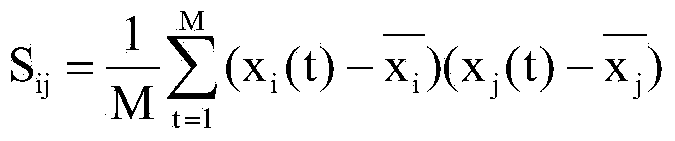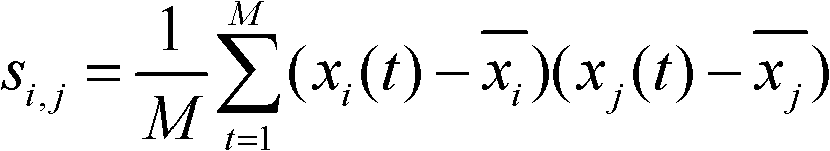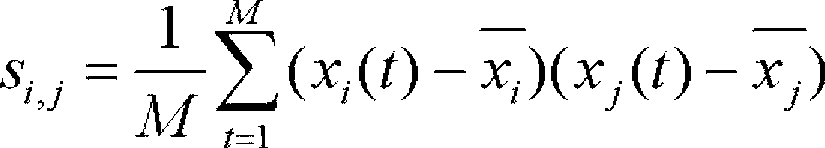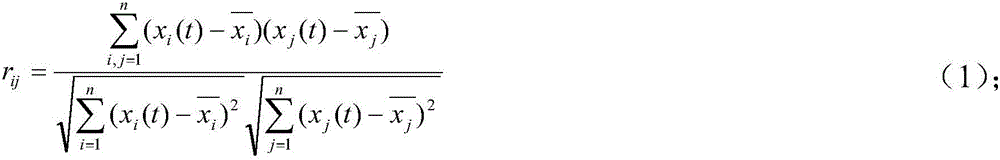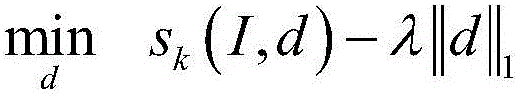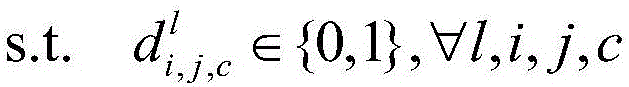Patents
Literature
96 results about "Functional magnetic resonance images" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
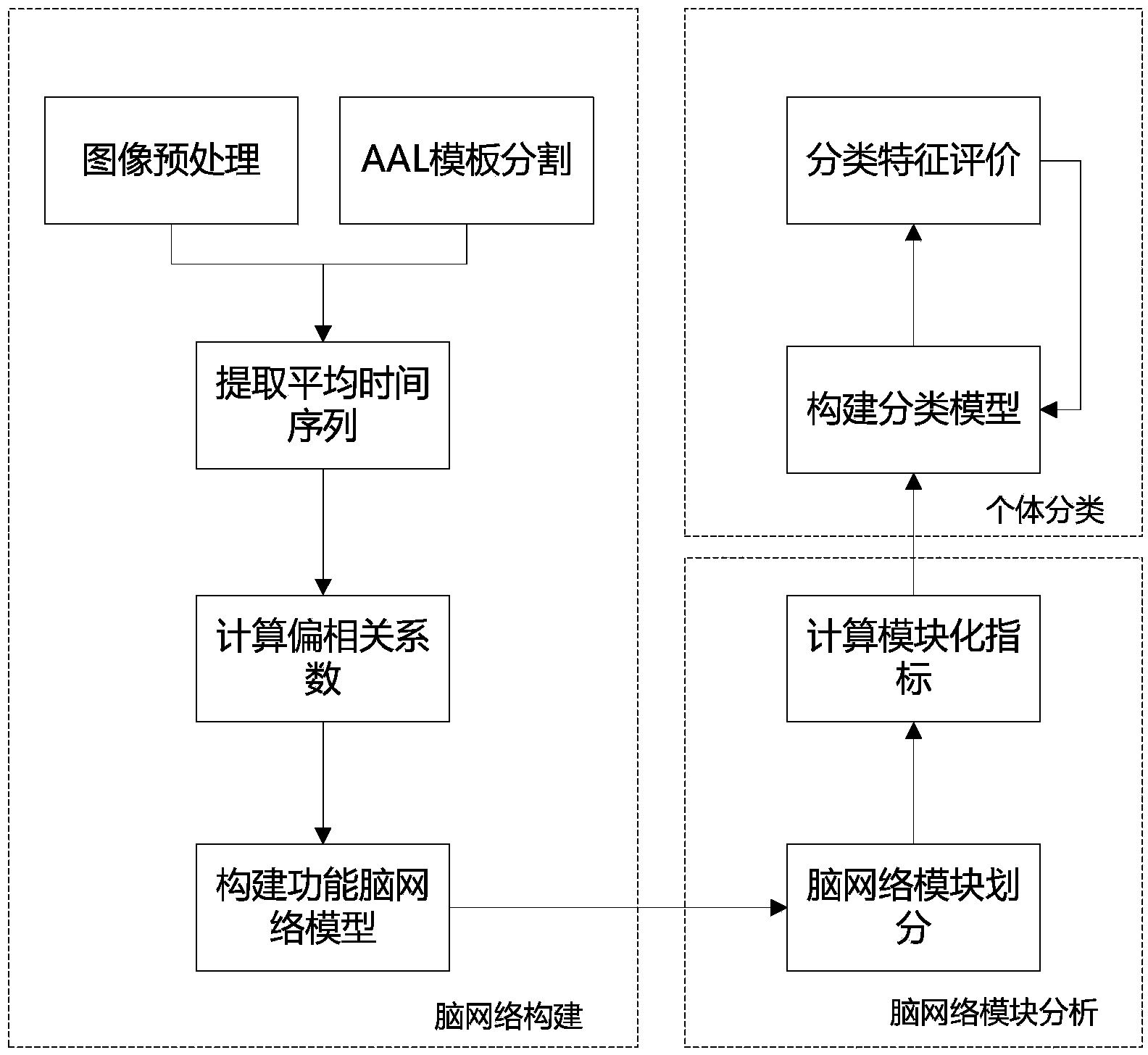
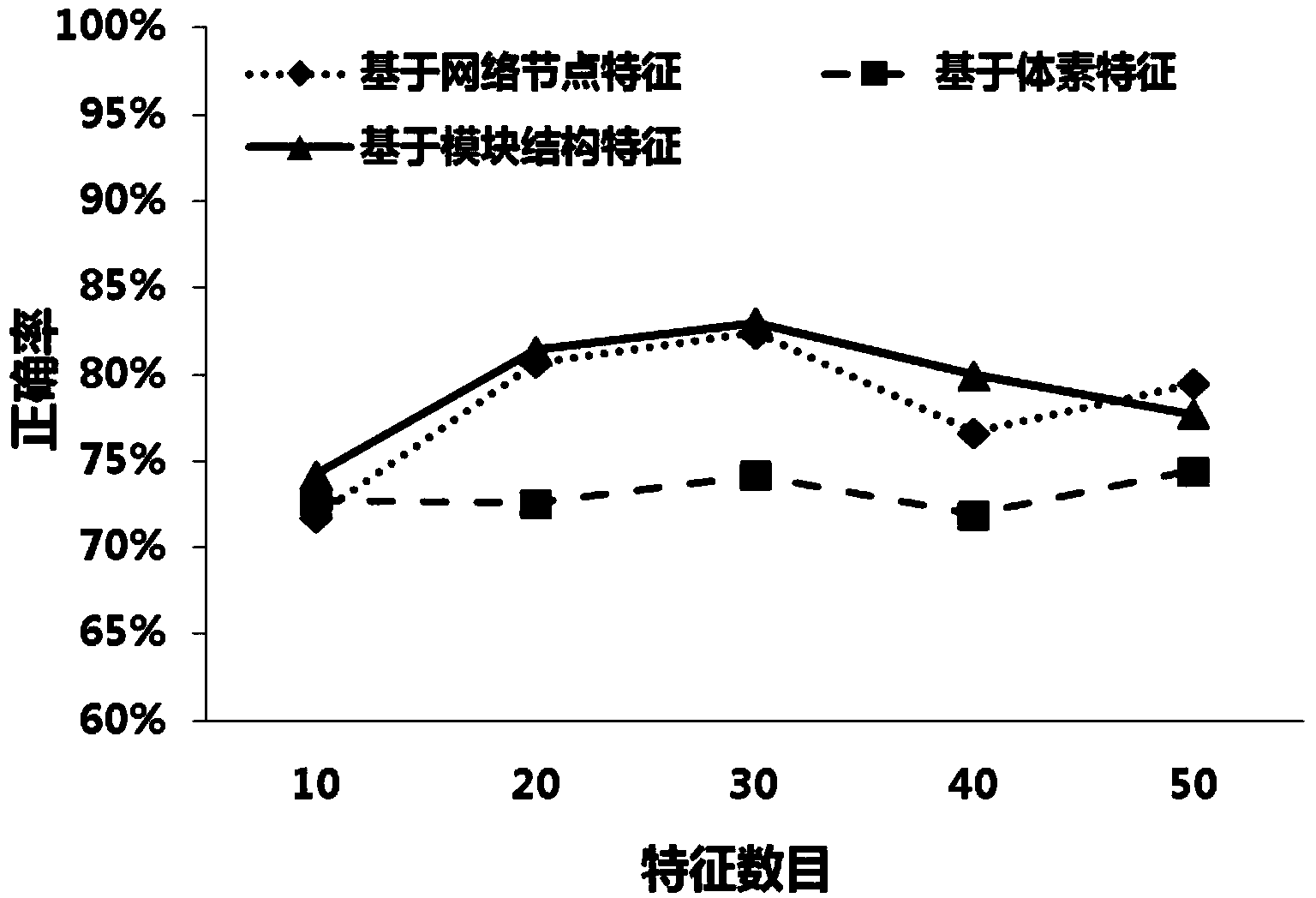
Functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on brain network modular structure characteristics
InactiveCN103886328AReflect the characteristics of the groupImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsClassification methodsBrain network
The invention discloses a functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on brain network modular structure characteristics. According to the functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on the brain network modular structure characteristics, network local gathering characteristics are described from the perspective of a modular structure, network collectivization characteristics are reflected, the potential relation between the structure and the function in the network is reflected, the defect that according to a traditional classification method, description of brain local characteristics is poor is overcome, and data classification accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
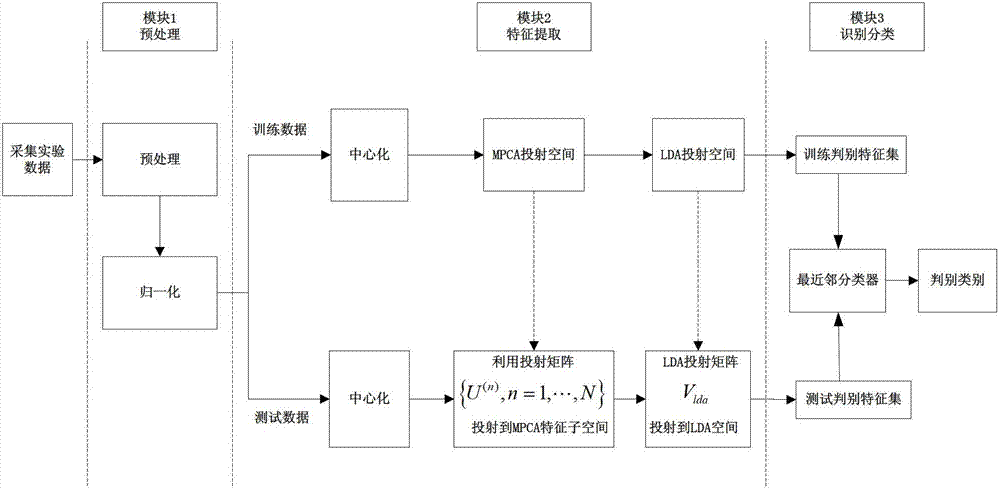
Brain cognitive state judgment method based on polyteny principal component analysis
InactiveCN103116764AGood recognition and classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses a brain cognitive state judgment method based on polyteny principal component analysis (PCA). The method includes the following steps of firstly, inputting sample sets, and processing input data; secondly, calculating characteristic decomposition of training sample sets, determining an optimal feature transformation transformational matrix, and projecting training samples into tensor characteristic subspace to obtain feature tensor sets of the training sets; thirdly, vectorizing lower dimension feature tensor data which are subjected to dimensionality reduction as input of linear discriminant analysis (LDA), determining an LDA optimal projection matrix, and projecting the vectorized lower dimension feature tensor data into LDA feature subspace for further extracting discriminant feature vectors of the training sets; and fourthly, classifying features, subjecting the discriminant feature vectors obtained by projection of training images and test images to feature matching, and further classifying the features . According to the brain cognitive state judgment method, PCA is utilized to directly perform dimensionality reduction and feature extraction to multi-level tensor data, the defect that structures and correlation of original image data are destroyed and redundancy and structures in the original images can not be completely maintained due to the fact that traditional PCA simply performs dimensionality reduction is overcome, and space structure information of functional magnetic resonance image (fMRI) imaging data is kept.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Real-time functional magnetic resonance data processing system based on brain functional network component detection
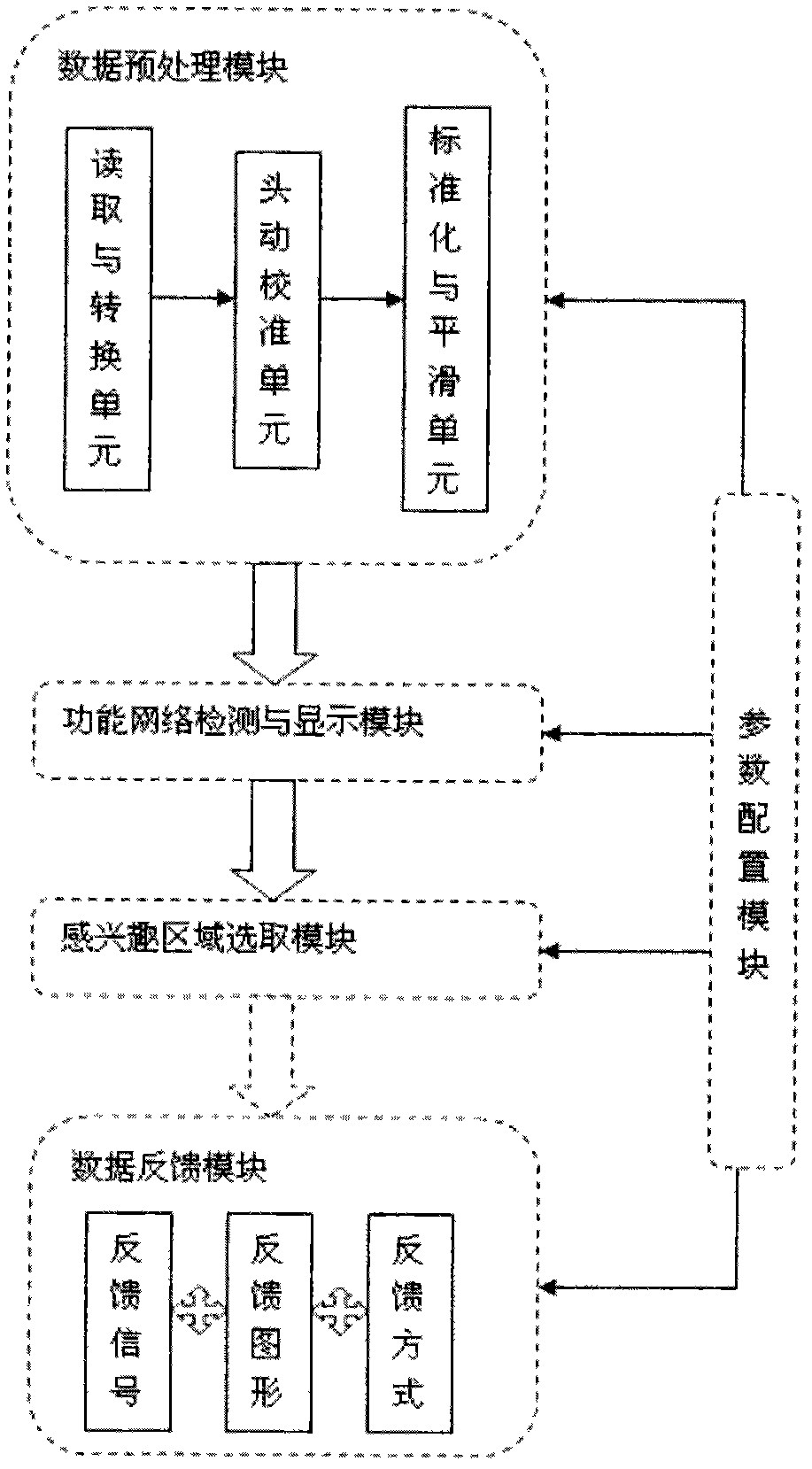
The invention provides a real-time functional magnetic resonance data processing system based on brain functional network component detection, which realizes real-time network analysis of brain functional magnetic resonance images obtained on line. The system comprises a data preprocessing module, a functional network detection and display module, a region-of-interest selection module, a data feedback module and a parameter configuration module, wherein the data preprocessing module is used for improving the signal to noise ratio of the data by image denoising, artifacts removing, etc after carrying out online reading and format conversion on the brain functional magnetic resonance images and for reducing the interference of noises and other factors in the magnetic resonance images; then the functional network detection and display module is used for carrying out real-time network analysis and extracting the functional network components of brain activity in specific state; the region-of-interest selection module is used for recording and saving the activity conditions of one or more node regions of interest in the network; the data feedback module is used for feeding the result data of the regions of interest back to the persons to be tested in real time according to different application requirements or by various ways or judging the result data by categories; and the parameter configuration module is used for providing parameter setting, reading and saving functions for each module and each unit contained by the invention. The system has important application values in multiple fields such as online estimation of quality of data, mind reading, brain function adjustment, clinical treatment, etc.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
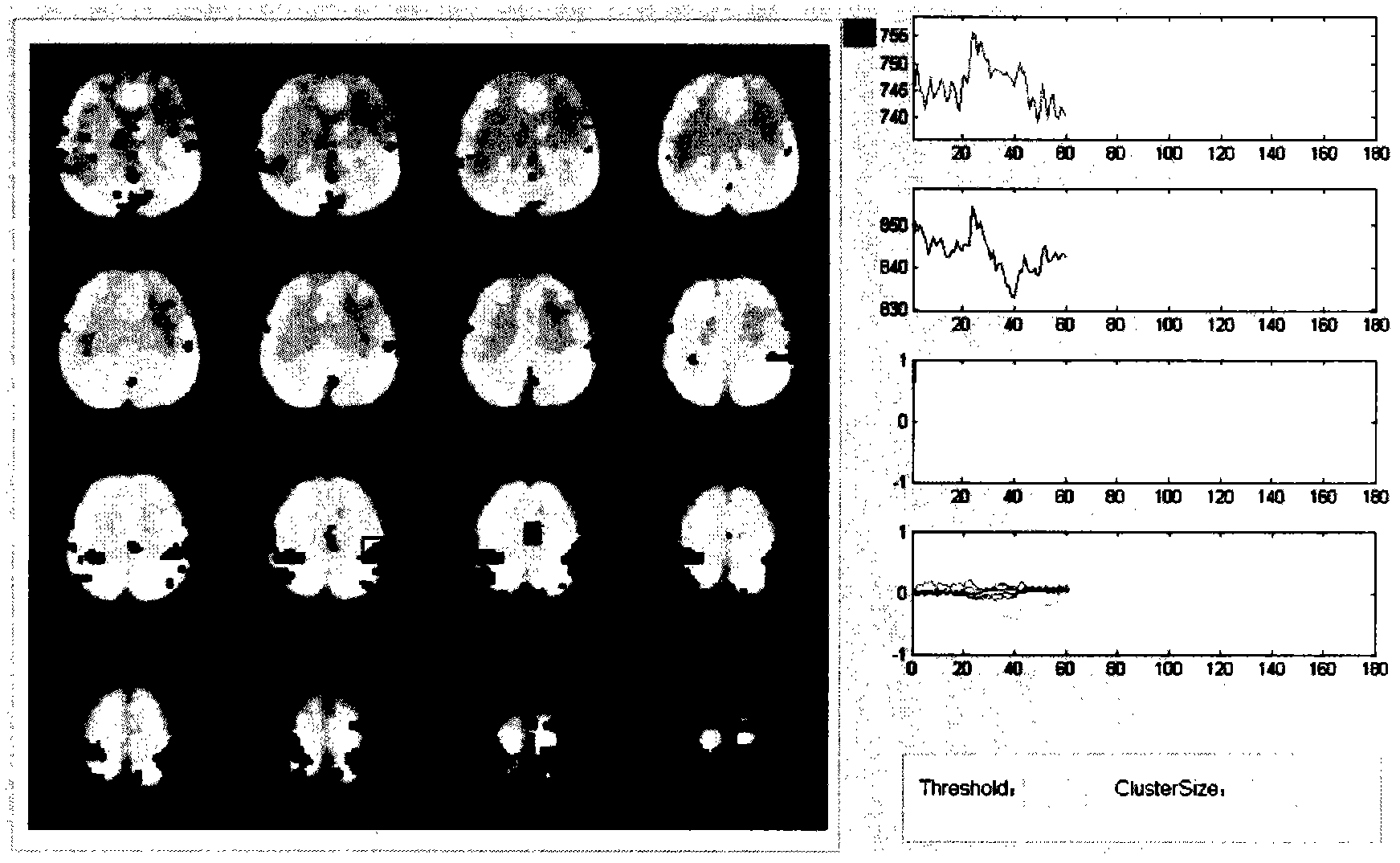
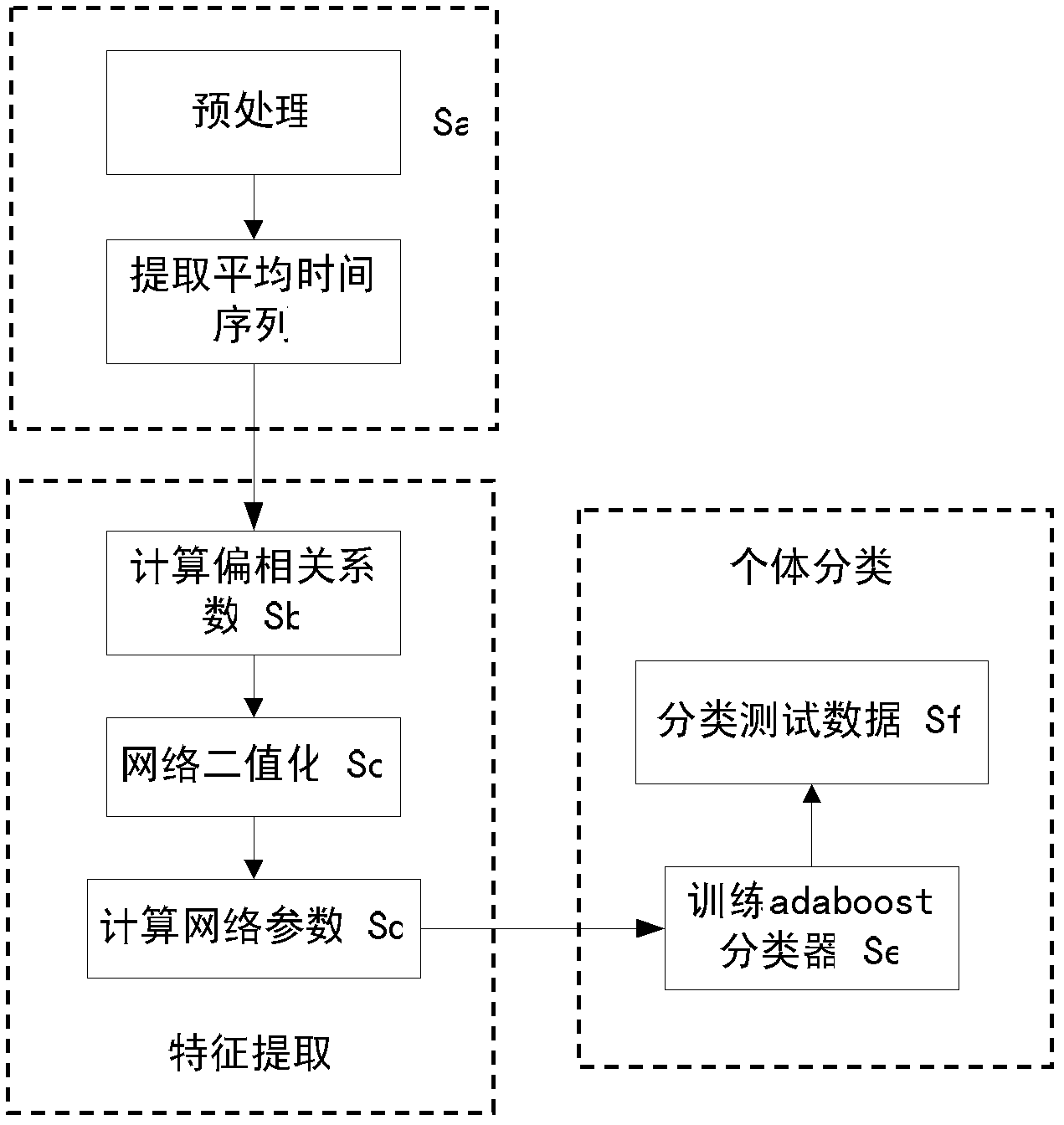
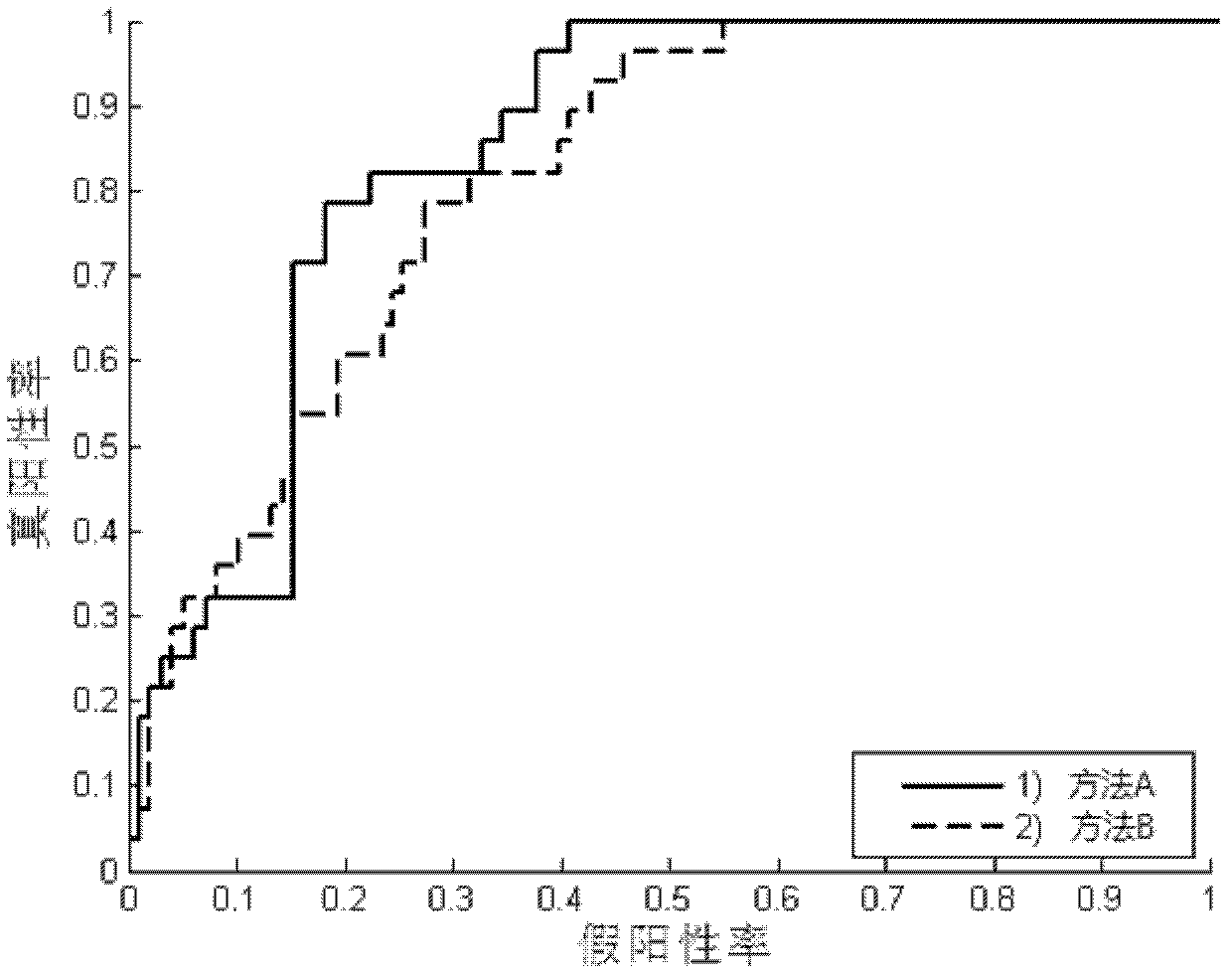
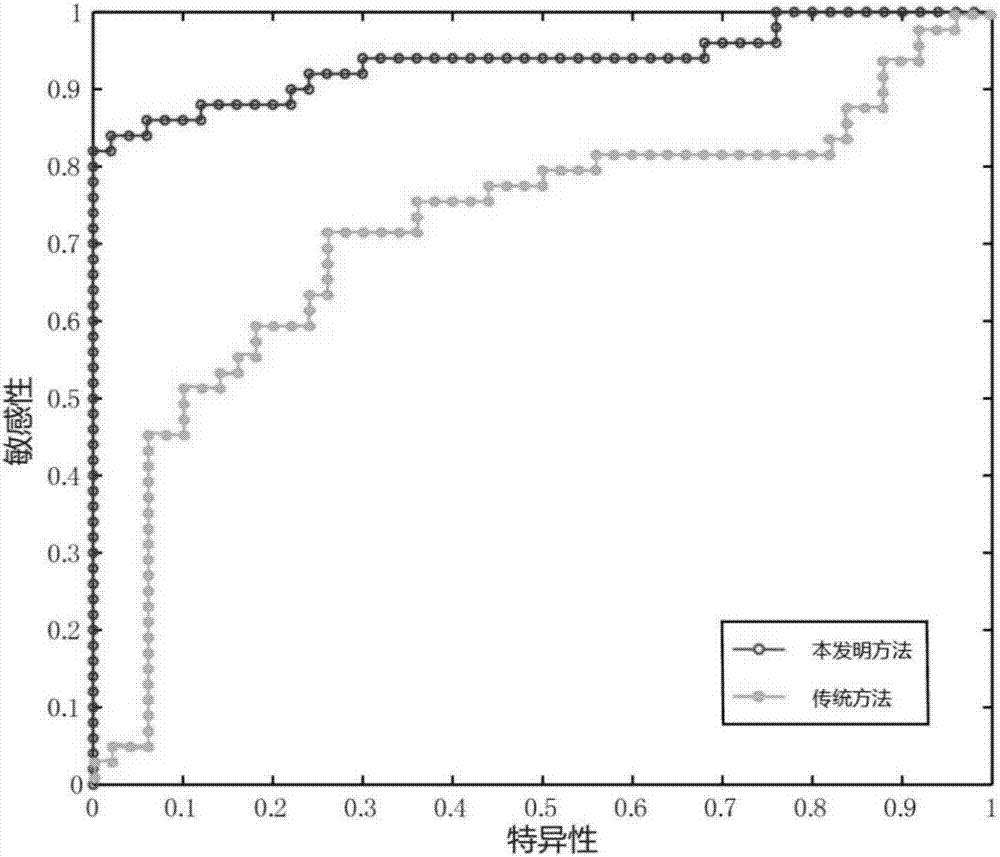
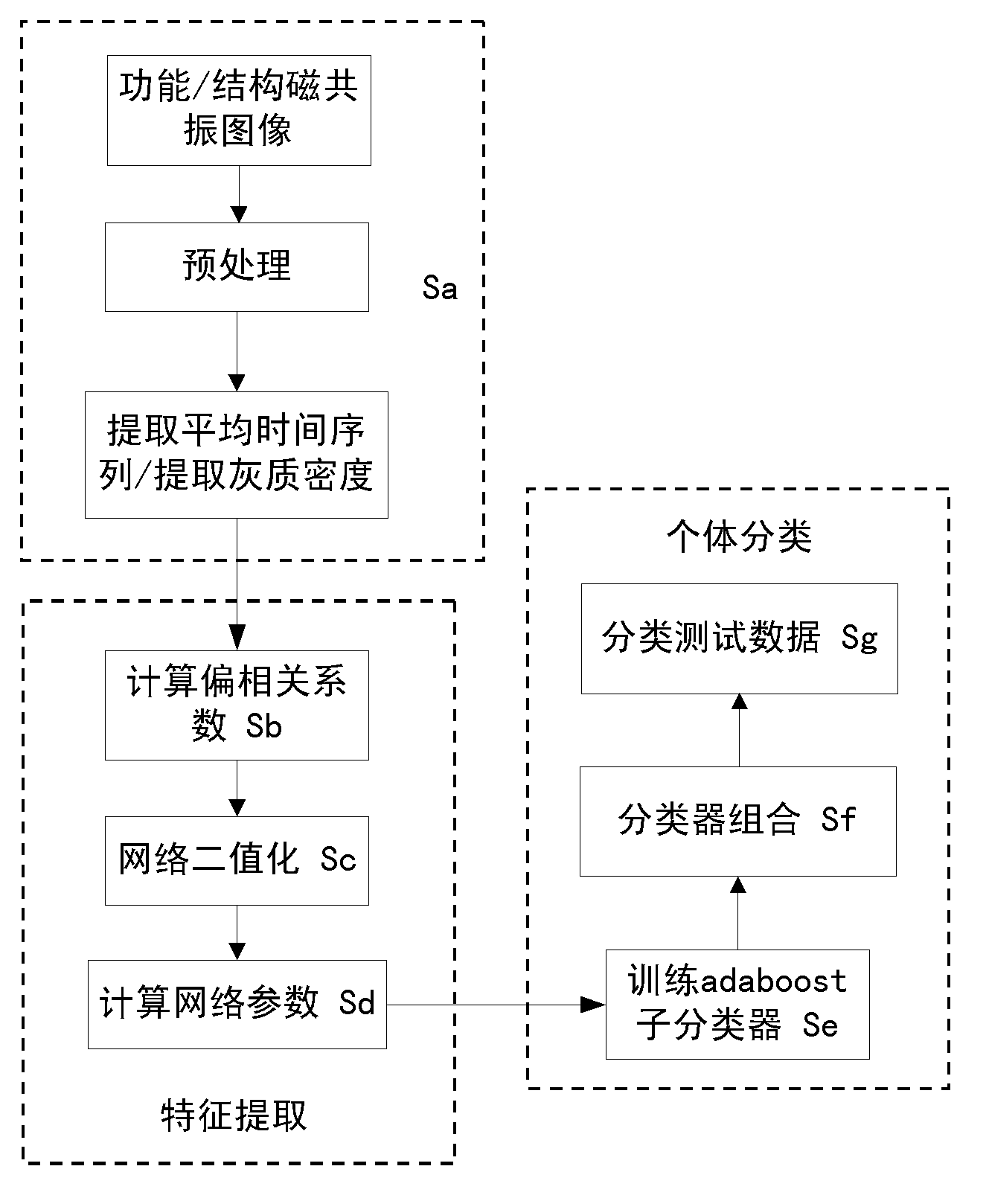
Brain functional magnetic resonance image classification method based on complex network
ActiveCN102509123AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpearman's rank correlation coefficientCorrelation coefficient
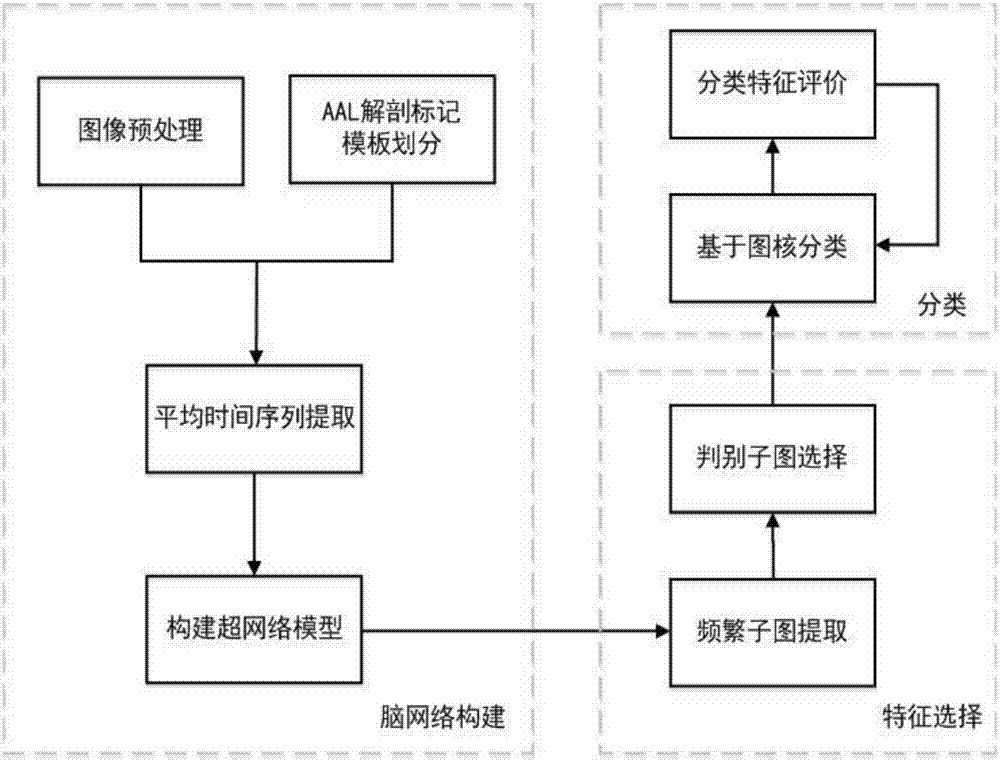
