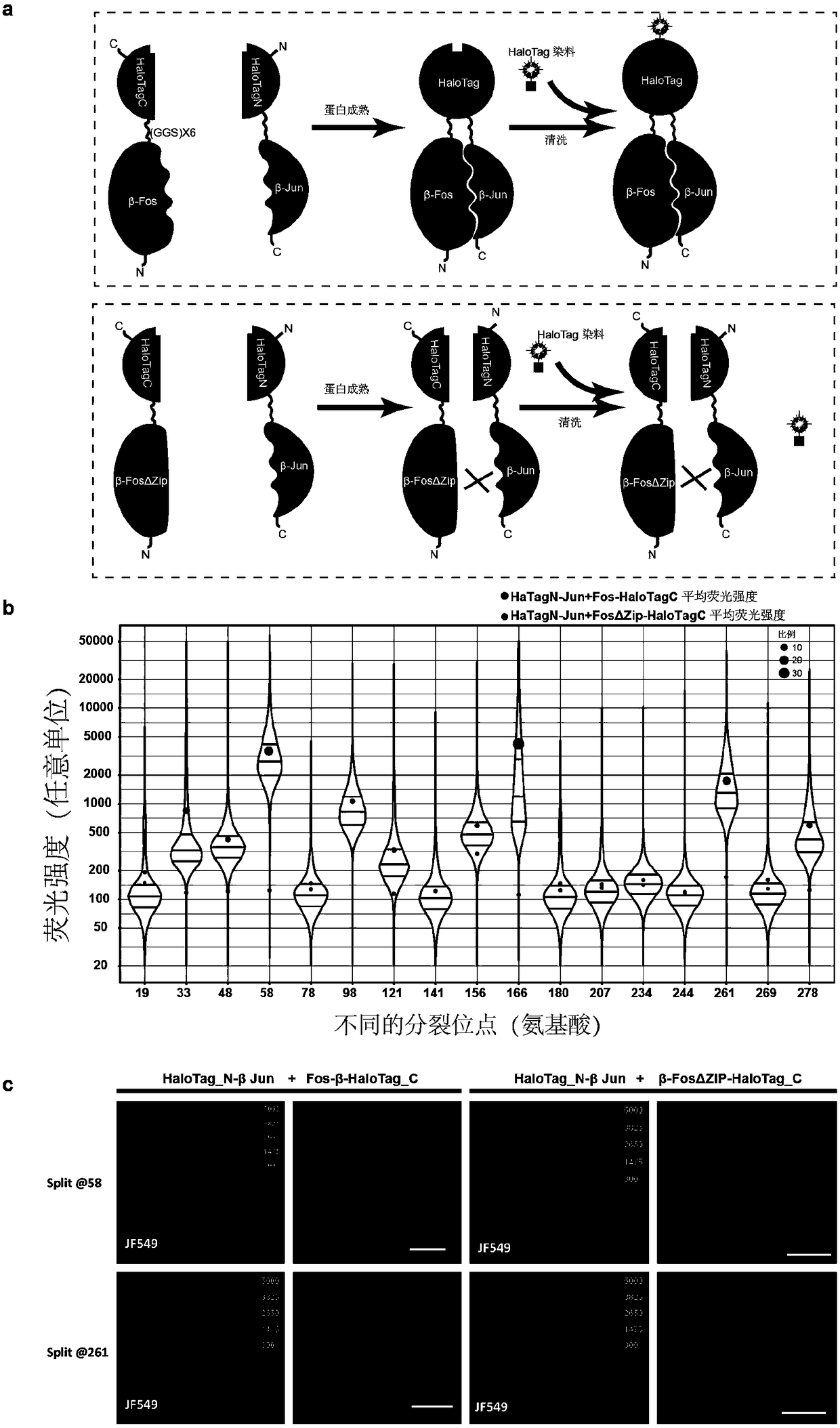
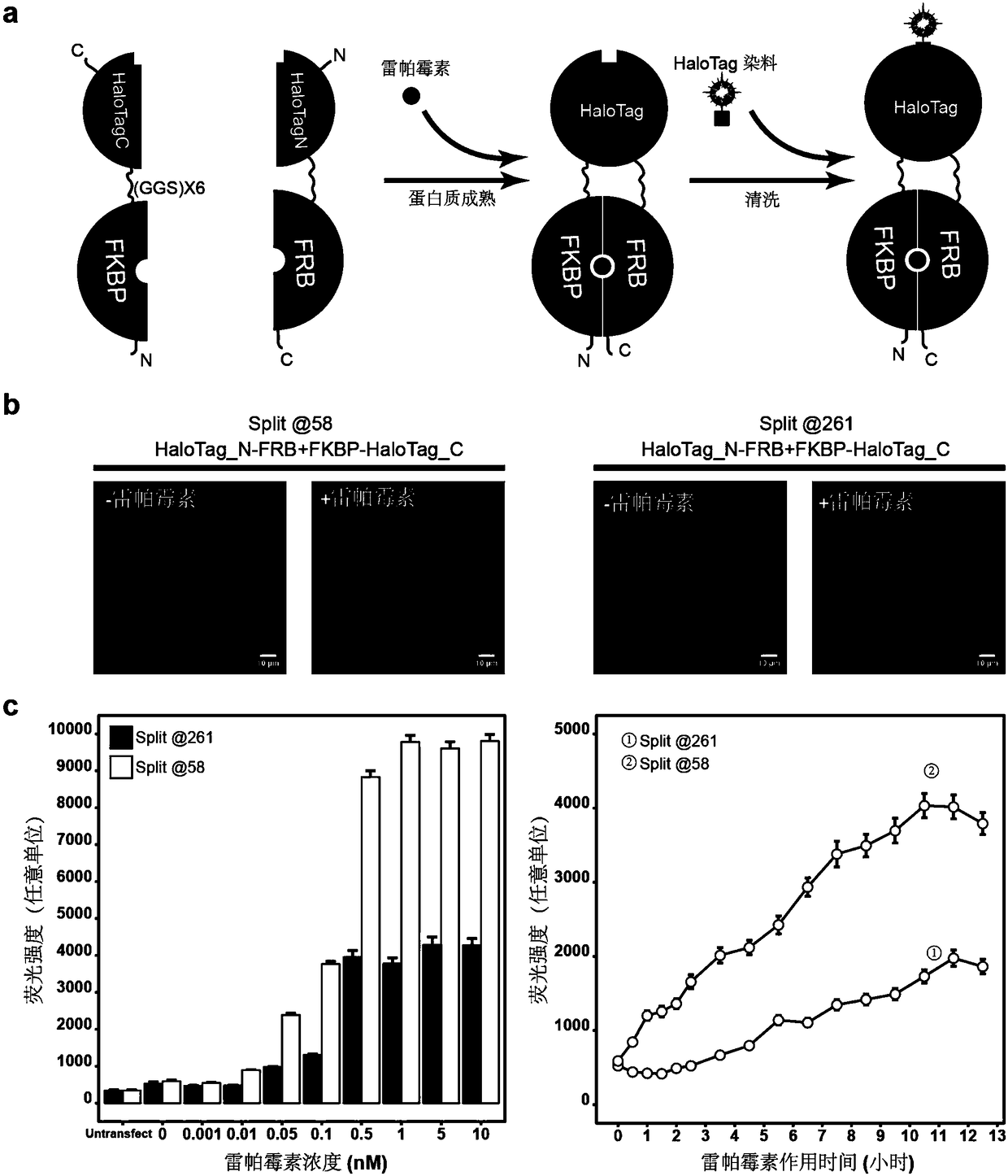
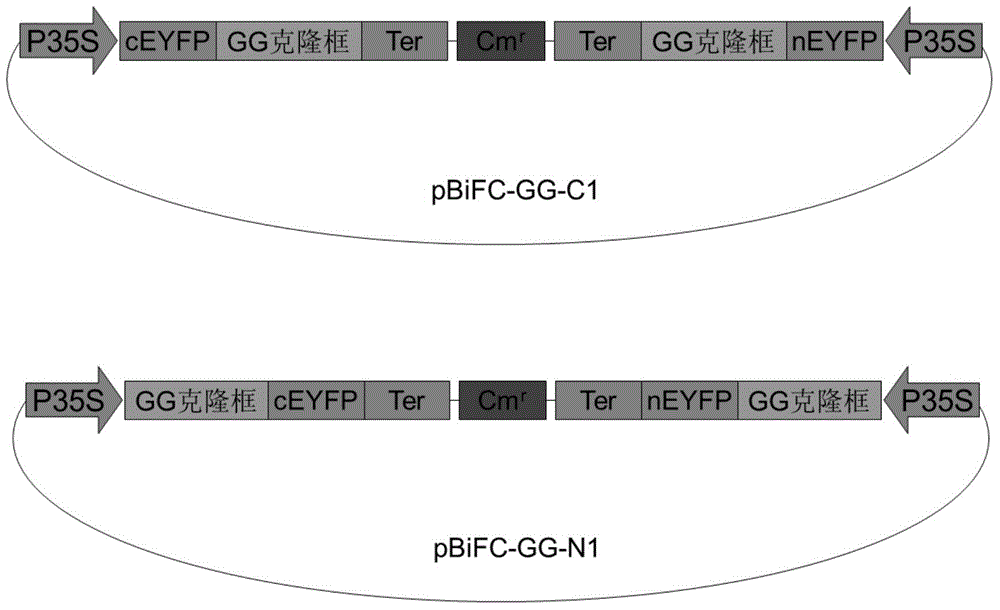
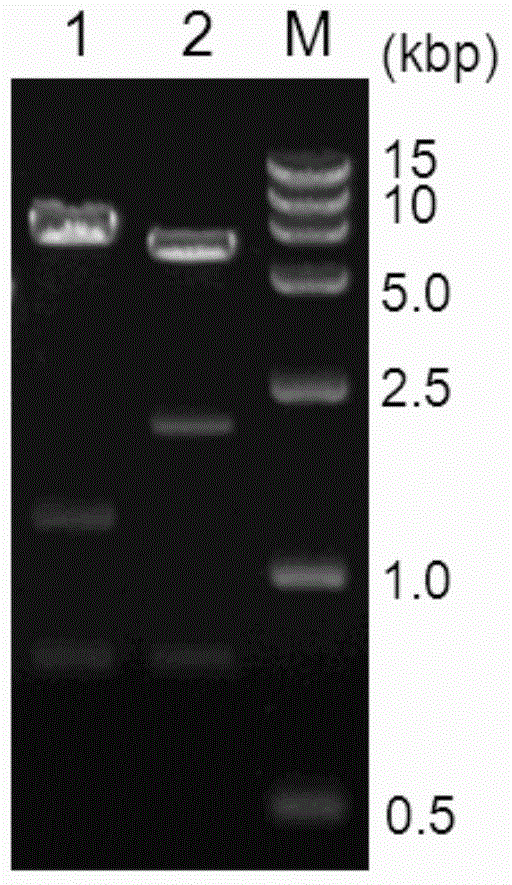
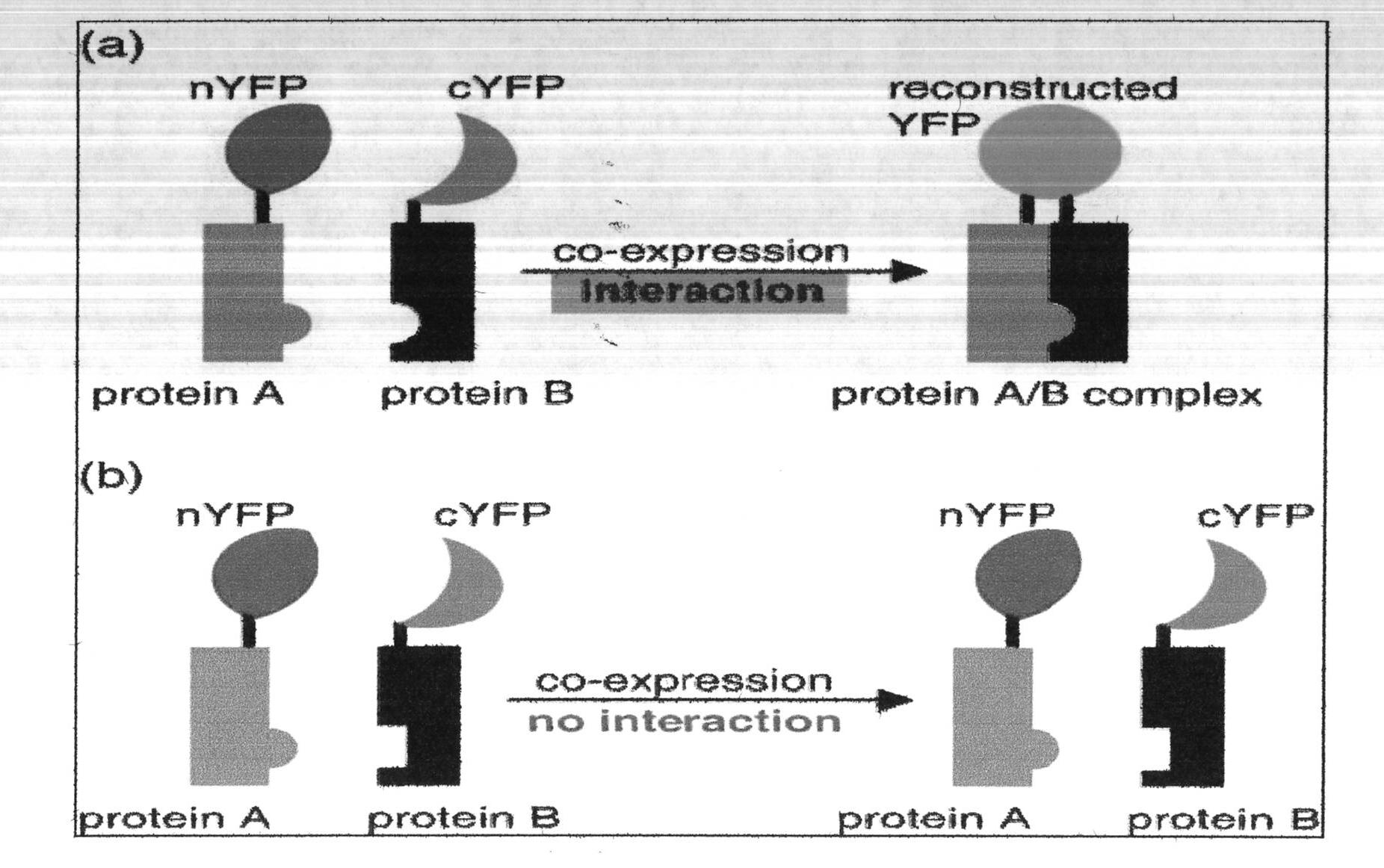
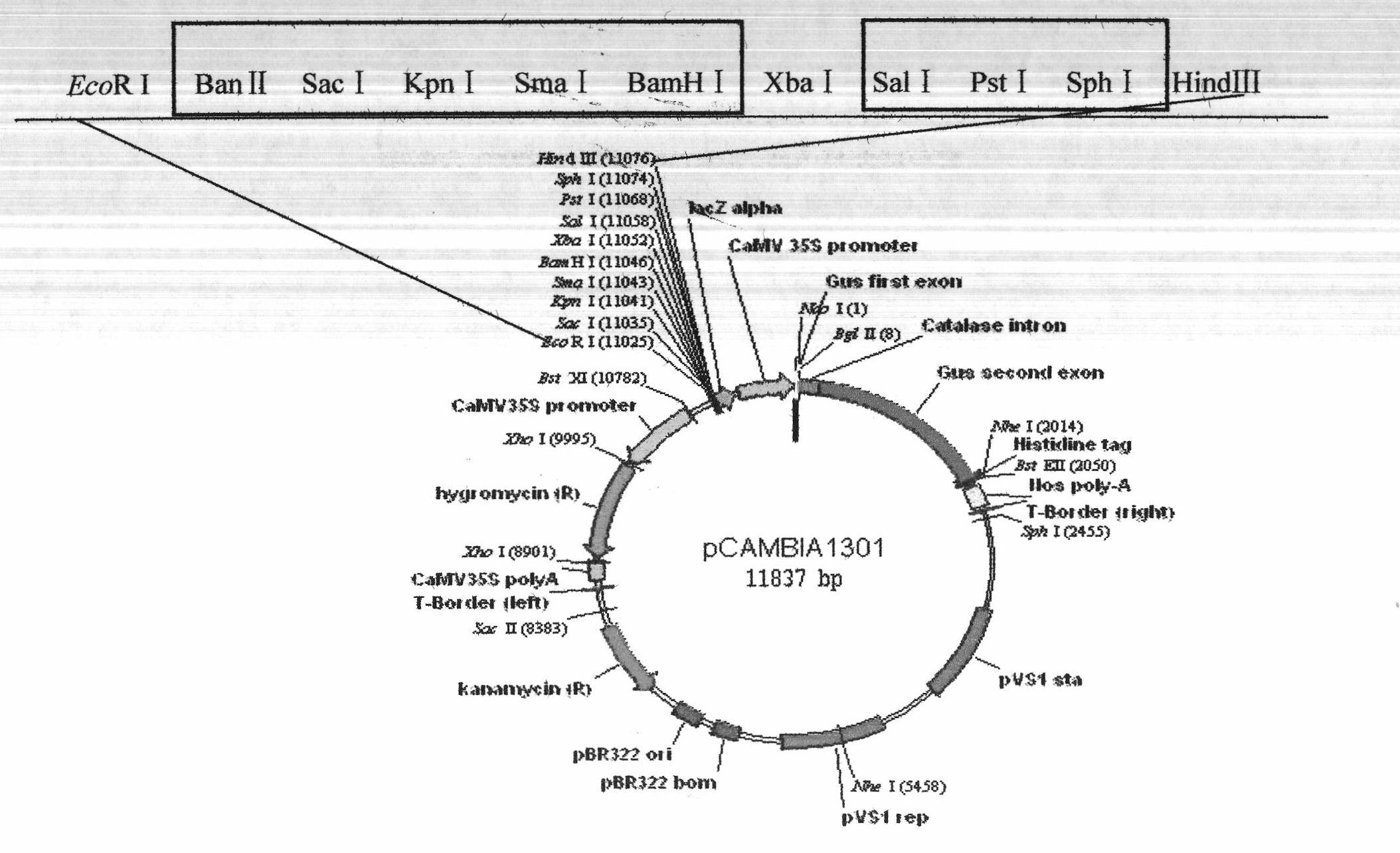
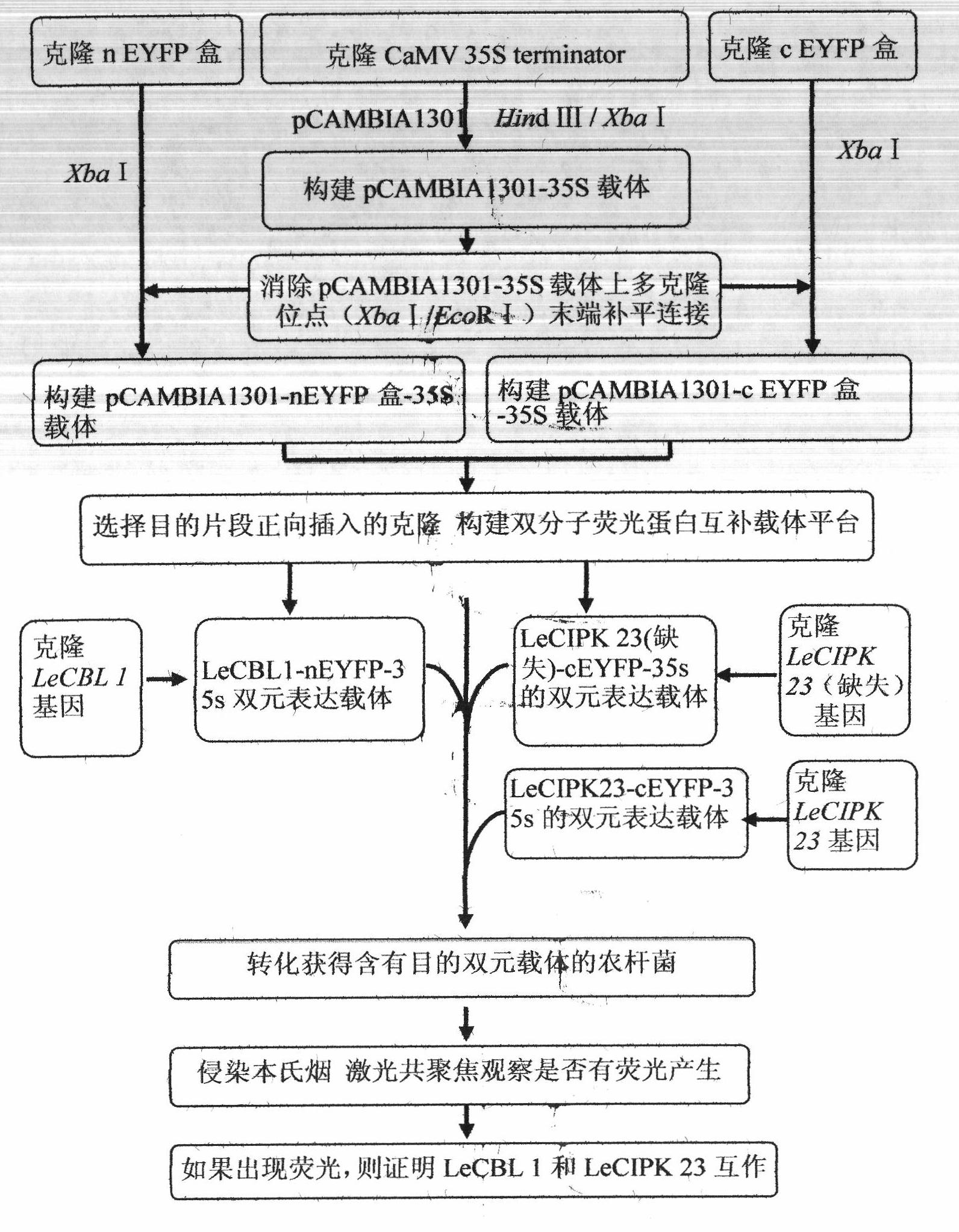
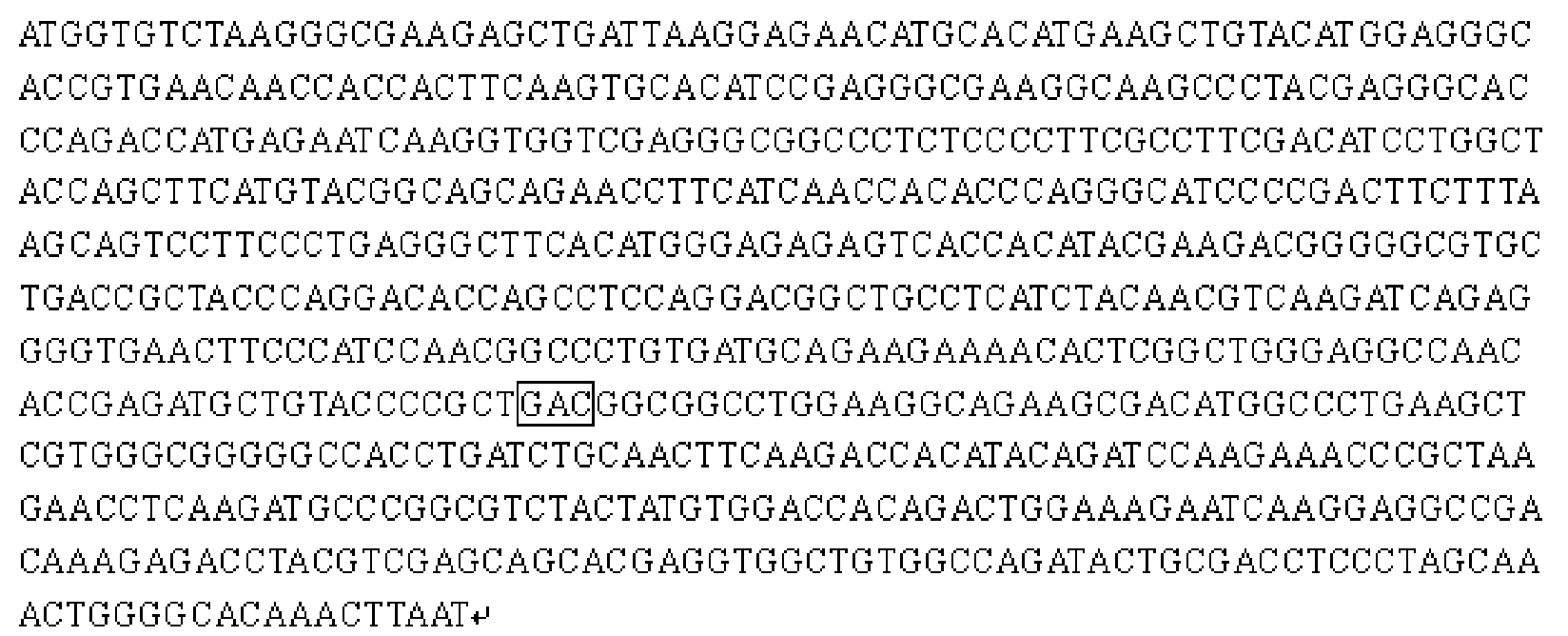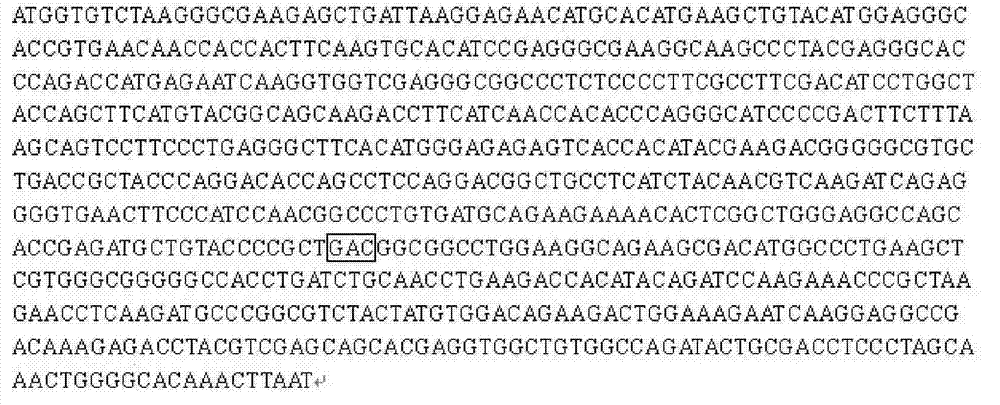Patents
Literature
48 results about "Bimolecular fluorescence complementation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
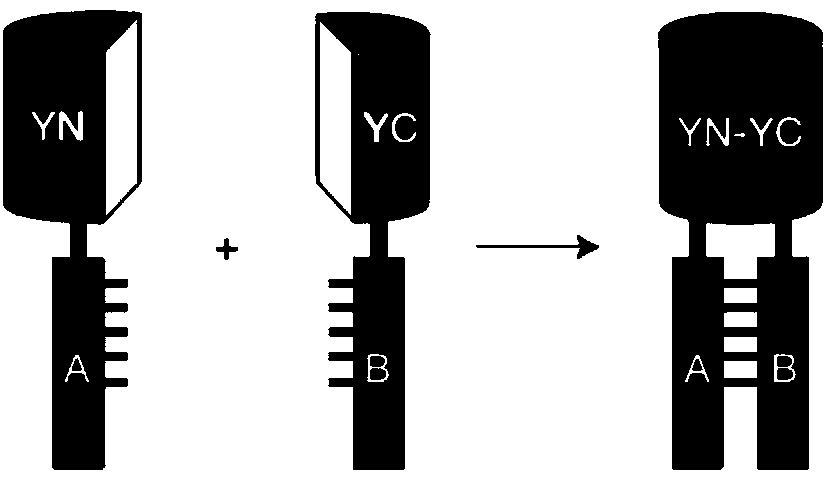
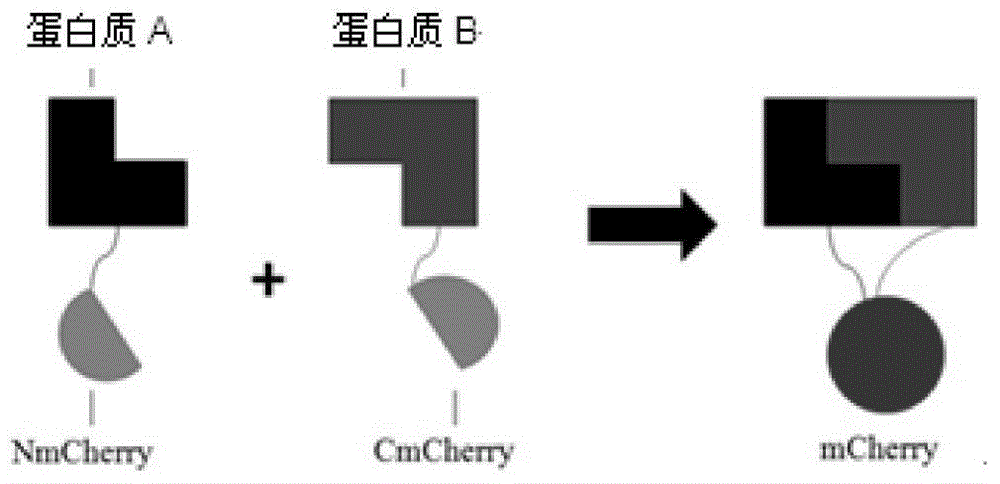
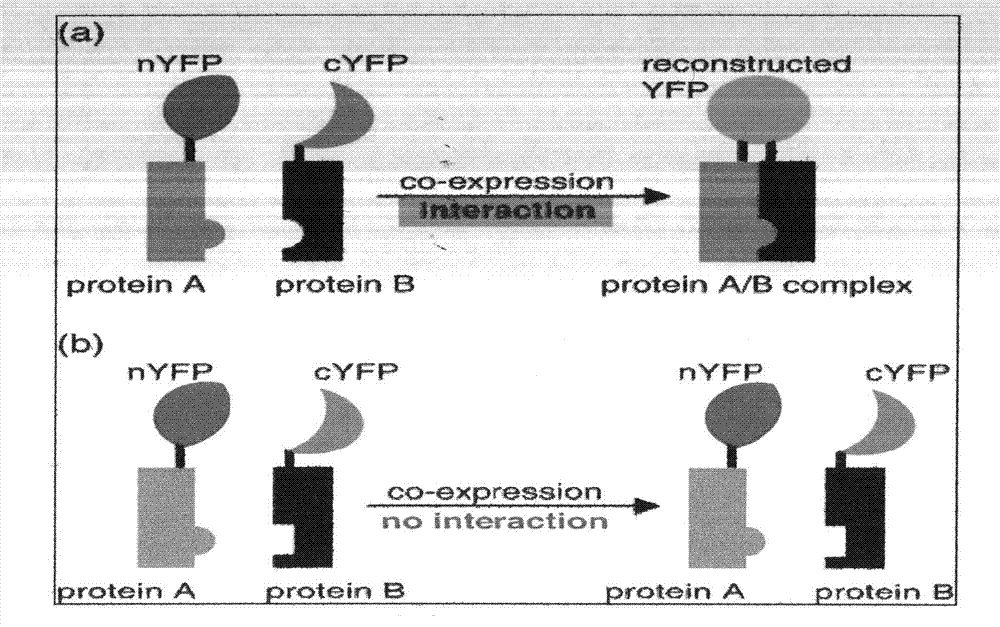
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (also known as BiFC) is a technology typically used to validate protein interactions. It is based on the association of fluorescent protein fragments that are attached to components of the same macromolecular complex. Proteins that are postulated to interact are fused to unfolded complementary fragments of a fluorescent reporter protein and expressed in live cells. Interaction of these proteins will bring the fluorescent fragments within proximity, allowing the reporter protein to reform in its native three-dimensional structure and emit its fluorescent signal. This fluorescent signal can be detected and located within the cell using an inverted fluorescence microscope that allows imaging of fluorescence in cells. In addition, the intensity of the fluorescence emitted is proportional to the strength of the interaction, with stronger levels of fluorescence indicating close or direct interactions and lower fluorescence levels suggesting interaction within a complex. Therefore, through the visualisation and analysis of the intensity and distribution of fluorescence in these cells, one can identify both the location and interaction partners of proteins of interest.
