Patents
Literature
48 results about "Fovea centralis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
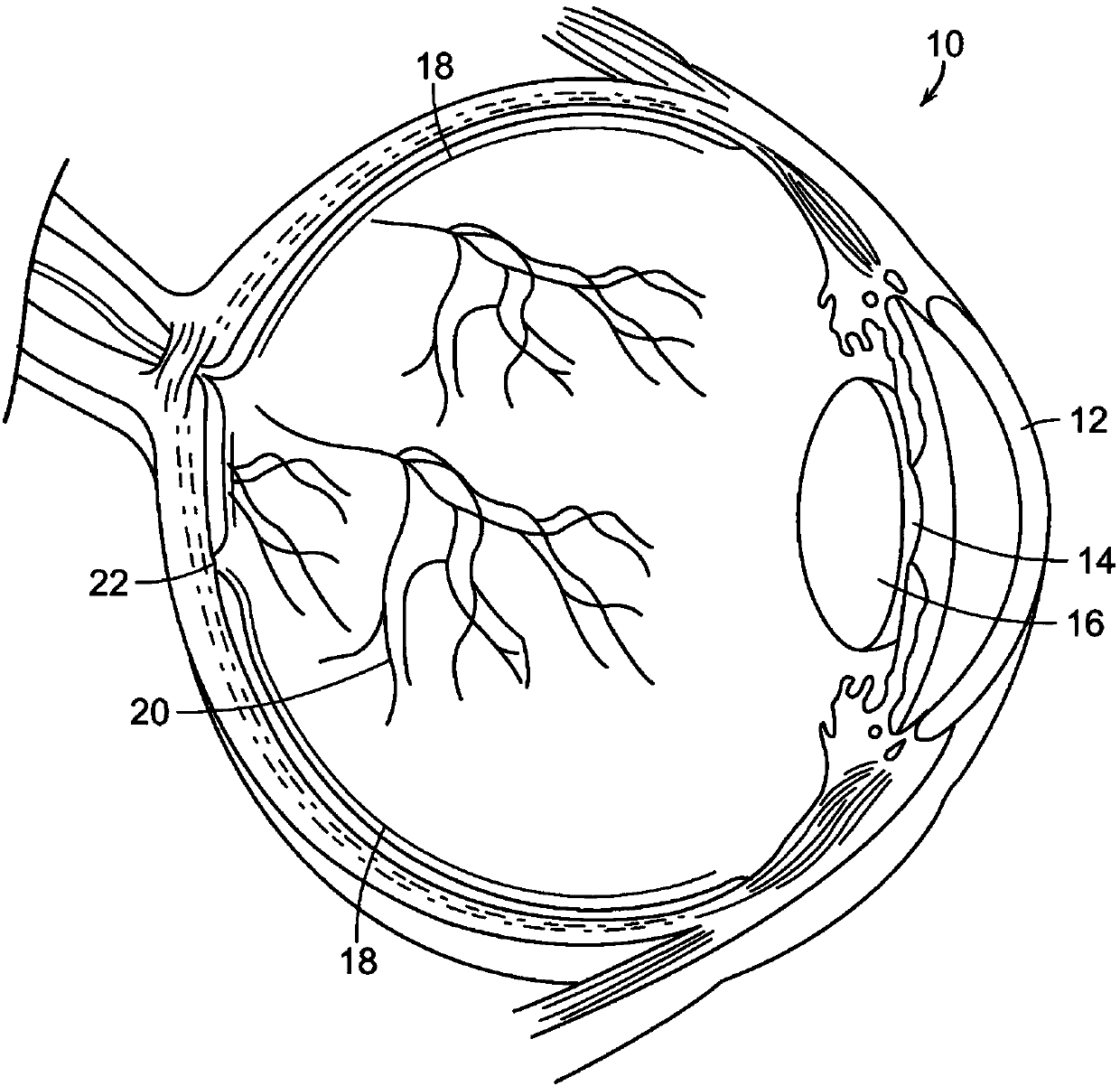
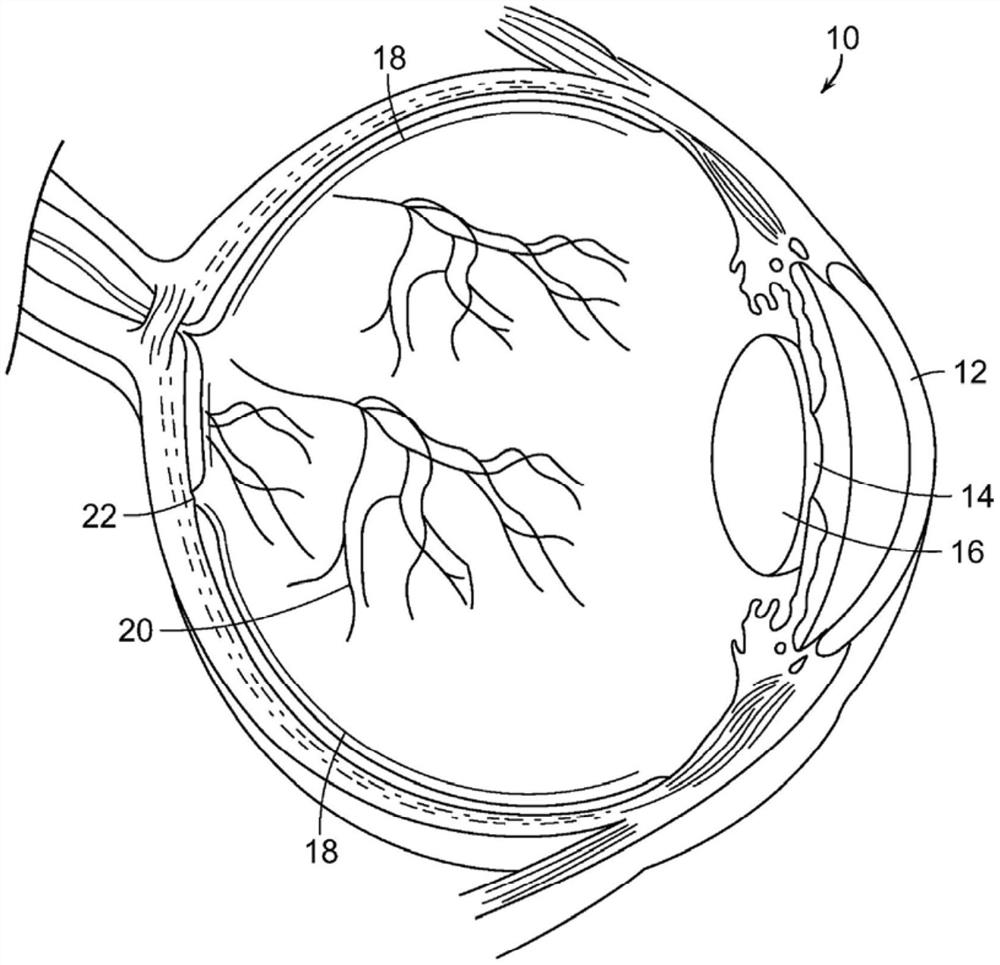
The fovea centralis is a small, central pit composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the macula lutea of the retina. The fovea is responsible for sharp central vision (also called foveal vision), which is necessary in humans for activities for which visual detail is of primary importance, such as reading and driving. The fovea is surrounded by the parafovea belt and the perifovea outer region.
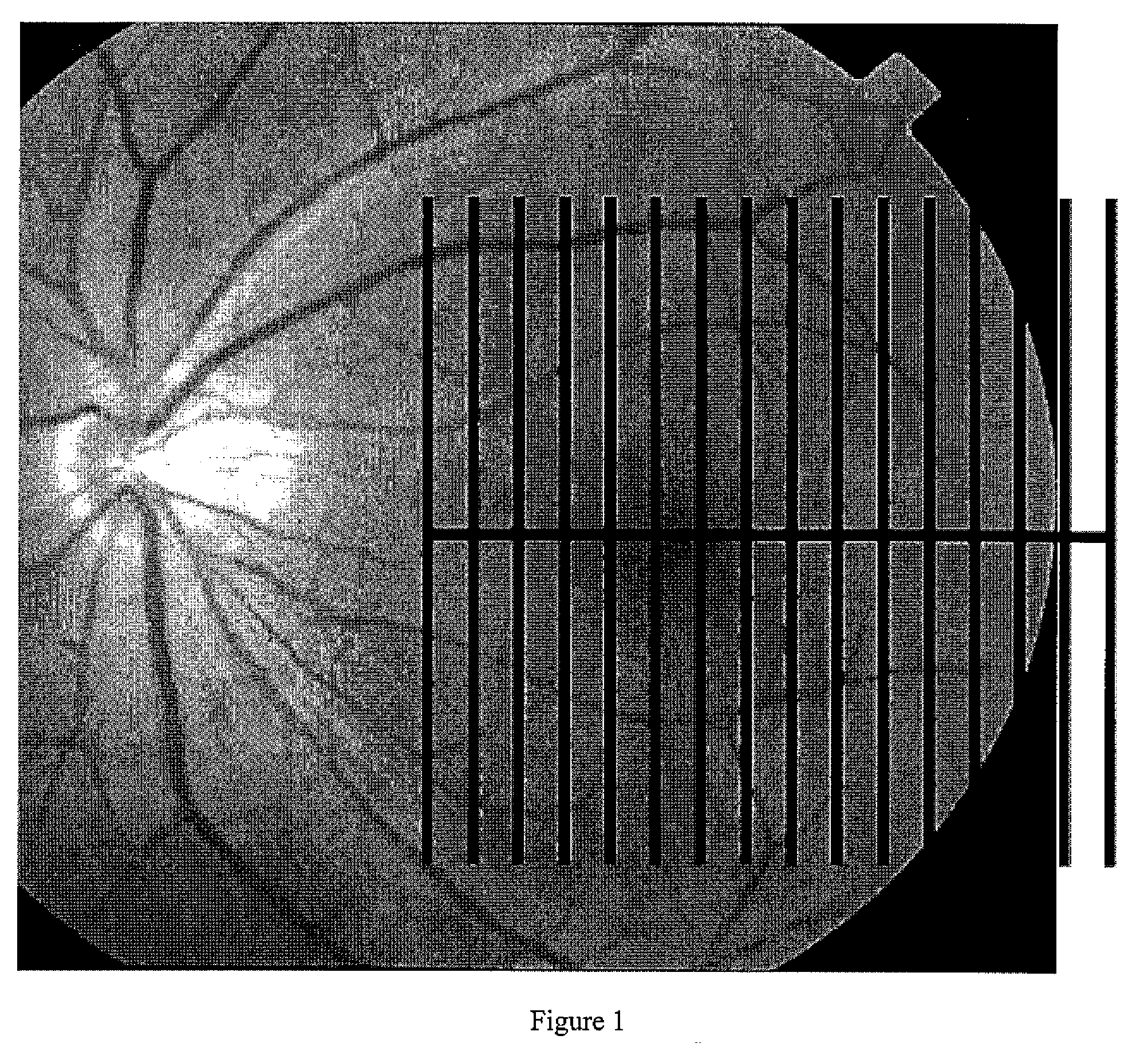
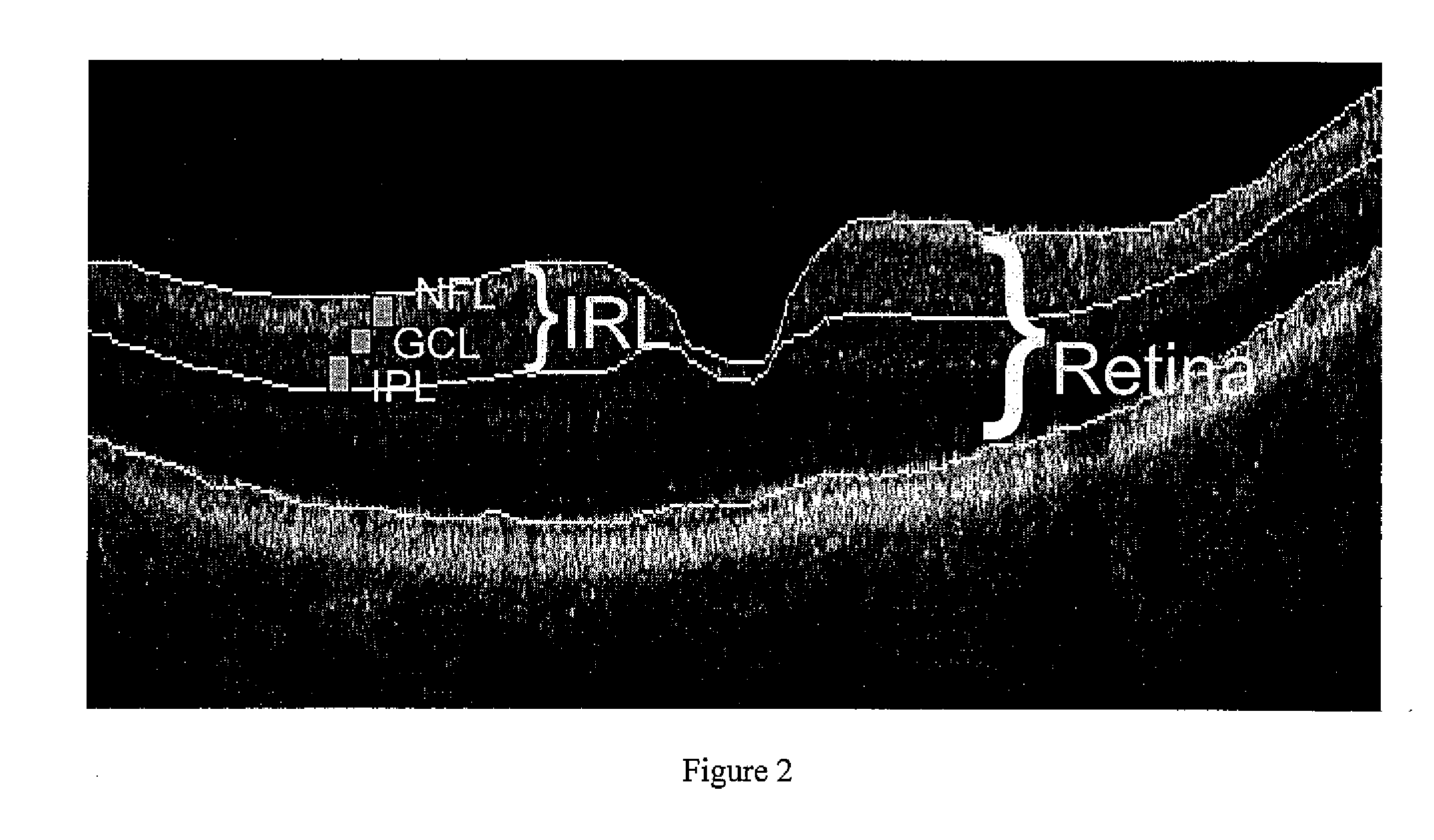
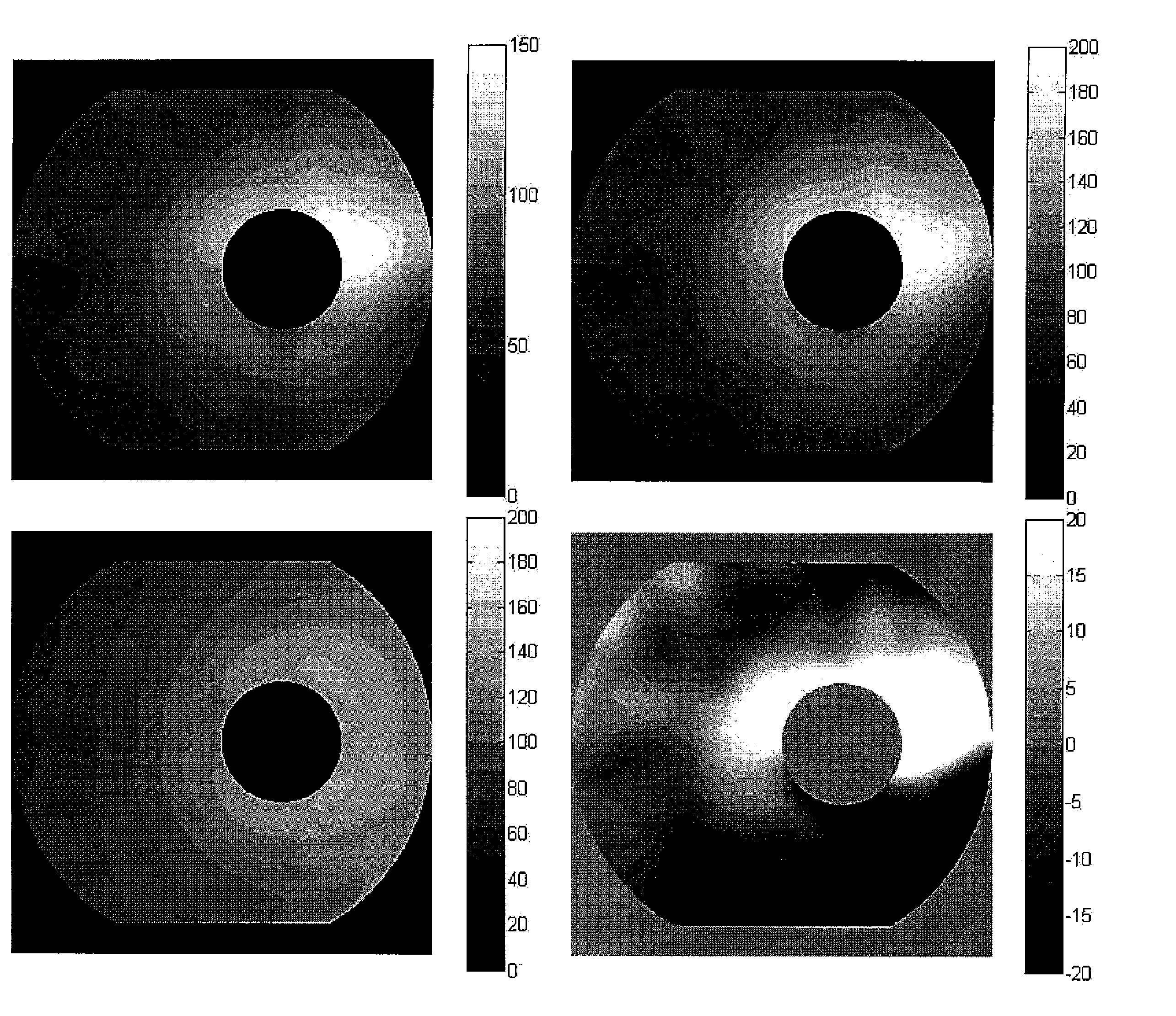
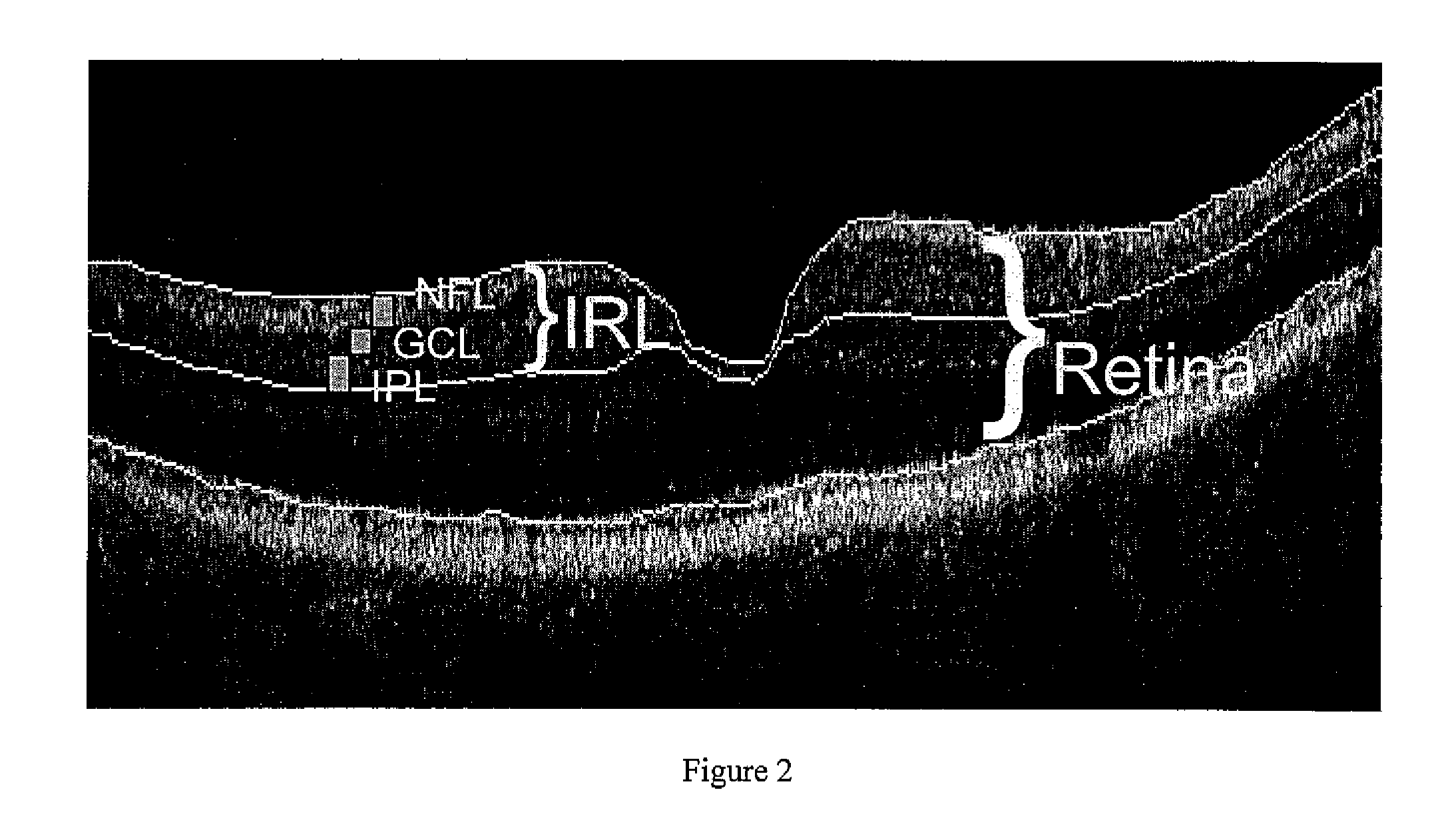
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
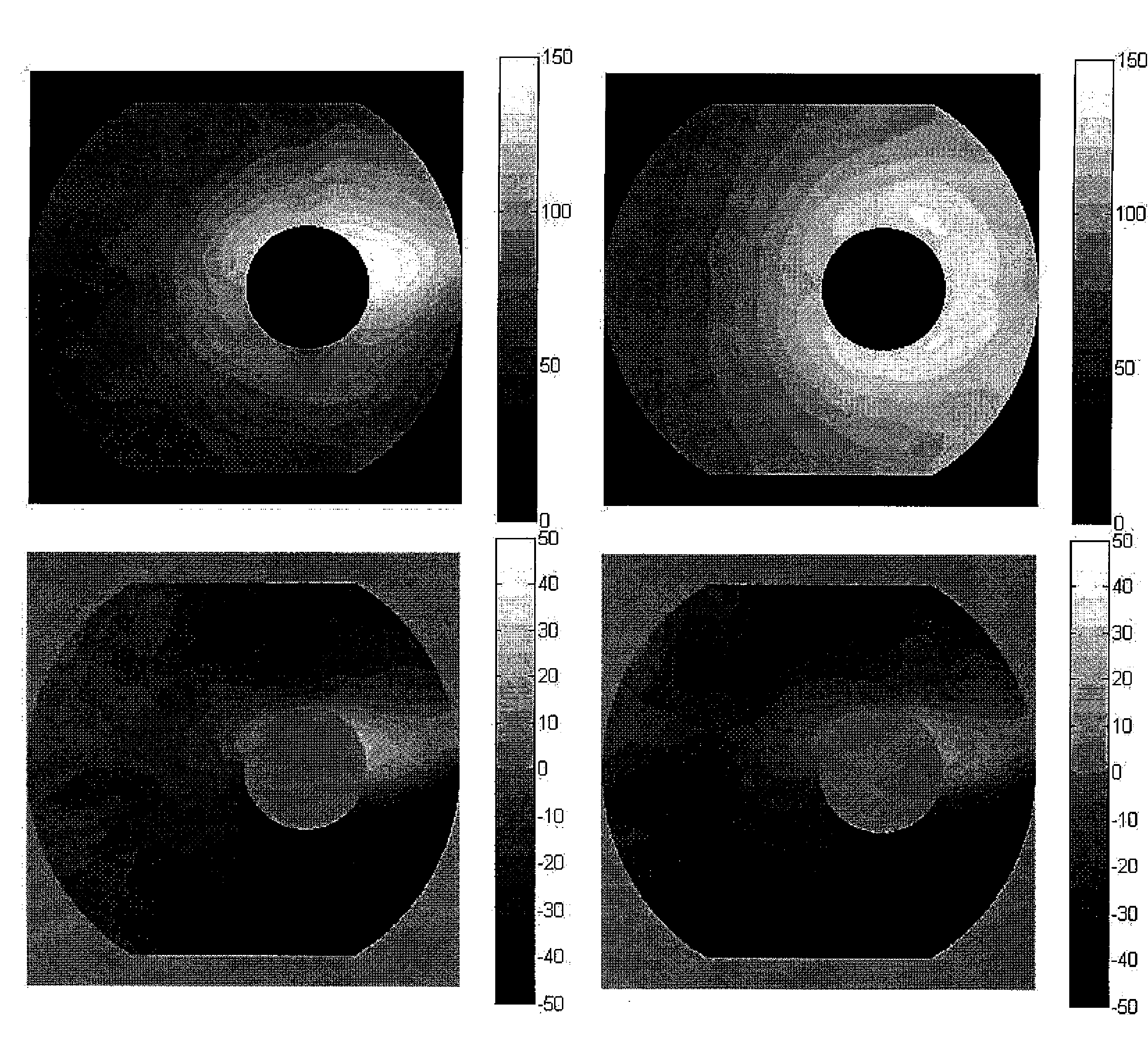
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
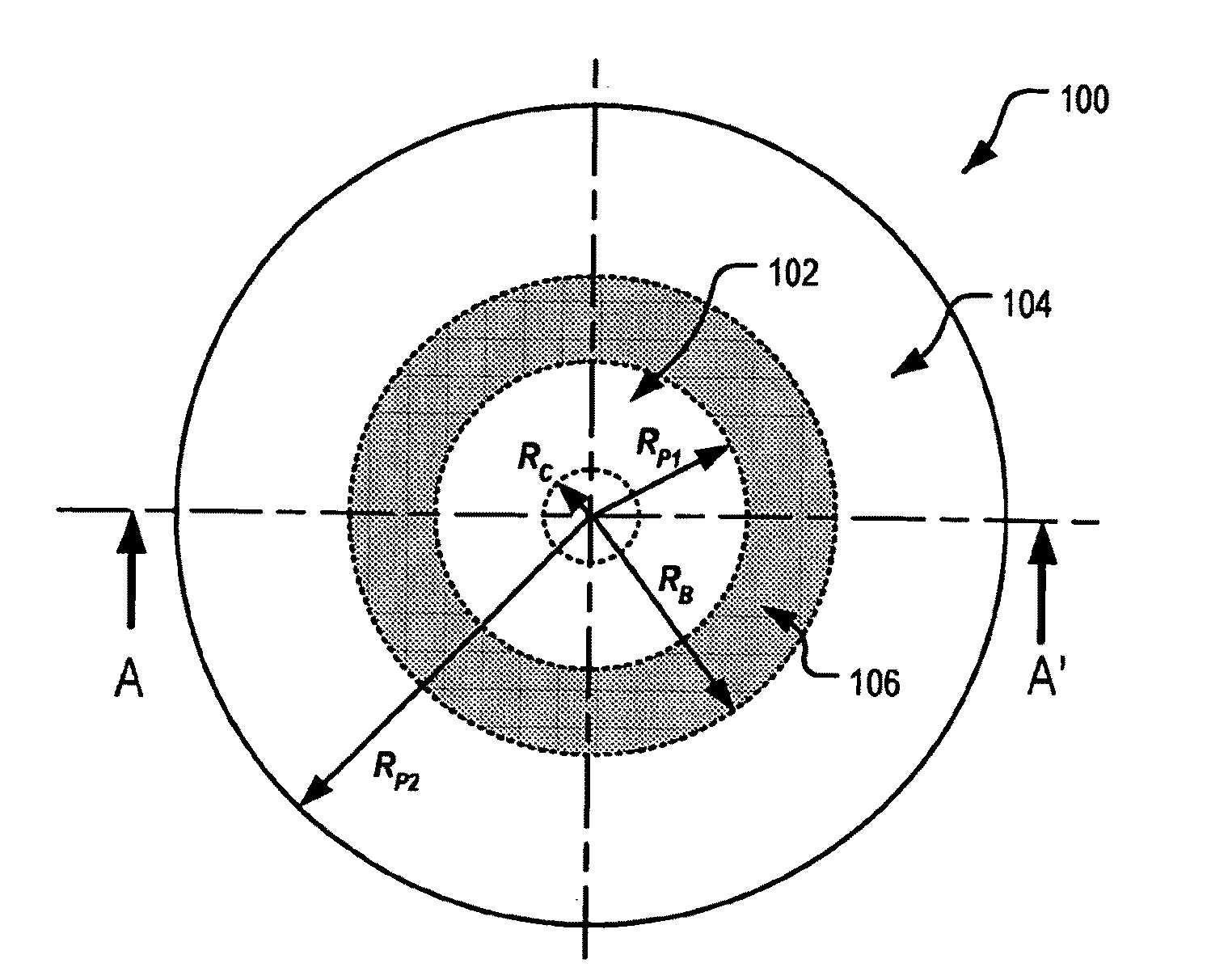
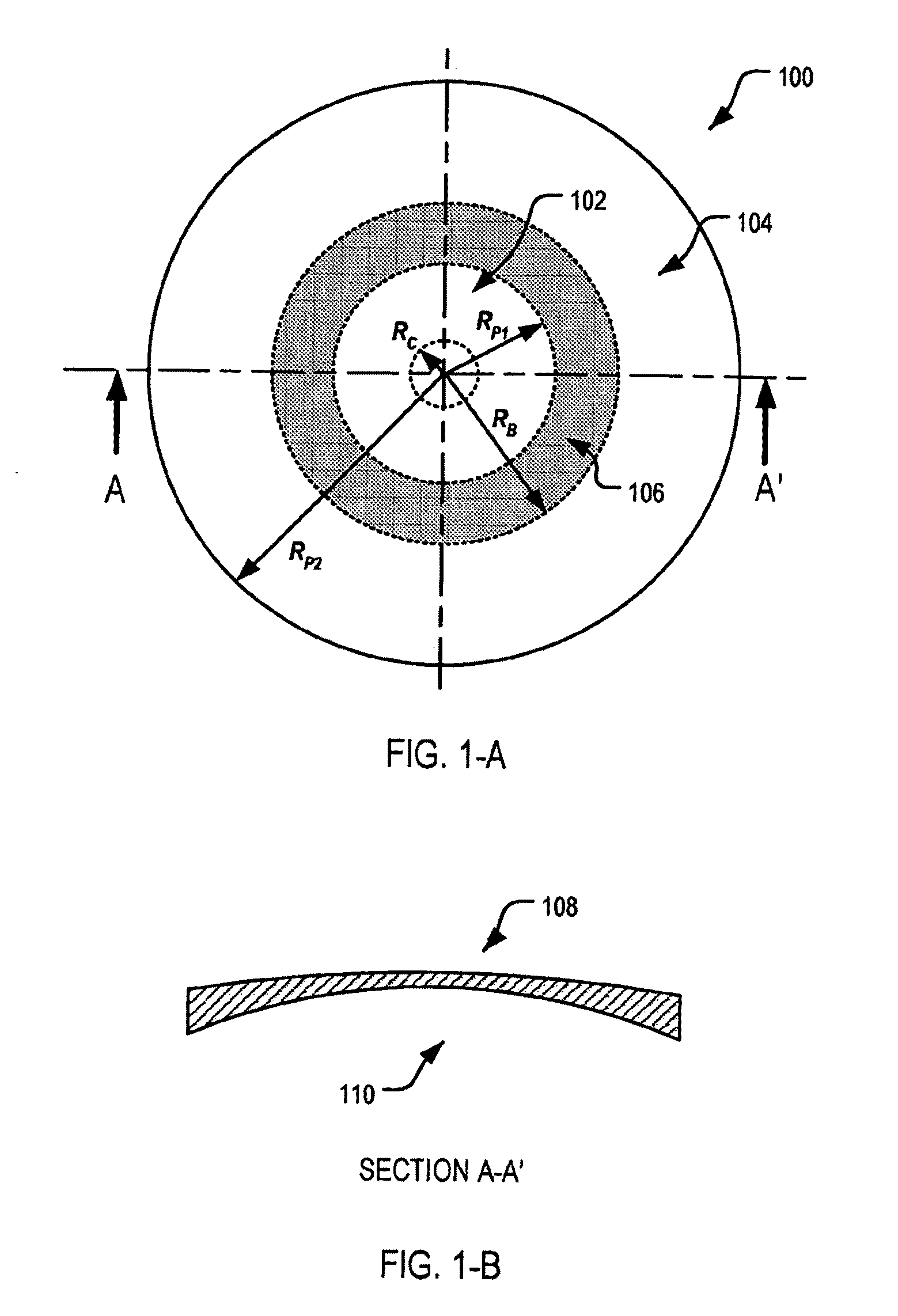
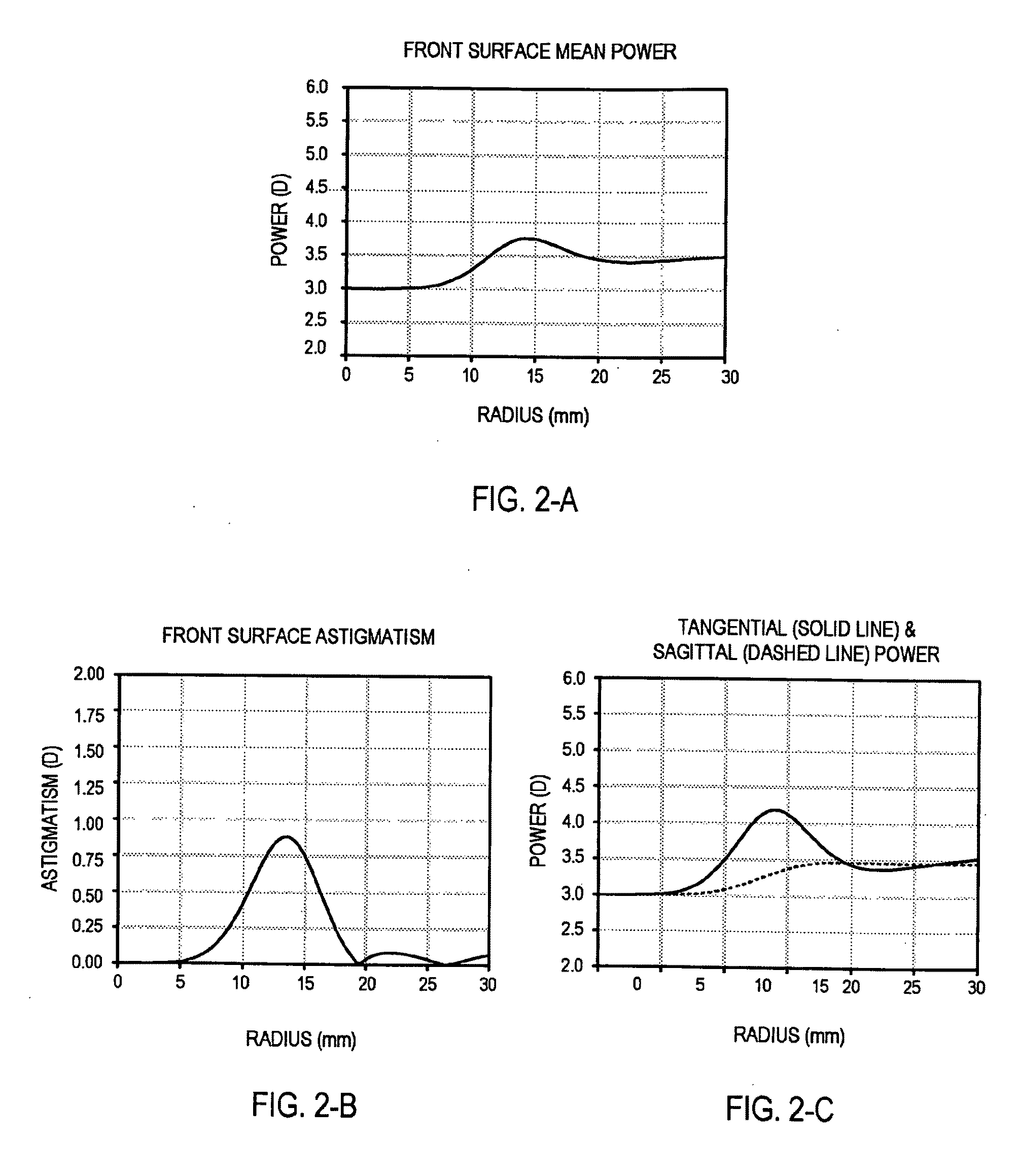
Ophthalmic Lens Element for Myopia Correction
ActiveUS20090257026A1Improve concentrationShorten the progressSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessOptical correction
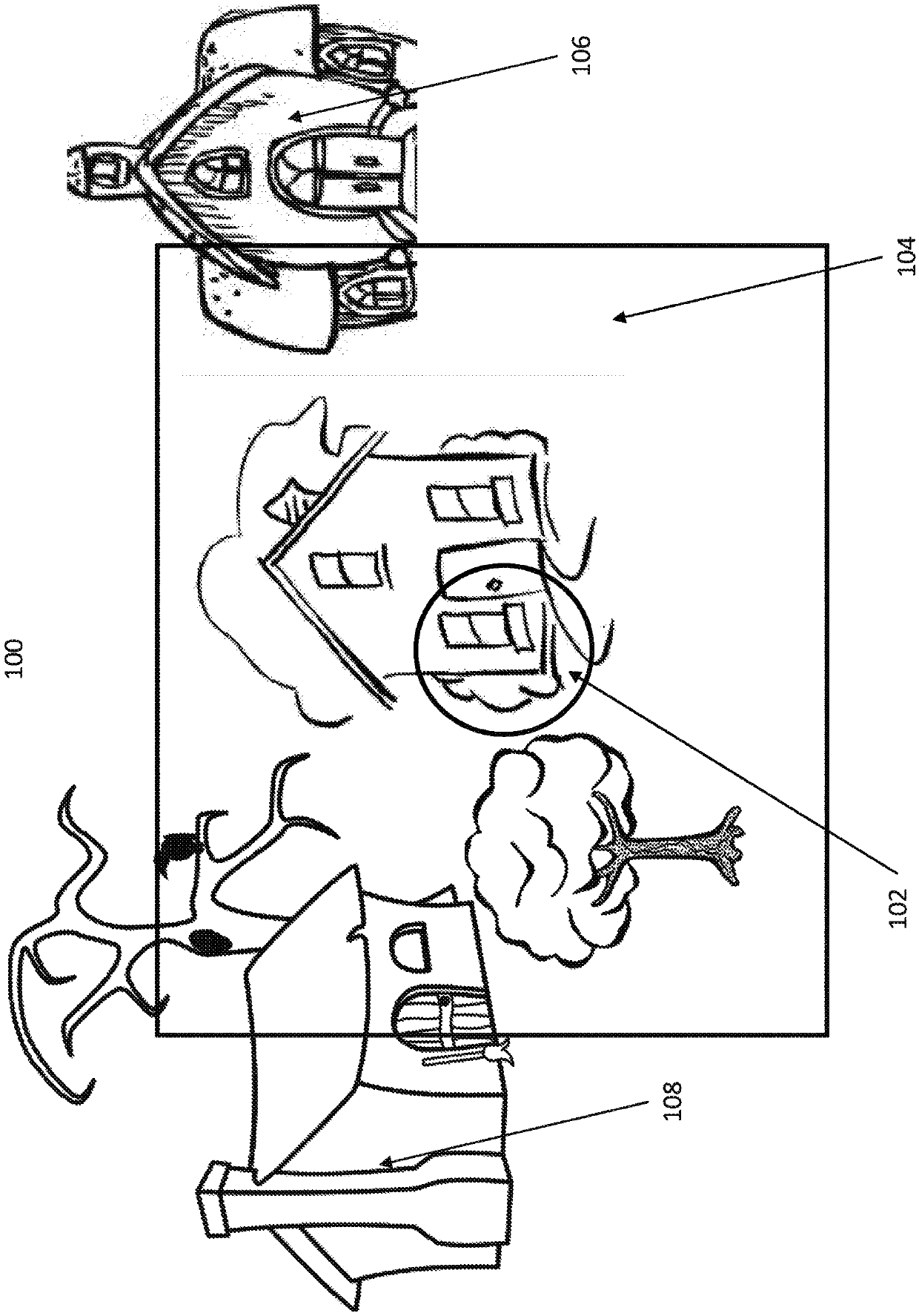
An ophthalmic lens element (100) for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is disclosed. The lens element (100) includes a central zone (102) and a peripheral zone (104). The central zone (102) provides a first optical correction for substantially correcting myopia associated with the foveal region of the wearer's eye. The peripheral zone (104) surrounds the central zone (102) and provides a second optical correction for substantially correcting myopia or hyperopia associated with a peripheral region of the retina of the wearer's eye. A system and method for dispensing or designing an ophthalmic lens element for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO +1
