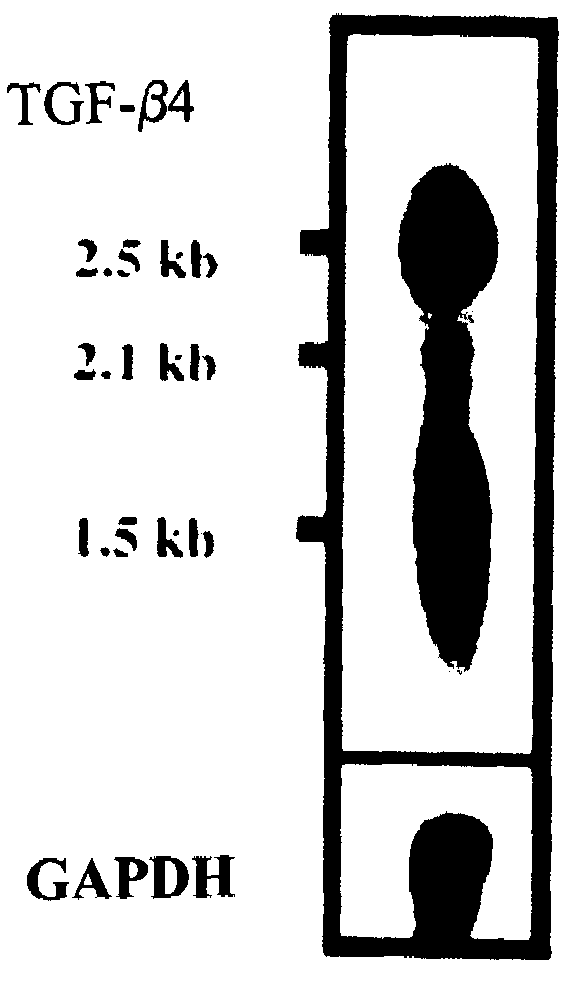
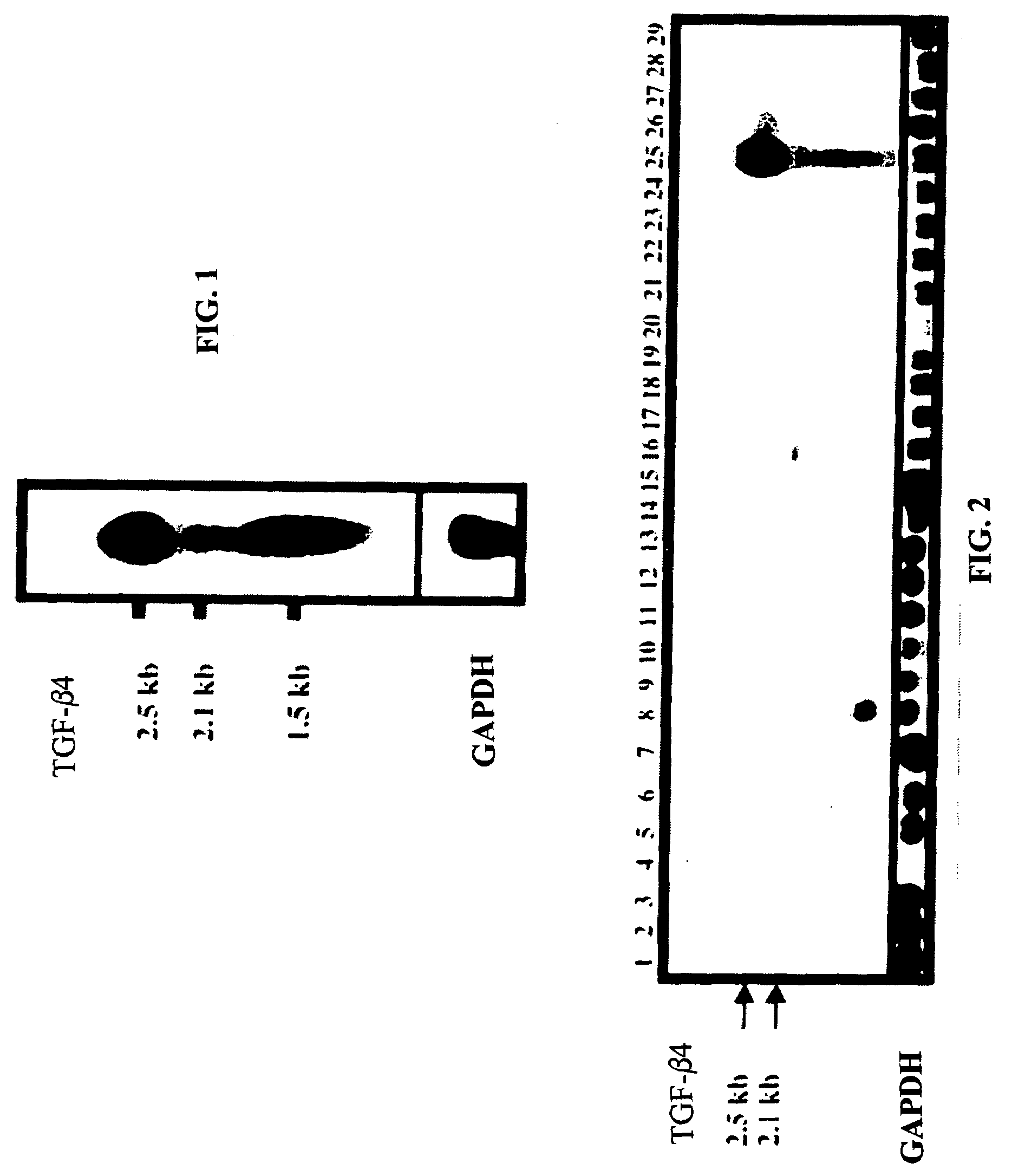
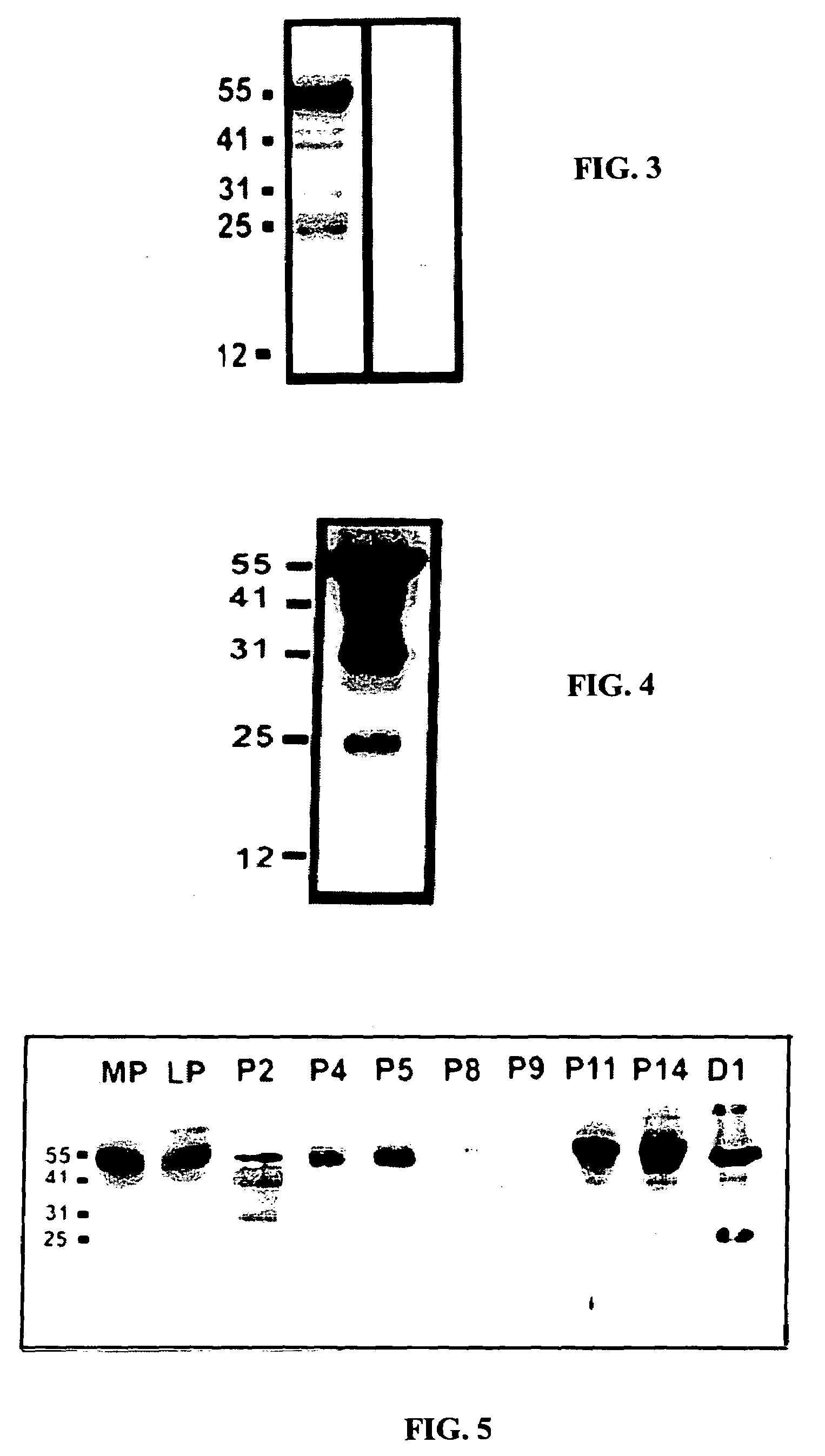
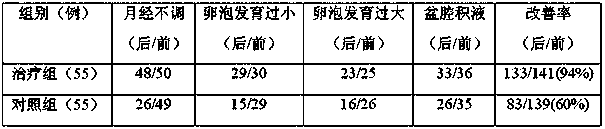
Patents
Literature
