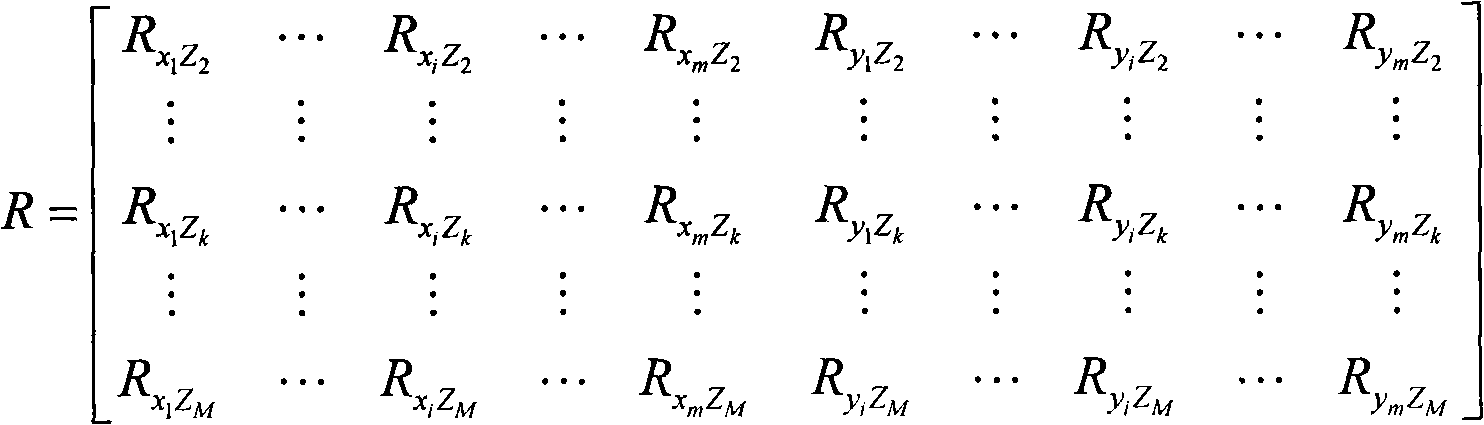Patents
Literature
201 results about "Retinal imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Retinal imaging is a high-resolution digital image taken of your retina, blood vessels and optic nerve located at the back of your eyes.
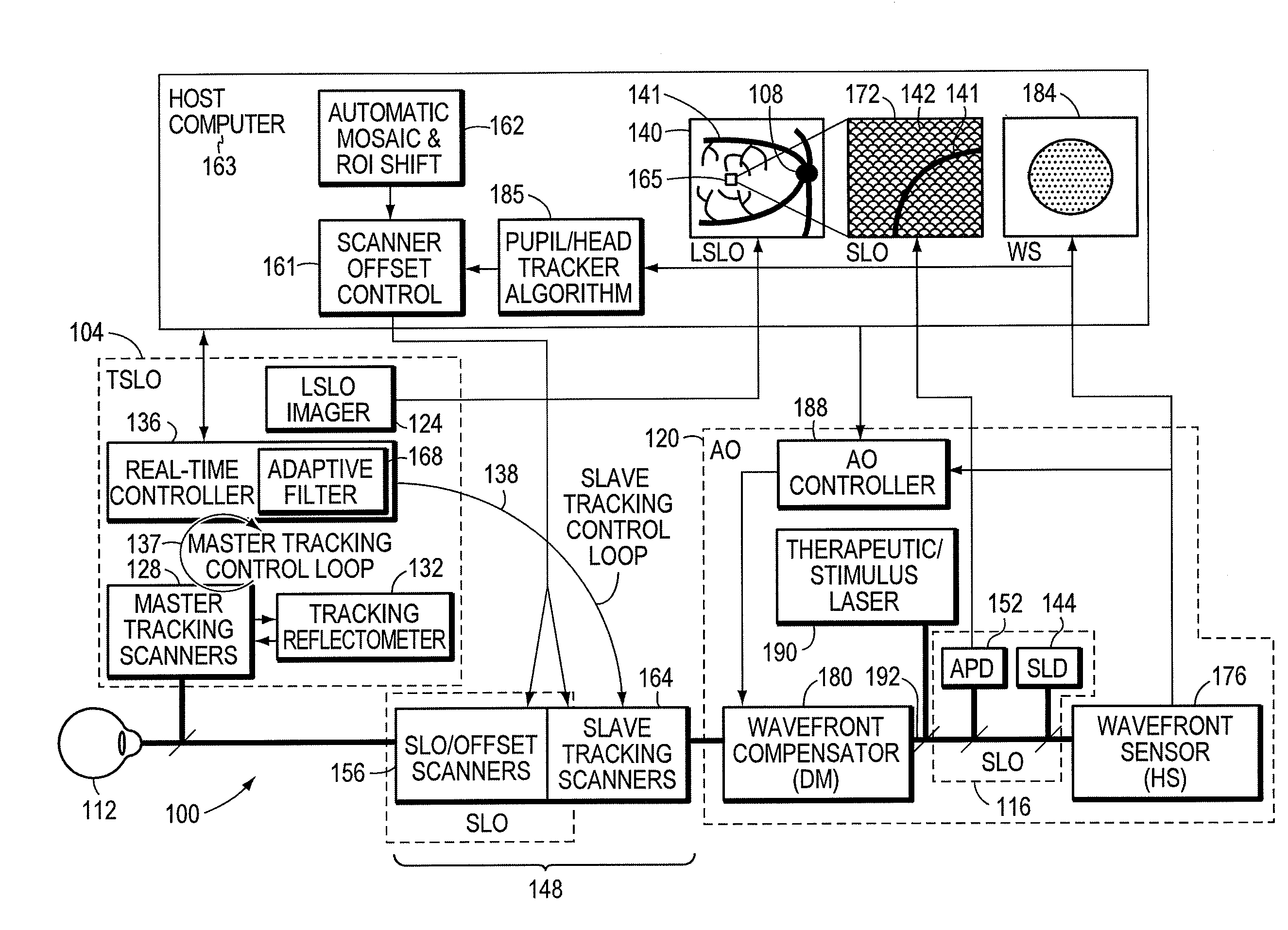
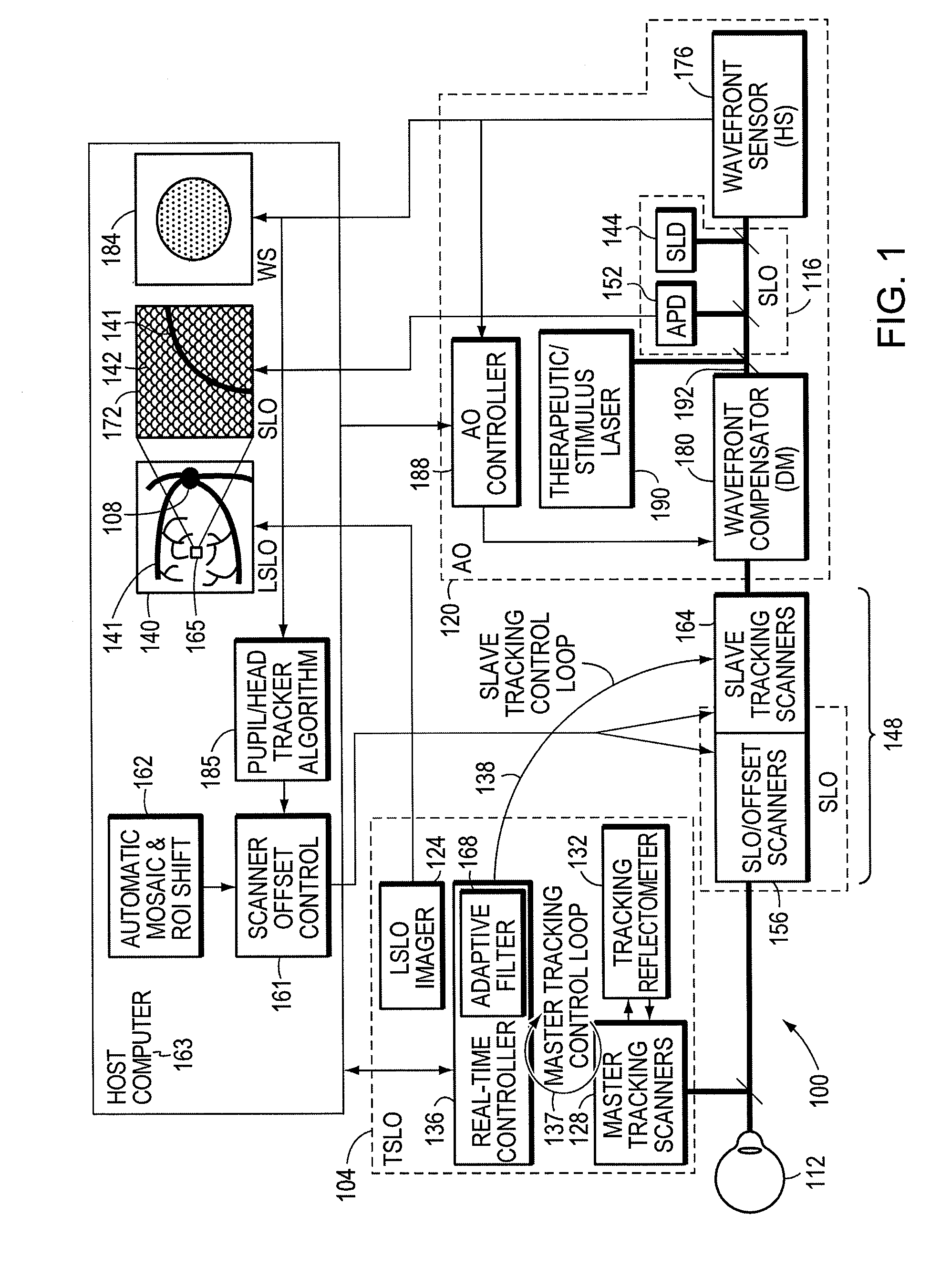
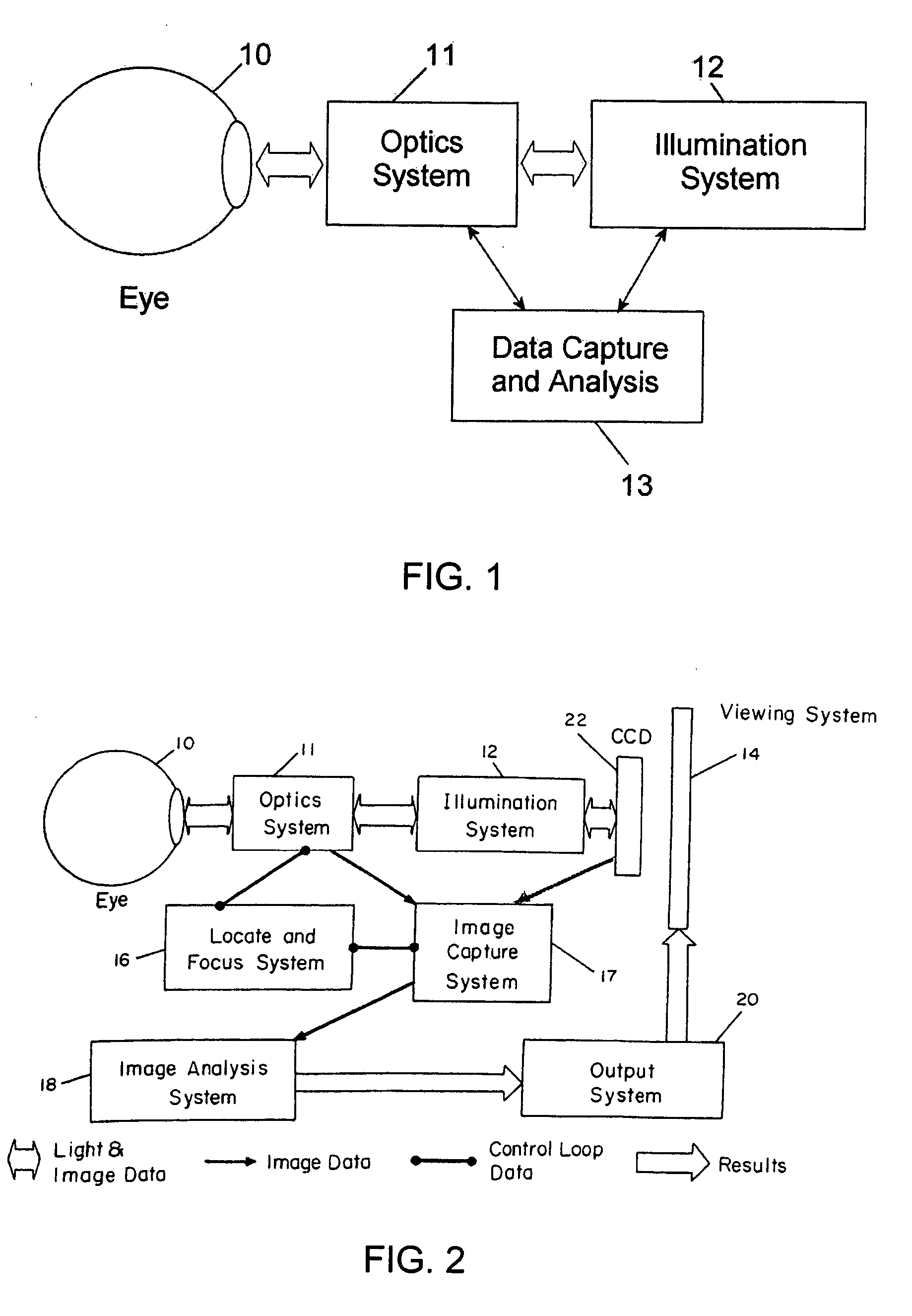
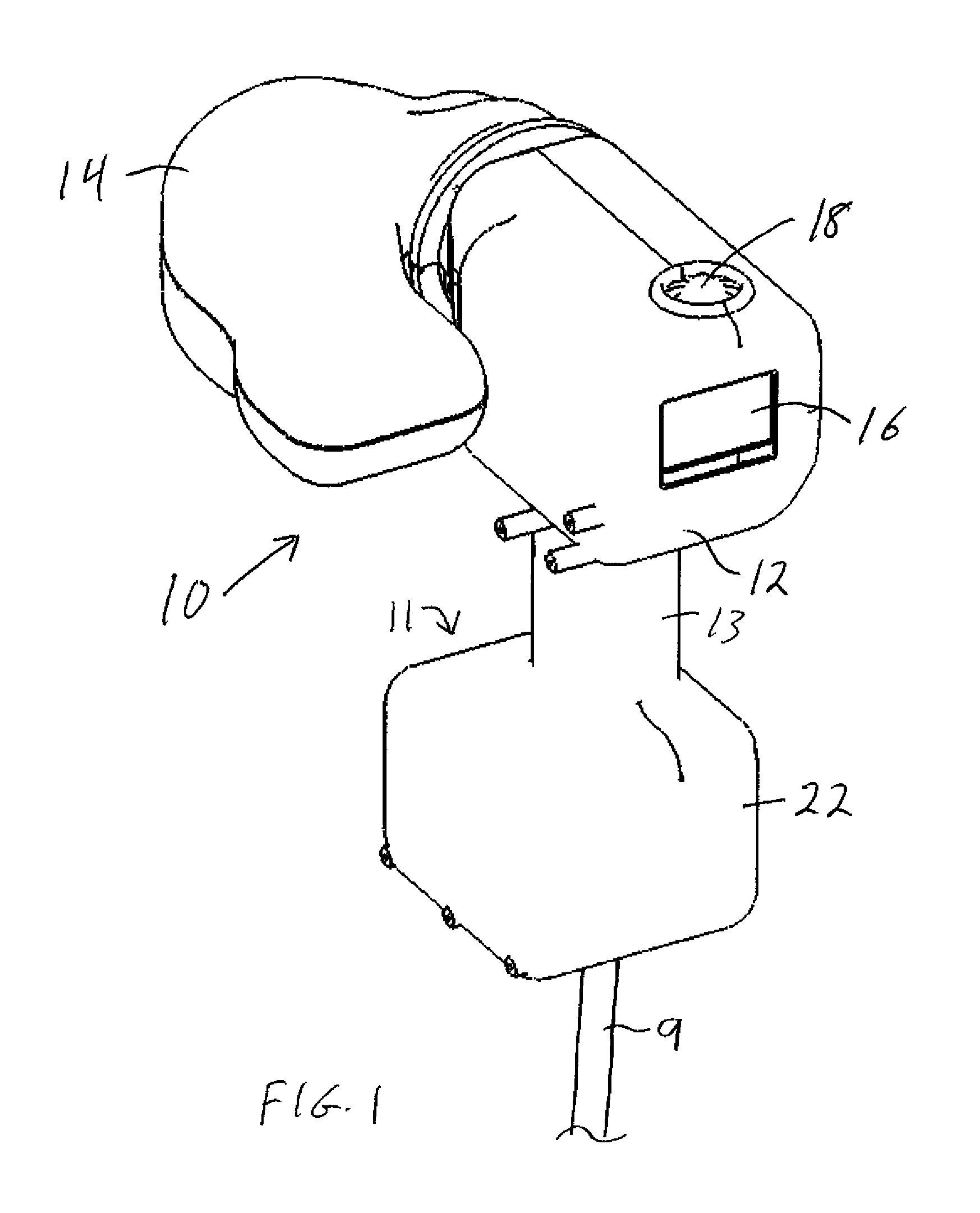
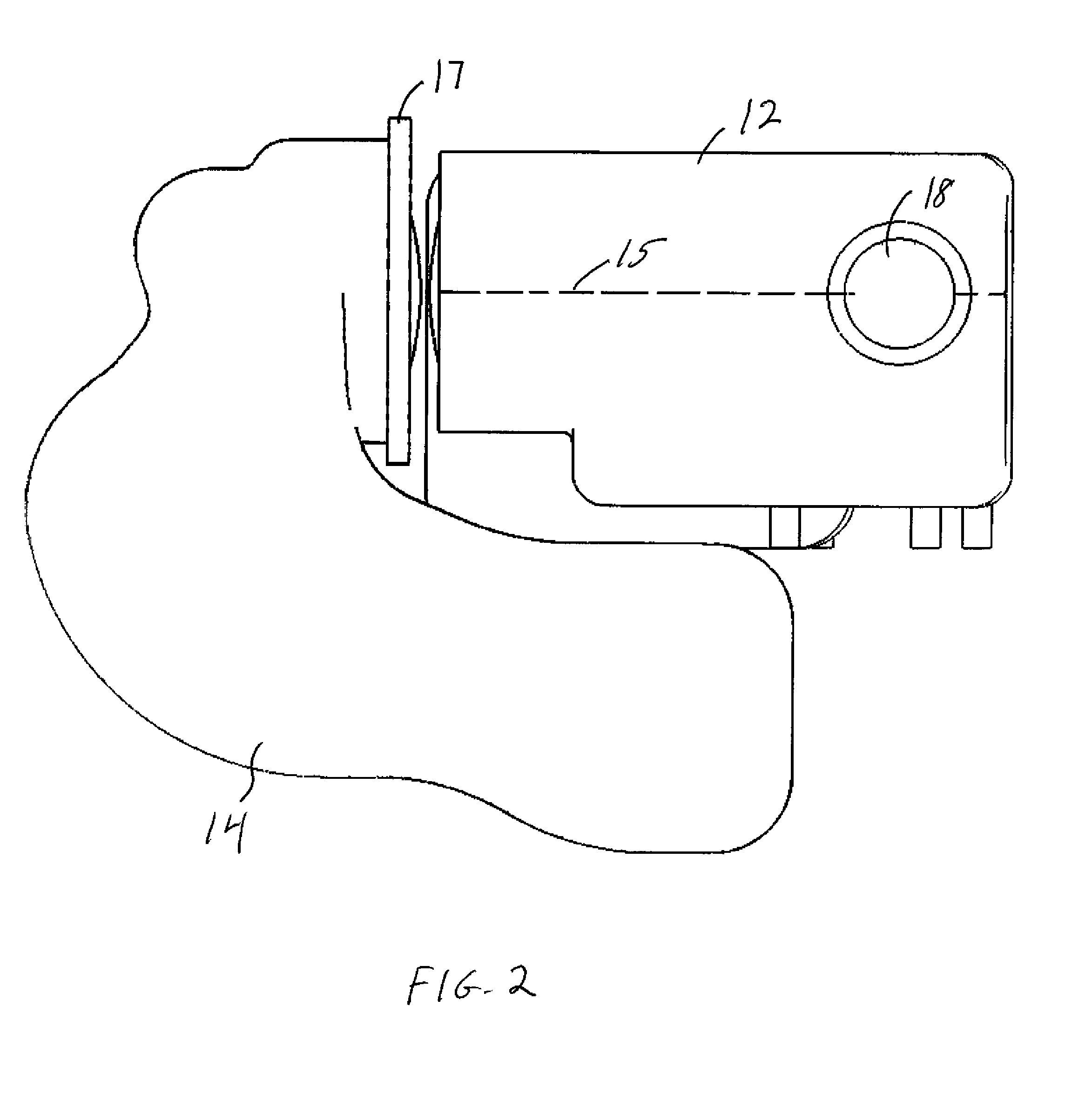
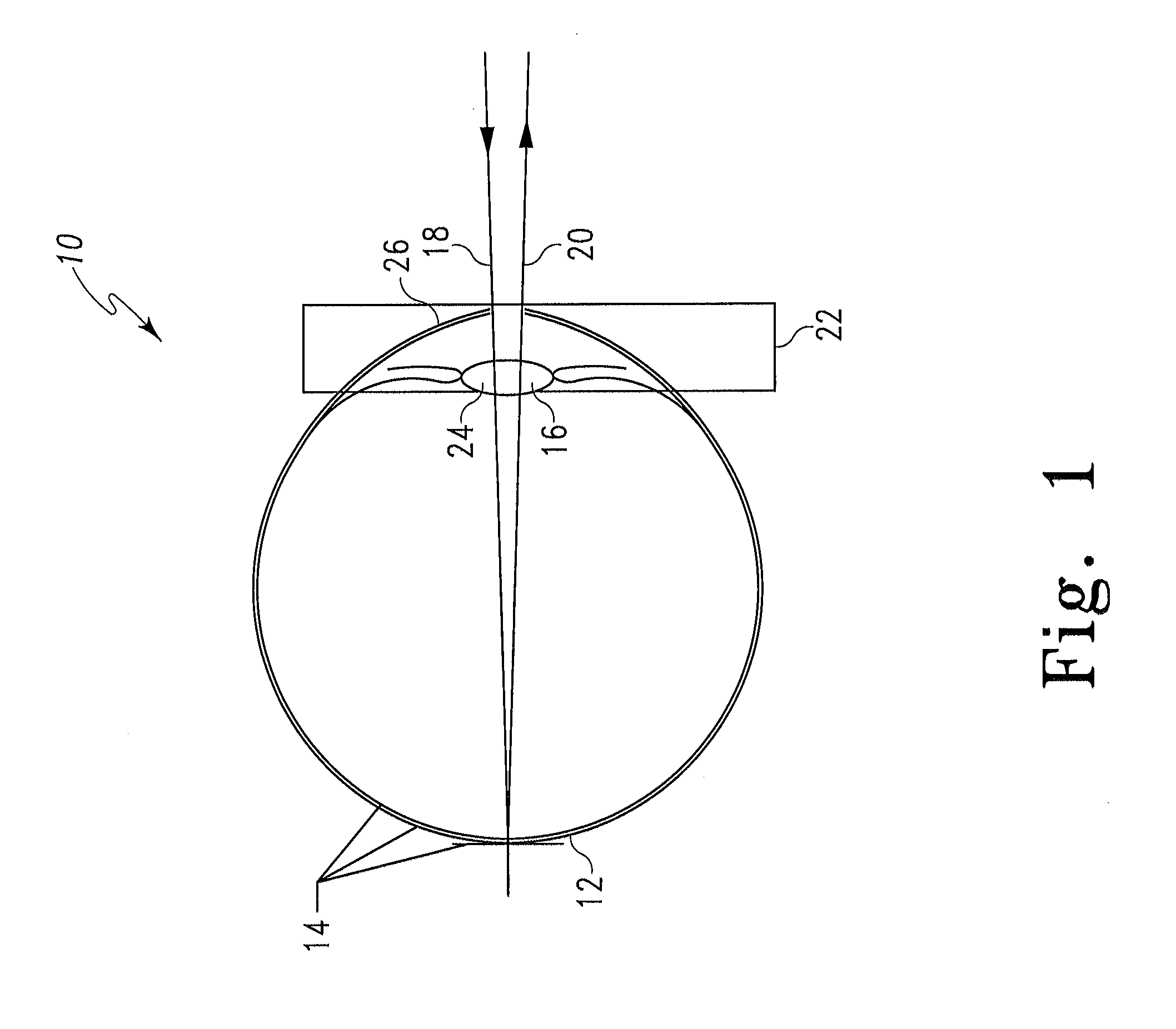
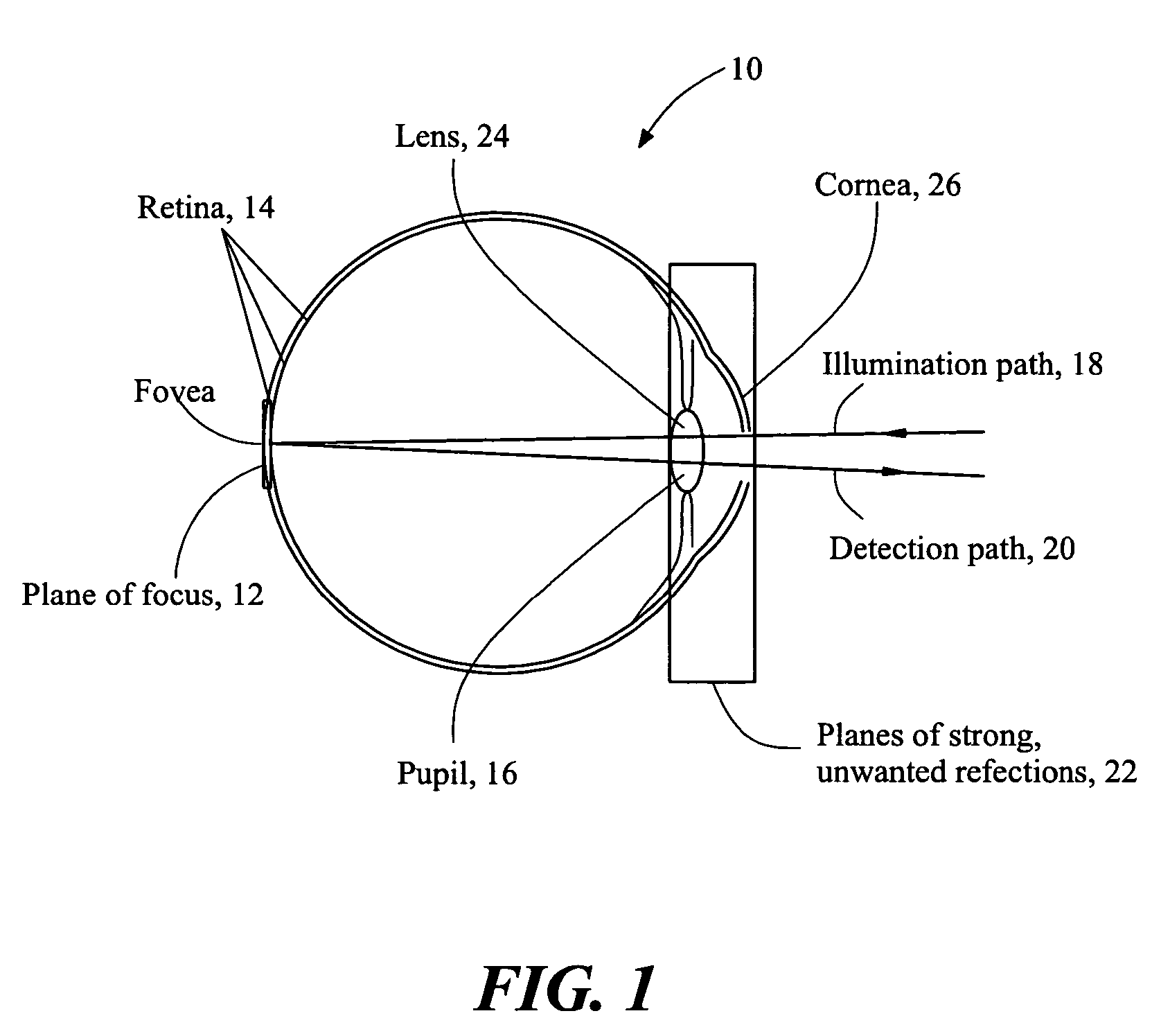
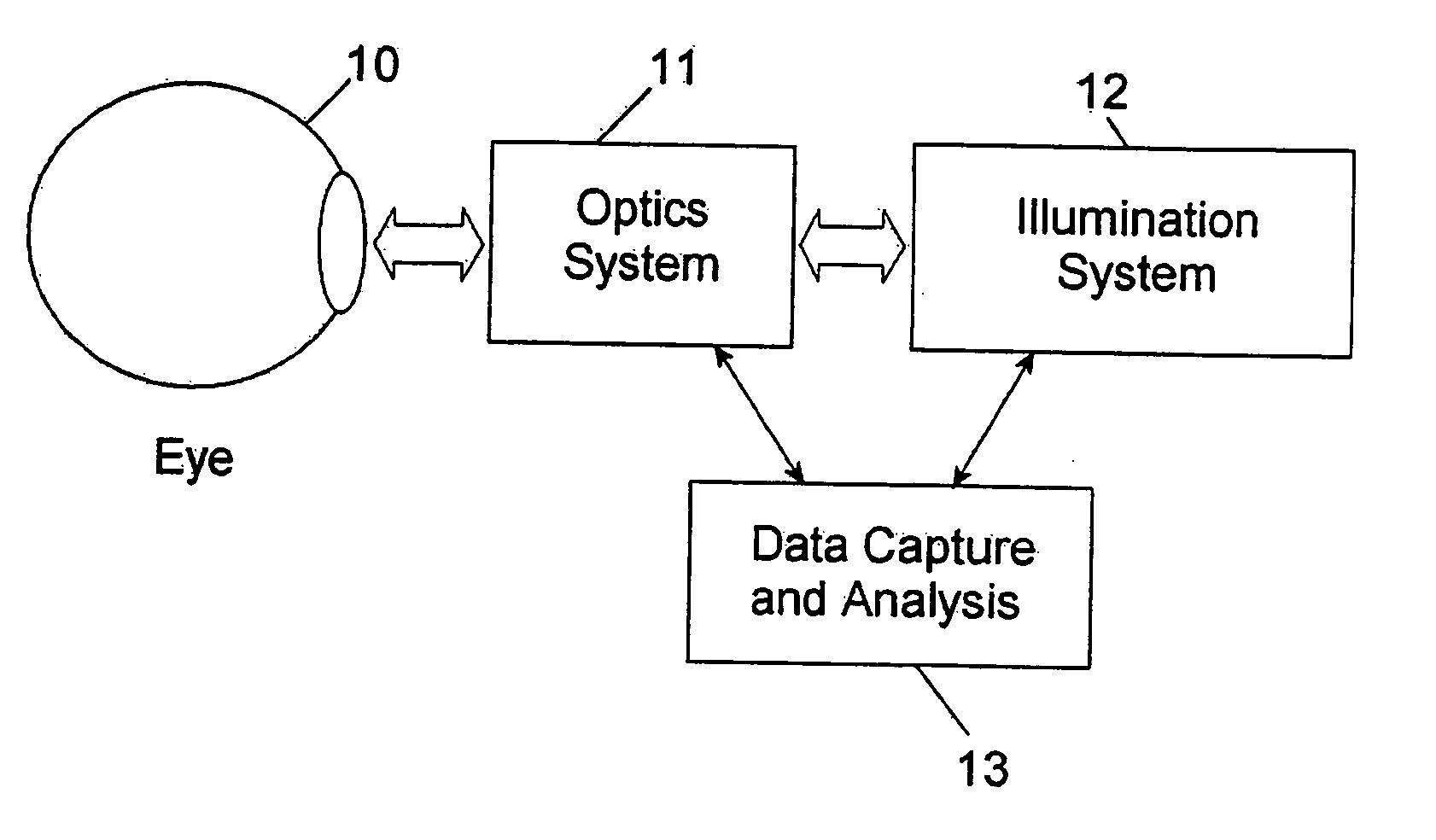
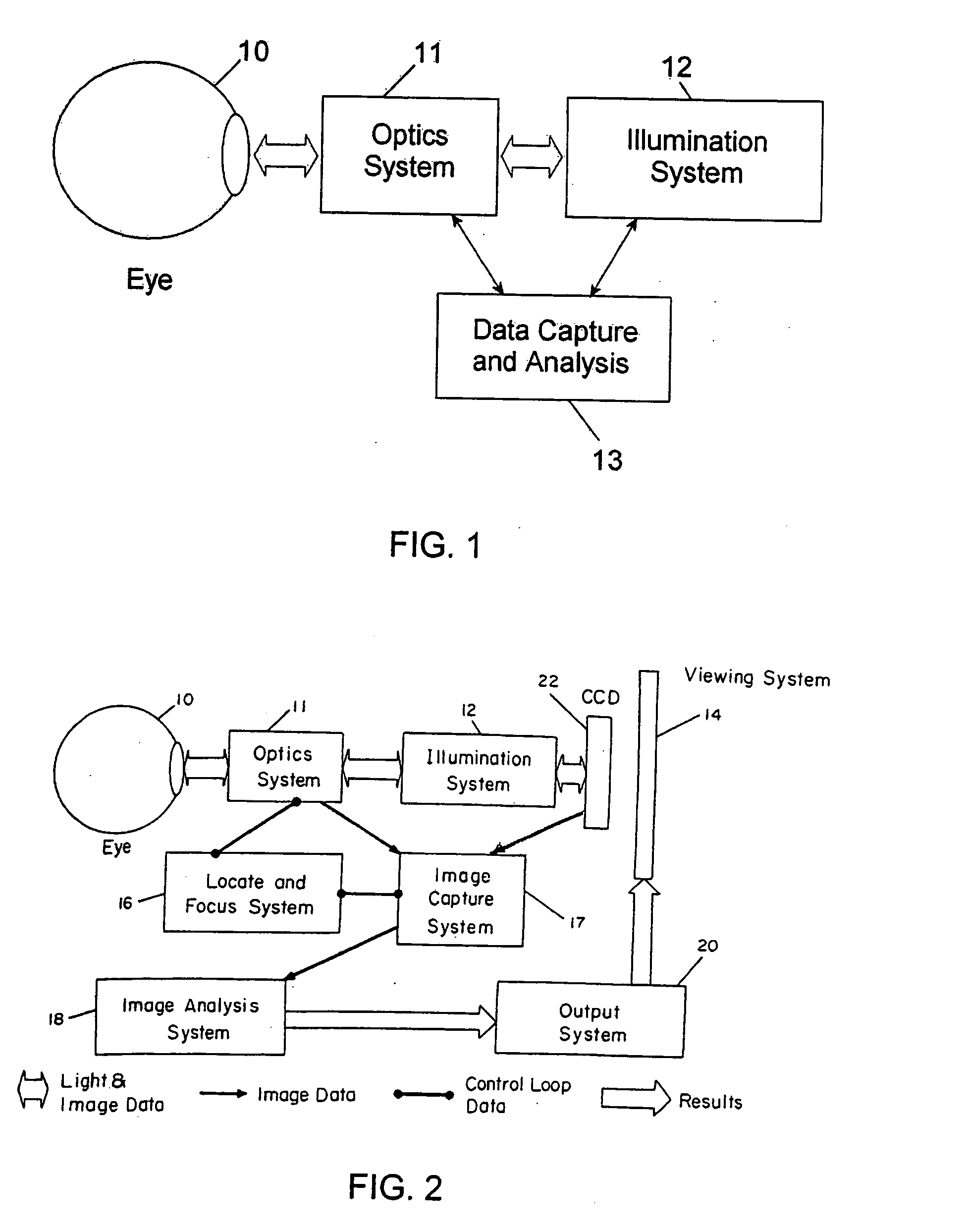
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS20070252951A1Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansRetinal imagingLight beam
A system provides an optical image of an object. A first module tracks a reference feature of the object. A second module includes a source for an imaging beam, a scanning device to move the imaging beam along a portion of the object and a detection device receives a signal associated with an image of the portion of the object. The first module controls the position of the imaging beam relative to the reference feature to correct for the motion of the object. A third module detects a distortion of the object and compensates for the distortion.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Non-invasive measurement of blood glucose using retinal imaging
InactiveUS20050010091A1Accurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineRetinal imaging
An apparatus carries out measurements of blood glucose in a repeatable, non-invasive manner by measurement of the rate of regeneration of retinal visual pigments, such as cone visual pigments. The rate of regeneration of visual pigments is dependent upon the blood glucose concentration, and by measuring the visual pigment regeneration rate, blood glucose concentration can be accurately determined. This apparatus exposes the retina to light of selected wavelengths in selected distributions and subsequently analyzes the reflection (as color or darkness) from a selected portion of the exposed region of the retina, preferably from the fovea.