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Real time eye tracking for human computer interaction
ActiveUS9311527B1Improve interactivityMore intelligent behaviorInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementLarge screenVisual axis
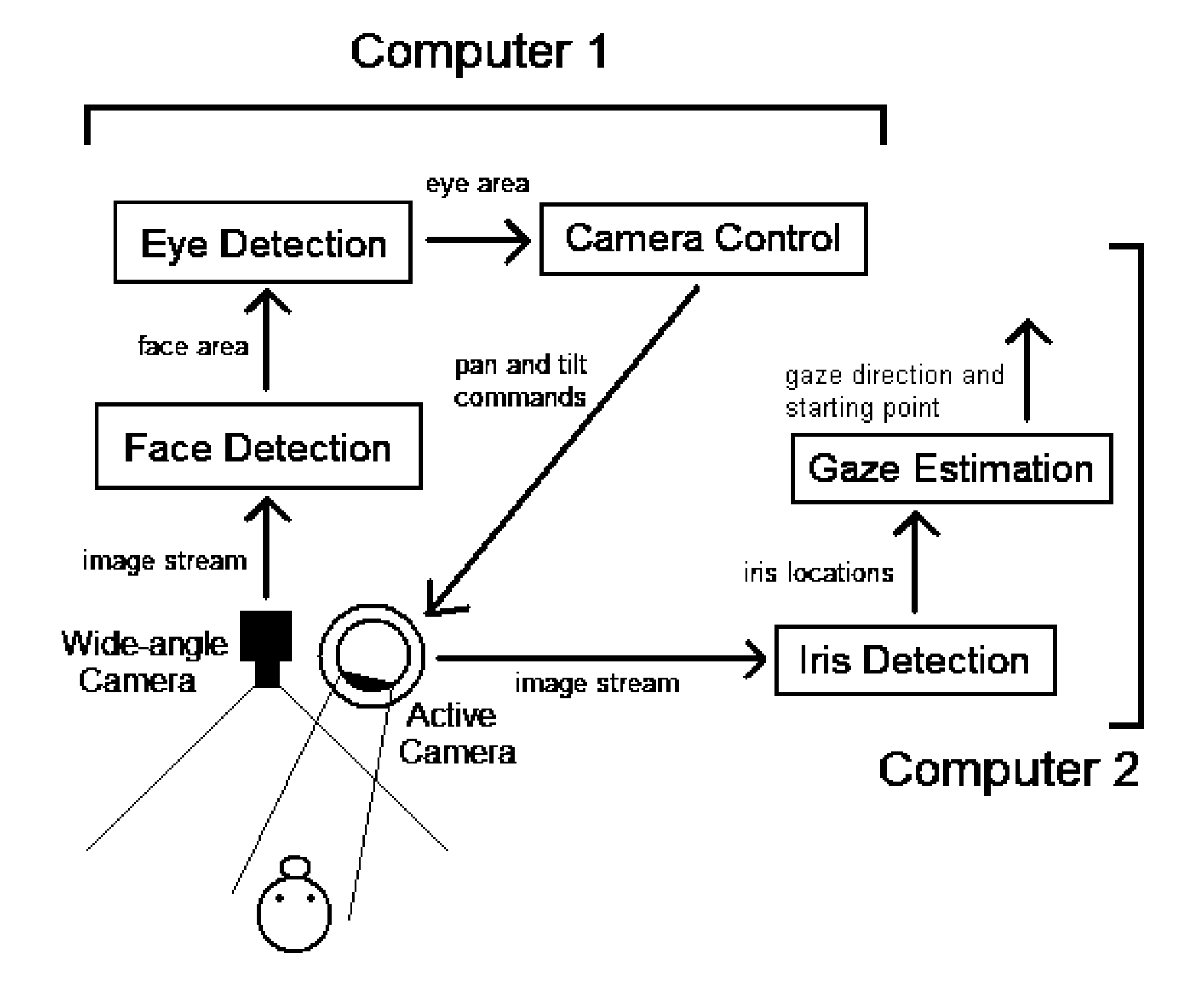
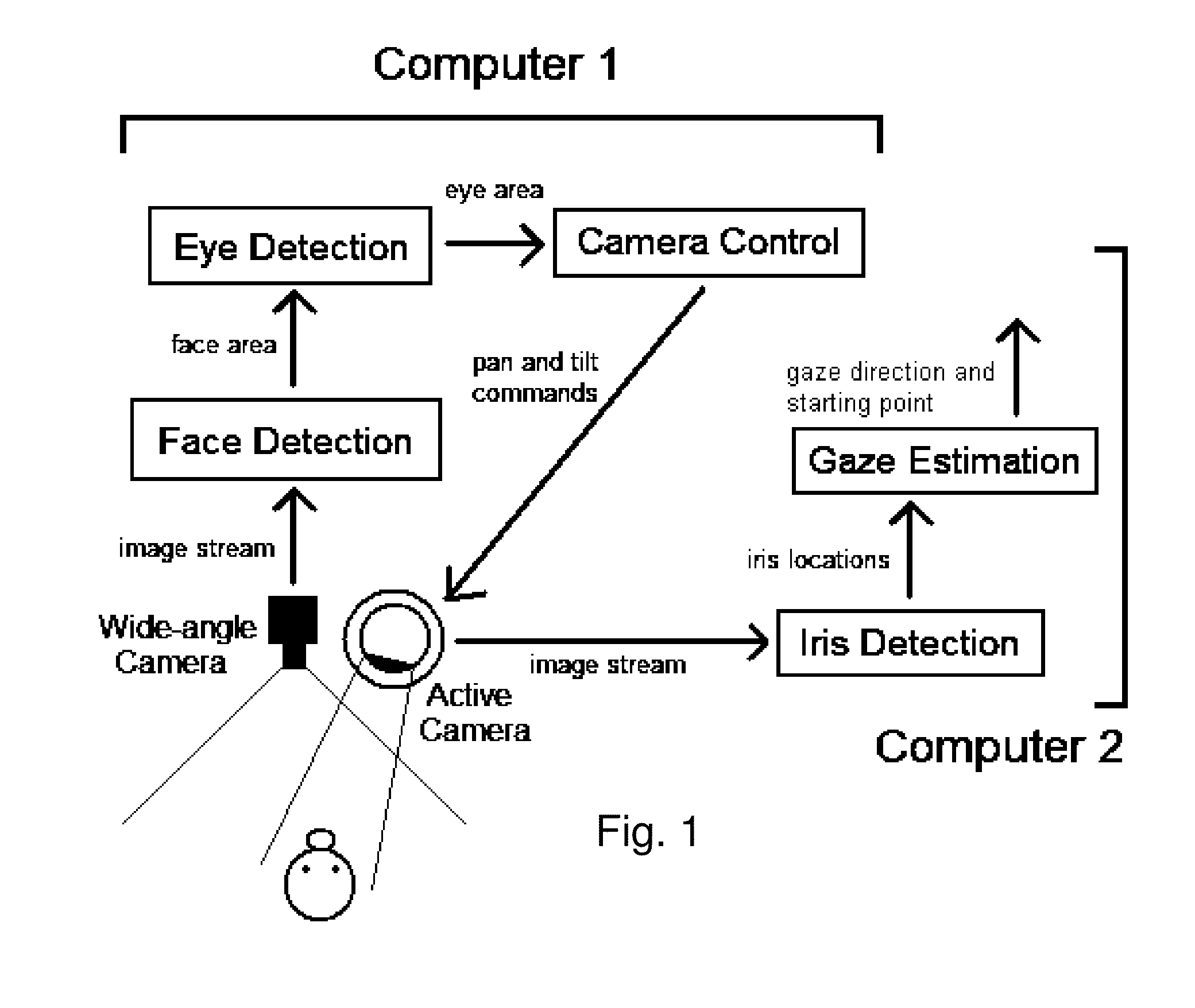
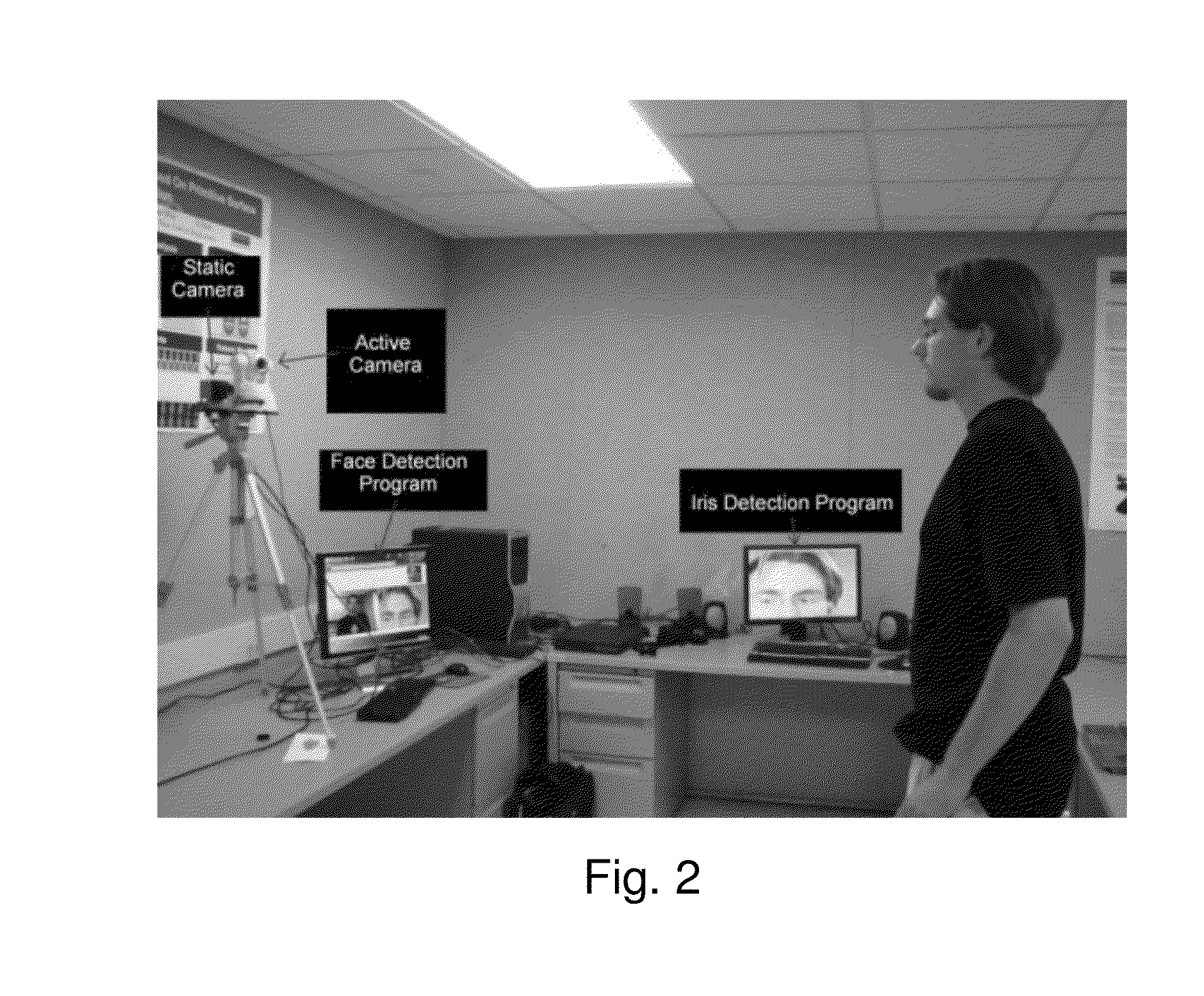
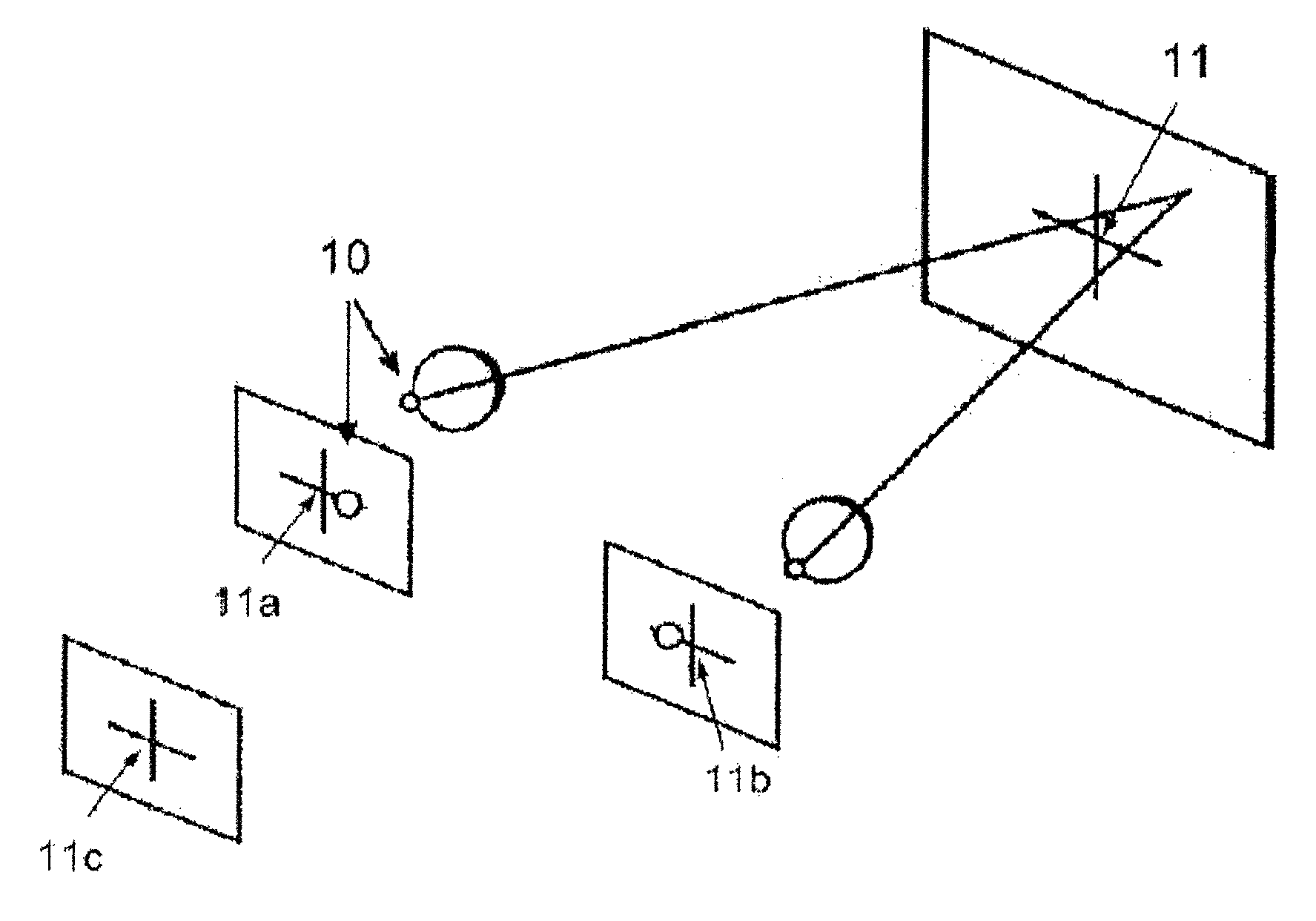
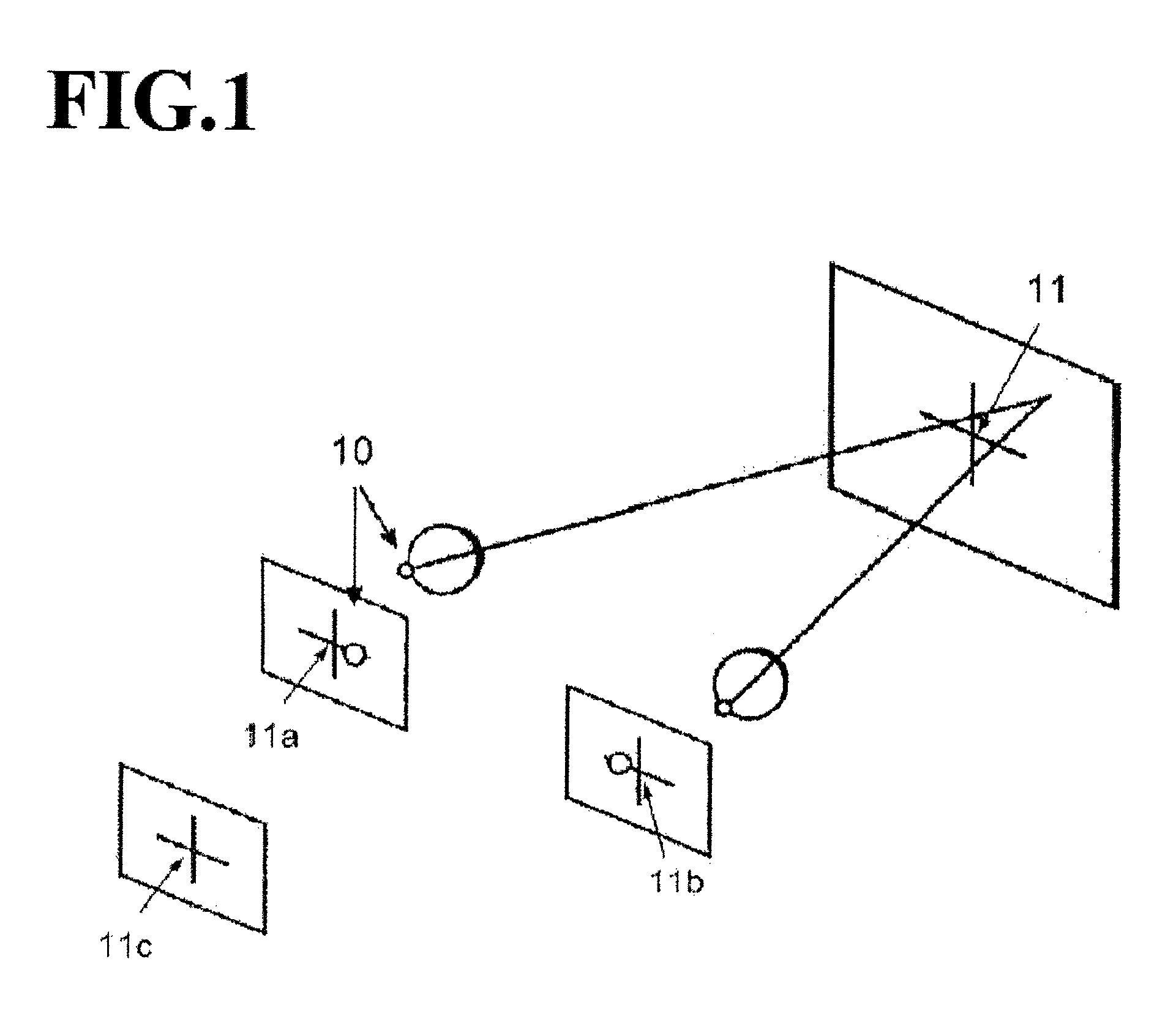
A gaze direction determining system and method is provided. A two-camera system may detect the face from a fixed, wide-angle camera, estimates a rough location for the eye region using an eye detector based on topographic features, and directs another active pan-tilt-zoom camera to focus in on this eye region. A eye gaze estimation approach employs point-of-regard (PoG) tracking on a large viewing screen. To allow for greater head pose freedom, a calibration approach is provided to find the 3D eyeball location, eyeball radius, and fovea position. Both the iris center and iris contour points are mapped to the eyeball sphere (creating a 3D iris disk) to get the optical axis; then the fovea rotated accordingly and the final, visual axis gaze direction computed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Retina fovea centralis detection method based on multi-feature model
ActiveCN106599804AHigh precisionImprove robustnessAcquiring/recognising eyesFeature extractionBlood vessel
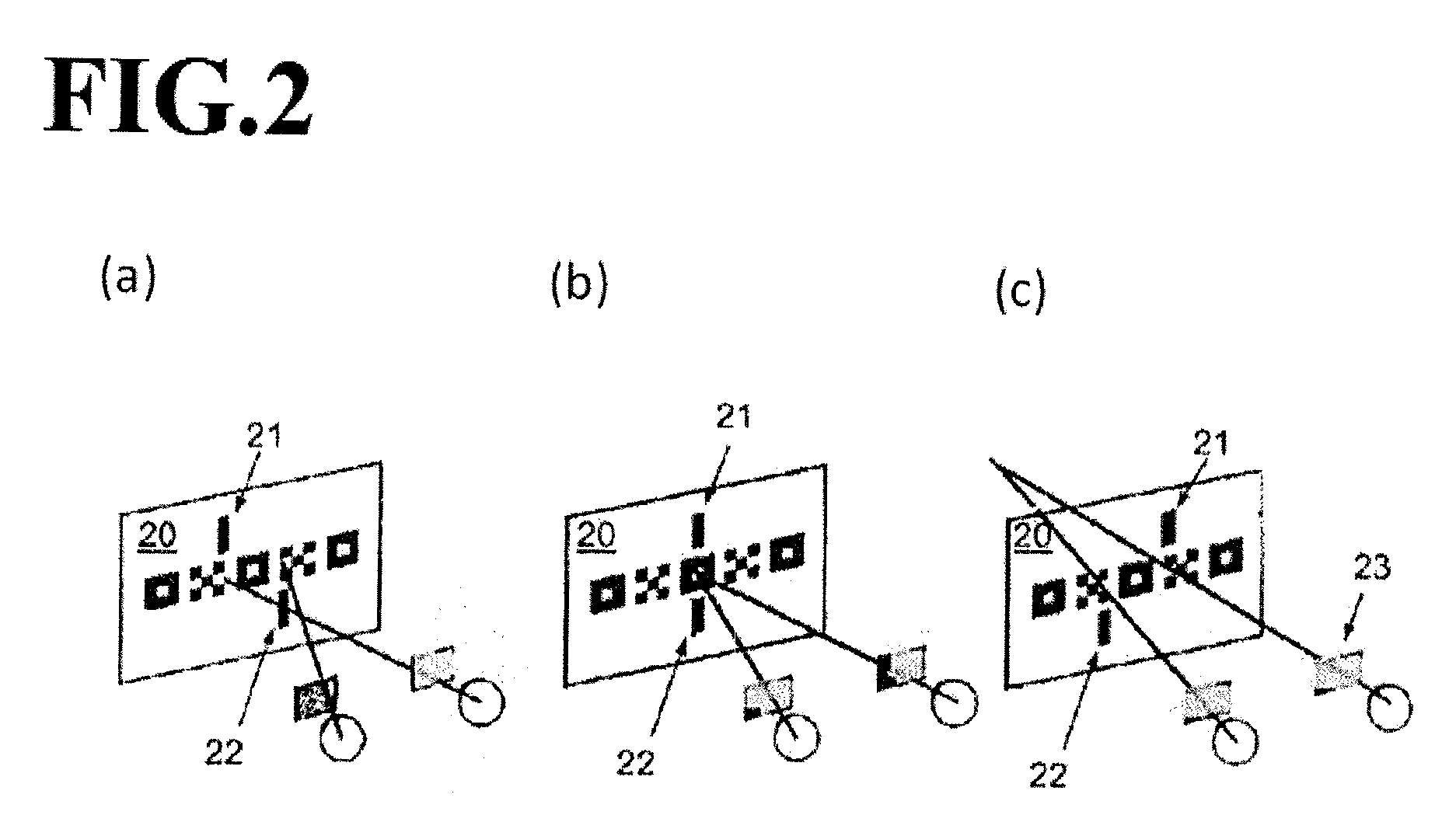
The invention discloses a retina fovea centralis detection method based on a multi-feature model. The retina fovea centralis detection method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out global prior feature extraction; 2) carrying out local prior feature extraction; 3) carrying out depth feature