173 results about "Female infertility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
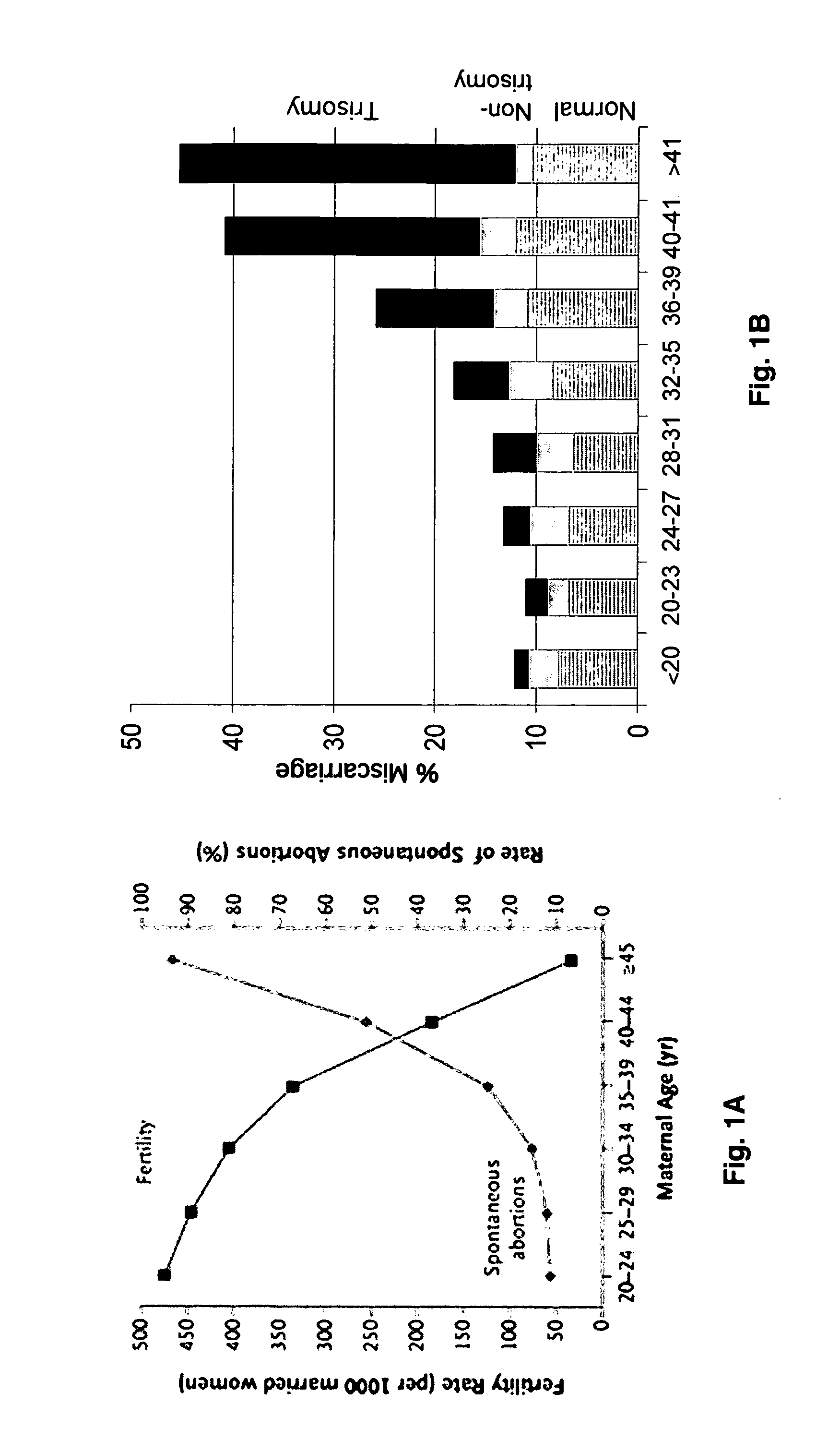
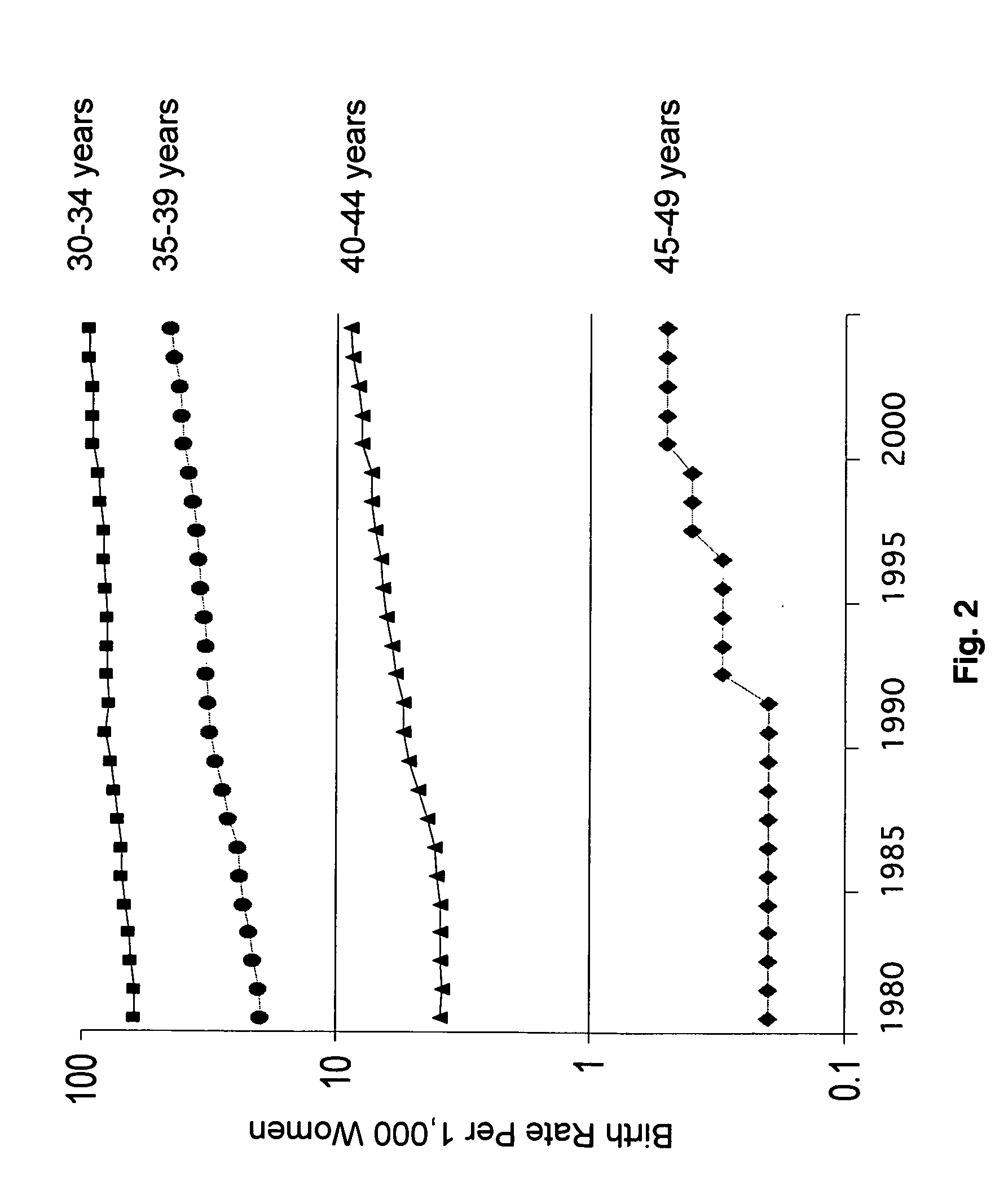
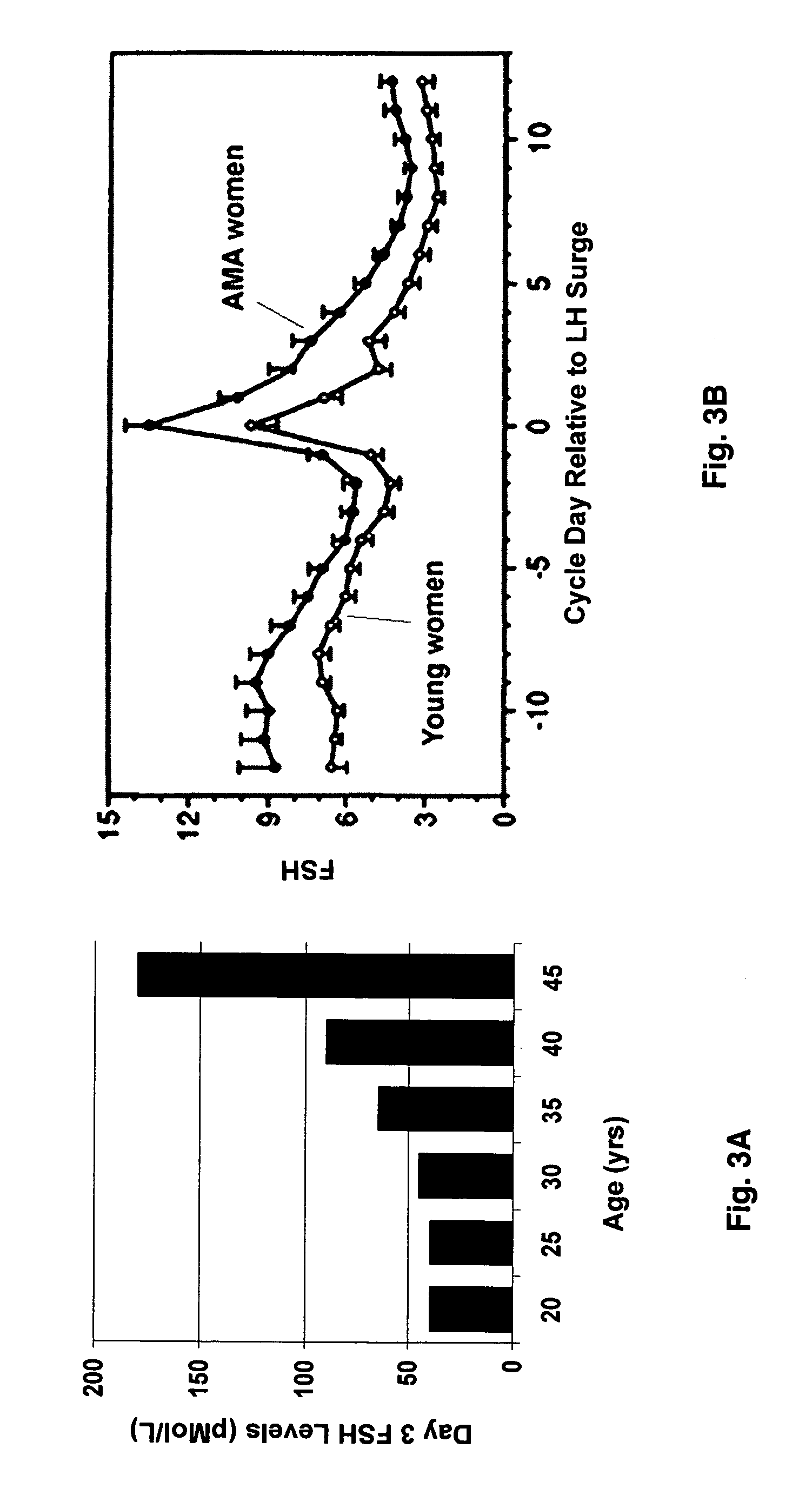
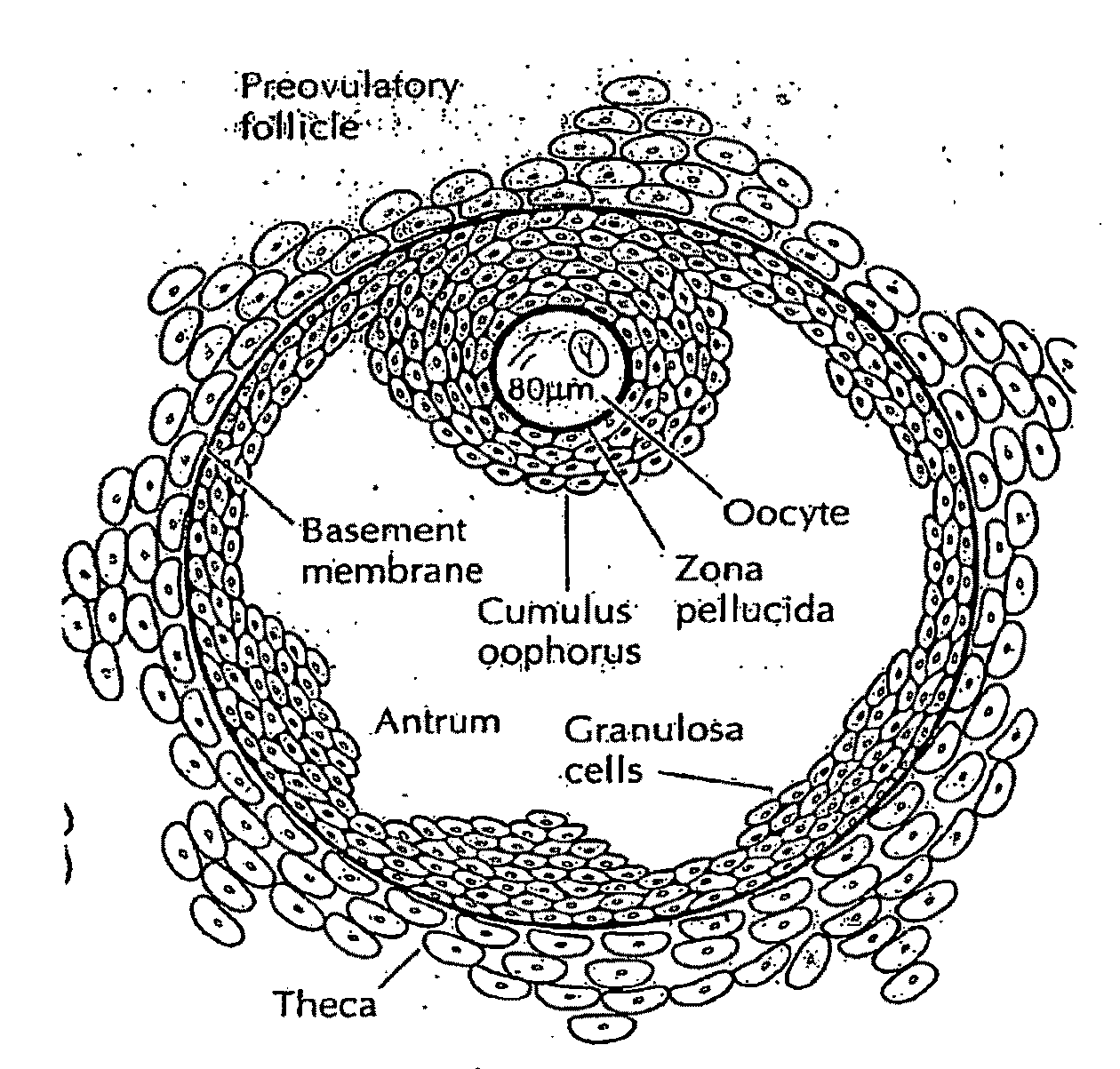
Infertility means not being able to get pregnant after at least one year of trying (or 6 months if the woman is over age 35). If a woman keeps having miscarriages, it is also called infertility.
