Framework for Abnormality Detection in Multi-Contrast Brain Magnetic Resonance Data
A technology of contrast and magnetic resonance, applied in the field of abnormal detection, can solve the problem of inability to improve patient-specific test benches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
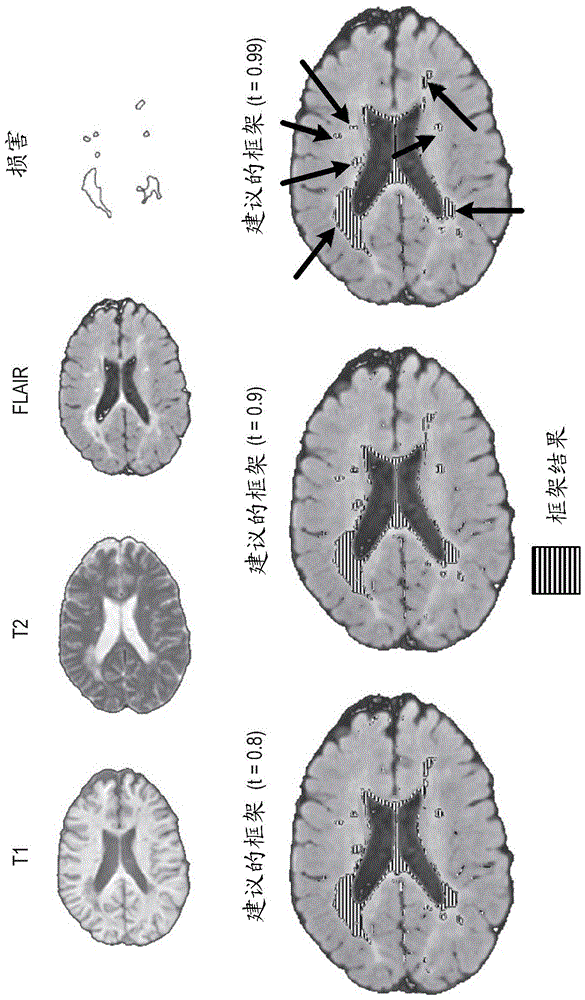
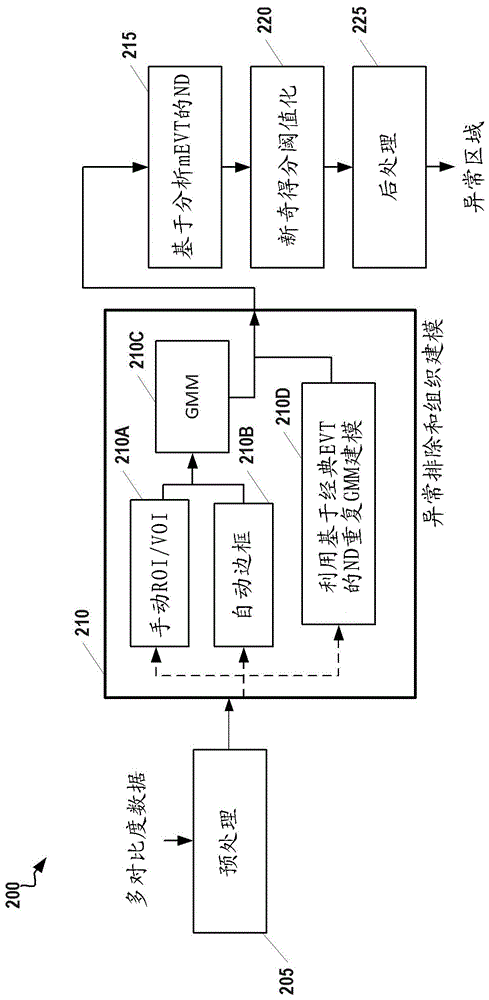
[0022] The following disclosure describes the invention in terms of several embodiments relating to methods, systems and devices related to a complete medical image analysis framework for detecting abnormalities in multi-contrast brain magnetic resonance (MR) data. More specifically, the medical image analysis framework described here accepts multi-contrast (T1 / T2 / PD / FLAIR / SWI) brain MR data of a single subject, identifies normal tissue with or without user guidance, performs these Normal tissue is parametrically modeled, and a slightly modified version of novelty detection (ND) using multivariate extreme value theory (EVT) is applied to all image data in order to detect abnormalities, if any, in the subject's brain. This framework can be applied, for example, to the detection of multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, ischemic stroke, and atypical gliomas, and thus, can be used to monitor treatment.
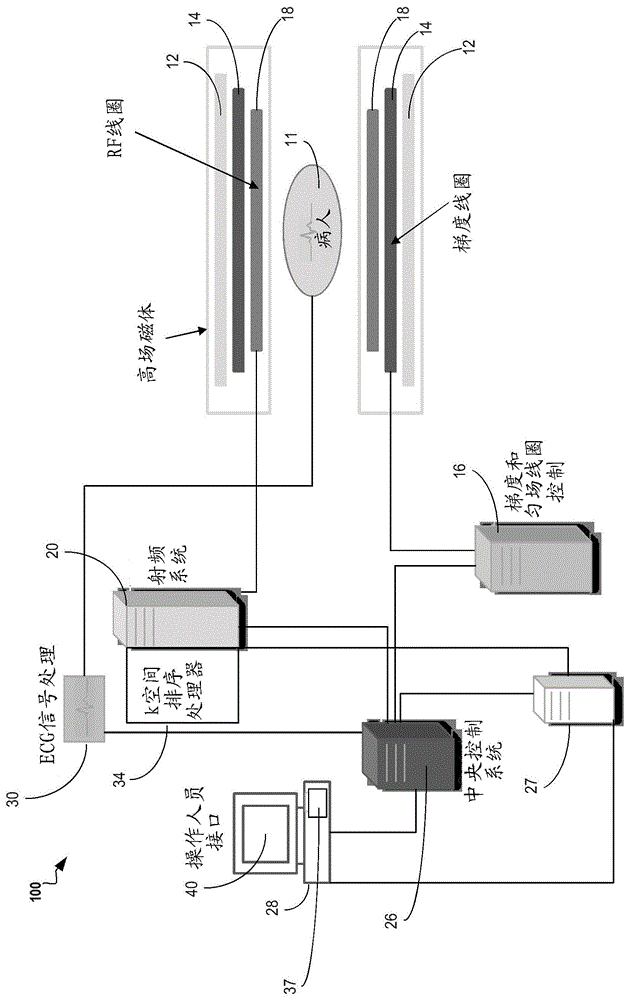
[0023] figure 1 A system 100 for sequencing the acquisition of frequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com