Method for detecting interaction of proteins
InactiveCN101620233AIncrease brightnessStrong penetrating powerBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein insertionLiving body
The invention relates to a detection method which belongs to the field of biomolecules. The method can be used for detecting the interaction among proteins by a dimolecular fluorescent complement technology on the basis of orange red fluorescent protein and infrared fluorescent protein. The invention can be applied to detect the interaction of the proteins by living body imaging and can synchronously detect the interaction of multiple pairs of proteins in parallel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
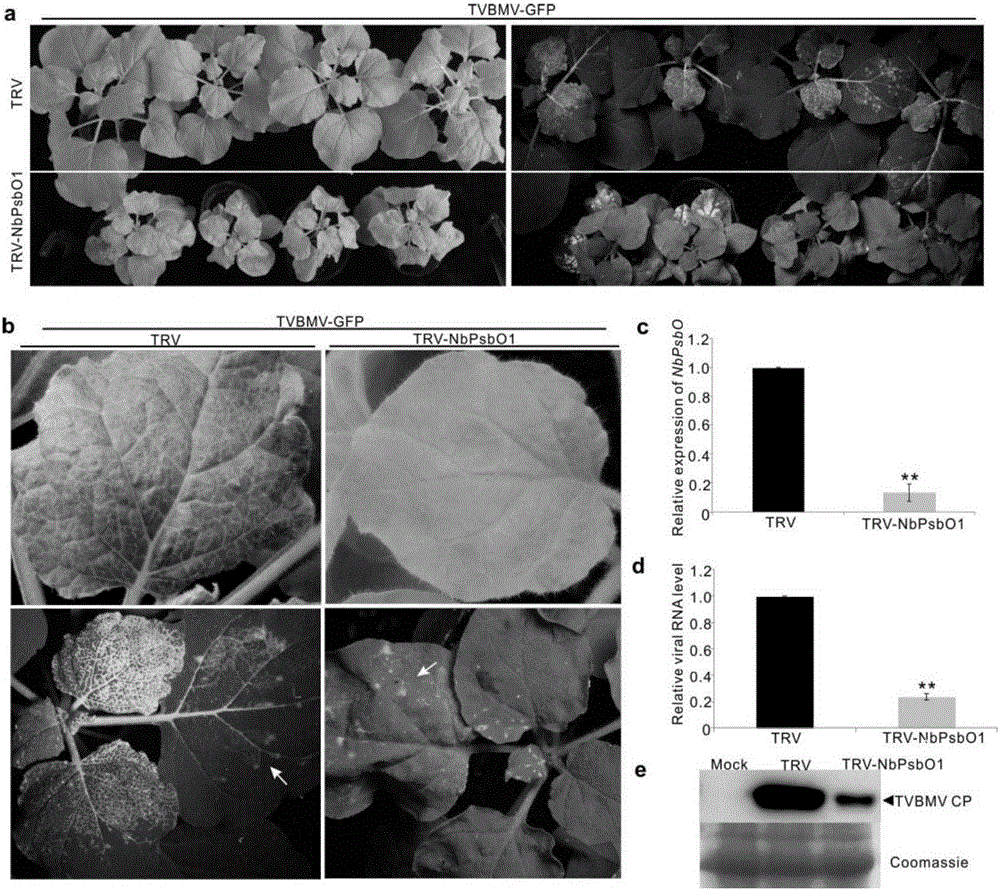
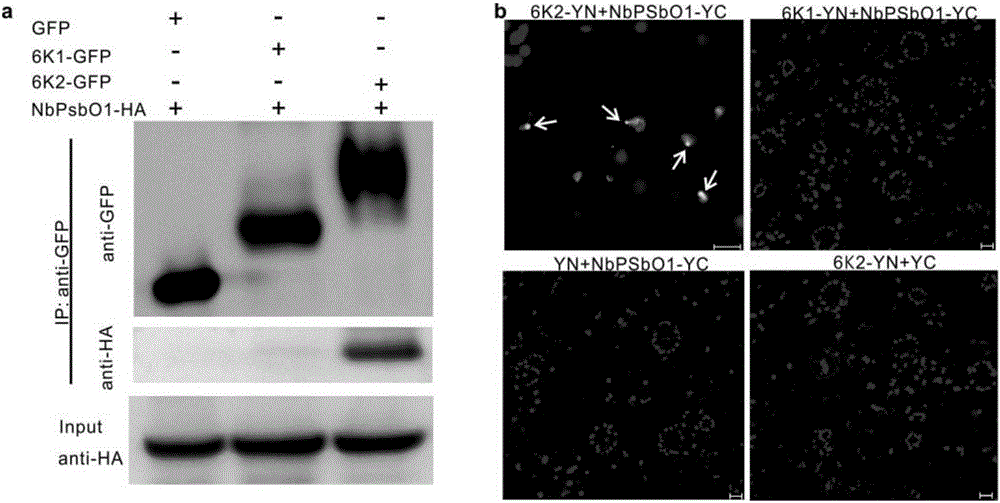
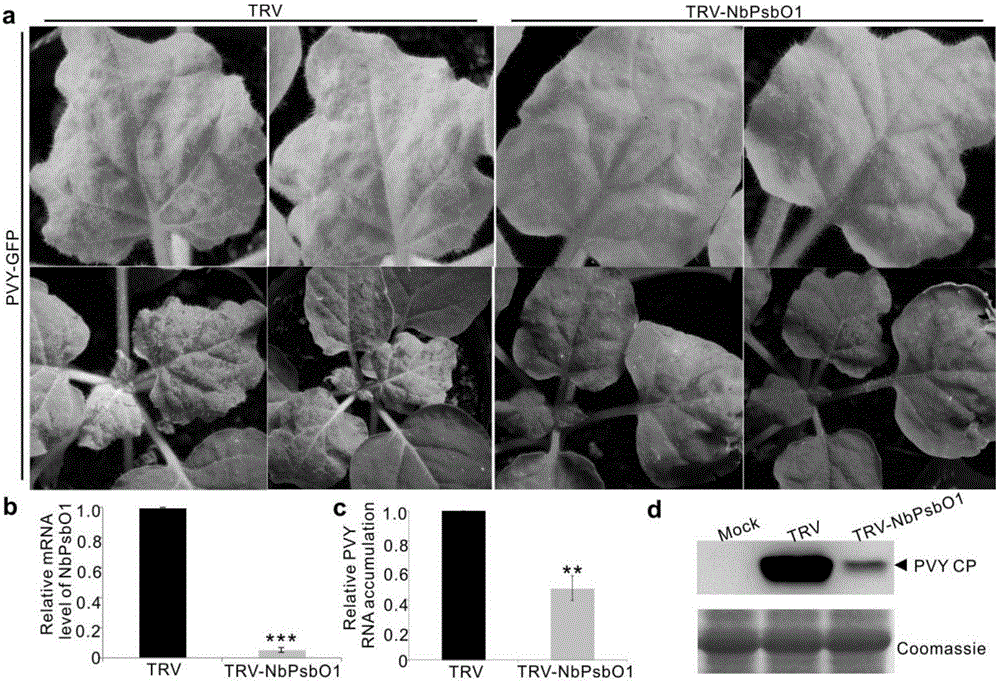
Screening and application of plant antiviral new target PsbO1
InactiveCN106699857AReduce infestationPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringNicotiana tabacumPotato virus Y PVY
The invention relates to the field of plant antiviral genetic engineering, and provides a plant antiviral new target. On the basis of tobacco vein banding mosaic virus infection cloning, photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex protein PsbO1 is screened through immunoprecipitation and mass spectrography, and a PbsO1 gene is obtained through reverse transcription PCR amplification. Immunoprecipitation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation prove that the PsbO1 can interact with the tobacco vein banding mosaic virus 6K2. Reduction in expression of the PsbO1 gene enables an infected plant to generate resistance to the tobacco vein banding mosaic virus and potato virus Y.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
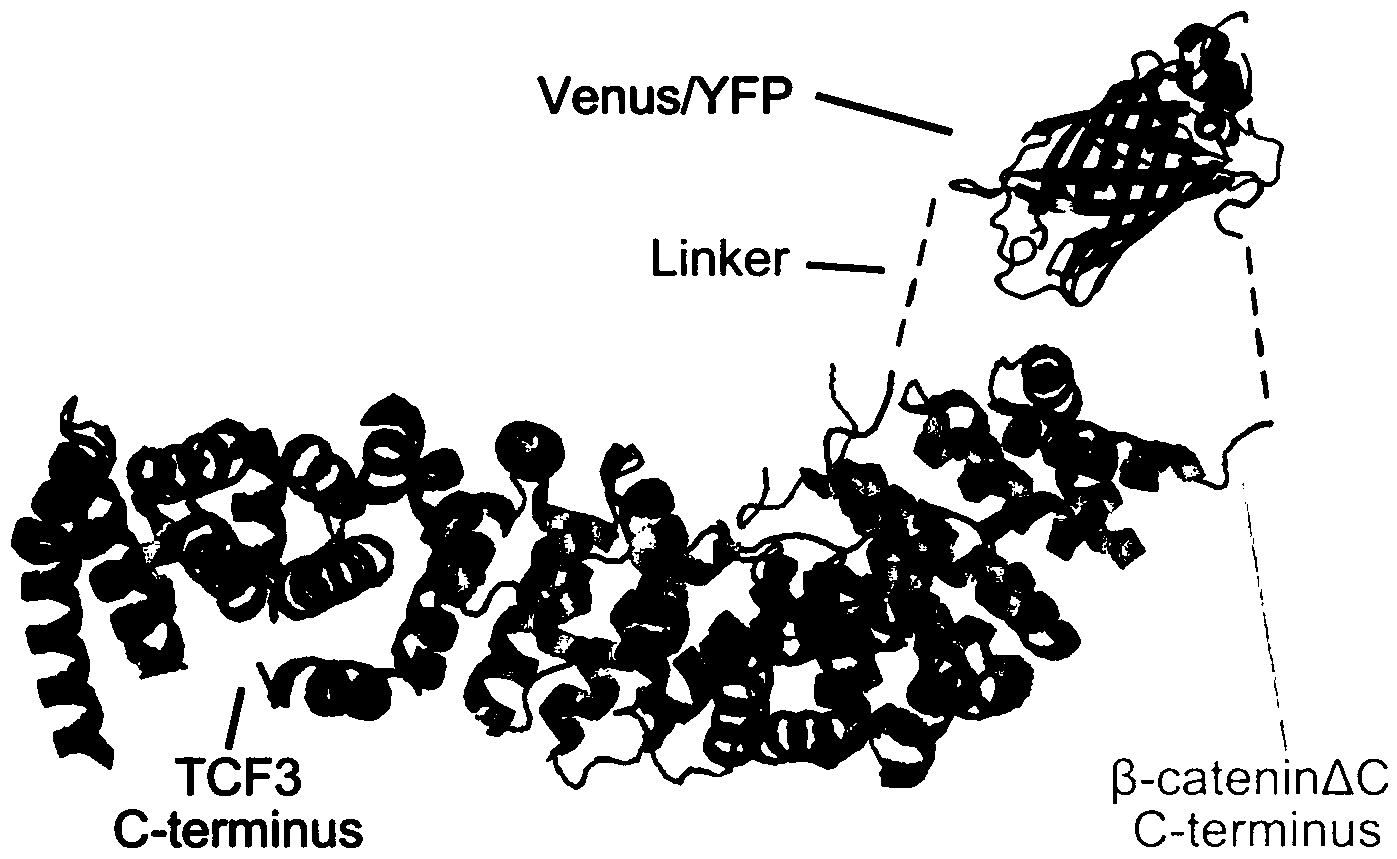
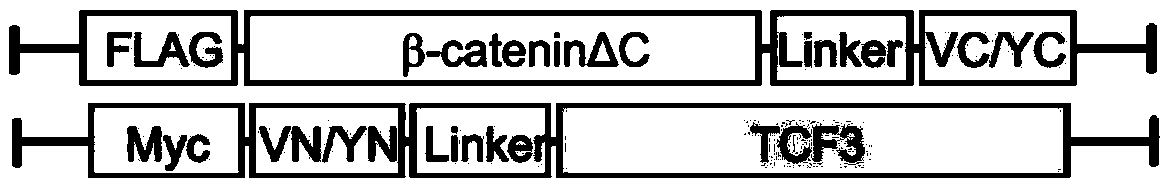
Vector composition for indicating active state of Wnt signal in cell by using BiFC (Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation) and application of vector composition
InactiveCN104004098ASimple methodEfficient formationBiological testingHybrid peptidesBeta-cateninActive state
The invention discloses a system for indicating the active state of a Wnt signal in a cell by using BiFC (Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation) and application of the vector composition. The invention provides a fusion protein group which consists of fusion protein A and fusion protein B, wherein the fusion protein A comprises a core effector beta-catenin fragment and a fluorescent protein fragment A located at a fragment C of the core effector beta-catenin fragment; the fusion protein B comprises a transcription factor (TCF) and a fluorescent protein fragment B located at a fragment N of the TCF. Proved by experiments, a complex formed by the core effector beta-catenin and the TCF in a Wnt signal channel is visualized by using a strategy on the basis of BiFC, so that the active state of Wnt in the cell is directly displayed; a BiFC system is used for instantaneously transfecting cells or constructing a stable expression cell line, so that specific signals formed in a cell nucleus can be observed and can specifically display and reflect the active state of the Wnt signal channel in a living cell and variation thereof.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Construction methods and applications of PVX (potato virus X) over-expression vectors and BiFC (bimolecular fluorescence complementation) vector
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering and provides construction methods and applications of two PVX (potato virus X) over-expression vectors and one BiFC (bimolecular fluorescence complementation) vector. A genome of a PVX 1985 isolate is cloned to a downstream 35S promoter through genetic recombination, obtained infectious clone can infect solanaceae crops such as tobacco, tomatoes, potatoes and the like through agrobacterium infiltration. Infectious clone is reconstructed, and the over-expression vectors capable of effectively expressing one or two types of heterologous protein in a host plant body as well as the BiFC vector capable of identifying interactions between protein are obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Protein interaction detection method with low false positive rate
ActiveCN103290091AReduce false positivesSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePlasmid VectorFluorescent protein
The invention provides a protein interaction detection method with low false positive rate, relates to a detection system and belongs to the field of a molecular biological technology. According to the method, two generally needed bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) detection systems based on single expression plasmid vectors are built in a dual expression plasmid vector system by a BiFC technology based on fluorescent protein, so the false positive rate of the BiFC detection method in research on protein-protein interaction can be reduced obviously, and quantitative analysis can be realized. The method also can be applied to screening research on unknown protein-protein interaction based on a gene library and detection on protein-protein interaction in living animals.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