Hormone normalization therapy and uses therefor
InactiveUS20090137478A1Reduce morbidityAvoid infertilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisMiscarriageAromatase inhibitor
The present invention discloses a novel method of prevention of birth defects, miscarriages and infertility in women. The two therapies, disclosed herein, the hormone normalization therapy and the aromatase inhibitor-hormone normalization therapy, focus on restoring young hormonal levels in women in order to prevent female infertility and miscarriages, guide follicular and oocyte maturation, and promote correct chromosomal segregation in oocytes and early embryos.
Owner:BERNSTEIN LORI R
Chinese medicinal composition for treating female infertility and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101966313AImprove self-coordinationEffective treatmentAnthropod material medical ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRhizomeAstragalus mongholicus
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal composition for treating female infertility and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicinal composition comprises the following raw material medicaments: glossy privet fruit, medlar, tuber fleeceflower root, ginseng, raw astragalus, dioscorea root, achyranthes root, white paeony root, szechwon tangshen root, raw rehmannia root, prepared rehmannia root, Chinese angelica, red paeony root, oriental waterplantain rhizome, looasa lateritia gill, mongolian snakegourd root, cassia bark, medcinal evodia fruit, tangerine peel, costus root, nutgrass flatsedge, medicated leaven, malt, motherwort herb, south dodder seed, Chinese leek seed and the like. The Chinese medicinal composition can be prepared into any common oral preparations by a conventional method for preparing traditional Chinese medicinal preparation. The Chinese medicinal composition can improve symptoms such as female infertility and the like caused by deficiency of chon and ren channels, deficiency-cold of uterus, depressed emotion, qi-blood disharmony, stagnation of qi activity, obstruction of chon and ren channels, blood stagnation and coagulation, accumulation of abdominal mass, agglomeration of uterus and the like obviously, has the definite and obvious clinical curative effect and is quick in response. The Chinese medicinal composition also has the advantages of low cost, no toxic or side effect and the like.
Owner:TAIYI HEPU BEIJING RES INST OF TCM
Methods for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Female Infertility Using Molecular Markers
InactiveUS20100055730A1Improve fertilityFavorable assisted reproductive therapy outcomeMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisRetinol bindingFemale infertility
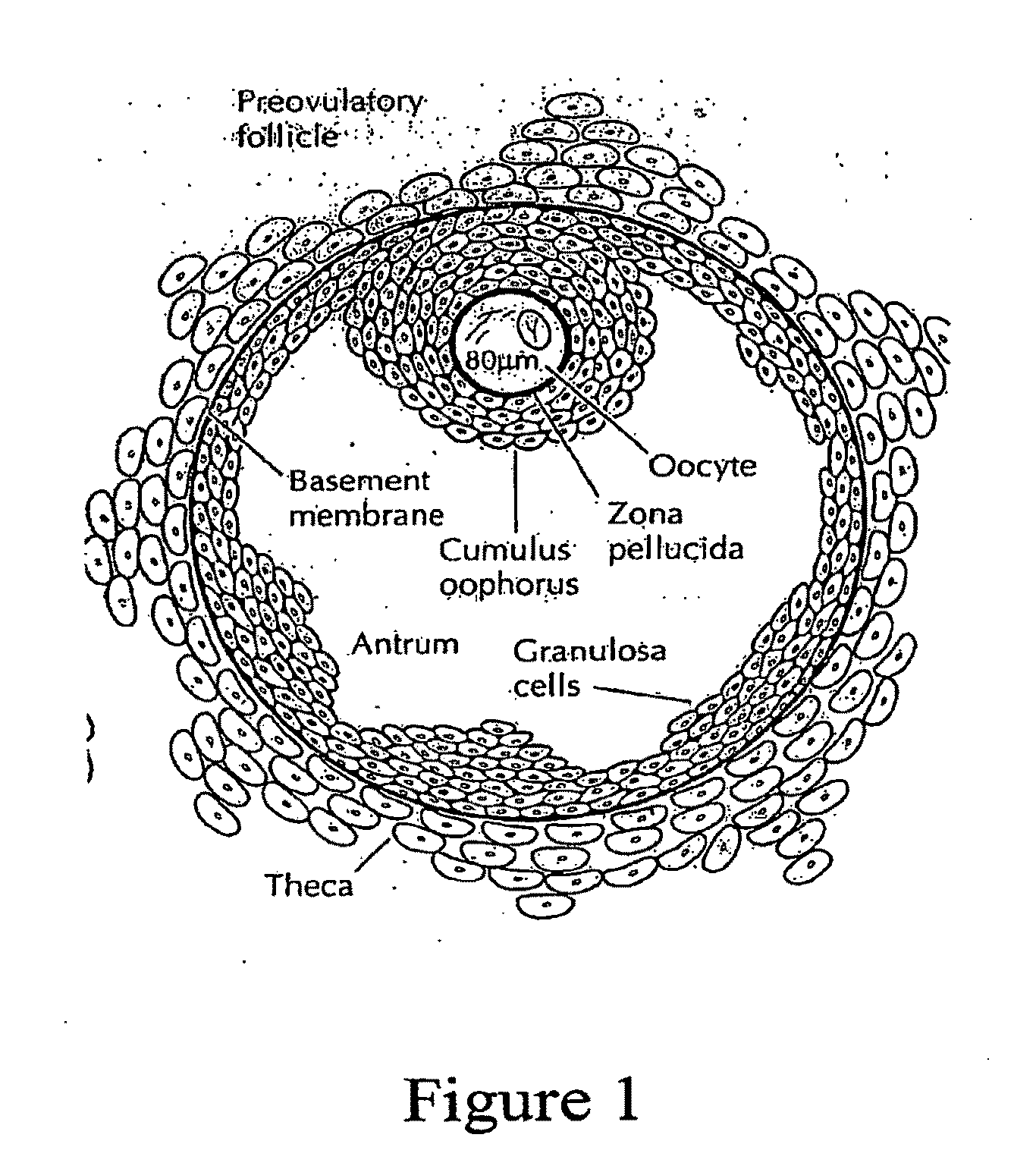
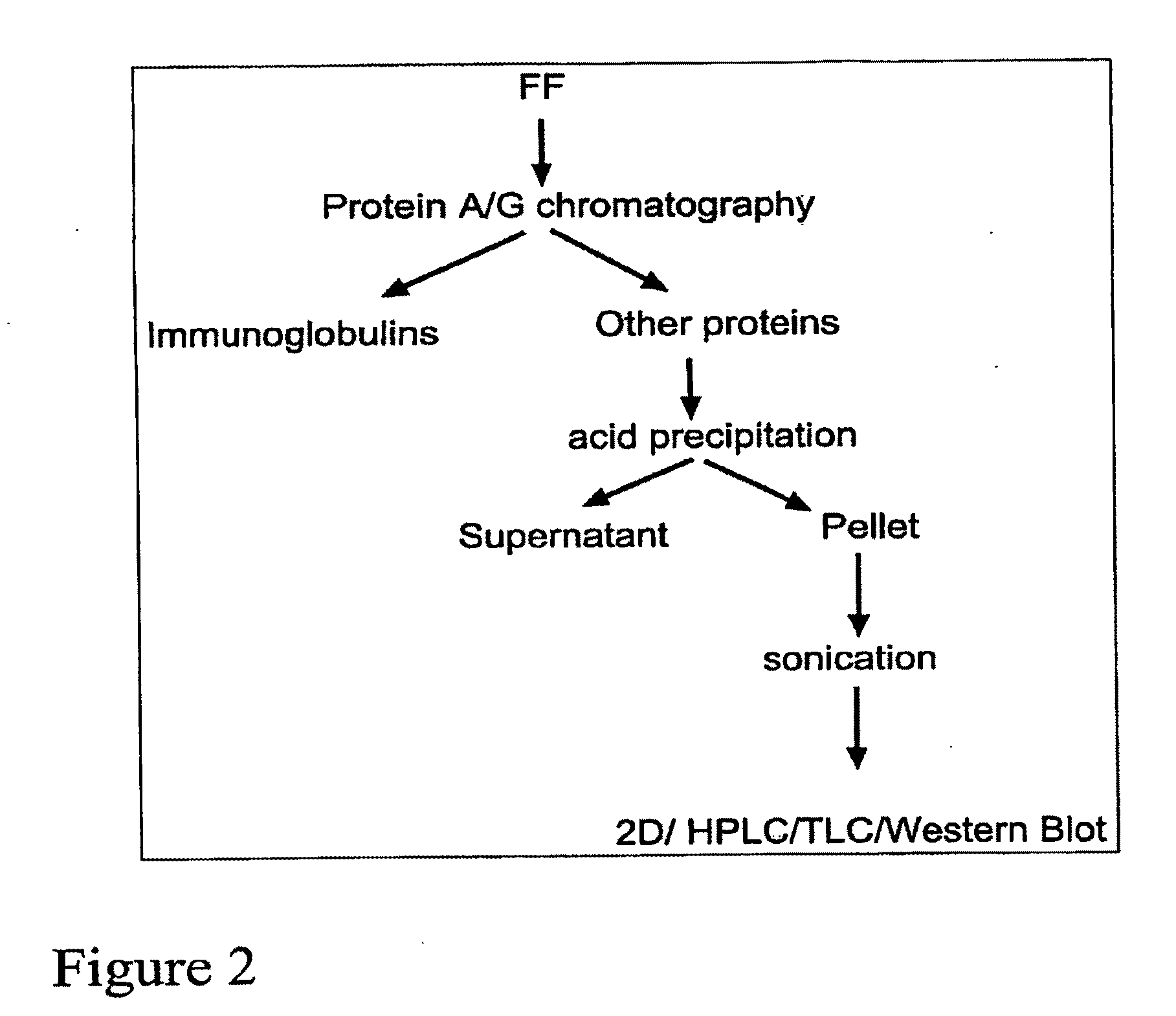
The present invention features methods of evaluating the fertility of a female subject, or the fertilization competence of an oocyte extracted from an ovarian follicle, using measurements of one or more differentially expressed components of follicular fluid. The methods of the invention include the steps of measuring the level of a component of follicular fluid. Examples of components of follicular fluid useful in the methods of the invention include apolipoprotein IA, apolipoprotein A, apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein E, prothrombin, CD 133 (prominin), alpha-2 macroglobulin, alpha crystallin B chain, ATP synthase alpha chain, neuropilin, heparin, heparin-like molecules, heparin receptors, bile acids, Aid, CS, Cortisol, Ang1, Ang2, cholesterol and its derivatives, cholesterol receptors, phospholipids, HDL, LDL, VLDL5 chylomicrons, retinoids, carotenoids, retinol-binding proteins, retinoic acid receptors, transthyretins, leptin, fibrin, ADPases, metal ions, and cytokines, e.g., IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-IO, IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-13, VEGF, VEGF receptors, PlGF, INF-γ, Aid, CS, Ang1, Ang2, TNF-α, C-reactive protein, and angiopoetin, and comparing the measured level to a reference range in order to determine whether the subject is likely to be fertile, or whether the oocyte is likely to be fertilization-competent. The invention also features methods of treatment of an infertile subject, wherein the treatment methods utilize measurements of one or more differentially expressed components of follicular fluid to determine optimal conditions for performing assisted reproductive therapy, e.g., in vitro fertilization.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Diagnostic markers of human female infertility
Methods and reagents for the diagnosis of female infertility, prognostic indicators for female infertility, compounds for the treatment of female infertility, compounds and methods for contraception. Methods and compounds are based on the levels of ebaf in endometrial tissue. Methods for diagnosing endometrial receptivity and bleeding function by screening a biological sample such as an endometrial tissue sample, or bodily fluid for the presence of ebaf. A contraceptive compound containing an effective amount of ebaf and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A diagnostic kit for timing contraception containing reagents for screening a sample for the presence of ebaf. A method of treating endometrial irregularities by down-regulating the expression of ebaf.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Protein chip for female infertility detection and kit thereof