The invention relates to a brain functional magnetic resonance image classification method based on a complex network, which comprises the following steps: pre-processing training sample images and test sample images, carrying out region segmentation, and extracting an average time sequence from each region; calculating the partial correlation coefficient among the average time sequences, carrying out matrix binarization on the partial correlation coefficient to obtain a complex network model, and calculating the feature path length, cost and clustering degree of the complex network model to respectively obtain network features of the training sample images and the test sample images; training to obtain an adaboost classifier; and by using the adaboost classifier obtained by training, classifying the test sample images. By using information in the brain functional magnetic resonance images as much as possible, the method can accurately classify the brain functional magnetic resonance images.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
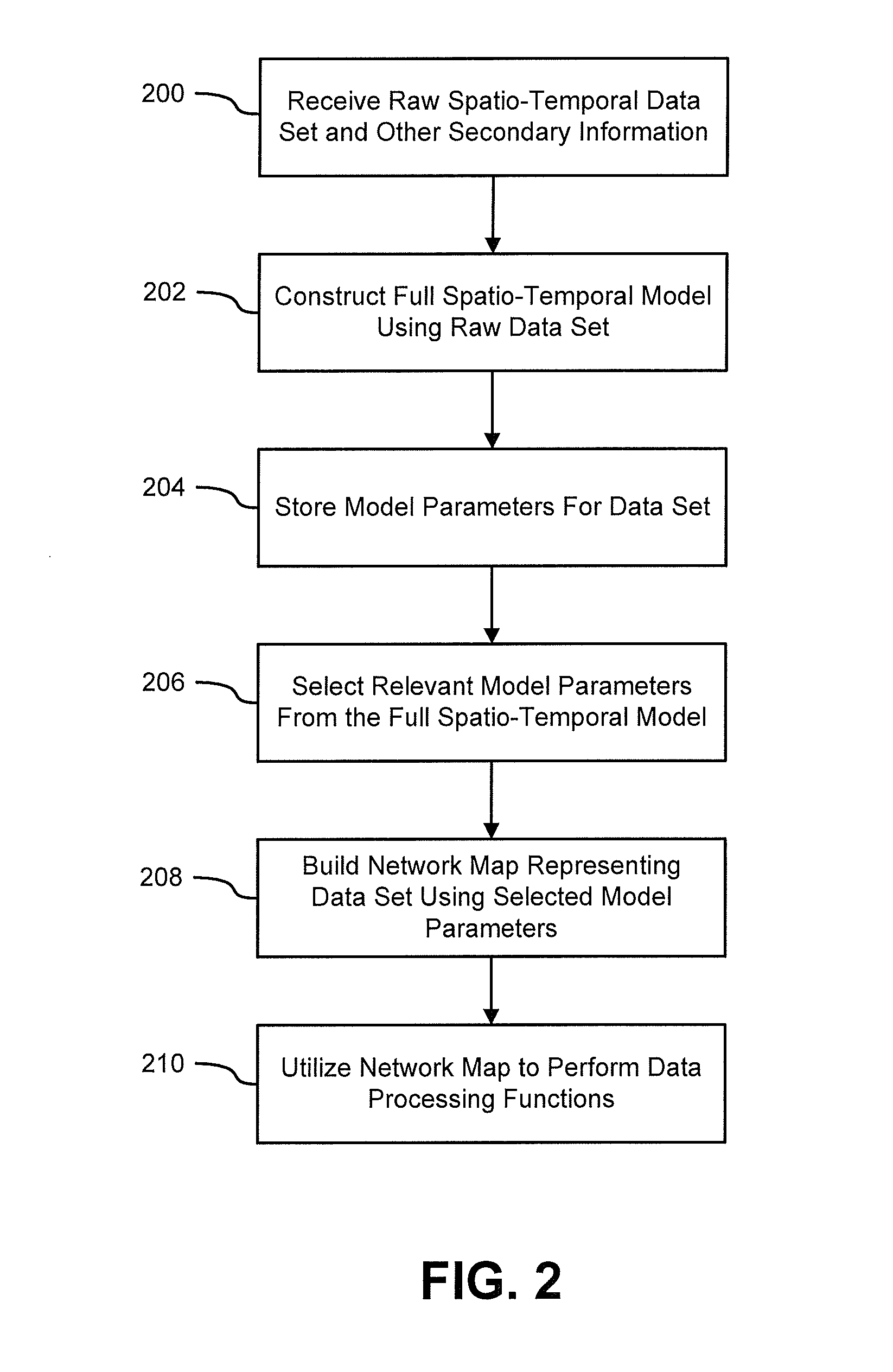
Systems and methods for modeling and processing functional magnetic resonance image data using full-brain vector auto-regressive model
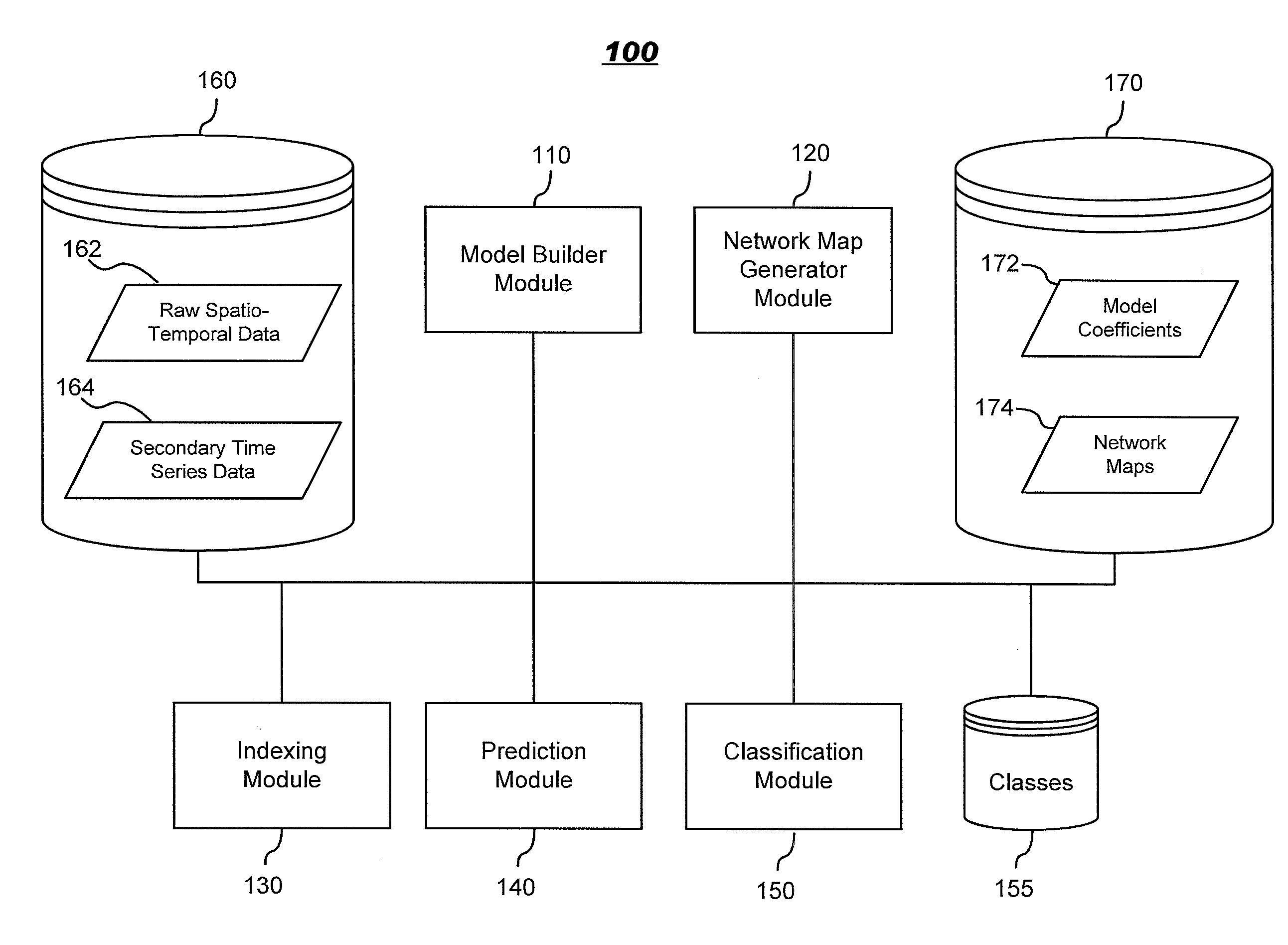
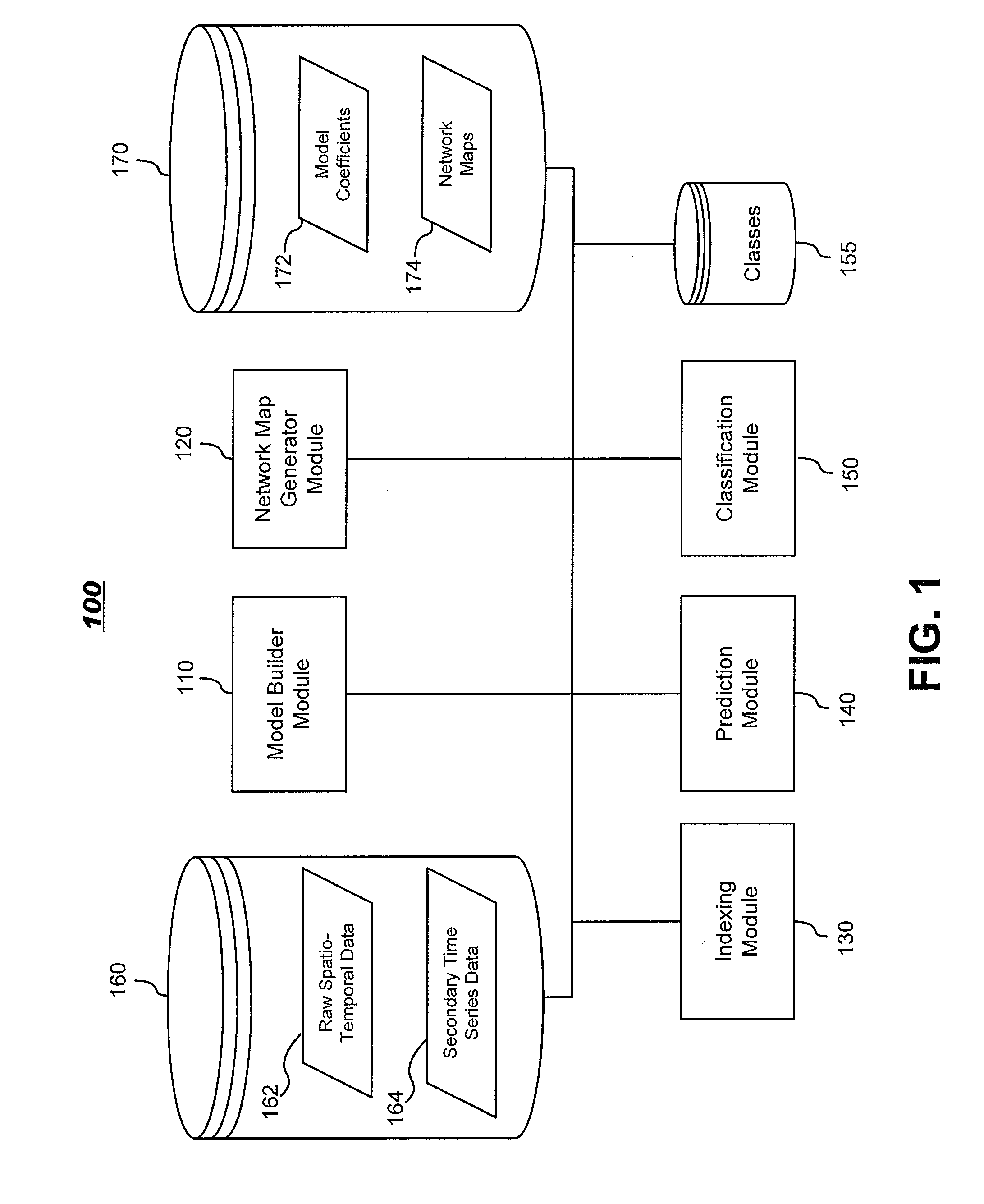
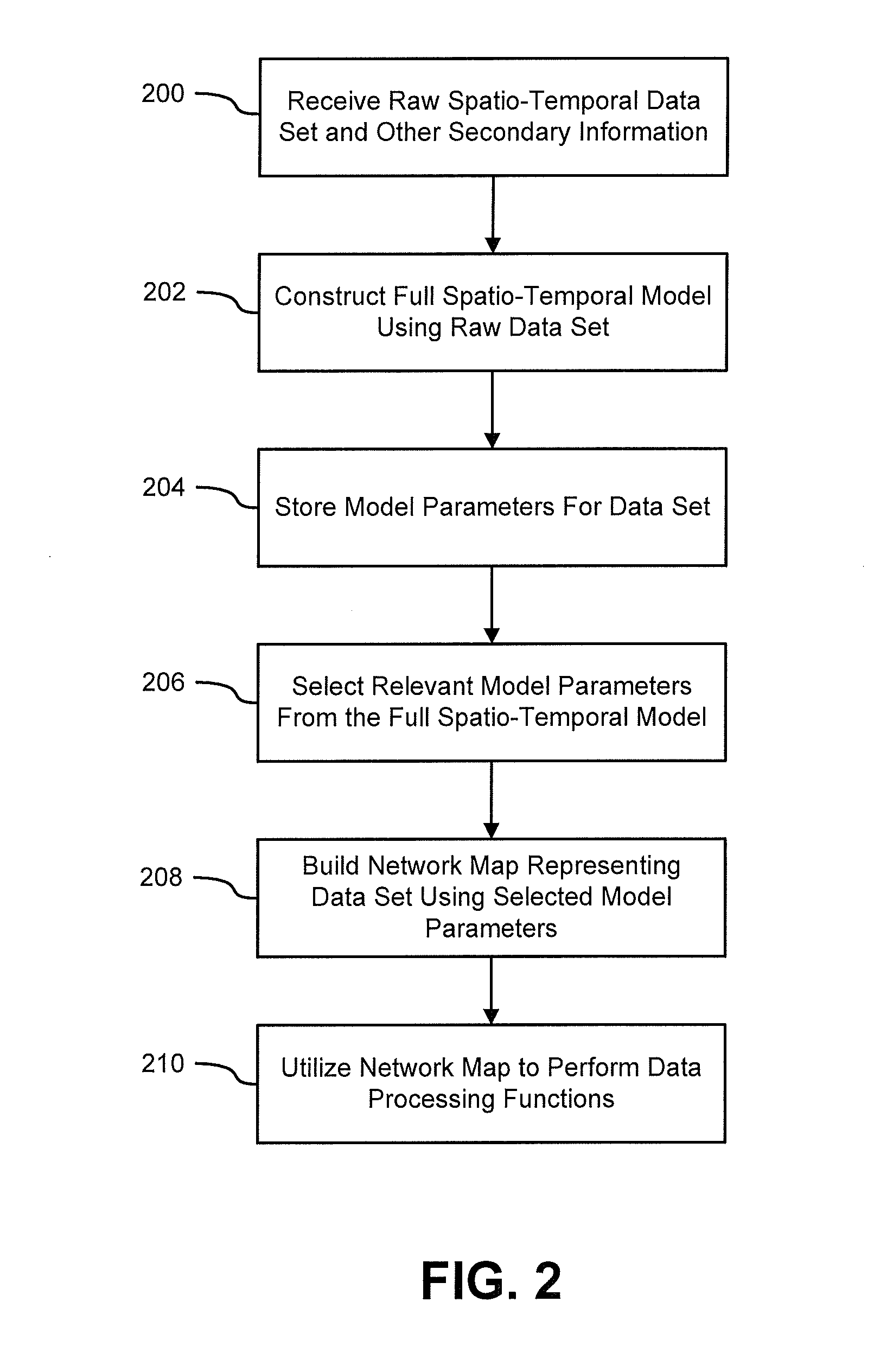
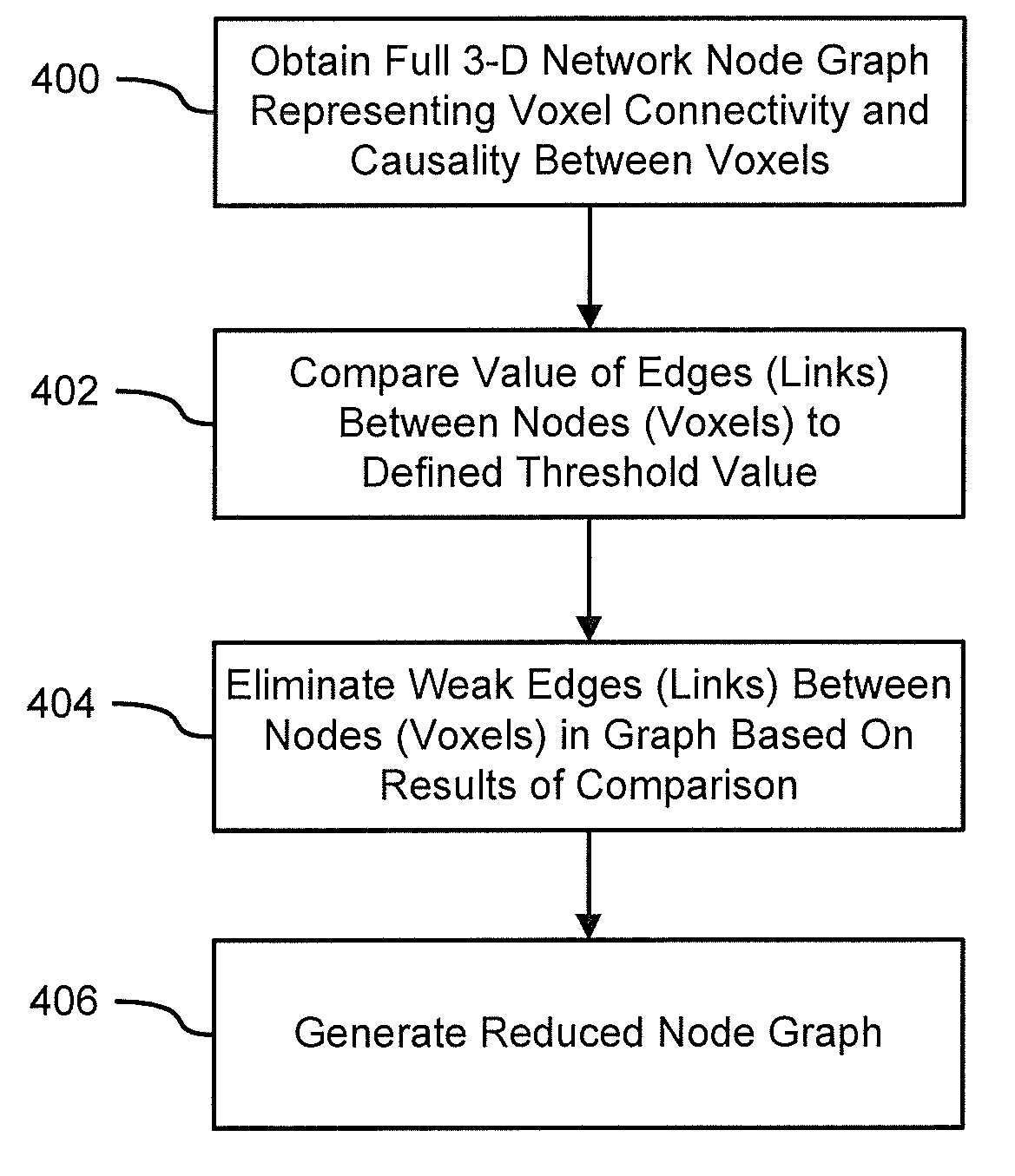
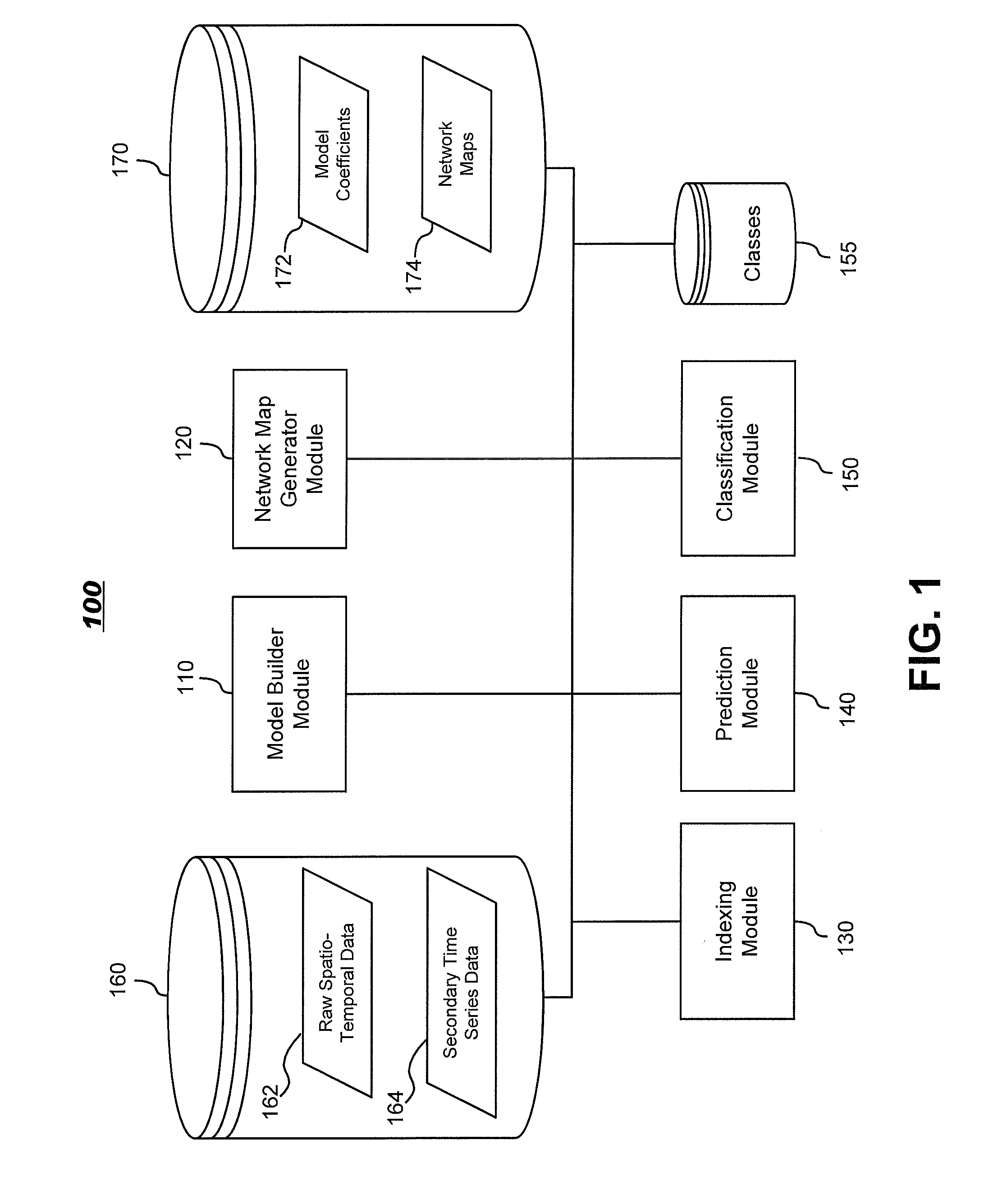
InactiveUS20130034277A1Reduced representation of dataReduced representationMedical simulationImage enhancementFunctional connectivityData set
Systems and methods for modeling functional magnetic resonance image datasets using a multivariate auto-regressive model which captures temporal dynamics in the data, and creates a reduced representation of the dataset representative of functional connectivity of voxels with respect to brain activity. Raw spatio-temporal data is processed using a multivariate auto-regressive model, wherein coefficients in the model with high weights are retained as indices that best describe the full spatio-temporal data. When there are a relatively small number of temporal samples of the data, sparse regression techniques are used to build the model. The model coefficients are used to perform data processing functions such as indexing, prediction, and classification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on super-network discriminant subgraphs
ActiveCN107133651APreserve integrityWithout loss of discriminabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse learningGraph kernel
The invention discloses a functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on super-network discriminant subgraphs. The method includes the steps of preprocessing a resting-state functional magnetic resonance image, and extracting the average time series of divided brain regions; using a sparse linear regression method and sparse learning to optimize an objective function to generate a super-network; extracting each super-edge in the super-network as a sub-graph, calculating the frequency of each sub-graph, selecting a frequency threshold, filtering the frequent sub-graphs, and taking a frequent sub-graph mode as a feature; in a training set, adopting a frequent score feature selection method, and then obtaining an optimal feature subset and a regularization parameter C based on the performance of a test set; adopting a classification algorithm based on a graph kernel and using discriminant subgraphs as features for classification; and quantifying the importance and redundancy of the selected features. For the diagnosis of brain diseases, the method of the invention retains the integrity of an original network topology, without the loss of discrimination of the features, and shows a higher level and more complex interaction among the brain regions.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
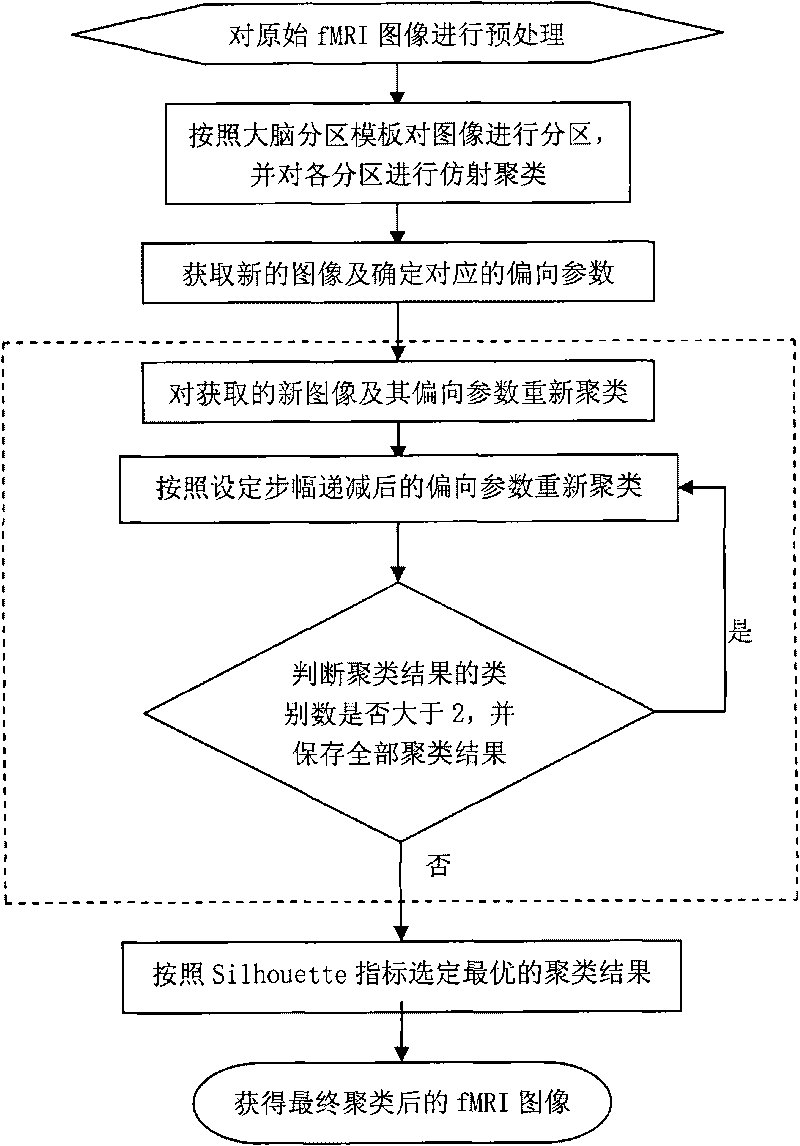
Clustering method for functional magnetic resonance images
InactiveCN101706561ASolve the objective choice problemObjective choice improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention relates to a clustering method for functional magnetic resonance images, belonging to biological information technologies. The method comprises the following steps of pre-processing an original fMRI image, clustering an affine in regions, acquiring a new image and determining a corresponding bias parameter, acquiring clustering results corresponding to all bias parameters, determining an optimal clustering result and acquiring a finally clustered fMRI image. Because the hierarchical clustering, the affine clustering and the self-adapting affine clustering are organically combined, and the images are comprehensively processed, the invention overcomes the defects that the conventional clustering methods are affected by the subjective factor of people, heavily dependent on the personal experience and cannot effectively carry out the clustering processing on the images with large data quantity, and effectively solves the problem of objectively selecting the optimal clustering result. Therefore, the invention has the characteristics of having strong ability for processing the images with large data quantity and effectively improving the objectivity in the fMRI image processing procedure as well as the accuracy of selecting the optimal clustering result.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method based on network analysis
ActiveCN103020653AAccurate classificationMake up for the inability to reflect the inherent properties of brain activityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBrain magnetic resonance
The invention provides a structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method based on network analysis. The method includes firstly, establishing a structure and function brain network model, calculating characteristic path length, an agglomeration degree and a network centrality of a brain network to represent different image models, and then training a self-adaption improving classifier by using network parameters. The structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method can use as many messages as possible in a magnetic resonance image, the brain network parameters can reflect brain activities in nature, and simultaneously, a technology of multiple classifiers is used, so that the defect that inherent attributes of the brain activities can not be reflected by traditional classification methods is made up, and the brain magnetic resonance image can be accurately classified.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
