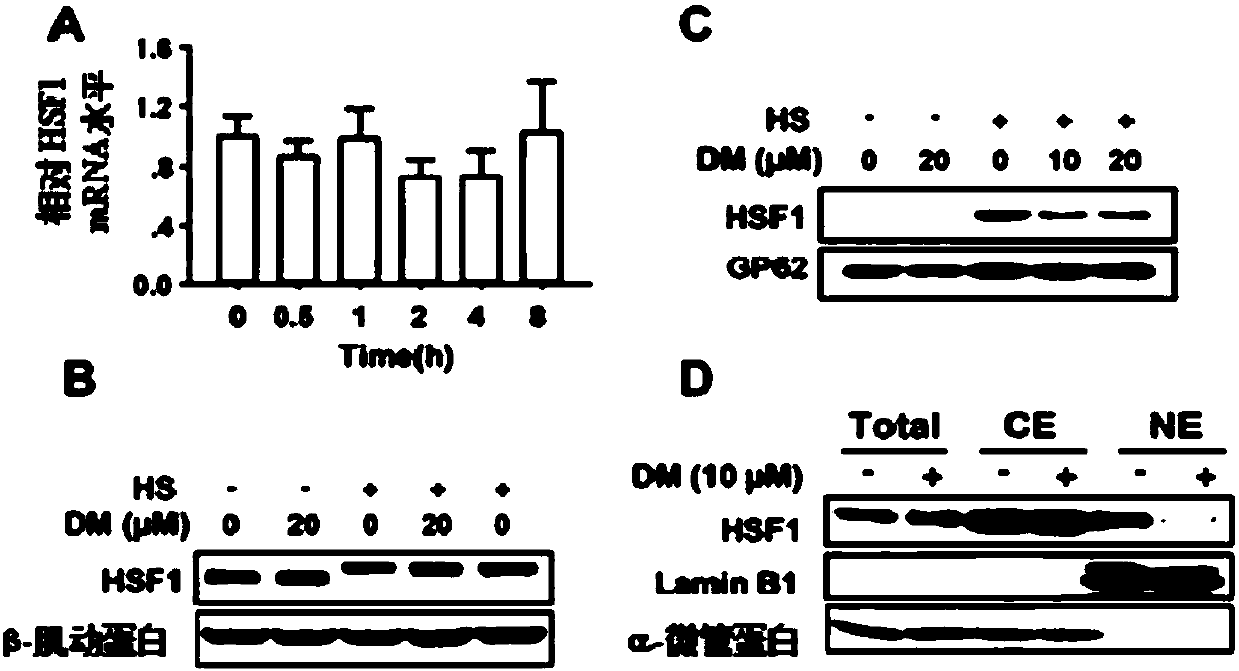
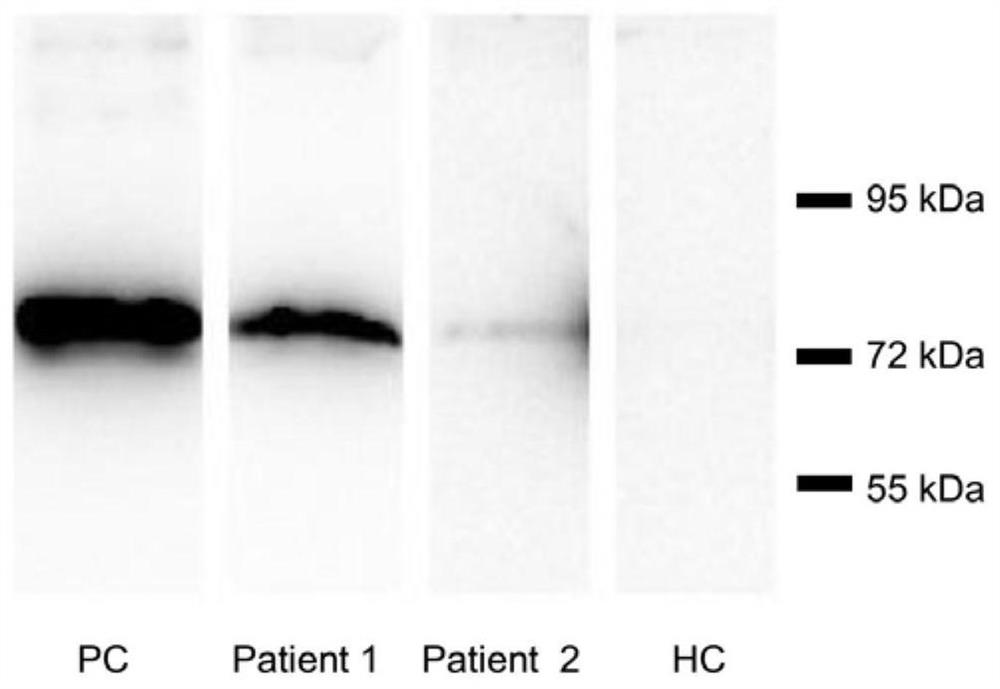
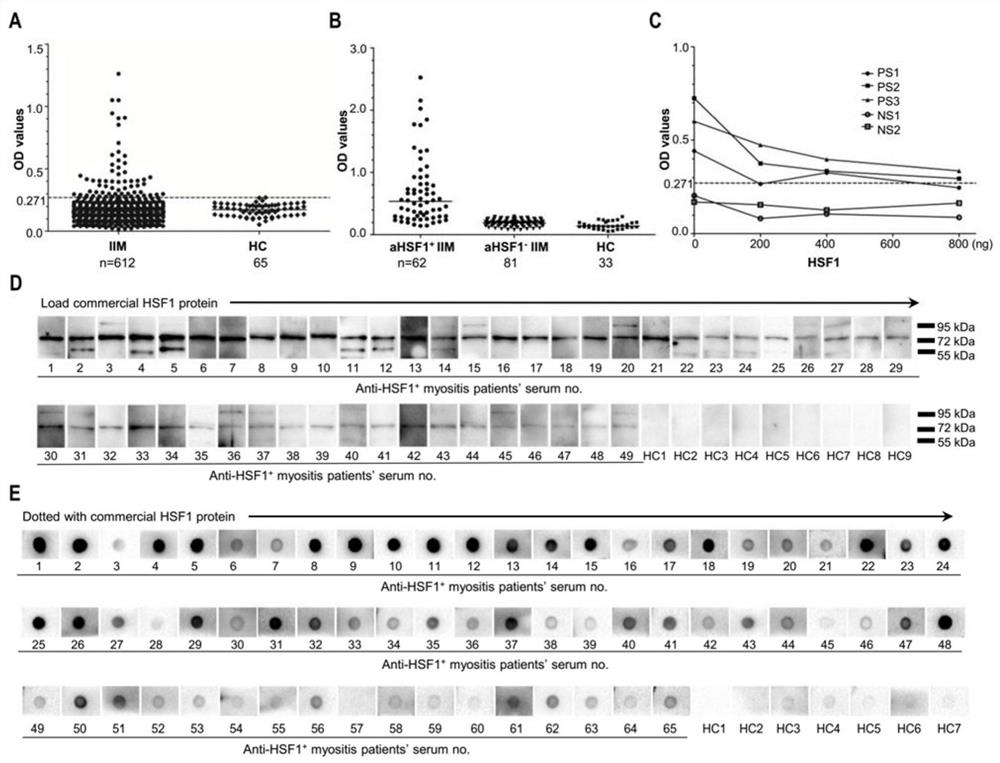
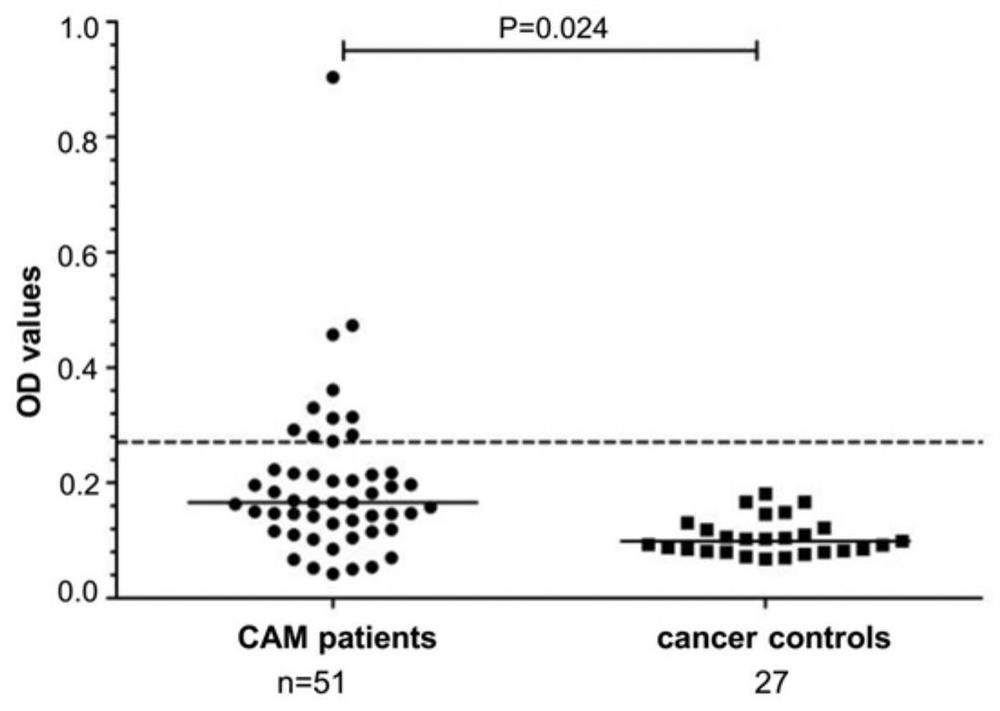
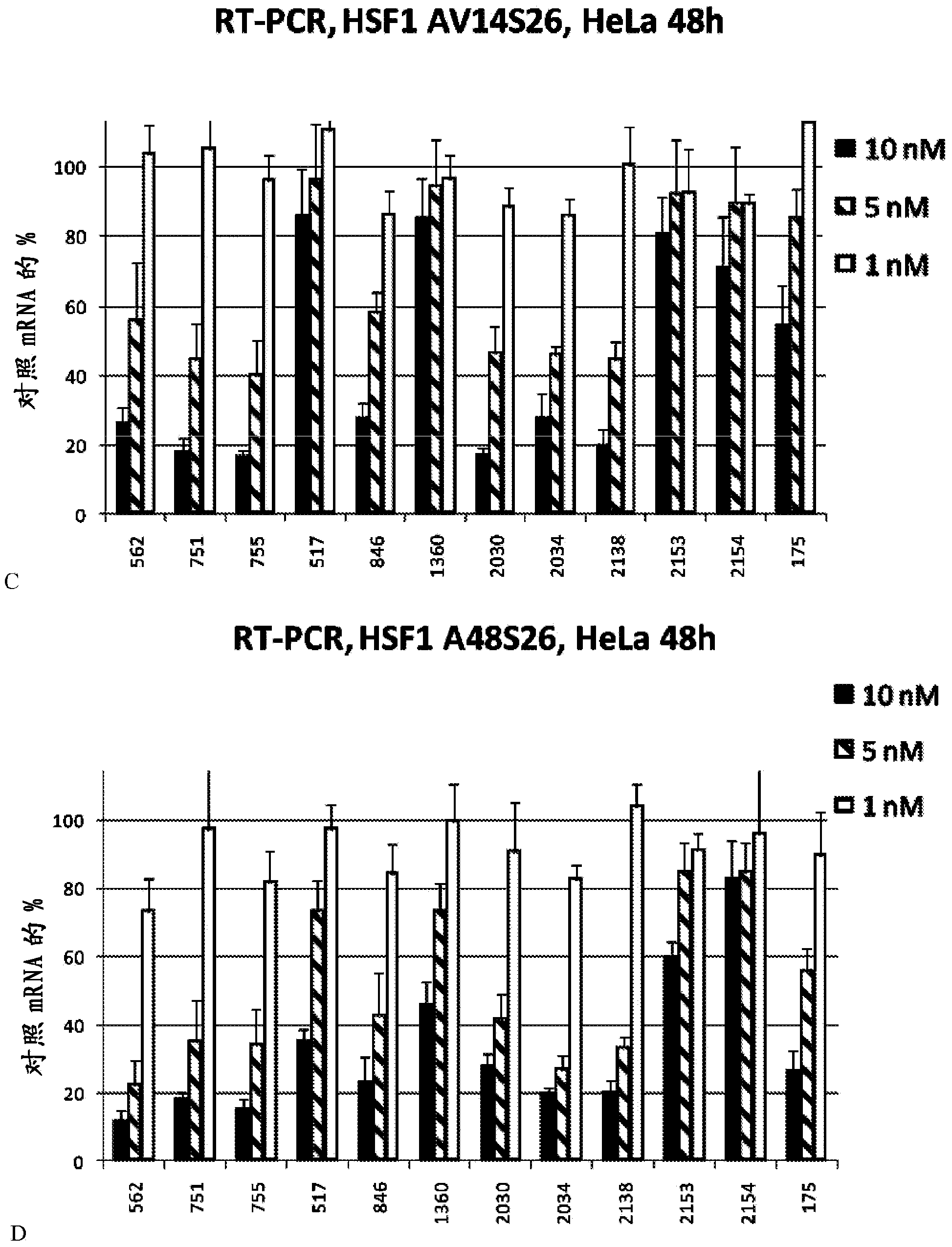
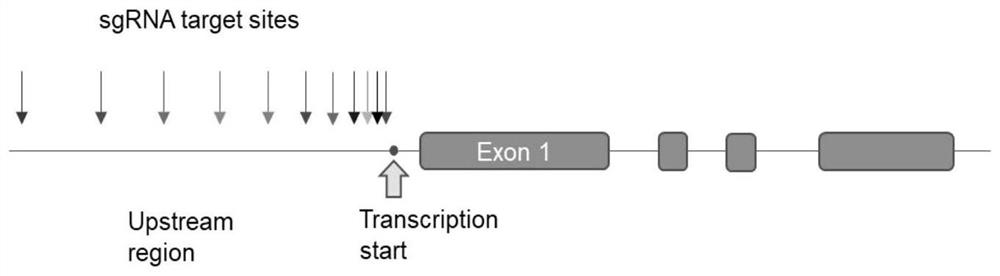
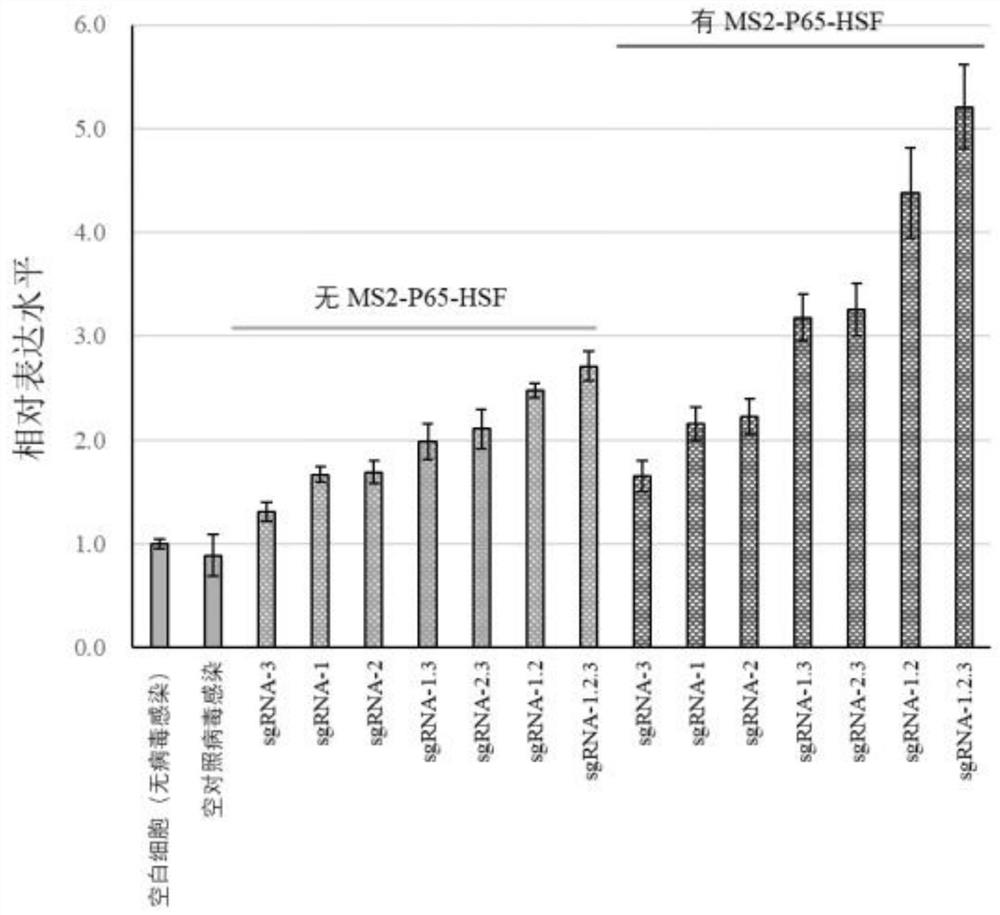
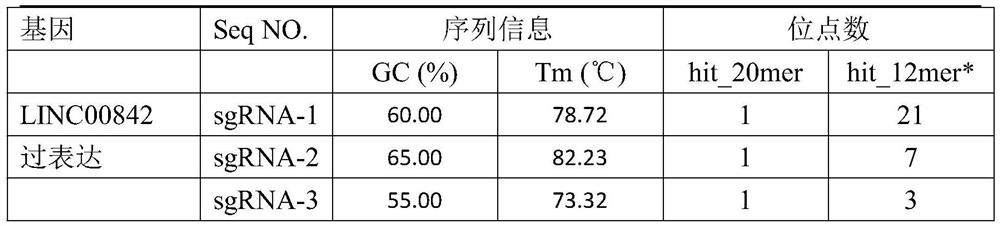
Patents
Literature
30 results about "HSF1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
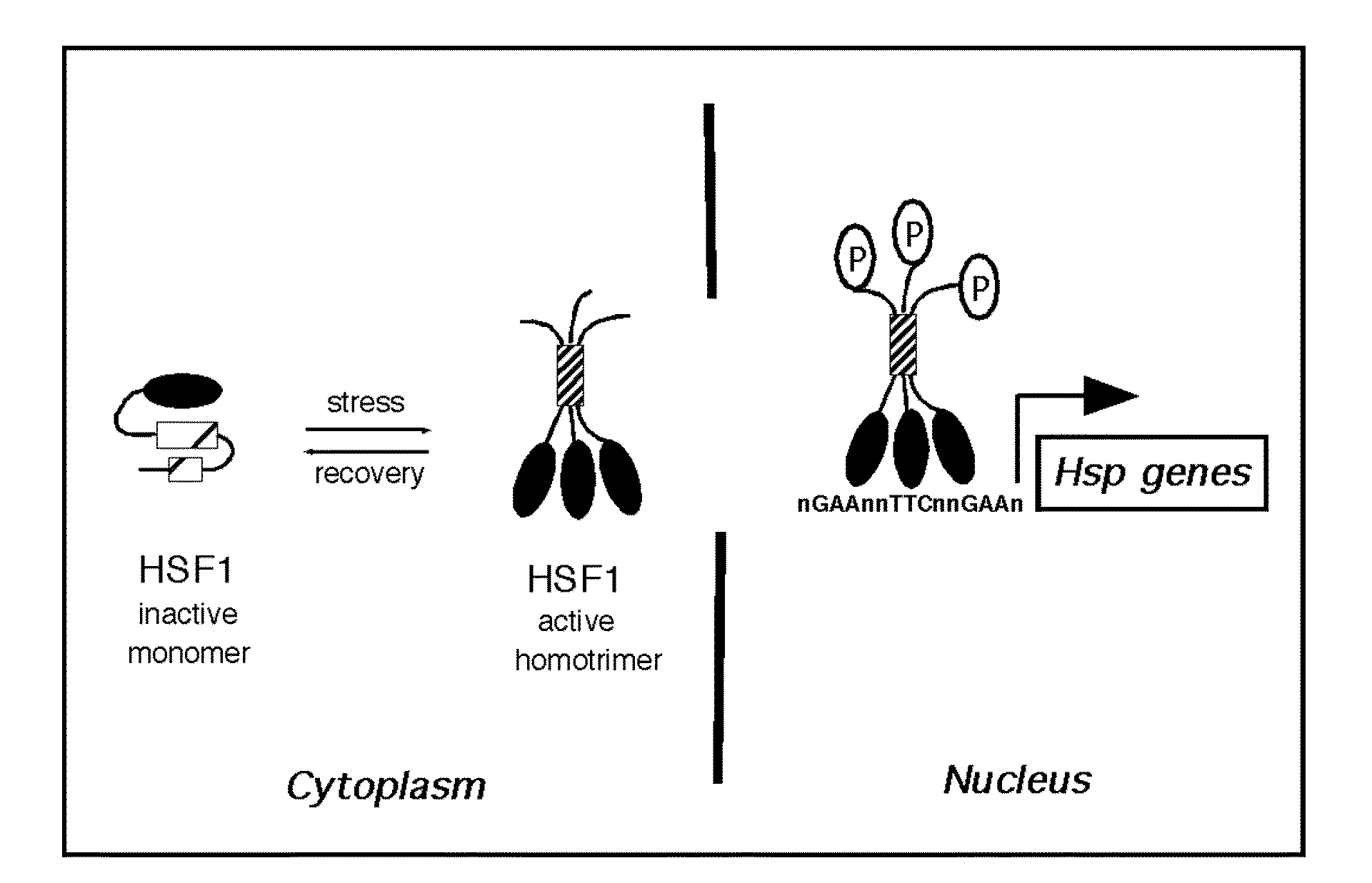
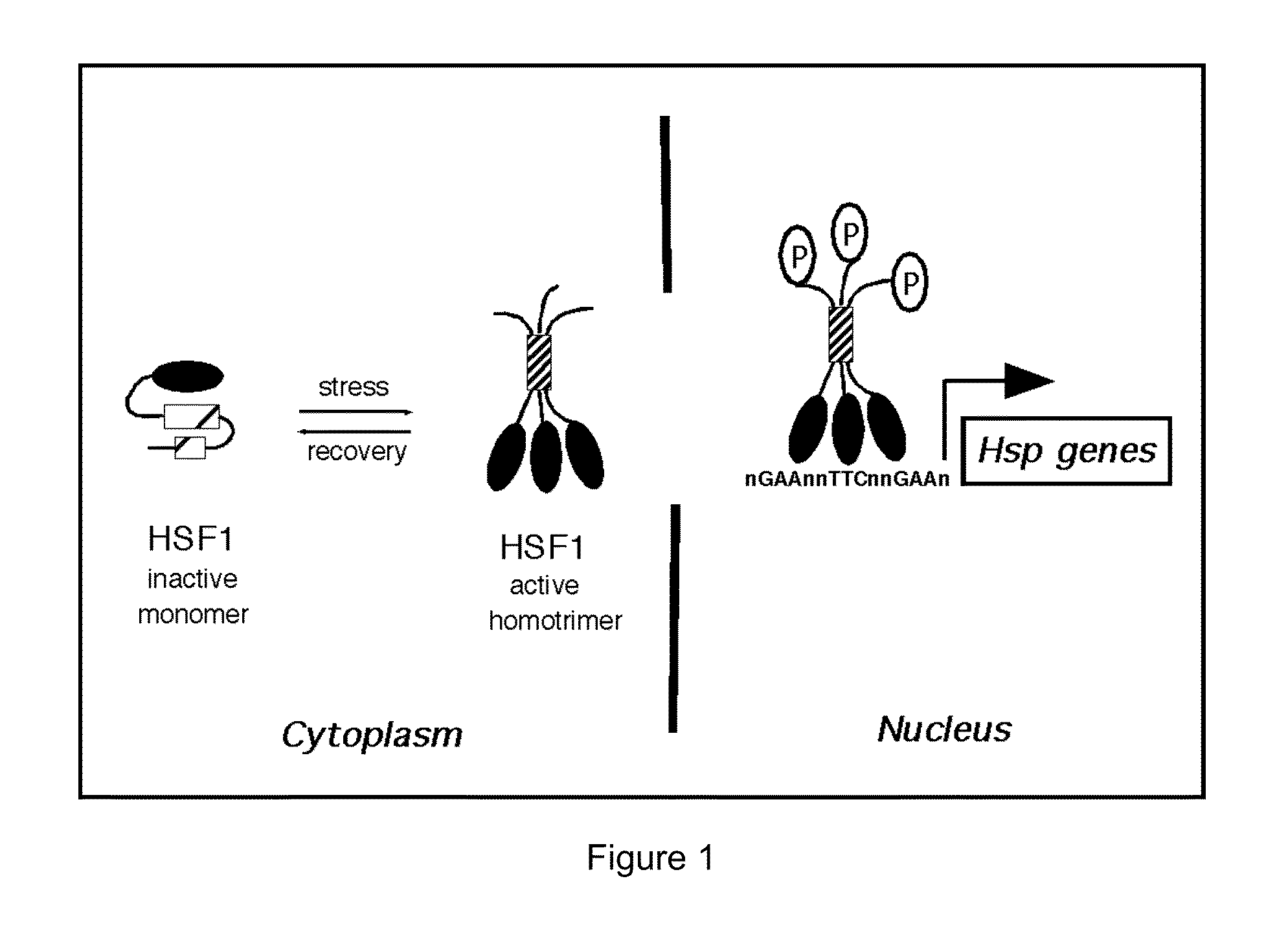
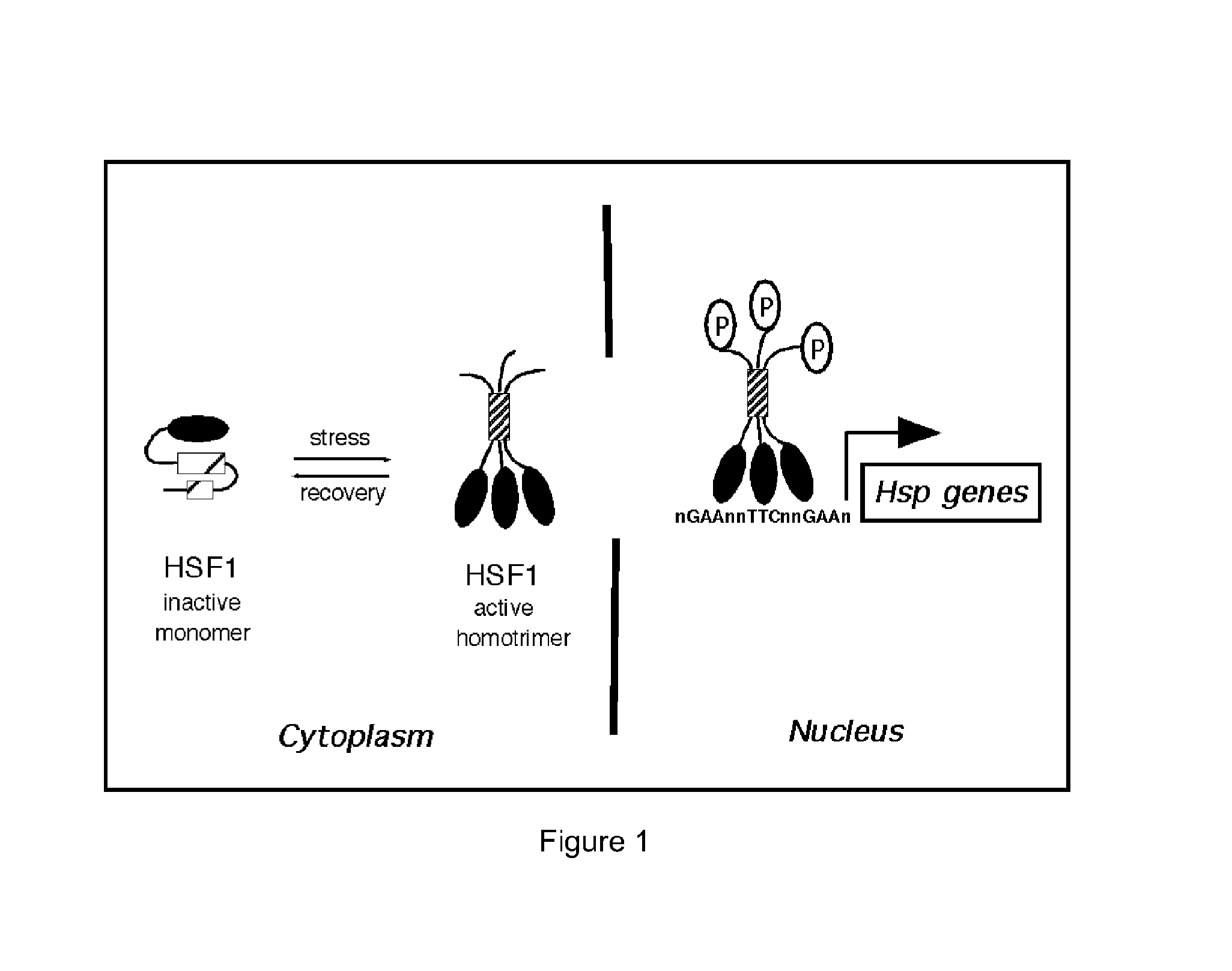
Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSF1 gene. HSF1 is highly conserved in eukaryotes and is the primary mediator of transcriptional responses to proteotoxic stress with important roles in non-stress regulation such as development and metabolism.
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
ActiveUS20110112073A1Improve intracellular quality controlImprove quality controlBiocideSenses disorderHeat Shock Transcription FactorPharmaceutical formulation
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Hsf1 as a marker in tumor prognosis and treatment
ActiveUS20140234858A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTreatment choicesNeoplasm diagnosis
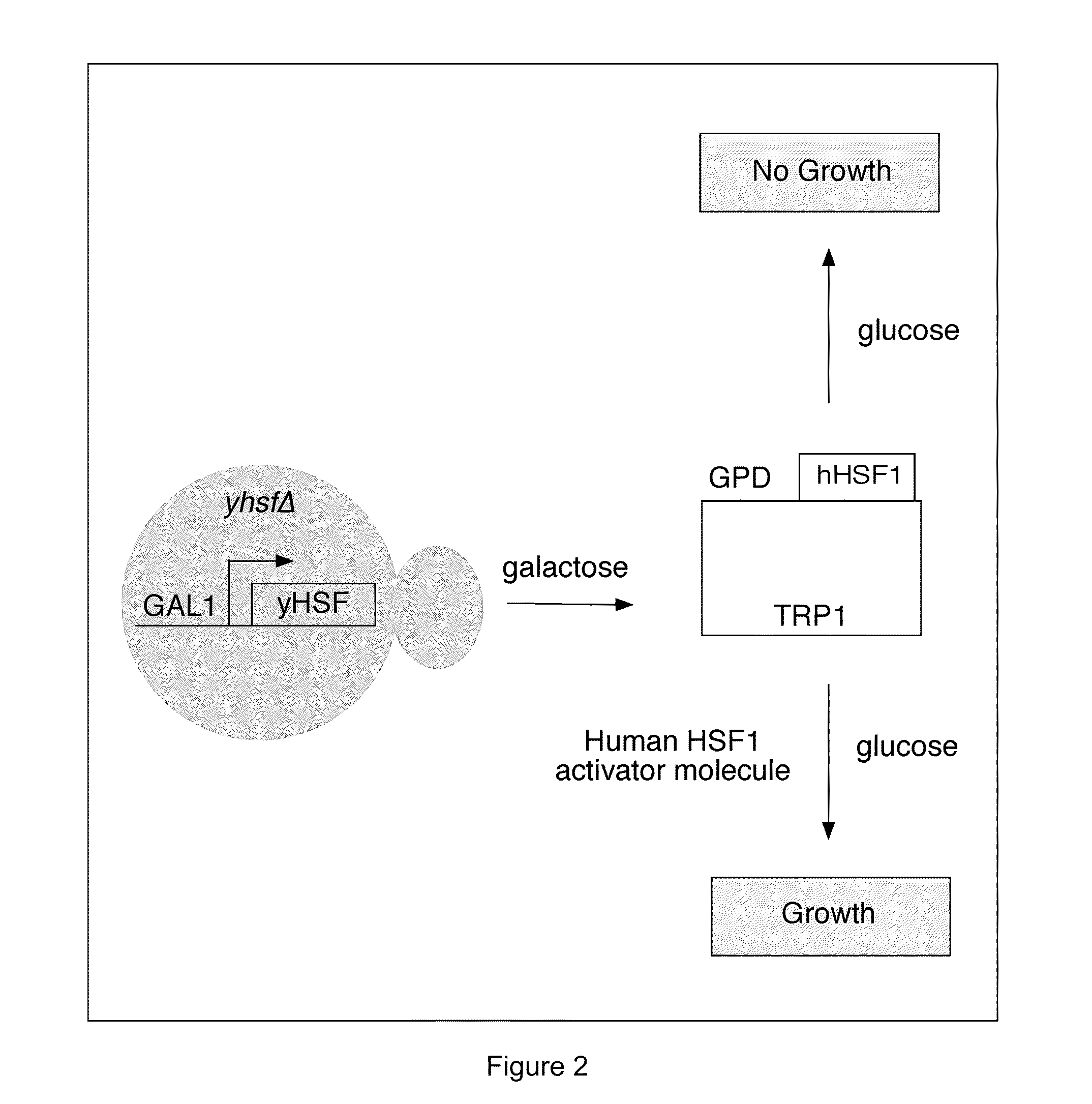
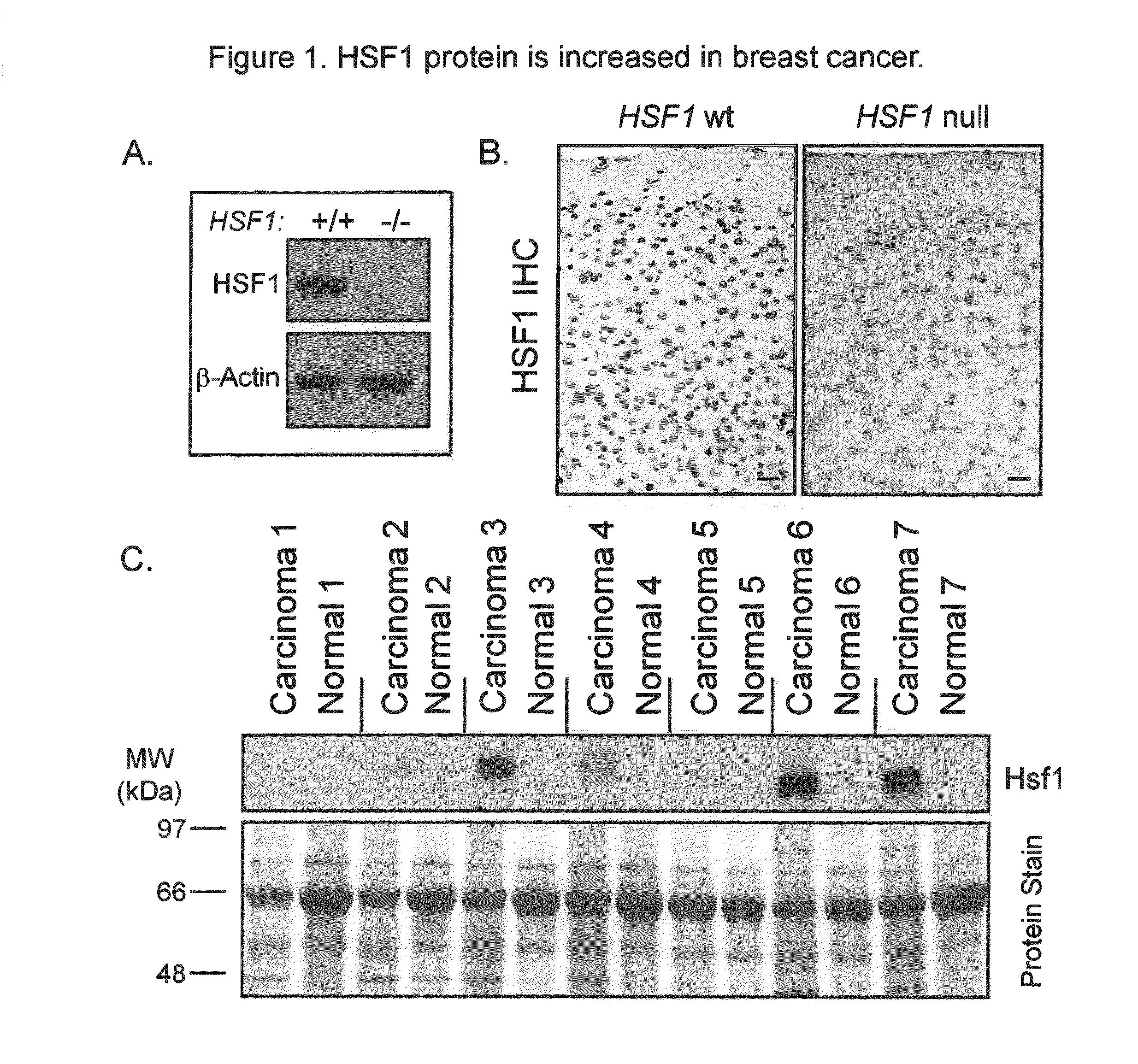
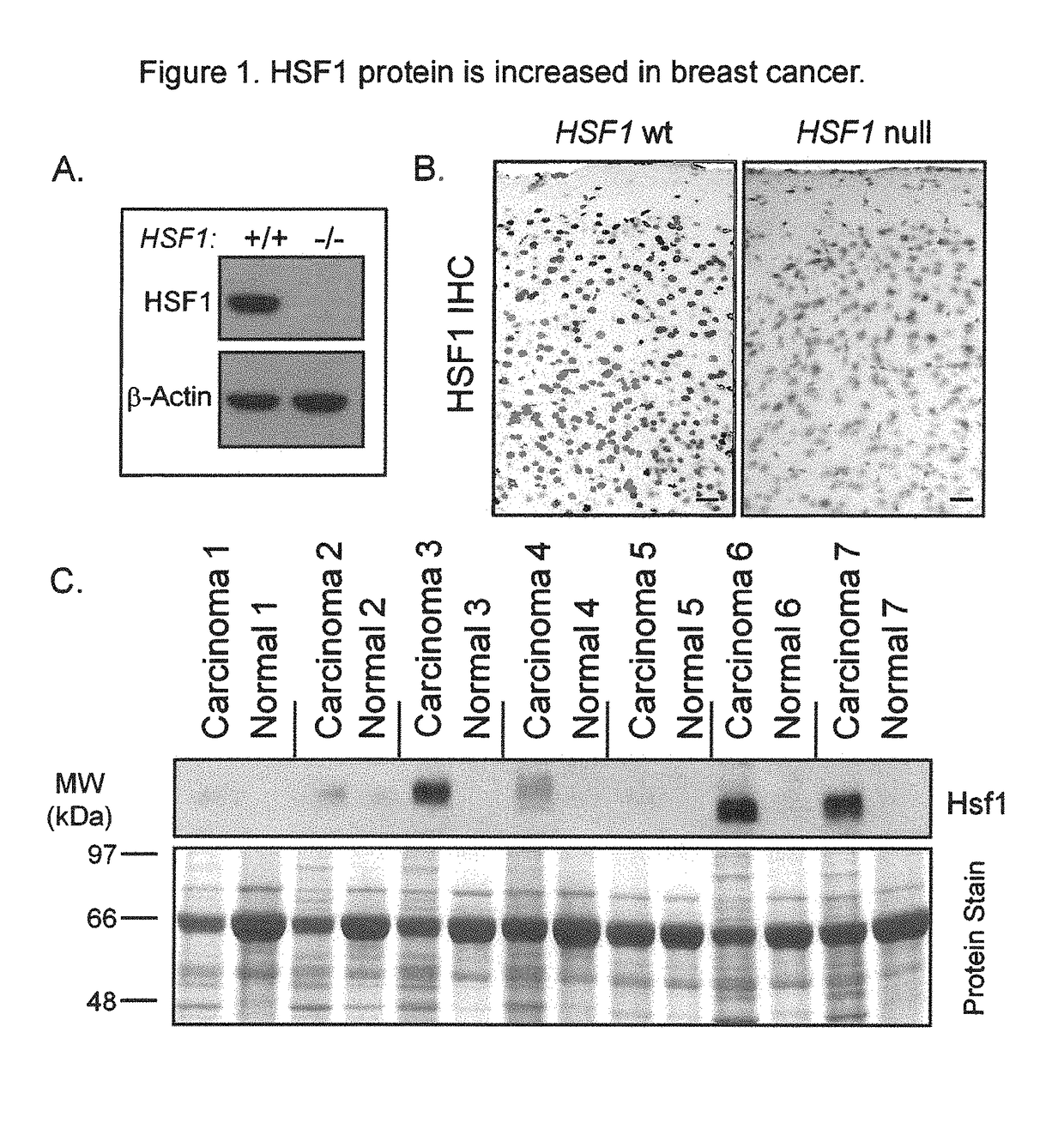
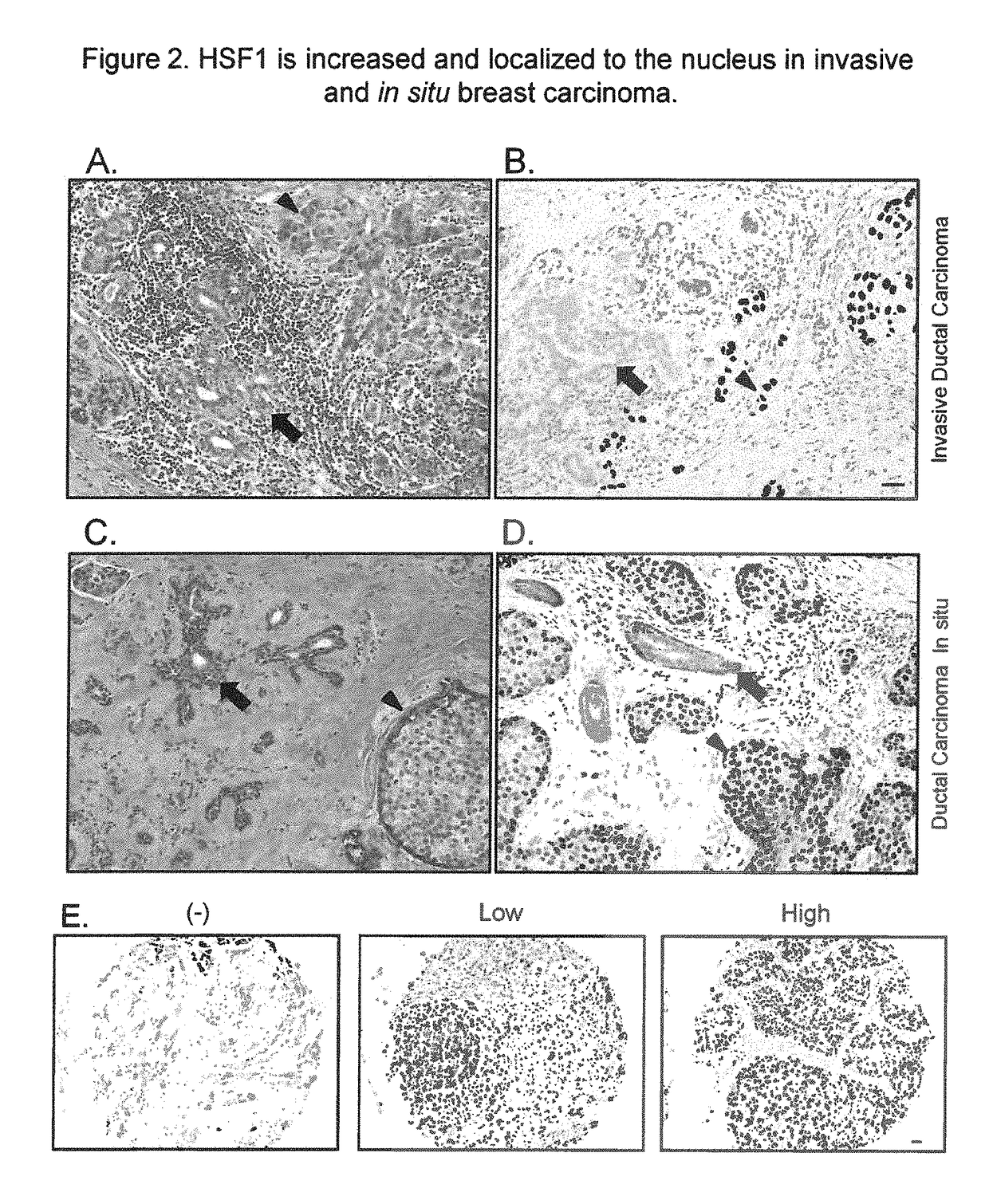
In some aspects, the invention relates to Heat Shock Protein-1 (HSF1) gene and HSF1 gene products. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of tumor diagnosis, prognosis, treatment-specific prediction, or treatment selection, the methods comprising assessing the level of HSF1 expression or HSF1 activation in a sample obtained from the tumor. In some aspects, the invention relates to the discovery that increased HSF1 expression and increased HSF1 activation correlate with poor outcome in cancer, e.g., breast cancer.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
Plant heat-resistant gene HSF1 and application thereof
The invention relates to a plant heat-resistant gene HSF1 and application thereof. A new plant heat-resistant gene is separated from brassica plants for the first time and can improve the heat-tolerant capacity of plants obviously. The invention also provides proteins of gene codes and a preparation method thereof, a carrier and a host cell containing the gene and a method for preparing transgenic plants carrying the gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for simultaneously activating transcriptional activity of multiple porcine endogenous stem cell factors by adopting tandem sgRNAs