The present invention discloses a dedicated multi-index protein chip for female infertility detection and a kit thereof. The protein chip consists of a substrate, protein detection indexes arranged on the substrate in an array mode and a contrast coating for the detection indexes. The protein detection indexes cover ovary antigen (OAg), endometrium antigen (EAg), sperm antigen (SAg), zona pellucida antigen (ZAg), human chorionic gonadotropin antigen (HCG), trophoblast antigen (TAg) and cardiolipin antigen (CAg). The present invention overcomes the defects of the existing autoimmunological detection products on market, such as single detection function, lagged detection indexes and no integration. Besides the indexes of the product (patent application No: 200510102466.3), the protein chip also has the ACA index. The density of all indexes can be quantitatively detected, and the cross reaction of all indexes is eliminated. The present invention not only has high specificity and high sensitivity, but also has high accuracy and precision.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
Drug for treating male infertility
InactiveCN101007138APromote secretionFunction increasePowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsMale infertilityTreatment effect
The invention discloses a medicament for treating male infertility, which is prepared from astragalus root, Siberian solomonseal rhizome, epimeddium, cnidium fruit, plantain seeds, ginseng, raspberry, deer horn gum, asparagus root, poria cocos, leek seeds, broomrape, anemarrhena rhizome and eucommia bark through steps of disintegrating, grilling, extracting concrete, and the medicament can be prepared into powders, granules, tablets or capsules.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Diagnostic markers of human female infertility
InactiveUS20080200379A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman FemalesEndometrial receptivity
The subject invention pertains to methods and reagents for the diagnosis of female infertility, prognostic indicators for female infertility, compounds for the treatment of female infertility, compounds and methods for contraception. Methods and compounds are based on the levels of ebaf in endometrial tissue. Methods for diagnosing endometrial receptivity and bleeding function by screening a biological sample such as an endometrial tissue sample, or bodily fluid for the presence of ebaf. A contraceptive compound containing an effective amount of ebaf and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A diagnostic kit for timing contraception containing reagents for screening a sample for the presence of ebaf. A method of treating endometrial irregularities by down-regulating the expression of ebaf.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating female infertility and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103585378AConvenient treatmentMammal material medical ingredientsCapsule deliveryMetaplasiaFollicle
The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines and in particular relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating female infertility and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of epimediums, 10-15 parts of semen cuscutae, 10-60 parts of astragalus membranaceus, 5-15 parts of human placenta, 10-15 parts of white atractylodes rhizome, 5-15 parts of angelica, 6-12 parts of ossa sepiae, 5-10 parts of pulp of dogwood fruit, 10-15 parts of fructus lycii, 3-10 parts of scutellaria baicalensis, 6-12 parts of rhizoma cyperi and 3-10 parts of ligusticum wallichii. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has the effects of warming yang, benefiting vital energy, nourishing blood, replenishing essence, regulating vital energy and removing blood stasis; the raw materials are carefully selected, metaplasia of follicle and restoration of reproductive function and organs such as the kidney, the heart, the liver and the spleen are promoted, and a remarkable treatment effect on the female infertility is achieved.
Owner:湖南庆春祥中医药有限公司
Dendrobium candidum medicine for treating female infertility
InactiveCN103816390APromote absorptionPromote physiological and biochemical functionsSexual disorderPlant ingredientsLycopus lucidusOvulation times
The invention discloses a dendrobium candidum medicine for treating female infertility. The effective components of the dendrobium candidum medicine for treating the female infertility are prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 15-30g of dendrobium candidum, 10-15g of blood ganoderma, 10-20g of mulberry, 8-12g of polygonatum, 8-15g of Chinese wolfberry, 6-10g of motherwort, 6-12g of cyperus rotundus, 8-12g of liquorice, 8-12g of lycopus lucidus, 6-10g of safflower, 4-8g of folium artemisiae argyi, 4-8g of angelica, 4-8g of ginseng, 6-12g of cinnamon, 4-10g of limonium sinense and 4-8g of glossy privet fruit. Pills or capsules of the dendrobium candidum medicine are prepared by uniformly mixing the 16 Chinese herbs, grinding, sieving, pilling or encapsulating. The dendrobium candidum medicine can improve ovarian development, adjust female menstruation and the ovulation state, promote uterine development and improve the pregnancy condition, has a good therapeutic effect in clinical trials, takes the Chinese herbs as the raw materials, and is small in toxic and side effects, easy to prepare and popularize.