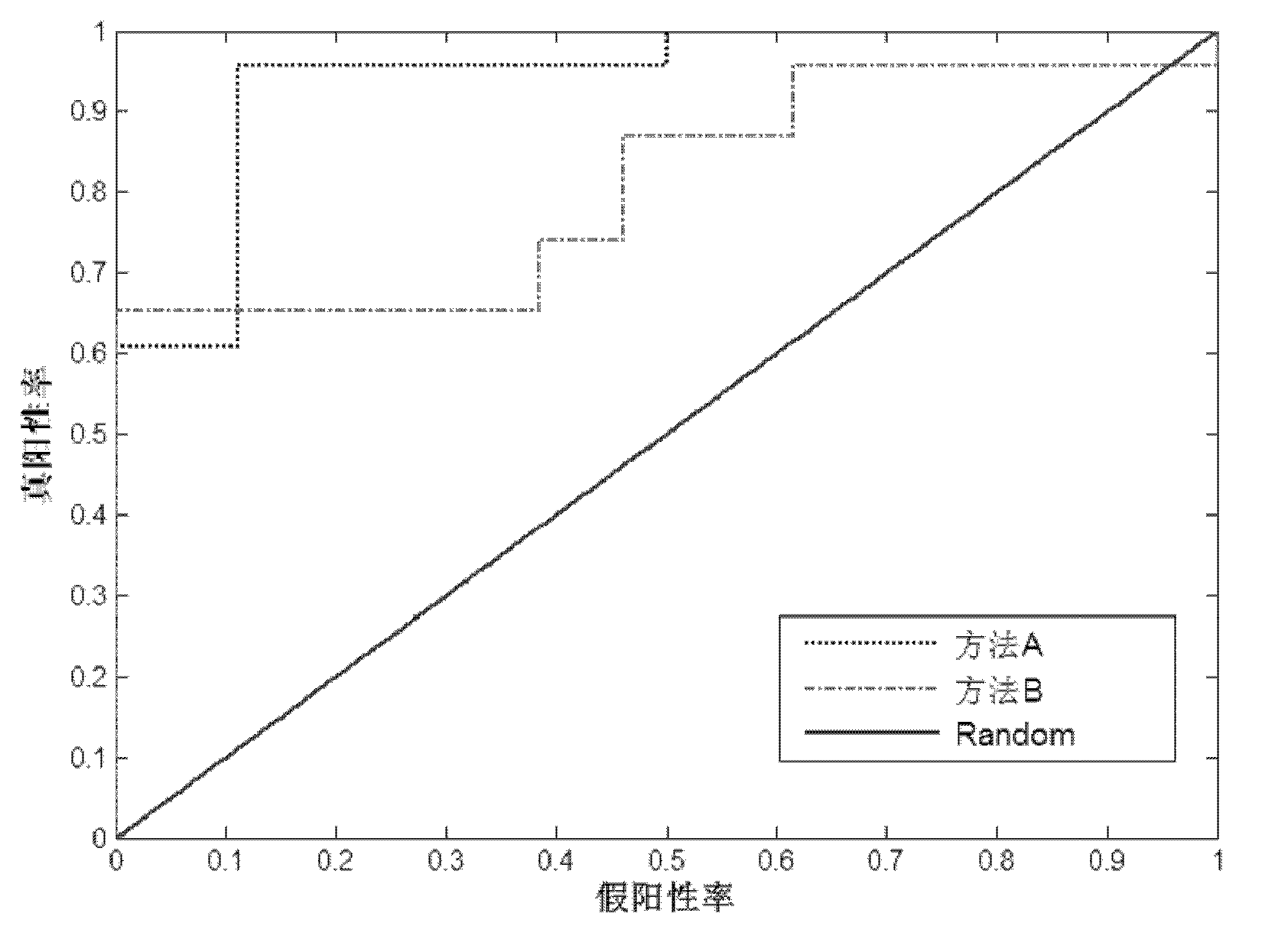
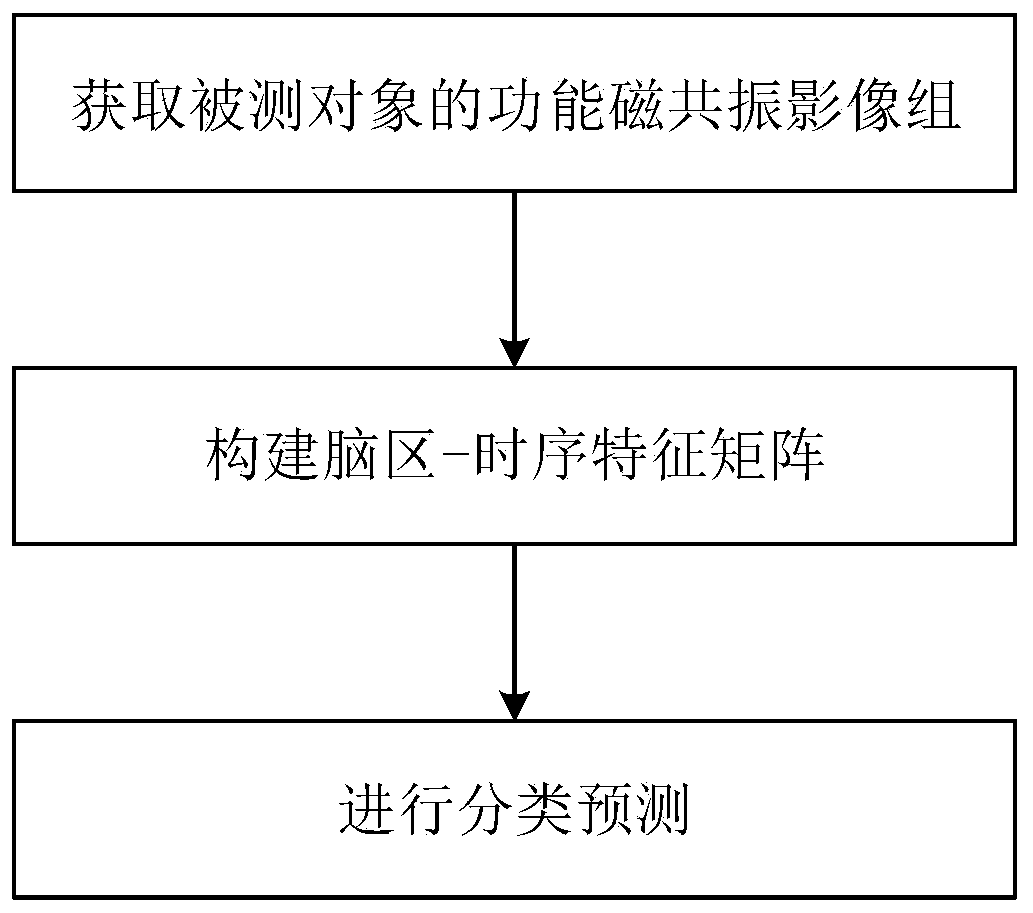
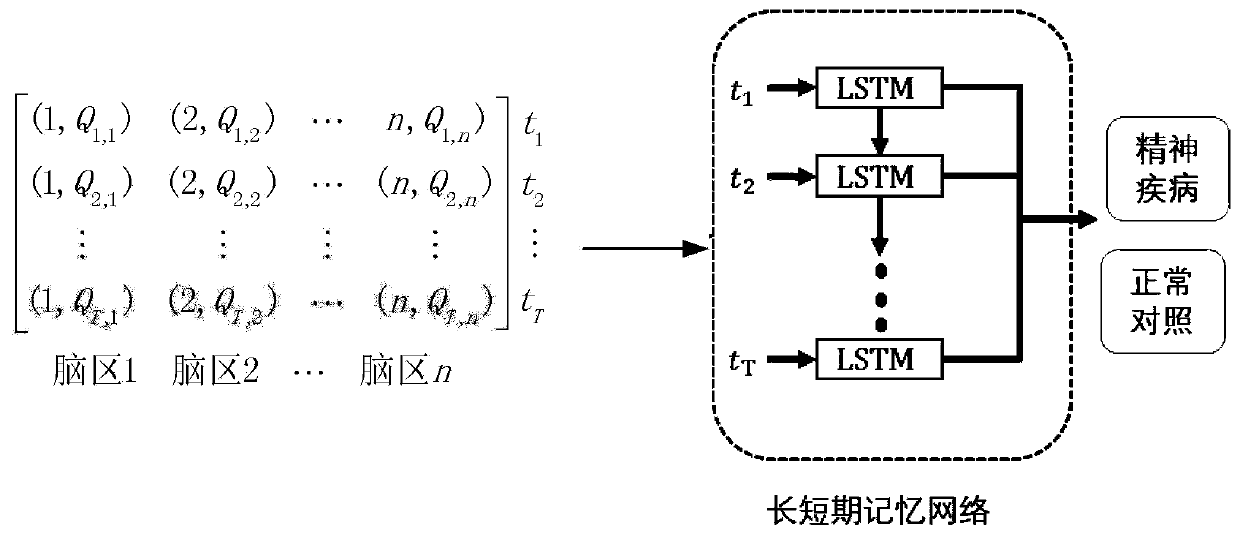
Method, system and device for classifying and predicting functional magnetic resonance images
ActiveCN109770903AEffective classificationPrecise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDimensionality reductionComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of computational medicines, particularly relates to a method, system and device for classifying and predicting functional magnetic resonance images, and aims at solving the problem of functional magnetic resonance image classification including time sequence information. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a functional magnetic resonance image group of a measured object which comprise a plurality of the functional magnetic resonance images; respectively performing feature dimensionality reduction on each brain region of each functional magnetic resonance image, and based on each of time sequences of the functional magnetic resonance images in the functional magnetic resonance image group, constructing brain region-time sequence feature matrix; classifying and predicting the brain region-time sequence feature matrix by a pre-trained classification model. The method achieves the functional magnetic resonance image classification including the time sequence information quickly and conveniently by computer means.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
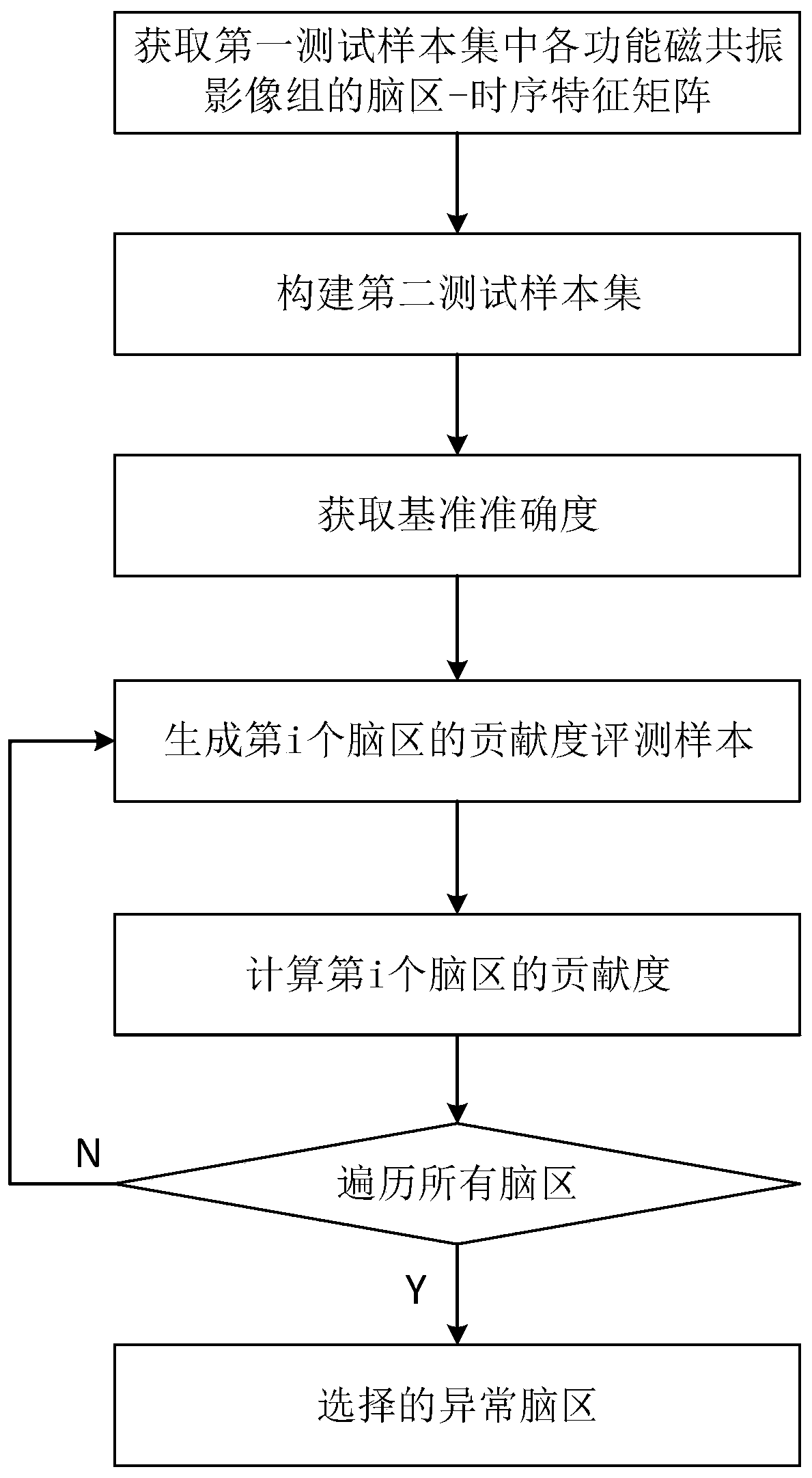
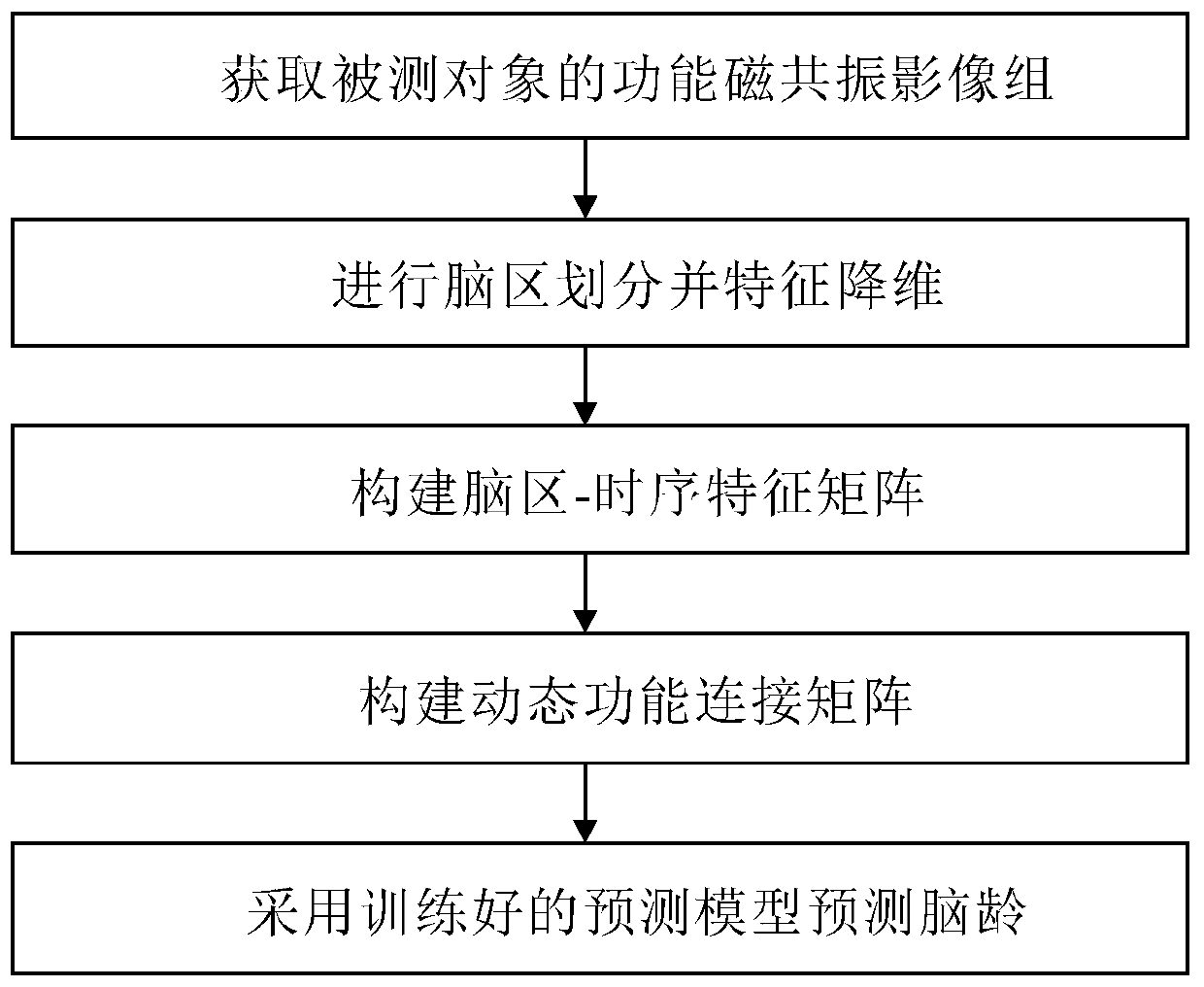
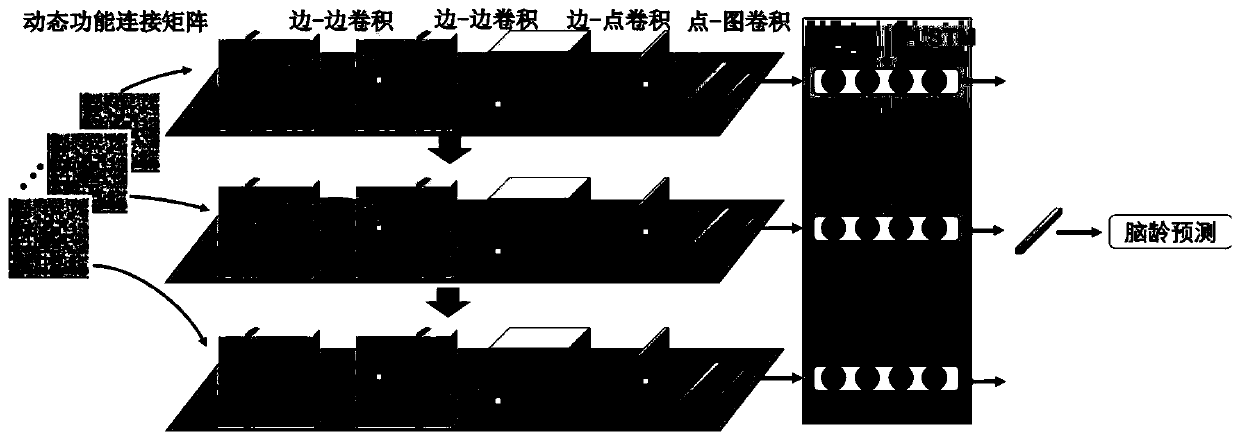
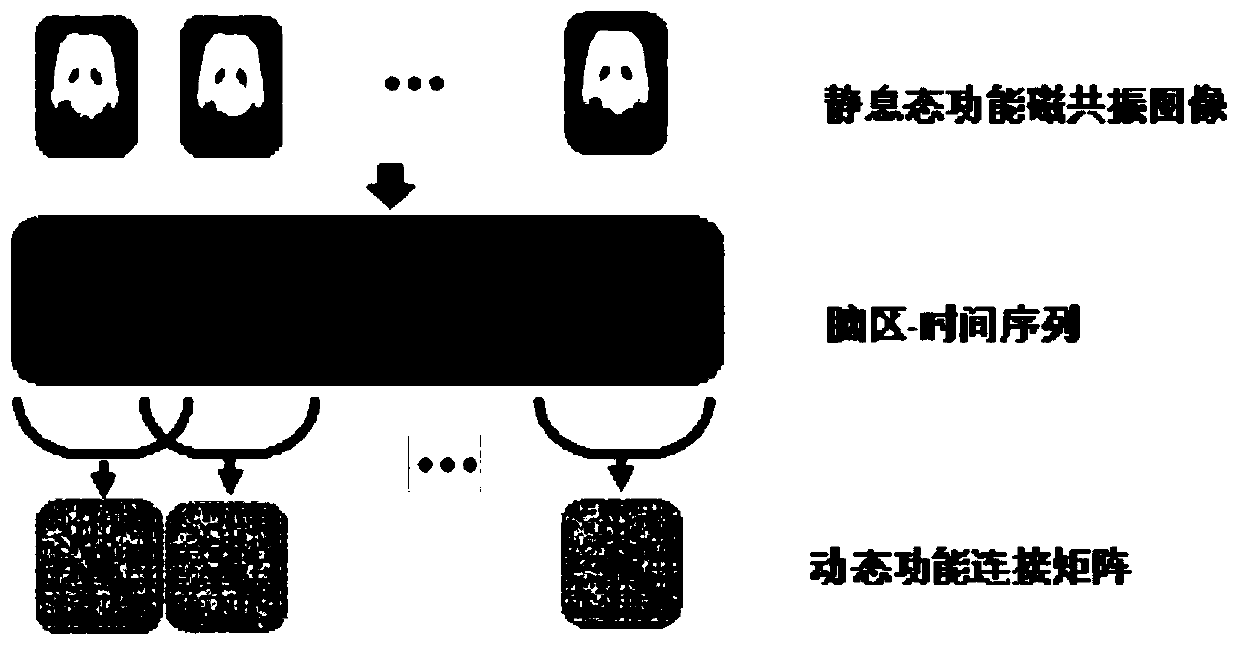
Baby brain age predicting method based on resting state functional magnetic resonance image and system
ActiveCN110097968AThe test result is accurateImprove practicalityMedical simulationImage enhancementIn silico medicineBrain growth
The invention belongs to the field of computer medicine, and particularly relates to a baby brain age predicting method based on a resting state functional magnetic resonance image and a system. The method and the system aim to settle a problem of incapability of predicting the baby brain age based on the functional magnetic resonance image based on dynamic function connection. The method according to the invention comprises the steps of acquiring a functional magnetic resonance image set of a measured object; performing brain area segmenting on each image, and performing characteristic dimension reduction on each brain area; based on the functional magnetic resonance image set after dimension reduction and a time sequence, constructing a brain area-time sequence characteristic matrix; constructing a dynamic function connecting matrix based on the brain area-time sequence characteristic matrix; and performing brain age predicting through a pre-trained classification model. The method and the system quickly and conveniently realize functional magnetic resonance image brain age predicting based on the dynamic function connection through a computer means, thereby quickly determining whether the brain growth degree of the baby matches an actual age, finding a possible brain retardation in time, and facilitating assistance to clinical decision of a doctor.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Brain cognitive state judgment method based on non-negative tensor projection operator decomposition algorithm
InactiveCN103425999APreserve spatial structure informationStrong orthogonalityCharacter and pattern recognitionCompositional dataCognitive status
Disclosed is a brain cognitive state judgment method based on a non-negative tensor projection operator decomposition algorithm. The method includes the steps of S1, collecting brain functional magnetic resonance images under different cognitive tasks to form a data sample set, carrying out preprocessing, and forming a sample set according to tensor modes, wherein the sample set is divided into a training set and a testing set according to the cognitive tasks, and the training set comprises functional magnetic resonance data in similar proportion of different cognitive states, S2, computing non-negative tensor projection operator decomposition of the training sample set to solve out a non-negative feature transformation matrix, projecting training samples to a non-negative tensor feature sub-space for dimensionality reduction to obtain a non-negative feature tensor set of the training set, S3, using lower-dimension non-negative feature tensor data after dimensionality reduction as input of an STM for training to solve out the optimum projection direction of the STM, and S4, projecting brain functional magnetic resonance data of tested samples to the non-negative tensor feature sub-space obtained through training to obtain non-negative feature tensors of the brain functional magnetic resonance data in the sub-space, and inputting the non-negative feature tensors of the tested samples to the trained STM to judge cognitive state types of the non-negative feature tensors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Feature selection method for FMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) data
InactiveCN104504373AFully reflect the structuralStable Feature Importance MeasureCharacter and pattern recognitionFault toleranceResonance