extraction; and 4) establishing a multi-feature-fusion fovea centralis detection model. Through global, local and depth feature information extraction of fovea centralis and effective fusion, accurate detection of the retina fovea centralis is finished. The method can effectively overcome the influence of fundus illumination noise, fundus lesions and abnormal blood vessel distribution on fovea centralis automatic detection, thereby improving fovea centralis detection precision and robustness, and providing more robust identity characteristic information for identity identification based on retinal images.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Mutual acting staring vision-training system and method
InactiveCN101084857AWon't be aloneRich contentEye exercisersEye treatmentProtecting eyeProjection screen
An interactive gazing vision training system comprises software loaded in a computer, gaming handle connected to the computer. Computer generated signal can be projected on projection screen after being input in projector. The total system can project 4-8 wickets controlled independently by gaming handle on projection screen. The gaming handle has buttons corresponding to each corresponding sighting direction. Sighting target in the wicket can wane continually under the control of the computer. Trainee sit at a place 2-5 m away from the projection screen, light ray emitted by any point on the projection screen enter the eyeball of the trainee via optical lens, and the hearth in the eye is located at a place 0.5-2mm in front of fovea centralis of niacula lutea retinae. The inventive interactive gazing vision training system integrates multiple modern theories for preventing and treating myopia, adopts the advantages of games, utilizes 3Dexaggeration technology, increases entertaining quality, and becomes an easily persistent eyes protection method.
