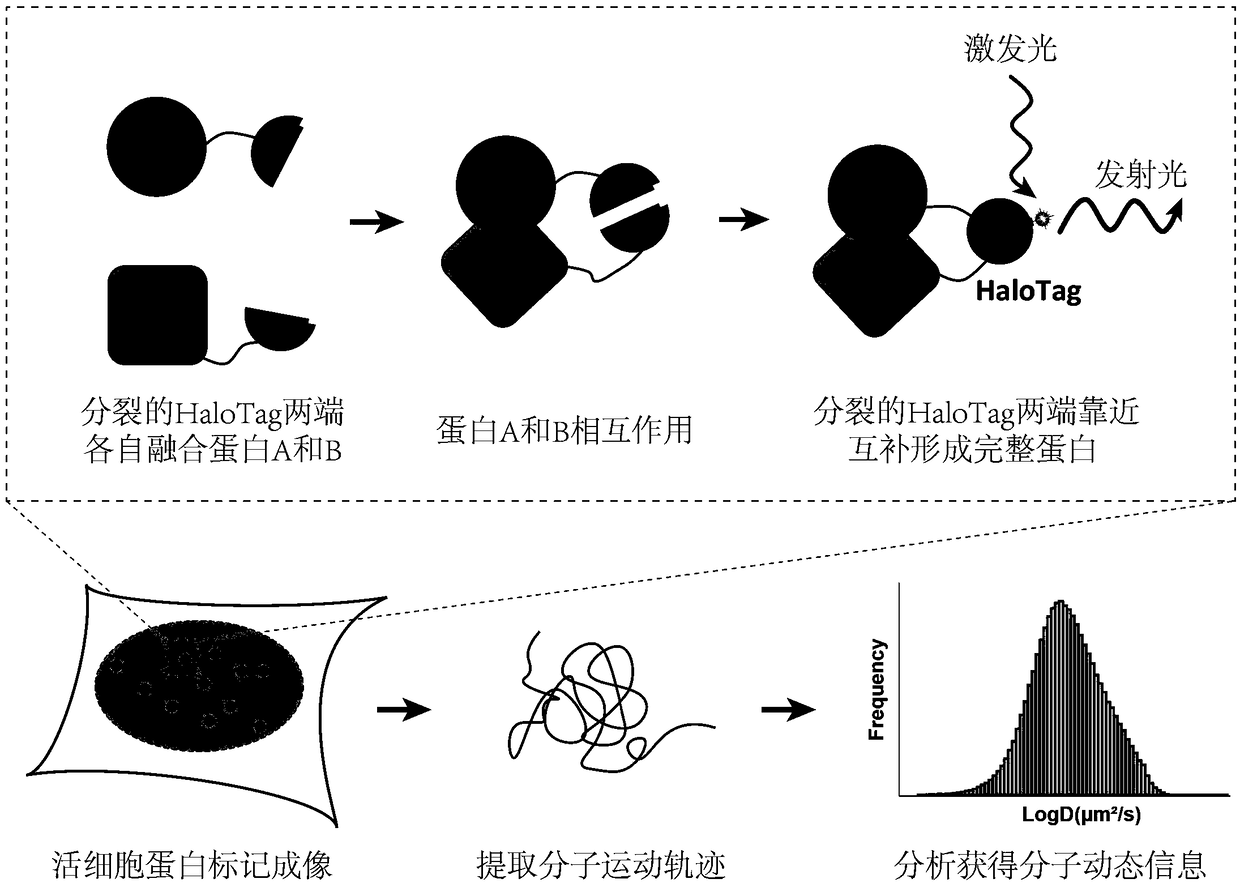
Imaging and tracking of interaction between proteins in living cells by utilizing bimolecular fluorescence complementation technology based on self-linkage label
A self-ligating, protein-based technology for use in cell biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
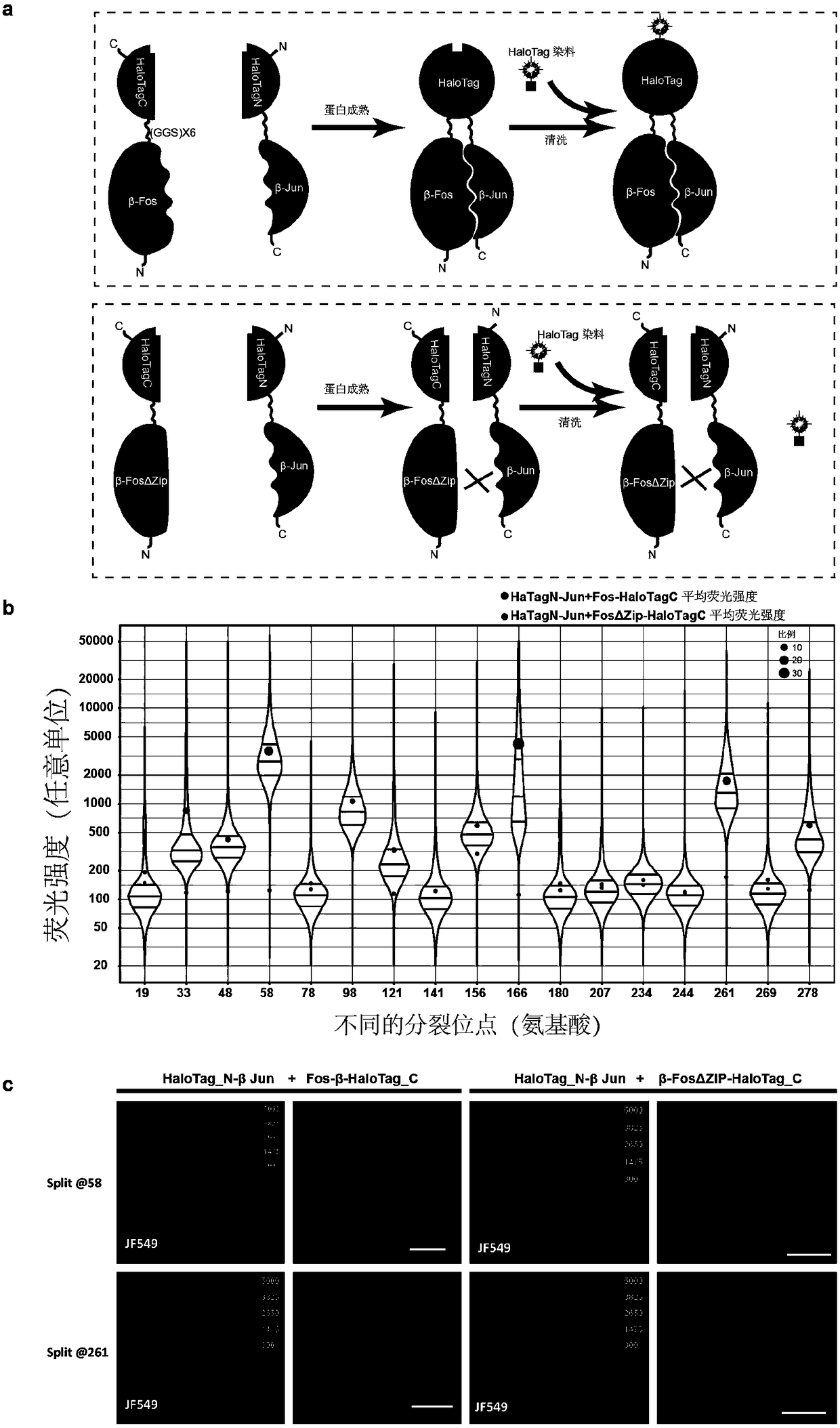
[0025] Example 1: Screening for suitable splitting sites of self-ligation tags:
[0026] (1) The requirement for the cleavage site is an irregular region between protein secondary structures, which does not affect the function of the protein. Because HaloTag is transformed from Escherichia coli dehalogenase, the crystal structure of Escherichia coli dehalogenase has been resolved but there is no crystal structure of HaloTag, so the cleavage site is designed according to the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli dehalogenase. Compare the protein sequences of HaloTag and E. coli dehalogenase to determine the cleavage site of HaloTag. A total of 17 split sites were designed in this experiment, namely 19, 33, 48, 58, 78, 98, 121, 141, 156, 166, 180, 207, 234, 244, 261, 269, and 278.
[0027] (2) The corresponding DNA fragments were amplified from the plasmids containing β-Fos, β-Fos(ΔZIP), and β-Jun by PCR. Add restriction enzyme sites to the amplified primers. Purifi...
