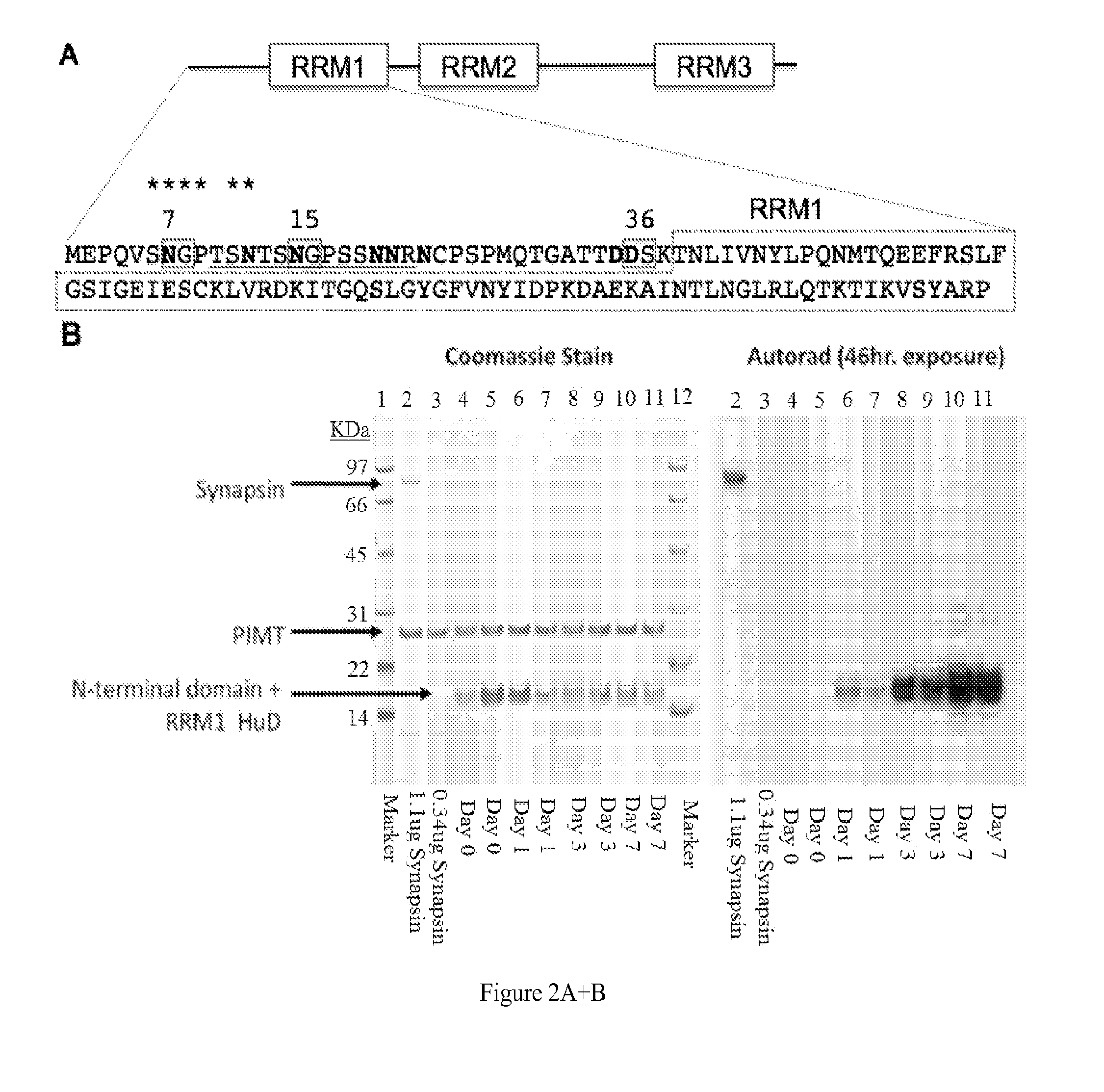
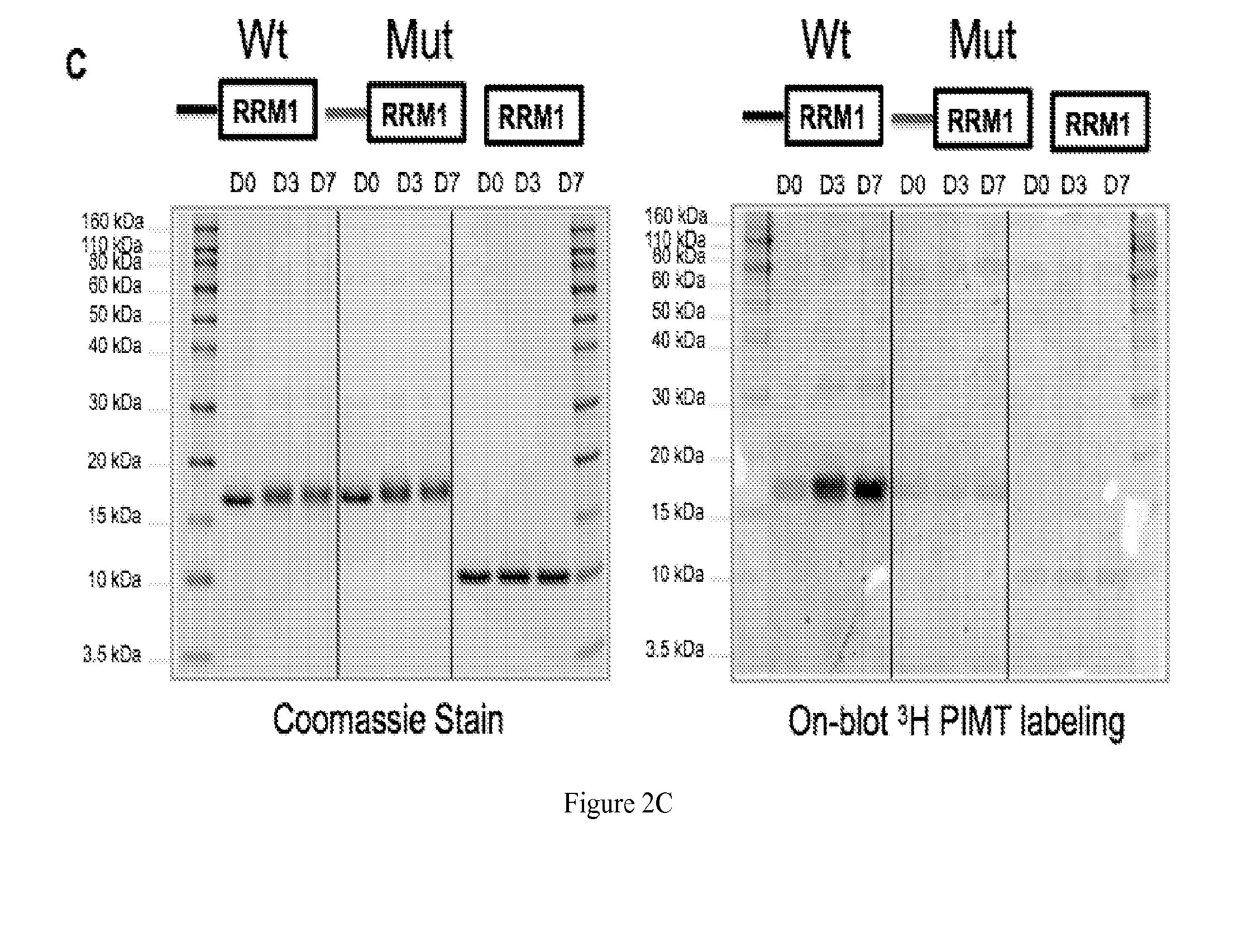
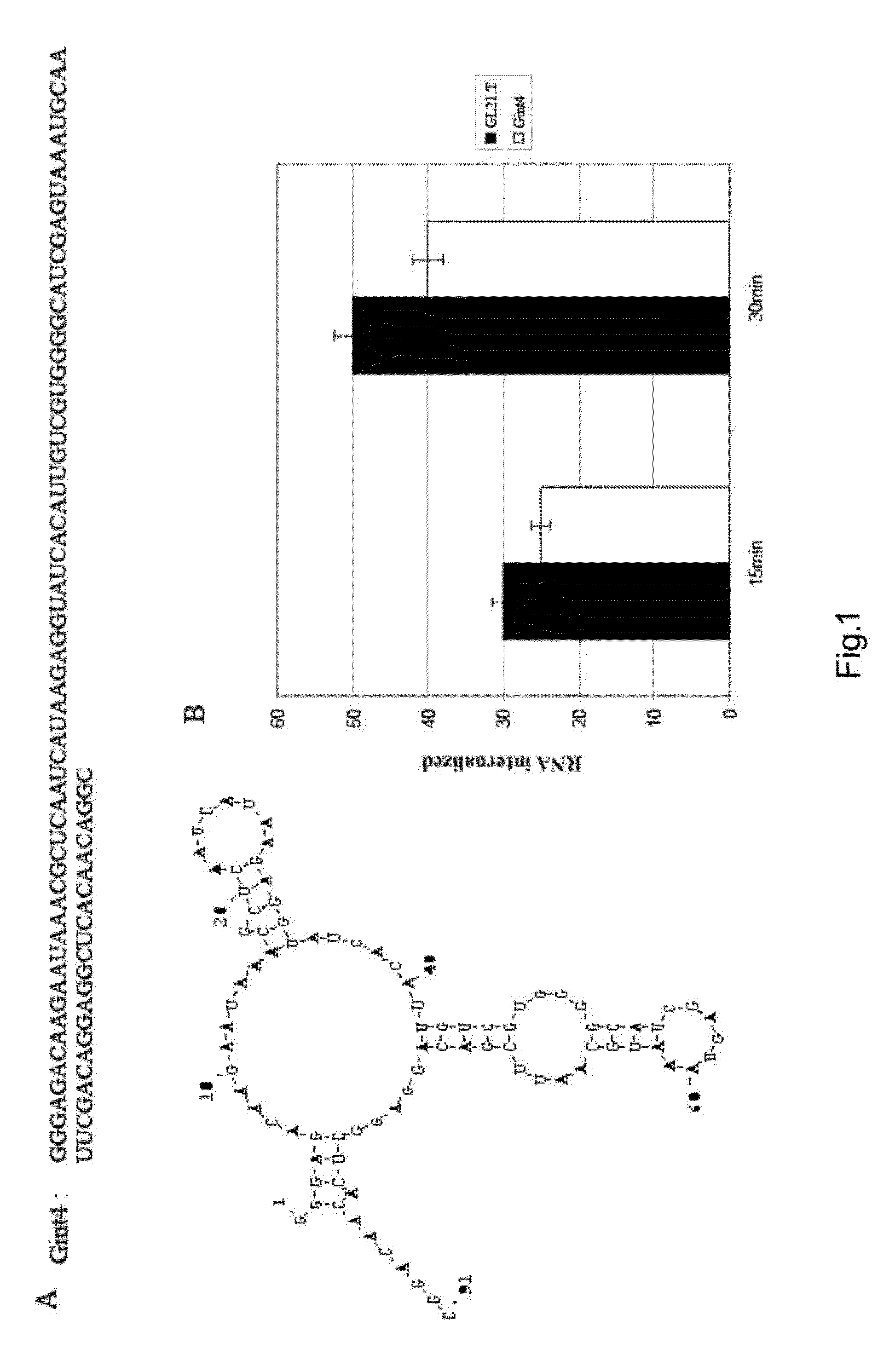
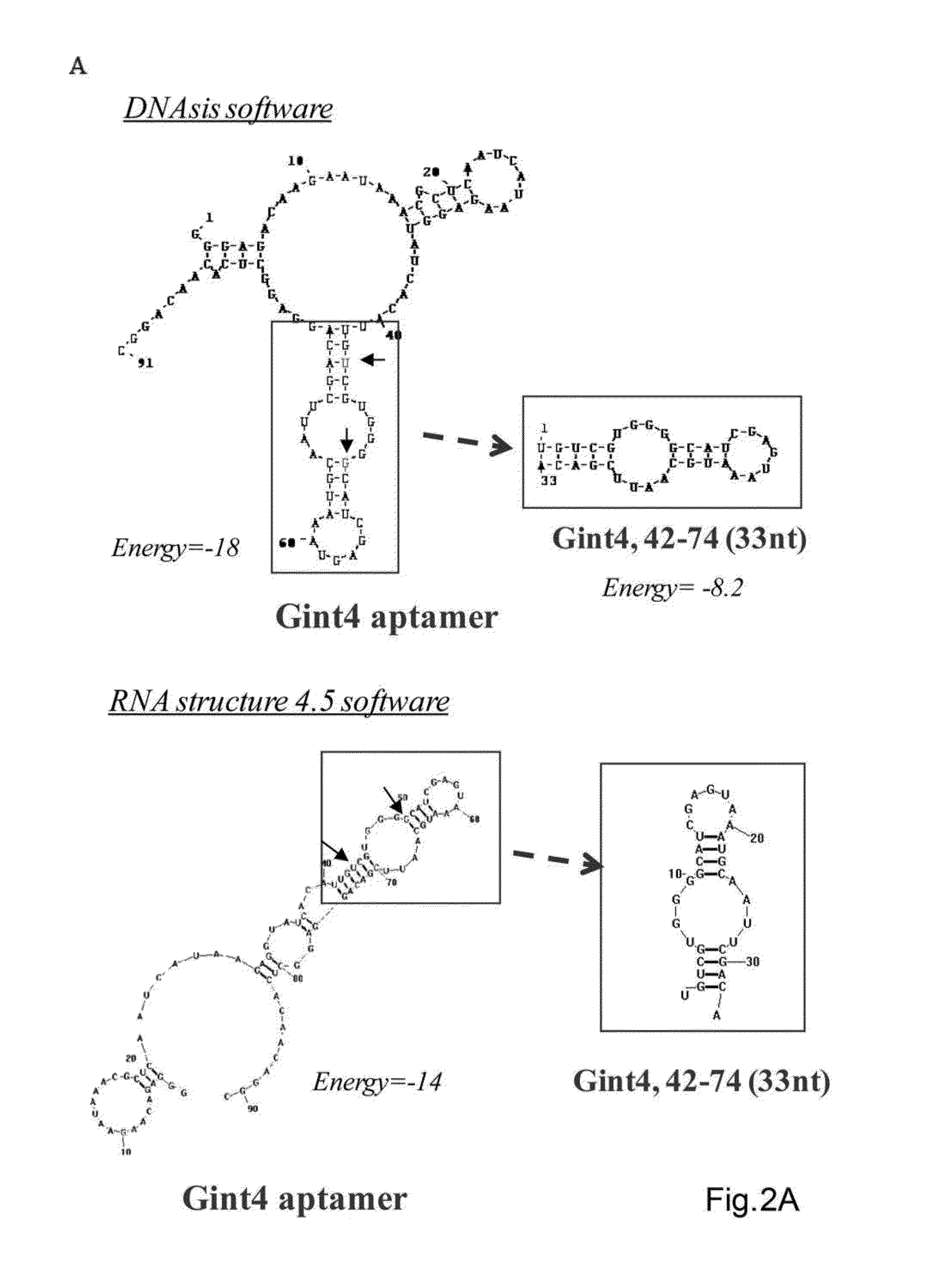
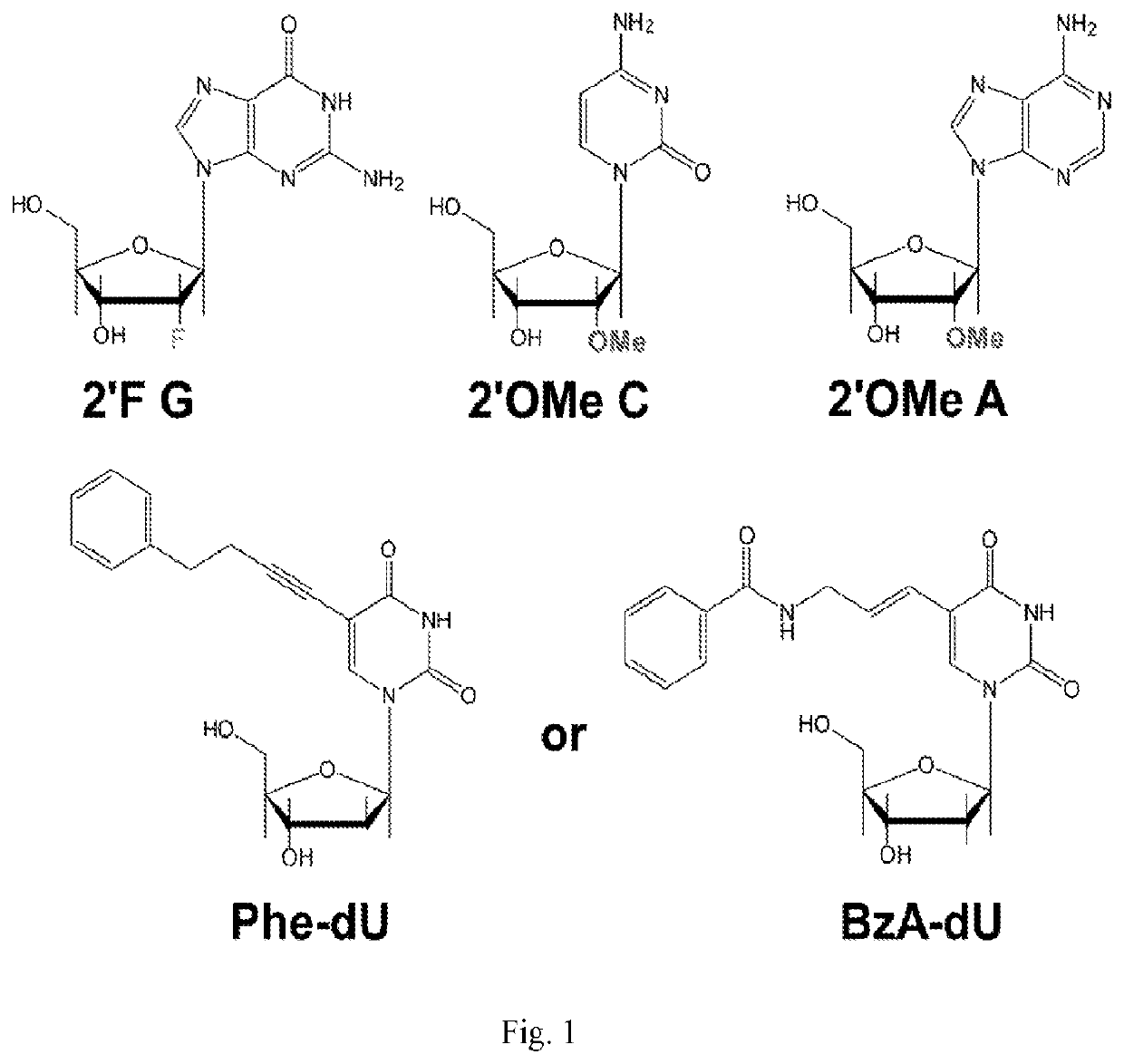
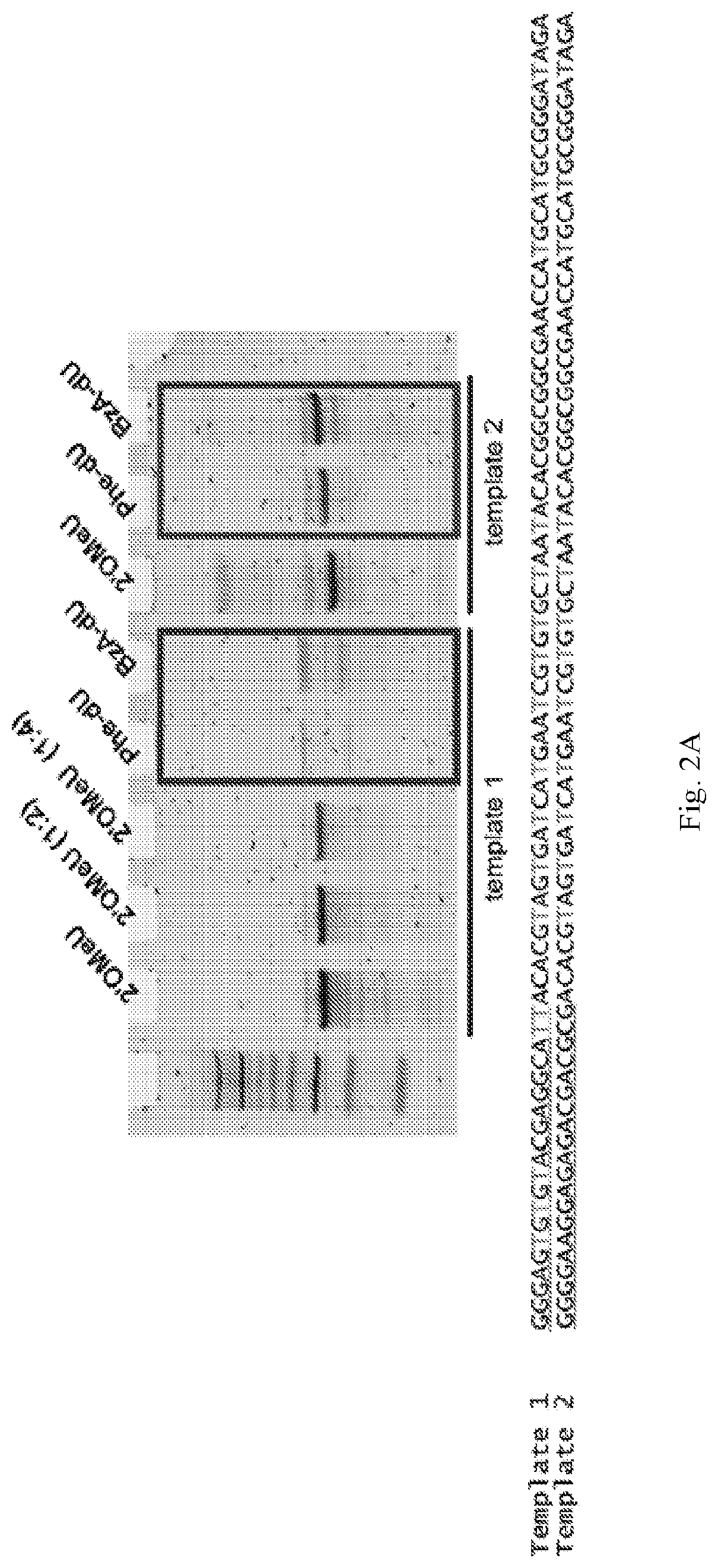
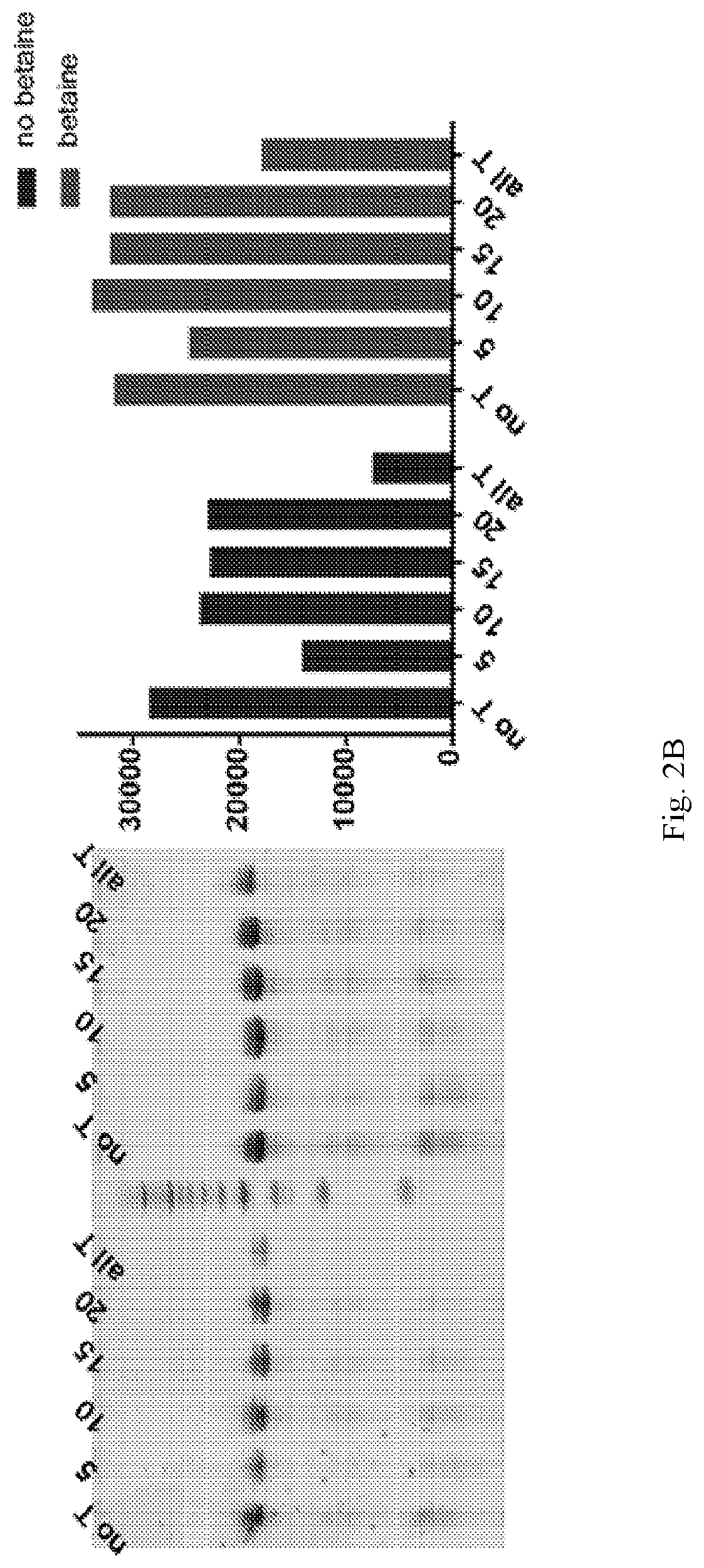
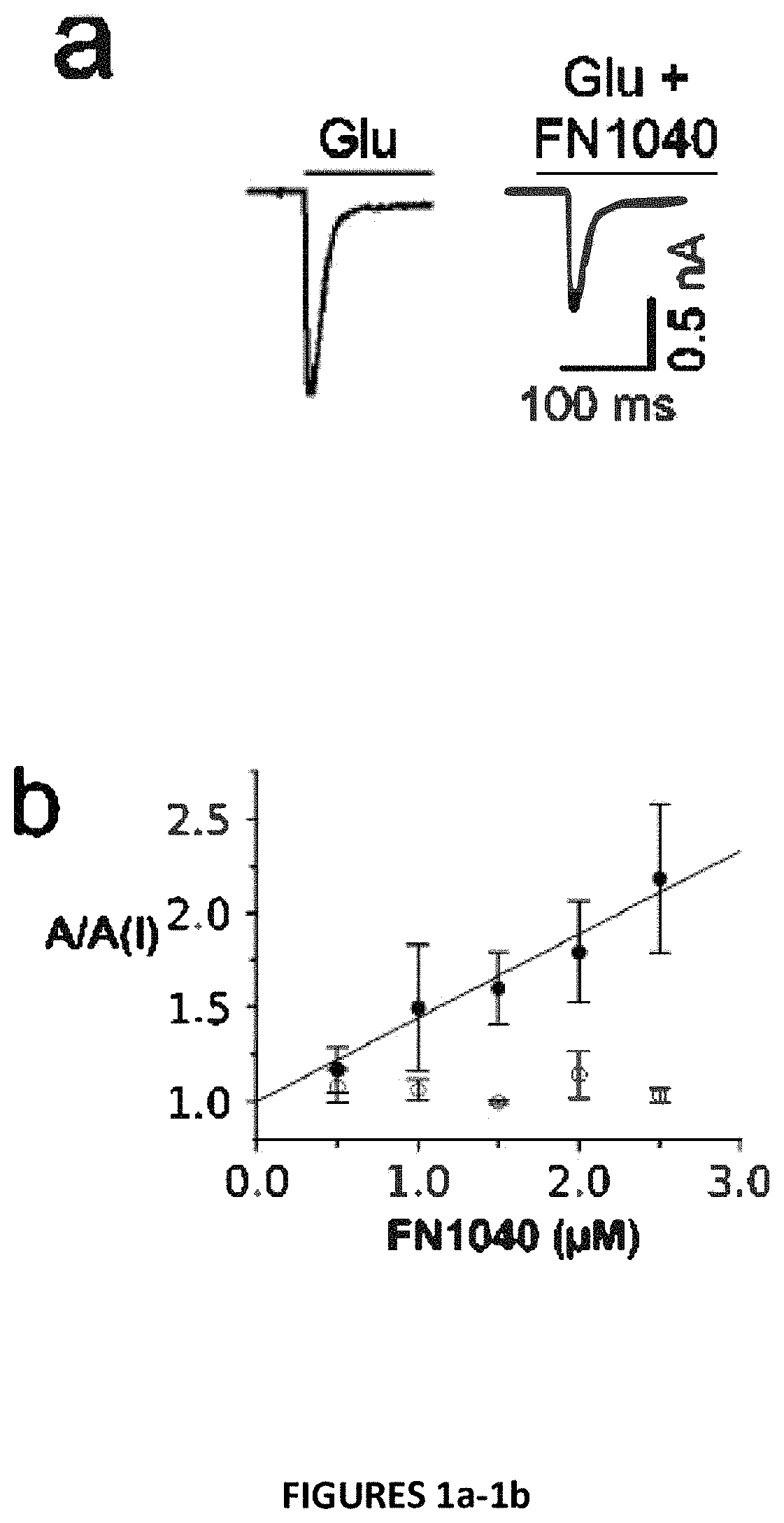
Patents
Literature
33 results about "RNA Aptamers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An L-ribonucleic acid aptamer (L-RNA aptamer, trade name Spiegelmer) is an RNA-like molecule built from L-ribose units. It is an artificial oligonucleotide named for being a mirror image of natural oligonucleotides. L-RNA aptamers are a form of aptamers.