Owner:北京眼吧科技有限公司
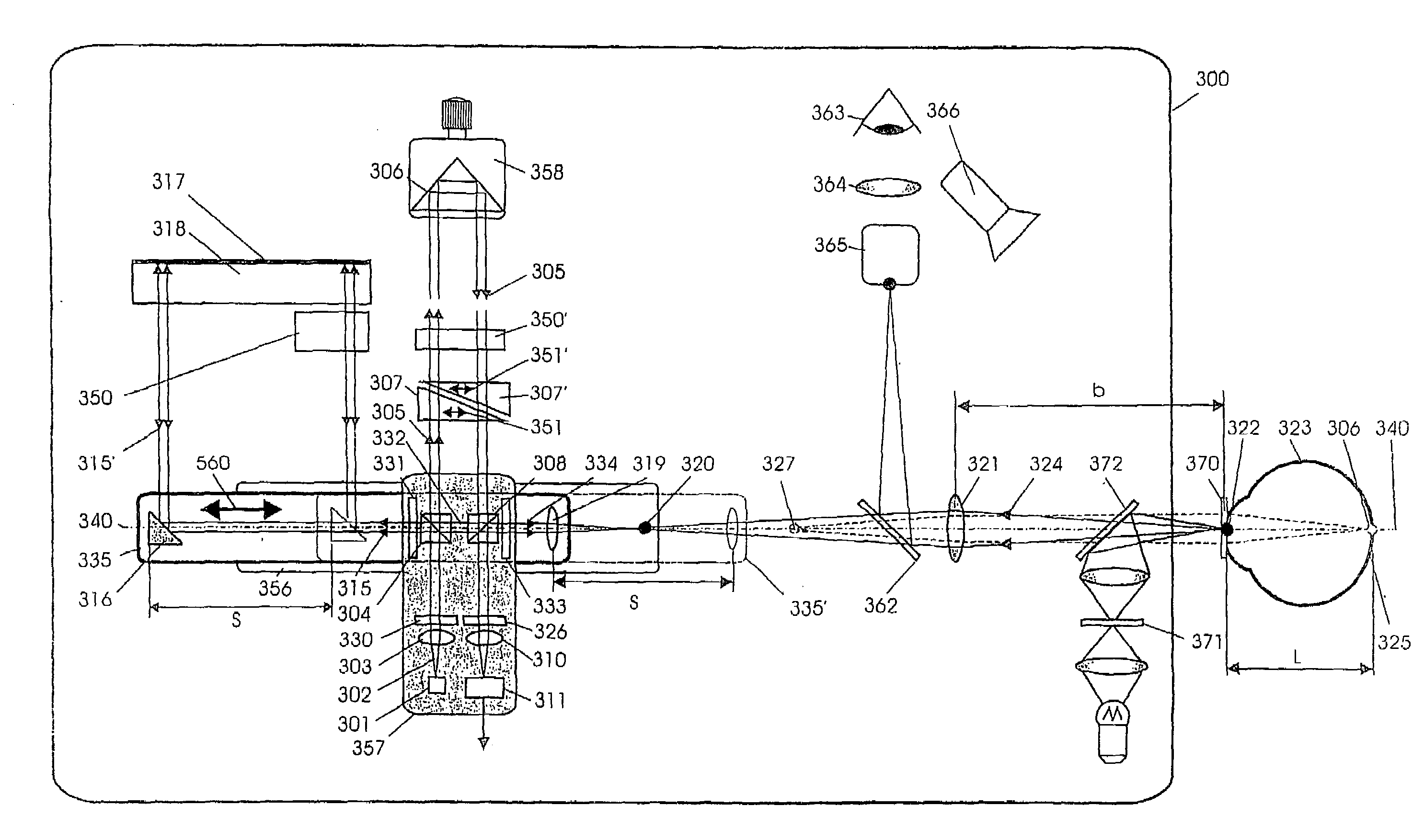
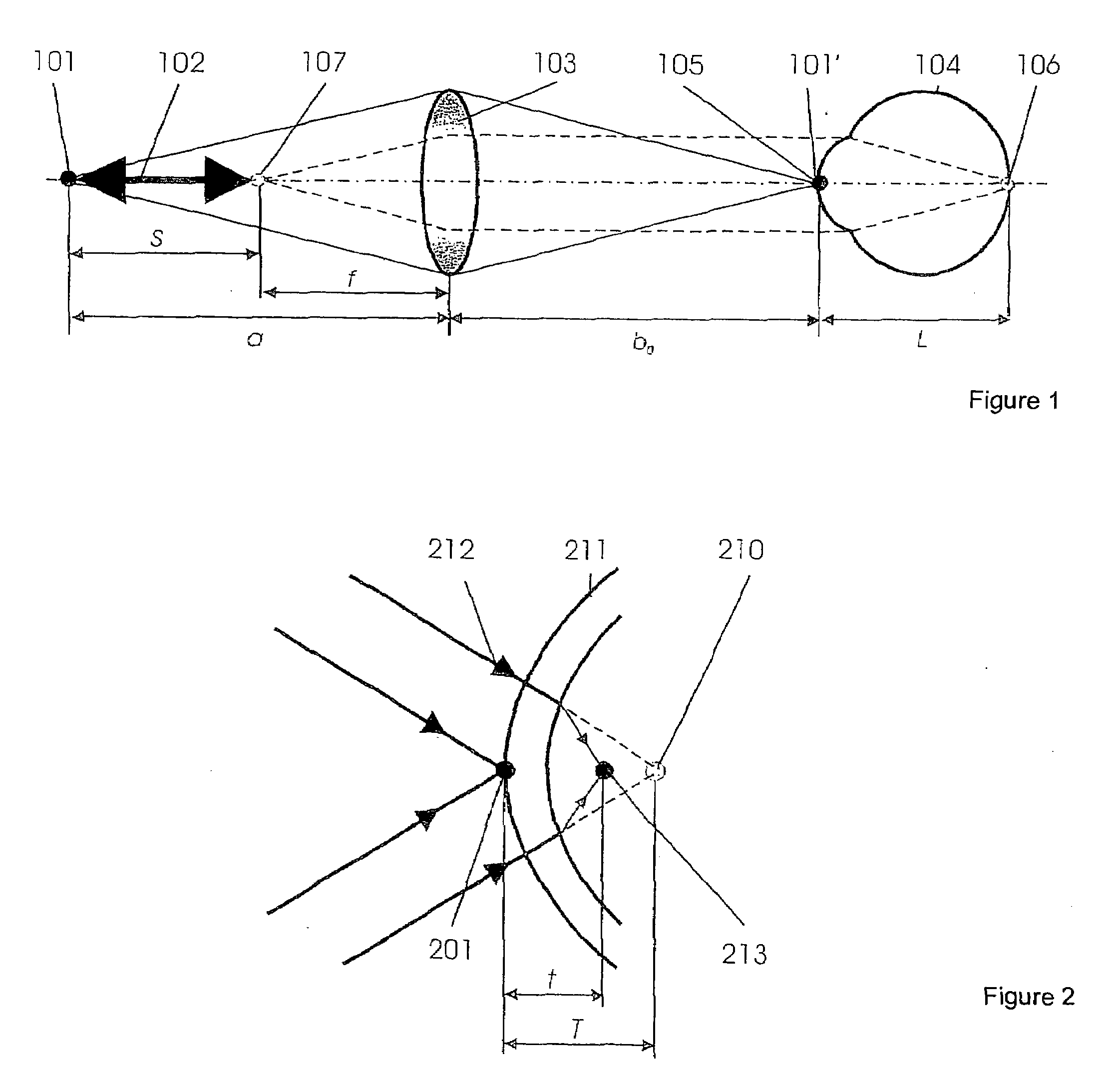
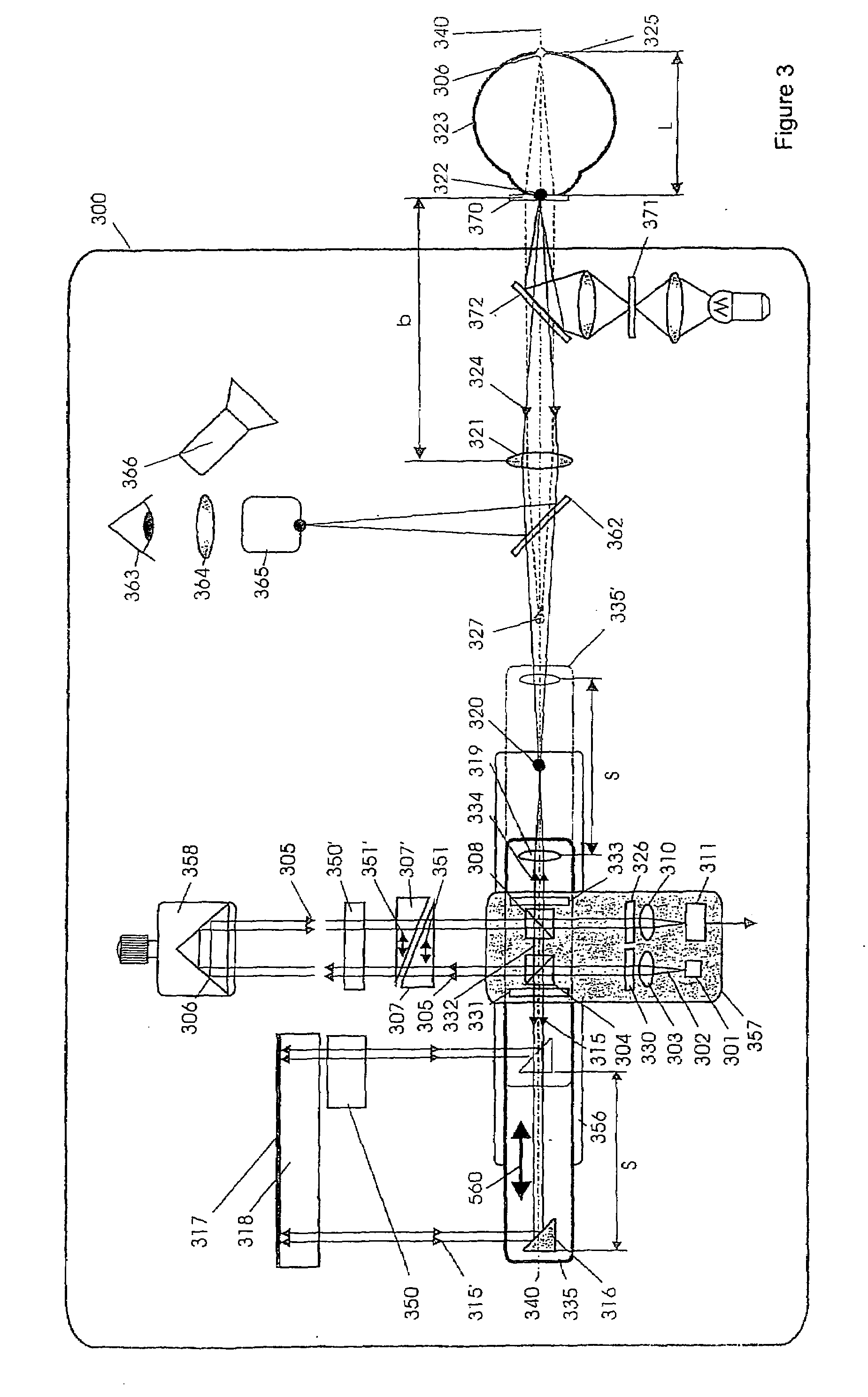
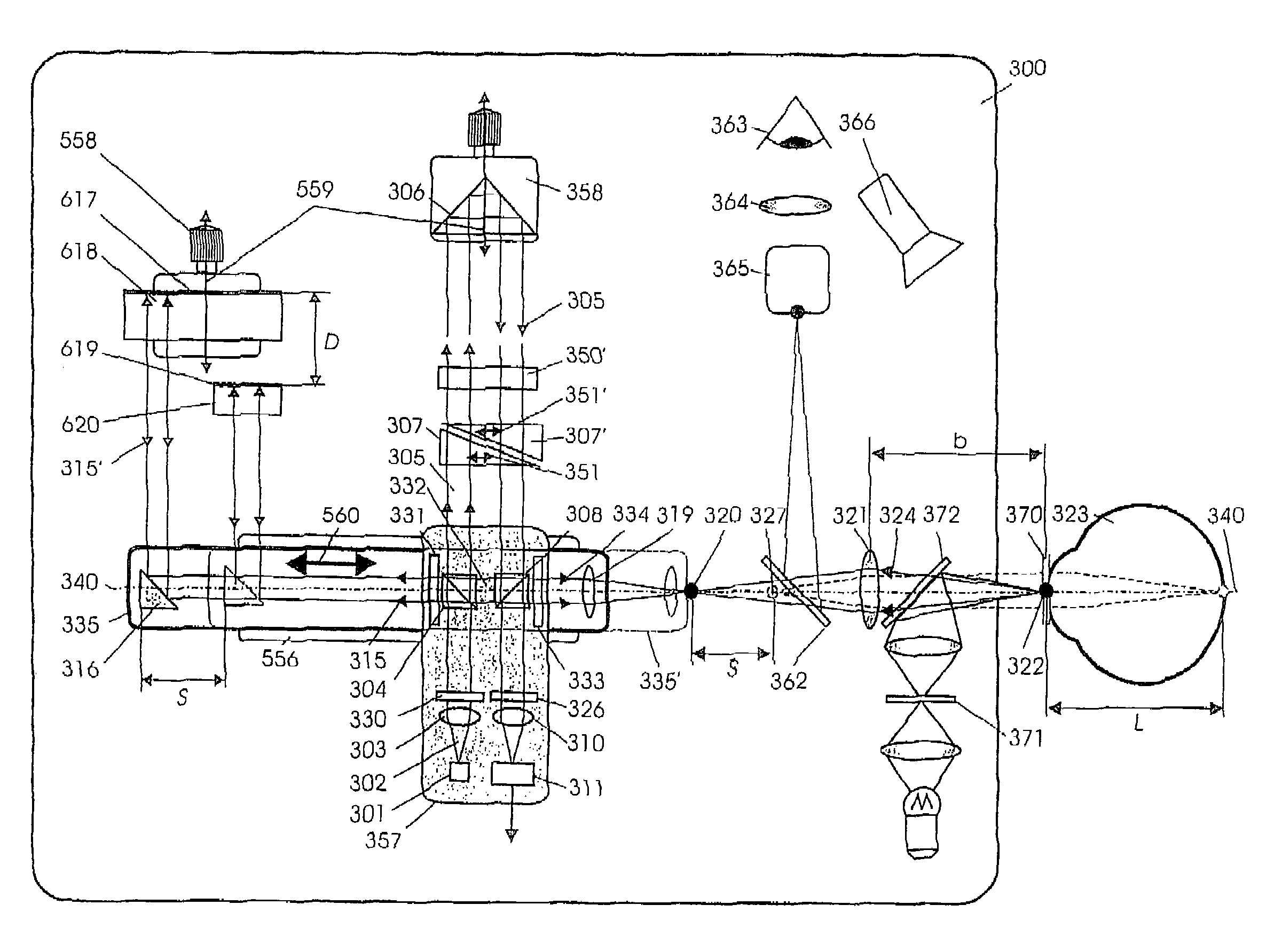
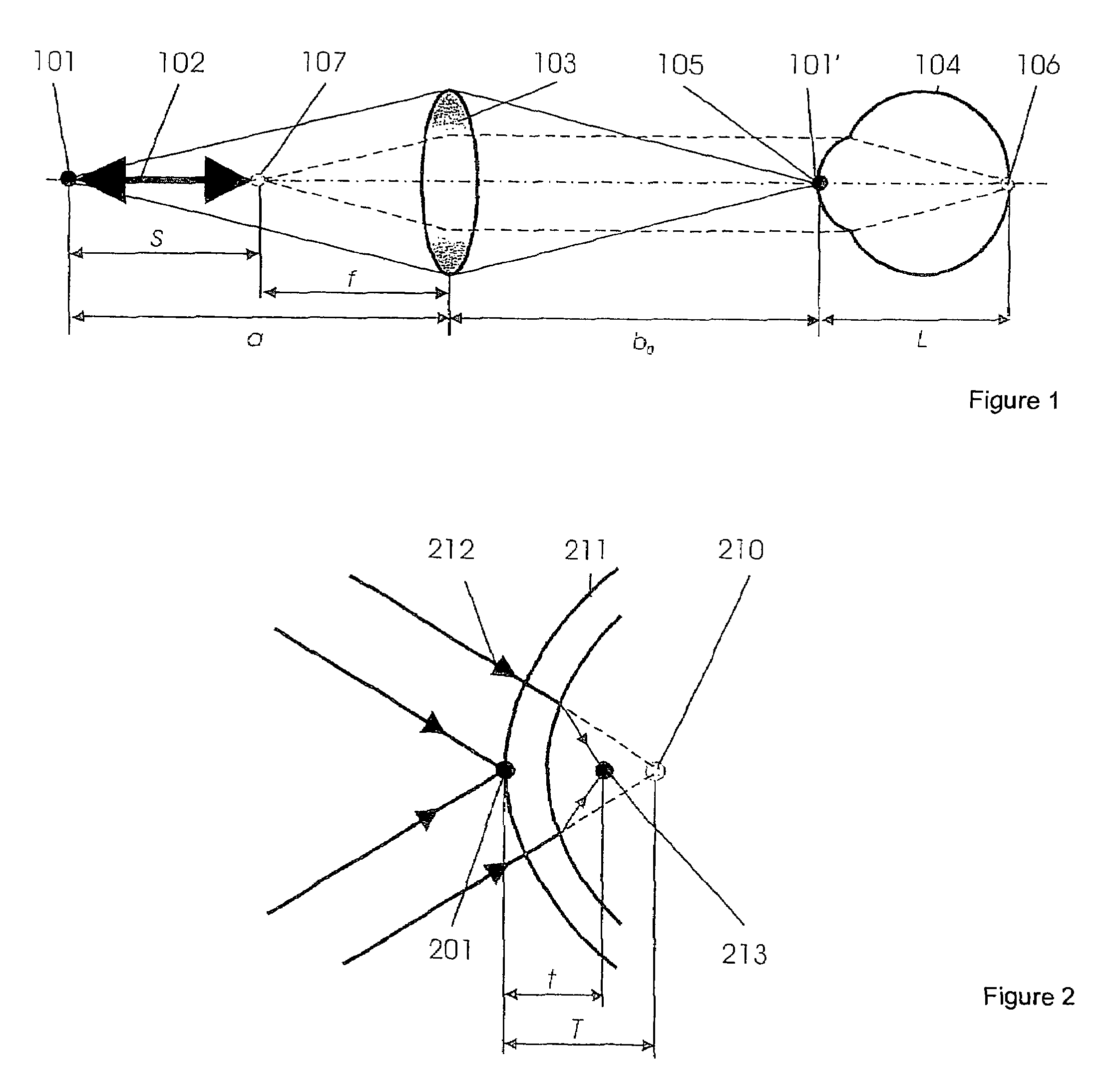
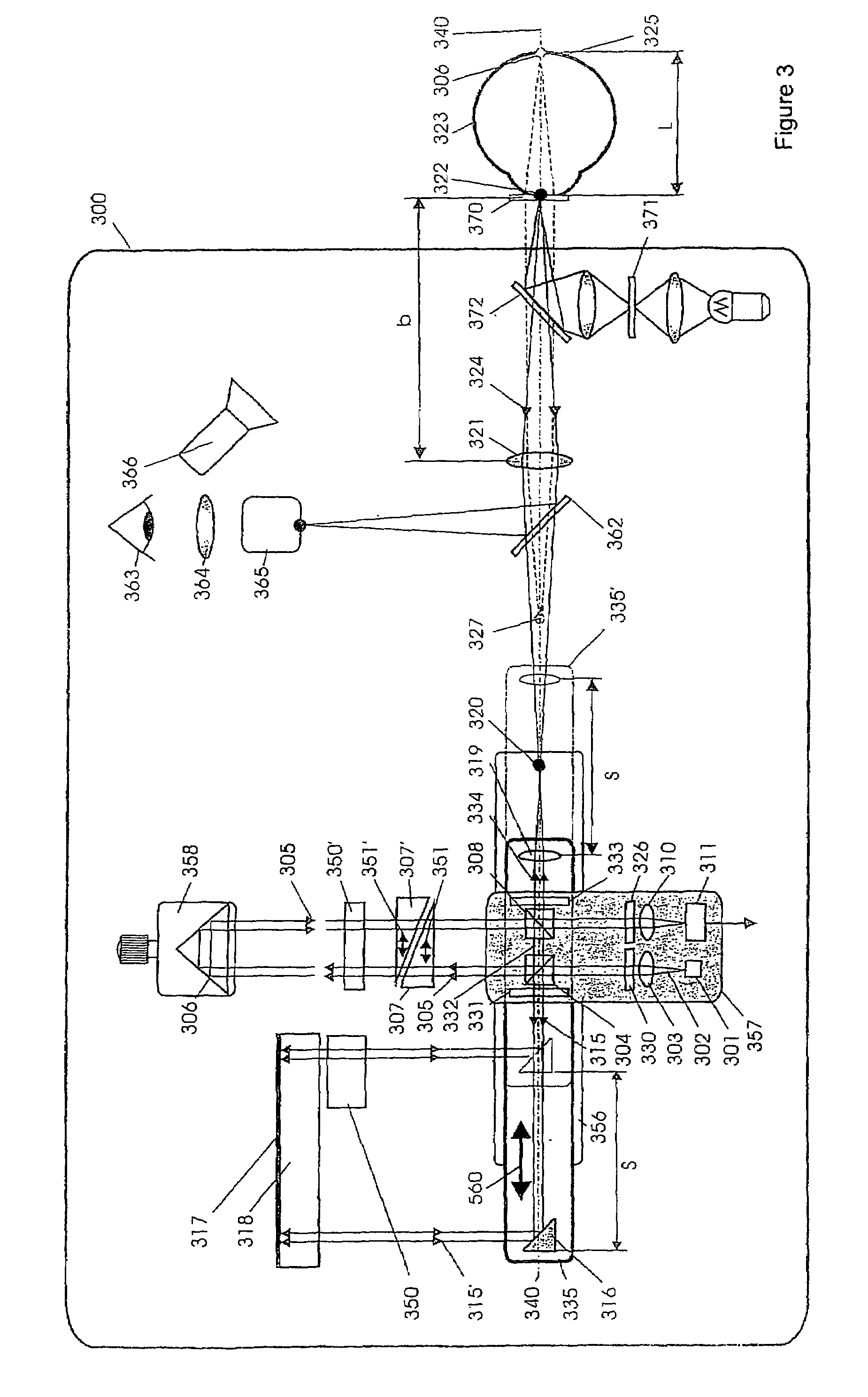
Short-Coherence Interferometeric Measurement of Length on the Eye
Two problems arise when measuring length at the eye by short-coherence interferometry. First, the measurement focus and coherence window usually do not coincide. Second, the scanning process along the eye axis is time-consuming. Both result in poor signal quality and inaccurate measurements. The present application is directed to a short-coherence interferometer in which a right-angle mirror and focusing optics jointly carry out a periodic back-and-forth movement in such a way that the measurement beam focus which is generated by the focusing optics and imaged on the eye by relay optics is moved synchronously with the coherence window from the cornea along the optic axis of the eye to the fovea centralis. Further, different path lengths are generated in the measurement beam path and reference beam path by means of a plurality of reflectors, so that the scanning process is limited to distances which are smaller than the optical length of the eye. The present invention is advantageously implemented using on a fiber-optic interferometer. According to the invention, the reference interferometer arm and measurement interferometer arm are combined with the arms of a fiber-optic interferometer.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
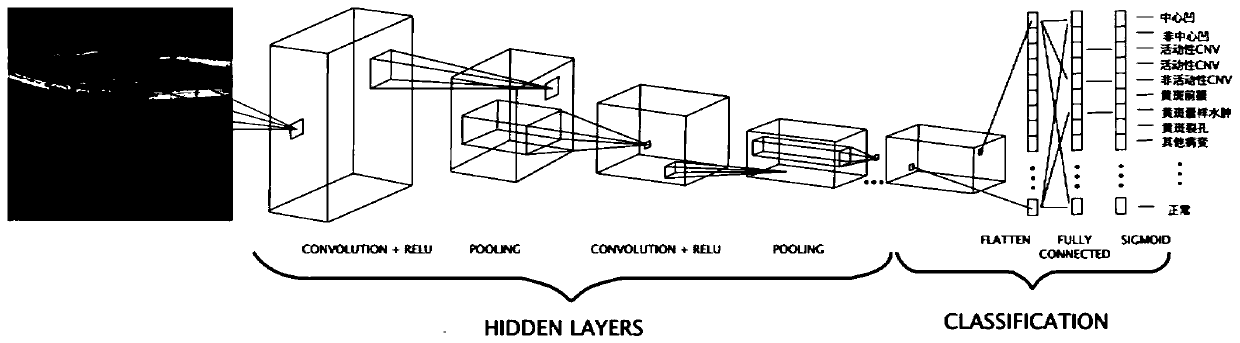
Fundus OCT image recognition method and device
PendingCN110555845AImprove reading efficiencyPracticalImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSize determination
The invention provides a fundus OCT image recognition method and device, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the recognition of a fundus OCT image through a neural network, and obtaininga recognition result related to lesion and fovea centralis; determining a region of interest according to the identification result; and determining the lesion degree according to the position and / orsize of the region of interest.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAGLEVISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
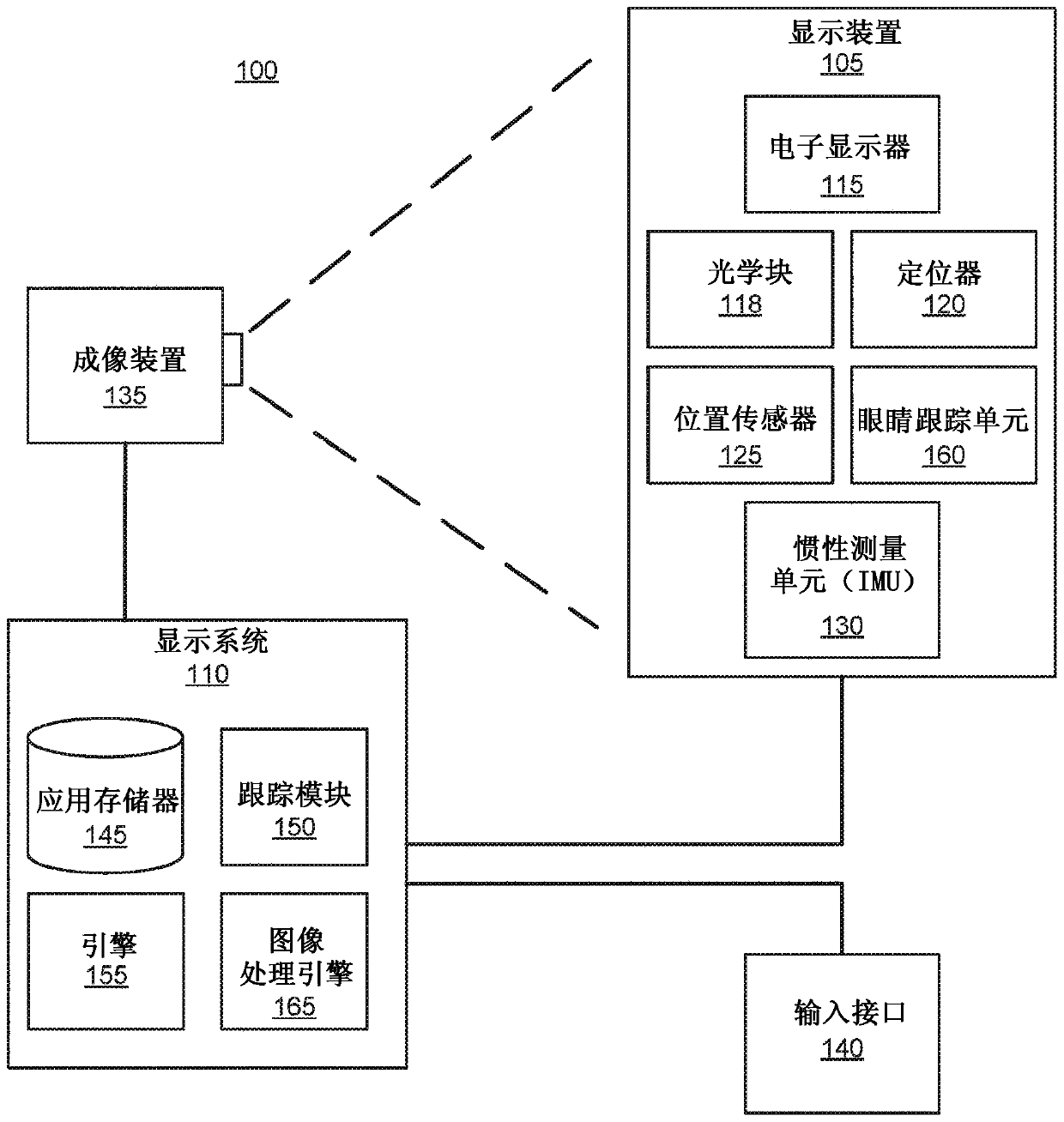
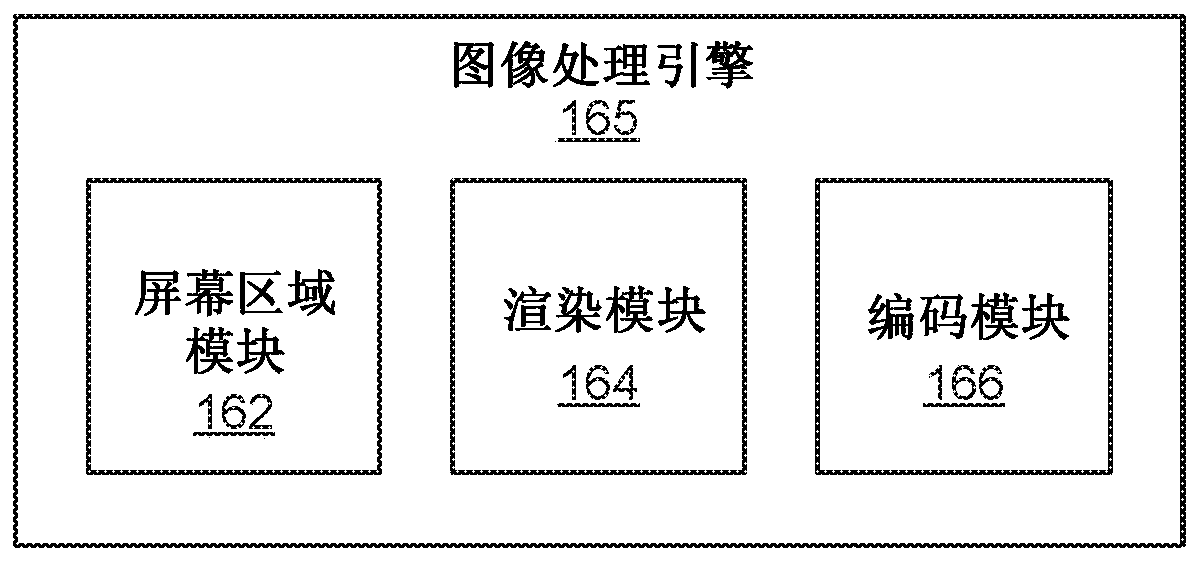
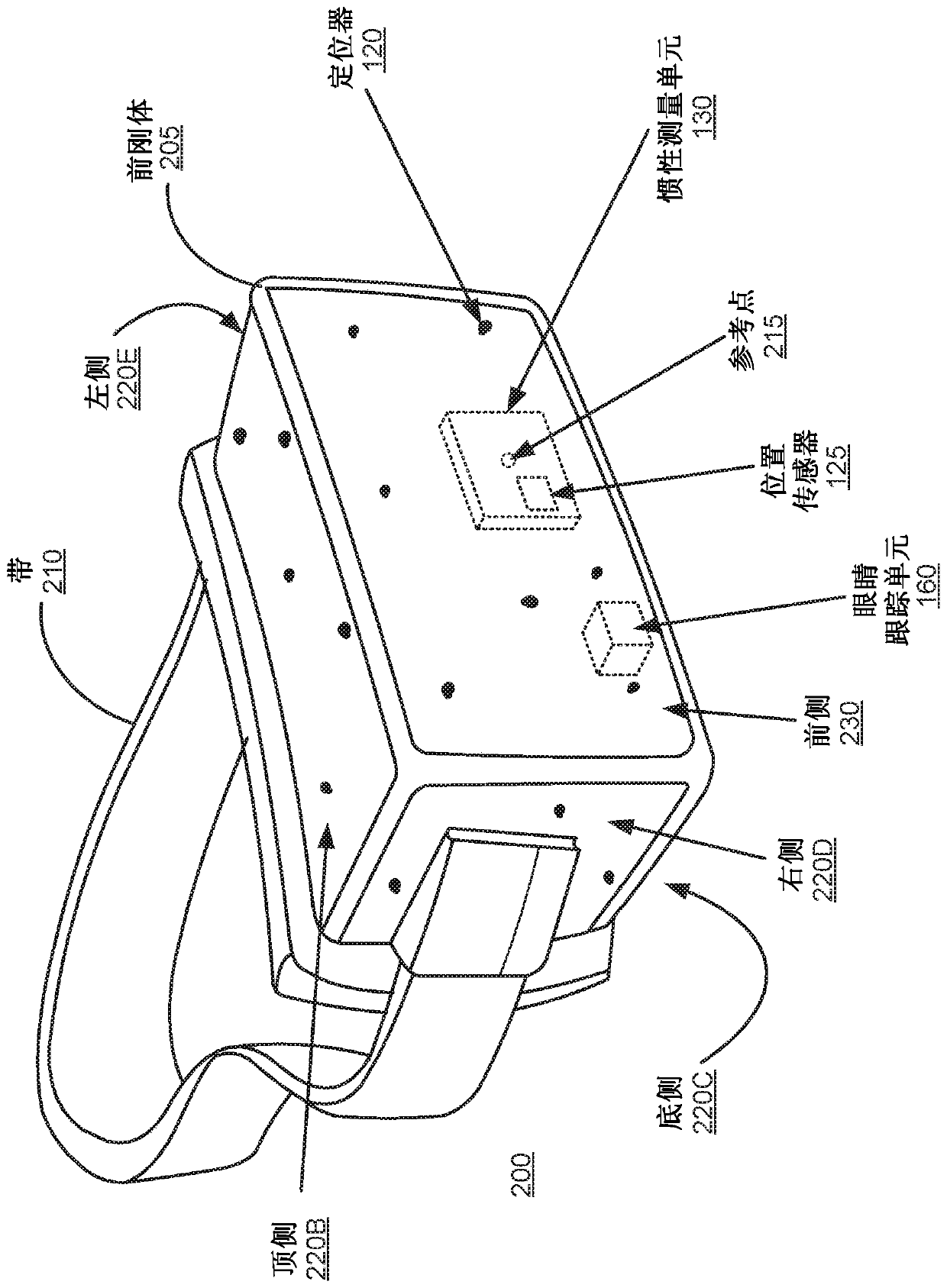
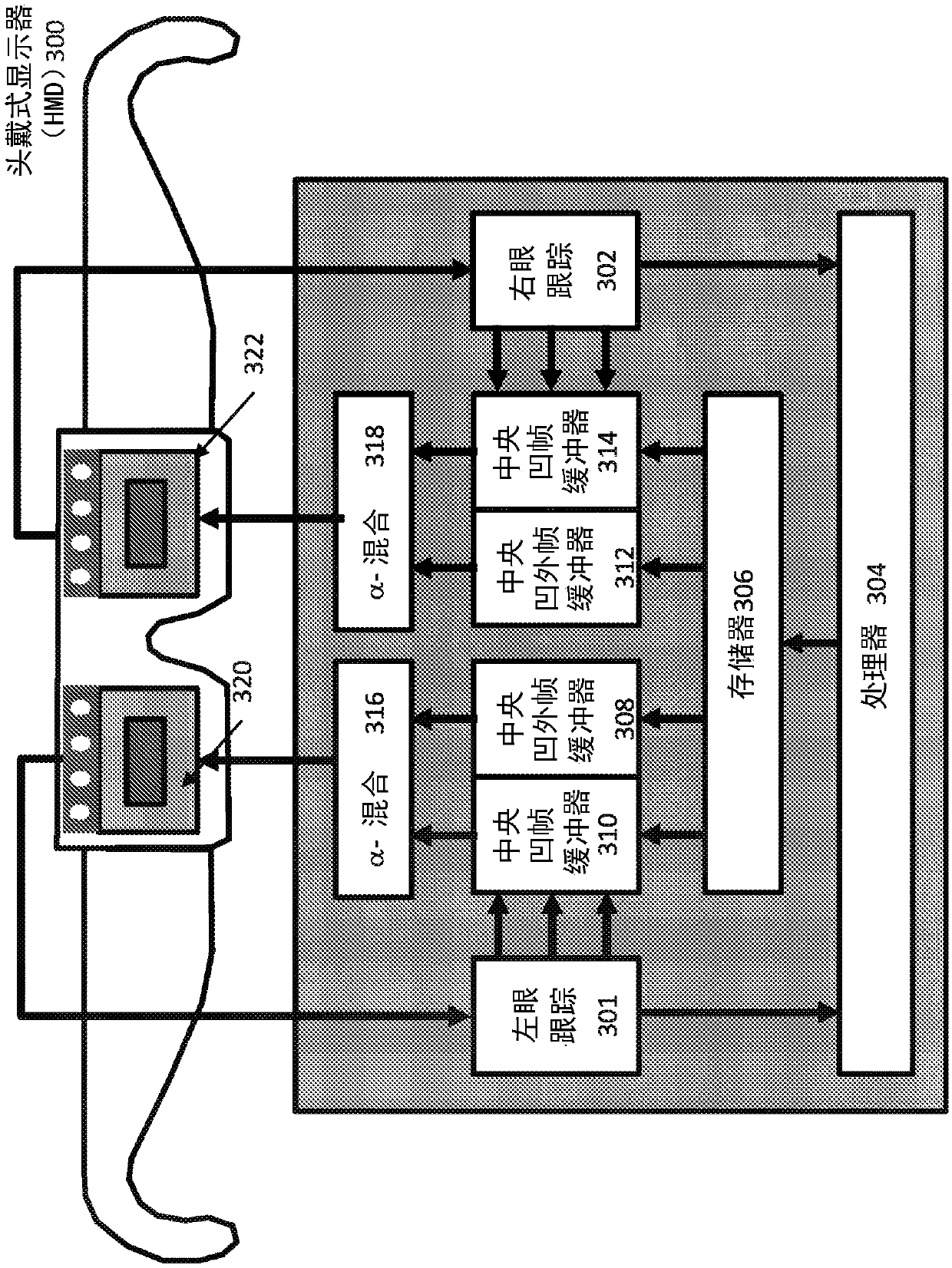
Adaptive parameters in image regions based on eye tracking information
A display system divides a screen into regions and applies a different set of rendering / encoding parameters to each region. The system applies a first set of parameters to a first region that is beingviewed by a fovea of an eye of a user. The system may also apply a second set of parameters to a second region that is being viewed by a parafovea of the eye, and apply a third set of parameters to athird region that is being viewed by the area of the eye outside of the parafovea. The first set of parameters is selected to yield relatively high image quality, while the second set of parameters are yield intermediate quality, and the third set of parameters yield lower quality. As a result, the second region and the third region can be rendered, encoded, and transmitted with less computing power and less bandwidth.
Owner:CTRL LABS CORP
Apparatus, method, and system for providing tunable circadian lighting at constant perceived brightness and color
ActiveCN109479357AElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOphthalmologyVisual perception
ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE The newly discovered retinal ganglion cell photoreceptor melanopsin absent in the central fovea of the eye but distributed throughout the remaining human retinal body provides both non-visual biological / physiological input inducing circadian entrainment, and visual input affecting perceived brightness; this perceived brightness is not the object brightness commonly associated with luminance and perceived color of an object in central view, but the perception of brightness of a whole space or task background. Discussed are improvements to circadian lighting systems based on melanopsin stimulation whereby ambient and / or device background lighting may be temporally tuned over a range of prescribed color temperatures from a first subset of lighting having a higher melanopic content to a second subset of lighting having a lower melanopic content or vice versa in accordance with a desired circadian cycle, and in a manner where net light output is of a constant perceived brightness and color throughout temporal tuning.
Owner:MUSCO
Prism prescription value acquisition system, acquisition method, acquisition apparatus and program for correcting fixation disparity
A prism prescription value acquisition system that includes a calculation part for numerically transforming a fixation disparity amount (unit: angle), which indicates a degree at which the visual axis is shifted from the central fovea of the retina when a subject conducts visual fixation of a target, into a prism prescription value by multiplying the fixation disparity amount by a coefficient when the fixation disparity amount is within ±4 minutes. Herein, the prism prescription value is calculated according to the following equation: APver=kver*FDver, APhor=khor*FDhor providing that each of coefficients khor and kver satisfies the following conditions: 0.3≦kver≦0.7, 1.4≦khor≦2.0.
