Patents
Literature
377 results about "Adaptive optics systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
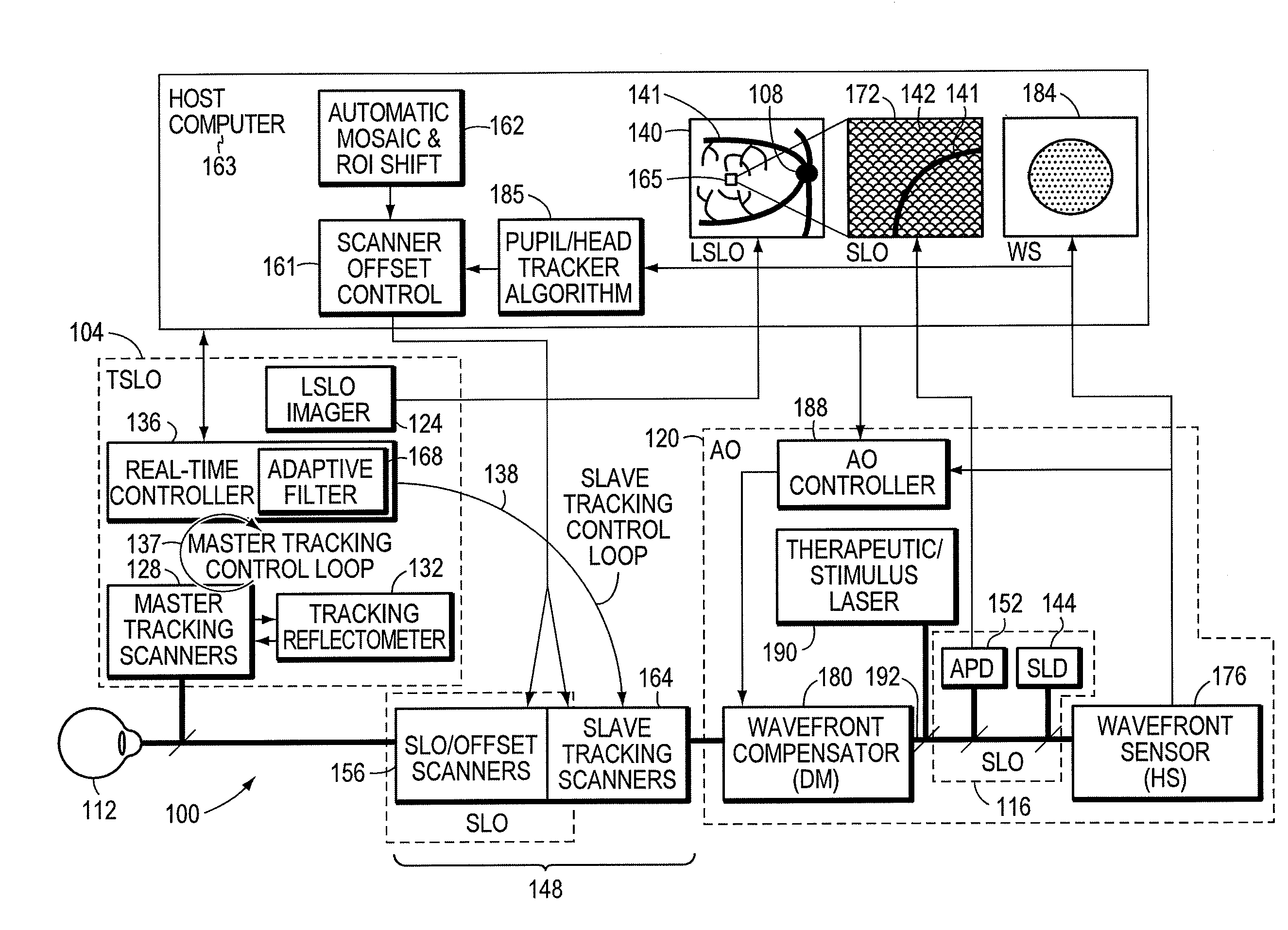
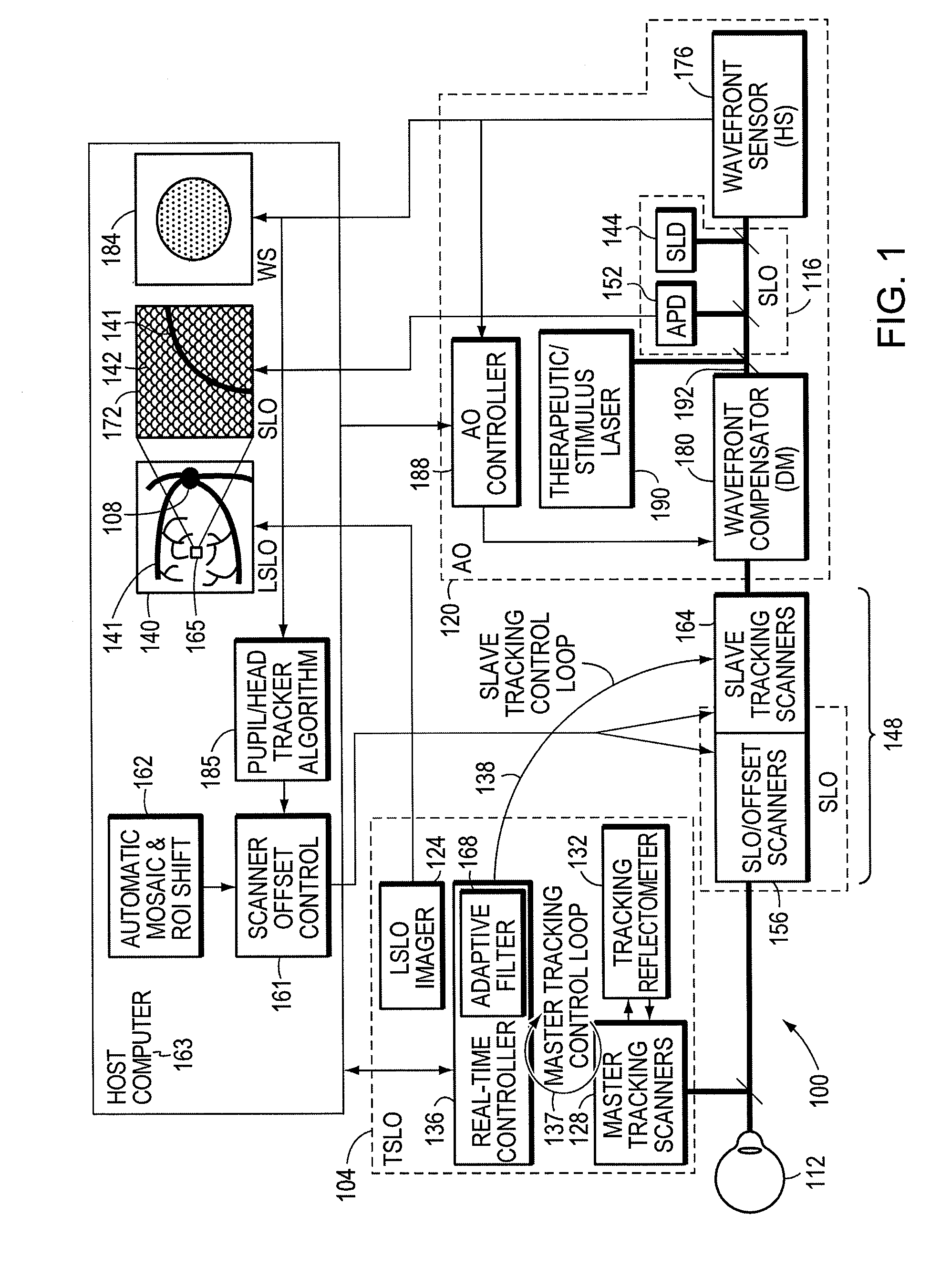
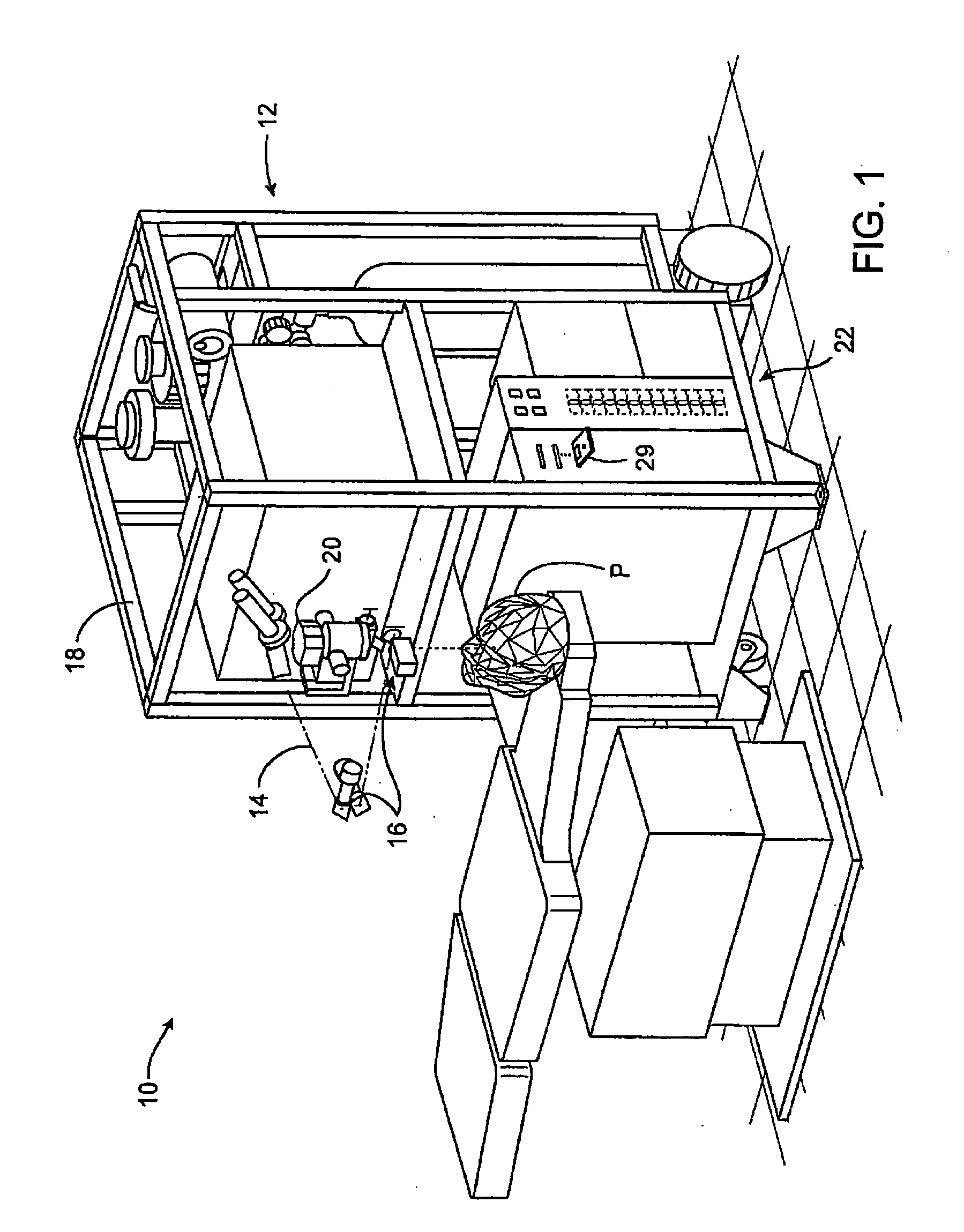
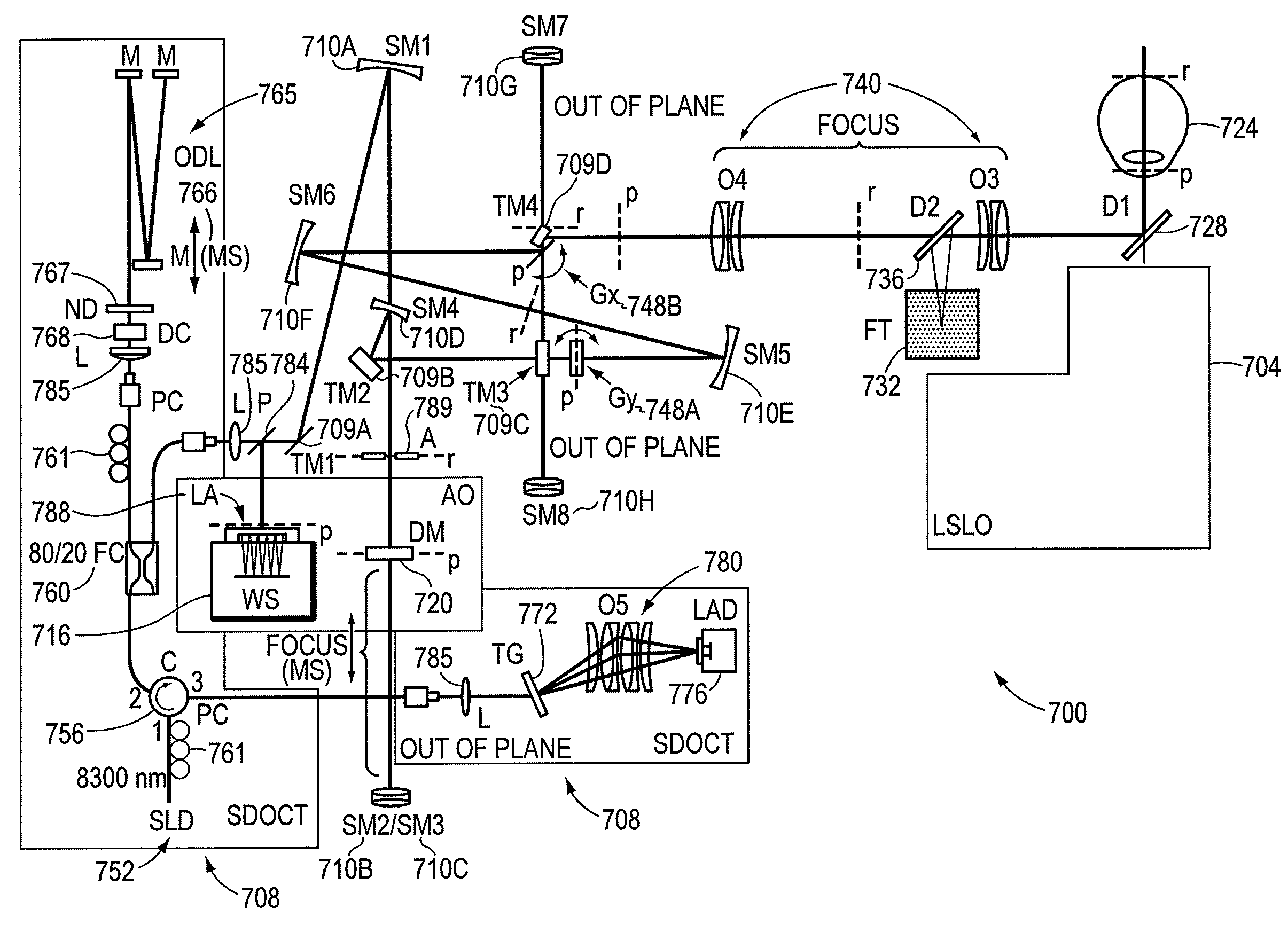
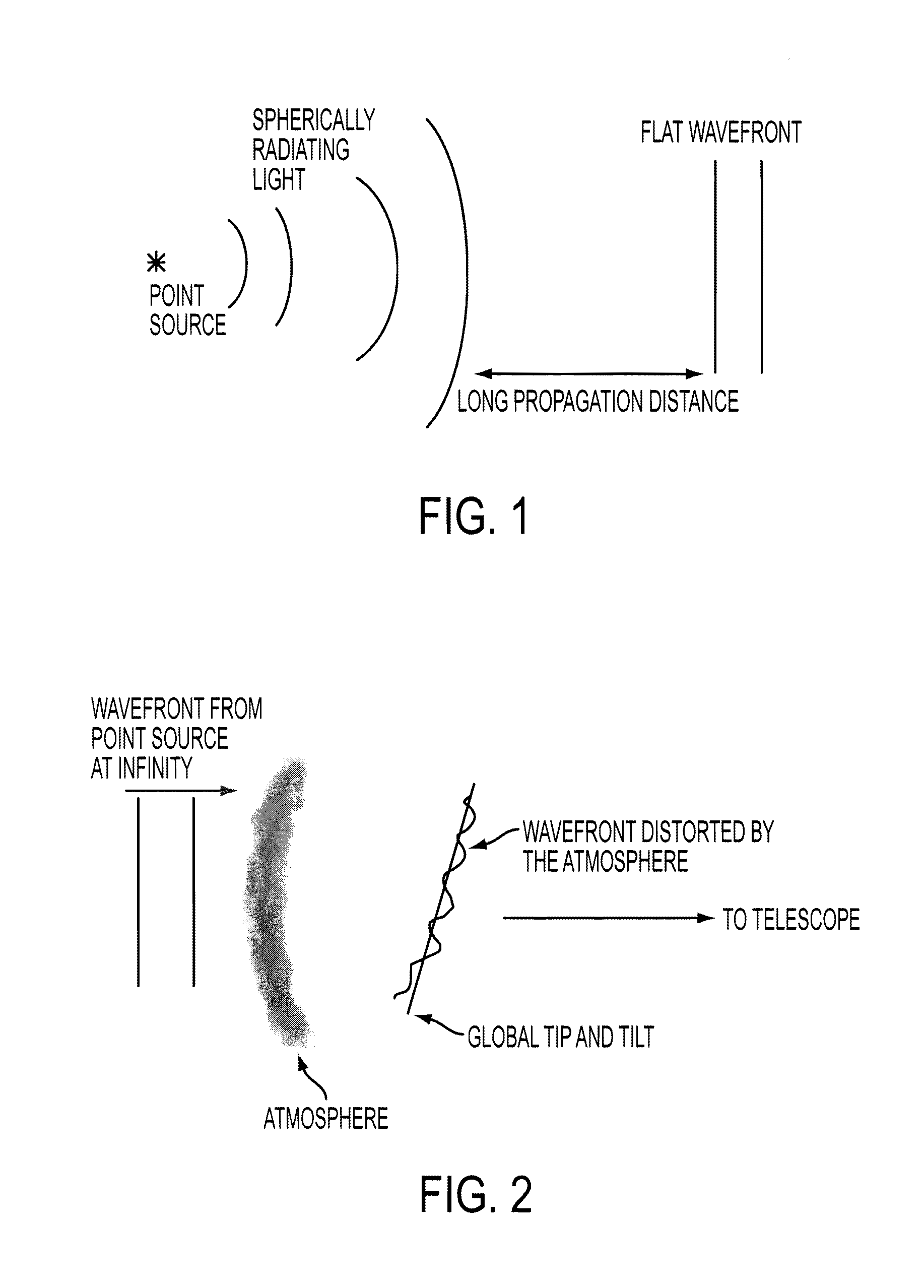
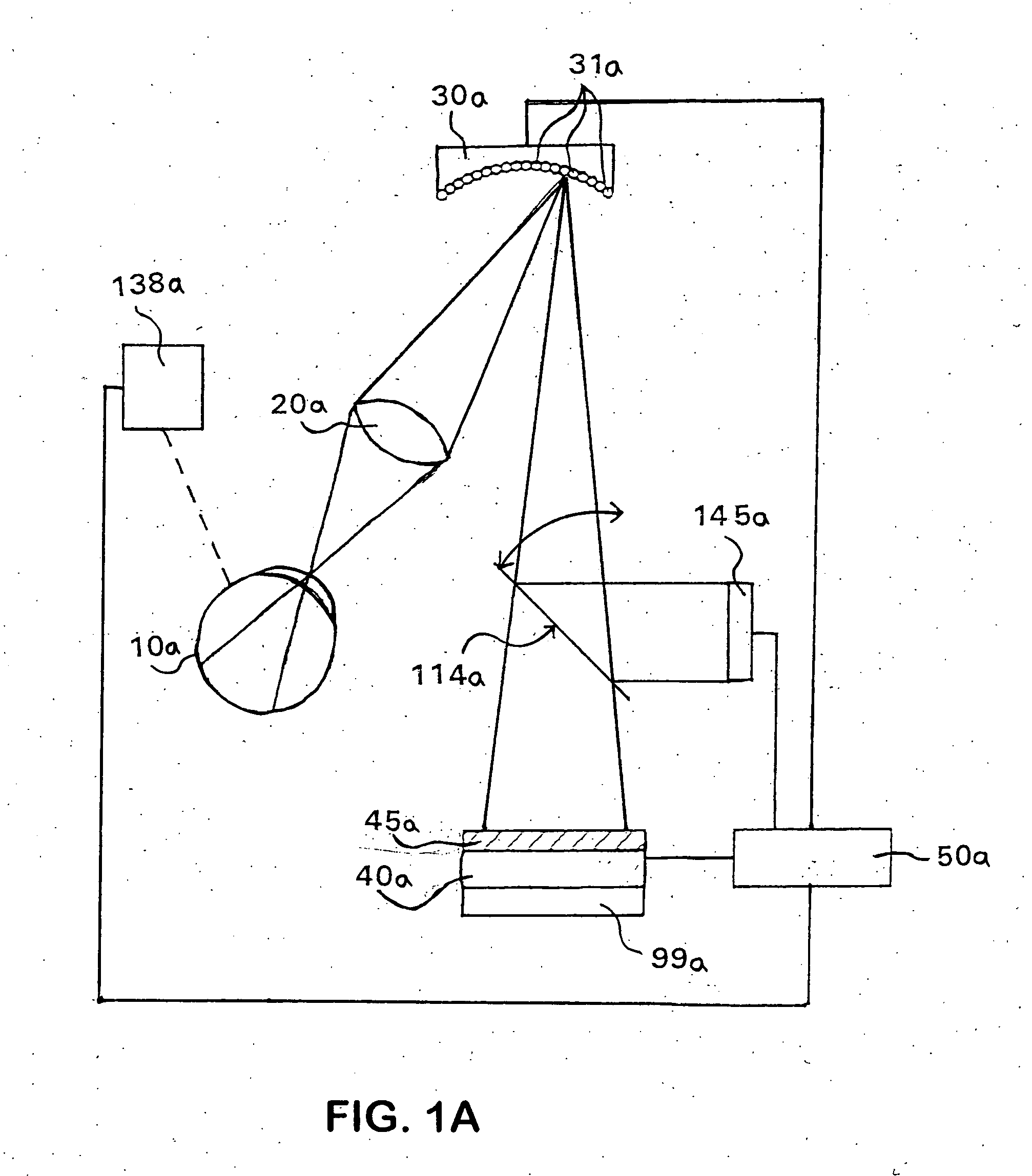
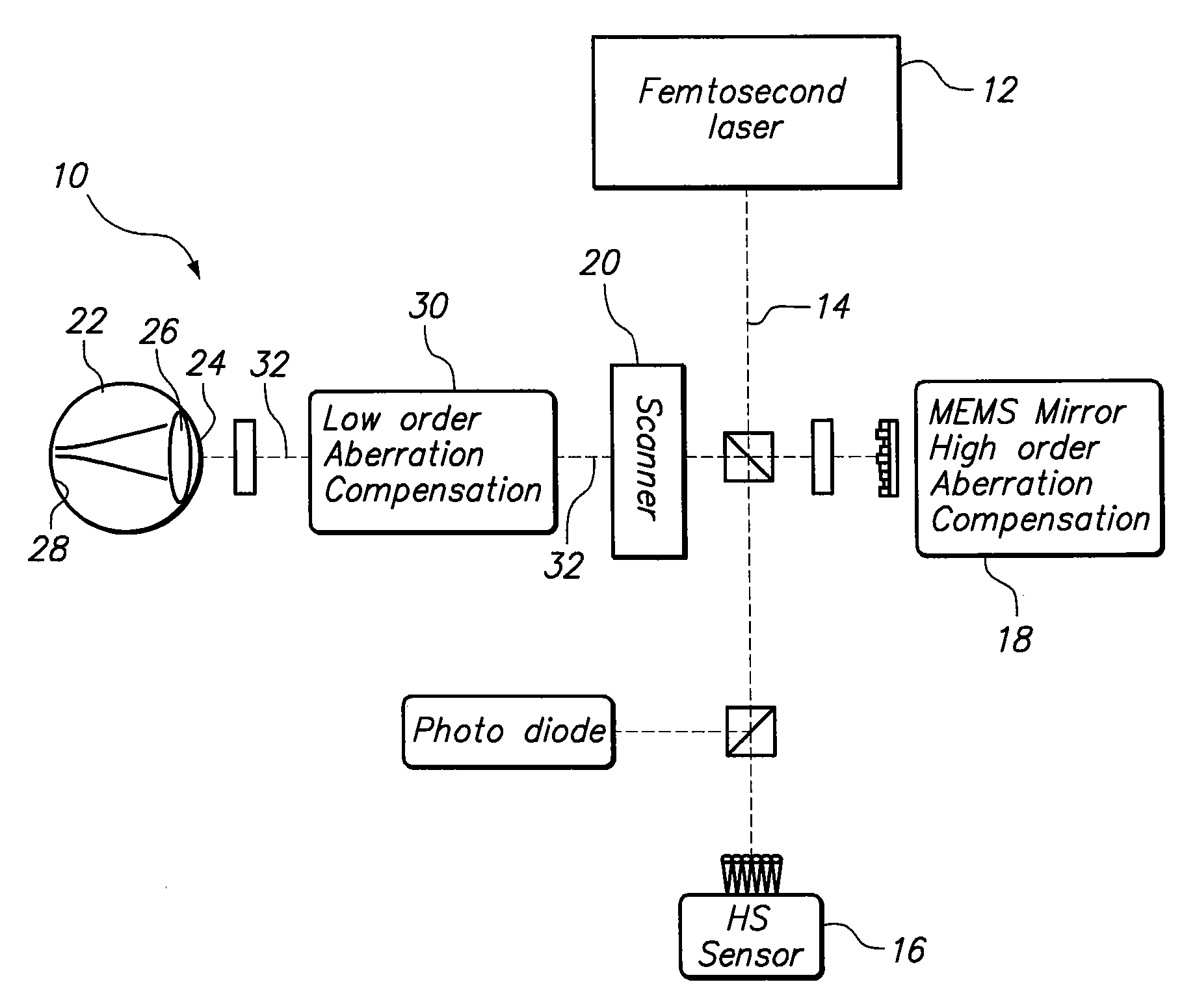
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS20070252951A1Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansRetinal imagingLight beam
A system provides an optical image of an object. A first module tracks a reference feature of the object. A second module includes a source for an imaging beam, a scanning device to move the imaging beam along a portion of the object and a detection device receives a signal associated with an image of the portion of the object. The first module controls the position of the imaging beam relative to the reference feature to correct for the motion of the object. A third module detects a distortion of the object and compensates for the distortion.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Correction of presbyopia using adaptive optics and associated methods
Devices, systems, and methods measure, diagnose, and / or treat one or both eyes of a patient. Adaptive optics systems (such as those having a deformable mirror) may be configured to an aspherical or multi-spherical presbyopia-mitigating prescriptive shape to allow objective and / or subjective measurements of a candidate prescription. A plurality of viewing distances allow subjective and / or objective evaluations of performance using a light spot or a test viewing image. Measurements of aberrations at selected viewing conditions (including distances and / or brightness) with correlating pupil sizes may also be provided.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Multidirectional selective plane illumination microscopy
ActiveUS20110115895A1Improve imagingColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsWavefrontMicroscope
A method and device for multi-directional selective plane illumination microscopy is provided. A detector focal plane is alternately illuminated with at least two counter-propagating, coplanar light sheets, and an image of a specimen cross-section positioned in the focal plane is detected while only one light sheet illuminates the specimen. The wavefront of the illumination beams may be deformed with adaptive optics using feedback from light transmitted through the specimen. Multiple images of the specimen