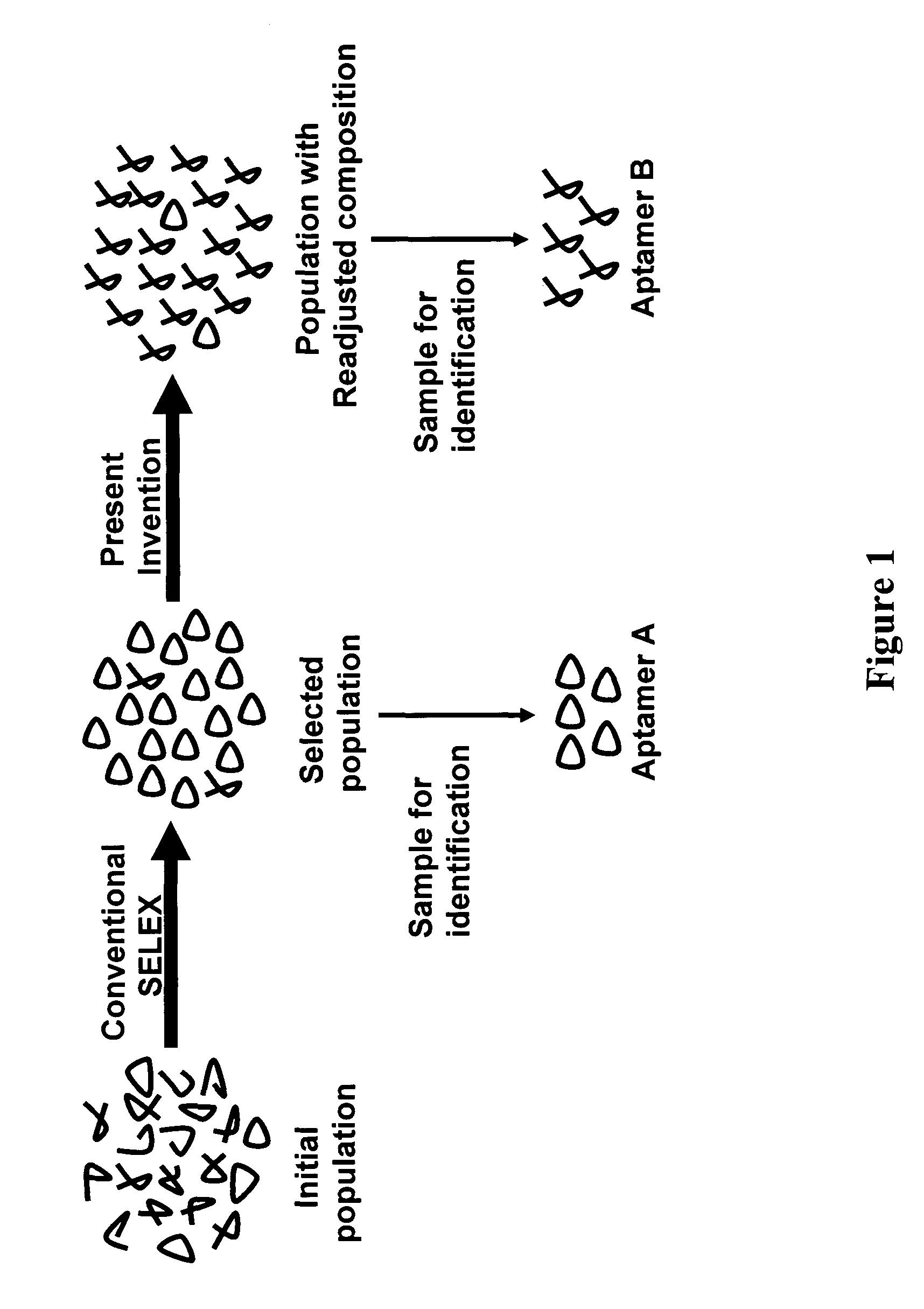
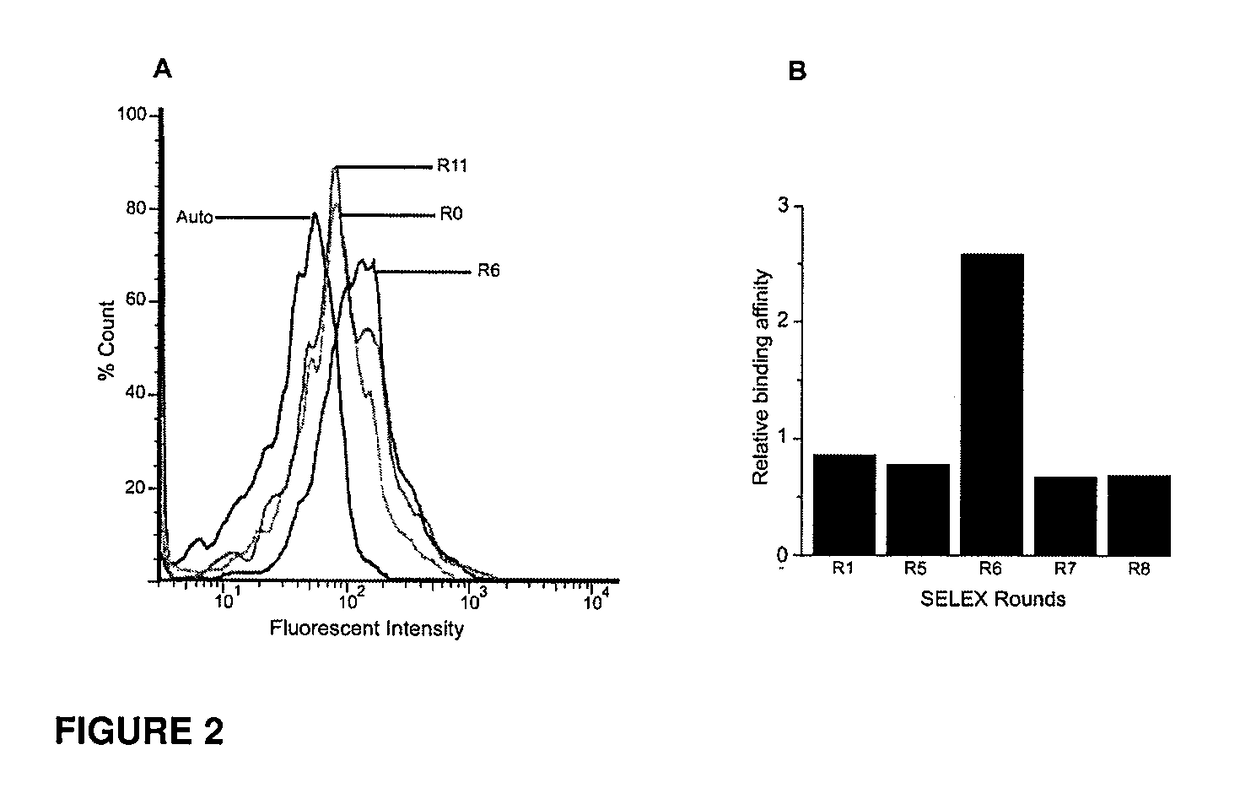
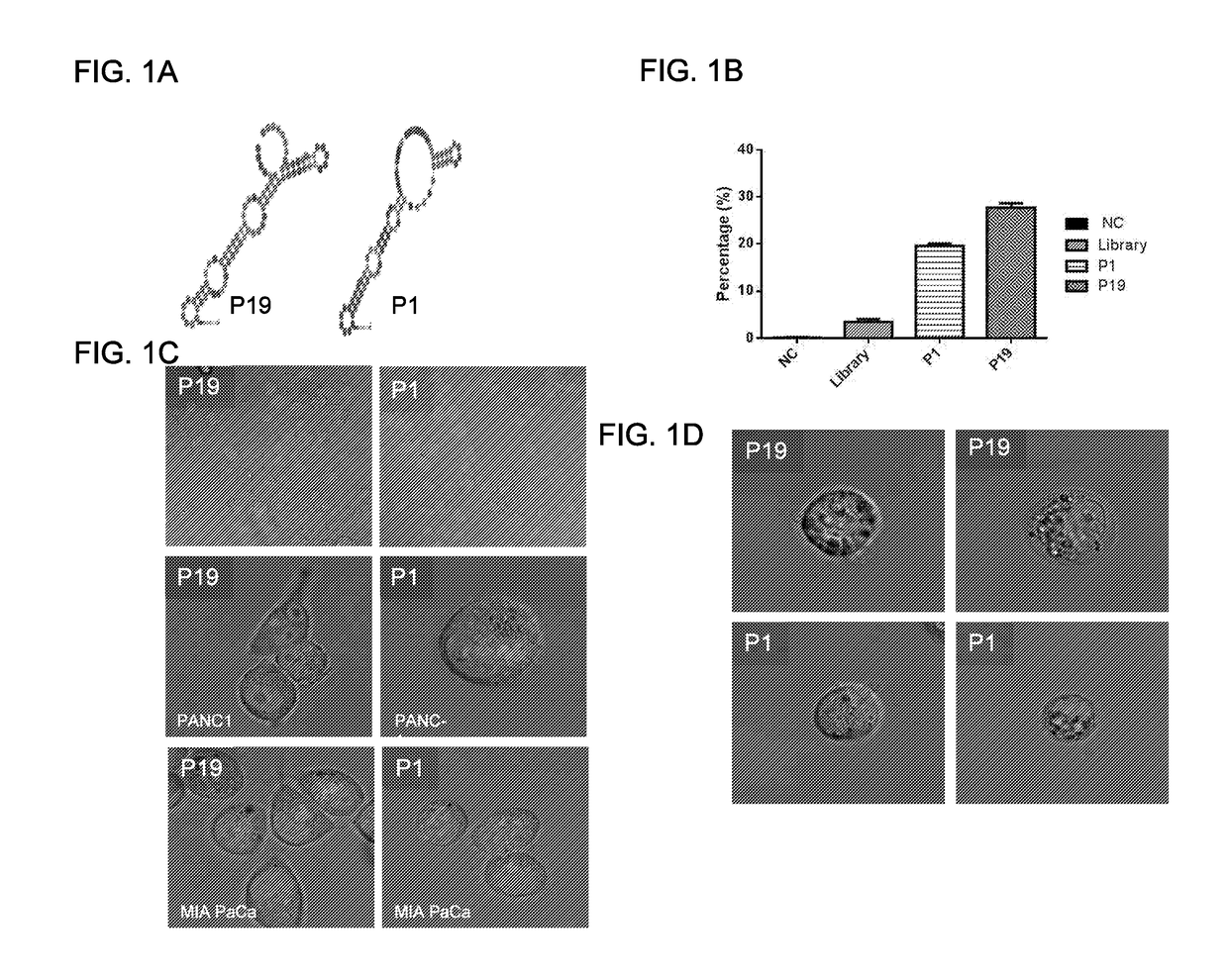
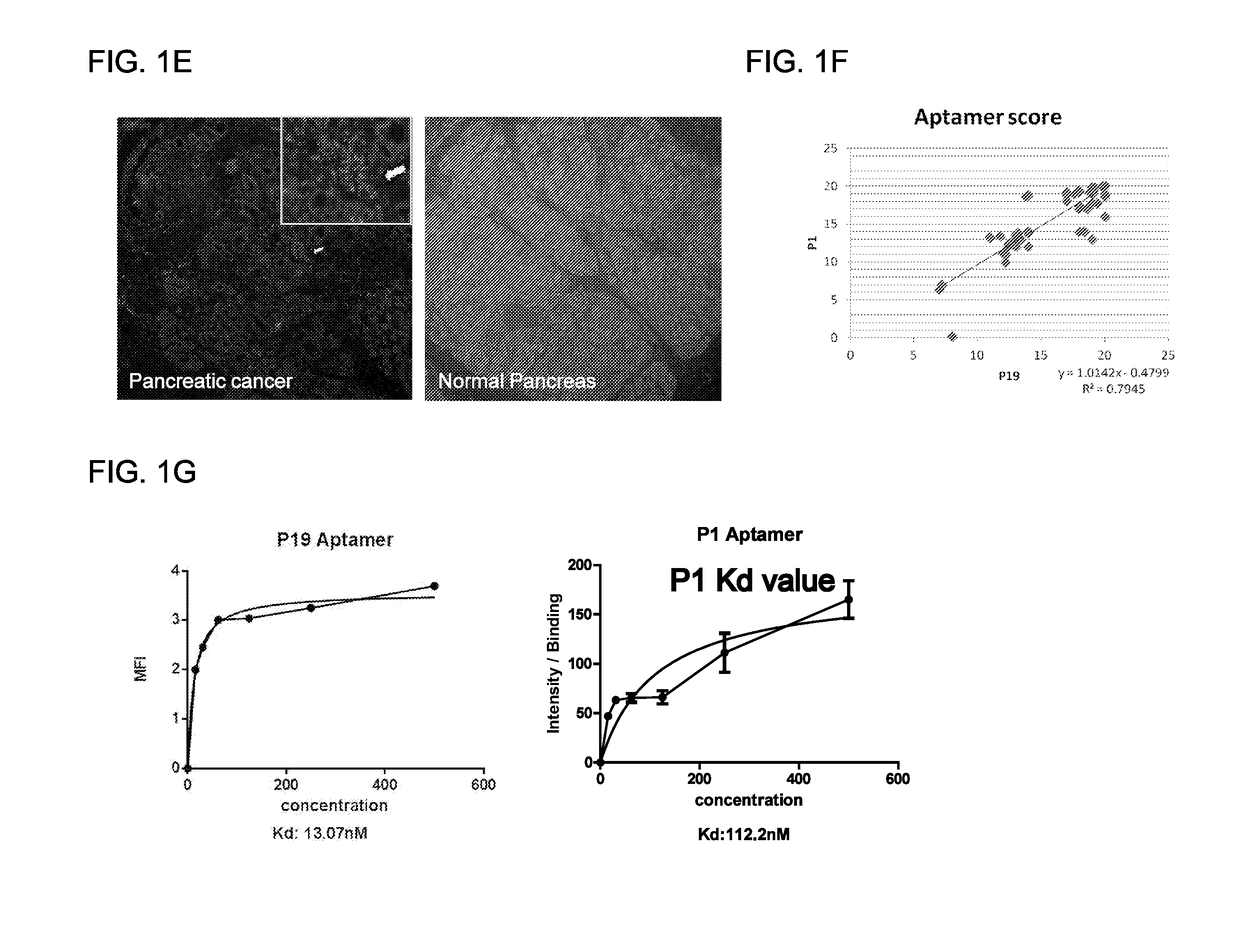
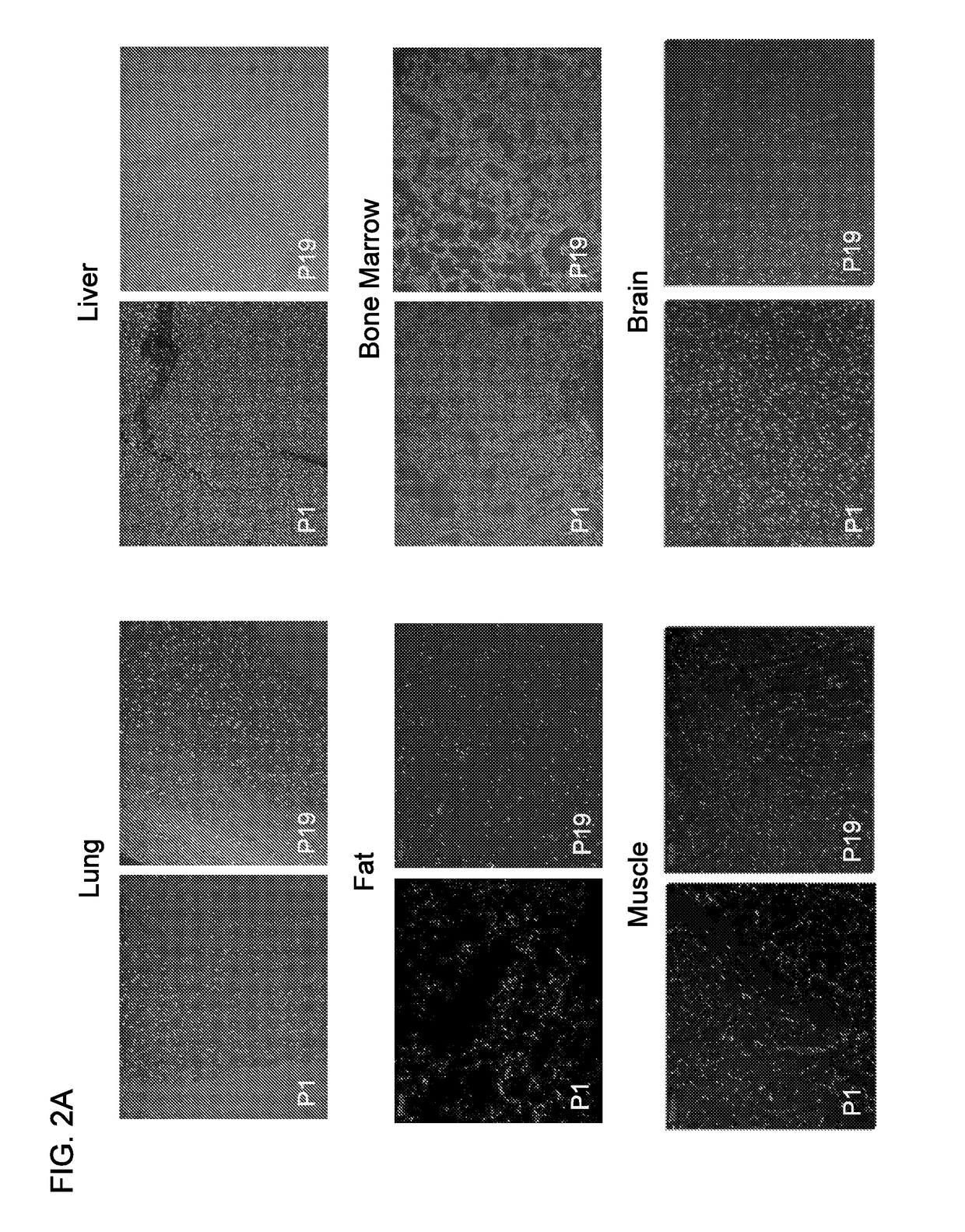
Exhaustive selection of RNA aptamers against complex targets
InactiveUS7435542B2Reduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processHigh concentrationHeat Shock Transcription Factor
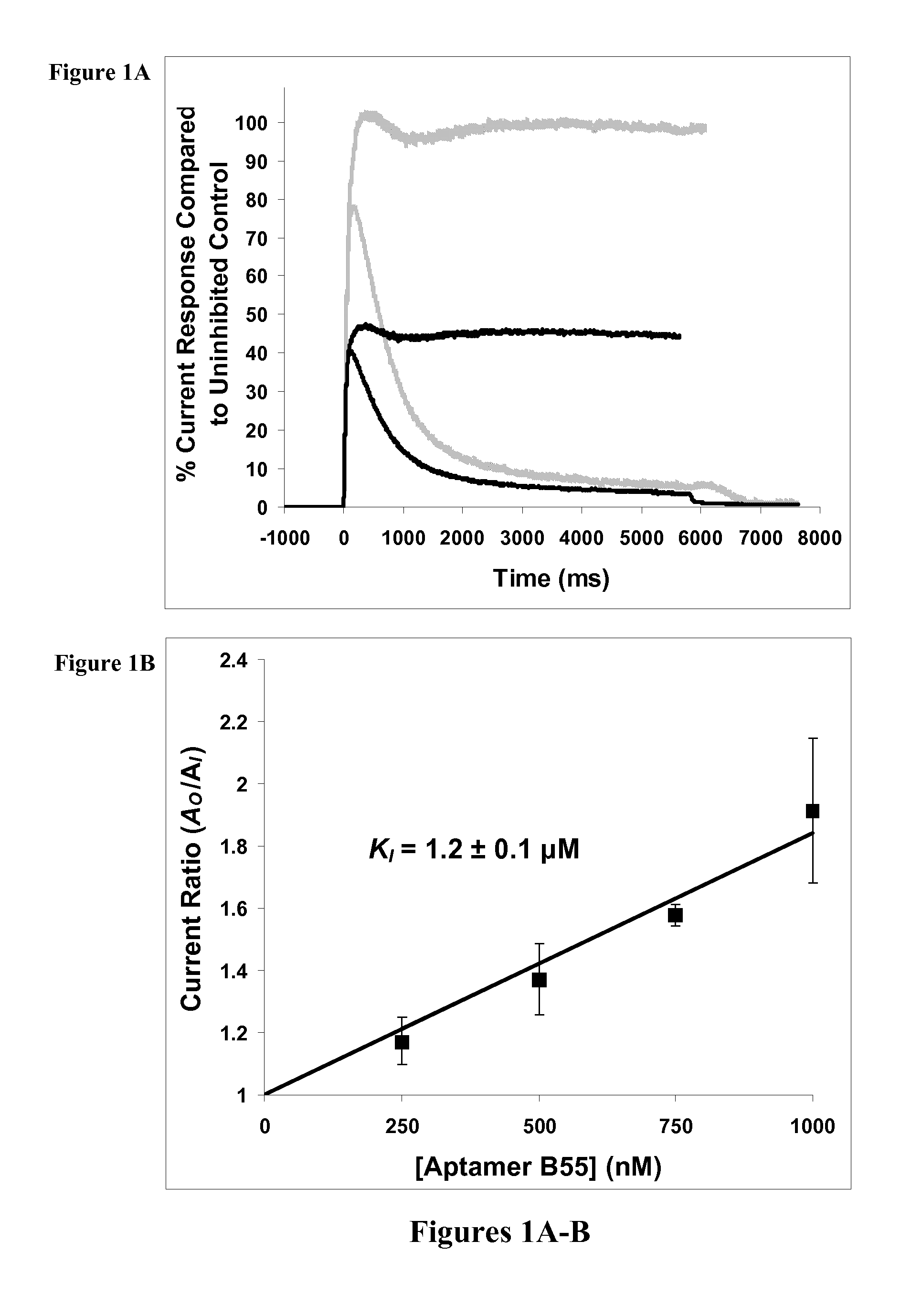
A method of identifying RNA ligands which bind to a target molecule by treating a first pool of RNA ligands that collectively bind more than one target under conditions effective to reduce the concentration or eliminate the presence of one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands from the first pool of RNA ligands; amplifying the RNA ligands in the treated first pool, thereby forming a second pool of RNA ligands that is enriched in one or more non-predominate target-binding RNA ligands of the first pool but not the one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands thereof; and identifying one or more predominate target-binding RNA ligands that are present in the second pool at a higher concentration than other target-binding RNA ligands. Oligonucleotides and kits which can be used in practicing the present invention are also disclosed, as are aptamers that bind to a heat shock factor protein and their use.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
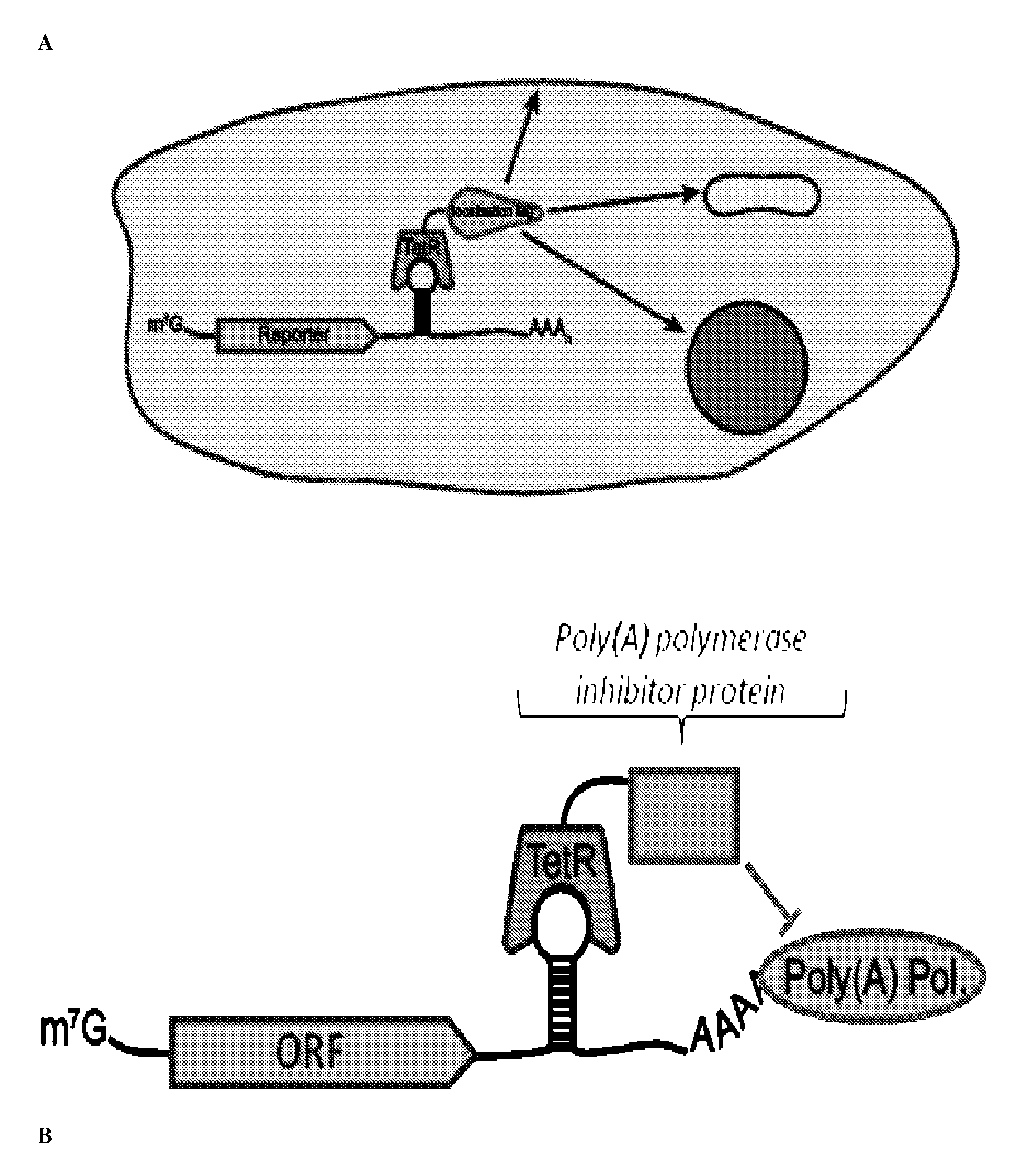
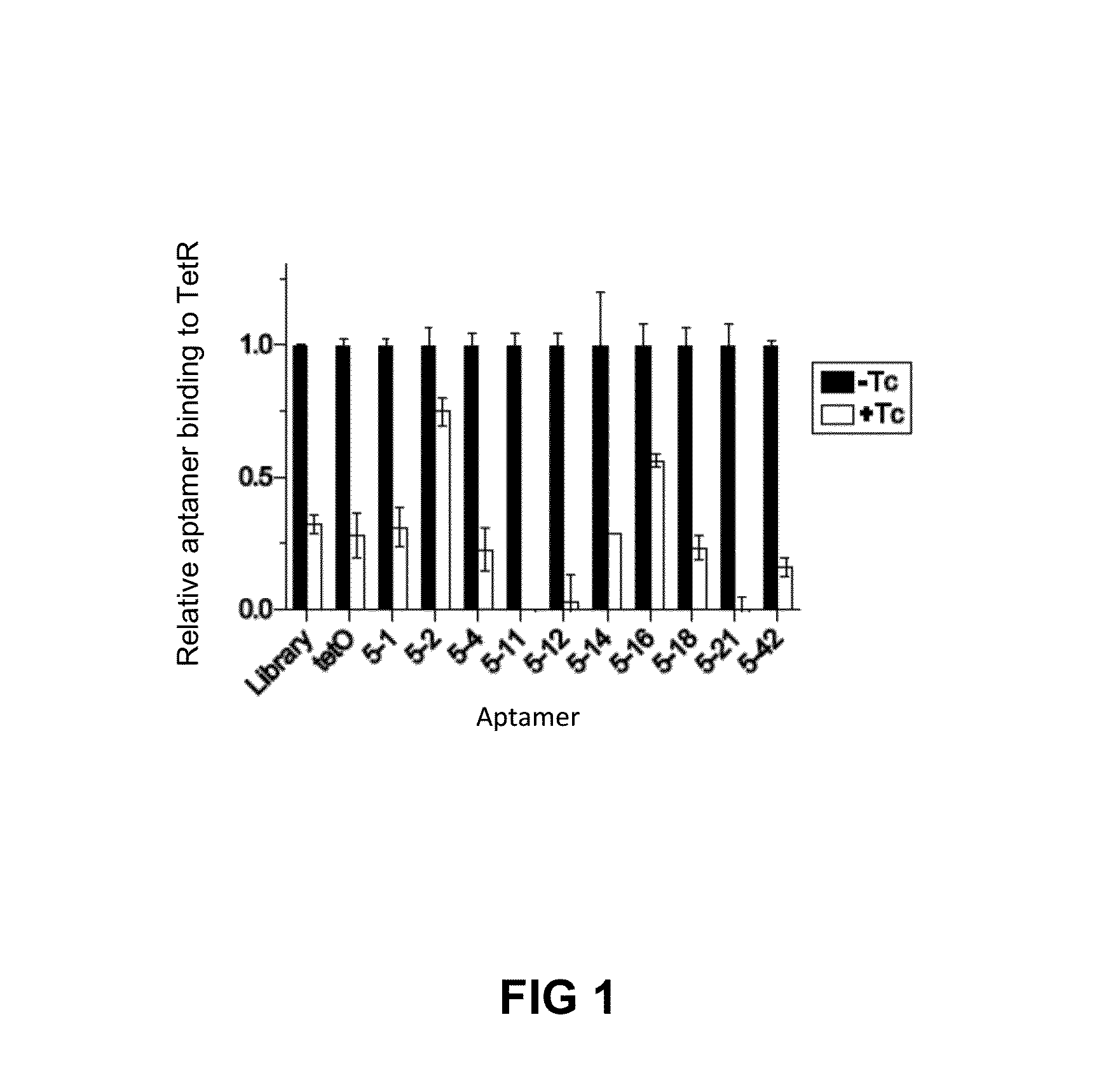
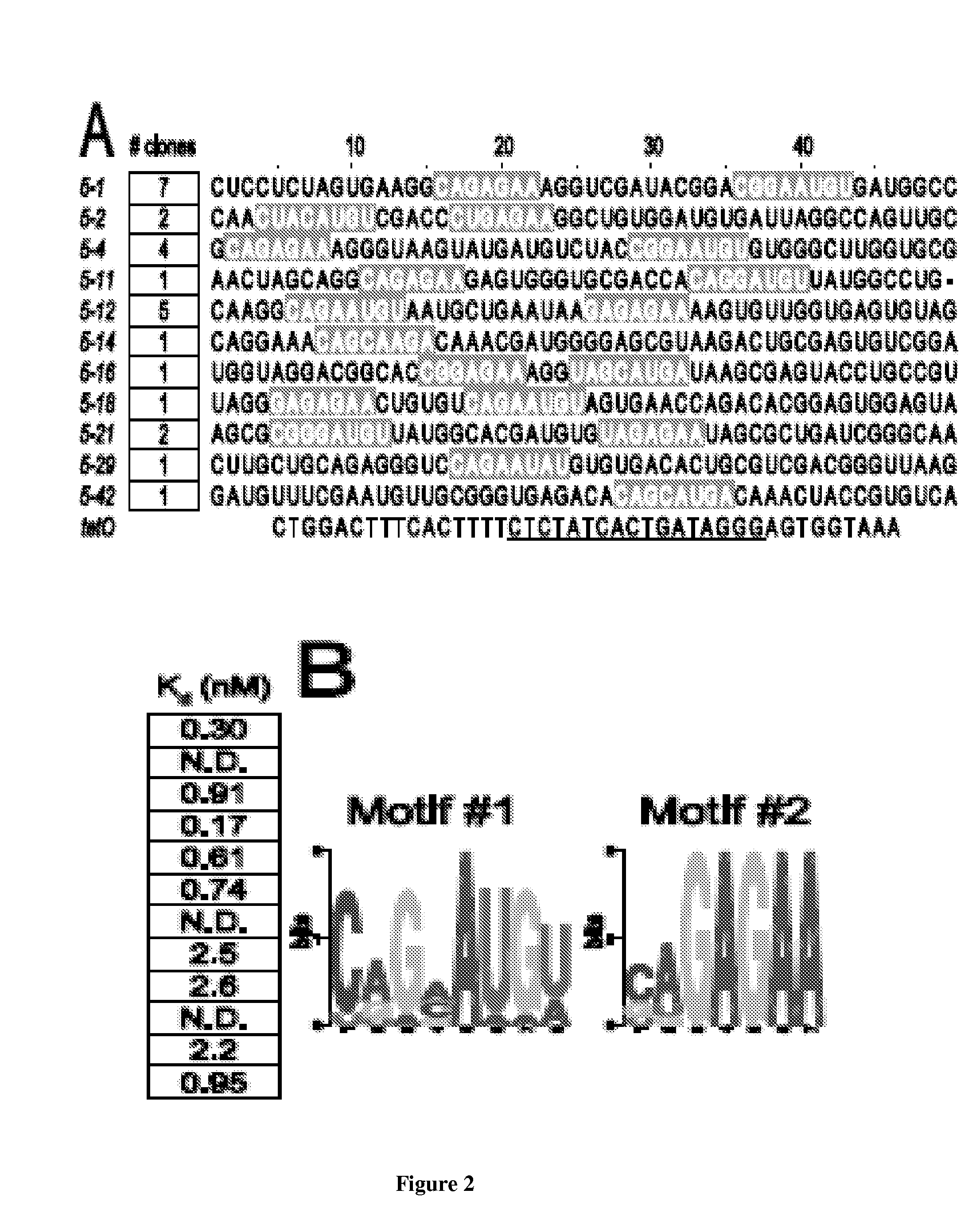
Post-Transcriptional Regulation Of RNA-Related Processes Using Encoded Protein-Binding RNA Aptamers
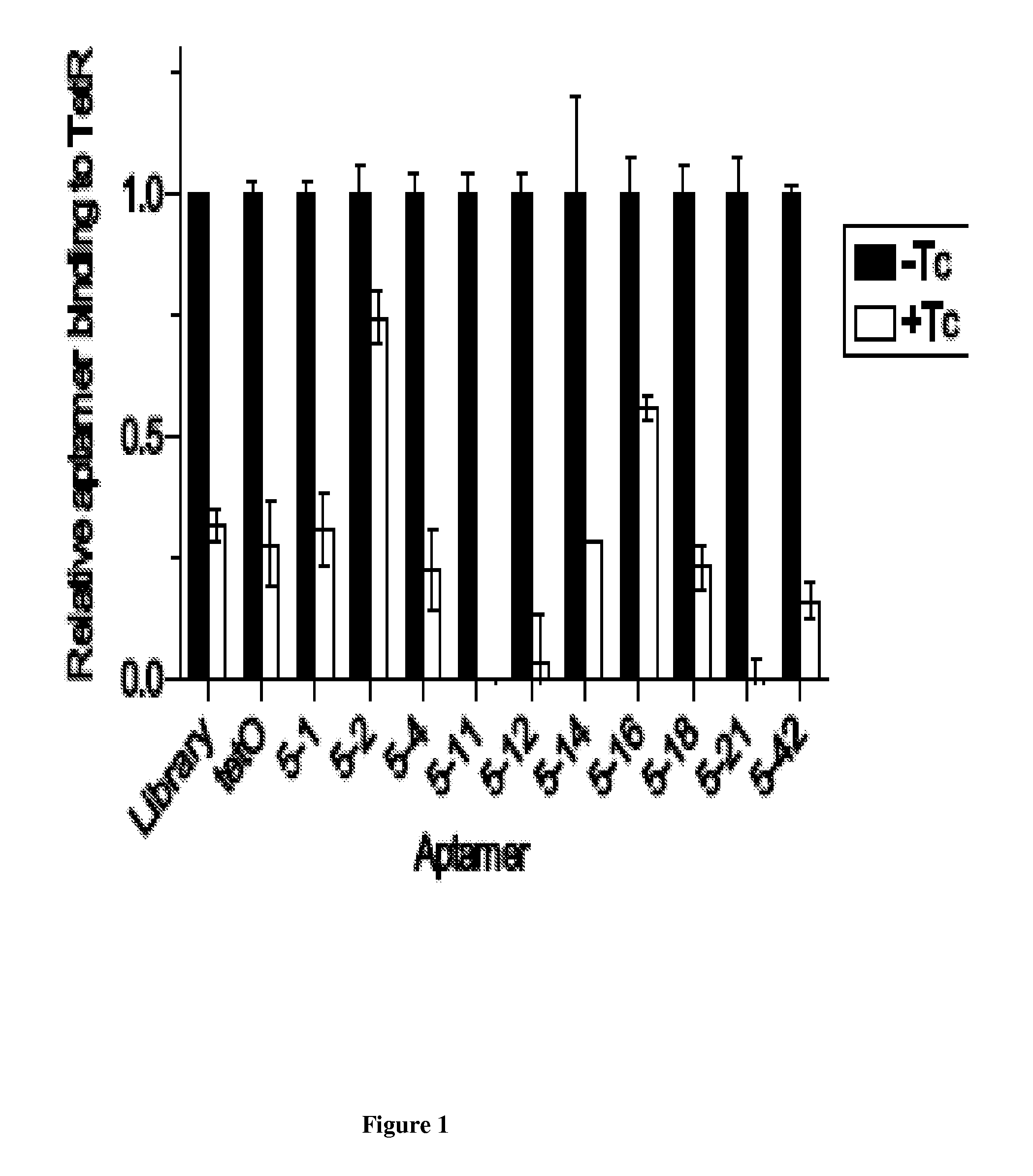
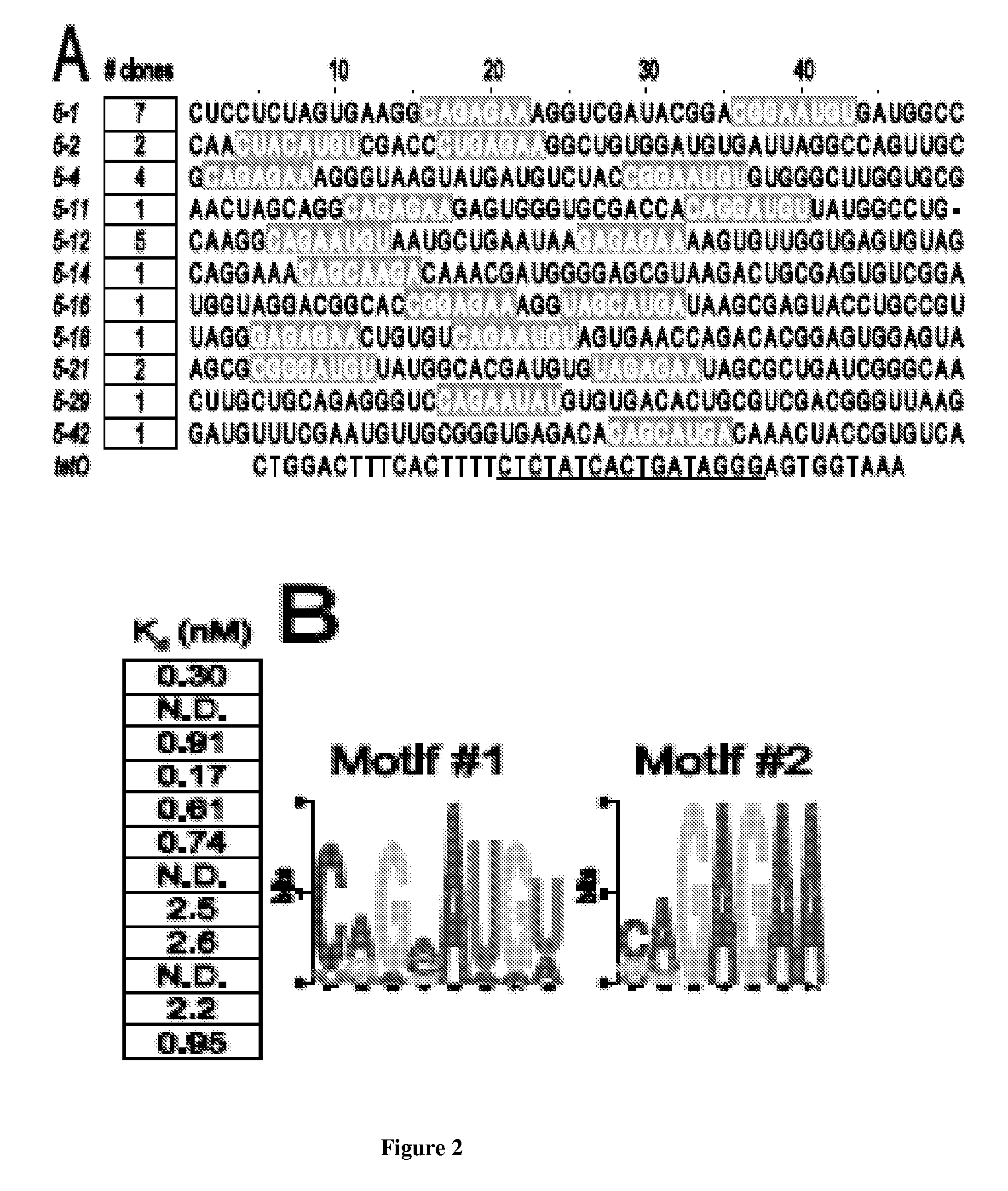
In vitro SELEX has been used to discover high affinity RNA aptamers interacting with the tetracycline repressor protein in a tetracycline-dependent manner. Using in silico RNA folding predictions to guide the design of both aptamer truncations and mutants, minimized tetracycline repressor protein high affinity binding aptamers have been defined. Using one such aptamer, inducible post-transcriptional regulation in vivo has been demonstrated that is predicated on a direct interaction between a tetracycline repressor protein and a RNA aptamer element. These aptamer components can be integrated in any organism to inducibly regulate RNA translation of a gene of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Aptamer capable of identifying hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, derivatives thereof and screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN102229933ALow costEfficient preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideScreening method
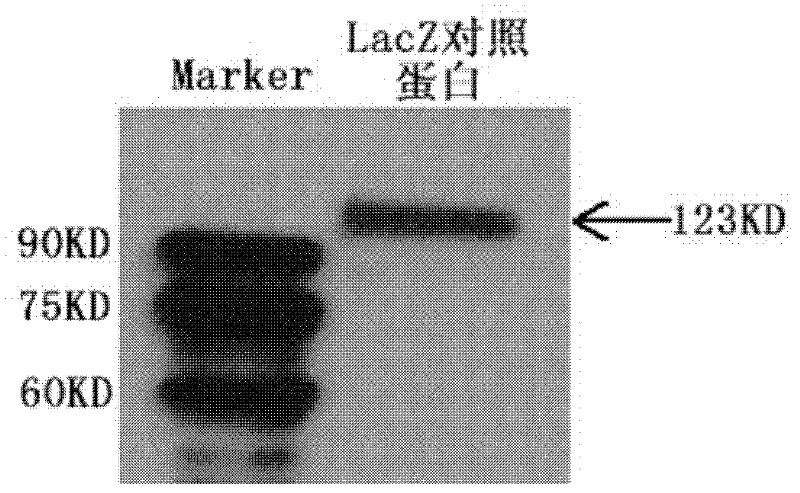
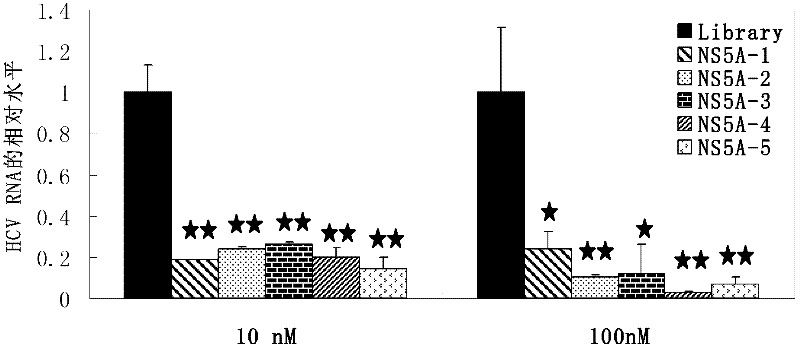