Owner:HOYA CORP
System and process for neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma
Provided is neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma which includes generating a micropulsed laser light beam having parameters and characteristics, including pulse length, power, and duty cycle, selectedto create a therapeutic effect with no visible laser lesions or tissue damage to the retina. The laser light beam is applied to retinal and / or foveal tissue of an eye having glaucoma or a risk of glaucoma to create a therapeutic effect to the retinal and / or foveal tissue exposed to the laser light beam without destroying or permanently damaging the retinal and / or foveal tissue and improve function or condition of an optic nerve and / or retinal ganglion cells of the eye.
Owner:OJAI RETINAL TECH
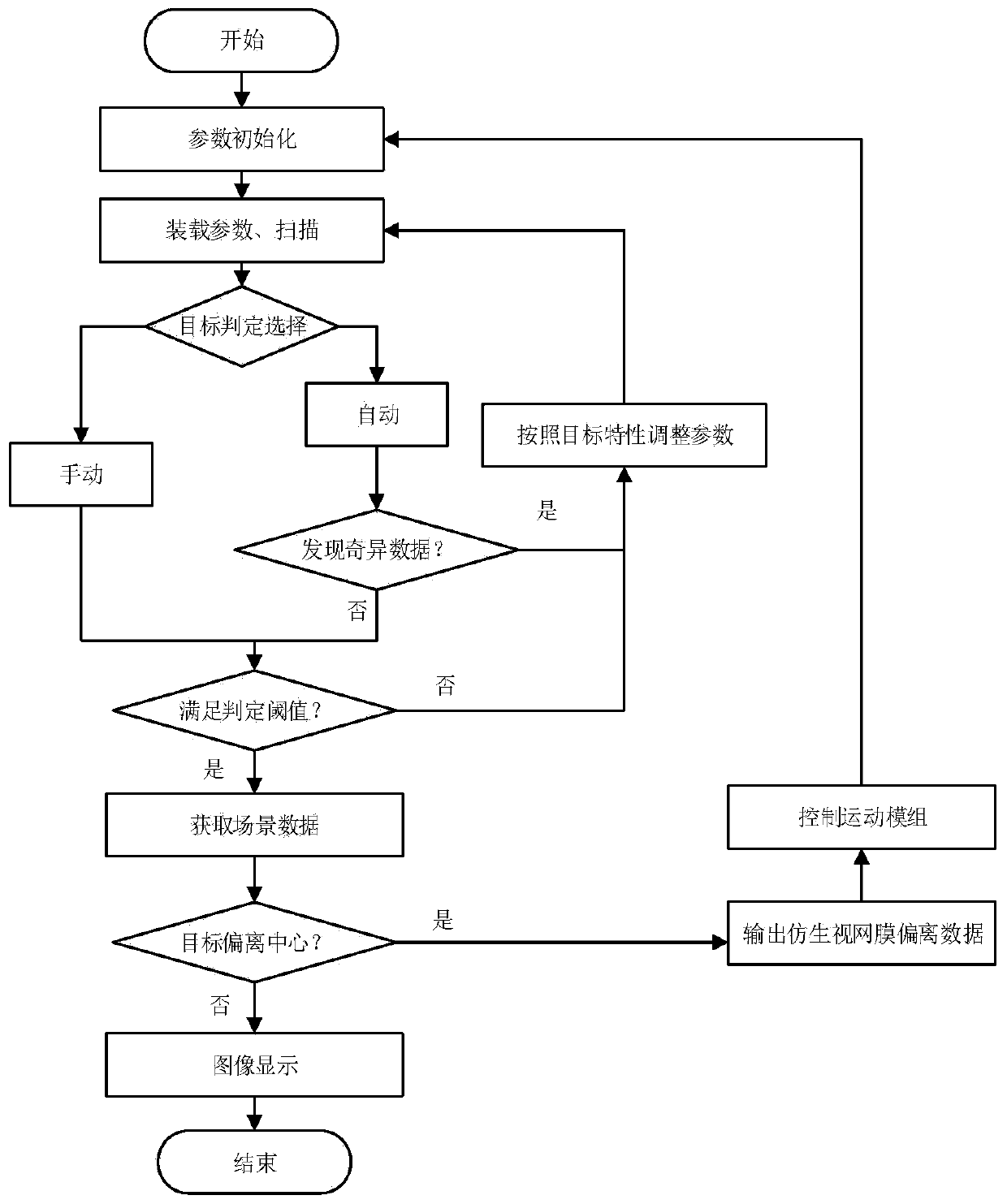
Visual target tracking method of bionic retina
ActiveCN111292376AImprove acquisition efficiencyAccurateImage analysisOphthalmologyVariable resolution
The invention discloses a visual target tracking method of a bionic retina, and belongs to the field of photoelectric target tracking. According to the invention, the variable resolution characteristic of bionic retina imaging is mainly utilized, and the field of view is mapped to the logarithm polar coordinates for target tracking. Firstly, logarithm polar coordinate mapping imaging of a bionic retina is utilized, a target tracking algorithm is improved through the staring effect of a fovea centralis, the information compression effect of an edge and real-time parameters, redundant data are compressed, detail information of an interested target is enhanced, and the information acquisition efficiency in a view field range is improved. And meanwhile, target information in a scene is accurately grasped by utilizing singular points and imaging threshold judgment, and the reliability of target screening is improved. And finally, real-time target tracking is realized by comparing an eccentricity judgment algorithm with higher speed with the motion control module. Compared with a traditional method, under the condition of a large field of view and high resolution, real-time target tracking is achieved on the basis of a bionic retina vision mechanism, efficiency is higher, and precision is higher.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Short-coherence interferometric measurement of length on the eye
Two problems arise when measuring length at the eye by short-coherence interferometry. First, the measurement focus and coherence window usually do not coincide. Second, the scanning process along the eye axis is time-consumin g. Both result in poor signal quality and inaccurate measurements. The present application is directed to a short-coherence interferometer in which a right-angle mirror and focusing optics jointly carry out a periodic back-and-forth movement in such a way that the measurement beam focus which is generated by the focusing optics and imaged on the eye by relay optics is moved synchronously with the coherence window from the cornea along the optic axis of the eye to the fovea centralis. Further, different path lengths are generated in the measurement beam path and reference beam path by means of a plurality of reflectors, so that the scanning process is limited to distances which are smaller than the optical length of the eye. The present invention is advantageously implemented using on a fiber-optic interferometer. According to the invention, the reference interferometer arm and measurement interferometer arm are combined with the arms of a fiber-optic interferometer.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
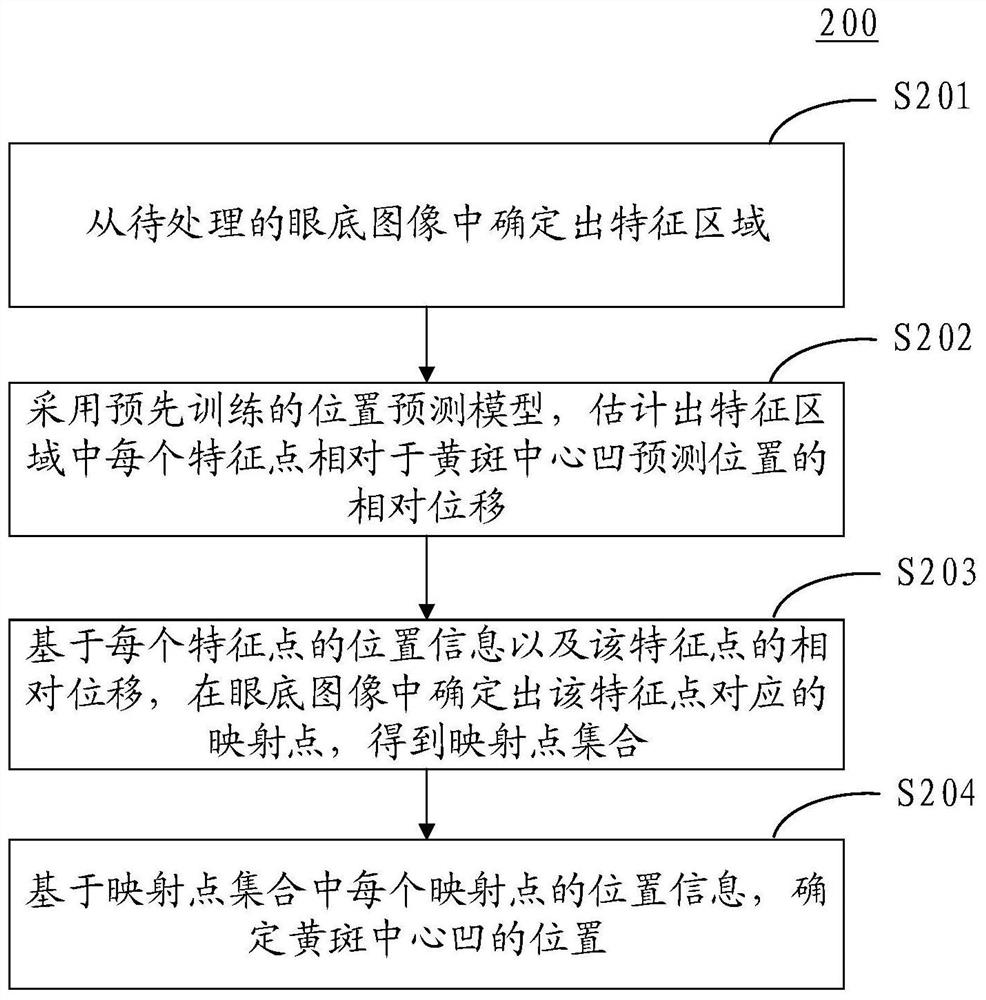
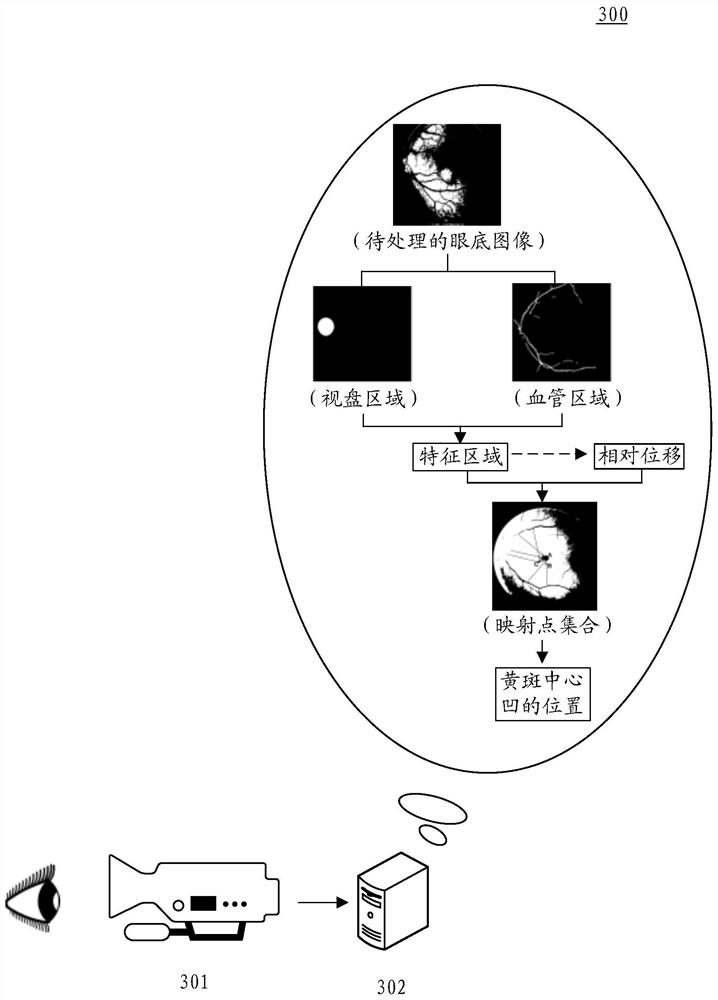
Method and device for determining macular fovea centralis position
PendingCN112150463ASolve the problem of low positioning accuracyImprove positioning accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOphthalmologyVisual perception
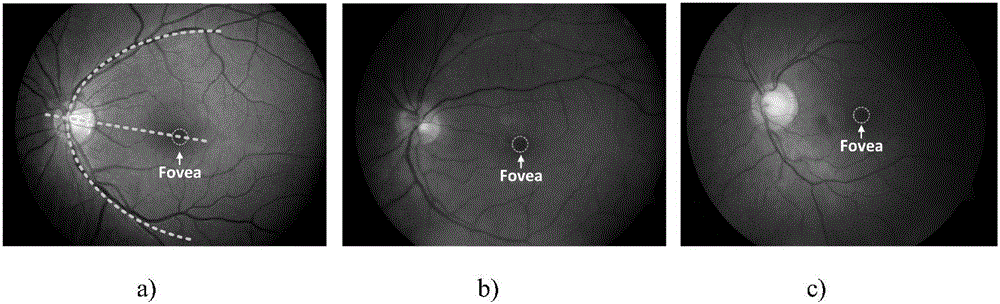
The invention discloses a method and a device for determining a macular fovea centralis position, and relates to the technical field of artificial intelligence such as smart medical treatment and computer vision. According to the specific implementation scheme, the method comprises the steps of determining a feature region from a to-be-processed fundus image, wherein the feature region comprises an optic disc region and a blood vessel region in the fundus image; adopting a pre-trained position prediction model to estimate the relative displacement of each feature point in the feature region relative to the macular fovea central fovea prediction position; based on the position information of each feature point and the relative displacement of the feature point, determining a mapping point corresponding to the feature point in the fundus image to obtain a mapping point set; and determining the position of the macular fovea based on the position information of each mapping point in the mapping point set. The positioning accuracy of macular fovea centralis is improved, and the influence of lesion shielding on the positioning accuracy can be avoided.