cross-section may be detected at different times and specimen positions and orientations to produce multi-view image stacks which may be processed using image fusion to produce a reconstructed image representation of the specimen. Additionally, the direction of propagation of the alternating light sheets may be pivoted in the focal plane while detecting the image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
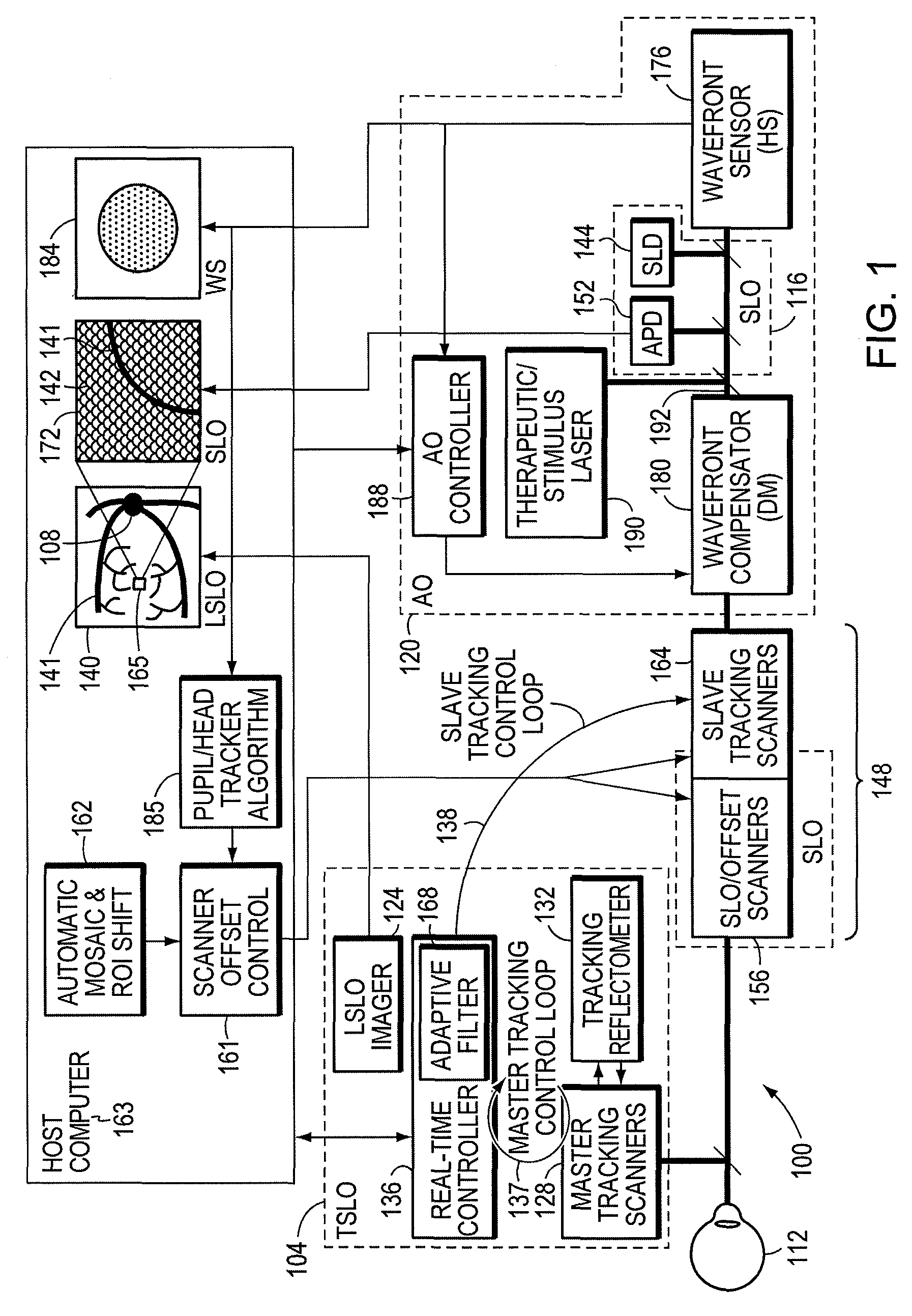
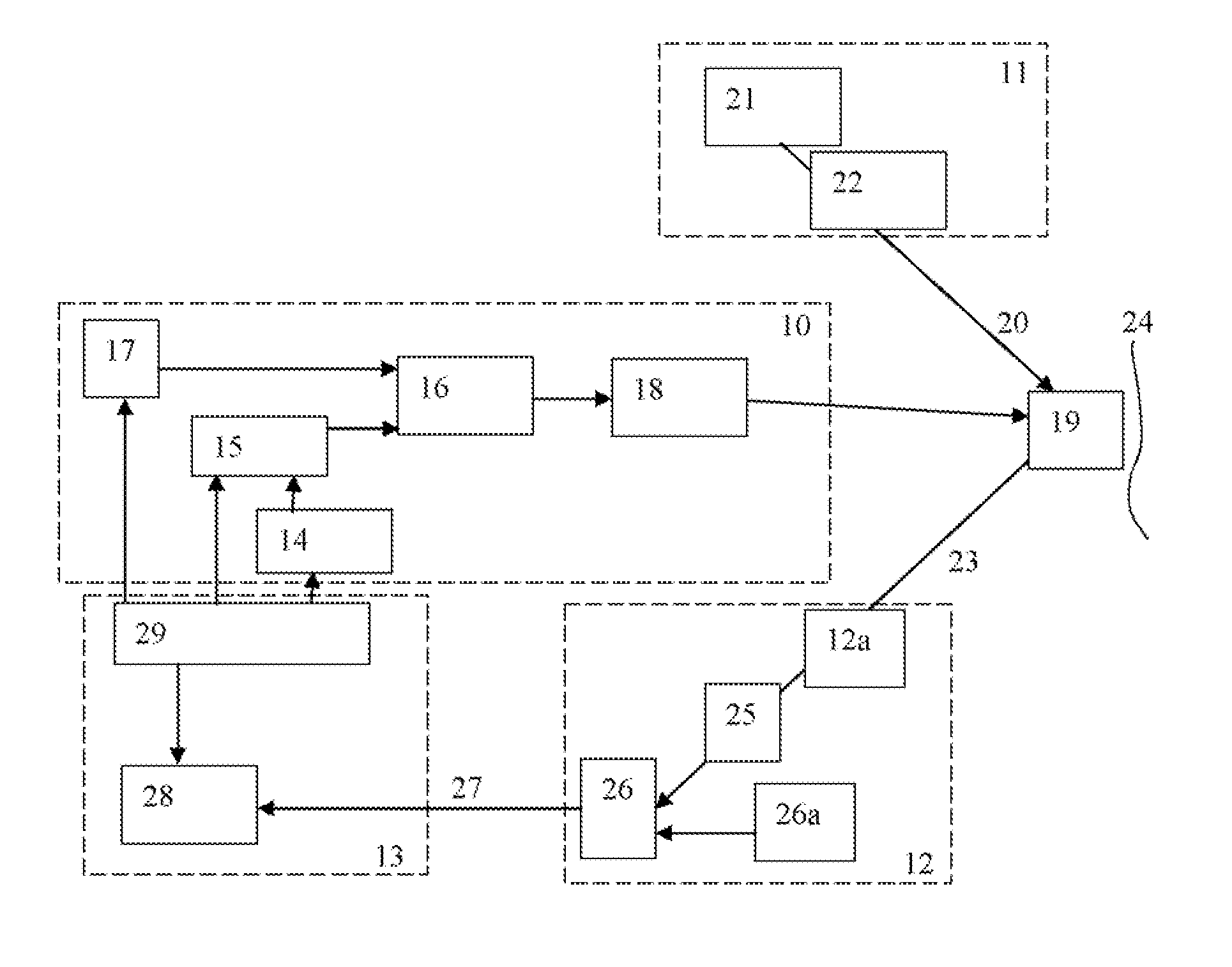
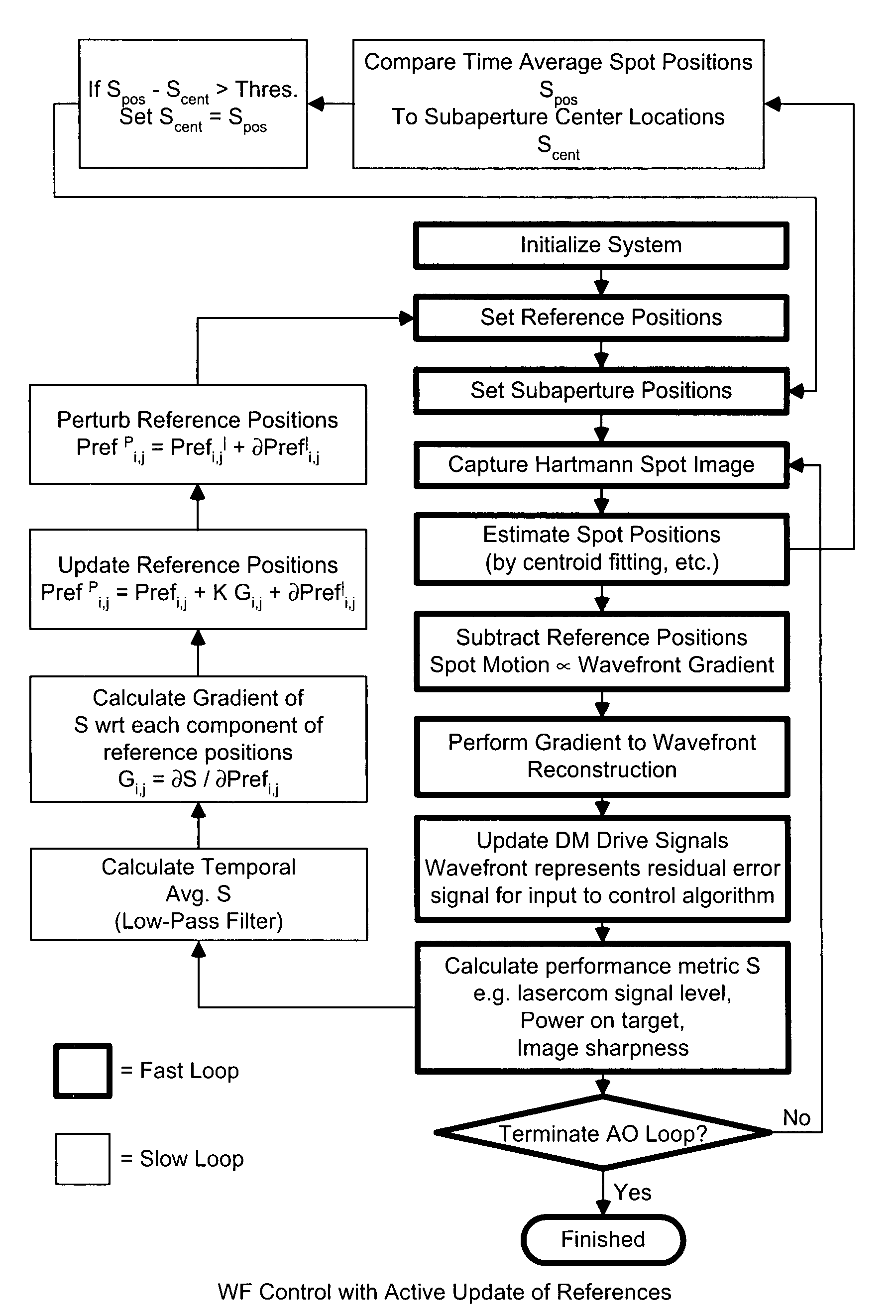
Wavefront sensing system employing active updating of reference positions and subaperture locations on wavefront sensor
ActiveUS20060024061A1Improve the situationSmall sizePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorCommunications system
A free-space adaptive optical laser communication system having signal transmission and reception channels at all terminals in the communication system, wherein wavefront sensing (WFS) and wavefront correction mechanisms are employed along signal transmission and reception channels of all terminals in the communication system (i.e. adaptive optics) to improve the condition of the laser beam at the receiver (i.e. reduce the size of the spot a the detector plane). in the illustrative embodiment, the WFS mechanisms employ a novel WFS control process, in which active updating of reference positions and subaperture locations on the wavefront sensor. These WFS mechanism can be used in diverse application environments, including but not limited to FSO laser communication systems.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Optical mapping apparatus
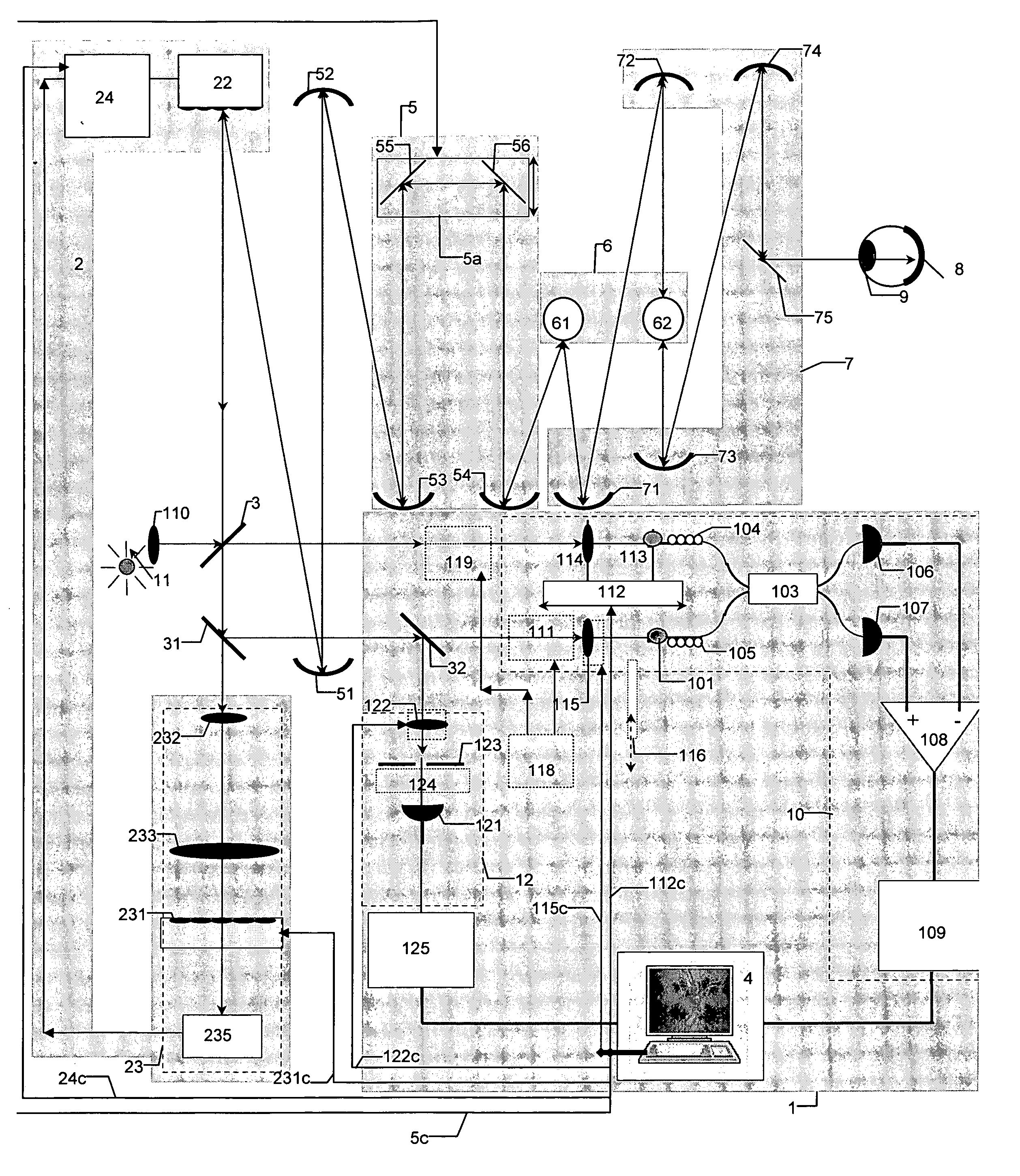
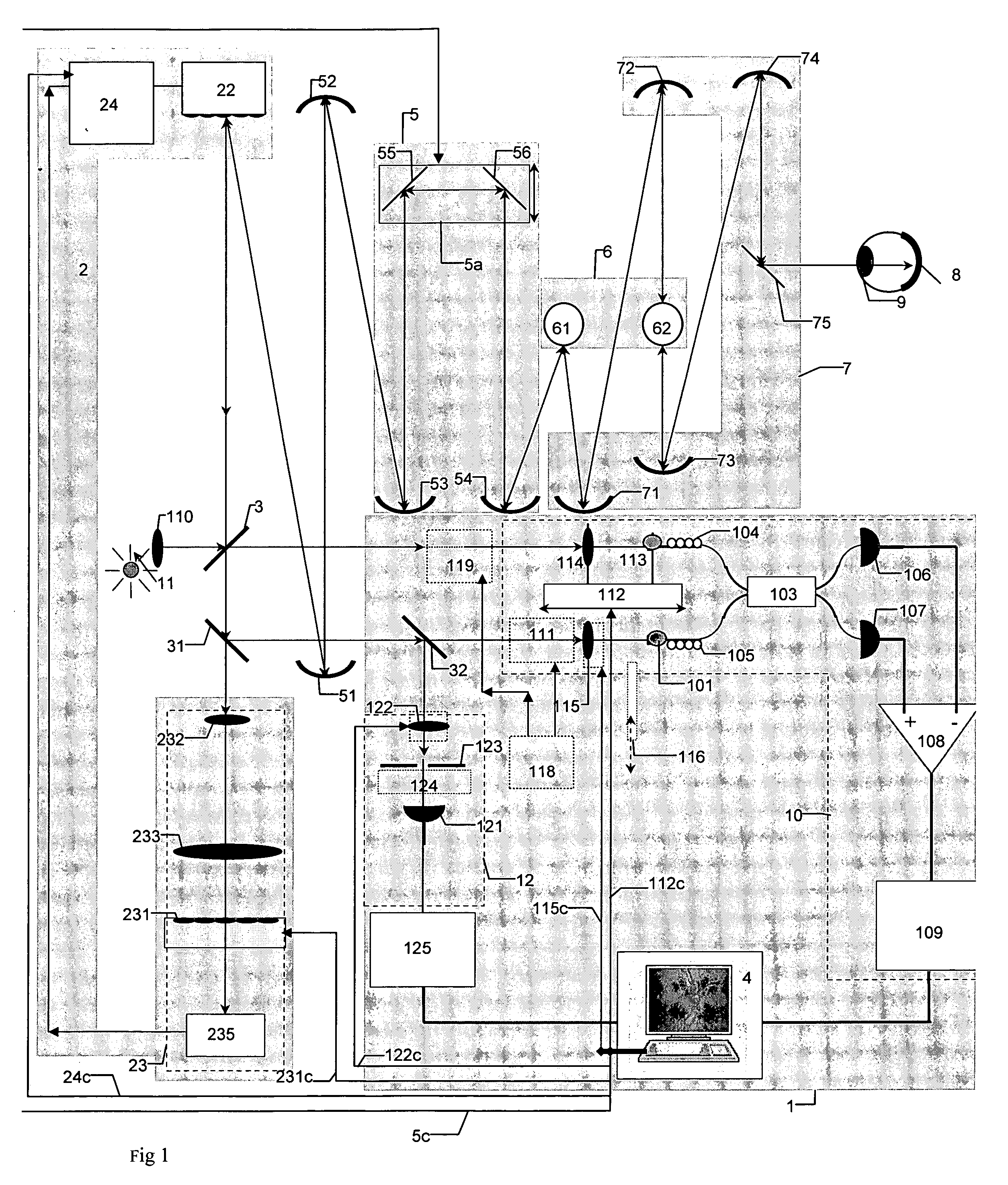
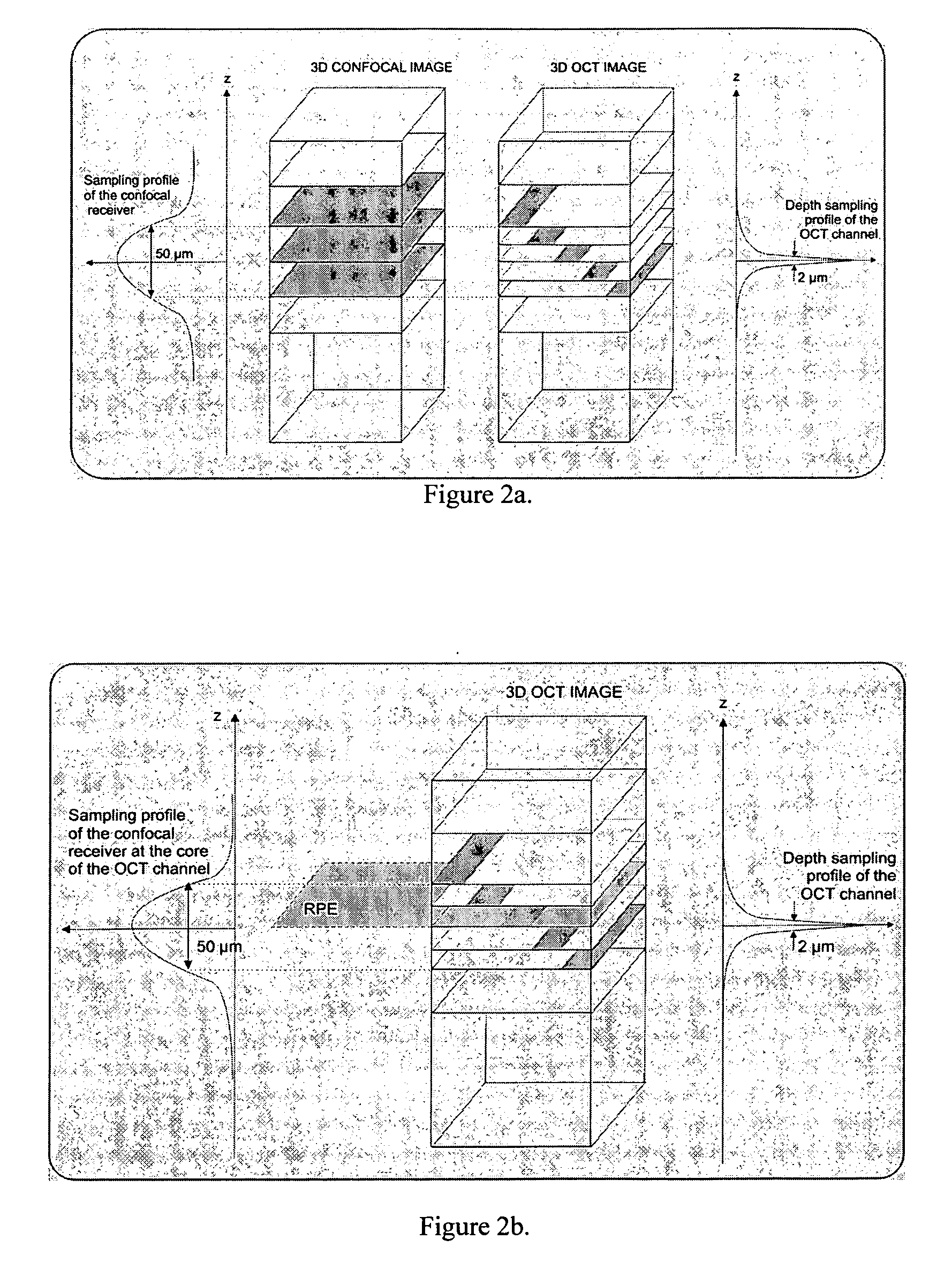
InactiveUS20070046948A1Easy to useHigh depth resolutionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesOptical mappingTomography
Optical mapping apparatus for imaging an object, comprising an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including an OCT source, an OCT reference path leading from the OCT source to an OCT receiver, an OCT object path leading from the object to the OCT coupler, an OCT depth scanner adapted to alter at least one of the OCT reference path and the OCT receiver path. A confocal system is provided including a confocal optical receiver a confocal path leading from the object to the confocal optical receiver via a confocal input aperture. An adaptive optics (AO) system is provided to correct optical aberrations in the OCT object path and the confocal path.