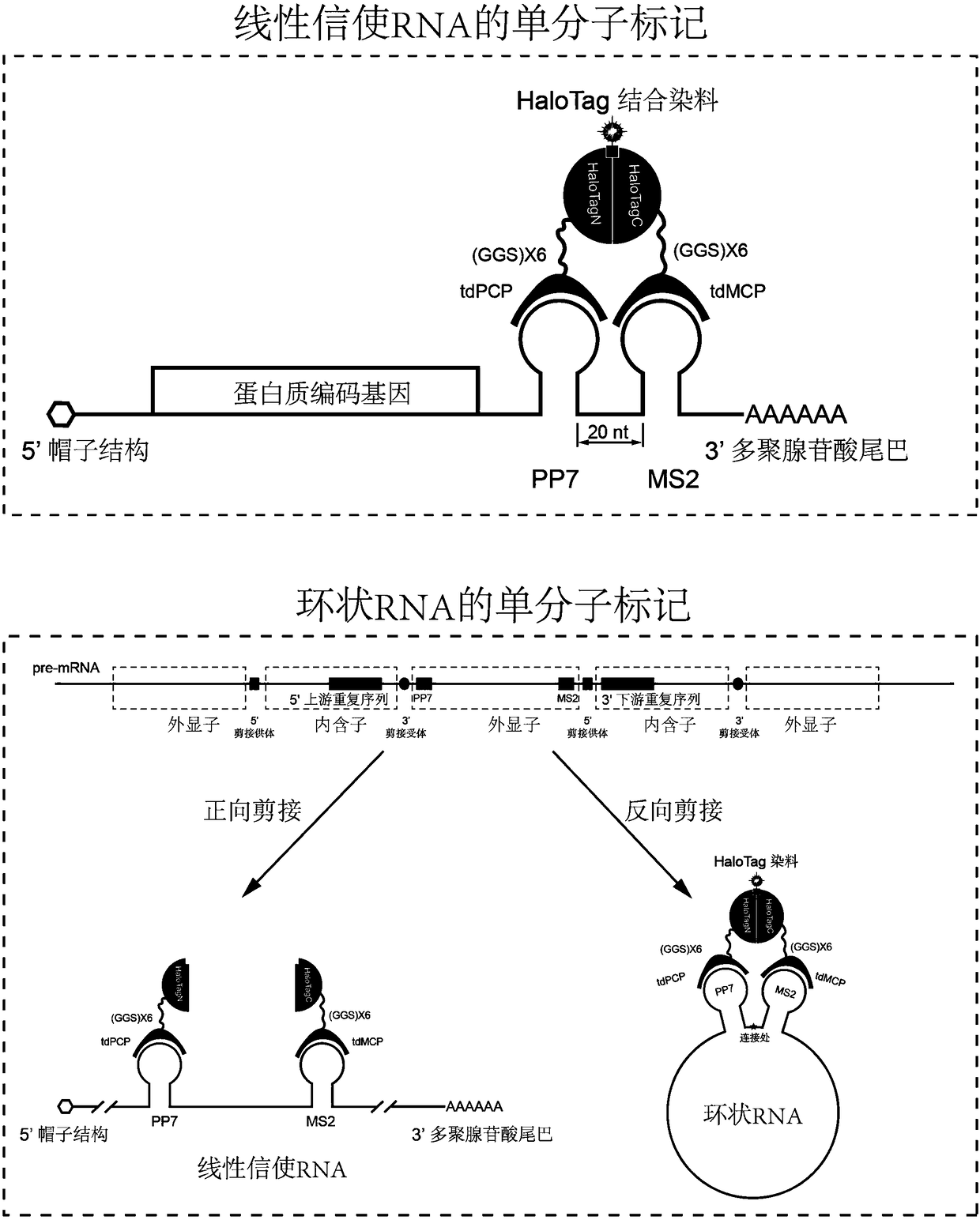
Novel labeling method for messenger RNA and circular RNA based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation
RNA molecules are an important member of an intracellular genetic information delivery system. Conventional RNA labeling methods cannot simultaneously have the characteristics of living cells, no invasion, high temporal and spatial resolution, single molecules, etc., so a novel method for labeling and tracking RNA need to be developed. The invention discloses a novel labeling method for messengerRNA and circular RNA based on self-ligation label bimolecular fluorescence complementation. A RNA aptamer subsystem is cooperatively used, aptamers are inserted at proper positions in the RNA, and twoparts of a self-ligation label are respectively fused with the binding proteins of the RNA aptamers. When the fusion proteins do not bind to RNA, RNA molecules do not fluoresce; when and only when the fusion proteins bind to RNA, the RNA molecules fluoresce, so the fluorescence background of an intracellular RNA marker is reduced. The novel RNA labeling method based on self-ligation label bimolecular fluorescence complementation can be used for long-term interference-free single-molecule imaging observation and tracking of messenger RNA and circular RNA of living cells and fixed cells, and has good application prospects in cell biology.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Manufacturing method and application of insect in-vitro protein interaction detecting system
InactiveCN104991072AEfficient transfectionSimple methodBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein insertionPolyhedral virus
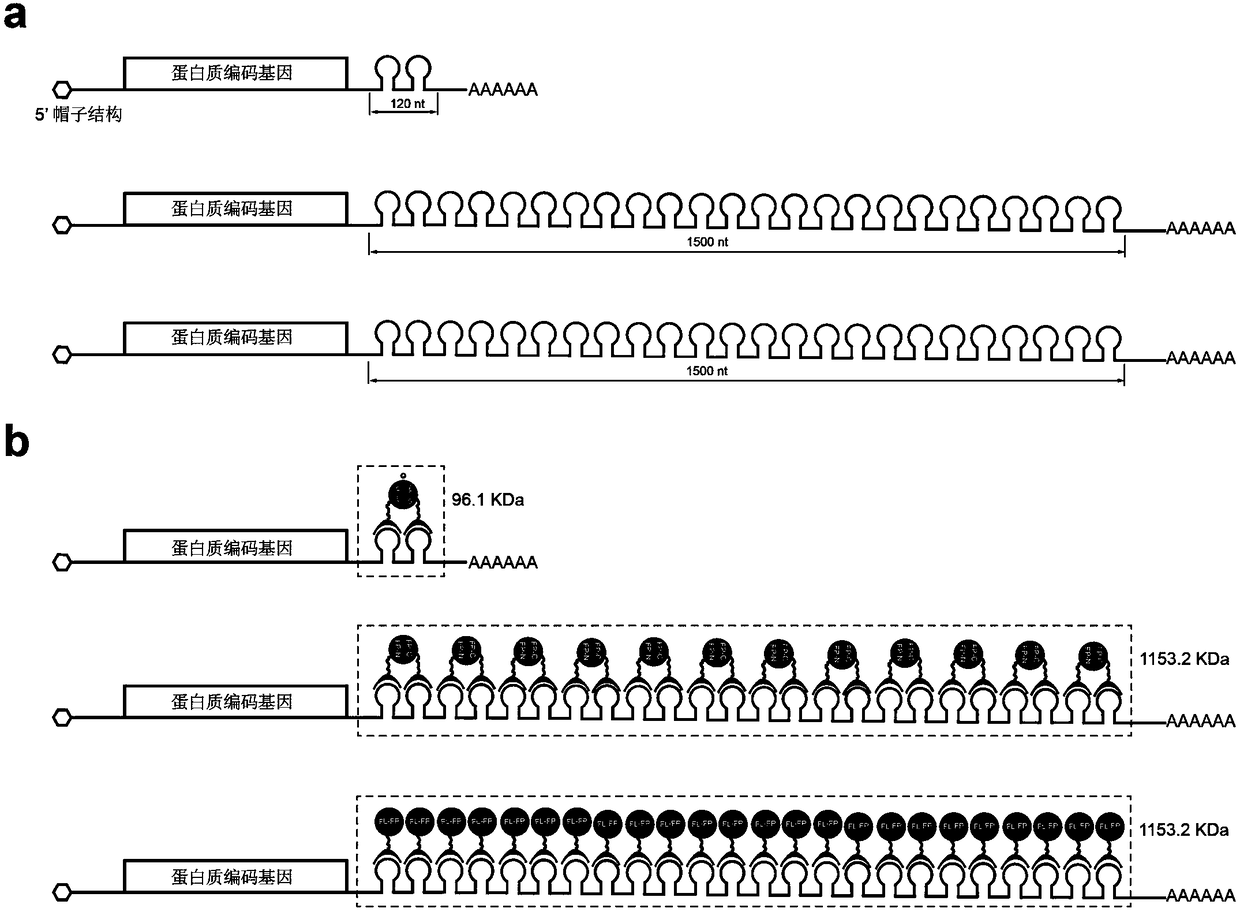
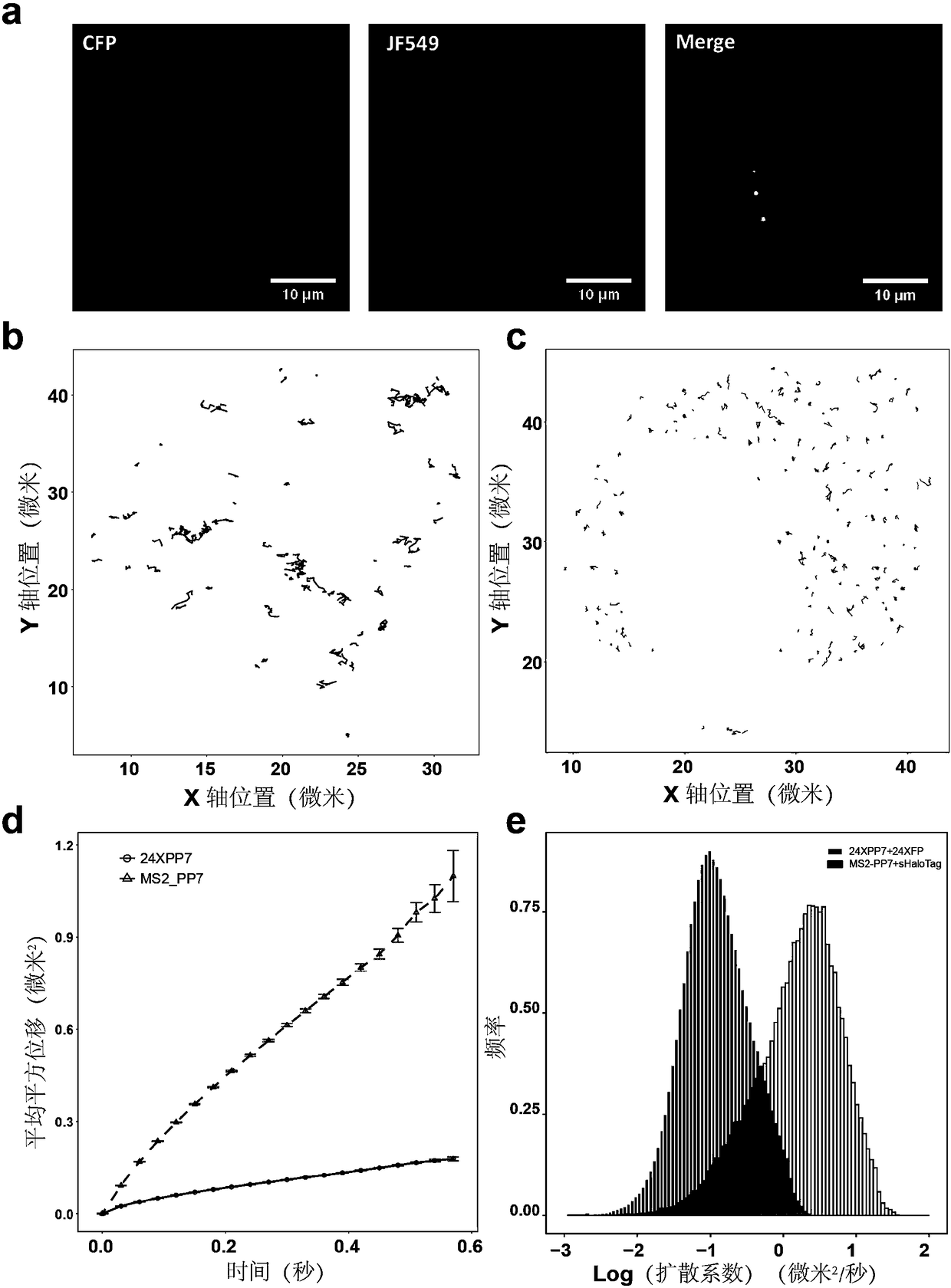
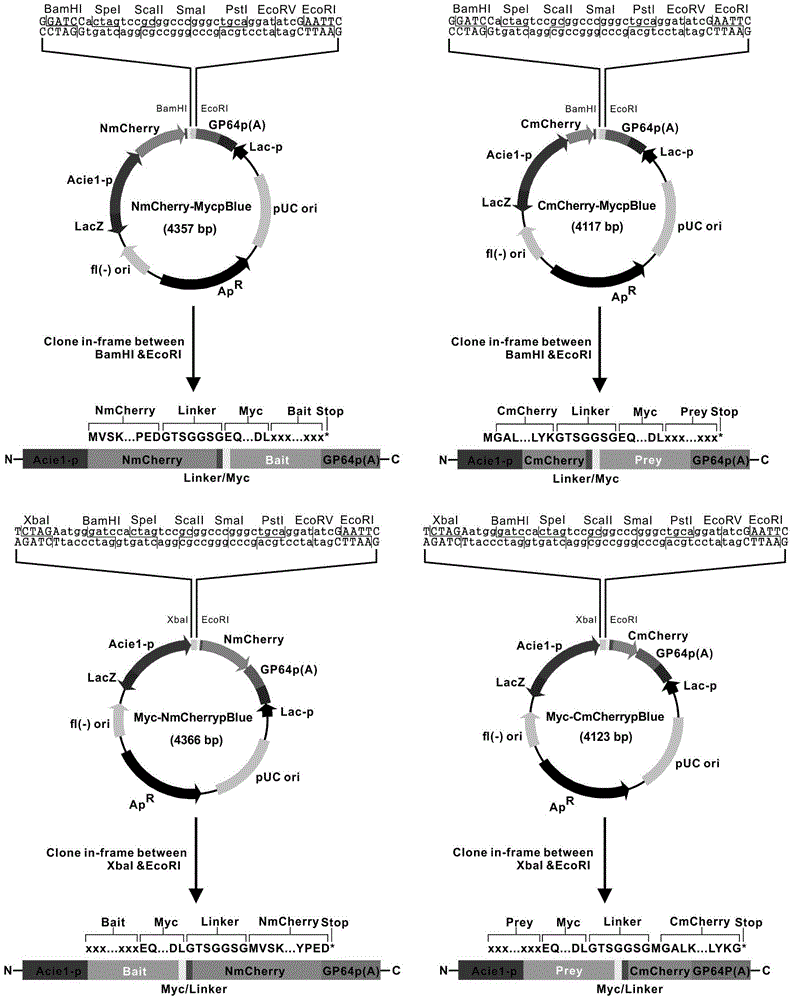
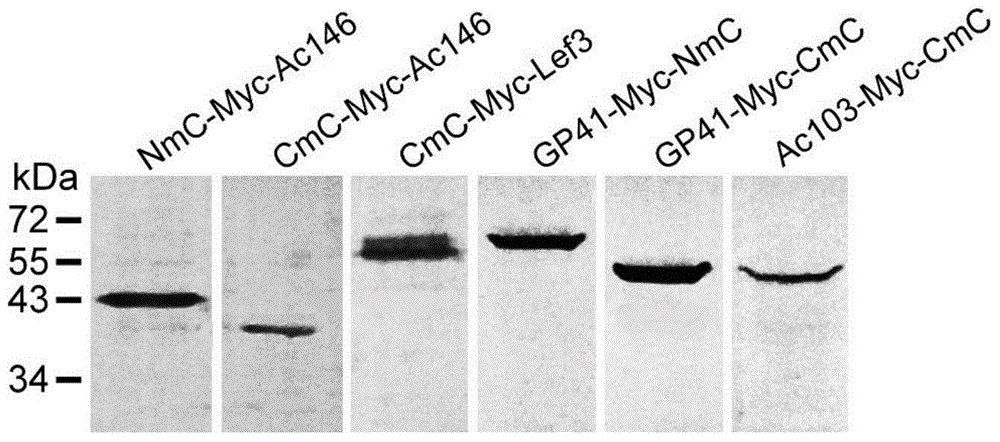
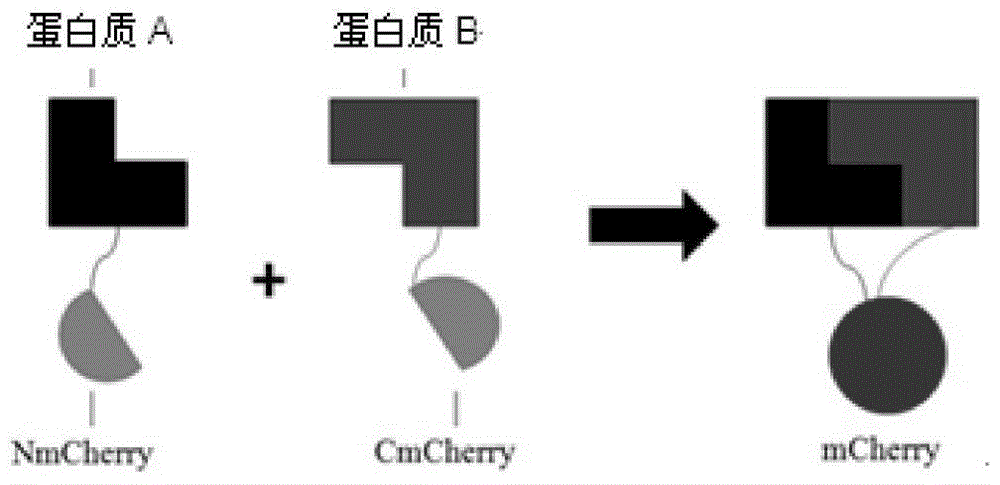
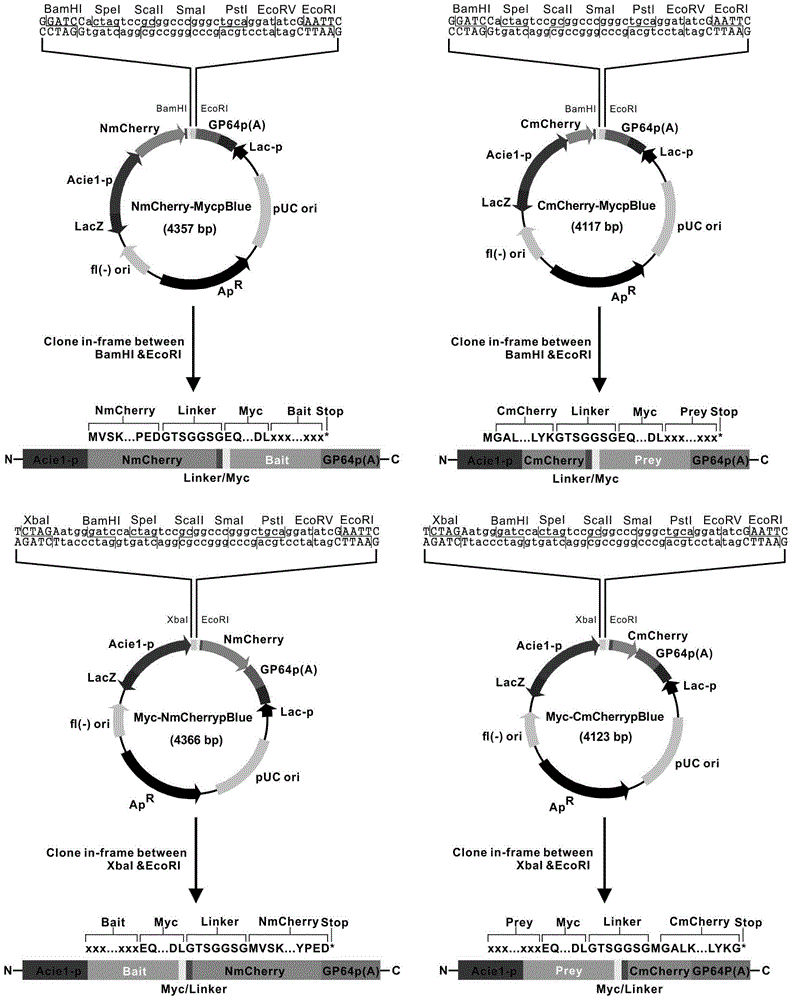
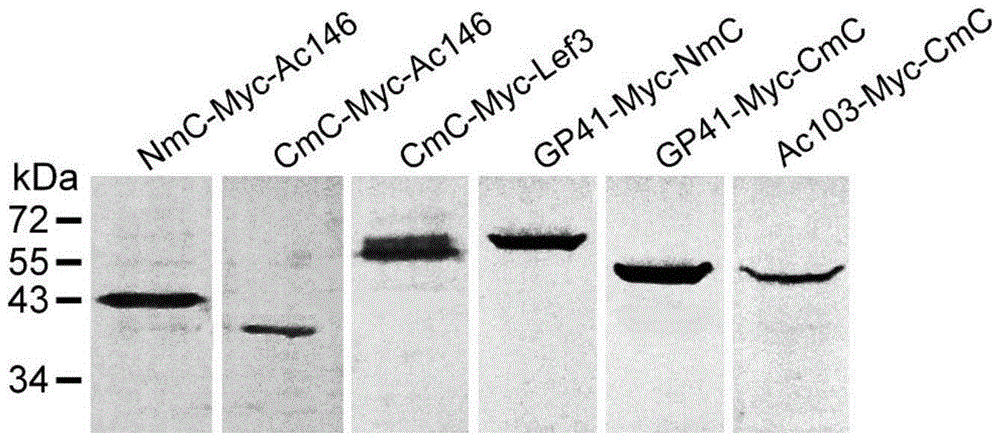
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and application of an insect in-vitro protein interaction detecting system. At the positions of amino acid residues at the 159th bit and the 160th bit, mCherry is divided into a segment NmC and a segment CmC through a PCR method, and then the segment NmC and the segment CmC are each fused with a connecting zone sequence, a c-Myc label and a poly(A) sequence to form four fused segments; the four fused segments are each connected with a pIE-MCS plasmid with an autographa californica multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus ie1 gene promoter and a gp64 gene poly(A) sequence to establish expression plasmids; the expression plasmids are combined to form an insect cell dimolecular fluorescent complementary detecting system. The method is simple and easy to implement, and the established dimolecular fluorescent complementary detecting system expands the application of an insect cell expression system and provides a convenient and effective technological means for insect proteomics and research on protein interaction between insects and pathogenic microorganisms of the insects.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for screening interacting protein based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation technique
ActiveCN107034228AIncrease credibilityIncreased sensitivityNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionYeastProtein target
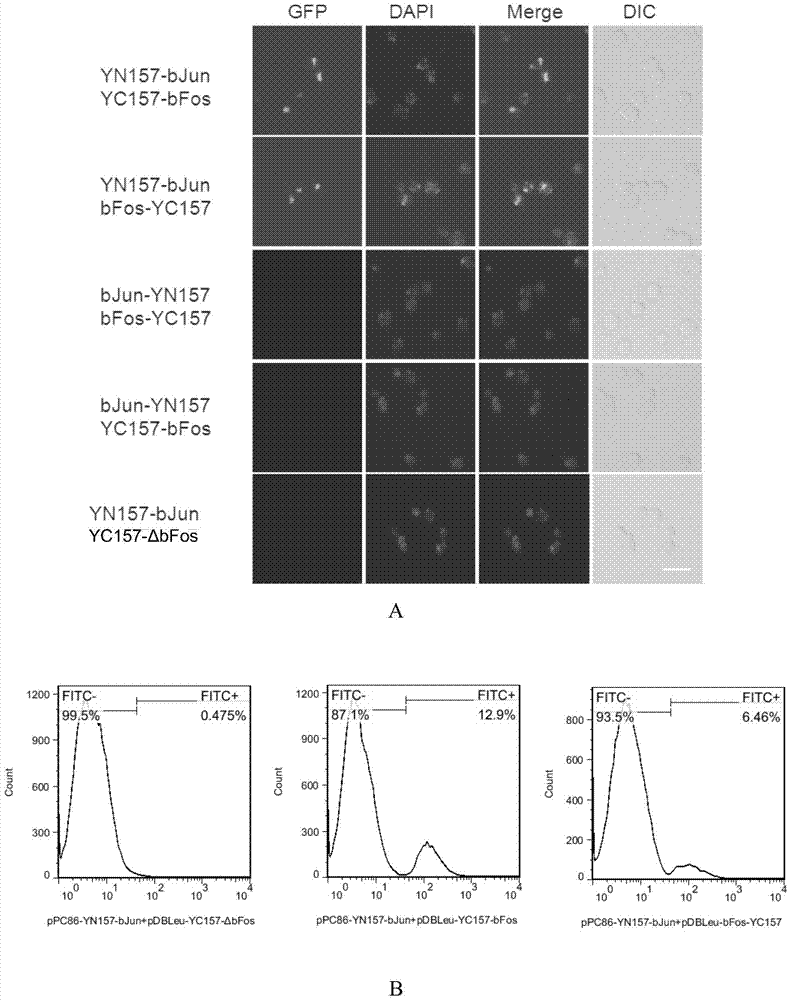
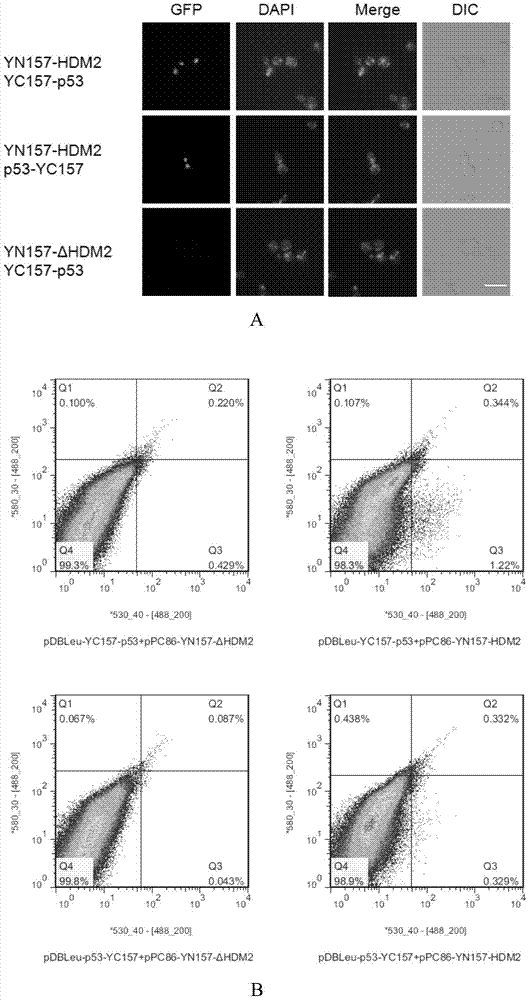
The invention discloses a method for screening interacting protein based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) technique. The method comprises the steps of 1, dividing YGFP into an N end (sequence 1, 1-157) and a C end (sequence 1, 158-238); connecting a coding gene of target protein A to the 3' terminal of an N-end coding gene through a connecting sequence (connecting peptide as shown in coding sequence 2), so as to form a fusion gene fragment A; connecting a coding gene of target protein B to the 5' terminal or 3' terminal of a C-end coding gene through the connecting sequence, so as to form a fusion gene fragment B; and 2, importing the fusion gene fragments A and B into receptor yeast cells, conducting culture to obtain transgenic yeast cells, and detecting whether the transgenic yeast cells generate green fluorescence, wherein an interaction or candidate interaction relation exists between the target protein A and the target protein B if yes, and no interaction or candidate interaction relation exists between the target protein A and the target protein B if not. The BiFC technique has high sensitivity and specificity, and is suitable for high-throughput protein-protein interaction screening in yeast.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Improved bimolecular fluorescence complementation carrier for researching protein interaction
InactiveCN102168102BImprove conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyProtein C
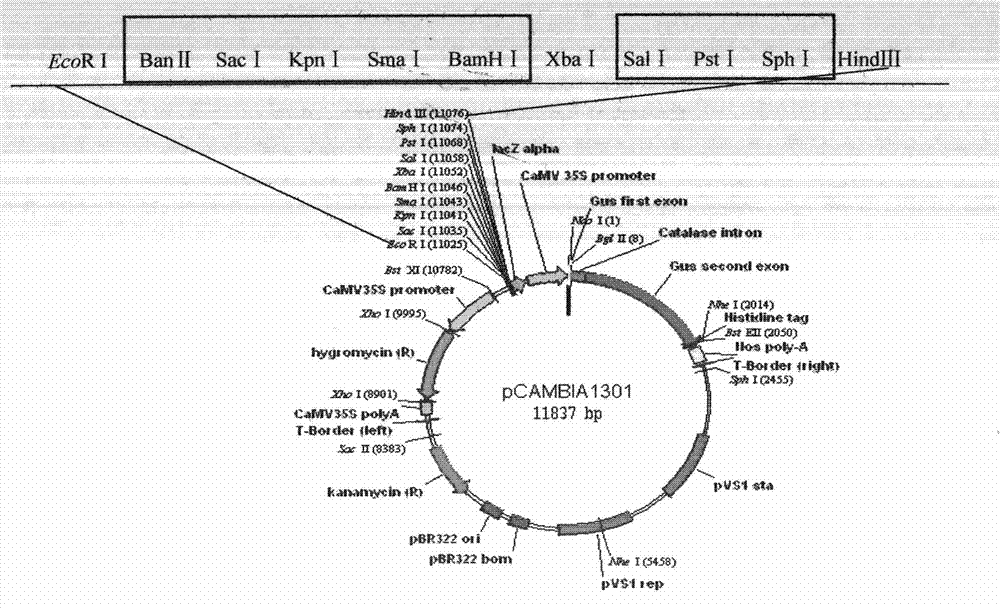
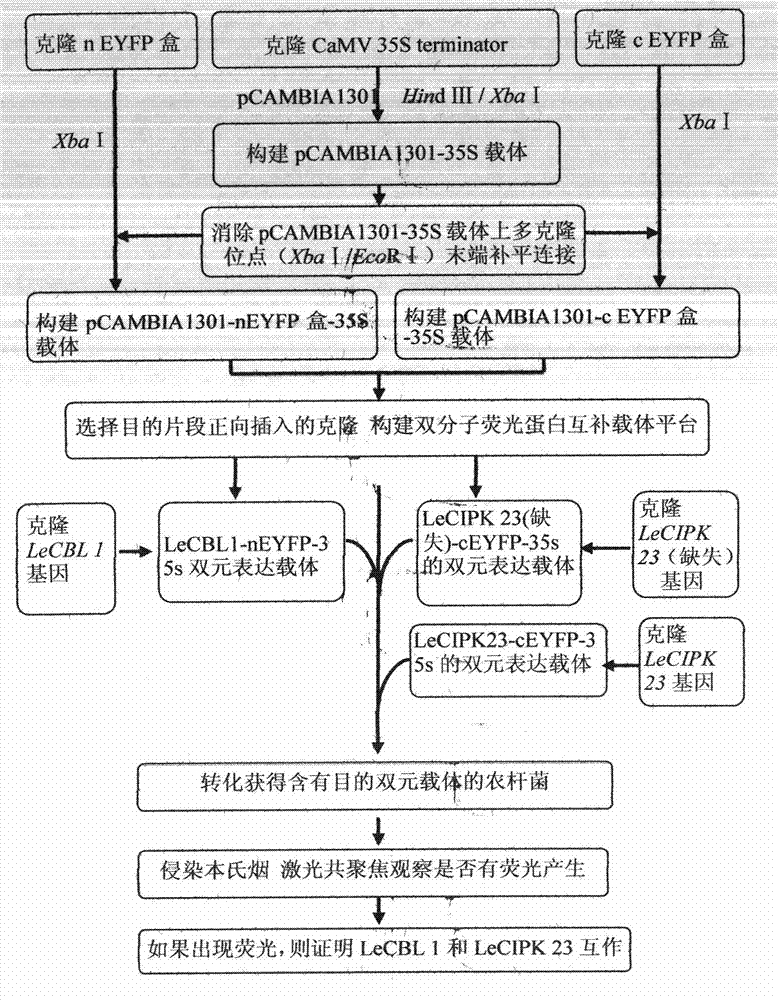
The invention provides an improved bimolecular fluorescence complementation carrier for researching the protein interaction. The carrier includes a CaMV 35S promoter and a CaMV 35S terminator, and a cEYFP box or a nEYEP box is included between the CaMV 35S promoter and the CaMV 35S terminator. The construction cost of the carrier is low, while the construction efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Imaging and tracking of interaction between proteins in living cells by utilizing bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology based on self-linkage label