The invention discloses an aptamer capable of identifying a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, which is a DNA fragment represented by any of sequences from SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.5. The derivatives of the aptamer comprise nucleotide substituted RNA aptamers, skeleton-restructured derivatives, restructured peptide nucleic acid derivatives and radioactive molecule connected derivatives. The screening method of the aptamer comprises: preparing HCV NS5A protein with histidine marker, and preparing protein pET200 / D / LacZ; immobilizing the proteins, and designing a random nucleic acid library; and finally, screening the aptamer by pretreating the DNA library, performing reverse screening, screening and repeated screening and other steps, wherein the obtained aptamer has high competition power and optimized sequence length. The aptamer and the derivatives thereof can be used in the preparation of detection kit or diagnosis reagent for the HCV NS5A protein and can also be used in preparation of reagents for inhibiting replication of hepatitis C virus in liver cells.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
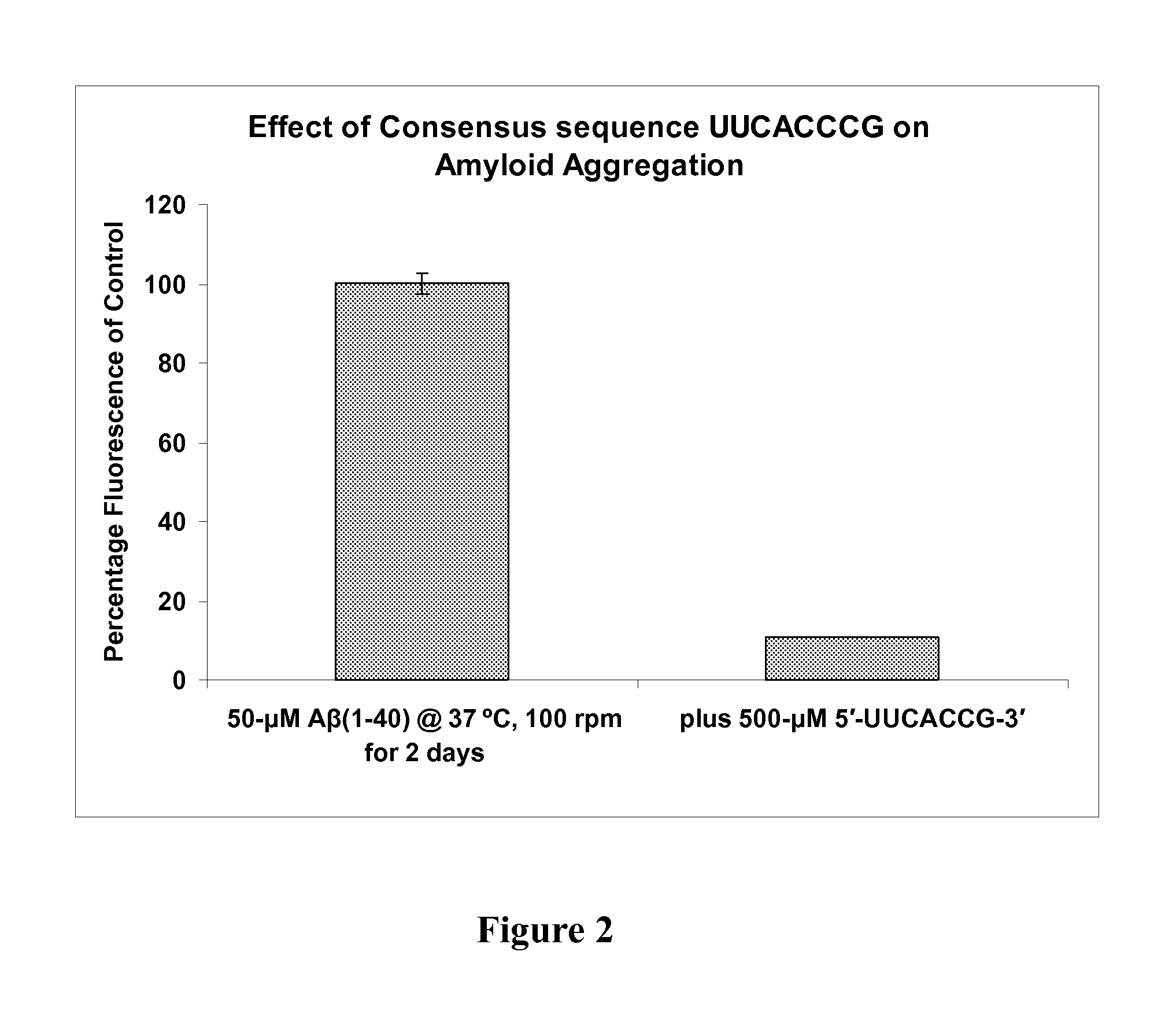
Inhibition of beta-amyloid peptide aggregation
ActiveUS20100069468A1Inhibit aggregationReduce processing stepsBiocideNervous disorderBinding siteMedicine
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods of producing interachain fluorophore-quencher FRET-aptamers and assays
InactiveUS20060257914A1Maximize sensitivityMaximize specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
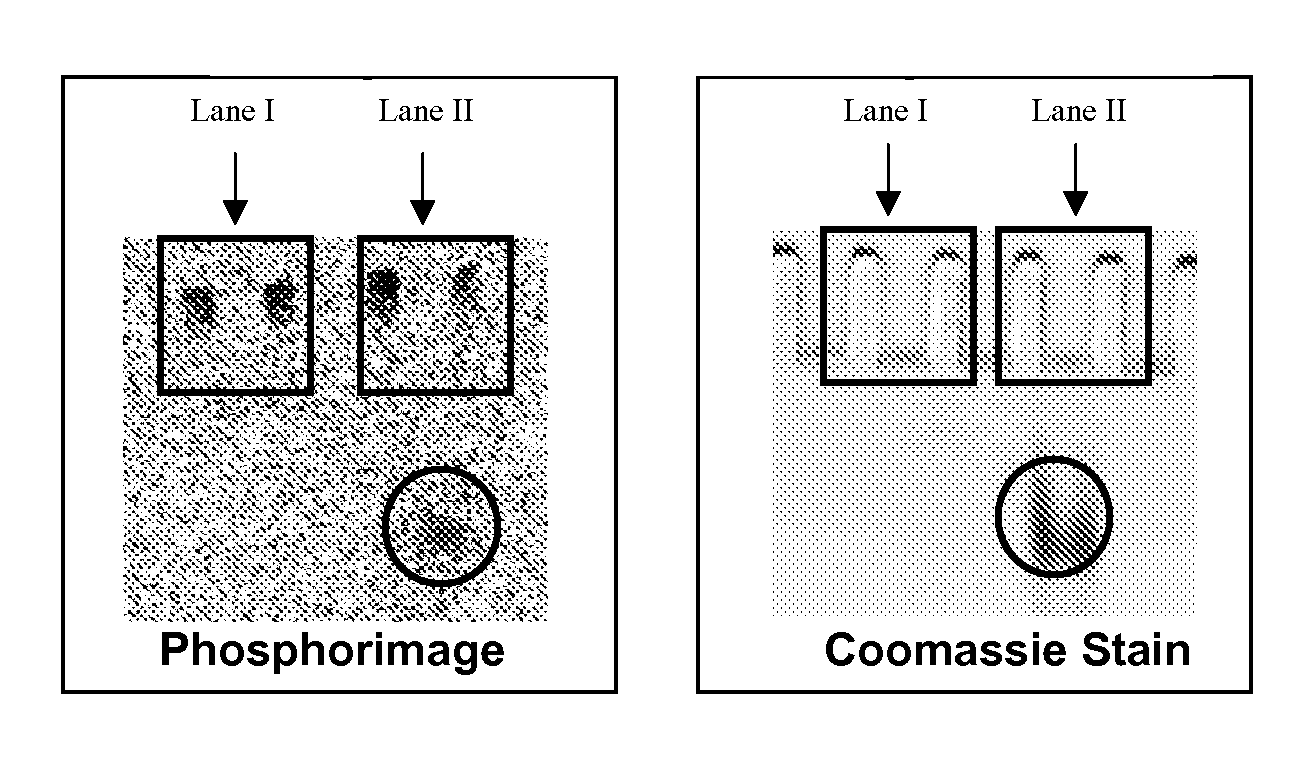
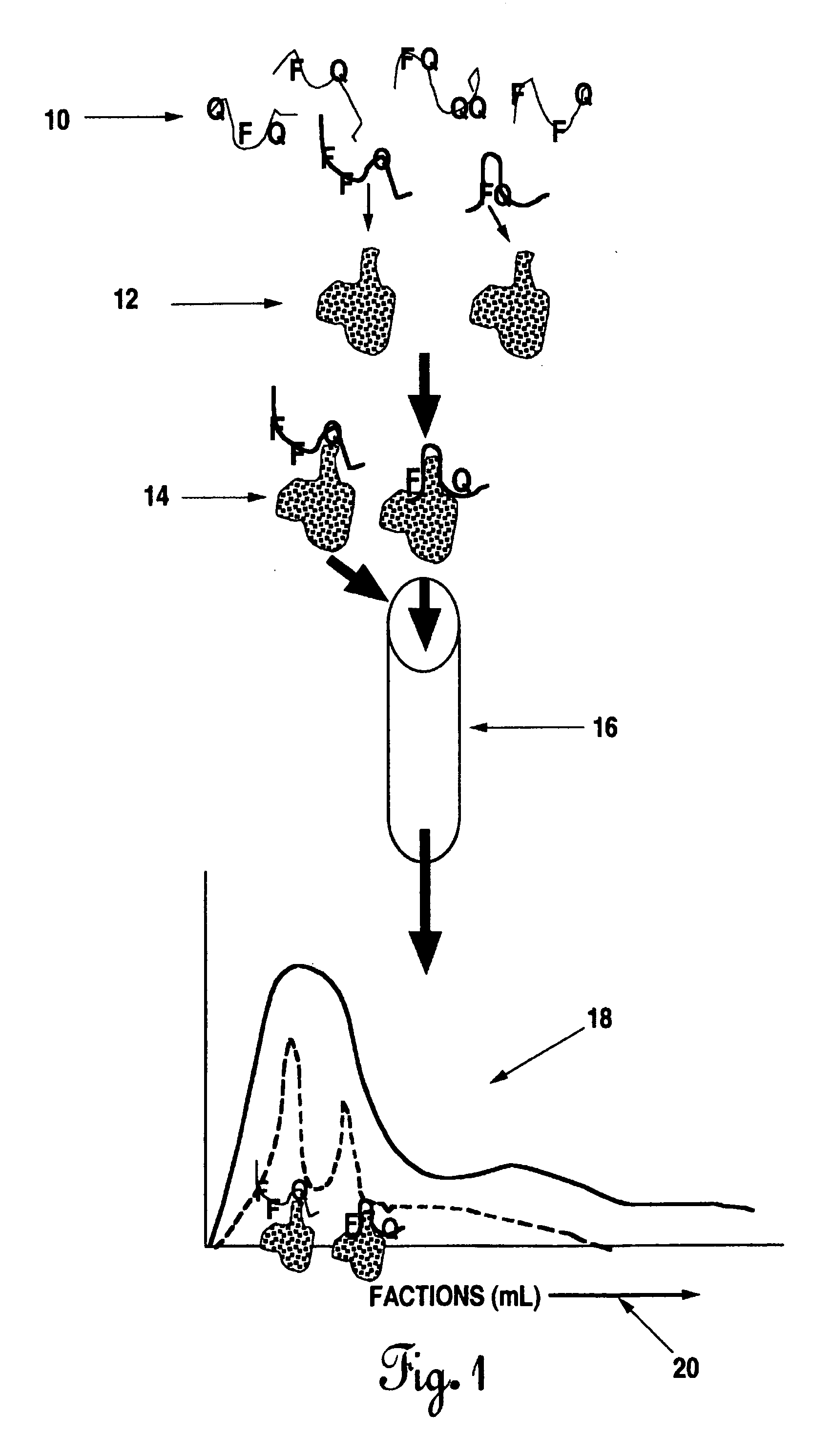
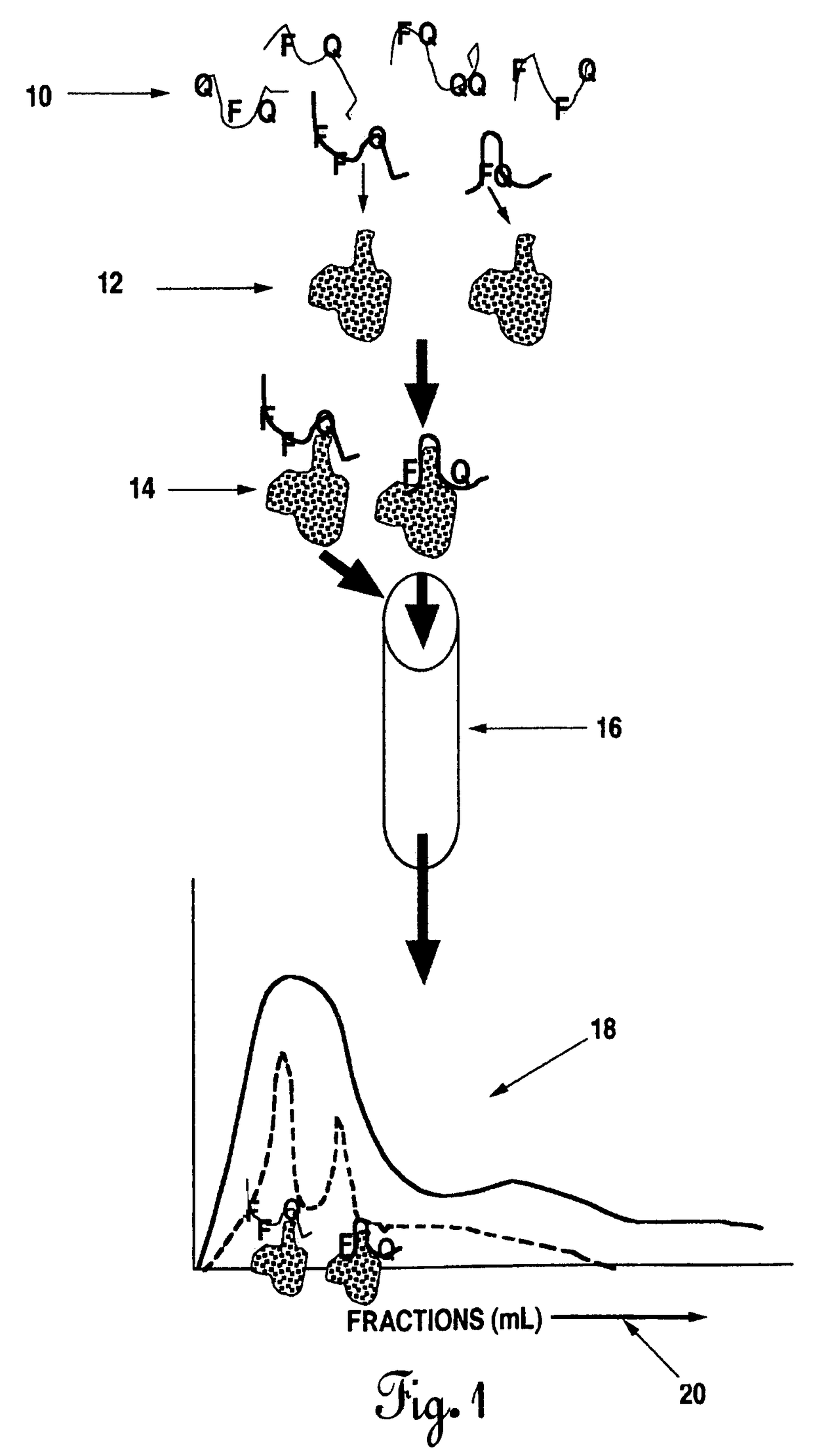
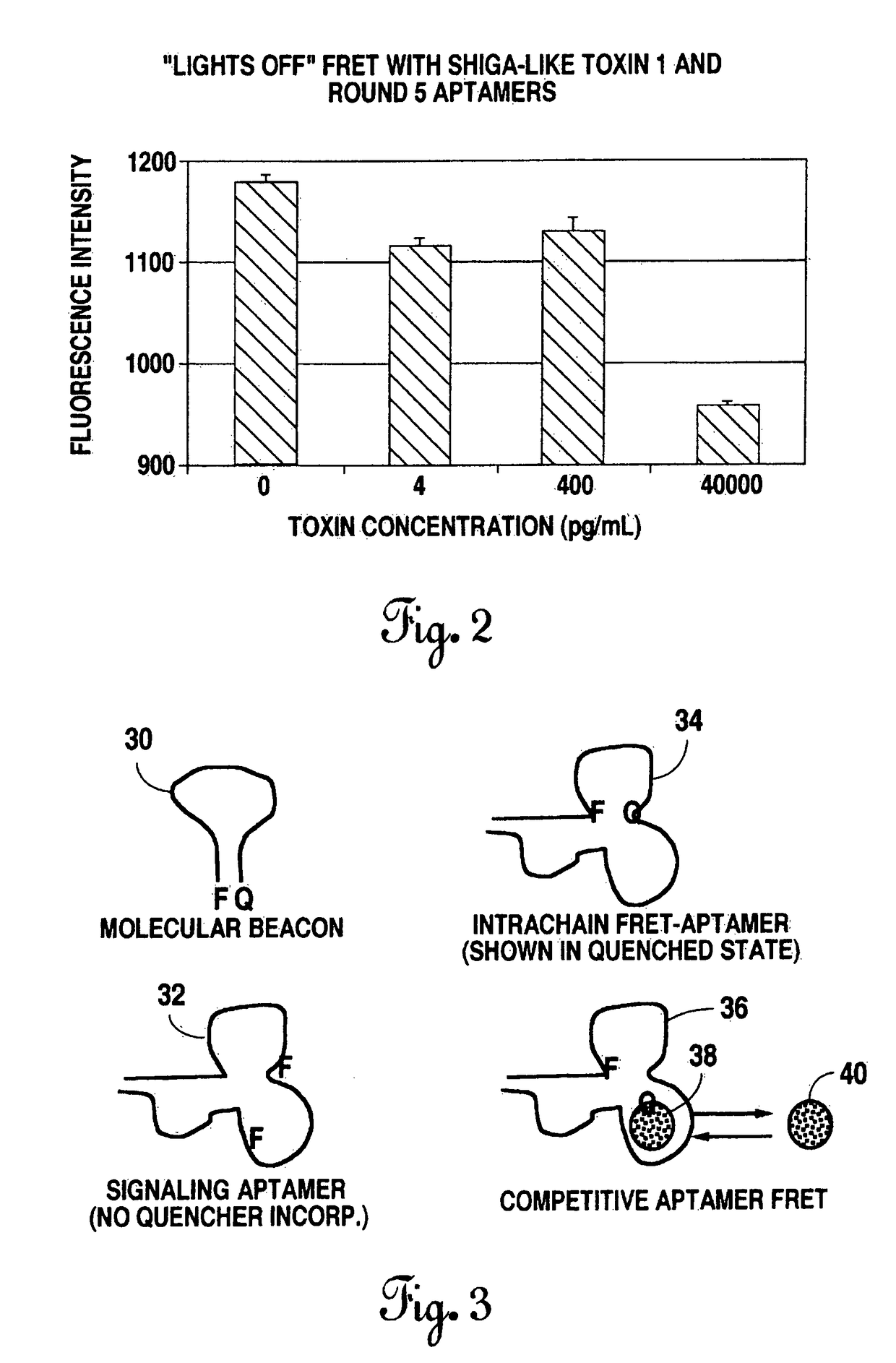
The present invention describes methods for the production and use of single chain (single-stranded) fluorescence resonance energy transfer (“FRET”) DNA or RNA aptamers containing fluorophores (F) and quenchers (Q) at various loci within their structures, such that when its specific matching analyte is bound and the FRET-aptamers are excited by specific wavelengths of light, the fluorescence intensity of the system is modulated (increased or decreased) in proportion to the amount of analyte added. F and Q are covalently linked to nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs), which are incorporated by various nucleic acid polymerases such as Taq polymerase during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and then selected by affinity chromatographic, size-exclusion or molecular sieving, and fluorescence techniques. Further separation of related FRET-aptamers can be achieved by ion-pair reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or other types of chromatography. Finally, FRET-aptamer structures and the specific locations of F and Q within FRET-aptamer structures are determined by digestion with exonucleases and mass spectral nucleotide sequencing analysis.