ActiveCN110218741AImprove activation efficiencyIncrease transcriptional activityGenetically modified cellsFermentationHigh activityCytokine
The invention provides a method for simultaneously activating multiple porcine endogenous stem cell factors by adopting a tandem sgRNA strategy. Blasticidin and hygromycin drugs are adopted for screening and constructing a PK-15 cell line (PK-15-dCas9-MS2) capable of stably expressing dCAS-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1 first, sgRNAs capable of targeting promoters of the porcine stem cell factors Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc and miR-302 / 367 are designed and constructed separately, high-activity sgRNA screening is carried out on the cells, the five sgRNAs with the highest gene transcription activation efficiency are serially combined and constructed into an expression vector, and the expression vector is introduced into the PK-15-dCas9-MS2 cells to simultaneously activate the transcriptional activity ofporcine OSKM and miR-302 / 367. The method has a potential application value in induced generation of porcine iPSC.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Recombinant pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN113046256AEnhance biofilm-forming abilitySolve the problem that the film-forming ability is weak and cannot be used for continuous immobilized fermentationFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisBiofilm
The invention discloses a recombinant pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium is constructed by over-expressing a transcription inhibition factor and an activating factor HSF1 in pichia pastoris. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on a pichia pastoris genome to obtain an HSF1 gene segment; (2) cloning the HSF1 gene segment to an expression plasmid to obtain a recombinant plasmid; and (3) introducing the linearized recombinant plasmid into pichia pastoris, and screening to obtain the pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium. The pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium can effectively improve the biofilm forming ability of the pichia pastoris, so that the