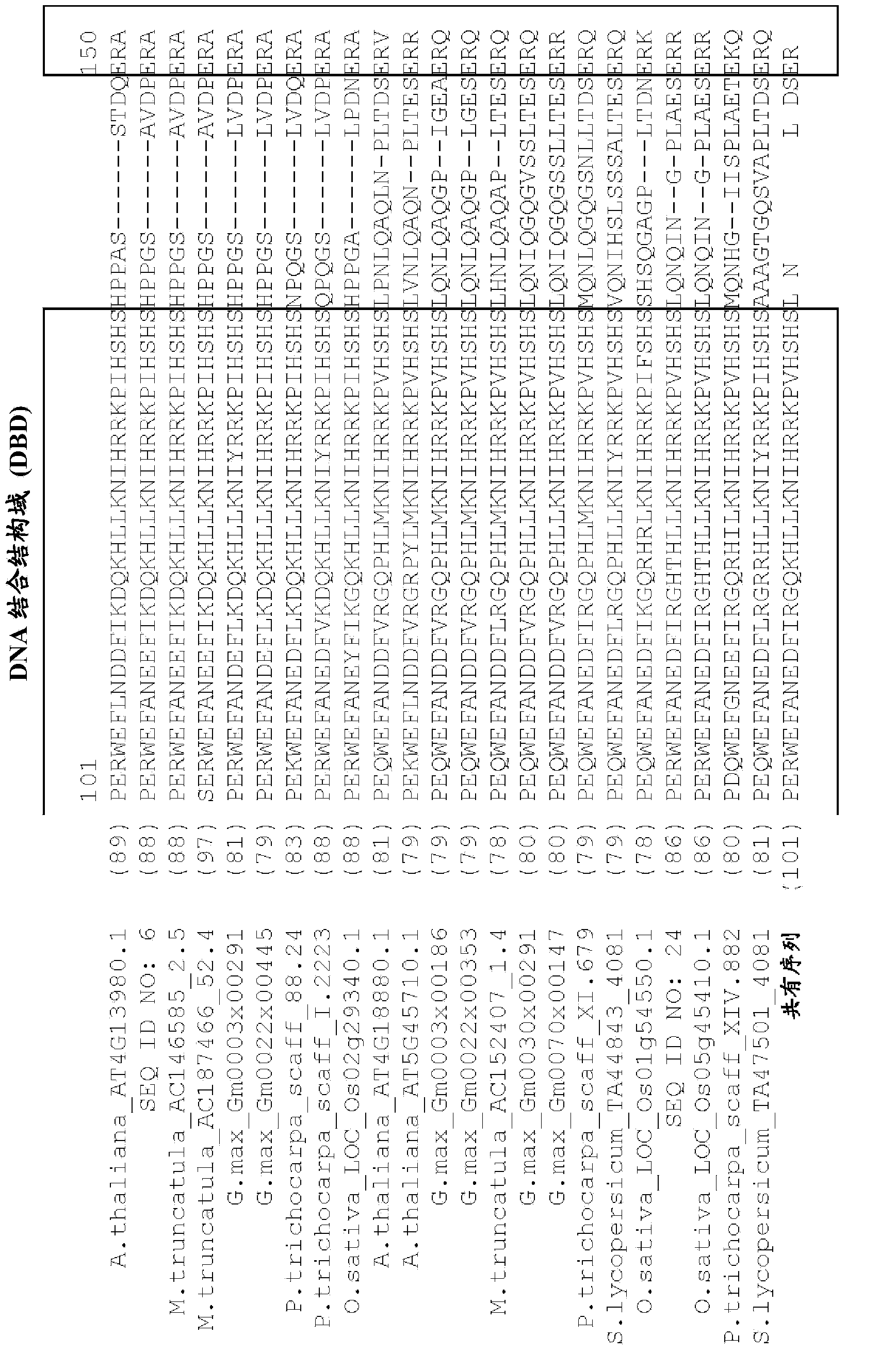
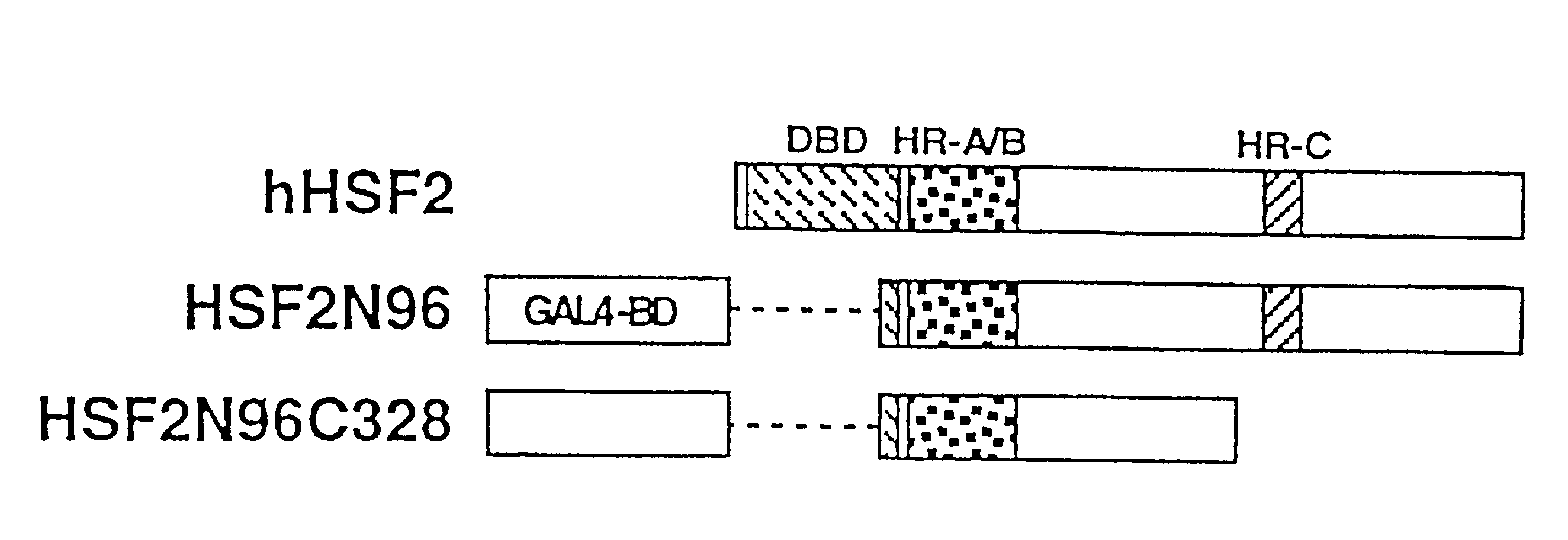
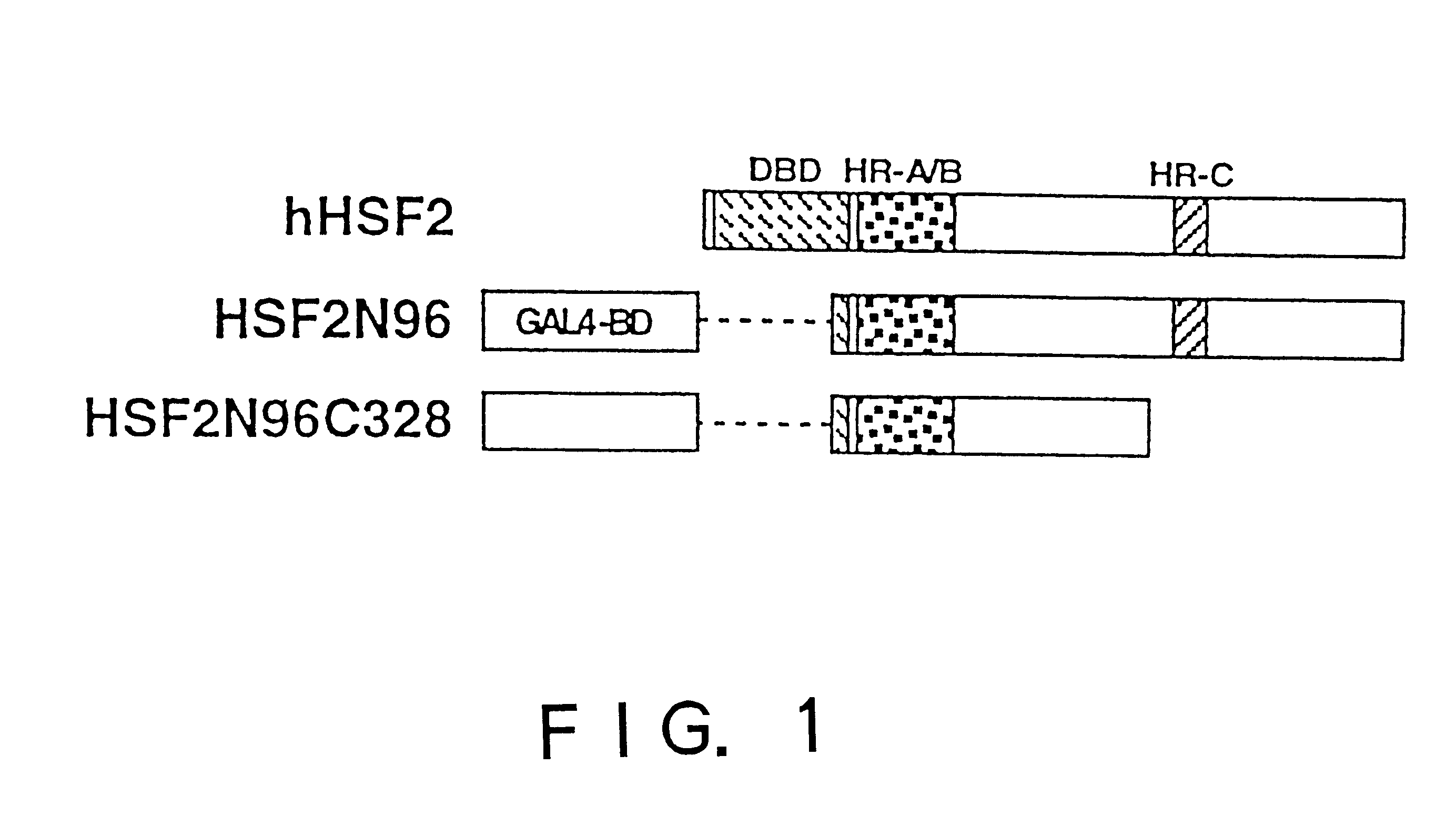
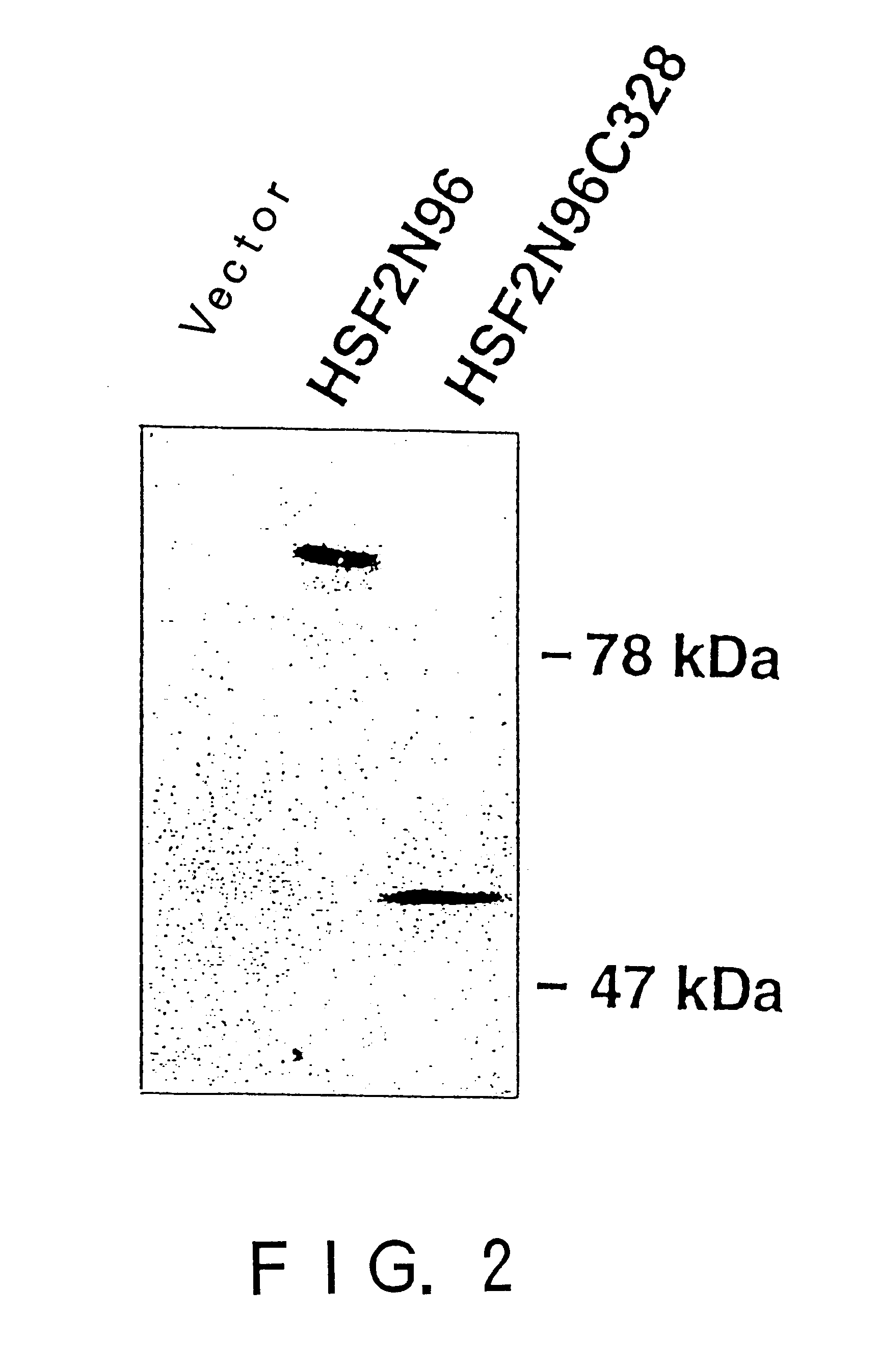
To provide a heat shock transcription factor (HSF) 2 binding factor, which can be involved in the transcriptional regulation of HSP70.2 playing an essential role in spermatogenesis; a DNA encoding the binding factor; an expression vector carrying the DNA; a transformant harboring the expression vector; a process for preparing a recombinant protein comprising the step of culturing the transformant; an antibody or a fragment thereof capable of specifically binding to the binding factor; an antisense DNA or antisense RNA complementary to the DNA; and an oligonudeotide probe or primer capable of specifically hybridizing to the DNA.