Owner:CIBUSDX INC
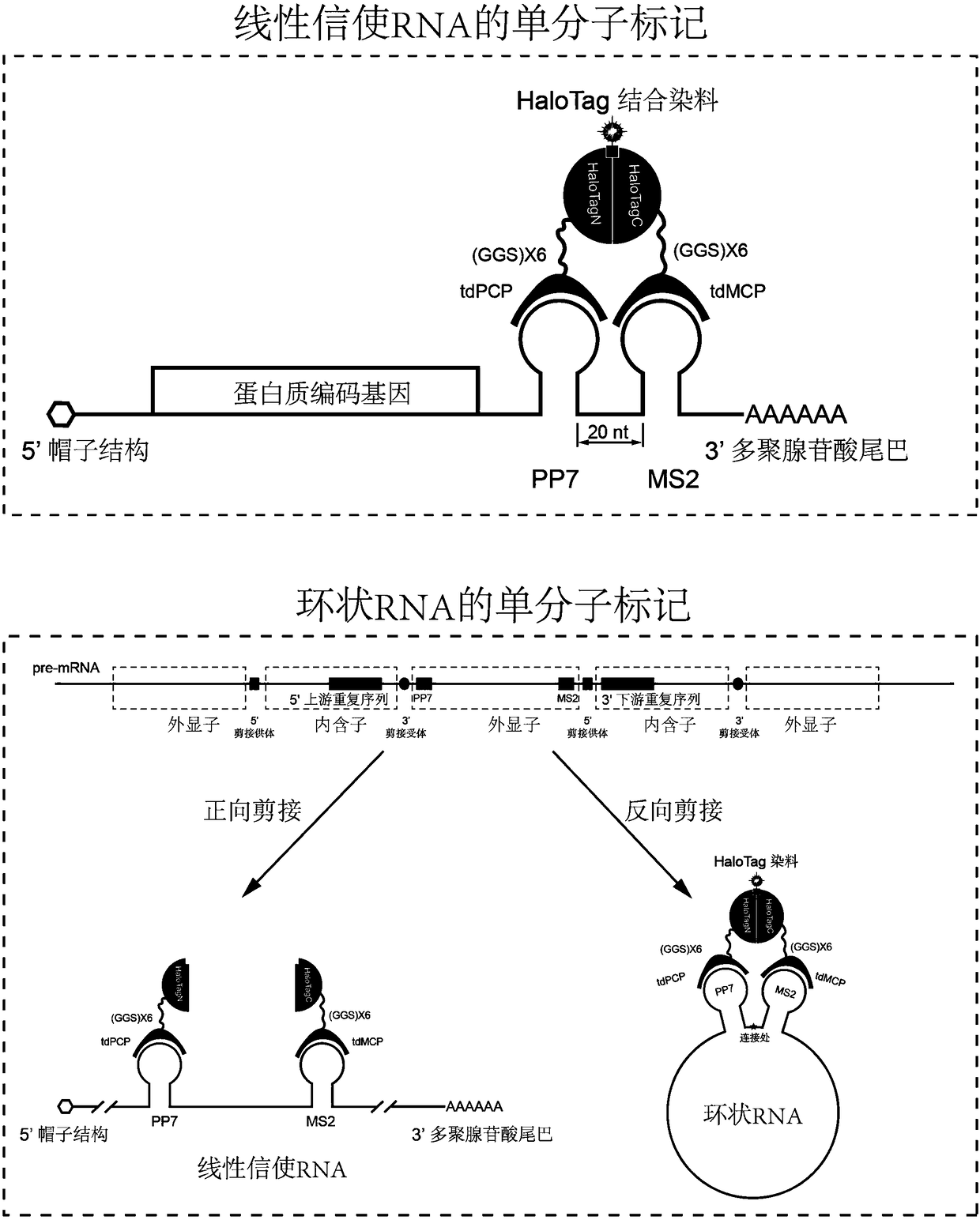
Novel labeling method for messenger RNA and circular RNA based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation
RNA molecules are an important member of an intracellular genetic information delivery system. Conventional RNA labeling methods cannot simultaneously have the characteristics of living cells, no invasion, high temporal and spatial resolution, single molecules, etc., so a novel method for labeling and tracking RNA need to be developed. The invention discloses a novel labeling method for messengerRNA and circular RNA based on self-ligation label bimolecular fluorescence complementation. A RNA aptamer subsystem is cooperatively used, aptamers are inserted at proper positions in the RNA, and twoparts of a self-ligation label are respectively fused with the binding proteins of the RNA aptamers. When the fusion proteins do not bind to RNA, RNA molecules do not fluoresce; when and only when the fusion proteins bind to RNA, the RNA molecules fluoresce, so the fluorescence background of an intracellular RNA marker is reduced. The novel RNA labeling method based on self-ligation label bimolecular fluorescence complementation can be used for long-term interference-free single-molecule imaging observation and tracking of messenger RNA and circular RNA of living cells and fixed cells, and has good application prospects in cell biology.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Methods of producing intrachain fluorophore-quencher FRET-aptamers and assays
InactiveUS7906280B2Maximize sensitivityMaximize specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerNucleotide
The present invention describes methods for the production and use of single chain (single-stranded) fluorescence resonance energy transfer (“FRET”) DNA or RNA aptamers containing fluorophores (F) and quenchers (Q) at various loci within their structures, such that when its specific matching analyte is bound and the FRET-aptamers are excited by specific wavelengths of light, the fluorescence intensity of the system is modulated (increased or decreased) in proportion to the amount of analyte added. F and Q are covalently linked to nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs), which are incorporated by various nucleic acid polymerases such as Taq polymerase during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and then selected by affinity chromatographic, size-exclusion or molecular sieving, and fluorescence techniques. Further separation of related FRET-aptamers can be achieved by ion-pair reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or other types of chromatography. Finally, FRET-aptamer structures and the specific locations of F and Q within FRET-aptamer structures are determined by digestion with exonucleases and mass spectral nucleotide sequencing analysis.
