Patents
Literature
108 results about "Nominal size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In manufacturing, a nominal size or trade size is a size "in name only" used for identification. The nominal size may not match any dimension of the product, but within the domain of that product the nominal size may correspond to a large number of highly standardized dimensions and tolerances. For example, dimensional lumber sizes such as "2 by 4" refers to a board whose finished dimensions are closer to 1 ¹⁄₂ inches by 3 ¹⁄₂ inches. A "3 ¹⁄₂-inch" floppy disk's standard dimension is 90 mm, or 3.54 inches, and is advertised to hold "1.44 megabytes" although its capacity is 1,474,560 bytes. A "³⁄₄-inch pipe" in the Nominal Pipe Size system has no dimensions that are exactly 0.75 inches. A screw thread has a number of dimensions required to assure proper function but is referred to by a nominal size and a thread design family, for example "¹⁄₄ inch, 20 threads per inch, Unified National Coarse". In the UK, pipe is available that is quoted in both metric size and imperial size. The metric size is larger than the imperial size.
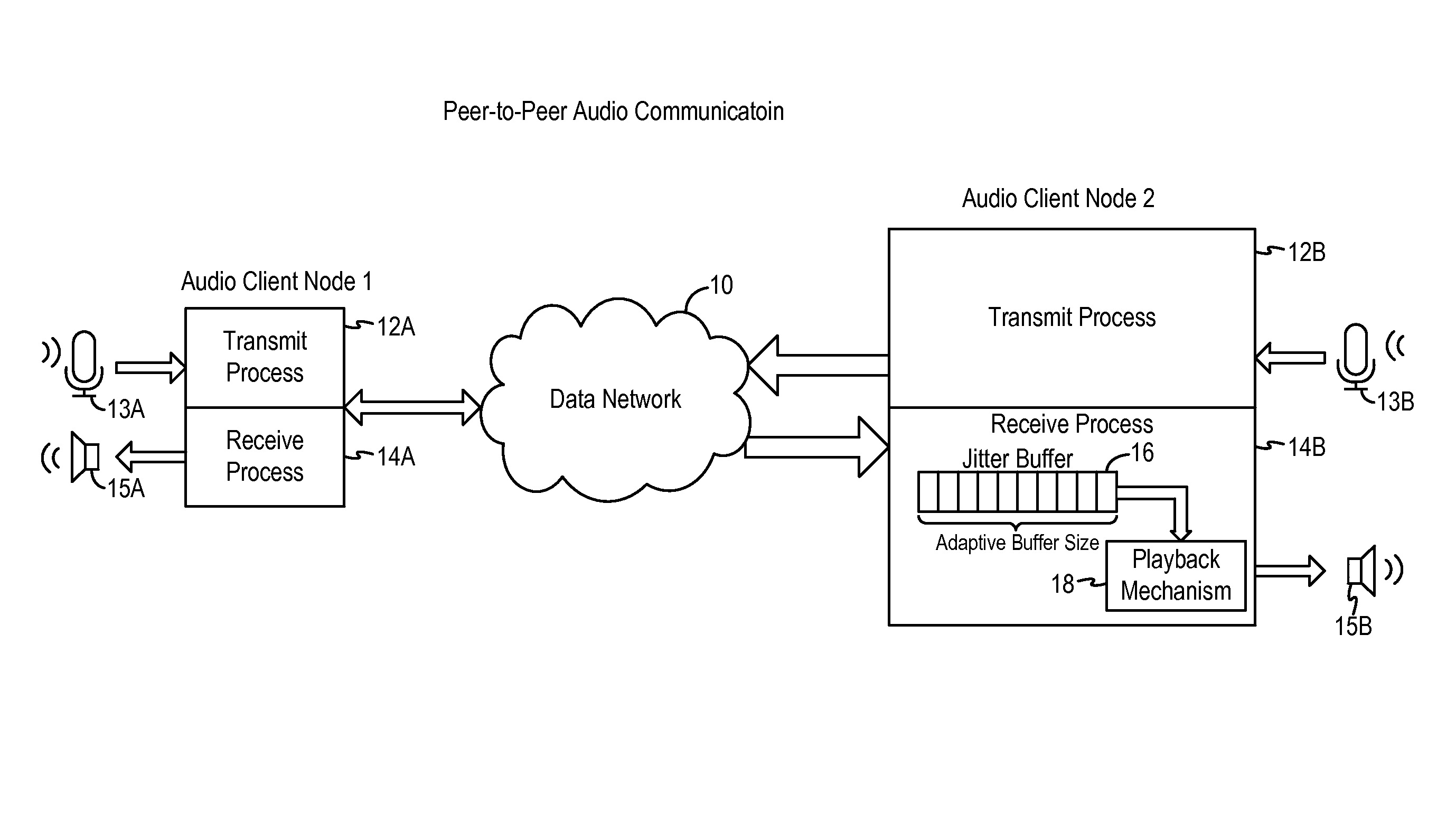
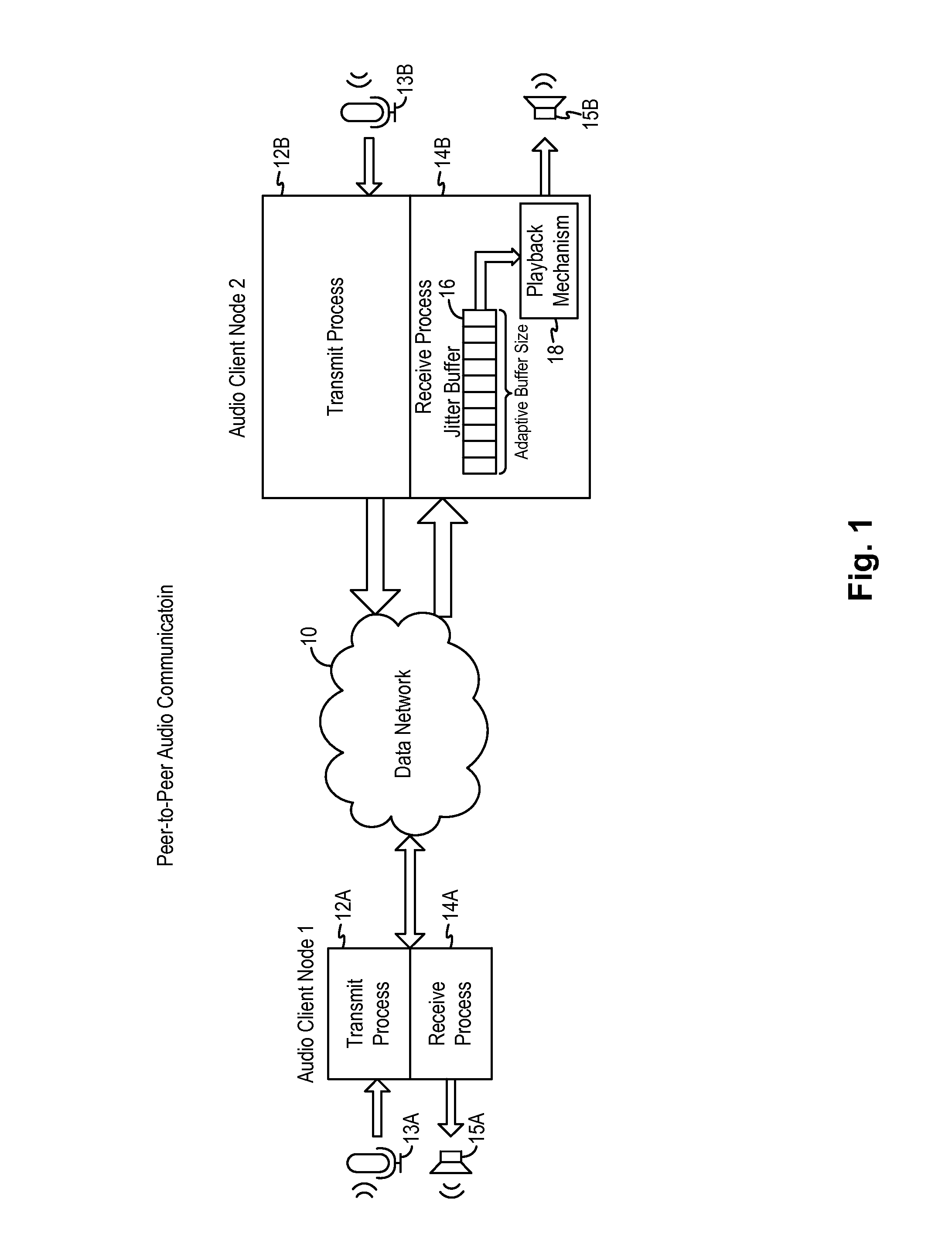
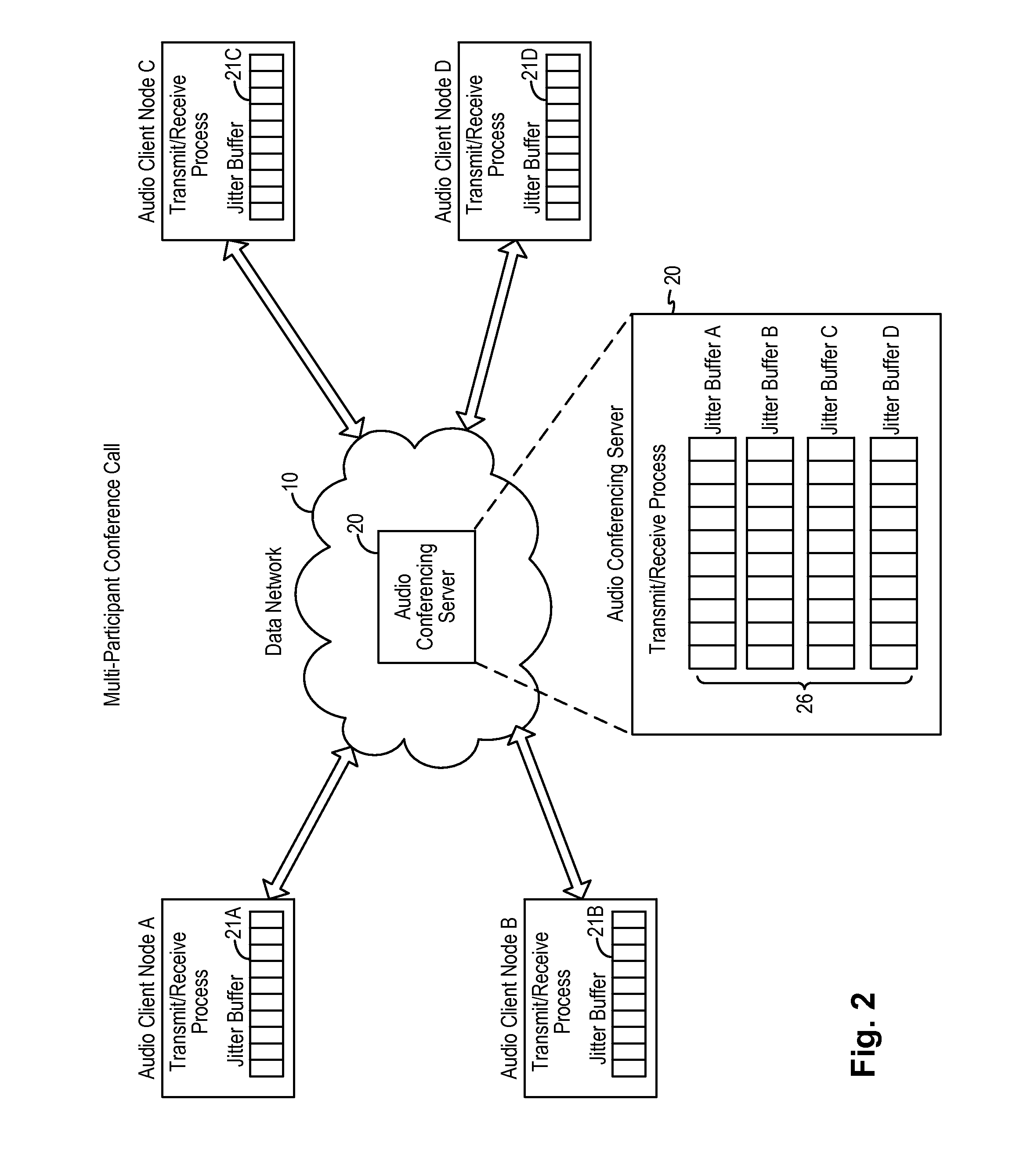
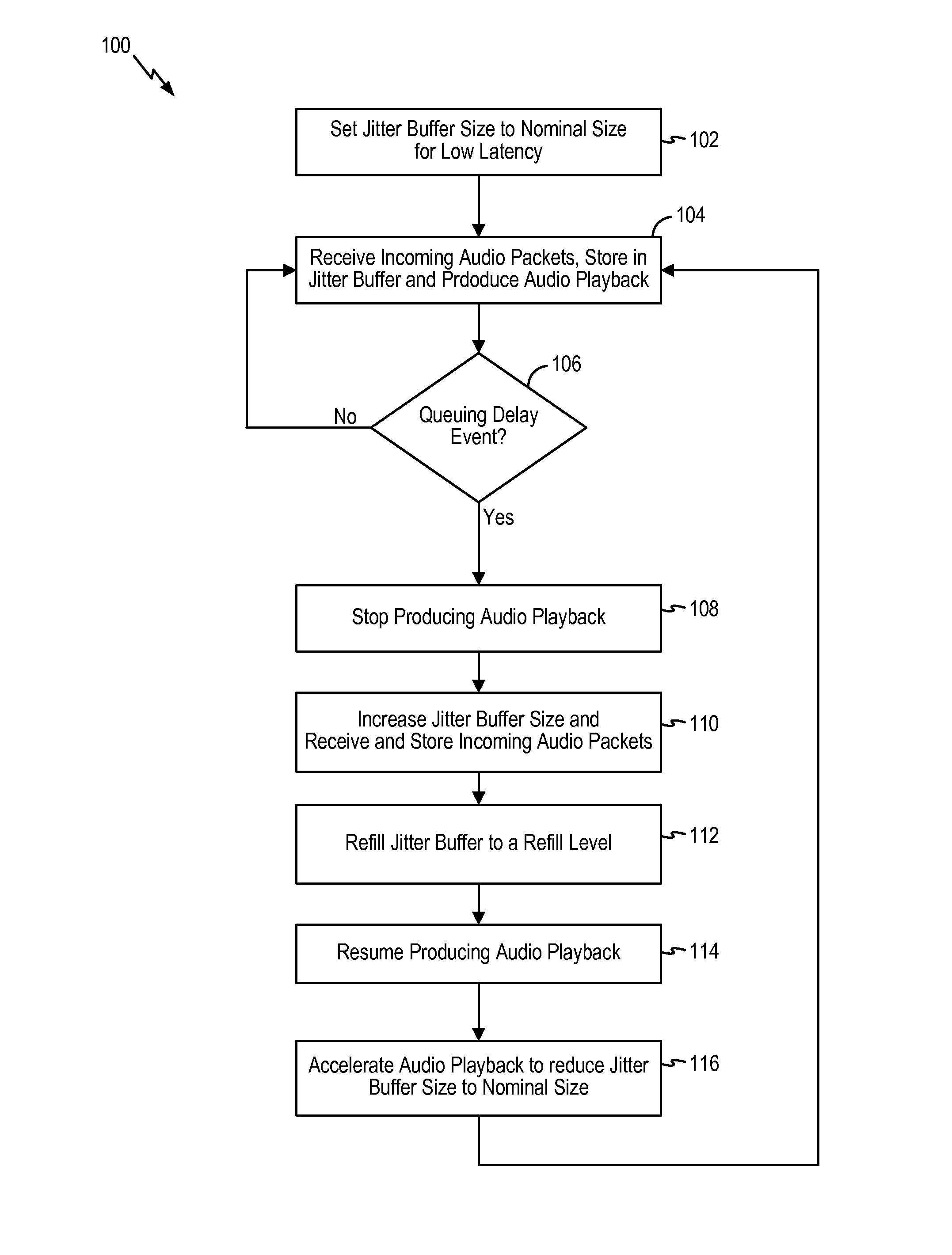
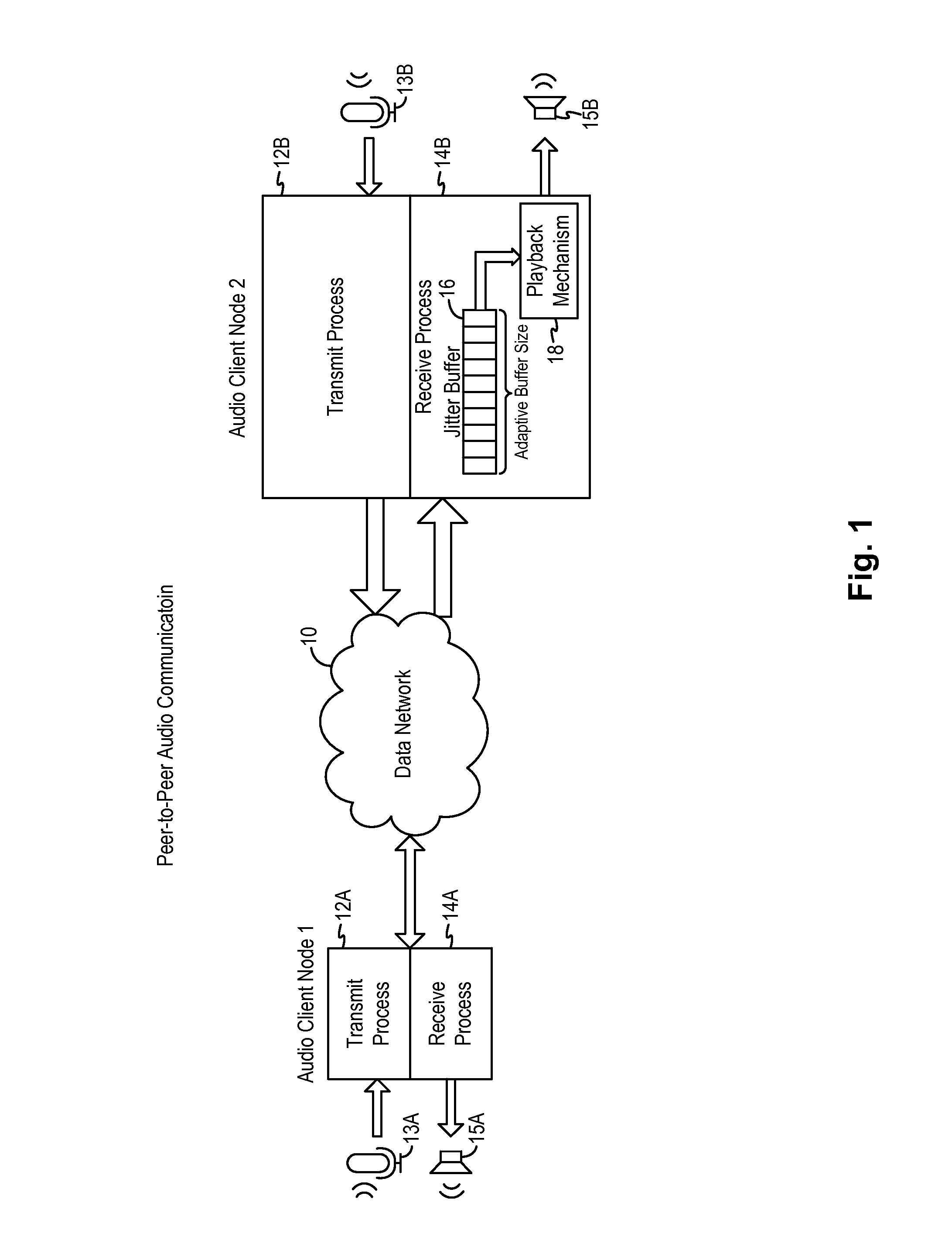
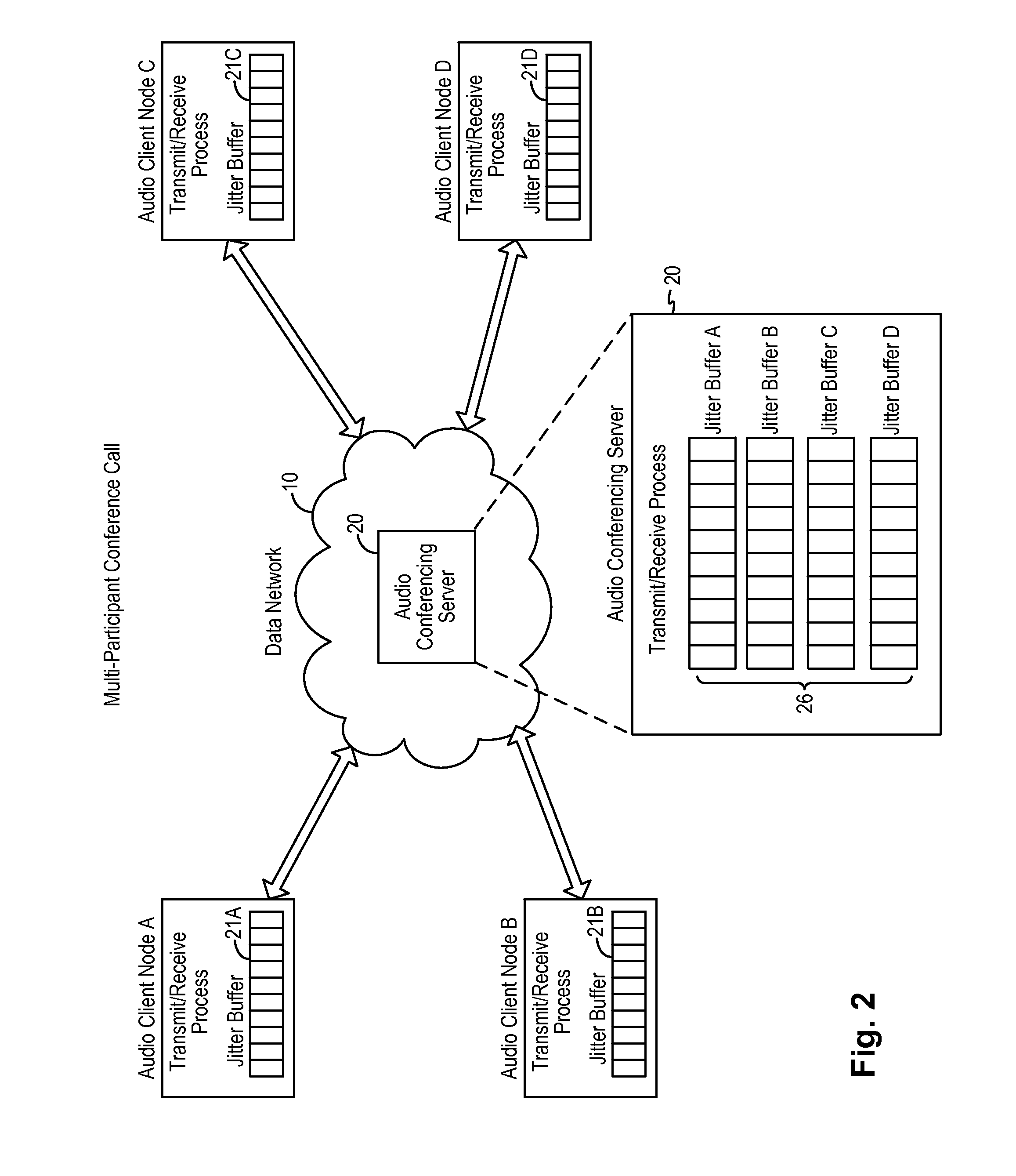
Adaptive audio stream with latency compensation
ActiveUS20160105473A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationUser devicePacket loss