Owner:GUANGXI JIANBAO SHIHU
Medicine patch for treating infertility caused by cold uterus and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101700288AGood curative effectQuick resultsSexual disorderSheet deliverySide effectGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACT
The invention provides a medicine patch for treating infertility caused by cold uterus and a preparation method thereof, which aims at the patients with infertility caused by cold uterus and irregular menstruation. The medicine patch is patched and applied on the Shenque point and is fixed with an adhesive tape; one patch is used for two days and replaced with a new patch every two days; and the medicine patch is applied by a hot-water bag for 30-60 minutes in the morning and at night every day until the interior of the abdomen feels hot. The purpose of treating infertility is achieved by warming the channel and eliminating stagnated blood, nourishing yin and blood, eliminating dampness and dispelling cold, consolidating the constitution and reinvigorating, and dispersing blood stasis and alleviating pain. The medicine patch is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-6 parts of angelica, 2-4 parts of white peony root, 2-4 parts of ginseng, 3-6 parts of cassia twig, 2-4 parts of root bark of peony, 2-4 parts of cyathula root, 2-4 parts of motherwort, 3-6 parts of hemlock parsley, 2-4 parts of moxa leaf, 1-2 parts of safflower and 1-2 parts of liquorice. The medicine patch of the invention is prepared from pure traditional Chinese medicines, and the traditional Chinese medicine patch is patched and applied on the Shenque point to treat female infertility caused by cold uterus and has the characteristics of cheapness, convenience and proved effects and no toxic or side effects.
Owner:刘丰伟
Medicament for treating multiple diseases such as climacteric syndrome and osteoporosis of women
ActiveCN101172103AInhibit apoptosisIncrease contentNervous disorderSkeletal disorderDiseaseStress syndrome
A medicine for treating various diseases such as women's climacteric syndrome, osteoporosis, mental depression, premature ovarian failure, premenstrual tension syndrome, hyperthyroidism, male and female infertility, hair loss and white hair, and is characterized in that it It is composed of fatty acids in the following weight percent range: hexadecanoic acid 8-32%, hexadecenoic acid 11-35%, octadecenoic acid 13-33%, octadecanoic acid 0.3-2.5%, octadecanoic acid Carbadienoic acid 11-33%, octadecatrienoic acid 3-15%. Compared with other drugs, the drug composition is simple, belongs to the target organ agonist, and has an independent reversible regulation function on the second messenger of the body. It is a medicine with high curative effect, safety and simplification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INNOVATION WISDOM VALLEY TECH CO LTD
Male and female infertility herbal composition
InactiveUS20180028591A1Enhances and promotes fertilityNourishingPlant ingredientsAdditive ingredientAdemetionine
An herbal composition that enhances and promotes fertility in both males and females by nourishing the kidney, regulating the liver and spleen, improving circulation of Qi and blood, and balancing the Yin and Yang through a unique composition consisting of natural herbs known in traditional Chinese medicine. The herbs create a synergy between each other that works to enhance fertility for both males and females. The composition consists of the following herbal ingredients mixed in varying weight percentages. goji berry, dodder seed, red sage root, green orange peel, processed fleece flower root, horny goat weed, codonopsis, raspberry, astragalus root, Chinese yam, white peony root, false daisy, mulberry, curcuma tuber, and cynomorium. The herbal ingredients are cleaned, purified and / or processed prior to formulation. The formulation process is at least partially dependent on the desired means of preparation and administering the composition.
Owner:KE SHAOBIN
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for nourishing yin and strengthening kidney and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for nourishing yin and strengthening kidney, and a preparation method thereof, the traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared by the following pharmaceutical raw materials: raw membranous milkvetch root, Indian buead, Chinese thorowax root, common anemarrhena rhizome, stir-fried eucommia bark, rehmannia root, radix rehmanniae preparata, Chinese angelica, pilose Asiabell root, Chinese wolfberry root-bark, stir-fried largehead atractylodes rhizome, dwarf lilyturf tuber and chrysanthemum; and the traditional Chinese medicine composition is processed into any one formulation of clinically acceptable tablets, capsules, granules and the like by extraction, refining and other processes. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has the effects of nourishing yin and strengthening kidney and is used for treating soreness and weakness of waist and knees, waist-back pain, insomnia, more dreams, tinnitus caused by kidney deficiency, endocrine disorders, female infertility caused by cold uterus, leucorrhea abnormal and other symptoms.
Owner:BEIJING TIANKE RENXIANG MEDICAL SCI TECH
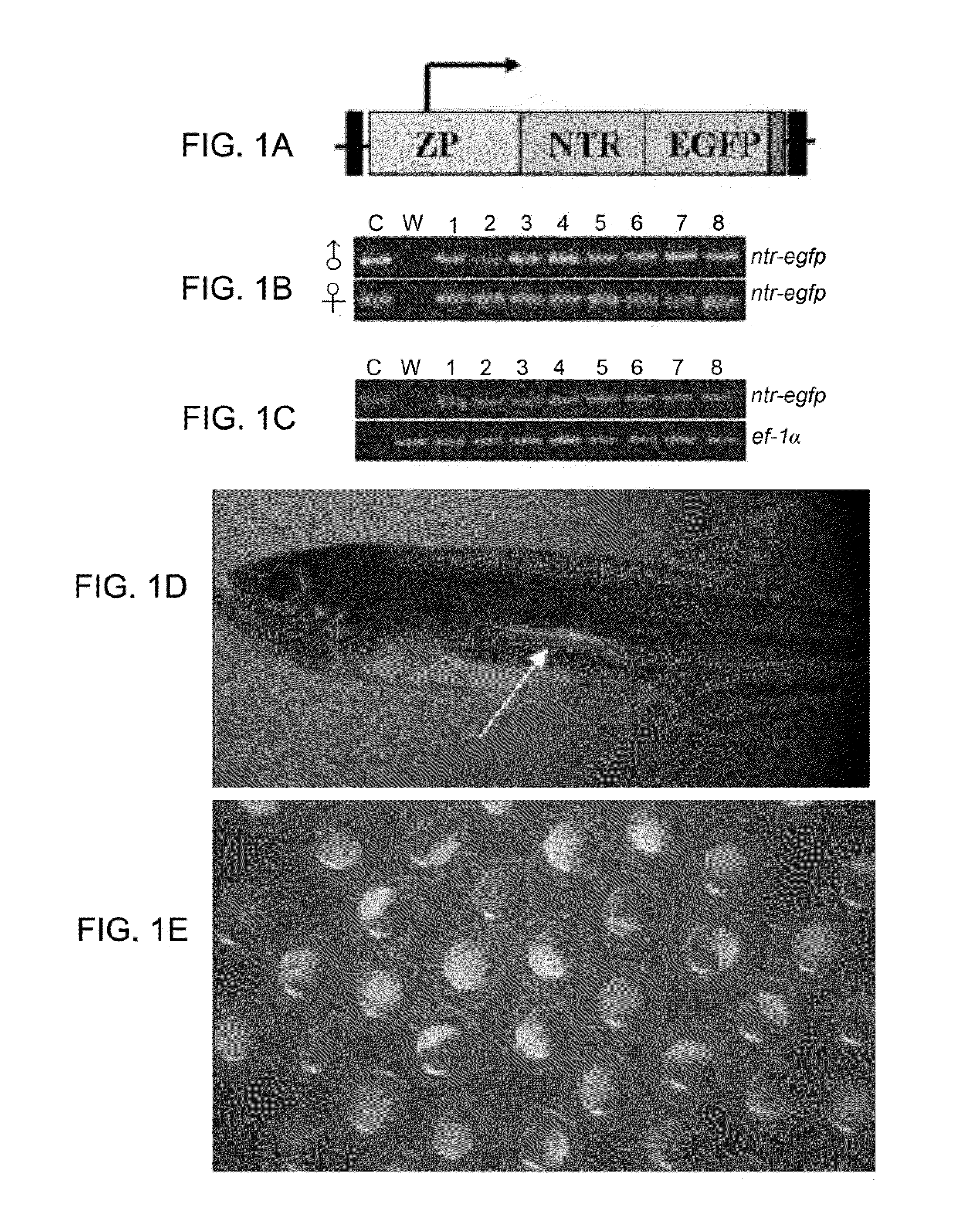
Infertility control of genetically modified fish
A method of inducing male and / or female infertility in a genetically modified (GM) fish is disclosed. Also disclosed is a method of generating an infertile GM fish with a phenotype and / or genotype of interest. The method involves generation of a GM fish whose genome comprises a foreign transgene operably linked to a fish gonad-specific promoter selected from the group consisting of an ovary-specific promoter and a testis-specific promoter. The transgene comprises a suicide gene selected from the group consisting of a reductase and a photosensitizer, in which the reductase is operably linked to a reporter gene. Infertility of the GM fish is induced if the GM fish expressing the reductase is treated with an effective amount of a reductase-activated cytotoxic prodrug or if the GM fish expressing the photosensitizer is treated with light irradiation.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
Penis cervi health-care wine
ActiveCN103484322APromote absorptionImprove immunityAlcoholic beverage preparationMammal material medical ingredientsLycium chinenseFemale infertility
The invention discloses penis cervi health-care wine. The penis cervi health-care wine is made in the following method comprising the steps that penis cervi, deer kidneys, deer tails, polygonatum rhizomes, mulberries, raspberries, ginseng, pawpaws, cortex cinnamomi, garter snakes, wolfberries and chinaroot greenbrier rhizomes are prepared, washed, taken out, sliced, mixed with pure grain white spirit at 60% alcohol by volume, put in a jar in a sealed mode, soaked for 30 days, poured into an extraction tank, extracted in a pressure reduction mode, and moved in a seal tank to be stored for 60 days after medicine dregs are filtered out, and the penis cervi health-care wine is obtained. The penis cervi health-care wine plays a role in enhancing human immunity, has health-care effects on prematurely senile symptoms of male and female kidney qi weakness, male and female infertility, unsatisfactory sexual life, male impotence, premature ejaculation, a low survival rate of sperms, female sexual apathy, and female uterus cold infertility, and also has health-care effects on lumbar disc herniation, osteoproliferation, apoplexia, hemiplegic paralysis, lumbar vertebrae strain, cervical spondylosis, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, brain atrophy and the like which are caused by kidney insufficiency.