InactiveCN108519484ARealize dynamic changesSolving Imaging ProblemsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage resolutionMolecular level
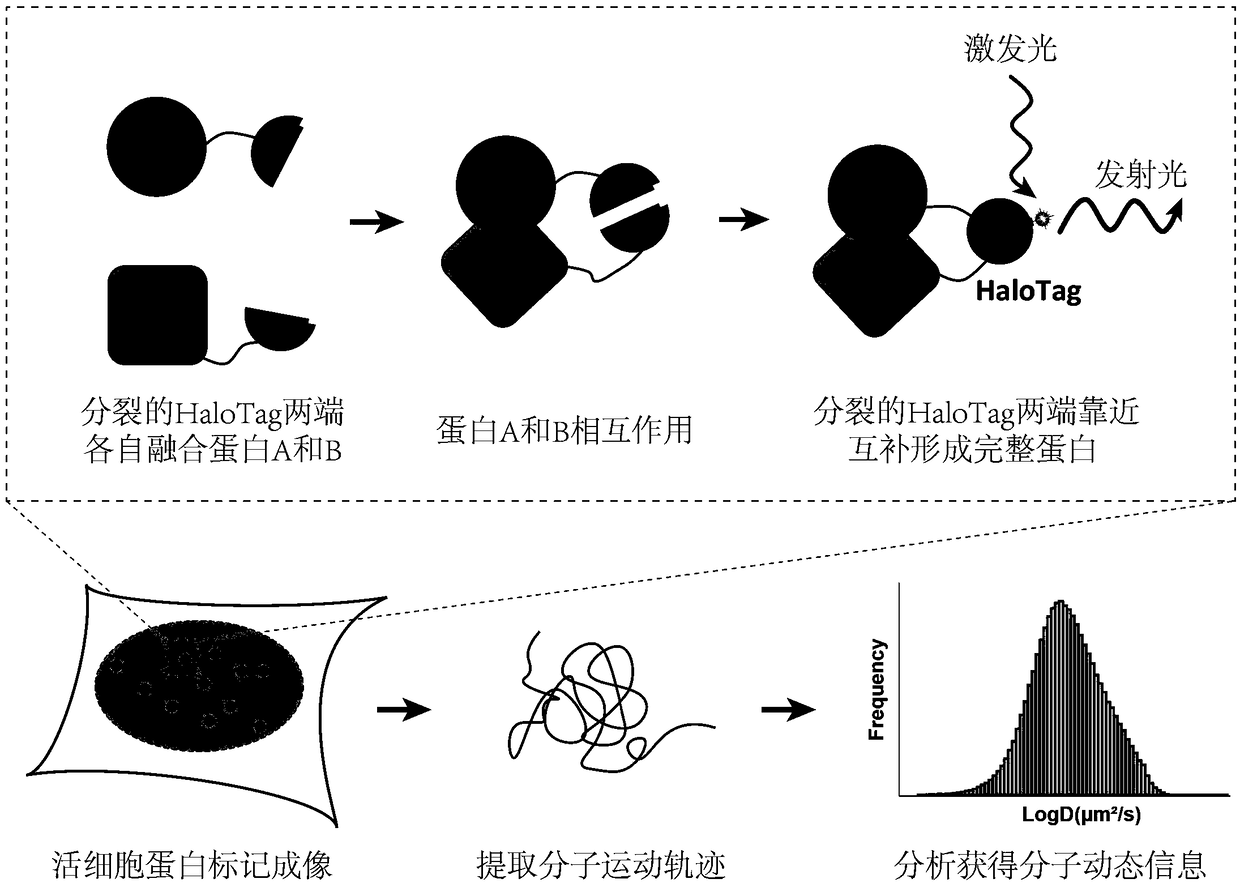
The invention discloses imaging and tracking of interaction between proteins in living cells by utilizing bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology based on a self-linkage label, and revealsan interaction relation between the proteins and explores that a dynamic behavior of an interaction compound is already become a hot spot for proteomics research. The interaction between proteins forms a basis of cellular activity. An existing method for researching the interaction of the proteins do not simultaneously have the characteristics of living cells, high temporal-spatial resolution, single molecules and the like, and therefore, a new method for making and tracking the interaction between the proteins needs to be developed. The invention discloses a method for novel marking the interaction compound of the proteins by adopting the bimolecular fluorescence complementation based on the self-linkage label. The self-linkage label is split into two parts at the proper site, and two proteins having the interaction effect are fused respectively, and due to the interaction of the two proteins, the split self-linkage labels are pulled spatially and closely so as to form a complete self-linkage label; by adding dyes, the interaction compound can give out fluorescent light. The novel marking method utilizing the bimolecular fluorescence complementation based on the self-linkage label is widely applied to cell biology, and single molecular horizontal detection and tracking on the interaction of the pair of proteins in the cells in a high temporal-spatial resolution manner can berealized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Expression vector for bimolecular fluorescence complementation) research and application thereof
ActiveCN105177041AIncrease flexibilityBiological testingVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetGolden gate
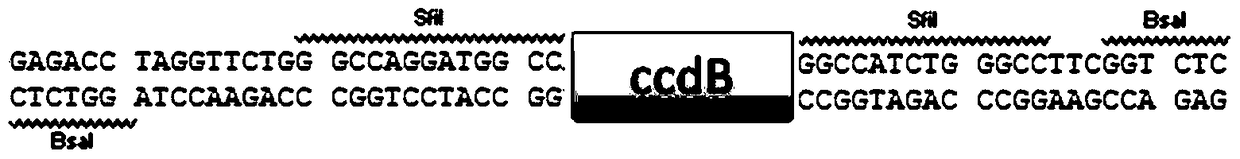
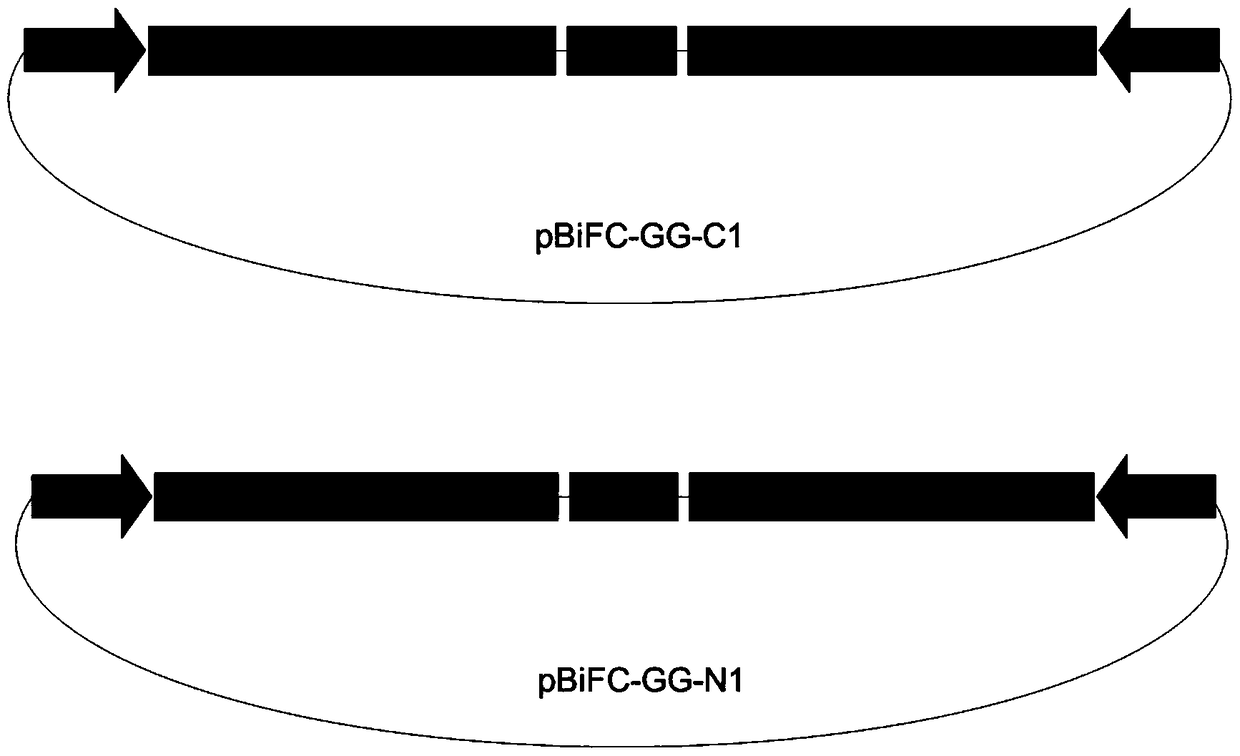
The invention provides a novel expression vector for bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) research. Expression cassettes of 2 segments of a fluorescent protein are integrated onto the vector; and gene sequences of 2 target proteins can be simultaneously cloned to the vector by one-step reaction (Golden Gate cloning or closed-loop Gibson splicing process) and respectively form fusion expression with the 2 segments of the fluorescent protein. Therefore, when the vector is used for BiFC research, only one vector is needed and introduced into cells, thereby greatly facilitating the operation of the plant BiFC experiment. The vector is compatible with the two novel cloning methods of Golden Gate cloning or closed-loop Gibson splicing. The vector is a high-copy plant expression vector containing T-DNA sequence, and can be simultaneously used for instantaneous and stable expression of plants.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Improved bimolecular fluorescence complementation carrier for researching protein interaction
InactiveCN102168102AImprove conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyBimolecular fluorescence complementation
The invention provides an improved bimolecular fluorescence complementation carrier for researching the protein interaction. The carrier includes a CaMV 35S promoter and a CaMV 35S terminator, and a cEYFP box or a nEYEP box is included between the CaMV 35S promoter and the CaMV 35S terminator. The construction cost of the carrier is low, while the construction efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
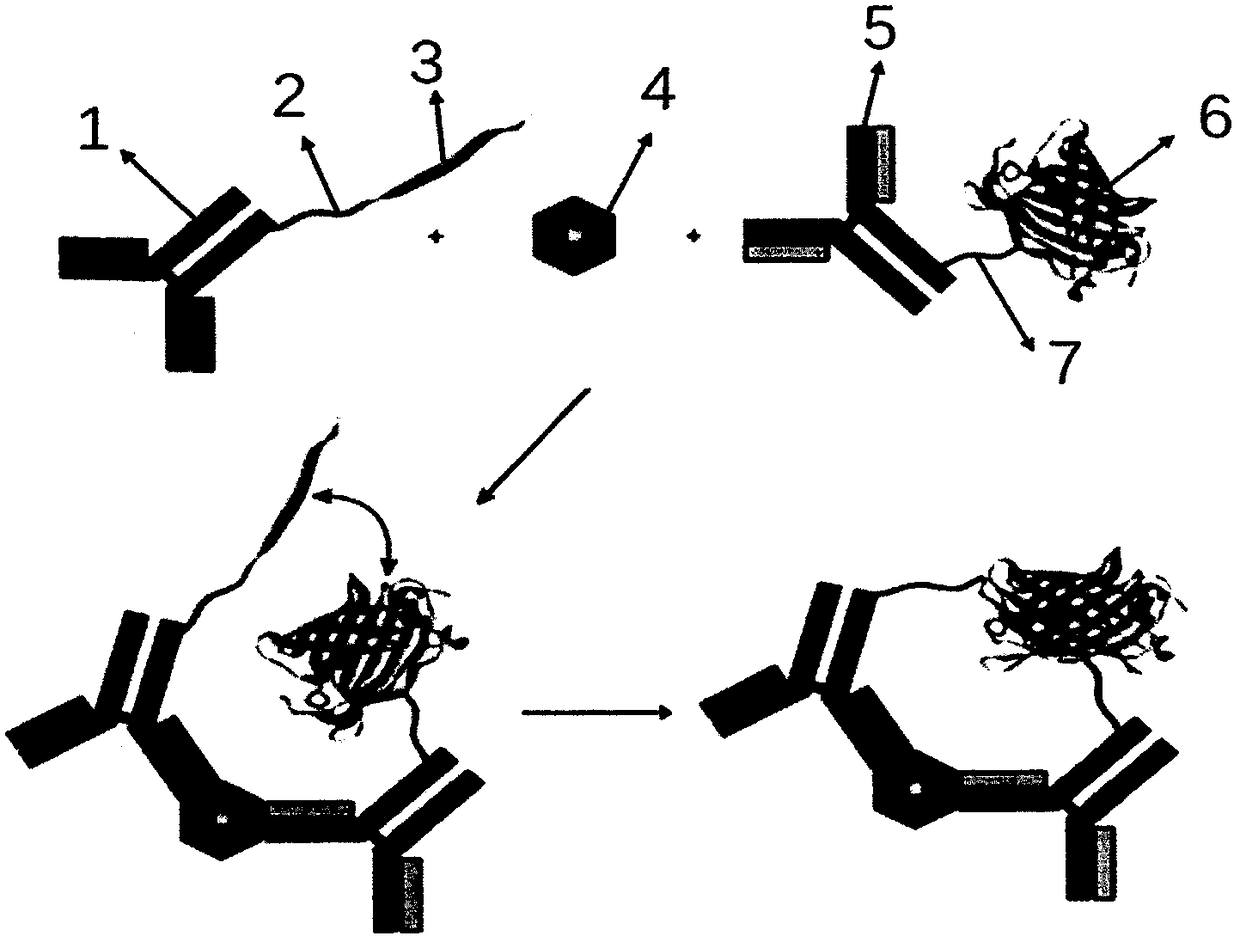
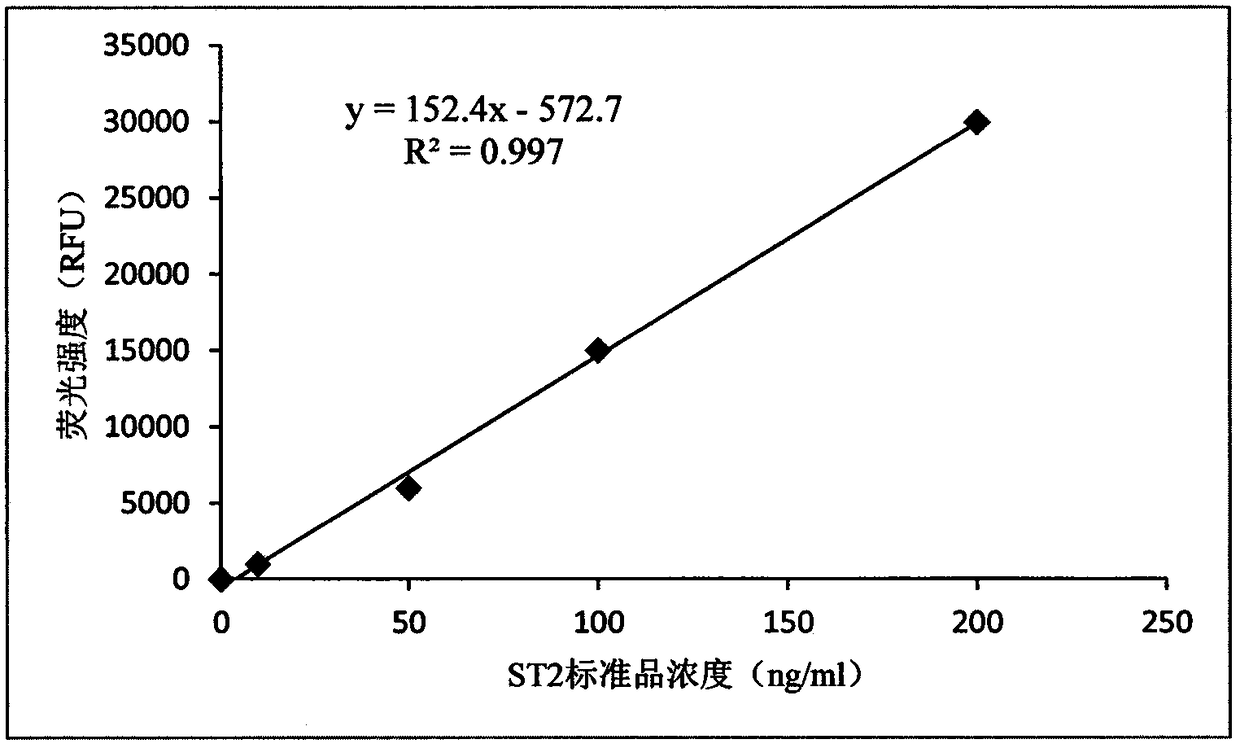
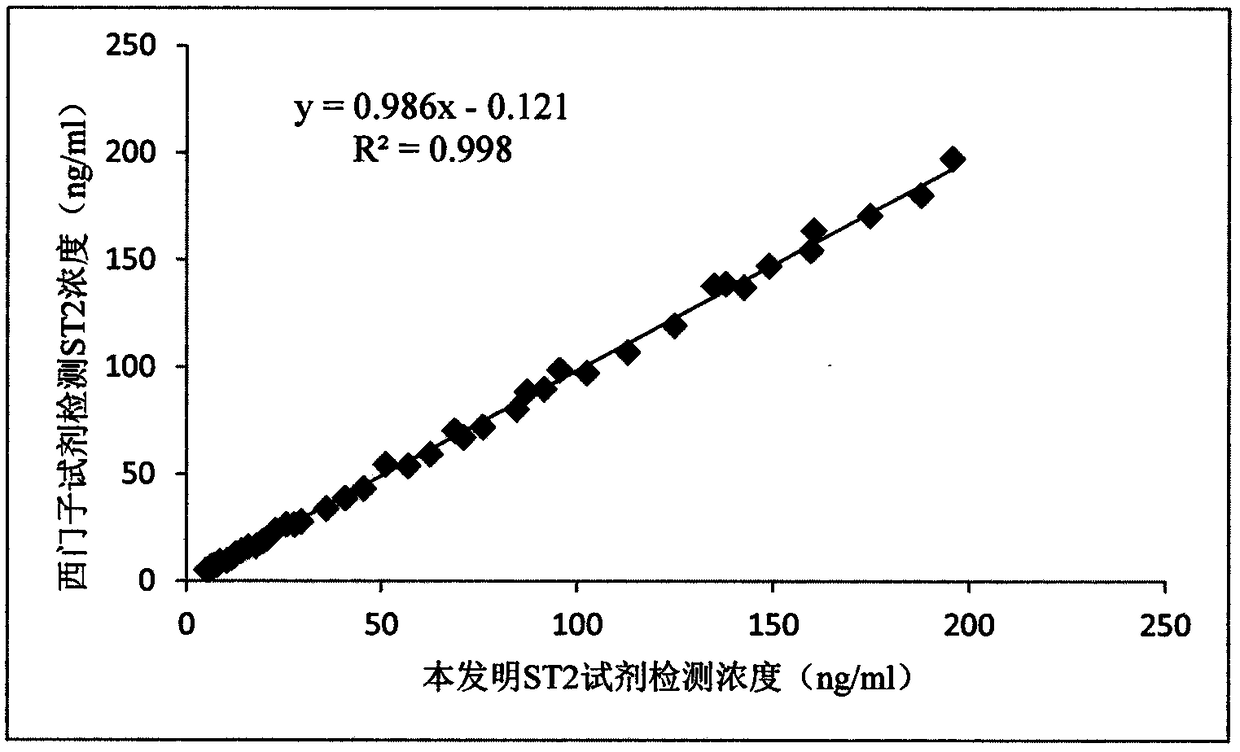
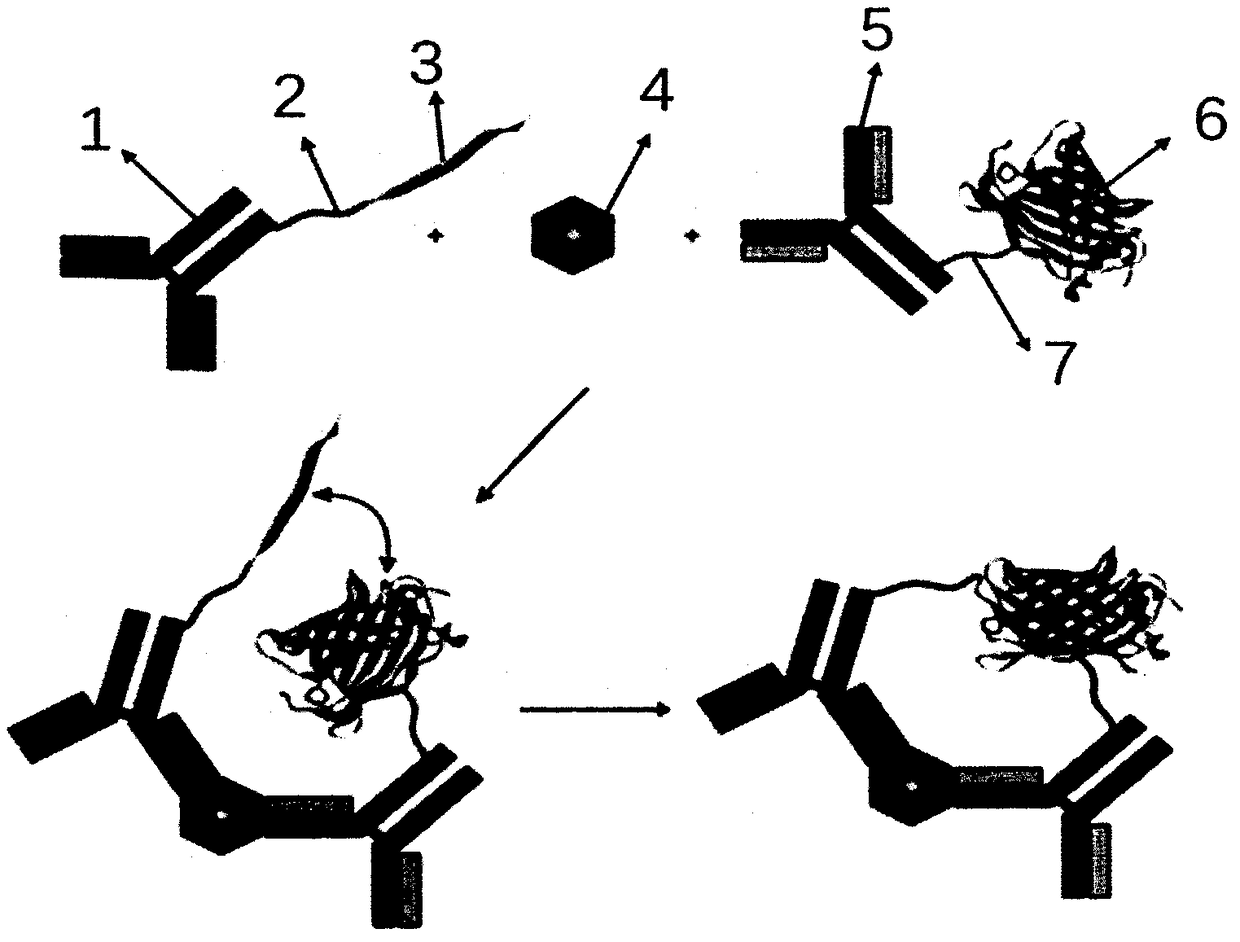
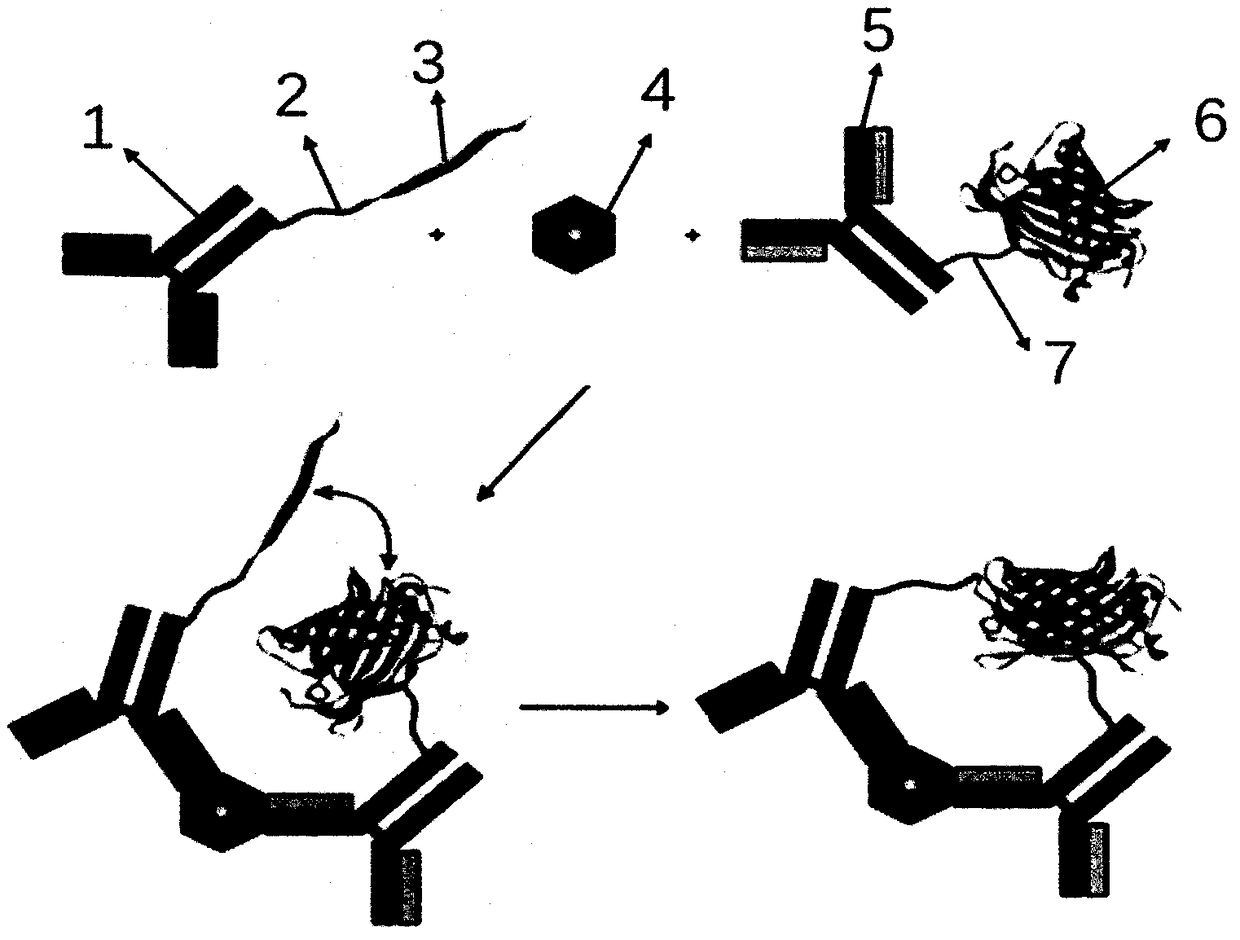
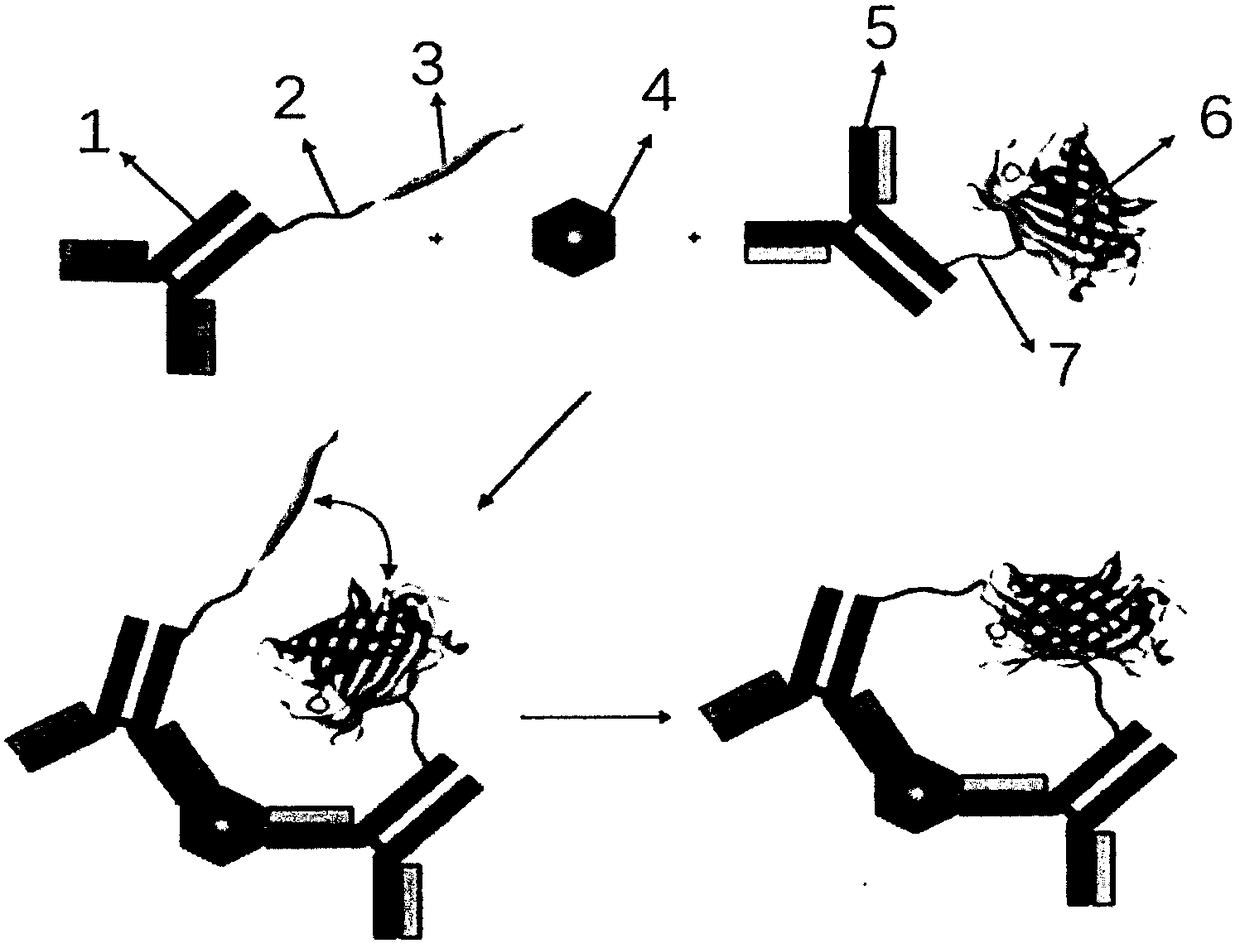
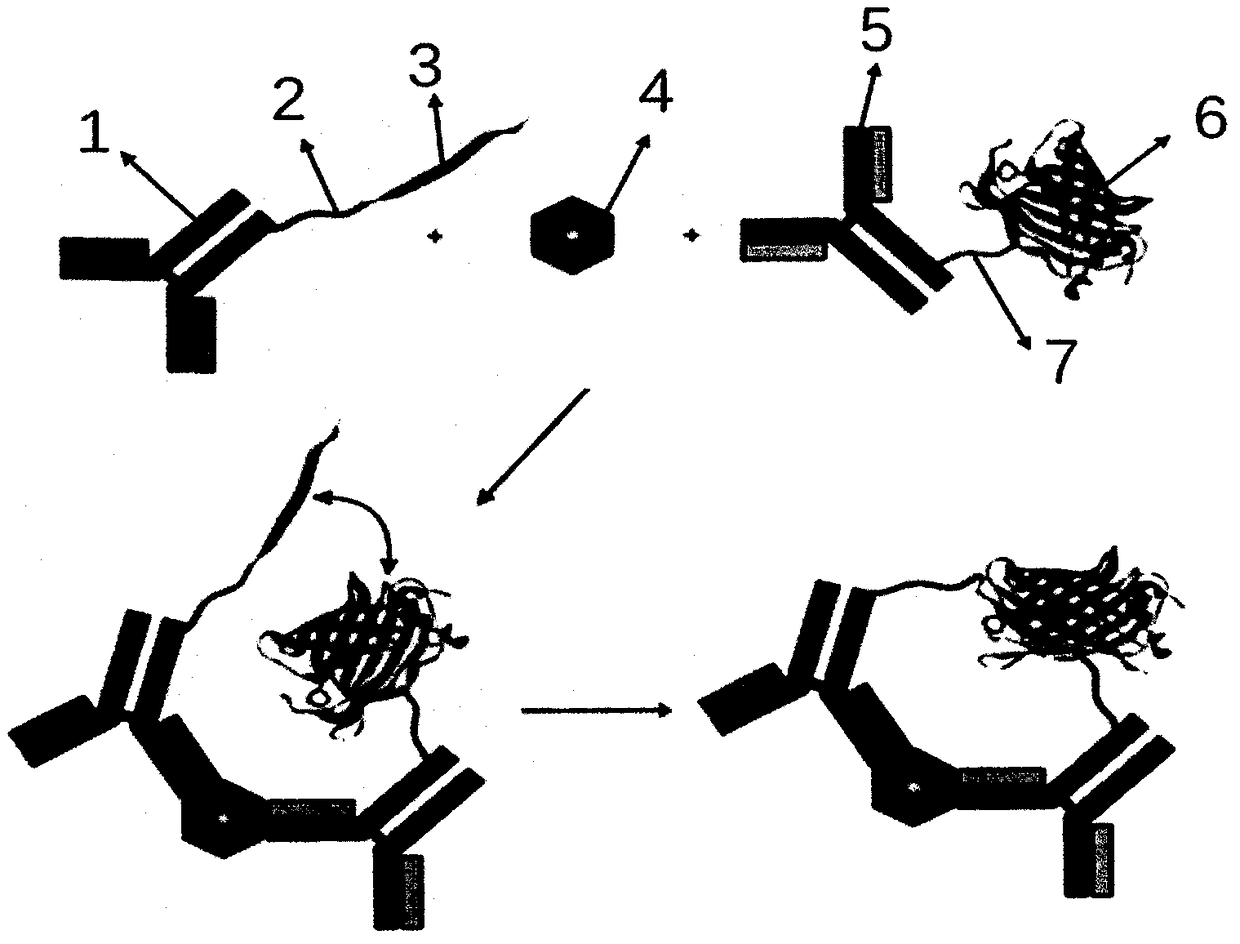
ST2 detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology and preparation and use method thereof
InactiveCN108267594ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological material analysisBiological testingCoronary artery diseaseBiology
The invention provides an ST2 detection kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology and a preparation and use method thereof. The kit includes a fluorescent protein N-end segment resistant to ST2 antibody coupling and a fluorescent protein C-end segment resistant to ST2 antibody coupling. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the ST2 diagnosis kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology. The preparation method includes preparation of the fluorescent protein N-end segment resistant to ST2 antibody coupling and preparation of the fluorescent protein C-end segment resistant to ST2 antibody coupling. Finally, the invention also discloses the use method of the kit. The kit has the advantages of being easy to operate, wide in linear range, excellent in specificity, free of cleaning, high in accuracy and the like and can provide convenience for clinical detection and usage; the kit is used for predicting unfavorable prognosis cardiovascular events happening to patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and monitoring the capacity of evaluating the coronary artery disease degree; by means of the kit, the clinical evaluation and risk stratification accuracy of clinicians on AMI patients or AMI high-risk groups are improved, and therefore the kit has a considerable market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