A latency compensating adaptive jitter buffer method is implemented in an audio client running on a user device or in an audio server to adaptively adjust the size of a jitter buffer to optimize latency while minimizing packet loss during audio signal transmission. In some embodiments, the jitter buffer is kept to a nominal size for low latency. In response to a queuing delay event being detected, audio production is temporarily stopped and the size of the jitter buffer is temporarily increased to receive all incoming audio packets up to a certain refill level. The method then resumes audio production using accelerated playback to reduce the jitter buffer size back to the nominal size.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Ultra-thin wearing layer of pavement
The invention belongs to the technical field of a building material used in road engineering, and specifically relates to drainage asphalt mixture for an ultra-thin wearing layer. The mixture comprises aggregated material, stuffing, high-performance asphalt and warm mixing additive; the maximal nominal size of the mixture is 6.7mm; the thickness of a pavement layer is 10-20mm; the aggregated material is basalt or dolerite; the used stuffing is mixture of limestone powder and common silicate cement, and the used high-performance asphalt is prepared from general modified asphalt by adding waste tire rubber powder which is 20-28% of weight of the asphalt and modifying. An ultra-thin finishing coat and low-temperature construction are realized by the asphalt mixture by adding the warm mixing additive; the ultra-thin wearing layer has the advantages of low construction cost, convenience in construction and the like, and is suitable for building of an asphalt concrete pavement and function-improving works of the pavement.