enzyme activity of the recombinant pichia pastoris under a single immobilized fermentation condition is improved by 28.3% compared with that of a free fermentation starting bacterium, and the fermentation period is shortened by 36.6%. The recombinant bacteria can be stably and continuously subjected to at least seven batches of immobilized fermentation enzyme production, and after seven batches of immobilized fermentation, the enzyme activity of the fermentation enzyme production of the recombinant bacteria is about 7 times higher than that of starting bacteria.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
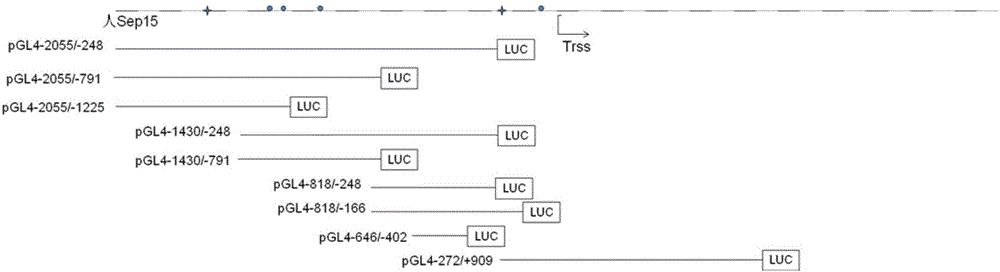
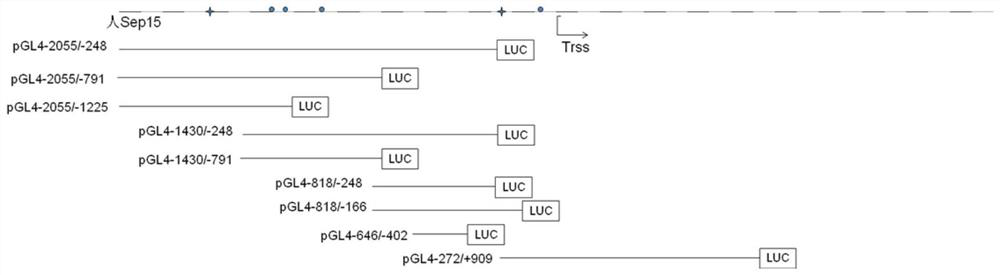
Application of heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating expression of 15kDa selenoprotein
The invention discloses an application of a heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating expression of a 15kDa selenoprotein. The application provided by the invention is specifically any one of the applications of the heat shock transcription factor 1: (a1) promoting expression of a Sep15 protein in a target cell; (a2) promoting transcription of a Sep15 gene; and (a3) enhancing the activity of a Sep15 promoter in the target cell. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a transcription factor HSF1 can be combined with the Sep15 promoter to adjust transcription of the Sep15 gene and accelerate expression of the Sep15 protein. Under a heat shock and fever of a physiological status, the transcription factor HSF1 can start transcription of Sep15 and improve expression of Sep 15 so as to participate the physiological process and help the protein being corrected folded or help the protein being unfolded and delivered to other proteins to help the proteins to be folded correctly. Under endoplasmic reticulum stress, the HSF1 also can promote expression of Sep 15 to participate protein quality control of endoplasmic reticulum so as to further promote cell survival. The application disclosed by the invention is of important significance in preventing and / or treating endoplasmic reticulum stress related diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
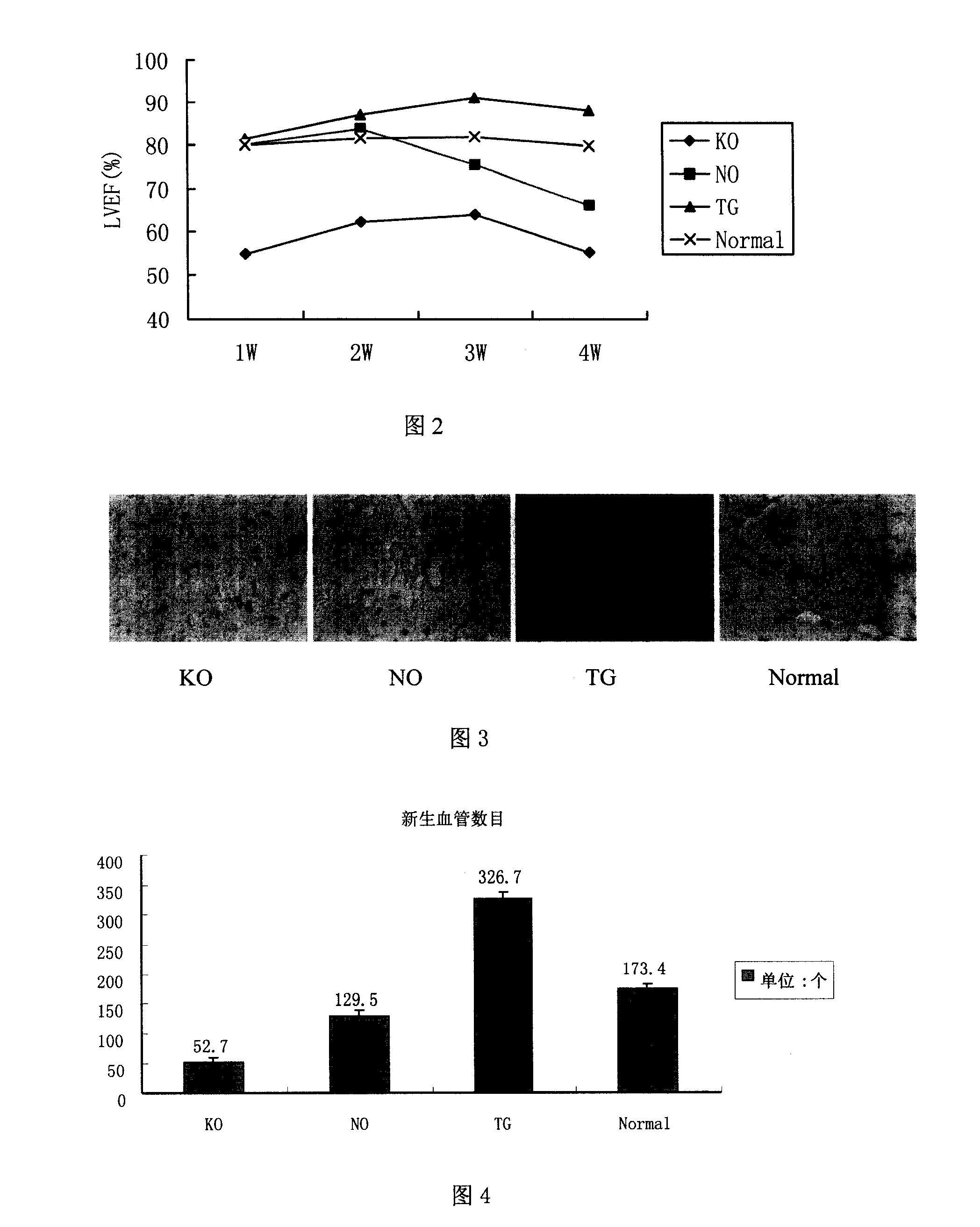
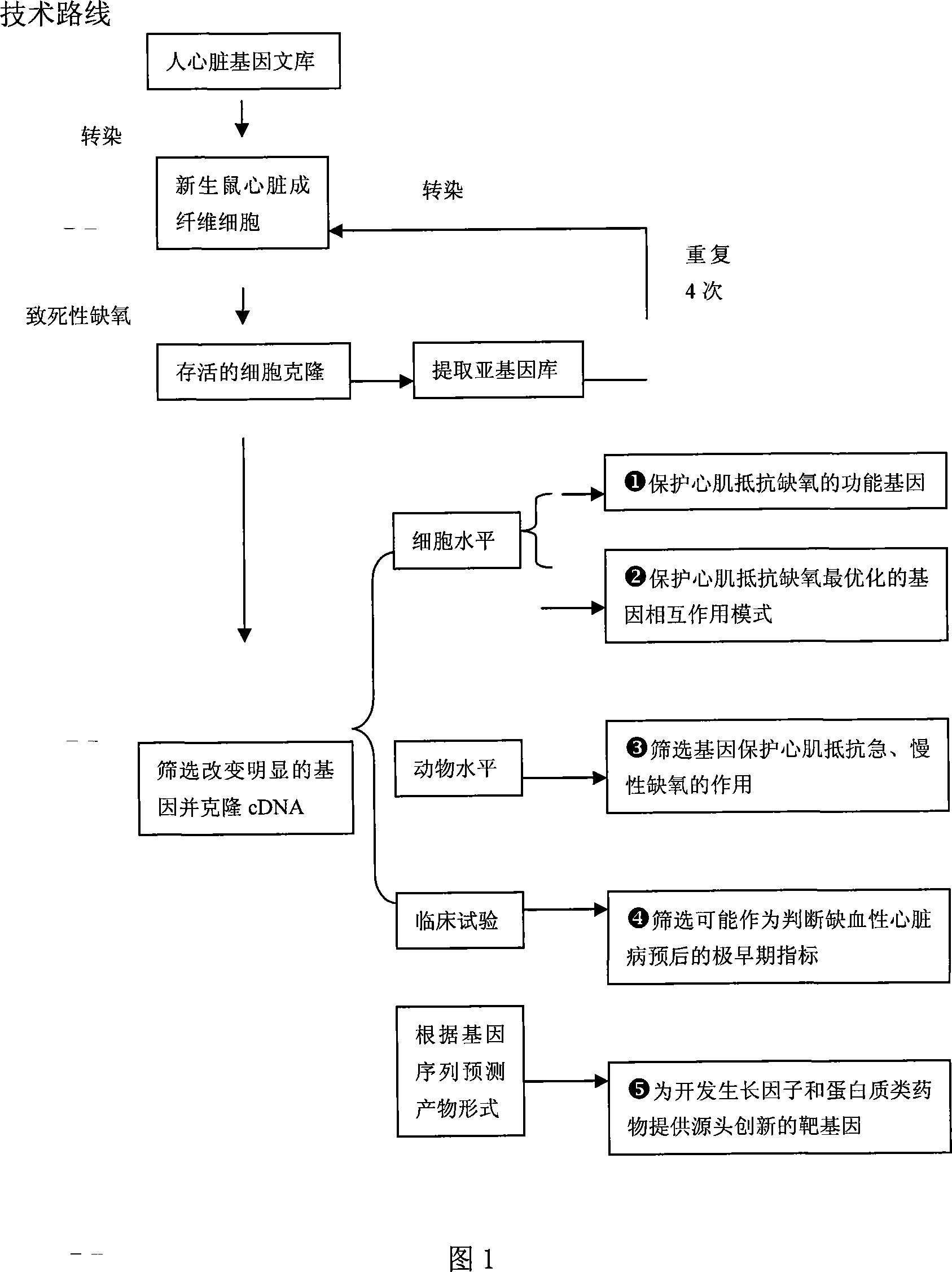
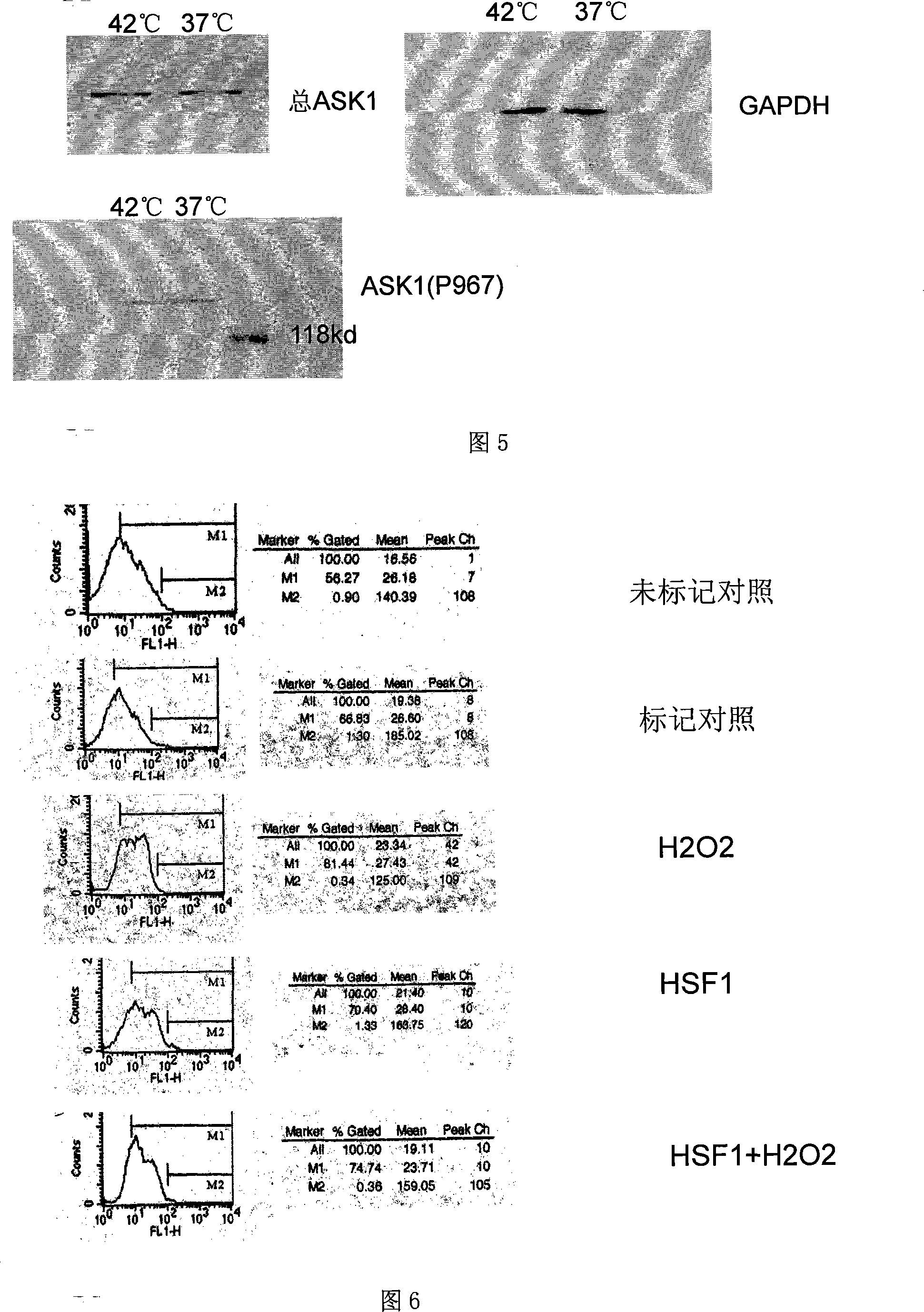