Owner:FOVIOPTICS INC
Portable digital medical camera for capturing images of the retina or the external auditory canal, and methods of use
InactiveUS20080259274A1Convenient reviewFacilitate interpretationPrintersOtoscopesExternal Auditory CanalsOtoscope
A hand-held digital camera for obtaining images of a portion of a patient's body and having a hand-held housing, a visible light source located within the housing for providing light along an illumination path from the housing aperture to the patient's body, an image sensor located within the housing that detects light returning from the patient's body along an imaging path that passes into the housing aperture, an optical system located within the housing with separate illumination and imaging paths, an external optical aperture common to the illumination and imaging systems, wherein the illumination and imaging sub-apertures are wholly contained within the common external aperture, are longitudinally coincident, and are laterally separated and non-overlapping, a digital memory device for storing captured images, an output display carried by the housing, and the ability to electronically transmit stored images. The camera can be used for retinal imaging and for otoscopy.
Owner:CHINNOCK RANDAL B
Choroid and retinal imaging and treatment system
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC
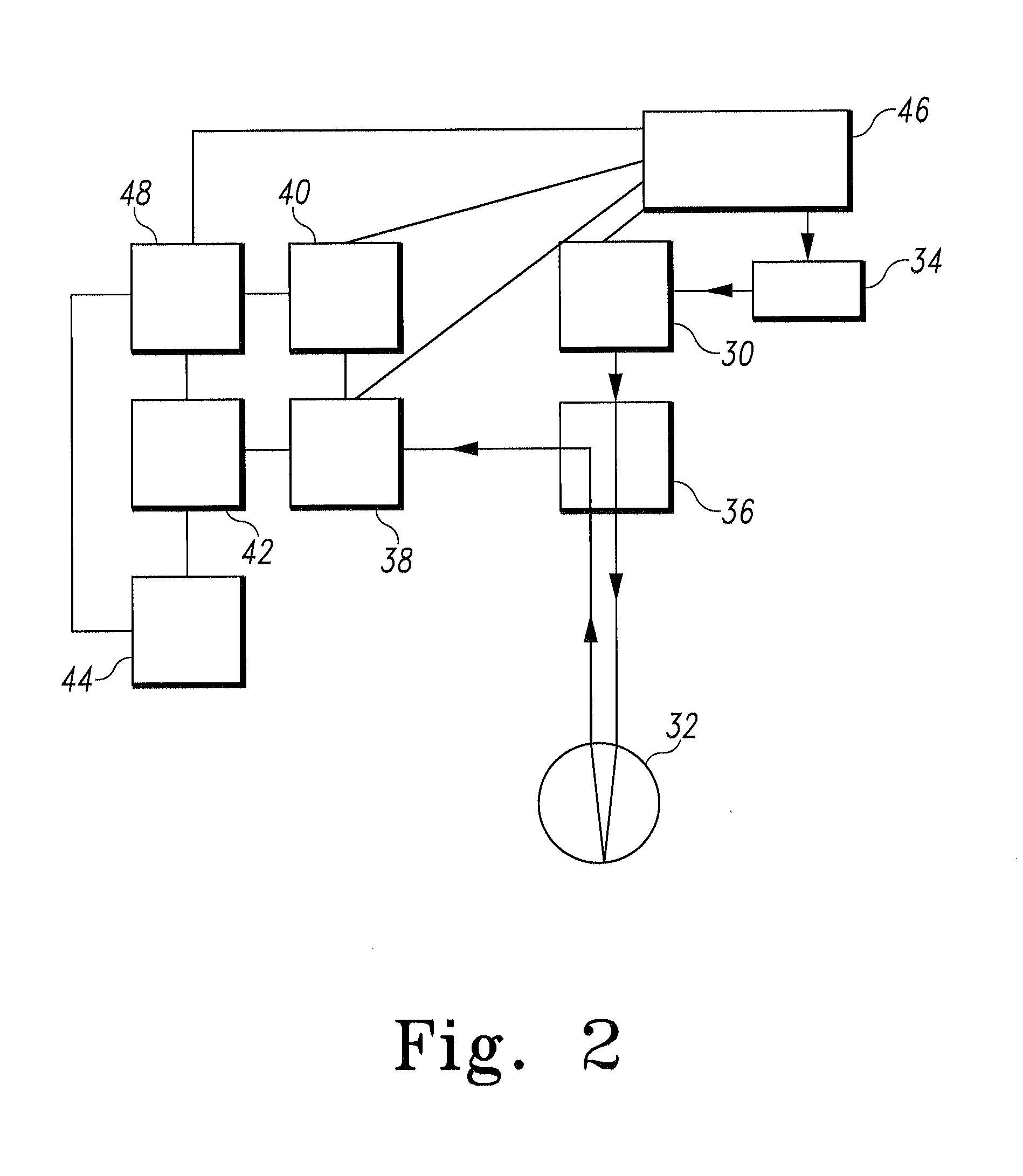
High-resolution retinal imaging using adaptive optics and fourier-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20070258095A1Precise positioningMinimize eye motionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesMicroscopic blood vesselHuman eye
This invention permits retinal images to be acquired at high speed and with unprecedented resolution in three dimensions (4×4×6 μm). The instrument achieves high lateral resolution by using adaptive optics to correct optical aberrations of the human eye in real time. High axial resolution and high speed are made possible by the use of Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Using this system, we have demonstrated the ability to image microscopic blood vessels and the cone photoreceptor mosaic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Portable Digital Medical Camera for Capturing Images of the Retina or the External Auditory Canal, and Methods of Use
Owner:CHINNOCK RANDAL B
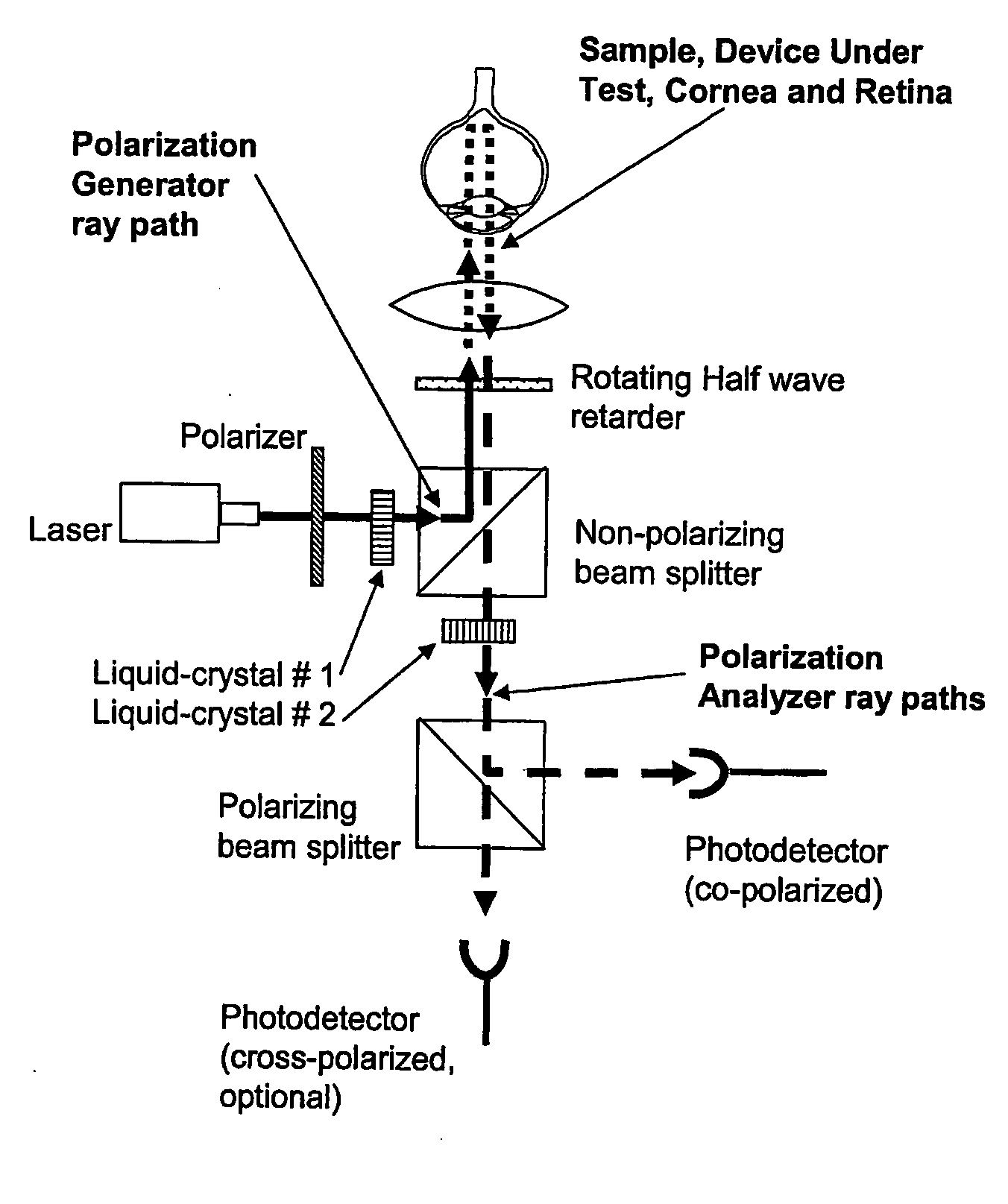
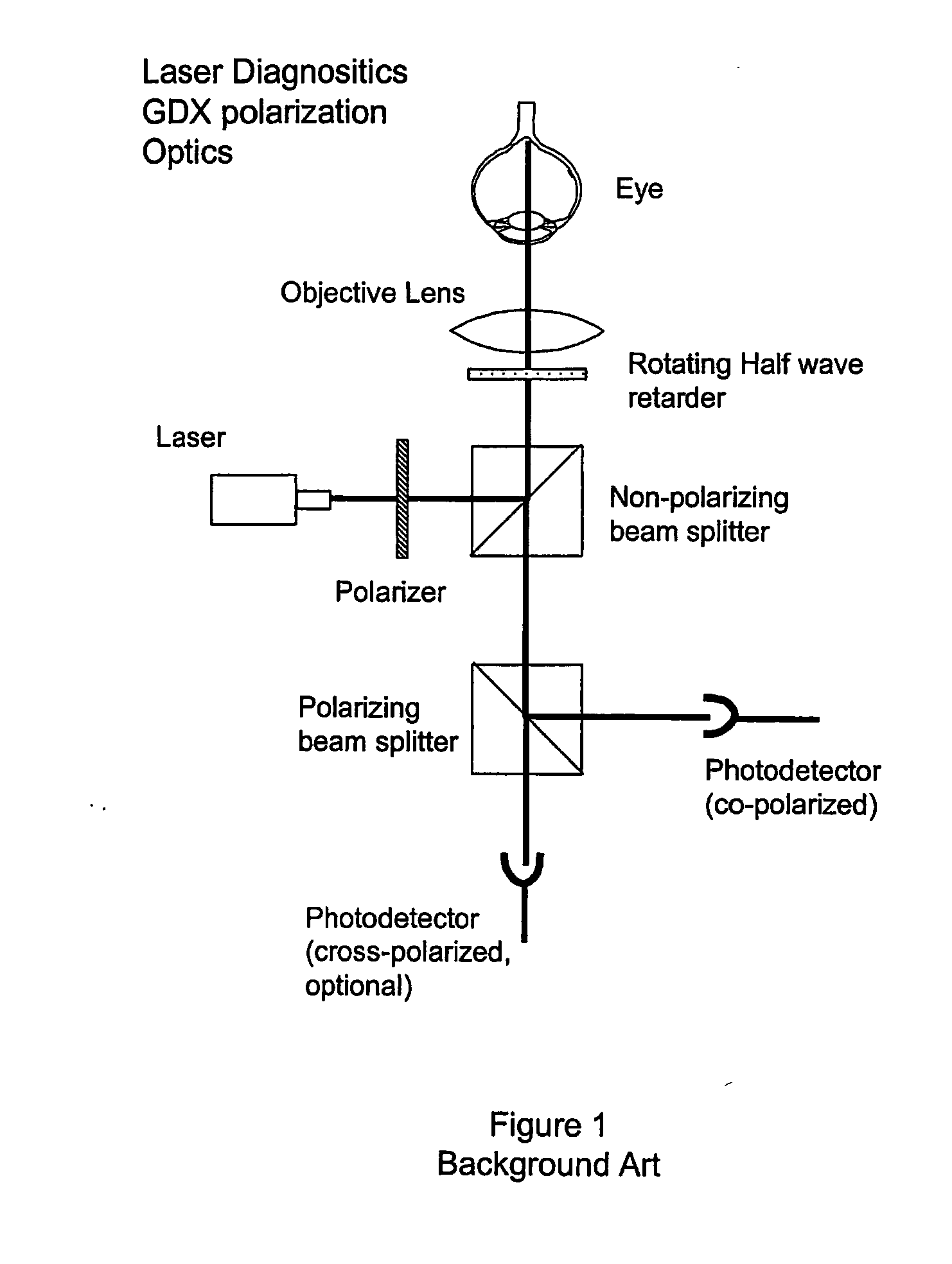
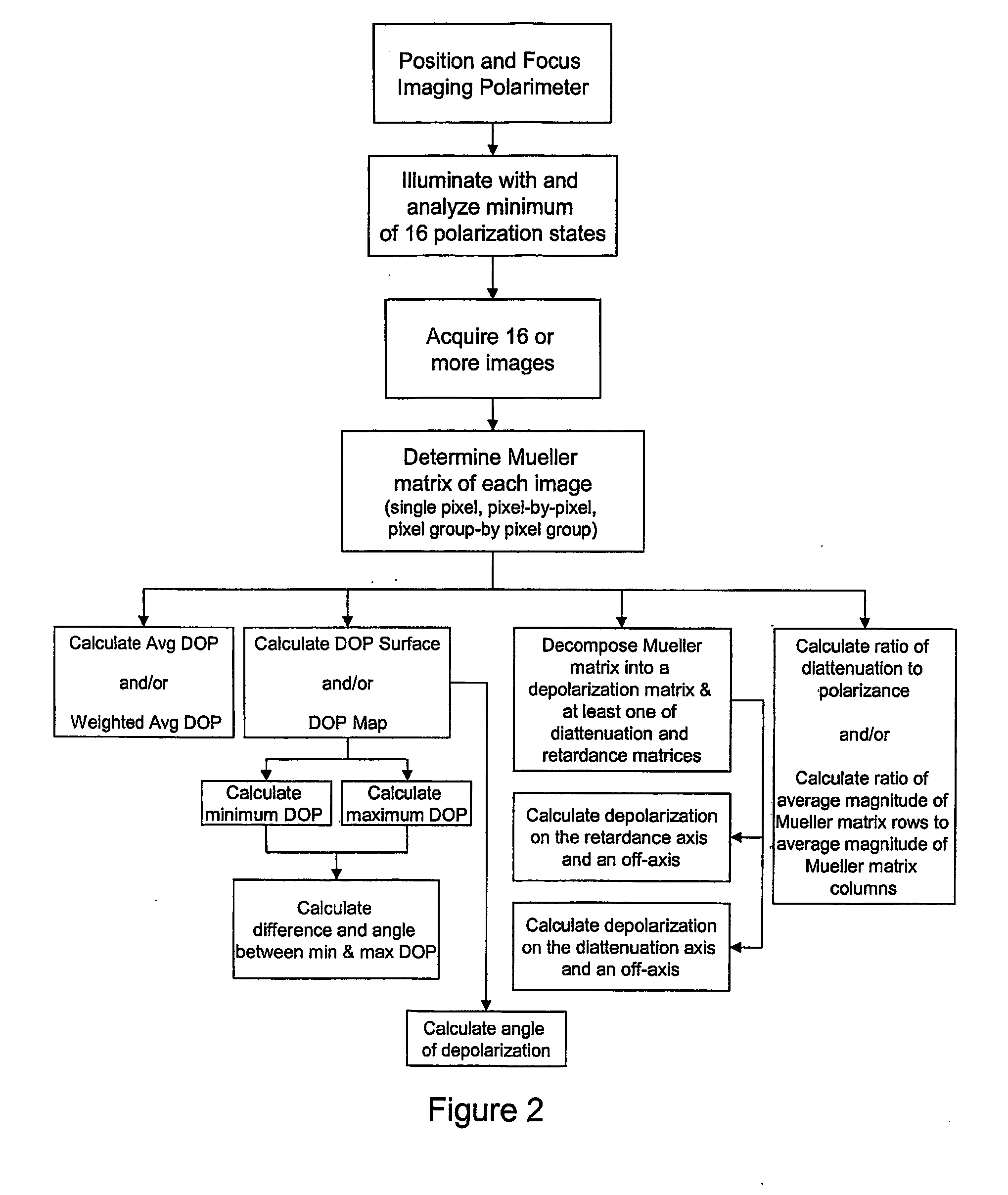
Advanced polarization imaging method, apparatus, and computer program product for retinal imaging, liquid crystal testing, active remote sensing, and other applications
InactiveUS20070146632A1Improve classificationEasy to identifyPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementRetinal imagingPolarimetry
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for identifying features in a sample by analyzing Mueller matrices to calculate an average degree of polarization, a weighted average degree of polarization, a degree of polarization map, a degree of polarization surface. Also, a method, apparatus, and computer program product for identifying features in a sample by analyzing Mueller matrices to calculate depolarization relative to a retardance axis and / or a diattentuation axis, and to calculate a ratio of diattenuation to polarizance or ratios of row and column magnitudes. Also, a method for retinal polarimetry, including a non-depolarizing light tube configured for insertion into the eye.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
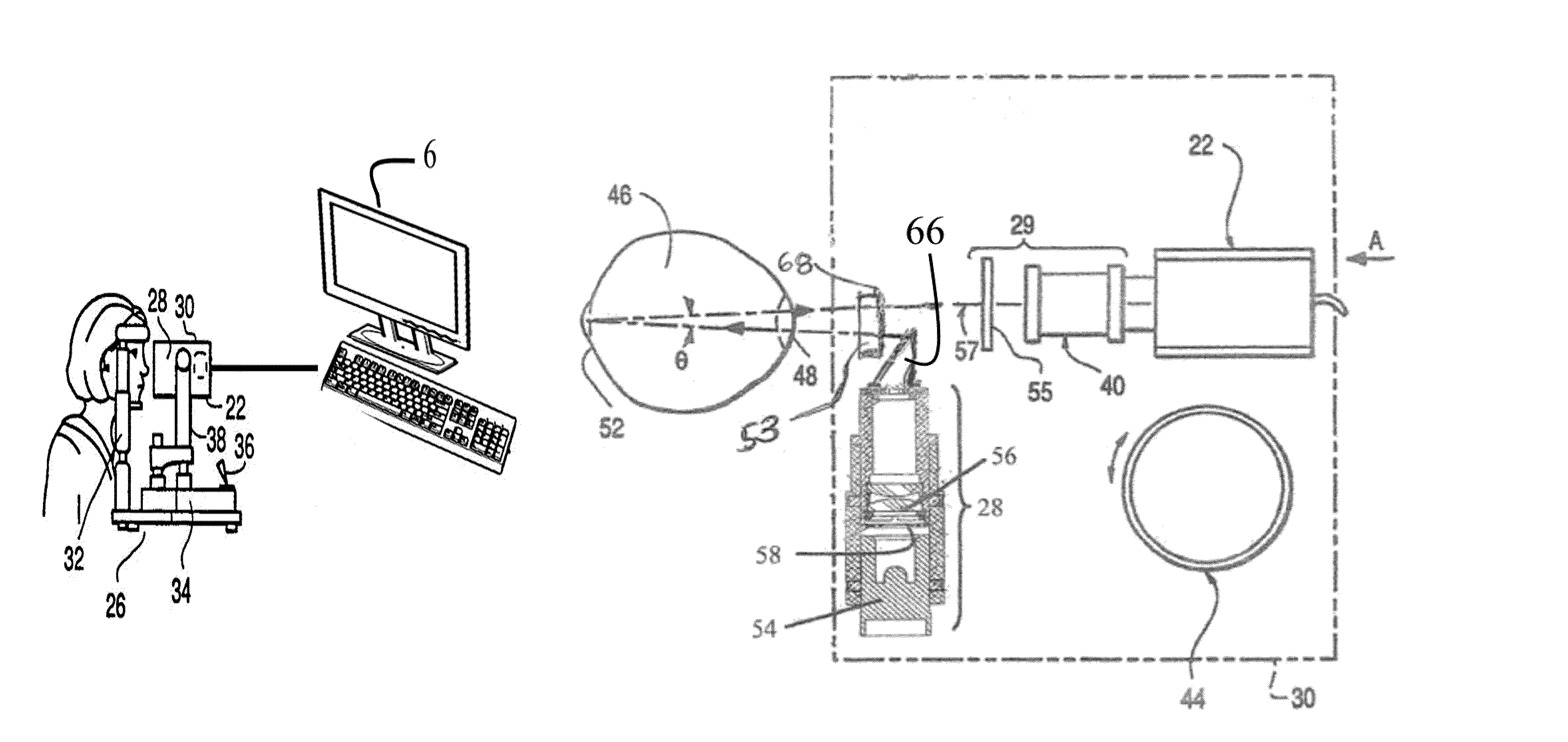
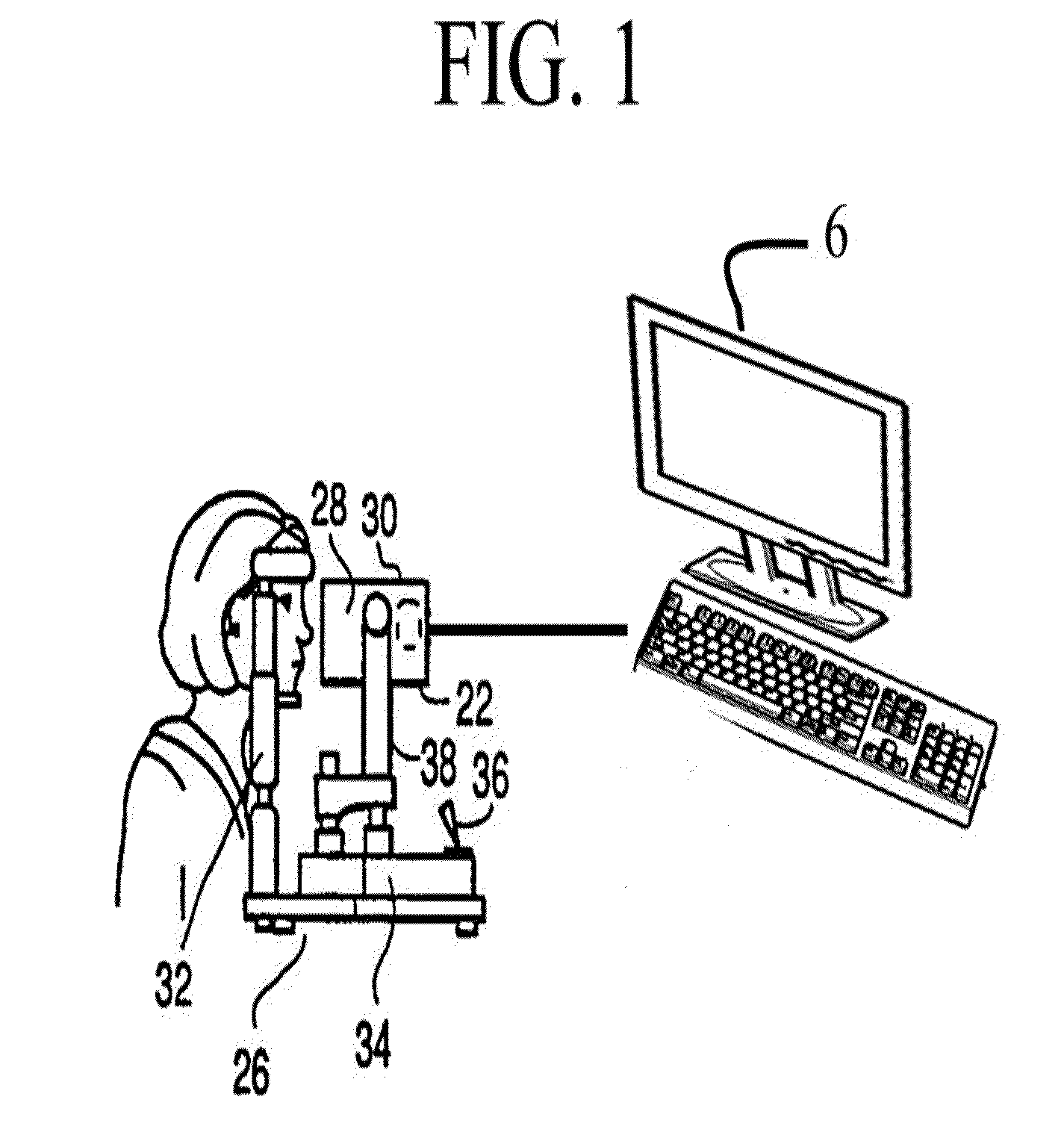
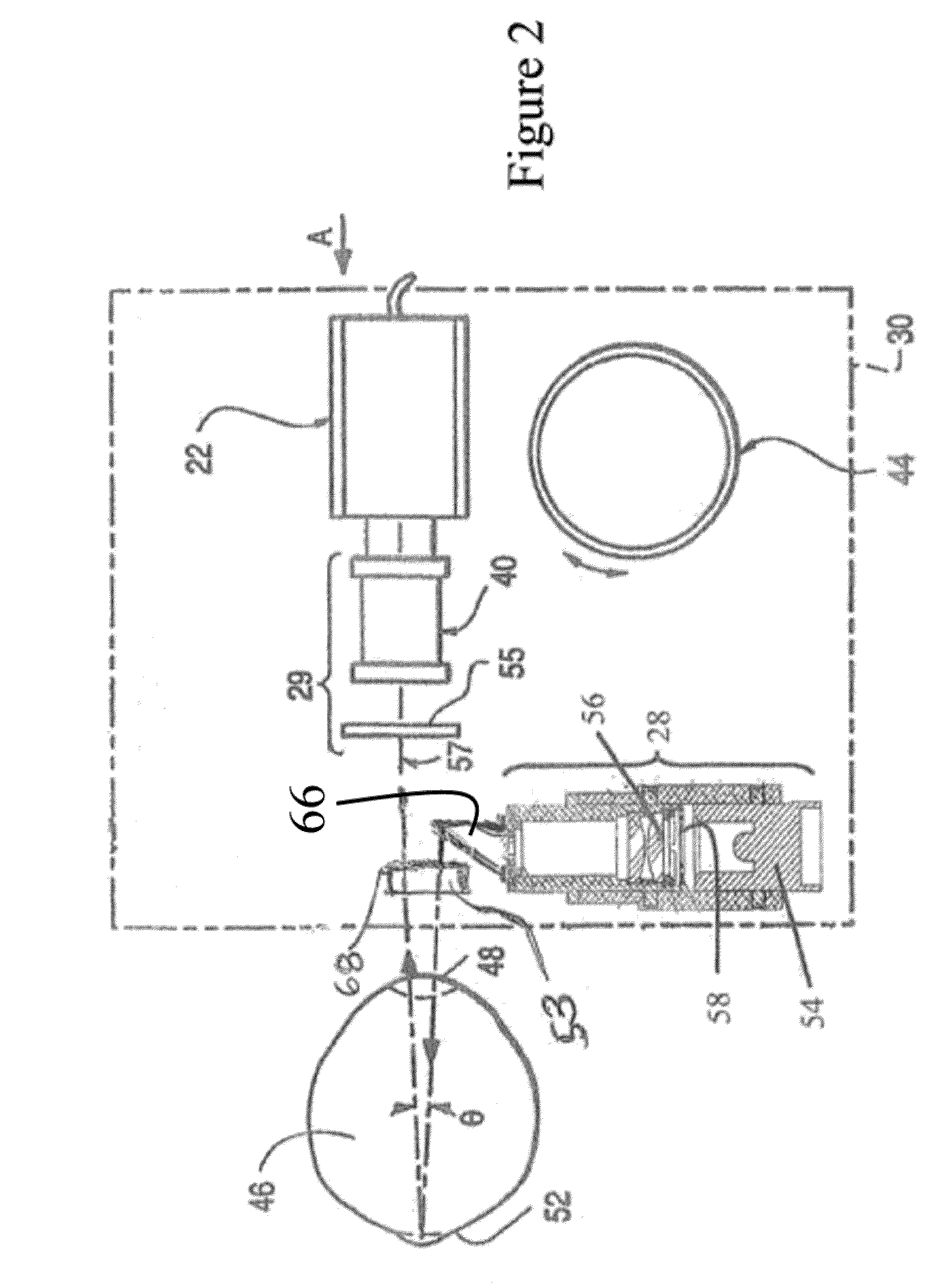
Apparatus and method for imaging the eye
ActiveUS20100097573A1Reduce glareEliminate artifactsGonioscopesOthalmoscopesWide fieldImaging processing
A slit lamp mounted eye imaging device for viewing wide field and / or magnified views of the retina or the anterior segment through an undilated or dilated pupil. The apparatus images posterior and anterior segments of the eye, and sections / focal planes in between and contains an illumination system that uses one or more LEDs, shifting optical elements, and / or aperture stops where the light can be delivered into the optical system on optical axis or off axis from center of optical system and return imaging path from the retina, thereby creating artifacts in different locations on retina. Image processing is employed to detect and eliminate artifacts from images. The device is well suited for retinal imaging through an undilated pupil, non-pharmacologically dilated, or a pupil as small as 2 mm. Two or more images with reflection artifacts can be created and subsequently recombined through image processing into a composite artifact-free image.
Owner:NEUROVISION IMAGING INC
Apparatus and method for imaging the eye
A slit lamp mounted eye imaging device for viewing wide field and / or magnified views of the retina or the anterior segment through an undilated or dilated pupil. The apparatus images posterior and anterior segments of the eye, and sections / focal planes in between and contains an illumination system that uses one or more LEDs, shifting optical elements, and / or aperture stops where the light can be delivered into the optical system on optical axis or off axis from center of optical system and return imaging path from the retina, thereby creating artifacts in different locations on retina. Image processing is employed to detect and eliminate artifacts from images. The device is well suited for retinal imaging through an undilated pupil, non-pharmacologically dilated, or a pupil as small as 2 mm. Two or more images with reflection artifacts can be created and subsequently recombined through image processing into a composite artifact-free image.