Owner:TIELING XIFENG YULIN DEER IND GRP
Anti-inflammation and tissue regeneration-promoting sanitary towel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102008741APreventing and Treating InfertilityAnti-inflammatoryAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsBlumeaPutrefaction
The invention relates to the technical field of daily necessities with the function of medical treatment and healthcare, more particularly to a anti-inflammation and tissue regeneration-promoting sanitary towel and a manufacturing method thereof. The sanitary towel includes a cotton cushion layer, which contains traditional Chinese medicine powders formed by mixing the following components: plaster, boneol, cinnabar and Balsamiferou Blumea. The sanitary towel of the invention has the efficacies of anti-inflammation, hemostasis, clear away heat, anti-putrefaction, promoting tissue regeneration and the curative effect for chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, cervical erosion, vaginitis and the like, and can be used, in case of long-term usage, for the prevention and treatment for female infertility caused by the above symptoms.
Owner:董莉莉
Blood invigorating and menses regulating medicine for treating female infertility
InactiveCN101700291ASignificant effectNo side effectsAnthropod material medical ingredientsSexual disorderDiseaseSequela
The invention discloses a blood invigorating and menstruation regulating medicine for treating female infertility, which is prepared from the following components: 6g of rhizoma of chuanxiong, 5g of rhizoma corydalis, 5g of trogopterus dung, 20g of leonurus, 3g of leech, 8g of eupolyphaga, 6g of trumpet creeper, 10g of red flower, 7g of angelica, 12g of white paeony root, 9g of peach kernel and 10g of liquorice; the above medicines are mixed together and pulverized to prepare watered pills according to the process of the watered pill, and each package is 9g. The medicine belongs to an internal medicine, mainly treats various refractory gynecologic diseases, including irregular menstruation, early occurrence and deferral of the menstruation, abnormal color of the menstruation, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis, infertility after marriage, blood incapable of nourishing the fetus, habitual abortion, pelvic inflammation and cervicitis and the like, and has obvious effects on sequela of abortion. The medicine takes menstruation regulation and blood circulation invigoration as core, has no toxic and side effects and low price, is easy to be manufactured and is applicable to popularization and application.
Owner:陈坤
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating female infertility
InactiveCN103301423AQuick resultsGood curative effectSexual disorderAlkali/alkaline-earth metal chloride active ingredientsAngelica Sinensis RootMedicine
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine for treating female infertility. The traditional Chinese medicine is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: fructus evodiae, cassia twig, dried ginger, ligusticum wallichii, angelica sinensis, radix paeoniae alba, ginseng, liquorice, herba epimedii, morinda officinalis, the root of red-rooted salvia, amethyst, herba lycopi, leonurus, semen cuscutae, szechwan Chinaberry fruit and radix curcumae; all the raw materials are added with 700 ml of water and decocted to 200 ml for the first time, and then added with 500 ml of water and decocted to 200 ml for the second time; for the first time of use, the medicine is taken till menses, and stopped at the end of the menses; later, the medicine is taken for three days during the menses of each month, twice a day, in the morning and the evening before eating.
Owner:闫玉枝
Medicine for treating male infertility
InactiveCN1634296AMedicinal and calmImprove male performanceUnknown materialsCapsule deliveryMale infertilityINFERTILITY MALE
Disclosed is a medicine for treating male infertility, which mainly comprises curculigo rhizome, epimeddium, raspberry, leek seeds, dodder seed, wolferry fruit, plantain seeds, schisandra fruit, mulberry seeds, pilose asiabell root, and licorice root. The medicine is made into the dosage form of oral liquid.
Owner:广州华博生物制药研究所
Medicine for female infertility
InactiveCN1504214AEffective treatmentMammal material medical ingredientsSexual disorderCurative effectAdemetionine
A medicament for treating women's barrenness which is related to the field of medical preparation. The medicament comprises the following constituents (by weight proportions), dried human placemta 100-300 parts, doddor seed 50-150 parts, eucommia bark 25-100 parts, deglued antler powder 25-50 parts, amethyst 50-150 parts, Chinese angelica root 100-200 parts, prepared rehmannia root 25-100 parts, rhizome of Sichuan lovage 25-50 parts, white peony root 25-100 parts, ginseng 25-100 parts, white atractylodes rhizome 25-100 parts, poria cocos wolf 25-100 parts, and epimedium 50-100 parts, the medicament has shown good curative effect for treating women's barrenness.
Owner:朱永革
Traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating female infertility and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating female infertility, which comprises the following traditional Chinese medicine ingredients in parts by weight: 18g of Atractylodes macrocephala, 7g of ginseng, 18g of Poria cocos, 6g of roasted licorice, 10g of tangerine peel, 7g of pinellia, 6g of woody root, and Jen 10g, Angelica 16g, Salvia miltiorrhiza 16g, Frankincense 16g, Myrrh 16g. The preparation and use method of the traditional Chinese medicine composition of the present invention: put a pair of Chinese medicinal materials in pottery, add cold water to 4-6cm above the surface of the medicine, boil with strong fire, then decoct with slow fire for 20-30min, and decoct the medicine for 20-30min. Filtrate the liquid and pour it into a bowl, then add water to the filter residue to exceed the surface of the medicinal residue by 3-4cm, then decoct with a slow fire for about 20 minutes, filter out the second decoction liquid, add water to the medicinal residue once more to exceed the surface of the medicinal residue 3-4cm, decoct with slow fire for about 20 minutes, mix the filtrate of 3 times as 1 dose, take 1 dose a day, take it warmly in 3 times, 7 days is a course of treatment, and 3~6 courses of treatment are required.
Owner:曹秀娟
Chinese medicine preparation for regulating menstruation and helping pregnancy
InactiveCN101468126AImprove plasticityWell mixedMammal material medical ingredientsSexual disorderRhizomeANGELICA ROOT
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating female infertility, capable of regulating menstruation and breeding, composed of raw materials by weight parts: Chinese angelica root 100, Chuanxiong rhizome 20-50, parched white peony root 20-40, prepared rehmannia root 30 -50, Chinese teasel root 2040, red sange root 20-40, medlar 18-22, dodder 18-22, corydalis tuber 20-50, ass-hide gelatin bead 20-30, cyperirhizome 20-30, eucommia 20-30, deglued antler powder 18 -25, tortoise plastron 18-30, atractylodes rhizome 20-40, radix codonopsis pilosulae 20-40, placenta hominis 18-25, cinnamon 20-40. 368 clinical cases of infertility patients show that: the traditional Chinese medicine preparation has obvious curative effect, 353 patients are basically healed and the curative rate is not less than 95%.