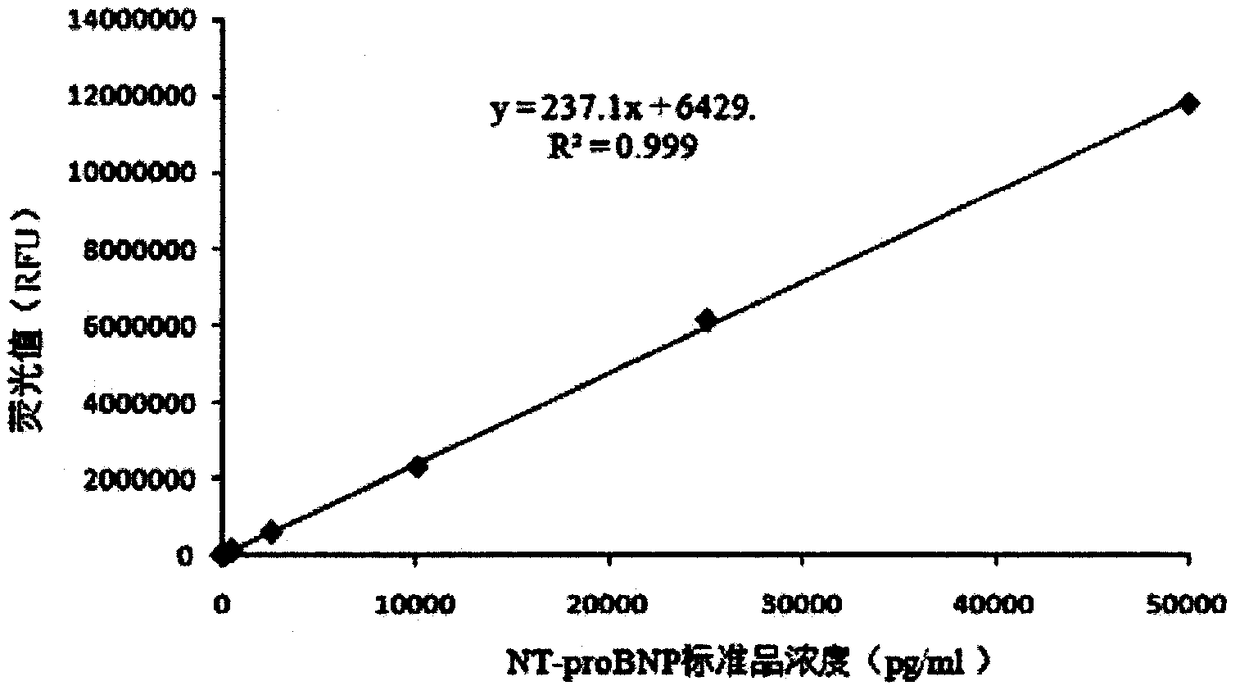
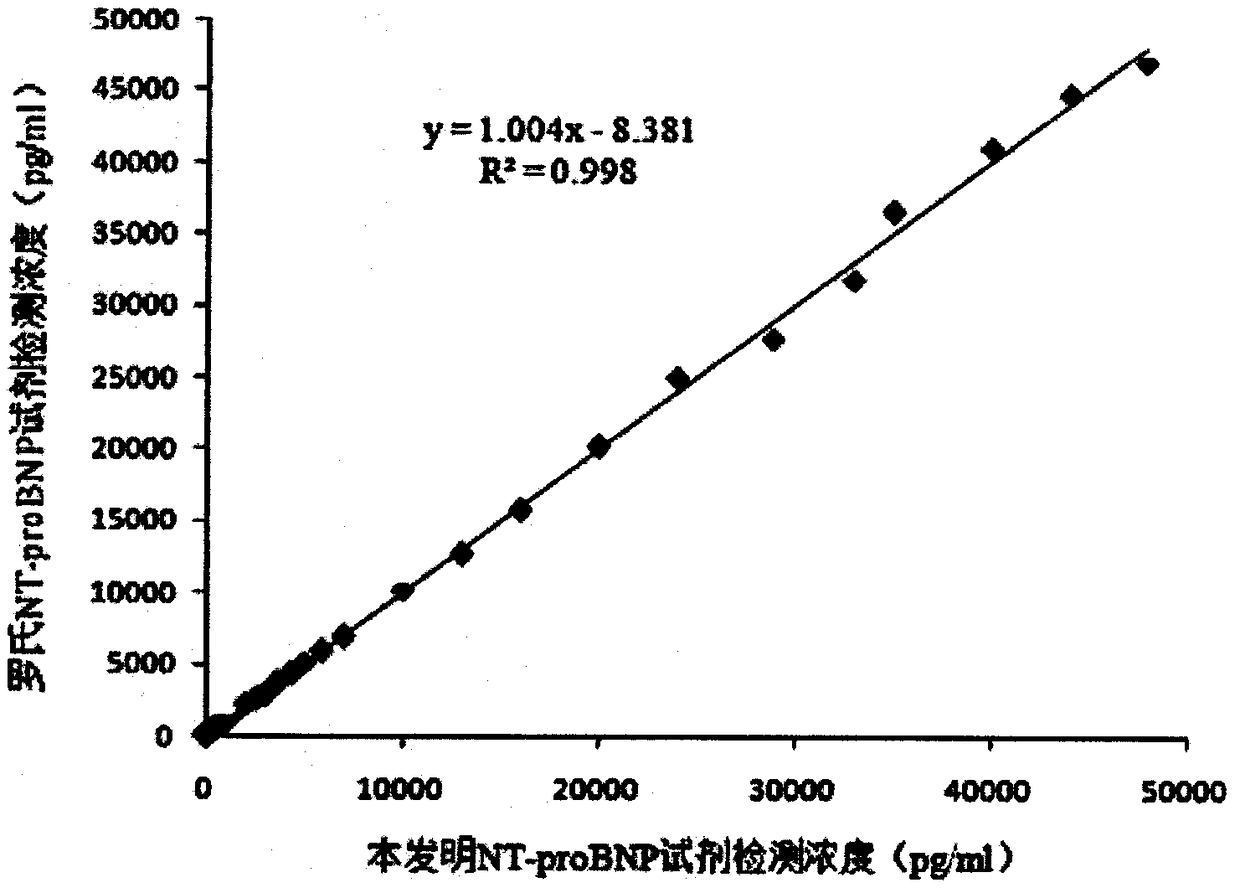
NT-proBNP detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology as well as preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108226529ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceBioinformaticsAntibody
The invention provides an NT-proBNP diagnostic kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-NT-proBNP antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment andan anti-NT-proBNP antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the NT-proBNP diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The method comprises the steps of preparing the anti-NT-proBNP antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and preparing the anti-NT-proBNP antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminalfragment. Finally, the invention further discloses a use method of the kit. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of good specificity, convenience in operation, rapidness in detection,wide linear range, free from cleaning, high accuracy and the like, is convenient in clinical detection use and can be used for improving the accuracy of heart failure diagnosis when the kit is appliedto heart failure monitoring, thereby having a great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
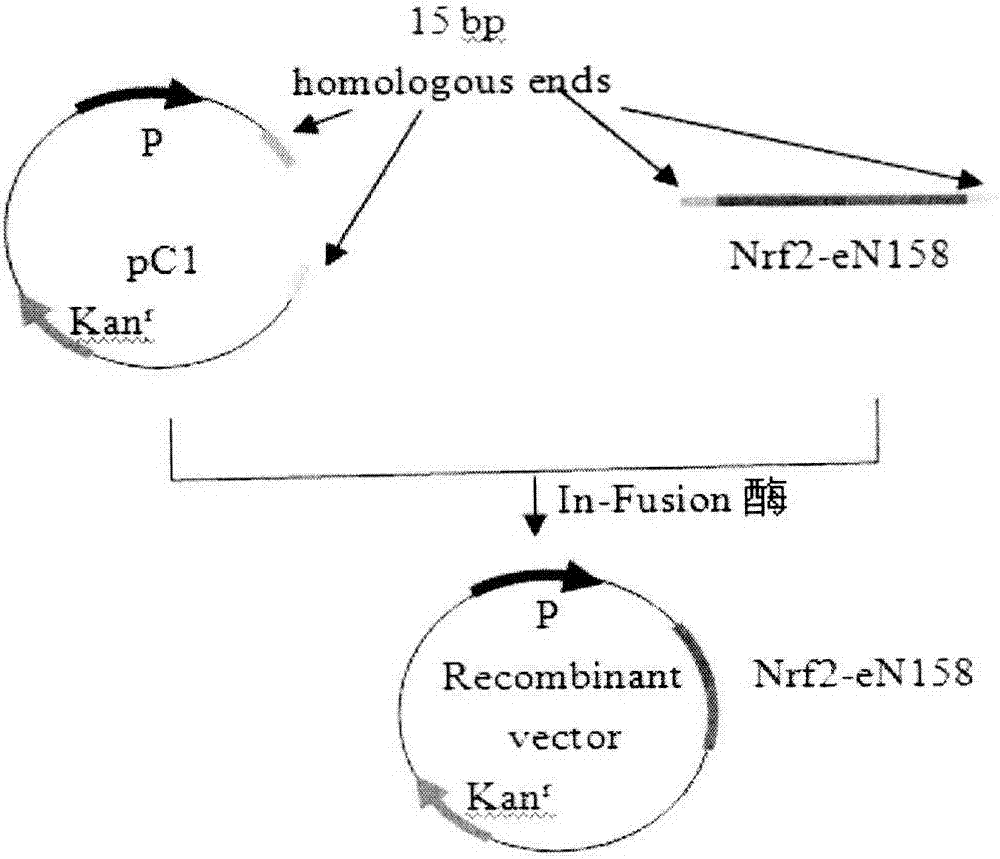
BiFC (Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation) intracellular detection method and system for indicating NrF2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor)-Keap1 (Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1) interaction
InactiveCN107236813AVisualize InteractionsSpecific formationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionWilms' tumorKEAP1 Protein
The invention discloses a BiFC (Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation) intracellular detection method and system for indicating NrF2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor)-Keap1 (Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1) interaction. A recombinational expression vector constructed by Nrf2 protein which is fused with eGFP N-end 158-locus amino acid and a Keap1 protein coding gene which is fused with eGFP C-end 159-locus amino acid is provided; meanwhile after cells are transfected, a complete fluorescent protein is reconstructed through fused N-end and C-end of fluorescent protein eGFP under the expressed NrF2-Keap1 interaction. By adopting the BIFC system, cells are transfected instantly or constructed into a stable expression cell line, a specific signal generated in a cell nucleus can be observed, the signal can be displayed specifically and reflect the activity state and change of a Nrf2-Keap1 signal path in a living cell, and a foundation is laid for screening of small molecule compounds capable of influencing Nrf2-Keap1 interaction and antitumor medicaments by detecting BiFC fluorescence change.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
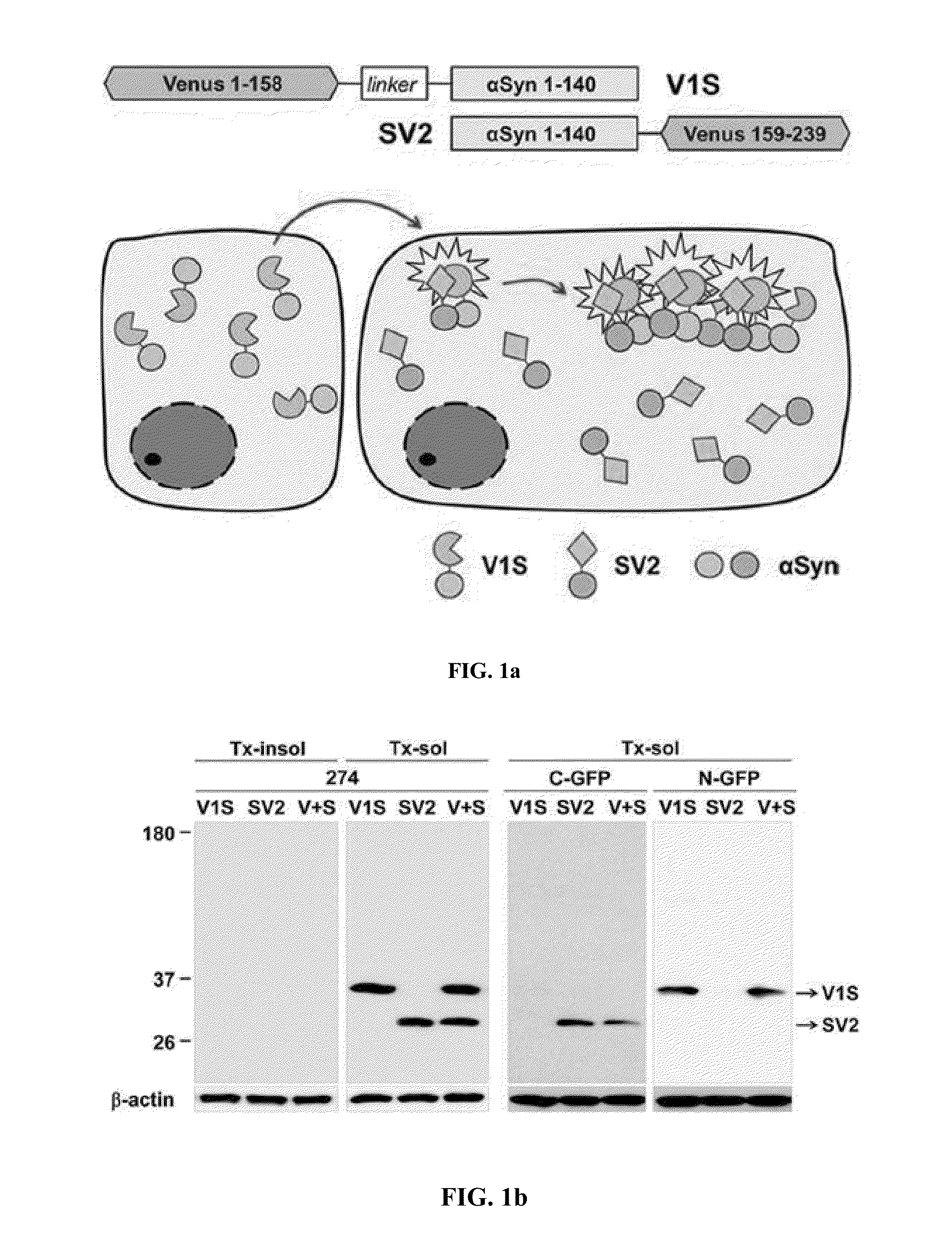
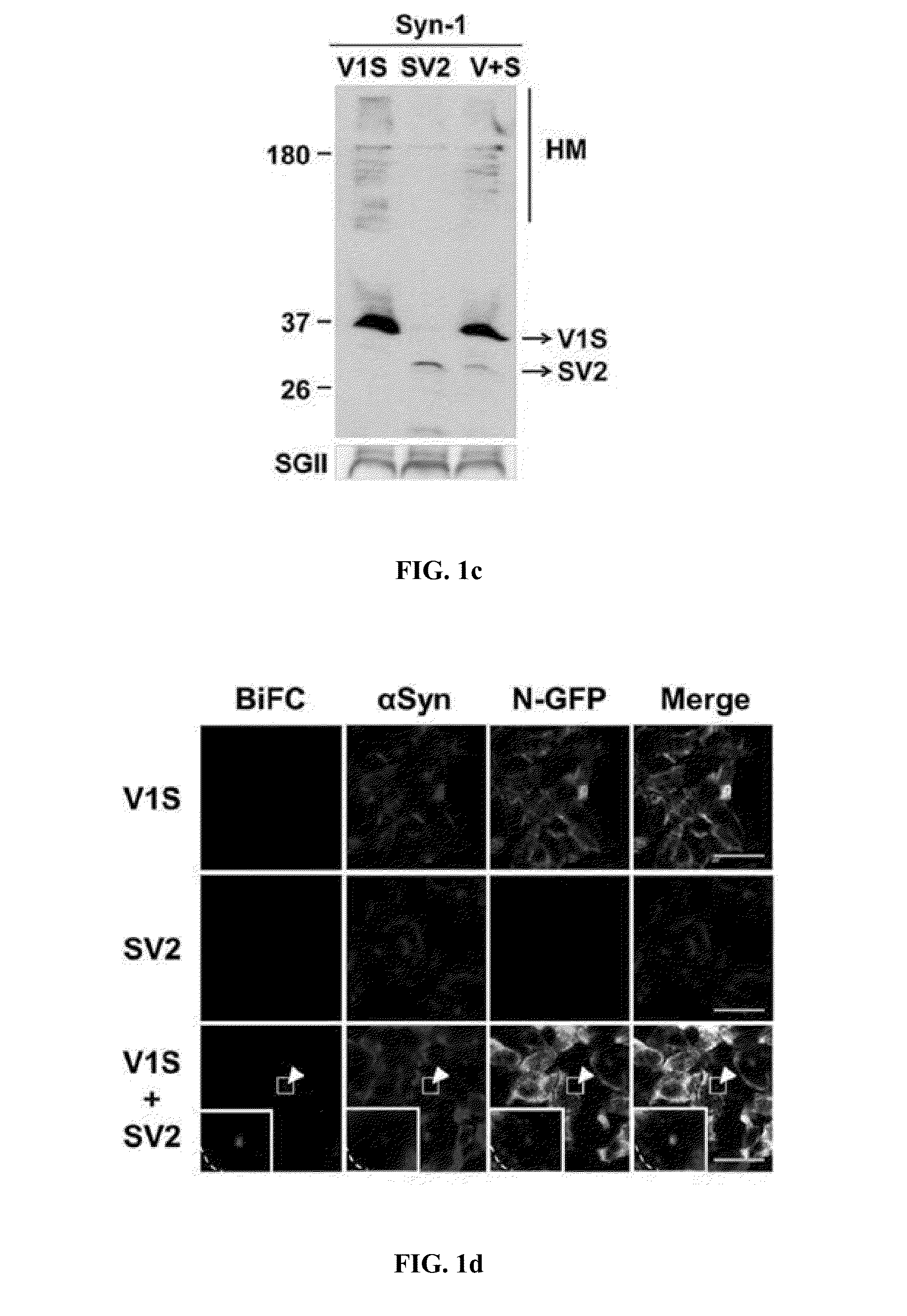
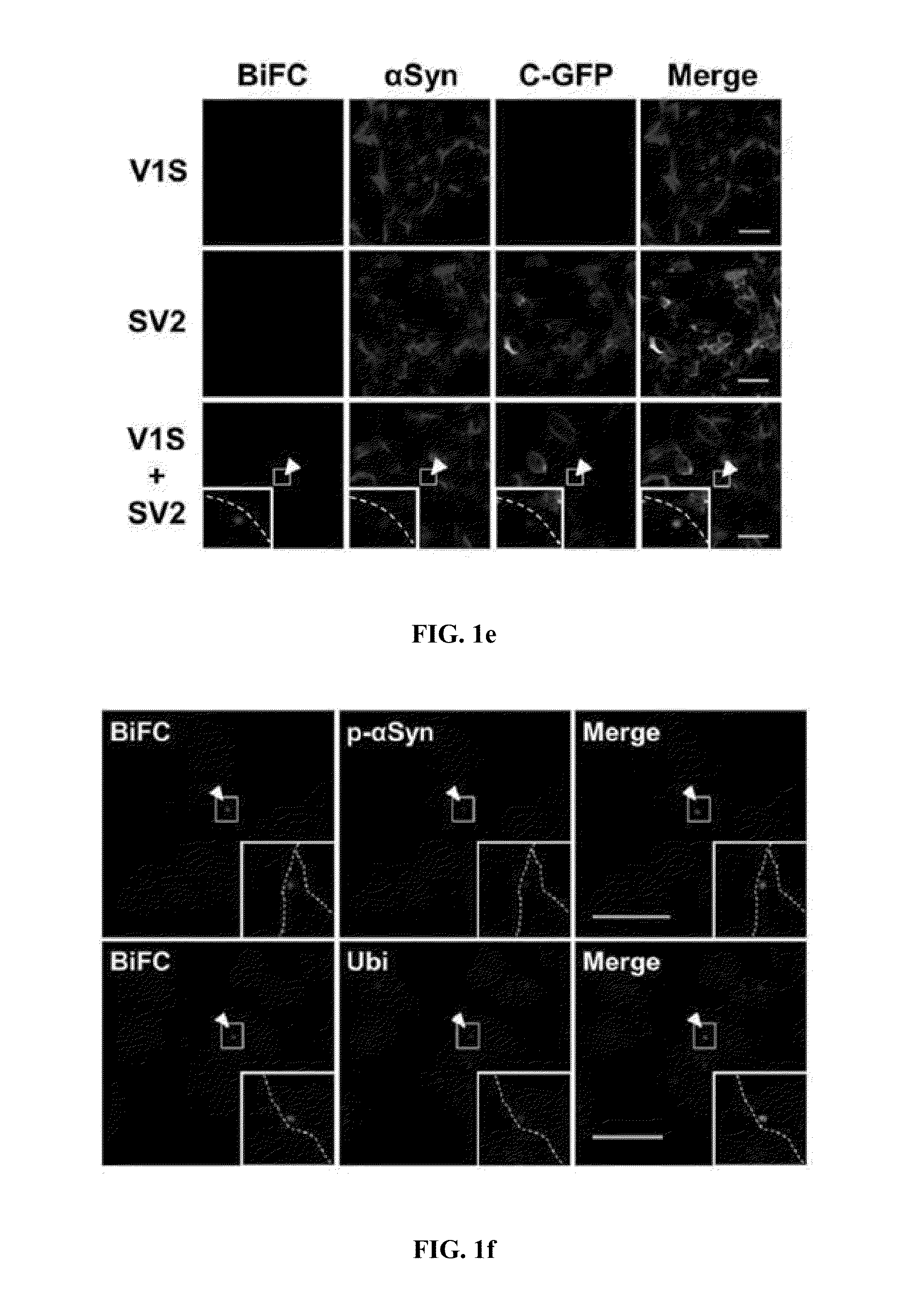
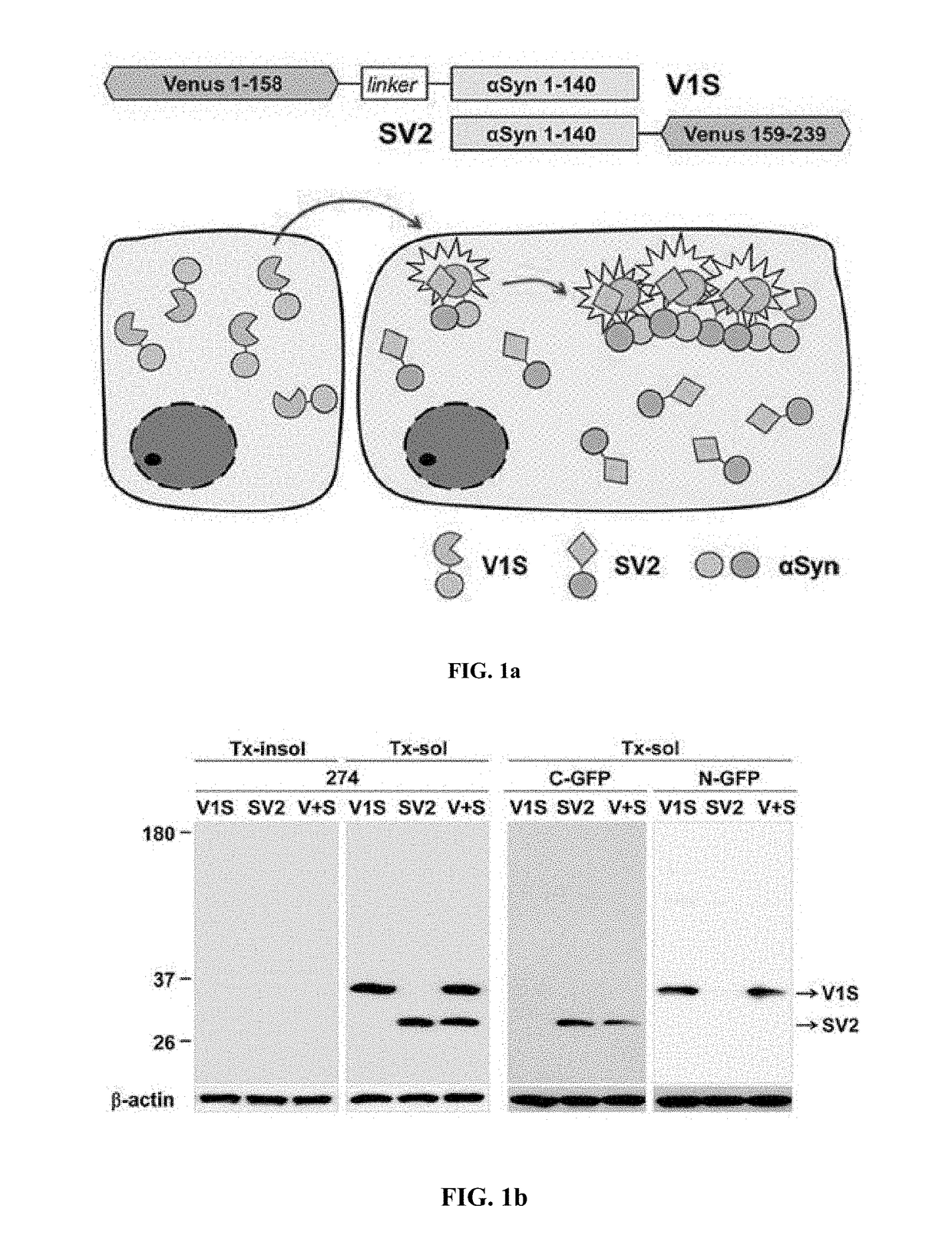
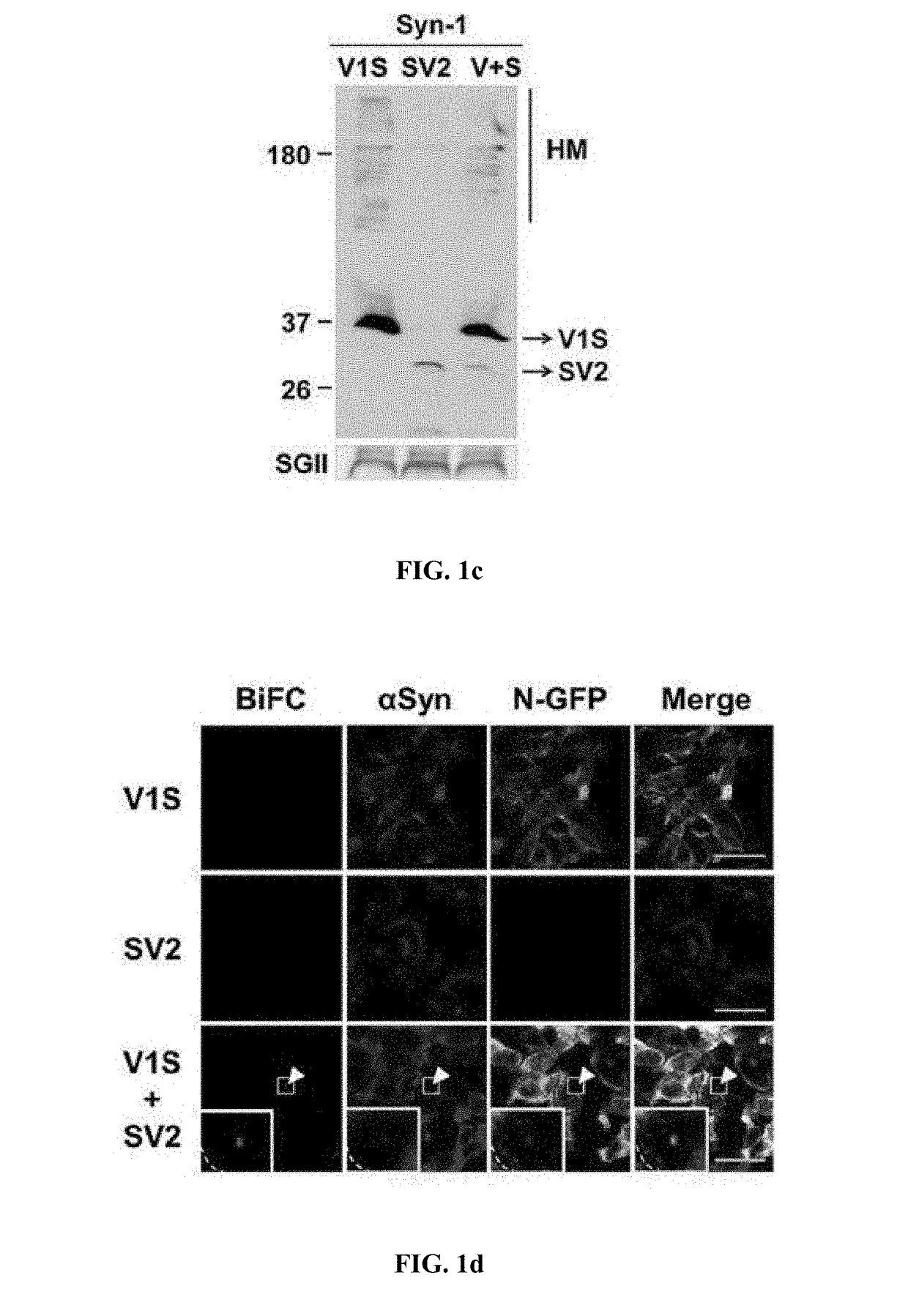
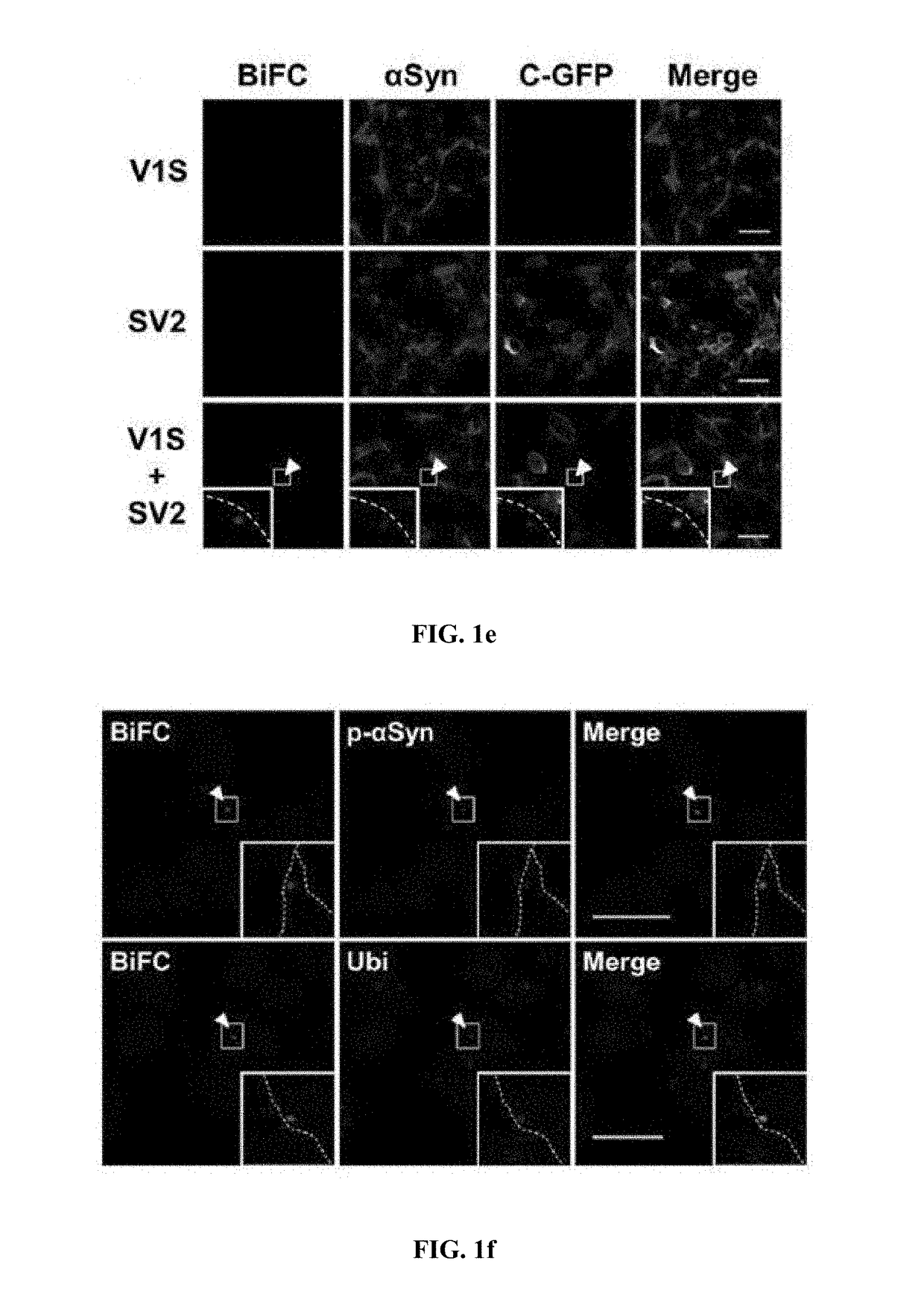
Method for measuring cell-to-cell transmission of alpha-synuclein aggregates using bimolecular fluorescence complementation system and method for screening a substance for preventing or treating neurodegenerative disease using the same
ActiveUS20160123961A1Restoring activity of proteinSlow spreadCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningProtein aggregationModel system
The present disclosure relates to dual-cell model and Caenorhabditis elegans model systems for measuring neuron-to-neuron transmission of protein aggregates, and more particularly to transgenic cell and animal model systems expressing fusion proteins of N-terminus or C-terminus of fluorescent proteins with α-synuclein proteins, methods for measuring continuous cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using the same, and methods for screening substances for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:NEURAMEDY CO LTD
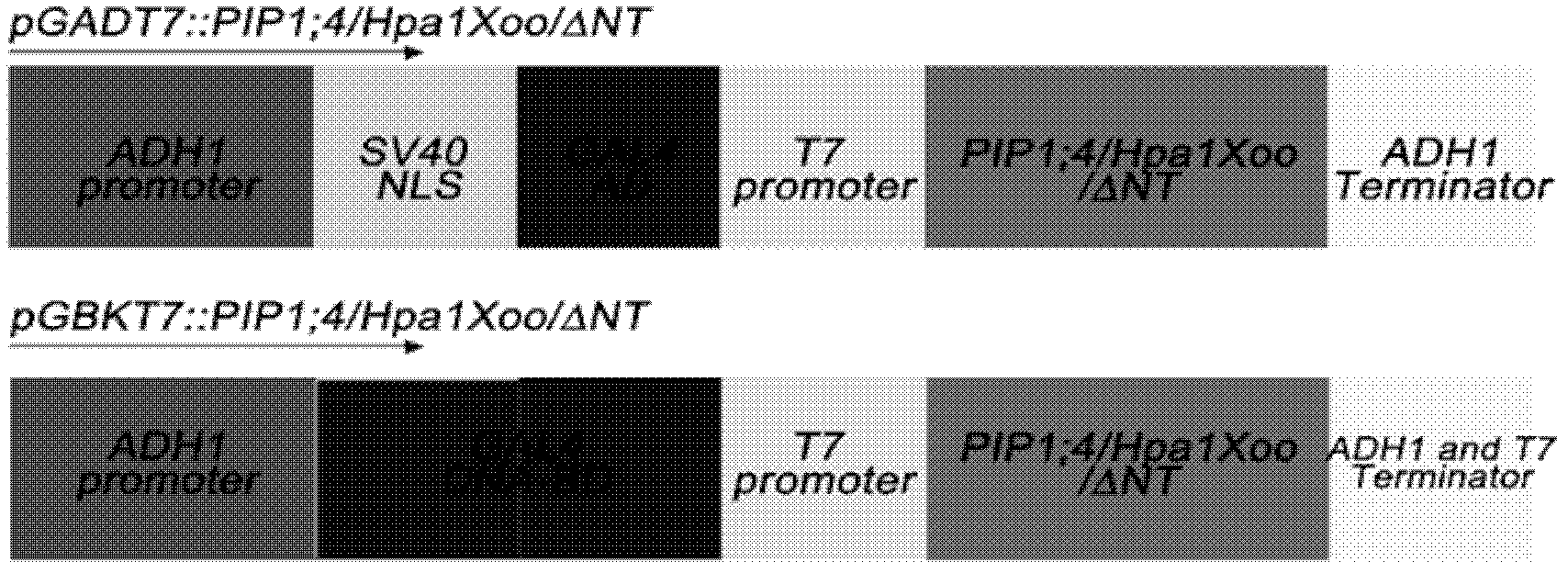
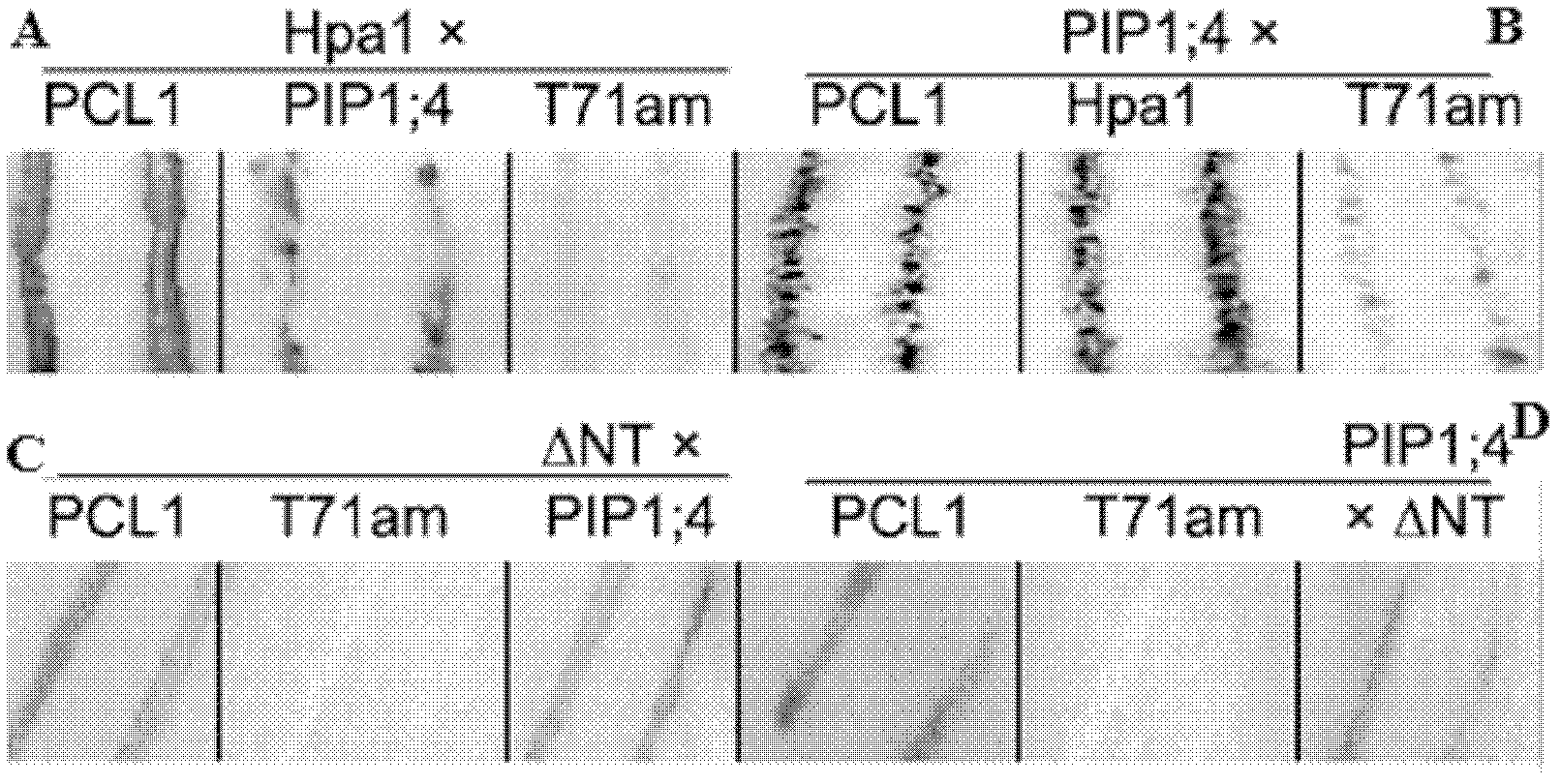
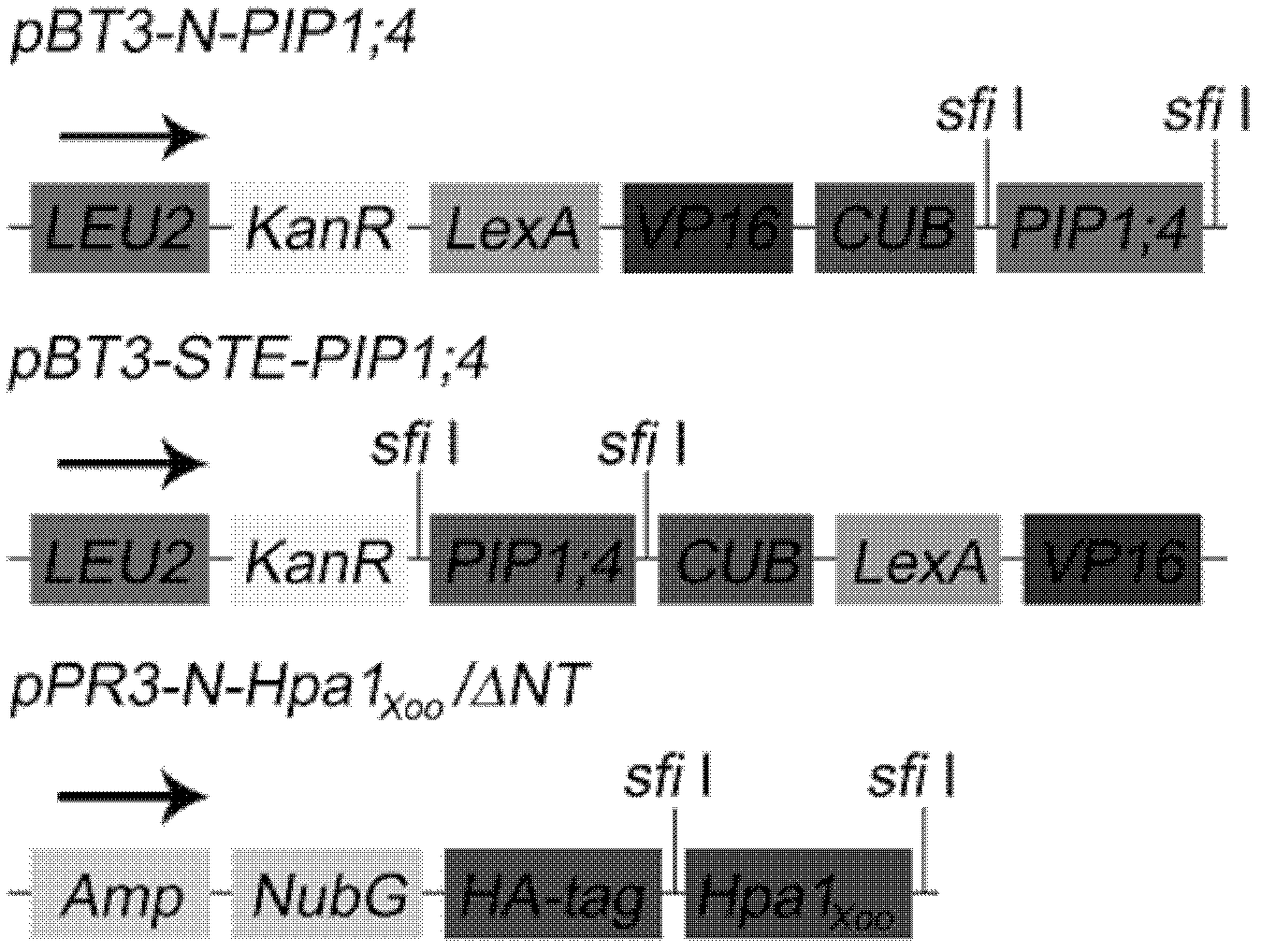
Application of aquaporin gene in construction of interaction carrier capable of interacting with Hpa1Xoo