Owner:NEUROVISION IMAGING INC
Laser scanning digital camera with pupil periphery illumination and potential for multiply scattered light imaging
ActiveUS8488895B2Increase illuminationConvenient lightingCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsTwo dimensional detectorDigital imaging
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
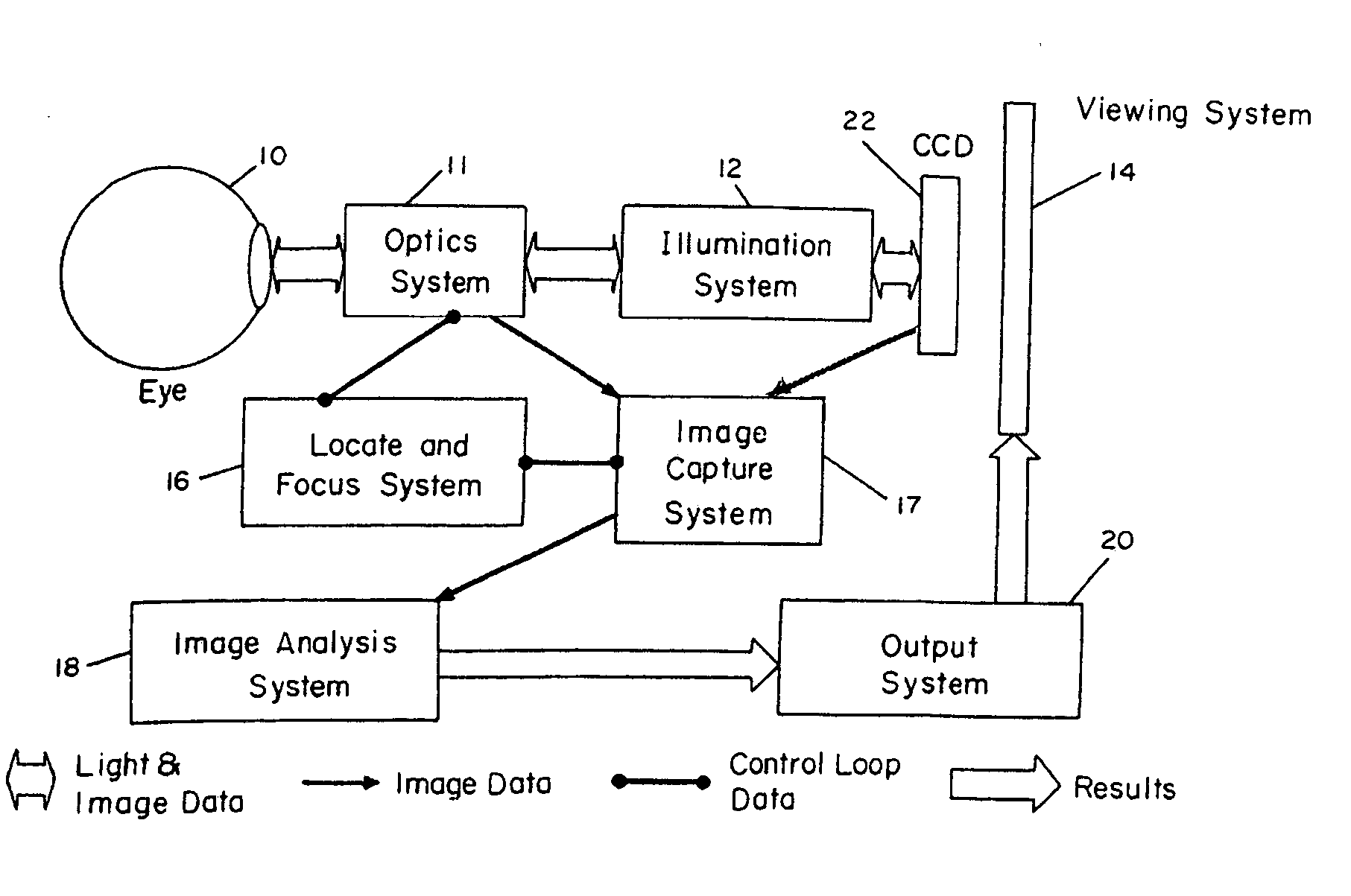
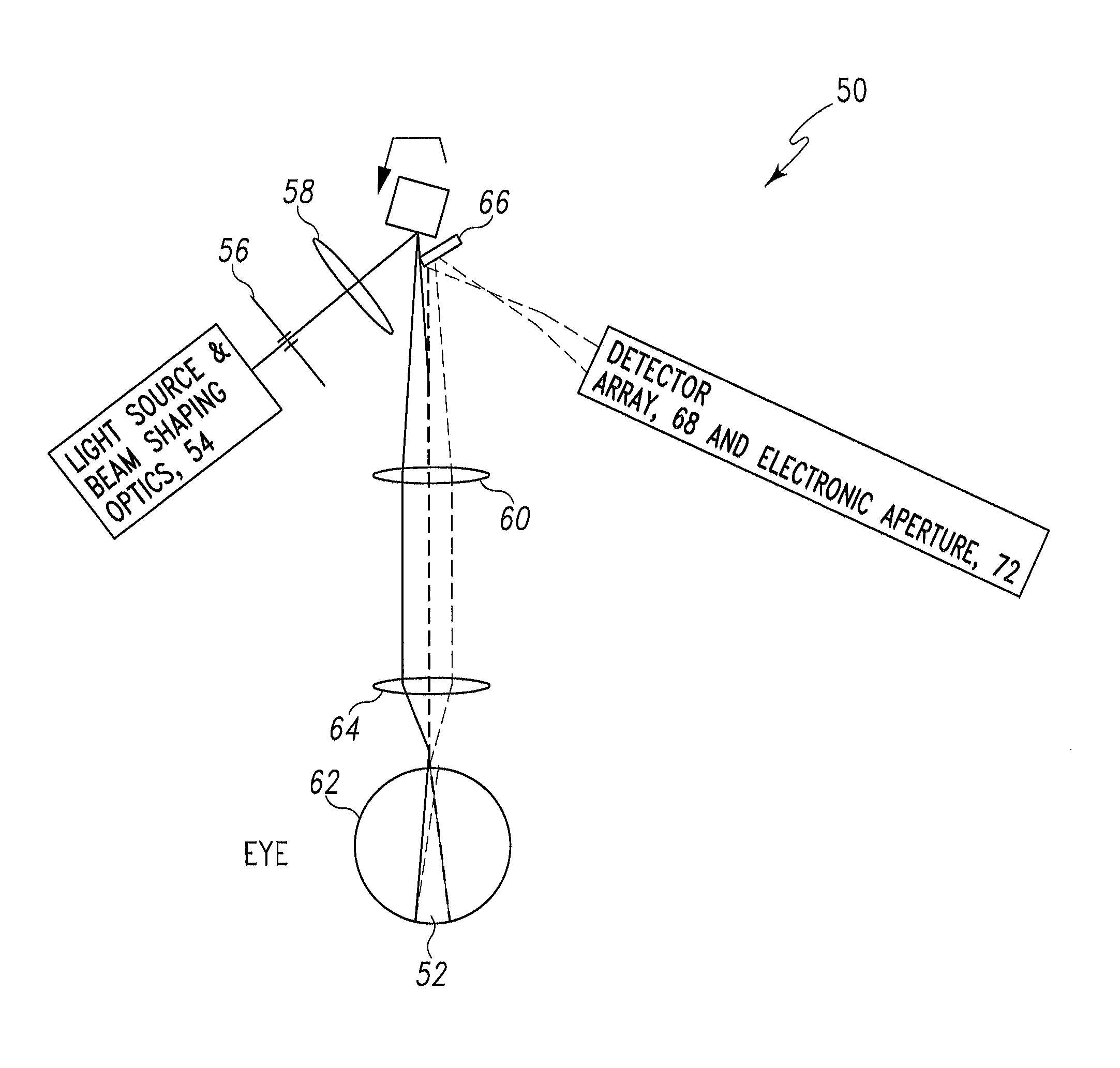
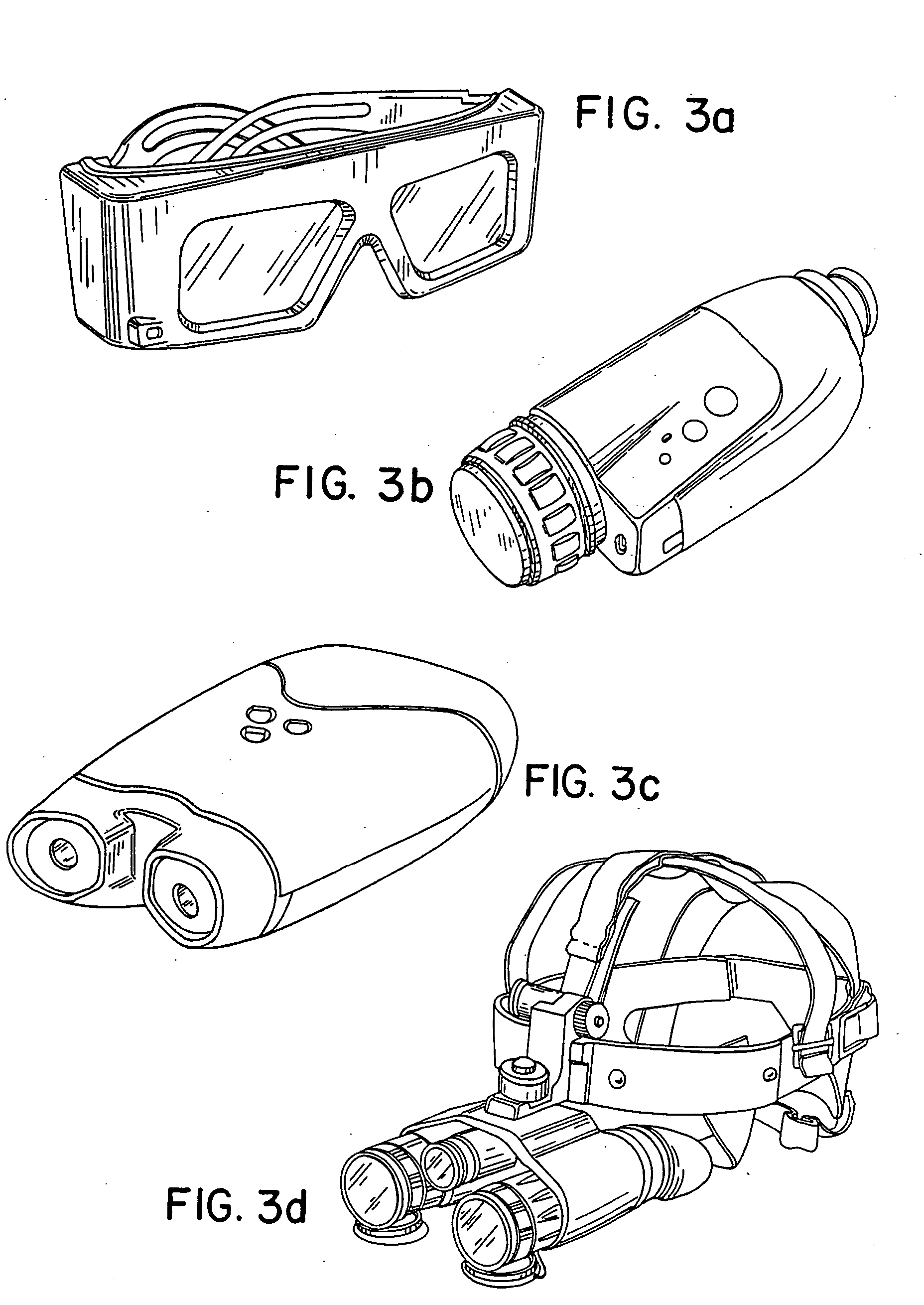
Device for digital retinal imaging
A portable, lightweight digital imaging device uses a slit scanning arrangement to obtain an image of the eye, in particular the retina. The scanning arrangement reduces the amount of target area illuminated at a time, thereby reducing the amount of unwanted light scatter and providing a higher contrast image. A detection arrangement receives the light remitted from the retinal plane and produces an image. The device is operable under battery power and ambient light conditions, such as outdoor or room lighting. The device is noncontact and does not require that the pupil of the eye be dilated with drops. The device can be used by personnel who do not have specialized training in the eye, such as emergency personnel, pediatricians, or general practitioners. Images can be viewed in the device or transmitted to a remote location. The device can also be used to provide images of the anterior segment of the eye or other small structures.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics
ActiveCN101862178AIncrease horizontal resolutionIncrease vertical resolutionOthalmoscopesRetinal imagingData acquisition
The invention relates to a reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics, which can accurately obtain the high-resolution images of vital human eye retinae in real time and comprises a light source, a reflection-type beam shrinking and expanding system, a two-dimension scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, a photoelectric detection system, a data acquisition and processing