Human myocardium protecting gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101200721APurposefulWith precisionGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringHSF1Organism
The present invention belongs to the biotechnological field and relates to a human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor (HSF1) and a sieving method and a purpose thereof. The present invention adopts the method of ''death trap'' that the gene which resists myocardial cell death is sieved from human cardiac gene, and the human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor 1 is cloned from the obtained gene. The result of transfection cell and animal experiment shows that the obtained human myocardial protection gene has the function of resisting cell death and also has the function of resisting ischemia, protecting myocardial cell and preventing and remedying the heart failure occurrence and development inside the heart of a living organism. The present invention can prepare for the medicine for remedying the ischemic heart disease and preventing the cardiac insufficiency and provides a novel target gene for the further function research and the gene engineering medicine development, which has important meaning for the early prevention and treatment of the heart failure and the research and the development of the related medicines and measures.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Compositions and methods relating to heat shock transcription factor activating compounds and targets thereof
InactiveUS20130267543A1Improve quality controlBiocideSenses disorderHeat Shock Transcription FactorHSF1
Owner:CHAPERONE THERAPEUTICS +1
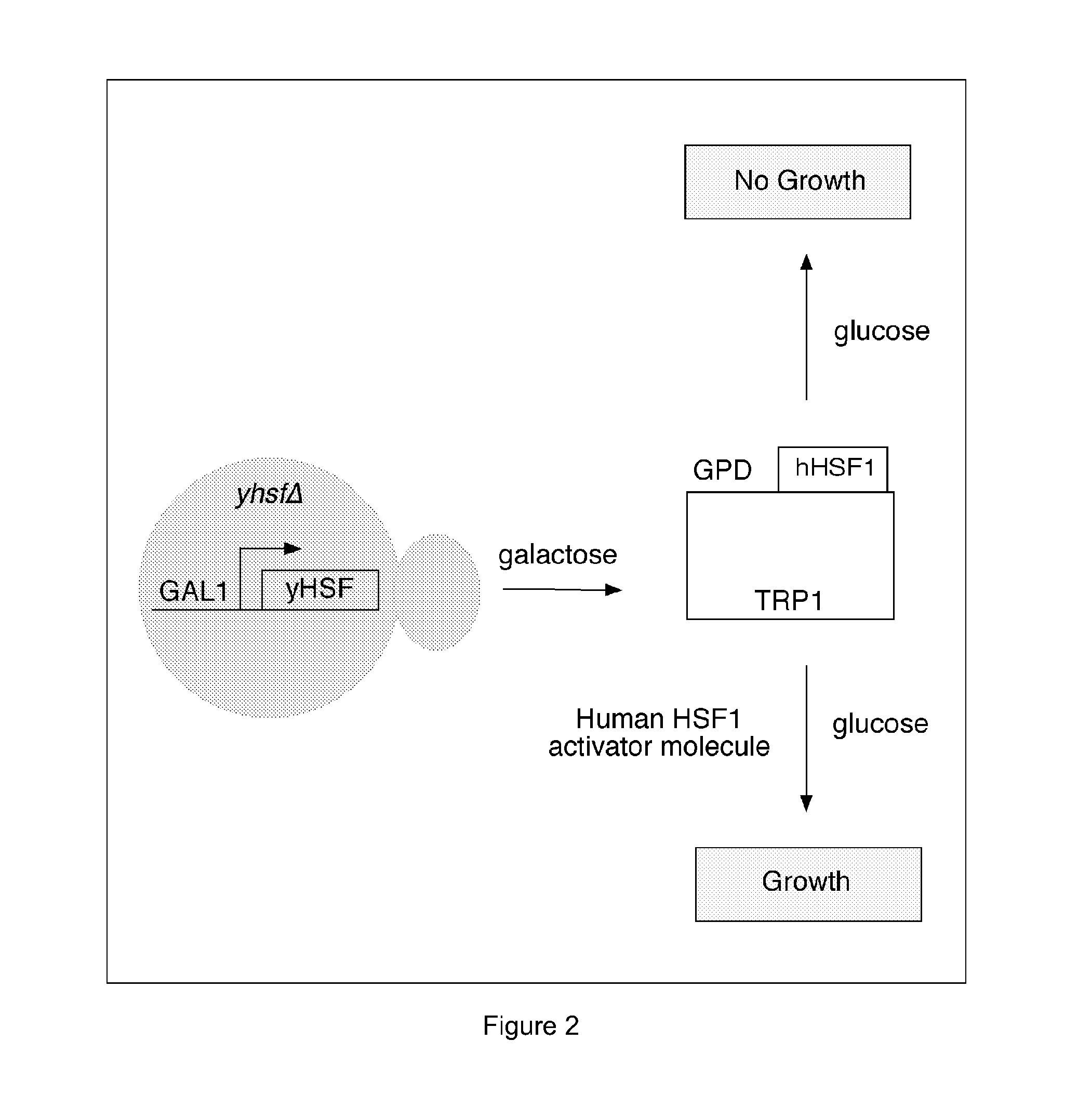
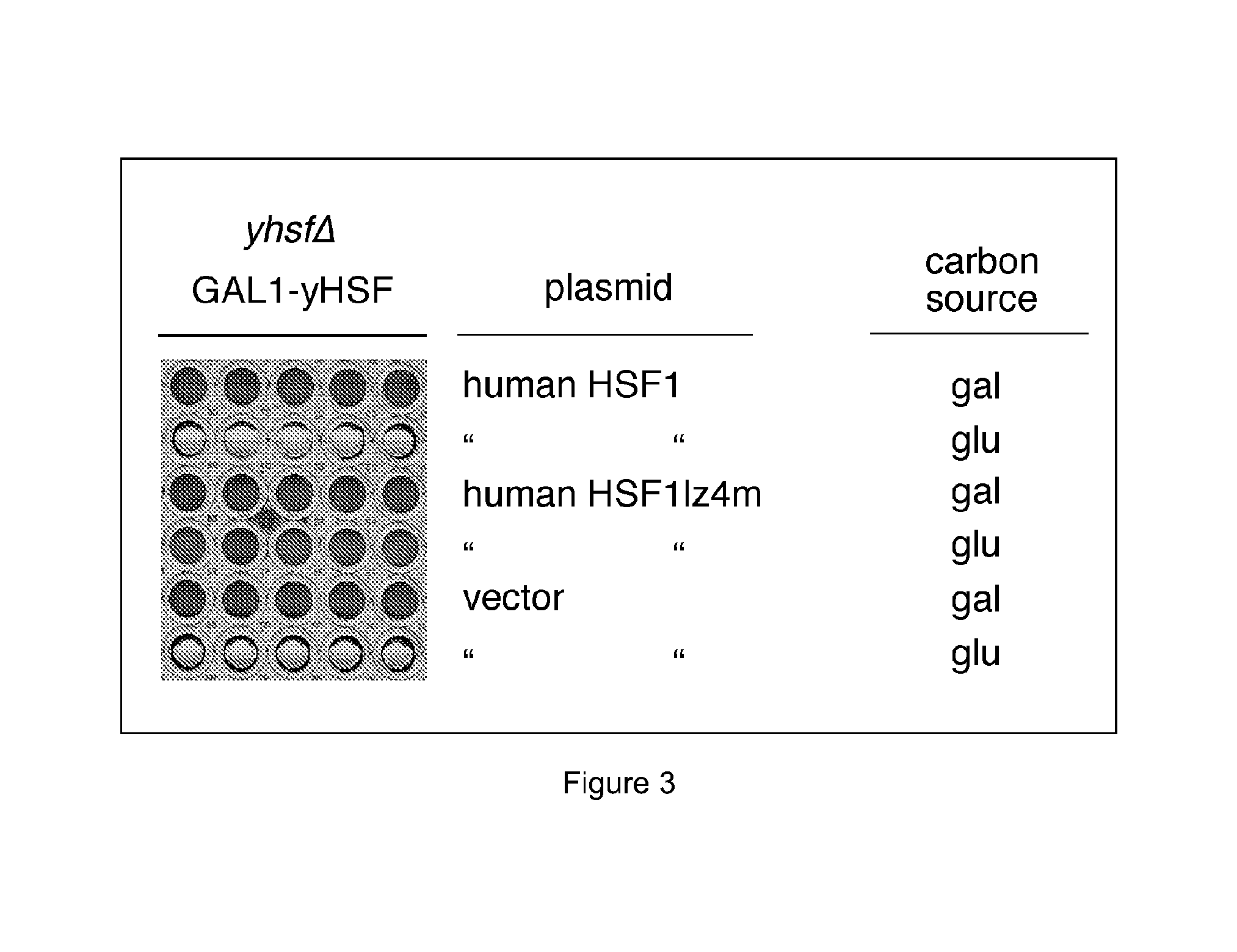
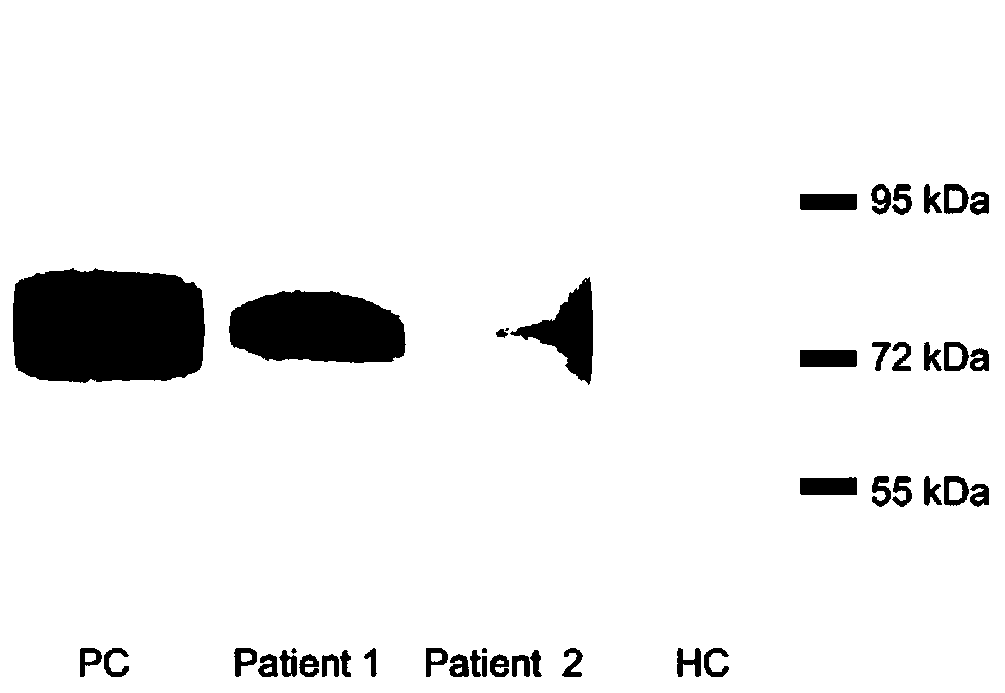
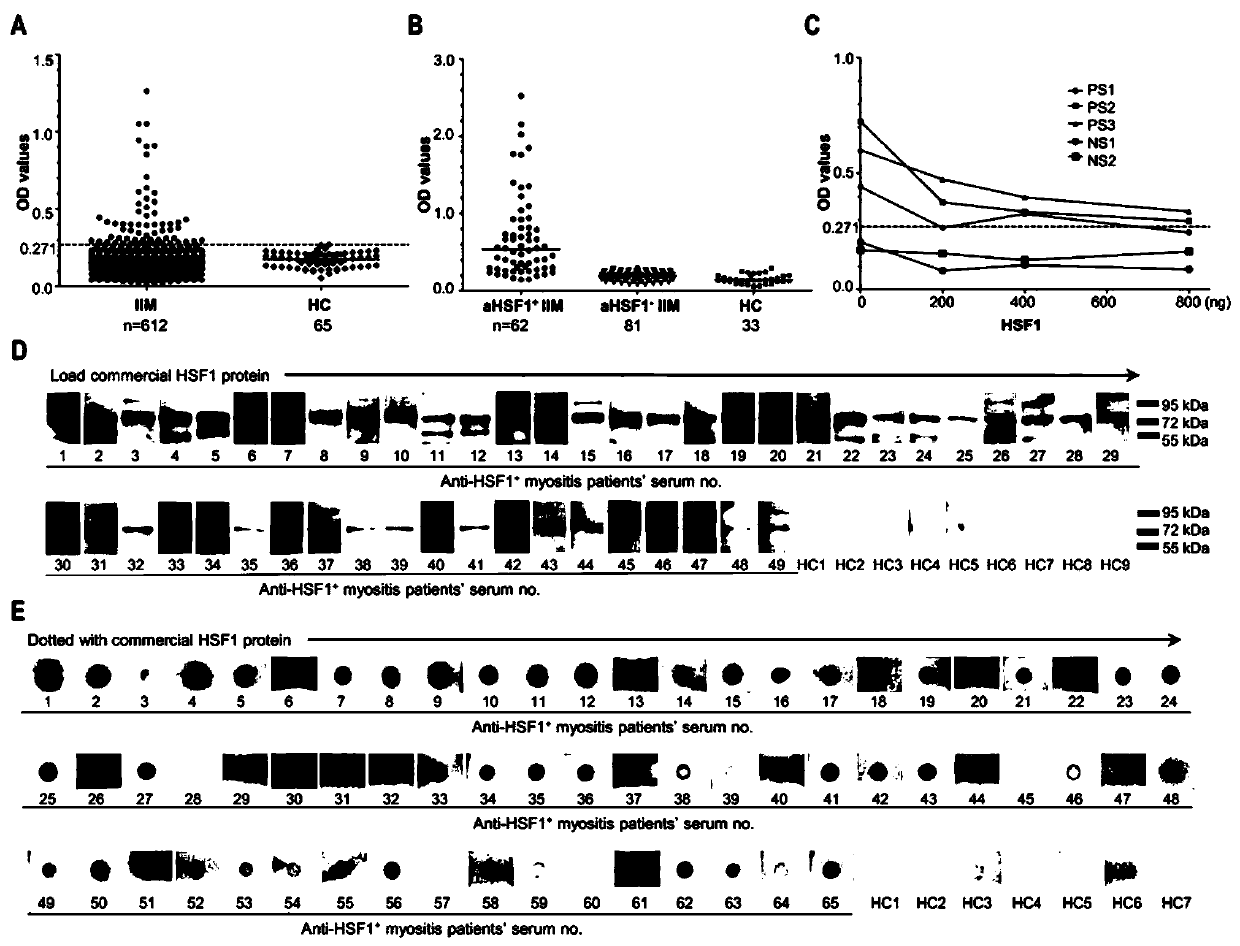
Molecular marker for diagnosing idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and application thereof
The invention relates to a molecular marker for diagnosing idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and an application thereof. The molecular marker is an autologous heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) antibody in a serum. The antibody is IgG. The idiopathic inflammatory myopathy is polymyositis (PM) or dermatomyositis (DM). The diagnosis is to distinguish the idiopathic inflammatory myopathy from a healthy population or to predict a disease progress of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM).