Owner:HSP RES INST
Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2 and coding protein and application thereof
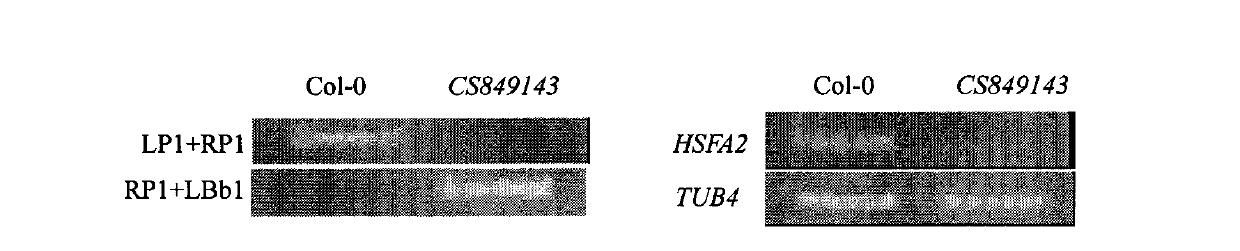
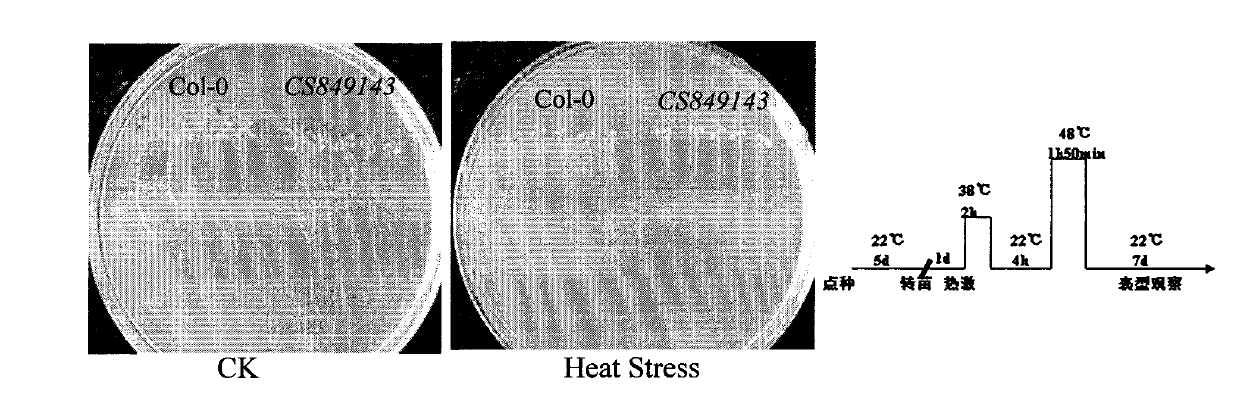
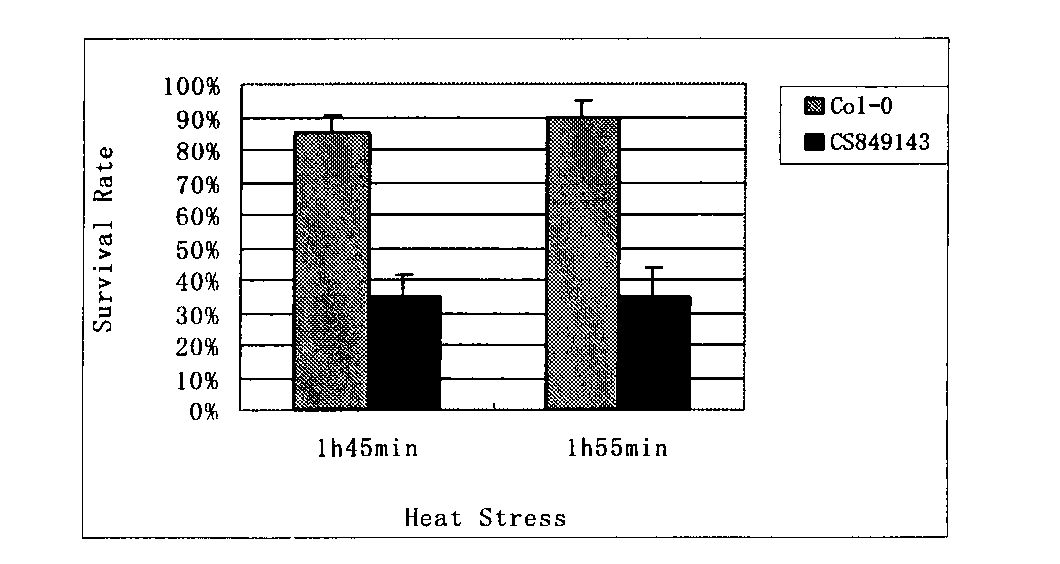
The invention belongs to the field of technology related to plant molecular biology and transgenosis. Concretely, the invention relates to verification of high temperature resistance function of the Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2, and the application of the gene in high temperature resistance plant new species cultivation. According to the invention, a model plant Arabidopis thaliana is used as material, and a HSFA gene T-DNA is inserted into a homozygous mutant lines CSS 849143 for researching high temperature resistance function of the HSFA2 gene in plants. The experiment result displays that the HSFA2 gene knock-out mutant appears a sensitive phenotype with heat shock stress, and survival rate, conductivity and osmotic pressure and other physiological indexes are significantly or highly significantly different from those of the wild type; The invention instructs that the HSFA2 gene plays an important effect in the signal transduction pathway of plant response low nitrogen stress, and predicts that the excessive expression of the gene can improve the heat resistance capability of plant and has a larger economic value in the plant stress-resistance molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Heat shock transcription factor and application thereof
InactiveCN103923198AImprove heat resistanceImprove salt toleranceBacteriaPlant peptidesHeat resistanceNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a heat shock transcription factor, a nucleotide sequence encoding the heat shock transcription factor and an application thereof in improving the heat resistance of the plant. Overexpression of the heat shock transcription factor can remarkably improve the heat resistance of a transgenic plant without bringing harmful effects such as growth delay and stuntedness to the plant, so that the heat shock transcription factor has a unique advantage in improving the heat resistance of the plant.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
Heat shock transcription factor gene TaHsfA2i of wheat, and encoded protein, and application of heat shock transcription factor gene TaHsfA2i
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and molecular breeding, and relates to a sequence of a heat shock transcription factor gene TaHsfA2i of wheat and application of the gene sequence. The nucleotide sequence of the heat shock transcription factor gene of the wheat is shown as in SEQ ID No.1. The gene TaHsfA2i is acquired from a heat resistant variety Cang 6005 of the wheat through cloning, the expression is obviously improved because of heat stress, and moreover, the expression of a downstream stress resistance gene is activated. The gene genetically transforms a yeast and arabidopsis, and the heat resistance capability of the yeast and the arabidopsis is obviously improved. A heat shock transcription factor encoding gene of wheat plays an important role in cultivating a crop variety with strong heat resistance.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Application of arabidopsis gene ROI1 in aspect of high temperature stress resistance of plants