Owner:CIBUSDX INC
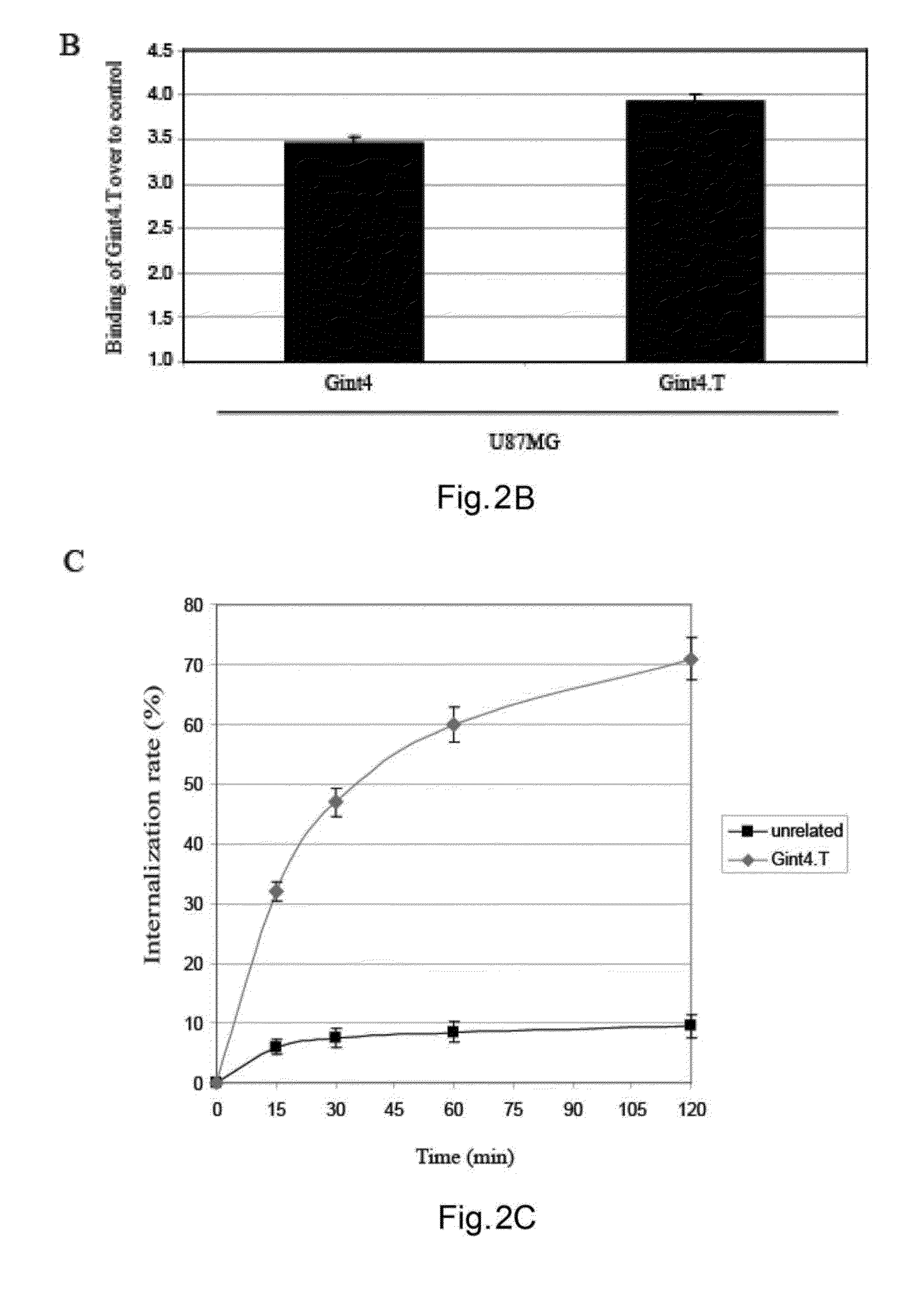
Anti-cancer RNA aptamers
Provided herein, inter alia, are compounds capable of binding HSP70 (e.g. mHSP70) on a cell and internalizing into said cell. The compositions provided herein may be useful for delivering therapeutic and diagnostic agents to a cell. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment using nucleic acid compounds provided herein.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
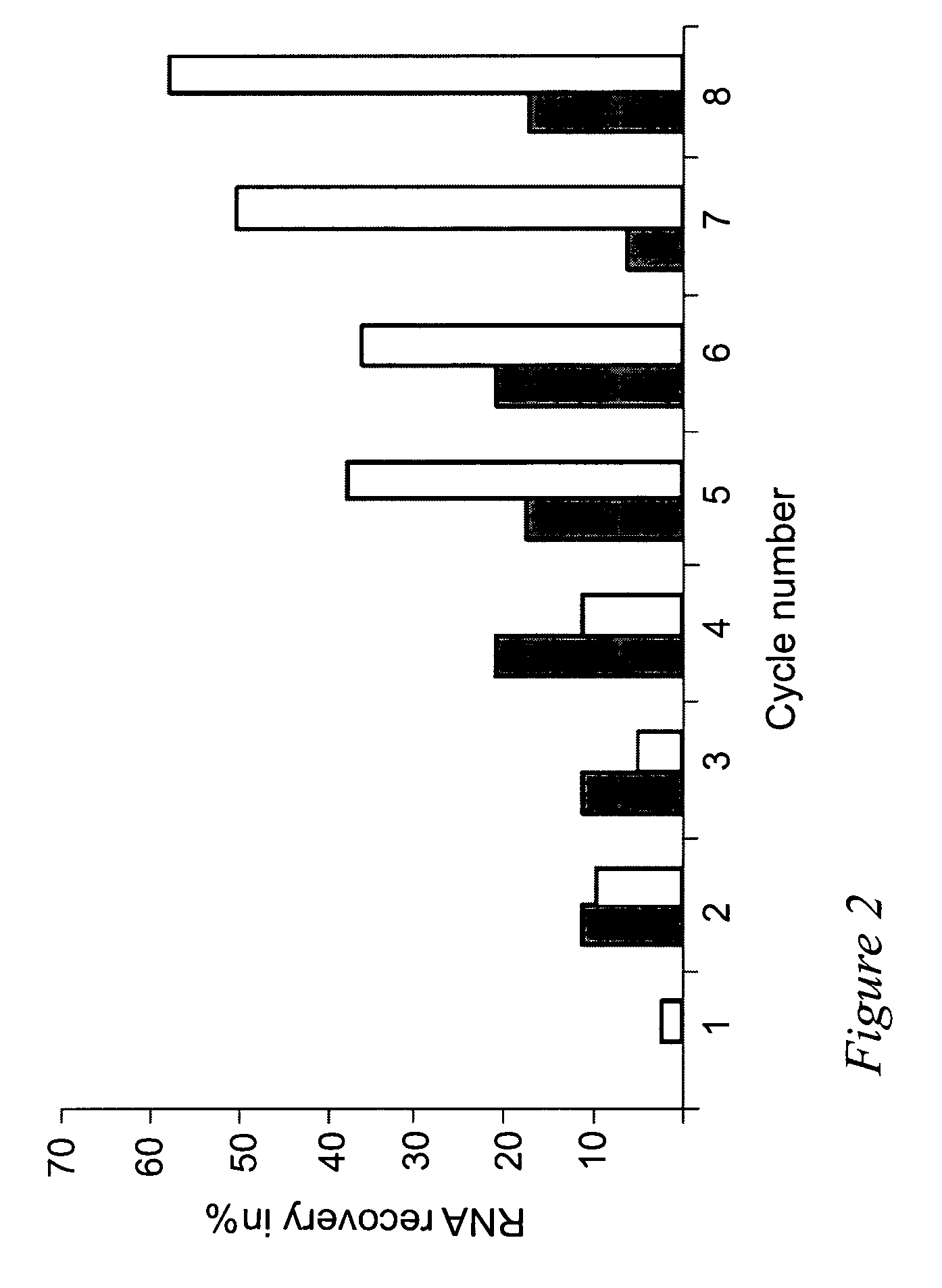
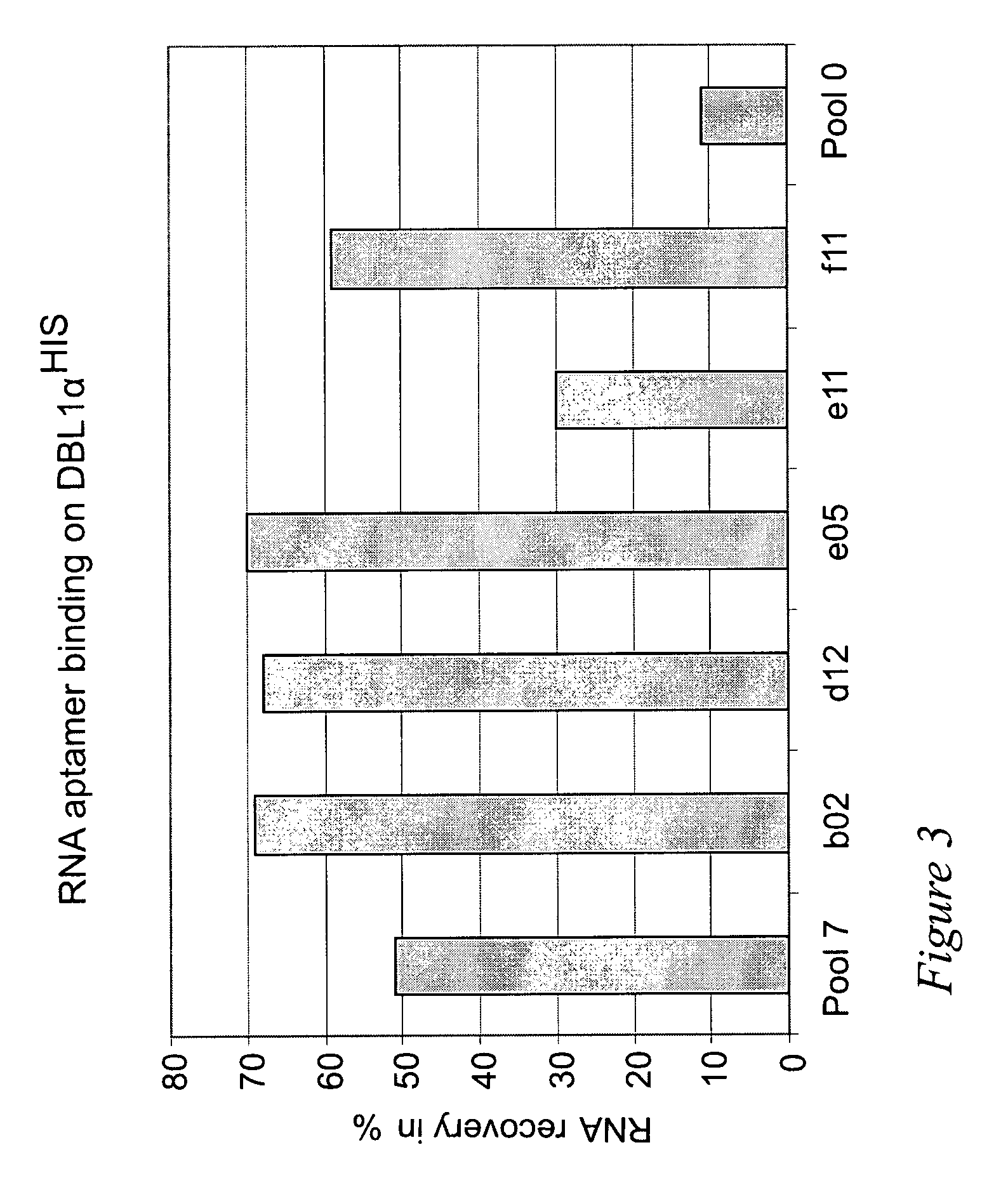
Selection of RNA aptamers as Anti-malaria agents
The present invention relates to an aptamer or an active fragment thereof raised against the semi-conserved duffy binding ligand domain 1α, DBL1α, region of the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1, PfEMPI, which aptamer has an effect against malaria, in particular severe cerebral malaria.
Owner:APTAHEM
Neutralizing RNA aptamers against pdgfbeta and uses thereof in the therapy and diagnosis of hyperproliferative diseases
InactiveUS20150275215A1Improve stabilitySugar derivativesDNA/RNA fragmentationPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
Nuclease-resistant RNA aptamers are provided which are capable of neutralizing PDGFRβ and are therefore useful in the diagnosis and / or therapy of PDGFRβ-associated and hyperproliferative-associated diseases, such as cancer and primary tumour metastasis. RNA aptamers provided herein include a modified synthetic RNA sequence wherein at least one pyrimidine residue is modified to 2′-fluoropyrimidine. Pharmaceutical compositions and diagnostic kits comprising RNA aptamers are also provided.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
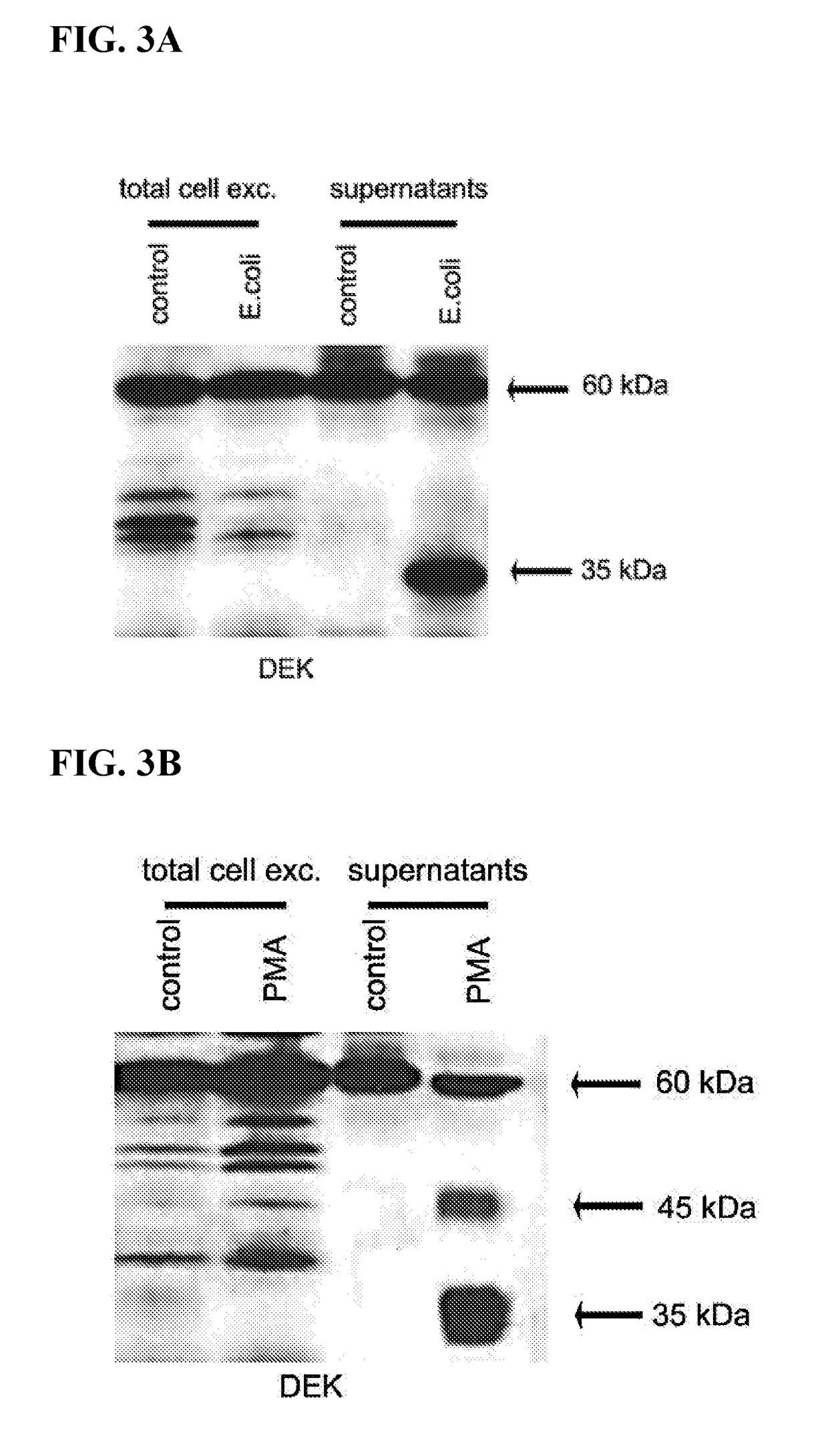
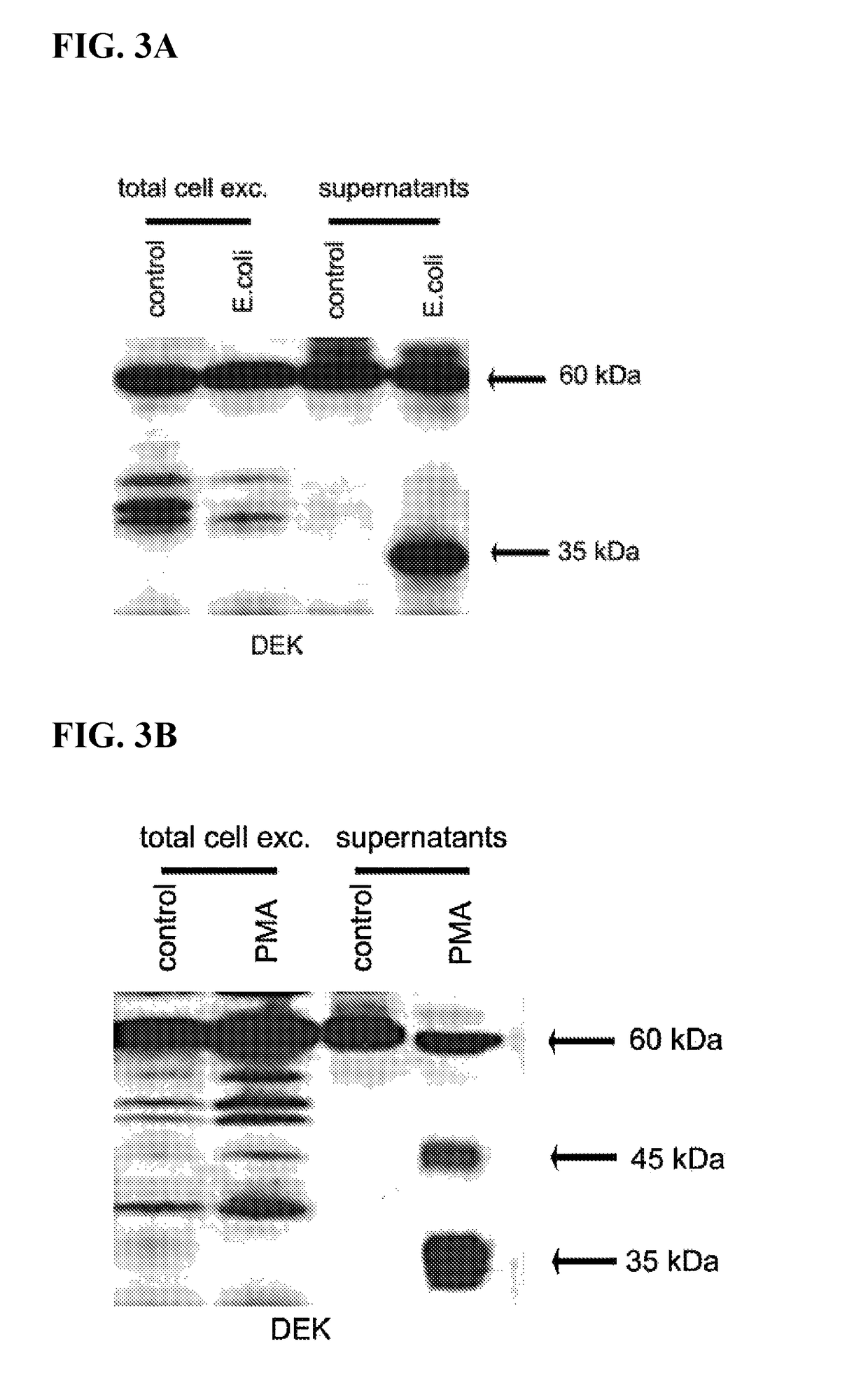
Inhibitors of dek protein and related methods
ActiveUS20180187196A1Prevents and reduces bindingReduce signalingOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticAutoimmune diseaseSingle strand dna
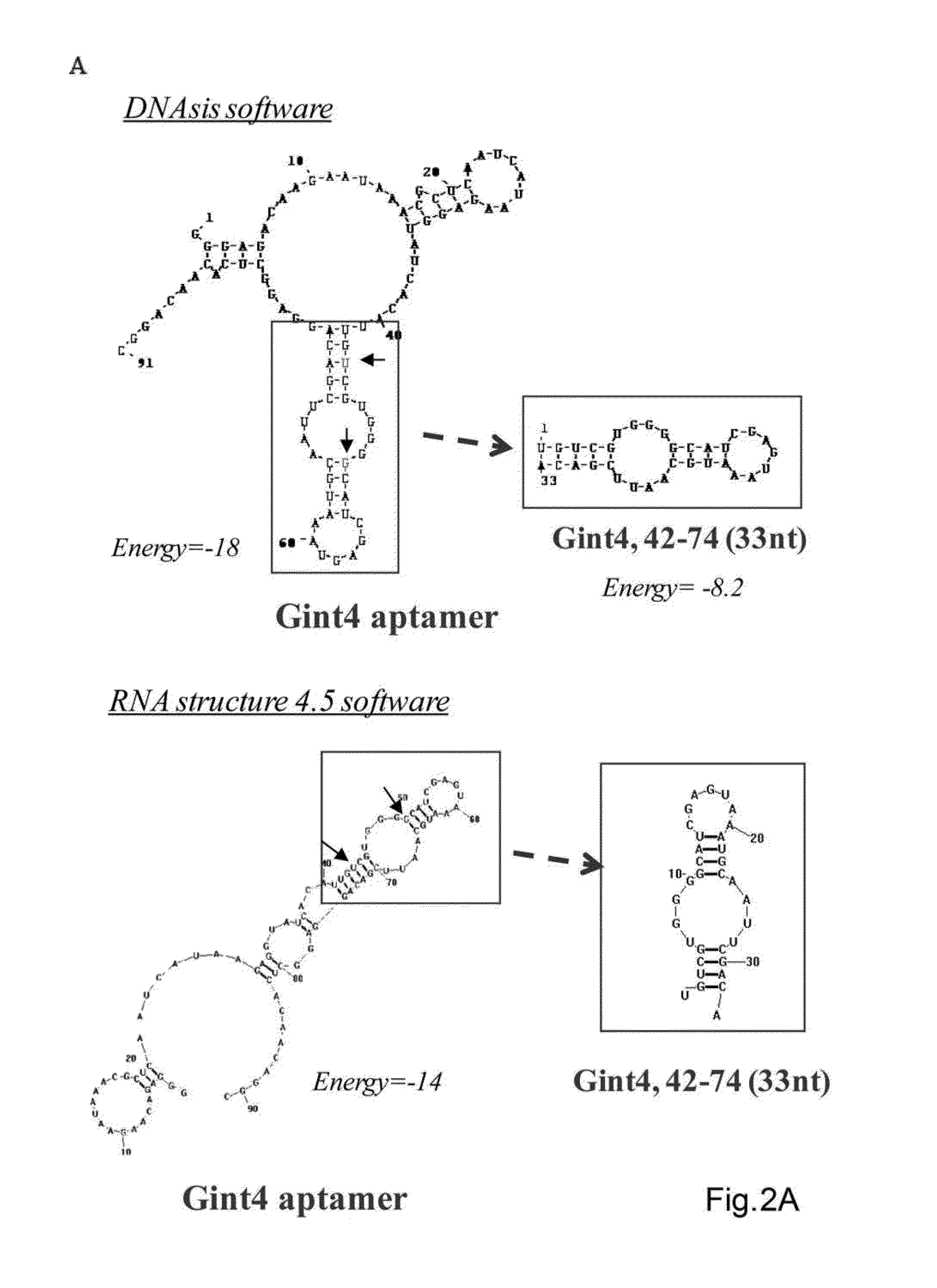
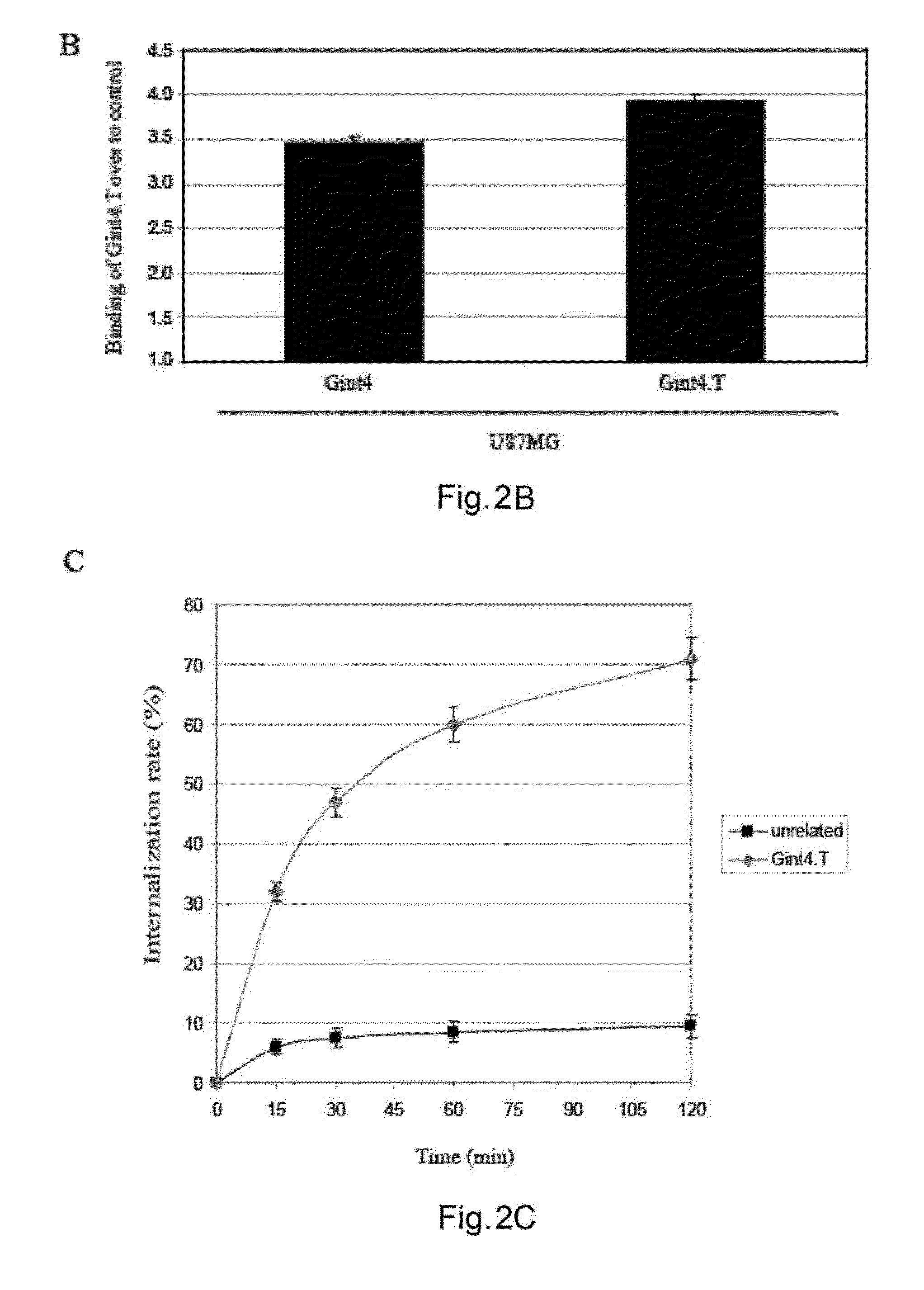
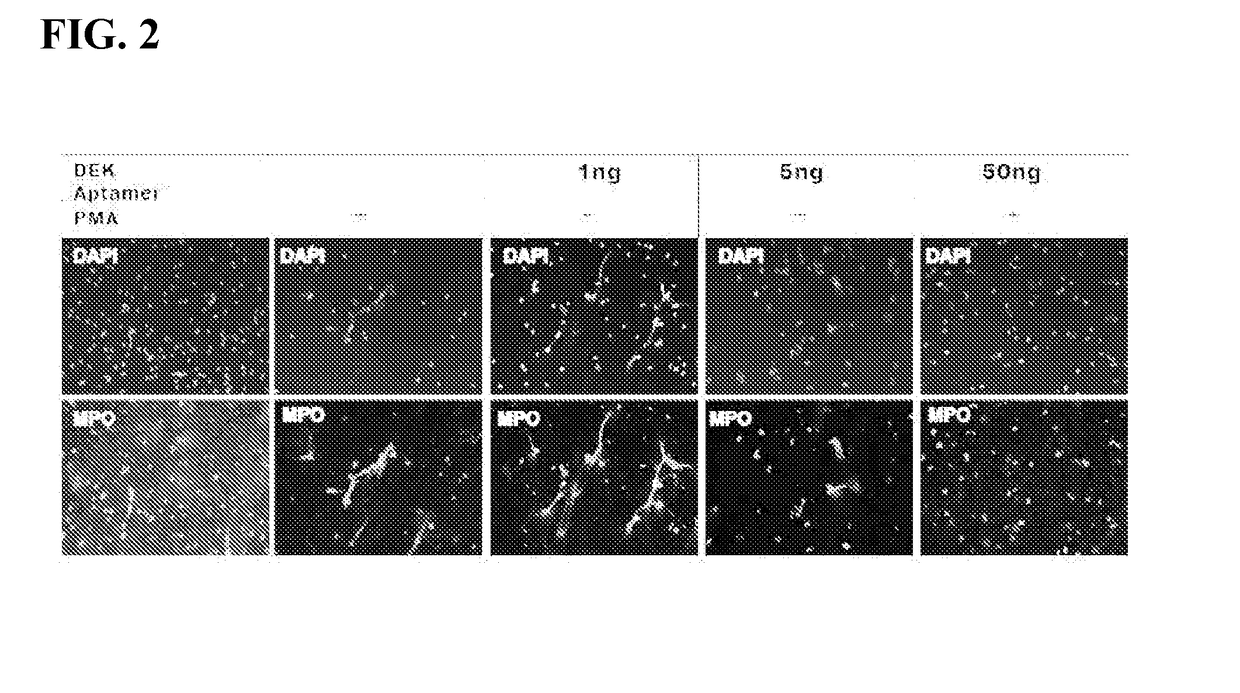
The present invention provides methods of treatment using inhibitors of DEK protein and DEK activity. Such methods include, but are not limited to, methods of preventing, treating, and / or ameliorating inflammatory diseases, infections, autoimmune diseases, malignant diseases, and other diseases or conditions in which DEK has been implicated. Such inhibitors of DEK protein include, but are not limited to, pharmaceutical compositions including single stranded DNA or RNA aptamers capable of binding to DEK. In some embodiments, such aptamers are useful for diagnosing DEK related diseases or conditions. Related kits and compositions are further provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
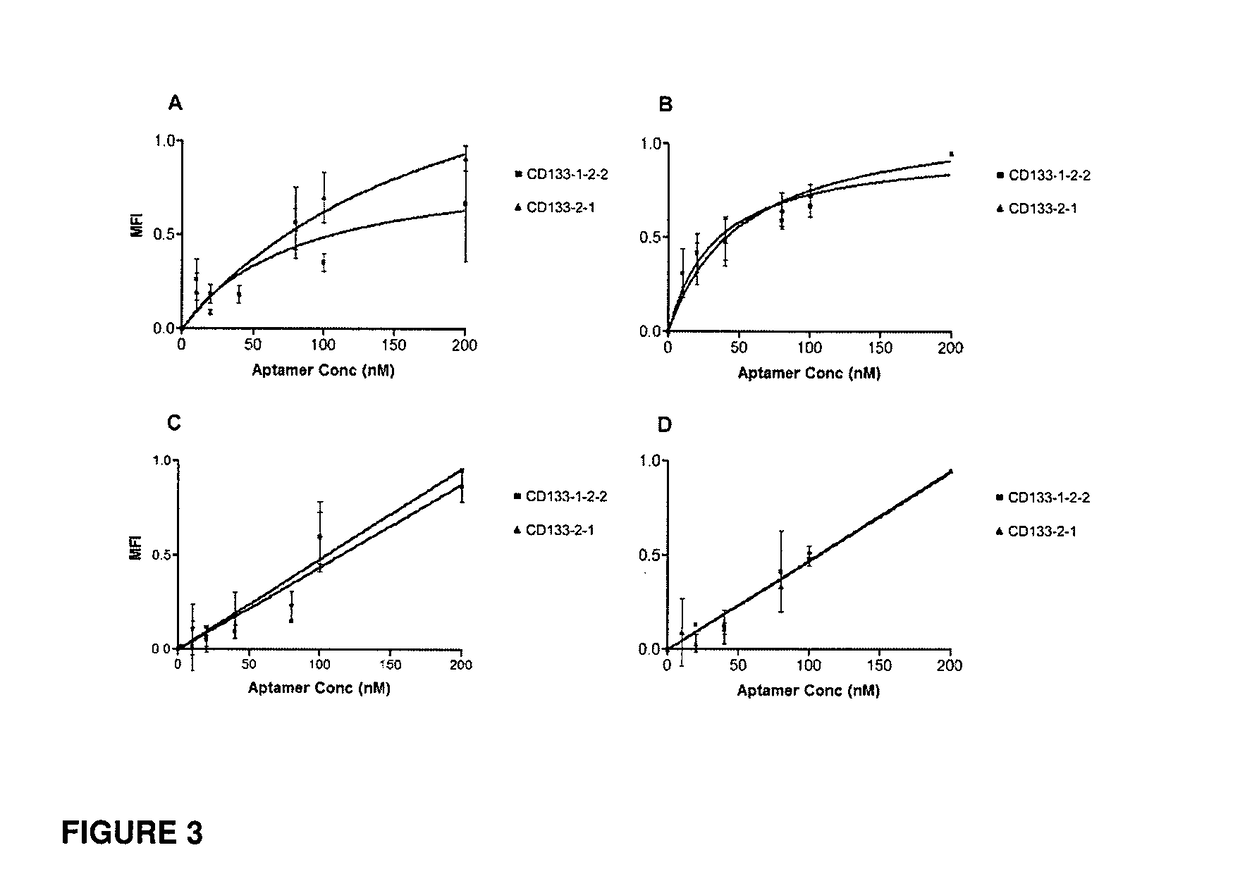
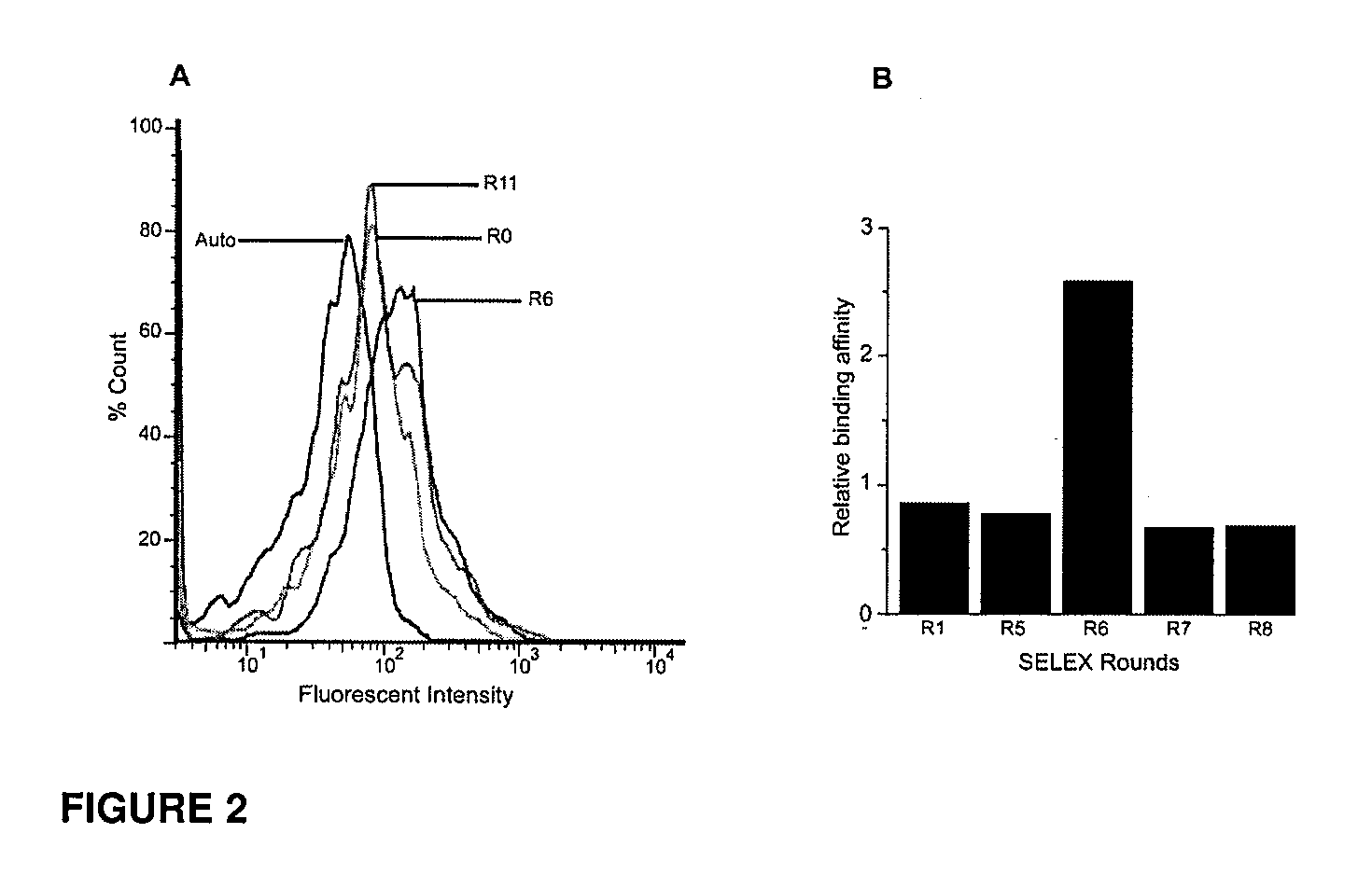
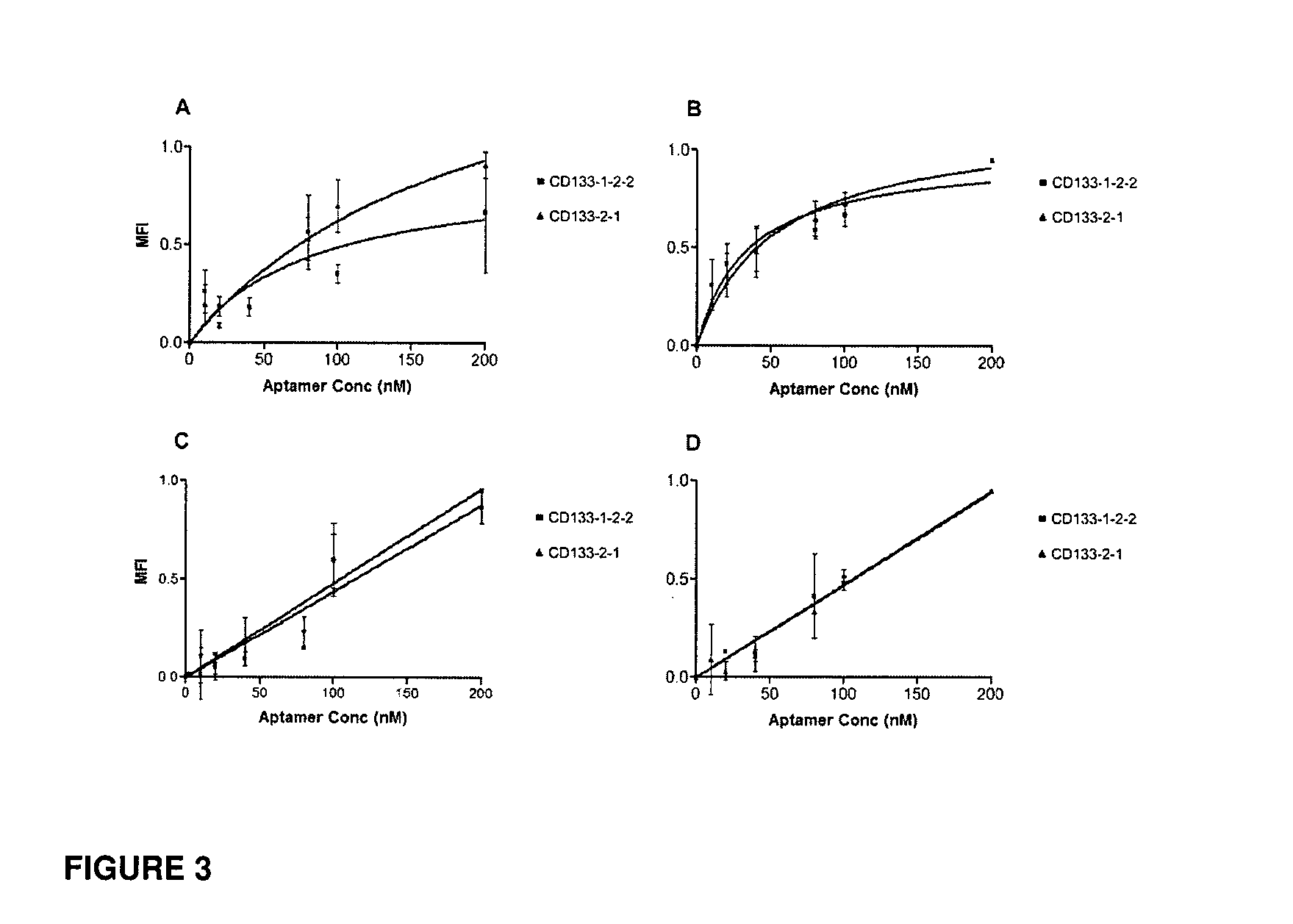
CD133 aptamers for detection of cancer stem cells
InactiveUS9840712B2Rapidly internalisedImprove permeabilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAptamerCancer cell
Owner:DEAKIN UNIVERSITY
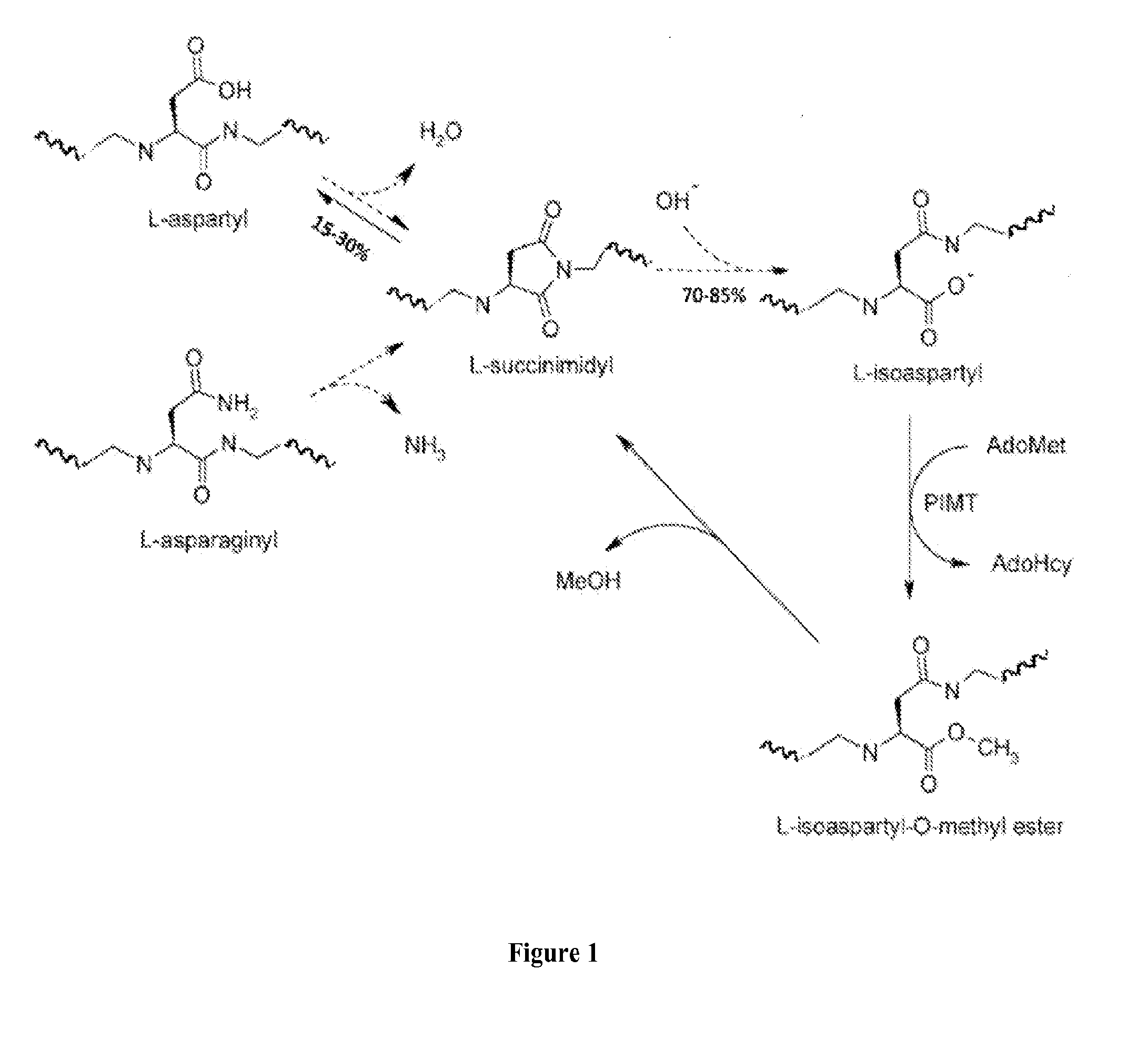
Methods and Compositions for Detecting, Imaging, and Treating Small Cell Lung Cancer Utilizing Post-Translationally Modified Residues and Higher Molecular Weight Antigenic Complexes in Proteins