Owner:KENT UNIVERITY OF +1
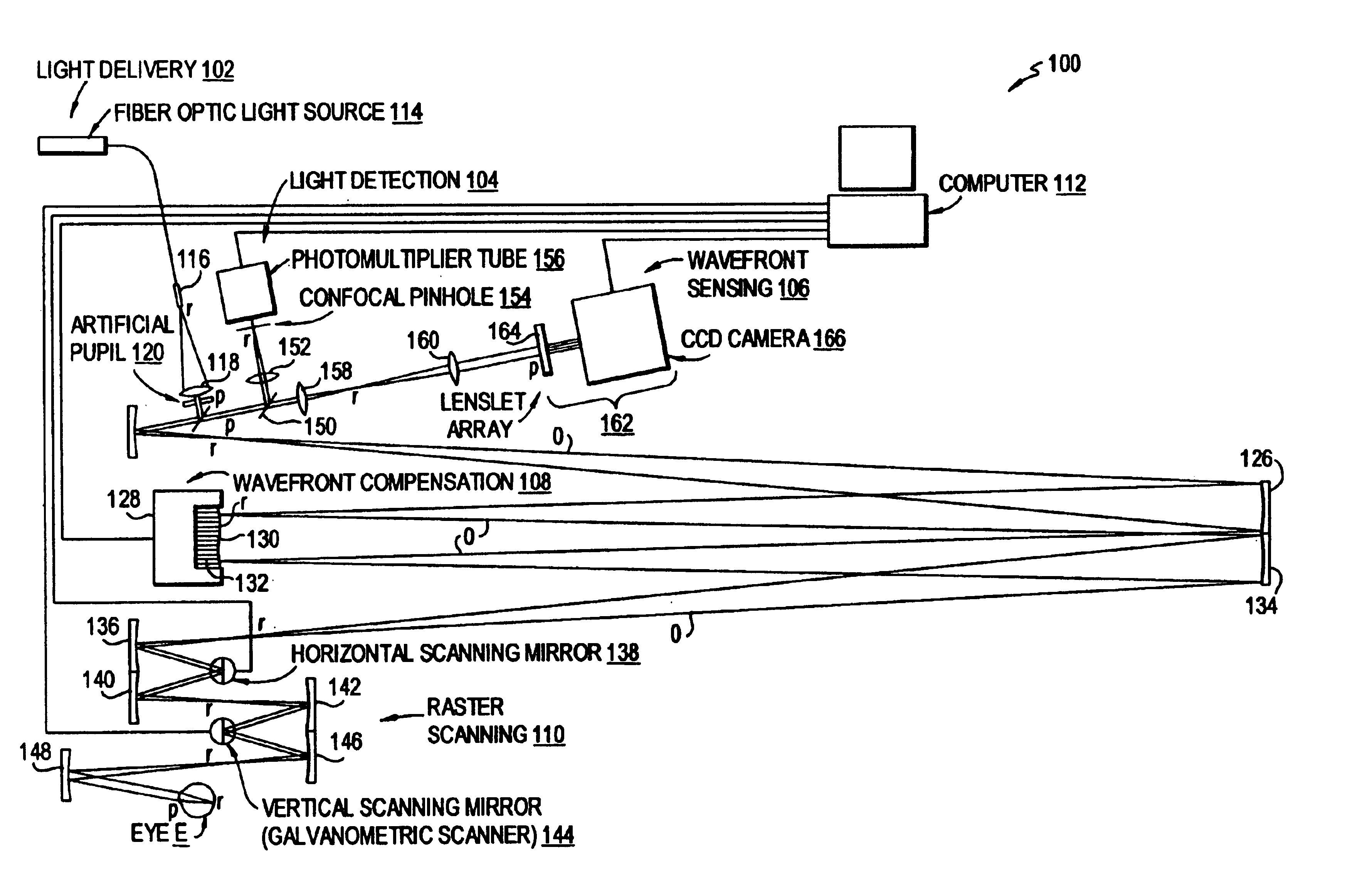
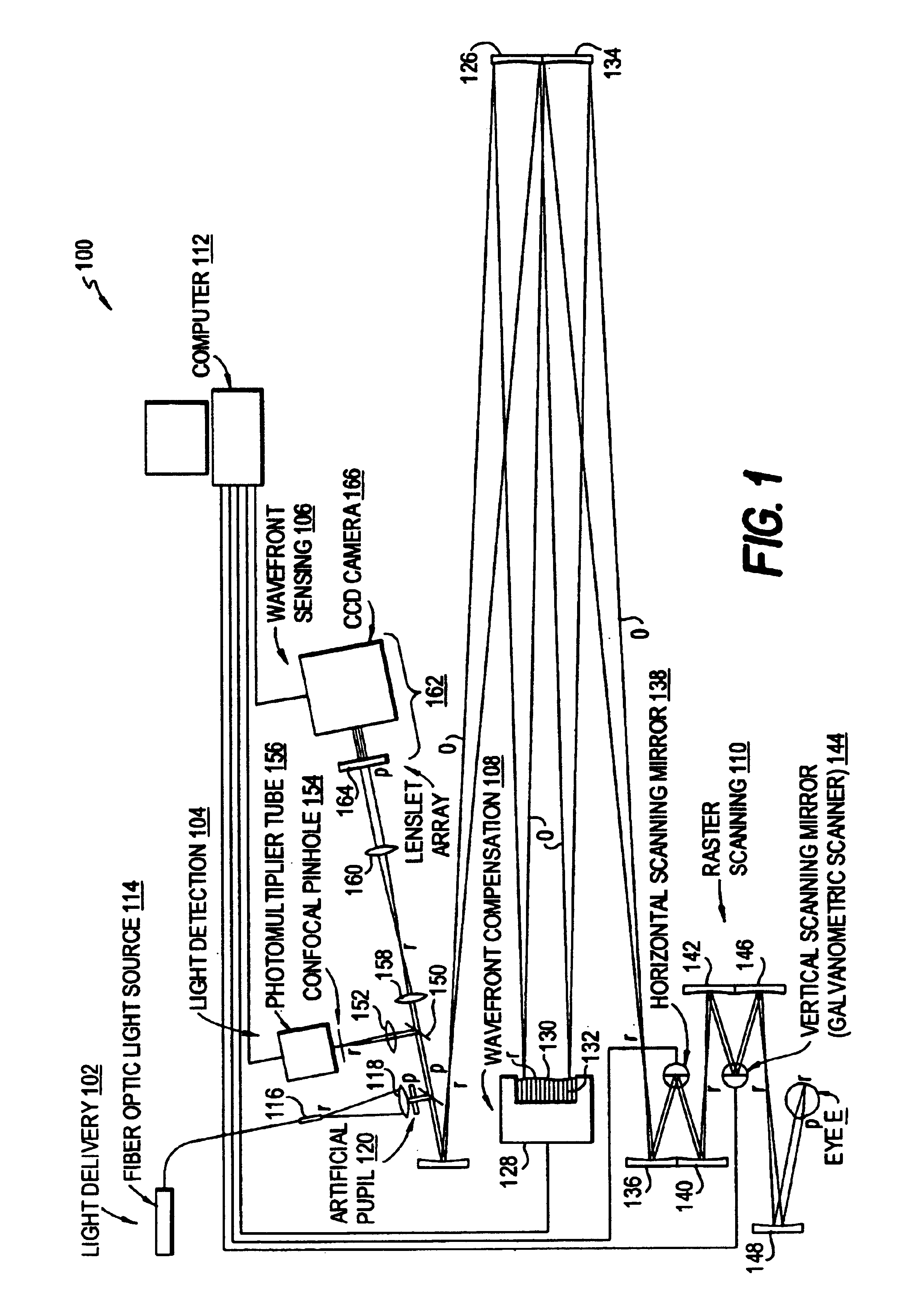
Method and apparatus for using adaptive optics in a scanning laser ophthalmoscope
InactiveUS6890076B2Efficient and effective implementationImprove abilitiesOptical measurementsOthalmoscopesScanning laser ophthalmoscopeEyewear
A scanning laser ophthalmoscope incorporates adaptive optics to compensate for wavefront aberrations in the eye. Light from a light source is scanned onto the retina. Light reflected from the retina is detected for imaging and is also used for wavefront sensing. The sensed wavefront aberrations are used to control an adaptive optic device, such as a deformable mirror, disposed in the path of the light from the source in order to compensate for the aberrations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
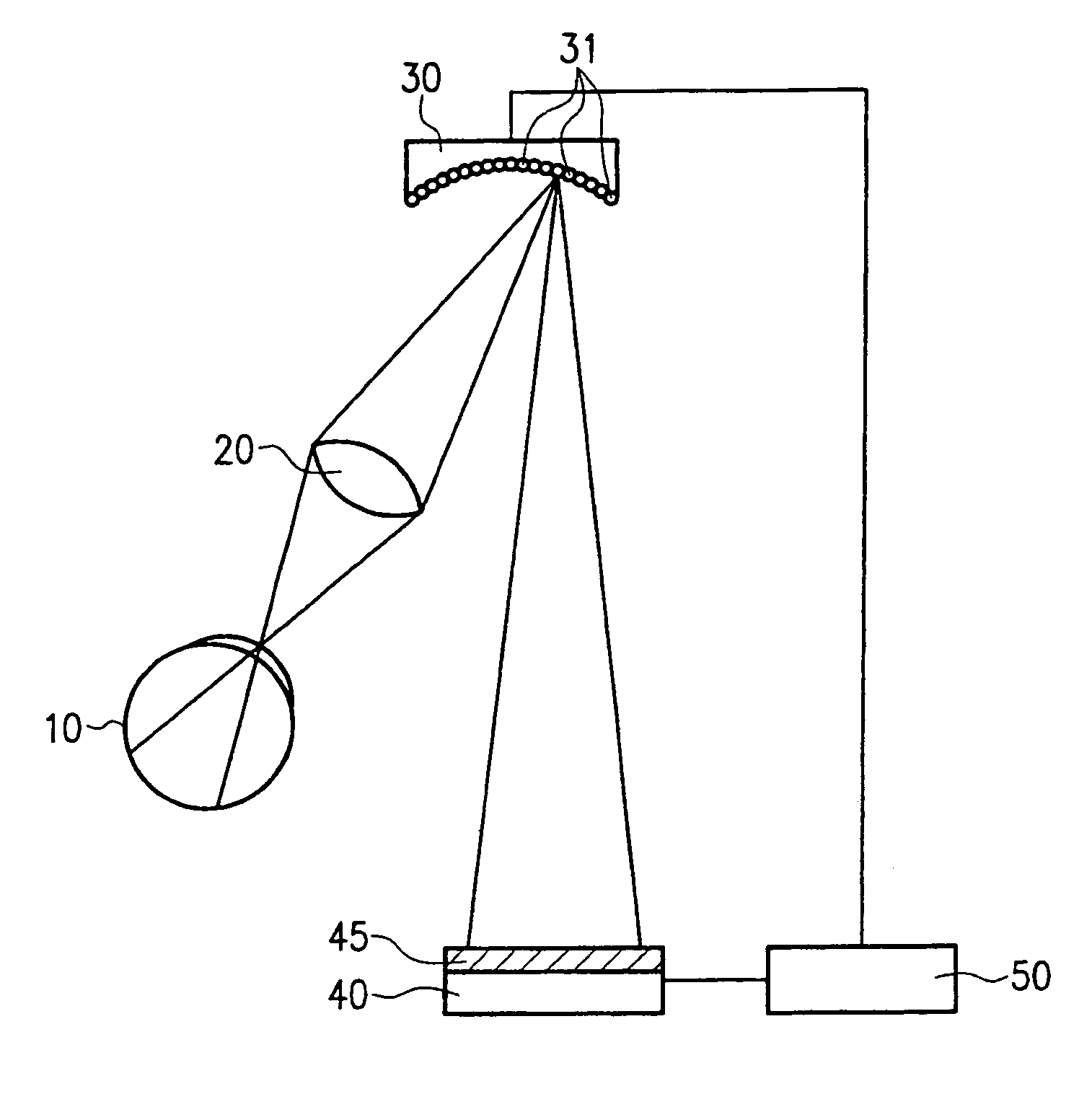
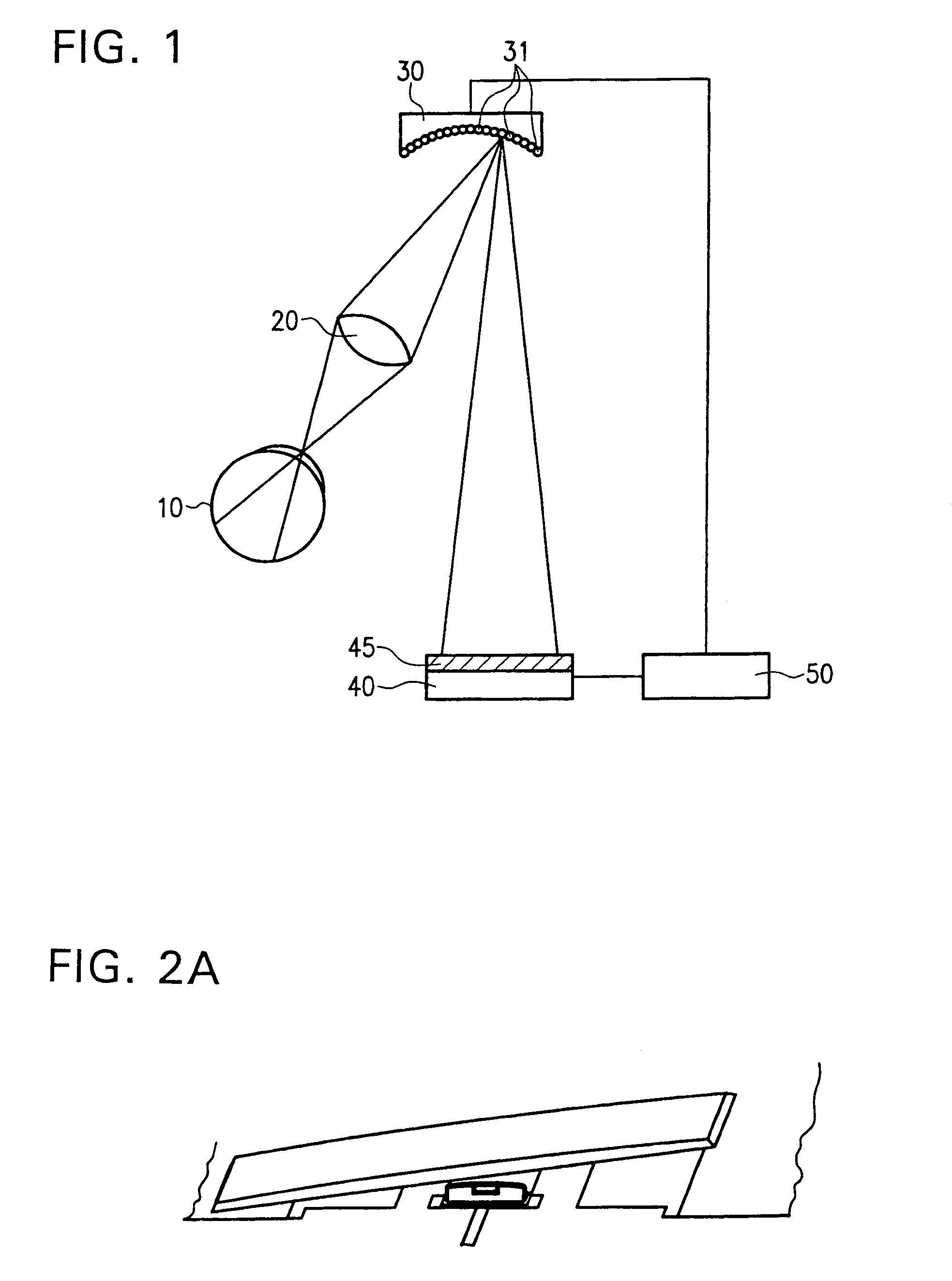
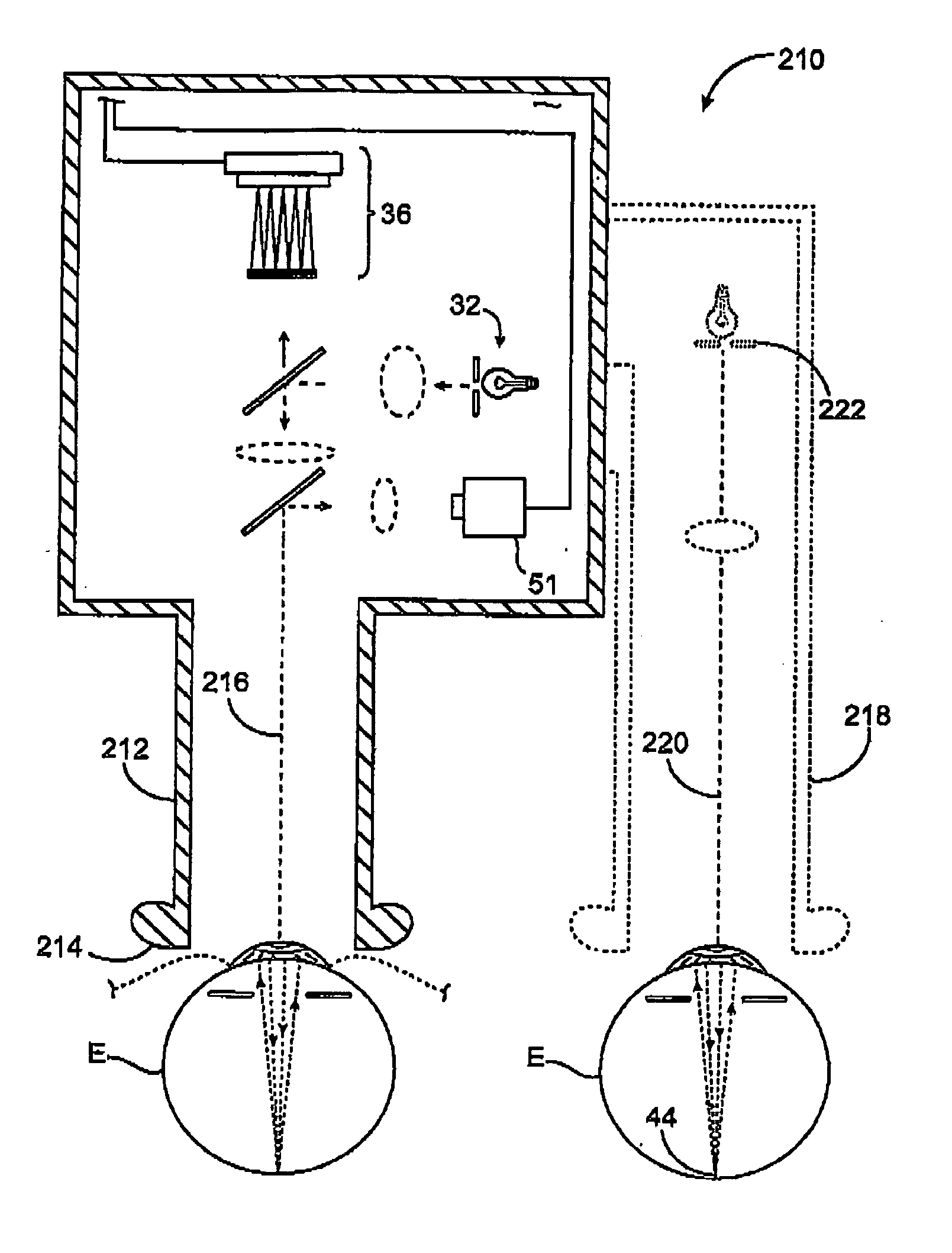
Method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye by interaction of a patient with an examiner and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6997555B2Easy to catchGood utilization basisRefractometersSkiascopesElectronic control systemComputer science
There is now provided a method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye. The method comprises projecting an image into the eye of the patient with an adaptive optical system having adaptive optical elements. The optical characteristics of the optical elements can be individually changed by an electrical signal. The presence of distortions of the image as perceived by the patient is determined by interaction of the patient with the examiner. By way of an electronic control system the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements are changed through outputting of an electrical signal to obtain a modified image with minimized distortions in the eye of the patient. The optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified, are determined and vision correcting data for the eye being examined are computed from the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified. The method not only takes into consideration the aberrations of the optical imaging system but also the properties of reception and signal processing in the human brain. The method is further characterized in that the correction data for the aberrations of the human eye that impair the vision can be obtained by a measuring method that is actively physiologically evaluated beforehand. There is also provided an apparatus for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
STED super-resolution microscope based on first-order Bessel beams and adjustment method thereof
ActiveCN105182523AHigh-resolutionGood spot shapeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSelf-healingCollection system
The invention discloses an STED super-resolution microscope based on first-order Bessel beams and an adjustment method thereof. The STED microscope comprises an excitation light source, a loss light source, an excitation light beam expanding and collimation system, a loss light beam expanding and collimation system, a spiral phase plate, a Bessel beam generation system, a loss light focusing lens, a beam combining system, an object lens, a piezoelectric scanning system, a filter plate, a signal collection system and a single-photon detector. Loss light is the first-order Bessel beams and has scattering-resistant and self-healing characteristics, and great light spot form of the deep position of a sample can be maintained so that resolution of the deep area of the sample can be enhanced. Compared with a method of realizing STED super-resolution microscope deep imaging through adjusting an object lens correction ring, the method is relatively simple in experiment operation without active adjustment. Compared with a method of using a self-adaptive optical system, the experiment device is relatively simple and cheap.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
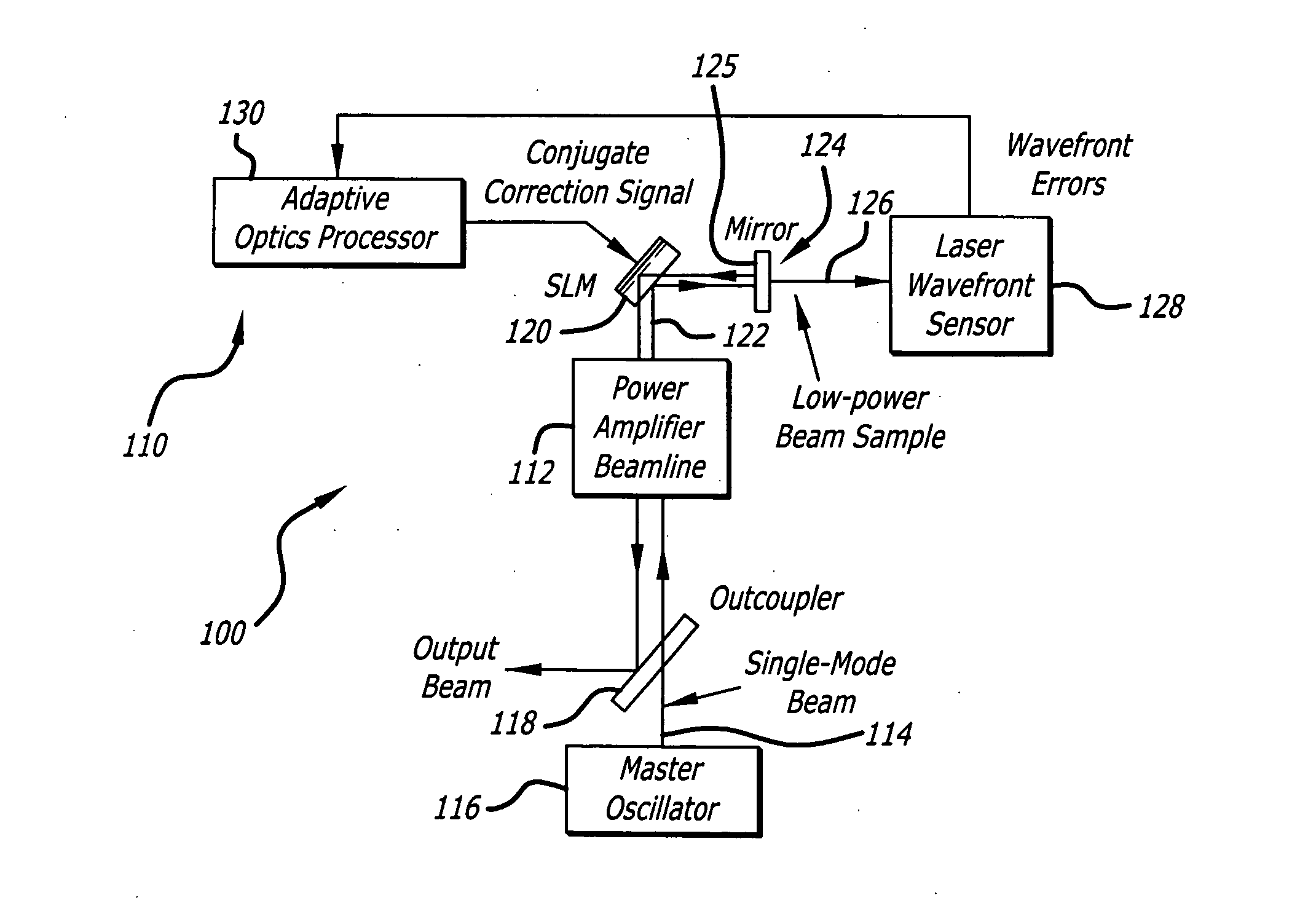
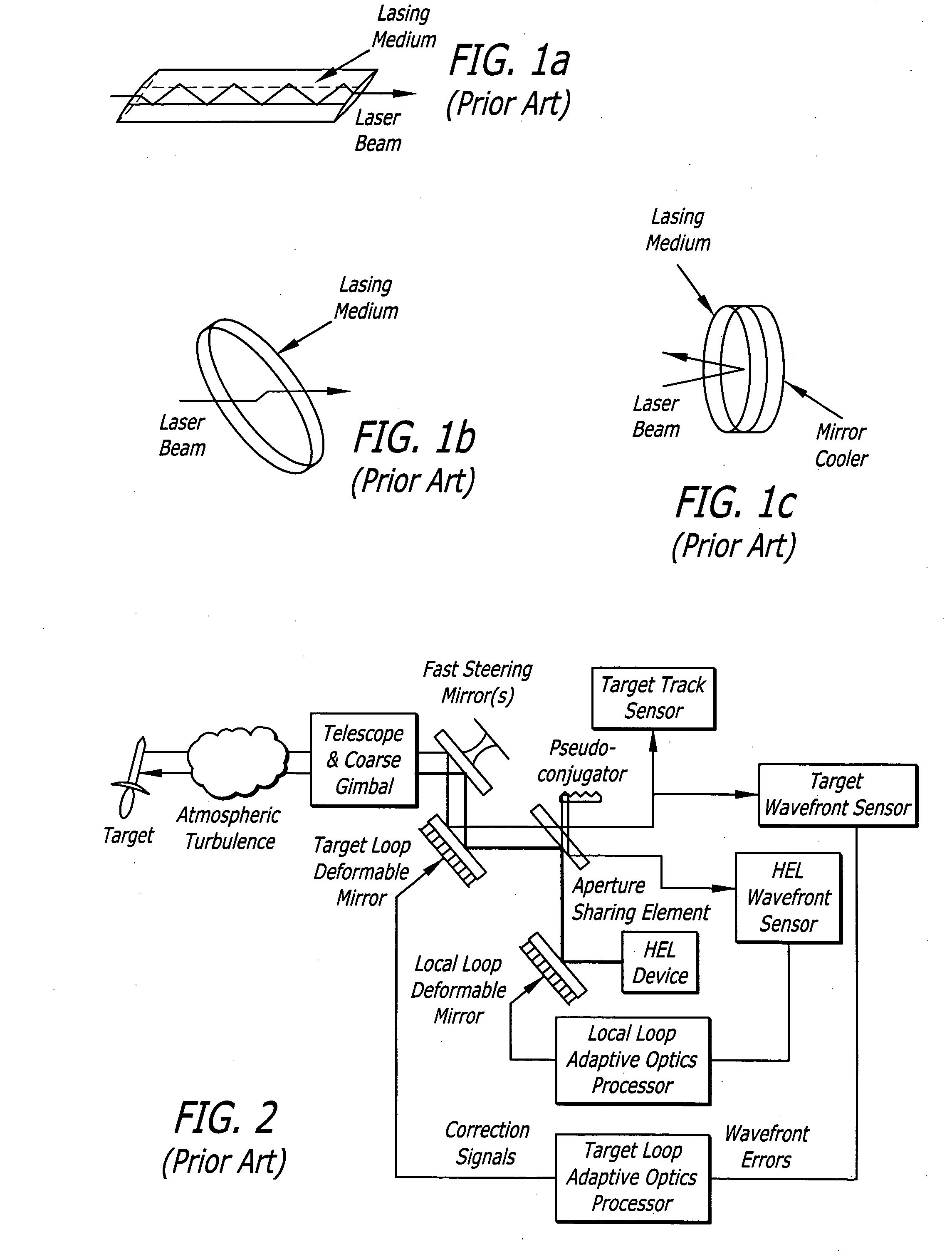
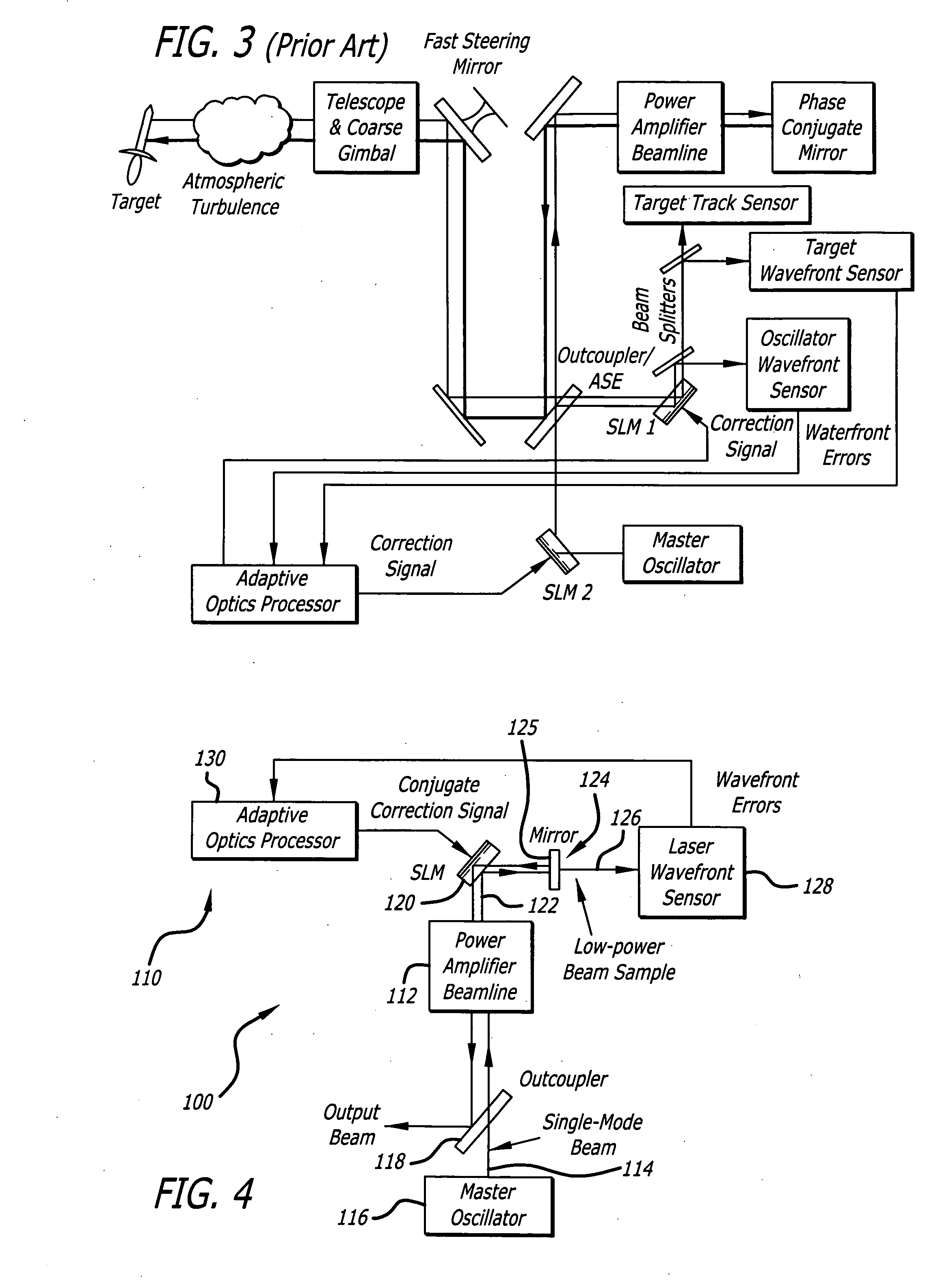
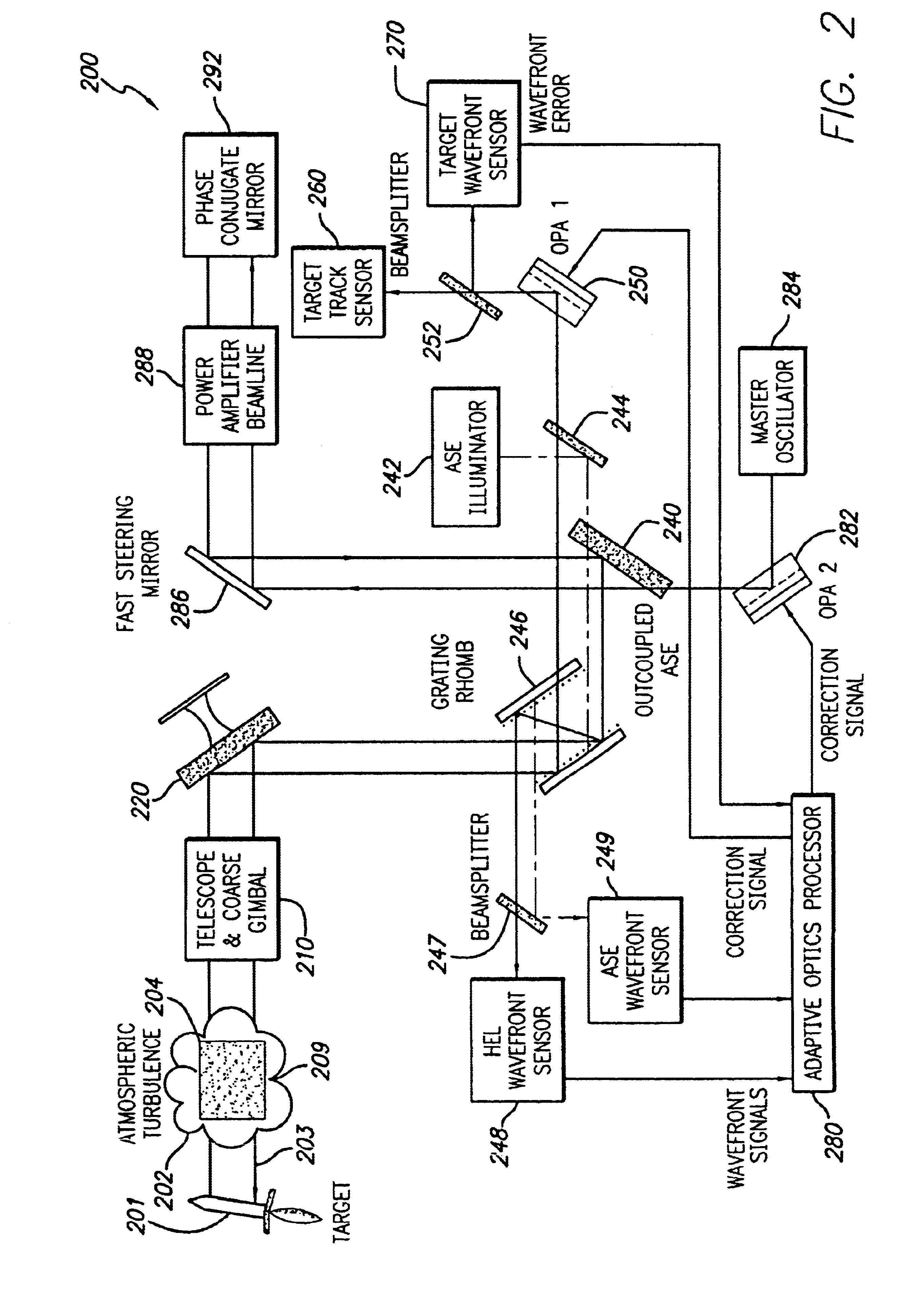
Linear adaptive optics system in low power beam path and method
InactiveUS20100232007A1Aberration correctionDirection controllersDirected energy weaponsDielectricWavefront sensor