InactiveCN101781659AImprove resistance to high temperature stress responseVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsTemperature stressSignalling molecules
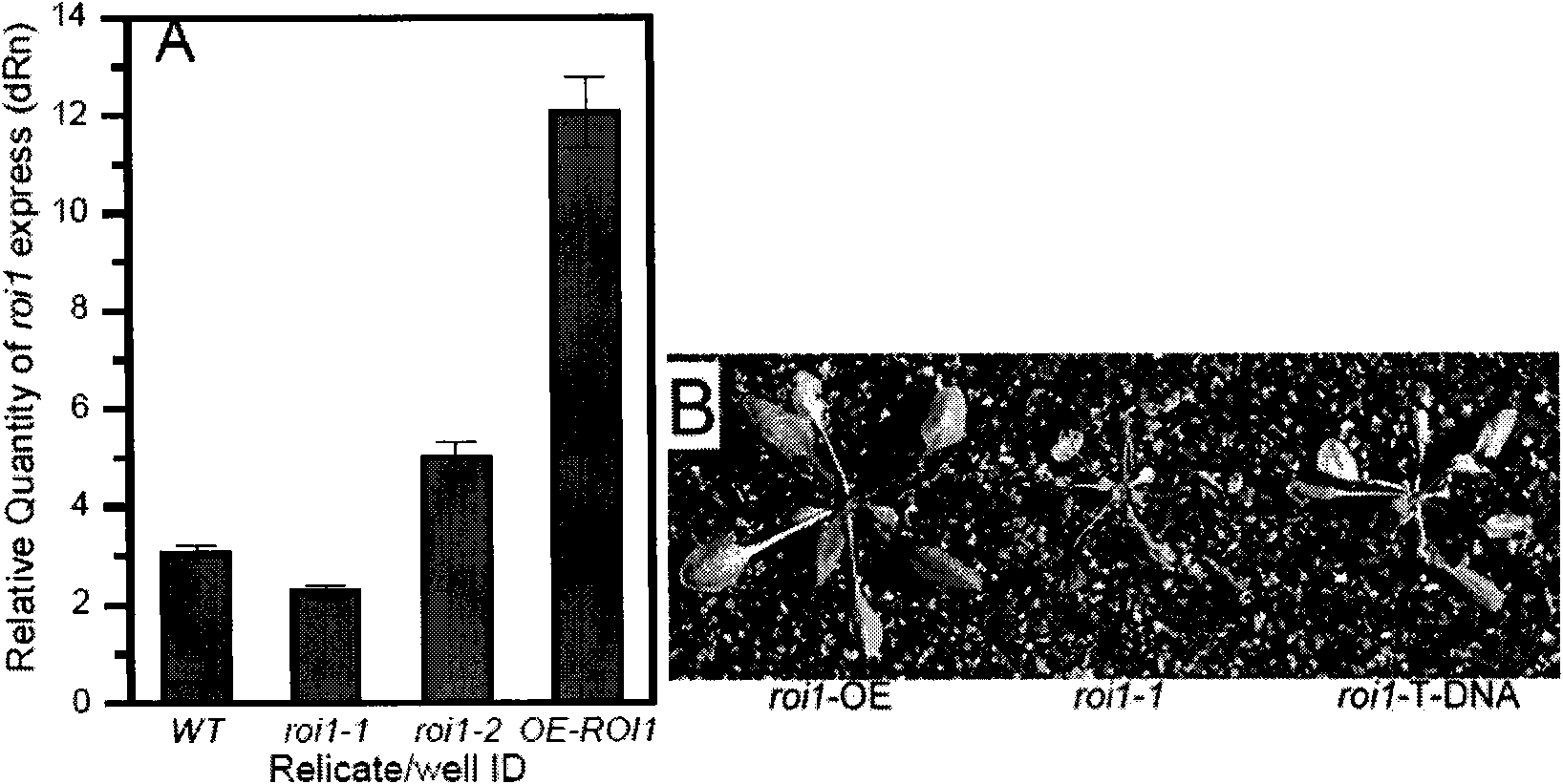
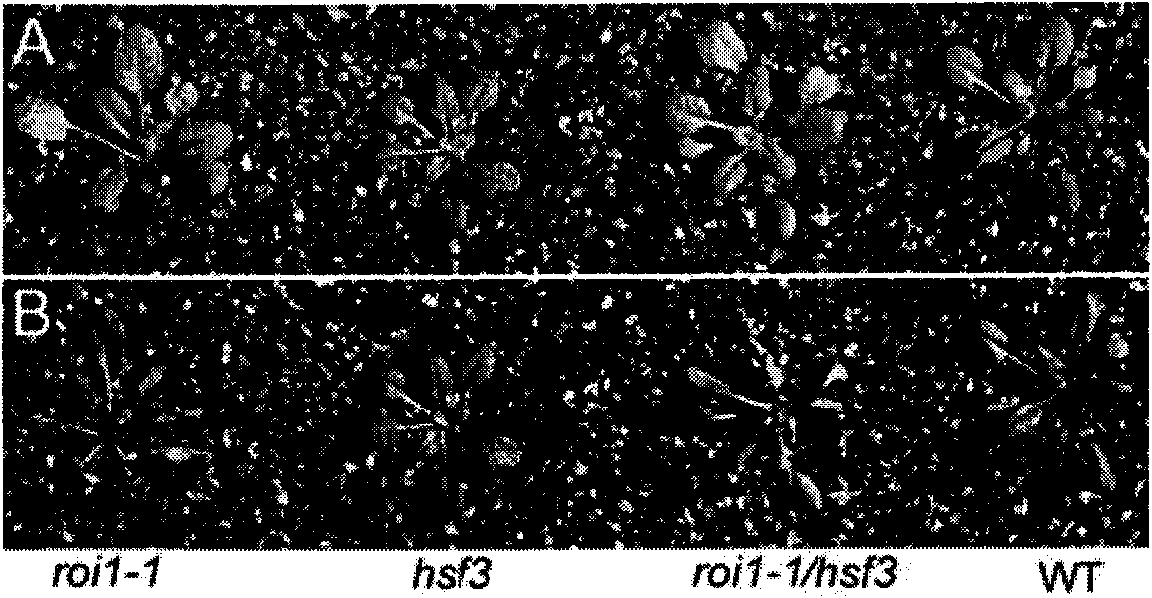
The invention discloses application of an arabidopsis gene ROI1 in the aspect of high temperature stress resistance of plants. An arabidopsis mutant roi1 sensitive to high temperature and oxidation stress is obtained through screening; and the ROI1 gene is obtained by separating the arabidopsis mutant roi1. Experiments show that the arabidopsis ROI1 gene is induced to express by high temperature stress, regulates generation of H2O2 in plant bodies, is combined with heat shock transcription factors HSF3, regulates the activity of the HSF3 and downstream signal molecules in a mode of phosphorylation regulation, and regulates and improves high temperature stress resisting reaction of the plants. Functional analysis and identification of the ROI1 provide basis of theory and method for obtaining new varieties of high temperature stress resisting plants.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Methods for increasing red blood cell levels and treating ineffective erythropoiesis
ActiveUS20170274077A1Decrease ineffective erythropoiesisAlleviates disease pathologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeat Shock Transcription FactorGastroenterology
In certain aspects, the present disclosure provides compositions and methods for increasing red blood cell and / or hemoglobin levels in a subject in need thereof. Subjects in need include, for example, subjects having anemia and / or ineffective erythropoiesis as a result of having reduced GATA-1, heat shock factor and / or NFE2 levels as compared to the levels in a reference population.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC +1
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a HSFA4 or HSFA5 (Heat Shock Factor of the class A4 or A5) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a HSFA4 or a HSFA5 polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various yield-related traits by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an oligopeptide transporter protein (OPT4-like) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an OPT4-like polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The invention also provides hitherto unknown OPT4-like-encoding nucleic acids, and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various yield-related traits by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a plastochron2-like (PLA2-like) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a PLA2-like polypeptide.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Heat-resistance related protein of plant maintaining stability of thylakoid membrane and application thereof
InactiveCN103288940AGuaranteed thermal stabilityImprove survivabilityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyHeat resistance
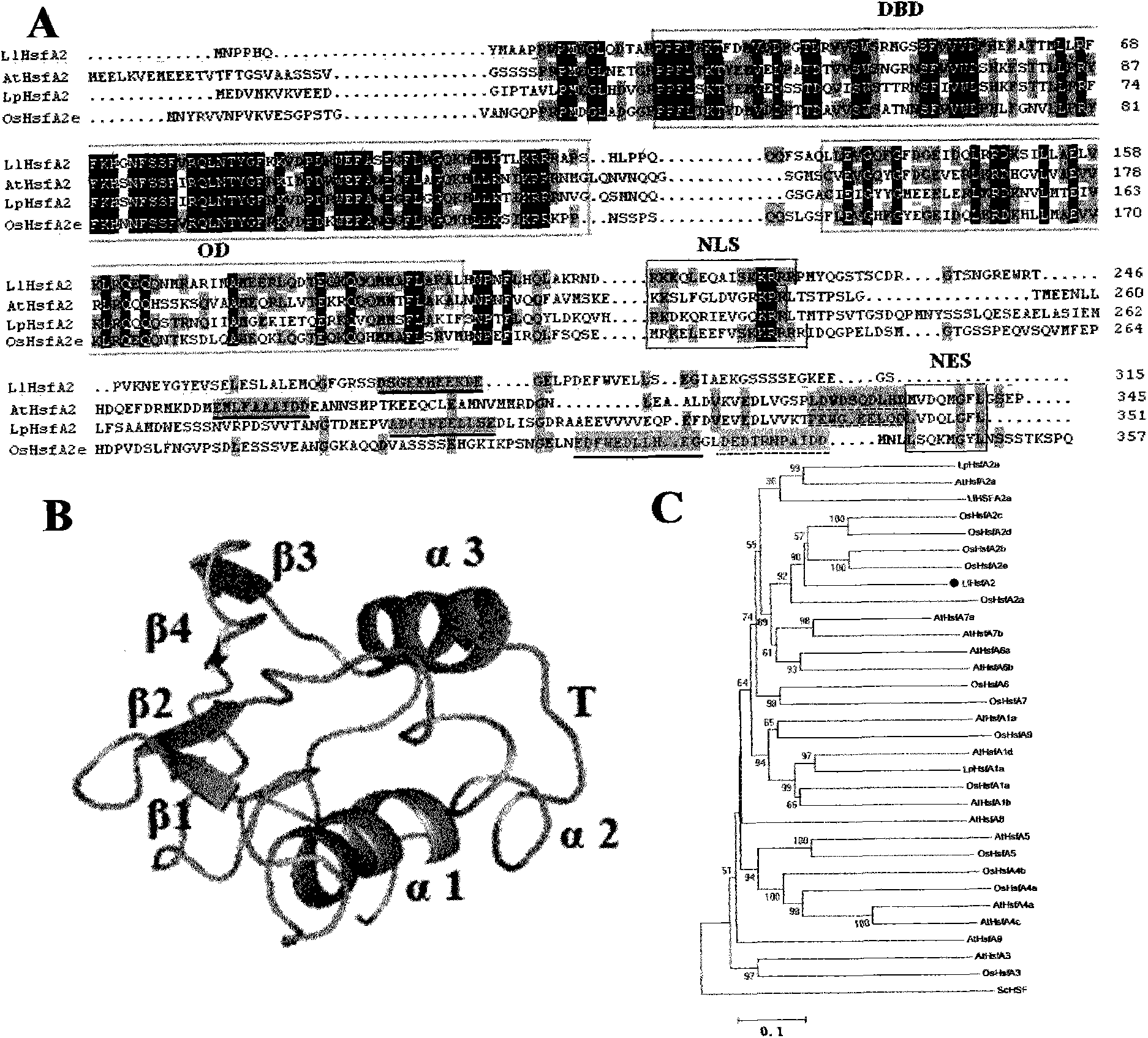