InactiveUS20150232539A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPotential biomarkersBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention discloses ectopically expressed isoaspartylated proteins and antigenic peptide fragments thereof as potential biomarkers for cancer such as small cell lung cancer. Also disclosed are antigen recognition agents capable of specifically recognizing and binding to isoaspartylated proteins and / or antigenic peptide fragments thereof. Antigen recognition agents of the invention may be formed from proteins, antibodies, RNA aptamers, or other small molecules capable of specifically binding to an isoaspartylated protein or an antigenic peptide fragment thereof. Other aspects disclosed herein include imaging methods for using the isoaspartyl antigen recognition agents, therapeutic methods for treating small cell lung cancer and compositions for performing the same.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Neutralizing RNA aptamers
Nuclease-resistant RNA aptamers are provided which are capable of neutralizing PDGFRβ and are therefore useful in the diagnosis and / or therapy of PDGFRβ-associated and hyperproliferative-associated diseases, such as cancer and primary tumor metastasis. RNA aptamers provided herein include a modified synthetic RNA sequence wherein at least one pyrimidine residue is modified to 2′-fluoropyrimidine. Pharmaceutical compositions and diagnostic kits comprising RNA aptamers are also provided.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Anti-cancer RNA aptamers
Provided herein, inter alia, are compounds capable of binding HSP70 (e.g. mHSP70) on a cell and internalizing into said cell. The compositions provided herein may be useful for delivering therapeutic and diagnostic agents to a cell. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment using nucleic acid compounds provided herein.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
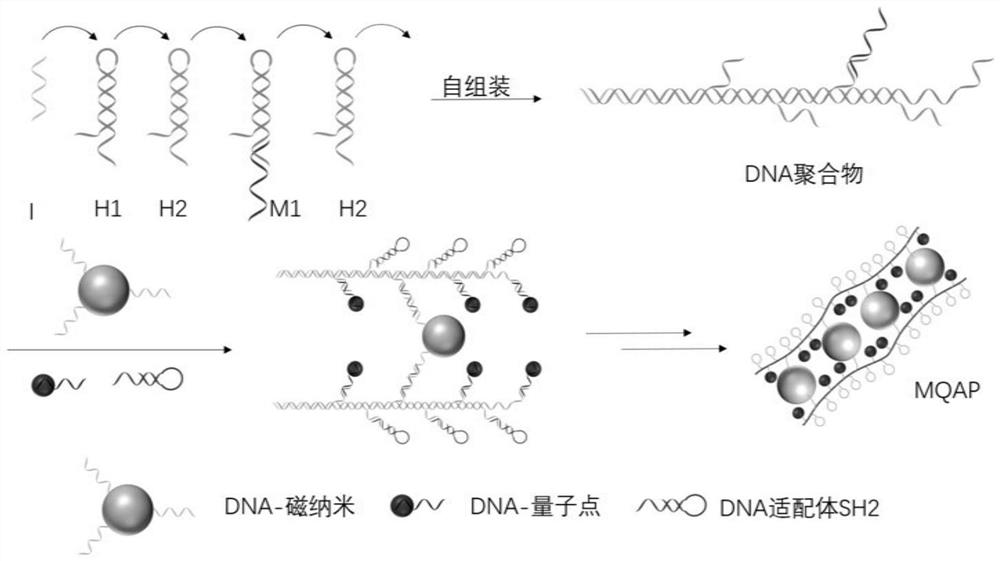
Magnetic fluorescent copolymer nano probe taking DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as template and application
ActiveCN108254346AActive influenceReduce testing costsFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsAptamerFluorescence
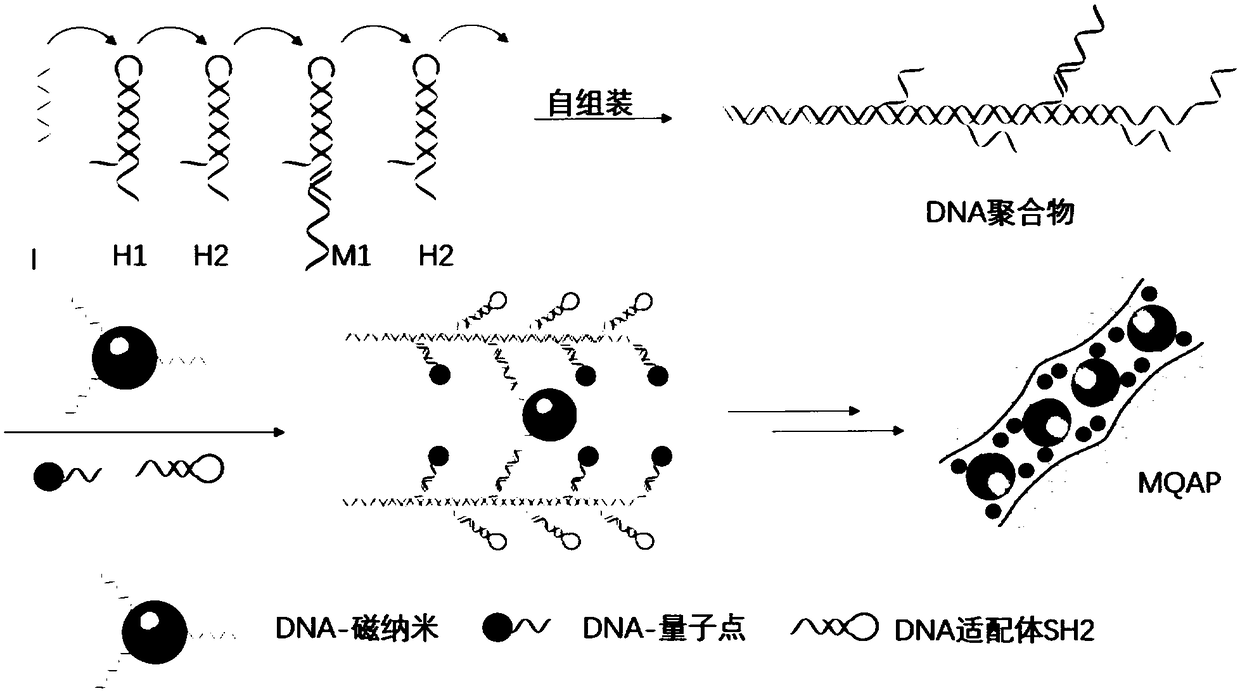
The invention relates to a magnetic fluorescent copolymer nano probe taking DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template. The probe comprises a linear template DNA chain, wherein the template DNA chain is connected with magnetic nano particles with superparamagnetism, quantum dot nano particles with fluorescence and DNA or RNA (ribonucleic acid) aptamers capable of specifically identifying a tumor cell by identifying a DNA sequence; and the magnetic nano particles or the quantum dot nano particles and the DNA or RNA aptamers are alternately connected onto the template DNA chain. The invention further discloses an application of the magnetic fluorescent copolymer nano probe in a preparation for identifying a circulating tumor cell. The nano probe can amplify a magnetic signal and a fluorescentsignal, and has higher specific selection on tumor cells and lower non-specific absorption on normal blood cells.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Inhibitors of DEK protein and related methods
ActiveUS10138486B2Prevents and reduces bindingPreventing, and/or ameliorating inflammatory diseasesSugar derivativesAntipyreticAutoimmune diseaseSingle strand dna
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
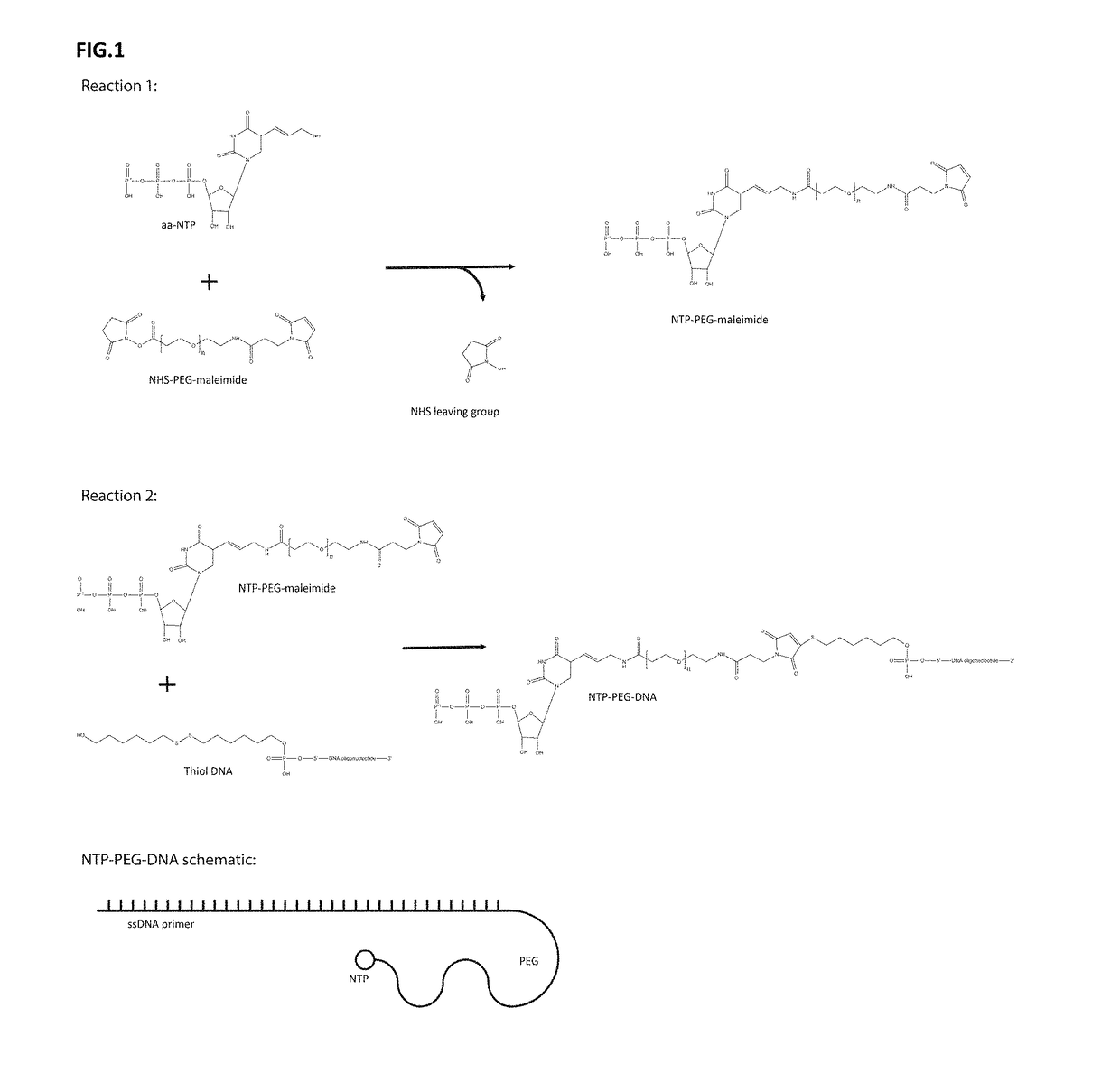
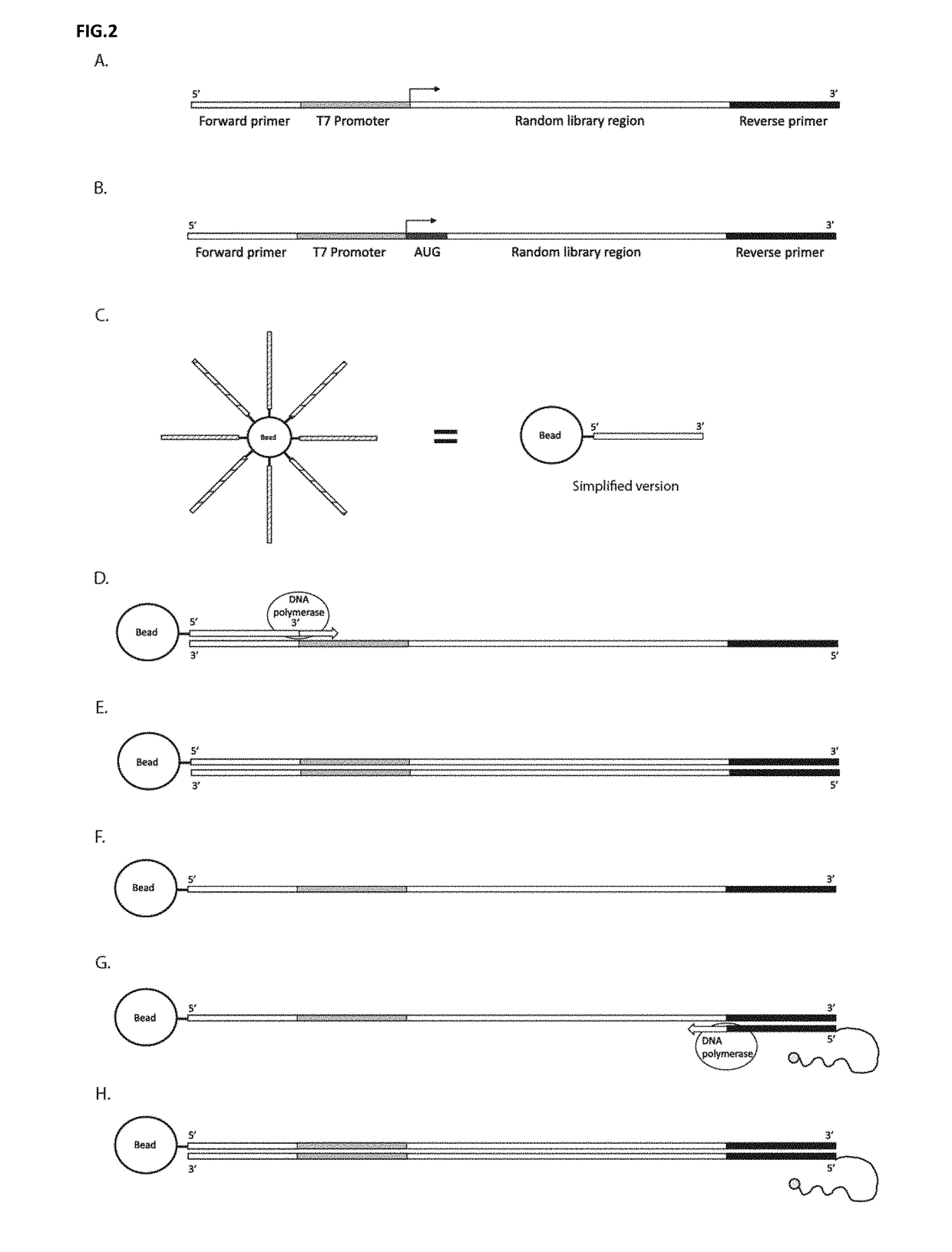
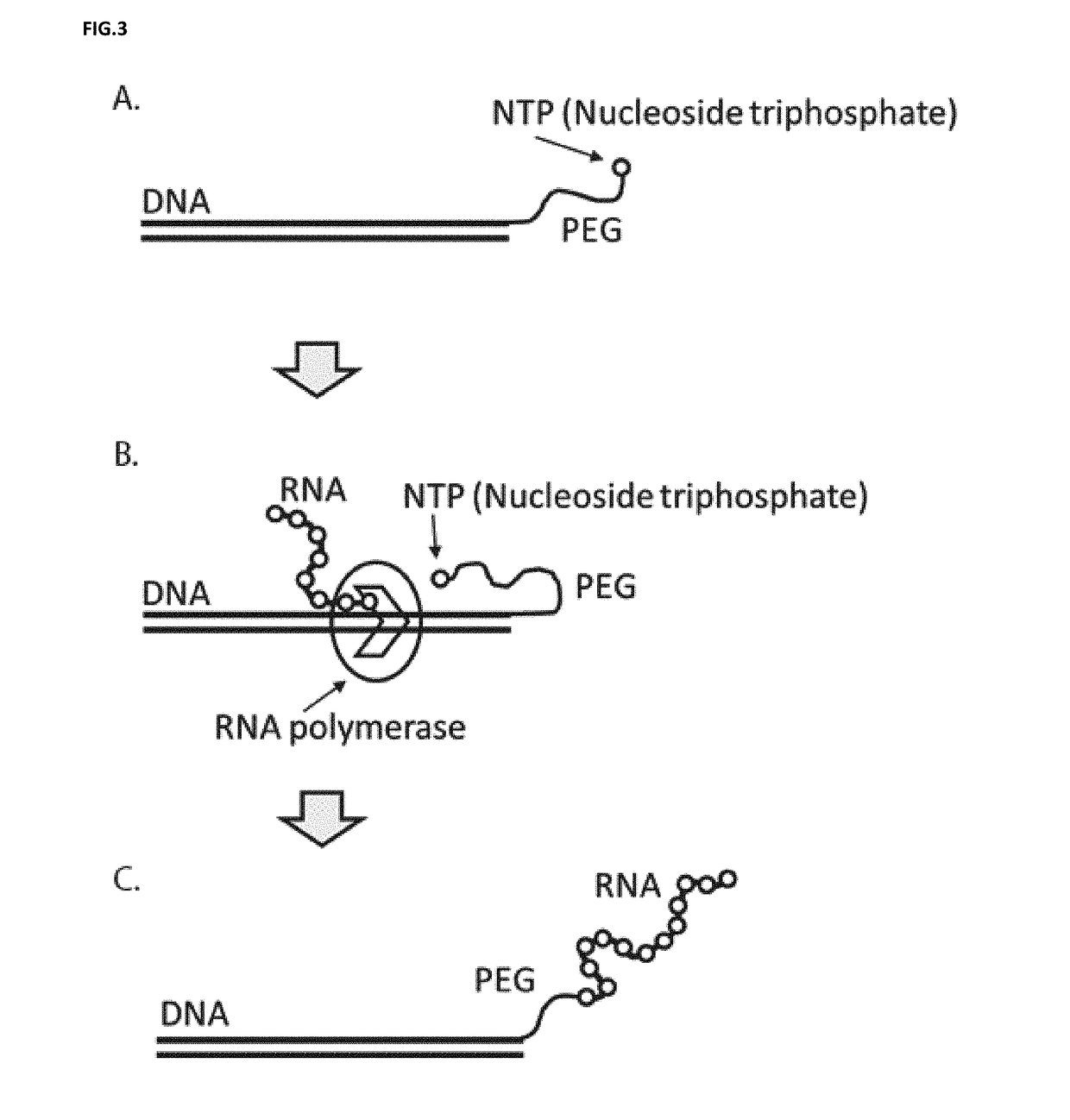
DNA display and methods thereof
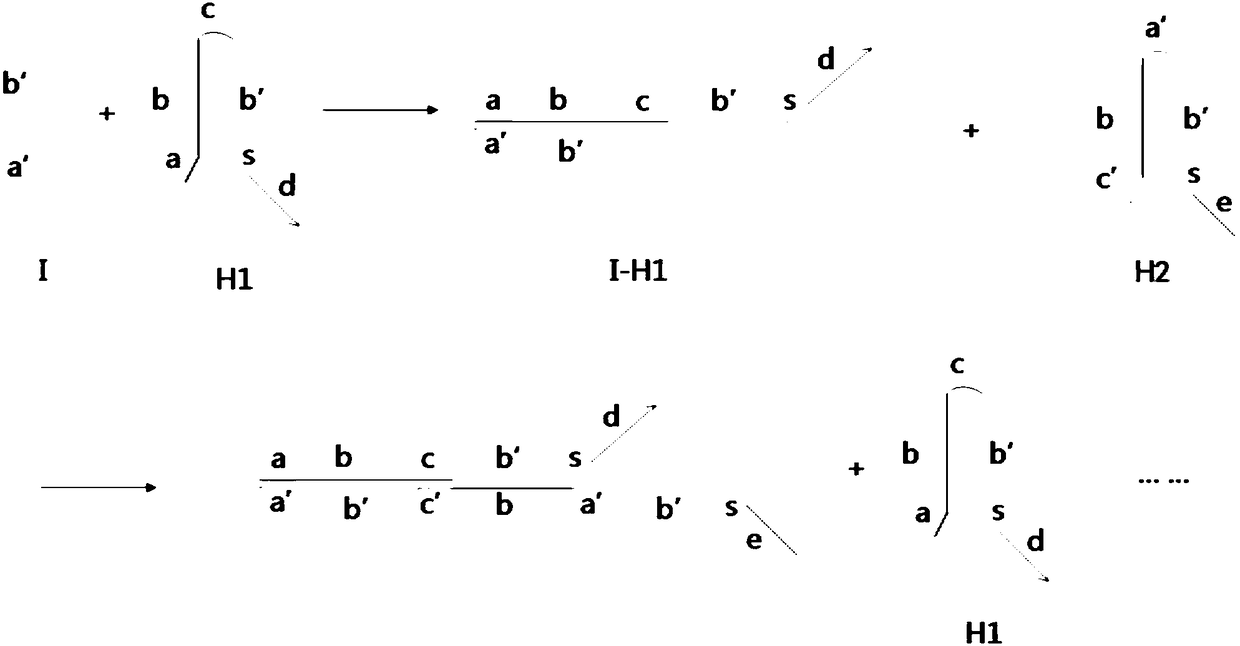
Described herein is a method that displays RNA on the DNA from which it was encoded, enabling enhanced selection of RNA aptamers and proteins. The covalent link between RNA and the DNA which encodes it can be used to negate the spatial informational loss following transcription. This method has applications in the selection of binding ligands such as RNA aptamers and antibodies as well as catalytic molecules such as aptazymes and enzymes.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Chemically modified RNA aptamers and uses thereof