The invention discloses a feature selection method for FMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) data, belongs to the technical field of biomedical image mode identification, and particularly relates to the feature selection method of a functional magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the following steps of randomly selecting a submatrix of data, calculating the weight vectors of selected features by using an elastic net method, and converting the obtained weight vectors into stable score vectors; repeating the process p (p is greater than 1,000) times to obtain the selected time vector of each feature, acquiring feature importance metrics according to the calculated accumulated stable score vectors and time vectors, and performing feature sequencing and selection. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high fault tolerance, high stability and the like. A novel effective technology is provided for feature selection and sequencing in the fields of magnetic resonance data mode identification and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Brain function network classification method based on variational auto-encoder
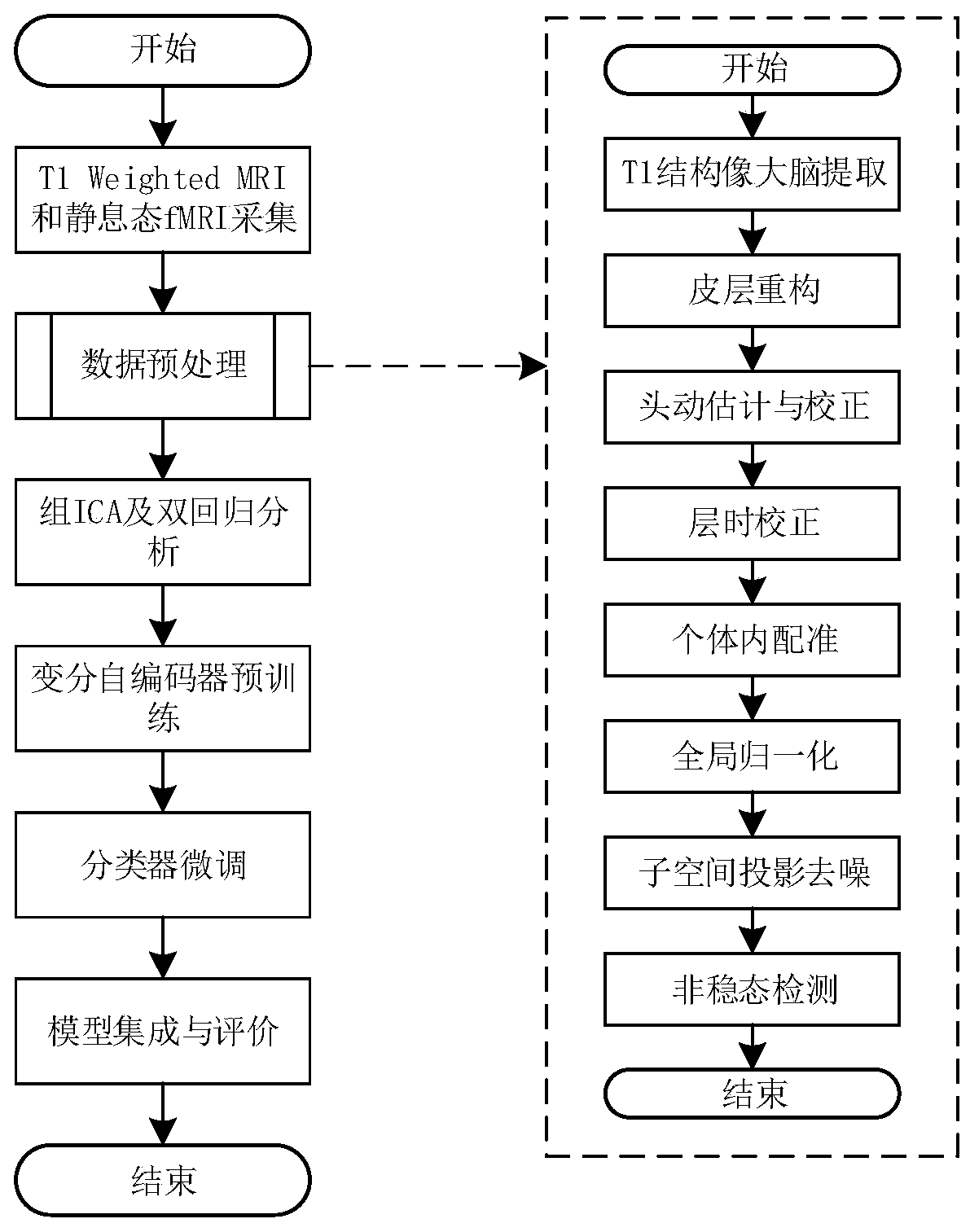
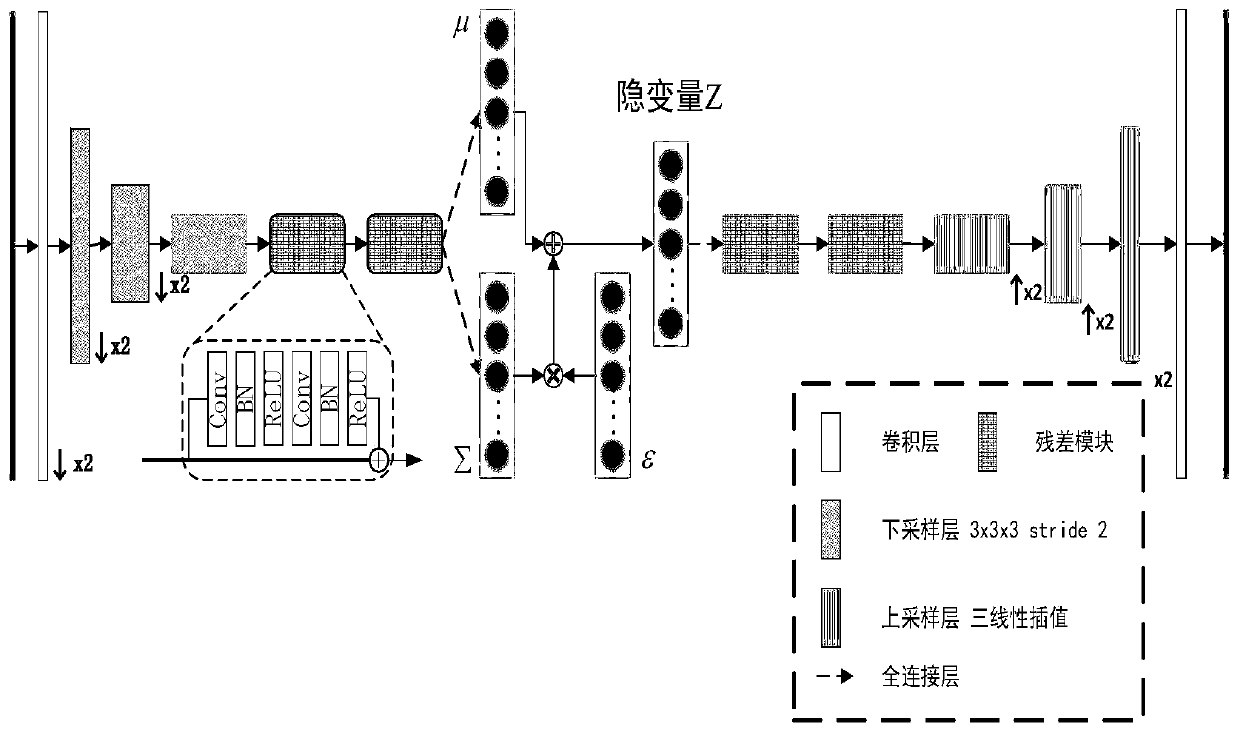
ActiveCN110188836AImprove generalization abilityOvercome the disadvantage of poor fitting abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesRegression analysisClassification methods
The invention discloses a brain function network classification method based on a variational autoencoder. The method comprises the following steps: The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring T1 weighted MRI and rs-fMRI of a plurality of normal people and patients with brain cognitive impairment; carrying out pretreatment; carrying out double regression analysis by taking the preprocessed rs-fMRI as a regression dependent variable and the brain function network as a regression independent variable to obtain an individual level brain function network; constructing a deep variationalautoencoder (VAE) model, taking the obtained individual level brain function network diagram as the input and output of the VAE, and taking the encoder part as a feature extraction module for obtaining the implicit code of the individual function network; constructing a multi-layer sensor network to classify the codes obtained by the VAE in the step 4; and deducing samples in the test set by using the trained classifiers for different brain function networks, and fusing deduction results of the classifiers to obtain a final classification result.acquiring T1 weighted magnetic resonance imagesT1 Weighted MRI and resting state functional magnetic resonance images rs-of a plurality of normal persons and patients with brain cognitive impairment; fMRI; carrying out pretreatment; pretreated rs- Performing double regression analysis by taking fMRI as a regression dependent variable and taking the brain function network as a regression independent variable to obtain an individual level brainfunction network; constructing a depth variation auto-encoder (VAE) model, taking the obtained individual level brain function network diagram as input and output of the VAE, and taking the encoder part as a feature extraction module for obtaining hidden codes of the individual function network; constructing a multi-layer perceptron network to classify the codes obtained by the VAE in the step 4;inferring samples in the test set by utilizing a plurality of trained classifiers for different brain function networks, and fusing inference results of the plurality of classifiers to obtain a finalclassification result; according According to the invention, the classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Functional magnetic resonance imaging synchronous monitoring and triggering stimulation control system
ActiveCN105078455AImprove performanceHighly integratedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceControl system
The invention discloses a functional magnetic resonance imaging synchronous monitoring and triggering stimulation control system. The technical scheme includes that the system comprises an upper computer, a lower computer and magnetic resonance imaging equipment; the upper computer is used for carrying out man-machine interaction and controlling the lower computer; the lower computer is used for processing communication and interaction with the magnetic resonance imaging equipment, stimulation tasks can be generated by a stimulation task generating module in the lower computer on the basis of instructions emitted by the upper computer, a monitoring module in the lower computer is communicated with the upper computer, and reaction parameters, which are measured by the magnetic resonance imaging equipment, of tested objects can be recorded when the stimulation tasks are carried out, and can be fed to the upper computer. The functional magnetic resonance imaging synchronous monitoring and triggering stimulation control system has the advantages that central control and hardware interfaces can be unified, triggering signals can be synchronously received when magnetic resonance images are scanned, various physiological parameters of primates can be synchronously recorded, and the functional magnetic resonance imaging synchronous monitoring and triggering stimulation control system is suitable for software and hardware technical platforms for the stimulation tasks for vision, touch and the like of the primates.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Classifying method for functional magnetic resonance image data based on multi-scale brain network characteristics