system and a contraocular sighting target system. Lasers emitted from the light source are hit into human eye ground; light reflected from the eye ground returns along the original path, enters the photoelectric detection system and passes through the data acquisition and processing system to obtain the real-time images of the human eye ground. Simultaneously, an adaptive optics system comprising the Hartmann sensor and the deformable mirror can synchronously detect and correct human eye aberration, and thereby, the high resolution of the images is ensured.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
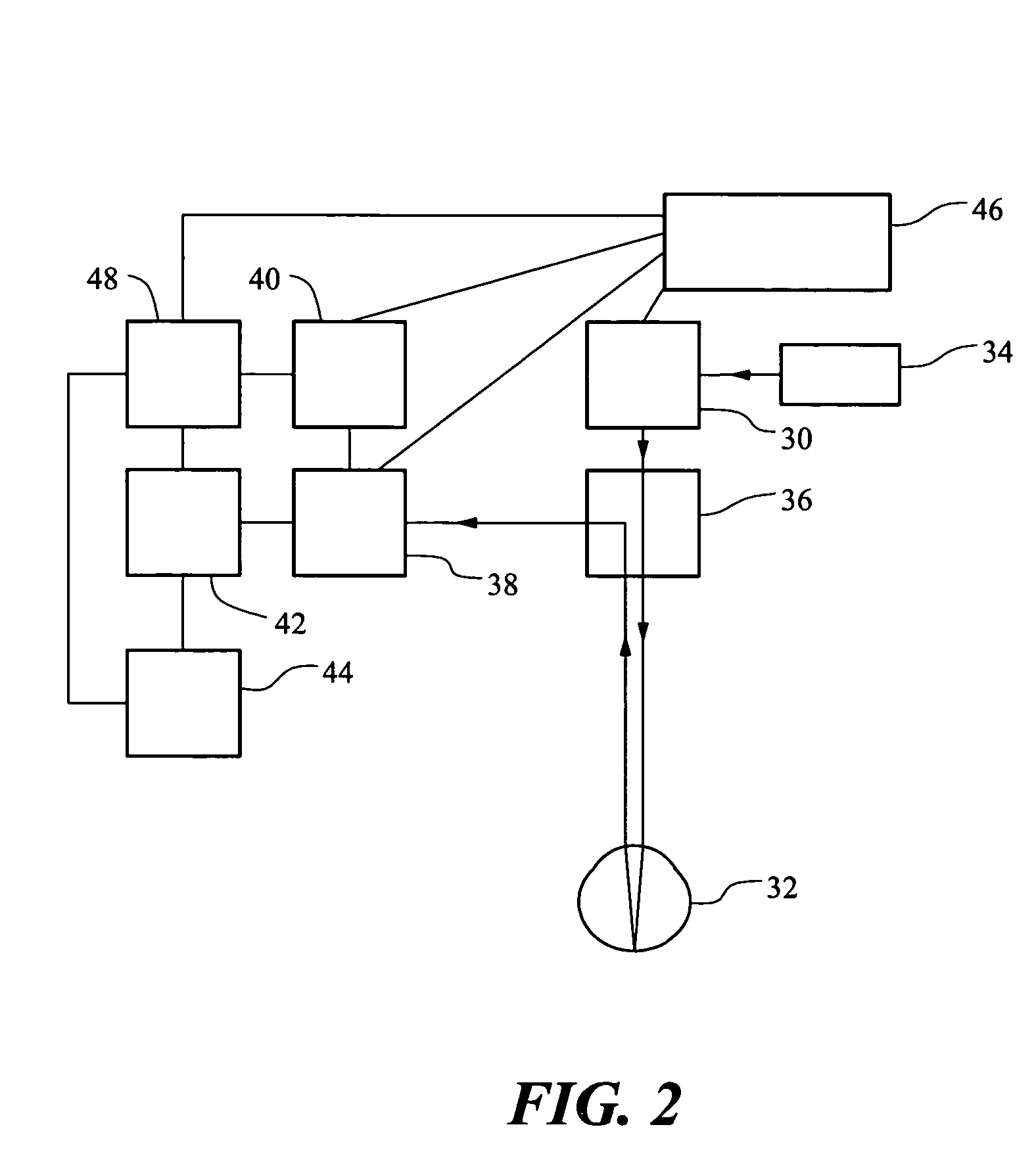
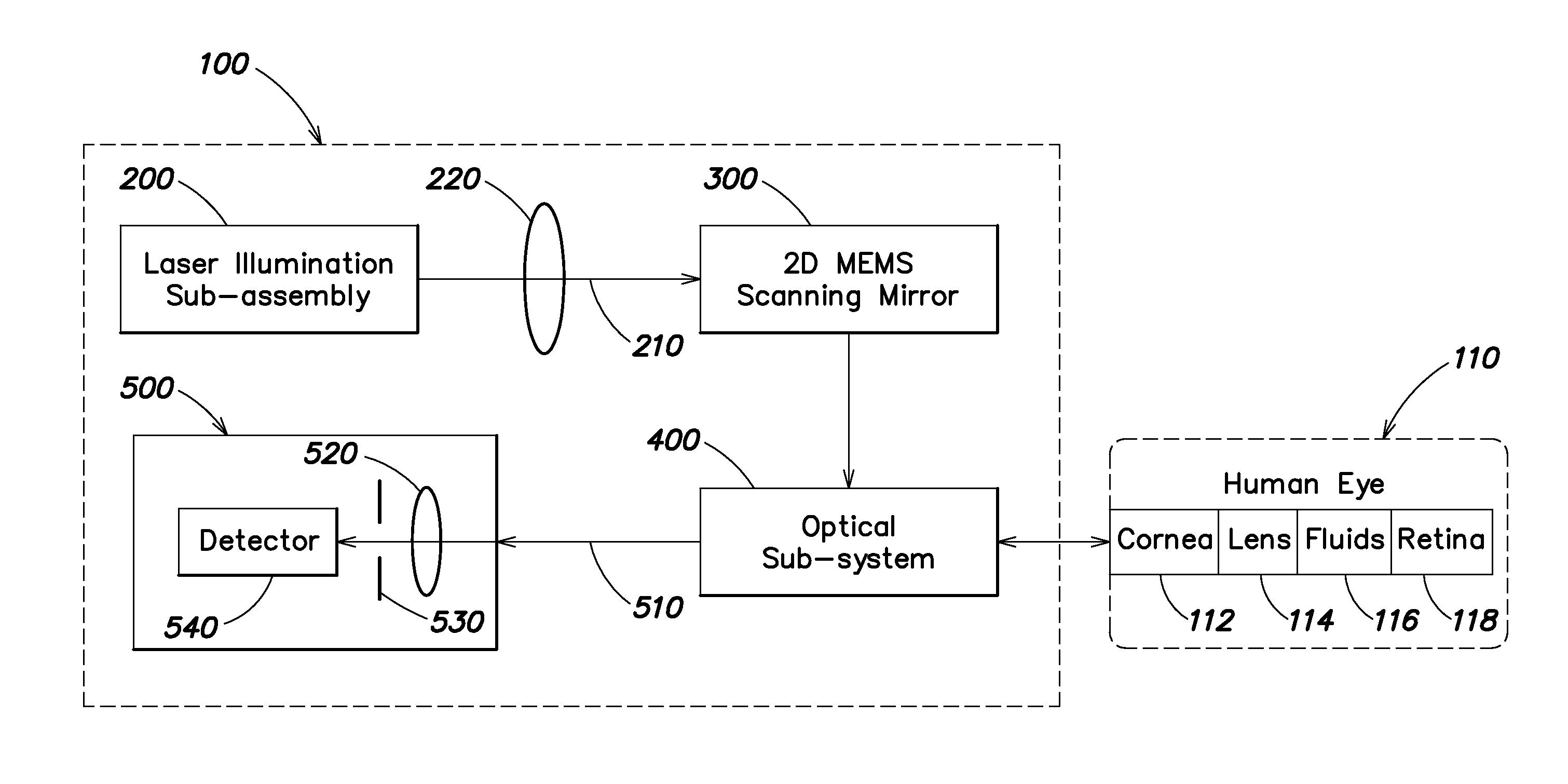
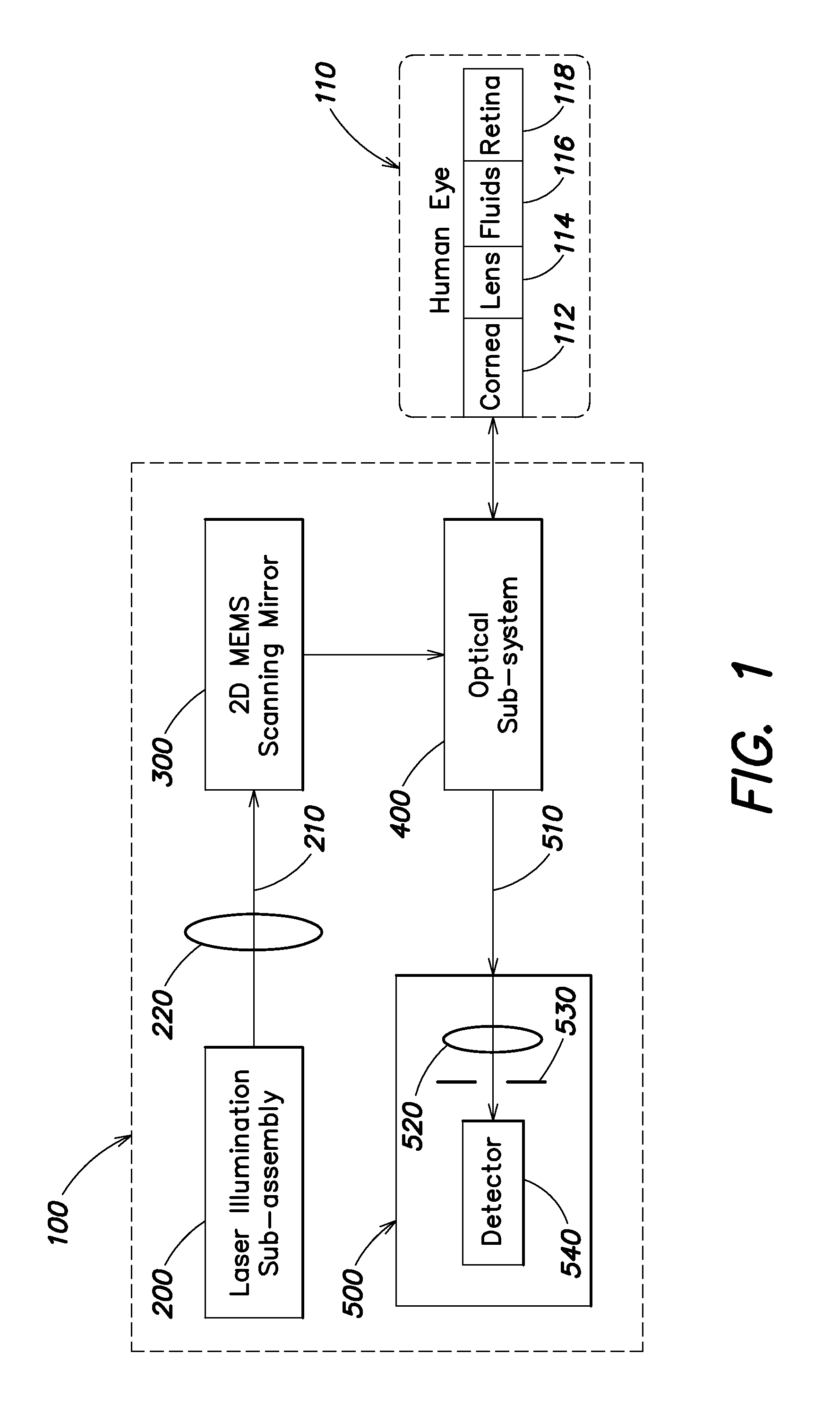
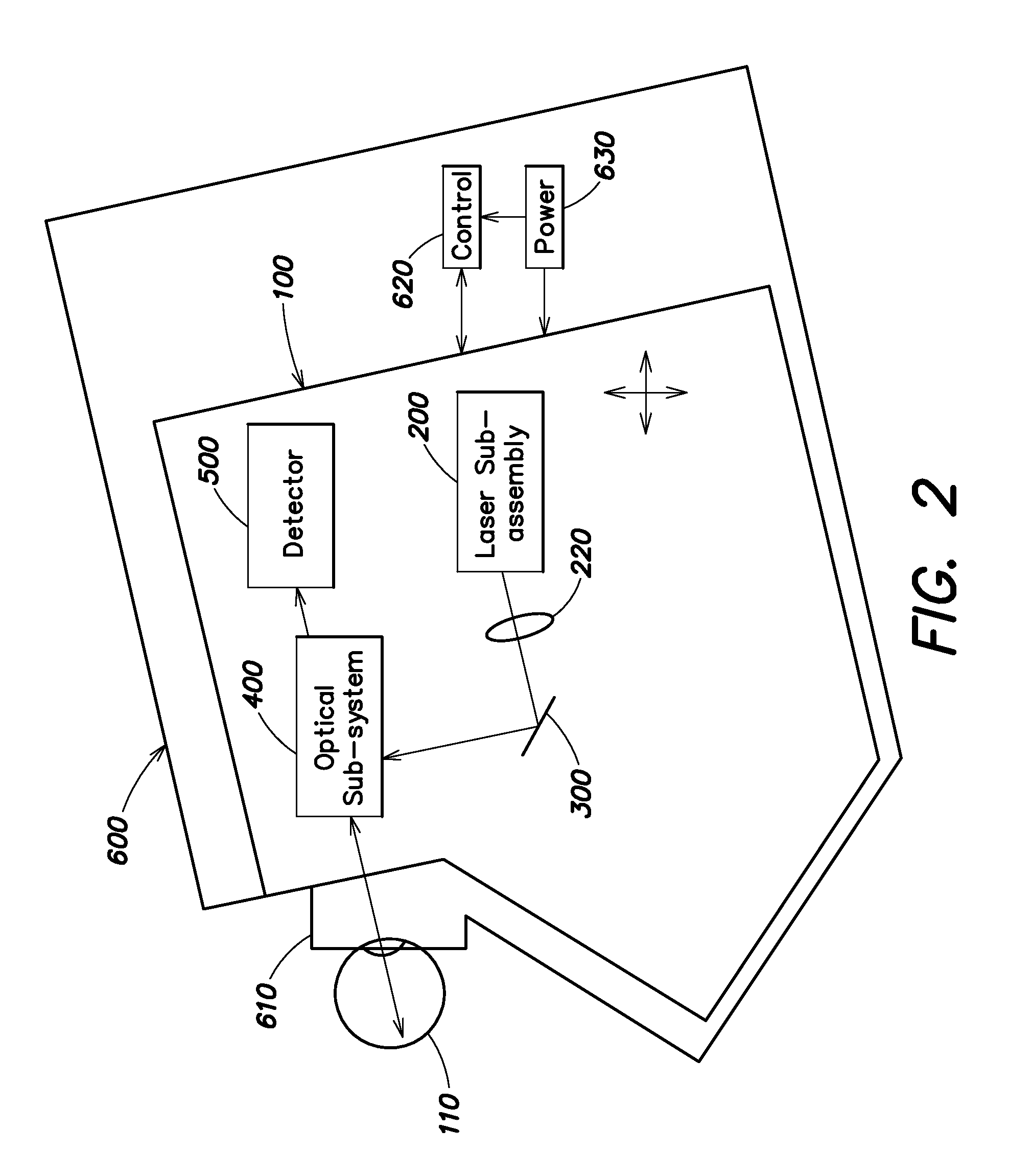
Portable retinal imaging device
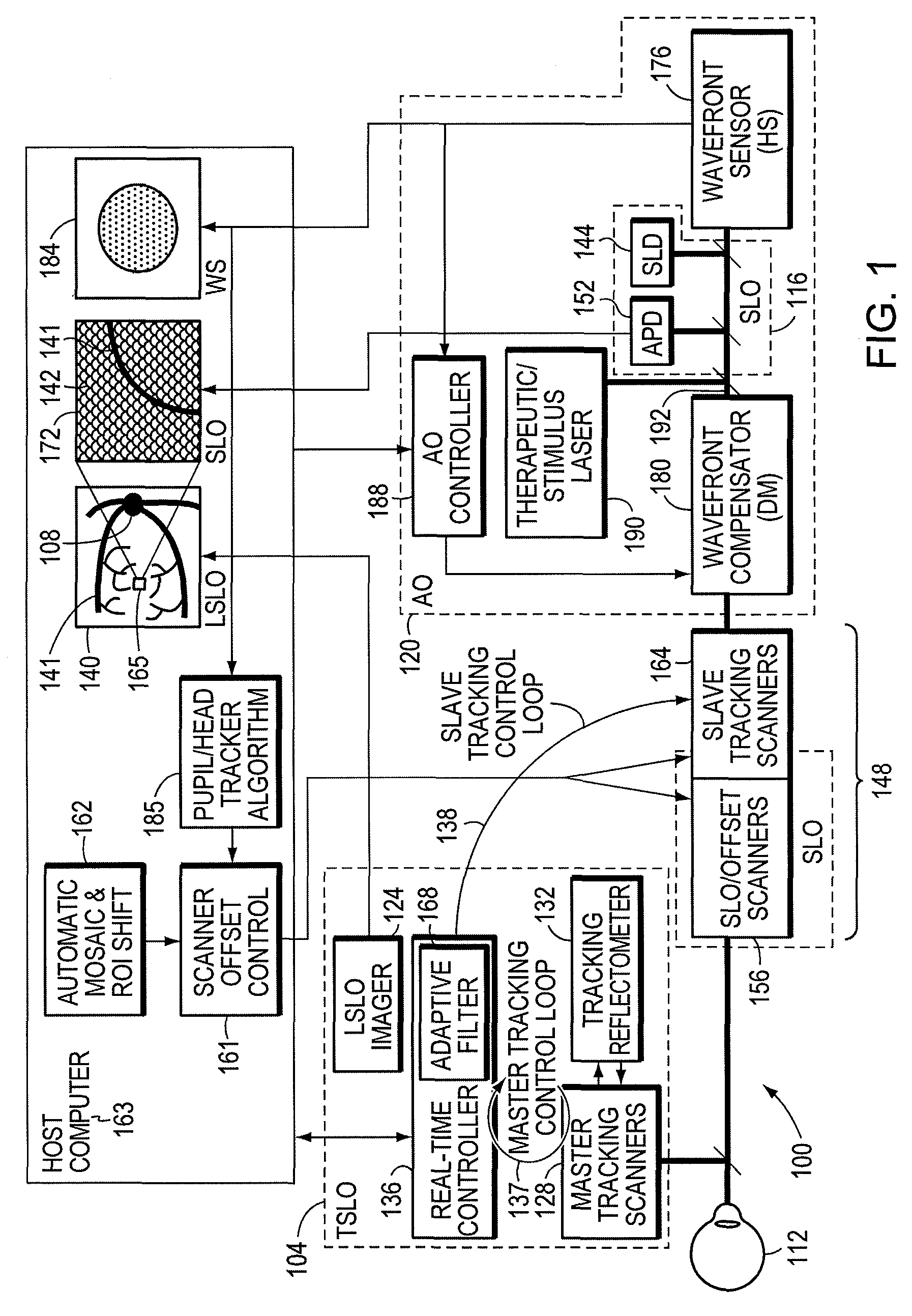
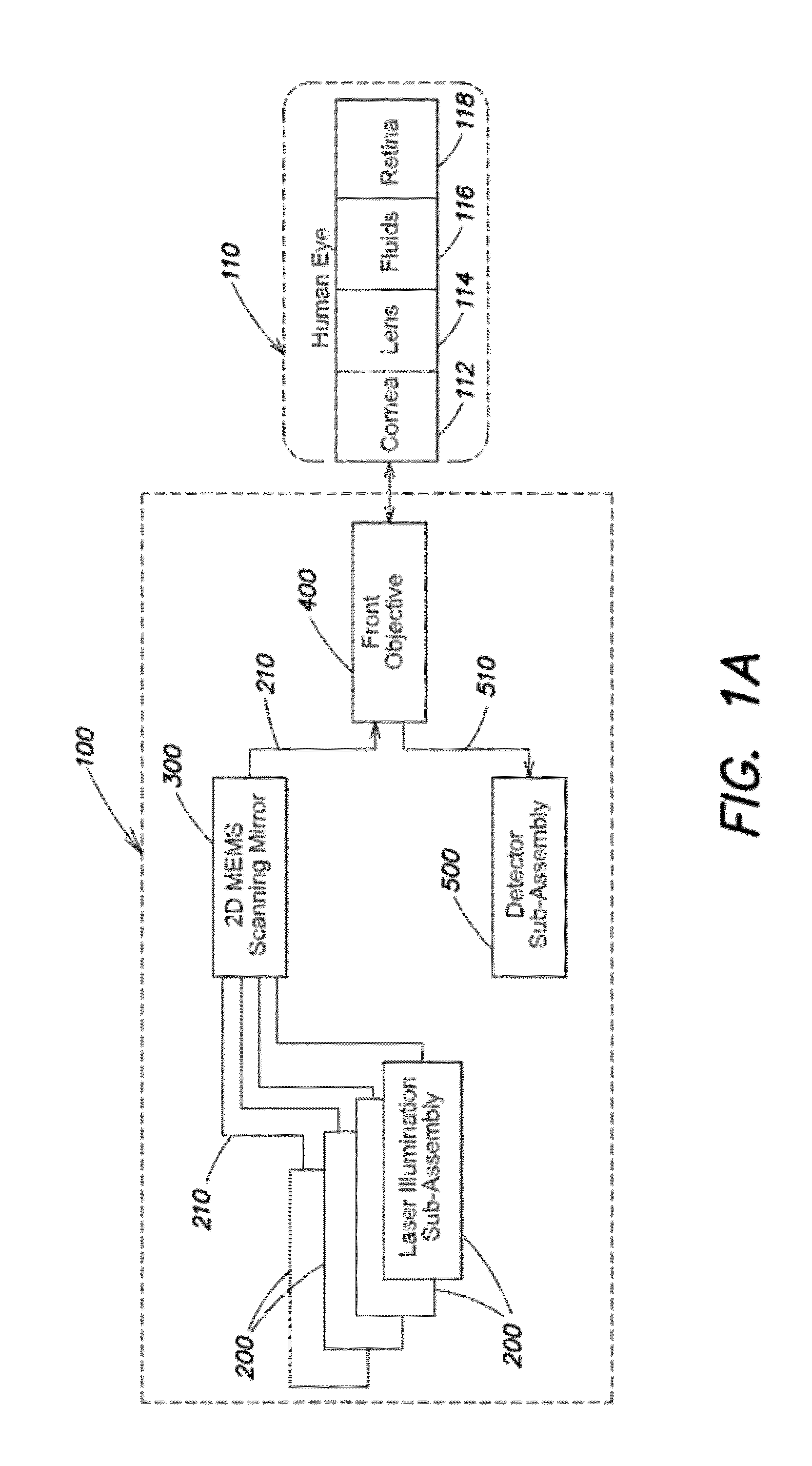
InactiveUS20130194548A1Robust scanningMicroscopesOthalmoscopesOptical radiationScanning laser ophthalmoscope
A portable MEMS-based scanning laser ophthalmoscope (MSLO). In one example the MSLO includes a laser illumination sub-assembly that generates a laser illumination beam, a two-dimensional MEMS scan mirror configured to receive and scan the laser illumination beam over at least a portion of the retina of an eye to be imaged, an optical system configured to direct the laser illumination beam from the scan mirror into the eye to illuminate the retina, and a detector sub-assembly configured to intercept optical radiation reflected from the eye to generate an image of the retina. The optical system includes a polarized beamsplitter positioned between the scan minor and the eye and configured to direct the laser illumination beam to into the eye and to direct the optical radiation reflected from the eye to the detector sub-assembly.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
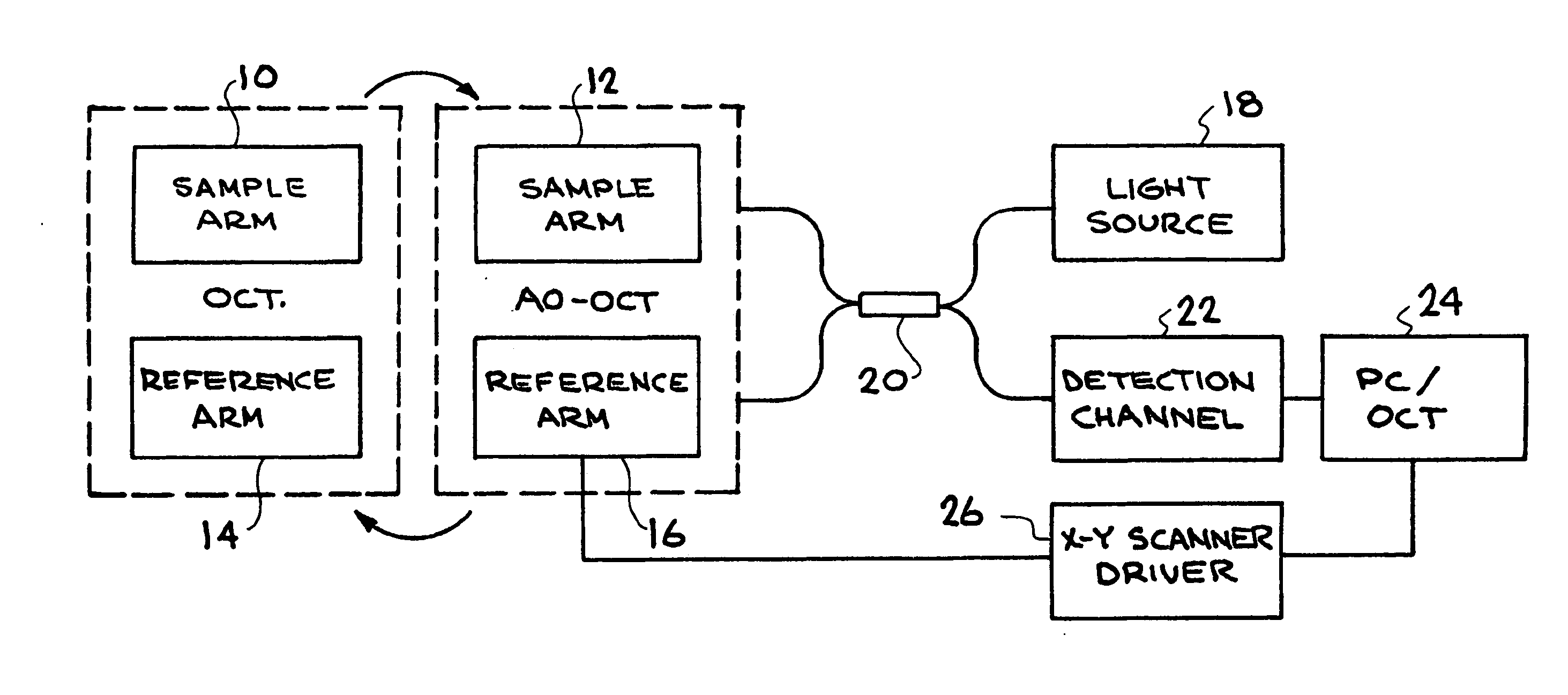
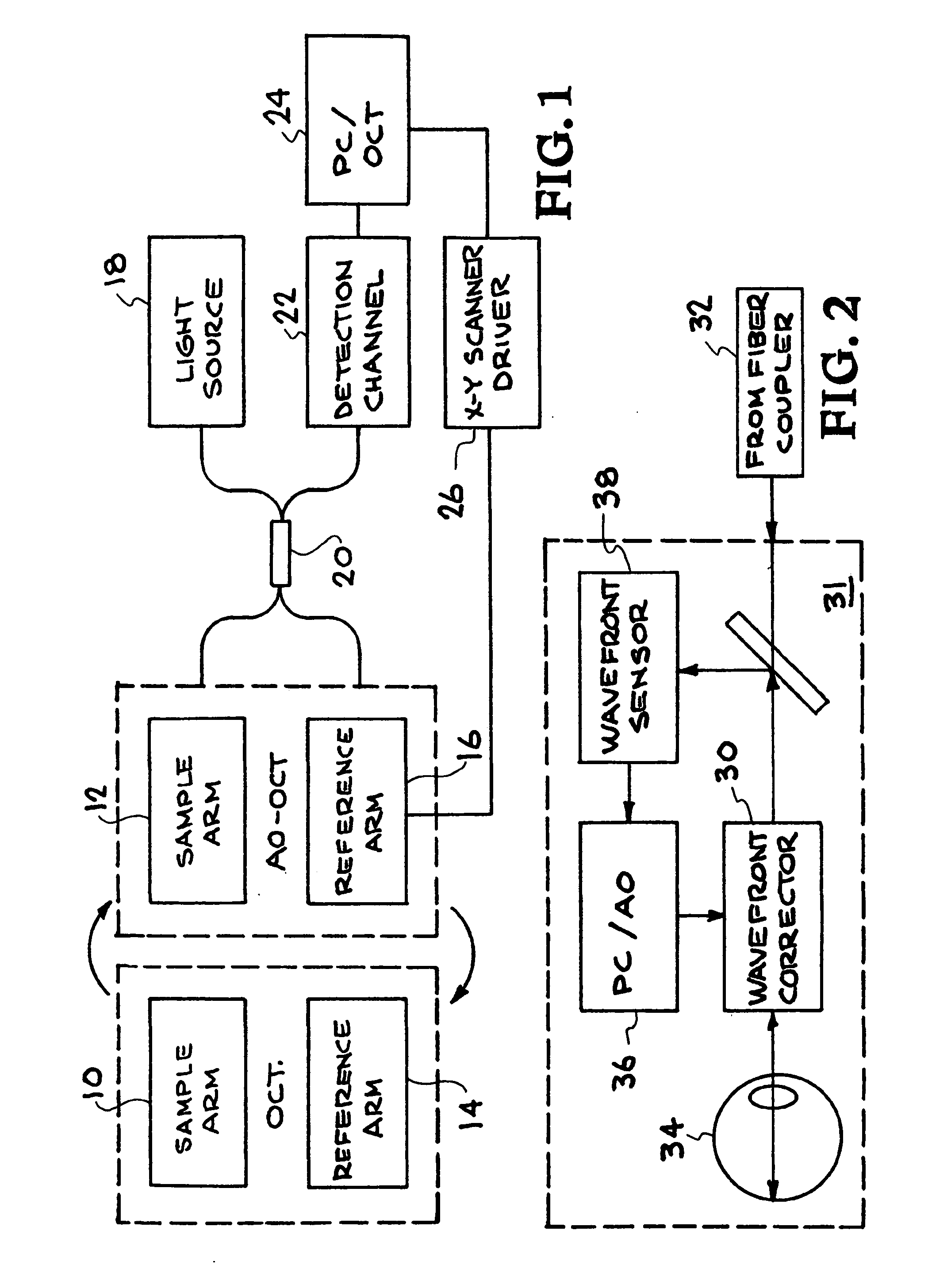
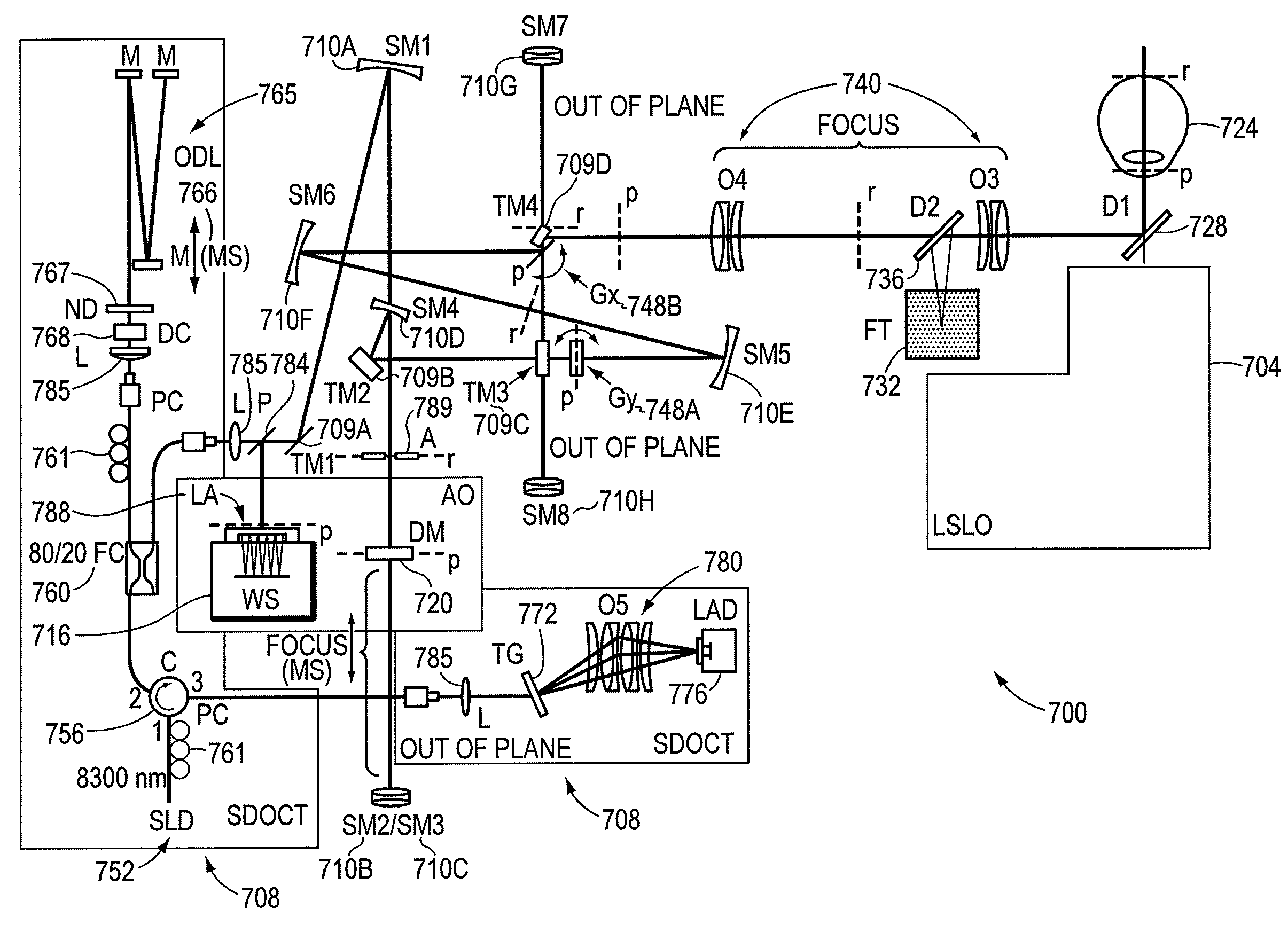