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Chemically modified AMPA receptor RNA aptamers
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Magnetic Fluorescent Copolymer Nanoprobe Using DNA as Template and Its Application
ActiveCN108254346BHave diversityActive influenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsAptamerA-DNA
The invention relates to a magnetic fluorescent copolymer nano probe taking DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template. The probe comprises a linear template DNA chain, wherein the template DNA chain is connected with magnetic nano particles with superparamagnetism, quantum dot nano particles with fluorescence and DNA or RNA (ribonucleic acid) aptamers capable of specifically identifying a tumor cell by identifying a DNA sequence; and the magnetic nano particles or the quantum dot nano particles and the DNA or RNA aptamers are alternately connected onto the template DNA chain. The invention further discloses an application of the magnetic fluorescent copolymer nano probe in a preparation for identifying a circulating tumor cell. The nano probe can amplify a magnetic signal and a fluorescentsignal, and has higher specific selection on tumor cells and lower non-specific absorption on normal blood cells.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A method for detecting the expression of cellular RNA
ActiveCN113686829BImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerRna expression
This application discloses a method for detecting cellular RNA expression. According to the principle of bimolecular fluorescence complementation, different RNA binding proteins or structural domains are fused at the N-terminal and C-terminal of the fluorescent molecule, and two exogenously expressed RNA aptamers pass through The principle of complementary base pairing is combined with the RNA to be detected, and the two RNAs expressed exogenously contain RNA binding protein binding sequences, and when the two fusion expressed different RNA binding proteins bind to them, they will emit fluorescence.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Chemically modified ampa receptor RNA aptamers
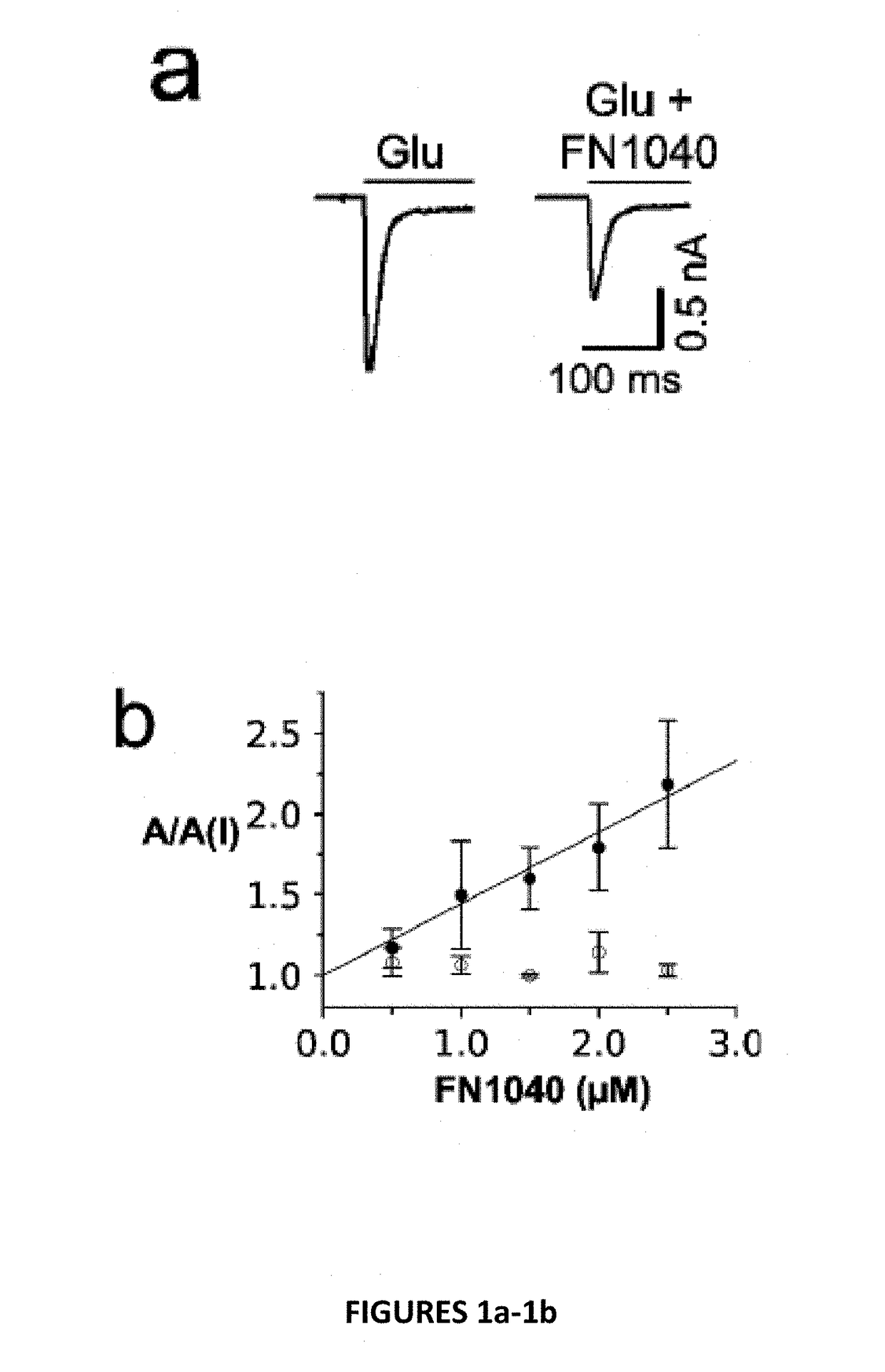
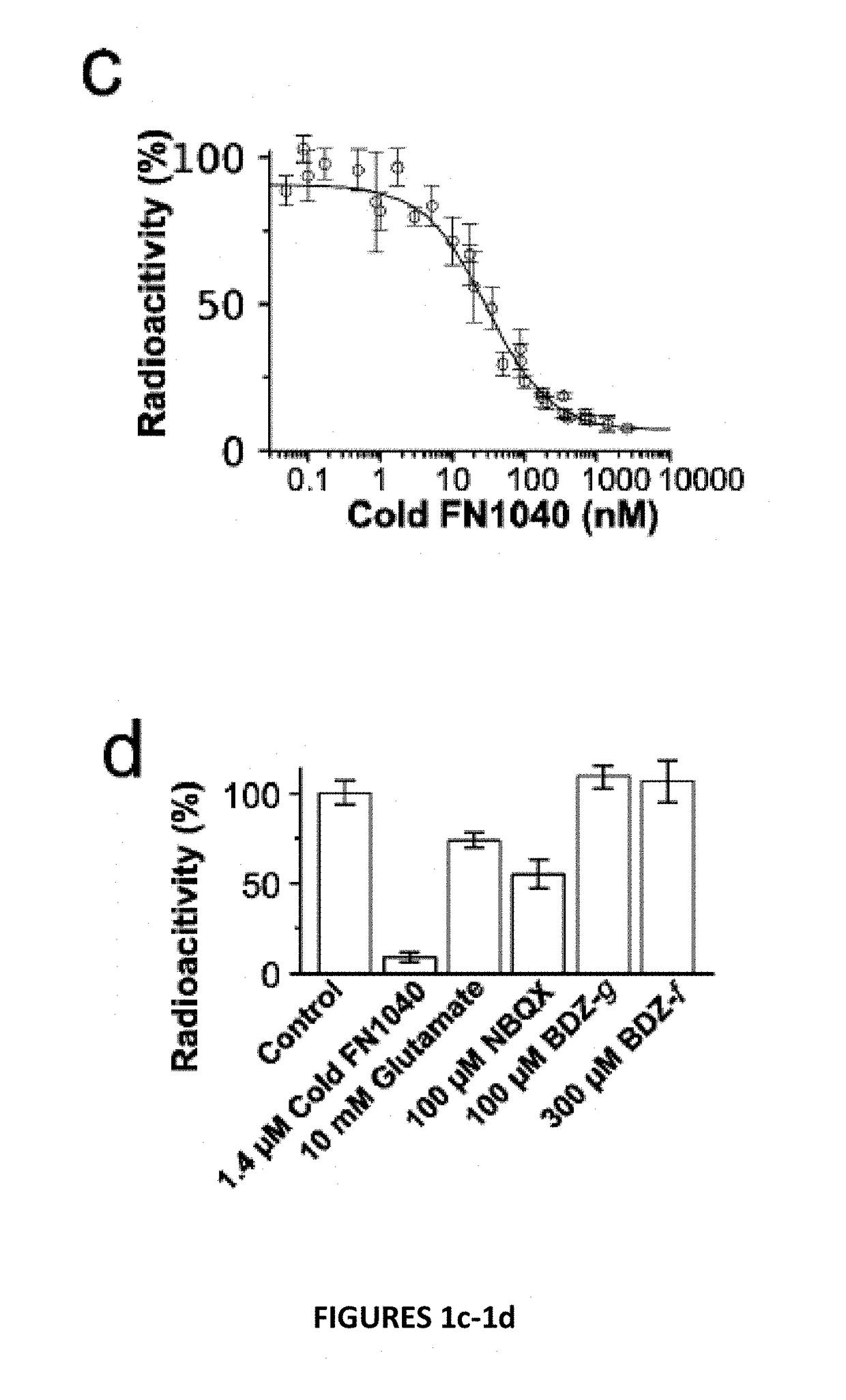
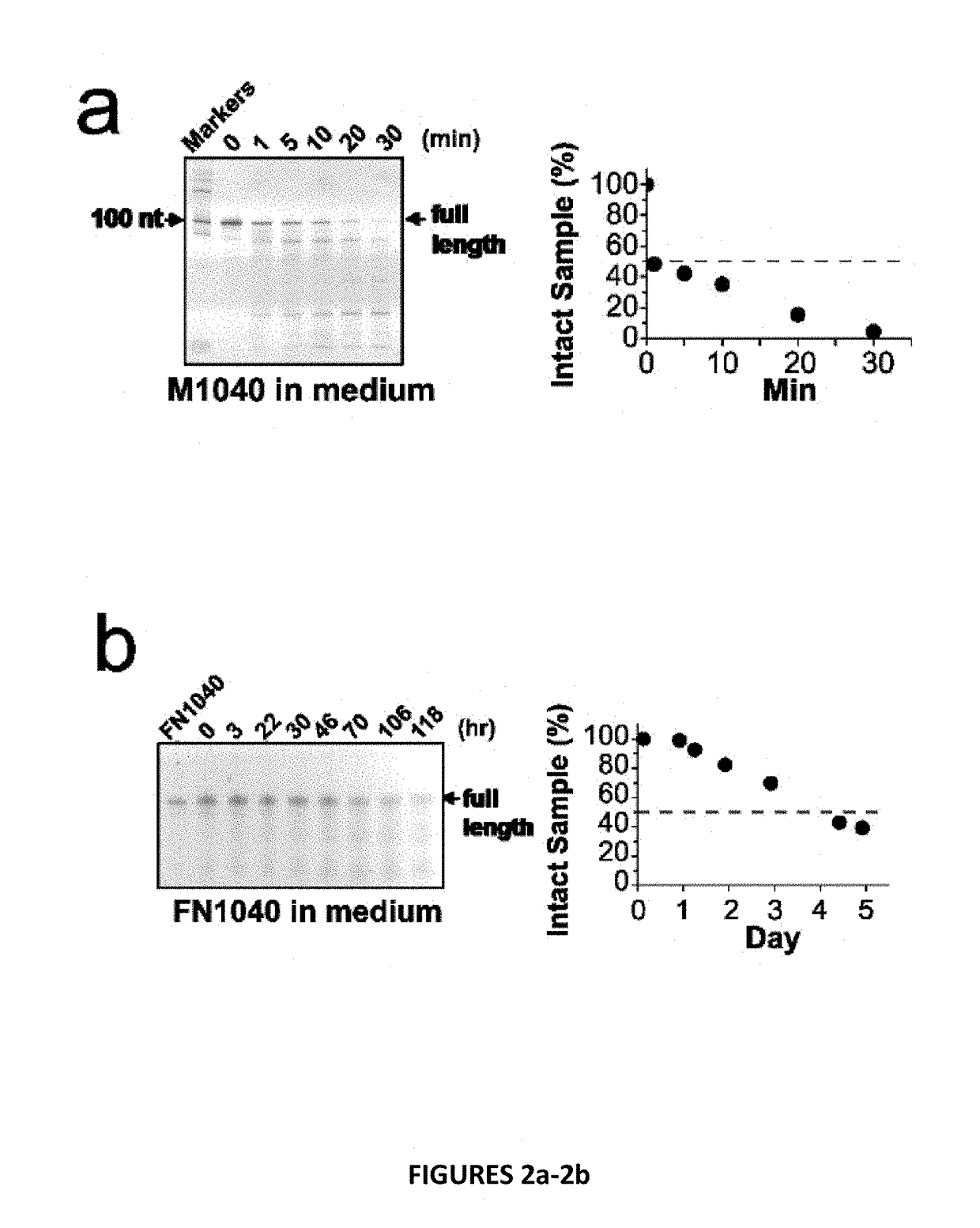
Disclosed is an RNA aptamer, a synthetic oligonucleotide of 2′-fluoro-modified A, U, and C nucleotides, with improved stability compared to its unmodified counterpart. Like the unmodified aptamer, however, the modified version is a potent glutamate receptor antagonist. Additionally, the RNA aptamers described herein are water soluble by nature, and generally exhibit nano- to micromolar potency making them potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of neurological disorders involving glutamate receptor activity.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cd133 aptamers for detection of cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20150299708A1Easy to detectEnhance the imageSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsAptamerOncology
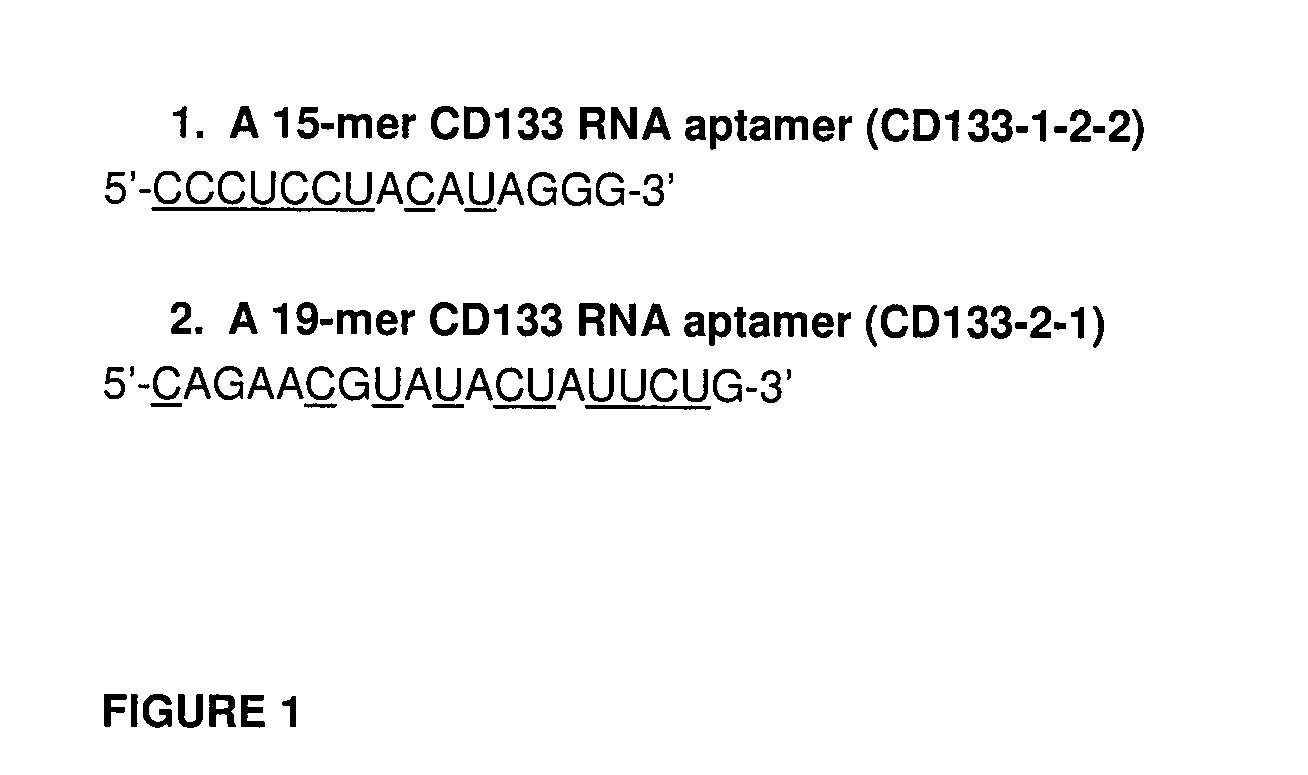
The present disclosure relates to RNA aptamers and uses thereof, in particular, aptamers which specifically bind to CD 133 and which demonstrate superior tumour penetration.
Owner:DEAKIN UNIVERSITY
A kind of production method and application of recombinant small RNA