Owner:上海砼仁环保技术发展有限公司
Adaptive audio stream with latency compensation
A latency compensating adaptive jitter buffer method is implemented in an audio client running on a user device or in an audio server to adaptively adjust the size of a jitter buffer to optimize latency while minimizing packet loss during audio signal transmission. In some embodiments, the jitter buffer is kept to a nominal size for low latency. In response to a queuing delay event being detected, audio production is temporarily stopped and the size of the jitter buffer is temporarily increased to receive all incoming audio packets up to a certain refill level. The method then resumes audio production using accelerated playback to reduce the jitter buffer size back to the nominal size.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
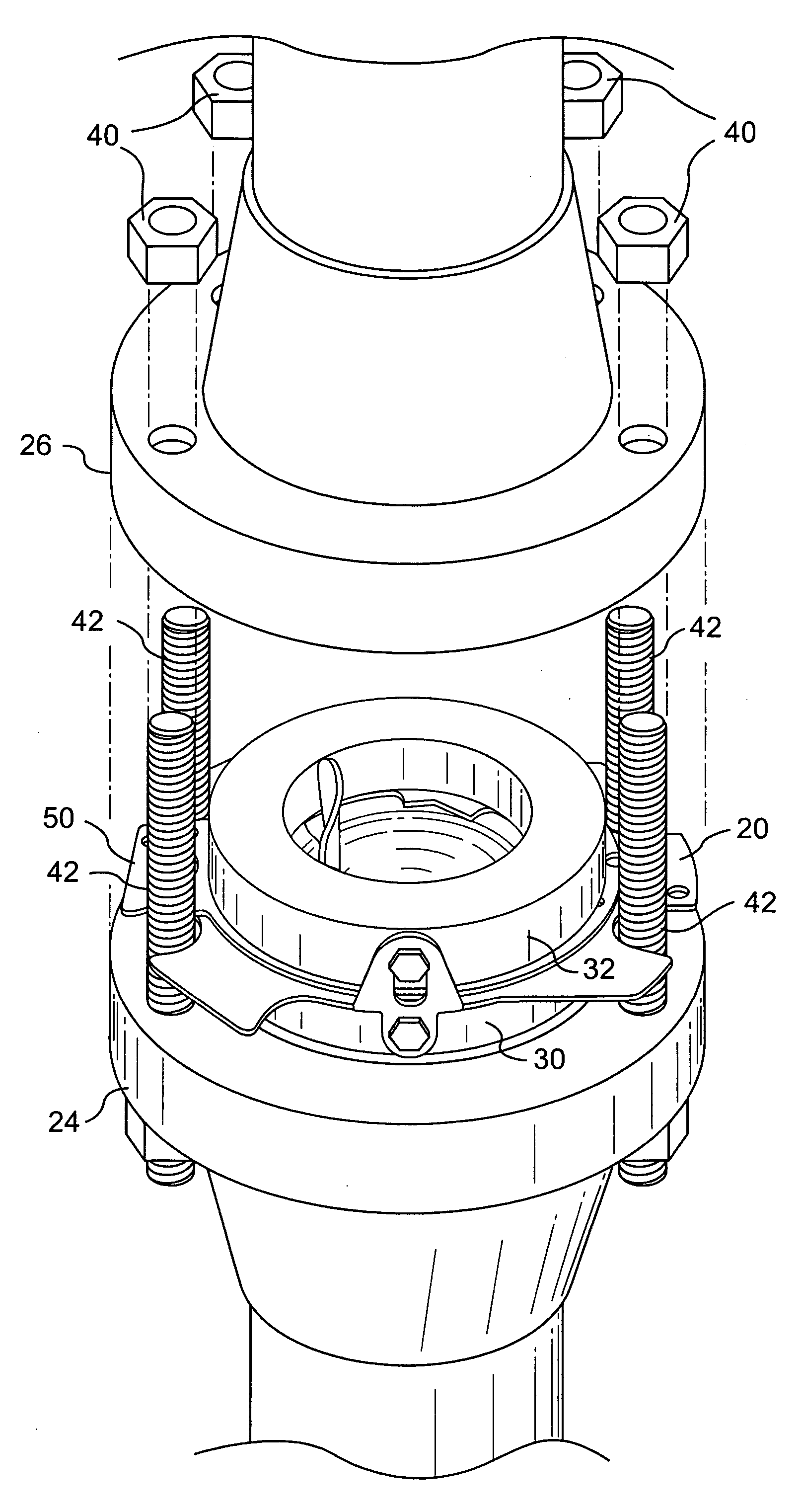
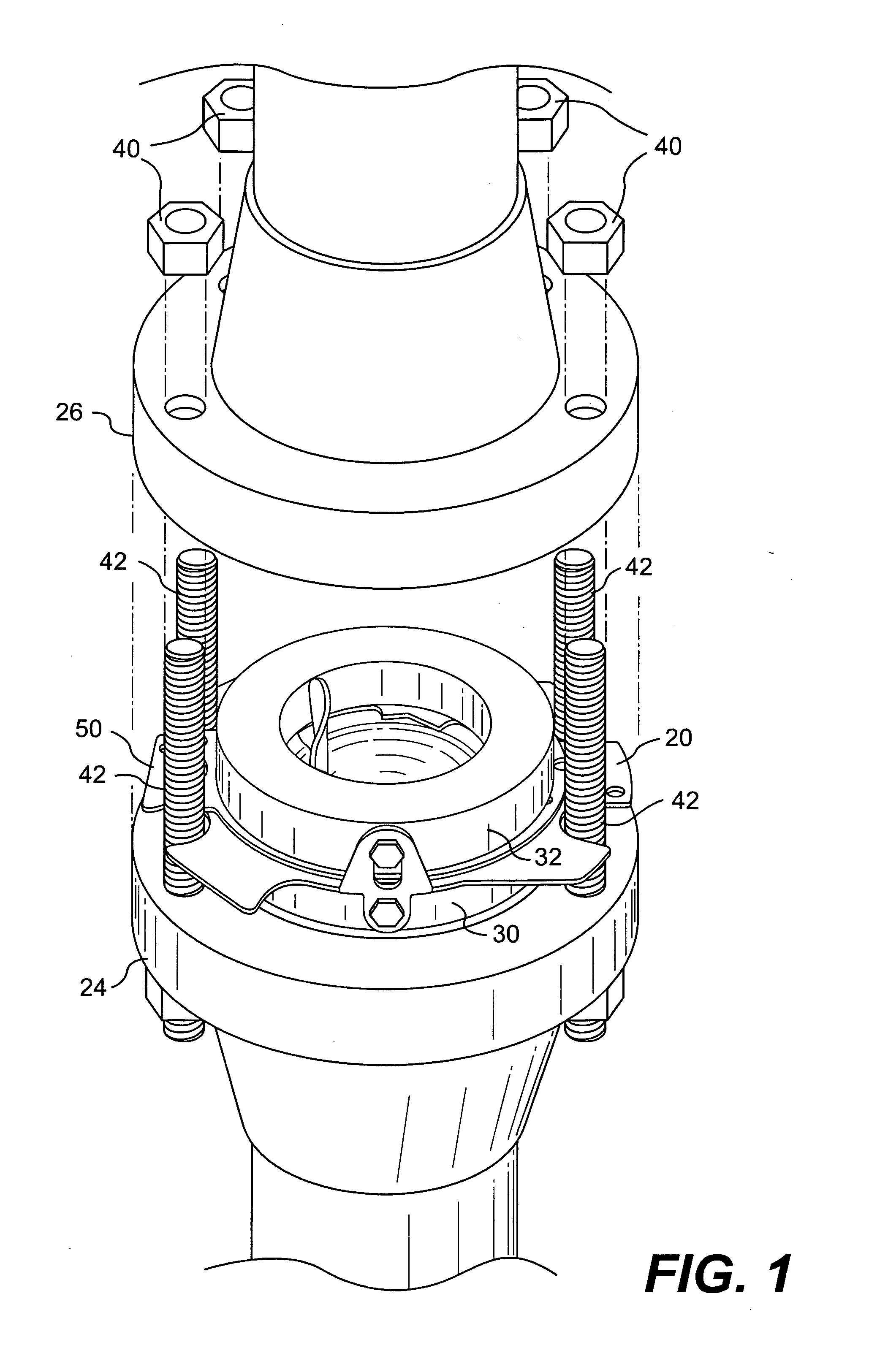
Flange adapter
ActiveUS20060049635A1Improve standardizationLess costlyFlanged jointsEqualizing valvesNominal sizeBiomedical engineering
A flange adapter is provided for positioning an insert device within a pressurized fluid system. A flange adapter assembly includes a pressure containing boundary and a flange adapter configured to be selectively connected to the pressure containing boundary. The adapter is configured to interchangeably fit a plurality of flange standards for the same nominal size. The adapter may also interchangeably fit a plurality of pressure ratings for the same nominal size. The flange adapter may be manufactured separate from the pressure containing boundary to allow for utilizing less costly material and to increase standardization of safety heads. The present invention also includes a gasket design having multi-flange compatibility for use in pressurized fluid systems.
Owner:BS&B SAFETY SYST LTD
Porous structures and methods for forming porous structures
InactiveUS20060273005A1Improve ductilityReduce differential pressureLoose filtering material filtersGravity filtersInorganic particleNominal size
A porous element is produced from a slurry of inorganic particles including a first plurality of inorganic particles having a first nominal size and a second plurality of inorganic particles having a second nominal size. The first nominal size is less than the second nominal size. The inorganic particles are sinter bonded.
Owner:PALL CORP
Transparent filtered capillaries
InactiveUS20050214737A1Improve throughputEnhance the imageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNominal sizeEngineering
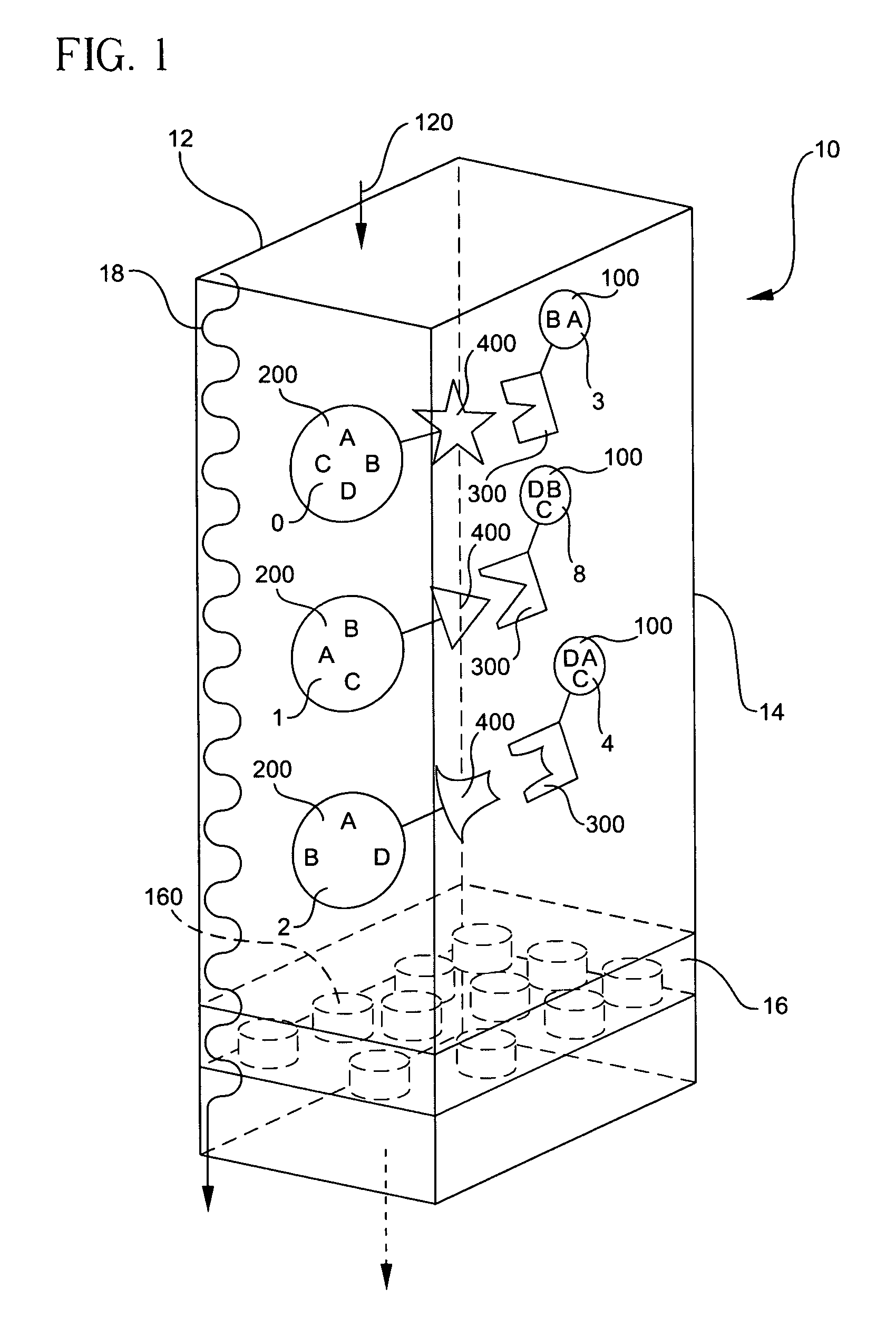
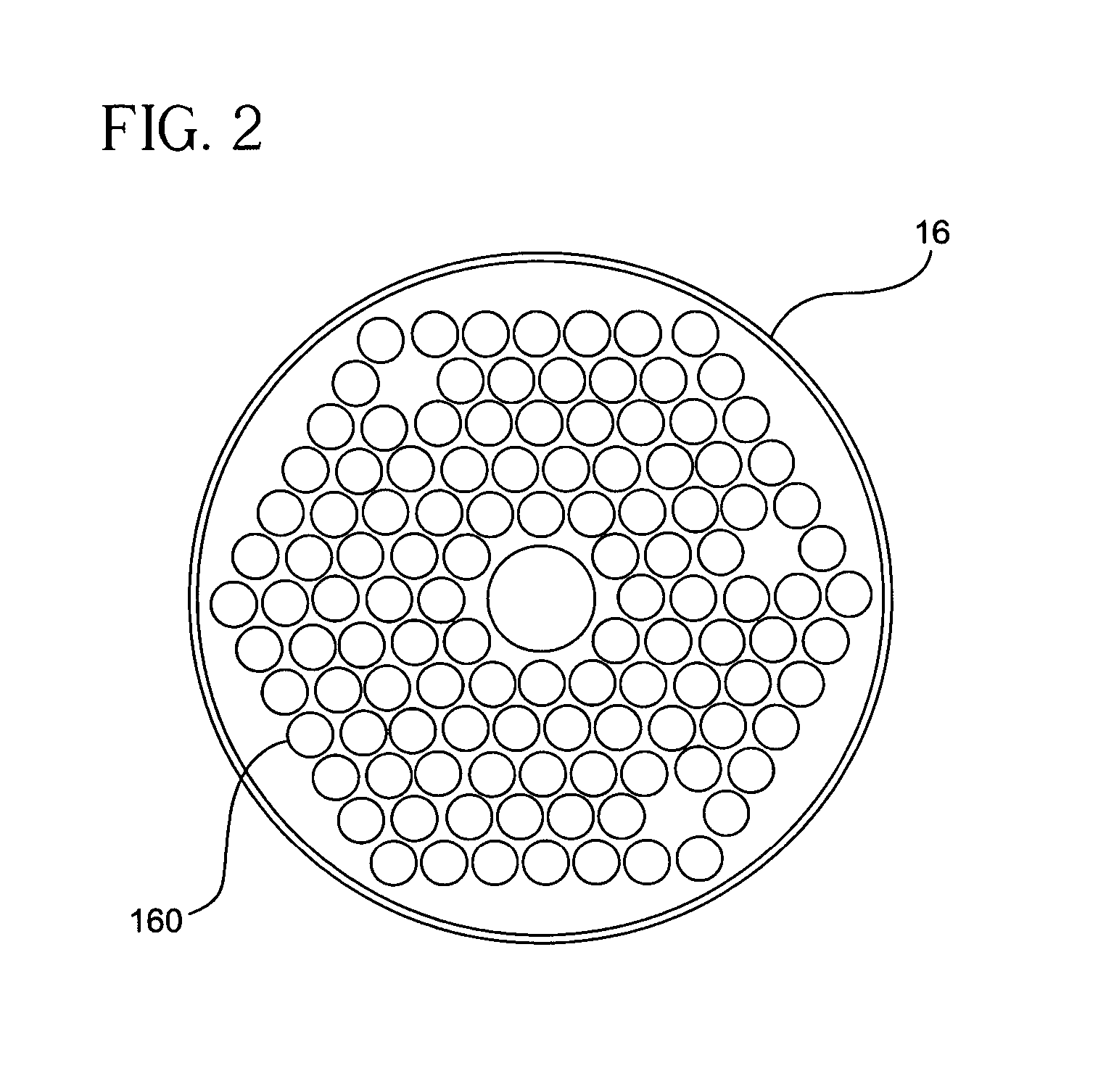
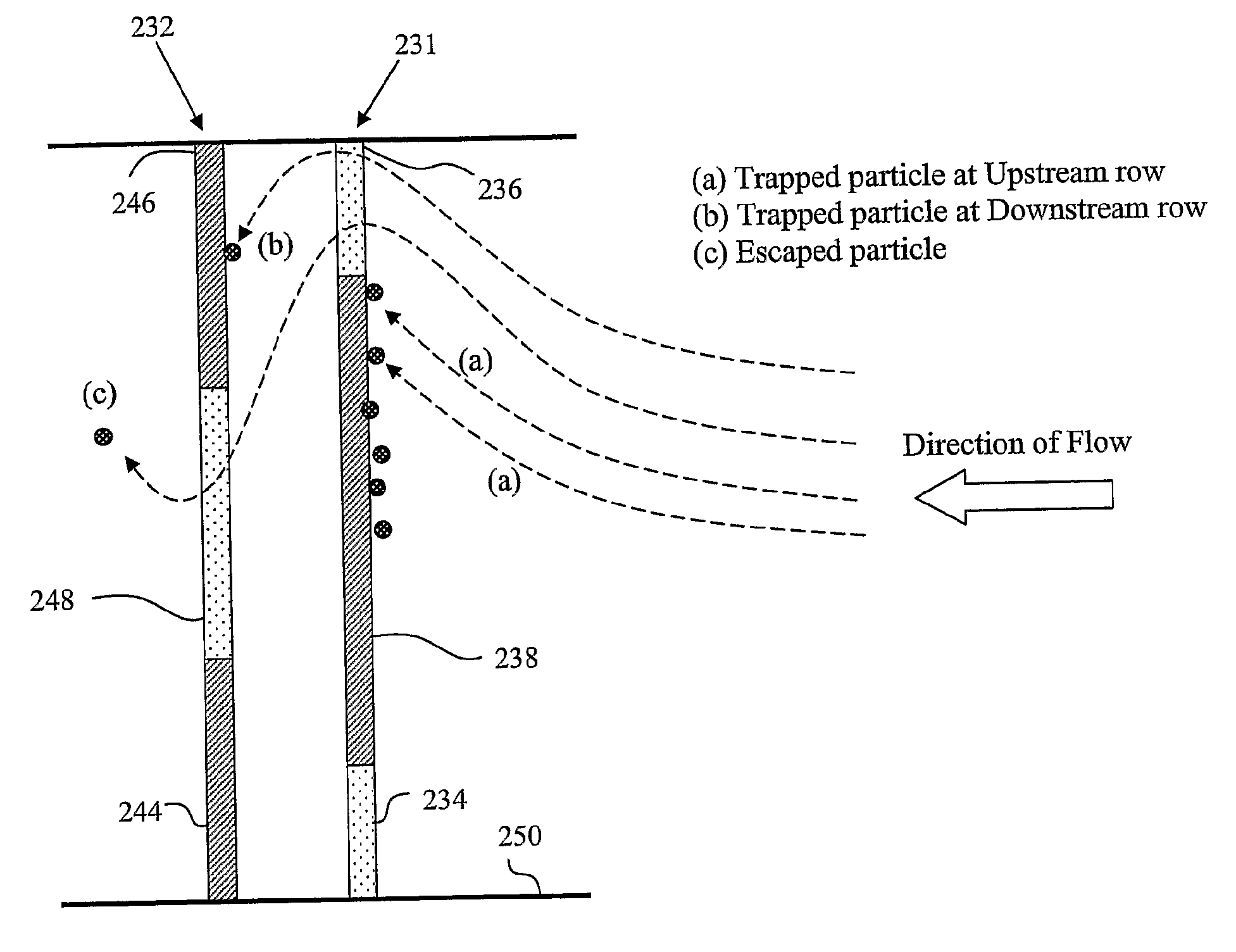
A microfluidic reactor (10) for trapping one or more particles of predetermined nominal size or range of sizes that have entered a flow inlet (12) includes a transparent reaction zone (14) which also serves as an in-situ detection zone wherein the detection zone is arranged so as substantially to correspond in shape to an optical detector (456). A porous filter (16) having a plurality of holes (160) being smaller than the nominal size or range of sizes of the particles (200) are arranged so as to trap the particles in the reaction zone (14) while a fluid (18) flows from the flow inlet (12) through the reaction zone (14) and the filter (16).
Owner:CORNING INC
Diamond abrasive particles and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS6565618B1Smoother finished surfaceAvoid it happening againPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCrystal structureNominal size
Diamond particles are provided having a nominal size of 5 mum or less by D50 measurement and which comprise an explicit thermal effect such as a minute crack in the crystal structure due to a heat treatment at a temperature at least of 1000° C. The diamond particles include diamond converted non-diamond carbon in an amount of at least 0.5% by weight relative to the whole diamond particle. A method for synthesizing the diamond particles includes providing diamond particles having a primary particle D50 average size of 50 nm or greater, subjecting the diamond particles to a heat treatment at a temperature of at least 1000° C. in either a non-oxidizing atmosphere or in a vacuum, and converting the diamond partly to non-diamond carbon.
Owner:ISHIZUKA