Owner:北京康夫子健康技术有限公司
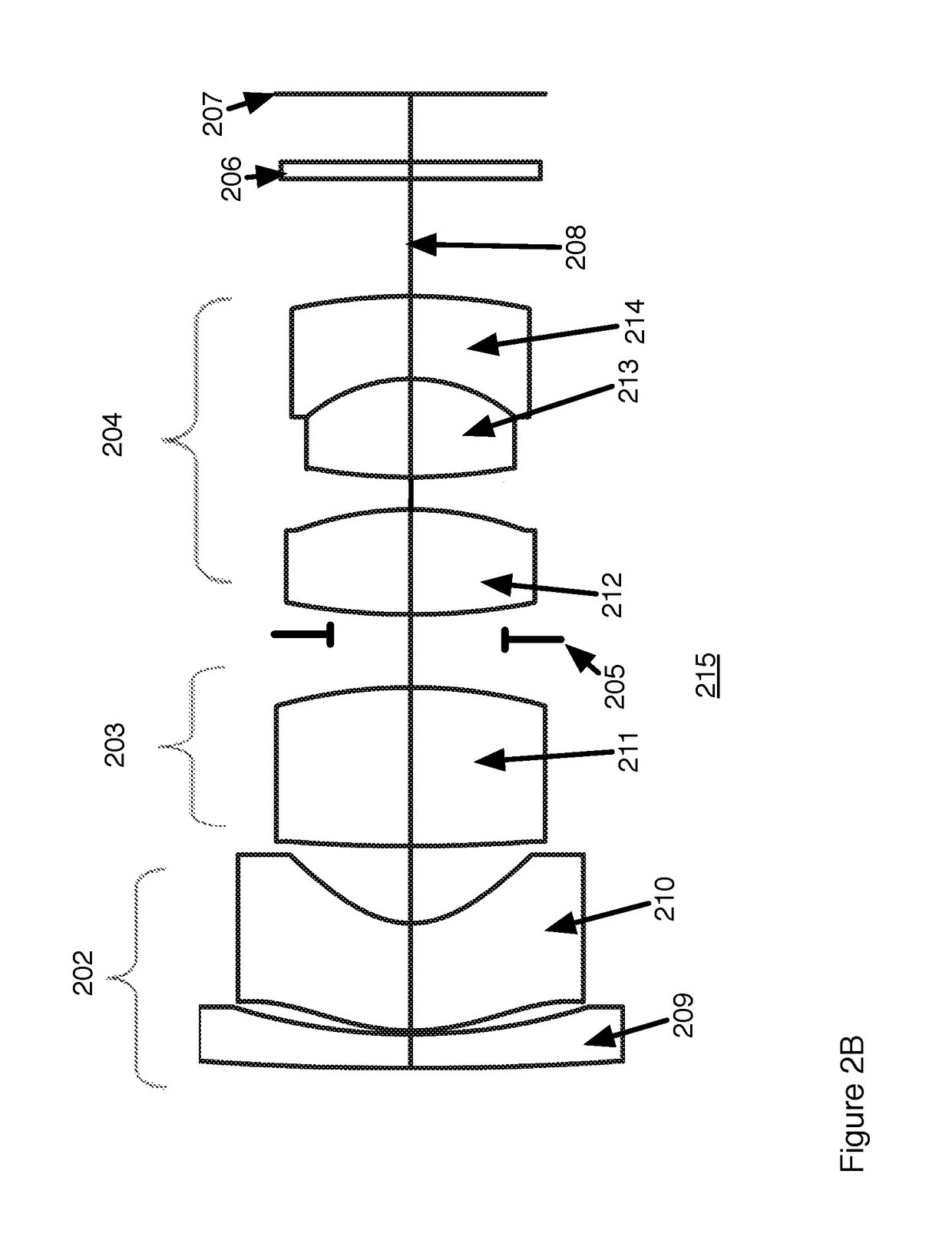
Intraocular lenses that improve peripheral vision
ActiveUS10588738B2Improve Optical Imaging QualityPoor visionIntraocular lensRefractive errorImaging quality
Lenses and methods are provided for improving peripheral and / or central vision for patients who suffer from certain retinal conditions that reduce central vision or patients who have undergone cataract surgery. The lens is configured to improve vision by having an optic configured to focus light incident along a direction parallel to an optical axis at the fovea in order to produce a functional foveal image. The optic is configured to focus light incident on the patient's eye at an oblique angle with respect to the optical axis at a peripheral retinal location disposed at a distance from the fovea, the peripheral retinal location having an eccentricity between −30 degrees and 30 degrees. The image quality at the peripheral retinal location is improved by reducing at least one optical aberration at the peripheral retinal location. The method for improving vision utilizes ocular measurements to iteratively adjust the shape factor of the lens to reduce peripheral refractive errors.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
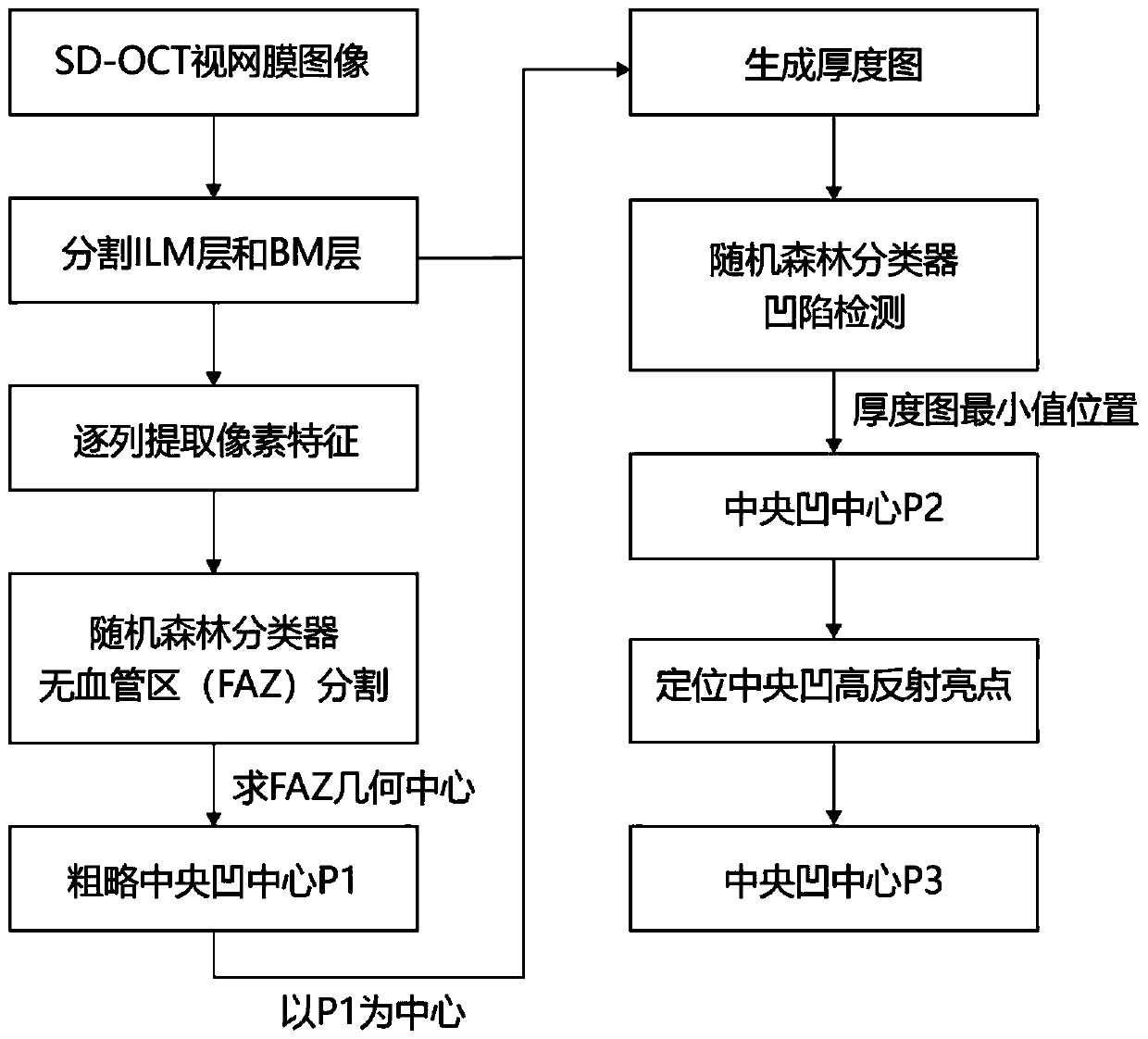
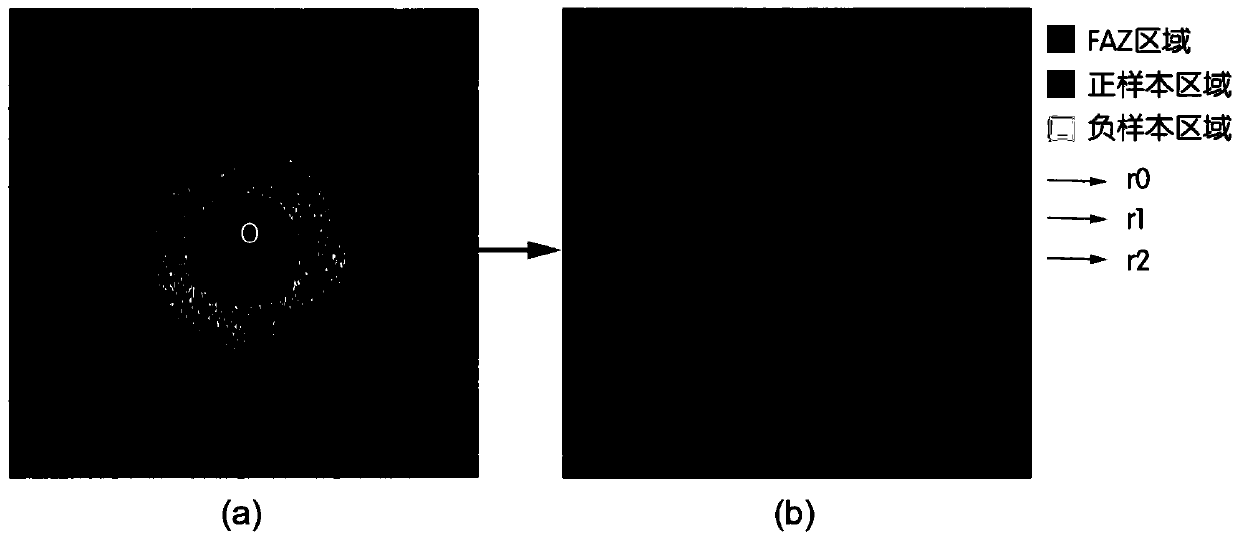
SD-OCT image macular fovea centralis center positioning method
ActiveCN110378333AReduce laborHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisOphthalmologyFoveal avascular zone
The invention discloses an SD-OCT image macular fovea centralis center positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting an inner boundary film layer and a Bloom film layer of an SD-OCT image; extracting each column of pixels between the inner boundary film layer and the Bloom film layer as features; training a random forest classifier to segment a fovea centralis non-vascular region, and calculating the geometric center position of the fovea centralis non-vascular region as the rough center position P1 of the macular fovea centralis; a retina thickness image is generated within a certain range with P1 as the center; judging whether the retina in the area is sunken or not, and if yes, taking the position at the minimum thickness value as a new foveal fovea central position P2; if not, the P2 is still the position of the P1; and searching a central concave high-reflection region around the position P2, if the high-reflection region exists, taking the central position of the high-reflection region as a final central concave central position P3, and otherwise, taking the P3 as the position P2. Compared with the conventional method for positioning only accordingto the thickness change of the retina, the robustness and the precision of the method are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
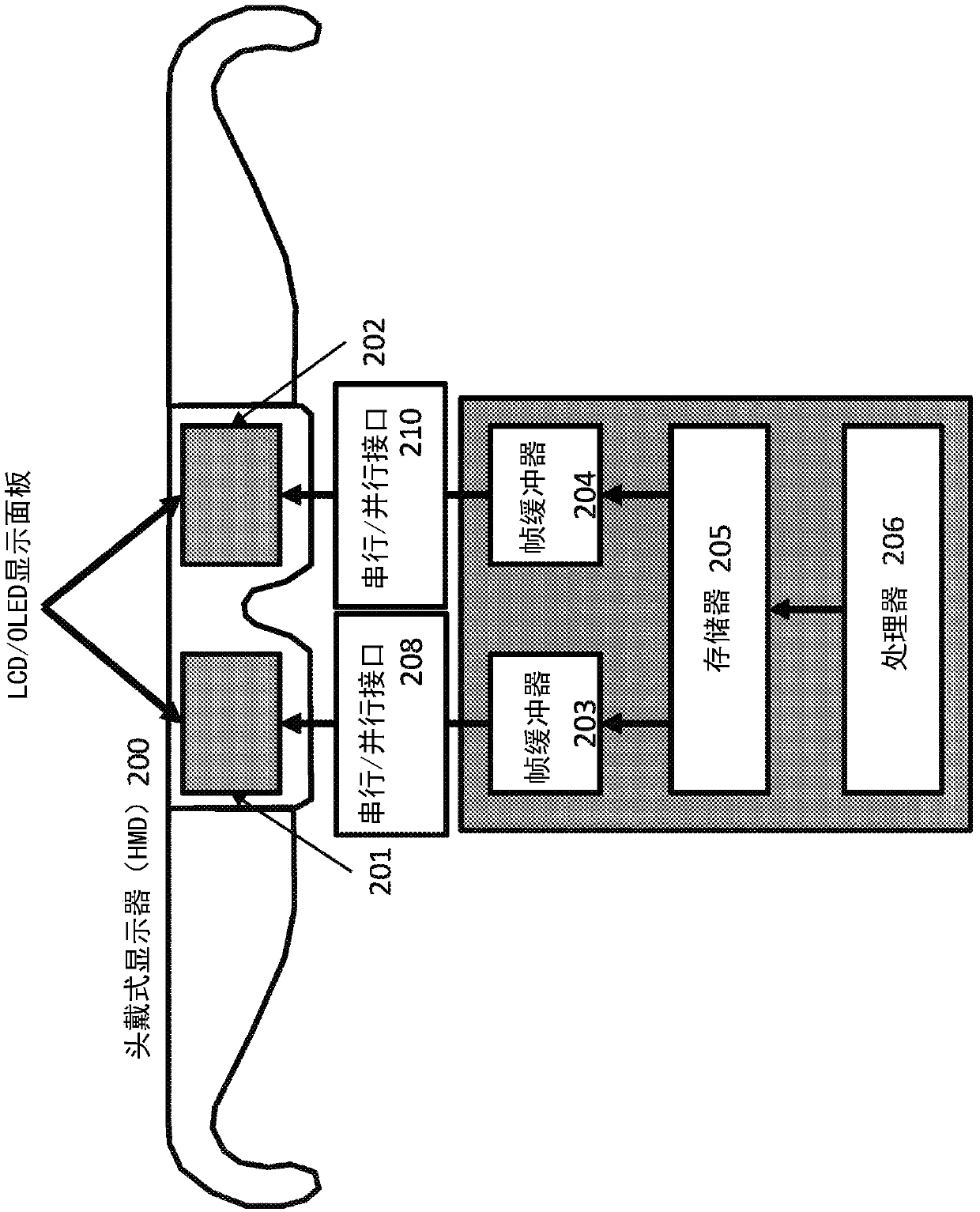
Systems and methods for head-mounted display adapted to human visual mechanism
InactiveCN110140353ACharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectro encephalogramComputer graphics (images)
Systems and methods are provided for rendering of a dual eye-specific display. The system tracks the user's eye movements and / or positions, in some implementations, based on electroencephalography (EEG) of the user, to correctly label the central (foveal) and peripheral (extra-foveal) areas of the display. Foveal data is fully rendered while extra-foveal data is reduced in resolution and, in someimplementations, shared between the two displays.
Owner:MOVIDIUS LTD
Prism prescription value acquisition system, acquisition method, acquisition apparatus and program for correcting fixation disparity
Owner:HOYA CORP
System and process for retina phototherapy
A process for performing retinal phototherapy or photostimulation includes generating a laser light that creates a therapeutic effect to retinal and / or foveal tissues exposed to the laser light without destroying or permanently damaging the retinal or foveal tissue. The laser light is applied to a first treatment area of the retina. After a predetermined interval of time, within a single treatmentsession, the laser light is reapplied to the first treatment area of the retina. During the interval of time between the laser light applications to the first treatment area, the laser light is applied to one or more additional areas of the retina that is spaced apart from the first treatment area and one another. The laser light is repeatedly applied to each of the areas to be treated until a predetermined number of laser light applications to each area to be treated has been achieved.
Owner:OJAI RETINAL TECH
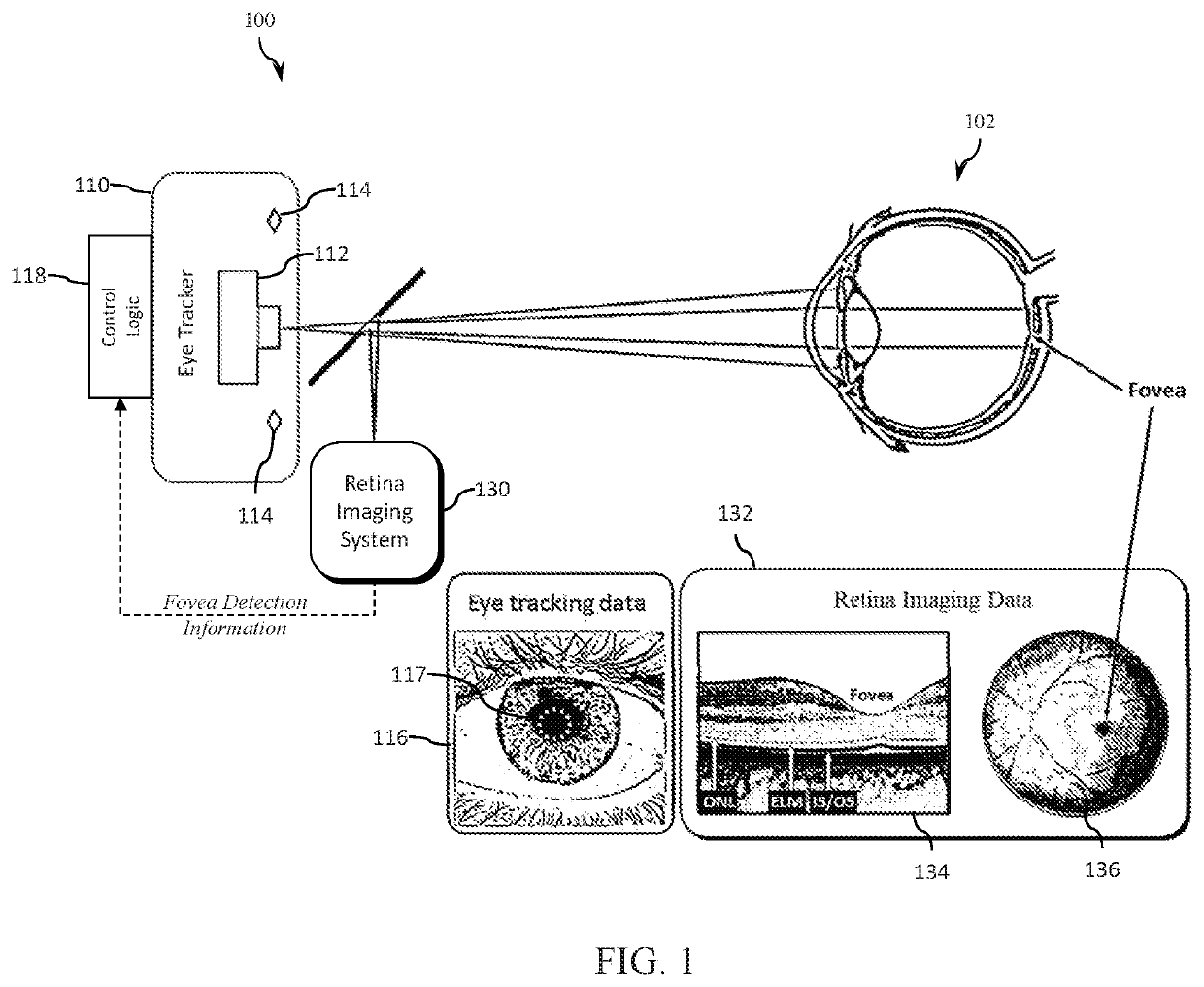
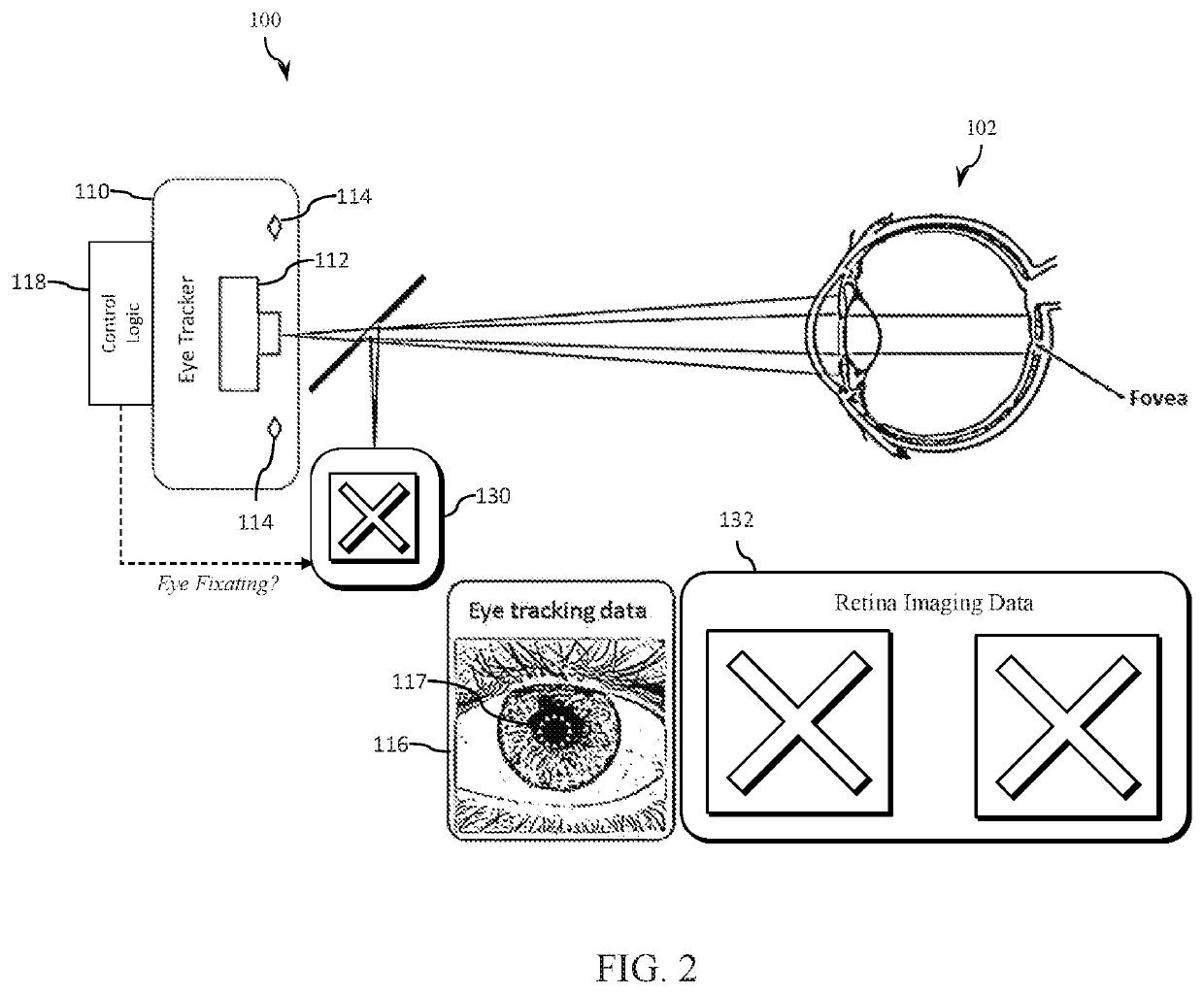
Eye tracking fixation monitoring systems and methods
ActiveUS20210045630A1Complete understandingImage enhancementImage analysisRetinal imagingFovea centralis
Systems and methods for tracking eye movement during a diagnostic procedure include a retina imaging system configured to capture a first plurality of images of an eye and detect a presence of a fovea, an eye tracker configured to capture a second plurality of images of the eye and track a position and orientation of the eye; and a control processor configured to synchronize the first and second plurality of images, determine a time at which the fovea is detected in the first plurality of images, and determine one or more images from the second plurality of images to be classified as representative of fixation. The classified images are analyzed to determine eye fixation status during the diagnostic procedure based on eye tracking data.