InactiveCN106295709AImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention relates to an image processing technique and specifically relates to a classifying method for functional magnetic resonance image data based on multi-scale brain network characteristics. The invention solves the problem of low classifying accuracy of the traditional magnetic resonance image data classifying method. The classifying method for functional magnetic resonance image data based on multi-scale brain network characteristics comprises the following steps: S1) pre-processing the resting state functional magnetic resonance image; S2) adopting a dynamic random seed method for performing region segmentation on the image and extracting mean time sequences for the cut brain areas; S3) calculating a relevance degree of each two mean time sequences of the brain areas; S4) performing binarization processing on the incidence matrix; S5) calculating a local property of the resting state functional brain network and an AUC value thereof in a specific threshold space; S6) constructing a classifier; S7) quantizing the importance and redundancy of the selected characteristics in the classifier. The classifying method provided by the invention is fit for the classification of the magnetic resonance image data.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for clustering videos by using brain imaging space features and bottom layer vision features
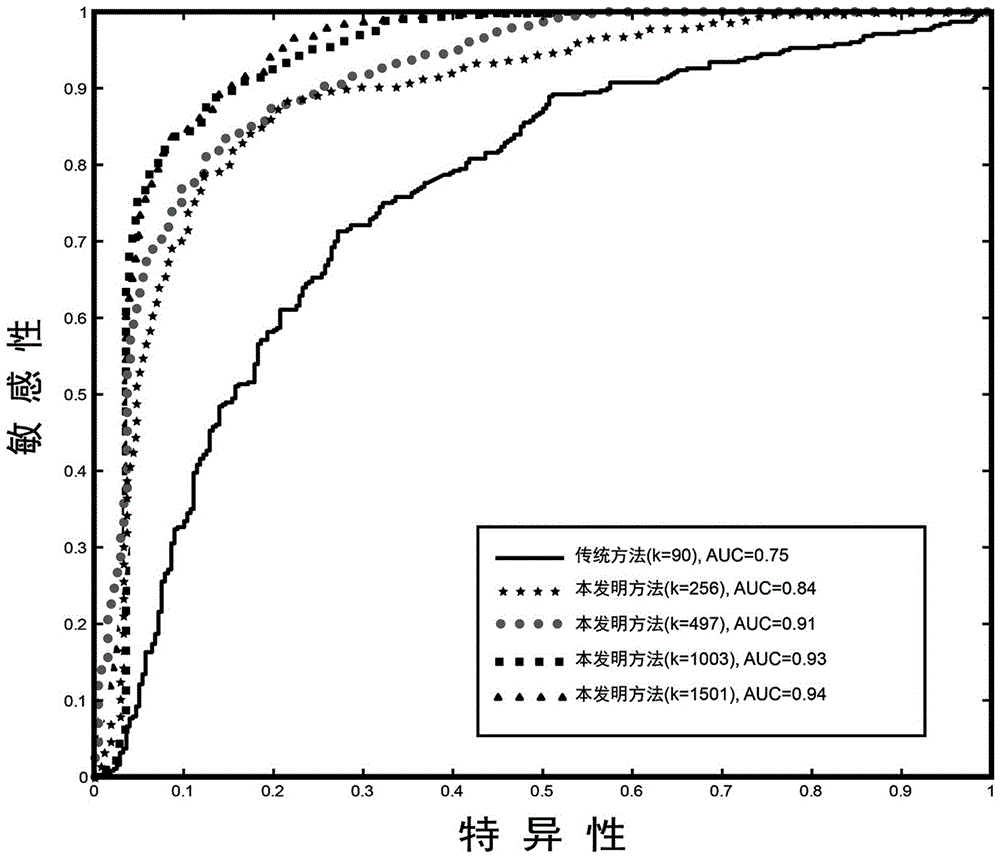
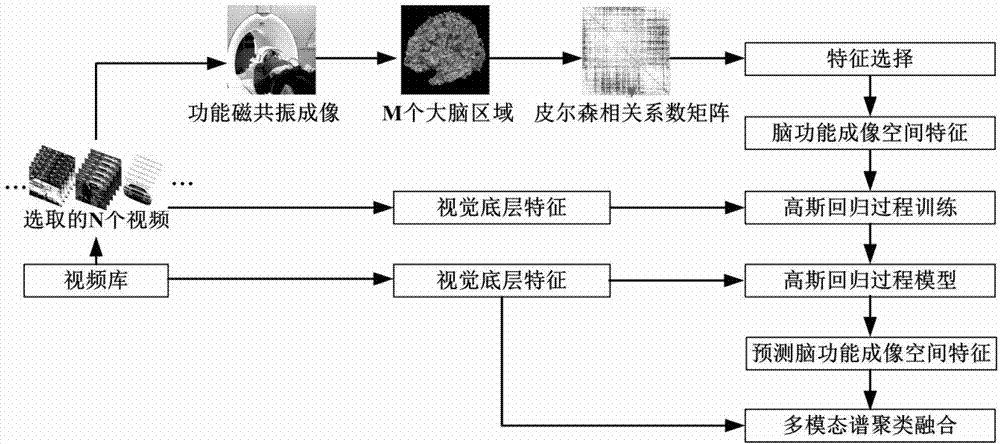
InactiveCN102855352AImprove accuracyImprove clustering accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFunctional imagingComputer vision
The invention relates to a method for clustering videos by using brain functional imaging space features and bottom layer vision features. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: extracting a brain signal vector in a functional magnetic resonance image sequence, calculating a Pearson relevant coefficient matrix of the signal vector, extracting the brain function imaging space features from the Pearson relevant coefficient matrix by using a single-factor variance analysis and relevant feature selection method, establishing a Gaussian process regression model according to the bottom layer vision features of partial videos and the brain function imaging space features, mapping the bottom layer vision features of the rest videos into the brain function imaging space features, and performing multi-modal spectrum clustering on the brain function imaging space features and the bottom layer vision features of all the videos. By the method, the brain function imaging space features and the bottom layer vision features can be combined and clustered; and compared with the conventional video clustering method based on the bottom layer vision features such as colors and shapes as well as the conventional space clustering method by independently using the brain functional features, the method has the advantage that the clustering accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging method and system
InactiveCN103932710AImprove time resolutionImprove spatial resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTikhonov regularizationImaging data
The invention discloses a dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging method and system. The method includes the steps that high-time low-space-resolution navigation data S<NAV> and high-space low-time-resolution dynamic image data S are collected in (k,t) space; the navigation data S<NAV> are decomposed through singular values to obtain a model order L and a time primary function phi[l](t), and Tikhonov regularization constraint is conducted by combining with the image data S to solve a space primary function cl(k); interpolation recovery with the high-time high-space coverage density is conducted on the (k,t) space through the model order L, the time primary function phi[l](t) and the space primary function cl(k), Fourier inversion is then conducted, and therefore a high-time-resolution and high-space-resolution dynamic brain function magnetic resonance image is obtained. By means of the method and the system, quality of the reconstructed image is improved, and meanwhile the high-time-resolution and high-space-resolution dynamic brain function magnetic resonance image is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
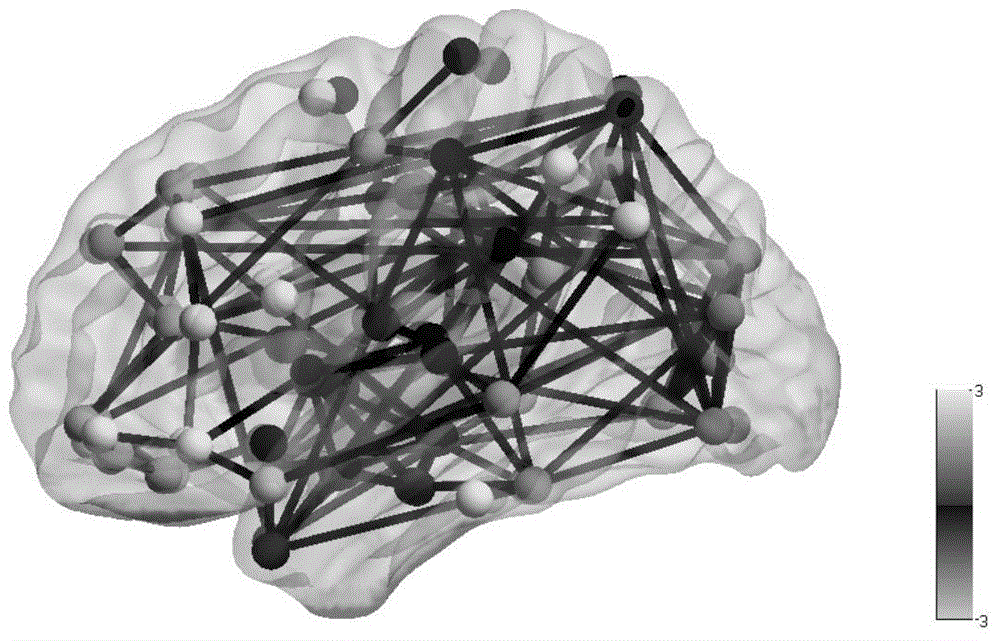
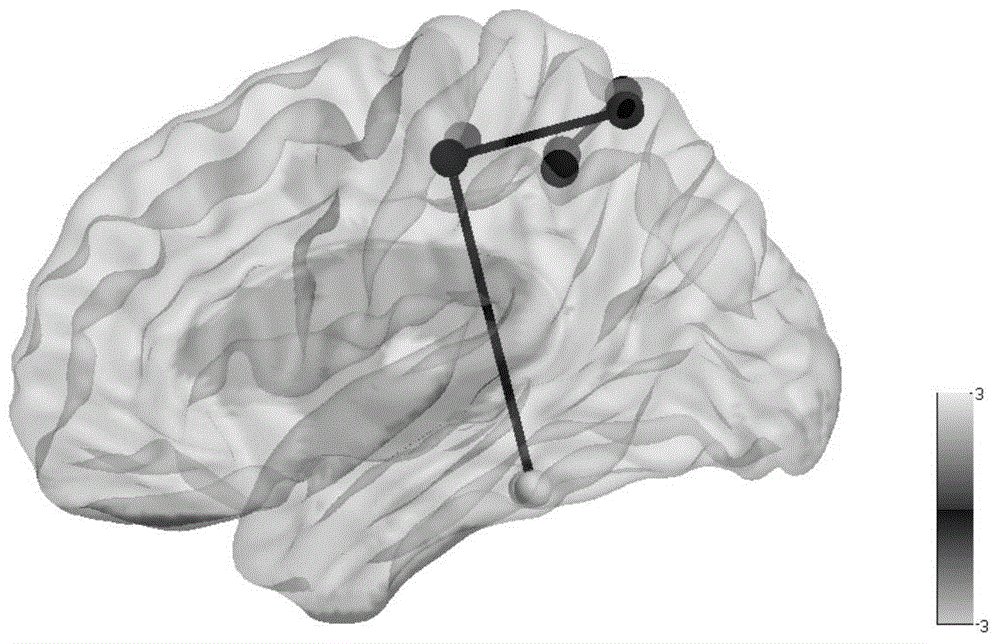
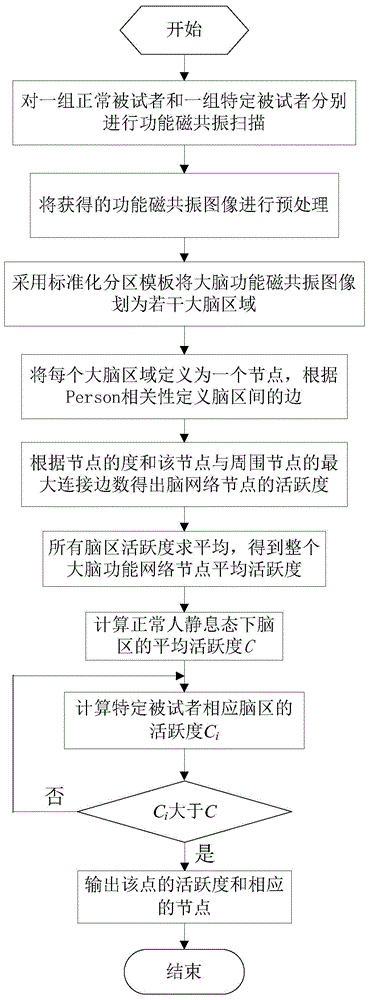
Brain functional network activity level measurement method
The invention discloses a brain functional network activity level measurement method. The method includes the steps: respectively carrying out functional magnetic resonance imaging on a normal subject and a specific subject, and subjecting brain functional magnetic resonance images acquired under identical conditions to preprocessing operations; using a standard partition template to divide the brain functional magnetic resonance images into a plurality of brain areas, defining each brain area as a node and defining connection between each two brain areas as a side for connection of the corresponding nodes to enable a whole brain to form a functional network with a plurality of nodes and the connection sides among the nodes; according to a level of each node and a maximum number of the connection sides among each node and the surrounding nodes, respectively calculating a corresponding node activity level of each brain area of the specific subject and an average node activity level of the whole brain functional network of the normal subject, comparing and taking the brain areas high in activity level as active areas. According to the brain functional network activity level measurement method, connection closeness of the brain areas is reflected by the node activity levels of the brain functional network, and the activity level of each single area can be observed specifically. The brain functional network activity level measurement method has a certain application value in the fields of brain functional regulation, cognitive function research, mental disease diagnosis and treatment and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
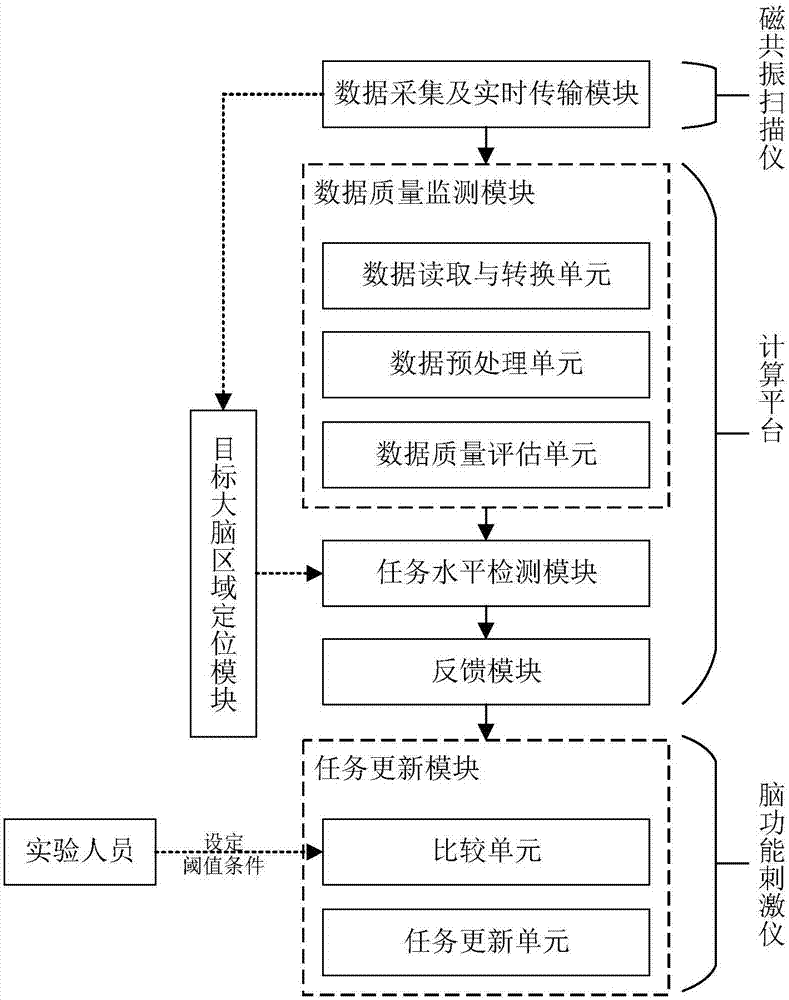
Brain function experimental task stimulation system with real-time feedback and task update functions