Substrates with small particle size metal oxide and noble metal catalyst coatings and thermal spraying methods for producing the same
A substrate having a catalytic surface thereon characterized as a coating of metal oxide and noble metal particles in the nominal diameter size distribution range of <3 microns, and more particularly <1 micron, is produced by thermal spraying a mixture of large size particles (e.g., in a nominal size distribution range of >10 micrometers) of hydroxides, carbonates or nitrates of the metals: cerium, aluminum, tin, manganese, copper, cobalt, nickel, praseodymium or terbium particles; and hydroxides, carbonates or nitrates of the noble metals: ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, iridium, platinum and gold onto the substrate. The coating adheres to the surface and provides desirable catalyst properties.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Toy container for volumetrically reduced diaper
InactiveUS20050155875A1Consumes small amountAmount of spaceContainers for flexible articlesContainer decorationsVacuum packNominal size
A toy for a child serves as a container for storing a volumetrically reduced diaper. The toy includes an interior compartment in which the volumetrically reduced diaper is disposed. The toy has an outward appearance such that it is not evident that said toy contains a diaper. Furthermore, the compartment has a size and configuration that corresponds to a size and configuration of the volumetrically reduced diaper such that the volumetrically reduced diaper completely fits within and consumes the space of the interior compartment. The size of the toy also may be substantially smaller than a nominal size of the diaper disposed therein. Preferably, the diaper is vacuum-packed.
Owner:KDS DEVING LLC
Disguisedly packaging absorbent article
ActiveUS20050155327A1Consumes small amountAmount of spaceSurgical needlesCoin-freed apparatusNominal sizeEngineering
A method of disguisedly packaging an absorbent article includes the steps of: volumetrically reducing an absorbent article such that the volume of the absorbent article is less than a nominal volume of the absorbent article; and disposing the volumetrically reduced absorbent article within a package. The package includes a deceptive size and outward appearance such that it is not visually evident that an absorbent article is disposed therein. Indeed, the size of the package is substantially smaller than the nominal size of the absorbent article, whereby the size of the package contributes to the deceptive outward appearance of the package.
Owner:KDS DEVING LLC
Disguisedly packaged absorbent article
InactiveUS20050155899A1Consumes small amountAmount of spaceDiagnosticsSurgical needlesNominal sizeElectrical and Electronics engineering
A disguisedly packaged absorbent article includes a package in which a volumetrically reduced absorbent article is disposed. The package includes a deceptive outward appearance such that it is not evident that an absorbent article is disposed therein. A size of the package is substantially smaller than a nominal size of the absorbent article, whereby the size of the package contributes to the deceptive outward appearance of the package. A shape and indicia of the package also may contribute to the deceptive outward appearance of the package.
Owner:KDS DEVING LLC
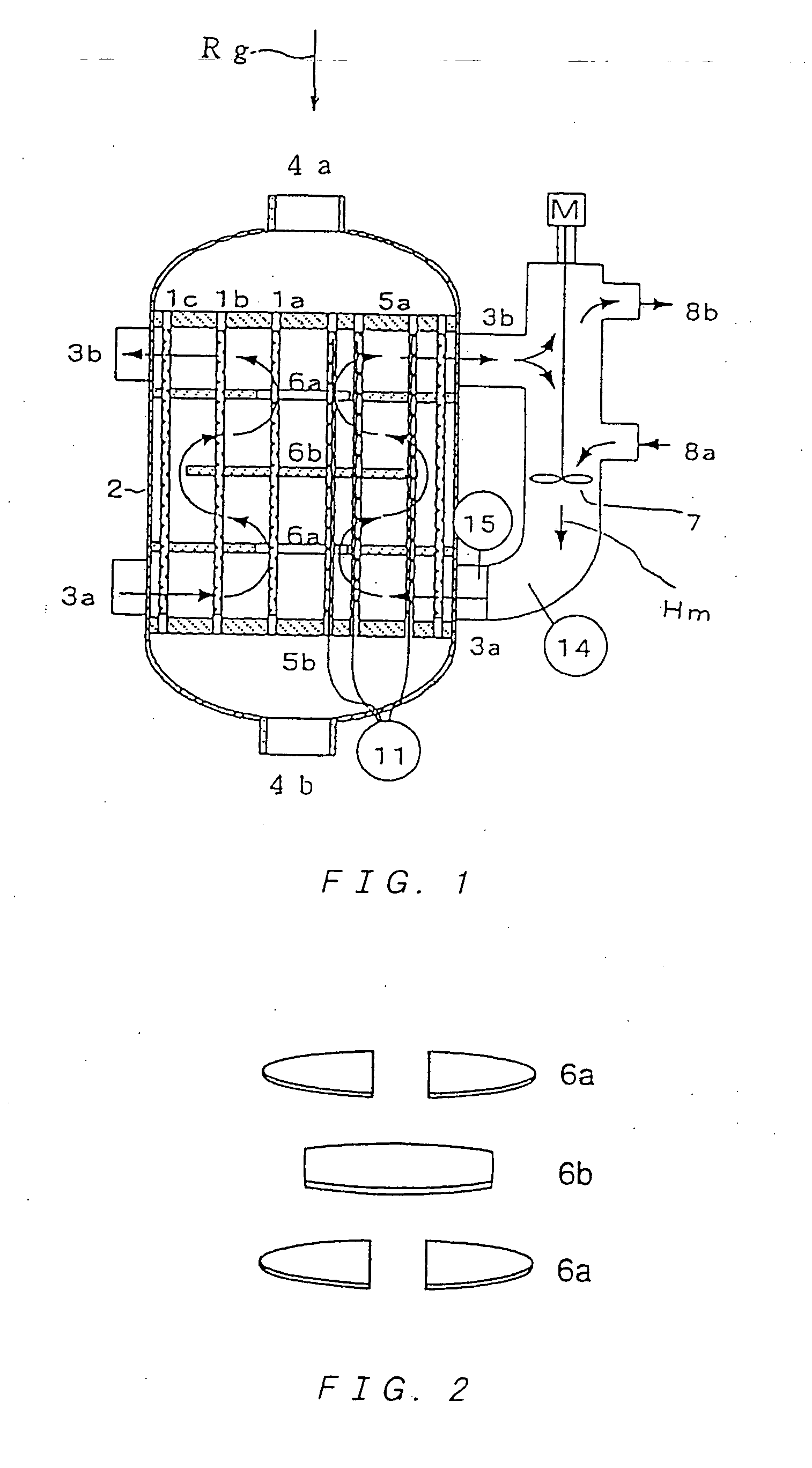
Multitube reactor, vapor phase catalytic oxidation method using the multitube reactor, and start up method applied to the multitube reactor
InactiveUS7144557B2Long catalyst lifeAvoid YieldOrganic compound preparationSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusCatalytic oxidationNominal size
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Tool kit
A tool kit includes a number of wrenches of various sizes and a corresponding number of go-through type sockets. Each wrench includes a handle with a box end with a nominal size. Each socket includes an engaging portion for engaging with the box end of a corresponding one of the wrenches. The engaging portion includes a nominal size the same as that of the corresponding one of the wrenches. Each socket further includes a driving portion having a driving hole with a nominal size the same as that of the corresponding one of the wrenches.