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and discloses application of an aquaporin gene in the construction of an interaction carrier capable of interacting with Hpa1Xoo. The interaction relationship between a plant aquaporin PIP1;4 and the Hpa1Xoo is obtained through a yeast two-hybrid system, membrane yeast two hybrid, pull-down assay, bimolecular fluorescence complementation and other protein interaction technologies. Therefore, the aquaporin PIP1;4 as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 (sequence identity number 1) can be applied to the construction of the interaction carrier enabling an expression product of the aquaporin PIP1;4 to interact with the Hpa1Xoo.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
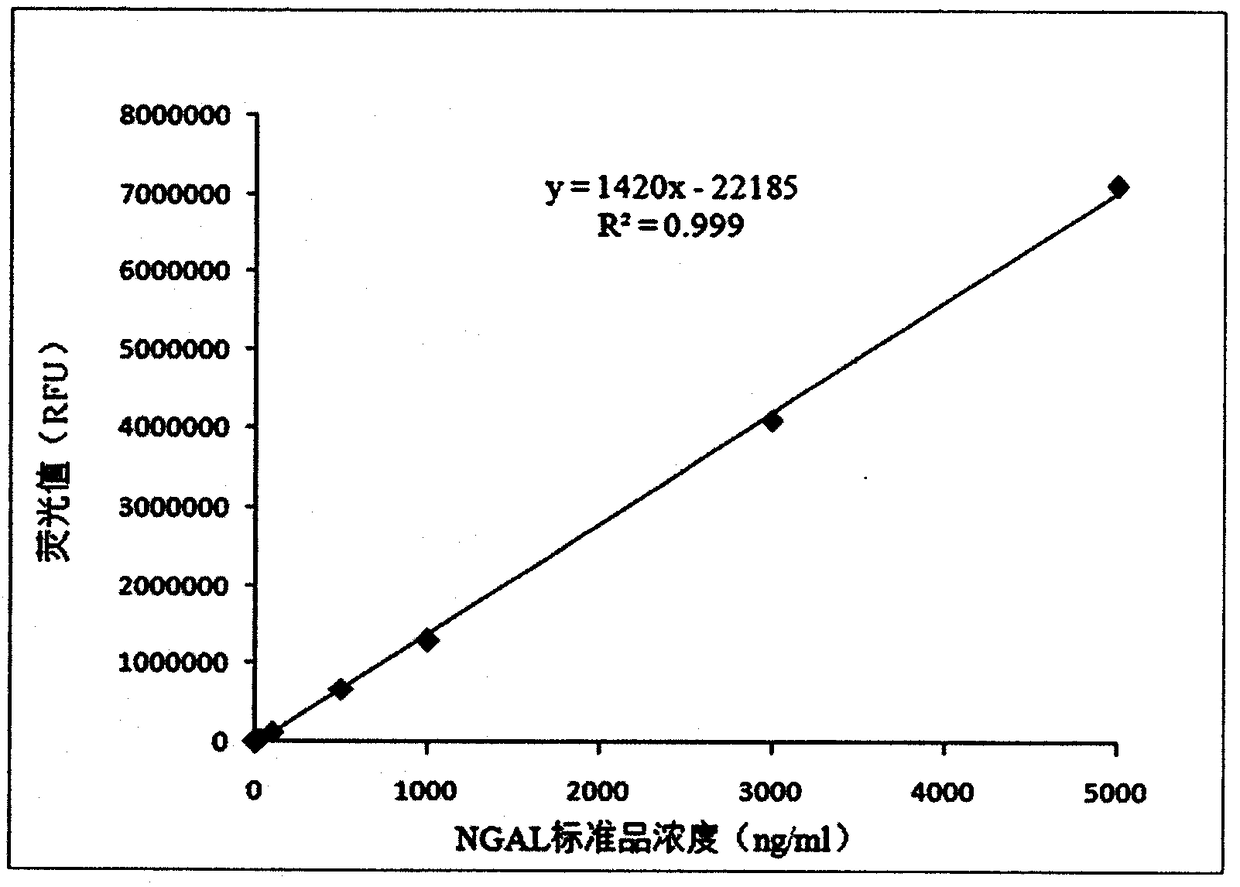
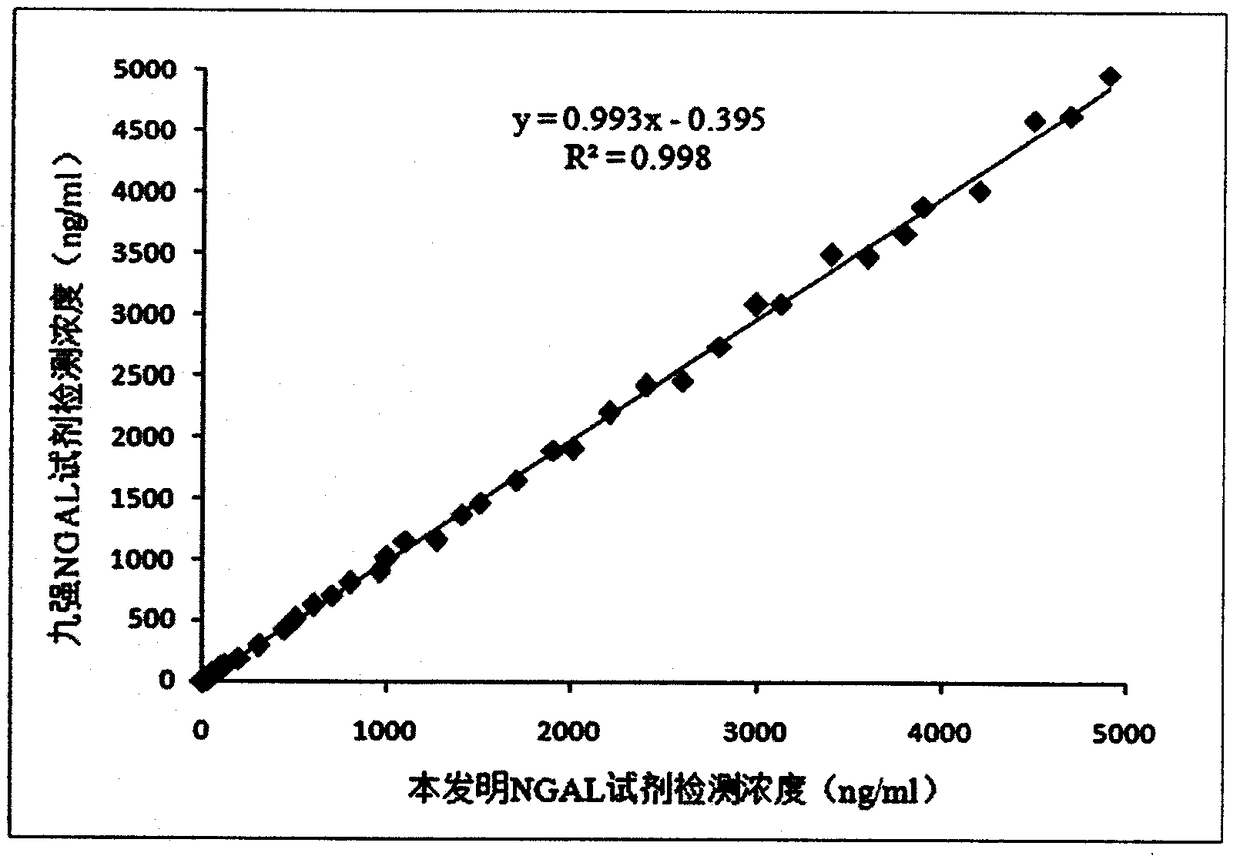
NGAL detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology, preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108254567ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescent proteinYellow fluorescent protein
The invention provides a NGAL diagnostic kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-NGAL antibody conjugation fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment andan anti-NGAL antibody coupled fluorescent protein C-terminal fragment. The present invention also discloses a preparation method of the NGAL diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The preparation method comprises preparation of the anti-NGAL antibody coupled fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment and preparation of the anti-NGAL antibody coupled fluorescent protein C-terminal fragment. The present invention also finally discloses a use method of the kit. The kit has the advantages of fast detection, simple operation, good specificity, no cleaning, highprecision, and the like, is convenient for clinical detection, can be used for monitoring of acute kidney injury, has great significance for preventing the acute kidney injury, and has great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
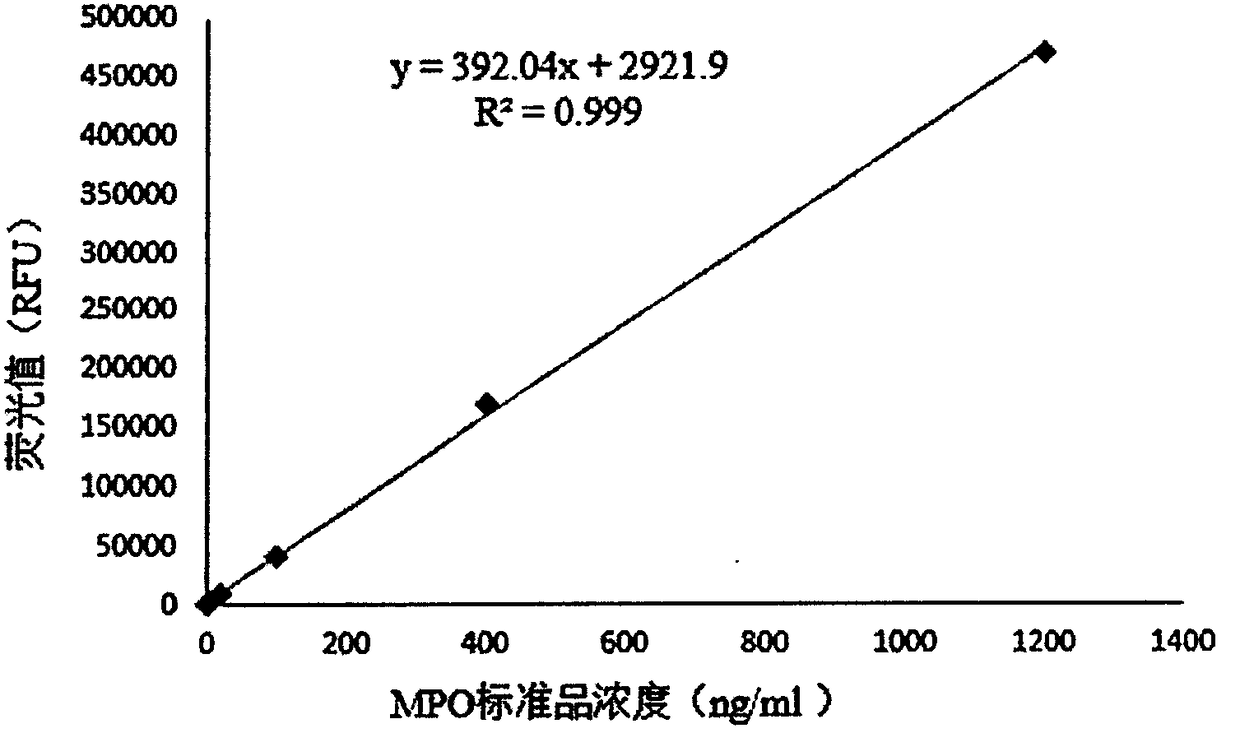
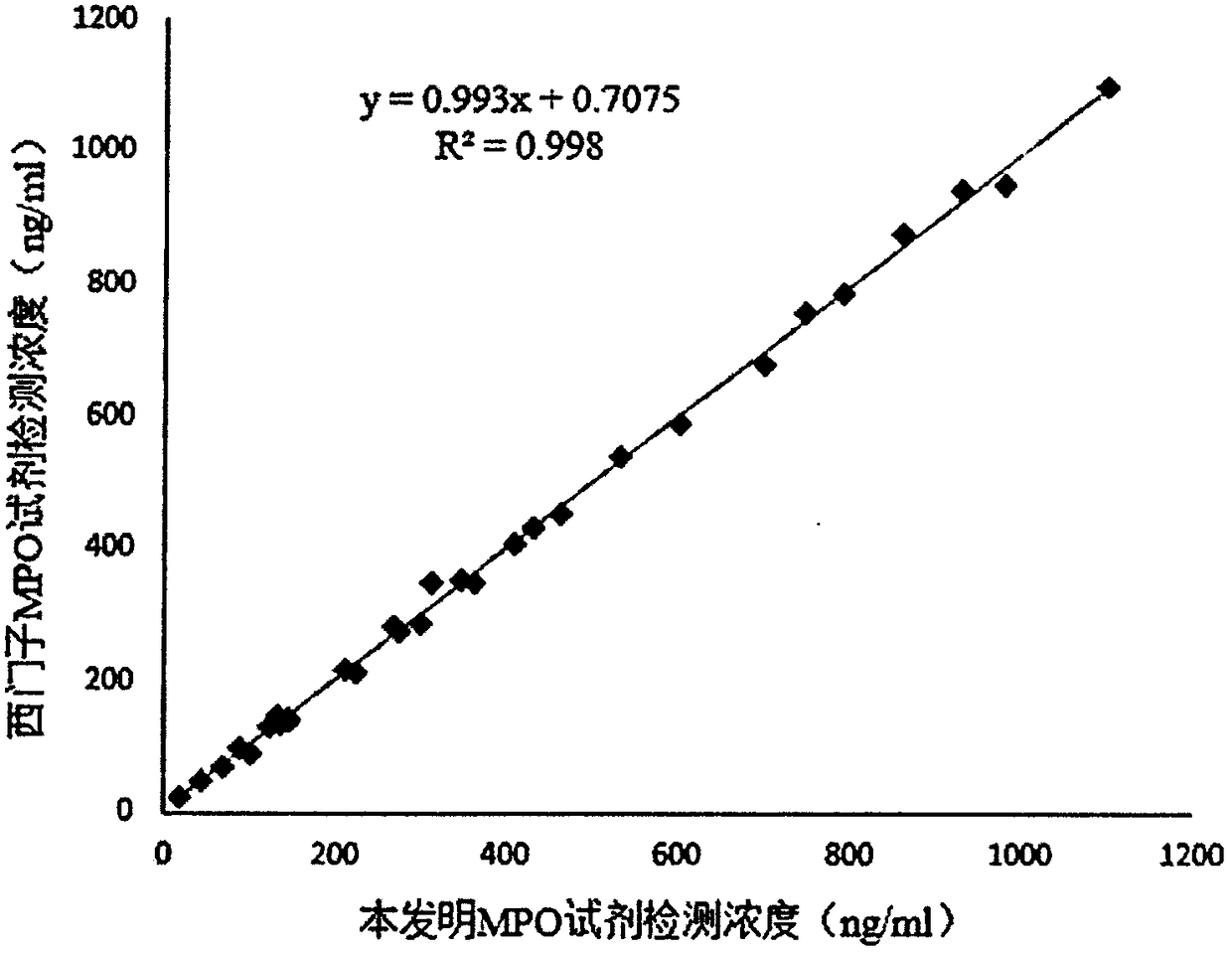
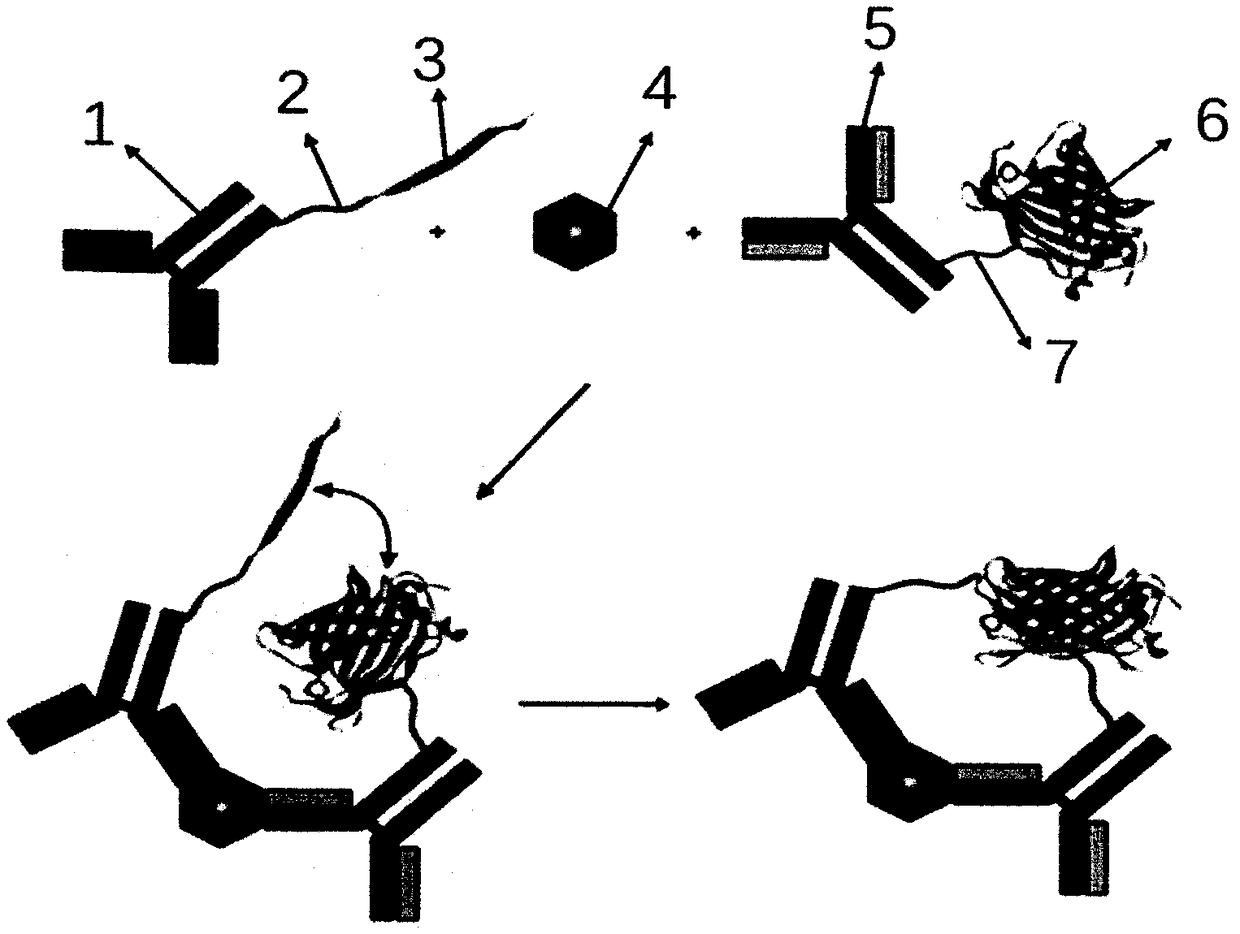
MPO detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology, preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN108387732ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingAntibody conjugateCardiovascular disorder diagnosis
The invention provides a MPO detection kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology, a preparation method and a use method thereof, wherein the kit comprises an anti-MPO antibodyconjugated fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment and an anti-MPO antibody conjugated fluorescent protein C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the MPO diagnosis kit, wherein the preparation method comprises: preparation of an anti-MPO antibody conjugated fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment, and preparation of an anti-MPO antibody conjugated fluorescentprotein C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a use method the kit. According to the present invention, the kit has advantages of simple operation, good specificity, no cleaning, highaccuracy and the like, is conveniently suitable for clinical detection, can increase the accuracy of the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases in the monitoring of cardiovascular diseases, and has great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
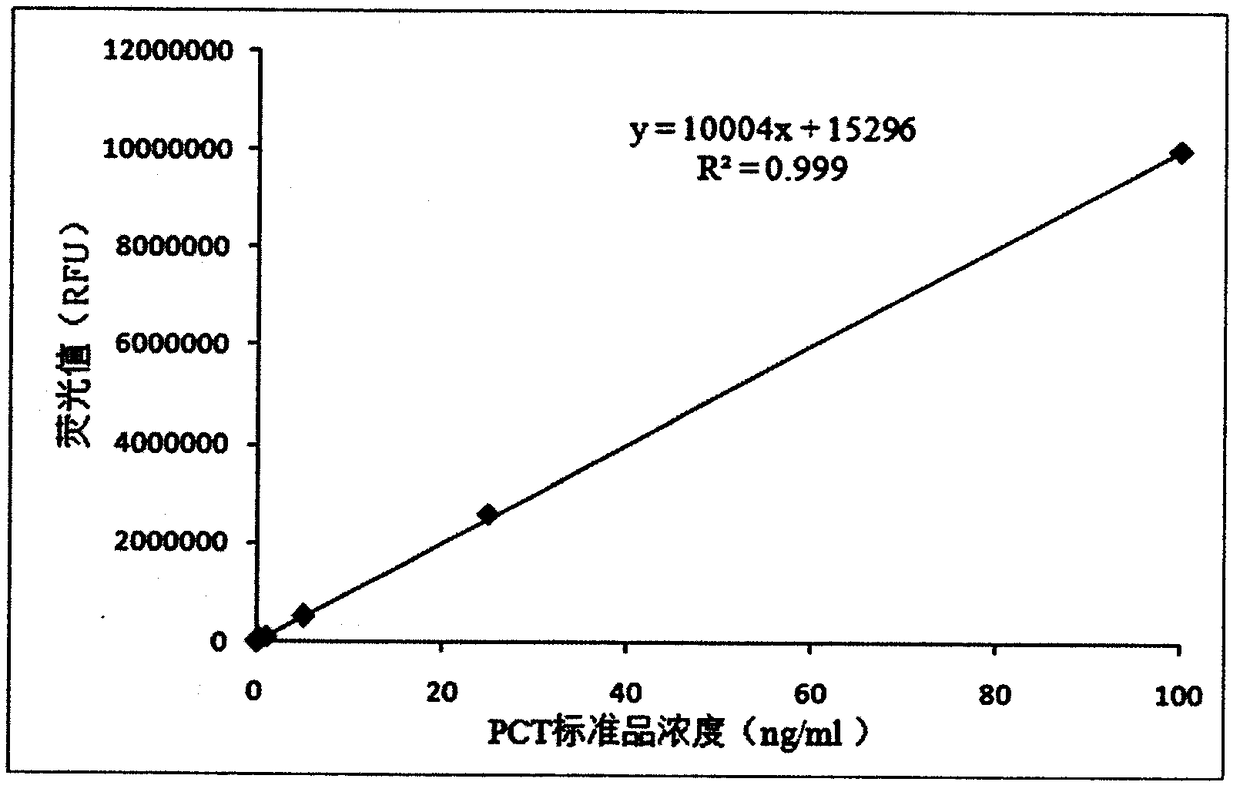
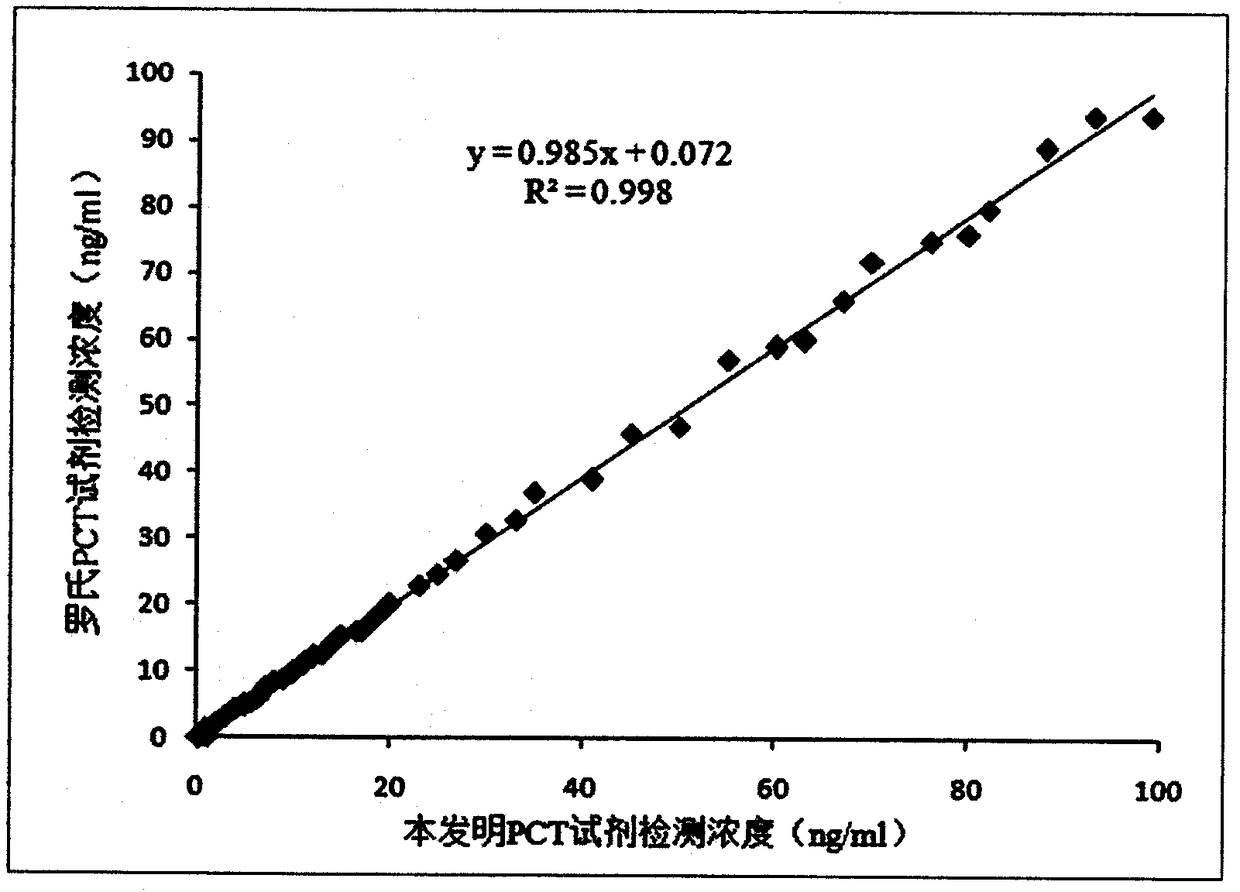
PCT detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology, preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN108387734ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingAntibody conjugateFluorescent protein
The invention provides a PCT diagnosis kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology, wherein the kit comprises an anti-PCT antibody conjugated fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment and an anti-PCT antibody conjugated fluorescent protein C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the PCT diagnosis kit, wherein the preparation method comprises: preparation of an anti-PCT antibody conjugated fluorescent protein N-terminal fragment, and preparation of an anti-PCT antibody conjugated fluorescent protein C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a use method the kit. According to the present invention, the kit has advantages of simple operation, good specificity, rapid detection, no cleaning, good precision and the like, is conveniently suitable for clinical detection, can increase the accuracy of the diagnosis of sepsis in the monitoring of infections, and has great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Method for detecting interaction of proteins
InactiveCN101620233BIncrease brightnessStrong penetrating powerBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceLiving bodyBiology
The invention relates to a detection method which belongs to the field of biomolecules. The method can be used for detecting the interaction among proteins by a dimolecular fluorescent complement technology on the basis of orange red fluorescent protein and infrared fluorescent protein. The invention can be applied to detect the interaction of the proteins by living body imaging and can synchronously detect the interaction of multiple pairs of proteins in parallel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
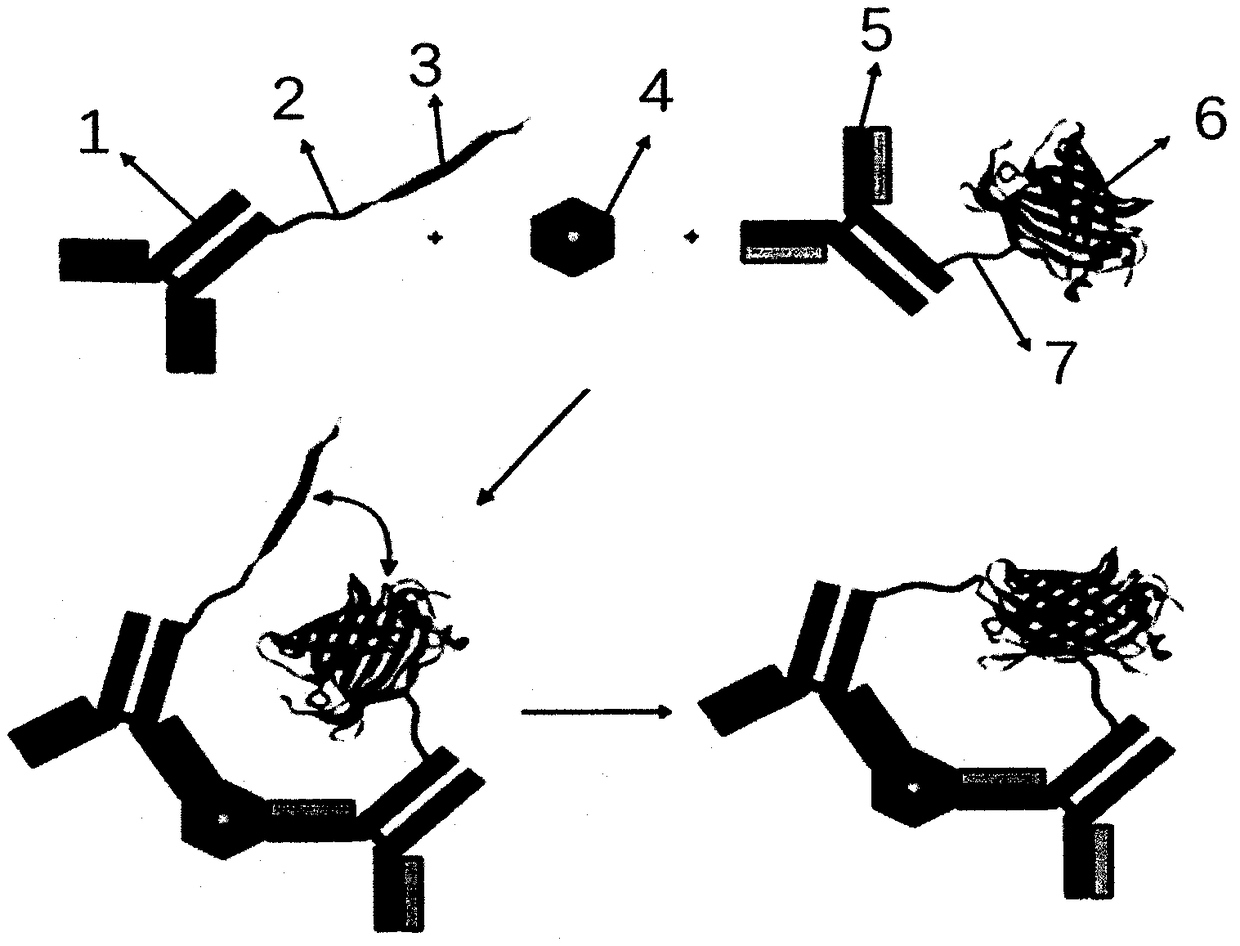
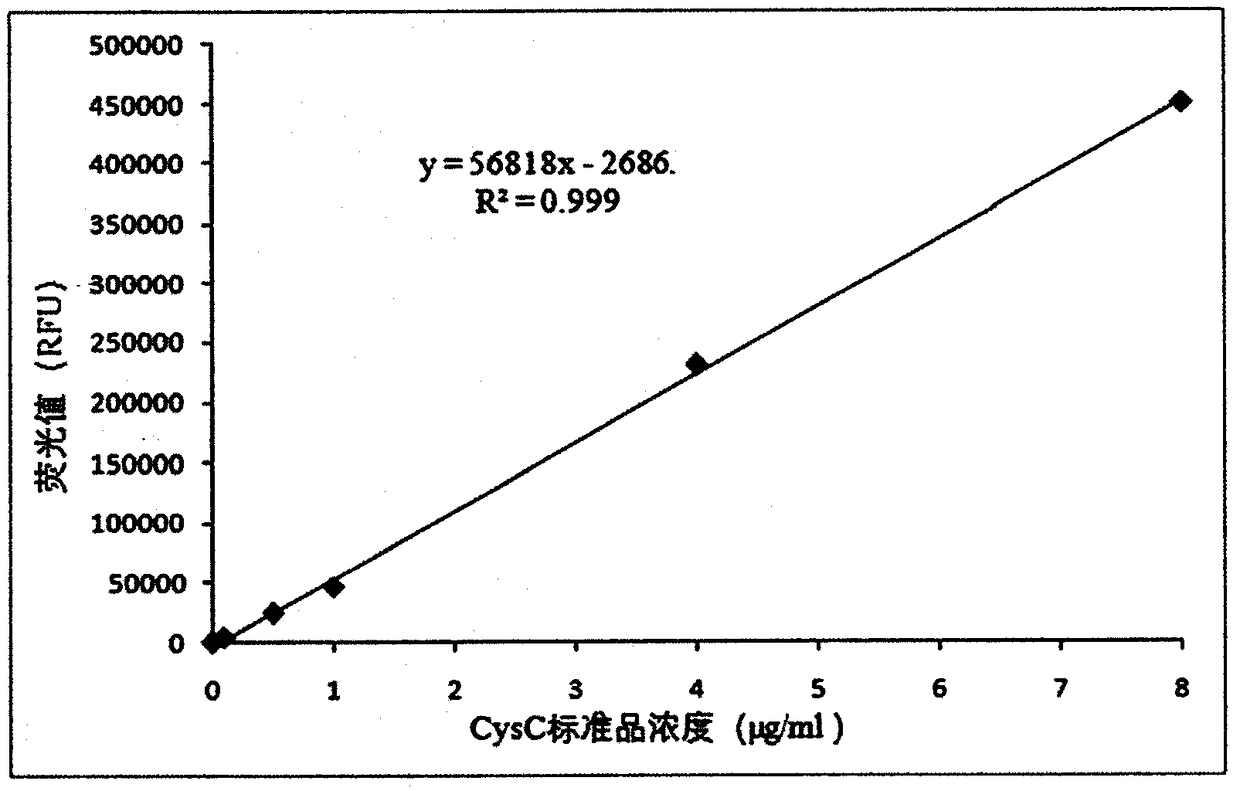
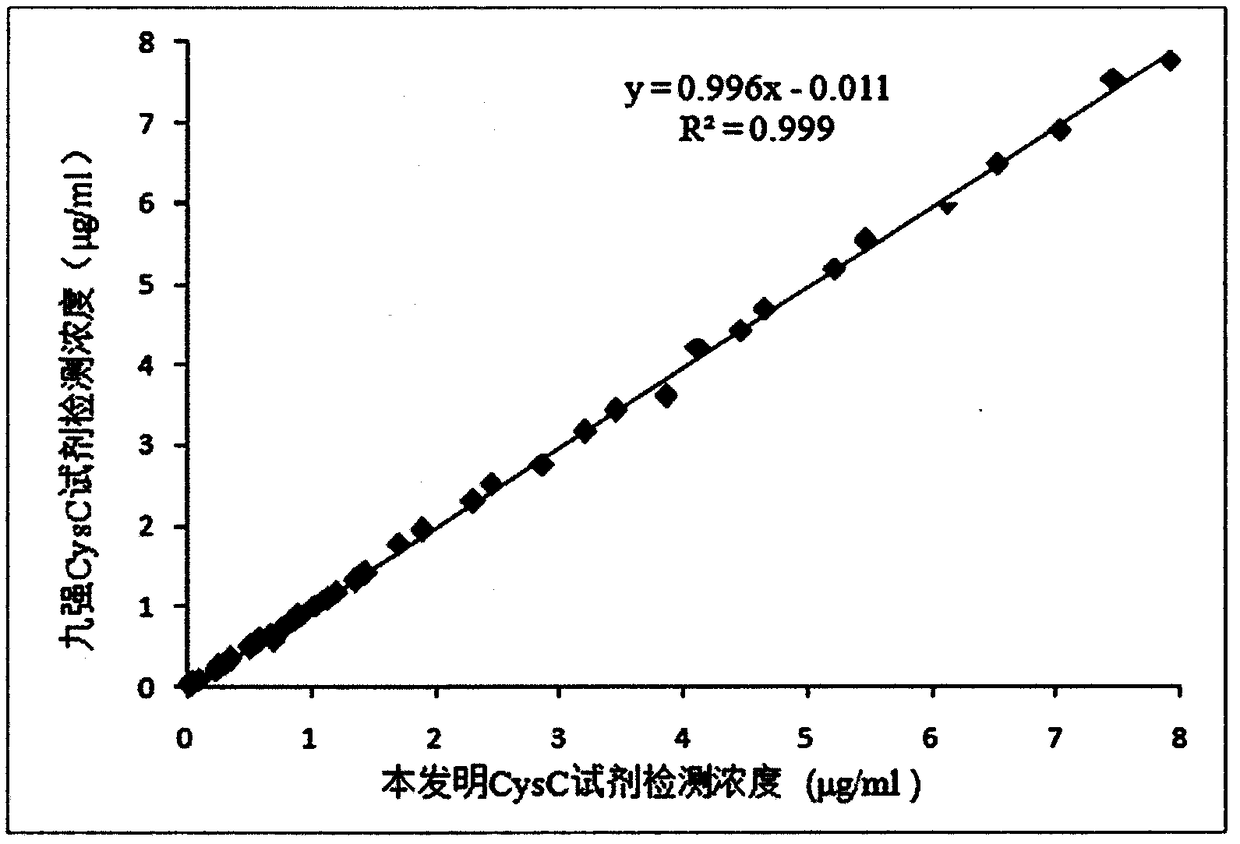