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
Methods of treating or preventing insulin resistance and associated diseases and conditions
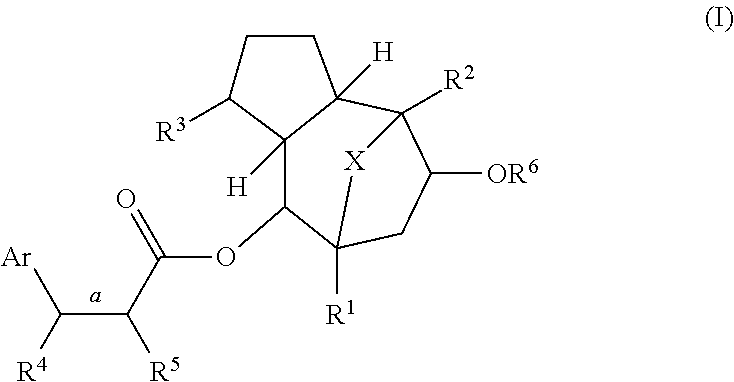
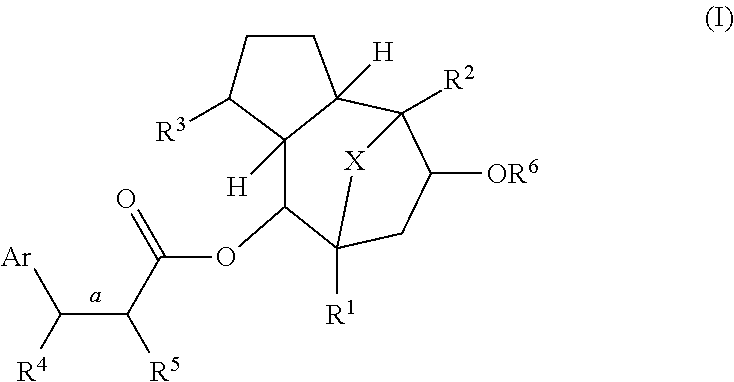
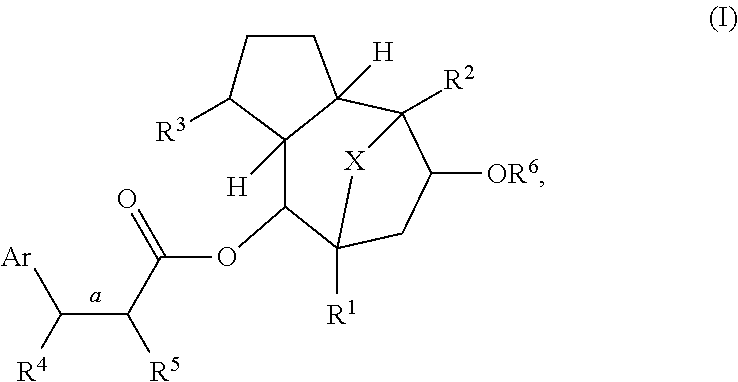
Disclosed are methods of treating an animal for insulin resistance and associated diseases or conditions, activating the transcriptional activity of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), or inducing the expression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) in an animal in need thereof, wherein the methods involve administering an effective amount of one or more compounds of formula (I) or an epimer thereof, wherein Ar, and R1-R6 are described herein. Examples of diseases or conditions associated with insulin resistance include diabetes, obesity, inflammation, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary disease, arteriosclerosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, reproductive abnormality in a female, and growth abnormality.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
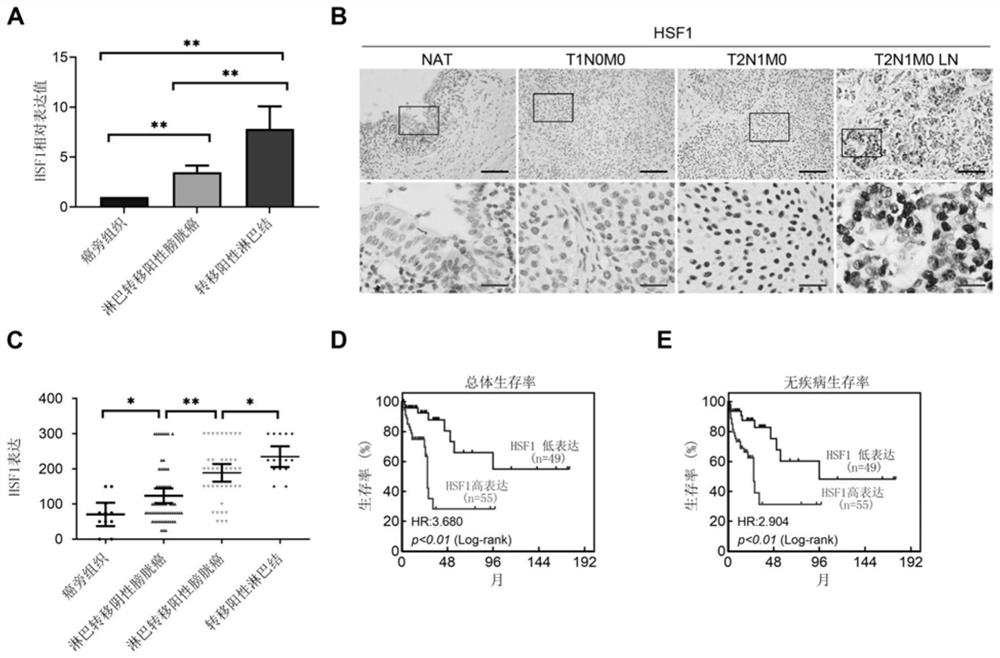
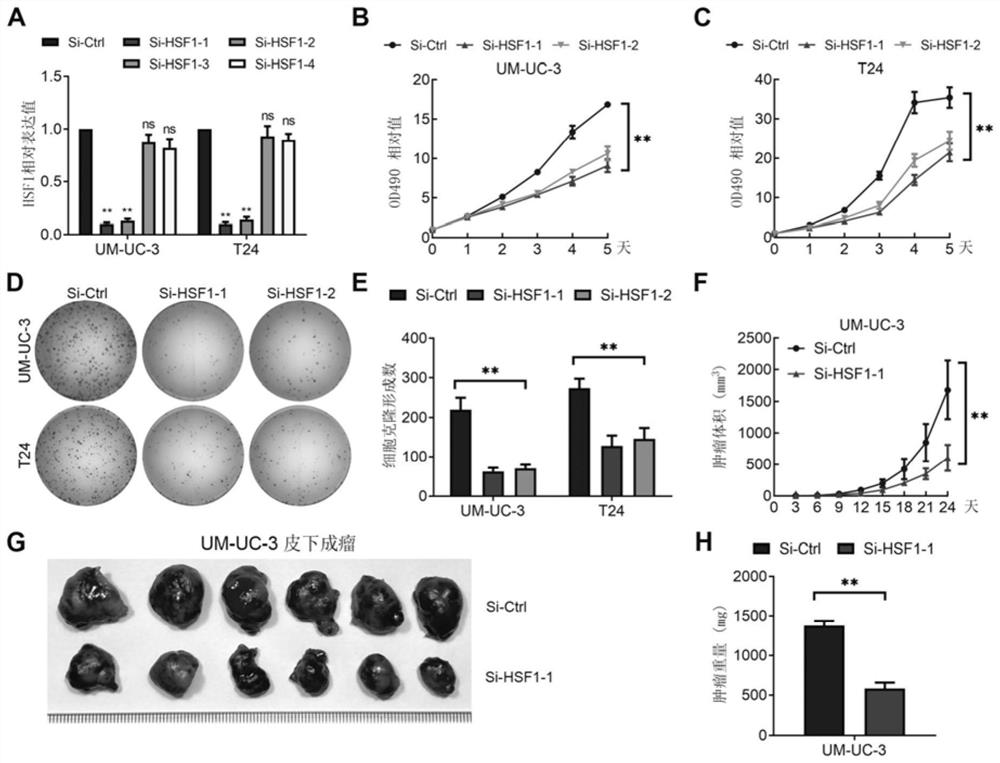
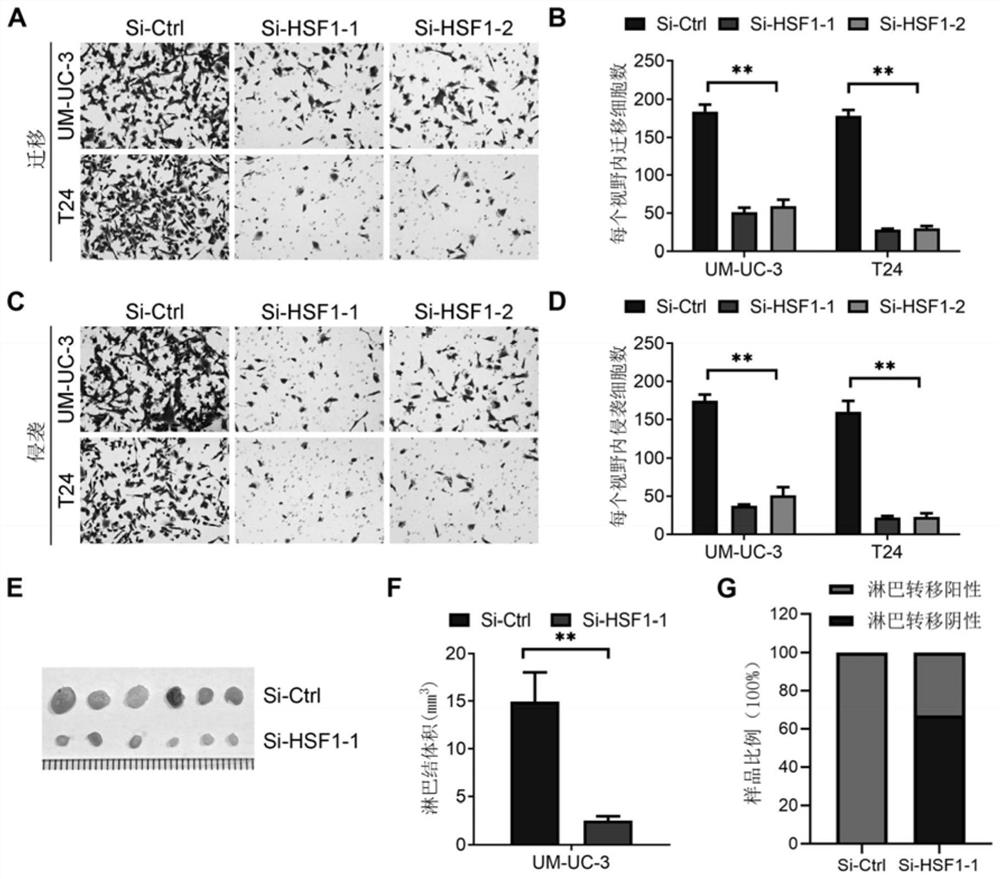
Molecular marker HSF1 for diagnosing and treating bladder cancer and application thereof
PendingCN113862361APrevent proliferationInhibit lymphatic metastasisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSurvival prognosisBladder cancer cell
The invention provides a molecular marker HSF1 for diagnosing and treating bladder cancer and an application thereof. Comparison of gene expression results in a bladder cancer clinical specimen shows that HSF1 is highly expressed in bladder cancer tissue with positive lymphatic metastasis, and negatively correlated with overall survival prognosis. The molecular marker can be used as a marker to indicate lymphatic metastasis in bladder cancer, and as an independent indicator to predict survival prognosis of a patient. In-vivo and in-vitro function experiments of bladder cancer cells show the silencing HSF1 can inhibit proliferation of bladder cancer cells and lymphatic metastasis. The invention discovers that HSF1 is an important carcinogenic factor of bladder cancer for the first time, and the HSF1 can be used as a molecular marker for diagnosing bladder cancer and judging prognosis, and as a new target for treating bladder cancer.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Small molecule peptides in hd therapeutic drugs and their application
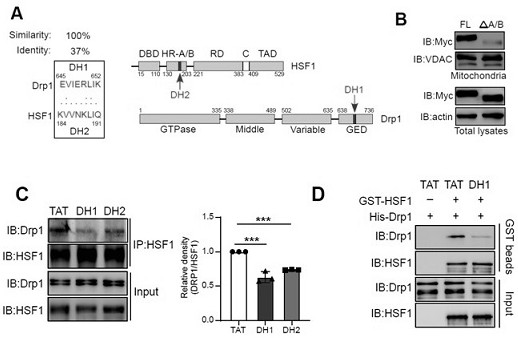
ActiveCN113087783BChange in normal functionNo cytotoxicity was foundNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeurophysinsMitochondrial translocation
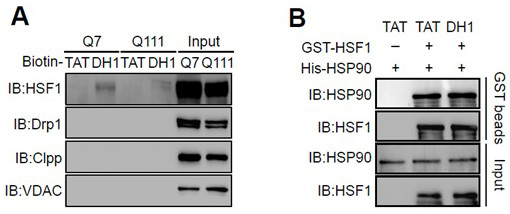
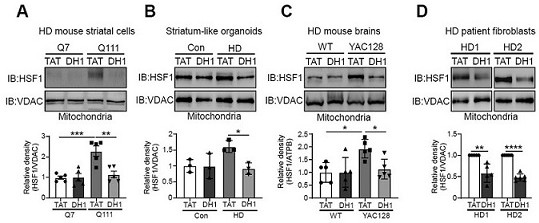
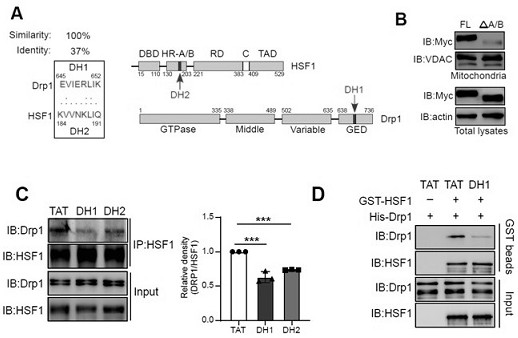
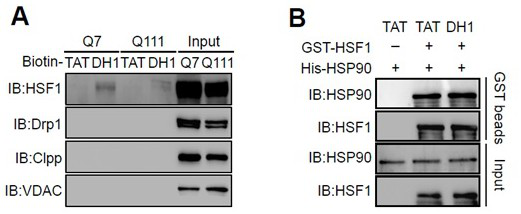
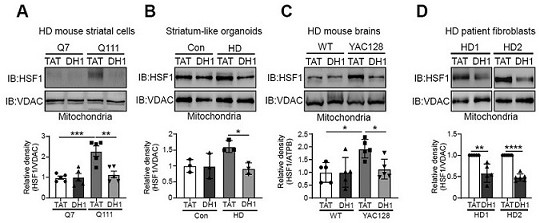