Owner:HU BOBBY
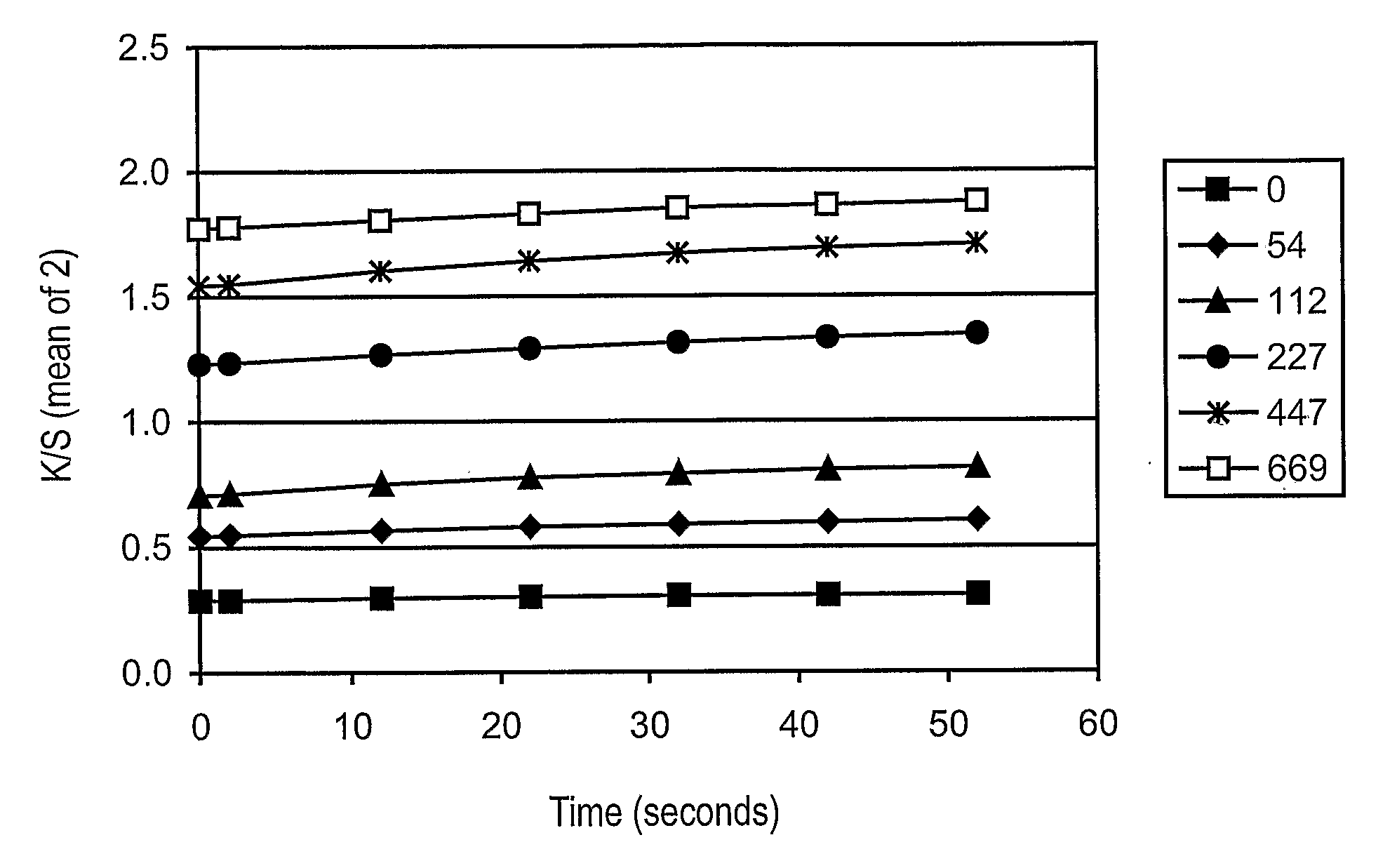
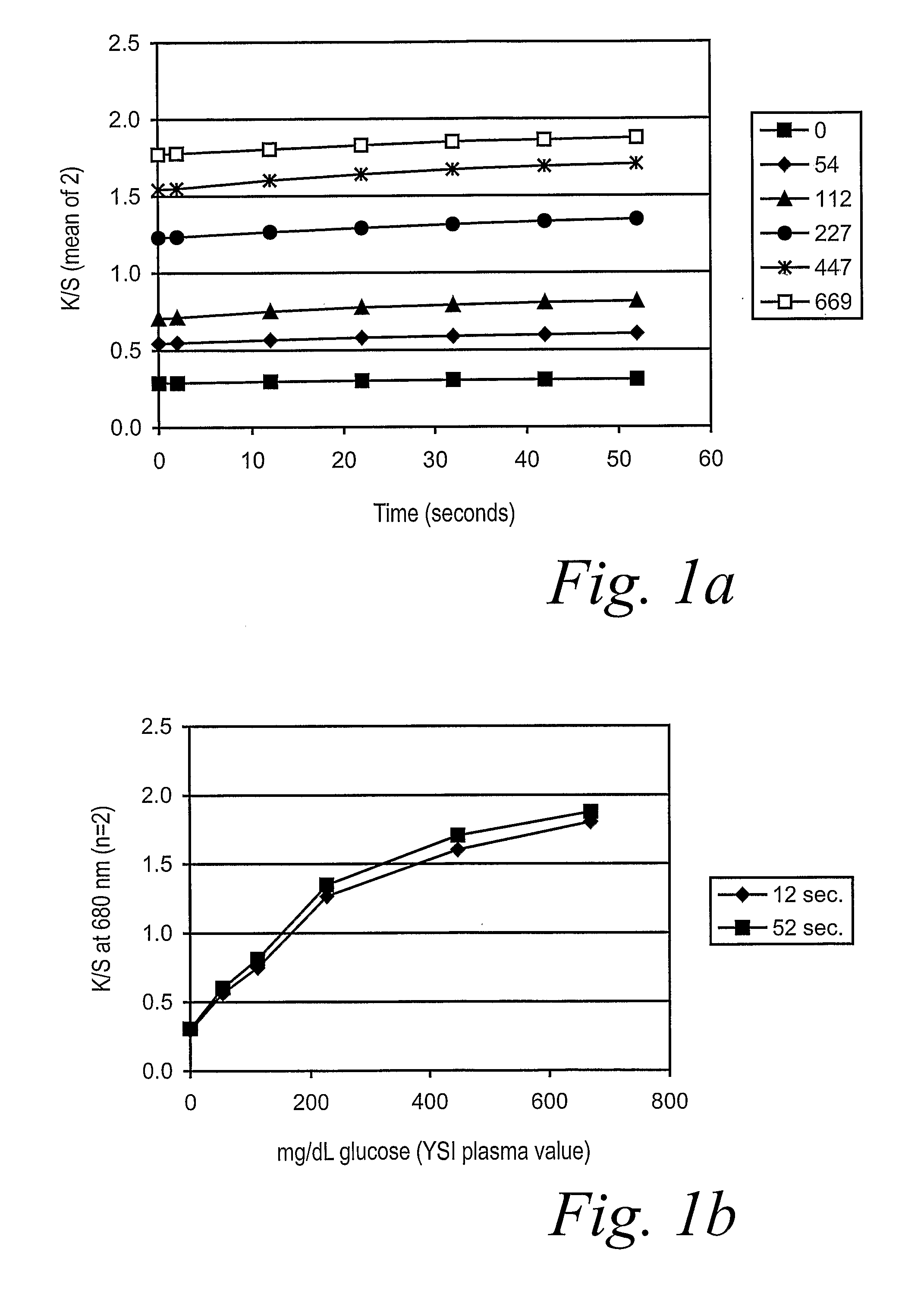
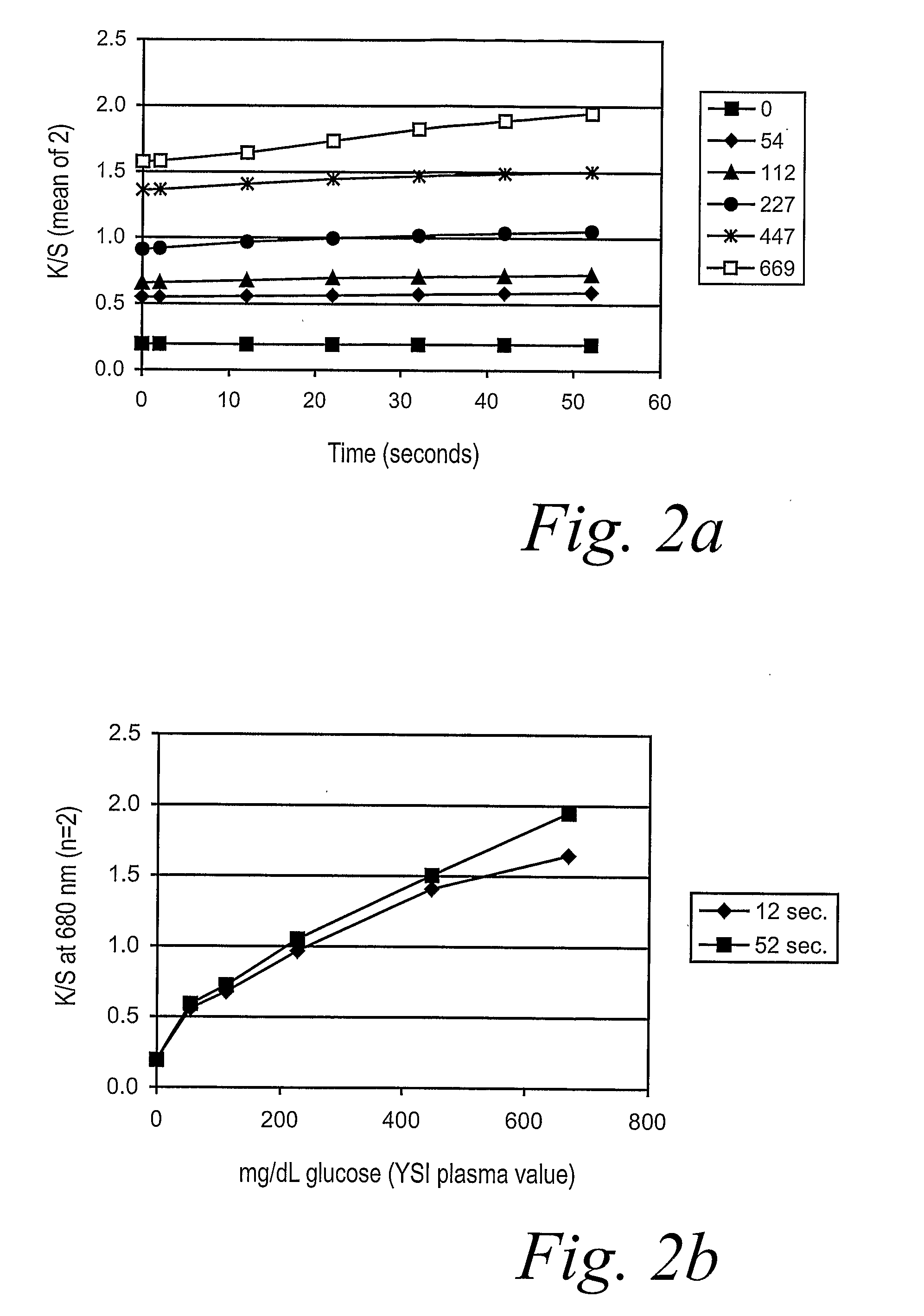
Size self-limiting compositions and test devices for measuring analytes in biological fluids
ActiveUS7964372B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPorous substrateWater insoluble
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Microfluidic filtration unit, device and methods thereof
InactiveUS20100288689A1Reduce flow of fluidLess sensitiveSamplingFixed microstructural devicesFiltrationNominal size
A microfluidic filtration unit for trapping particles of a predetermined nominal size present in a fluid is provided. The unit comprises a fluid chamber connected to an inlet for introducing the fluid to be filtered and an outlet for discharging filtered fluid, a filtration barrier arranged within the fluid chamber, said filtration barrier comprising a plurality of pillars arranged substantially perpendicular to the path of fluid flow when fluid is introduced into the fluid chamber, said pillars being aligned to form at least one row extending across said path of fluid flow, wherein each of said at least one row of pillars in the filtration barrier comprises at least one fine filtration section comprising a group of pillars that are spaced apart to prevent particles to be filtered from the fluid from moving between adjacent pillars, and at least one coarse filtration section comprising a group of pillars that are spaced apart to permit the movement of particles between adjacent pillars.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Fast curing optical adhesive
An adhesive composition for joining optical components is described. The adhesive composition comprises at least one epoxy resin, a visible light photoinitiating system comprising at least one of a cationic photoinitiator and a sensitizer, a polyol and at least 50 wt. % of a nanoparticle filler. The visible light photoinitiating system includes at least one of a cationic photoinitiator and a sensitizer and the nanoparticle filler comprises a first nanoparticle having a first nominal size and a second nanoparticle having a second size. The adhesive composition has a refractive index between 1.44 and 1.47 and a dn / dT of less than −2E−4 when cured.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Integrated circuit structures for increasing resistance to single event upset
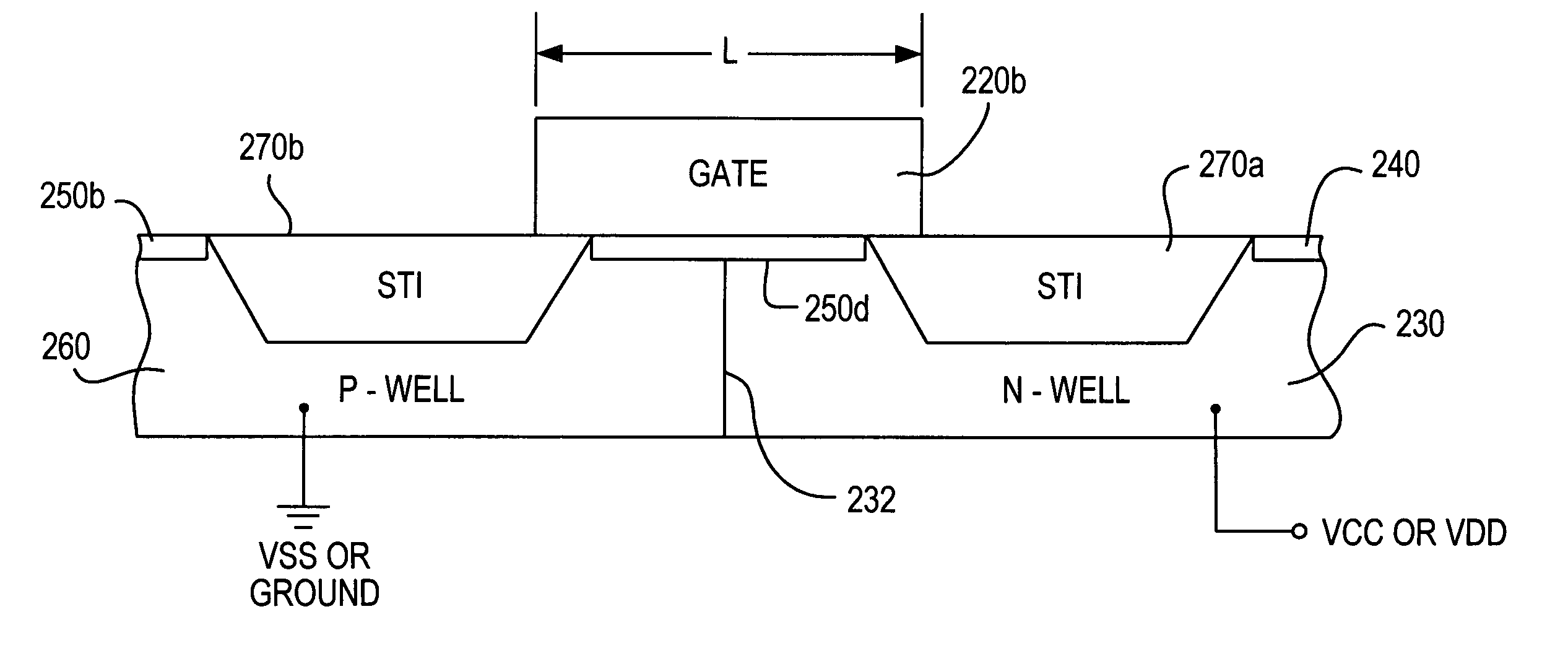
InactiveUS20060001045A1Improve the immunityImprove robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceNominal size
A configuration memory cell (“CRAM”) for a field programmable gate array (“FPGA”) integrated circuit (“IC”) device is given increased resistance to single event upset (“SEU”). A portion of the gate structure of the input node of the CRAM is increased in size relative to the nominal size of the remainder of the gate structure. Part of the enlarged gate structure is located capacitively adjacent to an N-well region of the IC, and another part is located capacitively adjacent to a P-well region of the IC. This arrangement gives the input node increased capacitance to resist SEU, regardless of the logical level of the input node. The invention is also applicable to any node of any type of memory cell for which increased resistance to SEU is desired.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
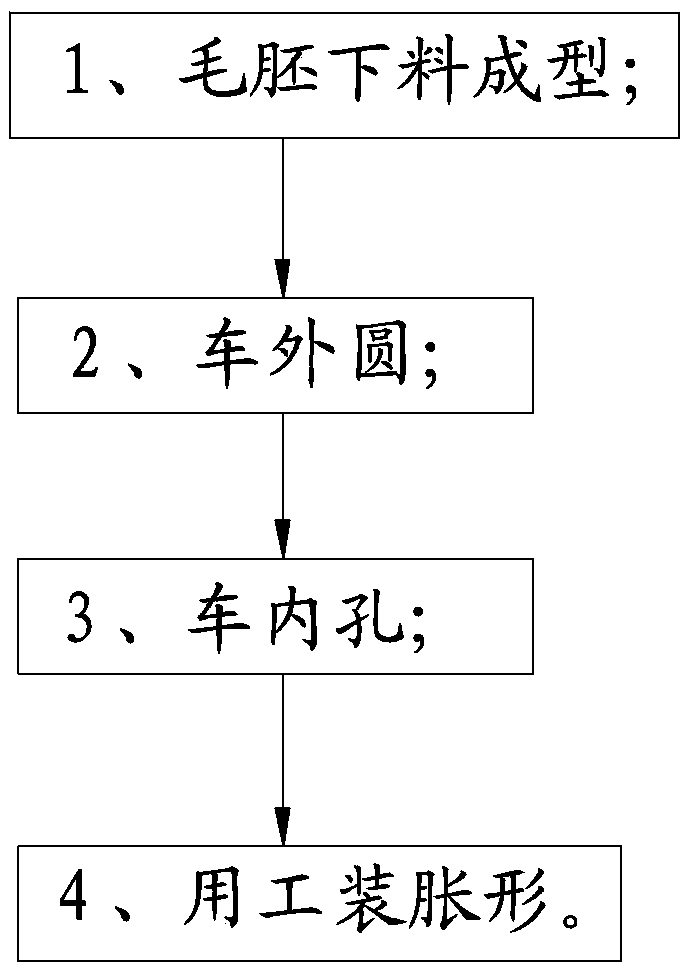
Cabin processing method and bulging tooling used in same
The invention relates to the technical field of aerospace industries, in particular to an aircraft cabin processing method and a bulging tooling used in the same. The method comprises the following steps: 1, blank blanking; 2, machining an excircle; 3, machining an inner hole, wherein the size of the machined inner hole is smaller than that of a nominal size; 4, using a tooling to perform bulging up to meet a required size. According to the method, the machining and the bulging processing are adopted, so that the precision requirements on the machining are greatly reduced, the production efficiency is improved, the consistency and the qualification rate of finished products are greatly improved, the manufacturing cost is relatively reduced, the cost is greatly reduced, and the economic efficiency is improved.
Owner:北京新航钛空天技术有限公司
Apparatus and method for treating products
InactiveCN102792475AShort reaction timeReduce the total massCalendersMetal working apparatusNominal sizeEngineering
An apparatus (10) for treating products continuously fed to the apparatus comprises a first roller (18) rotatable around a first rotation axis (19) and a second roller (20) rotatable around a second rotation axis (39) parallel to the first rotation axis (19). A treatment gap (16) is formed between the first roller (18) and the second roller (20). The apparatus further comprises an adjusting means (30) for inline adjusting the nominal size of the treatment gap (16), wherein the adjusting means comprises at least one piezoelectric element (30) for shifting the position of the first rotation axis (19) and / or the second rotation axis (39).
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