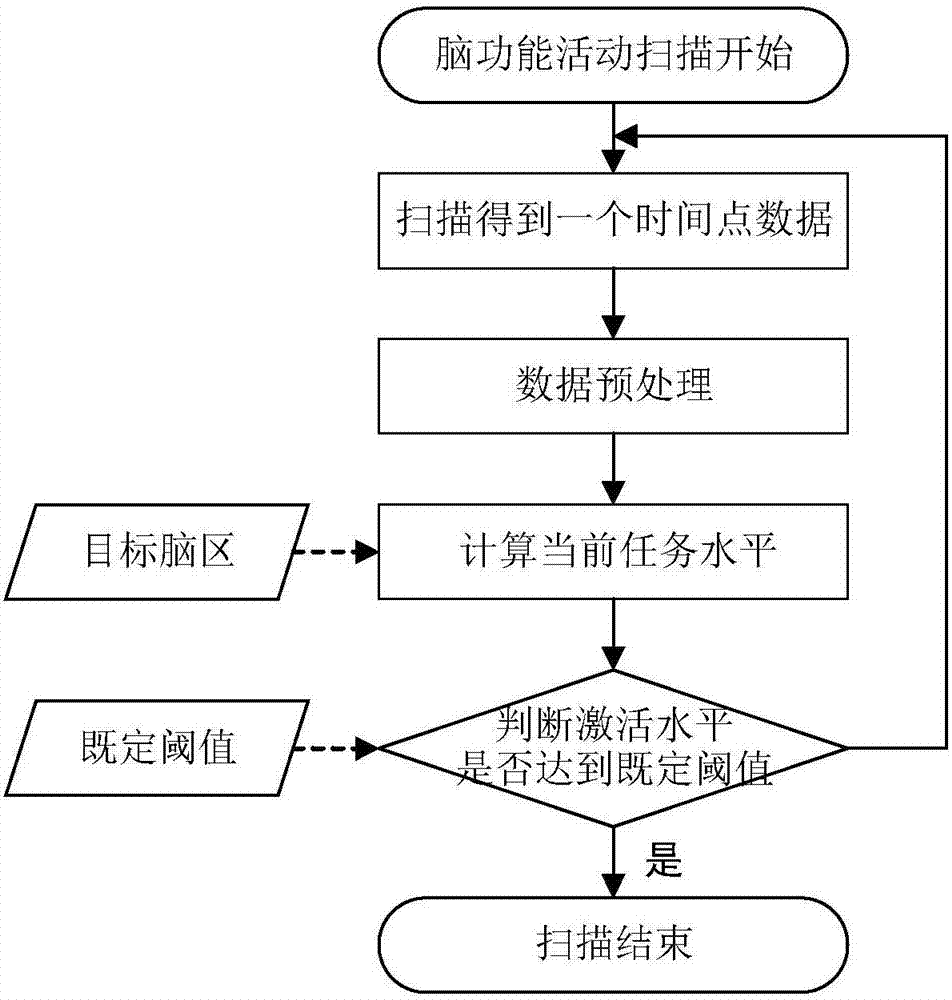
ActiveCN107045593AMonitor task levels in real timeImprove the efficiency of brain function activity scanningImage enhancementMedical imagingImaging qualityData acquisition
The present invention discloses a brain function experimental task stimulation system with real-time feedback and task update functions. The system comprises a computing platform, for detecting and positioning a brain functional area in real time, monitoring image quality of brain function imaging in real time, and detecting and feed backing the current task response level of the brain; the computing platform is provided with a target brain area positioning module, a data quality monitoring module, a task level detection module and a feedback module; the computing platform is also provided with a data acquisition and real-time transmission module, wherein the original function magnetic resonance image is transmitted to the computing platform after acquisition and reconstruction by using a magnetic resonance scanner; and the computing platform is further provided with a task update module, for presenting new experimental task material by comparing and determining to trigger and control the brain function stimulator. According to the system disclosed by the present invention, efficiency of the statistical determination on the active level of the specific brain area is improved, the total time of brain function signal acquisition is shortened, and the system has great practical significance to improve the scanning efficiency of brain function activity and fast positioning of the functional area in clinical patients, and can be applied to the neurological research related to brain functional area detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
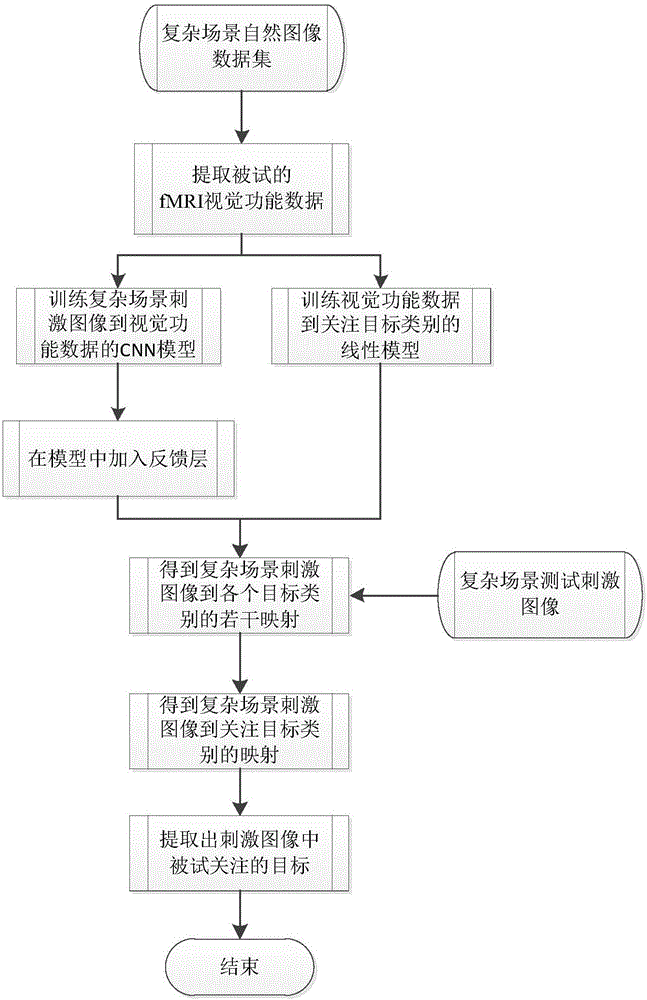
CNN (convolutional neural network)-based fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) visual function data object extraction method
ActiveCN106056602AImprove accuracyImprove analytical abilityImage enhancementImage analysisVisual functionNetwork model
The present invention relates to a CNN (convolutional neural network)-based fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) visual function data object extraction method. The method includes the following steps that: the fMRI visual function data of an examinee under the stimulation of a complex scene natural image are acquired, a stimulus image-to-fMRI visual function data deep convolution neural network model is trained, and at the same time, an fMRI visual function data-to-focus target category linear mapping model is trained; feedback layers are added into the deep convolution neural network model, the trained linear mapping model is compounded with the deep convolution neural network model, category score mappings are obtained for different target categories in one test image; and the category score mappings are utilized to analyze the fMRI visual function data of the examinee in viewing a new test image, and a target focused by the examinee can be extracted. With the method of the invention adopted, the fMRI visual function data of the examinee which are caused by viewing the complex scene natural image can be analyzed, and the target in the image focused by the examinee can be extracted, and the accuracy of the extraction of the focused target can be improved.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method and device for functional magnetic resonance imaging
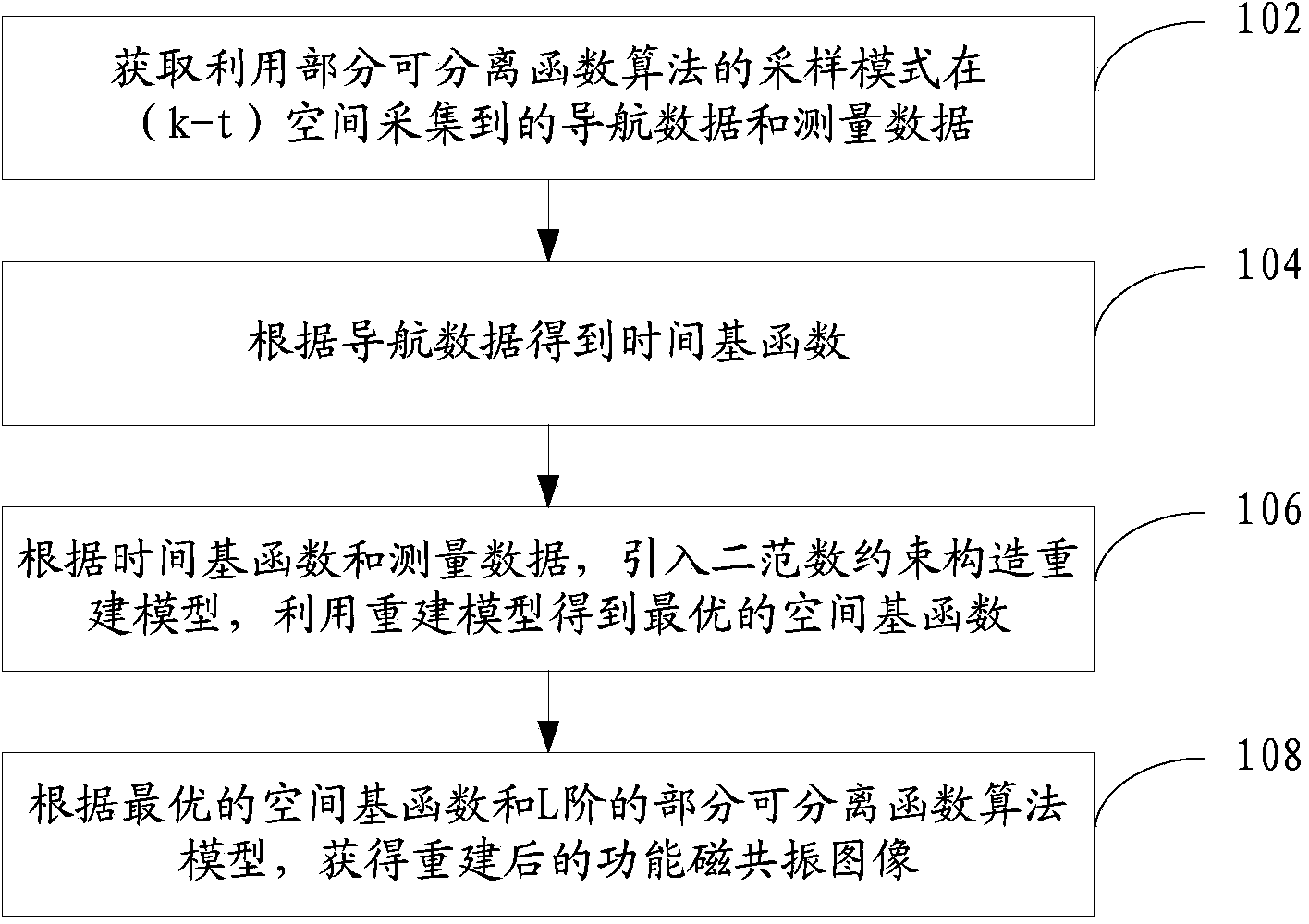
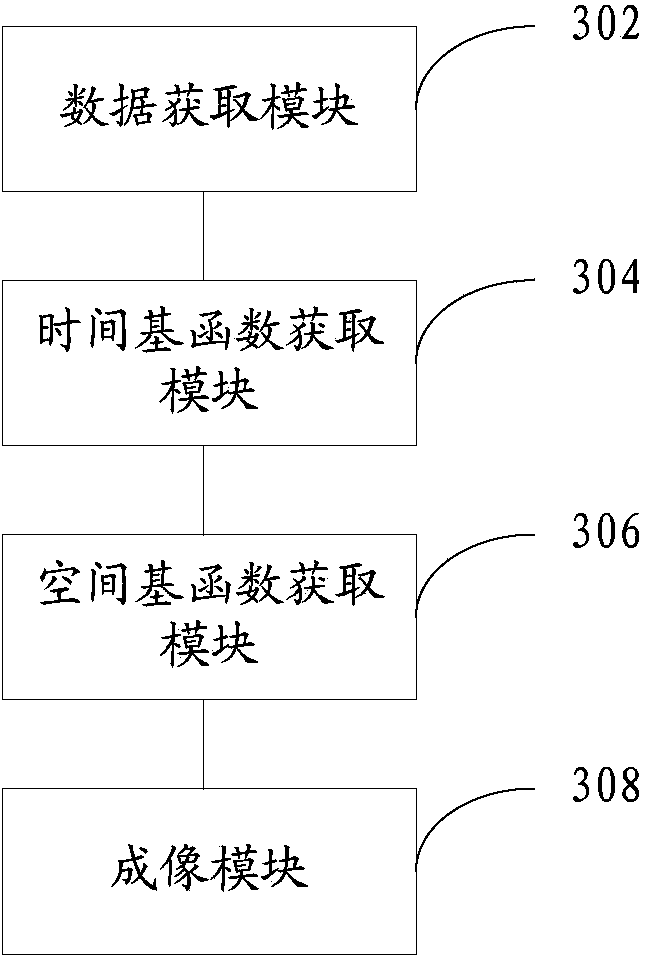
ActiveCN104337517AQuality improvementOvercome the problem of inaccurate fitSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringSample ModeImaging quality
The invention provides a method for functional magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining navigation data and measurement data which are collected in a (k-t) space by utilizing a sampling mode of partial separable functions algorithm; obtaining a time primary function according to the navigation data; introducing a two norm constraint structure to rebuild a model according to the time primary function and the measurement data, and obtaining an optimal space primary function by utilizing the rebuilt model; obtaining a rebuilt functional magnetic resonance image according to the optimal space primary function and L-order partial separable functions algorithm model. Through the use of the method, an image artifact and rebuilding noise can be effectively reduced, so that the image quality is improved. In addition, the invention also provides a device for the functional magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
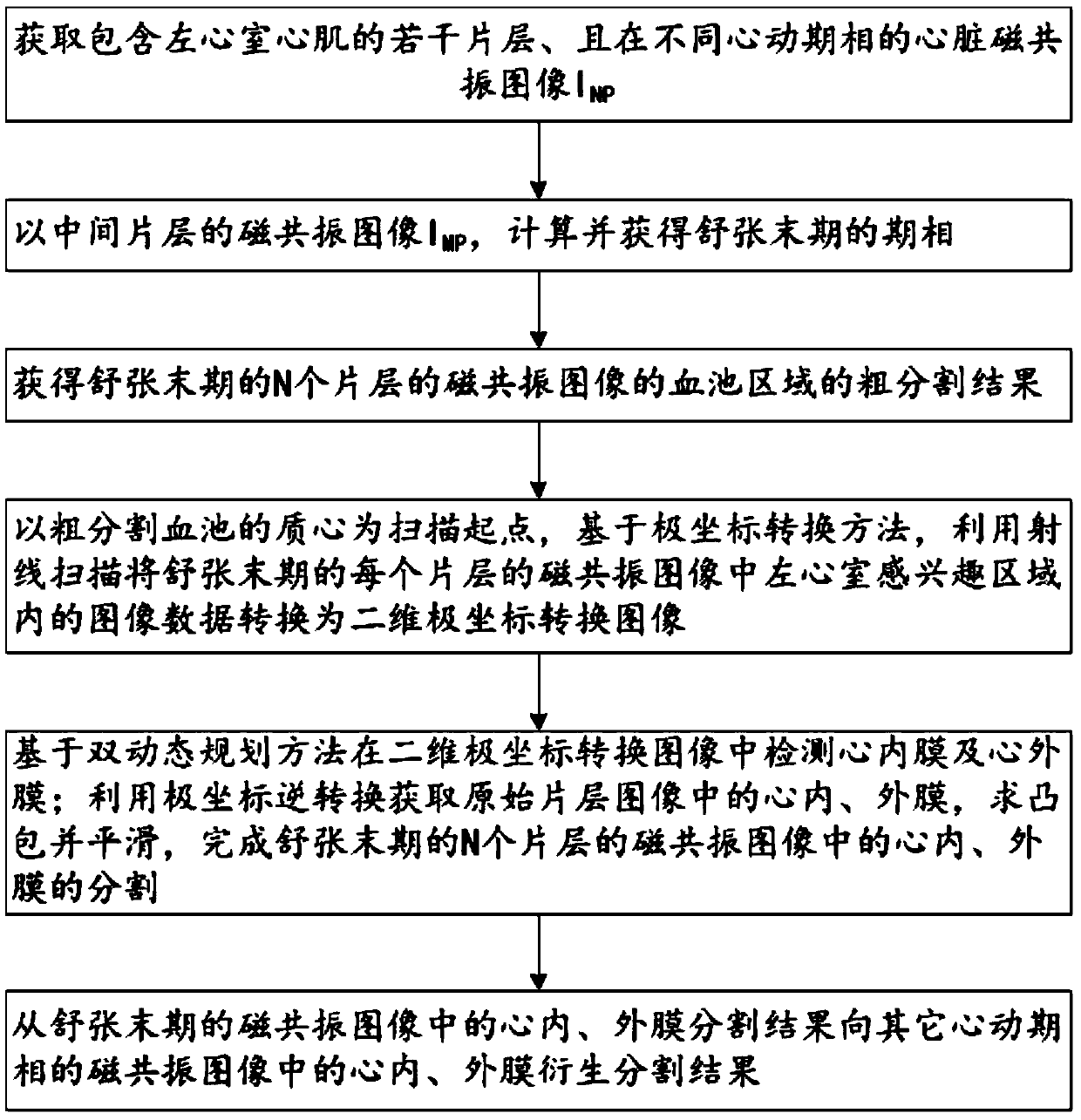
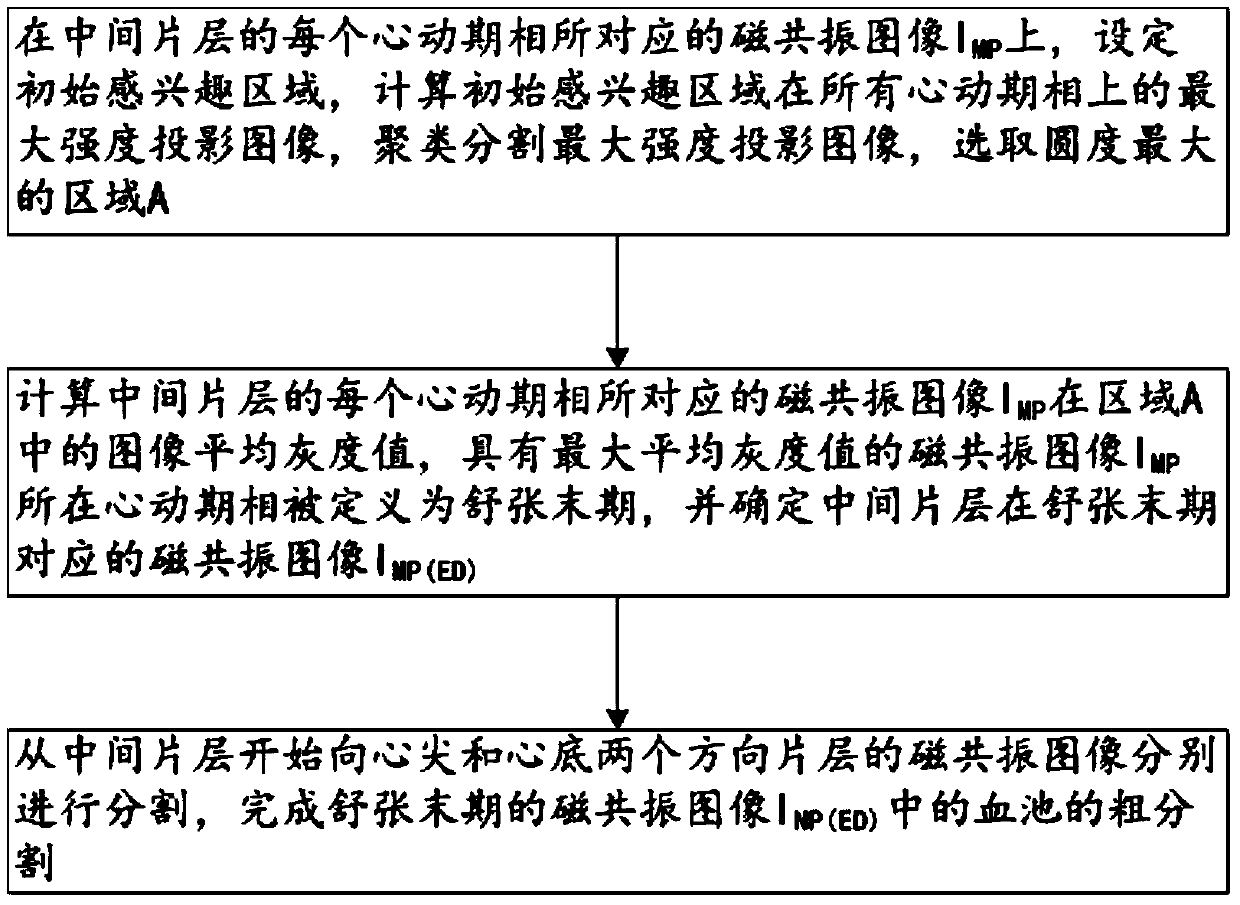
Method for segmenting endocardium and epicardium in heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN106910194ARealize detectionAccurate and effective detectionImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleLeft ventricle wall
The invention discloses a method for segmenting the endocardium and the epicardium in a heart cardiac function magnetic resonance image. The method comprises positioning the diastasis in heart magnetic resonance images I<NP> including several lamellas of the left ventricular myocardium and in different cardiac cycle phases, and obtaining a coarse segmentation result of blood pools of magnetic resonance images of N lamellas in the diastasis; converting image data in the left ventricle region-of-interest in the magnetic resonance image of each lamella in the diastasis into a two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image by means of ray scanning based on a polar coordinate conversion method; detecting the endocardium and the epicardium in the two-dimension polar coordinate conversion image based on a bidynamic programming method; obtaining the endocardium and the epicardium in an original lamella image by means of polar coordinate inverse conversion, calculating the convex hull and smoothing the convex hull, and completing segmentation of the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images of the N lamellas in the diastasis; and deriving the segmentation result of the in the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in the diastasis to the endocardium and the epicardium in the magnetic resonance images in other cardiac cycle phases.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