The invention relates to a heat-resistance related protein of a plant maintaining stability of a thylakoid membrane and an application thereof. Specifically, through massive screen to plant genes, the inventor accidentally obtain a heat-resisting gene of a plant related to maintaining the stability of the thylakoid membrane. The gene is a heat shock transcription factor A2 (HfA2) of the plant. The gene and protein provided by the invention can effectively maintain the thermal stability of the thylakoid membrane, improve the viability and the photosynthetic efficiency of plants under heat stress, improve the crop yield, and avoid or reduce adverse effect of high temperature to the plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Substituted 1,3-thiazoles as heat shock transcription factor 1 activators
InactiveUS9156775B2Improve quality controlBiocideSenses disorderThiazoleHeat Shock Transcription Factor
Owner:CHAPERONE THERAPEUTICS +1
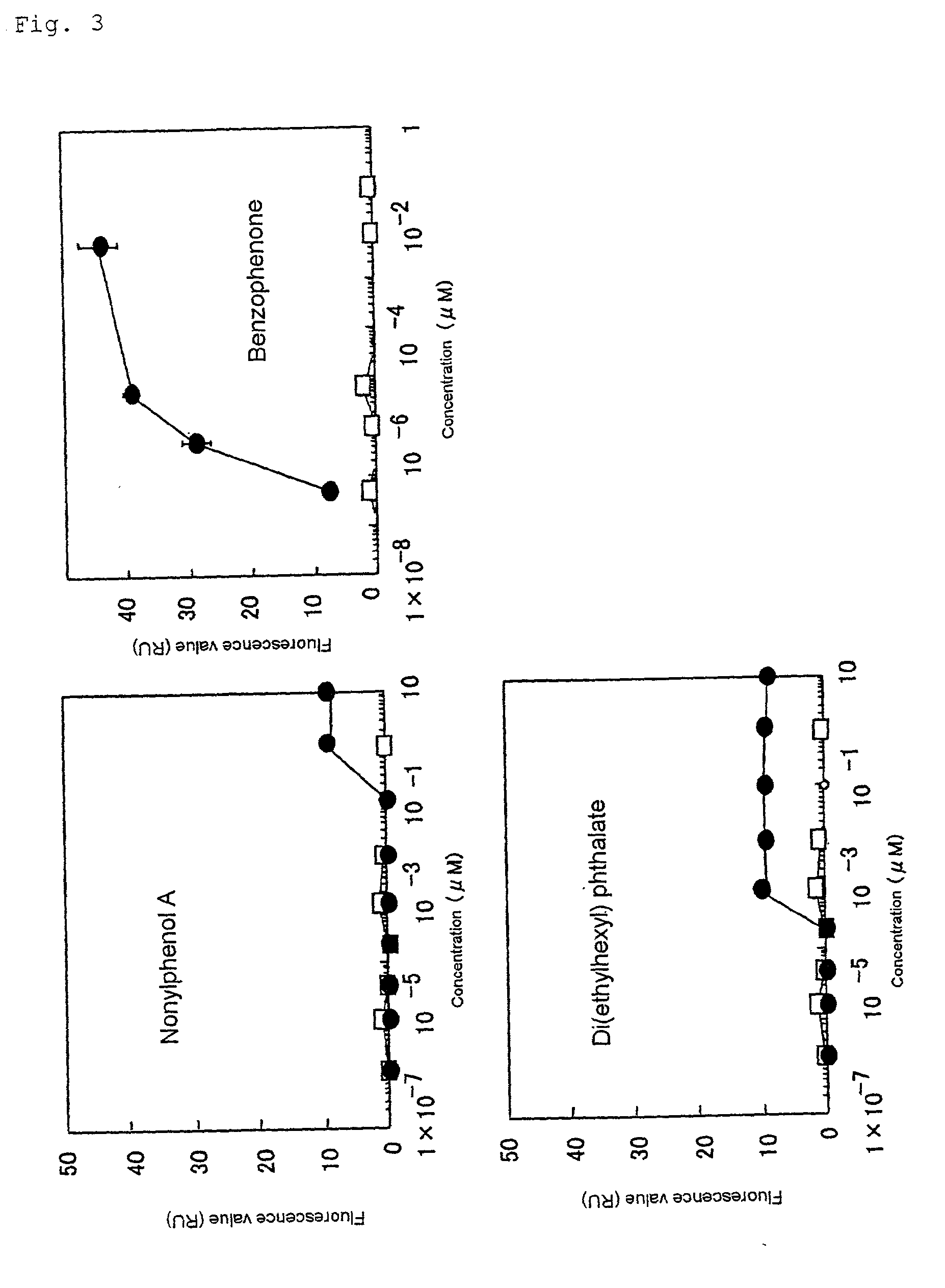
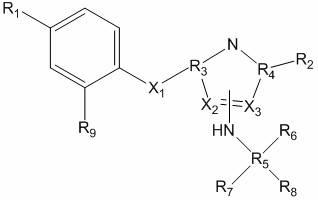
High-sensitive detection of environmental pollutants
The present invention is aimed to provide a bioassay system that can detect hazardous chemical substances or natural toxic substances in the environment, inclusive of the unknown homologs, with high sensitivity, simplicity and speed. The present invention is a method for detecting a hazardous chemical substance or a natural toxic substance, which comprises culturing a cell in a test sample-containing medium and then measuring a reporter gene protein inducing activity. Said cell is obtained by transferring a promoter containing a heat shock factor binding DNA sequence and a transcriptional regulatory sequence necessary on an occasion of stress induction as a transcriptional regulatory factor binding site, as well as a reporter gene under the control of said promoter into a chromosome, said reporter gene being connected, on the downstream side thereof, to the SV40pA signal without any intervening intron.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECHNOLGOY AIST ADMINISTATIVE INSTION IAI UNDER MINIST OF ECONOMY TRADE & IND +1
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
InactiveCN102088973AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBiological activationHeat Shock Transcription Factor
The present invention relates to HSF activating compounds, methods for their discovery, and their research and therapeutic uses. In particular, the present invention provides compounds capable of facilitating HSFl activation, and methods of using such compounds as therapeutic agents to treat a number of conditions associated with protein misfolding.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Promoter of cotton heat shock transcription factor GhHsf 39 genes and application of promoter
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and molecular breeding and discloses a promoter of cotton heat shock transcription factor GhHsf 39 genes and application of the promoter. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. When a plant is subjected to abiotic stress, the expression of target genes can be regulated by pghhsf39. When the pghhsf39 sequence cloned from upland cotton is subjected to different abiotic stress stimulus, the expression quantity of the GhHSF 39 genes can be increased. The pghhsf39 promoter disclosed by the invention is connected with the target genes so as to form an expression cassette, and transgenic plants subjected to adversity stress to regulate the expression of the target genes can be obtained. The invented pghhsf39 provides an important promoter element for researching plant stress resistance and disease resistance. Therefore, the promoter has wide application values.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