Lithographic processing method and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20040265710A1Low costImprove toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistNominal size
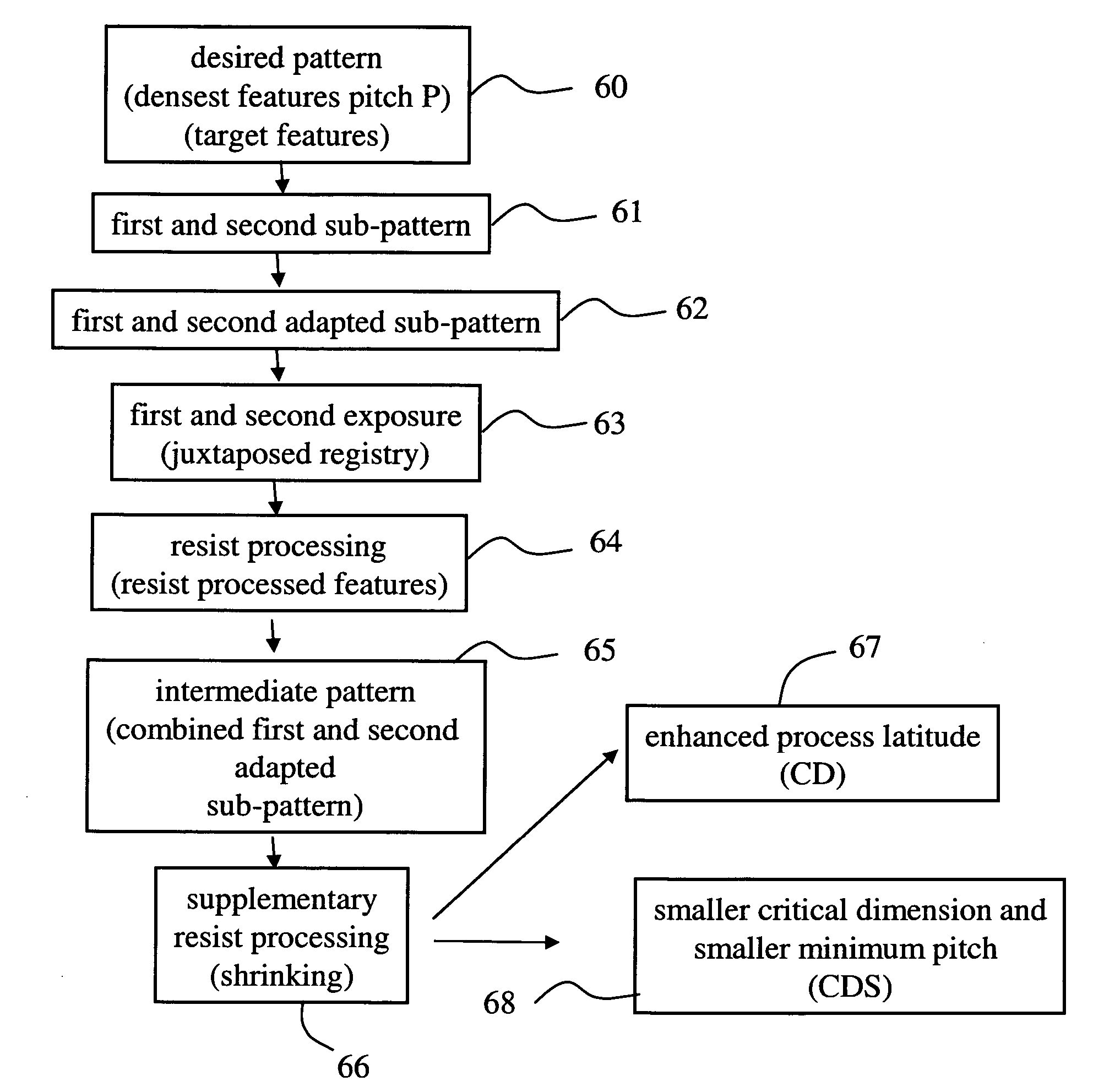
A lithographic double exposure processing method for providing to a device layer a pattern comprises the steps of expanding each feature of a first mask pattern and second mask pattern with a preselected dilatation distance before the first and second exposure steps, resist-processing the exposed radiation sensitive layer of a substrate to provide resist-processed features corresponding to said pattern whereby each resist-processed feature is expanded with respect to its nominal size, and shrinking said resist-processed features over a preselected shrinking distance by applying supplementary resist-processing to said resist-processed features.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multitube reactor, vapor phase catalytic oxidation method using the multitube reactor, and start up method applied to the multitube reactor
ActiveUS20050131254A1Long catalyst lifeAvoid YieldOrganic compound preparationSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusRoom temperatureNominal size
A multitube reactor, wherein tubes having smaller tolerance between a nominal size and actual sizes are used as reaction tubes to stably perform a high yield reaction for a long period, a catalyst is filled into the reaction tubes so that the catalyst layer peak temperature portions of the reaction tubes are not overlapped with the connection sites thereof with baffles to effectively prevent hot spots from occurring and stably perform a reaction for a long period without the clogging of the reaction tubes, a heat medium and raw material gas are allowed to flow in the direction of a countercurrent and a specified type of catalyst is filled into the reaction tubes so that activity is increased from the inlet of the raw material gas to the outlet thereof to prevent the autooxidation of products so as to prevent equipment from being damaged due to the reaction, and, at the time of starting, gas with a temperature of 100 to 400° C. is led to the outside of the reaction tubes to increase the temperature of the reaction tubes and, a heat medium, which is solid at the room temperature, is heated to circulate to the outside of the reaction tubes to efficiently start up the reactor without affecting the activity of the catalyst.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Size Self-Limiting Compositions and Test Devices for Measuring Analytes in Biological Fluids
ActiveUS20090123955A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementPorous substrateWater insoluble
A test strip or electrochemical sensor for measuring the amount of an analyte in a hiological fluid, e.g., the glucose content of whole blood, includes a size self-limiting reagent formulation employing an enzyme system for reaction with the analyte, the reactive system mixed into a water-soluble swellable polymer matrix containing small water-insoluble particles having a nominal size of about 0.05 to 20 μm, preferably about 1 to 10 μm. The weight ratio of the water-insoluble particles to the water-soluble swellable polymer matrix is about 1 / 2 to 2 / 1. The reagent formulation is deposited onto a non-porous substrate to form a thin layer about 6-16 μm thick, providing a rapid and stable response to application of a sample, while being insensitive to the amount of the sample.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Asphalt mixture mineral aggregate gradation composition design method using internal friction angle as design index
InactiveCN106351099AReduced potential for shear flow deformationImprove stabilityIn situ pavingsFilling materialsNominal size
The invention belongs to the technical field of traffic civil engineering application, and particularly relates to an asphalt mixture mineral aggregate gradation composition design method using the internal friction angle as a design index. A stage-by-stage filling theory is used; materials with the lower stage of particle diameter D1 are filled into maximum-nominal-size NMAS; by measuring the internal frictional angle phi of aggregates at different proportions, the proportion corresponding to the maximum internal frictional angle is used as an optimum composition proportion for forming the mineral stable framework; by such analogy, the optimum composition proportion relationship of each grade of coarse aggregates in the asphalt mixture can be obtained, so that a stable coarse aggregate framework structure is formed. Then, a bailey method is used for designing the fine aggregate and filling material proportion; the mineral aggregate gradation designed by the method provided by the invention realizes shearing resistance and compactness. The method has the advantages that the targeted performance is good; by aiming at the physical damage features of track damages of the asphalt pavement in Guangxi high-temperature hot and humid area, i.e., the insufficient high-temperature stability, the track-resistant asphalt mixture mineral aggregate gradation is designed; the mineral aggregate gradation has a stable framework compact structure.