A system and method for providing a wavefront corrected high-energy beam of electromagnetic energy. In the illustrative embodiment, the system includes a source of a first beam of electromagnetic energy; an amplifier for amplifying said beam to provide a second beam; a sensor for sensing aberration in said second beam and providing an error signal in response thereto; a processor for processing said error signal and providing a correction signal in response thereto; and a spatial light modulator responsive to said correction signal for adjusting said beam to facilitate a correction of said aberration thereof. In more specific embodiments, the source is a laser and the sensor is a laser wavefront sensor. A mirror is disposed between said modulator and said sensor for sampling said beam. The mirror has an optical thin-film dielectric coating on at least one optical surface thereof. The coating is effective to sample said beam and transmit a low power sample thereof to said means for sensing aberration. The processor is an adaptive optics processor. The spatial light modulator may be a micro electro-mechanical system deformable mirror or an optical phased array. In the illustrative embodiment, the source is a master oscillator and the amplifier is a power amplifier beamline. An outcoupler is disposed between the oscillator and the amplifier.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics
ActiveCN101862178AIncrease horizontal resolutionIncrease vertical resolutionOthalmoscopesRetinal imagingData acquisition
The invention relates to a reflection-type confocal scanning retina imaging system based on adaptive optics, which can accurately obtain the high-resolution images of vital human eye retinae in real time and comprises a light source, a reflection-type beam shrinking and expanding system, a two-dimension scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, a photoelectric detection system, a data acquisition and processing system and a contraocular sighting target system. Lasers emitted from the light source are hit into human eye ground; light reflected from the eye ground returns along the original path, enters the photoelectric detection system and passes through the data acquisition and processing system to obtain the real-time images of the human eye ground. Simultaneously, an adaptive optics system comprising the Hartmann sensor and the deformable mirror can synchronously detect and correct human eye aberration, and thereby, the high resolution of the images is ensured.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
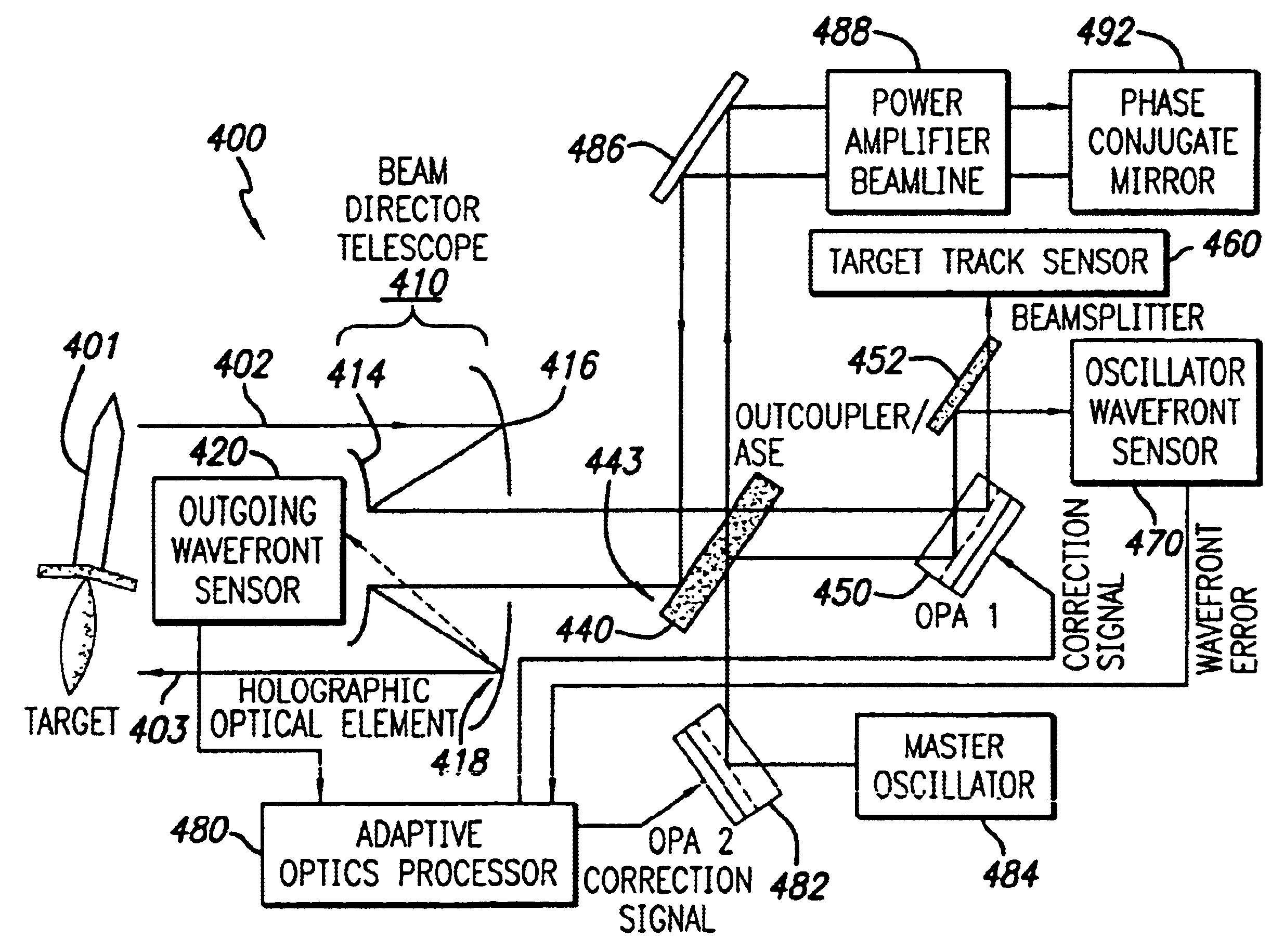
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS6849841B2Cancellation effectPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
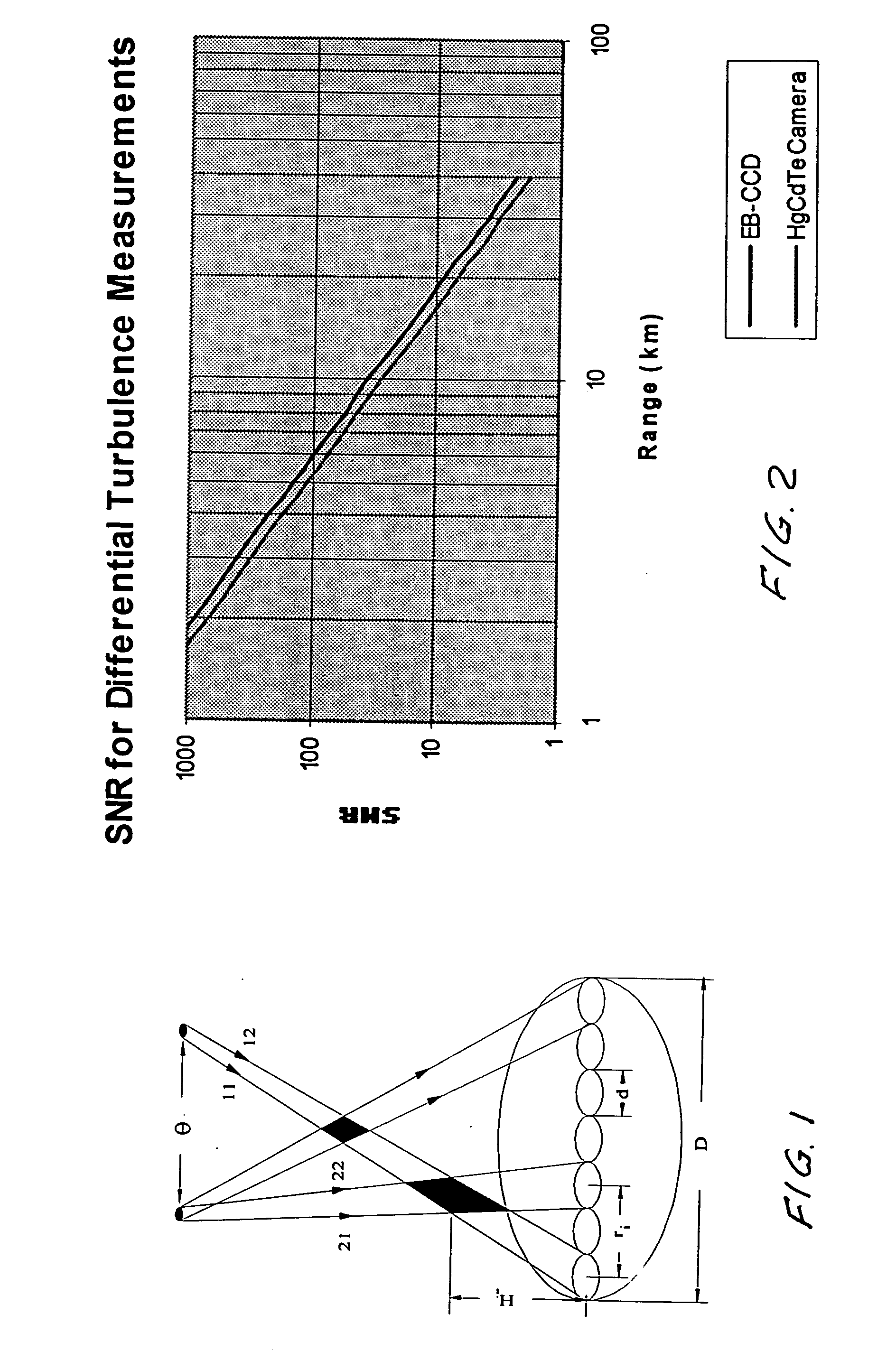
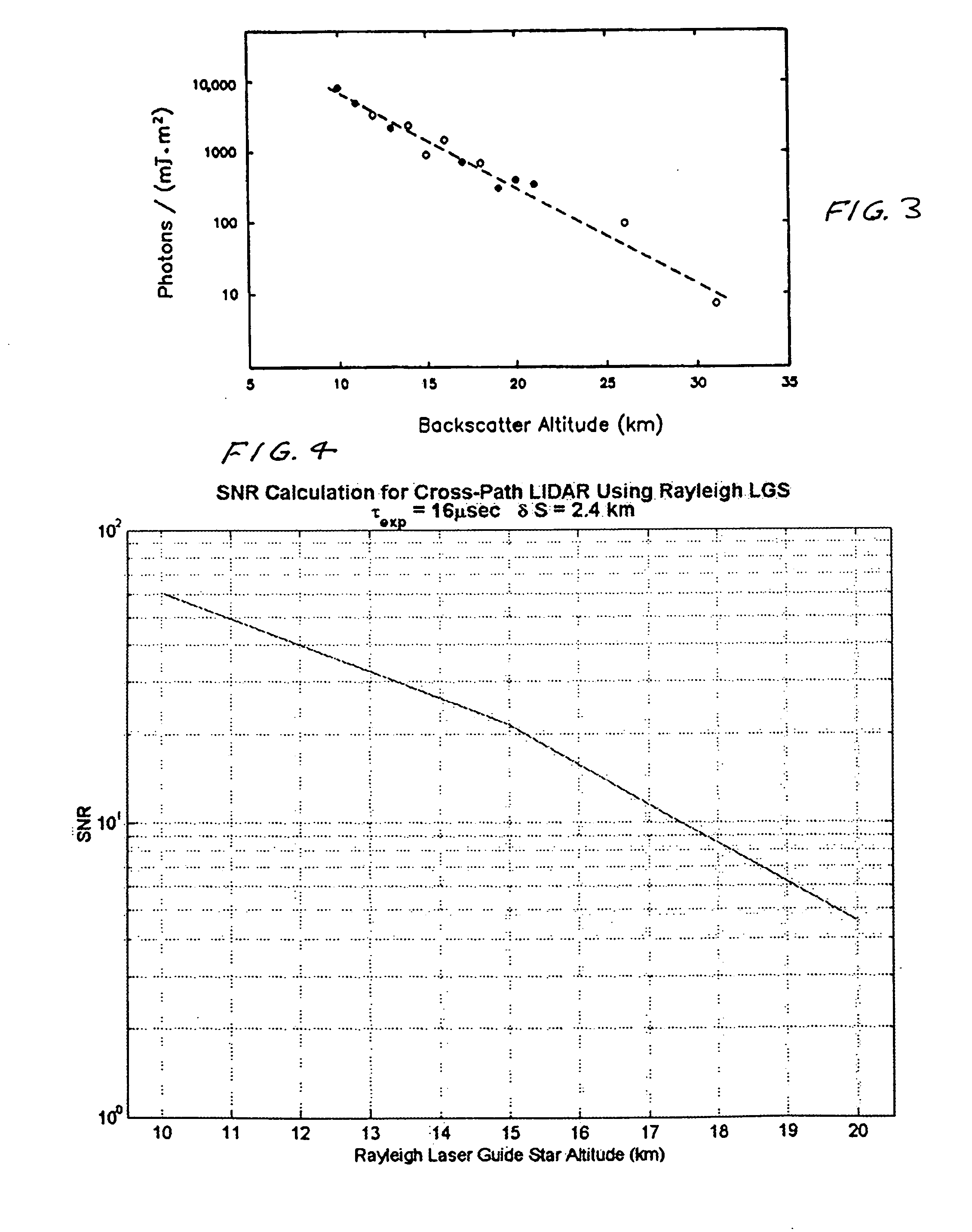
System for measuring atmospheric turbulence
InactiveUS20070077071A1Electromagnetic transmissionElectromagnetic wave reradiationWavefront sensorAngular distance
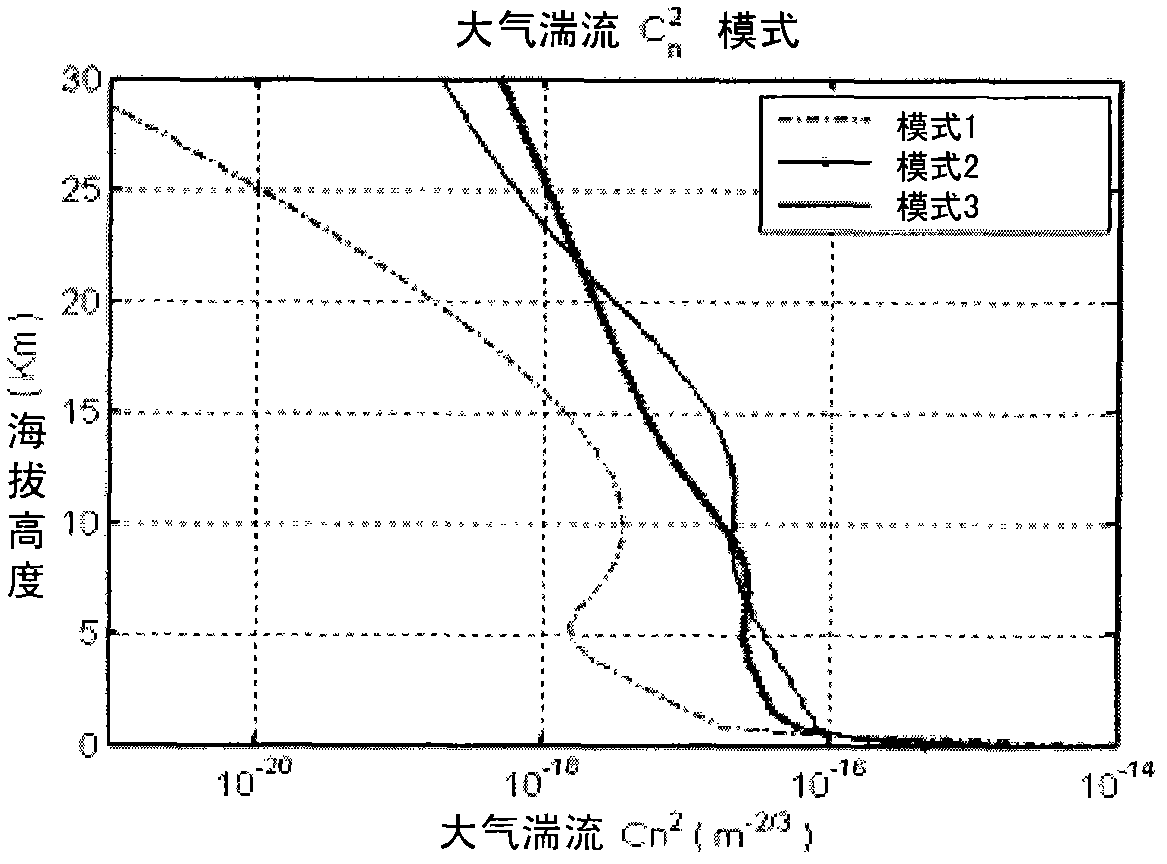
Equipment and techniques for the accurate estimates of the turbulence profile to improve the performance of adaptive optics systems designed to compensate the degradation effects of turbulence on directed energy systems, in astronomy, and in laser communication systems. The present invention is an optical turbulence profiler. The invention includes a cross-path LIDAR. The cross-path LIDAR technique uses laser guide star technology combined with a cross-path wavefront sensing method. In this method, two Rayleigh, or sodium, laser beacons separated at some angular distance are created by using a pulsed laser and a range-gated receiver. In preferred embodiments a Hartmann wavefront sensor measures the wavefront slopes from two laser guide stars. The cross-correlation coefficients of the wavefront slope are calculated, and the turbulence profile of refractive index structure characteristic Cn2(z) is reconstructed from the measured slope cross-correlations.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
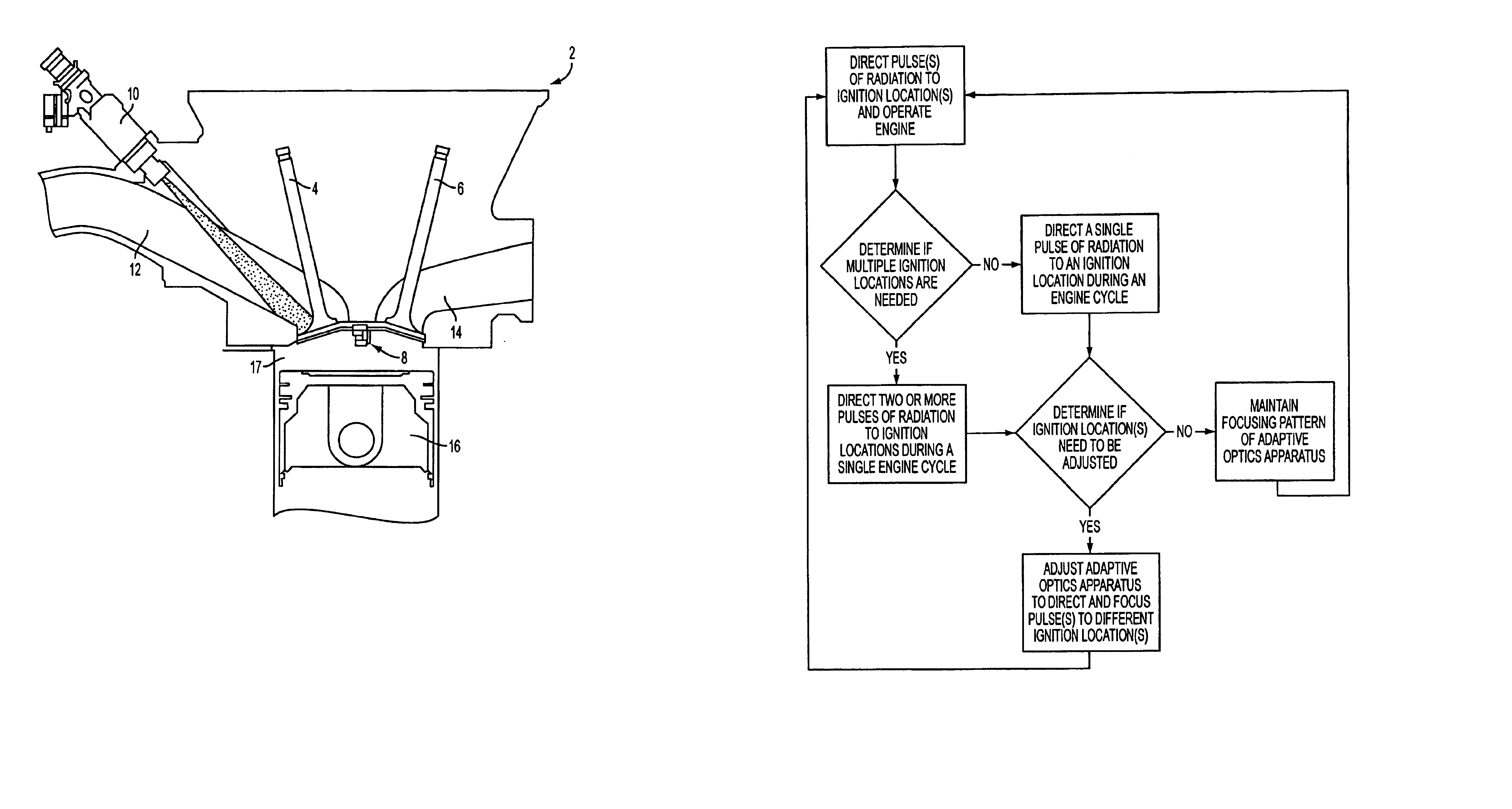
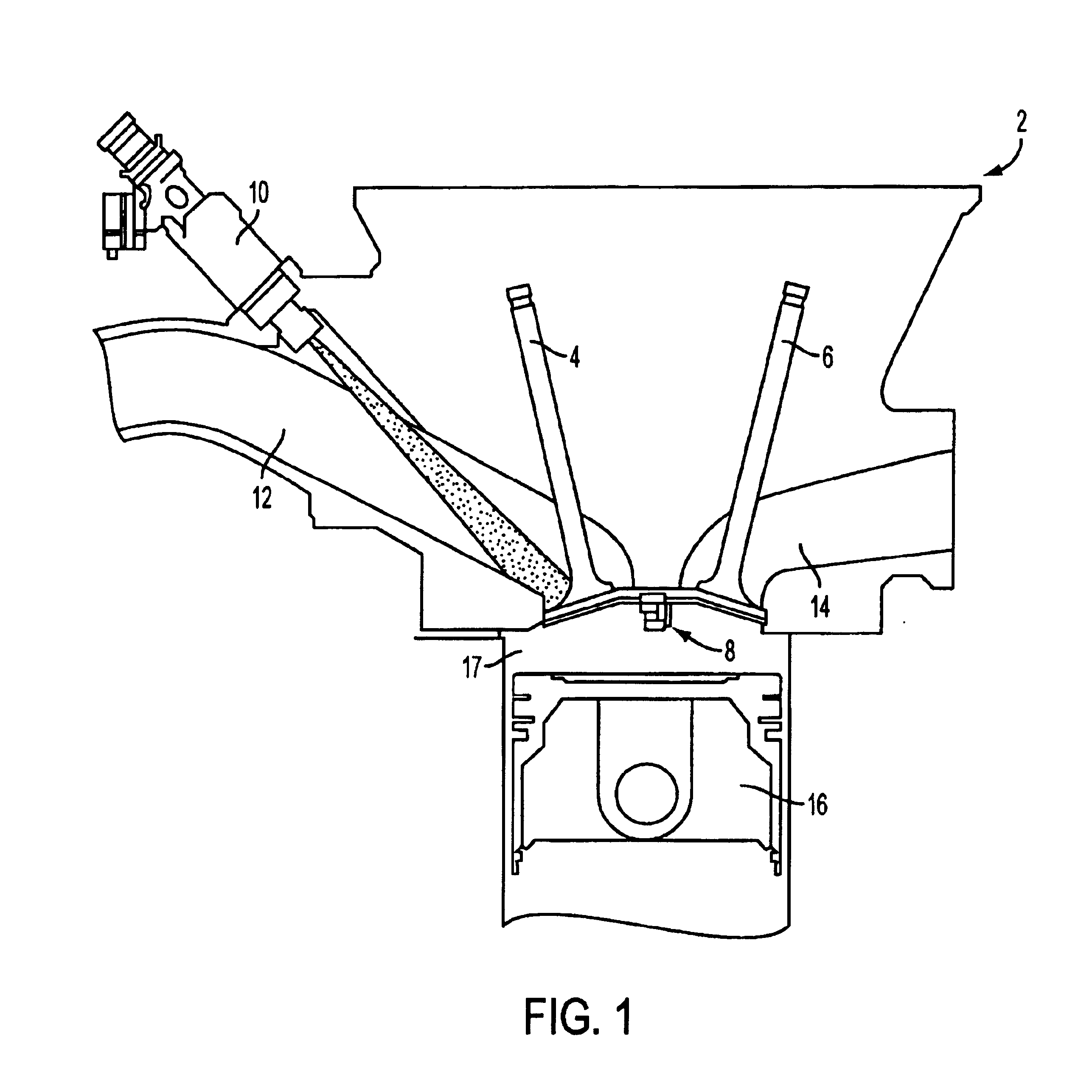
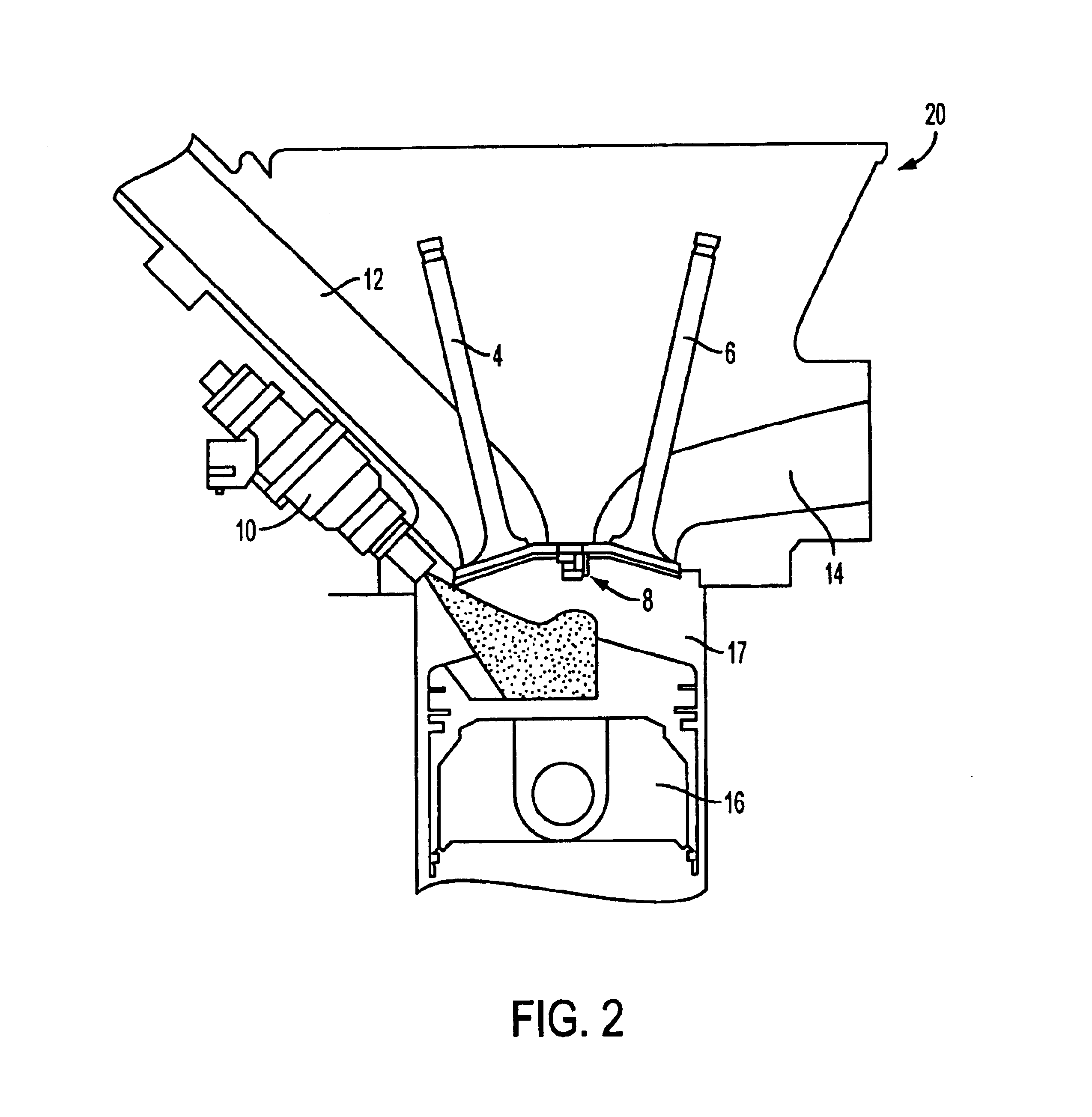
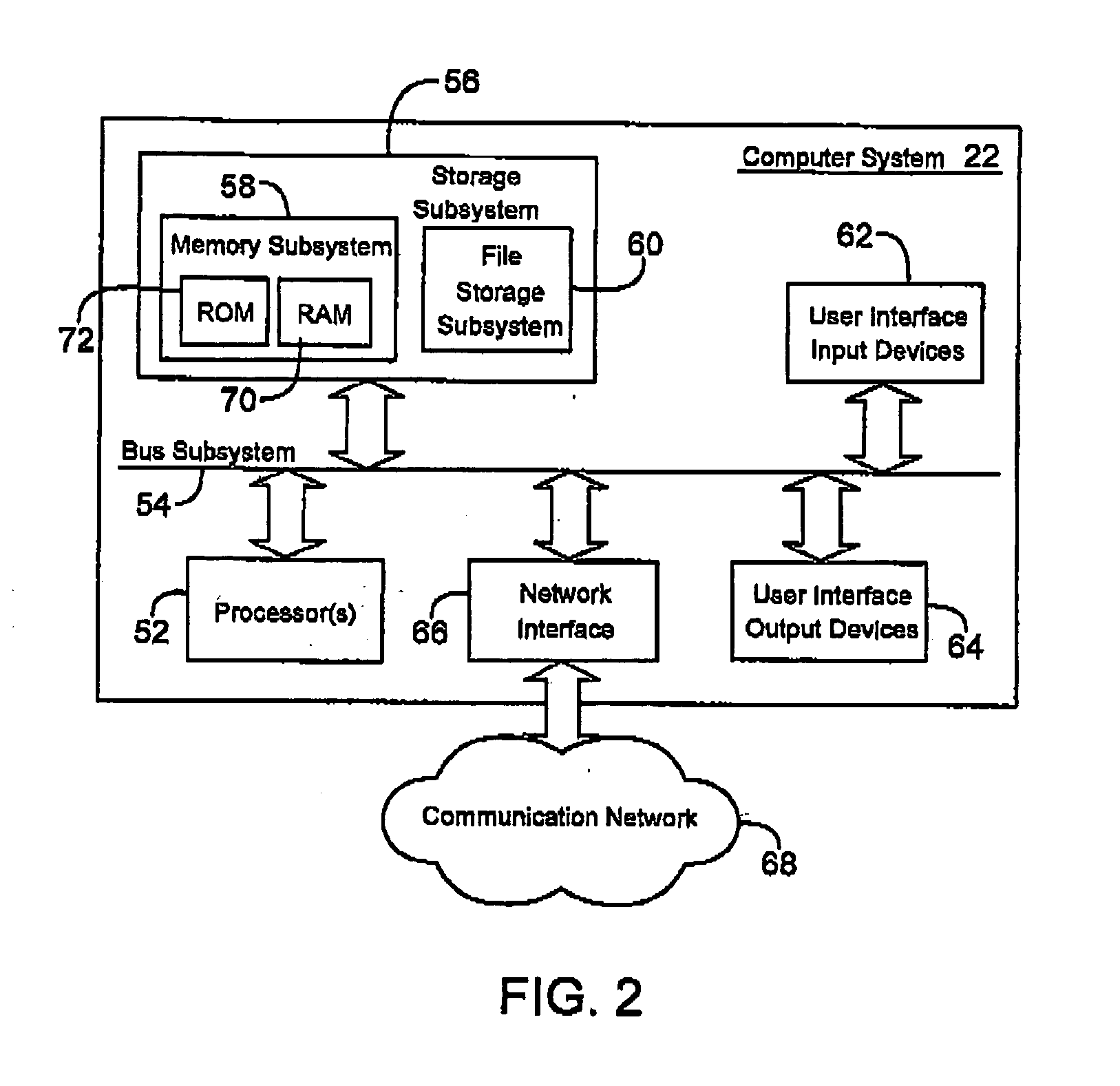
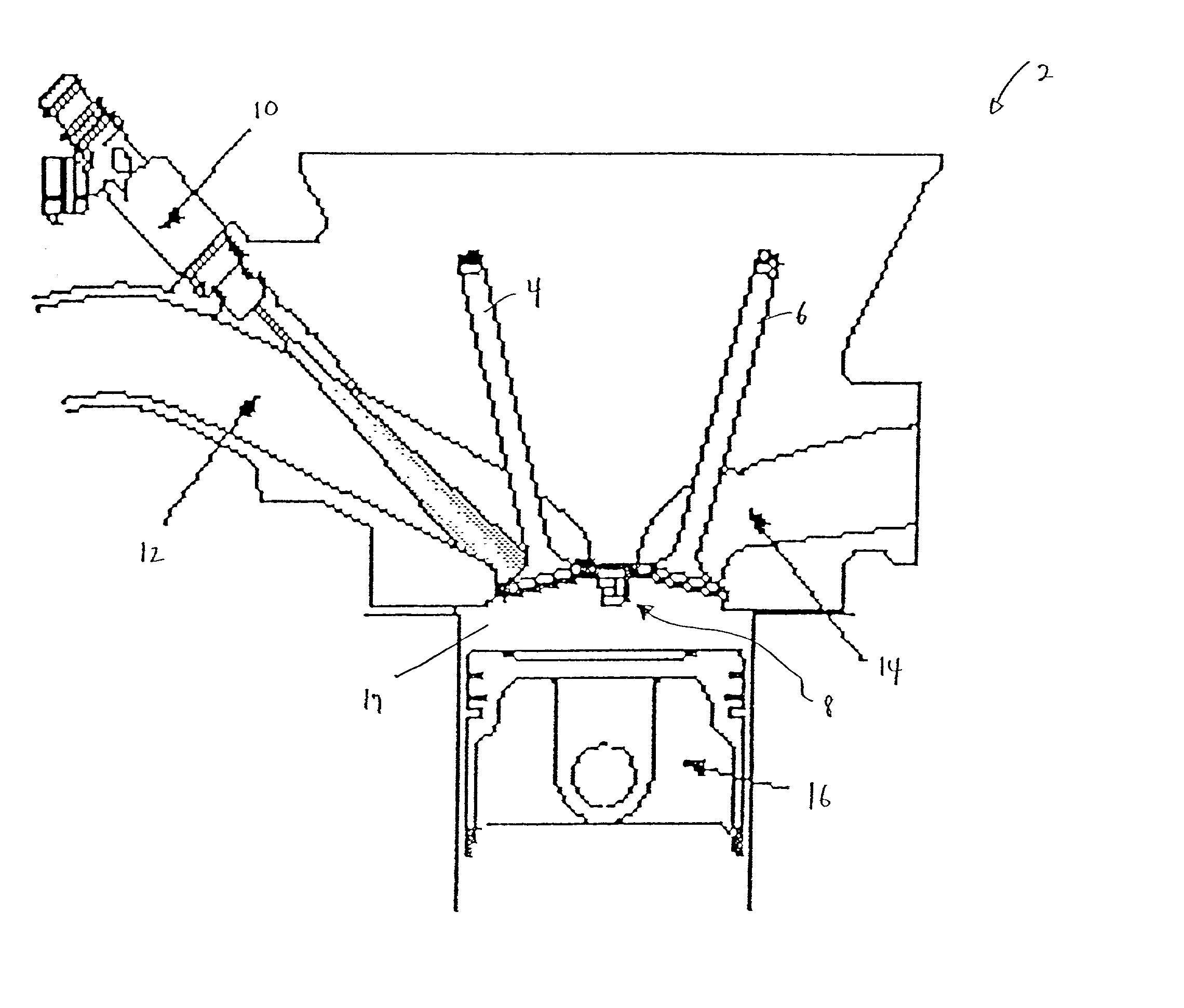
Methods and apparatuses for laser ignited engines
InactiveUS6796278B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
Methods and apparatuses for laser ignition in an internal combustion engine. Laser radiation is directed to an ignition location within a combustion chamber with adaptive optics, and the position of the ignition location is adaptively adjusted during operation of the engine using the adaptive optics. Multiple ignition locations may be provided during a cycle of an internal combustion engine. A first pulse of laser radiation is directed to a first ignition location within a combustion chamber with adaptive optics, and a second pulse of laser radiation is directed to a second ignition location within the combustion chamber using the adaptive optics.