The present invention relates to a small molecule polypeptide in HD treatment medicine and application thereof, the amino acid sequence of the small molecule polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention also provides the application of the small molecule polypeptide. The present invention designs a small molecule polypeptide DH1 through the research on the translocation mechanism and function of HSF1. The polypeptide inhibits the mitochondrial translocation of HSF1, weakens the fragmentation of mitochondria, increases the expression of mitochondrial DNA, and then achieves the purpose of protecting neurons and improving the disease process of HD, and provides a new target for HD treatment.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
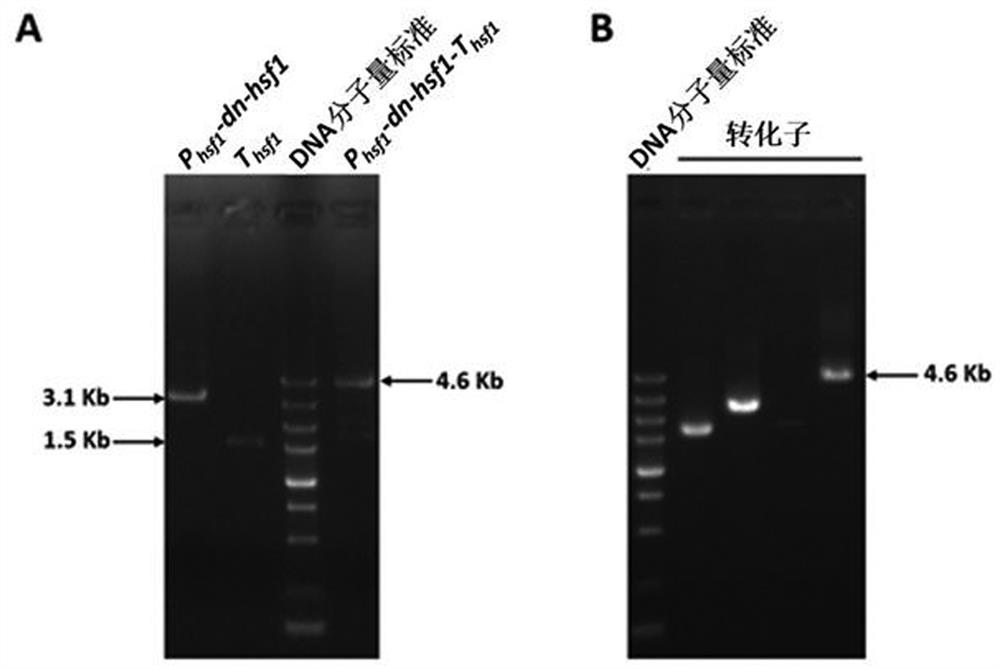
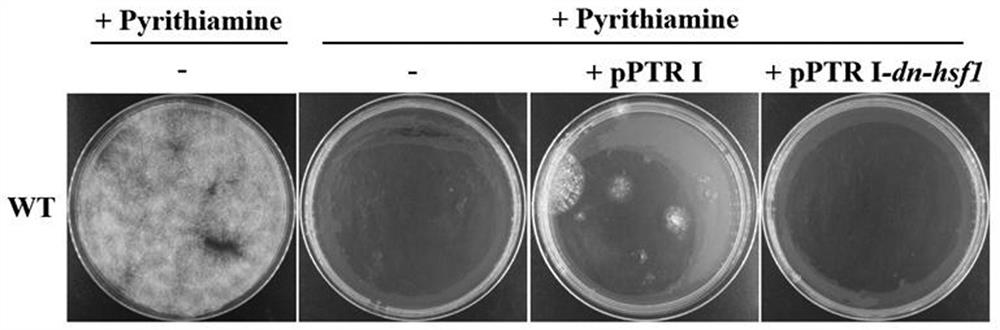
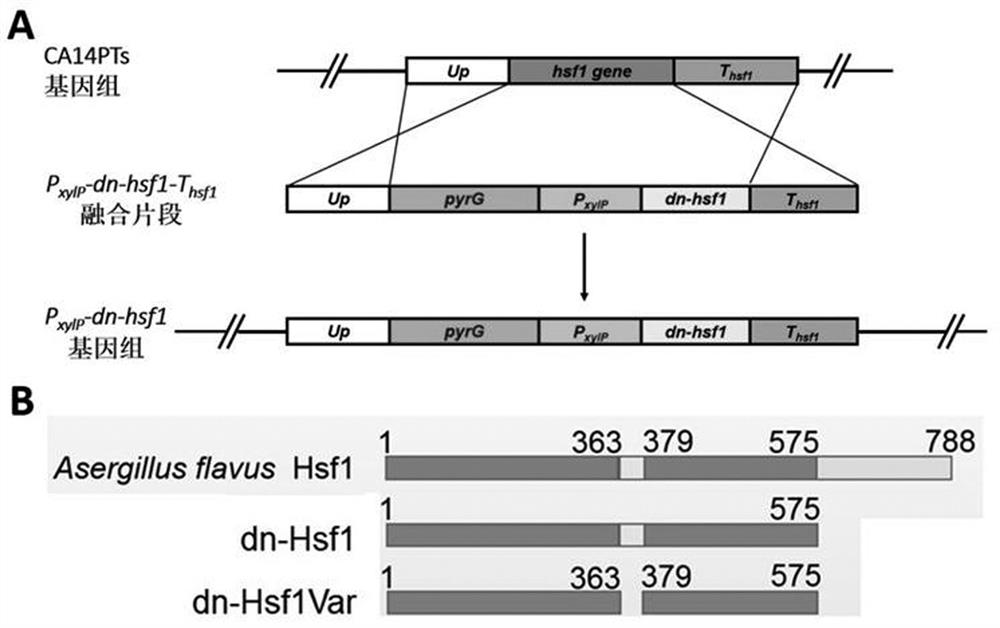
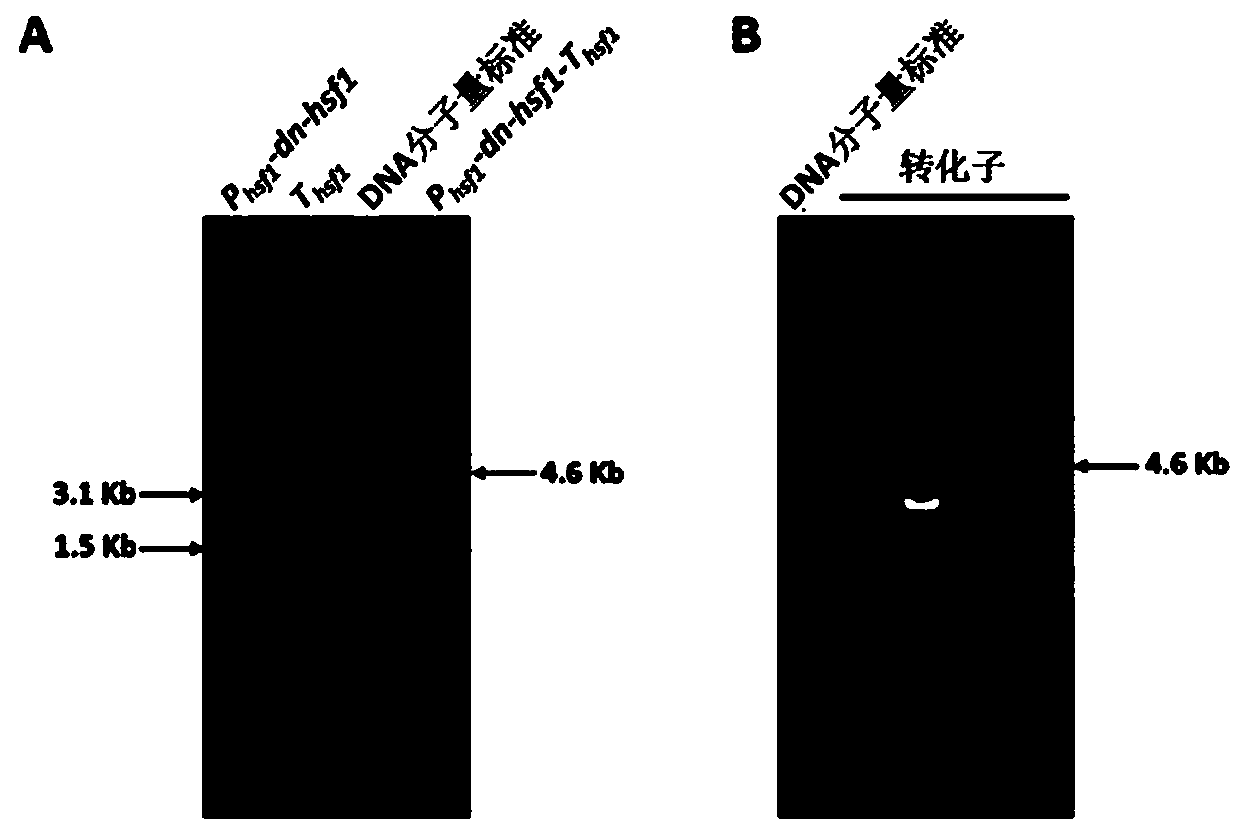
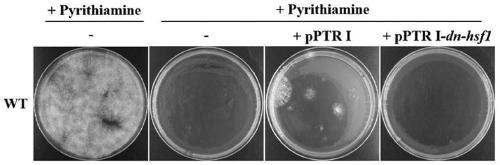
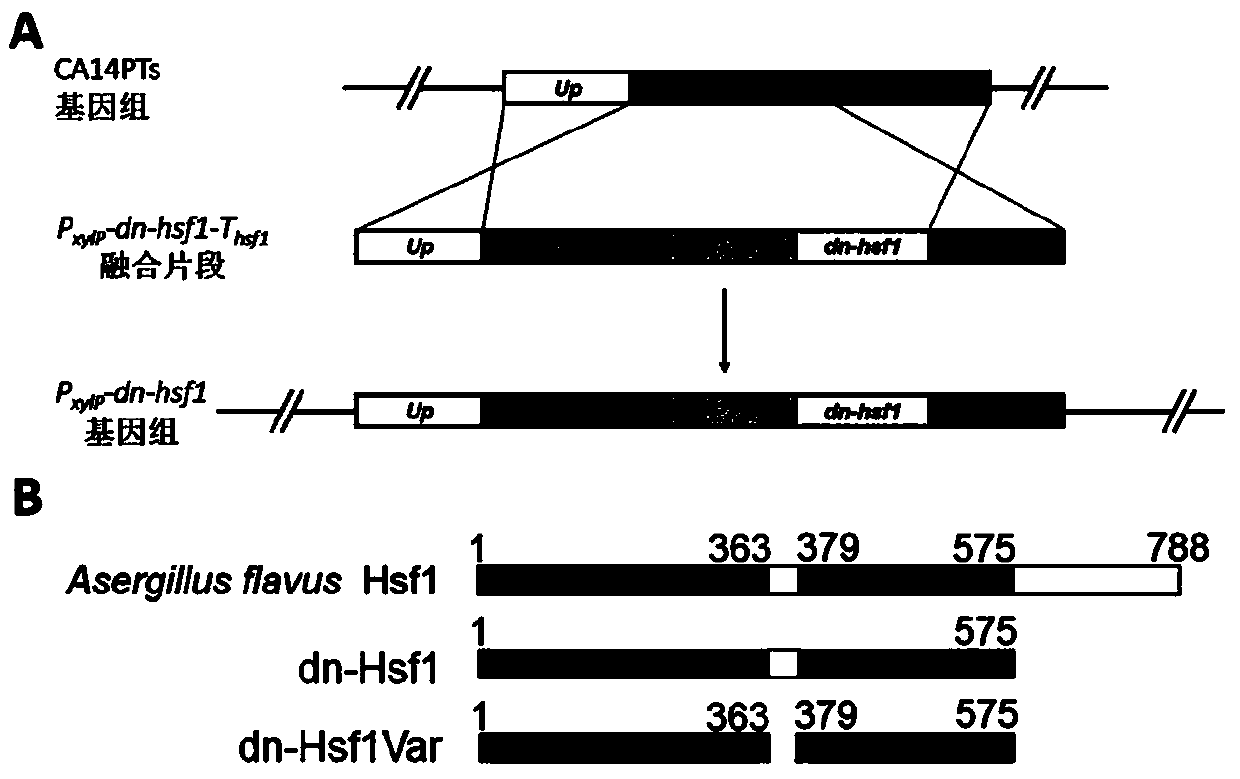
A dominant negative effect mutant of heat shock transcription factor 1 and its application
ActiveCN111087454BGrowth inhibitionLow homologyFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideAspergillus flavus
The invention discloses a heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 and its application, belonging to the field of biotechnology. Human and A. flavus ( Aspergillus flavus ) in the heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein, and a total of 213 amino acid residues from the 576th to the 788th position of the C-terminal of the Aspergillus flavus Hsf1 protein were deleted to obtain the heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative mutant dn in Aspergillus flavus The amino acid sequence of the -Hsf1 protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the coding nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The dominant-negative mutant dn-Hsf1 can inhibit the function of normal Hsf1 in fungi, thereby inhibiting the growth of fungi, and is used in the prevention and control of fungal pollution.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
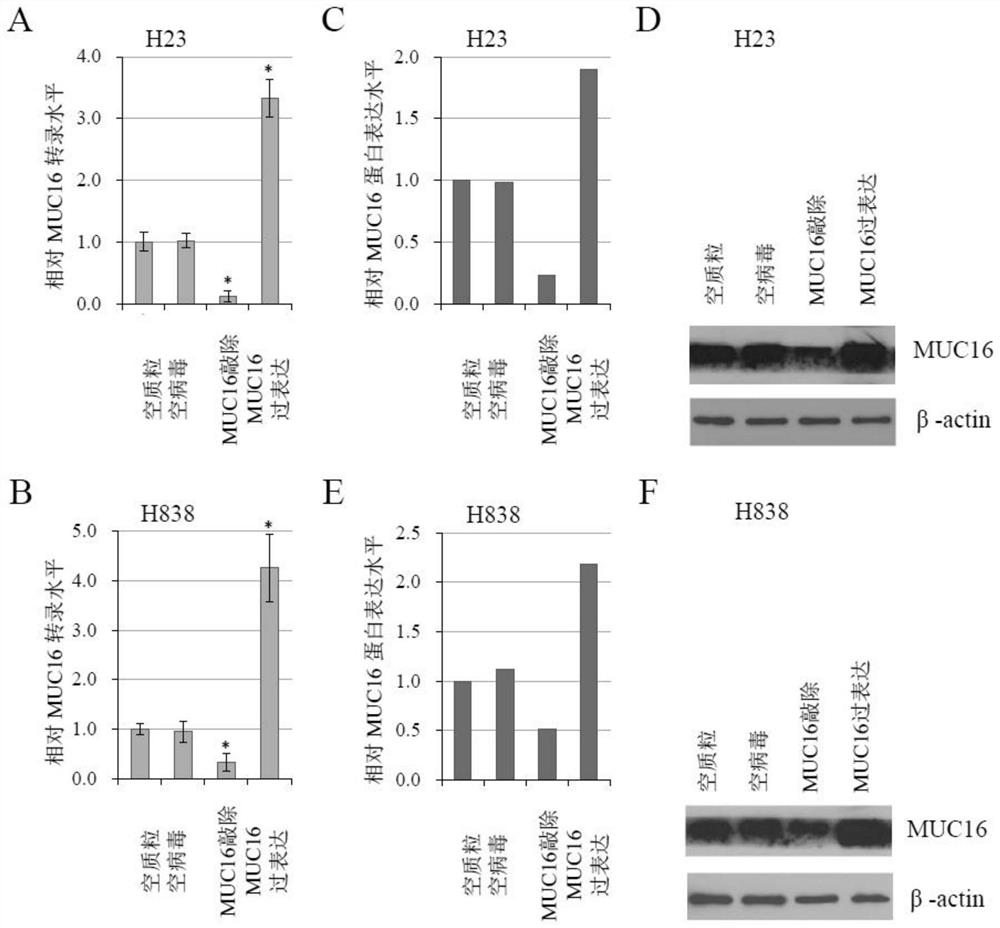
In-situ stable overexpression method of glycoprotein MUC16
InactiveCN112143757AIn situ transcriptional activationAchieve stable overexpression in situTumor rejection antigen precursorsMucinsCell divisionLentivirus
The invention discloses an in-situ stable overexpression method of glycoprotein MUC16, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. According to the invention, dCas9 is located to a promoter region of MUC16 gene on genome DNA by utilizing specific sgRNA of MUC16, and a transcription initiation complex is recruited to the greatest extent at a localization point through VP64 fused with dCas9 in combination with MS2-P65-HSF1, so that in-situ transcription activation of the MUC16 gene is effectively achieved. The lentivirus system can integrate the necessary elements for overexpression (MUC16-sgRNA, dCAS-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1) into genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a cell. Along with cell division and replication, the stable overexpression of MUC16 in cell strains is achieved. According to the invention, in-situ stable overexpression of macromolecular glycoprotein MUC16 which is difficult to clone by a conventional vector is realized.