Owner:GUANGXI TRANSPORTATION SCI & TECH GRP CO LTD
Testing system of steam hydrophobic valve type
InactiveCN104931243ARealize automatic controlFulfill the needs of the testMachine part testingAutomatic controlNominal size
The invention discloses a testing system of a steam hydrophobic valve type, and the system comprises a high-pressure tank device which is used for providing steam with the specific testing pressure and temperature and hot condensed water for a tested drain valve, steam and hot condensed water pipes which are connected between the high-pressure tank device and the front end of the tested drain valve, a discharge pipe which is disposed in the direction of the rear end of the tested drain valve, a pipe-type telescoping joint which is connected between the rear end of the tested drain valve and the discharge pipe, and a monitoring device which is used for monitoring the on / off of the tested drain valve. The monitoring device comprises a first sight glass which is disposed between the pipe-type telescoping joint and the rear end of the tested drain valve. The first sight glass moves along with the stretching and drawing of the pipe-type telescoping joint. The system can achieve automatic control, and is used for the type tests of different types of stream drain valves in different nominal sizes.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & TEST
Method for measuring deviation of nominal size of bore diameter of bearing inner ring
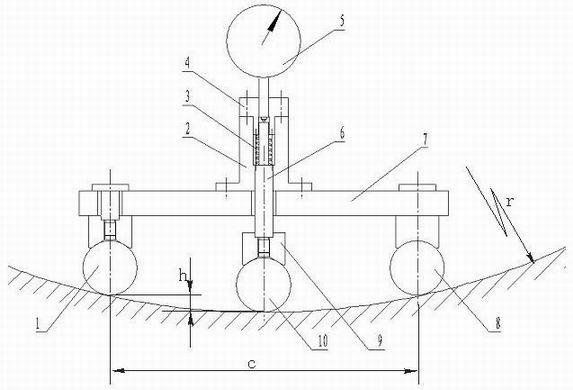
InactiveCN102278932ASimple structureLight structureMechanical diameter measurementsMeasurement deviceMeasuring instrument
Disclosed is a method for measuring the deviation of the nominal size of the bore diameter of a bearing inner ring. The measuring device is composed of a first positioning ball (1), a positioning sleeve (2), a pressure spring (3), a cover plate (4), a measuring instrument (5), a measuring rod (6), a balancing rack (7), a second positioning ball (8), a positioning sleeve (9) and a radial moving positioning ball (10). Reference calibration is based on h=r-1 / 2(4r2-C3)1 / 2, a first standard block (11), a second standard block (12), a third standard block (13) are provided, and an original value is obtained. The distance between two points where first positioning ball and the second positioning ball contact with the bearing inner ring is equal to the chord length of the bearing inner ring with a bore diameter of 2r, a height difference h formed by the connecting line of the horizontal line of the contact point of the radial moving positioning ball and the inner ring bearing, and the distance of the two points is equal to the chord height of the bearing inner ring with a bore diameter of 2r, so that the difference between the measuring value and the original value is the deviation of the nominal size of the bore diameter of the bearing inner ring.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for manufacturing a catheter
An intraparenchymal infusion catheter system for delivering drugs or other agents to selected sites in an organism, such as a human, includes a pump that may be implanted or disposed outside the organism. A catheter is coupled to the pump. The catheter comprises a flexible biocompatible tubular portion terminating in a free distal end. The distal end of the catheter bears a rounded tip, a portion of which is slidably disposed within the lumen of the tubular portion. The tip is porous for discharging an agent or drug to a selected site. The tip has a microporosity of less than or equal to 0.22 microns. The tubular portion is composed from a material that will expand from its nominal size when exposed to a stimulus such as heat or a solvent and return to its nominal size when the stimulus is withdrawn. By expanding the tubular portion, a physician can select the amount of the tip that is exposed to the organism, thereby customizing the catheter to the structural size of the selected site within the body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Pipe Fitting Wireform for Measuring Linear Distance and Method
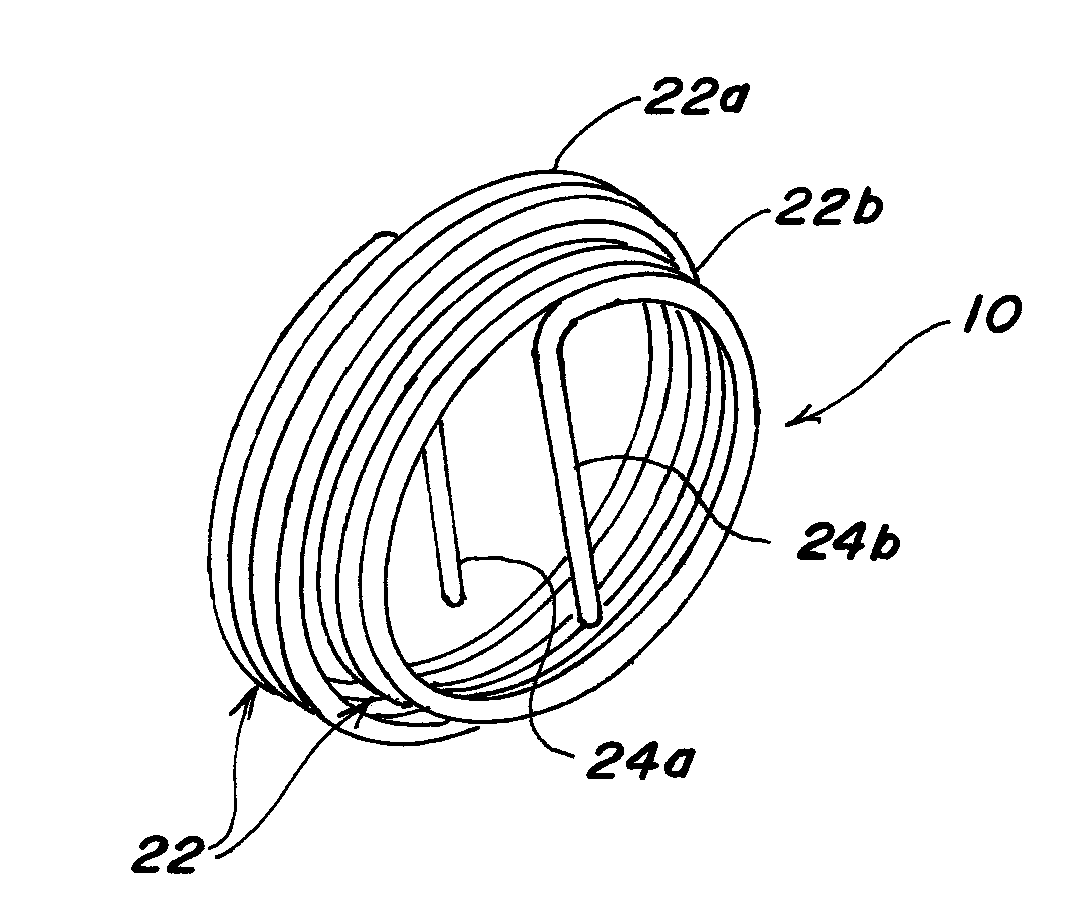
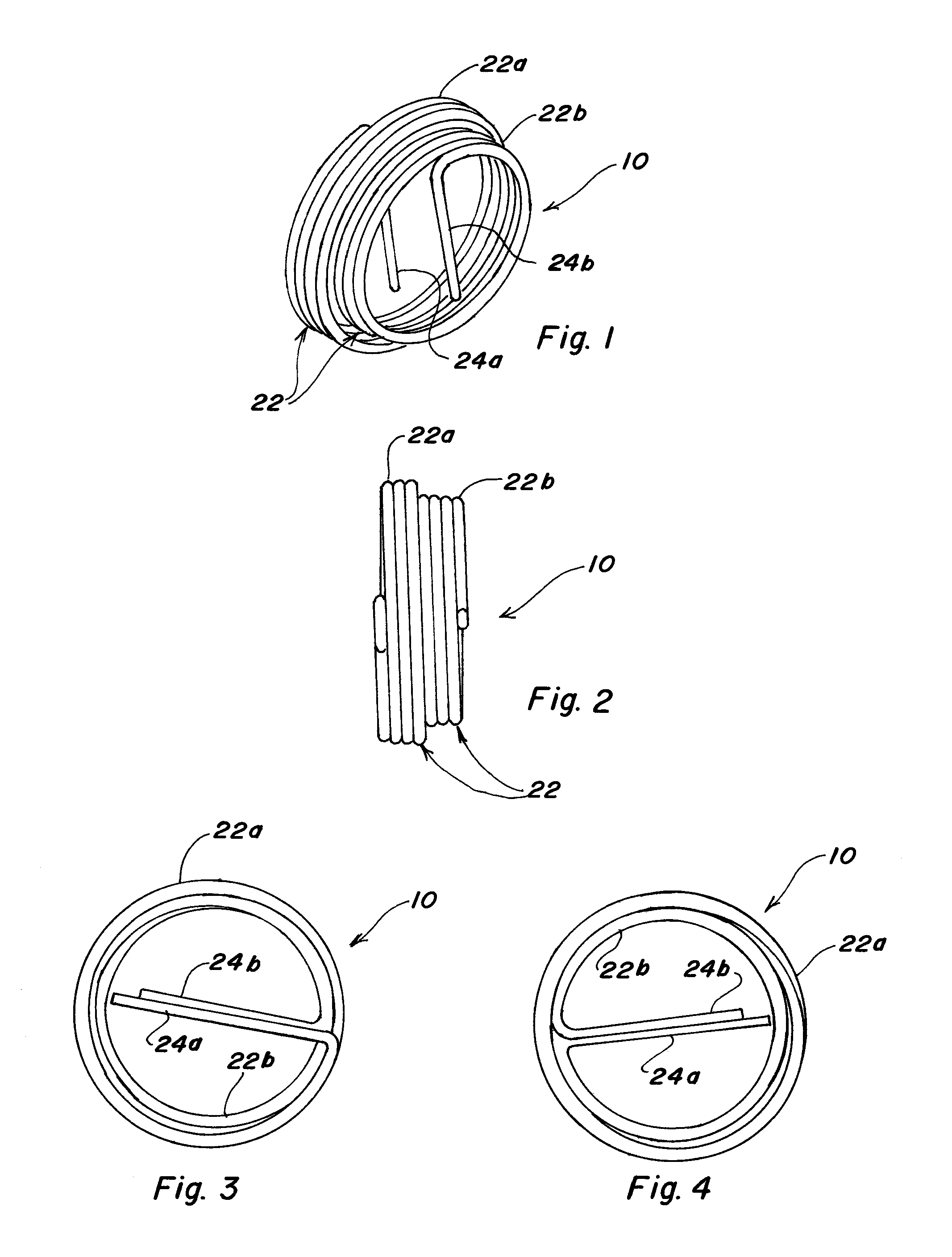
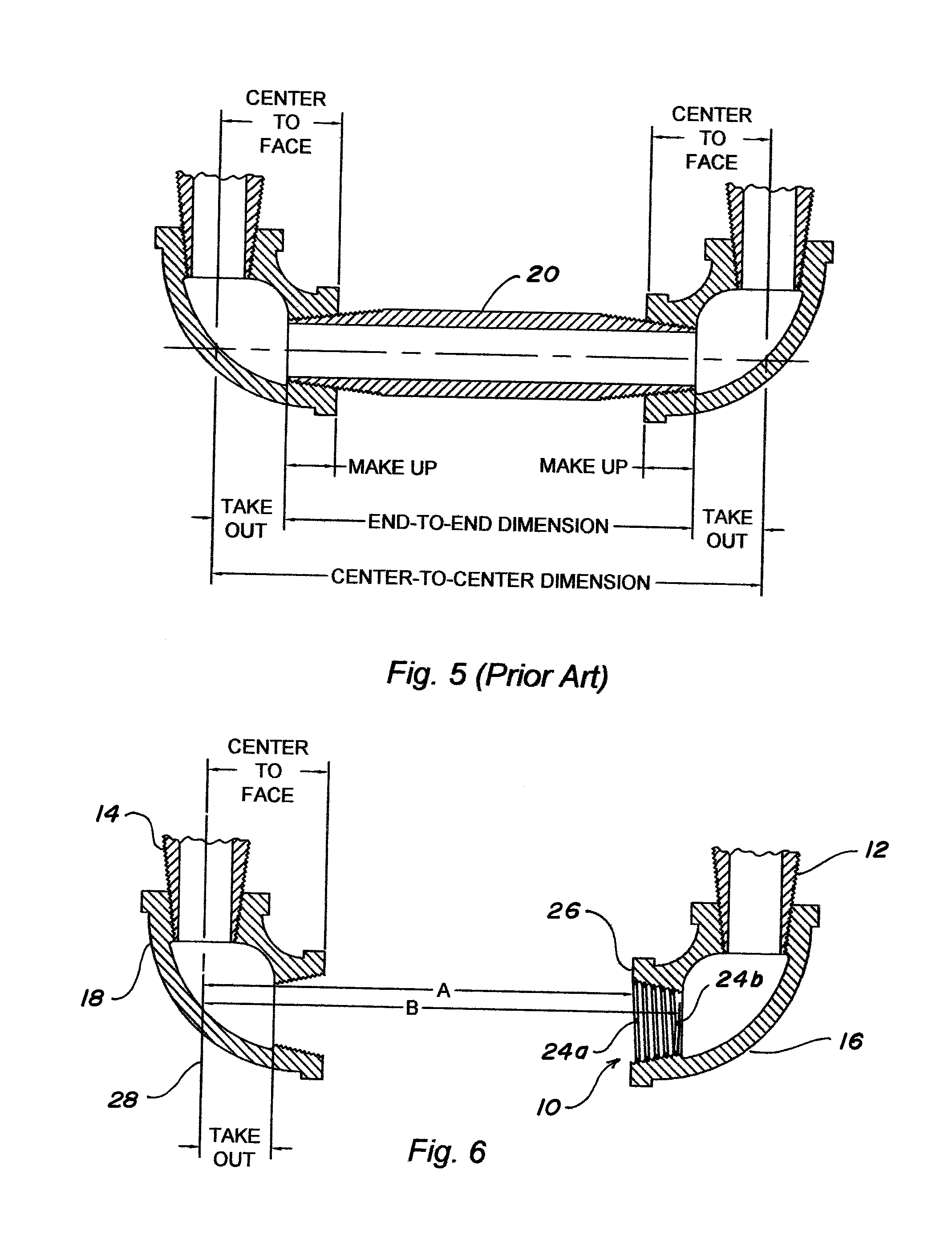
A pipe fitting wireform which when threaded into a fitting allows a user to measure center-to-end or end-to-center of the fitting to determine the length of a pipe needed to connect a pair of pipe fittings in a pipe assembly. The fitting wireform is a coil with a free end bent laterally to form a tang. The fitting wireform having an outside diameter substantially equal to the nominal size of the pipe fitting with substantially the same number of turns per inch as the pipe fitting such that the pipe fitting wireform can be threaded into the pipe fitting.