Retinal imaging system for the mouse or rat or other small animals
A small animal imaging system comprising a base element and a camera coupled to the base element, the camera being sized to image the eye of a small animal. A light-emitting diode is also included coupled to the base element. An OCT imaging apparatus is also included coupled to the base element. An X-Y scanner is also included coupled to the base element in communication with the OCT imaging apparatus.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
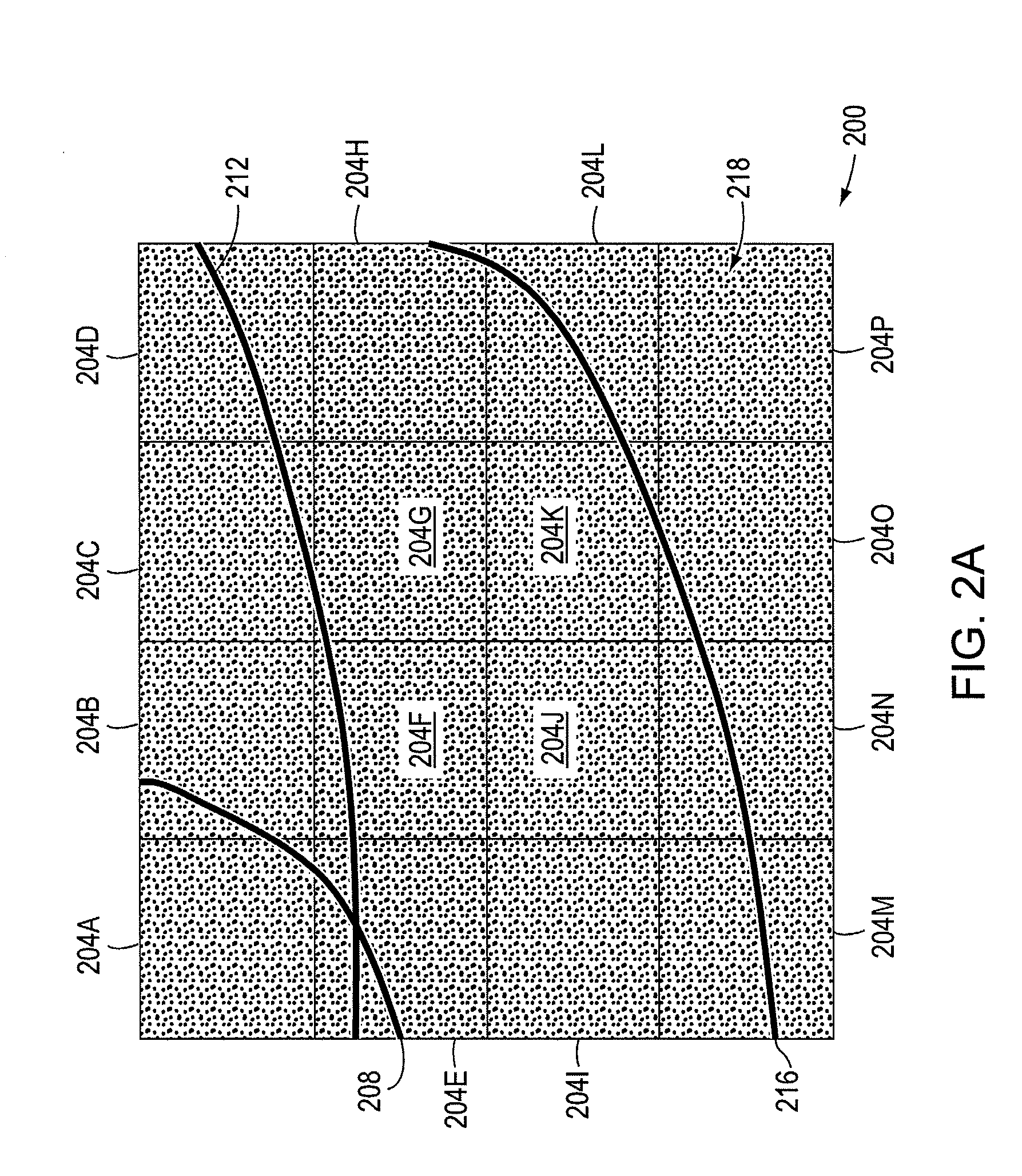
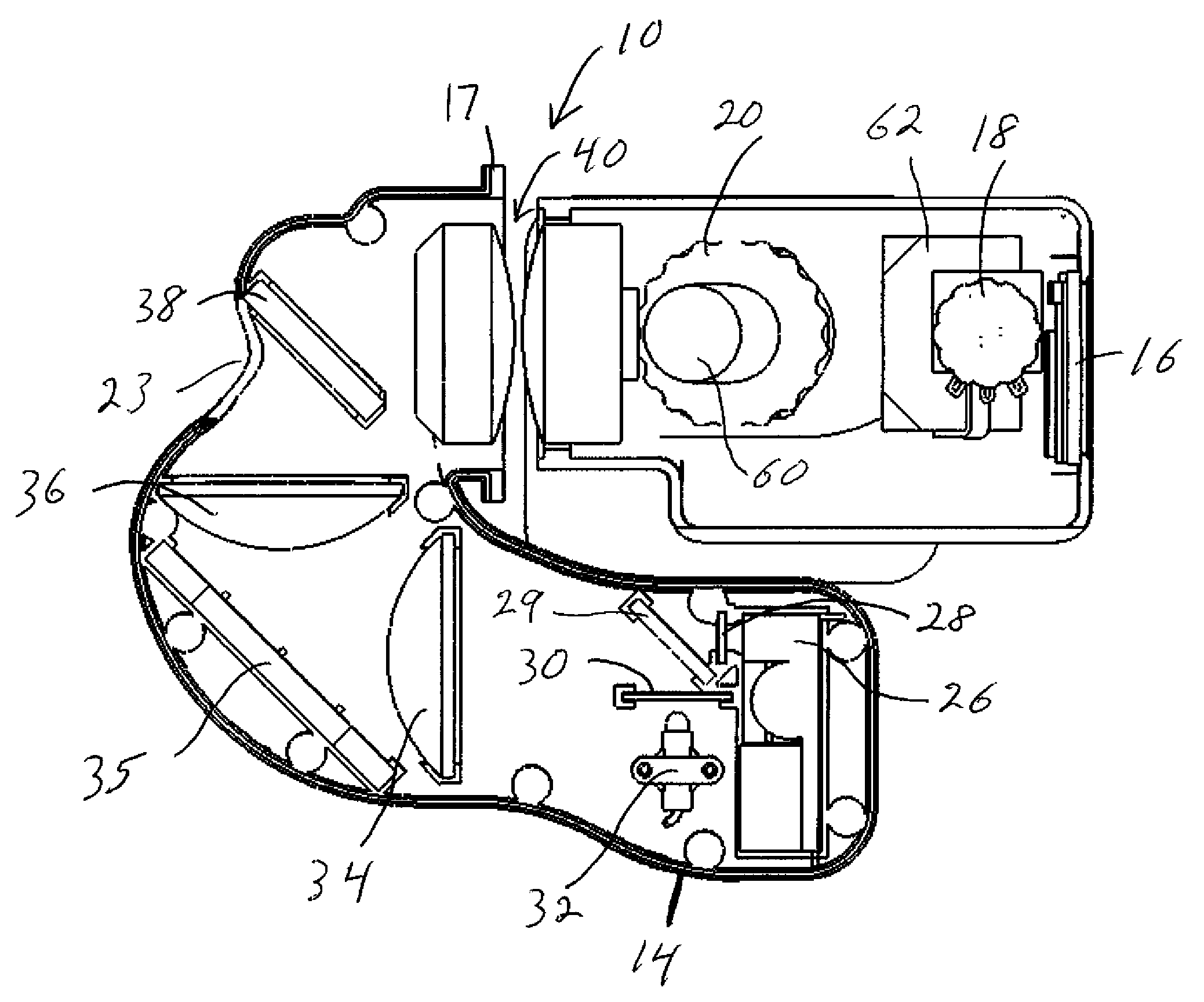
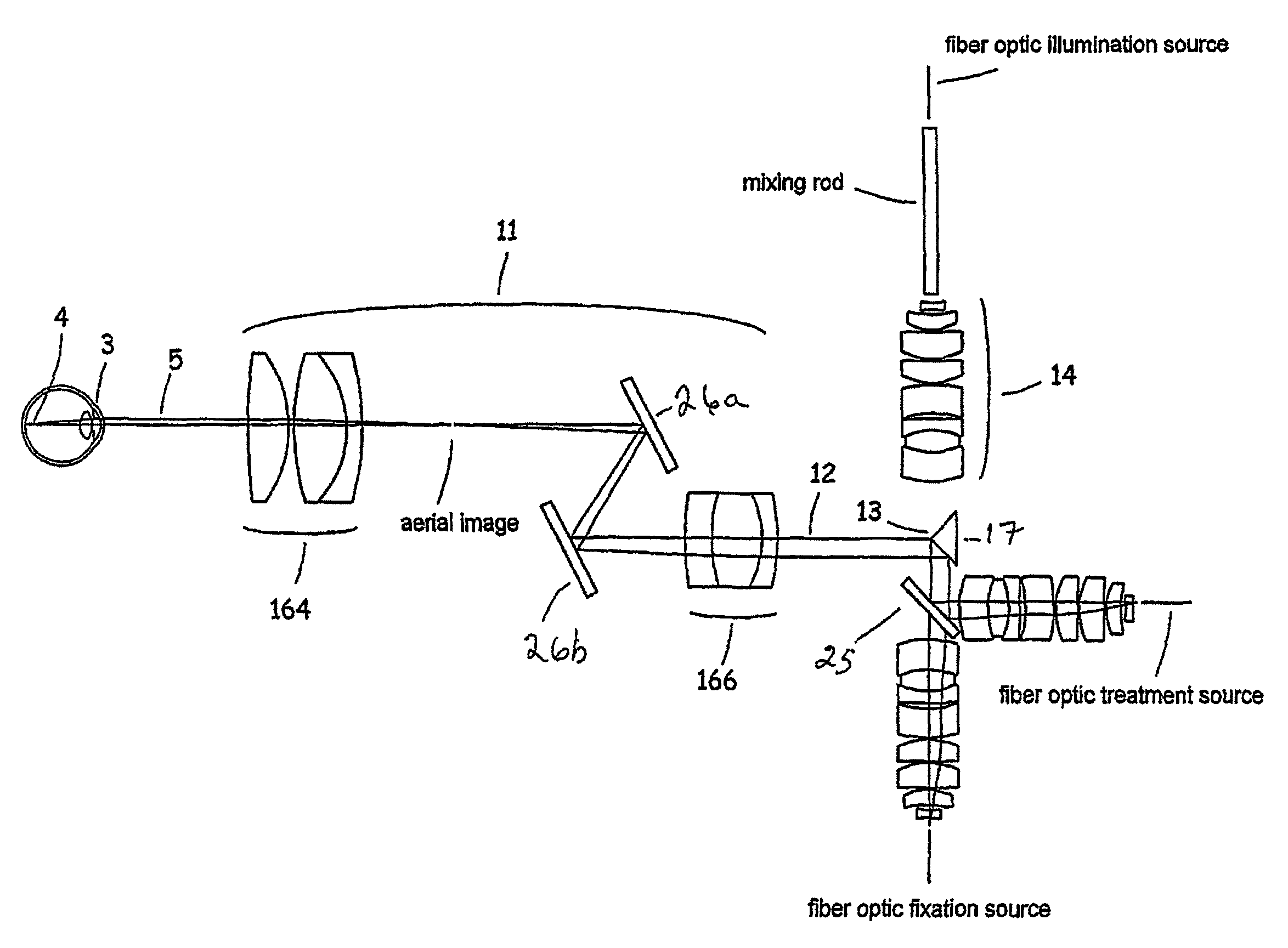
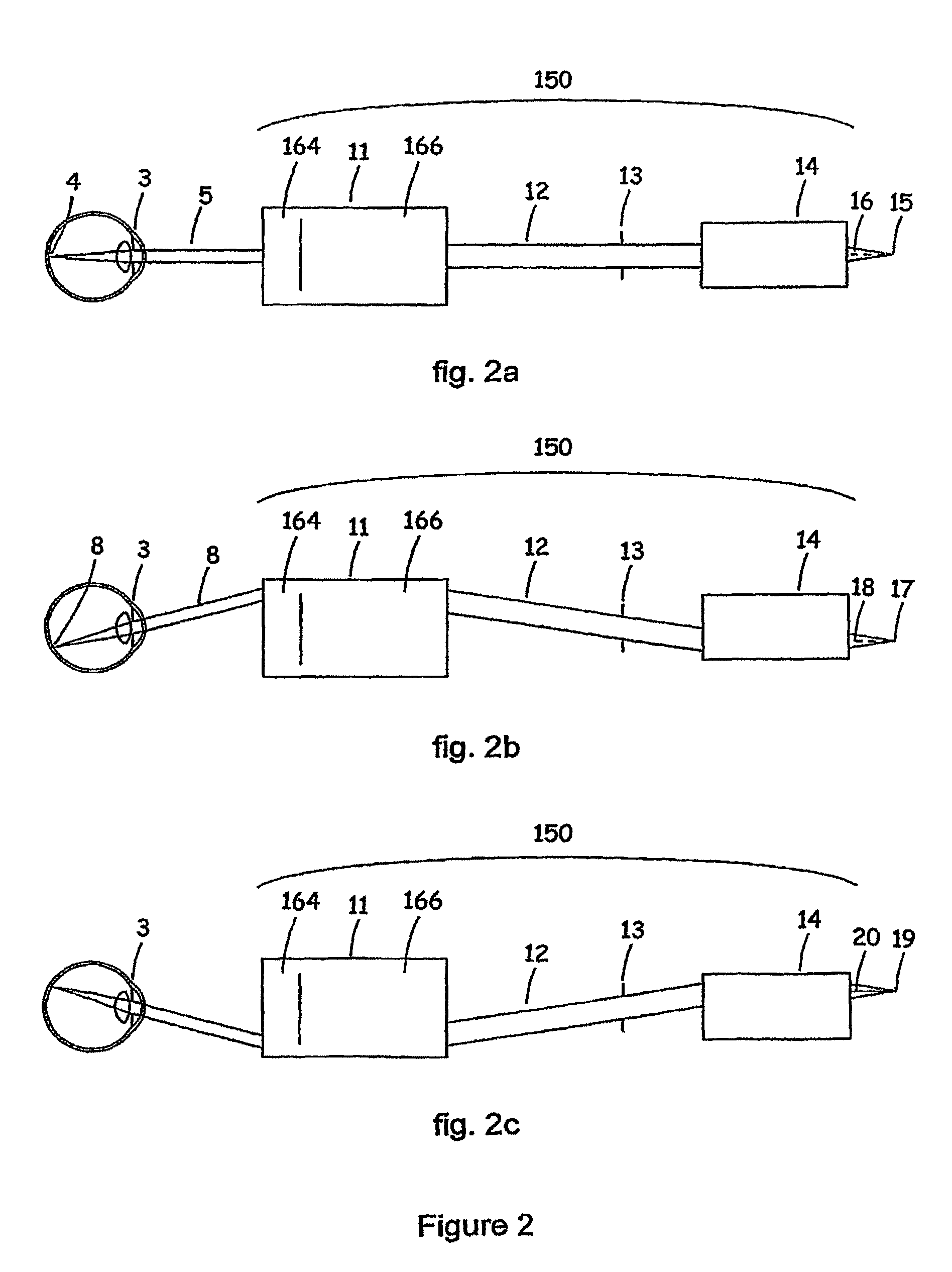
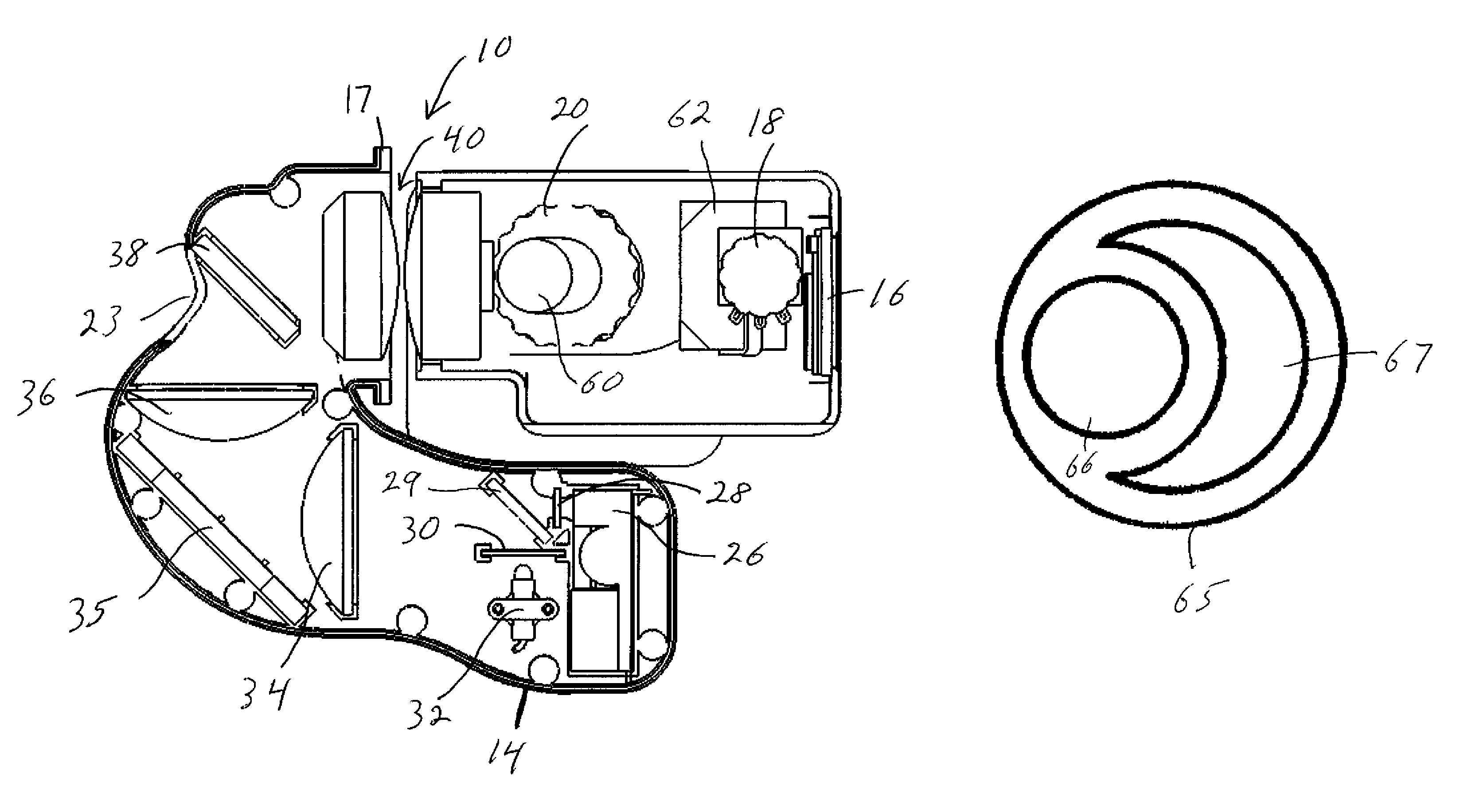
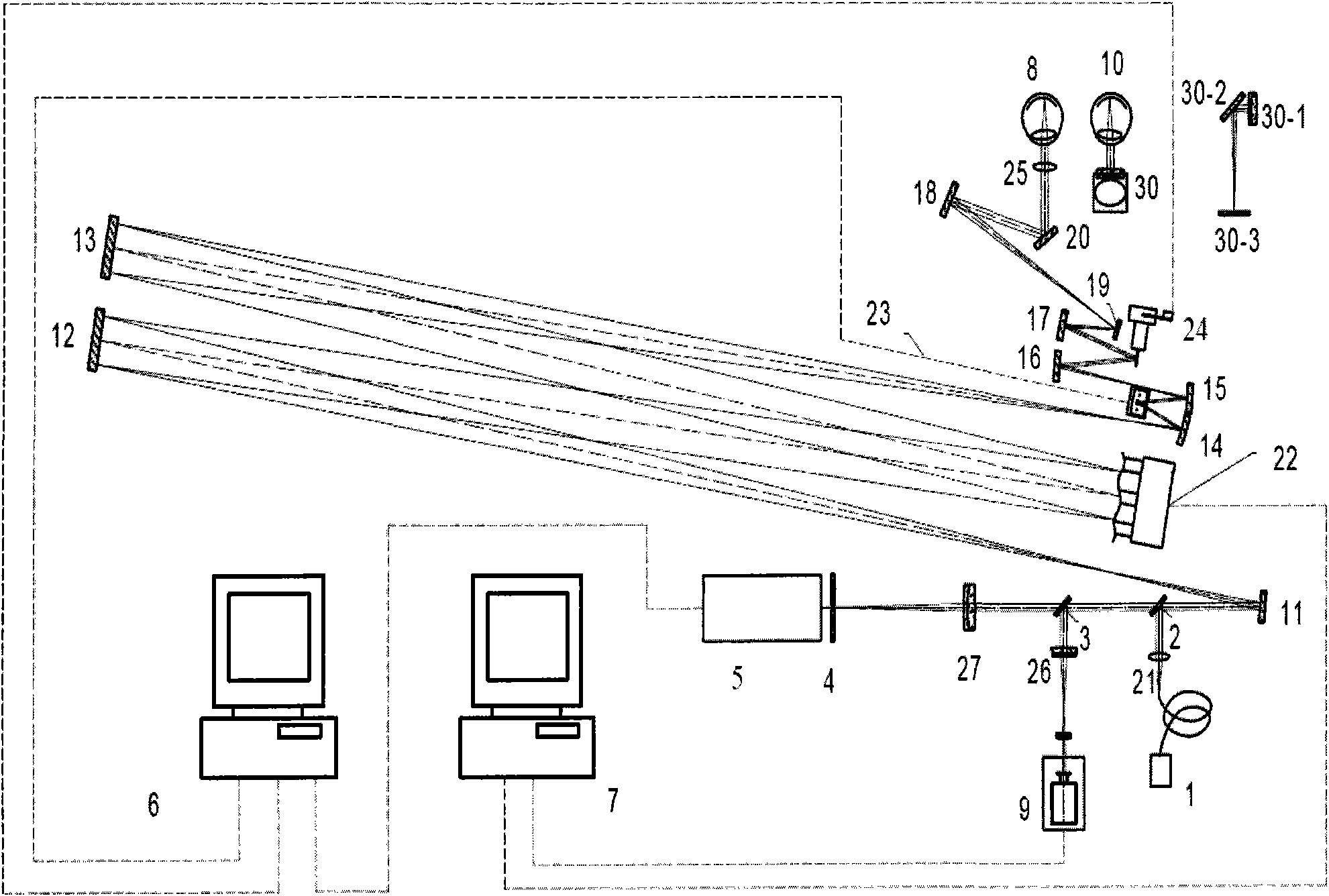
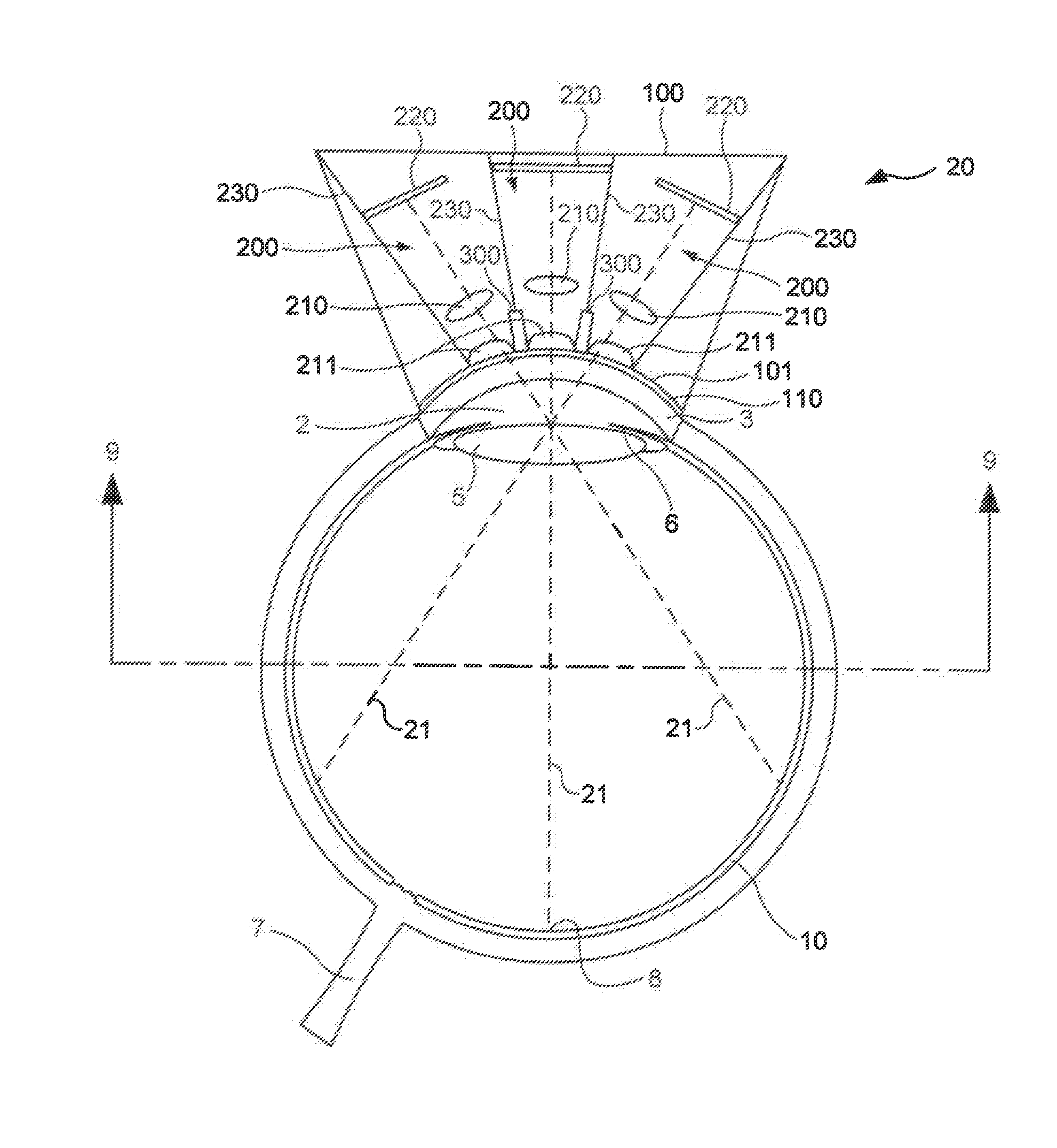
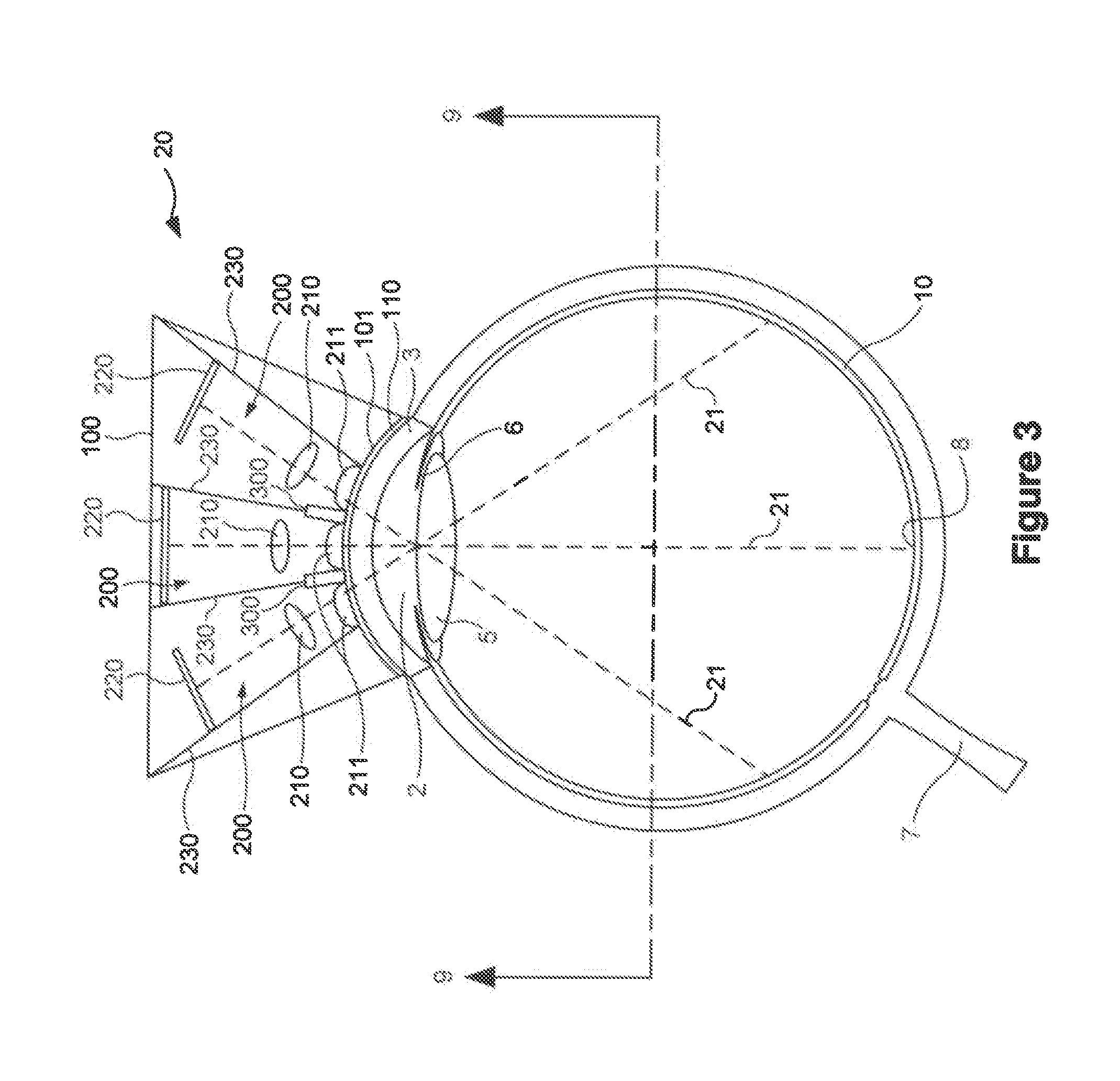
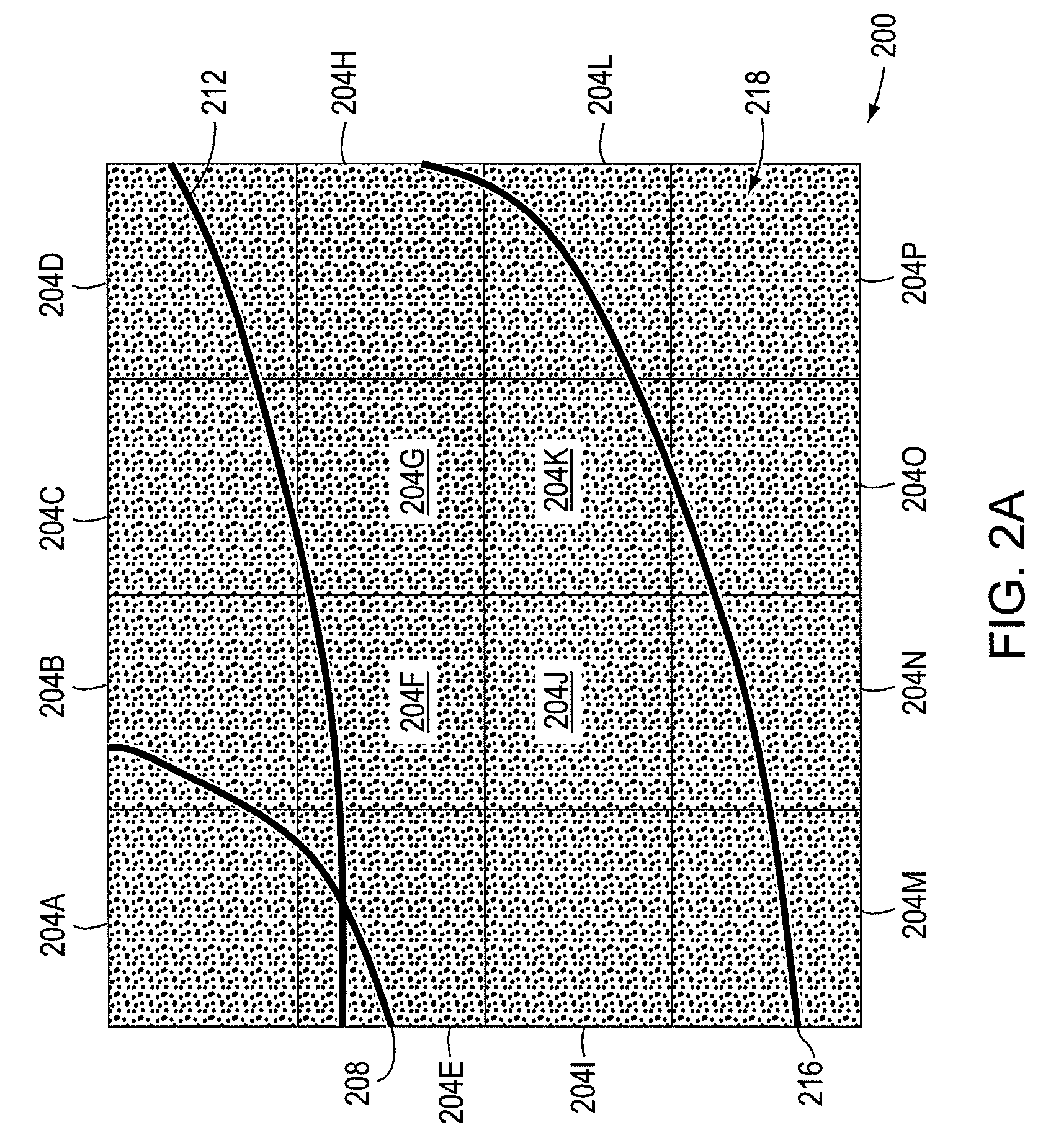
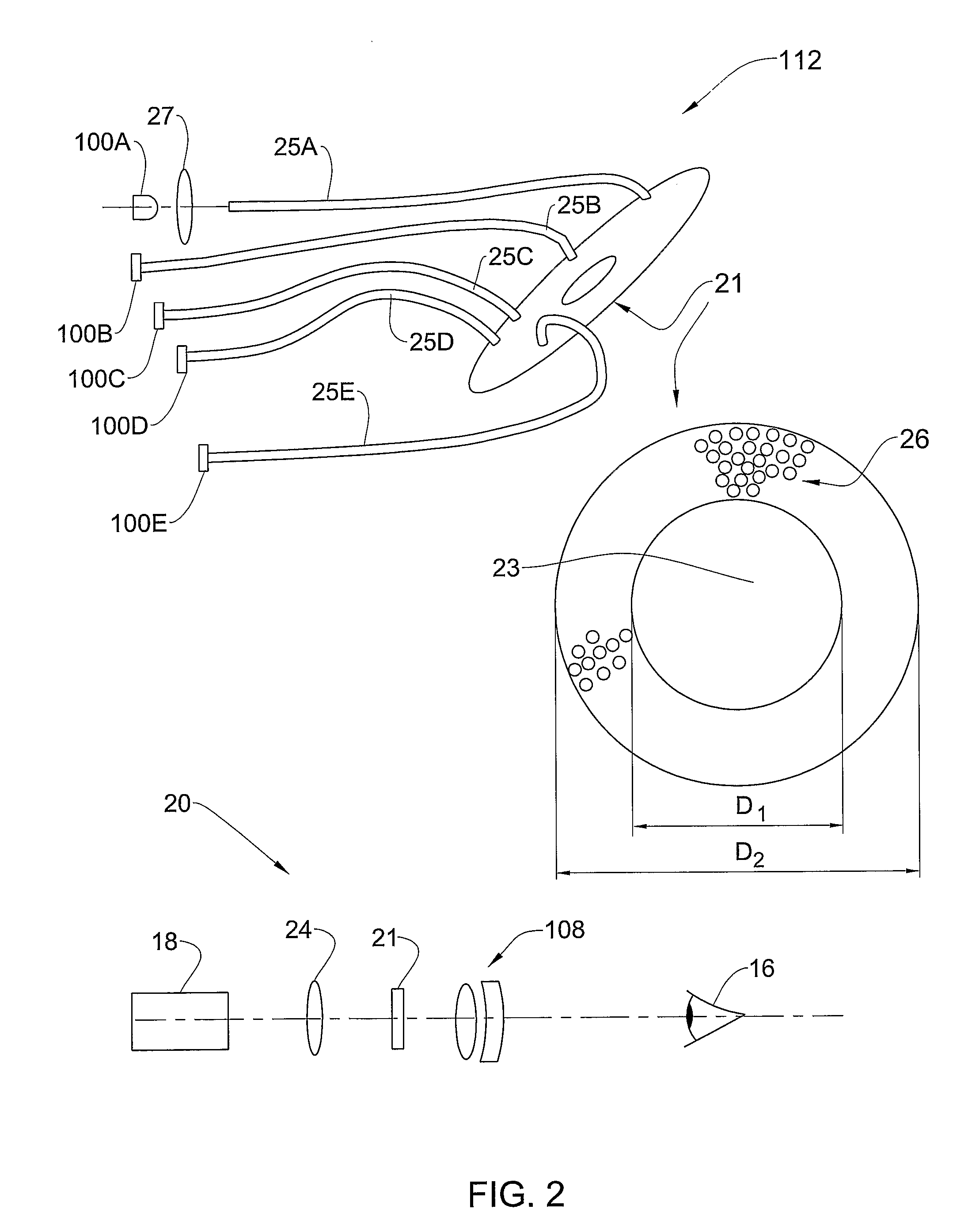
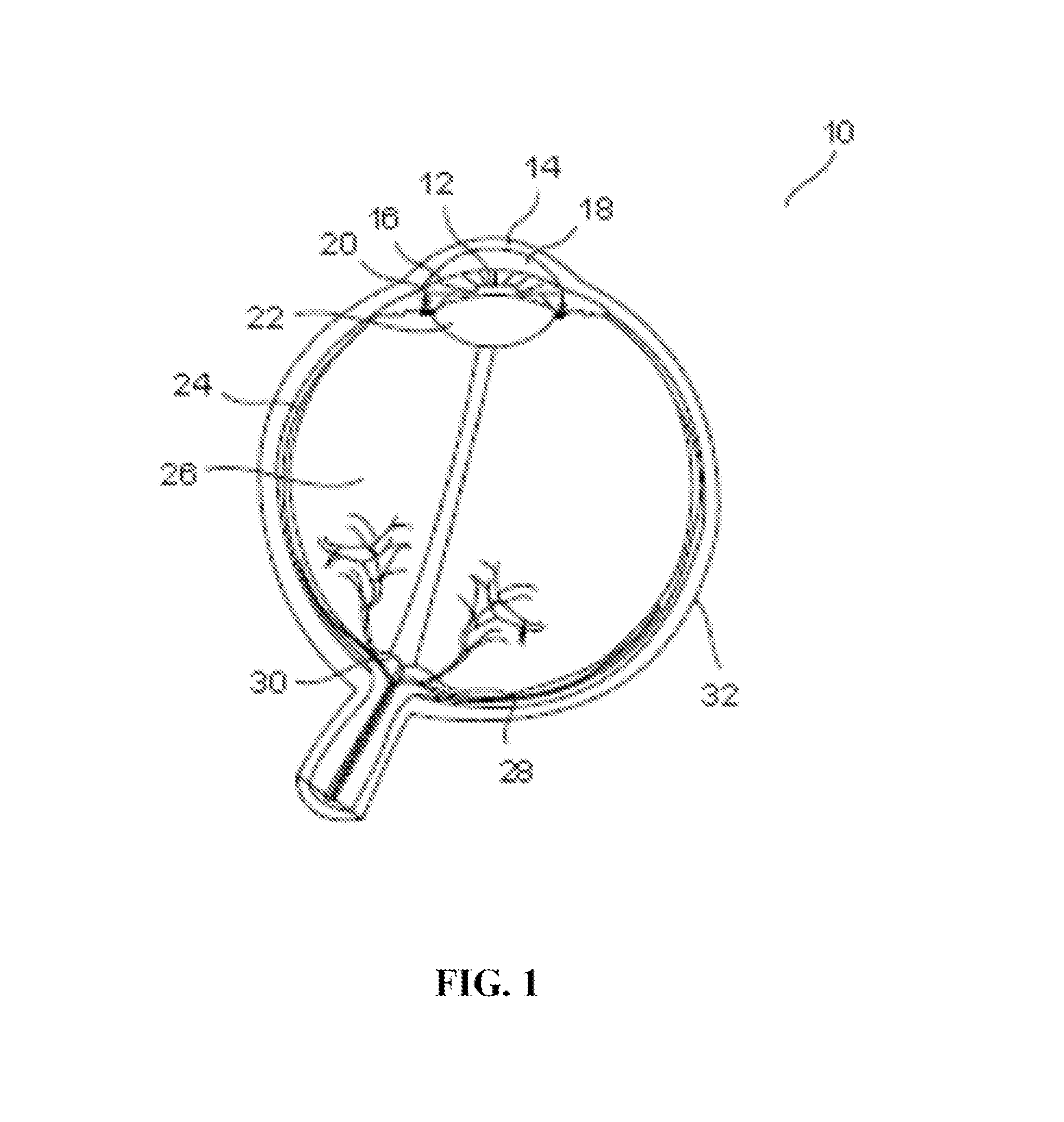
Multiple-lens retinal imaging device and methods for using device to identify, document, and diagnose eye disease
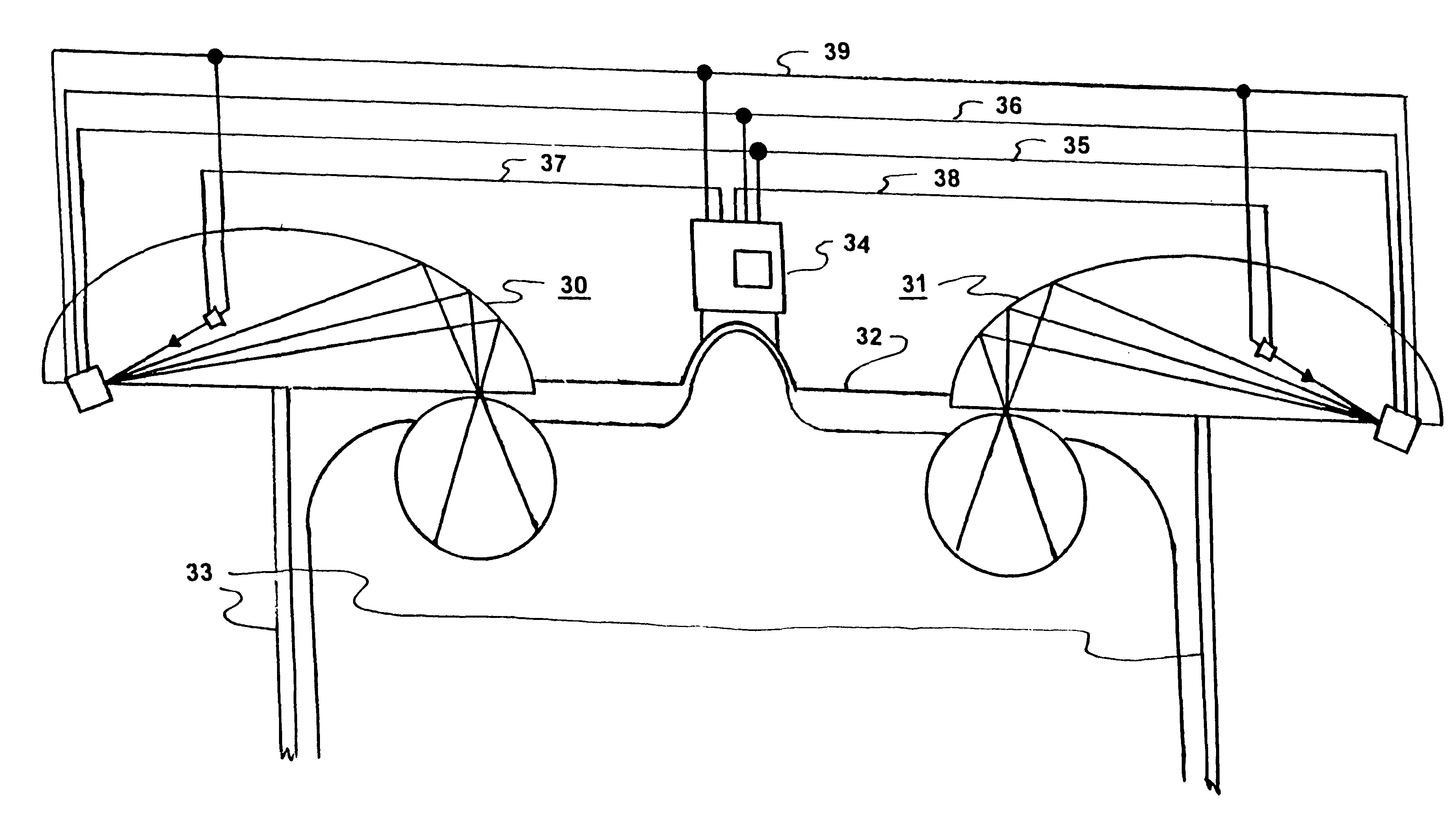
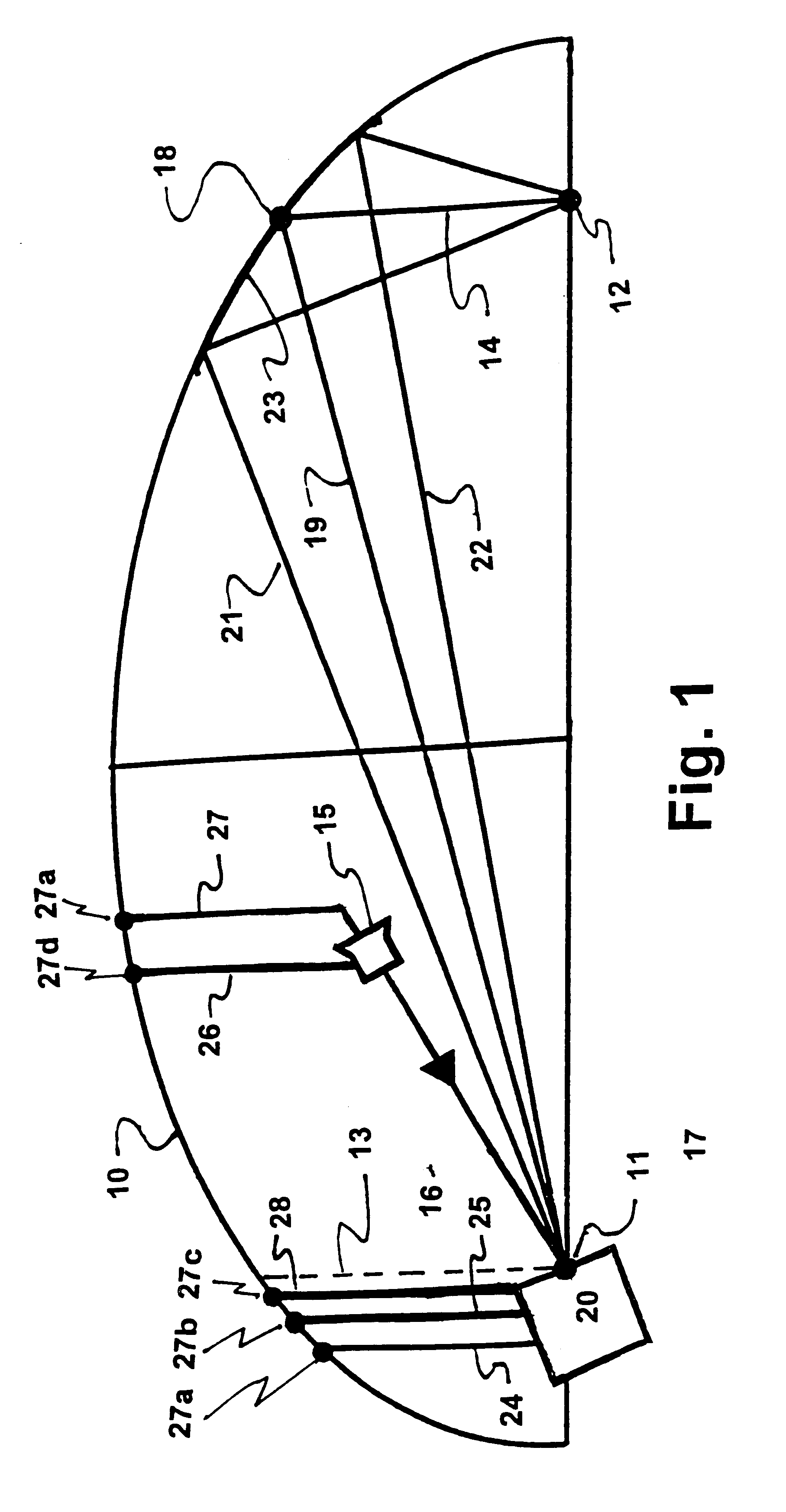
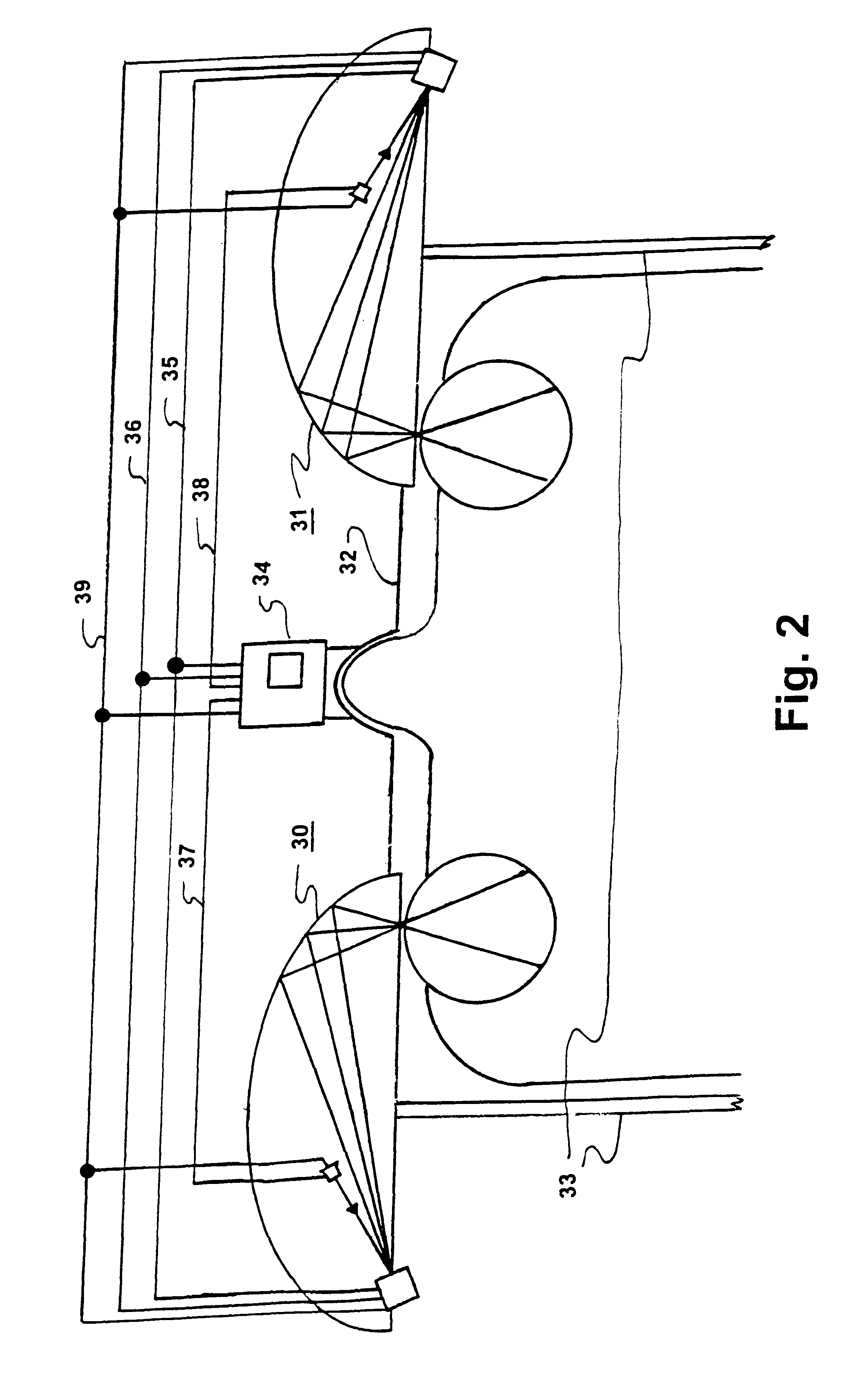
A device (20) for use in the screening, documentation, and diagnosis of various diseases of the eye (1). Several images (60) are taken substantially simultaneously, with the images (60) preferably taken in a non-coplanar orientation relative to each other (60). The images (60) represent multiple different zones (11) of the retina (10) taken using different optical imaging pathways (200). Image (60) distortion is minimized, because the individual optical imaging pathways (200) need to account for significantly less differential curvature of the object plane than a wide-field optical pathway that attempts to capture both the central and peripheral retina (10) in a single image. A single composite wide field image (61) can be generated, by merging the overlapping fields of multiple, concurrently captured images (60) taken at different angles.