Owner:云南省肿瘤医院
sgRNAs, recombinant plasmids, and cell lines for upregulating expression of human Dlk1-dio3 imprinted domain non-coding RNAs
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
HSF1 as a marker in tumor prognosis and treatment
In some aspects, the invention relates to Heat Shock Protein-1 (HSF1) gene and HSF1 gene products. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of tumor diagnosis, prognosis, treatment-specific prediction, or treatment selection, the methods comprising assessing the level of HSF1 expression or HSF1 activation in a sample obtained from the tumor. In some aspects, the invention relates to the discovery that increased HSF1 expression and increased HSF1 activation correlate with poor outcome in cancer, e.g., breast cancer.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +1
Application of heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating the expression of 15kda selenoprotein
ActiveCN106831975BConducive to survivalHigh expressionNervous disorderMuscular disorderDiseaseReticulum cell
The invention discloses an application of a heat shock transcription factor 1 in regulating expression of a 15kDa selenoprotein. The application provided by the invention is specifically any one of the applications of the heat shock transcription factor 1: (a1) promoting expression of a Sep15 protein in a target cell; (a2) promoting transcription of a Sep15 gene; and (a3) enhancing the activity of a Sep15 promoter in the target cell. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a transcription factor HSF1 can be combined with the Sep15 promoter to adjust transcription of the Sep15 gene and accelerate expression of the Sep15 protein. Under a heat shock and fever of a physiological status, the transcription factor HSF1 can start transcription of Sep15 and improve expression of Sep 15 so as to participate the physiological process and help the protein being corrected folded or help the protein being unfolded and delivered to other proteins to help the proteins to be folded correctly. Under endoplasmic reticulum stress, the HSF1 also can promote expression of Sep 15 to participate protein quality control of endoplasmic reticulum so as to further promote cell survival. The application disclosed by the invention is of important significance in preventing and / or treating endoplasmic reticulum stress related diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods of treating or preventing insulin resistance and associated diseases and conditions
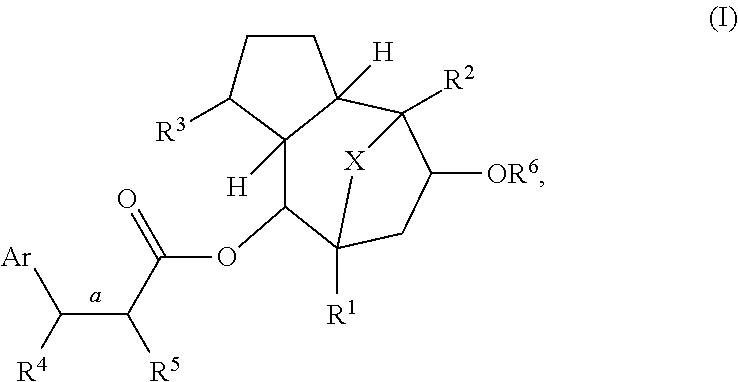
Disclosed are methods of treating an animal for insulin resistance and associated diseases or conditions, activating the transcriptional activity of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1), or inducing the expression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) in an animal in need thereof, wherein the methods involve administering an effective amount of one or more compounds of formula (I) or an epimer thereof, wherein Ar, and R1-R6 are described herein. Examples of diseases or conditions associated with insulin resistance include diabetes, obesity, inflammation, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary disease, arteriosclerosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, reproductive abnormality in a female, and growth abnormality.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Small molecule polypeptide in HD treatment medicine and application of small molecule polypeptide
ActiveCN113087783AChange in normal functionNo cytotoxicity was foundNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMitochondrial fragmentationMitochondrial translocation
The invention relates to a small molecule polypeptide in an HD treatment medicine and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the small molecule polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention also provides application of the small molecule polypeptide. According to the invention, a small molecule polypeptide DH1 is designed by researching a translocation mechanism and functions of HSF1. The polypeptide achieves the purposes of protecting neurons and improving the HD disease progress by inhibiting mitochondrial translocation of HSF1, weakening mitochondrial fragmentation and improving the expression quantity of mitochondrial DNA, and provides a new target for HD treatment.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Synchronous activation of transcriptional activity of multiple porcine endogenous stem cell factors using tandem sgRNAs
ActiveCN110218741BImprove activation efficiencyIncrease transcriptional activityGenetically modified cellsFermentationHSF1Cell strain
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
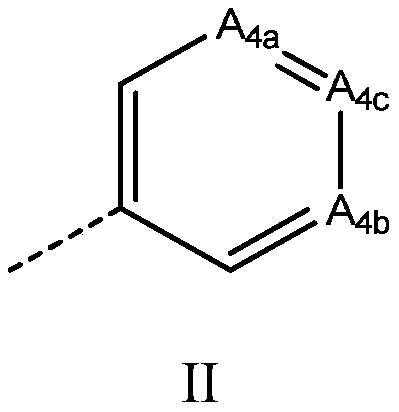
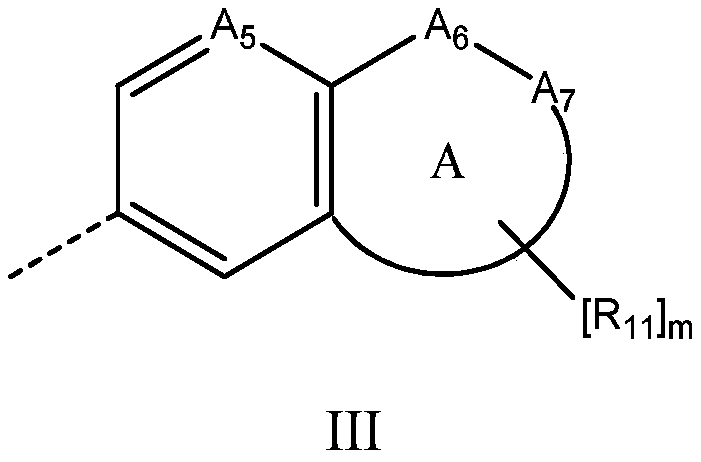
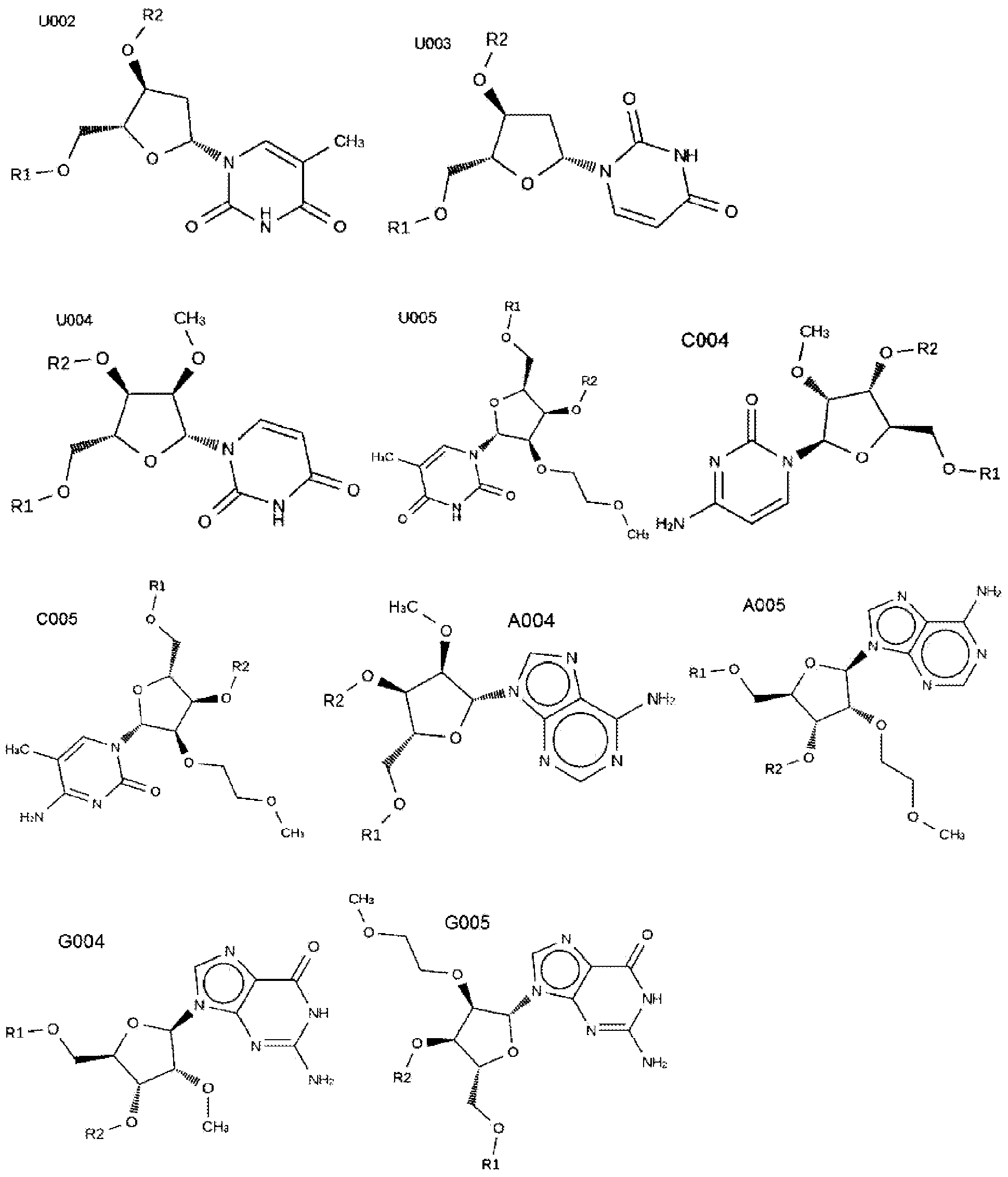
Fused 1,4-dihydrodioxin derivatives as inhibitors of heat shock transcription factor 1
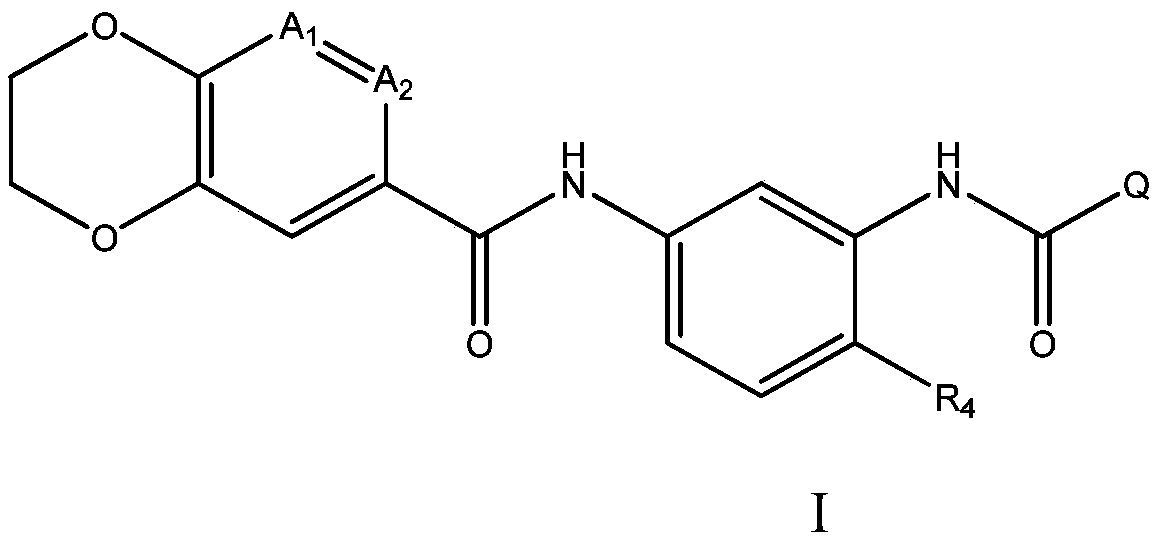
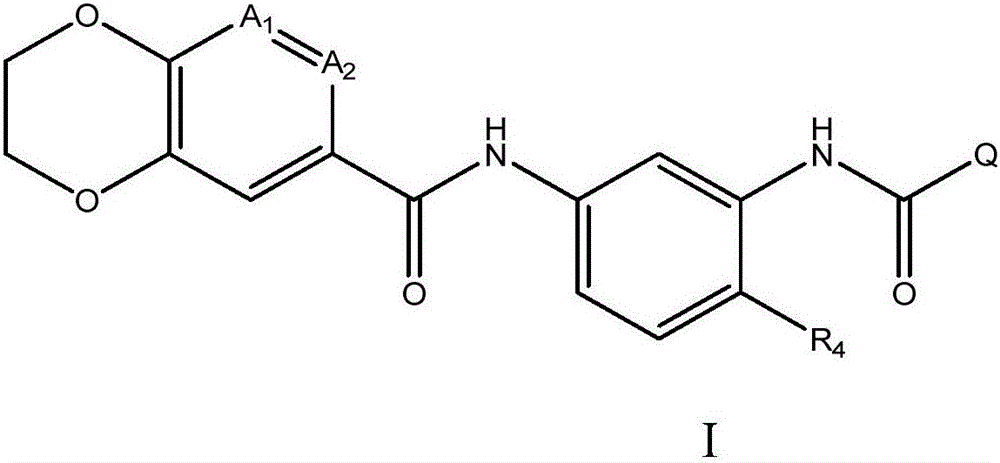
The present invention relates to compounds of formula I, wherein A 1 、A 2 , R 4 and Q are as defined herein. The compounds of the present invention are inhibitors of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1). In particular, the present invention relates to the use of these compounds as therapeutic agents for the treatment and / or prevention of proliferative diseases such as cancer. The invention also relates to processes for the preparation of these compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Inhibitor of heat shock factor 1, and preparation method and application of inhibitor
The invention provides an inhibitor of a heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) and an application of the inhibitor, particularly a compound as shown in a formula I or pharmaceutically-acceptable salt of the compound. The compound has excellent HSF1 restraining activity and tumor resisting effects. The invention further provides a medical composition containing the compound and an application of the medical composition in the respect of restraining HSF1.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A molecular marker for diagnosing idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and its application
The invention relates to a molecular marker for diagnosing idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and its application. The molecular marker is autologous anti-heat shock transcription factor 1 (heat shock factor 1, HSF1) antibody in serum. The antibody is IgG; the idiopathic inflammatory myopathy is polymyositis (polymyositis, PM) or dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis, DM); the diagnosis is to distinguish idiopathic inflammatory myopathy and healthy population or to predict the disease process of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM).
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
Fused 1,4-dihydrodioxin derivatives as inhibitors of heat shock transcription factor 1