Cys C detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology as well as preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108226522ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceNephropathyC-terminus
The invention provides a Cys C diagnostic kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-Cys C antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and an anti-Cys C antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the Cys C diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology.The method comprises the steps of preparing the anti-Cys C antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and preparing the anti-Cys C antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. Finally, the invention further discloses a use method of the kit. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, wide linear range, good specificity, free from cleaning, high accuracy and the like, is convenient in clinical detection use and can be used for reflecting symptoms of kidney diseases in time and accurately reflecting disease situation changes when the kit is appliedto kidney disease monitoring, thereby being extensively popular to the market and having a great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of an insect in vitro protein interaction detection system
InactiveCN104991072BEfficient transfectionSimple methodBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein insertionPolyhedral virus
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and application of an insect in-vitro protein interaction detecting system. At the positions of amino acid residues at the 159th bit and the 160th bit, mCherry is divided into a segment NmC and a segment CmC through a PCR method, and then the segment NmC and the segment CmC are each fused with a connecting zone sequence, a c-Myc label and a poly(A) sequence to form four fused segments; the four fused segments are each connected with a pIE-MCS plasmid with an autographa californica multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus ie1 gene promoter and a gp64 gene poly(A) sequence to establish expression plasmids; the expression plasmids are combined to form an insect cell dimolecular fluorescent complementary detecting system. The method is simple and easy to implement, and the established dimolecular fluorescent complementary detecting system expands the application of an insect cell expression system and provides a convenient and effective technological means for insect proteomics and research on protein interaction between insects and pathogenic microorganisms of the insects.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
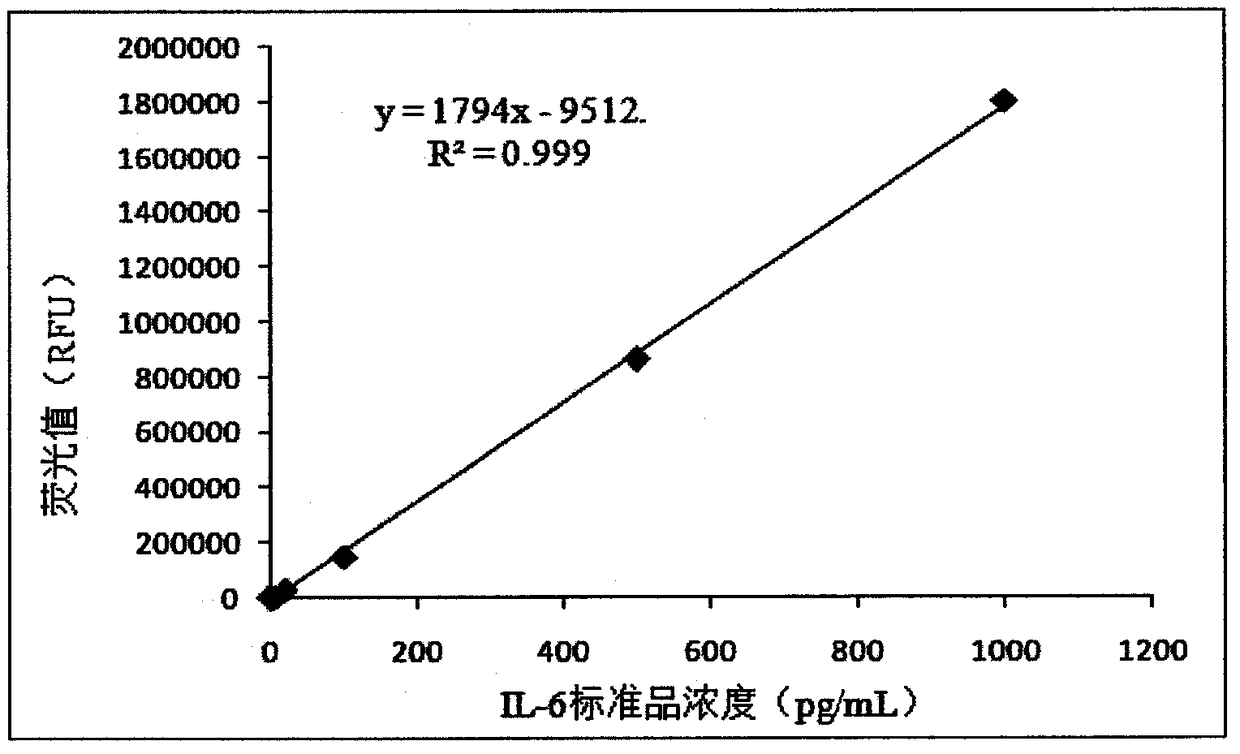
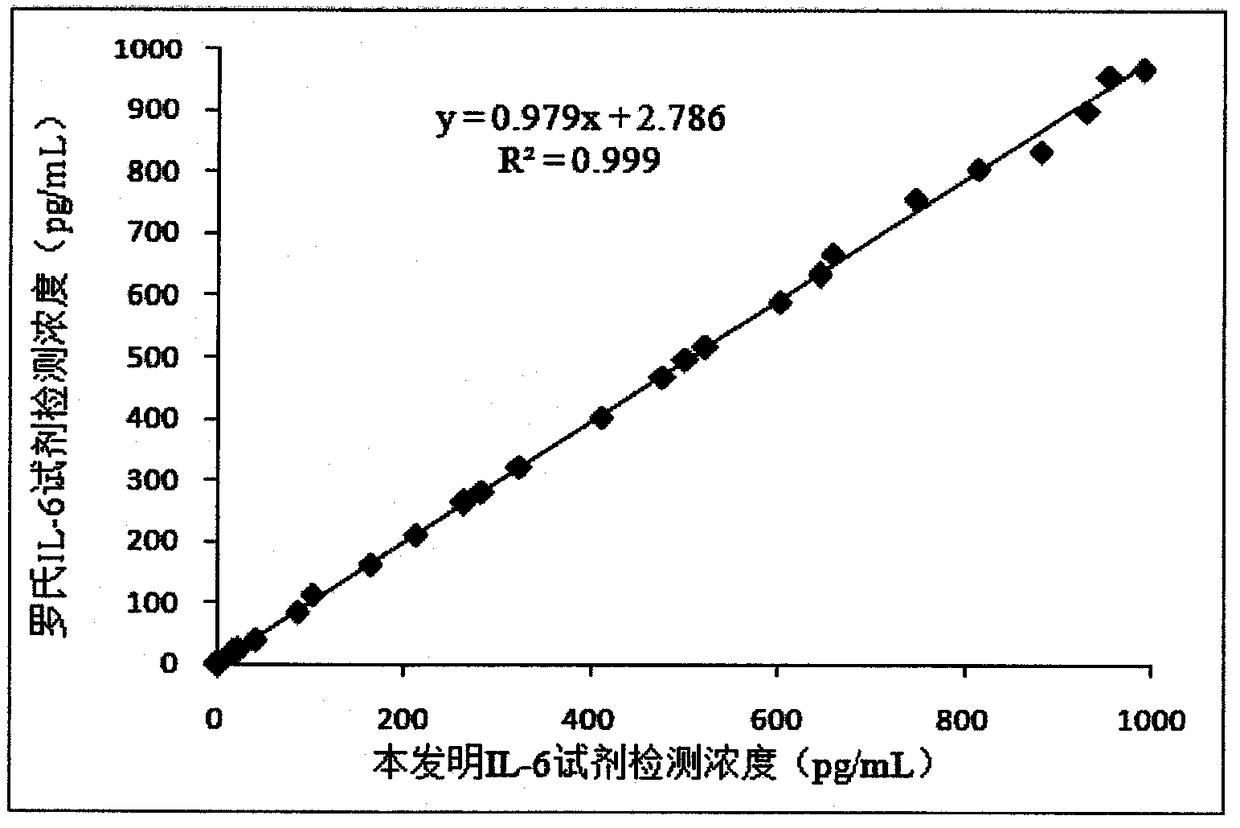
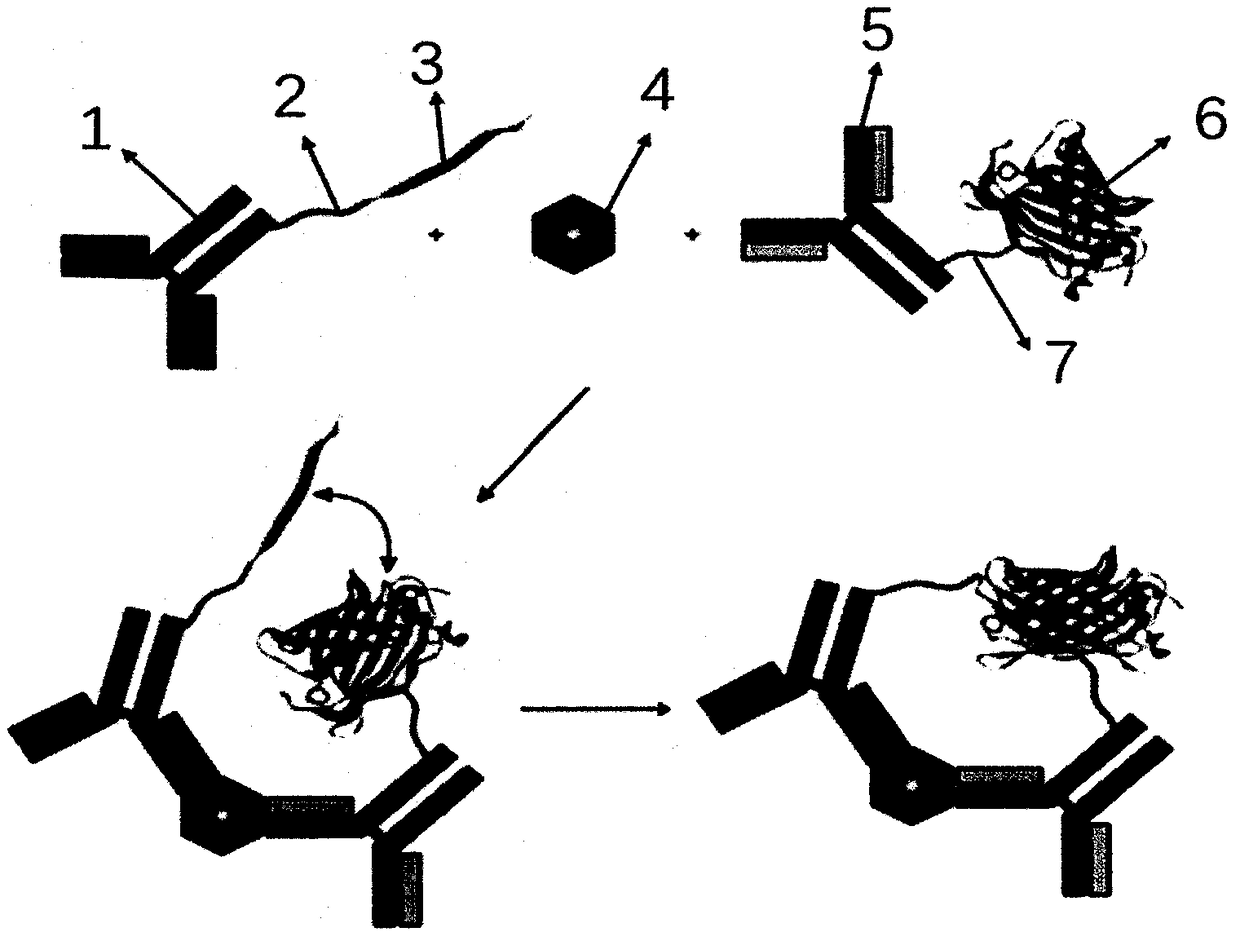
IL-6 detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology as well as preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108226525ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntibodyBioinformatics
The invention provides an IL-6 diagnostic kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-IL-6 antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and an anti-IL-6 antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the IL-6 diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. Themethod comprises the steps of preparing the anti-IL-6 antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and preparing the anti-IL-6 antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. Finally, the invention further discloses a use method of the kit. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, wide linear range, good specificity, free from cleaning, high accuracy and the like, is convenient in clinical detection use and can be used for improving the accuracy of sepsis diagnosis when the kit is applied to infection monitoring, thereby being extensively popular tothe market and having a great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
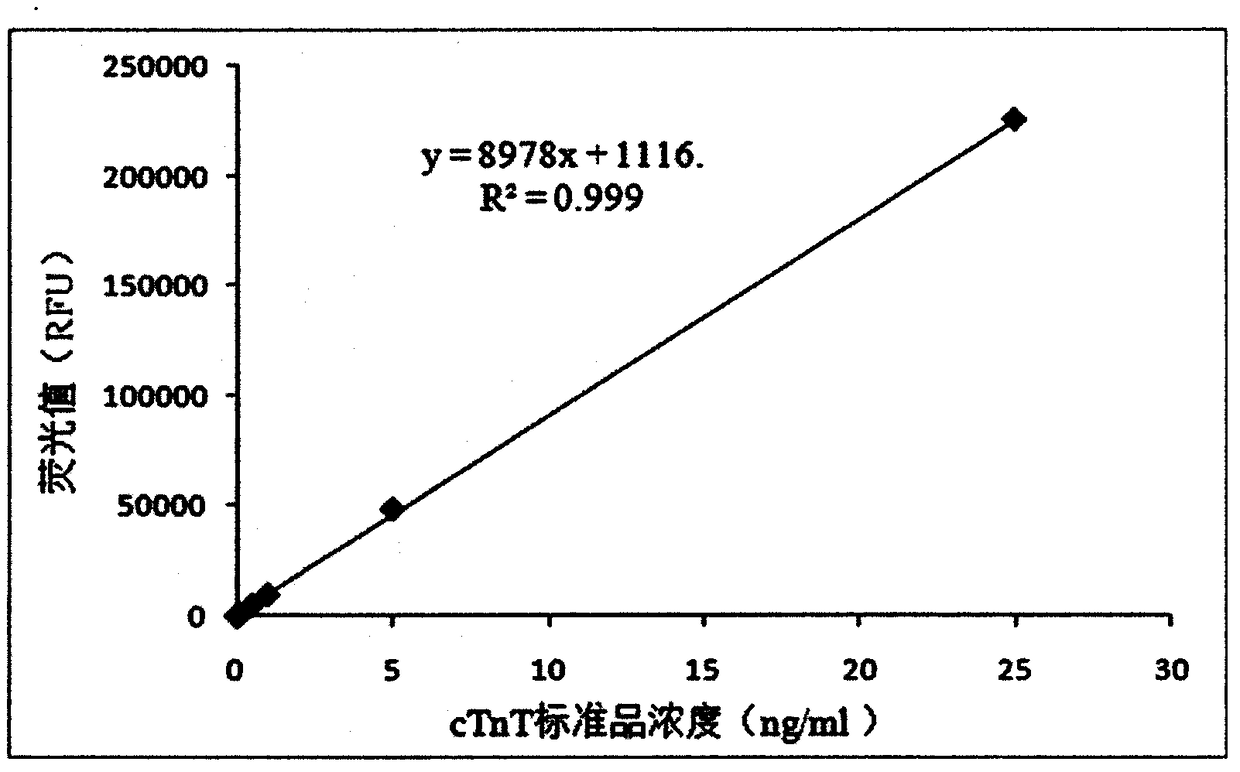
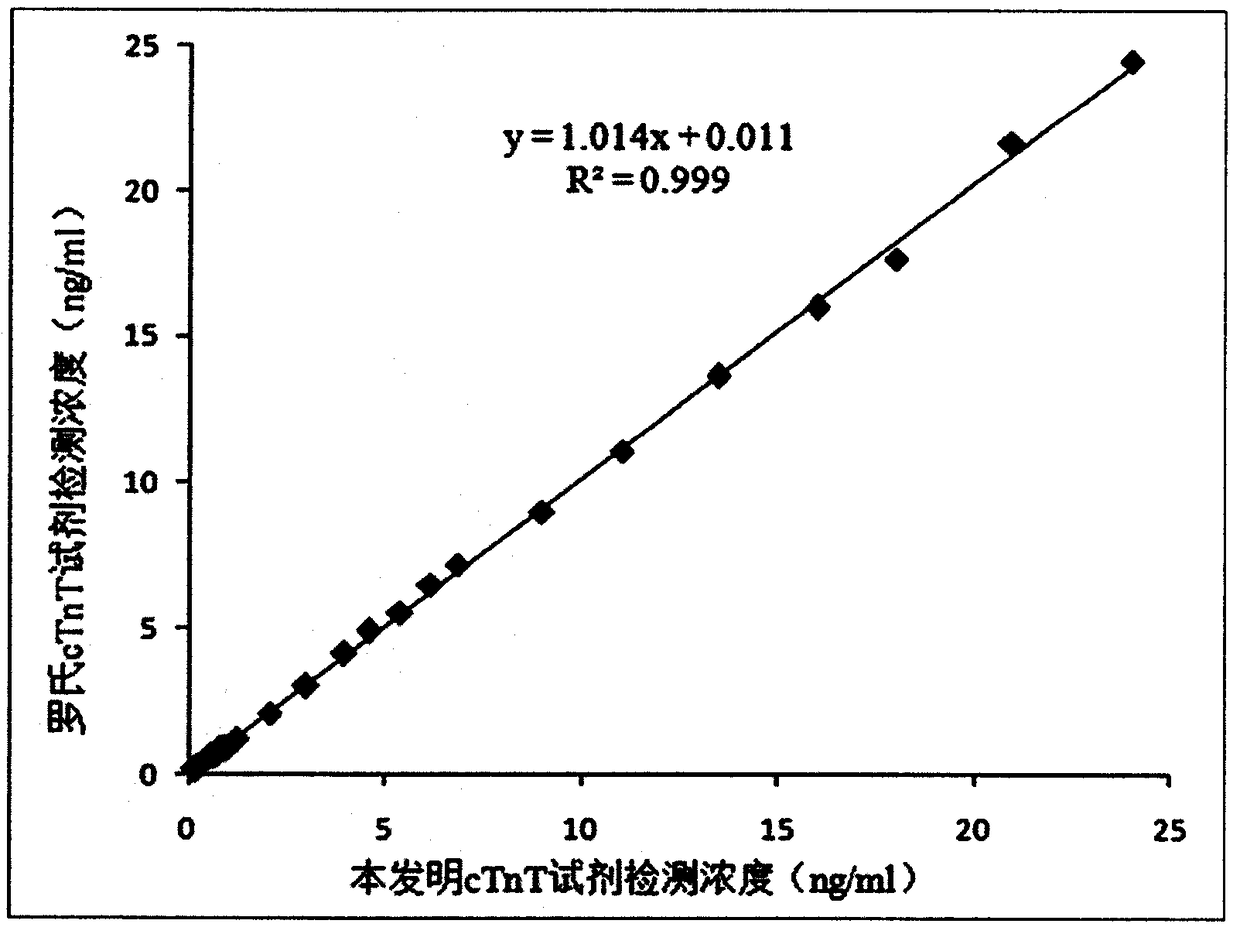
CTnT detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology as well as preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108226524ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingBiologyAntibody
The invention provides a cTnT diagnostic kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-cTnT antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and an anti-cTnT antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the cTnT diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. Themethod comprises the steps of preparing the anti-cTnT antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and preparing the anti-cTnT antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. Finally, the invention further discloses a use method of the kit. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of rapidness in operation, good specificity, good precision, high accuracy and the like, is convenientin clinical detection use and can be used for improving the accuracy of acute myocardial injury diagnosis when the kit is applied to myocardial injury monitoring, thereby having a great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
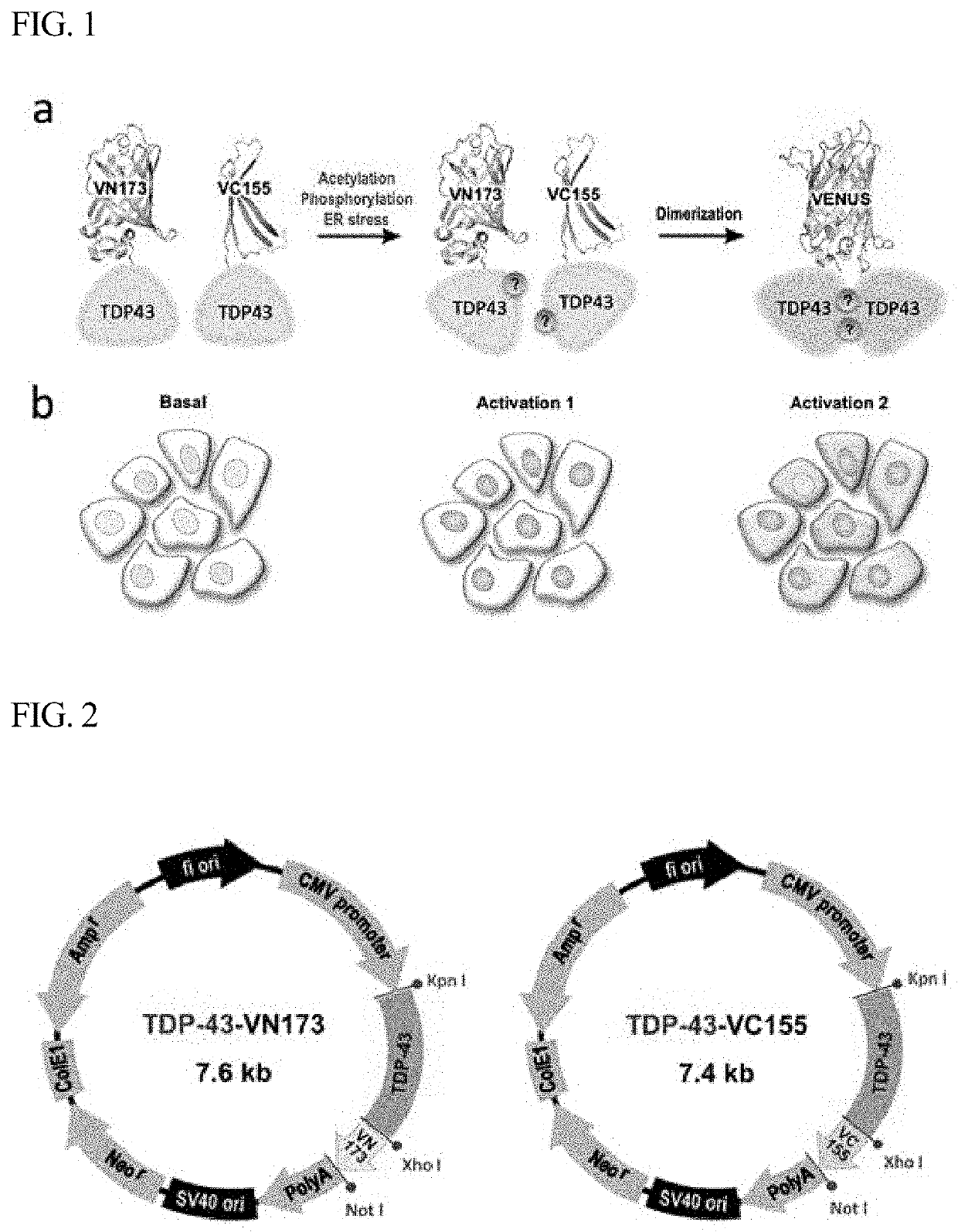
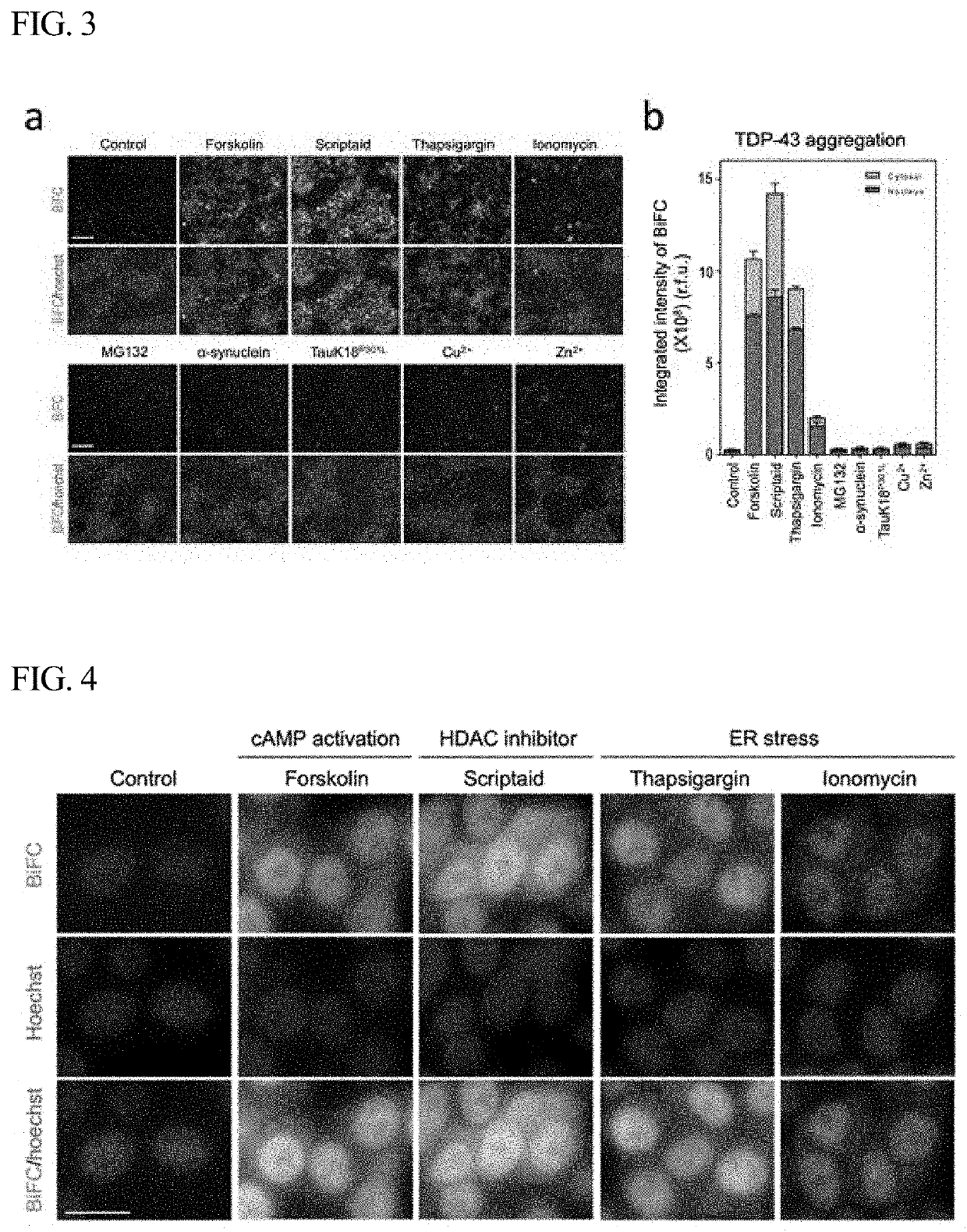
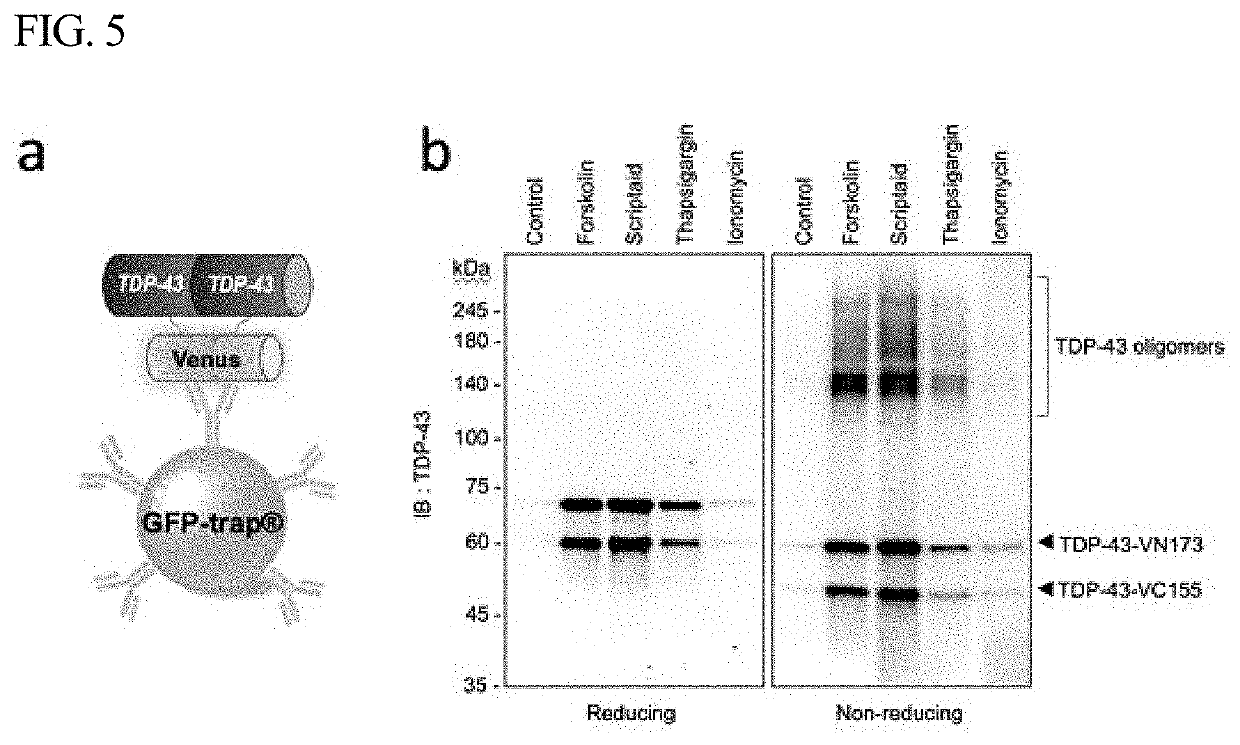