Owner:BROADSPOT IMAGING
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS7758189B2Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansOphthalmologyRetinal imaging
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Portable self-retinal imaging device
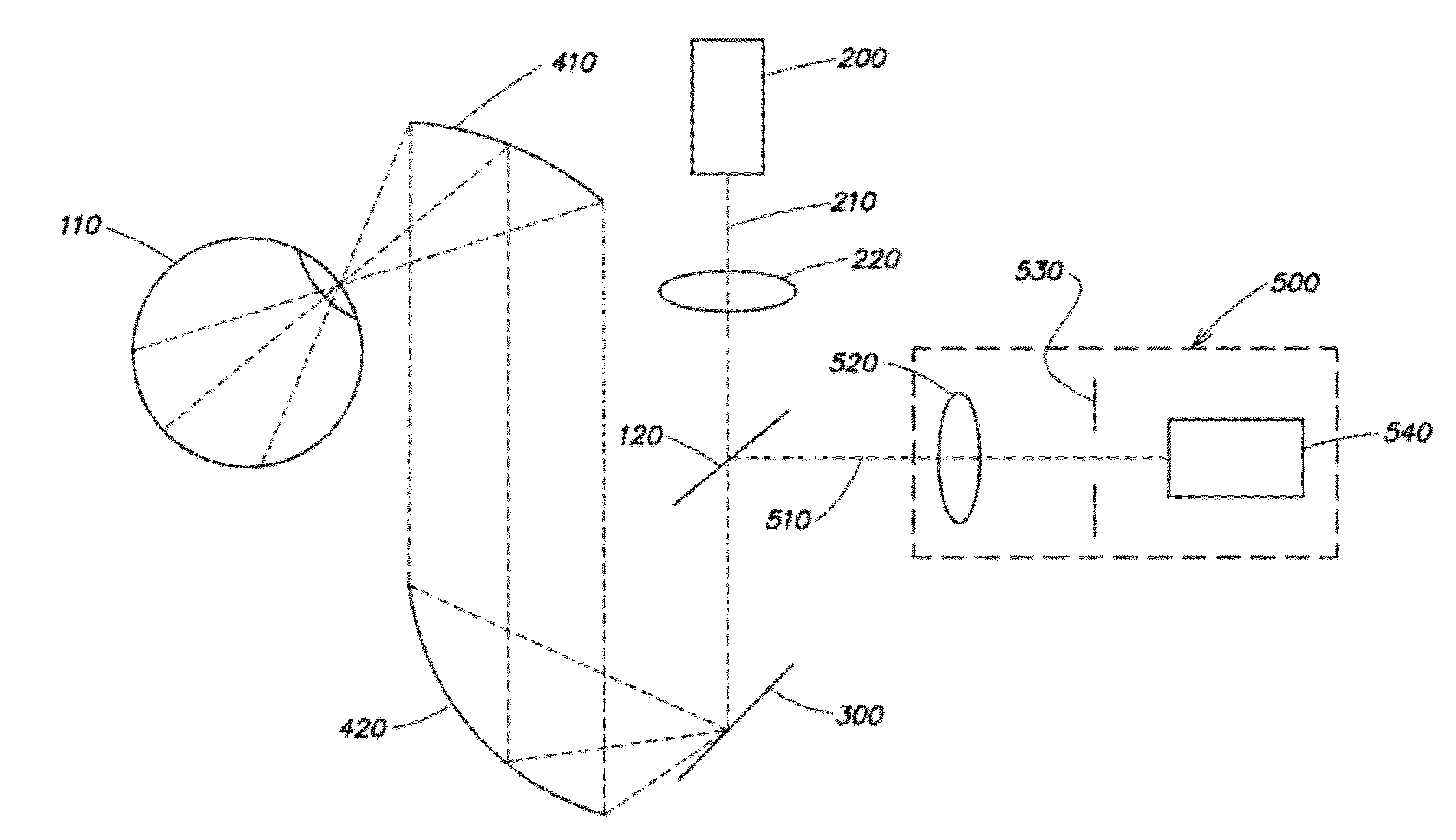
InactiveUS20120257166A1Robust scanningSmall sizeMicroscopesOthalmoscopesCamera lensScanning laser ophthalmoscope
A portable MEMS-based scanning laser ophthalmoscope (MSLO). In one example, the MSLO includes a laser illumination sub-assembly, a two-dimensional MEMS scanning mirror, a conic front objective, and a detector sub-assembly all disposed within a portable housing. A battery configured to provide power to components of the MSLO may also be included within the housing. In one example, the laser illumination sub-assembly includes at least one laser configured to generate in each of two orthogonal dimensions one or more illumination beams separated from one another by a predetermined angle of separation. The MEMS scanning minor and conic front objective are configured to produce a two-dimensional area of illumination from the illumination beam(s) in each dimension and to direct the illumination from the scanning minor to the eye to illuminate the retina.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
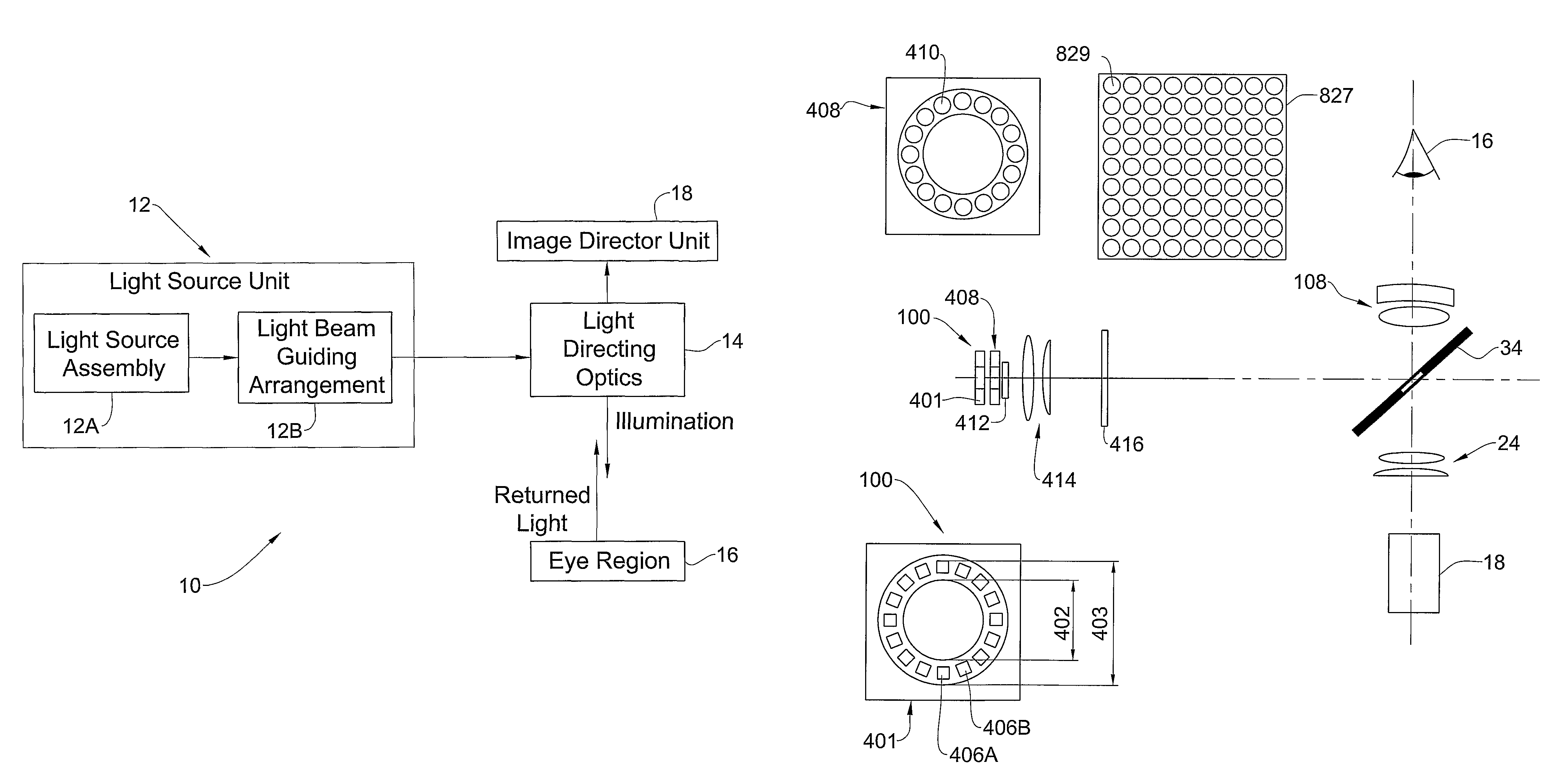
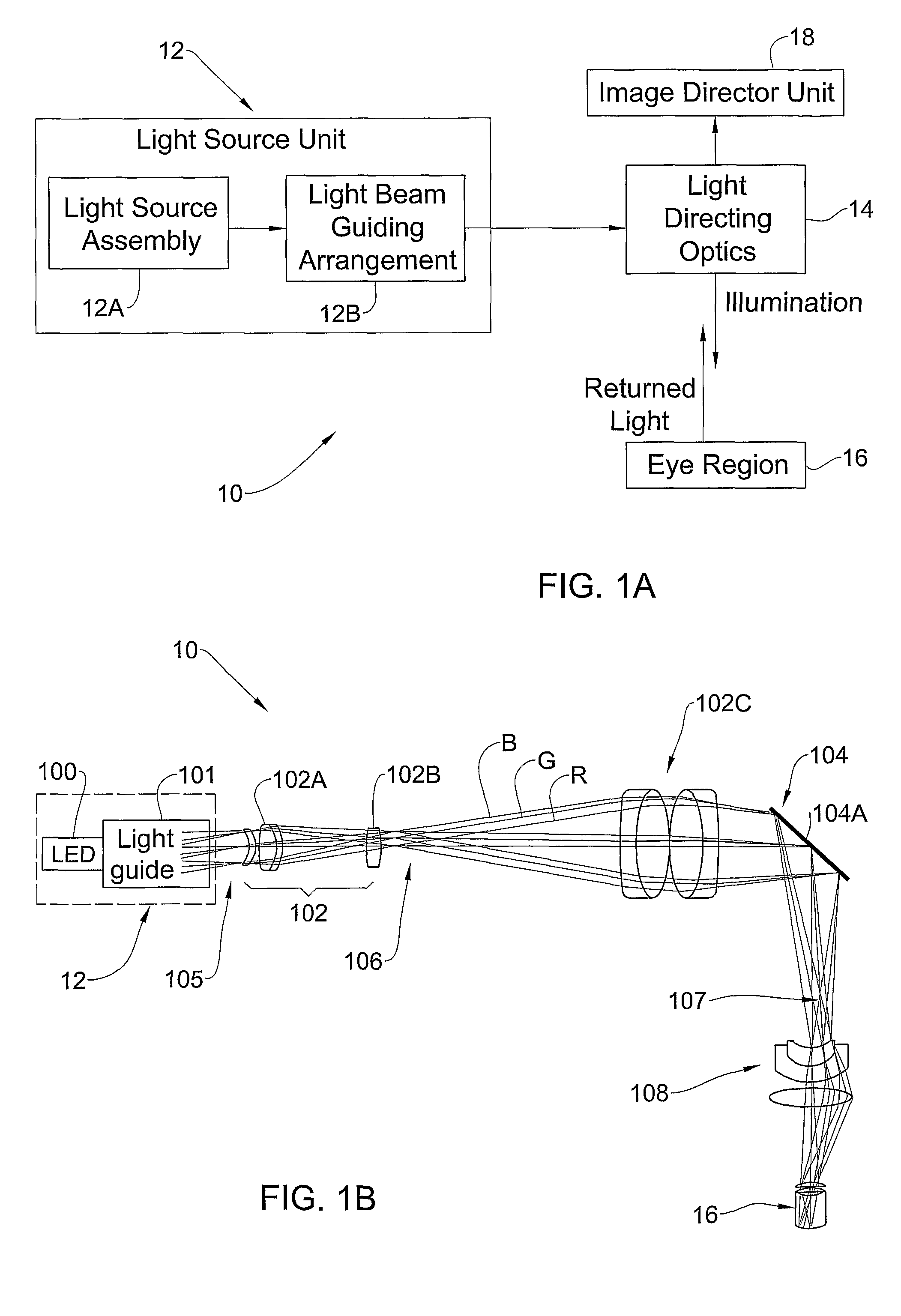
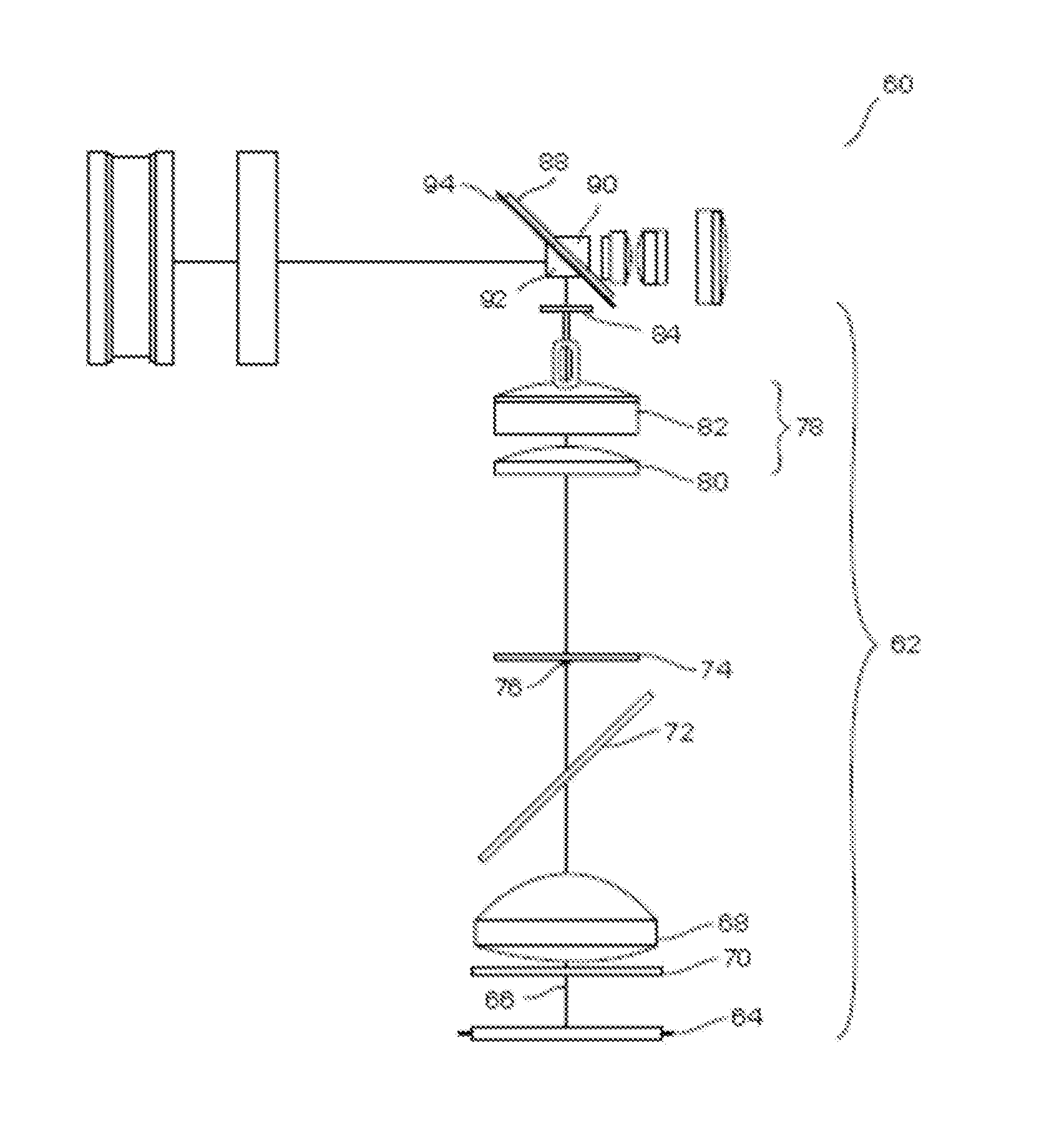
Integrated retinal imager and method
ActiveUS8109635B2Enhance the imageEfficient couplingOthalmoscopesPhotographyImaging qualityExposure control
A system and method are presented for use in imaging the patient's retina. A light source unit is provided including a light emitting diode (LED) arrangement comprising multiple LEDs of different wavelength ranges. A light guide arrangement is used with the LEDs arrangement and is configured for coupling light from the LEDs and providing output light beams of a desired shape. The illuminating light is directed towards a region on the retina, and light returned from the illuminated region is collected and directed to an image detector unit. The invention enables the use of LED light at high intensity as required in the eye retina imaging, while maintaining the required high-quality imaging. Also, the invention provides for simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous as well as high-speed imaging in FA and ICG imaging procedures, thereby satisfying a long felt need in ophthalmology. Also, the invention provides for automated illumination or light exposure control to optimize overall light exposure to the patient eye and best acquired image quality in terms of brightness, contrast and image signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
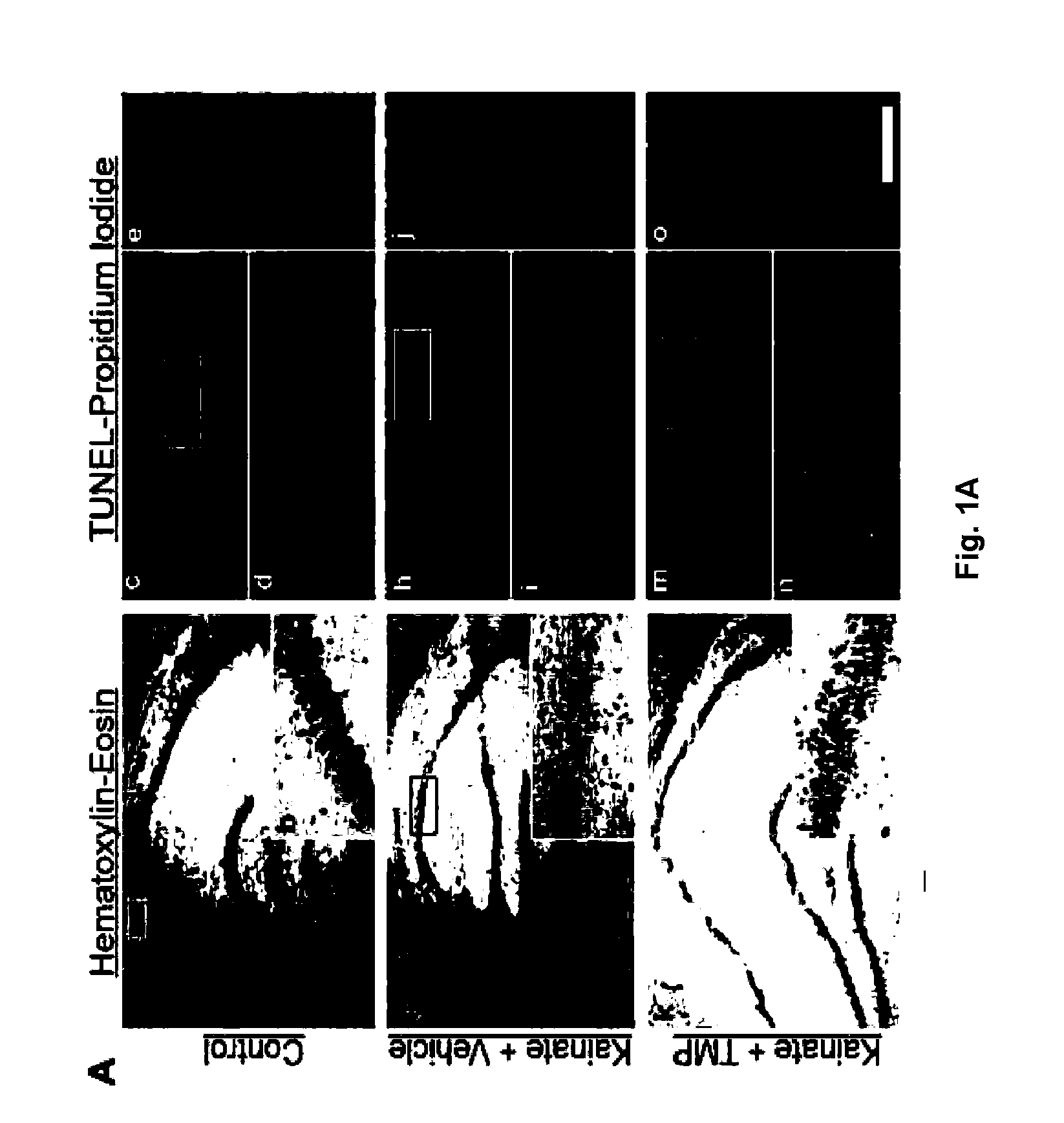
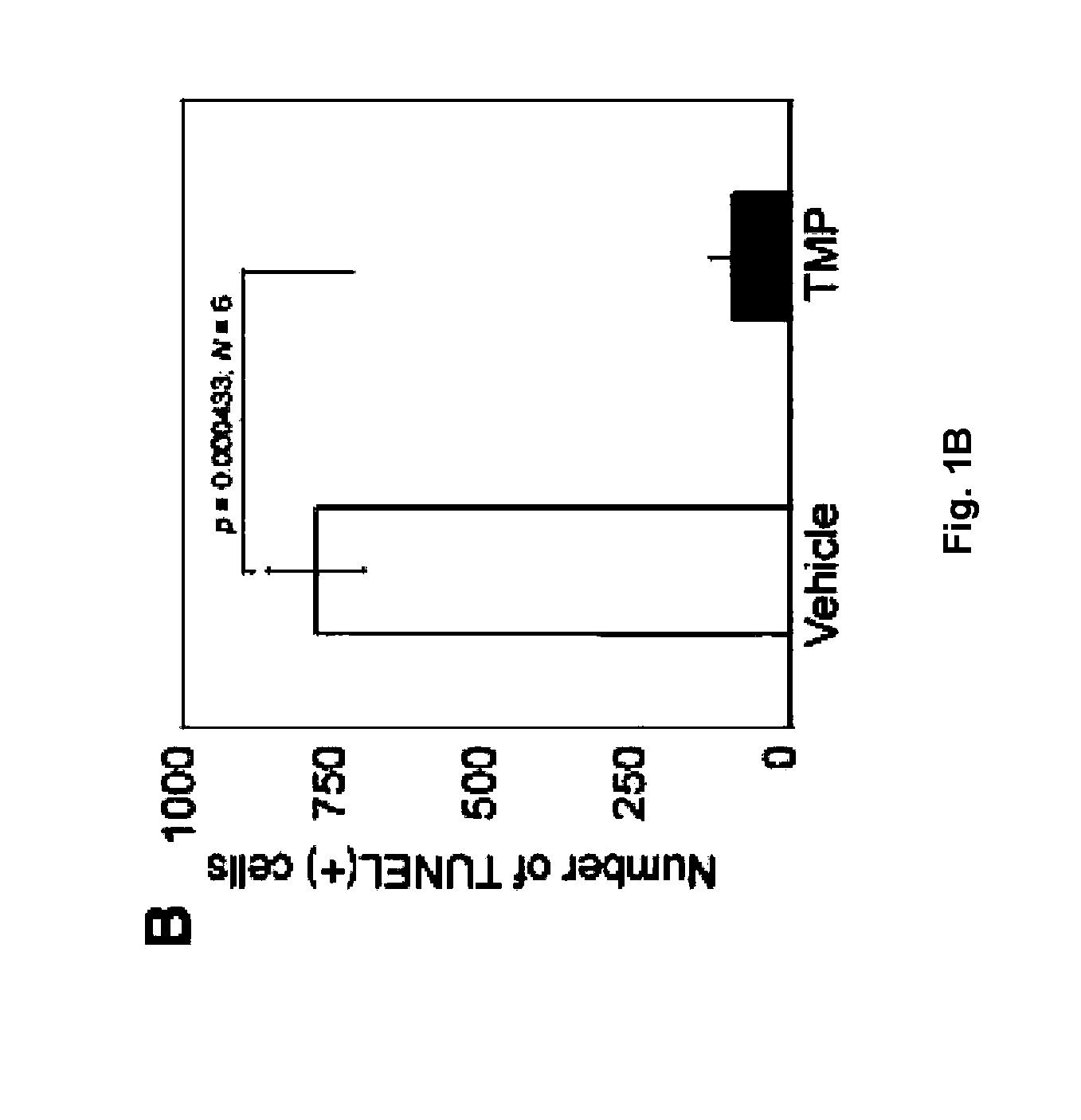
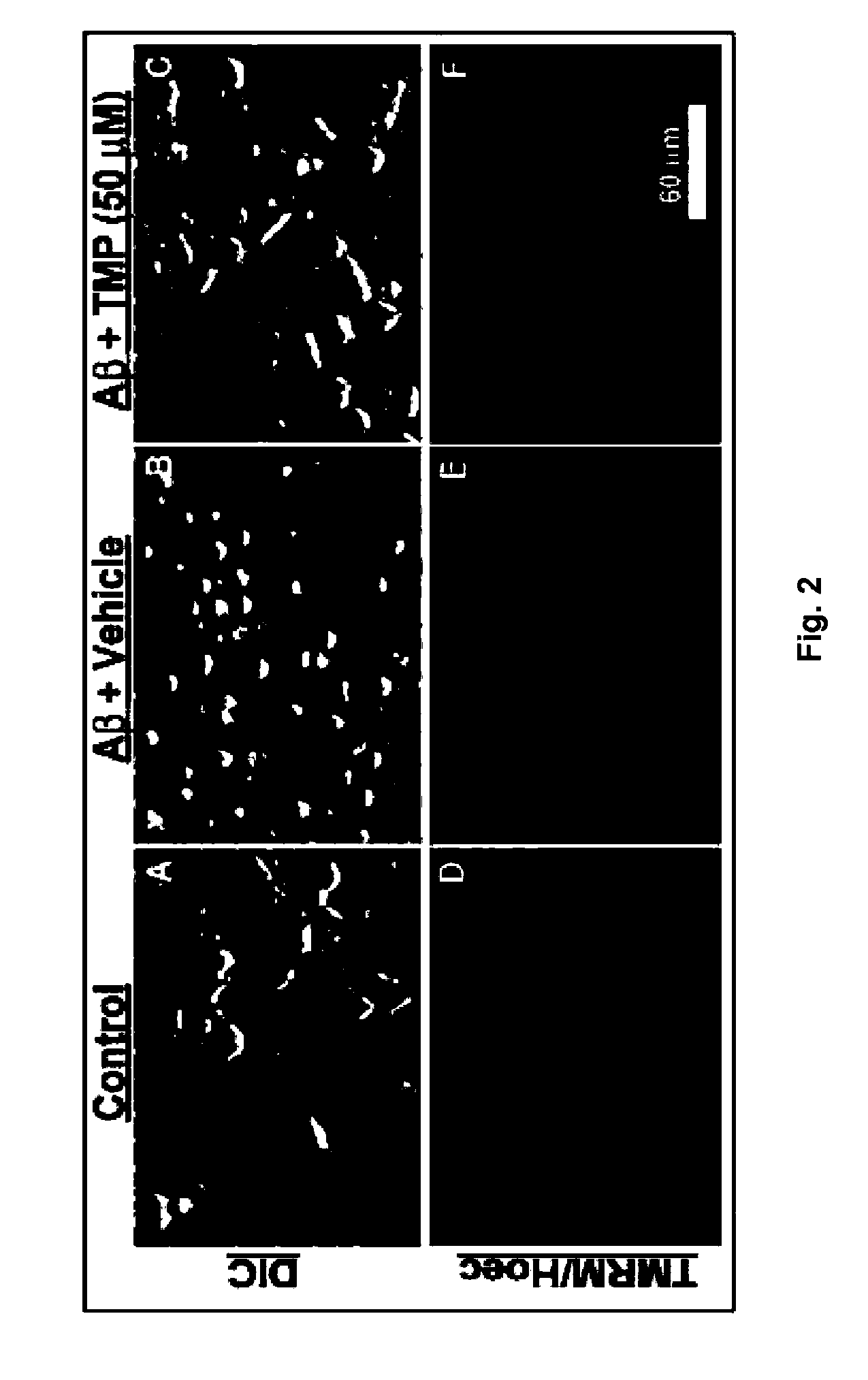
Treatment and diagnosis of central nervous system disorders
InactiveUS20110200531A1Reduce severityImprove survivalBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
The invention relates to the use of tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) for the treatment of patients at risk for the development of, or diagnosed as having, CNS disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), glaucoma, and Huntington's Disease (HD), as well as traumatic brain injury (TBI). The present invention also relates to the use of retinal imaging to diagnose and monitor efficacy of treatments for such CNS disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
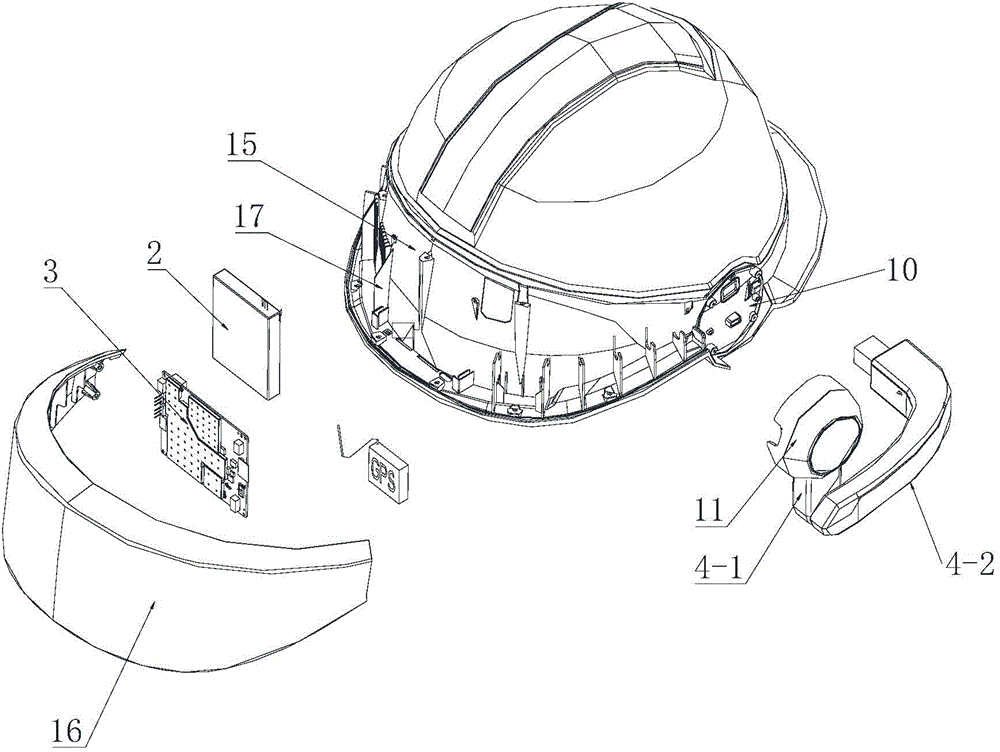
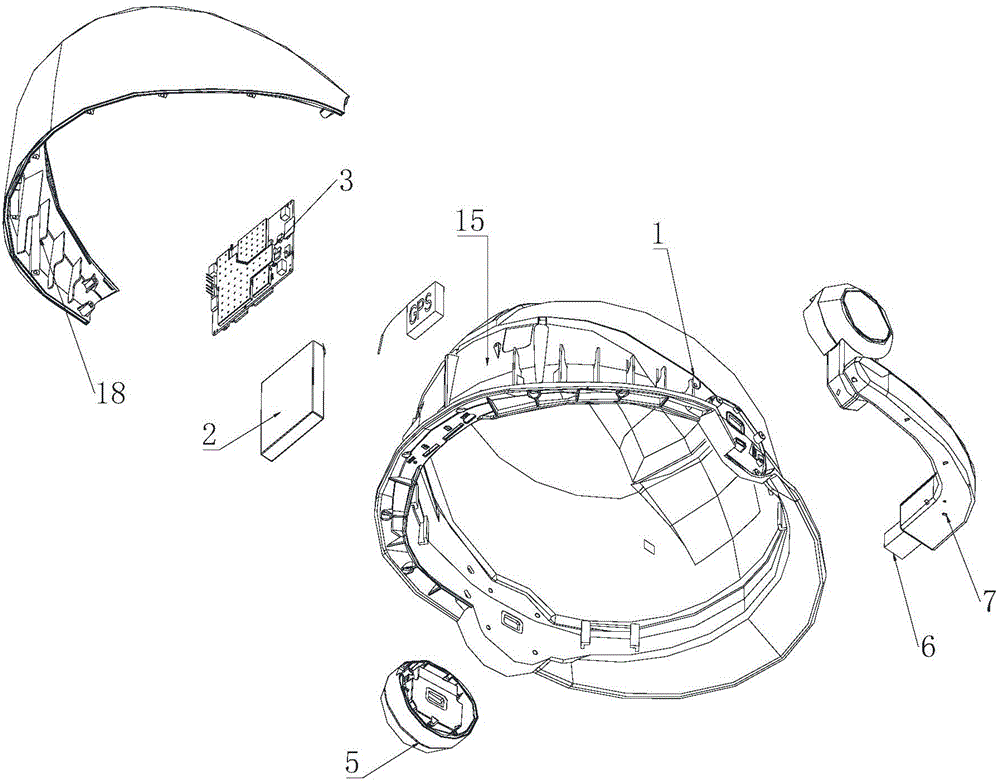
Reality augmenting intelligent safety helmet
The invention discloses a reality augmenting intelligent safety helmet. The reality augmenting intelligent safety helmet comprises a safety helmet body, and is characterized in that a power supply, a microcontroller and an optical machine arm are arranged on the safety helmet body, a control platform system is carried by the microcontroller, the power supply is connected with the microcontroller, the optical machine arm is provided with a retina imaging projector which is connected with the microcontroller, the included angle for preventing a shielding environment light source from entering human eyes is formed by the edge of the safety helmet and the optical machine arm, and the high-resolution display output of the microcontroller is imaged on retinas of the eyes through the retina imaging projector. By means of the reality augmenting intelligent safety helmet, a built-in microphone based on a connection rod, the video input and the imaging optical machine display are integrated in the safety helmet together with a voice control system, hands, tapping a keyboard, of an operator are liberated, the more portable on-site official business handling is achieved, and through the cooperation with a wireless network, the data exchange in an electric system can be achieved, and the remote control and the remote debugging can be achieved.
Owner:佛山市威格特电气设备有限公司
Non-invasive measurement of blood glucose using retinal imaging
InactiveUS20050267343A1Accurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineRetinal imaging
An apparatus carries out measurements of blood glucose in a repeatable, non-invasive manner by measurement of the rate of regeneration of retinal visual pigments, such as cone visual pigments. The rate of regeneration of visual pigments is dependent upon the blood glucose concentration, and by measuring the visual pigment regeneration rate, blood glucose concentration can be accurately determined. This apparatus exposes the retina to light of selected wavelengths in selected distributions and subsequently analyzes the reflection (as color or darkness) from a selected portion of the exposed region of the retina, preferably from the fovea.