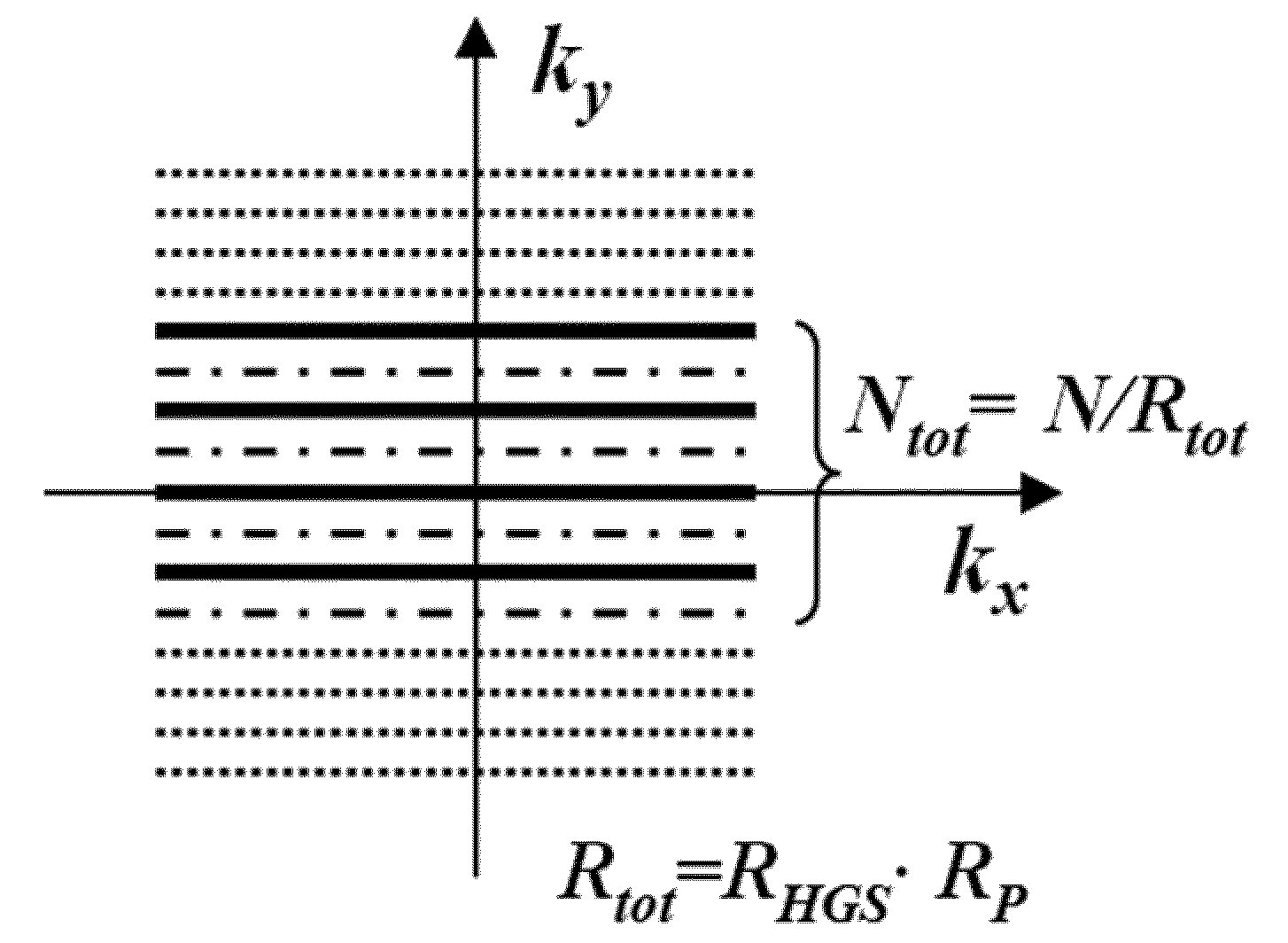
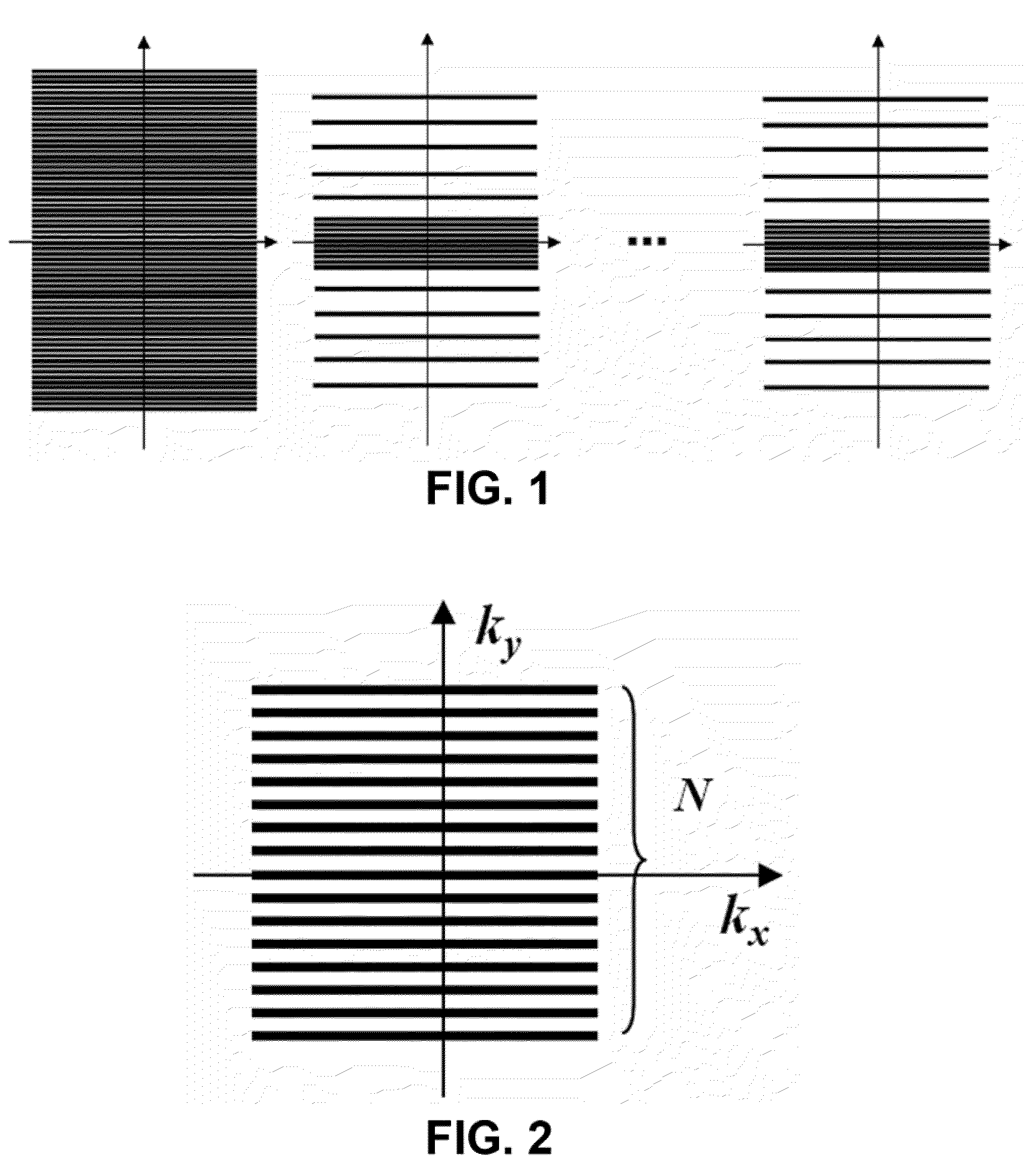
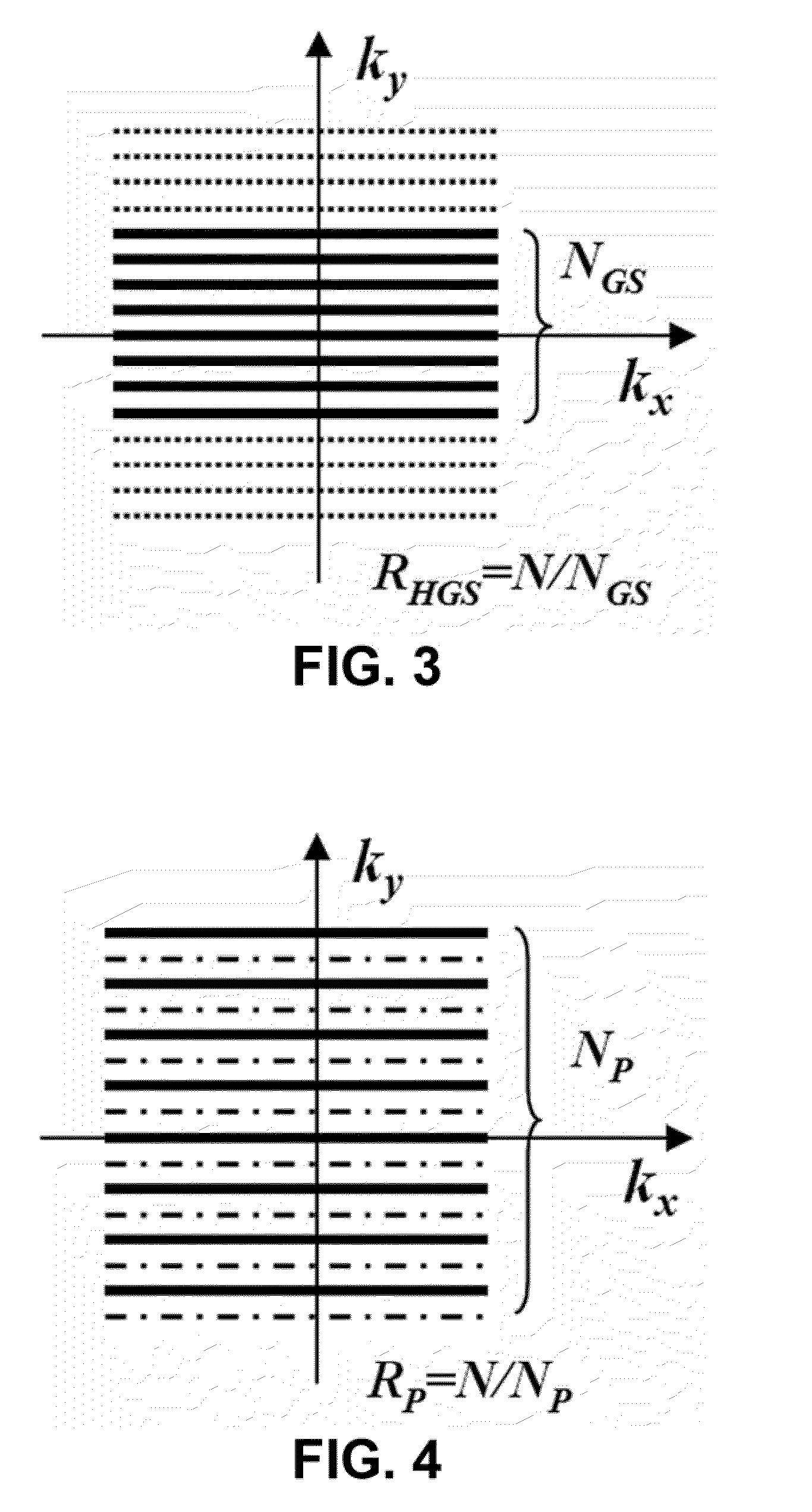
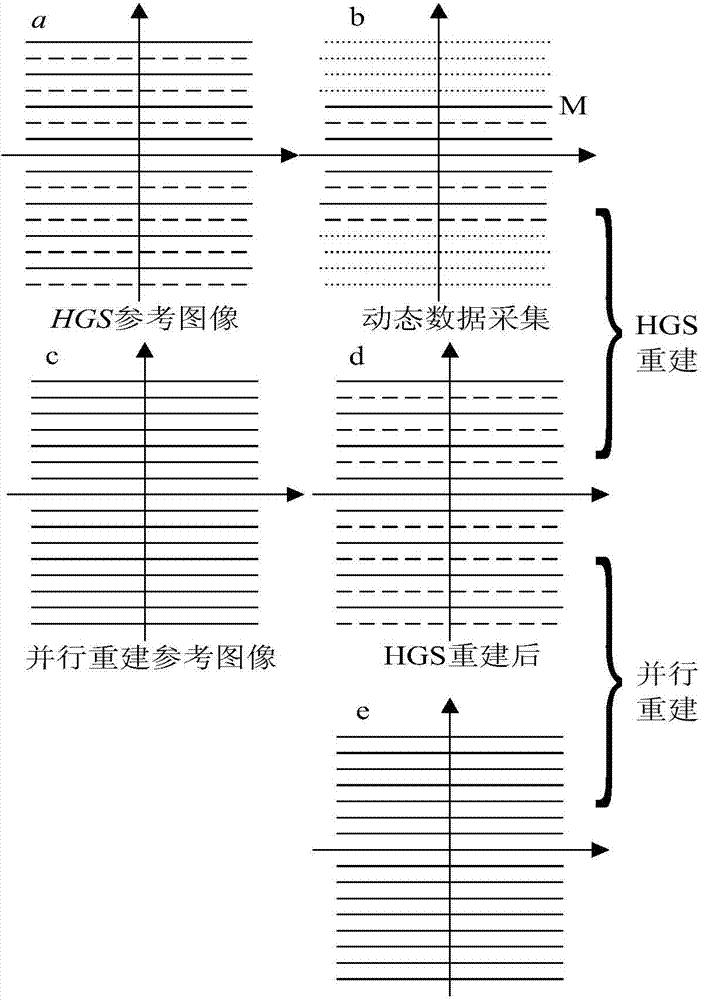
Higher-order generalized series parallel imaging method for acquiring high spatio-temporal resolution functional magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20100171496A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeHigh resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTemporal resolutionResonance
Disclosed area high-order generalized series parallel imaging method for acquiring high spatio-temporal resolution functional magnetic resonance images and a sampling method. The higher-order generalized series parallel imaging method for acquiring high spatio-temporal resolution functional magnetic resonance images includes: performing sampling of an input image in k-space; applying a high-order generalized series (HGS) reconstruction procedure to data acquired as the sampling result to acquire a first reconstructed image; and applying a parallel magnetic resonance reconstruction procedure to the first reconstructed image to acquire a second reconstructed image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
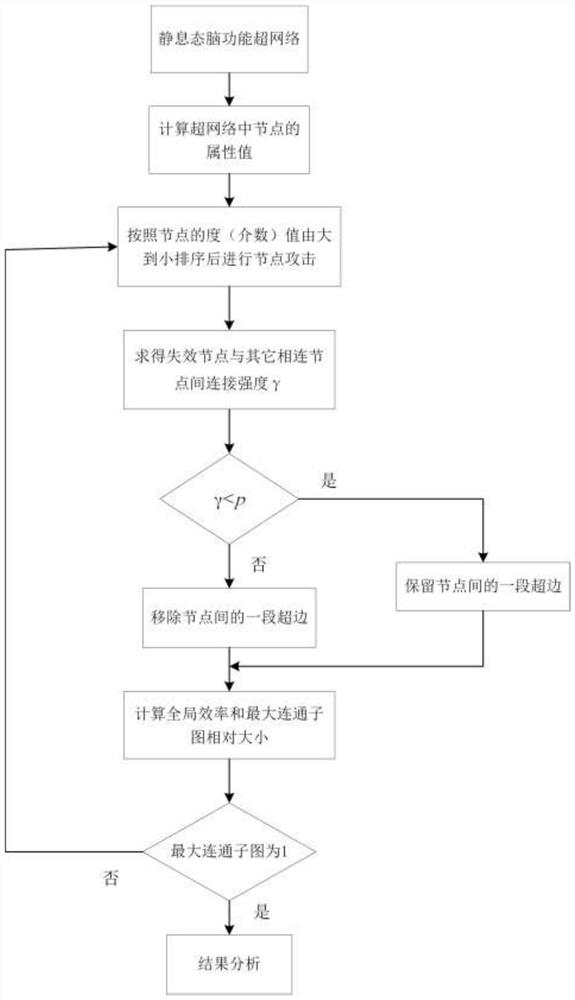
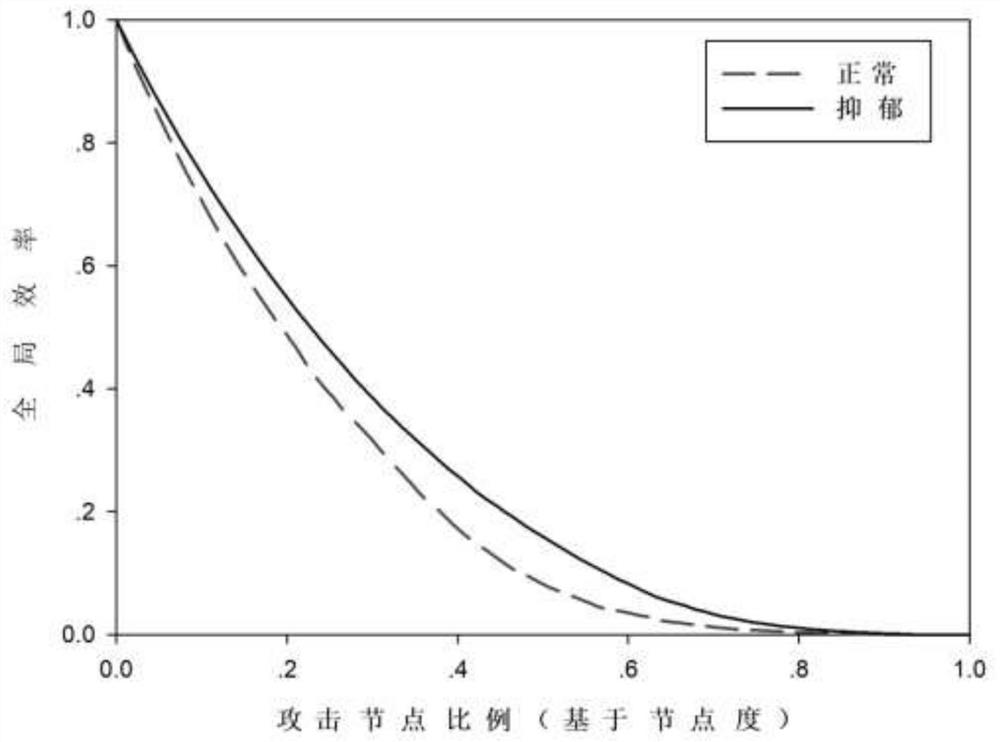
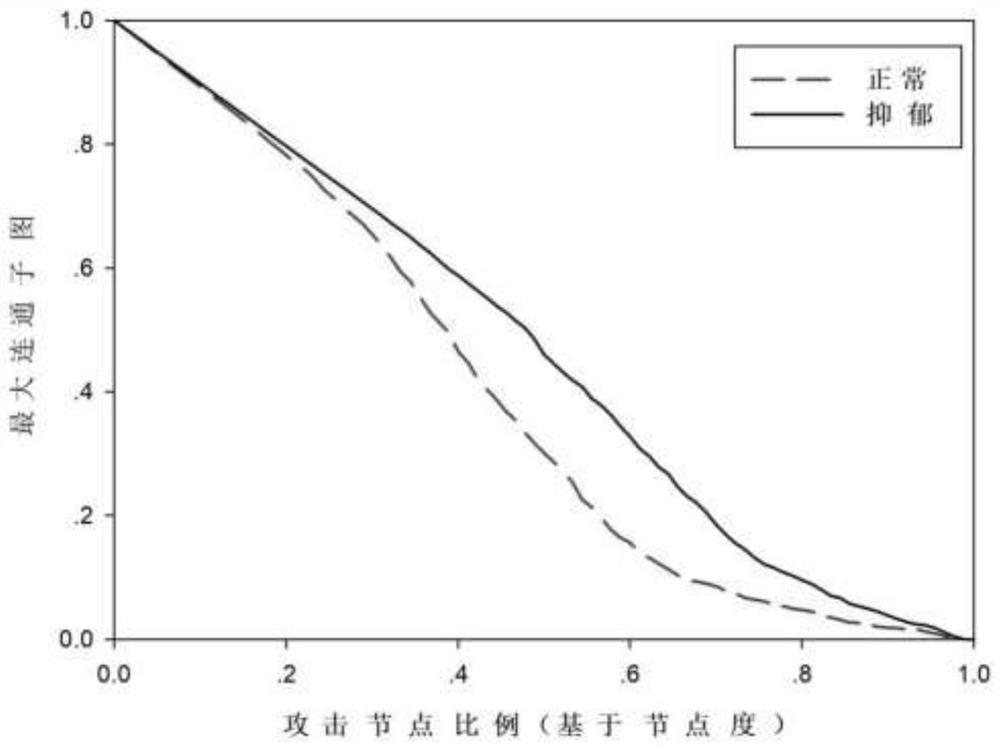
Robustness evaluation method for brain function super-network model
ActiveCN111754395ARobust Effective AnalysisImplementing Disorder SimulationsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage manipulation
The invention relates to an image processing technology, in particular to a robustness evaluation method based on a brain function super-network model, which is realized by adopting the following steps of: S1, preprocessing a resting state functional magnetic resonance image, and extracting an average time sequence of each brain region; s2, solving the sparse linear regression model based on a coverage group lasso method to obtain a brain function super-network model; s3, calculating attributes of the brain function super network; s4, simulating a failure process of the brain function super-network through the constructed super-network model; s5, calculating the global efficiency and the relative size of the maximum connected sub-graph according to the brain function super-network model after the fault; and S6, evaluating the robustness of the brain function super network. According to the method, on the basis of truly representing the complex multi-element interaction relationship ofthe human brain, robustness evaluation is carried out on a brain function super-network model so as to realize functional disorder simulation of the brain disease state in a complex multi-element interaction environment.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Biological safety detection method for LED (light-emitting diode) light
InactiveCN102885613AObserve the activationPracticalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood oxygenation level dependentEngineering
The invention discloses a biological safety detection method for LED (light-emitting diode) light, which belongs to the illuminating engineering field, and specifically relates to a safety detection method of a light source, in particular to the safety detection method of an LED light source. In order to better detect the biological safety of the LED light, the invention provides a novel biological safety detection method for the LED light; in the prior art, detecting the extent of the damage on retina is currently mainly used as a method for measuring the biological safety of the LED light. The inventor of the invention provides a new way, introduces a functional magnetic resonance imaging technology and analyzes the cerebral function by the functional magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate the biological safety of the LED light; the detection method is objective and belongs to a noninvasive test method; the change of a BOLD-fMRI (blood oxygenation level dependent-functional magnetic resonance imaging) signal caused by the change of the brain blood flow when the human eye is stimulated by different light sources is changes before the retina change obtained by various inspection methods. Therefore, using the fMRI to evaluate the biological safety of the LED light is feasible.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
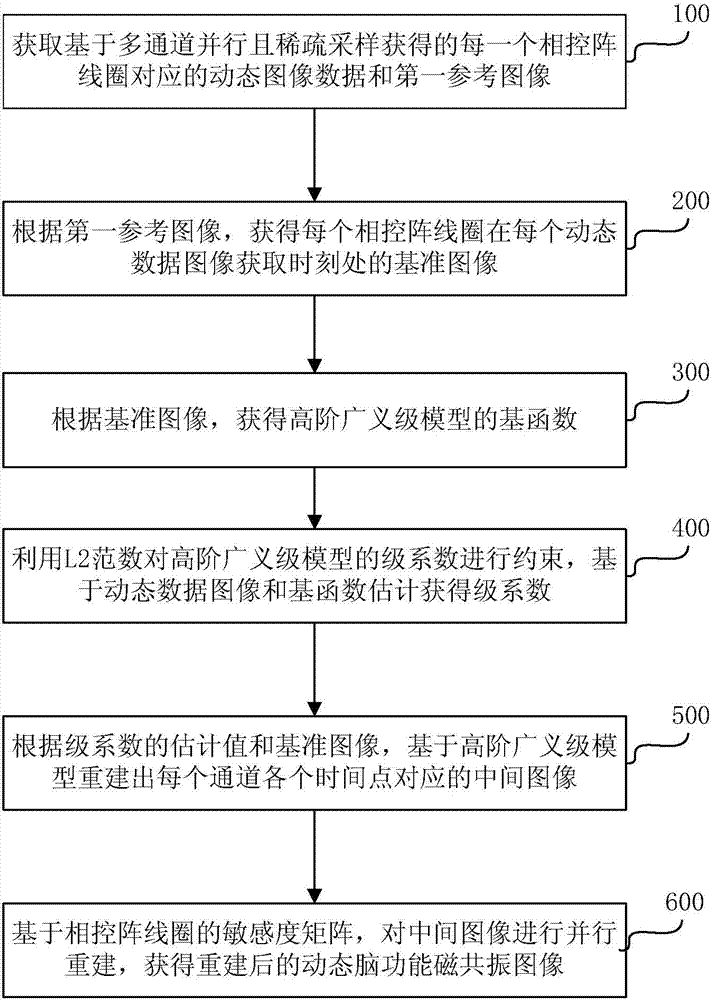
Brain function magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN104323776AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceReference image
The invention provides a brain function magnetic resonance imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a dynamic data image corresponding to each phased array coil based on multi-channel parallelism and sparse sampling; obtaining a standard image of each phased array coil at an obtaining moment of each dynamic data image according to a first reference image; obtaining a primary function of a high-order generalized-grade model according to the standard image; restraining a grade coefficient of the high-order generalized-grade model by using L2 norms; estimating the grade coefficient based on the dynamic data image and the primary function; reconstructing a middle image corresponding to each time point of each channel based on the high-order generalized-grade model according to an estimated value of the grade coefficient and the standard image; reconstructing the middle image based on a sensitivity matrix of each phased array coil to obtain a reconstructed brain function magnetic resonance image. According to the brain function magnetic resonance imaging method and system, image geometric distortion and Nyquist sampling artifact problems of an imaging technology in the prior art are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