Owner:ALCON INC
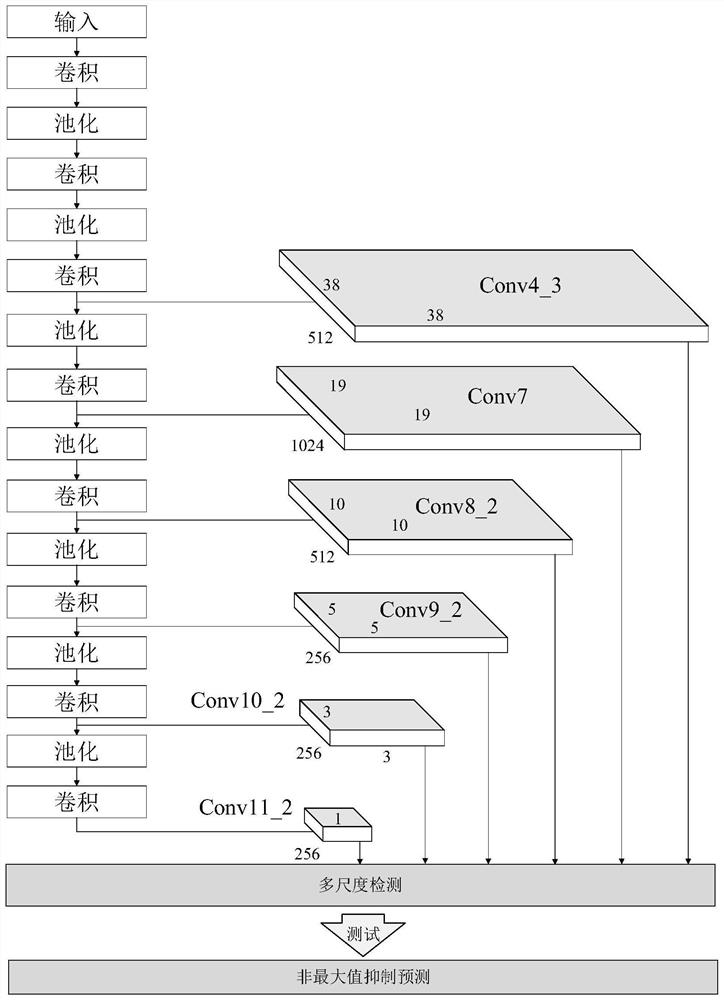
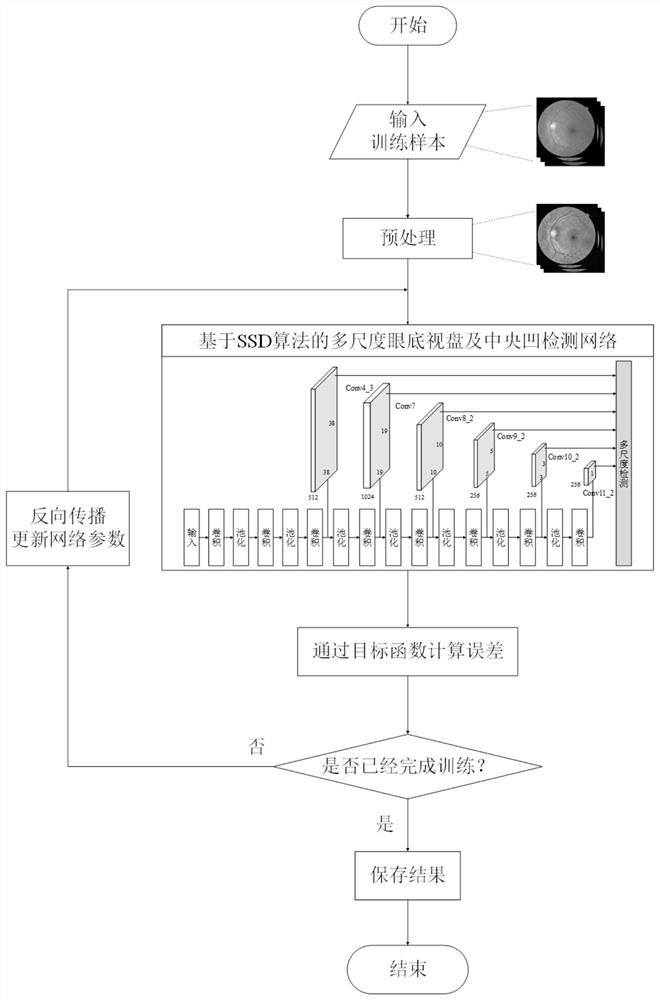
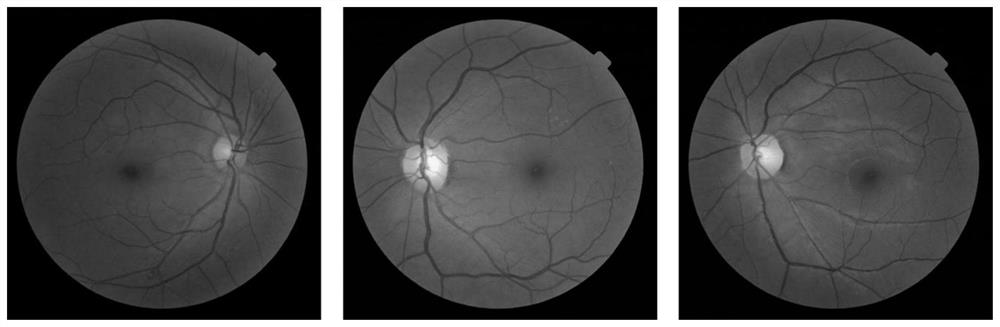
Fundus optic disc and fovea centralis real-time detection device and method based on deep learning
PendingCN112541883ARealize real-time detectionImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingOphthalmology
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and aims to realize real-time fundus optic disc and fovea centralis detection based on deep learning and improve the detectionprecision and speed of the optic disc and the fovea centralis. Therefore, according to the technical scheme, the fundus optic disc and fovea centralis real-time detection device and method based on deep learning are adopted, a fundus optic disc and fovea centralis detection network based on a single-stage multi-frame detection SSD algorithm is constructed, parameters of a network model are optimized through multiple times of iterative learning, and the detection precision of the network model is improved. And real-time positioning of the optic disc and the fovea centralis center in a large number of fundus images is realized. The method is mainly applied to medical image processing occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
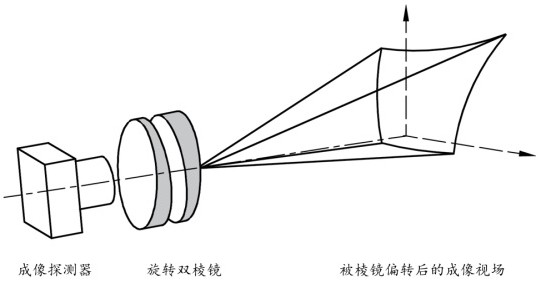
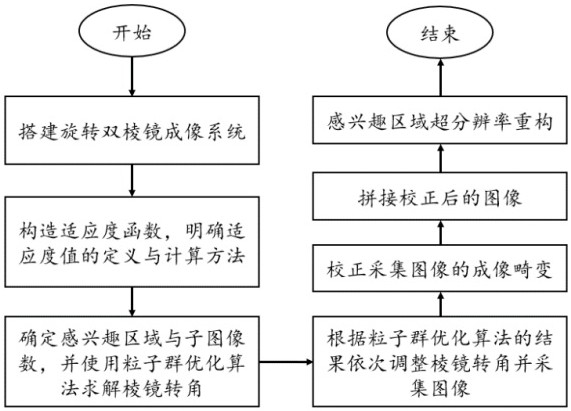
Method for realizing flexible central fovea imaging based on rotary biprism imaging system
ActiveCN113759543AReduce in quantityGuaranteed Foveal Imaging PerformanceImage enhancementPrismsImage resolutionEngineering
The invention relates to a method for realizing flexible central fovea imaging based on a rotary biprism imaging system. The method comprises the steps of S1, constructing a rotary biprism imaging system; S2, constructing a fitness function, and defining a definition and calculation method of a fitness value; S3, determining a region of interest and the number of sub-images, and solving a prism rotation angle by using a particle swarm optimization algorithm; S4, sequentially adjusting the rotation angles of the prisms according to the result of the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and collecting images; S5, carrying out distortion correction on the collected images; S6, splicing the distorted and corrected images to obtain a large field of view; and S7, performing super-resolution reconstruction on the region of interest to further improve the resolution of the central fovea region. According to the invention, central fovea imaging with flexible adjustment of the region of interest can be realized, and acquisition of an overall large field of view is considered. Besides, central fovea imaging can be realized only by using the single rotary biprism imaging system, so that the complexity of equipment is greatly reduced, and the method has excellent practical value.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
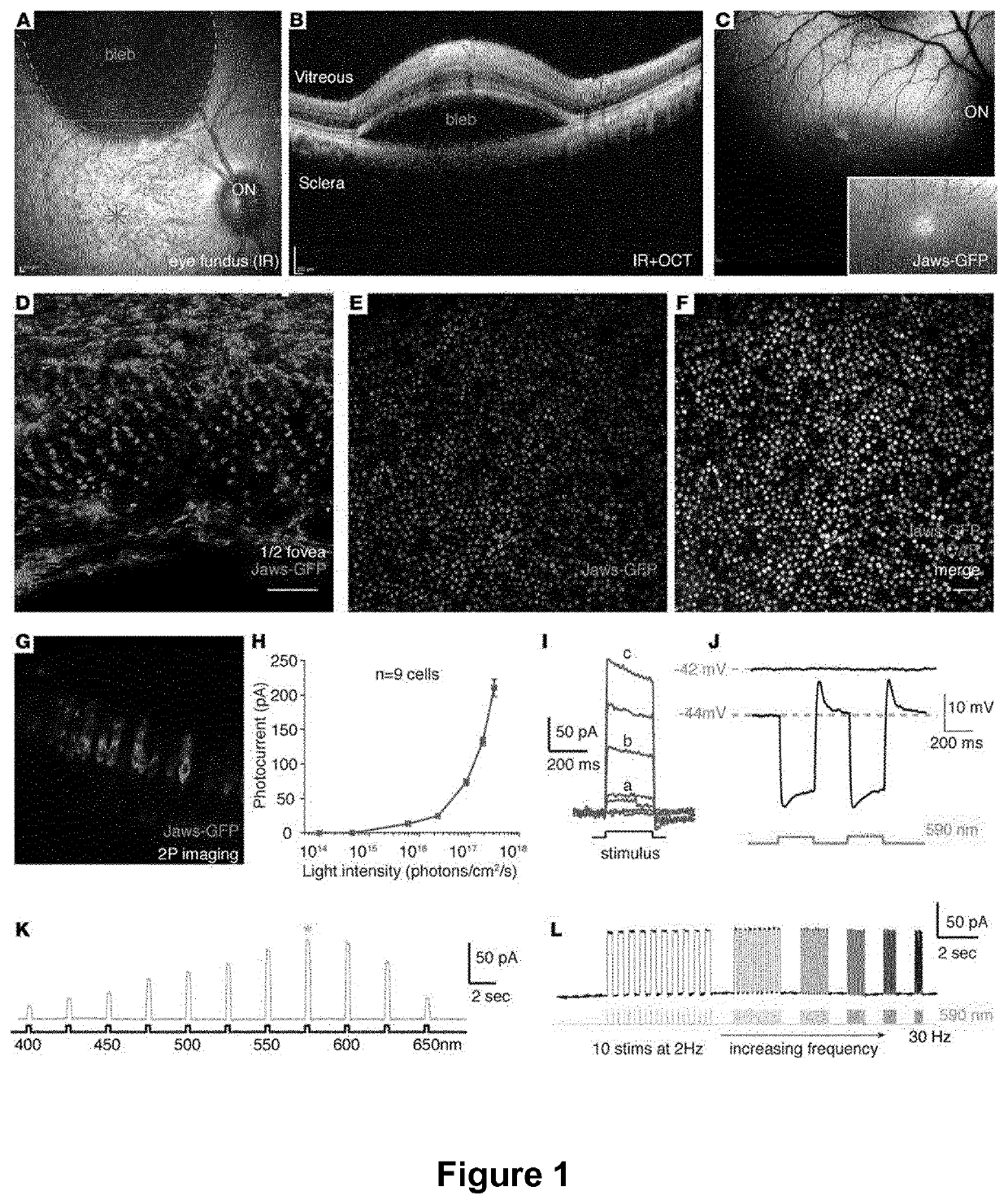
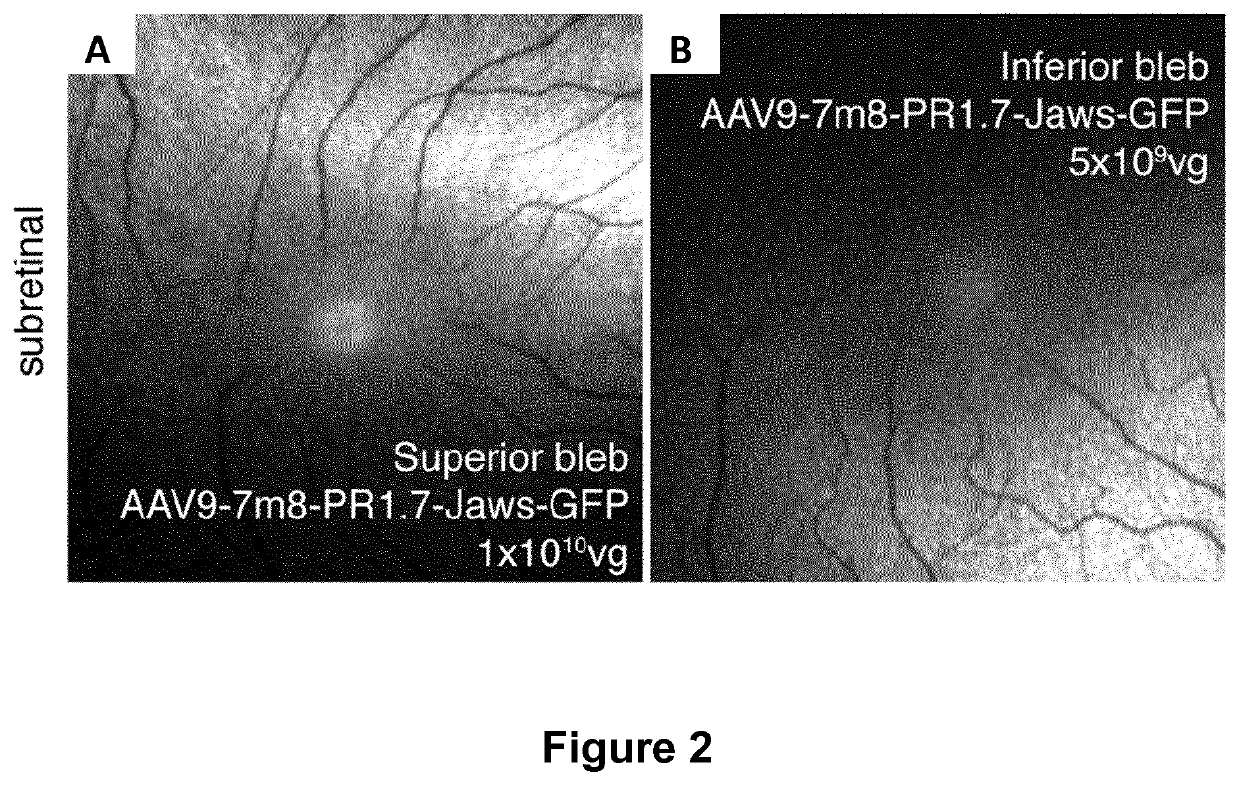
Methods of expressing a polynucleotide of interest in the cone photoreceptors of a subject comprising the subretinal delivery of a therapeutically effective amount of a recombinant aav9-derived vector
ActiveUS20210268125A1Efficient deliveryEfficient transductionSenses disorderVectorsOptogeneticsCone cell
Several new vector-promoter combinations to overcome the limitations associated with AAV-mediated cone transduction in the fovea are provided. The delivery modality relies on a cone-specific promoter and result in high-level transgene expression compatible with optogenetic vision restoration. Methods of expressing a polynucleotide of interest in the cone photoreceptors of a subject comprising subretinal delivery of a therapeutically effective amount of a recombinant AAV9-derived vector comprising a VP1 capsid protein as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 11 and the polynucleotide of interest under the control of the pR1.7 promoter as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 12 are also provided.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Methods of expressing a polynucleotide of interest in the cone photoreceptors of a subject comprising the subretinal delivery of a therapeutically effective amount of a recombinant aav9-derived vector
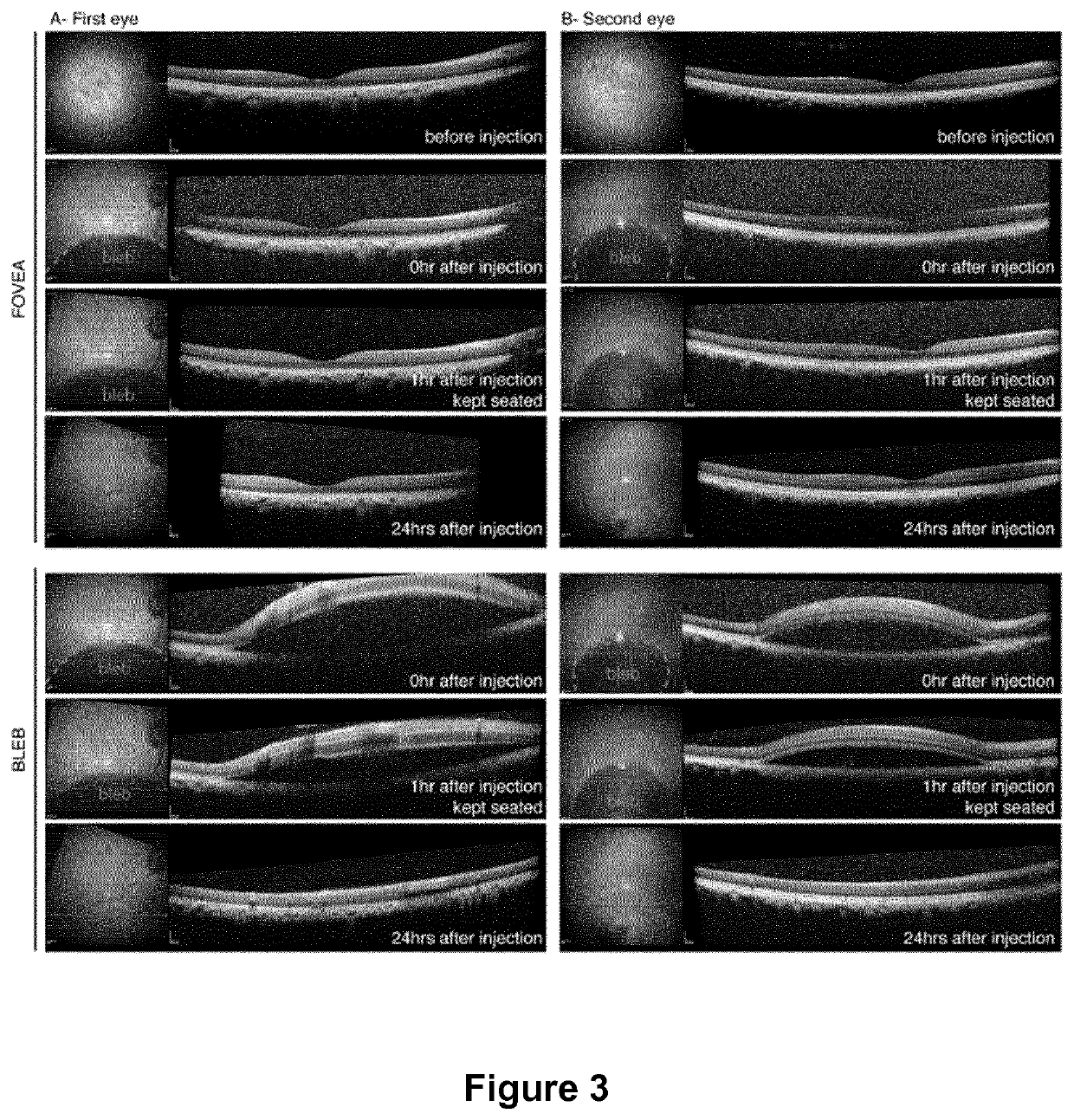
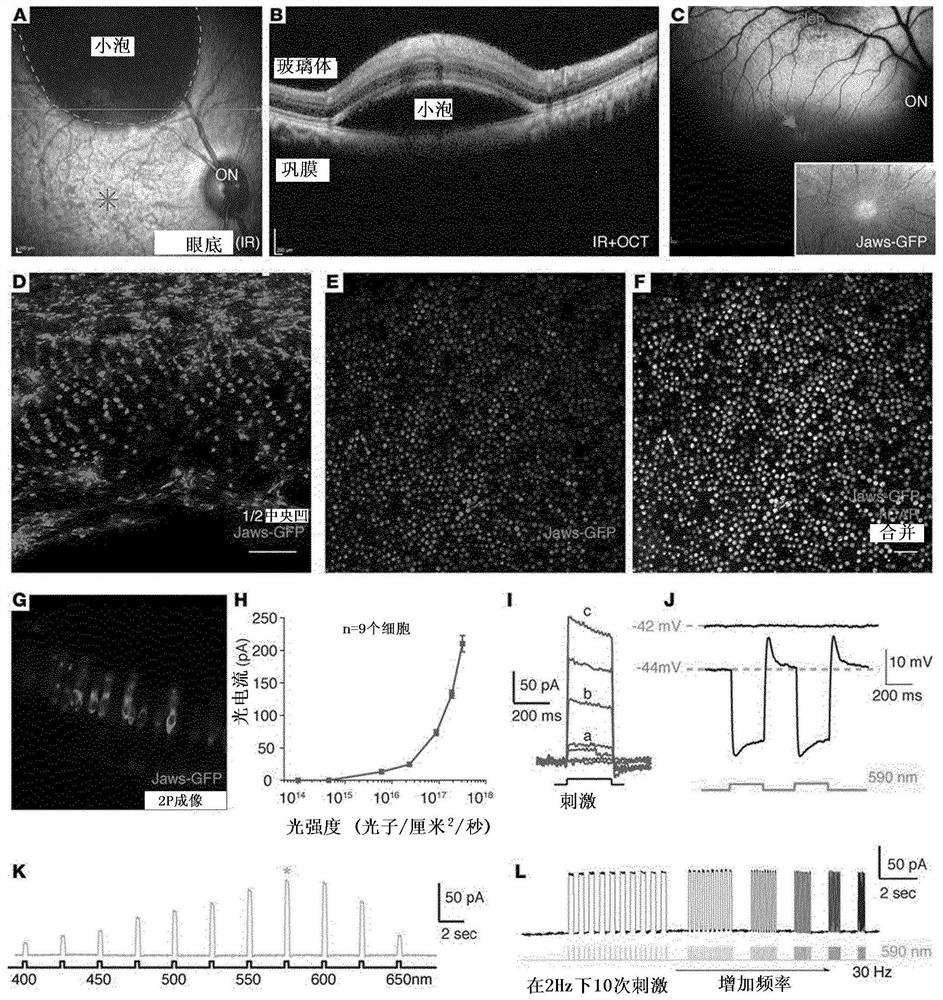
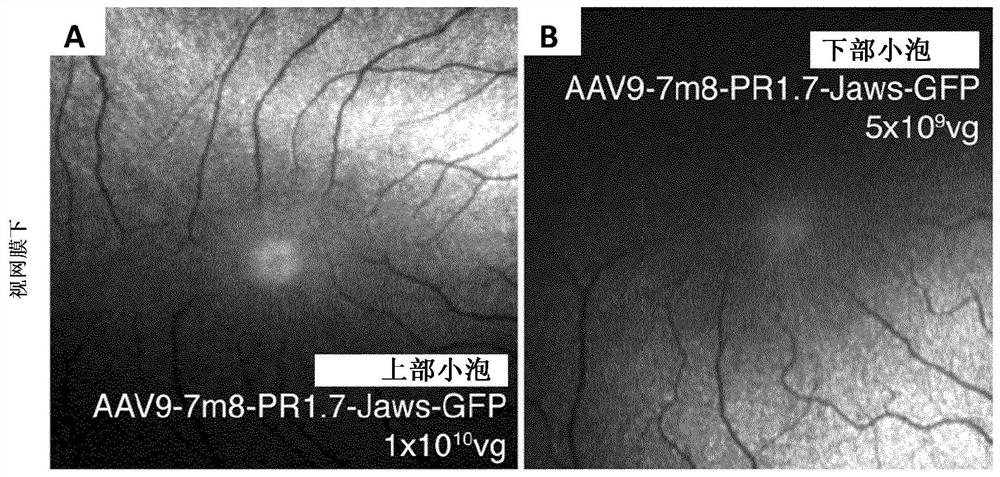
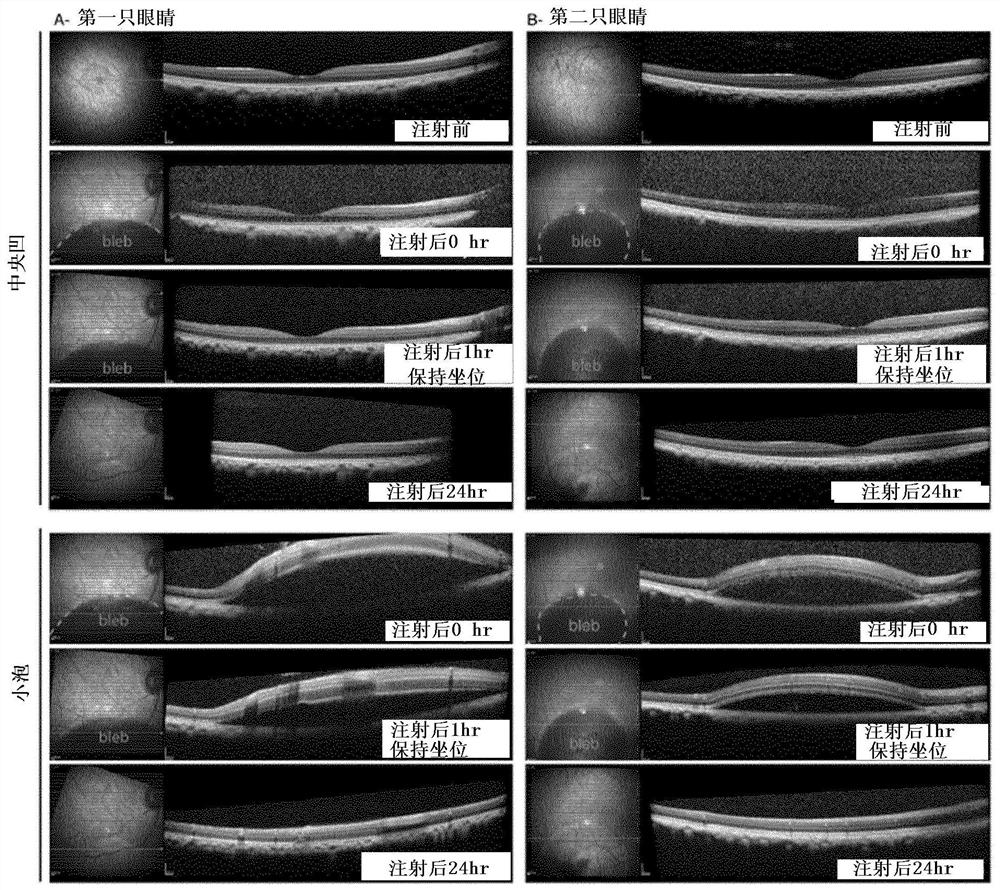