Owner:FOVIOPTICS INC
Elliptical cavity optical retinal display
An opto-mechanical configuration for direct laser scanned retinal imaging is described. The concept uses simple geometric properties of an ellipse in a reflective optical delivery system which allows a small scanned laser beam to create a two dimensional video image directly on the retina of the human eye. The system is best suited for use in head-mounted display applications where light weight is a priority.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
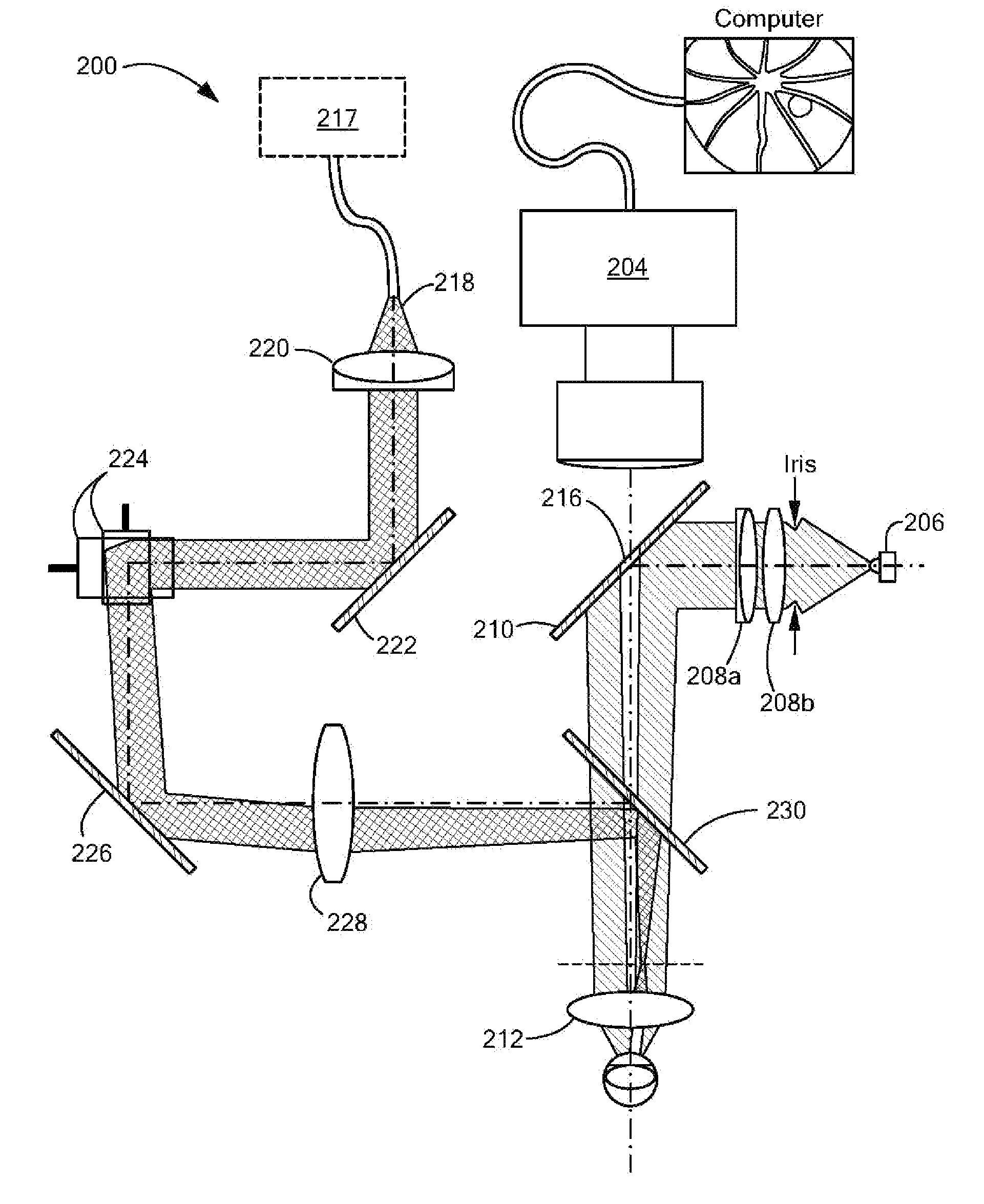
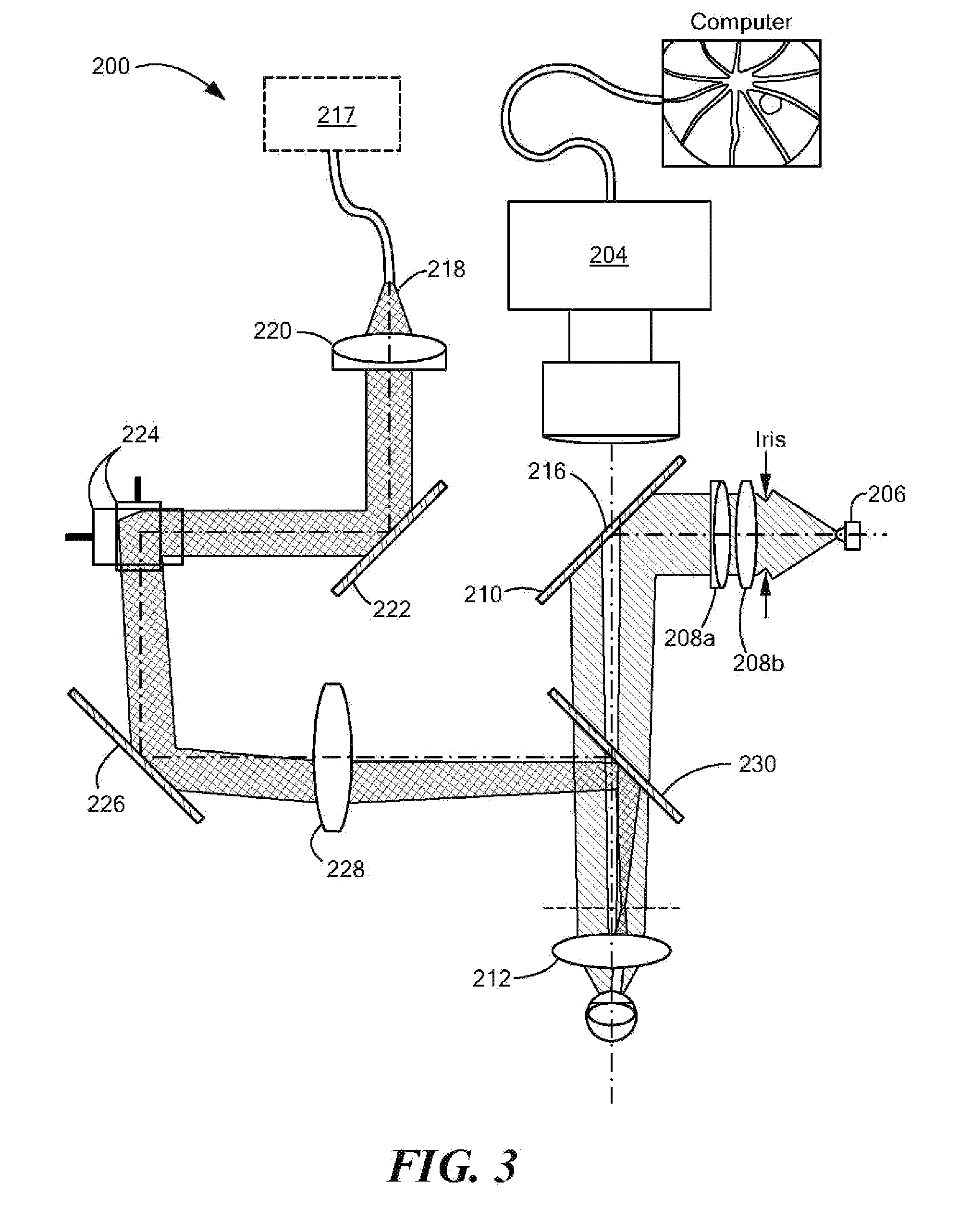
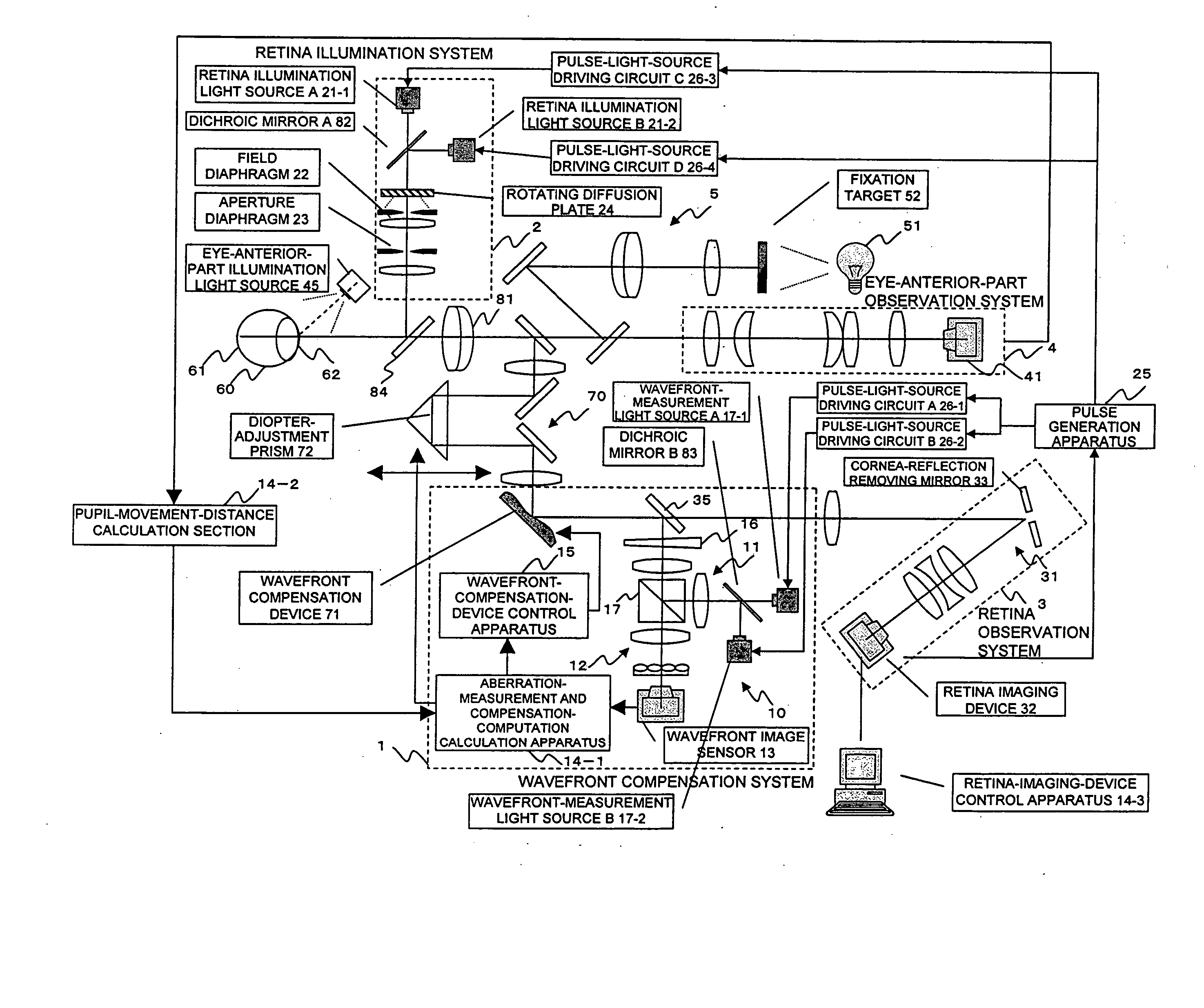
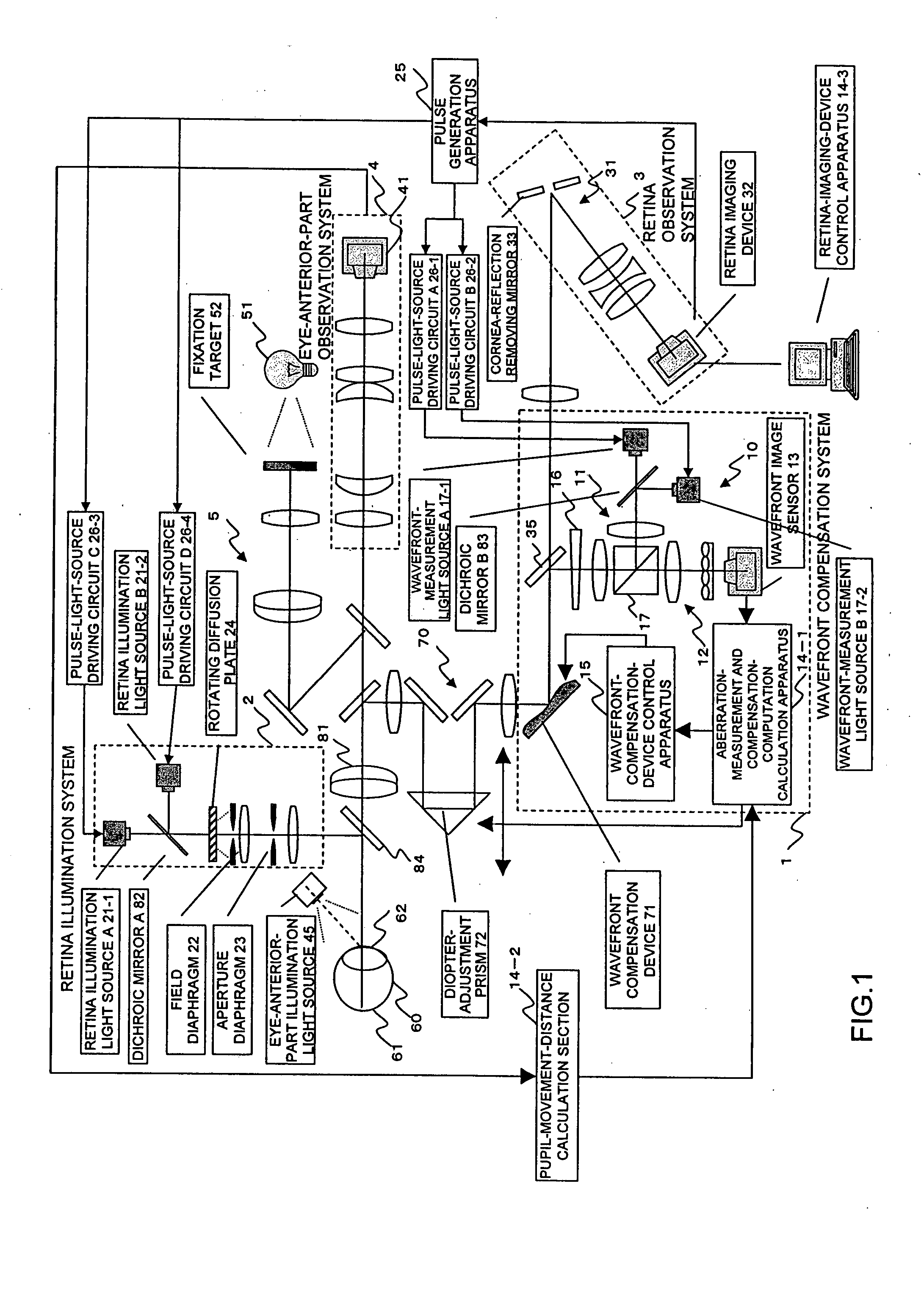
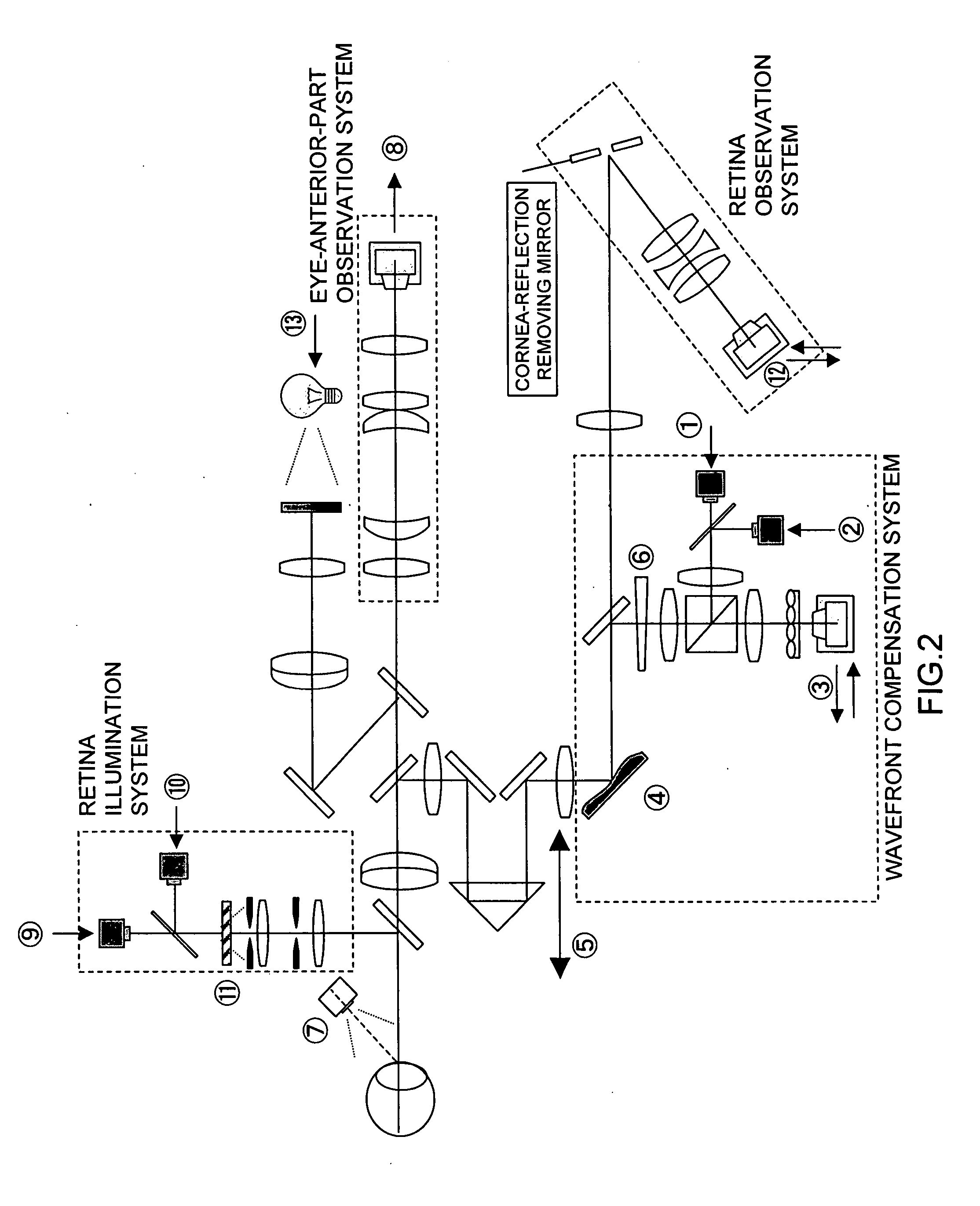
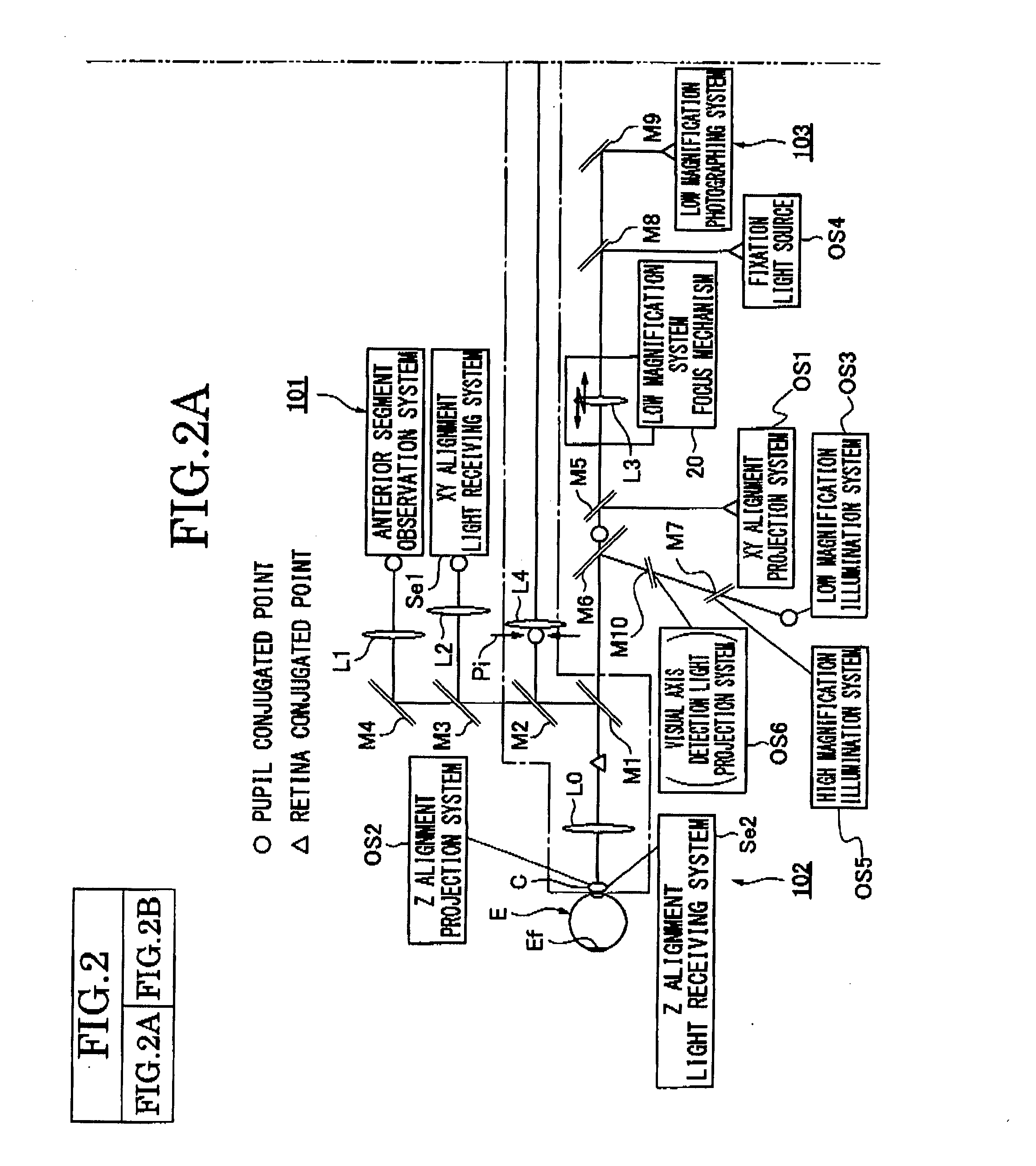
Ophthalmologic imaging apparatus
A first wavelength for measurement is selected from among a plurality of wavelengths. Aberrations at the first wavelength are measured with a wavefront-measurement light source having the first wavelength. A compensation optical section performs compensation so as to cancel out the measured aberrations. After the compensation, a retinal image is obtained from a retina imaging device using a retina illumination light source having the same wavelength as the wavefront-measurement light source. During image-data transfer from the retina imaging device, aberrations at a second wavelength are measured using another wavefront-measurement light source having the second wavelength. The compensation optical section performs compensation so as to cancel out the measured aberrations. After the compensation, a retinal image is obtained using another retina illumination light source having the same wavelength as the another wavefront-measurement light source. A difference image is obtained from the retinal images, and displayed or stored.
Owner:KK TOPCON
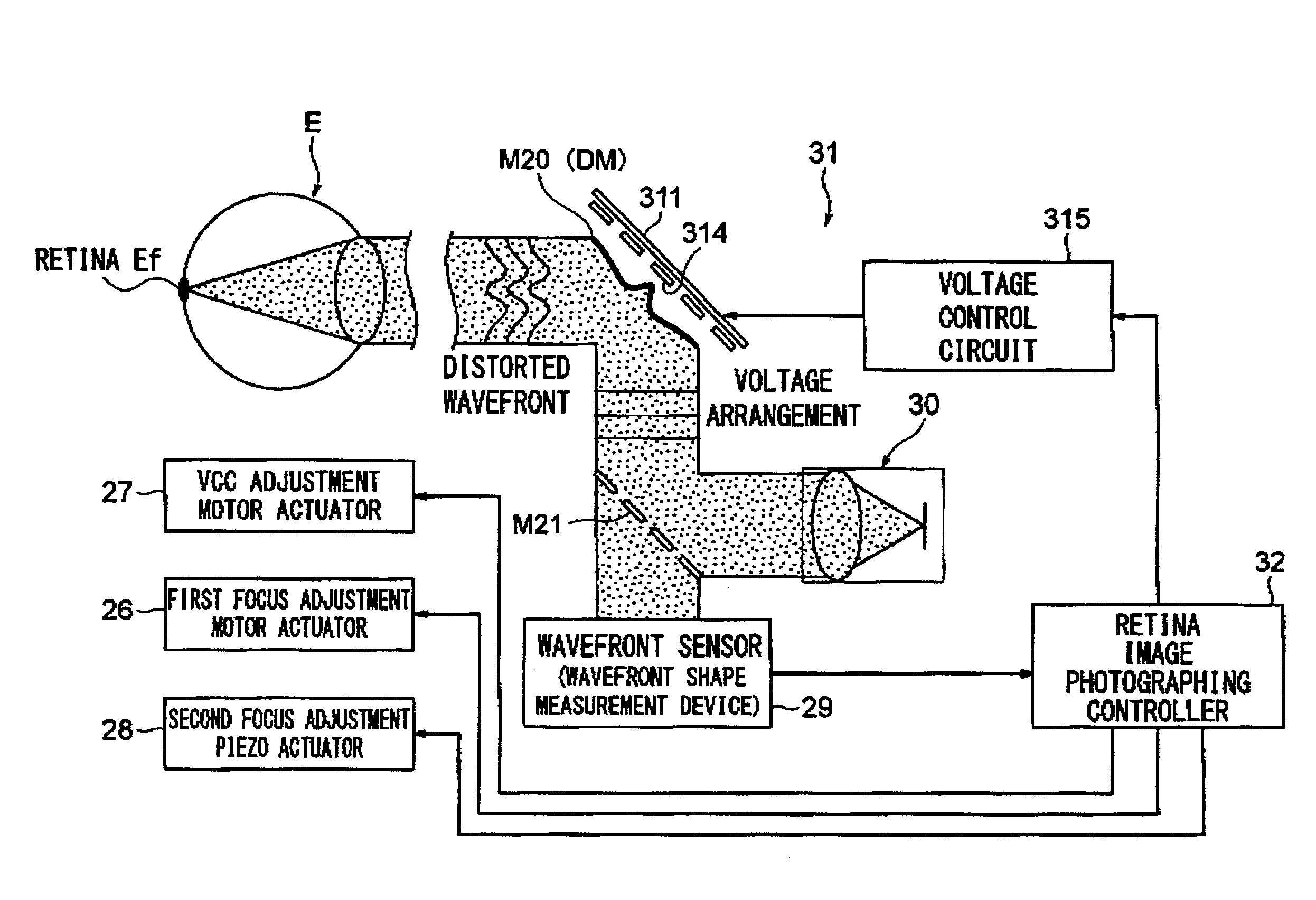
Ophthalmologic apparatus
An ophthalmologic apparatus includes an imaging system that illuminates a retina of an eye, and images the retina of the eye based on reflective luminous flux from the retina, an aberration measurement part that measures optical aberration of the eye, an aberration compensation device disposed in the imaging system to compensate the optical aberration of the eye based on a signal from the aberration measurement part, a first focusing device disposed in an optical path of the imaging system to perform focusing of the image of the retina of the eye according to a refractive property of the eye, and a second focusing device disposed in the optical path of the imaging system to compensate infinitesimal spherical aberration generated by the aberration compensation device after adjustment by the first focusing device.