Owner:牛海艳
Formula of Chinese medicament for treating female infertility and processing method of Chinese medicament
The invention relates to the field of Chinese medicaments, in particular to the field of the Chinese medicaments for treating female physiological maladies, and particularly provides a formula of a Chinese medicament for treating female infertility and a processing method of the Chinese medicament. The formula of the Chinese medicament for treating the female infertility comprises the following components: 5 to 20 grams of blister beetle, 500 grams of rhubarb, and 30 grams of common fennel. The formula of the Chinese medicament for treating the female infertility and the processing method of the Chinese medicament can disperse cold by warming meridians, nourish blood to activate channels, promote blood flow to induce menstrual flow, resolve blood stasis to relieve pain, nourish blood to regulate qi, and effectively relieve and cure female common diseases.
Owner:李鑫
New application of herba blumea riparia for treating gynecological diseases
InactiveCN102772465APromote maturityPromotes ovulationSexual disorderFood preparationMedicinal herbsMedicine
The invention discloses a new application of herba blumea riparia for treating gynecological diseases, and relates to a product prepared by raw powder of herba blumea riparia or extracts of herba blumea riparia and is used for treating female infertility. Particularly, drugs, functional foods and the like can be prepared by the raw powder of herba blumea riparia or extracts of herba blumea riparia and proper excipients or auxiliary components. The product is capable of improving ovulation of the uterus remarkably and has a good curative effect to the female infertility.
Owner:广西桂西制药有限公司
Chinese herbal medicine preparation for curing endometrial disease, infertility and habitual abortion
ActiveCN103405643AGood curative effectNo side effectsSexual disorderPlant ingredientsSagina subulataHabitual Abortions
The invention relates to a Chinese herbal medicine preparation for curing the endometrial disease, the infertility and the habitual abortion. The Chinese herbal medicine preparation is prepared through decocting the following Chinese herbal medicines with water: angelica sinensis, astragalus membranaceus, rubus idaeus, ciliatenerve knotweed root, spiranthes sinensis ames, polygonum perfoliatum, kalimeris indica root, herba lycopi, achyranthes aspera, ginseng, rubus pluribracteatus, rubus parvifolius root, rhizoma polygonat, solanum lyratum, cyperus rotundus, cistanche, daughters red, crneate lespedeza, Chinese rose, galium aparine, achyranthes root, sagina subulata, gold rattan, crowndaisy chrysanthemum, herba leonuri, sargentgloryvine stem, semen cuscutae, semen euryales and the like. The Chinese herbal medicine preparation is beneficial for the recovery of the physical function and the organ function, has no any toxic or side effects, achieves more than 93% of effective rate in treating the female infertility and the habitual abortion, achieves more than 94% of effective rate in treating the endometritis and the pelvic inflammation, achieves more than 89.4% of effective rate in treating the cervical hypertrophy, the cervical erosion, the xeromenia, the inflammatory mass, the uterine fibroid, the ovarian cyst and other gynecological diseases, and achieves more than 94.1% of effective rate in treating sterility due to oligozoospermia and the necrospermia.
Owner:屈力军
Traditional Chinese medicine pill for treating female infertility and preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine pill
InactiveCN104906183AEasy to prepareSmall side effectsPill deliverySexual disorderSalvia miltiorrhizaSide effect
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine pill for treating female infertility and a preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine pill. The traditional Chinese medicine pill is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-30 parts of angelica sinensis, 10-20 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, 10-30 parts of ligusticum wallichii, 5-15 parts of manis pentadactyla, 30-60 parts of fructus liquidambaris, 5-10 parts of leech, 15-30 parts of American ginseng, 15-30 parts of radix astragali and 5-10 parts of liquorice. According to the traditional Chinese medicine pill, all the traditional Chinese medicines are combined for use and can complement one another; the traditional Chinese medicine pill has the functions of activating blood and dissolving stasis, softening and resolving hard mass, boosting qi and nourishing yin, regulating both qi and blood, and eliminating blood stasis and promoting pregnancy, has the excellent effect of treating female infertility caused by factors such as tubal nowhere, amenorrhea, polycystic ovarian syndrome and premature ovarian failure, and is simple in preparation method, few in toxic and side effects, easy to produce and low in cost; the wide popularization of the traditional Chinese medicine pill is facilitated.
Owner:郭前进
Chinese medicinal composition for treating oviduct obstruction, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101897932AFast absorptionEffective fastGranular deliverySexual disorderAlcoholTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a Chinese medicinal composition for treating oviduct obstruction, and a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a Chinese medicinal composition for treating oviduct obstruction, and a preparation method of granules and application thereof, and belongs to the field of medicine. The oviduct obstruction or partially passable oviduct is the major cause for female infertility, and the oviduct obstruction cannot be treated by special-effect medicament at present. The Chinese medicinal composition consists of nine medicaments such as Chinese angelica, red paeony root, beautiful sweetgum fruit and the like, and the granules of the Chinese medicinal composition are prepared by aqueous extraction, filtering, alcohol extraction, concentration, drying under reduced pressure, pulverizing and pelleting by adding auxiliary materials. The Chinese medicinal composition has a strict formula, and is particularly suitable for treating the oviduct obstruction which belongs to qi depression to blood stasis in differentiation of traditional Chinese medical science. Experiments verify that the treatment effect is obvious. The Chinese medicinal composition has the advantages of reasonable and feasible preparation process, suitability for industrial production, quick absorption of the granules, quick response, moisture prevention, light resistance, good medicinal stability, clean and attractive appearance, small administration dosage and convenient production, transportation, carrying and storage.
Owner:广东爱民药业有限公司
Oligopeptide lyophilisate, their preparation and use
InactiveUS6863891B2Successful treatmentHigh activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAcetic acidFreeze-drying
A novel lyophilizate and method of preparation as well as the use of the lyophilizate to treat female infertility and for gonad protection. Cetrorelix is dissolved in acetic acid 30% v / v, the solution is transferred to water and freeze dried.
Owner:ZENTARIS IVF
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating female barrenness
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine for treating female infertility. The drug comprises the following components by weight percentages: 20-25% of Chinese angelica root, 10-15% of hemlock parsley, 10-15% of white paeony root, 15-20% of prepared rhizome of rehmannia, 20-25% of antler, 8-10% of moutan bark, 10-15% of fructus evodiae, 15-20% of motherwort and 8-10% of cornus officinalis. The traditional Chinese medicine can be suitable for various symptoms resulting from female endocrine dyscrasia, has low cost and no toxic and side effect. In clinical application, the curative ratio reaches 90% and the effective rate reaches 95%.
Owner:秦晓鹏
Composite medicinal composition for treating female infertility
InactiveCN102327536AGood effectSimple recipeUnknown materialsSexual disorderExcessive menstrual flowRhizome
The invention discloses a composite medicinal composition for treating female infertility, which comprises the following medicaments calculated according to weight percentage: 30-50 percent of saussurea involucrate, 10-20 percent of rhizome chuanxiong, 10-20 percent of dogwood fruit, 20-40 percent of artemisia leaf, 10-25 percent of Chinese angelica, 25-45 percent of Chinese cinnamon, 15-30 percent of Chinese wolfberry, 35-60 percent of peony, 30-50 percent of morinda officinalis, 15-30 percent of pilose antler, 20-30 percent of cassia twig, 30-50 percent of lesser galangal, 30-70 percent of China dodder, 20-30 percent of peach kernel, 30-50 percent of spatholobus stem and 50-70 percent of prepared rhizome of rehmannia. The composite medicinal composition can be used for specially treating female yin-cold excess, weak kidney qi, kidney essence deficiency, irregular menstrual period, unsmooth stem flow, disharmony between QI and blood, phlegm damp stasis residue, menstrual disorder, qi depression to blood stasis and other symptoms; and the quantity of traditional Chinese medicaments in each composition can be adjusted according to specific symptoms on the basis of a basic composition so as to achieve the aims of diagnosis and treatment based on an overall analysis of the illness and the condition of patients and find apt and specific ways to solve problems.
Owner:李国水
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com