The present invention relates to compounds of formula I wherein A1, A2 R4 and Q are as defined herein. The compounds of the present invention are inhibitors of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1). In particular, the present invention relates to the use of these compounds as therapeutic agents for the treatment and / or prevention of proliferative diseases, such as cancer. The present invention also relates to processes for the preparation of these compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising them.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Human myocardium protecting gene and uses thereof
The present invention belongs to the biotechnological field and relates to a human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor (HSF1) and a sieving method and a purpose thereof. The present invention adopts the method of ''death trap'' that the gene which resists myocardial cell death is sieved from human cardiac gene, and the human myocardial protection gene heat shock transcription factor 1 is cloned from the obtained gene. The result of transfection cell and animal experiment shows that the obtained human myocardial protection gene has the function of resisting cell death and also has the function of resisting ischemia, protecting myocardial cell and preventing and remedying the heart failure occurrence and development inside the heart of a living organism. The present invention can prepare for the medicine for remedying the ischemic heart disease and preventing the cardiac insufficiency and provides a novel target gene for the further function research and the gene engineering medicine development, which has important meaning for the early prevention and treatment of the heart failure and the research and the development of the related medicines and measures.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
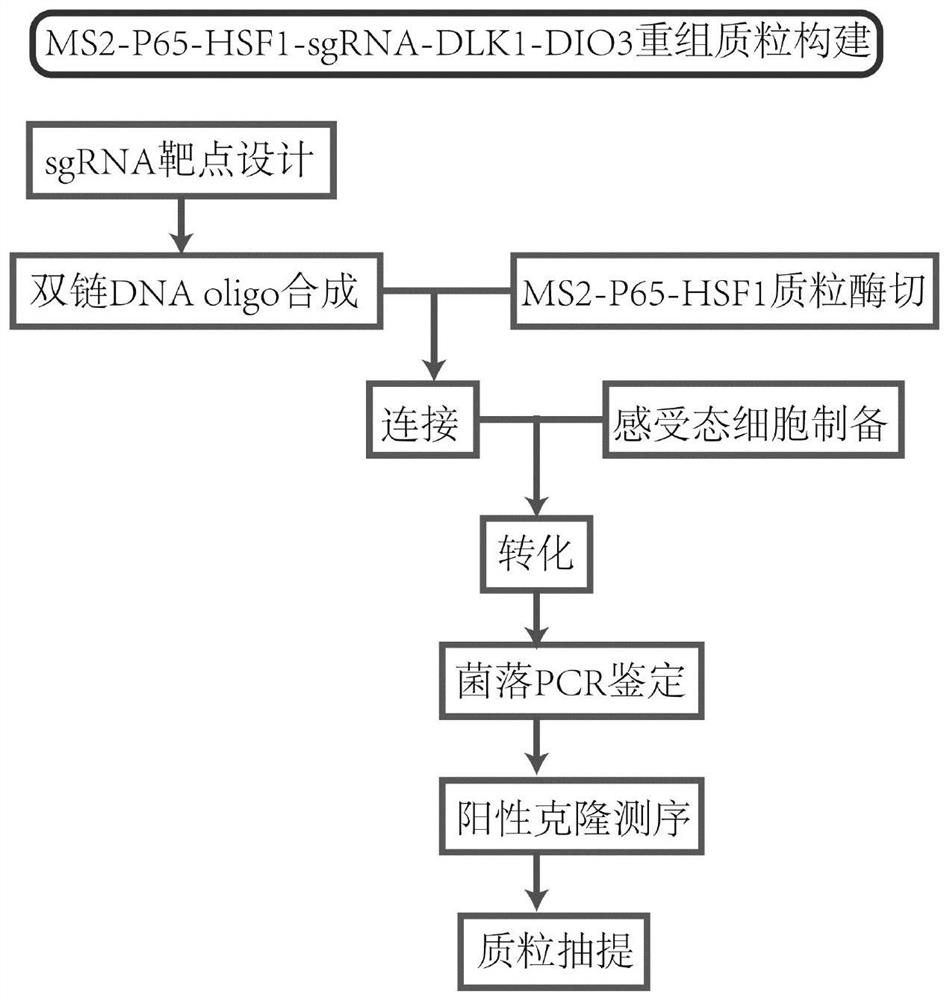
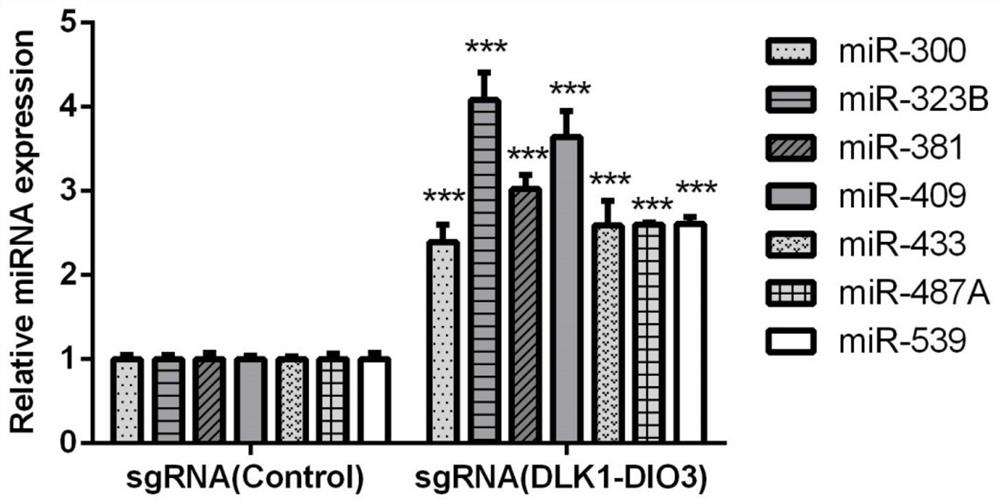
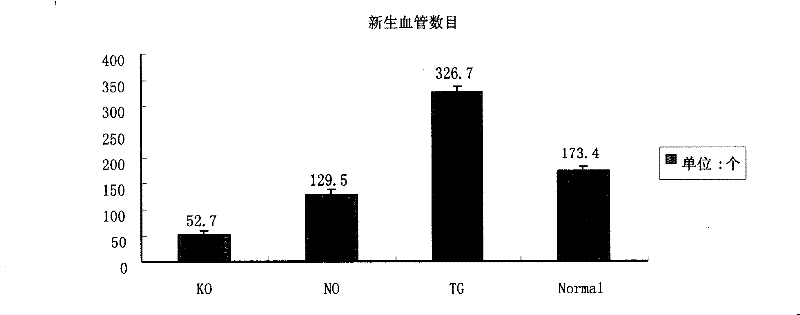
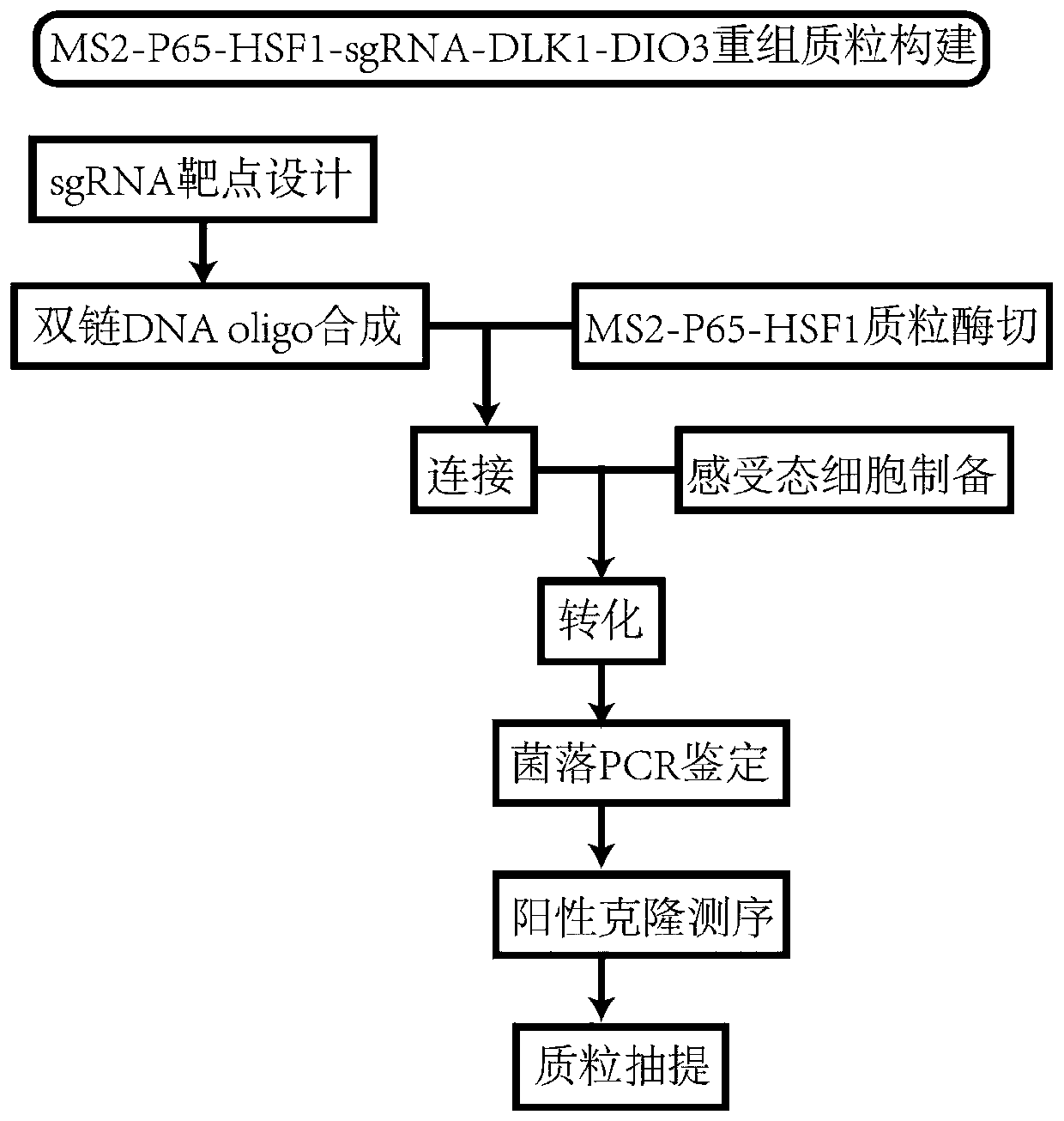
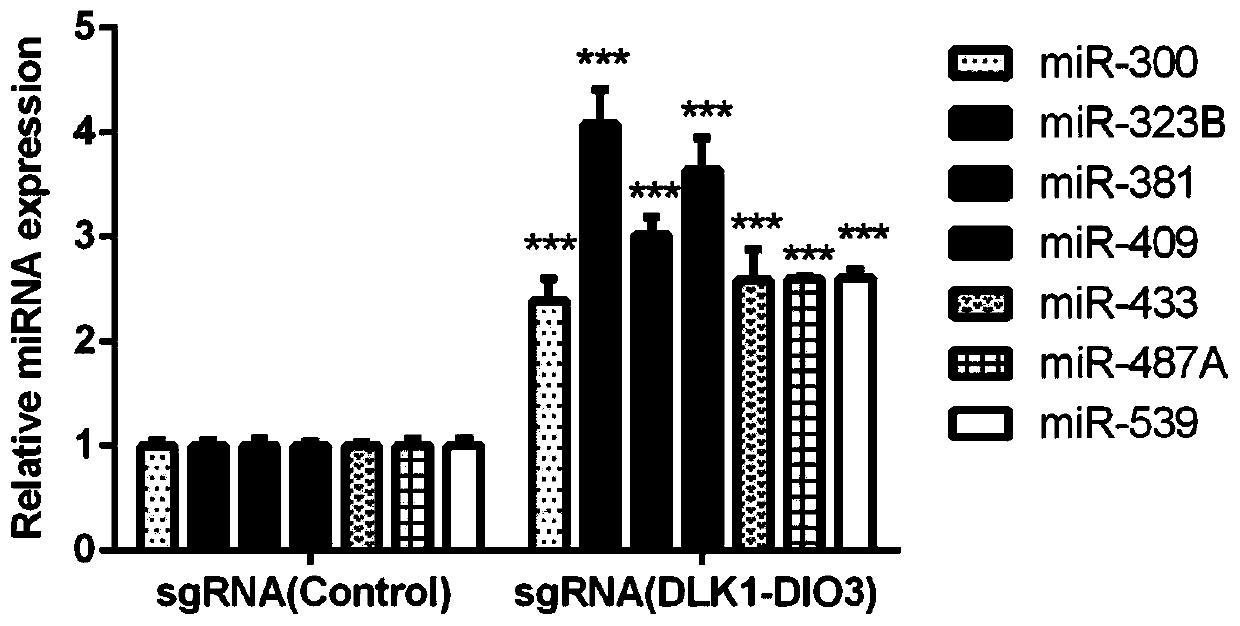
sgRNA for up-regulating non-coding RNA expression in human DLK1-DIO3 imprinted domain, recombinant plasmid and cell line
The invention discloses sgRNA for up-regulating non-coding RNA expression in a human DLK1-DIO3 imprinted domain, a recombinant plasmid and a cell line. The sgRNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, andspecifically as 5'-TTTATATGGAGGCGCAGAAG-3'; the method comprises the steps of: synthesizing a nucleic acid fragment of a sgRNA sequence and inserting into a multiple cloning site of the MS2-P65-HSF1expression plasmid vector and transforming, and selecting a monoclonal strain, extracting the recombinant plasmid of MS2-P65-HSF1-sgRNA-DLK1-DIO3, and transfecting the recombinant plasmid to the target cell line which is pre-transfected with dCAS9-VP64 plasmid to obtain the cell strain for up-regulating non-coding RNA expression in the DLK1-DIO3 imprinted domain. The application can rapidly, easily and accurately up-regulate the expression of non-coding RNA on the DLK1-DIO3 imprinted domain of the cell strain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
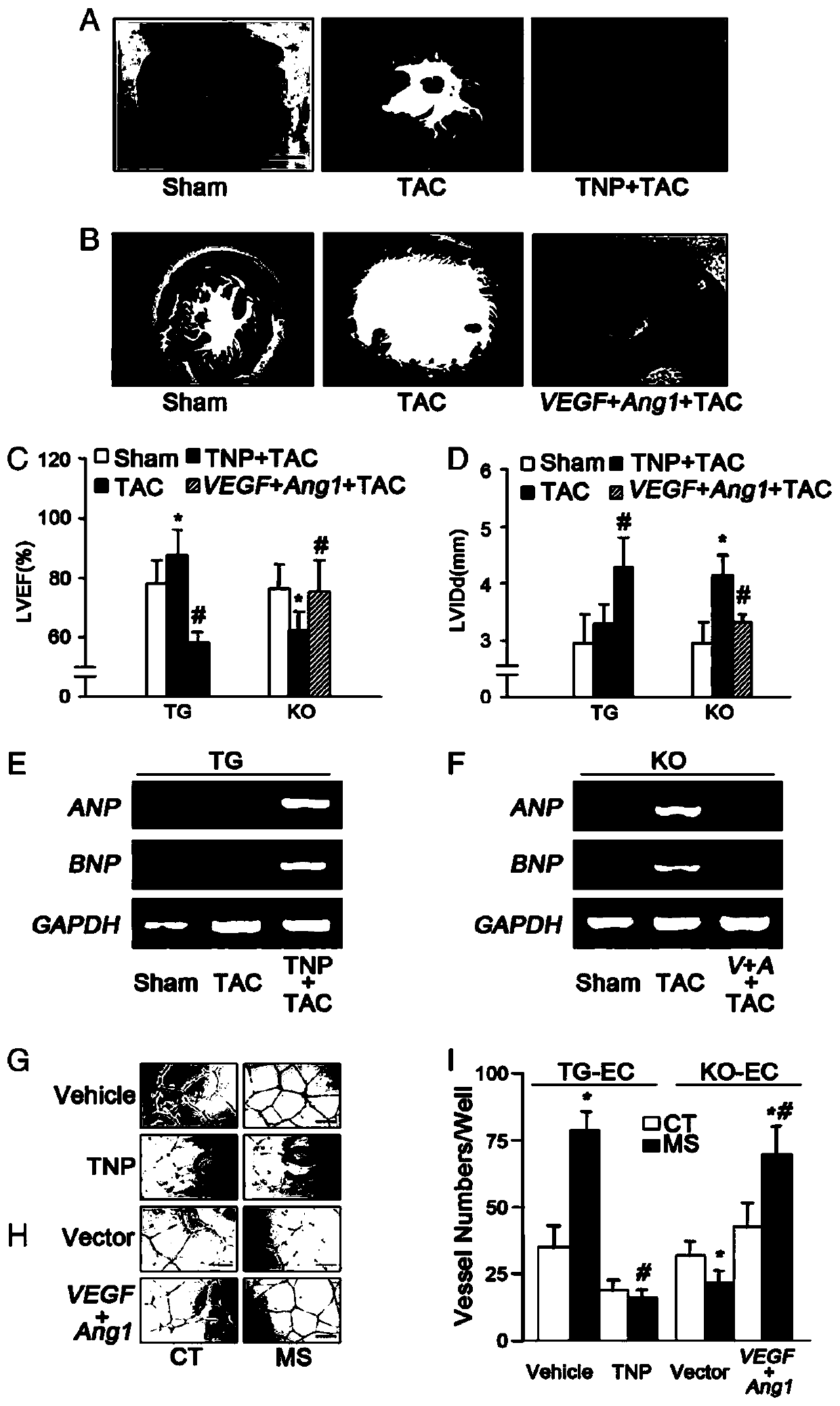
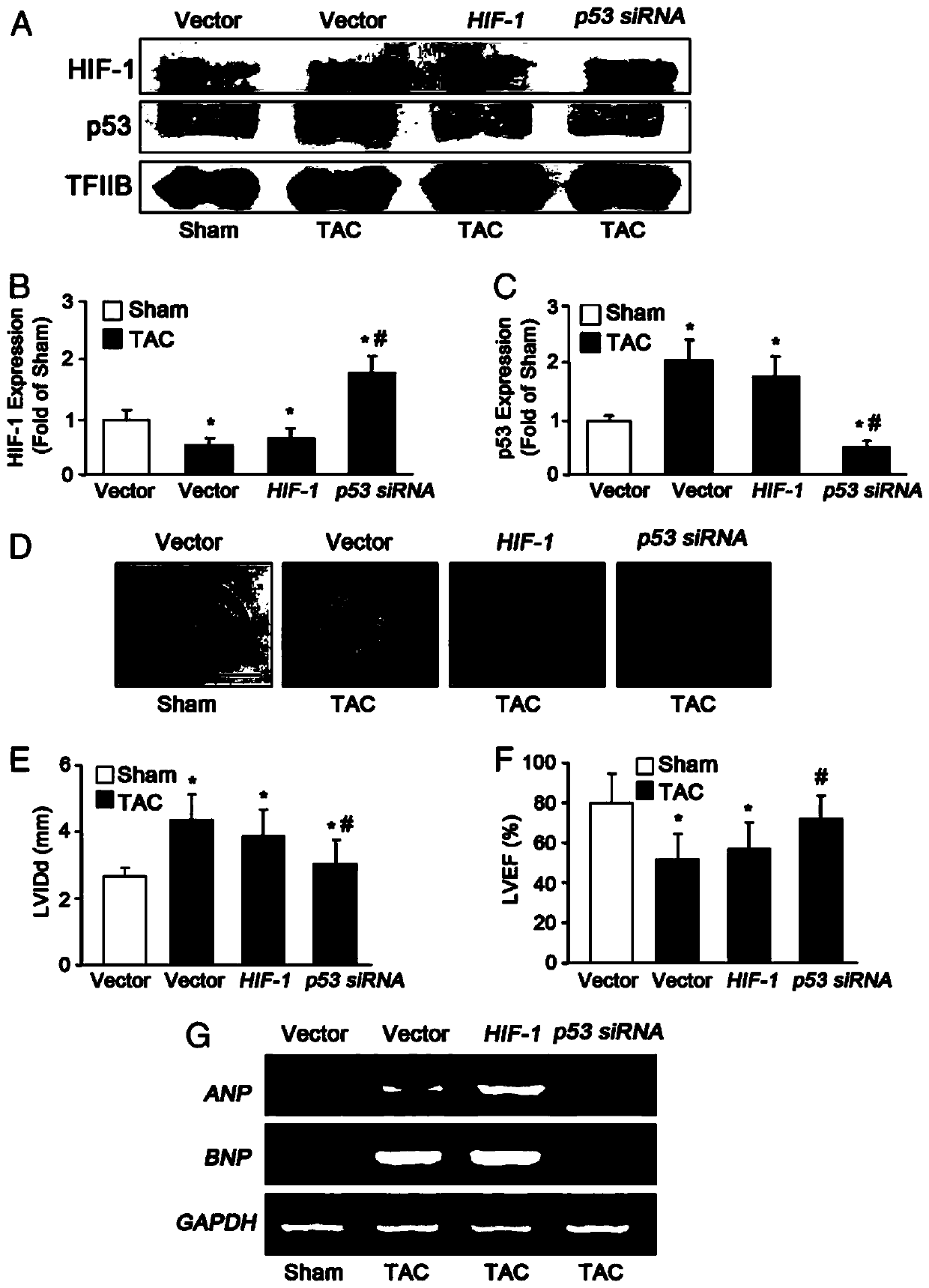
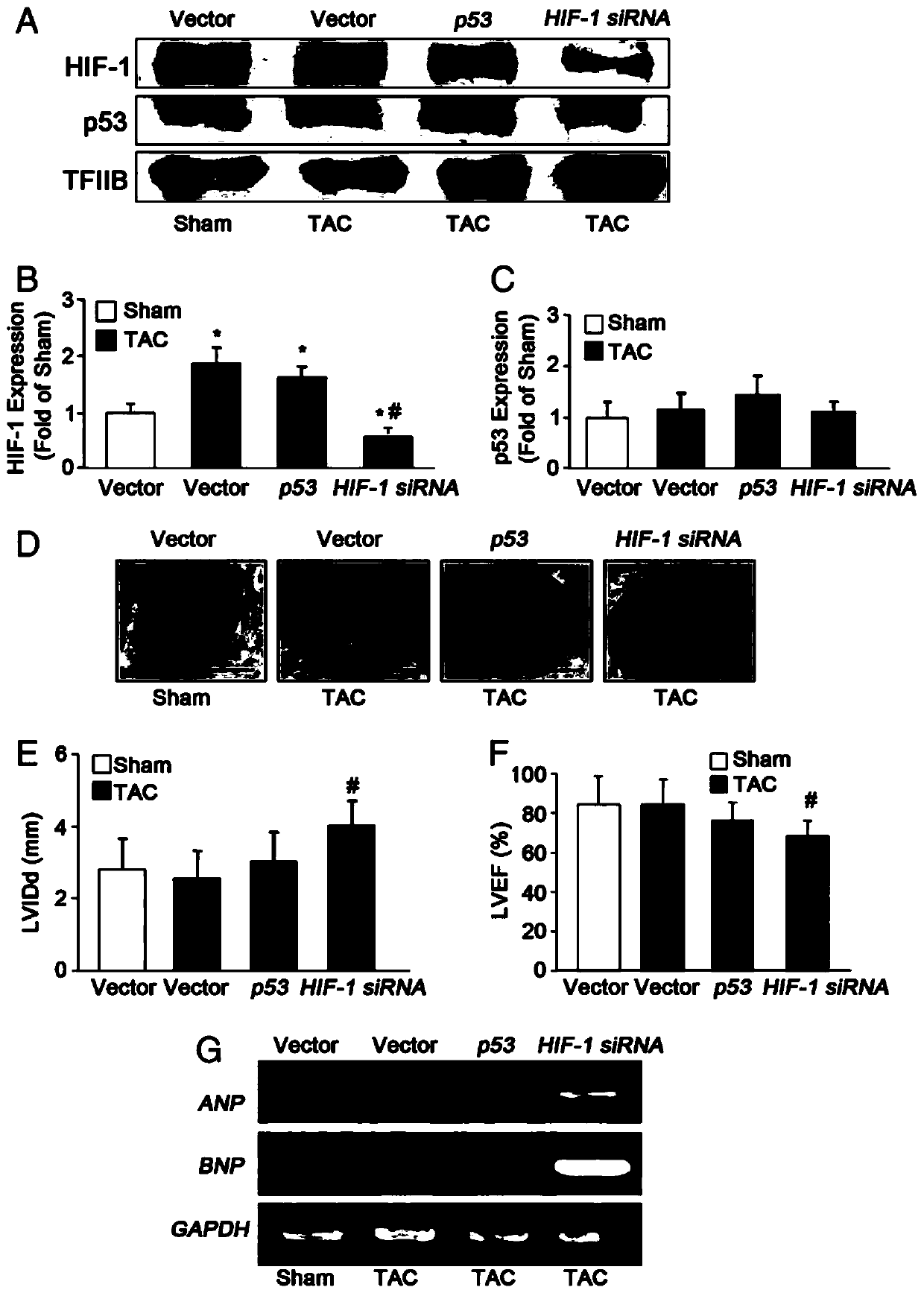
Adenovirus vector and application thereof in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating heart failure
InactiveCN111197059APromote generationMaintain cardiac fitnessOrganic active ingredientsFermentationPressure overloadPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a medicine for preventing and treating heart failure, which is characterized in that the medicine for preventing and treating heart failure comprises an adenovirus vector, theadenovirus vector comprises a polynucleotide sequence for encoding HSF1, and the polynucleotide sequence of HSF1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The HSF1 promotes cardiac angiogenesis by inhibiting p53 andthen up-regulating HIF-1 in endothelial cells during chronic pressure overload, so that cardiac adaptability is maintained, and the adenovirus vector has important significance in early prevention andtreatment of heart failure and further research and development of related drugs and means.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111087454AGrowth inhibitionLow homologyFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotide sequencingHSF1
The invention discloses a heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Through homologously comparing heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein in human and heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein in aspergillus flavus (Aspergillus flavus), 213 amino acid residues from 576th-site to788th site at the C terminal of aspergillus flavus Hsf1 protein are deleted, the amino acid sequence of the obtained protein of the heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 in aspergillus flavus is as shown in SEQID NO.1, and the coding nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQID NO.2. The dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 can restrain normal Hsf1 from exertingfunctions in fungi, so that the growth of the fungi can be restrained, and the heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 can be applied to the respect of preventing andcontrolling fungus pollution.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Organic compositions to treat HSF1-related diseases
The present disclosure relates to methods of treating heat shock factor 1 (HSF1)-related diseases such as cancer, autoimmune and viral diseases, using a therapeutically effective amount of a RNAi agent to HSF.
Owner:ARROWHEAD RES CORP
Stepped fine adjustment method for in-situ over-expression of long-chain non-coding RNA-LINC00842
InactiveCN112111523AStable expressionFacilitate the study of long-term physiological and pathological effectsStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorCell divisionTranscription initiation
The invention discloses a stepped fine adjustment method for the in-situ over-expression of a long-chain non-coding RNA-LINC00842. According to the method, LINC00842 specific sgRNA is used to positiondCas9 to a promoter region of an LINC00842 gene on a genome DNA, a transcription initiation complex is recruited in different degrees at a positioning site through the binding of MS2-P65-HSF1 with dCas9-fused VP64, and thereby the gradient adjustment of the in-situ over-expression of the LINC00842 gene is effectively realized. Moreover, a lentivirus system can integrate over-expression required elements (LINC00842-sgRNA, dCAS-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1) into a genome DNA of cells, the stable over-expression of LINC00842 in a cell strain is realized along with cell division and replication, and finally a cell strain series for stably over-expressing the LINC00842 gene with different amplitudes is obtained.
Owner:云南省肿瘤医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com