Owner:KK TOPCON
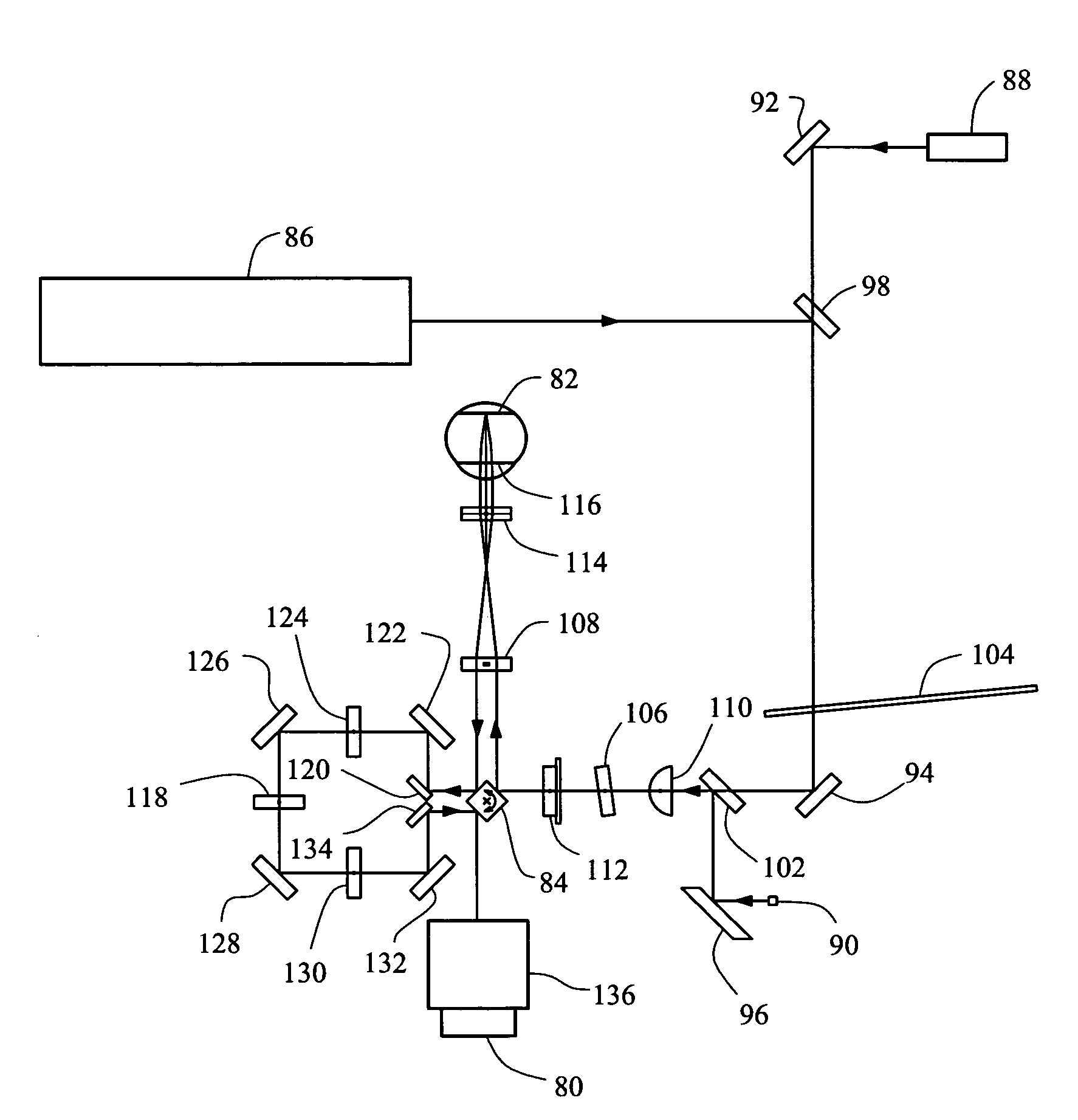
Liquid crystal adaptive aberration correction retinal imaging device with high-efficiency utilization of energy
InactiveCN101797149ALow costWork around sensitivity limitationsOthalmoscopesBeam splitterHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of adaptive optical imaging, and relates to an optical design of high resolution imaging of fundus oculi retina, which is a liquid crystal adaptive aberration correction retinal imaging device with high-efficiency utilization of energy. The imaging device is characterized in that a polarizing beam splitter prism which is normally arranged on a front light path of a liquid crystal corrector is moved to be behind the liquid crystal corrector; a beam splitter with a high transmission-reflection ratio is arranged at the position where the polarizing beam splitter prism is originally positioned; an annular diaphragm is inserted to shield the light vertically entering human eyes, so interference light directly reflected by a front cornea is basically eliminated. The polarizing beam splitter prism is placed corresponding to an e-light polarization direction of the liquid crystal corrector; the corrected e-light is separated from non-corrected o-light; the e-light is allowed to enter an imaging CCD camera in follow-up light paths, and the o-light enters a Hartmann wavefront detector; a controller drives the liquid crystal corrector to perform aberration correction according to wavefront detected by Hartmann to make the imaging in the CCD clear. The imaging device can increase the light energy utilization ratio for imaging and detection by about 1 time, so that the costs of the imaging cameras and detectors are greatly reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
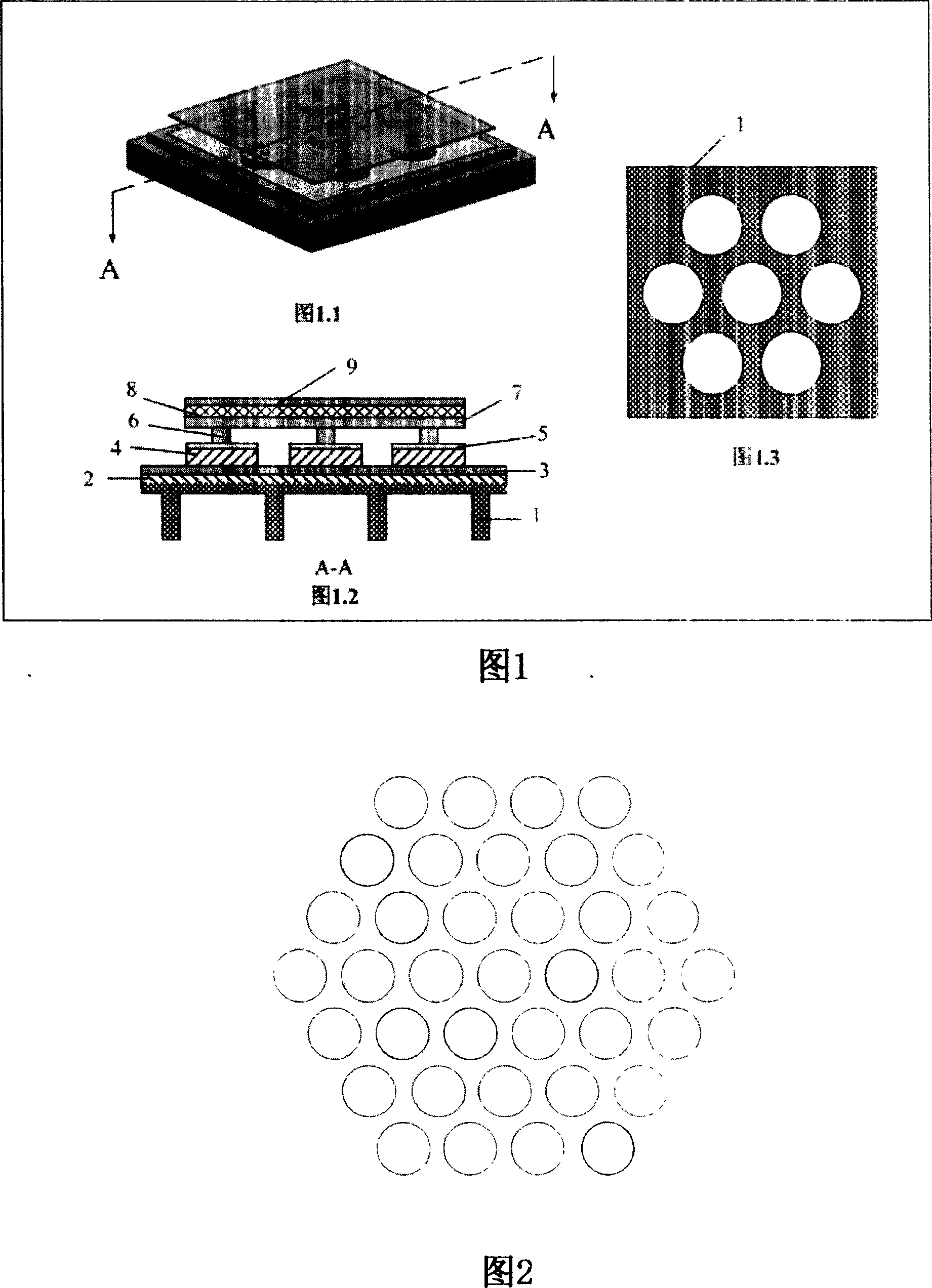
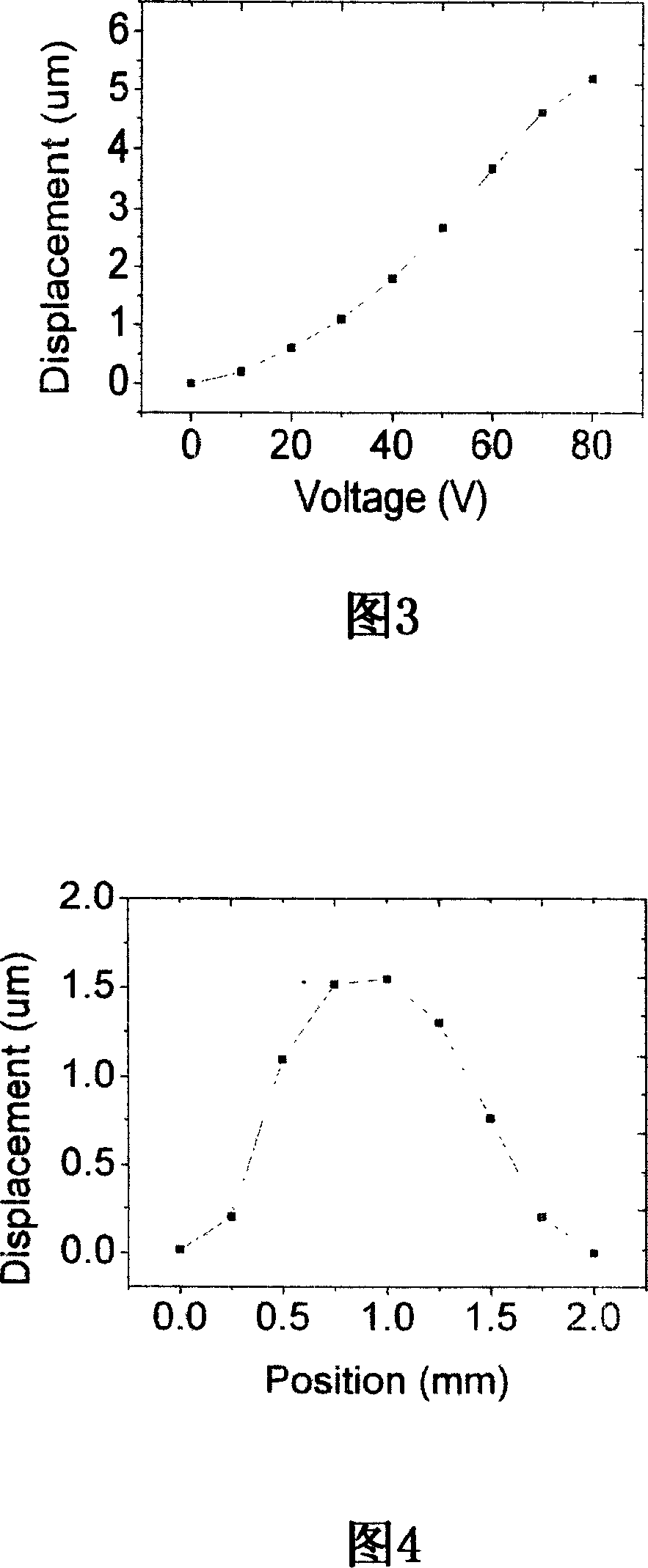
Piezoelectric thick diaphragm driving micro deformable mirror and producing method thereof
InactiveCN101021617AMeet the use requirementsAvoid decoupling control complexityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesEtchingMicro actuator
The invention belongs to a microdeformable mirror and the machining and preparing field thereof, concretely relating to a piezoelectric film drive-based microdeformable mirror and the preparing method thereof. And the mcirodeformable mirror comprises micro actuator array composed of actuating units and mirror surface, where the micro actuator array is of a centrosymmetric regular hexagonal structure and the mirror composed of monocrystalline silicon diaphragm is connected with upper electrodes through photosensitive high polymer boss; the preparing course comprises: preparing silicon substrate piezoelectric ceramic base film, using wet-etching process to etch the silicon substrate piezoelectric ceramic base film, using wet-etching process to etch silicon substrate piezoelectric ceramic thick film shape, preparing upper electrode array on the silicon substrate piezoelectric ceramic thick film array, and preparing connection boss on the upper surface of the upper electrode array and using photosensitive high polymer to fix the mirror surface on the actuator array. And the microdeformable mirror can drive the mirror to generate larger displacement so as to meet the requirements of the fields of astro-observation, amotio imaging, etc; and the preparing method has simple process, low cost and good commercial application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
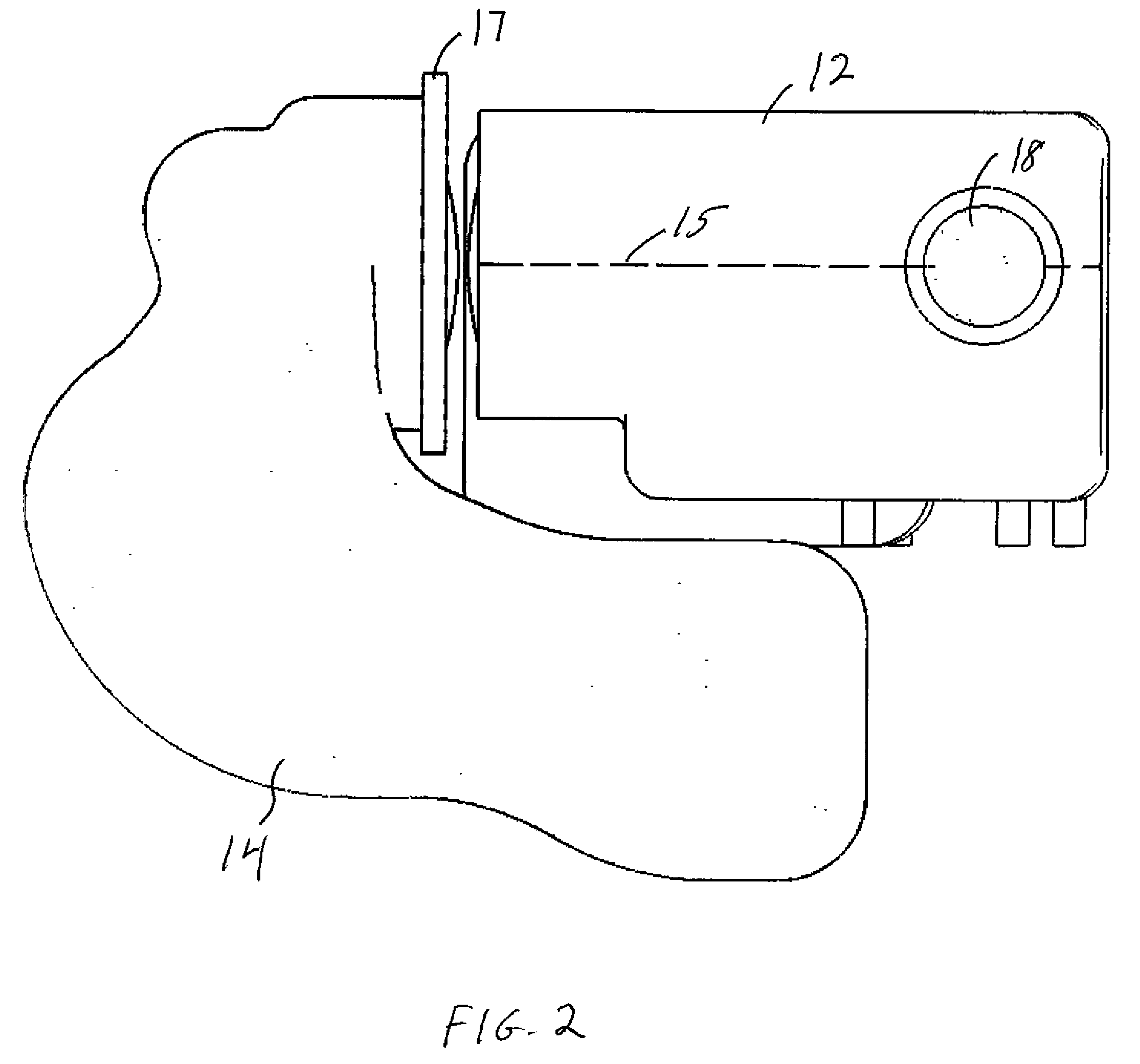
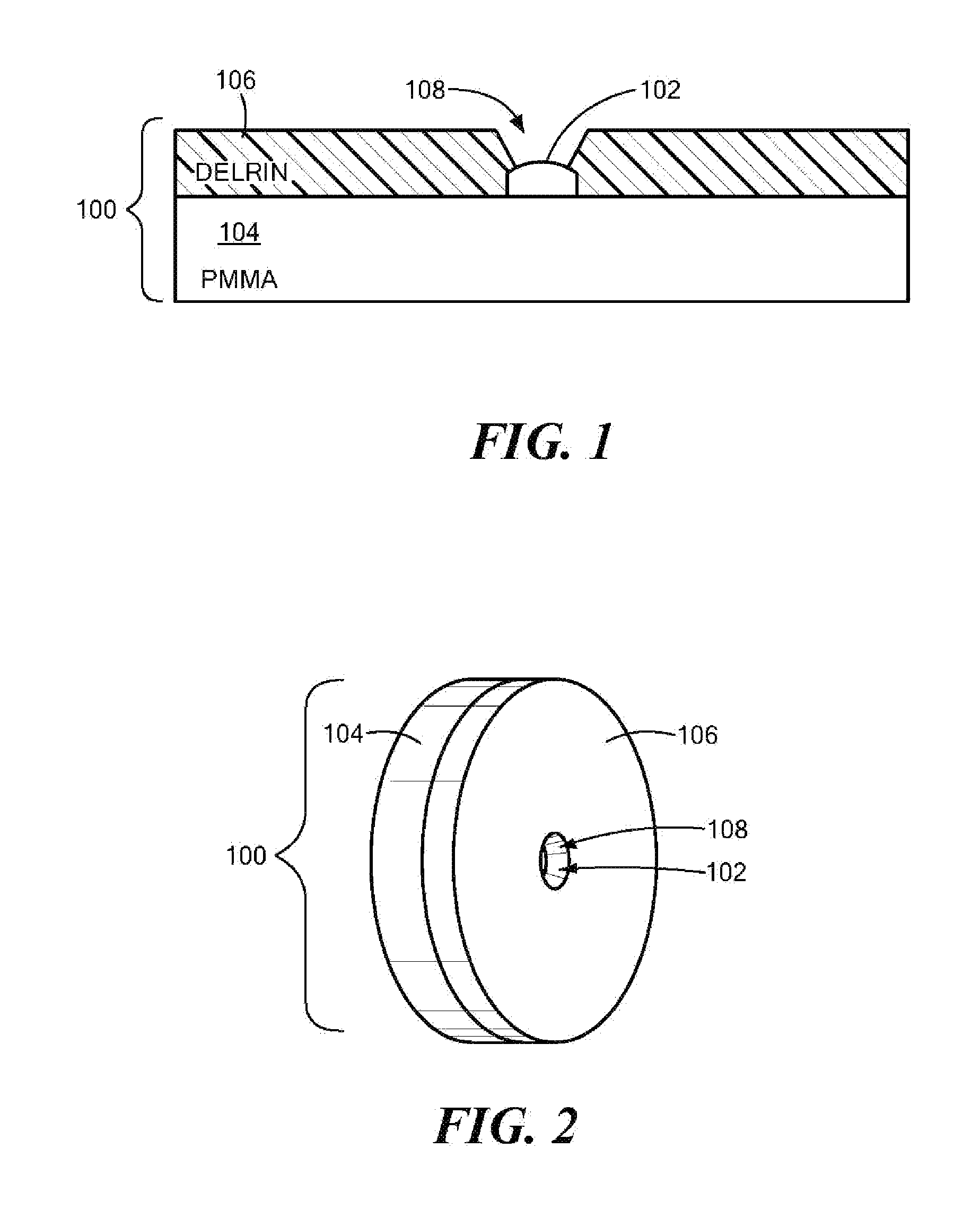
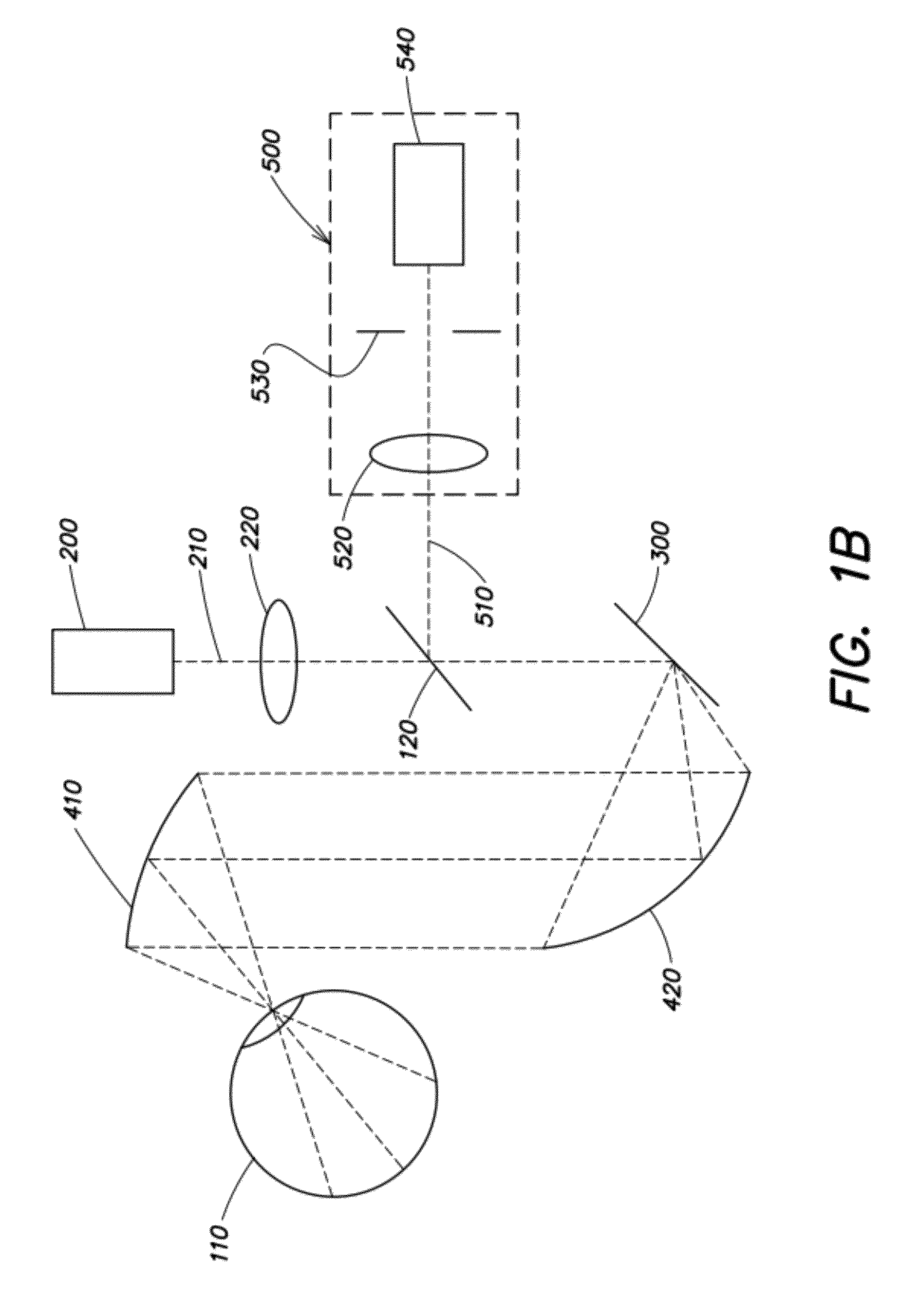
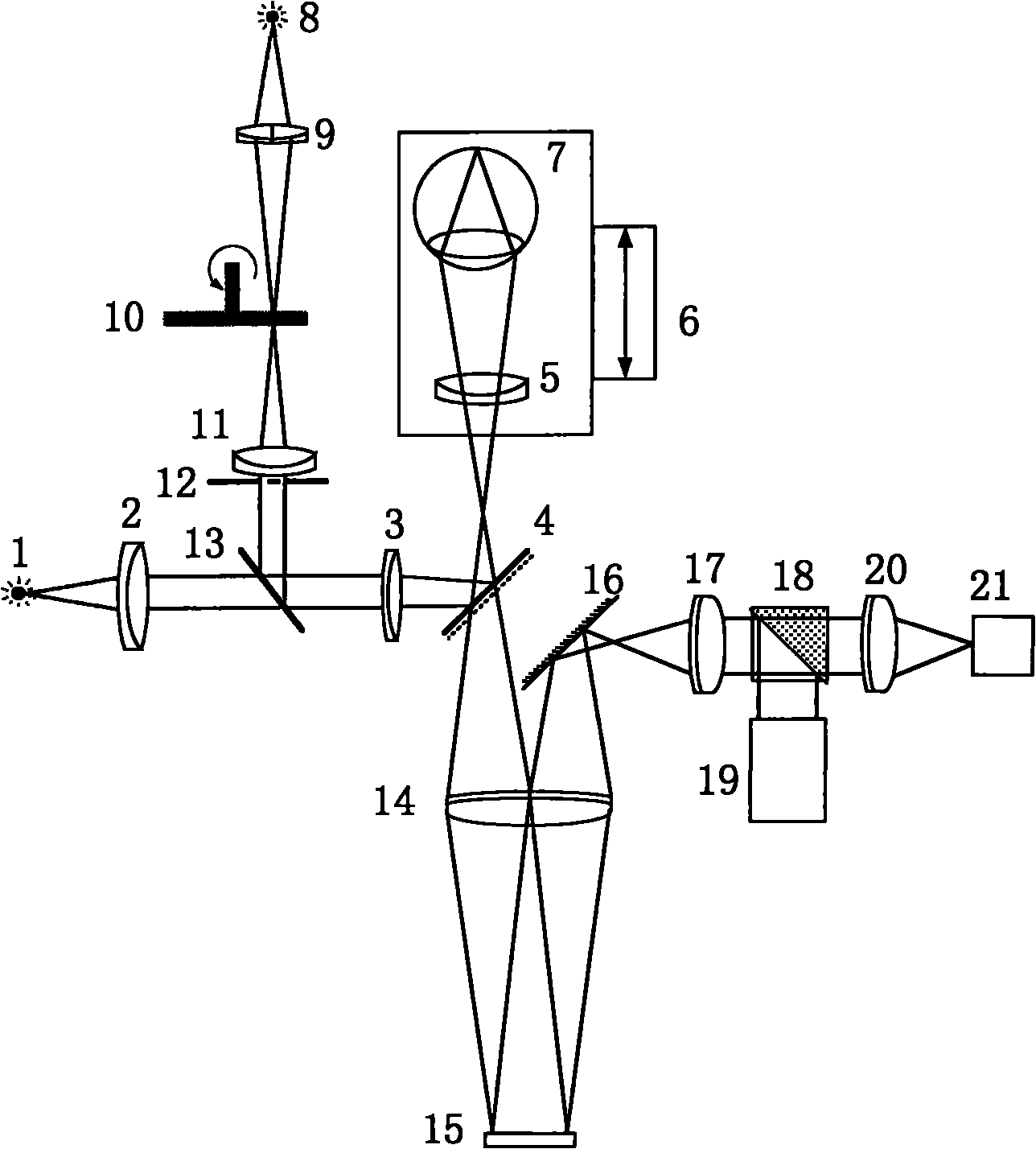
Retinal imaging device
A retinal imaging device and illumination module. The illumination module includes a light source to provide an incident beam along an illumination axis, a condenser lens at a spaced apart distance from the light source for condensing the incident beam and emanating a condensed incident beam, a transparent plate at a spaced apart distance from the condenser lens, wherein the transparent plate comprises a light absorber, at least one projections lens system to focus the condensed incident beam, a shield at a spaced apart distance from the projection lens system to yield a first partially blocked beam to form a comea illumination doughnut, and a perforated mirror comprising a hollow cylinder. A portion of the hollow cylinder protrudes out from a reflecting face of the mirror, forming an elliptical stopper to yield a second partially blocked beam to form a pupil illumination doughnut, enabling reflex-free imaging of the retina.
Owner:REMIDIO INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS PVT
Non-invasive measurement of blood glucose using retinal imaging
InactiveUS20050245796A1Accurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood Glucose MeasurementPhotopigment
An apparatus carries out measurements of blood glucose in a repeatable, non-invasive manner by measurement of the rate of regeneration of retinal visual pigments, such as cone visual pigments. The rate of regeneration of visual pigments is dependent upon the blood glucose concentration, and by measuring the visual pigment regeneration rate, blood glucose concentration can be accurately determined. This apparatus exposes the retina to light of selected wavelengths in selected distributions and subsequently analyzes the reflection (as color or darkness) from a selected portion of the exposed region of the retina, preferably from the fovea.
Owner:FOVIOPTICS INC
Ocular metrology employing spectral wavefront analysis of reflected light
ActiveUS20160135679A1Balanced detectionReduce artefactSpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsMetrologyNear sightedness
Method and systems are presented for analysing a wavefront using a spectral wavefront analyser to extract optical phase and spectral information at a two dimensional array of sampling points across the wavefront, wherein the relative phase information between the sampling points is maintained. Methods and systems are also presented for measuring an eye by reflecting a wavefront of an eye and measuring the wavefront at a plurality of angles to provide a map of the off-axis relative wavefront curvature and aberration of the eye. The phase accuracy between wavelengths and sample points over a beam aperture offered by these methods and systems have a number of ocular applications including corneal and anterior eye tomography, high resolution retinal imaging, and wavefront analysis as a function of probe beam incident angle for determining myopia progression and for designing and testing lenses for correcting myopia.
Owner:CYLITE
Method and apparatus for imaging using polarimetry and matrix based image reconstruction
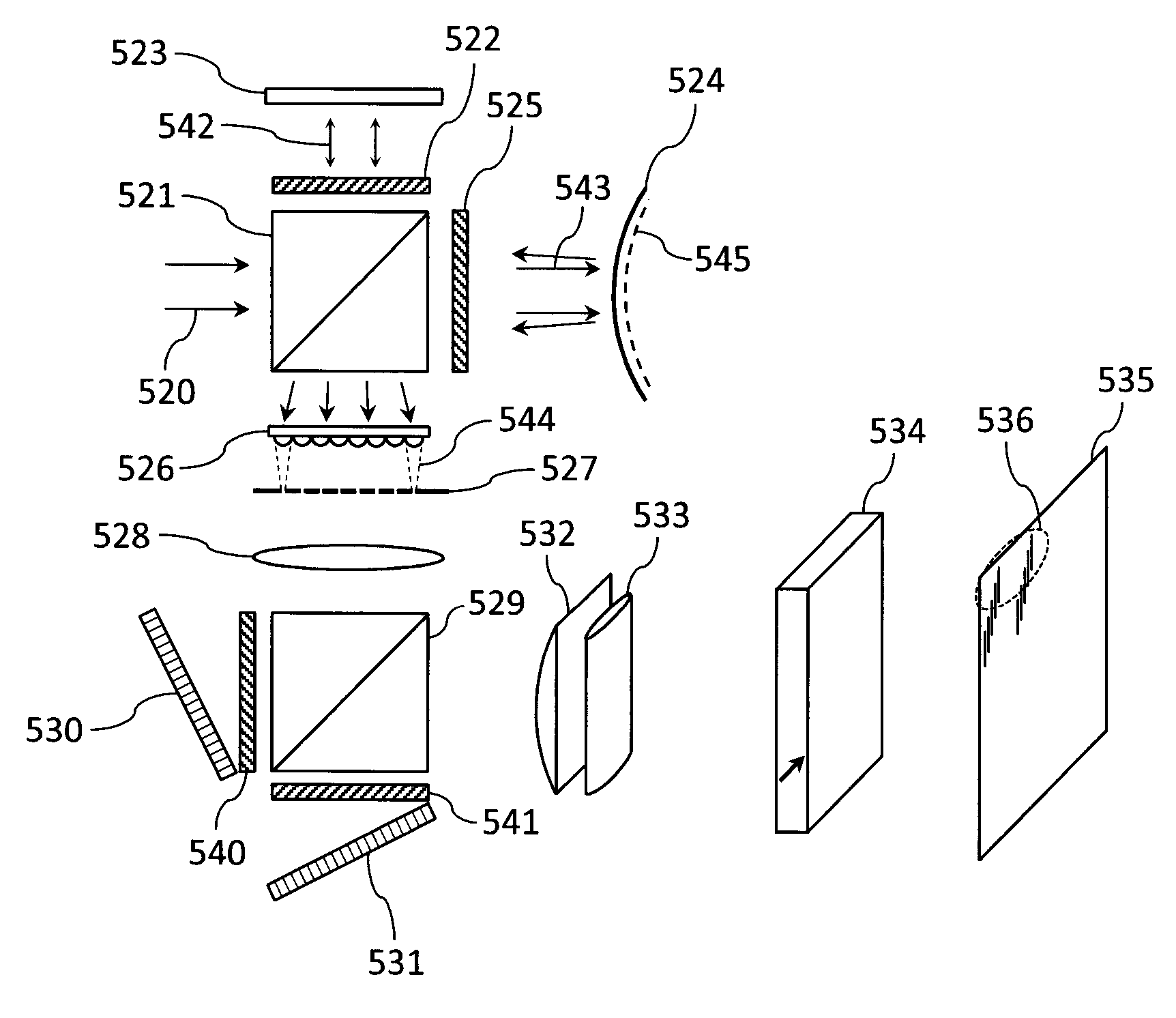
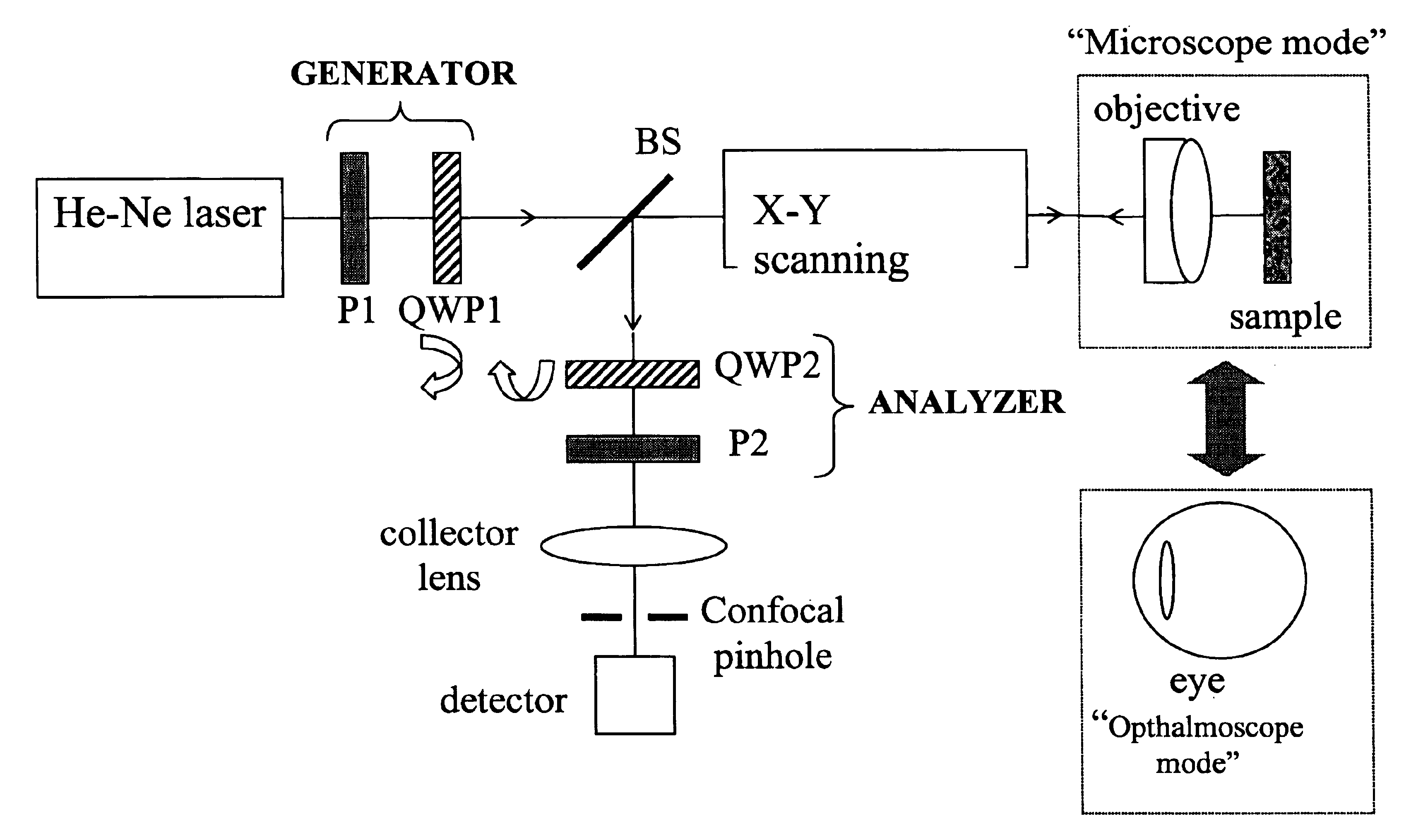
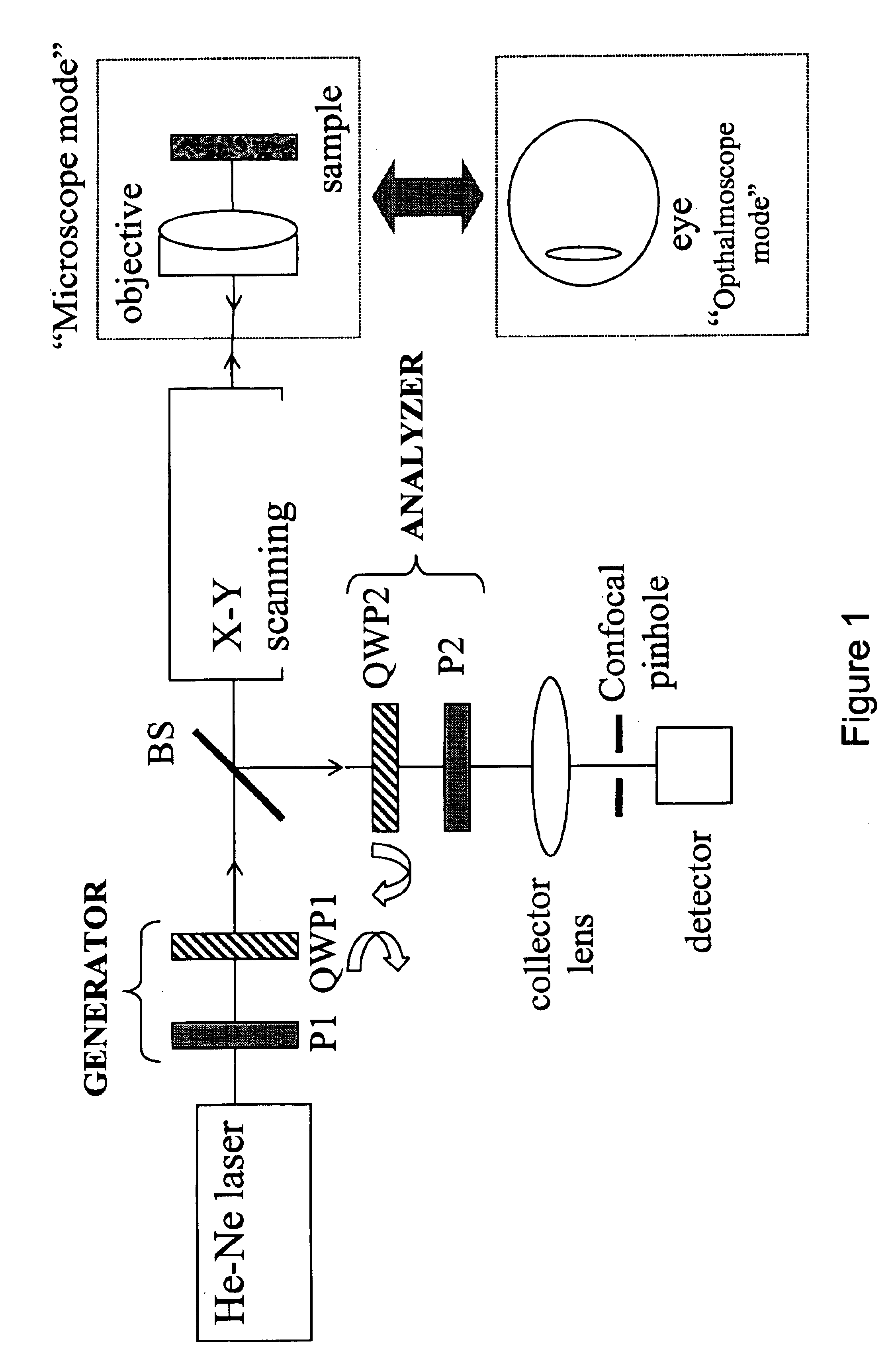
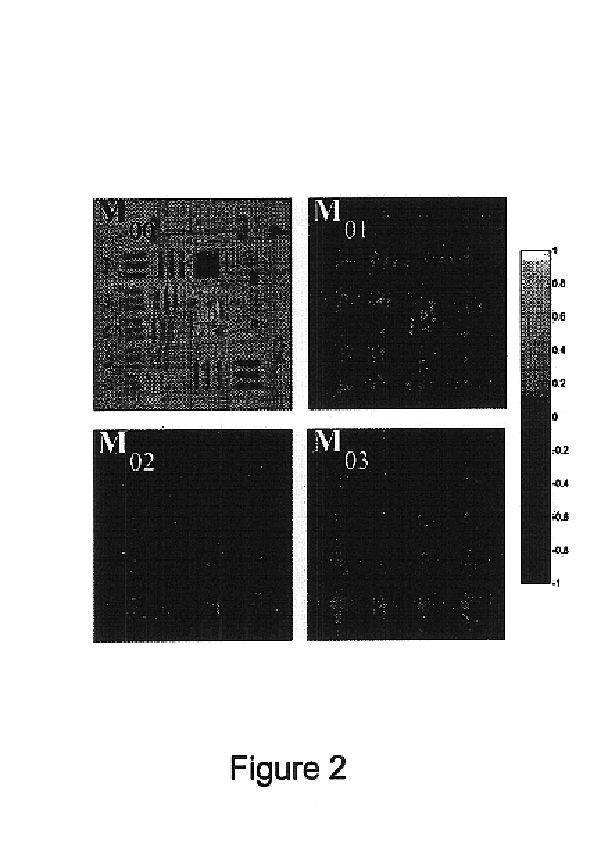
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for improving the signal to noise ratio, the contrast and the resolution in images recorded using an optical imaging system which produces a spatially resolved image. The method is based on the incorporation of a polarimeter into the setup and polarization calculations to produce better images. After calculating the spatially resolved Mueller matrix of a sample, images for incident light with different states of polarization were reconstructed. In a shorter method, only a polarization generator is used and the first row of the Mueller matrix is calculated. In each method, both the best and the worst images were computed. In both reflection and transmission microscope and Macroscope and ophthalmoscope modes, the best images are better than any of the original images recorded. In contrast, the worst images are poorer. This technique is useful in different fields such as confocal microscopy, Macroscopy and retinal imaging.
Owner:GARCIA JUAN MANUEL BUENO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com