Intraocular injection of adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors has been an evident route for delivering gene drugs into the retina. Currently, the vectors need to be injected into the subretinal spacein order to provide gene delivery to cones. In this approach, gene delivery is limited to cells that contact the local "bleb" of injected fluid. Furthermore, retinal detachment that occurs during subretinal injections is a concern in eyes with retinal degeneration. Here, the inventors establish several new vector-promoter combinations to overcome the limitations associated with AAV-mediated cone transduction in the fovea with supporting studies in mouse models, human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids, post-mortem human retinal explants and living macaques. They show that an AAV9variant provides efficient foveal cone transduction when injected into the subretinal space several millimeters away from the fovea, without detaching this delicate region. The delivery modality relies on a cone-specific promoter and result in high-level transgene expression compatible with optogenetic vision restoration. Accordingly, the present invention relates to method of expressing a polynucleotide of interest in the cone photoreceptors of a subject comprising subretinal delivery of a therapeutically effective amount of a recombinant AAV9-derived vector comprising a VP1 capsid protein asset forth in SEQ ID NO: 11 and the polynucleotide of interest under the control of the pR1.7 promoter as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 12.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +1
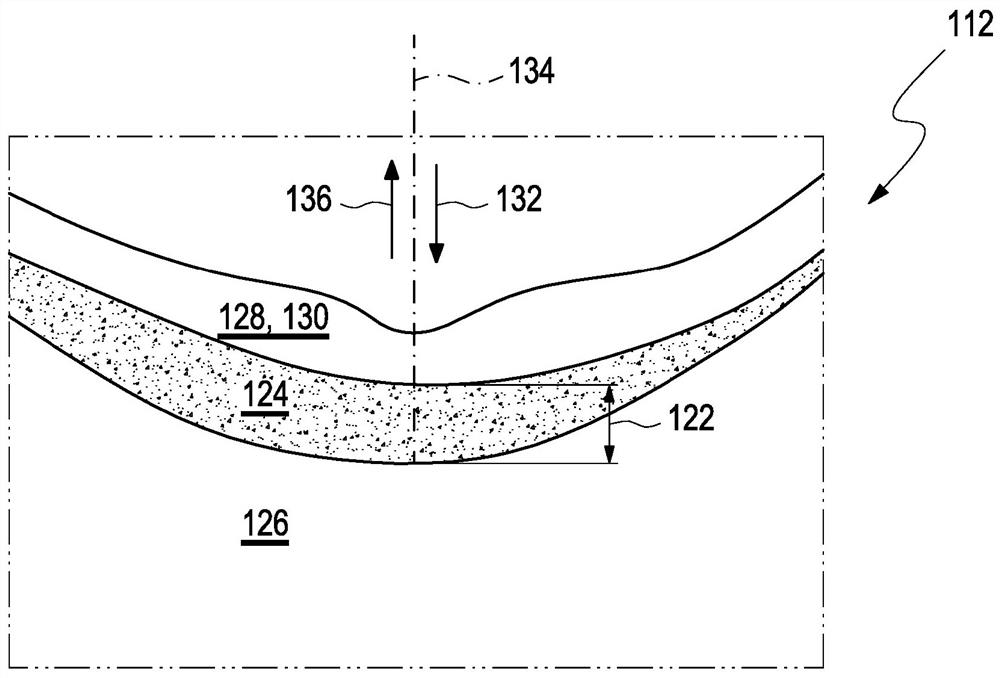
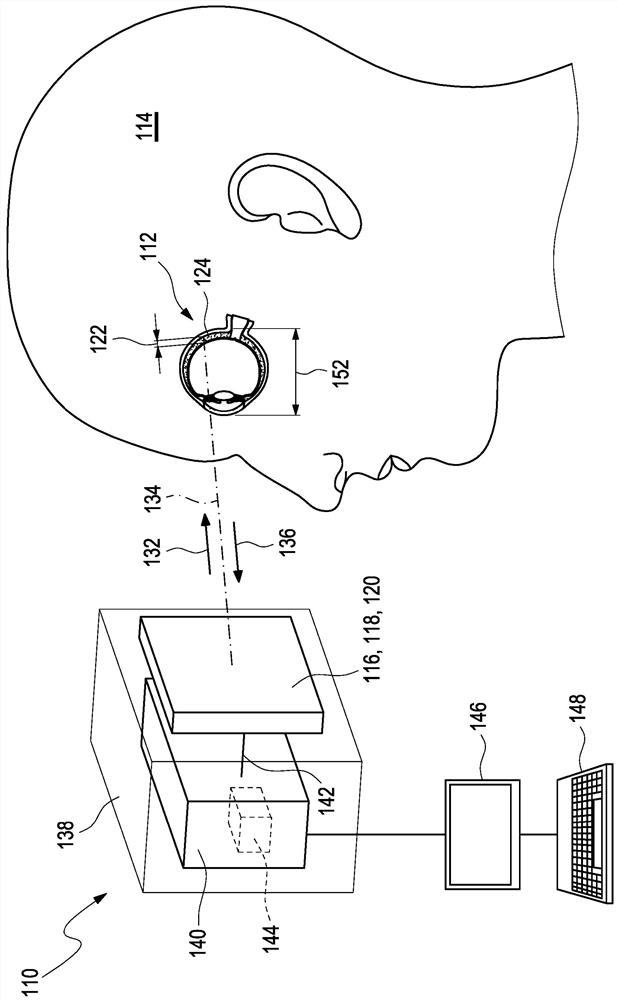
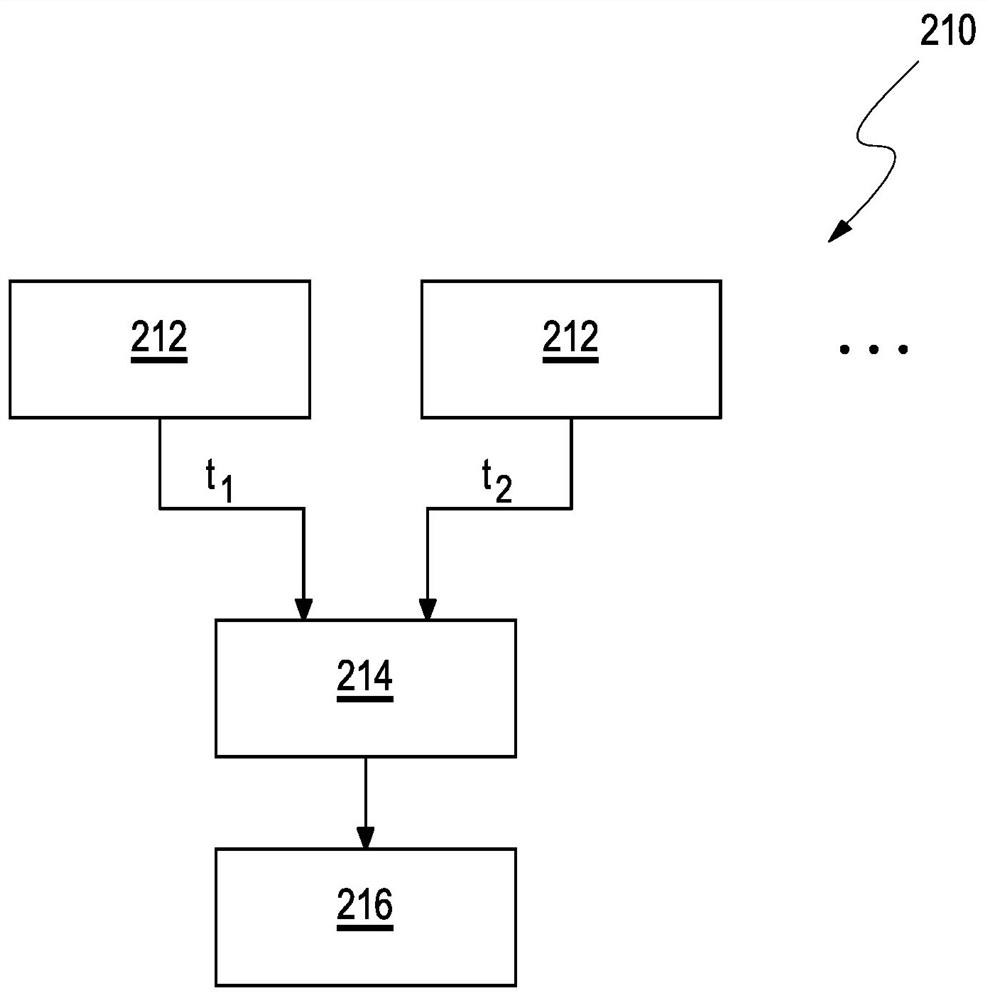
Determination of a change in the refraction error of an eye
The present invention relates to a method (210), a device (110) and a computer program for determining a refractive error of an eye (112) of a user (114). The method (210) for determining the refractive error of the eye (112) of the user (114), wherein the eye (112) of the user (114) has a choroid (124), comprises the following steps: a) determining at least one value for a layer thickness (122) of the choroid (124) of the eye (112) of the user (114) over at least one region (150) of the choroid (124); and b) determining a value (216) for the change in the refractive error of the eye (112) exclusively from at least two values for the layer thickness (122) of the choroid (124), each of which have been determined at different times for the at least one region (150) of the choroid (124), wherein the at least one region (150) is selected from a nasal perifoveal region (168) or a nasal parafoveal region (166).
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INT GMBH
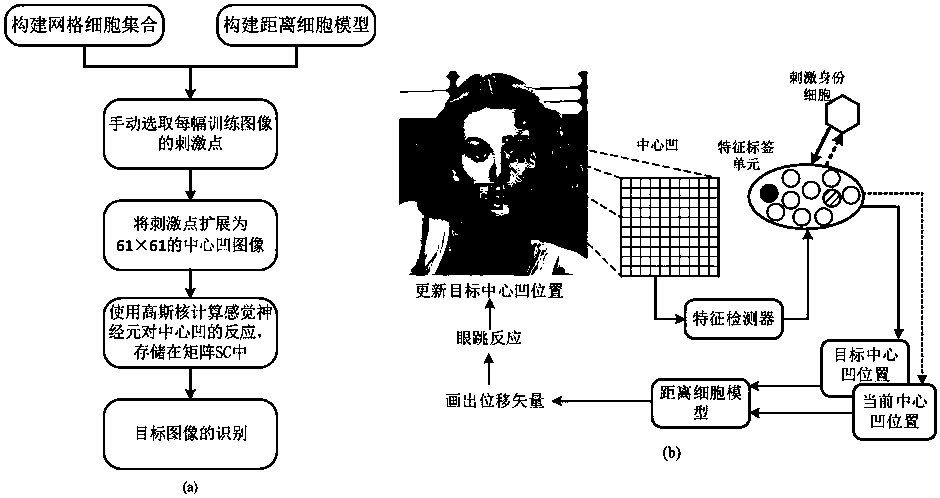
Bionic visual image target recognition method fusing dot-line memory information
ActiveCN110598534APrecise and detailed visual contentImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionSensory cellViewpoints
The invention discloses a bionic visual image target recognition method fusing dot-line memory information, and the method comprises the steps of constructing a grid cell set based on visual drive, constructing a distance cell model, and calculating a displacement vector between the positions coded by a grid cell group vector; calculating the response of all sensory neurons to each central concavepixel k through a Gaussian kernel, wherein the response is used for target recognition; calculating the fovea centralis of the current target image by using Gaussian nuclear sensory cells, taking thefeature tag unit with the strongest response as the next jump point, and accumulating the corresponding stimulated identity cells; selecting a next-hop viewpoint, and updating a foveal displacement vector through a distance cell model; and circularly repeating the calculation of the current position during the target identification process, selecting the next-hop viewpoint, and carrying out the vector calculation until the accumulation of a certain stimulated identity cell reaches a threshold value 0.9, and considering the stimulated identity as the finally identified target. The method provided by the invention has a relatively higher recognition rate for the position change, zooming and shielded images.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
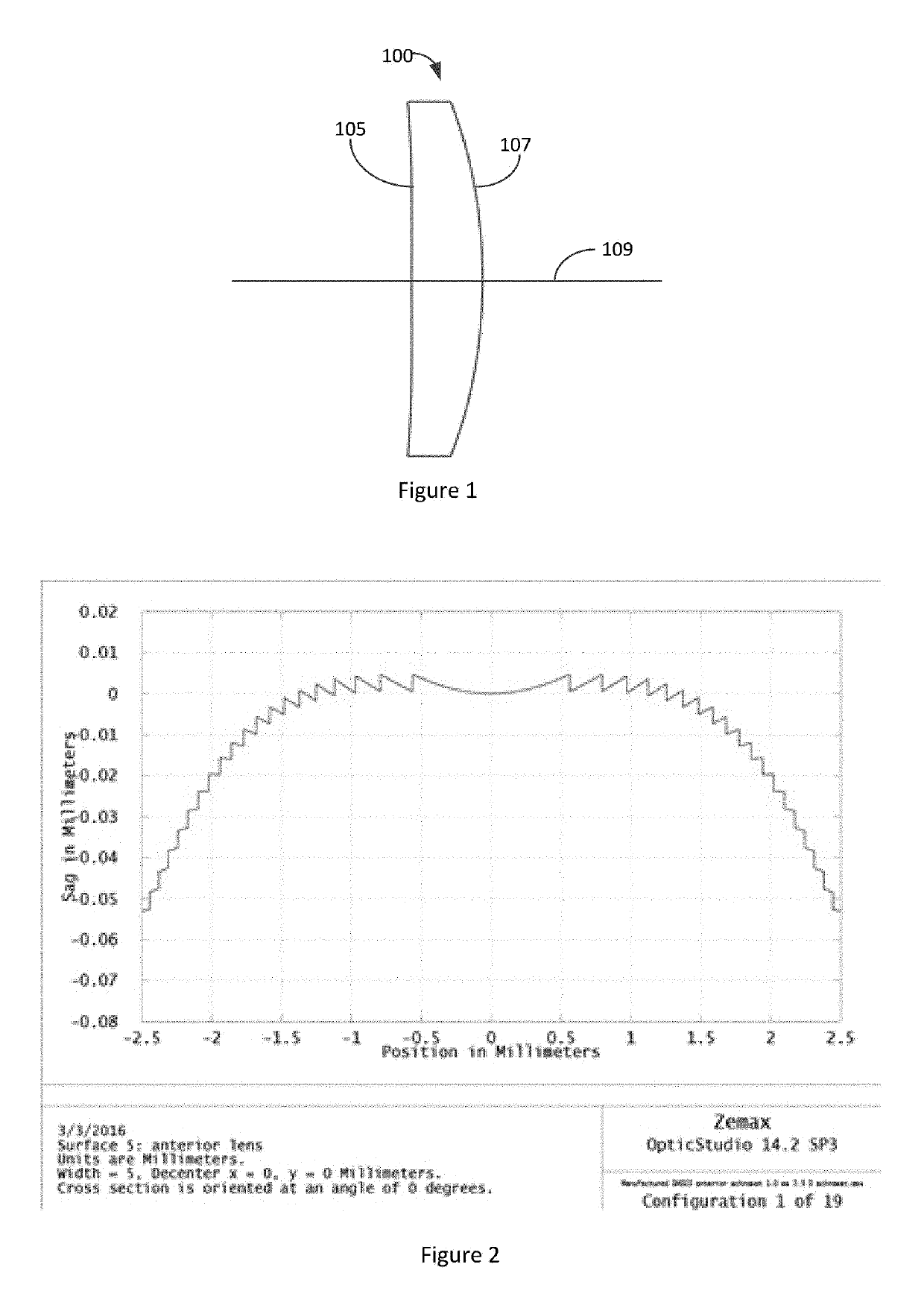
Fovea lens
ActiveUS10180562B1Reduce manufacturing riskDifficult to manufactureOptical elementsOptical axisHigh magnification
Wide angle fovea lens and a camera design using the lens are described. The lens has three lens groups and includes a single aspherical lens element. The lenses have higher magnification on the optical axis than at angles off the optical axis.
Owner:NING ALEX
Intraocular lens for extended macular vision in patients with macular degeneration
ActiveUS11147662B2Improve image qualityMinimized optical aberrationIntraocular lensImaging qualityPreferred retinal locus
Owner:SYNEOS HEALTH INT LTD
Systems and methods for neuroprotective therapy of glaucoma
Provides neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma, including the generation of micropulsed laser beams with parameters and characteristics, including pulse length, power, and duty cycle, selected to produce a therapeutic effect without visually visible laser lesions or damage to the retina tissue damage. Laser beams are applied to the retinal tissue and / or foveal tissue of eyes with or at risk of glaucoma to produce therapeutic effects on the retinal tissue and / or foveal tissue exposed to the laser beam without destroying or permanently Damage retinal tissue and / or foveal tissue, and improve the function or condition of the optic nerve cells and / or retinal ganglion cells of the eye.
Owner:OJAI RETINAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com