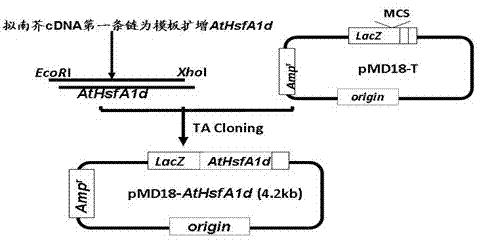
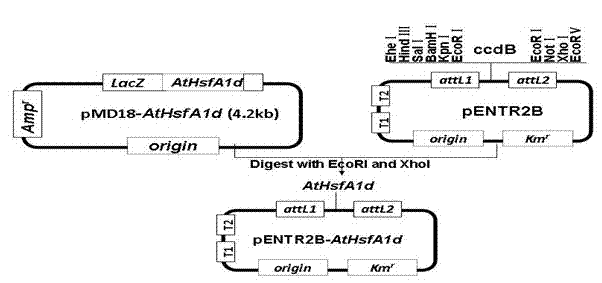
Heat-shock transcription factor gene AtHSFA1d, and coding protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the fields of plant molecular biology and transgenic correlation techniques, and particularly relates to verification of high-temperature-resistant functions of Arabidopsis thaliana heat-shock transcription factor gene AtHSFA1d and application of the gene in culture of new species of high-temperature-resistant plants. By using the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana as the material, the AtHSFA1d gene T-DNA insertion homozygous mutant strain system salk_058618 is utilized to research the functions of the AtHSFA1d gene in the plant high-temperature-resistance aspect. The experimental result shows that the AtHSFA1d gene knockout mutant is sensitive phenotype under heat shock stress and has obvious or extremely obvious differences from the wild type in the aspects of survival rate, electric conductivity, osmotic pressure, malondialdehyde, SOD (superoxide dismutase), POD (peroxidase) enzyme activities and other physiologic indexes, which indicates that the AtHSFA1d gene has important actions on signal transmission paths under plant response heat-shock stress. The overexpression of the gene is estimated to enhance the heat resistance of the plants and have great economic value in plant stress-tolerant molecule breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Arabidopsis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA5, its encoded protein and application
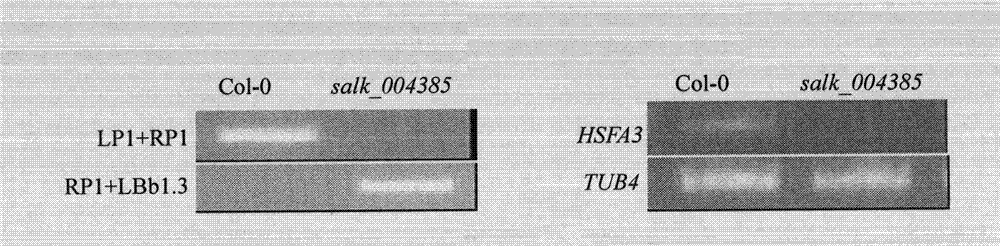
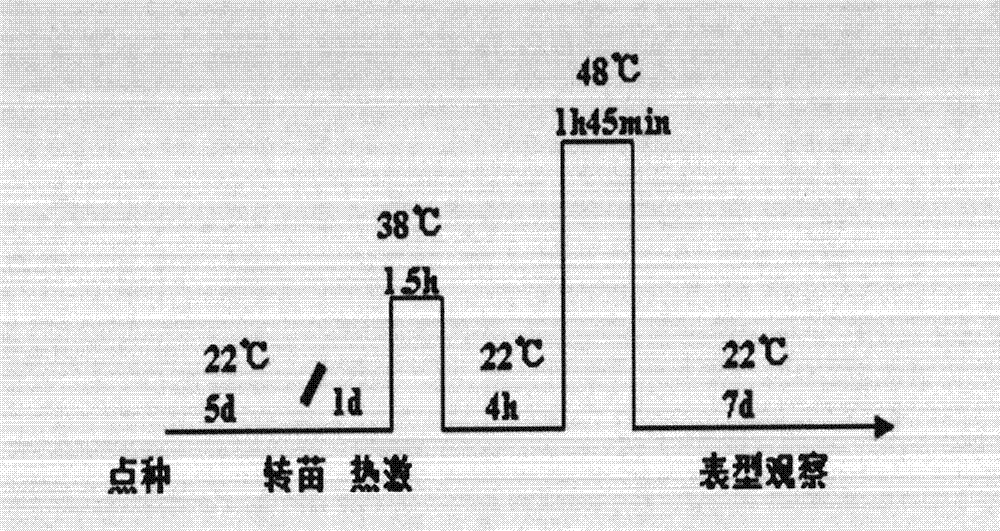
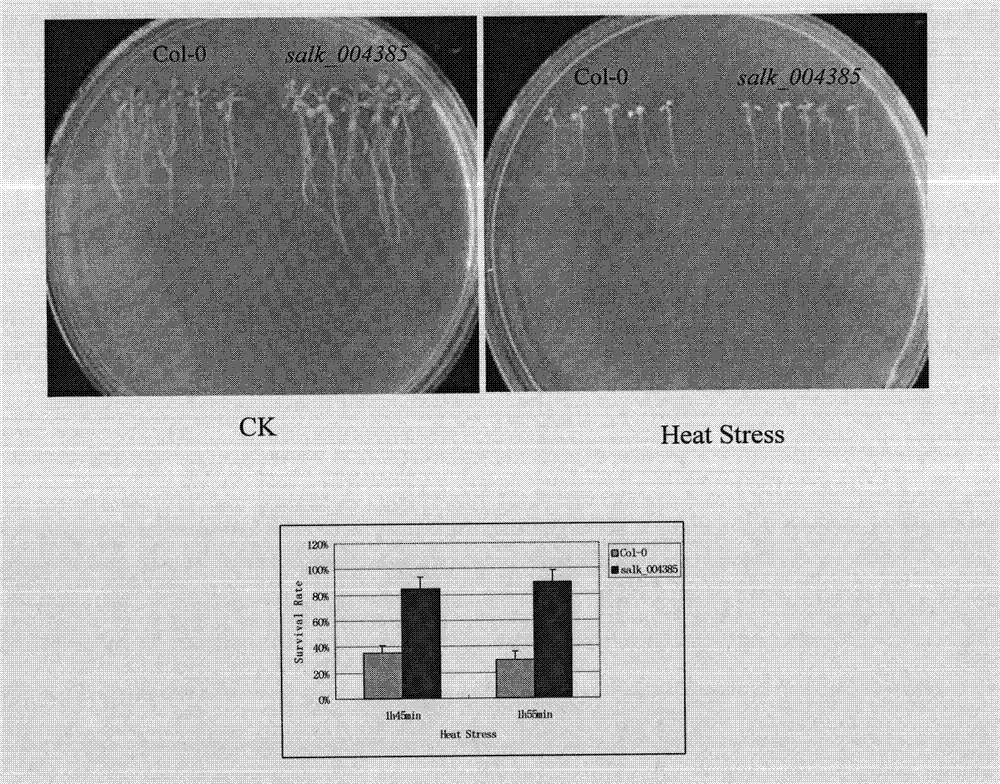
The invention belongs to plant molecular biology and transgenosis related technical field, and specifically relates to verification of the high temperature resistance function of the Arabidopsis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA5, and application of the gene in breeding new varieties of high temperature resistant plants. In the invention, the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana is adopted as the material, and T-DNA of the HSFA5 gene is inserted into a homozygous mutant strain salk_004385 to study the function of the HSFA5 gene in the aspect of plants' high temperature resistance. Experimental results show that: the HSFA5 gene knockout mutant shows a heat resistant phenotype under heat shock stress, and its survival rate is significantly higher than that of a wild type; and the HSFA5 gene plays an important role in a signal transduction pathway of plants' stress response to heat shock stress, and it is estimated that overexpression of the gene can improve heat resistance of plants and has great economic value in molecular breeding of plant stress resistance.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compositions and methods for regulating cellular protection
InactiveUS20090075948A1Increasing Hsp7 synthesisIncrease transcriptionBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaSalicylic acid