Owner:III HLDG 1
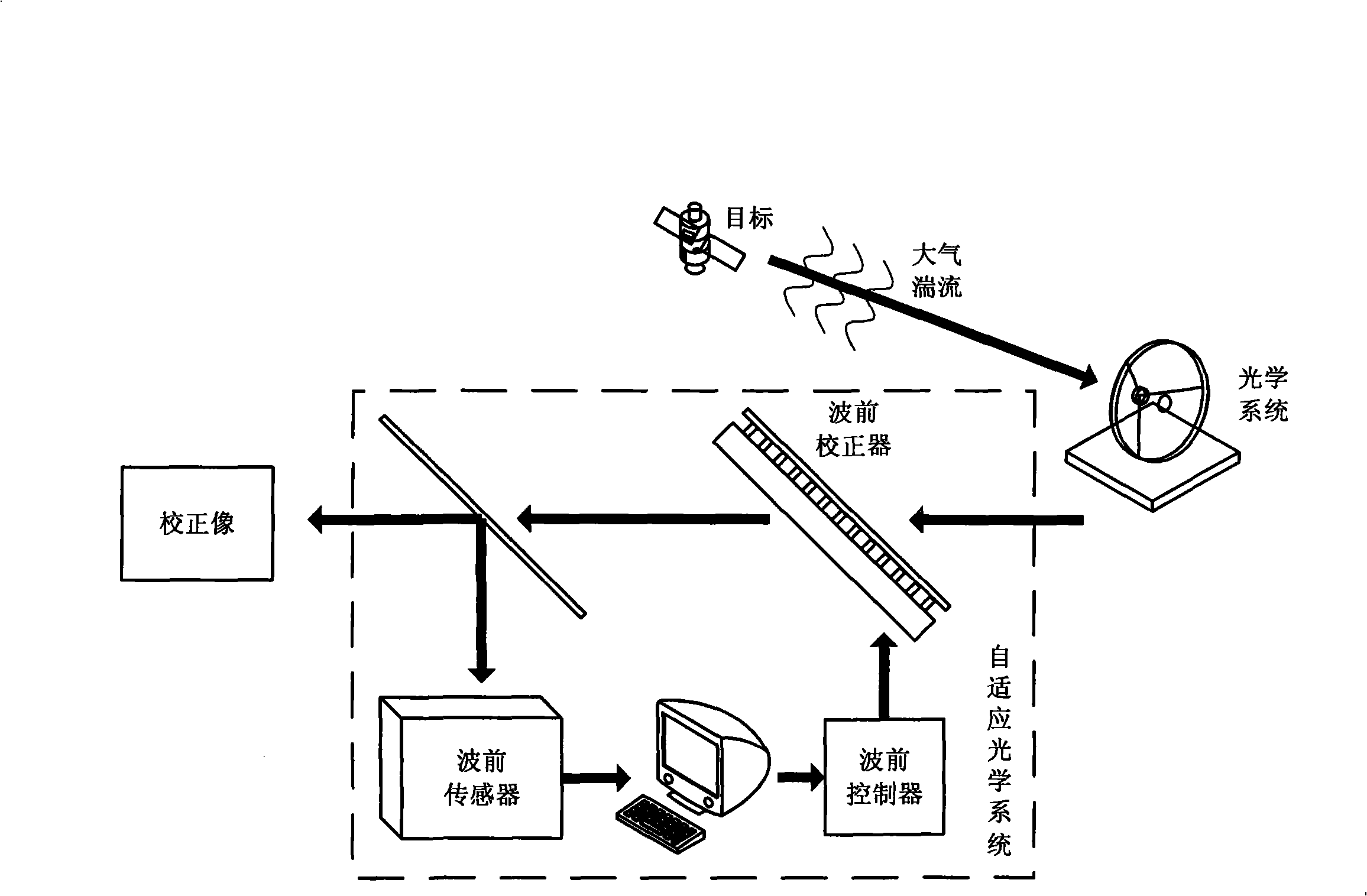
Self-adaptive optical star target imaging system based on image clearing principle
InactiveCN101078808AAvoid the cumbersome processLow costGenetic modelsTelescopesWavefront sensorImaging quality
The invention relates to an adaptive optical aster target imaging system based on image clearing principle, mainly comprising receiving telescope, spectroscope, reflection deformable mirror, high-voltage amplifier, photo detector, main control computer, control algorithm, high-speed digital processor and image-quality diagnosis system. The invention can make use aster target itself as beacon. It is not need that dear wave-front sensor is used to measure the wave-front error of beam from space target. Image clearing index, which can reflect wave-front error information, can be used to measure quality factor for system imaging ability. By controlling the reflection deformable mirror to correct the wave-front error the quality factor can achieve or approach the optimal value. The invention is provided with simple structure, easy regulation, real-time imaging, convenient control, and eliminating or decreasing bacon no-isoplanatic error. Under the condition of very strong atmospheric turbulence aster target can be imaged effectively. The cost of conventional adaptive optical system for imaging compensation of aster target can be decreased greatly.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS7758189B2Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansOphthalmologyRetinal imaging
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
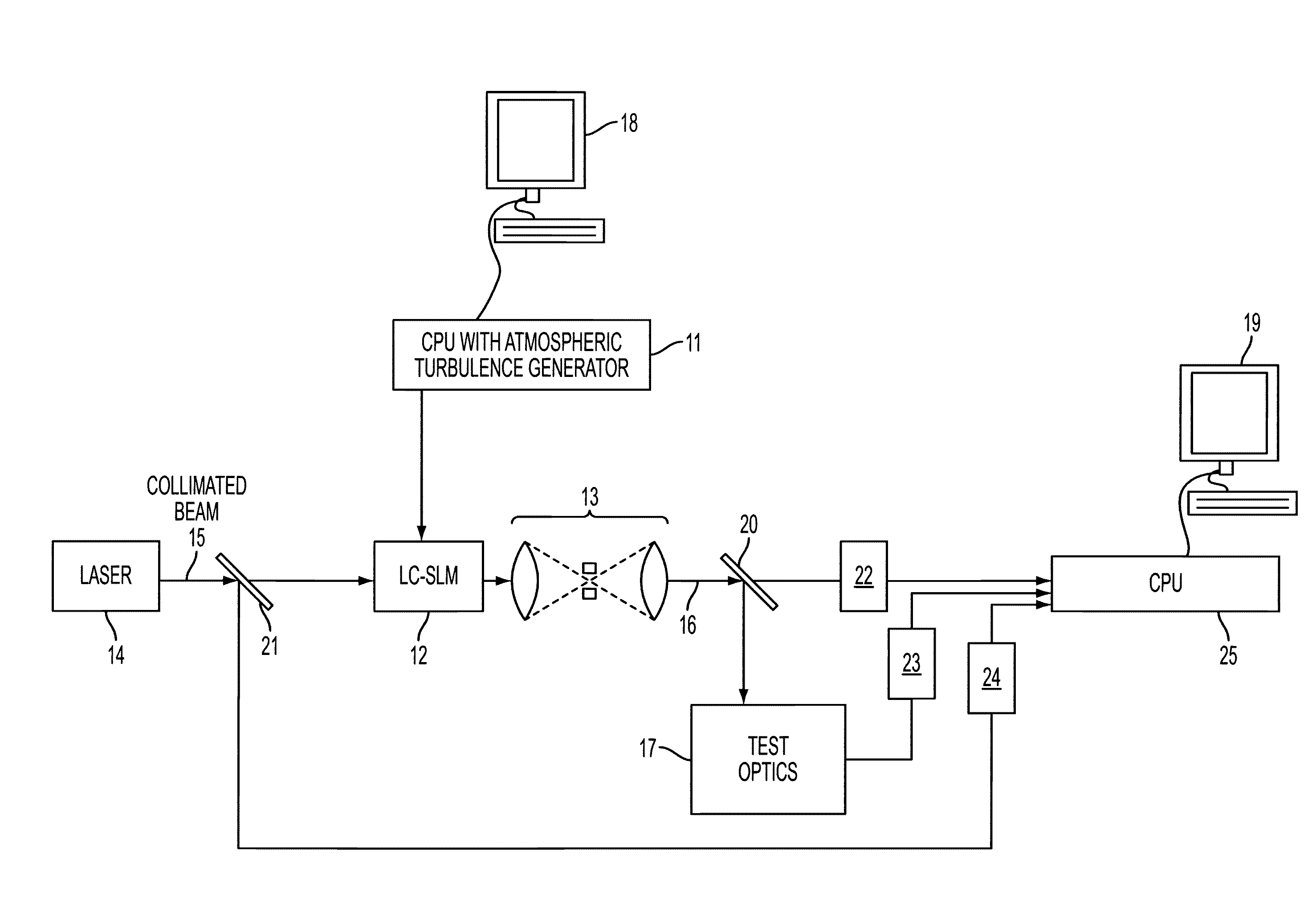
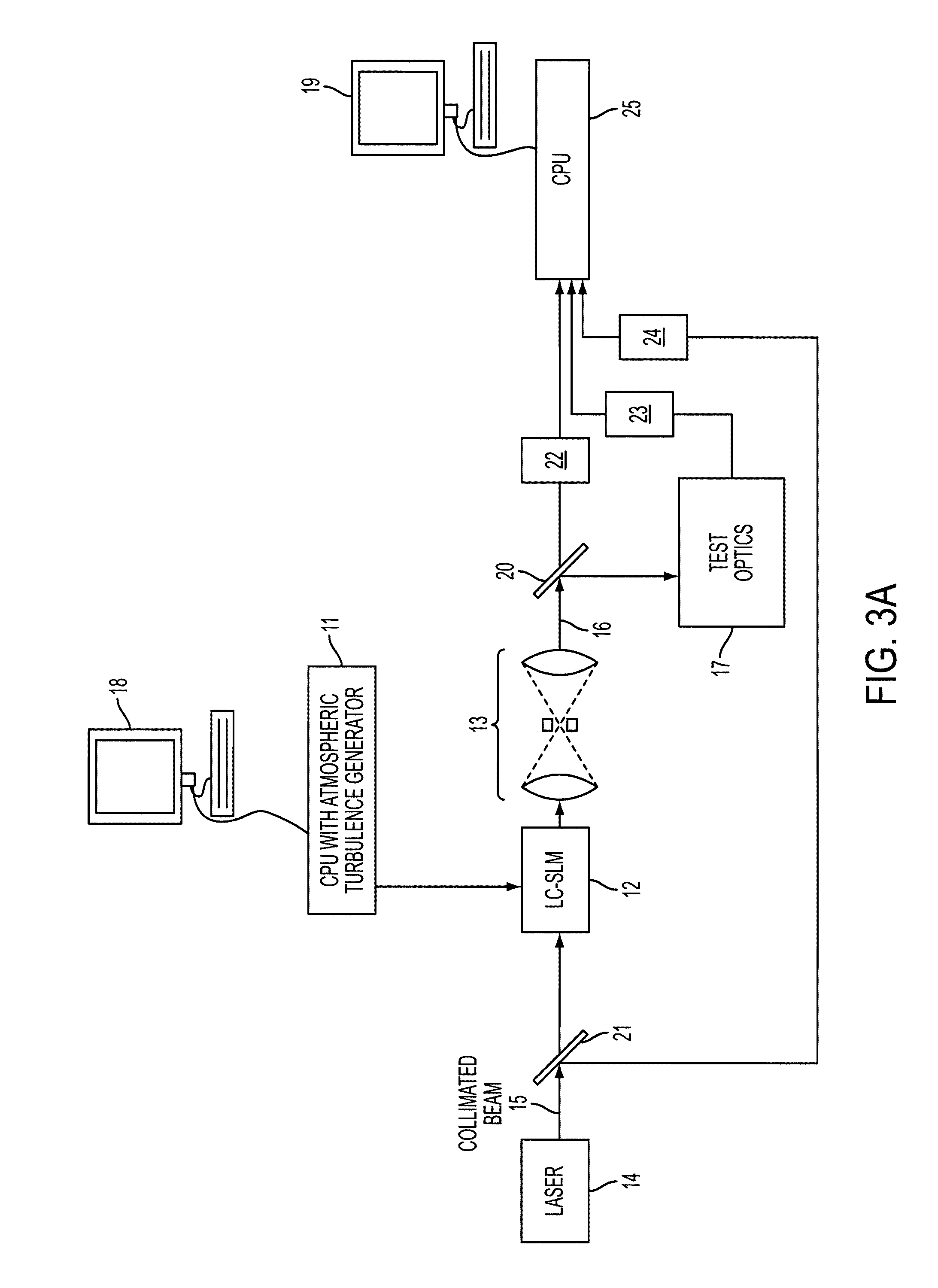
System and Method of Generating Atmospheric Turbulence for Testing Adaptive Optical Systems
ActiveUS20100192709A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial analysis by optical meansTime functionComputer science
A system and method for simulating atmospheric turbulence for testing optical components. A time varying phase screen representing atmospheric turbulence is generated using Karhunen-Loeve polynomials and a splining technique for generating temporal functions of the noise factor for each Zernike mode. The phase screen is input to a liquid crystal spatial light modulator. A computer display allows the user to set geometric characteristics, and select between methods for generating atmospheric turbulence including Karhunen-Loeve polynomials, Zernike polynomials, and Frozen Seeing.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT IN THE NAME OF THE SEC OF THE NAVY +1
Correction of presbyopia using adaptive optics and associated methods
InactiveUS20060017883A1Easy to deriveImprove aberrationRefractometersSkiascopesLight spotComputer science
Devices, systems, and methods measure, diagnose, and / or treat one or both eyes of a patient. Adaptive optics systems (such as those having a deformable mirror) may be configured to an aspherical or multi-spherical presbyopia-mitigating prescriptive shape to allow objective and / or subjective measurements of a candidate prescription. A plurality of viewing distances allow subjective and / or objective evaluations of performance using a light spot or a test viewing image. Measurements of aberrations at selected viewing conditions (including distances and / or brightness) with correlating pupil sizes may also be provided. Wavefront measurement systems and methods may help position and isolate the eye from ambient light.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
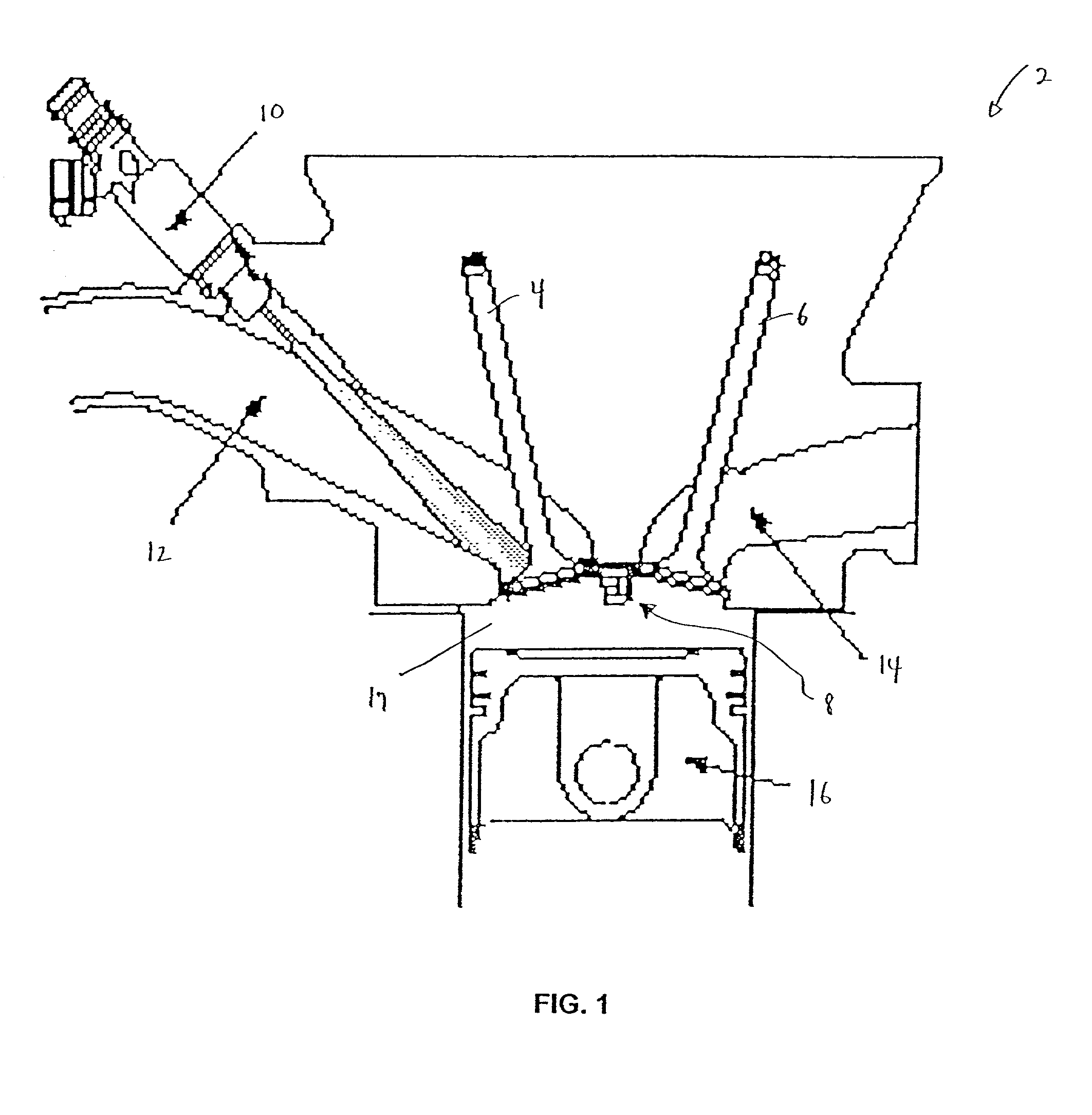
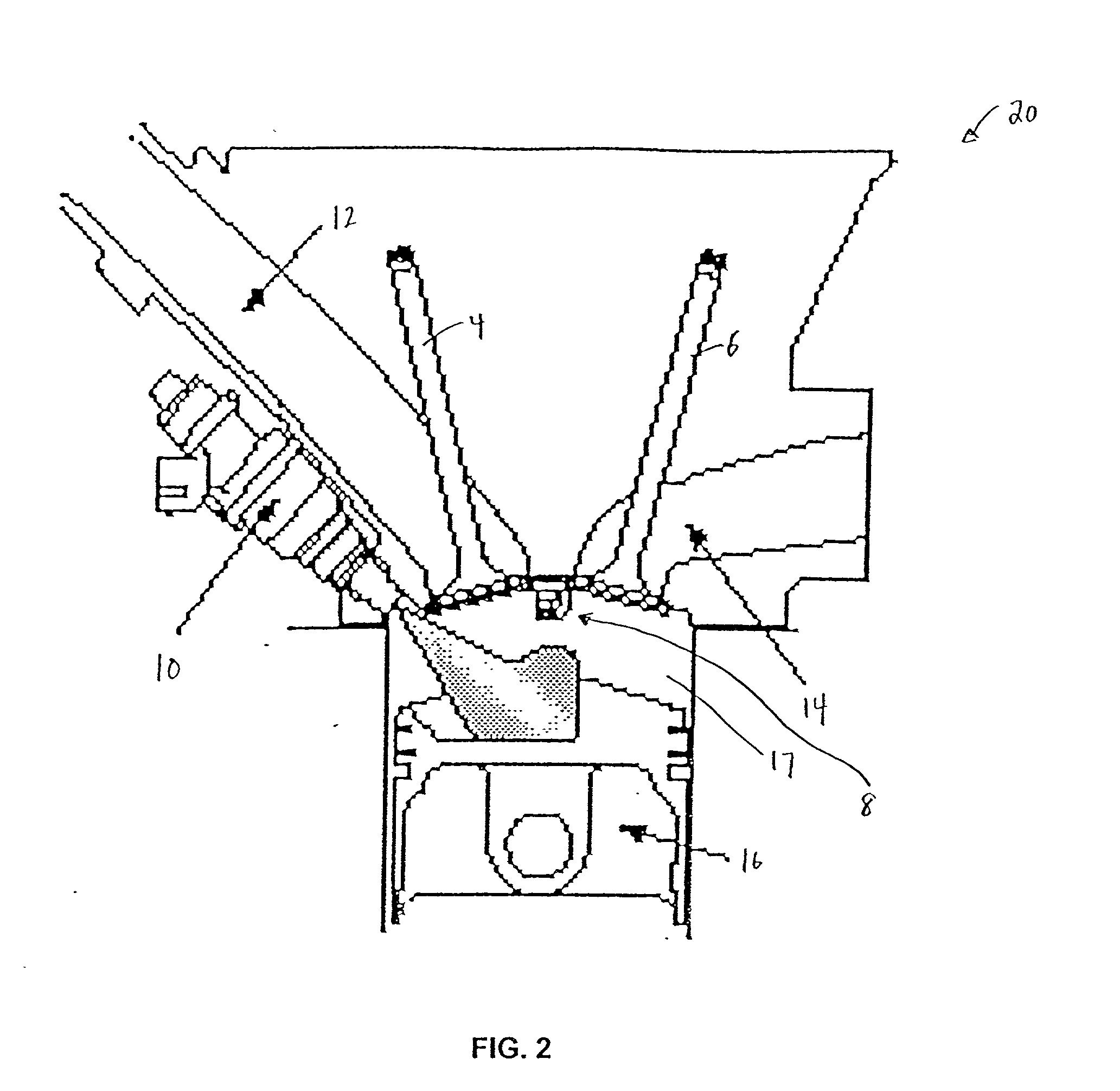
Methods and apparatuses for laser ignited engines
InactiveUS20020185097A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
Methods and apparatuses for laser ignition in an internal combustion engine. Laser radiation is directed to an ignition location within a combustion chamber with adaptive optics, and the position of the ignition location is adaptively adjusted during operation of the engine using the adaptive optics. Multiple ignition locations may be provided during a cycle of an internal combustion engine. A first pulse of laser radiation is directed to a first ignition location within a combustion chamber with adaptive optics, and a second pulse of laser radiation is directed to a second ignition location within the combustion chamber using the adaptive optics.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Atmospheric turbulence detection simulator used for self-adaptive optical system
InactiveCN102169048ARealize simulationRealize the target observation functionAerodynamic testingHigh elevationAtmospheric air
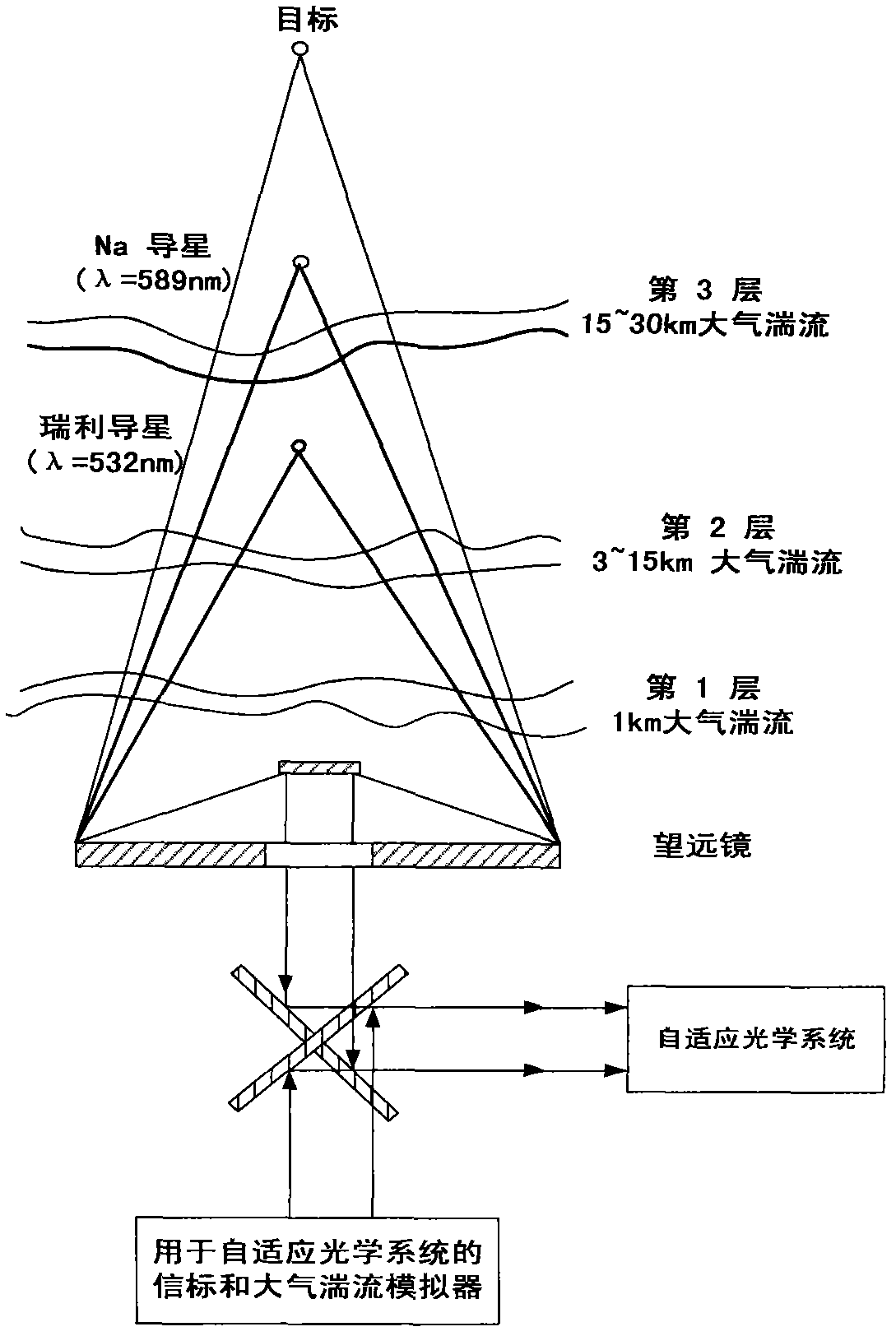
The invention discloses an atmospheric turbulence detection simulator used for an self-adaptive optical system, which comprises a beam contracting module, a first atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, a second atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, a first splitter, a third atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, a second splitter, a lens, a Rayleigh beacon, a natrium beacon, and a target; thefirst atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, the second atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, and the third atmospheric turbulence simulation unit respectively represent the atmospheric turbulencedistribution from lower elevation to higher elevation according to order from left to right in sequence; the Rayleigh beacon is arranged behind the first atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, the second atmospheric turbulence simulation unit, and the first splitter, before the third atmospheric turbulence simulation unit; the natrium beacon is arranged behind the third atmospheric turbulence simulation unit and the second splitter; and the target is arranged behind the second splitter and the lens, and represents an infinity target.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