ActiveCN108753780BShorten the lengthImprove stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a production method of recombinant small RNA. In the method, tRNA is used as a scaffold, and a chimeric miRNA precursor is used to express target small RNA in Escherichia coli. In addition, the invention also discloses the application of the recombinant small RNA produced by the method. The recombinant small RNA designed and prepared by the present invention is obtained through bioengineering technology, and has the advantages of simple and convenient equipment, rapid production, high yield, low cost, and good functionality; tests by various technical means show that the method of the present invention can conveniently and quickly Prepare a variety of miRNA / siRNA / RNA aptamers, and produce recombinant small RNAs to meet the needs of scientific research and drug development.
Owner:西安荣清畅生物科技有限公司 +1
DNA display and methods thereof
InactiveCN107614703AImprove bindingAvoid lossMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesADAMTS ProteinsDna encoding
Described herein is a method that displays RNA on the DNA from which it was encoded, enabling enhanced selection of RNA aptamers and proteins. The covalent link between RNA and the DNA which encodes it can be used to negate the spatial informational loss following transcription. This method has applications in the selection of binding ligands such as RNA aptamers and antibodies as well as catalytic molecules such as aptazymes and enzymes.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Selection of RNA-aptamers as anti-malaria agents
The present invention relates to an aptamer or an active fragment thereof raised against the semi-conserved duffy binding ligand domain 1α, DBL1α, region of the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1, PfEMPI, which aptamer has an effect against malaria, in particular severe cerebral malaria.
Owner:APTAHEM
Post-transcriptional regulation of RNA-related processes using encoded protein-binding RNA aptamers
In vitro SELEX has been used to discover high affinity RNA aptamers interacting with the tetracycline repressor protein in a tetracycline-dependent manner. Using in silico RNA folding predictions to guide the design of both aptamer truncations and mutants, minimized tetracycline repressor protein high affinity binding aptamers have been defined. Using one such aptamer, inducible post-transcriptional regulation in vivo has been demonstrated that is predicated on a direct interaction between a tetracycline repressor protein and a RNA aptamer element. These aptamer components can be integrated in any organism to inducibly regulate RNA translation of a gene of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
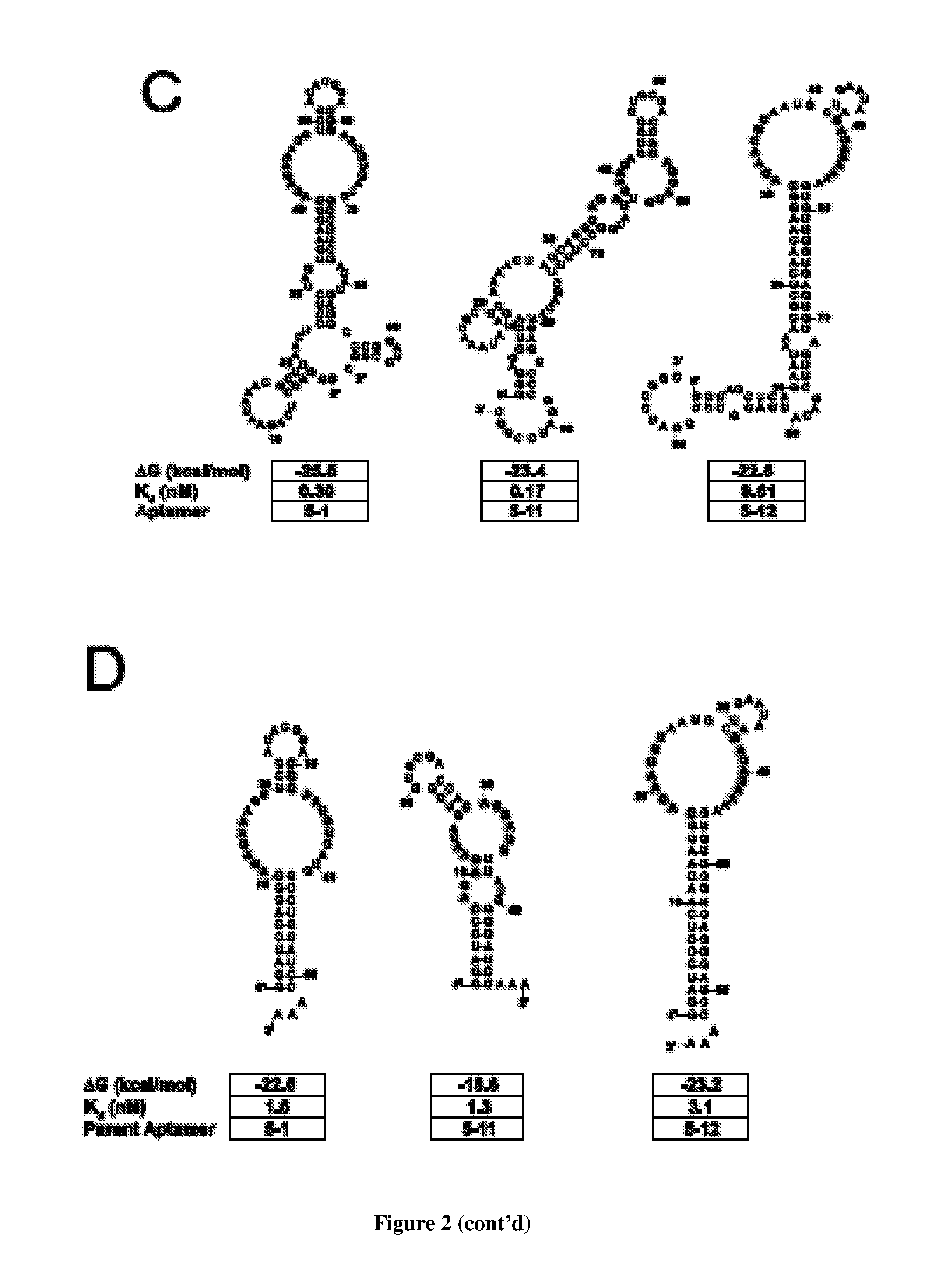
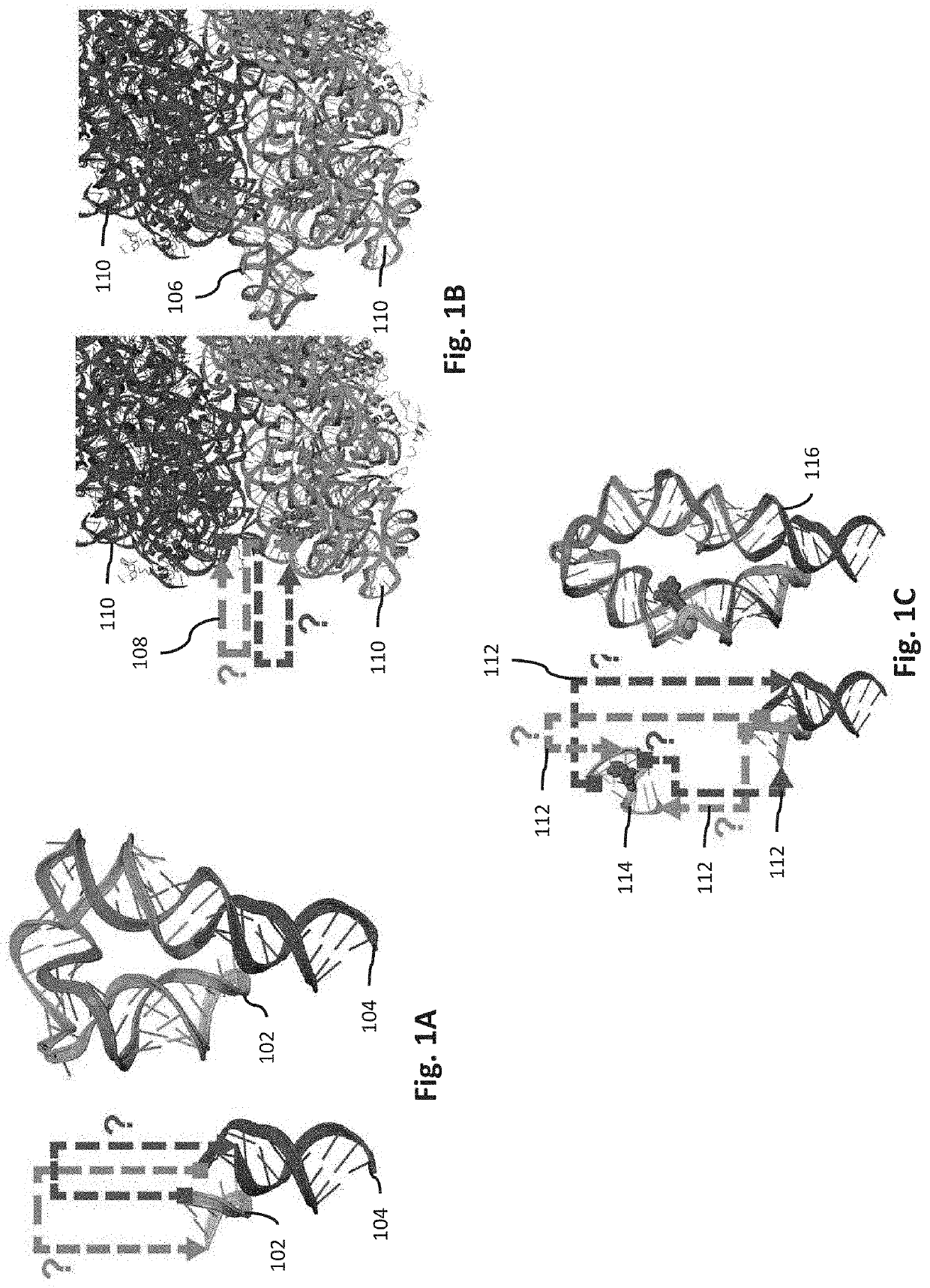
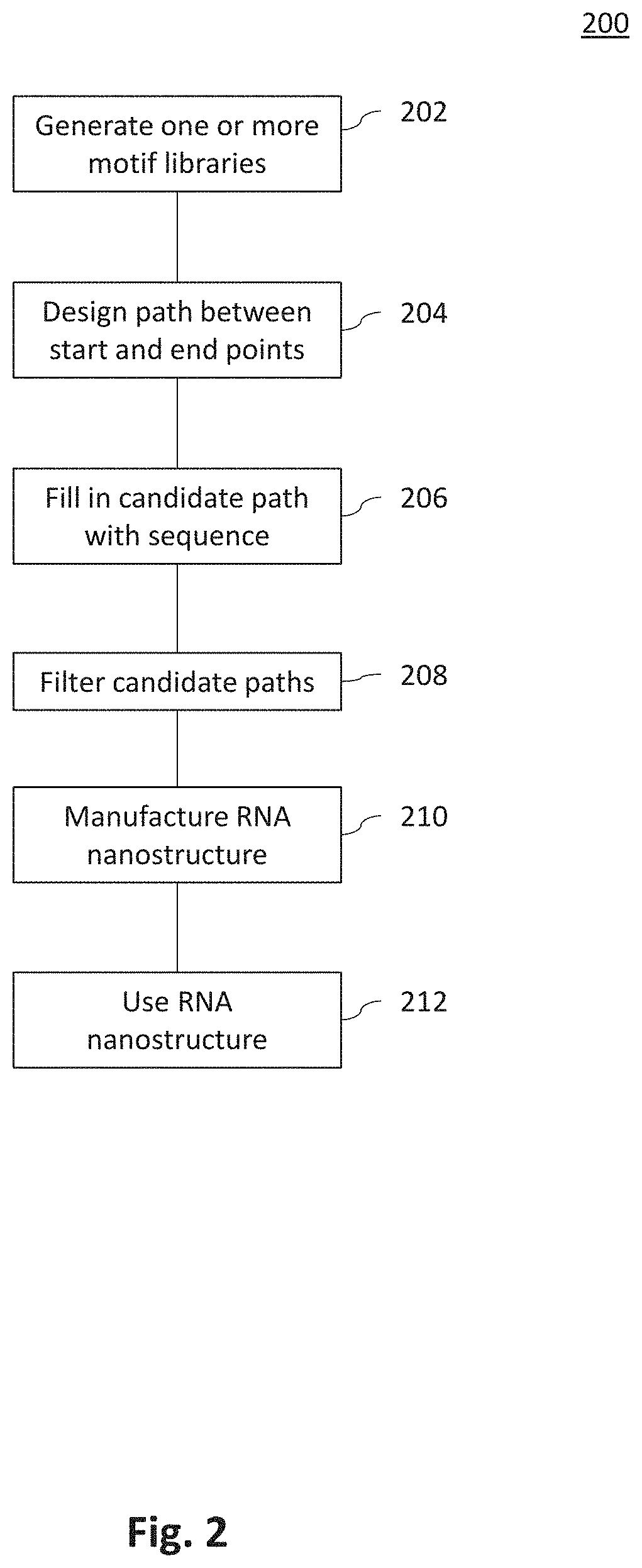
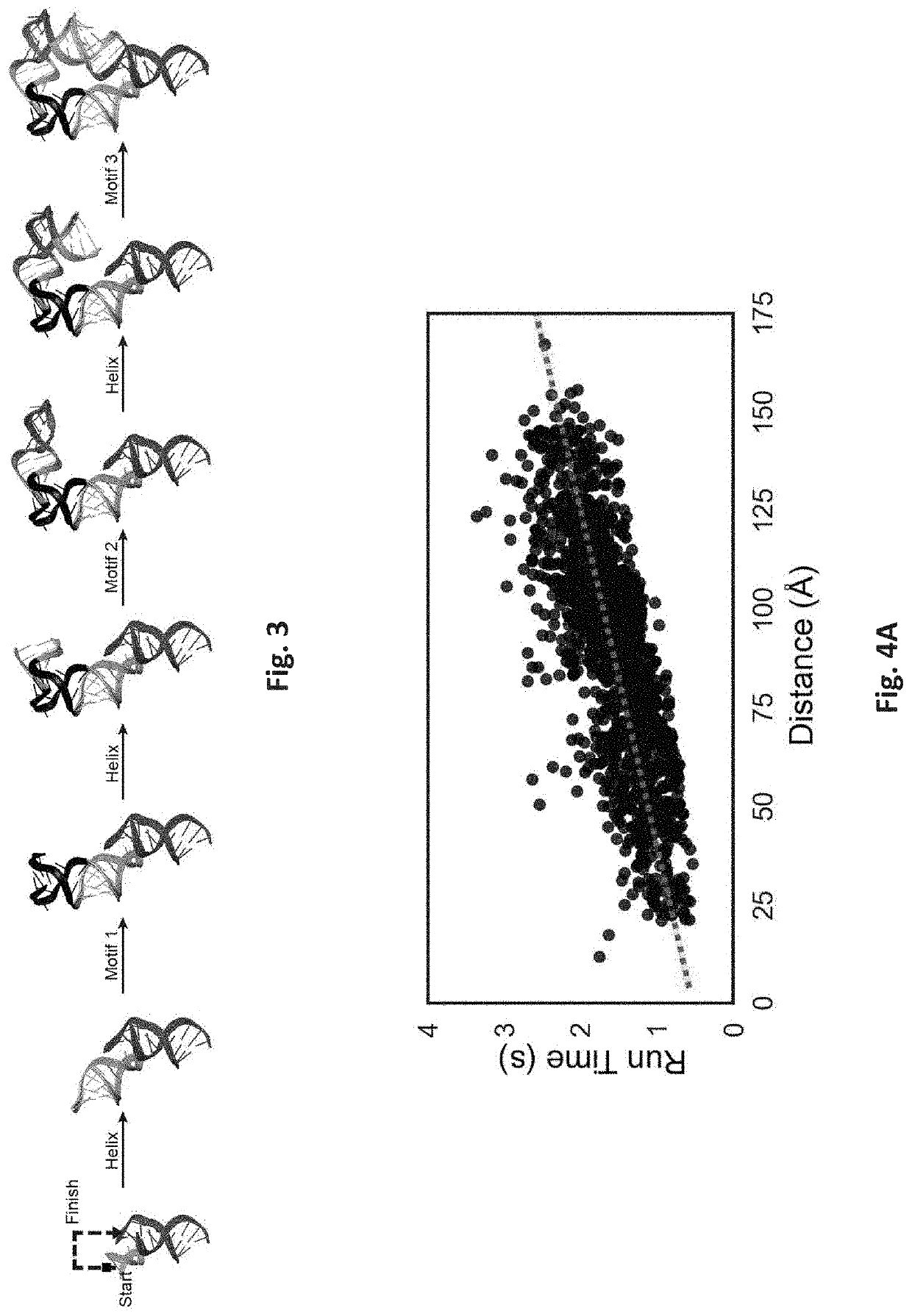
Systems and Methods for Designing RNA Nanostructures and Uses Thereof
Systems and methods for generating RNA nanostructures capable of linking RNA structures and capable of securing aptamers in an active and stable structure are disclosed. Generally, RNA possesses many structural properties to create novel nanostructures and machines. RNA tertiary structure is composed of discrete and recurring components known as tertiary ‘motifs’. Along with the helices that they interconnect, many of these structural motifs appear highly modular. Systems and methods herein generate a motif library including canonical and noncanonical motifs to design a candidate path to connect one or more RNA molecules. These paths can also be used to secure RNA aptamers to improve aptamer stability and activity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com