A pair of amino acid sequences for monitoring formation of tdp-43 oligomer in living cells via bimolecular fluorescence complementation
The present disclosure relates to a vector pair for screening TDP-43 (TAR DNA-binding protein 43 or TransActive Response DNA-binding protein 43) oligomer formation, a cell line transfected with the vector pair, and a method of monitoring TDP-43 oligomer formation using the cell line. More specifically, the vector pair includes: a first vector including a first TDP-43 gene and a first fluorescence protein gene; and a second vector including a second TDP-43 gene and a second fluorescence protein gene, wherein a protein expressed from the first fluorescence protein gene and a protein expressed from the second fluorescence protein gene bind to each other to display fluorescence, by association between a protein expressed from the first TDP-43 gene and a protein expressed from the second TDP-43 gene. The vector pair is effective in that it makes it possible to monitor TDP-43 oligomer formation in living cells.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
A method for detecting the expression of cellular RNA
ActiveCN113686829BImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerRna expression
This application discloses a method for detecting cellular RNA expression. According to the principle of bimolecular fluorescence complementation, different RNA binding proteins or structural domains are fused at the N-terminal and C-terminal of the fluorescent molecule, and two exogenously expressed RNA aptamers pass through The principle of complementary base pairing is combined with the RNA to be detected, and the two RNAs expressed exogenously contain RNA binding protein binding sequences, and when the two fusion expressed different RNA binding proteins bind to them, they will emit fluorescence.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
A kind of expression vector and its application for the study of bimolecular fluorescence complementation
ActiveCN105177041BBiological testingVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetClosed loop
The invention provides a novel expression vector for bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) research. Expression cassettes of 2 segments of a fluorescent protein are integrated onto the vector; and gene sequences of 2 target proteins can be simultaneously cloned to the vector by one-step reaction (Golden Gate cloning or closed-loop Gibson splicing process) and respectively form fusion expression with the 2 segments of the fluorescent protein. Therefore, when the vector is used for BiFC research, only one vector is needed and introduced into cells, thereby greatly facilitating the operation of the plant BiFC experiment. The vector is compatible with the two novel cloning methods of Golden Gate cloning or closed-loop Gibson splicing. The vector is a high-copy plant expression vector containing T-DNA sequence, and can be simultaneously used for instantaneous and stable expression of plants.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for measuring cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using bimolecular fluorescence complementation system and method for screening a substance for preventing or treating neurodegenerative disease using the same
ActiveUS9757402B2Reduce formationShorten the progressCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseModel system
The present disclosure relates to dual-cell model and Caenorhabditis elegans model systems for measuring neuron-to-neuron transmission of protein aggregates, and more particularly to transgenic cell and animal model systems expressing fusion proteins of N-terminus or C-terminus of fluorescent proteins with α-synuclein proteins, methods for measuring continuous cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using the same, and methods for screening substances for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:NEURAMEDY CO LTD
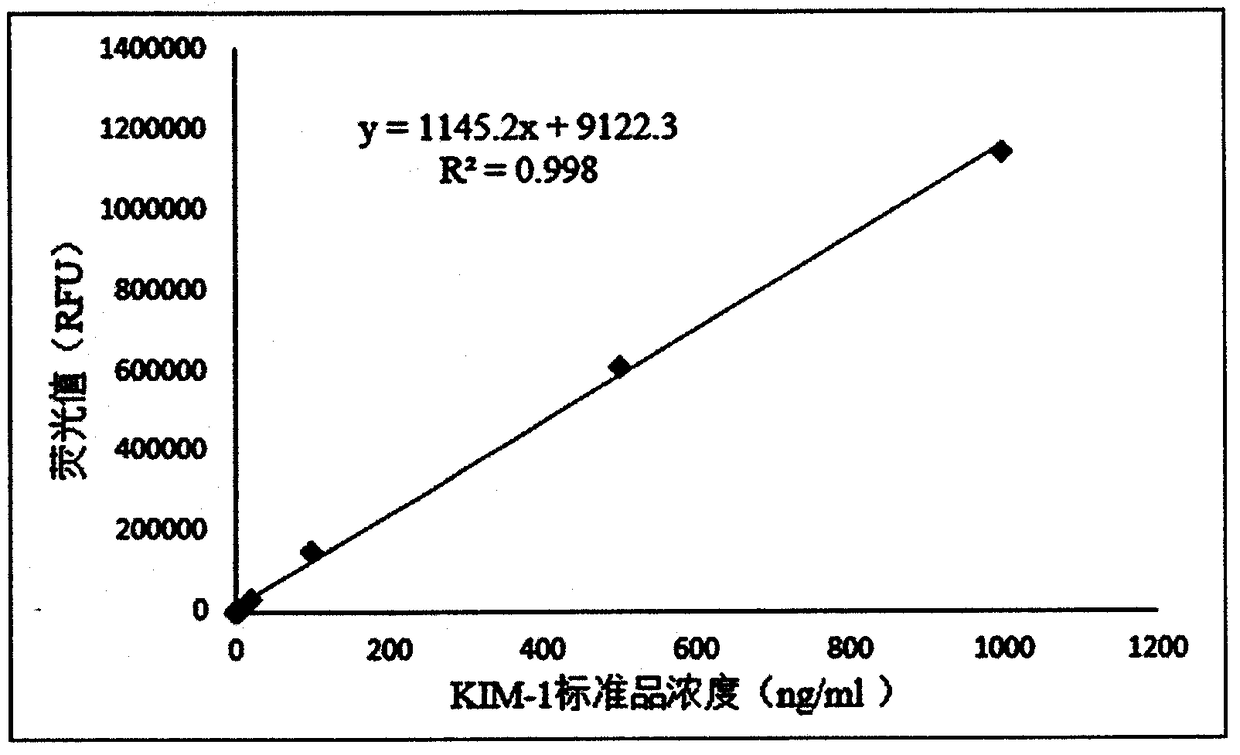
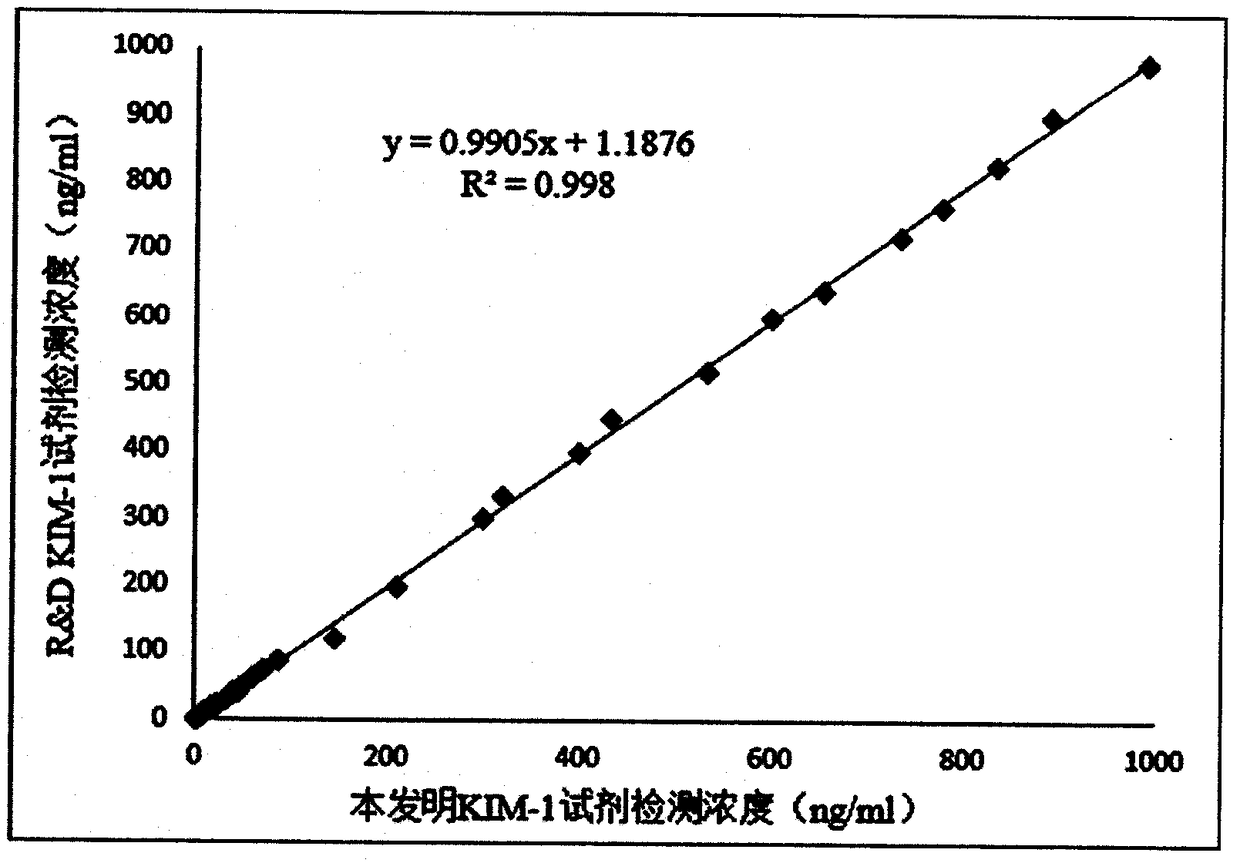
KIM-1 detection kit based on bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology as well as preparation and use methods
InactiveCN108226523ALower requirementHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAcute Renal InjuryBiology
The invention provides a KIM-1 diagnostic kit based on a bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology. The kit comprises an anti-KIM-1 antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and an anti-KIM-1 antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the KIM-1 diagnostic kit based on the bimolecular fluorescence complementary technology.The method comprises the steps of preparing the anti-KIM-1 antibody coupled fluorescin N-terminal fragment and preparing the anti-KIM-1 antibody coupled fluorescin C-terminal fragment. Finally, the invention further discloses a use method of the kit. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of rapidness in operation, good specificity, good precision, high accuracy and the like, is convenient in clinical detection use and can be used for improving the accuracy of acute renal injury diagnosis when the kit is applied to acute renal injury monitoring, thereby having a great market value.
Owner:NANJING TZONE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com