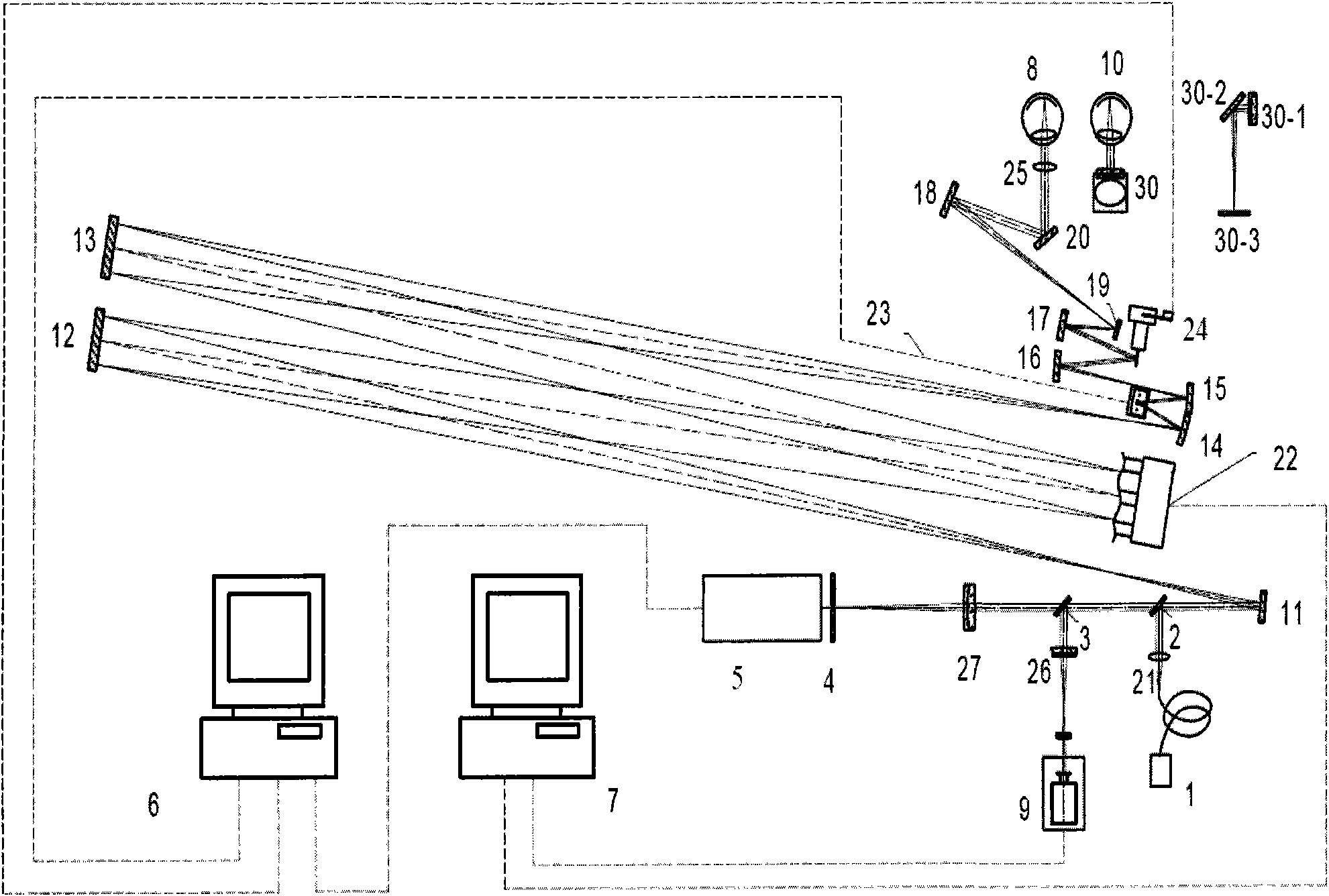
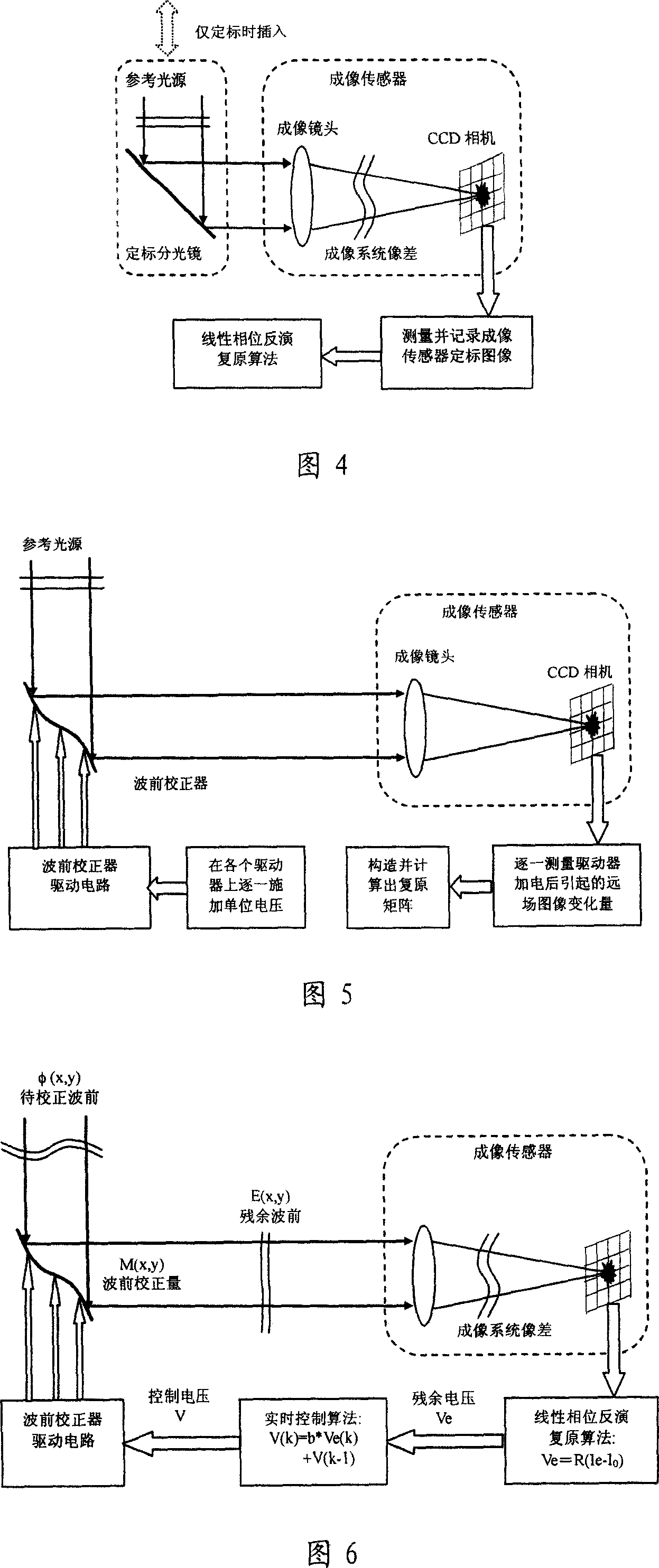
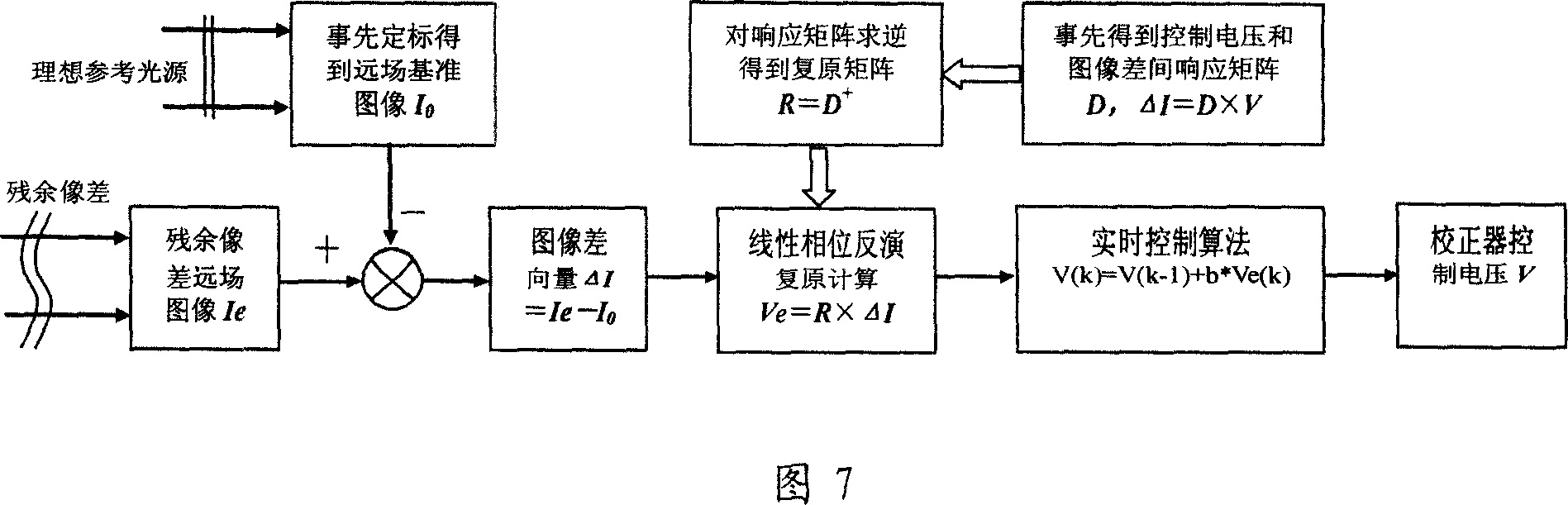
Self-adaptive optical system based on linear phase inversion restoration technology
InactiveCN101013195ASimple structureImprove light energy utilizationOptical measurementsOptical elementsInversion recoveryTime control
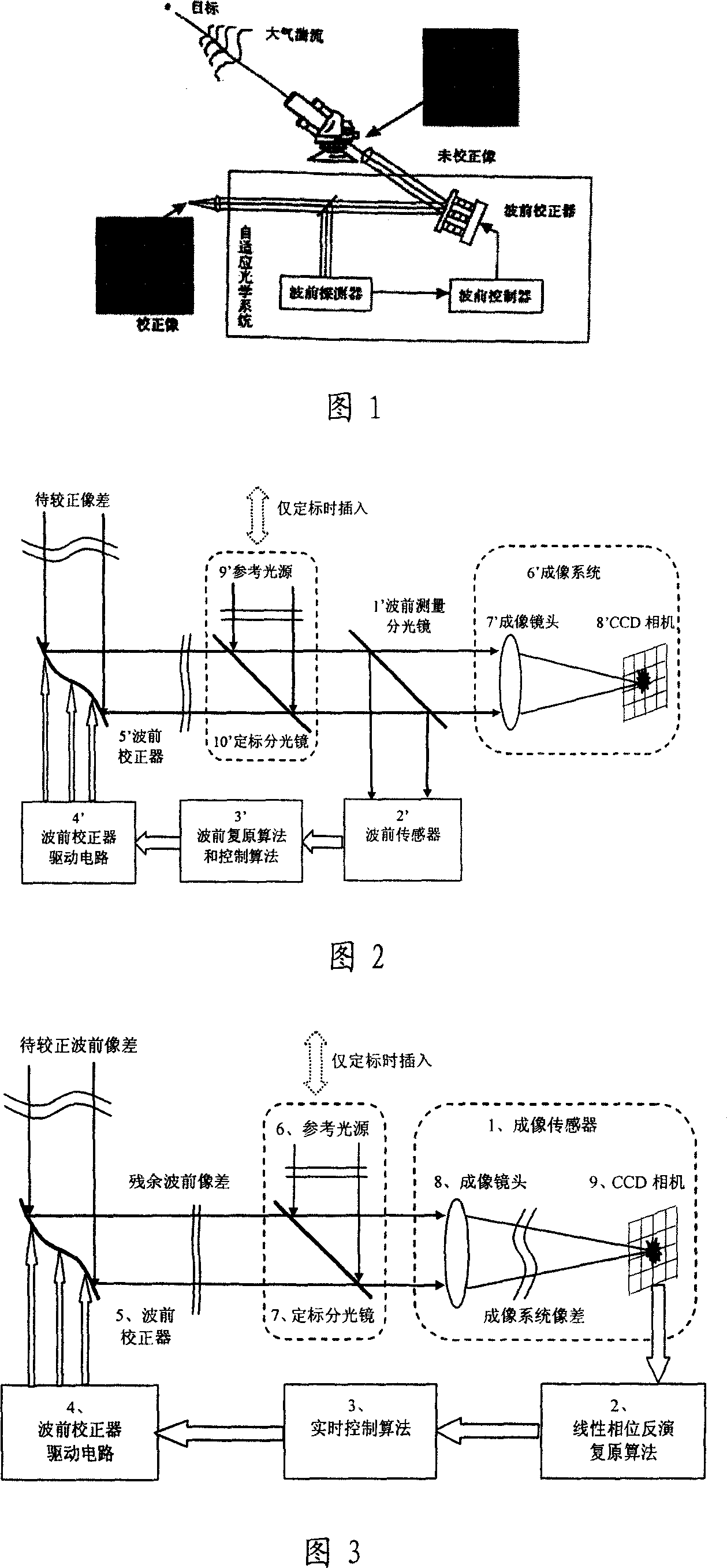
It is an adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique, comprising the imaging sensor, the linear phase inversion recovery algorithm, the real-time control algorithm, the wave-front correction and drive circuit, and the reference light source. During the system running, the imaging sensor measures the residual aberration far-field image after the compensation of the wave-front correction device, and subtracting with the benchmark image to obtain the image difference vector. In advance, using the reference light source to calibrate the imaging sensor to obtain the benchmark image, and according to the corresponding relations between the wave-front correction device and the imaging sensor, obtaining the recovery matrix between the image difference vector and control voltage. Multiply the image difference vector and the recovery matrix to obtain the corresponding control voltage of the residual wave-front, and use real-time control algorithms, such as proportional integral, to obtain the control voltage of the wave-front correction device, making the wave-front aberration to be corrected. Compared the adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique and the conventional adaptive optical technology, it has simple structure, high optical energy efficiency, and other advantages.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
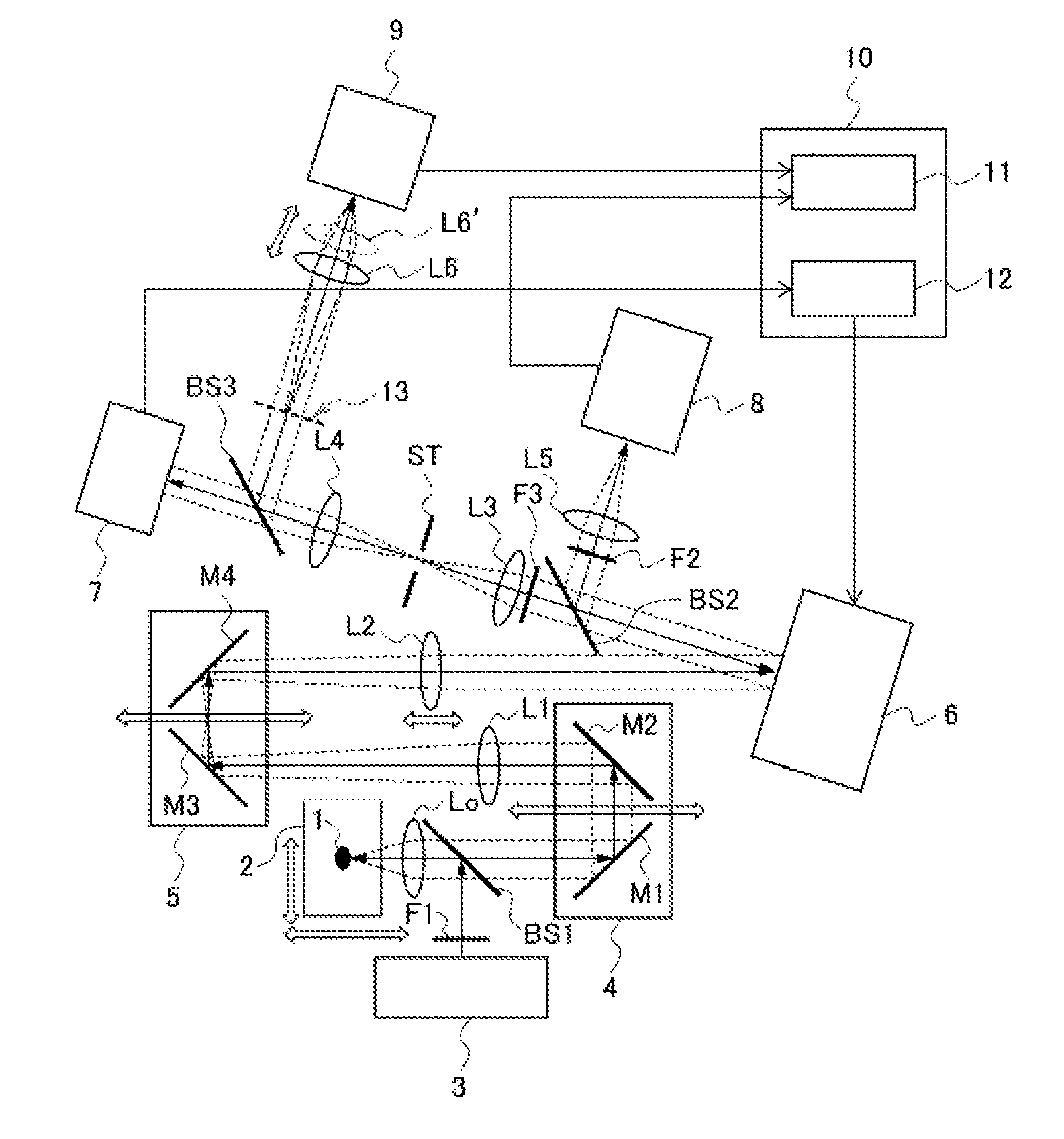
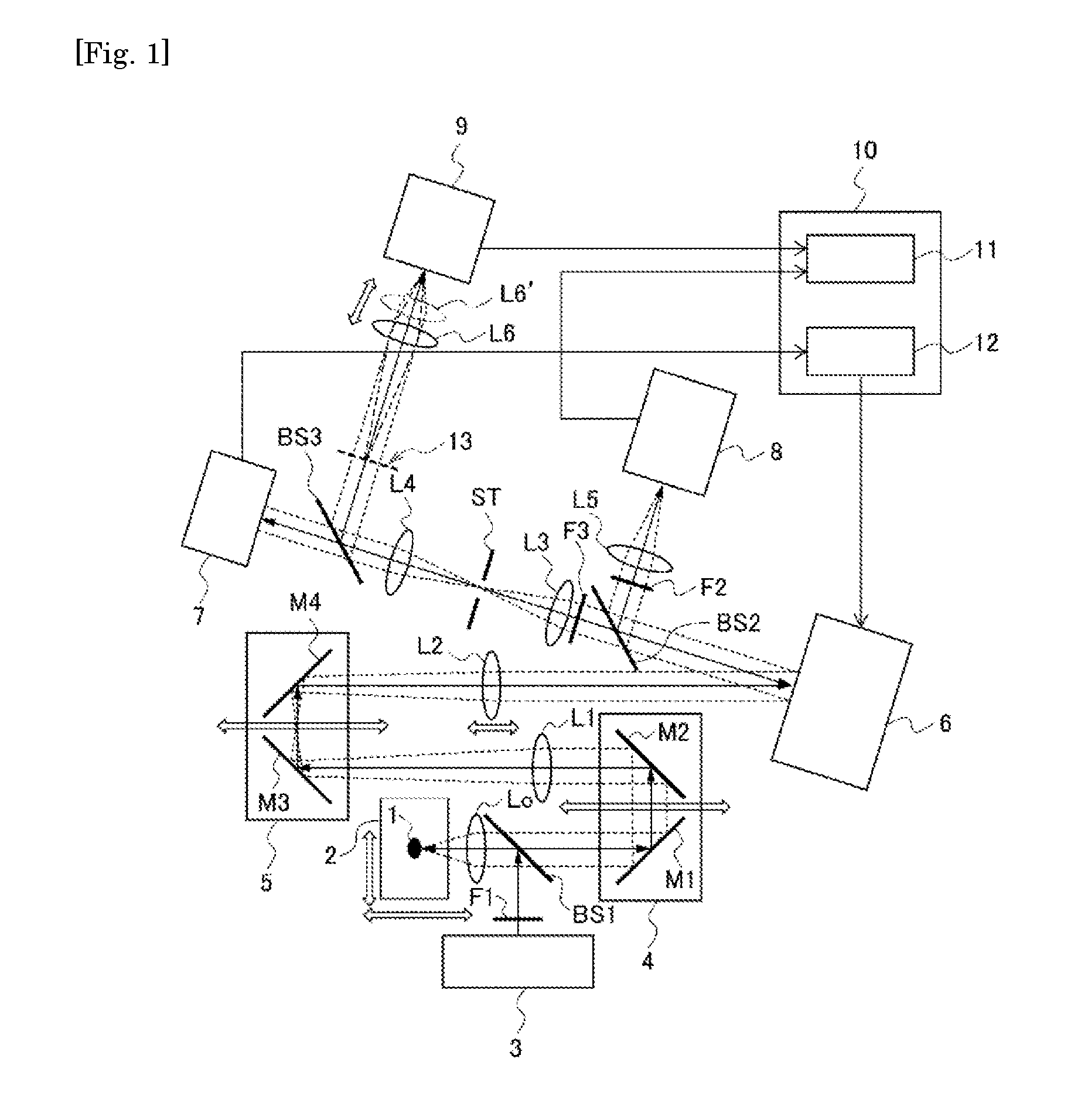
Adaptive optics system and optical device
ActiveUS20160209646A1Improve accuracyAberration correctionOptical measurementsDiagnostics using lightOptic systemPhase modulation
The present invention is intended to provide an adaptive optics system and an optical device that allow correction of wavefront phase aberration with higher accuracy than before and have a wider correction range than the conventional ones, regardless of the distance between the observation target and the fluctuation layer, and the size of the observation target. An adaptive optics system includes: a wavefront phase modulator that makes aberration correction to incident light and emits the corrected light; and an imaging-conjugated position adjustment mechanism that adjusts freely within a specimen the position of a surface imaging-conjugated with a fluctuation correction surface formed by the wavefront phase modulator. The imaging-conjugated position adjustment mechanism adjusts the fluctuation correction surface to be imaging-conjugated with a fluctuation layer existing in the specimen.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST NAT INST OF NATURAL SCI
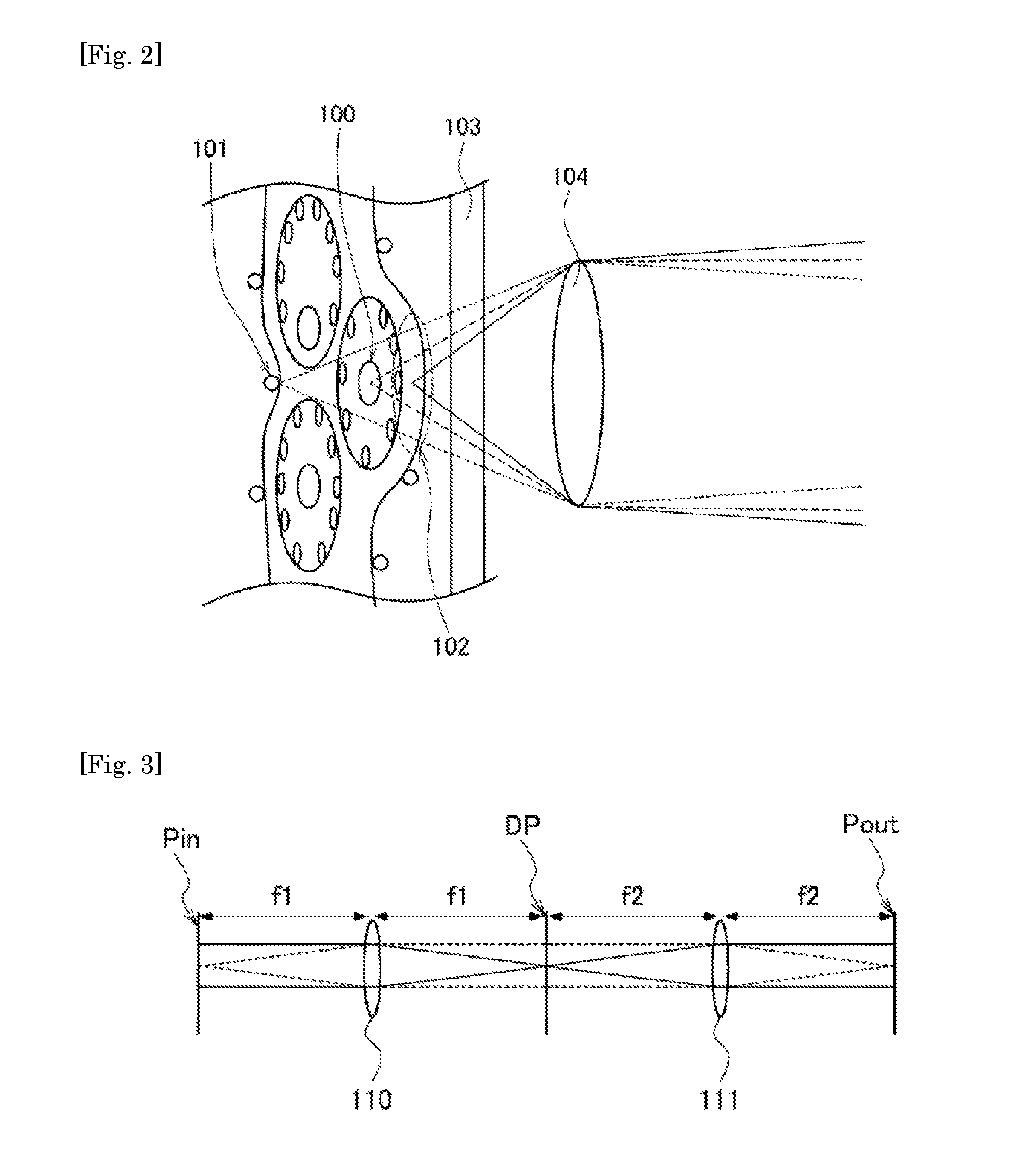
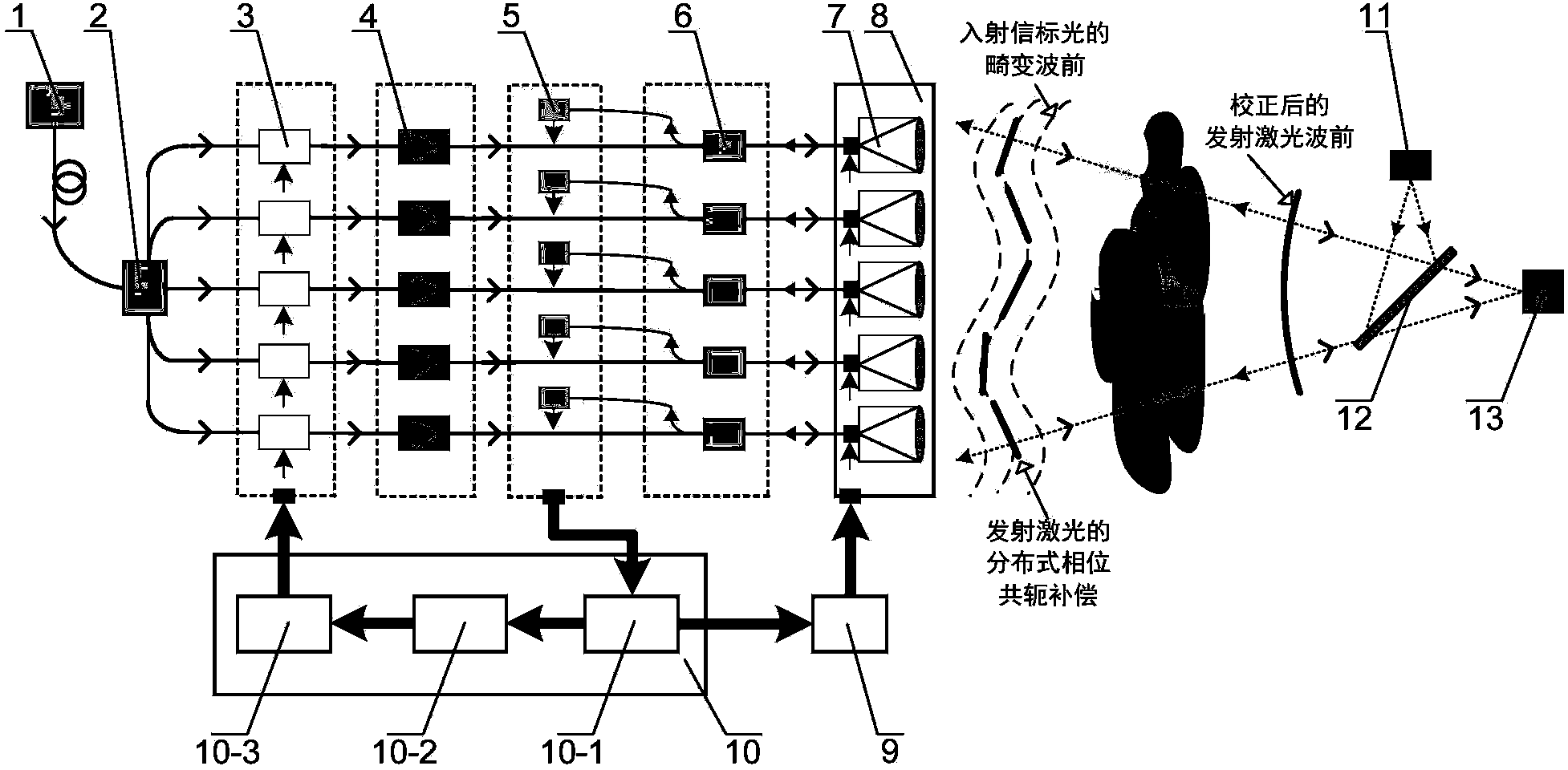
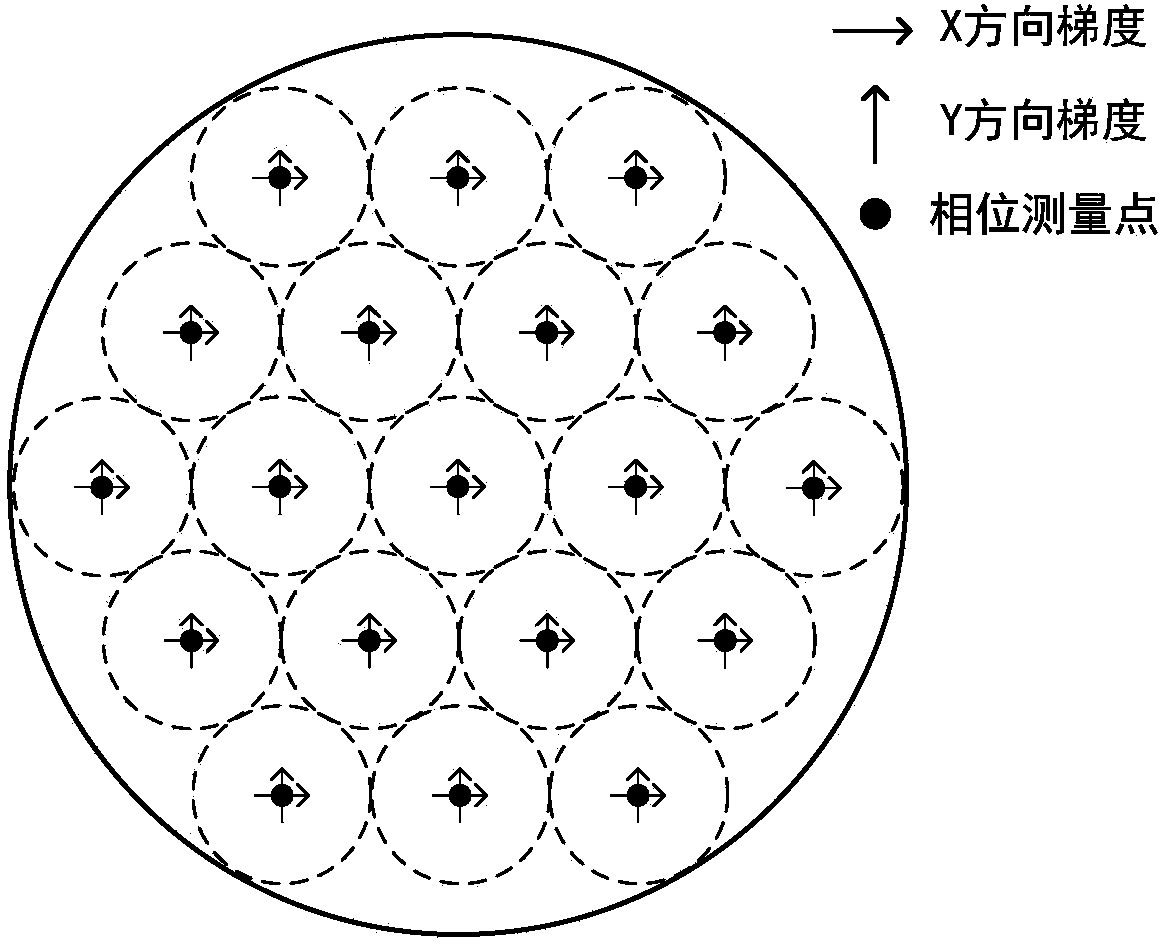
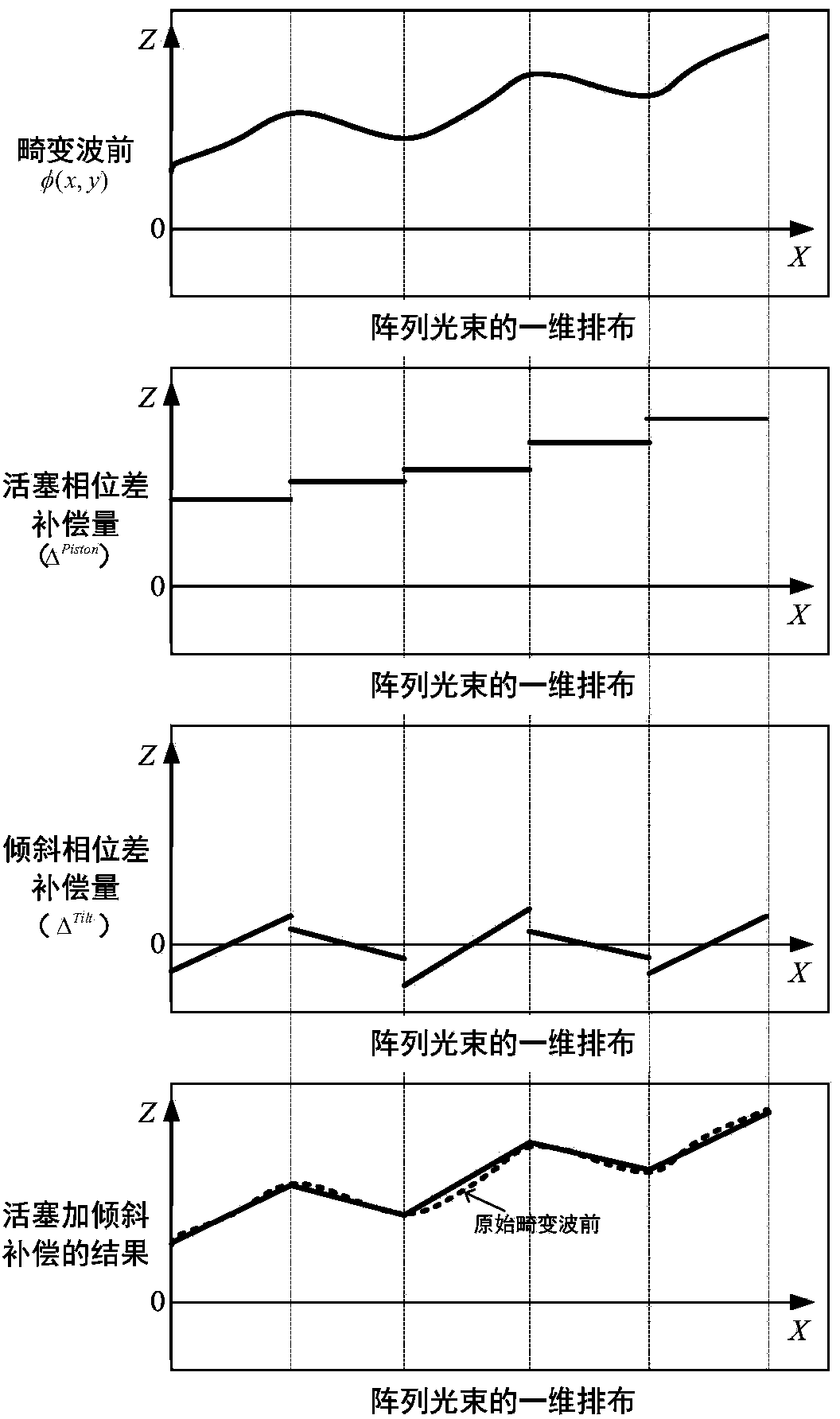
Distributed self-adaptive optical system based on optical fibers
ActiveCN104037606ASimple structureIncrease control bandwidthActive medium shape and constructionBeam splitterLaser array
The invention provides a distributed self-adaptive optical system based on optical fibers. The distributed self-adaptive optical system based on the optical fibers comprises an emitting laser, an optical fiber beam splitter, an optical fiber phase modulator, an optical fiber laser amplifier, a photoelectric detector, a three-port optical fiber circulator, a self-adaptive optical fiber collimator and coupler array, an integrated device, a multi-channel high-voltage amplifier, a wavefront controller as well as a beacon light source, a spectroscope and a far field target. The distributed self-adaptive optical system is based on the fiber laser technology in combination with a plurality of optical fiber devices, and is characterized in that a beacon light beam is divided by use of the self-adaptive optical fiber collimator and coupler array, the wavefront error of beacon light is measured in real time and the error is decomposed to each light sub-beam in a laser array, a piston for emitting the light sub-beams and a tilting phase are controlled independently and in parallel according to the principle of phase conjugation, and the influence of atmospheric turbulence effect on the quality of the light beam at the far field target is relieved. The distributed self-adaptive optical system based on the optical fibers has important application prospects in the fields such as laser atmospheric transmission, free space laser communication and laser radar.