The invention provides a method of inducing a protective response in cells by activating a heat shock response, via heat shock transcription factor (HSF), without stressing the cells. The invention is based on the surprising discovery that HSF can be activated in non-stressed cells by disrupting interaction with the repressive cognate protein, Hsc70. As described herein, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), including salicylic acid and ibuprofen, can stimulate HSF DNA binding, Hsp70 transcription and Hsp70 protein synthesis in non-stressed cells. By activating HSF, the degenerative effects of certain neurodegenerative proteins such as polyglutamine repeat proteins (Huntington's disease) and the α-synuclein protein (Parkinson's disease) can be offset. The invention thus provides a method of ameliorating symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Heat shock transcription factor gene AtHSFA6a, coding protein, and applications thereof
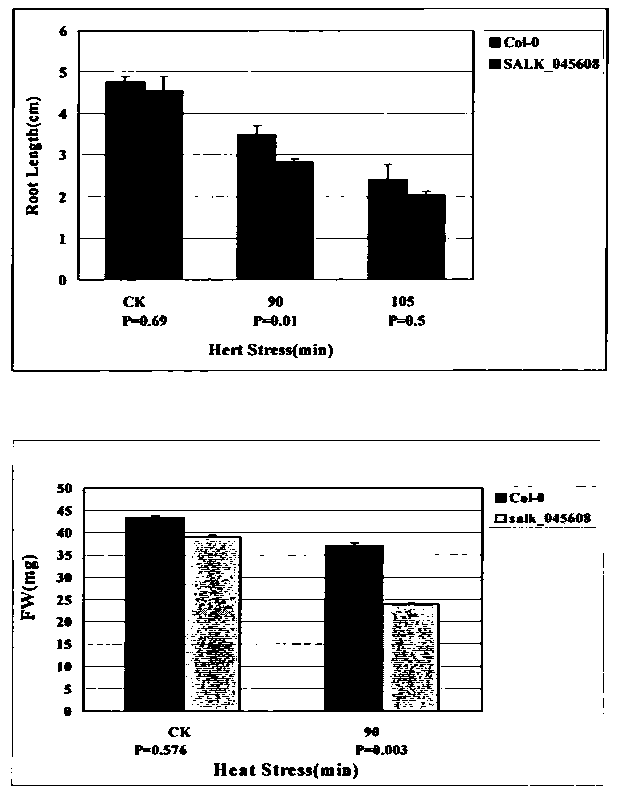
The invention belongs to the plant molecular biology and transgenosis related technical fields, concretely relates to verification of high temperature resistant function of arabidopsis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene AtHSFA6a, and provides applications of the gene in cultivation of high temperature resistant new varieties of plants. The model plant arabidopsis thaliana is employed as a material, the AtHSFA6a gene T-DNA is inserted into a homozygous mutant strain salk-045608, and the functions of the AtHSFA6a gene in the aspect of plant high temperature resistance are studied. Experiment results show that, the AtHSFA6a gene knockout mutant shows a sensitive phenotype under heat shock stress, and is significantly or highly significantly different from the wild type at aspects of physiological indices of root length, fresh weight of an overground part, conductivity, osmotic pressure, malondialdehyde content, SOD enzymatic activity and the like, which shows that the AtHSFA6a gene plays an important role in the signal transduction pathway of response to heat shock stress of plants, and predicts that overexpression of the gene can raise heat resistance of plants, which has large economic values in plant stress resistance molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
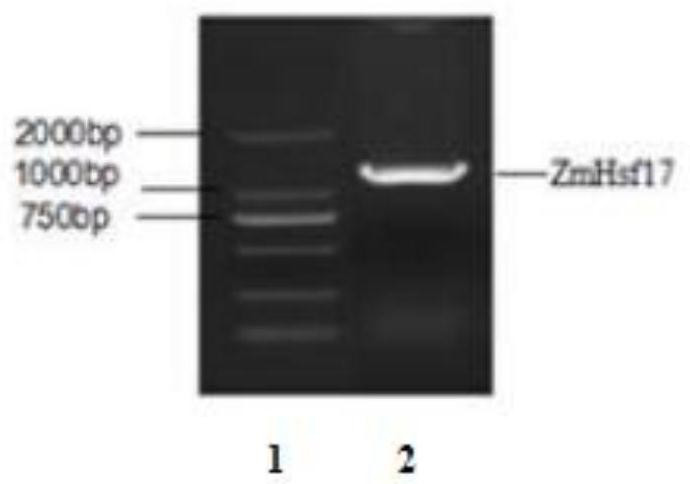
Antioxidant function of corn heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf17 encoding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN112625100AImprove antioxidant capacityIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an antioxidant function of a corn heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf17 encoding protein and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the corn heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf17 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, the gene ZmHsf17 is obtained by cloning from a corn (Zea mays L.) inbred line H21, and can activate the expression of a plurality of downstream stress-resistant functional genes, and the gene can significantly improve the antioxidant function of plants by transforming arabidopsis. The corn heat shock transcription factor encoding gene of the invention will provide a backup gene resource for crop stress resistance genetic improvement and germplasm innovation.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
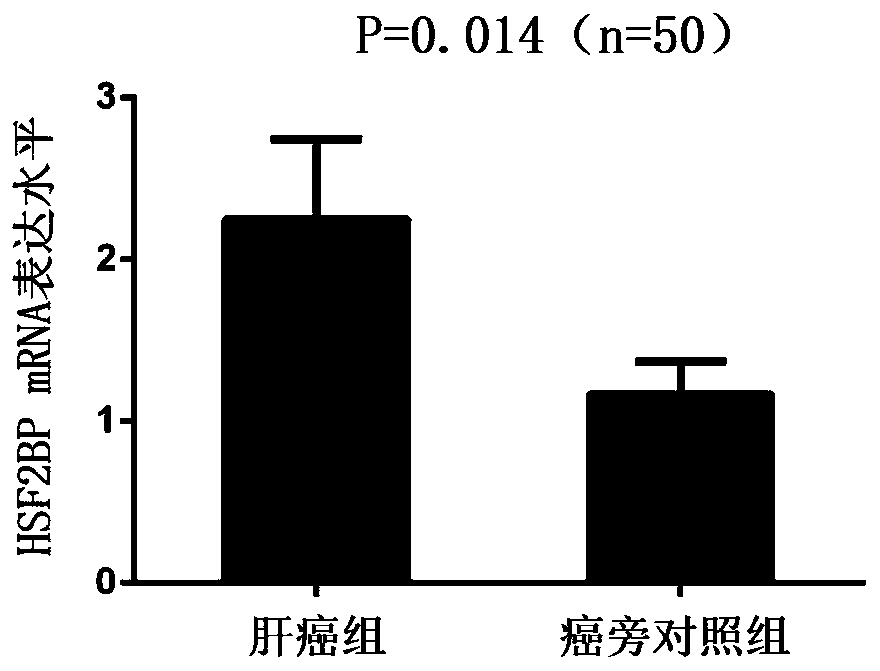
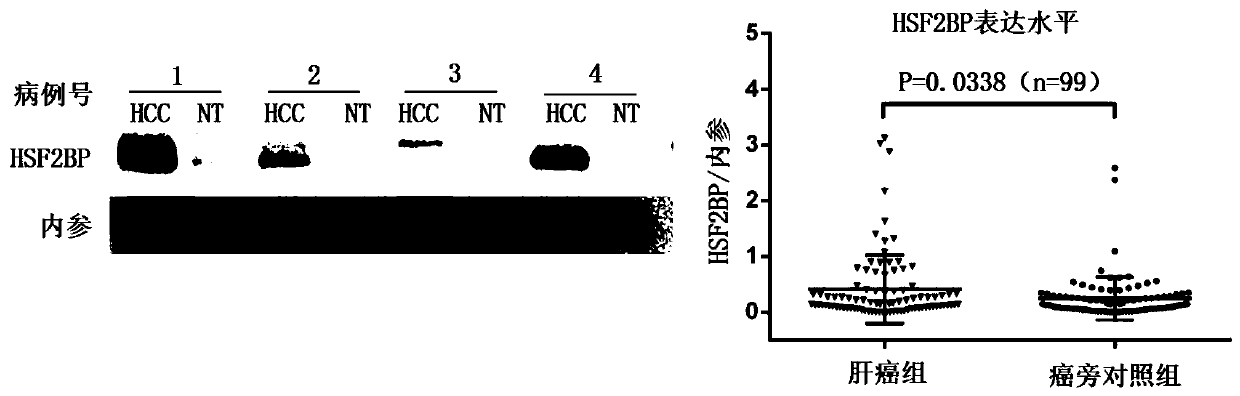
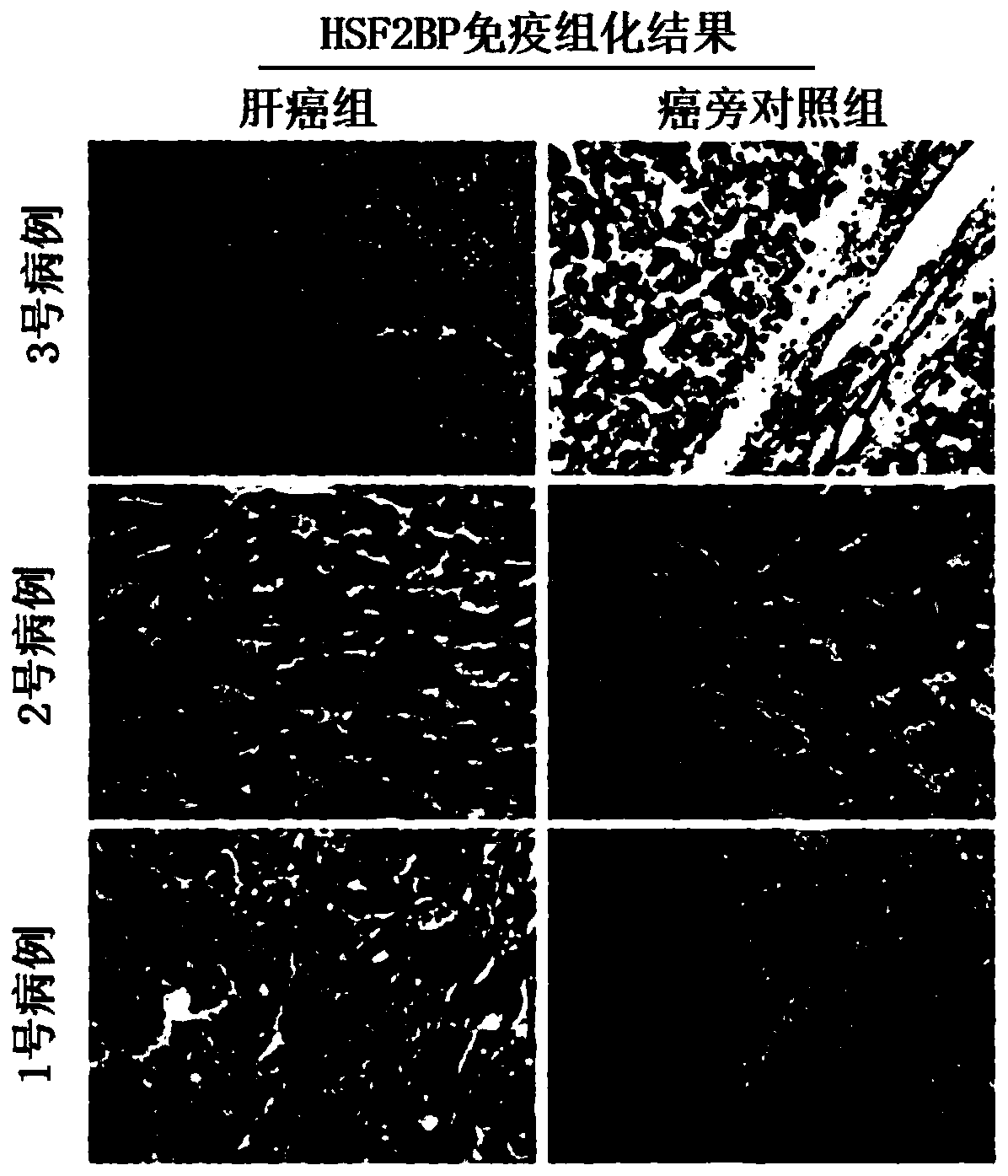
Liver cancer tumor marker heat shock factor 2 binding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN110885366AHigh clinical application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWestern blotHeat Shock Transcription Factor