Owner:LONG FREDRICK D
A composite body of silicon carbide and binderless carbon and process for producing
A composite body of silicon carbide having binderless, allotropic carbon granules distributed throughout is produced. The nominal size of the binderless allotropic carbon granules can range from 5 to 500 micrometers. The concentration of the binderless allotropic carbon particles can vary from 1.0 to 35.0 weight percent. The process to produce such a composite body is to sinter silicon carbide with binderless, carbon-yielding precursor granules. The composite body is utilized in tribological applications. The dense, impervious silicon carbide-binderless carbon composite exhibits excellent physical and tribological characteristics when used as a mechanical face seal, a sliding bearing arrangement, or some other rubbing component.
Owner:约翰格兰有限公司
Wheel Rim Assembly with Integral Air Cooled Lubricant Cavity and Hub
The two-piece wheel rim assembly includes first and second hub sections affixed together and rotatably mounted on an axle by a set of bearings which are longitudinally spaced apart on the axle. The hub sections have radially inboard wall segments and radially outboard segments. The inboard segments form a radial cavity about the axle longitudinally bounded by the bearings. An oil bath substantially fills the radial cavity except for a small thermal expansion air pocket. The thermal expansion air pocket is positioned above the axle and the bearings when the hub-tire combination is in use. The thermal expansion air pocket has a nominal size only sufficient to account for thermal expansion and contraction of the wheel.
Owner:HAMILTON THOMAS S
Heavy concrete
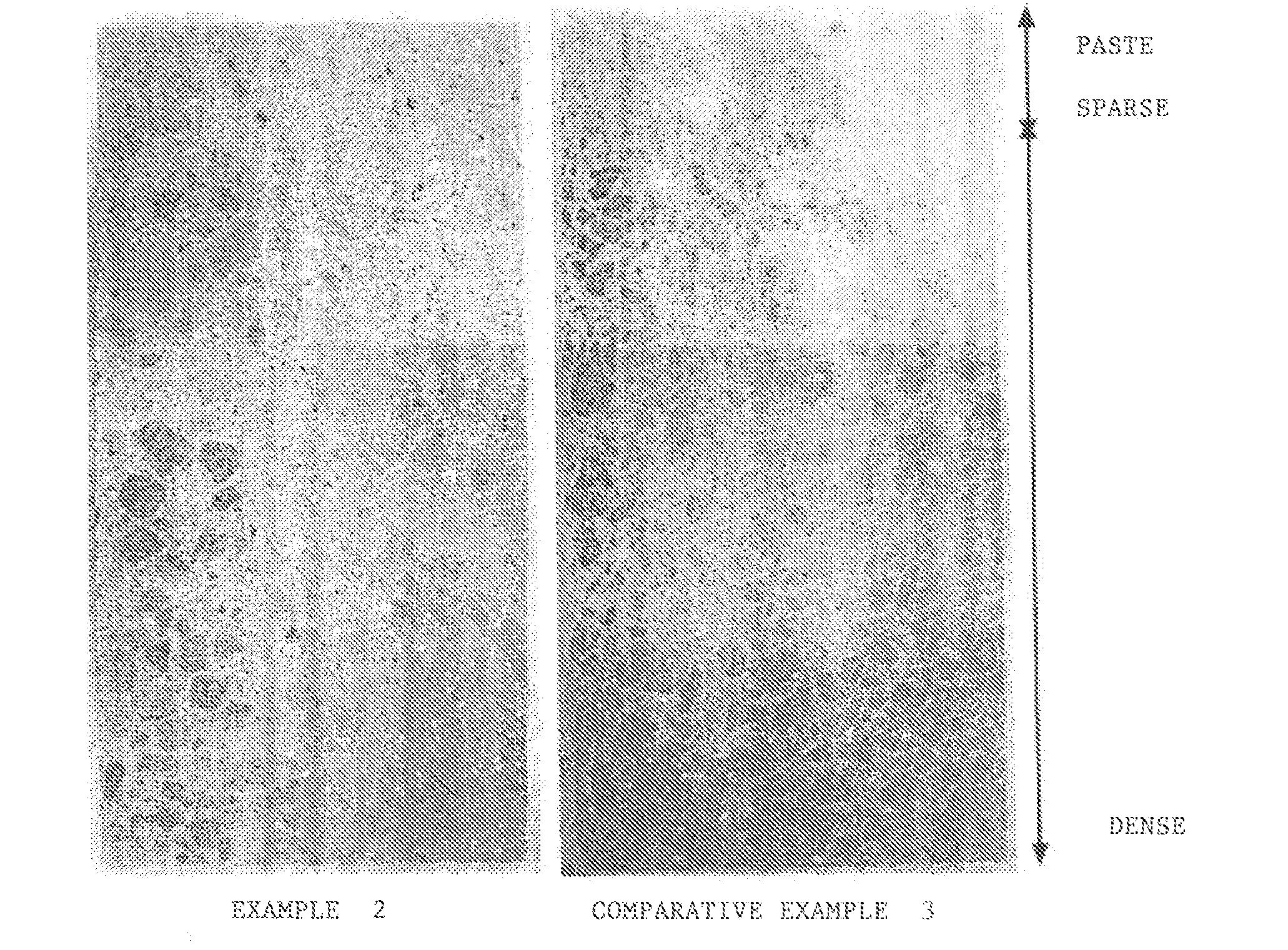
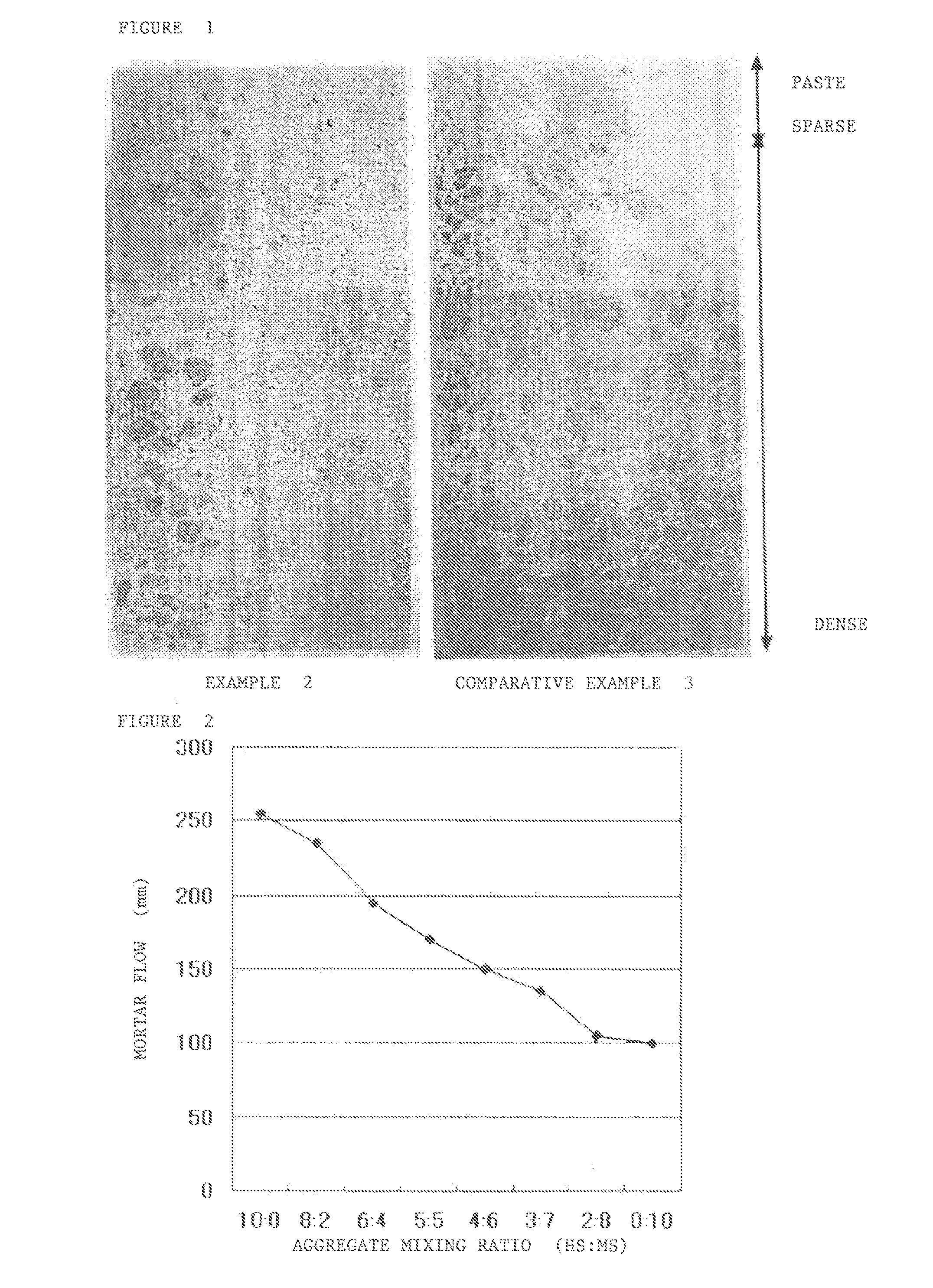
InactiveUS20100282130A1Improve liquidityHigh densitySolid waste managementShieldingMethyl celluloseNominal size
It is aimed at providing a heavy concrete, which does not require addition of a thickener such as methyl cellulose, which is less in segregation between a heavy aggregate and a cement paste, and which is high in flowability and excellent in construction ability. The present invention provides a heavy concrete comprising, at least, a cement, a heavy aggregate, and water, mixed with one another, characterized in that the heavy fine aggregate includes hot scarves brought about in a scarfing process of a steel slab surface. The present invention further provides the above-described heavy concrete characterized in that the heavy fine aggregate includes fine aggregate particles passing through a sieve having a nominal size of 0.15 mm, in an amount of 10% to 20% in mass percentage, and the heavy fine aggregate includes spherical particles each having a distortion irregularity of 3.3 or less as defined below, in an amount of 20% or more in the whole of particles having diameters between 50 μm inclusive and 5 mm inclusive in the heavy fine aggregate:[Distortion irregularity]=[Length of circumferential outline of particle] / [Diameter of true circle having the same area as the area of the particle providing the outline].
Owner:TAIHEIYO CEMENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com