Owner:北京鸿羚科技有限公司
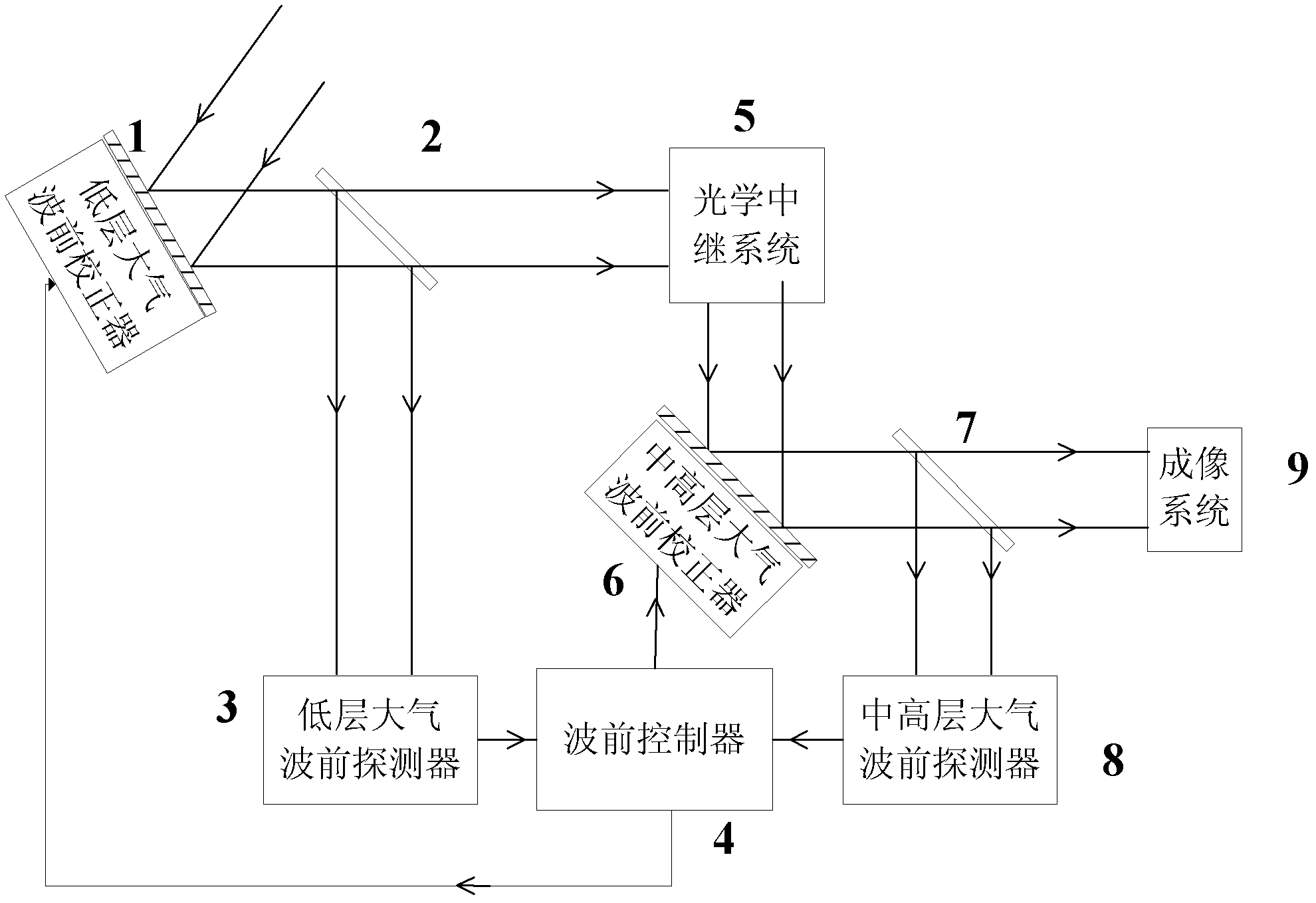
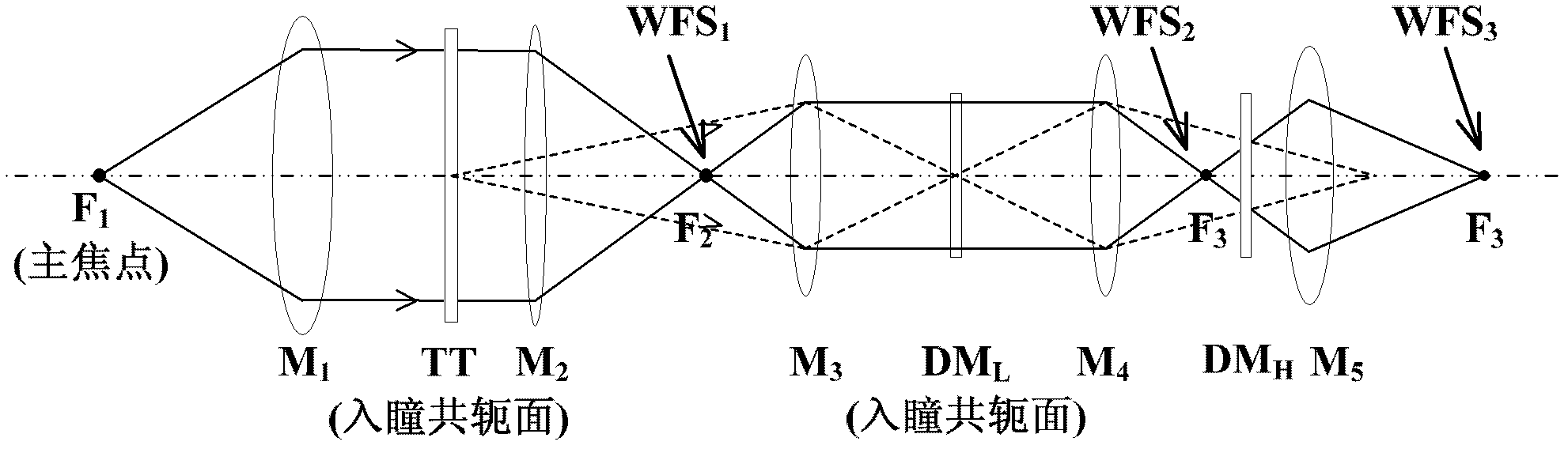
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system
ActiveCN102621687ARealize high-resolution imagingSimplify the difficulty of decouplingOptical measurementsOptical elementsHigh resolution imagingCoupling
The invention provides a solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system comprises a lower atmospheric wave front sensor, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front sensor, a lower atmospheric wave front corrector, a middle and upper atmospheric wave front corrector, a wave front controller, an optical relay system, an imaging subsystem and other necessary optical components. The system has the advantages that sunspots or grain structures on the surface of the sun are taken as beacons and wave front detection is conducted on multiple areas at the same time, so as to obtain wave front distortion caused by turbulence in a large field range; wave front aberration caused by different turbulent layers is calculated by utilizing a tomography algorithm; and at last, the wave front correctors positioned in conjugate positions of the corresponding turbulent layers are controlled to correct the atmospheric turbulence in a layered manner, so as to finally realize high-resolution imaging in the large field range. The solar multi-conjugate adaptive optical system has the advantages that the sequence of the conjugate positions of the high and the lower turbulent layers is adjusted through the optical relay system, so that the lower turbulent layer is firstly compensated and corrected and the accuracy of the detection and the correction is increased; and due to the use of the tomography algorithm, errors caused by the coupling of the wave front aberrations of the different turbulent layers are reduced.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High sensitivity coherent photothermal interferometric system and method for chemical detection
A photo-thermal interferometric spectroscopy system is disclosed that provides information about a chemical at a remote location. A first light source assembly is included that emits a first beam. The first beam has one or more wavelengths that interact with the chemical and change a refractive index of the chemical. A second laser produces a second beam. The second beam interacts with the chemical resulting in a third beam with a phase change that corresponds with the change of the refractive index of the chemical. A detector system is positioned remote from the chemical to receive at least a portion of the third beam. An adaptive optics system at least partially compensates the light beam degradation caused by atmospheric turbulence. A focusing system is used to bring together the light passed through the chemical; the focusing system includes a multimode fiber for the light collection, The detector system provides information on a phase change in the third beam relative to the second beam that is indicative of at least one of, absorption spectrum and concentration of the chemical.
Owner:CELIGHT
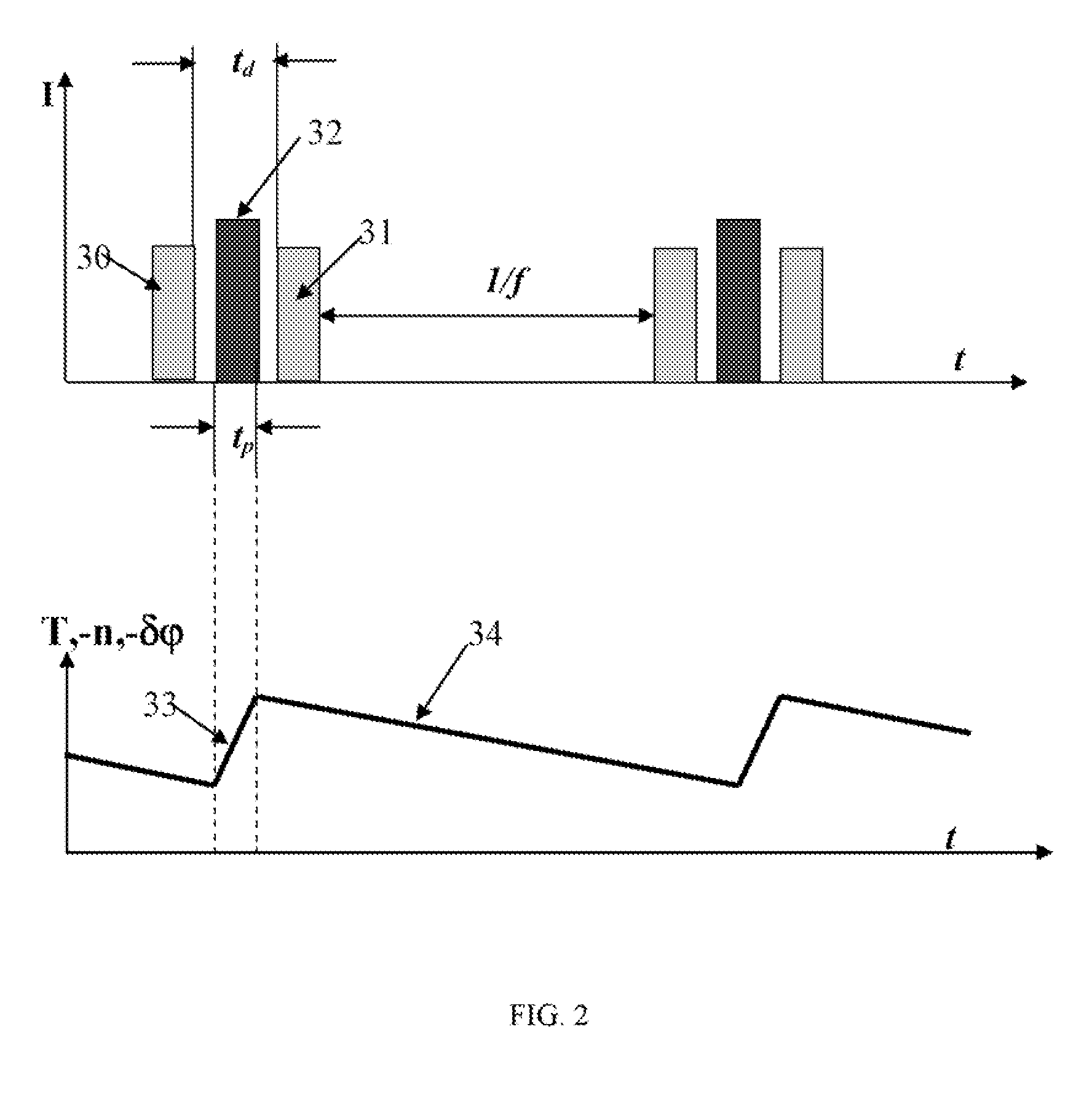
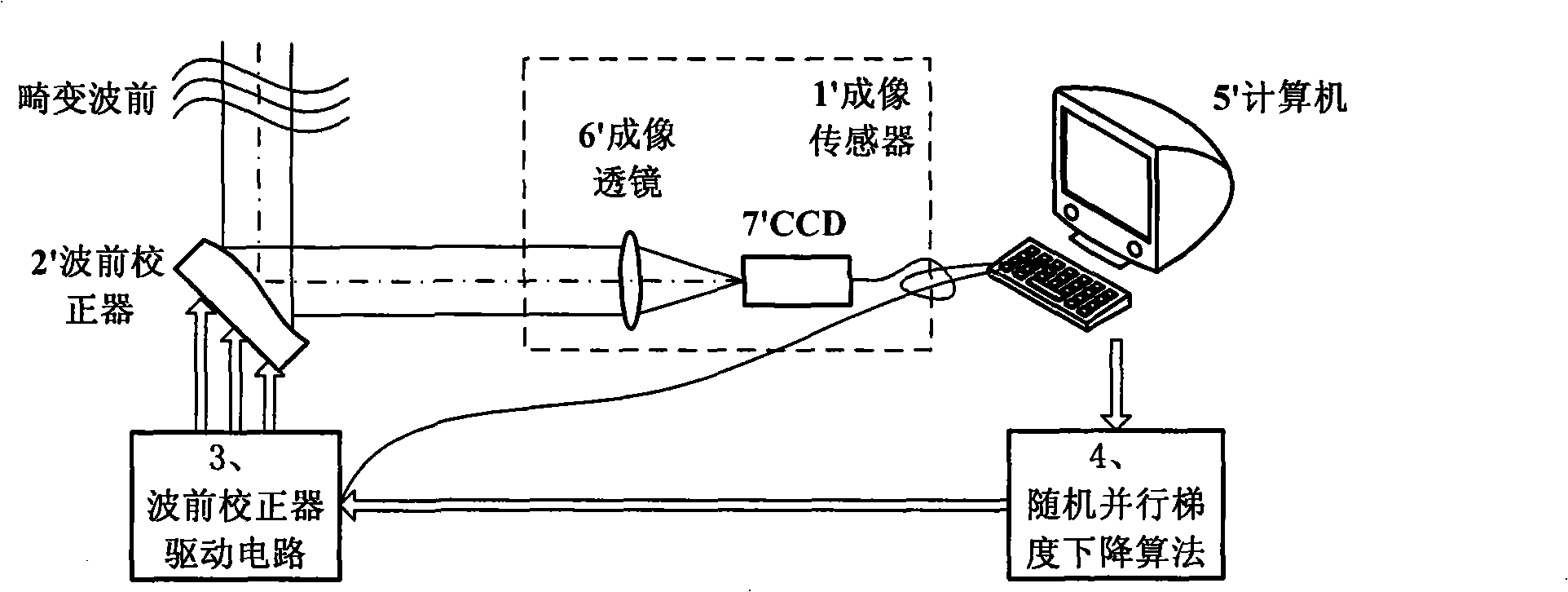
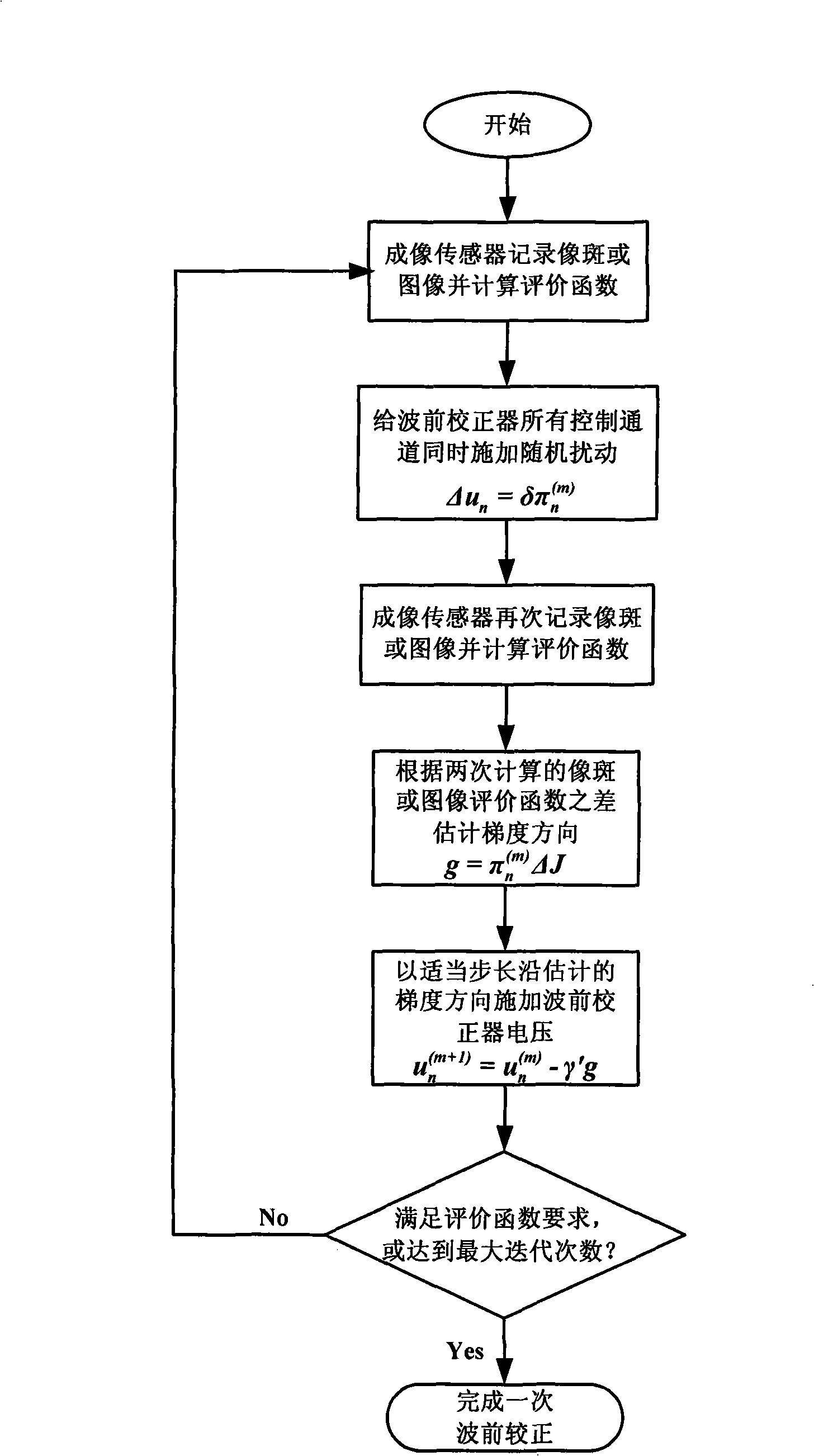
Wavefront-free detector self-adapting optical system based on random paralleling gradient descent algorithm
The invention relates to an adaptive optics system without wavefront detector based on the random paralleling gradient descent algorithm, comprising an imaging sensor, a wavefront corrector and a driving circuit thereof and a random paralleling gradient descent algorithm. The imaging sensor detects the blur image spot or image generated by the distortion wavefront at real time and the control pressure corresponding with the wavefront corrector for making the image spot or image clear is obtained by the random paralleling gradient descent algorithm and applied on the wavefront corrector by the driving circuit, therefore the wavefront corrector generates compensation dosage for removing the wavefront distortion, thus the above operation is repeatedly performed to correct the wavefront error, so as to obtain idea imaging effect. The adaptive optics system based on the random paralleling gradient descent algorithm does need the wavefront detector and influence function of the wavefront corrector, with features of simple structure, compactness, light weight and high efficiency for light energy utilization.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wavefront sensing system employing active updating of reference positions and subaperture locations on wavefront sensor