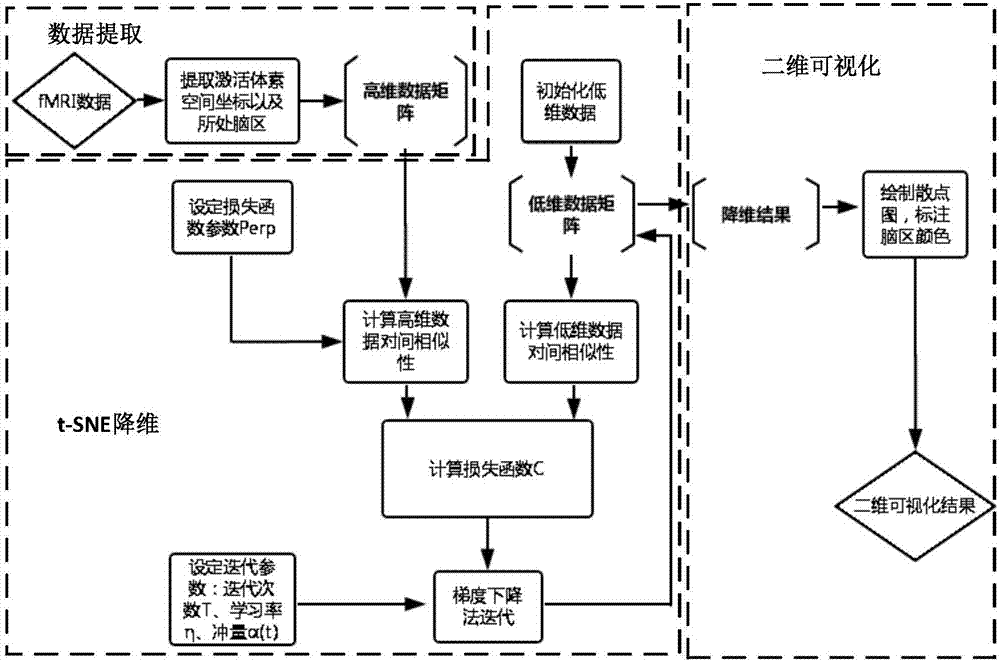
Two dimensional visualization method of fMRI data based on popular learning algorithm
ActiveCN107330948ARealize 2D visualizationEfficiencyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionNonlinear dimensionality reductionVoxel
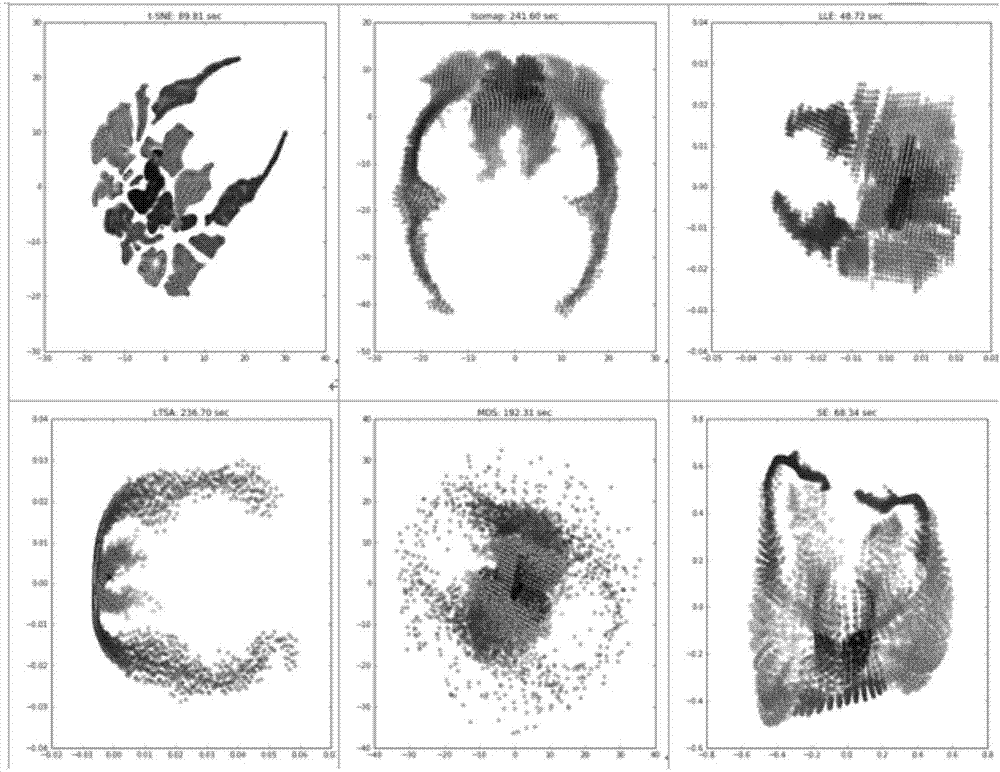
The invention discloses a two-dimensional visualization method of fMRI data based on a popular learning algorithm, the method belonging to the technical field of biomedical image pattern recognition, and in particular relates to a dimensionality reduction visualization method of functional magnetic resonance image data. According to the invention, by using a popular learning algorithm, dimensionality reduction is carried out for fMRI data and two-dimensional visualization of brain voxels is realized, with high efficiency and high stability. Moreover, a dimensionality reduction mechanism of the t-SNE algorithm also determines that the result of two-dimensional visualization can maintain an original spatial topological relationship of the data. The invention puts forward the new and effective method for the two-dimensional visualization of the functional magnetic resonance data, which applies the popular learning algorithm to the two-dimensional visualization of the brain fMRI data for the first time and can be used as a supplementary means of the traditional cortex developed view and expansion graph.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
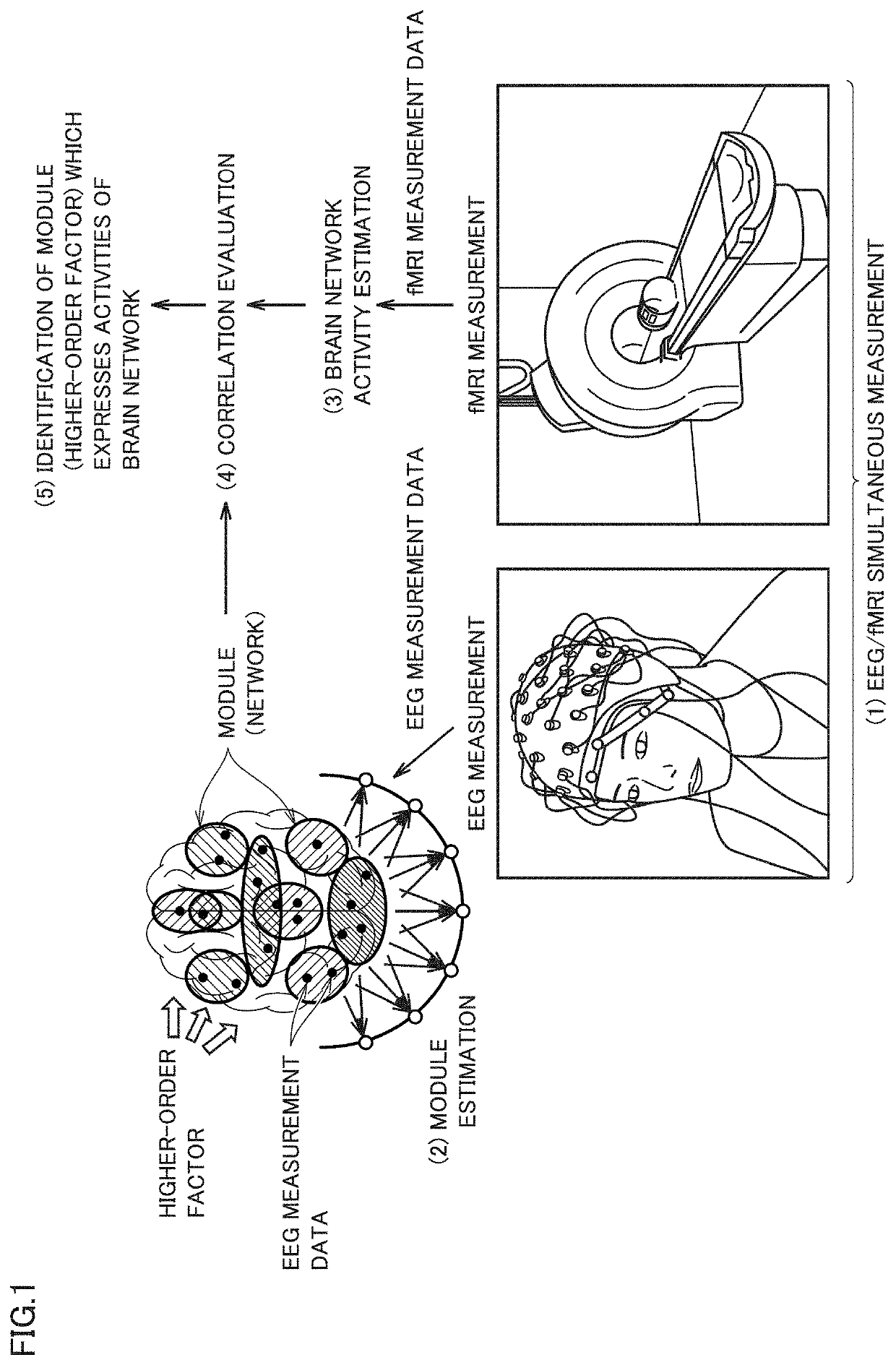
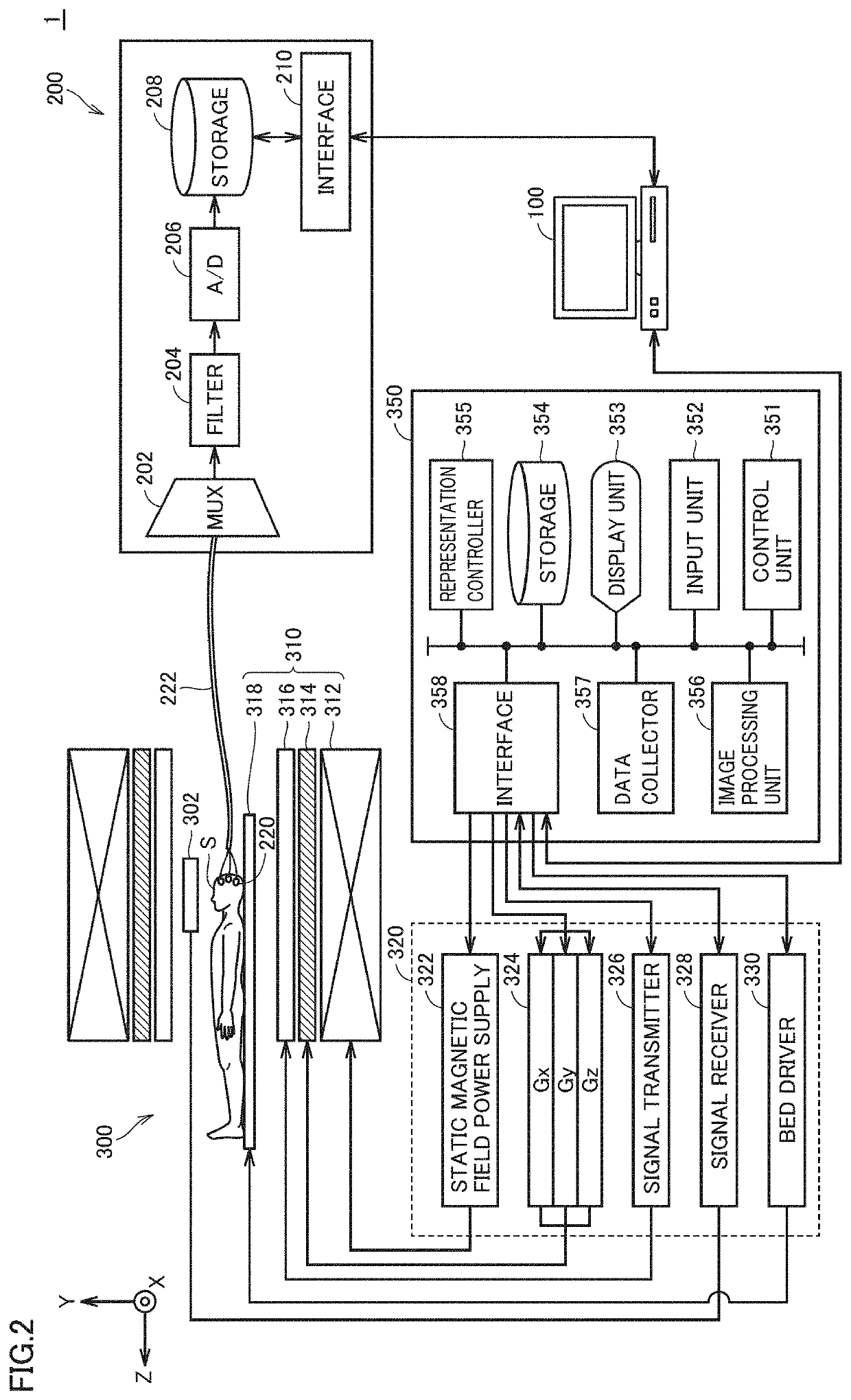
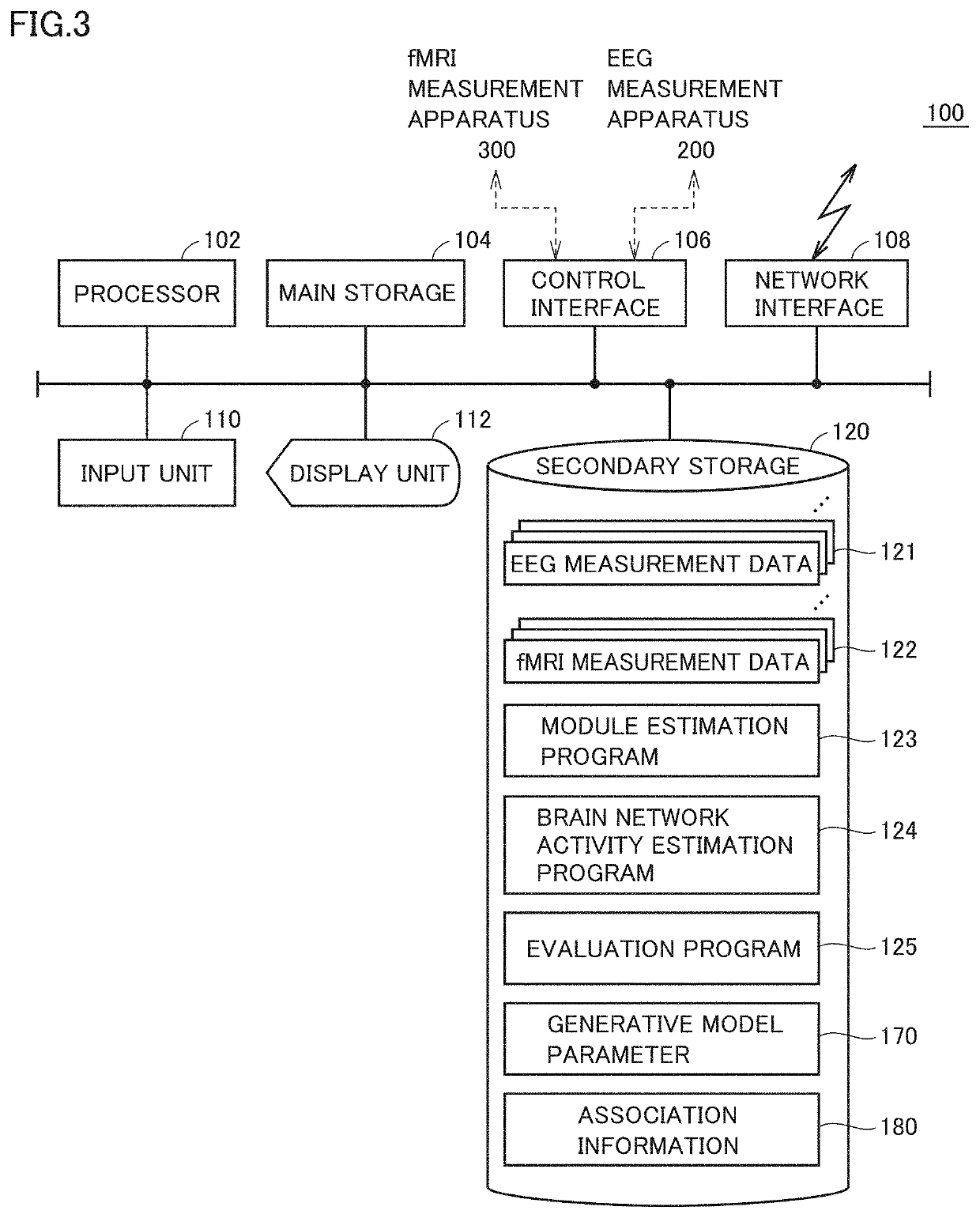
Brain network activity estimation system, method of estimating activities of brain network, brain network activity estimation program, and trained brain activity estimation model
PendingUS20210035665A1High activityElectroencephalographySensorsPattern recognitionFeature estimation
A brain network activity estimation system includes means for obtaining brain wave measurement data and functional magnetic resonance imaging measurement data simultaneously measured from a subject, means for constructing a feature estimation model which receives the brain wave measurement data as input data and determining a parameter which defines the feature estimation model, means for calculating a feature value for each module based on an output value from each module that is calculated when the brain wave measurement data is provided as the input data, means for calculating an image feature value for each brain network based on the functional magnetic resonance imaging measurement data, and means for determining one or more modules which express activities of a specific brain network among a plurality of modules by evaluating correlation between the feature value for each module and the image feature value for each brain network.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
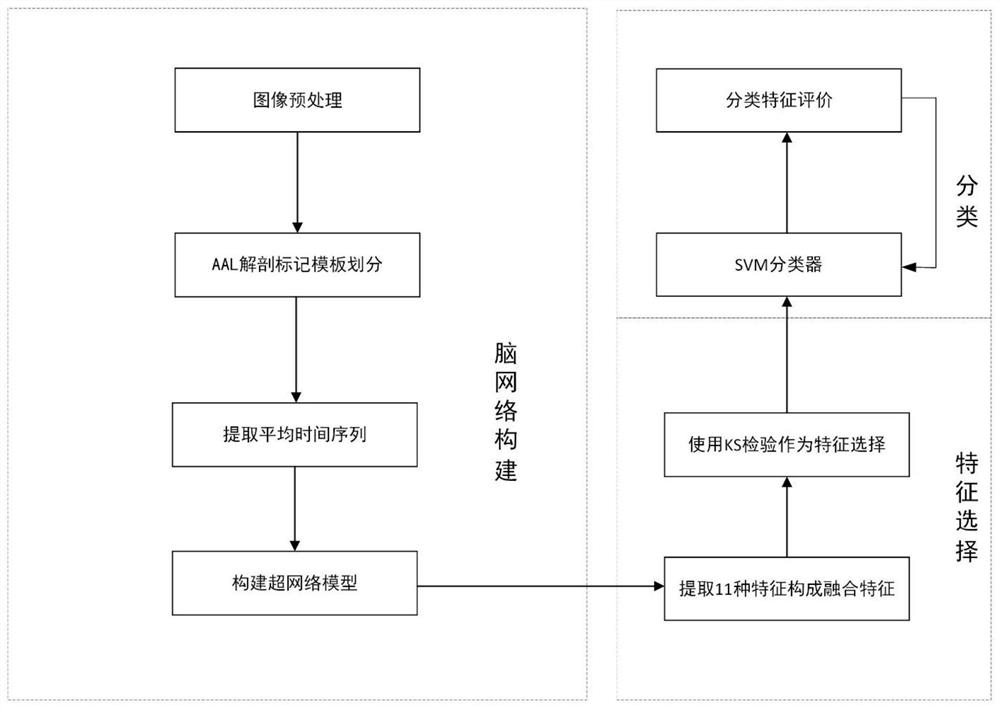
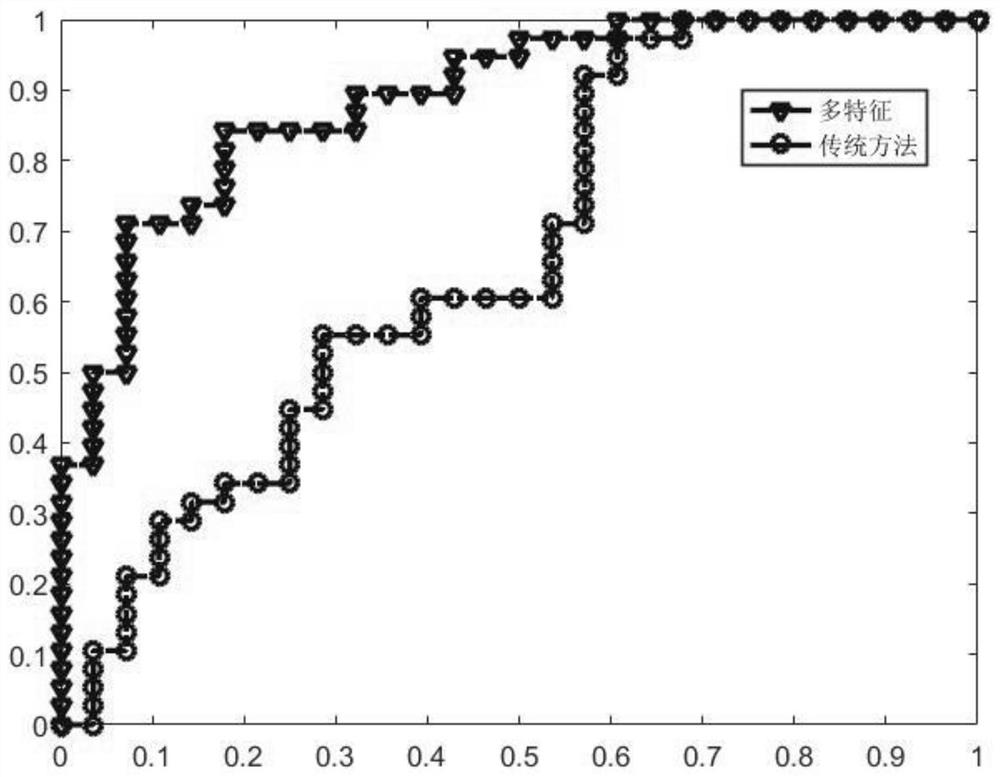
Multi-feature fusion data classification method based on brain function super network model
The invention relates to an image processing technology, in particular to a multi-feature fusion magnetic resonance image data classification method based on a brain function super network model. According to the invention, the problem of low accuracy caused by the fact that a traditional magnetic resonance imaging data classification method uses a single attribute feature is solved, the topological structure of the super-network is evaluated in a multi-angle three-dimensional mode, the integrity of topological information of the super-network is presented, the inter-group difference characterization capability is enhanced, and the method is suitable for related research of functional magnetic resonance image classification. According to the invention, firstly, a complex MCP method is usedfor constructing a super-network model, and then 11 different features are extracted from the super-network to serve as fusion features for classification, so that the defect that a single attributefeature contains single information is overcome. The feature set rich in sufficient information can represent omnibearing multi-angle topology in the brain super-network, and the integrity of a super-network topology structure is presented, so that it is ensured that a classifier constructed later can effectively extract discrimination information, and the upper limit of the classification precision of the classifier is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for modeling and processing functional magnetic resonance image data using full-brain vector auto-regressive model
Systems and methods for modeling functional magnetic resonance image datasets using a multivariate auto-regressive model which captures temporal dynamics in the data, and creates a reduced representation of the dataset representative of functional connectivity of voxels with respect to brain activity. Raw spatio-temporal data is processed using a multivariate auto-regressive model, wherein coefficients in the model with high weights are retained as indices that best describe the full spatio-temporal data. When there are a relatively small number of temporal samples of the data, sparse regression techniques are used to build the model. The model coefficients are used to perform data processing functions such as indexing, prediction, and classification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com