Owner:崇好科技有限公司
Plant expression vector of arabidopsis heat shock factor gene AtHsfA1d, and application thereof
InactiveCN102363790AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a plant expression vector of an arabidopsis heat shock factor gene AtHsfA1d, and the application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, the plant expression vector pK2-35S-AtHsfA1d is constructed by the arabidopsis heat shock factor gene AtHsfA1d, and is transferred into the plant via Agrobacterium mediation, so that the absorption capacity and the tolerance of the plant to the methanal are improved, and own defects of low absorption capacity and low tolerance to the methanal of the plant are solved; the experimental resultsshow that, after being cultred for 7 days in a MS solid culture medium containing 6mmol / L methanal, the transgenic tobacco with over-expression of an AtHsfA1d transcription factor has greater fresh weight than that of the wild tobacco, and the methanal absorption speed of the plant of the transgenic AtHsfA1d tobacco in 4mM methanal is higher than that of the wild tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
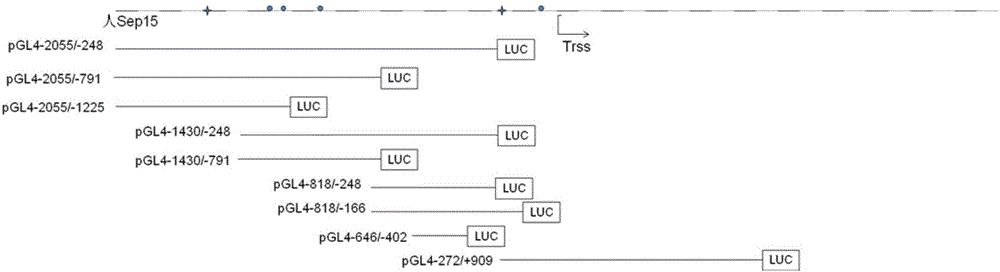
Application of heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating expression of 15kDa selenoprotein
The invention discloses an application of a heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating expression of a 15kDa selenoprotein. The application provided by the invention is specifically any one of the applications of the heat shock transcription factor 1: (a1) promoting expression of a Sep15 protein in a target cell; (a2) promoting transcription of a Sep15 gene; and (a3) enhancing the activity of a Sep15 promoter in the target cell. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a transcription factor HSF1 can be combined with the Sep15 promoter to adjust transcription of the Sep15 gene and accelerate expression of the Sep15 protein. Under a heat shock and fever of a physiological status, the transcription factor HSF1 can start transcription of Sep15 and improve expression of Sep 15 so as to participate the physiological process and help the protein being corrected folded or help the protein being unfolded and delivered to other proteins to help the proteins to be folded correctly. Under endoplasmic reticulum stress, the HSF1 also can promote expression of Sep 15 to participate protein quality control of endoplasmic reticulum so as to further promote cell survival. The application disclosed by the invention is of important significance in preventing and / or treating endoplasmic reticulum stress related diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
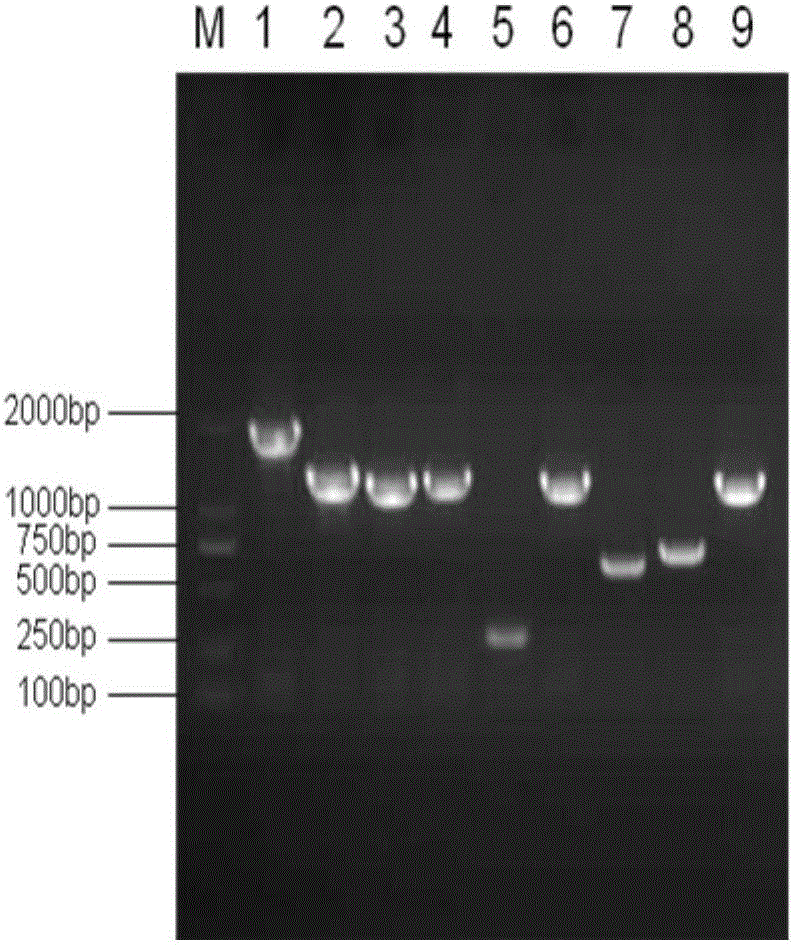
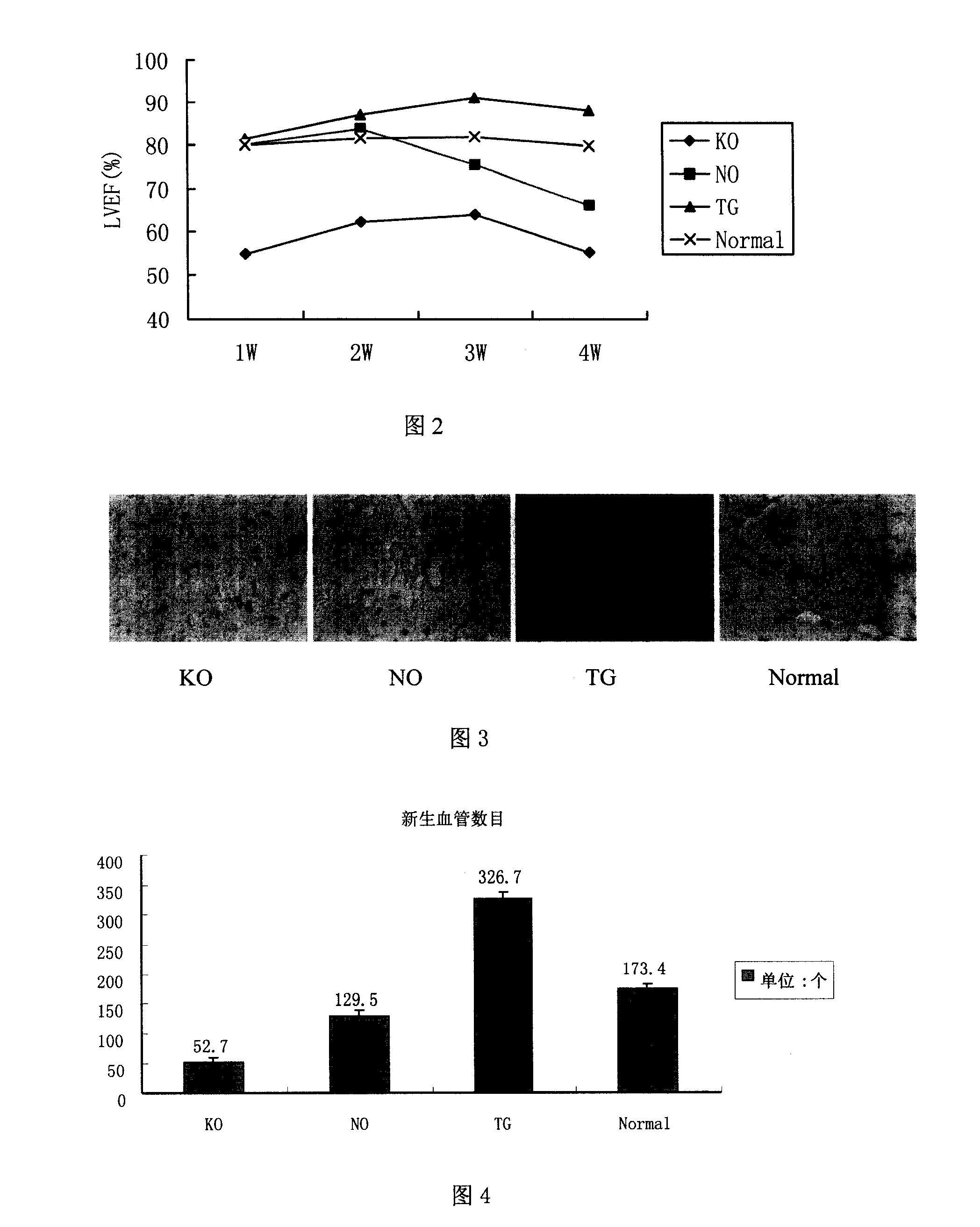
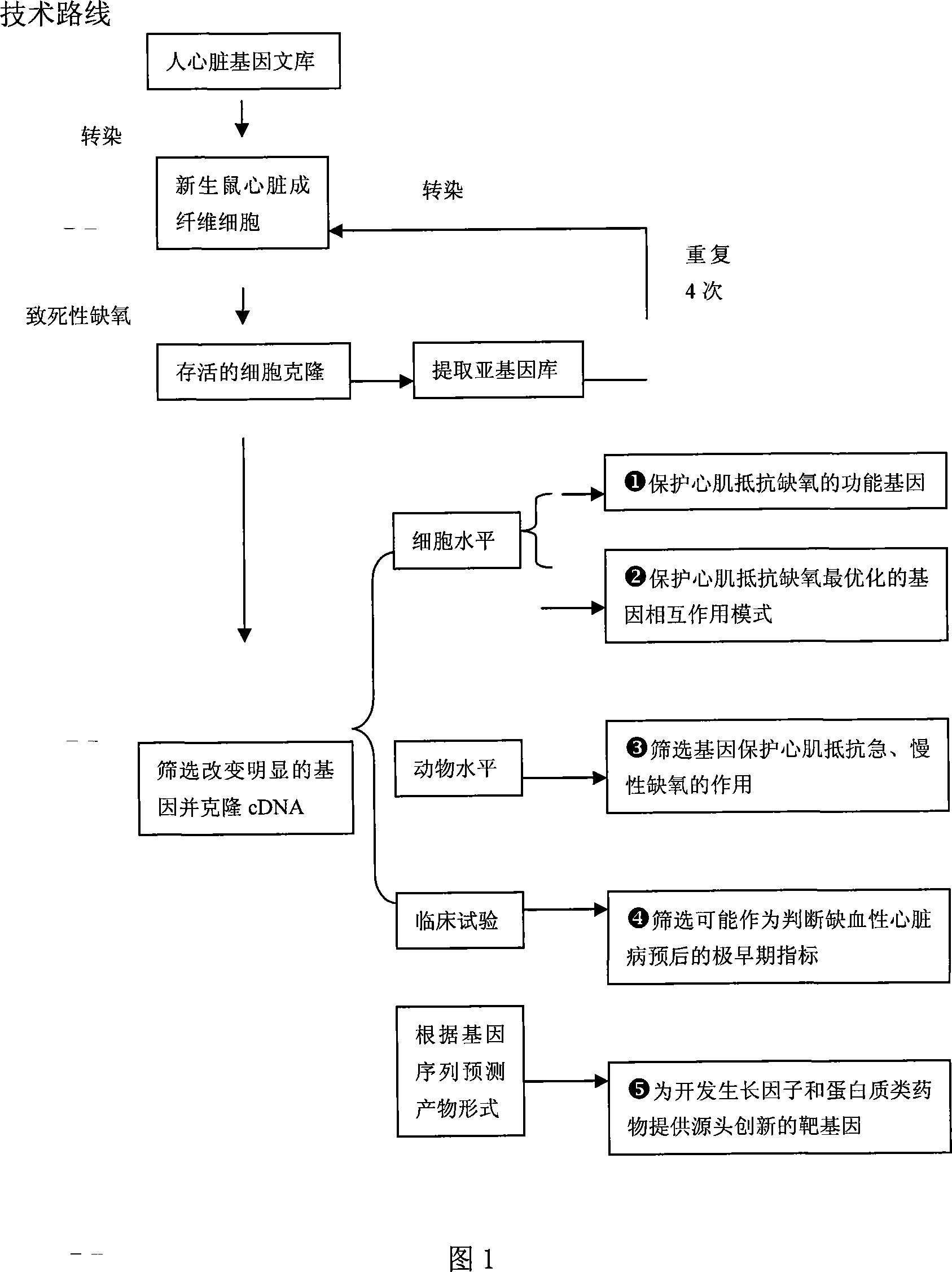
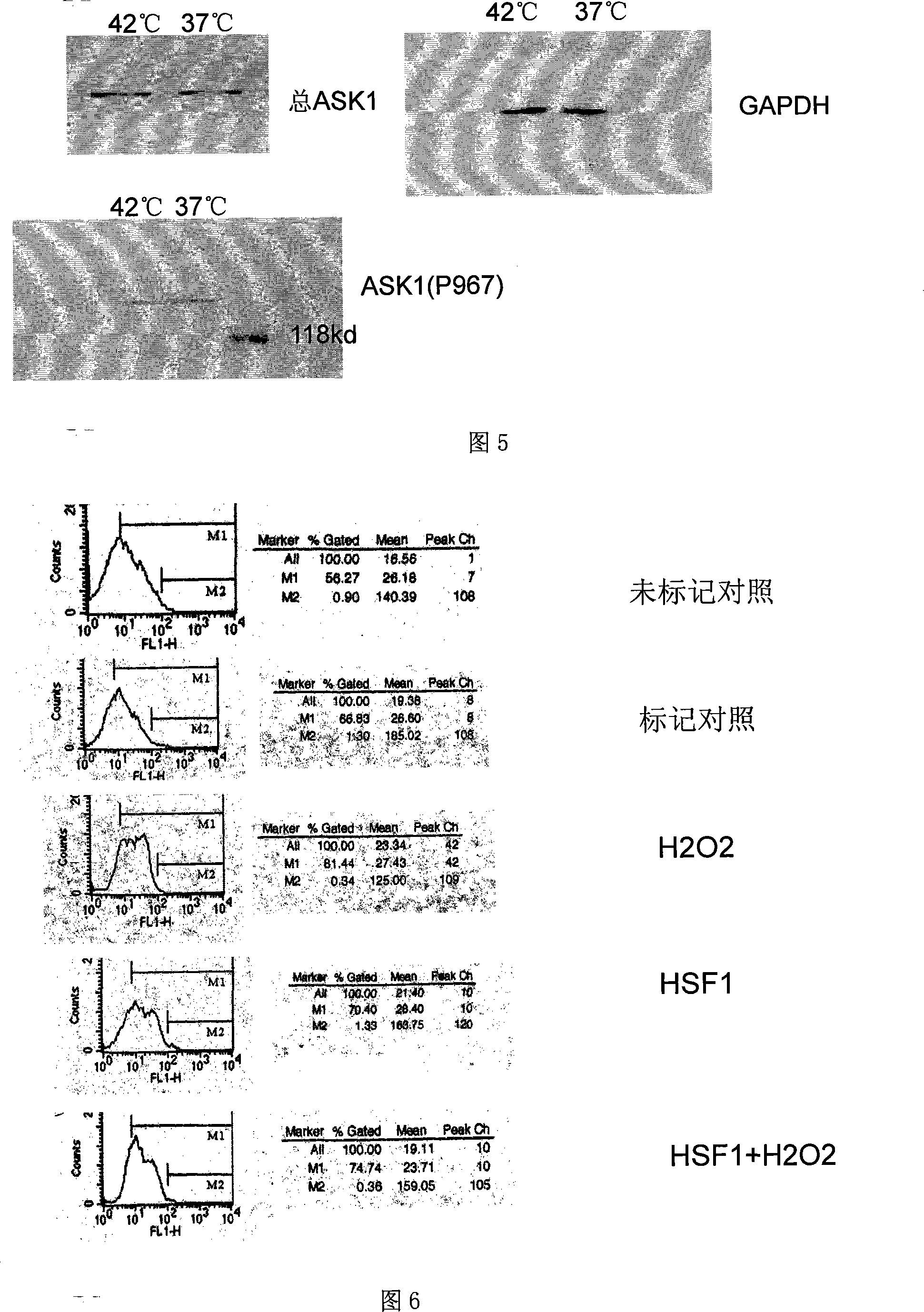
Human myocardium protecting gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101200721APurposefulWith precisionGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringHSF1Organism