ActiveUS7437077B2Avoiding shortcoming and drawbackPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorEngineering
A free-space adaptive optical laser communication system having signal transmission and reception channels at all terminals in the communication system, wherein wavefront sensing and wavefront correction mechanisms are employed along signal transmission and reception channels of all terminals in the communication system (i.e. adaptive optics) to improve the condition of the laser beam at the receiver (i.e. reduce the size of the spot the detector plane). Speckle-to-receiver-aperture tracking mechanisms are employed in the transmission channel of the communication system and laser beam speckle tracking mechanism in the reception channels thereof, so as to achieve a first level of optical signal intensity stabilization at signal detector of each receiving channel. Speckle-to-fiber / detector locking mechanisms are also employed in signal receiving channels of all terminals in the communication system so as to achieve a second level of optical signal intensity stabilization at signal detector of each receiving channel.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye by interaction of a patient with an examiner and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20060238710A1Easy to catchGood utilization basisRefractometersSkiascopesVisual acuityHuman eye
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
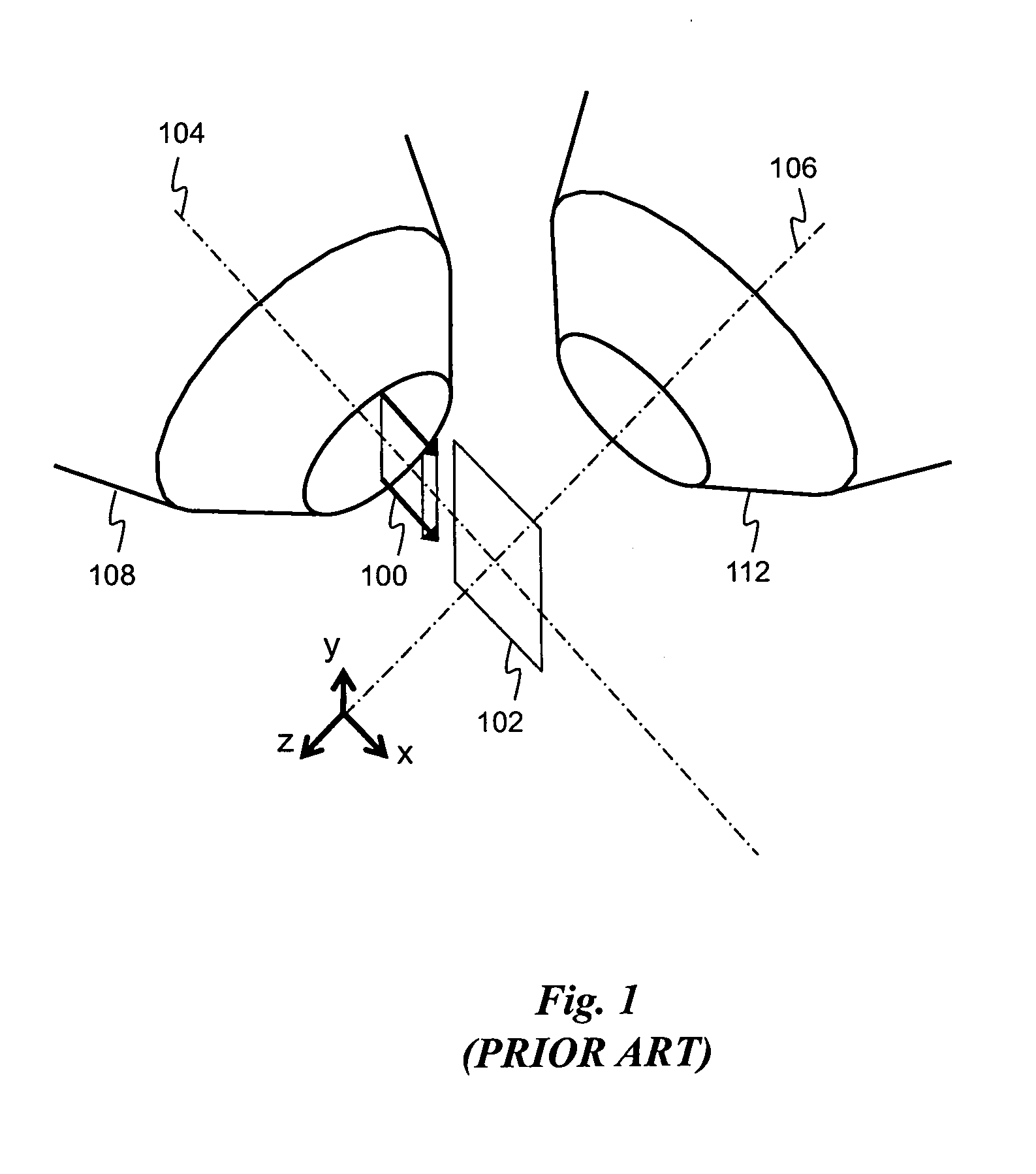
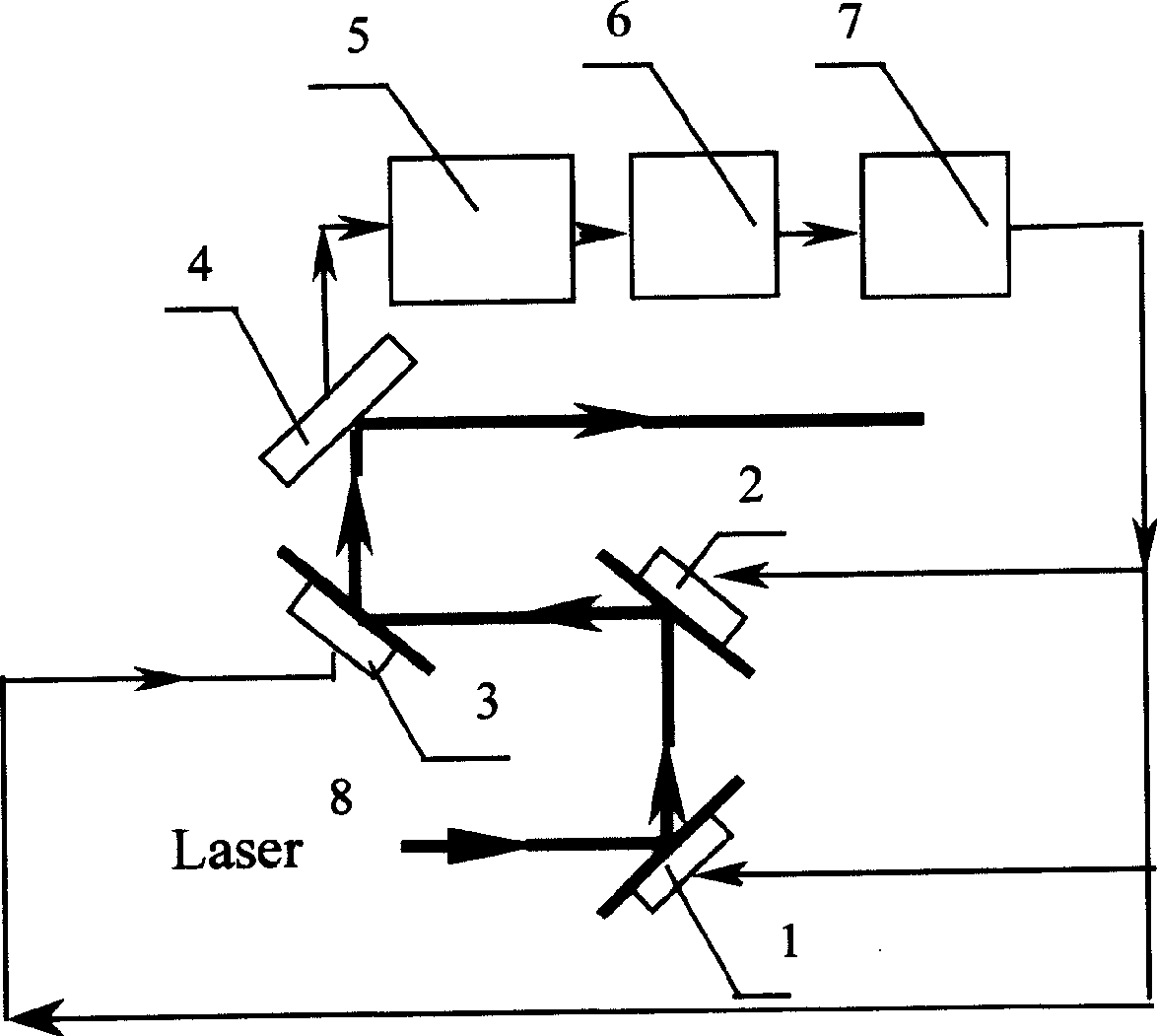
Double wave front calibrator self-adaptive optical system
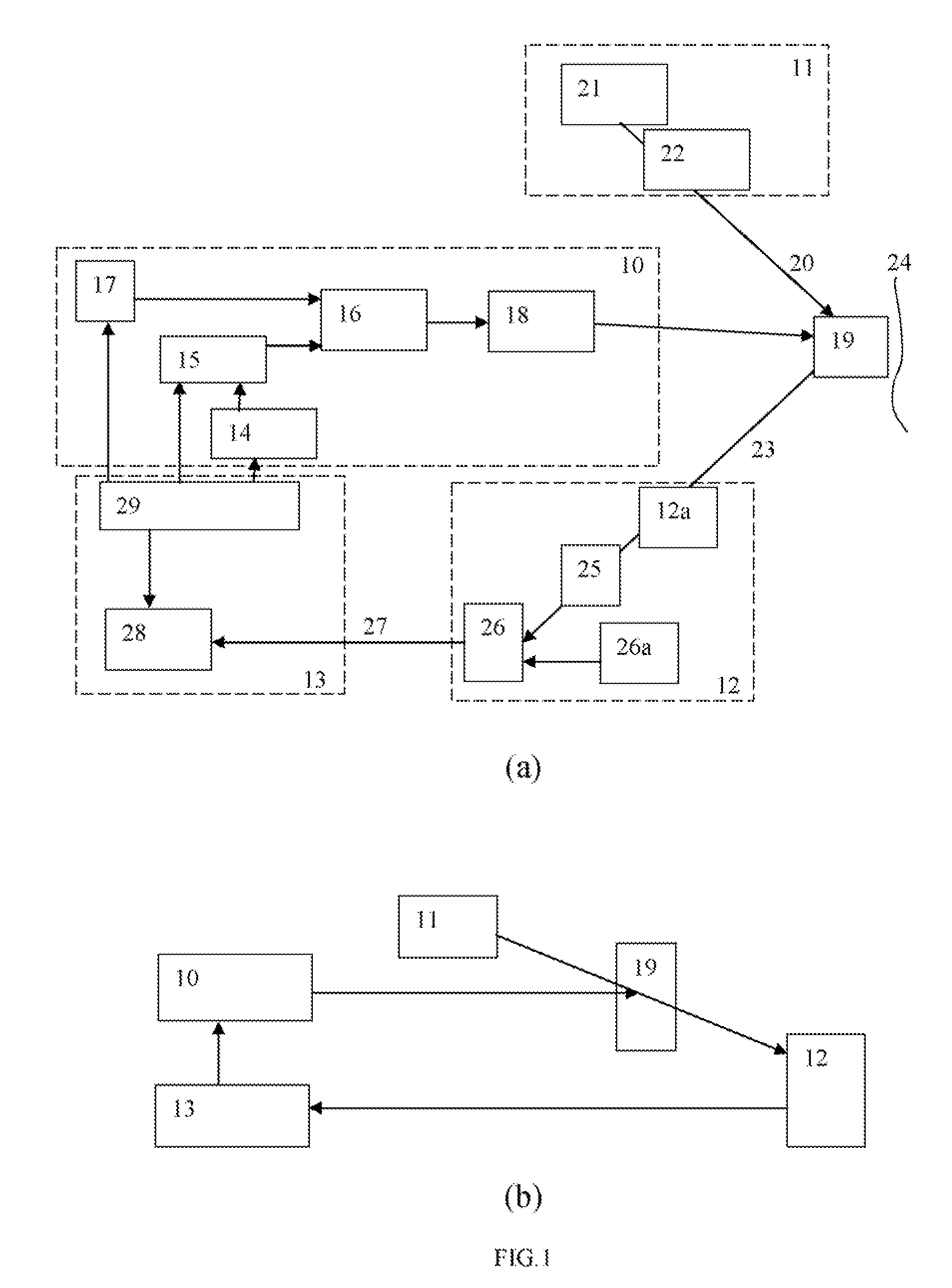
ActiveCN1664650AReduce production difficulty requirementsQuality improvementConverting sensor output opticallyOptical elementsWavefront sensorLight beam
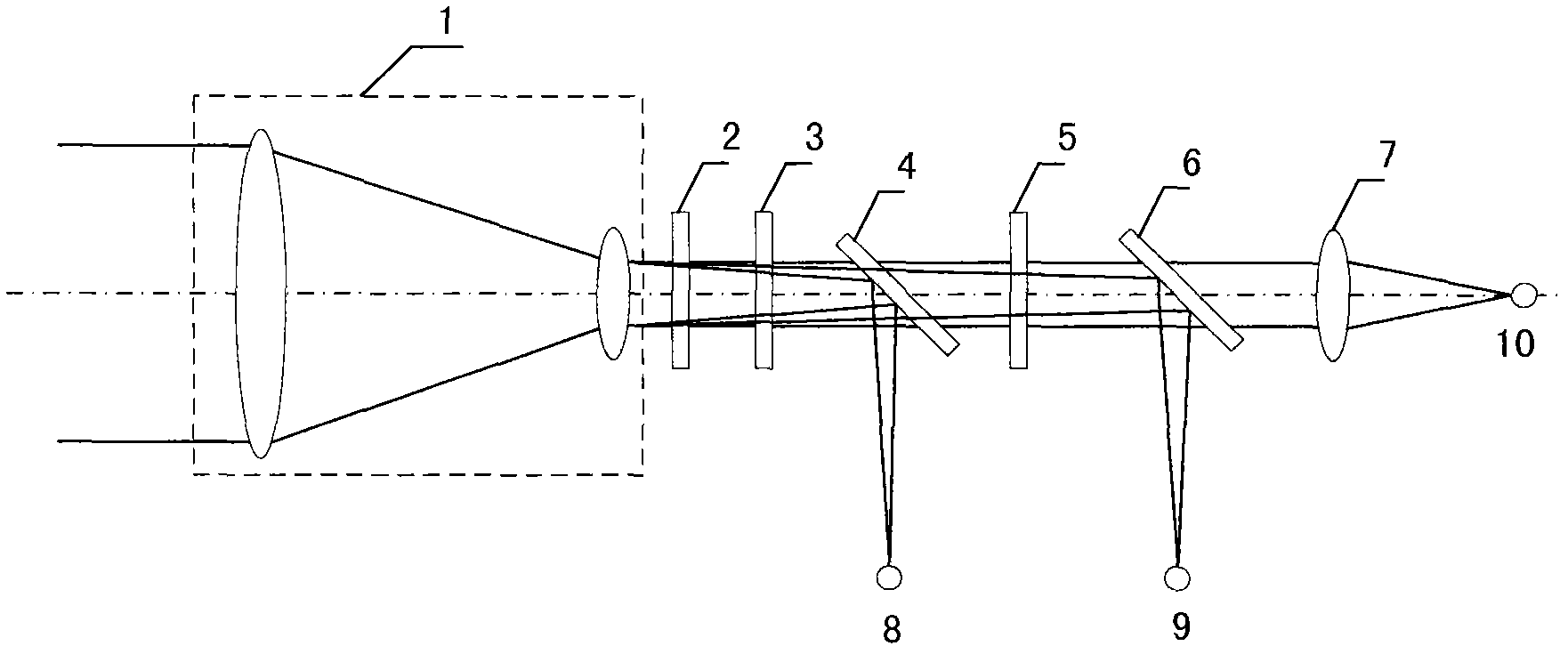
This invention relates to double wave pre-corrector self-adapting optical system, which comprises incline reflection lens, two before wave correctors, before wave sensor, splitter lens, before wave processor, two before wave correctors, which separately realize the low and high picture difference correction as needed. The before wave corrector needs large journey to correct the low picture difference and the before wave corrector has larger space frequency.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive optics for compensating for optical aberrations in an imaging process
Owner:HEIDELBERG ENGINEERING GMBH
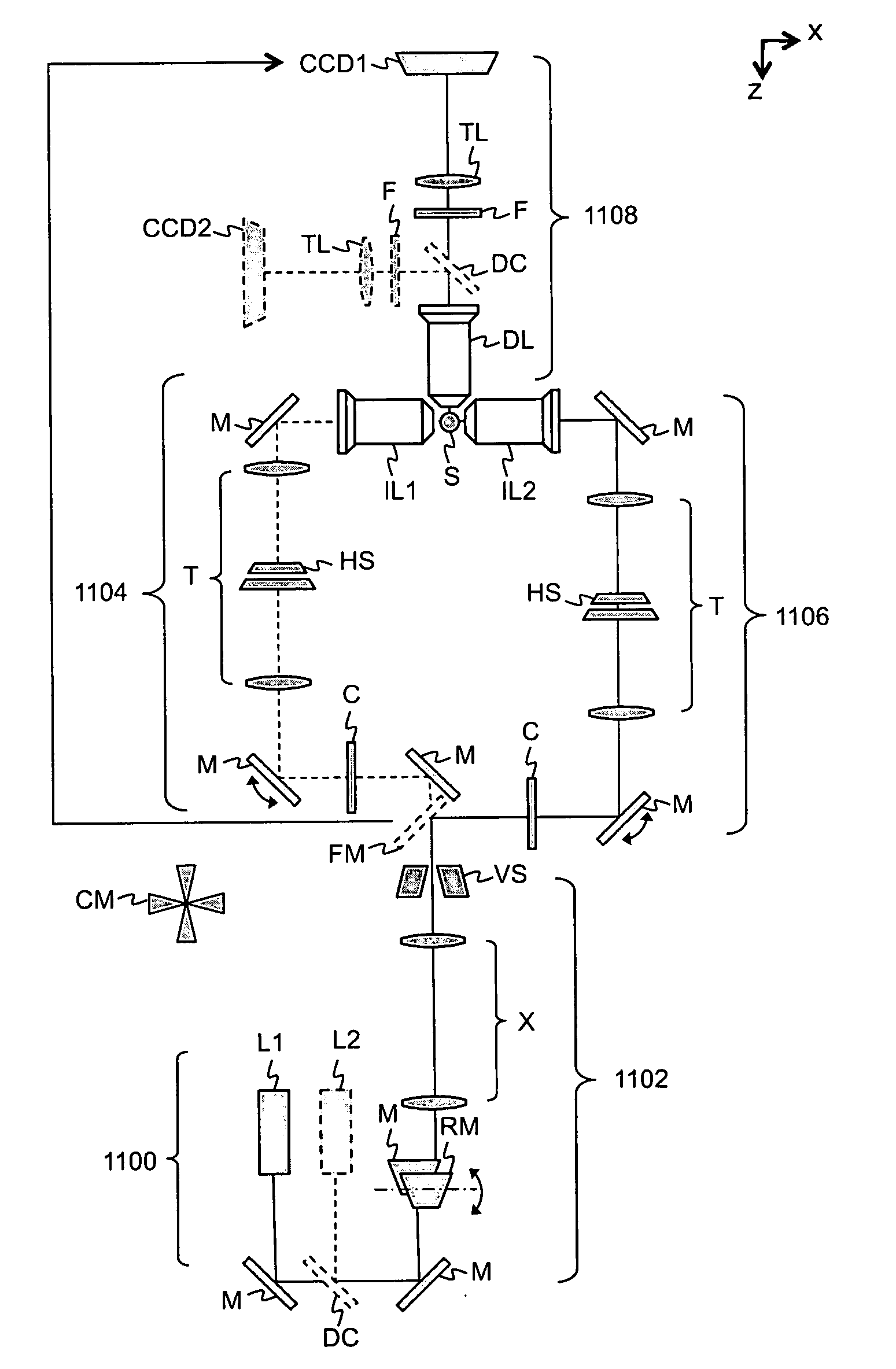
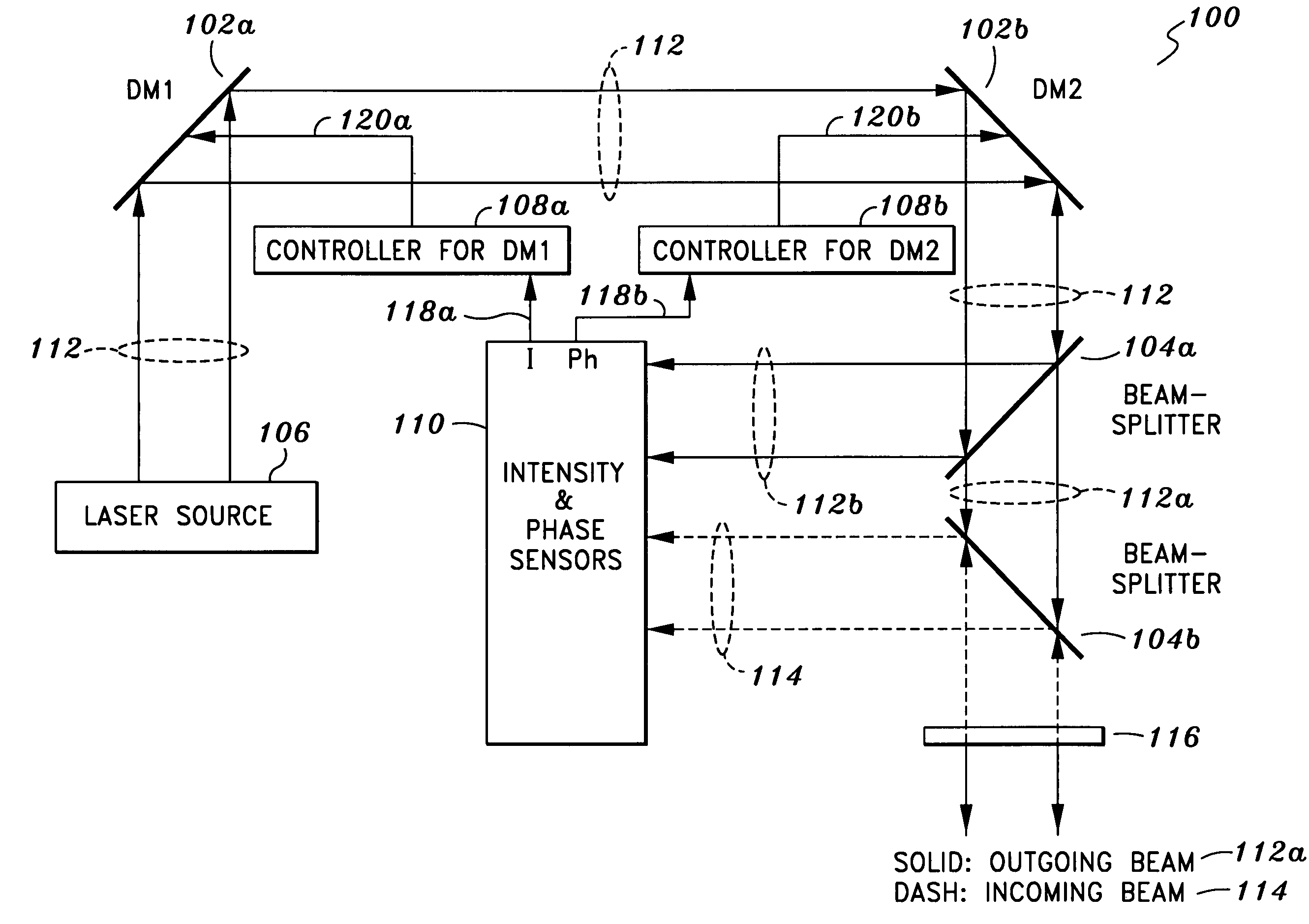
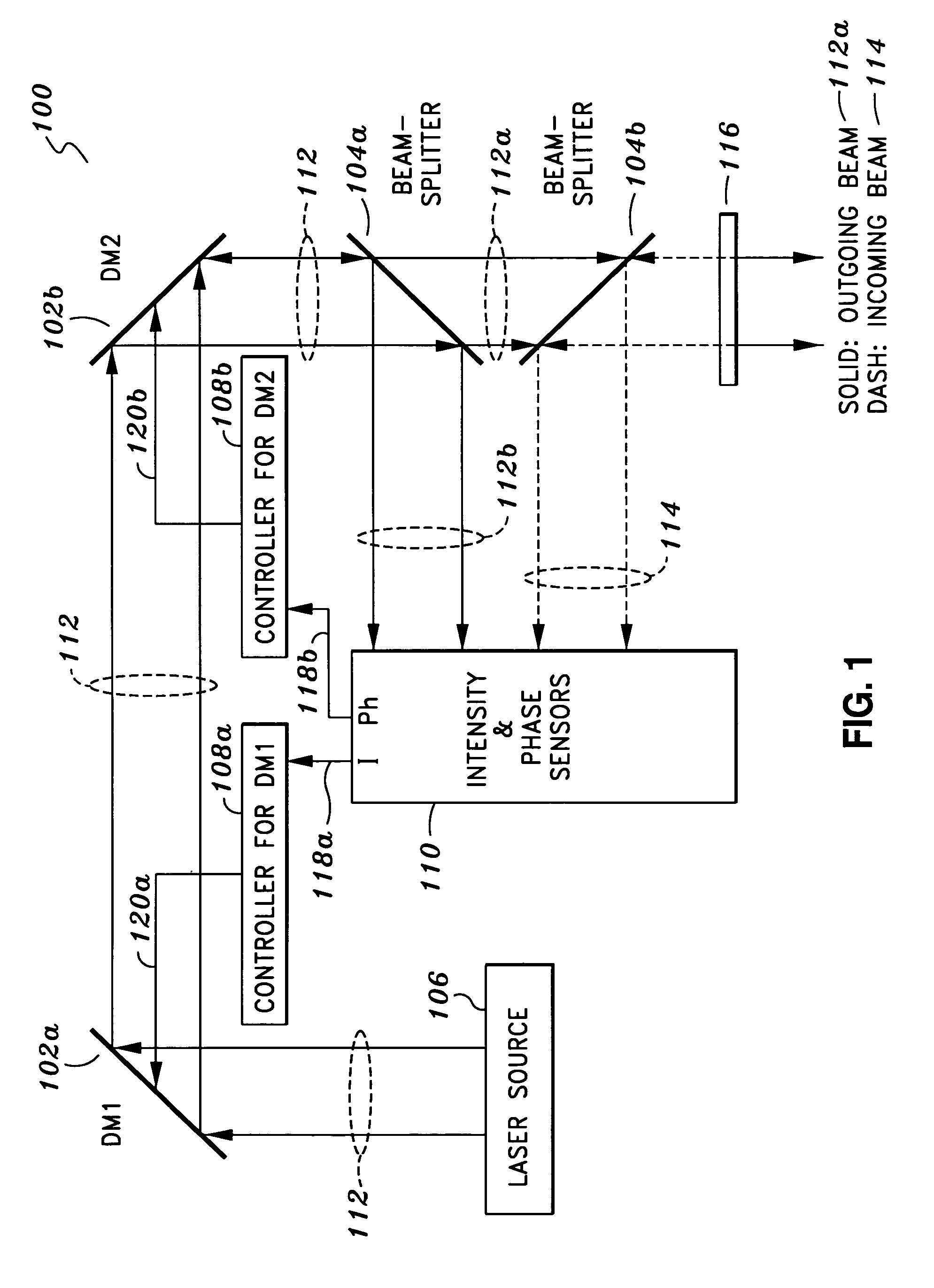
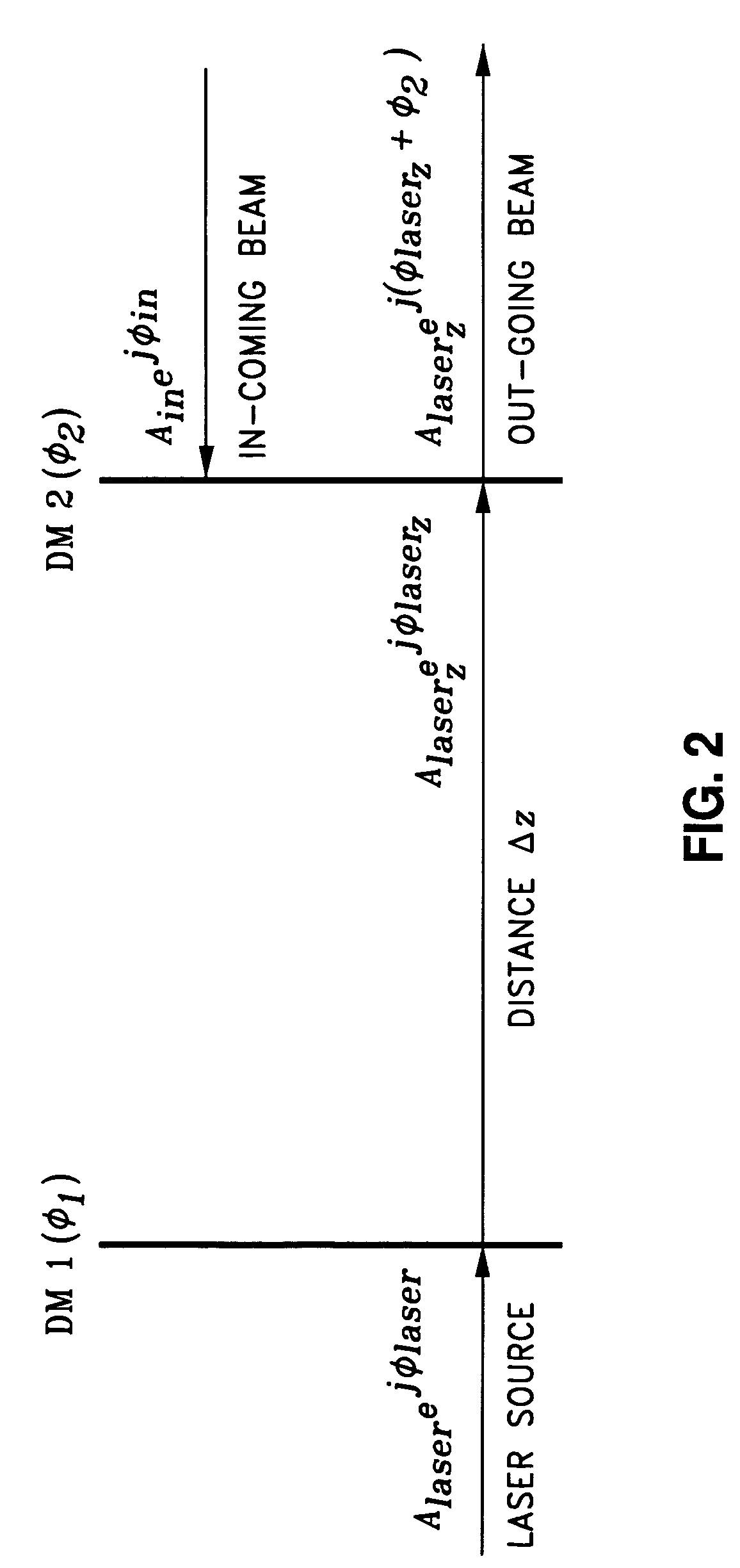
Amplitude and phase controlled adaptive optics system
ActiveUS7397018B1Good compensationPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamPhase control
An adaptive optics system is provided. The system includes a light source, a pair of deformable mirrors and a detection module. The light source is configured to provide an outgoing beam. The outgoing beam has an amplitude and a phase. The first deformable mirror is configured to reflect the outgoing beam and adjust its associated amplitude. The second deformable mirror is configured to reflect the outgoing beam reflected from the first deformable mirror and adjust its associated phase. The detection module is configured to detect an incoming beam and the reflected outgoing beam from the second deformable mirror and generate certain signals. The signals are used to control the first and second deformable mirrors such that the amplitude of the outgoing beam is the same as that of the incoming beam and the phase of the outgoing beam is opposite that of the incoming beam.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com