Dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging method and system
A magnetic resonance imaging and brain function technology, applied in medical science, sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient temporal and spatial resolution of imaging, and achieve the effect of improving the quality of reconstructed images and improving temporal and spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] figure 1 It is a flow chart of a dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method mainly includes the following steps:
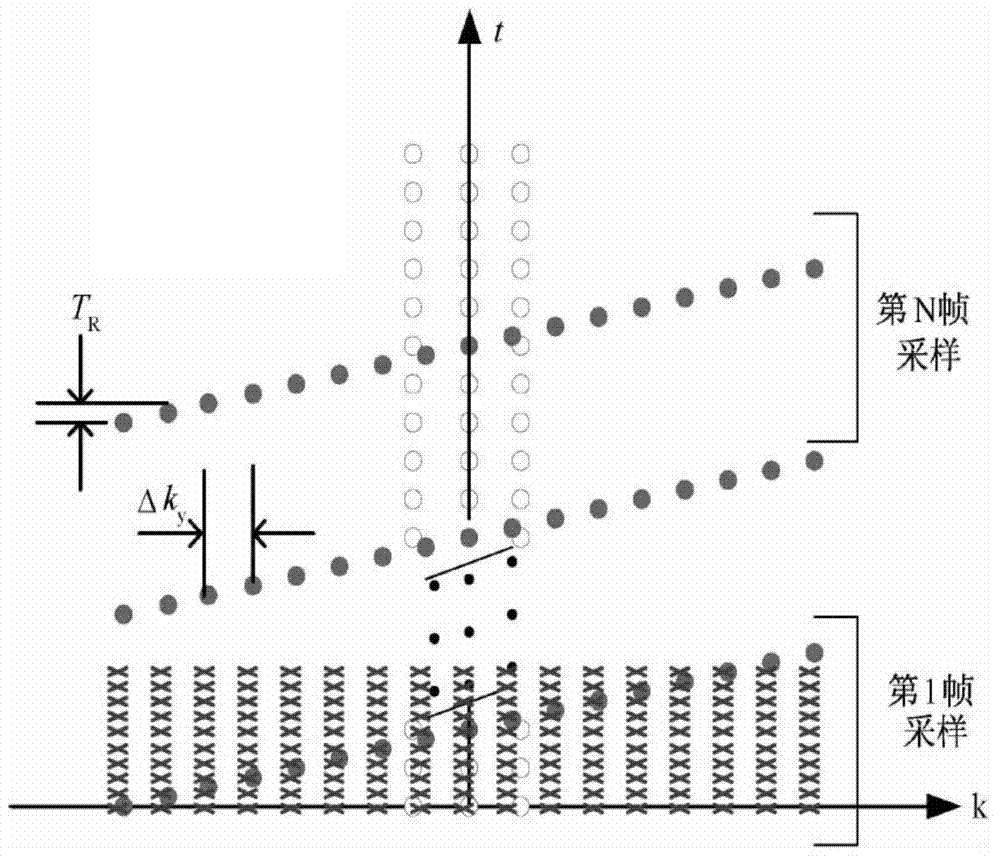
[0026] Step 11. Collect navigation data S with high time and low spatial resolution in (k, t) space NAV Dynamic image data with high spatial and low temporal resolution S IMG .
[0027] In the (k, t) space, each moment along the time axis t is a complete k-space, where k is a two-dimensional space.
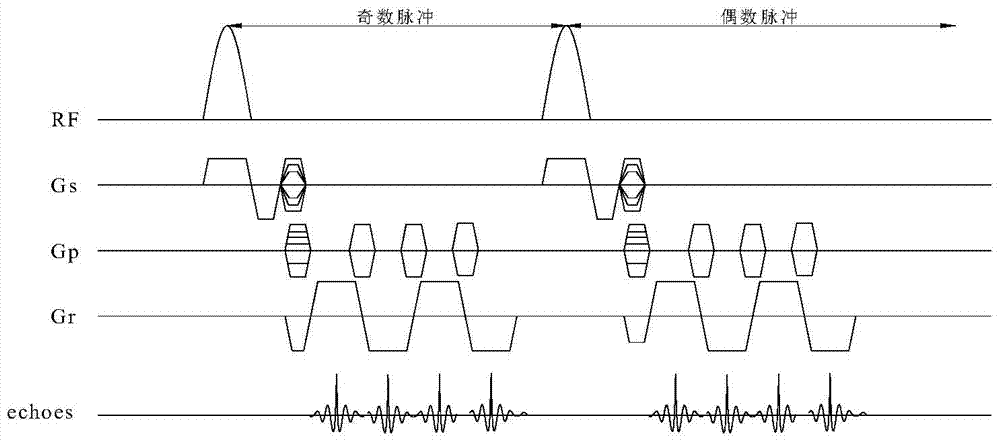
[0028] In the embodiment of the present invention, based on the preset number of phase encoding steps and the echo chain length (ETL), the corresponding number of excitations is generated; wherein, the number of K-space phase encoding lines is filled after each radio frequency pulse excitation, and in the same radio frequency cycle The navigation data SNAV and the image data SIMG are collected synchronously.
[0029] Step 12, using the singular value f...
Embodiment 2
[0045] In order to facilitate understanding of the present invention, below in conjunction with Figure 2-5 Make further introductions.
[0046] The embodiment of the present invention provides a dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging method, which fully exploits the advantages of the PSF model and the MS (multiple excitation echo planar imaging technology)-EPI sequence, and solves the partially separable function model using Tikhonov regular constraints The key parameters in the method can improve the quality of the reconstructed image while releasing the constraints of time and space.
[0047] Among them, brain functional imaging sequence (EPI) is developed on the basis of gradient echo, and can be divided into single-shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) and multiple-shot echo planar imaging according to the number of excitations. Technology (multi-shot EPI, MS-EPI). The raw data of all K-spaces can be obtained with a single shot, and the imaging time is signific...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of a dynamic brain functional magnetic resonance imaging system provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Such as Figure 6 As shown, the system mainly includes:
[0079] The data collection module 61 is used to collect navigation data S with high time and low spatial resolution in (k, t) space NAV Dynamic image data with high spatial and low temporal resolution S IMG ;
[0080] Calculation module 62, for using the singular value to calculate the navigation data S NAV Decompose to obtain the model order L and time basis function Combined with the image data S IMG Perform Tikhonov regularization constraints to solve the spatial basis function c l (k);
[0081] Imaging module 63, for using the model order L, time basis function and spatial basis functions c l (k) performing interpolation recovery of high temporal and high spatial coverage density on the (k, t) space, and then performing inverse Fourier transform, so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com