The present invention belongs to the biotechnological field and relates to a human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor (HSF1) and a sieving method and a purpose thereof. The present invention adopts the method of ''death trap'' that the gene which resists myocardial cell death is sieved from human cardiac gene, and the human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor 1 is cloned from the obtained gene. The result of transfection cell and animal experiment shows that the obtained human myocardial protection gene has the function of resisting cell death and also has the function of resisting ischemia, protecting myocardial cell and preventing and remedying the heart failure occurrence and development inside the heart of a living organism. The present invention can prepare for the medicine for remedying the ischemic heart disease and preventing the cardiac insufficiency and provides a novel target gene for the further function research and the gene engineering medicine development, which has important meaning for the early prevention and treatment of the heart failure and the research and the development of the related medicines and measures.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Method of enhancing gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20110131680A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellHeat Shock Transcription Factor
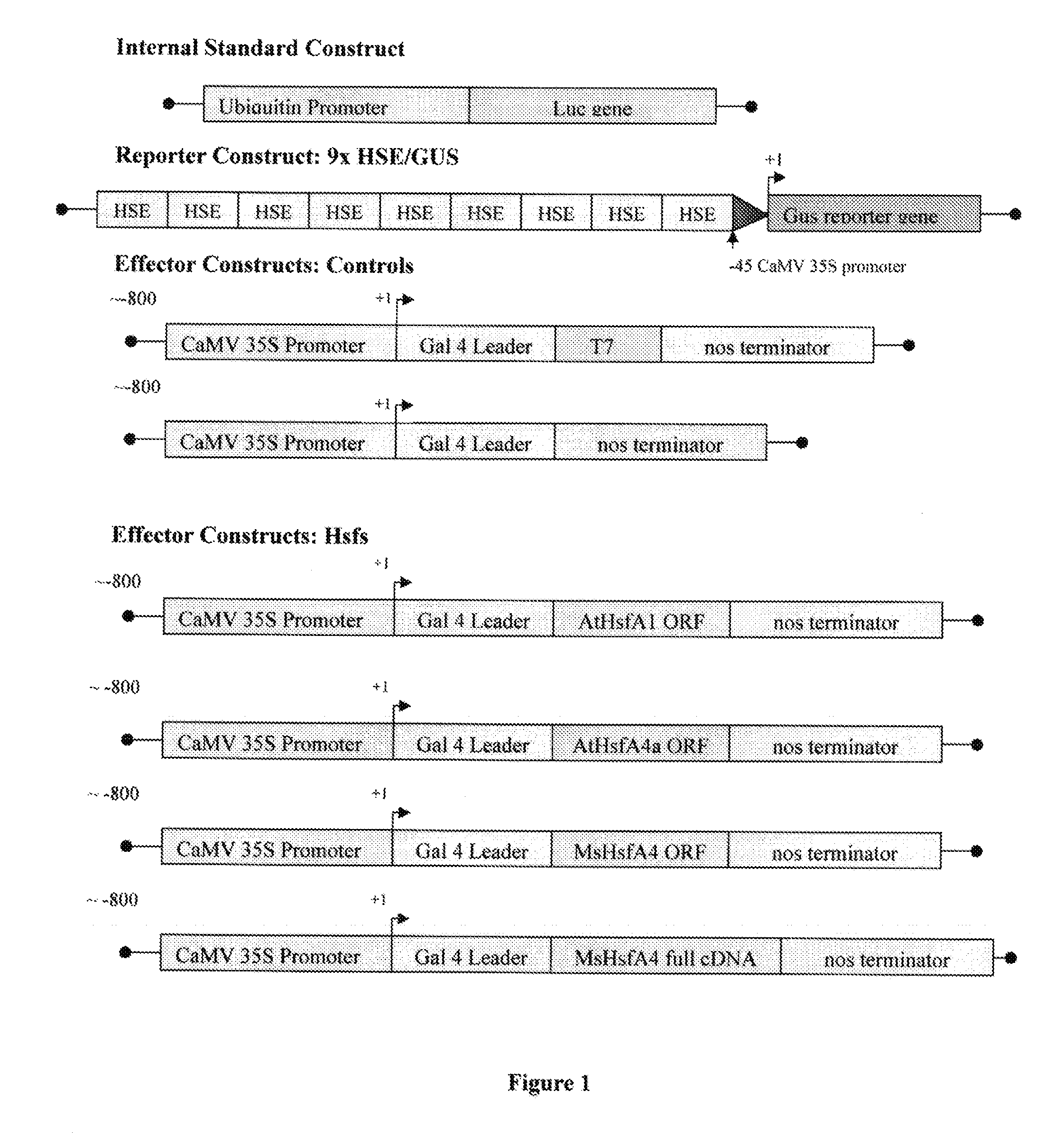
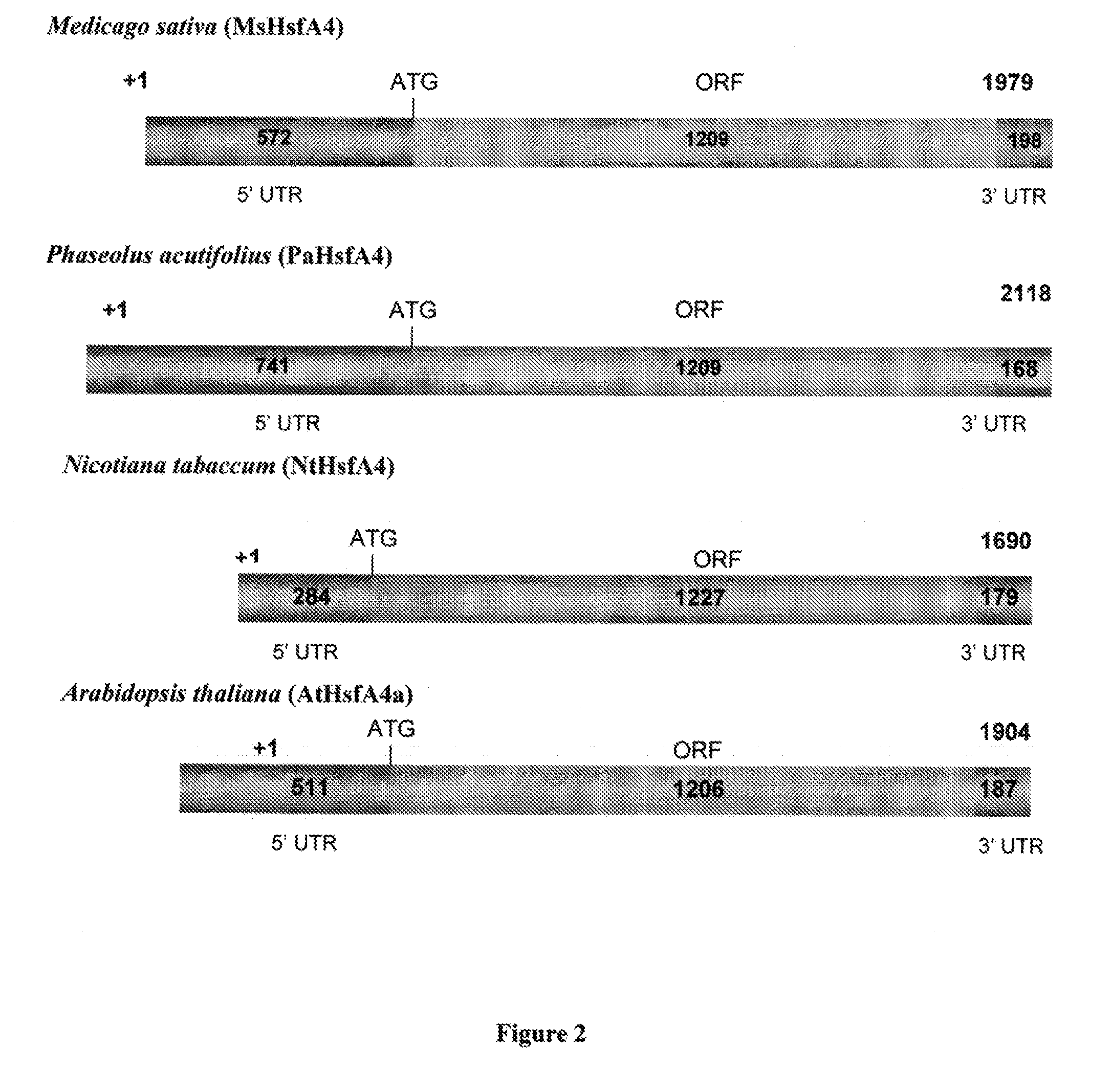
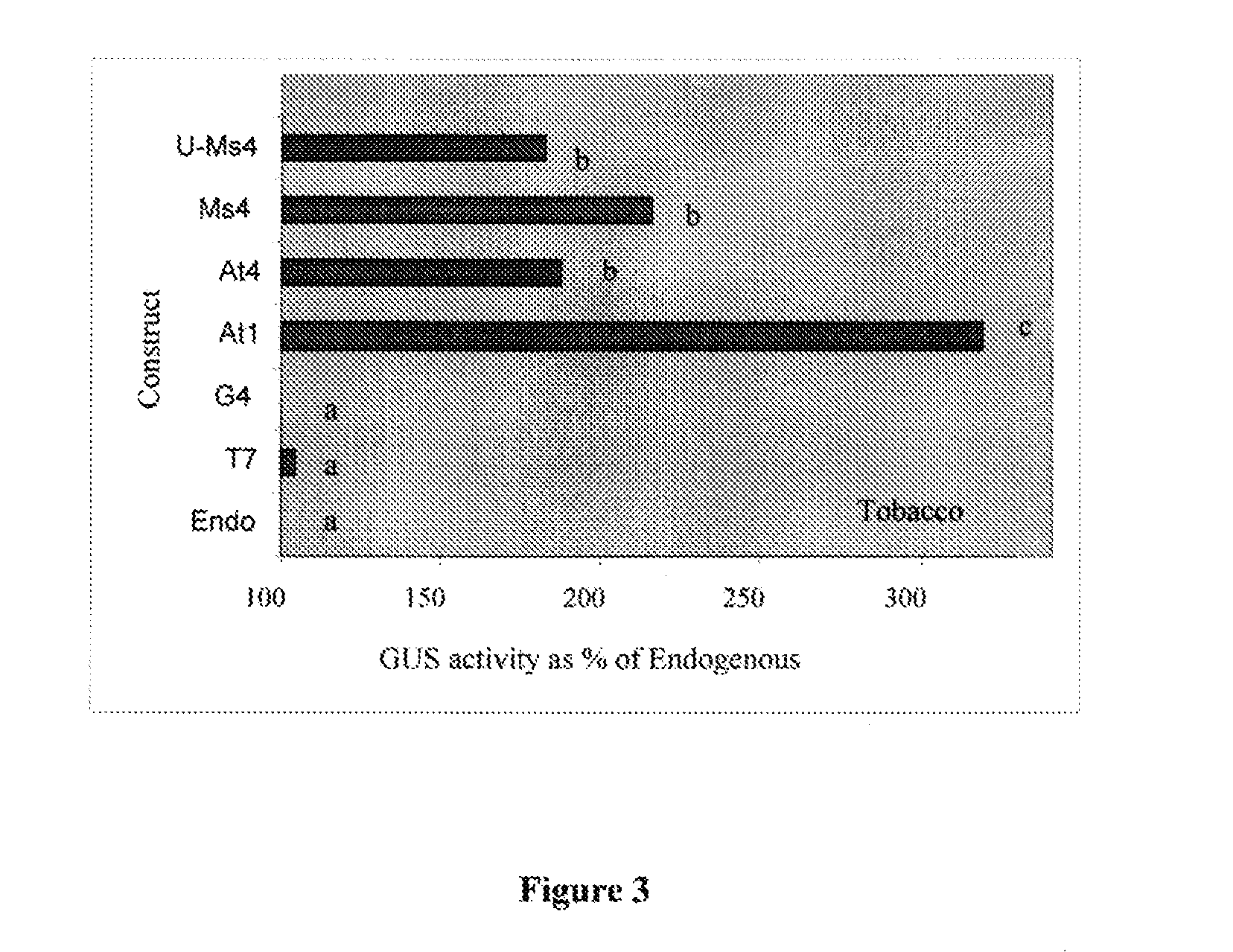
A method of enhancing the expression of a gene in a legume plant is provided comprising introducing into the cells of said plant a construct comprising at least a portion of a 5′-untranslated region of a heat shock transcription factor gene from Medicago sativa (MsHsfA4) upstream of a gene to be expressed. Plant cells capable of expressing enhanced levels of a gene are also provided. The cell comprises a construct comprising at least a portion of the 5′-UTR of the MsHsfA4 gene upstream of the gene to be expressed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
InactiveUS20130267543A1Improve quality controlBiocideSenses disorderHeat Shock Transcription FactorHSF1
Owner:CHAPERONE THERAPEUTICS +1
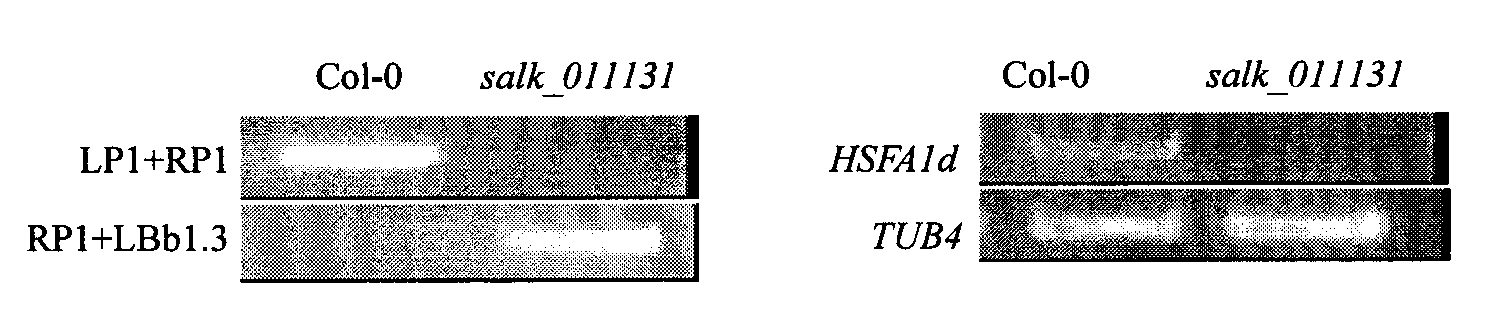
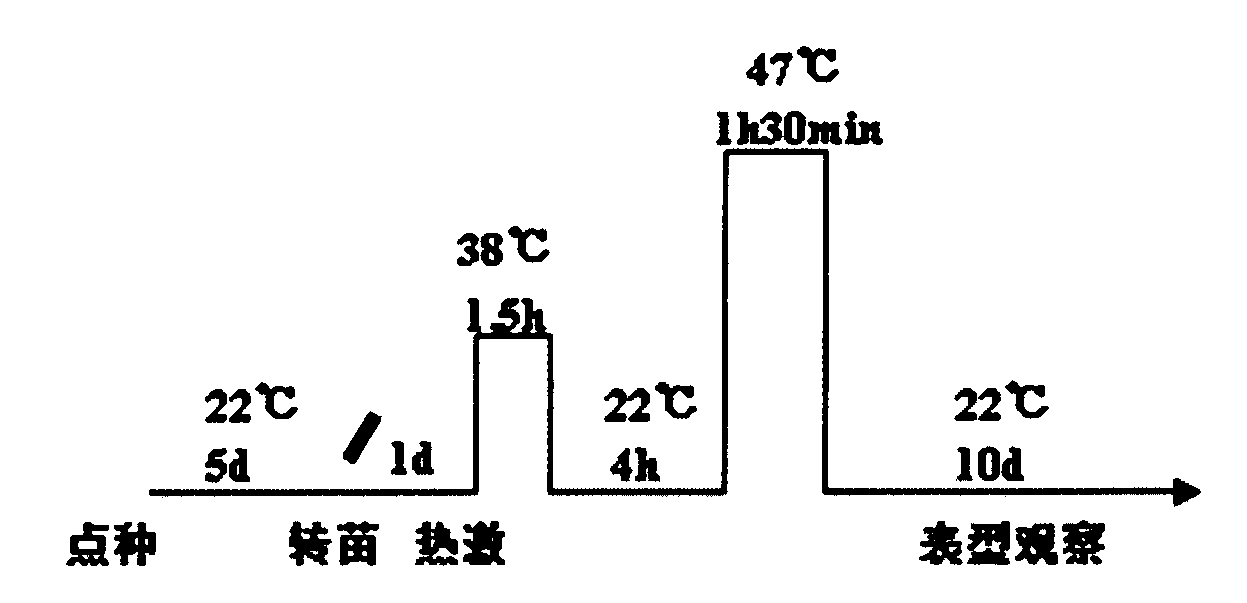
Arabidopsis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA3, encoding protein and applications thereof
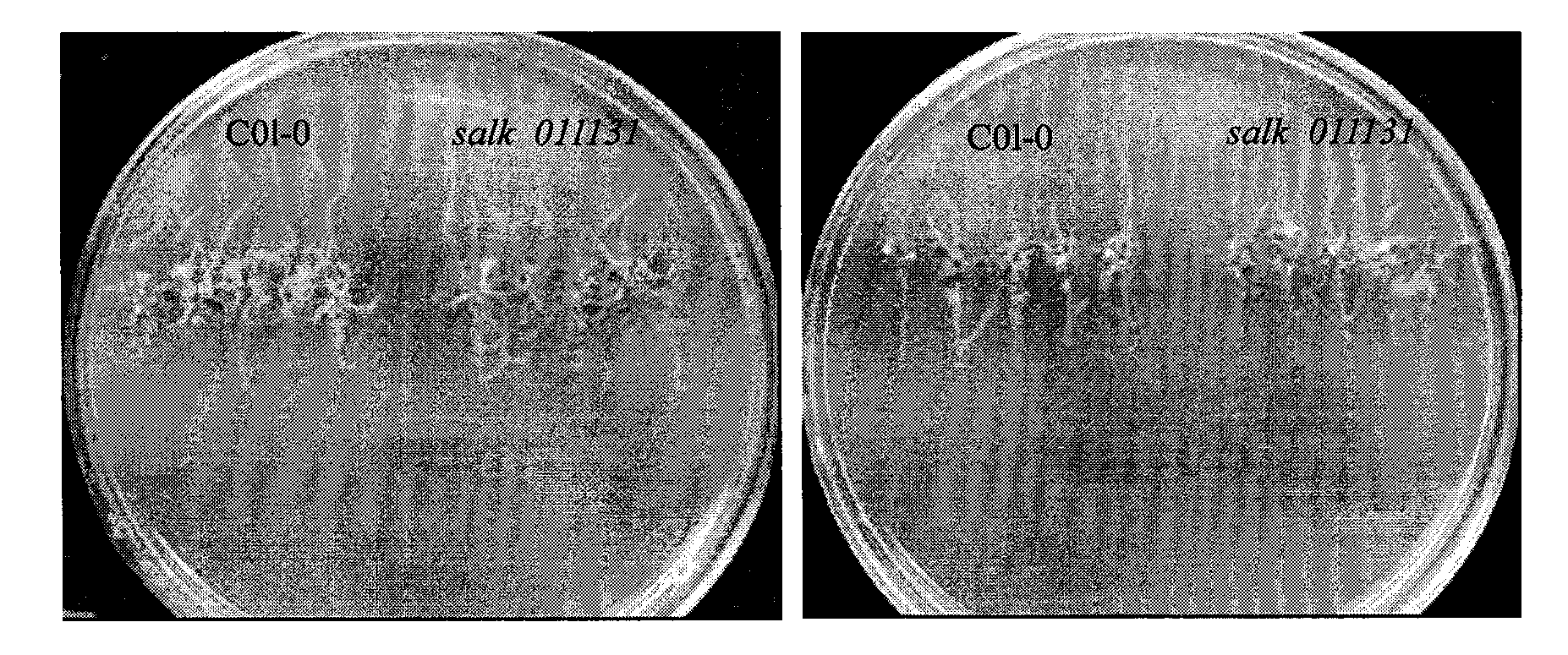
The invention belongs to the plant molecule biology and transgenic related technical field, and specifically relates to verification of high temperature resistance of arabidopsis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA3 and applications of the gene in breeding of new high temperature resistance varieties. According to the present invention, a model plant arabidopsis thaliana is adopted as a material, and HSFA3 gene T-DNA is adopted to insert into a homozygosis mutant line salk_011131 so as to research functions of the HSFA3 gene in the field of high temperature resistance of plants, wherein experiment results show that the HSFA3 gene knocked out mutant presents a heat resistance phenotype under heat shock stress, and a root length and above-ground biomass of the HSFA3 gene knocked out mutant are significantly more than a root length and above-ground biomass of the wild type, such that the HSFA3 gene provides important effects in a signal transduction pathway of the plant response to heat shock stress, and it can be predicted that overexpression of the gene can increase heat resistance of the plant and can provide high economic values in plant stress tolerance molecule breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com