Embodiment 2
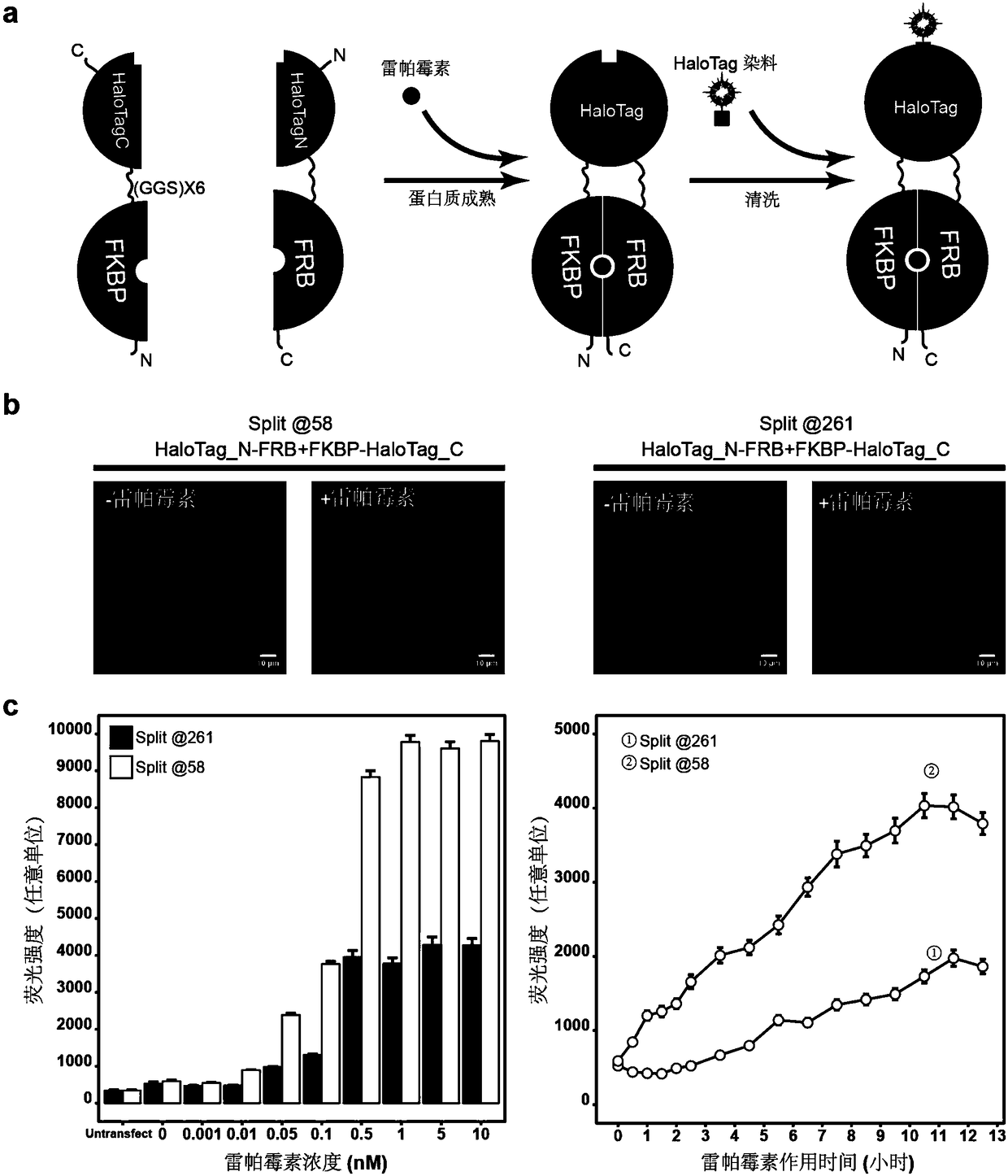
[0041] Example 2: Measuring the maturation kinetics of split self-attachment tags:
[0042] (1) The corresponding DNA fragments were amplified from the plasmids containing FKBP and FRB by PCR. Add restriction enzyme sites to the amplified primers. Purified DNA fragments were recovered by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis and a gel purification kit to obtain FKBP and FRB fragments. For the PCR amplification system used, refer to step (2) of Example 1.
[0043] (2) The vectors pcDNA3.1(+)-HaloTag N-β-Jun and pcDNA3.1(+)-β-Fos-HaloTag C were digested overnight with restriction enzymes respectively to obtain the cut vector pcDNA3.1( +)-HaloTag N and pcDNA3.1(+)-HaloTagC. At the same time, the FKBP and FRB fragments were double-digested overnight with the same restriction enzymes. Pure DNA fragments were recovered by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis and gel purification kit. For the enzyme digestion system used, refer to step (3) of Example 1.
[0044] (3) pcDNA3.1(+)-HaloTag N ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Comparison of bimolecular fluorescence complementation of self-linked tags and photoconvertible fluorescent protein bimolecular fluorescence complementation:
[0052] (1) The corresponding mMaple3N175 and mMaple3C174 fragments were amplified from the plasmid containing mMaple3 by PCR. Add restriction enzyme sites to the amplified primers. Purified DNA fragments were recovered by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis and gel purification kit to obtain mMaple3N175 and mMaple3C174 fragments. For the PCR amplification system used, refer to step (2) of Example 1.
[0053] (2) The vectors pcDNA3.1(+)-HaloTag N-β-Jun and pcDNA3.1(+)-β-Fos-HaloTag C were digested overnight with restriction enzymes respectively to obtain the cut vector pcDNA3.1( +)-β-Jun and pcDNA3.1(+)-β-Fos. At the same time, mMaple3 N174 and mMaple3C175 fragments were double digested overnight with the same restriction enzymes. Pure DNA fragments were recovered by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com